COPD. Topics for discussion. Clinical implications COPD. Genes and COPD: when to test for alpha-1- antitrypsin deficiency
|
|
|
- Claud Mathews
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Advances in Internal Medicine 2007 James K. Brown, M. D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Section, Department of Veterans Affairs Medical Center, San Francisco Topics for discussion Screening for genetic abnormalities Inhaled bronchodilators Short-acting Long-acting Inhaled corticosteroids Alone Combined with long-acting beta-agonists Treatment of exacerbations Antibiotics Systemic corticosteroids Non-invasive ventilation Confounding diagnoses Lung volume reduction surgery Genes and : when to test for alpha-1- antitrypsin deficiency Early onset dyspnea from prior to 50 years Prominent family history of early-onset Lower lobe-predominant emphysema Unexplained cirrhosis or HCC in a patient Early-onset : Risks to 1 st -degree relatives who smoke Goal: to assess the risk to relatives of those with early-onset for airflow obstruction and chronic bronchitis. Methods: Probands: 44 patients with severe, early-onset - FEV1 < 40% predicted - age < 53 years - absence of alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency - all cigarette smokers or ex-smokers Study subjects: 204 first-degree and 45 second-degree relatives of early-onset probands. Controls: smokers or ex-smokers matched with early-onset probands for smoking, age, and sex. Silverman EK et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1998; 157: Early-onset : Risks to 1 st -degree relatives who smoke Clinical implications Patients with early-onset should be identified. Definition: onset of dyspnea that limits ADL from prior to age 50. First-degree relatives should be counseled regarding their extra risk of lung disease from cigarette smoking. Silverman EK et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1998; 157:
2 severity stages: 2003 GOLD Guidelines Stage Characteristics 0: At Risk Normal spirometry Symptoms of chronic bronchitis (cough and sputum) is a heterogeneous disease I: Mild FEV1/FVC<70%; FEV1>80% predicted With or without symptoms II: Moderate III: Severe IV: Very Severe FEV1/FVC<70%; 50%<FEV1<80% predicted With or without symptoms FEV1/FVC<70%; 30%<FEV1<50% predicted With or without symptoms FEV1/FVC<70%; FEV1<30% predicted or FEV1<50% predicted plus chronic respiratory failure Reilly J. Proc Am Thor Soc 3: , 2006 Bronchodilators in stable Bronchodilators are central to symptom management of. No agent has been shown to modify the long-term decline in lung function. Inhaled therapy always is preferred. Bronchodilators may be prescribed on an asneeded or regular basis to reduce symptoms. Regular treatment with long-acting inhaled bronchodilators is more convenient than with short-acting agents, but also more expensive. From GOLD Guidelines, 2003 Effects of Susceptibility, Smoking, and Smoking Cessation on Normal Age-Dependent Decline in FEV1 Effects of smoking cessation on age-dependent FEV1 decline LUNG HEALTH STUDY Fletcher CM et al, 1977 Anthonisen et al, Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002; 166:
3 Bronchodilators in stable Duration and Administration of Inhaled Bronchodilators Bronchodilators are central to symptom management of. No agent has been shown to modify the long-term decline in lung function. Inhaled therapy always is preferred. Bronchodilators may be prescribed on an asneeded or regular basis to reduce symptoms. Regular treatment with long-acting inhaled bronchodilators is more convenient than with short-acting agents, but also more expensive. From GOLD Guidelines, 2003 Sutherland, ER et al. NEJM 2004;350: Sites of action of bronchodilators in airways Effects of Ipratropium (inhibitor of muscarinic cholinergic receptors) and Metaproterenol (beta-adrenergic agonist) on FEV1 in chronic stable Non-selective muscarinic antagonists (iptratroprium) mediators Beta-2-adrenergic agonists (albuterol) Inflammatory cell Structures of ipratropium and tioproprium bromide When should we be using tiotropium? In stage II - IV (moderate -> very severe) patients that benefit symptomatically from bronchodilators; AND When tiotropium is preferred over long-acting betaagonists because of: - tachycardia or tremor from beta-agonists; - strong preference for once-daily administration schedule.
4 Some unanswered questions about longacting bronchodilators for - are the once-daily administration schedule or other features of tiotropium worth the increased expense over long-acting beta-adrenergic agonists (LABA s) - should we be using tiotropium in combination with LABA, and if so, in which patients? - are there clinically important non-bronchodilator actions of these agents, such as antiinflammatory effects? Definition is a disease state characterized by airflow limitation that is not fully reversible. The airflow limitation is usually both progressive and associated with an abnormal inflammatory response of the lungs to noxious particles or gases. GOLD Guidelines. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001; 163: NORMAL RESPIRATORY BRONCHIOLE RESPIRATORY BRONCHIOLE IN : -Decreased tethering of alveolar septae -Inflamed, thickened airway wall -Luminal plugs of mucous and inflammatory cells pathogenesis: potential relationships to asthma Differences in Inflammation and its Consequences: Asthma and ASTHMA Allergens Cigarette smoke Y Y Y Smokers Asthma I. requires co-occurrence of asthma and smoking Ep cells Mast cell Alv macrophage Ep cells Smokers with Asthma Asthmatic Bronchitis or II. and asthma are distinct diseases with occasional co-occurrence Reversible CD4+ cell Eosinophil (Th2) Bronchoconstriction AHR Airflow Limitation CD8+ cell (Tc1) Neutrophil Small airway narrowing Alveolar destruction Irreversible
5 Decline in FEV1 in Patients on Inhaled Triamcinolone vs. Placebo Inhaled corticosteroids in stable : results of 4 RCT s Inhaled corticosteroids in stable : results of 3 recent RCT s Copenhagen EUROSCOP ISOLDE LHS Patients (n) Mean entry FEV1 (l) Active smokers (%) Exclusion criteria Asthma Yes Yes Yes No BD response Yes Yes Yes No Prednisone response Yes ND Done - but did not ND exclude responders Treatment Budesonide - (800 μg/day) - Budesonide Fluticasone 1 μg/day TAM 1200 ug/day Outcomes FEV1 Initial effect Not seen Yes - small Yes - small Not seen (3-6 months) Rate of decline (3 years) No effect No effect No effect No effect Exacerbations No effect Not reported 33% reduction Reduced Quality of life Not reported Not reported Mild beneficial effect Not measured Inhaled corticosteroids do not alter the accelerated agedependent decline in FEV1 in chronic stable NEJM 2000; 343: Inhaled Corticosteroids in Potential mechanisms for interactions between LABA and inhaled corticosteroids Consider in patients with: moderate or severe (FEV1< 50% predicted) plus frequent exacerbations (> 3 in past 3 years) OR: features suggesting concurrent asthma or atopy - unusual degree of BD reversibility on PFT testing; - background or FH suggestive of asthma or atopy; - eosinophilia. Weigh the risks. Barnes PJ et al. EurRespirJ.25: 1084, 2005 TORCH ( Towards a Revolution in Health ) Trial TORCH Trial: Results Patients: 6112 with Current smokers 43% FEV1 1.1 L (44% predicted) Exclusion: >10% FEV1 or FVC improvement with bronchodilator on PFT s Treatments: for 3 years [after 2-week run-in when ICS, LABA excluded in all patients] Placebo Fluticasone 50 μg BID Salmeterol 500 μg BID Fluticasone + Salmeterol BID Endpoints: Primary: mortality Secondary: health status, FEV1, # exacerbations N Engl J Med 356: , 2007 N Engl J Med 2007;356:
6 TORCH Trial Criticisms - Relatively high rates of withdrawal of study subjects - Increased pneumonia rates in subjects receiving fluticasone - Lack of cost-benefit analysis - No information as to whether benefit was the same in active smokers versus non-smokers/sustained quitters? Implications - Not completely clear! - For now: when the indication for inhaled corticosteroids is: moderate or severe (FEV1< 50% predicted) plus frequent exacerbations (> 3 in past 3 years) then consider adding a long-acting beta agonist Exacerbation: Definition An event in the natural course of the disease characterized by a change in the patient s baseline dyspnea, cough, and/or sputum that is beyond normal day-to-day variations, is acute in onset, and may warrant a change in regular medication in a patient with underlying. exacerbations: importance of infections Bacteria (40-50%) Common - Streptococcus pneumoniae - Hemophilus influenzae - Moraxella catarrhalis Rare - Pseudomonas aeroginosa (severe, bronchiectasis, recent hospitalizations, multiple recent courses of antibiotics) Viruses (30%) - rhinoviruses, influenza, parainfluenza, respiratory syncytial virus Atypical bacteria (5%) - Chlamydia pneumoniae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Legionella species exacerbations: evidence for effectiveness of antibiotics Meta-analysis of 9 placebo-controlled studies in 1995 indicated small but significant benefit. Since those studies, bacterial antimicrobial resistance has emerged. Beneficial effects of antibiotics have occurred particularly in patients with: FEV1 < 50% co-morbid conditions > 3 exacerbations in previous year A few recent studies have demonstrated benefits of using more advanced generation antibiotics though benefits have been subtle (e.g. times to next exacerbation, need for further courses of antibiotics). Sethi S. et al. Infect Dis Clin N Am 18: , 2004 Algorithm for antibiotic treatment of exacerbations Niewoehner DE, Erbland ML, Deupree RH, Collins D, Gross NJ, Light RW, Anderson P, and Morgan NA. Effect of systemic glucocorticoids on exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Department of Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study Group. N Engl J Med 1999; 340: Goal: to evaluate the efficacy of systemic glucocorticoids for exacerbations. Sethi S. et al. Infect Dis Clin N Am 18: , 2004 Methods: 221 patients with exacerbations, > 30 pack years, age > 50 years, and baseline FEV1 < 1.5 or unmeasureable. Exclusions: asthma, use of systemic glucocorticoids within past month. Treatments (3 groups): - 8-week group: MP 125 mg iv q 6h x 3 days, then prednisone slow taper (60 mg on days 4-7, 40 mg days 8-11, 20 mg days 12-43, 10 mg days 44-50, and 5 mg days 51-57). - 2-week group: MP 125 mg iv q 6h x 3 days, then prednisone rapid taper (60 mg on days 4-7, 40 mg days 8-11, and 20 mg days 12-15). - placebo.
7 Niewoehner DE, Erbland ML, Deupree RH, Collins D, Gross NJ, Light RW, Anderson P, and Morgan NA. Effect of systemic glucocorticoids on exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Department of Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study Group. N Engl J Med 1999; 340: Exacerbations: Beneficial Effects of Systemic Corticosteroids on FEV1 Recovery Methods (cont): Universal treatments: antibiotics x 7 days, inhaled beta-agonists and ipratropium bromide. Endpoints: Primary endpoint: treatment failure = death, intubation, re-admission, and/or intensification of pharmacologic therapy. Secondary endpoints: rate of improvement in FEV1, length of hospital stay. Niewoehner DE et al, NEJM 1999; 340: Exacerbations: Beneficial Effects of Systemic Corticosteroids on Treatment Failure Niewoehner DE et al, NEJM 1999; 340: Treatment of exacerbations with high-dose systemic corticosteroids: summary Beneficial Effects of NIPPV in Severe Exacerbations High doses (iv or oral) provide modest benefit in: increasing rate of rise in FEV1 reducing length of hospital stay No demonstrated benefits in: re-intubation rates mortality Duration of administration should be < 2 weeks Keenan, S. P. et. al. Ann Intern Med 2003;138:
8 Beneficial Effects of NIPPV in Severe Exacerbations exacerbations : are we missing pulmonary emboli? Keenan, S. P. et. al. Ann Intern Med 2003;138: Tillie-Leblond, I. et. al. Ann Intern Med 2006;144: Predictors of pulmonary embolism in patients with exacerbations Dyspnea without increased sputum volume/purulence, fever, or previous URI GOLD stage I severity (54%) Malignant disease (43%) Previous PE or DVT (25%) Decrease in arterial pco 2 by > 5 mm Hg Favorable and unfavorable predictors of beneficial response to LVRS Favorable Unfavorable Clinical Age < 75 y. Age > 75 y. Predominant emphysema. Predominant bronchitis. Off cigarettes > 6 months. Co-morbid conditions Severe dyspnea despite increasing surgical risk. maximal medical treatment Pulmonary hypertension including rehabilitation. PA syst >45 mmhg PA mean>35 mmhg. Severe obesity or cachexia. Previous thoracic procedure. Pleurodesis. Tillie-Leblond, I. et. al. Ann Intern Med 2006;144: From Martinez FJ. Chest Surgical Clinics North America 13: , 2003 Favorable and unfavorable predictors of beneficial response to LVRS - 2 LVRS: Which patients will benefit? Favorable Physiologic FEV1< 45% (post bd) RV>150%. TLC>100%. PaO2>45 mm Hg PaCO2<60 mm Hg Unfavorable NETT Research Group. Patients at high risk of death after lungvolume-reduction surgery. NEJM 345: , Radiologic Severe emphysema with Homogeneous and diffuse upper lung field predominance. emphysema. NETT Research Group. A randomized trial comparing lung-volumereduction surgery with medical therapy for severe emphysema. NEJM 348: , From Martinez FJ. Chest Surgical Clinics North America 13: , 2003
9 NETT: Identification of subgroup with high surgical risk FEV1 <20% predicted and Either diffusing capacity < 20% predicted or homogeneous pattern of emphysema NETT Research Group. NEJM 345: , 2001 NETT Research Group. NEJM 348: , 2003 NETT: Measurement of exercise capacity to predict benefit from surgery Incremental exercise test on bicycle ergometer. Starting with no-load pedaling, 5-10 watt increments every 3 minutes. Patient breathing 30% O 2 throughout. Low maximum exercise capacity defined as <40% predicted maximum value: Women: 25 watts Men: 40 watts.
10 Benefit from emphysema surgery in patient with upper lobe bullae Exercise Date FEV1/FVC Dsb Duration O2 requirement 1/99 0.8/ lpm 4/99(postrehab) 0.8/ lpm 8/99(postsurgery) 1.5/ RA 12/99 1.7/ RA 5/00 1.1/ RA 11/00 1.2/ /01 1.2/ RA Emphysema surgery: when to think of it? For lung volume reduction surgery: Measure PFT s Consider if FEV1 < 45%, TLC >100%, RV >150% Exclude if FEV1 < 20% predicted and DLCO < 20% predicted Perform high resolution chest CT scan Consider if emphysema is predominant in upper-lung fields with at least partial sparing of lower lobes Refer for incremental pulmonary exercise testing Presence of large bullous emphysema Topics for discussion Screening for genetic abnormalities Inhaled bronchodilators Short-acting Long-acting Inhaled corticosteroids Alone Combined with long-acting beta-agonists Treatment of exacerbations Antibiotics Systemic corticosteroids Non-invasive ventilation Confounding diagnoses Lung volume reduction surgery
Prevention of Acute COPD exacerbations
 December 3, 2015 Prevention of Acute COPD exacerbations George Pyrgos MD 1 Disclosures No funding received for this presentation I have previously conducted clinical trials with Boehringer Ingelheim. Principal
December 3, 2015 Prevention of Acute COPD exacerbations George Pyrgos MD 1 Disclosures No funding received for this presentation I have previously conducted clinical trials with Boehringer Ingelheim. Principal
RES/006/APR16/AR. Speaker : Dr. Pither Sandy Tulak SpP
 RES/006/APR16/AR Speaker : Dr. Pither Sandy Tulak SpP Definition of Asthma (GINA 2015) Asthma is a common and potentially serious chronic disease that imposes a substantial burden on patients, their families
RES/006/APR16/AR Speaker : Dr. Pither Sandy Tulak SpP Definition of Asthma (GINA 2015) Asthma is a common and potentially serious chronic disease that imposes a substantial burden on patients, their families
Pharmacology of the Respiratory Tract: COPD and Steroids
 Pharmacology of the Respiratory Tract: COPD and Steroids Dr. Tillie-Louise Hackett Department of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics University of British Columbia Associate Head, Centre of Heart
Pharmacology of the Respiratory Tract: COPD and Steroids Dr. Tillie-Louise Hackett Department of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics University of British Columbia Associate Head, Centre of Heart
COPD and Asthma Differential Diagnosis
 COPD and Asthma Differential Diagnosis Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is the third leading cause of death in America. Learning Objectives Use tools to effectively diagnose chronic obstructive
COPD and Asthma Differential Diagnosis Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is the third leading cause of death in America. Learning Objectives Use tools to effectively diagnose chronic obstructive
Bronchodilators in COPD
 TSANZSRS Gold Coast 2015 Can average outcomes in COPD clinical trials guide treatment strategies? Long live the FEV1? Christine McDonald Dept of Respiratory and Sleep Medicine Austin Health Institute for
TSANZSRS Gold Coast 2015 Can average outcomes in COPD clinical trials guide treatment strategies? Long live the FEV1? Christine McDonald Dept of Respiratory and Sleep Medicine Austin Health Institute for
Acute Care of COPD: Gaps in our knowledge. Robert A. Wise, M.D. May 20, 2010
 Acute Care of COPD: Gaps in our knowledge Robert A. Wise, M.D. May 20, 2010 Outline of talk Importance of COPD exacerbations Current treatments Areas for improvement Significant knowledge gaps Strategies
Acute Care of COPD: Gaps in our knowledge Robert A. Wise, M.D. May 20, 2010 Outline of talk Importance of COPD exacerbations Current treatments Areas for improvement Significant knowledge gaps Strategies
Management of exacerbations in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Primary Care
 Management of exacerbations in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Primary Care Acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are associated with significant morbidity and mortality.
Management of exacerbations in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Primary Care Acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are associated with significant morbidity and mortality.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the name for a group of lung diseases including chronic bronchitis, emphysema and chronic obstructive airways
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the name for a group of lung diseases including chronic bronchitis, emphysema and chronic obstructive airways
Department of Surgery
 What is emphysema? 2004 Regents of the University of Michigan Emphysema is a chronic disease of the lungs characterized by thinning and overexpansion of the lung-like blisters (bullae) in the lung tissue.
What is emphysema? 2004 Regents of the University of Michigan Emphysema is a chronic disease of the lungs characterized by thinning and overexpansion of the lung-like blisters (bullae) in the lung tissue.
Tests. Pulmonary Functions
 Pulmonary Functions Tests Static lung functions volumes Dynamic lung functions volume and velocity Dynamic Tests Velocity dependent on Airway resistance Resistance of lung tissue to change in shape Dynamic
Pulmonary Functions Tests Static lung functions volumes Dynamic lung functions volume and velocity Dynamic Tests Velocity dependent on Airway resistance Resistance of lung tissue to change in shape Dynamic
Prof. Florian Gantner. Vice President Respiratory Diseases Research Boehringer Ingelheim
 Prof. Florian Gantner Vice President Respiratory Diseases Research Boehringer Ingelheim Research and Development in Practice: COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Facts Main cause of COPD
Prof. Florian Gantner Vice President Respiratory Diseases Research Boehringer Ingelheim Research and Development in Practice: COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Facts Main cause of COPD
Objectives COPD. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) 4/19/2011
 Objectives Discuss assessment findings and treatment for: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Bronchitis Emphysema Asthma Anaphylaxis Other respiratory issues Provide some definitions Chronic Obstructive
Objectives Discuss assessment findings and treatment for: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Bronchitis Emphysema Asthma Anaphylaxis Other respiratory issues Provide some definitions Chronic Obstructive
COPD PROTOCOL CELLO. Leiden
 COPD PROTOCOL CELLO Leiden May 2011 1 Introduction This protocol includes an explanation of the clinical picture, diagnosis, objectives and medication of COPD. The Cello way of working can be viewed on
COPD PROTOCOL CELLO Leiden May 2011 1 Introduction This protocol includes an explanation of the clinical picture, diagnosis, objectives and medication of COPD. The Cello way of working can be viewed on
On completion of this chapter you should be able to: discuss the stepwise approach to the pharmacological management of asthma in children
 7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
Compare the physiologic responses of the respiratory system to emphysema, chronic bronchitis, and asthma
 Chapter 31 Drugs Used to Treat Lower Respiratory Disease Learning Objectives Describe the physiology of respirations Compare the physiologic responses of the respiratory system to emphysema, chronic bronchitis,
Chapter 31 Drugs Used to Treat Lower Respiratory Disease Learning Objectives Describe the physiology of respirations Compare the physiologic responses of the respiratory system to emphysema, chronic bronchitis,
PLAN OF ACTION FOR. Physician Name Signature License Date
 PLAN OF ACTION FOR Patient s copy (patient s name) I Feel Well Lignes I feel short directrices of breath: I cough up sputum daily. No Yes, colour: I cough regularly. No Yes I Feel Worse I have changes
PLAN OF ACTION FOR Patient s copy (patient s name) I Feel Well Lignes I feel short directrices of breath: I cough up sputum daily. No Yes, colour: I cough regularly. No Yes I Feel Worse I have changes
Understanding COPD. Carolinas Healthcare System
 Understanding COPD Carolinas Healthcare System 2013 This self-directed learning module contains information about the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of COPD. Target Audience: All RNs and LPNs
Understanding COPD Carolinas Healthcare System 2013 This self-directed learning module contains information about the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of COPD. Target Audience: All RNs and LPNs
Drug therapy SHORT-ACTING BETA AGONISTS SHORT-ACTING ANTICHOLINERGICS LONG-ACTING BETA AGONISTS LONG-ACTING ANTICHOLINERGICS
 Drug therapy 6 6.1 What is the role of bronchodilators in COPD? 52 SHORT-ACTING BETA AGONISTS 6.2 How do short-acting beta agonists work? 52 6.3 What are the indications for their use? 52 6.4 What is the
Drug therapy 6 6.1 What is the role of bronchodilators in COPD? 52 SHORT-ACTING BETA AGONISTS 6.2 How do short-acting beta agonists work? 52 6.3 What are the indications for their use? 52 6.4 What is the
Pre-Operative Services Teaching Rounds 2 Jan 2011
 Pre-Operative Services Teaching Rounds 2 Jan 2011 Deborah Richman MBChB FFA(SA) Director Pre-Operative Services Department of Anesthesia Stony Brook University Medical Center, NY drichman@notes.cc.sunysb.edu
Pre-Operative Services Teaching Rounds 2 Jan 2011 Deborah Richman MBChB FFA(SA) Director Pre-Operative Services Department of Anesthesia Stony Brook University Medical Center, NY drichman@notes.cc.sunysb.edu
Pathway for Diagnosing COPD
 Pathway for Diagnosing Visit 1 Registry Clients at Risk Patient presents with symptoms suggestive of Exertional breathlessness Chronic cough Regular sputum production Frequent bronchitis ; wheeze Occupational
Pathway for Diagnosing Visit 1 Registry Clients at Risk Patient presents with symptoms suggestive of Exertional breathlessness Chronic cough Regular sputum production Frequent bronchitis ; wheeze Occupational
Severe asthma Definition, epidemiology and risk factors. Mina Gaga Athens Chest Hospital
 Severe asthma Definition, epidemiology and risk factors Mina Gaga Athens Chest Hospital Difficult asthma Defined as asthma, poorly controlled in terms of chronic symptoms, with episodic exacerbations,
Severe asthma Definition, epidemiology and risk factors Mina Gaga Athens Chest Hospital Difficult asthma Defined as asthma, poorly controlled in terms of chronic symptoms, with episodic exacerbations,
Clinical Guideline. Recommendation 3: For stable COPD patients with respiratory symptoms
 Clinical Guideline Diagnosis and Management of Stable Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Clinical Practice Guideline Update from the American College of Physicians, American College of Chest Physicians,
Clinical Guideline Diagnosis and Management of Stable Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Clinical Practice Guideline Update from the American College of Physicians, American College of Chest Physicians,
understanding the professional guidelines
 SEVERE ASTHMA understanding the professional guidelines This guide includes information on what the European Respiratory Society (ERS) and the American Thoracic Society (ATS) have said about severe asthma.
SEVERE ASTHMA understanding the professional guidelines This guide includes information on what the European Respiratory Society (ERS) and the American Thoracic Society (ATS) have said about severe asthma.
Clinical Guideline. Recommendation 3: For stable COPD patients with respiratory symptoms
 Clinical Guideline Diagnosis and Management of Stable Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Clinical Practice Guideline Update from the American College of Physicians, American College of Chest Physicians,
Clinical Guideline Diagnosis and Management of Stable Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Clinical Practice Guideline Update from the American College of Physicians, American College of Chest Physicians,
medicineupdate to find out more about this medicine
 medicineupdate Asking the right questions about new medicines Seretide for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease What this medicine is 1 What this medicine treats 2 Other medicines available for this condition
medicineupdate Asking the right questions about new medicines Seretide for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease What this medicine is 1 What this medicine treats 2 Other medicines available for this condition
Irish Association for Emergency Medicine (IAEM) submission to the National COPD Strategy
 31 st Irish Association for Emergency Medicine (IAEM) submission to the National COPD Strategy 1 Introduction Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is an important disease for patients, the health
31 st Irish Association for Emergency Medicine (IAEM) submission to the National COPD Strategy 1 Introduction Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is an important disease for patients, the health
CLINICAL PATHWAY. Acute Medicine. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
 CLINICAL PATHWAY Acute Medicine Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Table of Contents (tap to jump to page) INTRODUCTION 1 Scope of this Pathway 1 Pathway Contacts
CLINICAL PATHWAY Acute Medicine Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Table of Contents (tap to jump to page) INTRODUCTION 1 Scope of this Pathway 1 Pathway Contacts
NICE Pathways bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic.
 bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published.
bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published.
Influenza (Flu) Influenza is a viral infection that may affect both the upper and lower respiratory tracts. There are three types of flu virus:
 Respiratory Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology General Manifestations of Respiratory Disease Sneezing is a reflex response to irritation in the upper respiratory tract and is associated with inflammation
Respiratory Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology General Manifestations of Respiratory Disease Sneezing is a reflex response to irritation in the upper respiratory tract and is associated with inflammation
The patient s response to therapy within the first hour in the Emergency Room is one of the most reliable ways to predict need for hospitalization.
 Emergency Room Asthma Management Algorithm The Emergency Room Asthma Management Algorithm is to be used for any patient seen in the Emergency Room with the diagnosis of asthma. (The initial history should
Emergency Room Asthma Management Algorithm The Emergency Room Asthma Management Algorithm is to be used for any patient seen in the Emergency Room with the diagnosis of asthma. (The initial history should
Pulmonary Disorders. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
 RCS 6080 Medical and Psychosocial Aspects of Rehabilitation Counseling Pulmonary Disorders Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Characterized by decreased expiratory airflow Reduction in expiratory
RCS 6080 Medical and Psychosocial Aspects of Rehabilitation Counseling Pulmonary Disorders Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Characterized by decreased expiratory airflow Reduction in expiratory
Topic: New Treatment = Better Outcome?
 Session on COPD: Novel Concepts and Promising New Drugs Topic: New Treatment = Better Outcome? Through a CME Grant sponsored by New Treatment = Better Outcome? Tim S. Trinidad, MD Disclosure Present: COPD
Session on COPD: Novel Concepts and Promising New Drugs Topic: New Treatment = Better Outcome? Through a CME Grant sponsored by New Treatment = Better Outcome? Tim S. Trinidad, MD Disclosure Present: COPD
Background information
 Background information Asthma Asthma is a complex disease affecting the lungs that can be managed but cannot be cured. 1 Asthma can be controlled well in most people most of the time, although some people
Background information Asthma Asthma is a complex disease affecting the lungs that can be managed but cannot be cured. 1 Asthma can be controlled well in most people most of the time, although some people
National Learning Objectives for COPD Educators
 National Learning Objectives for COPD Educators National Learning Objectives for COPD Educators The COPD Educator will be able to achieve the following objectives. Performance objectives, denoted by the
National Learning Objectives for COPD Educators National Learning Objectives for COPD Educators The COPD Educator will be able to achieve the following objectives. Performance objectives, denoted by the
F r e q u e n t l y As k e d Qu e s t i o n s. Lung Disease
 Lung Disease page 1 Q: What is lung disease? A: Lung disease refers to disorders that affect the lungs, the organs that allow us to breathe. Breathing problems caused by lung disease may prevent the body
Lung Disease page 1 Q: What is lung disease? A: Lung disease refers to disorders that affect the lungs, the organs that allow us to breathe. Breathing problems caused by lung disease may prevent the body
The asthmatic patient and sedation
 The asthmatic patient and sedation Introduction The sedation practitioner is often faced with difficult questions to answer before the administration of sedation. Our guidelines say clearly that we are
The asthmatic patient and sedation Introduction The sedation practitioner is often faced with difficult questions to answer before the administration of sedation. Our guidelines say clearly that we are
Interpretation of Pulmonary Function Tests
 Interpretation of Pulmonary Function Tests Dr. Sally Osborne Cellular & Physiological Sciences University of British Columbia Room 3602, D.H Copp building 604 822-3421 sally.osborne@ubc.ca www.sallyosborne.com
Interpretation of Pulmonary Function Tests Dr. Sally Osborne Cellular & Physiological Sciences University of British Columbia Room 3602, D.H Copp building 604 822-3421 sally.osborne@ubc.ca www.sallyosborne.com
COPD. What is COPD? How many people have COPD in Canada? Who gets COPD?
 What is COPD? COPD stands for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. It is a long-term lung disease that makes it difficult for air to move into and out of the lungs. COPD is used to describe a few lung
What is COPD? COPD stands for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. It is a long-term lung disease that makes it difficult for air to move into and out of the lungs. COPD is used to describe a few lung
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER)
 Guidance for Industry Acute Bacterial Exacerbations of Chronic Bronchitis in Patients With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Developing Antimicrobial Drugs for Treatment U.S. Department of Health
Guidance for Industry Acute Bacterial Exacerbations of Chronic Bronchitis in Patients With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Developing Antimicrobial Drugs for Treatment U.S. Department of Health
Stanley J. Szefler, MD National Jewish Medical and Research Center
 New Asthma Guidelines: Special Attention to Infant Wheezers Stanley J. Szefler, MD Helen Wohlberg & Herman Lambert Chair in Pharmacokinetics, & Professor of Pediatrics and Pharmacology, University of Colorado
New Asthma Guidelines: Special Attention to Infant Wheezers Stanley J. Szefler, MD Helen Wohlberg & Herman Lambert Chair in Pharmacokinetics, & Professor of Pediatrics and Pharmacology, University of Colorado
Exploring the Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Clinical Pathway. Health Quality Ontario s integrated episode of care for COPD
 Exploring the Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Clinical Pathway Health Quality Ontario s integrated episode of care for COPD Dr. Charlie Chan Health Quality Ontario Expert Panel Co-Chair May/June
Exploring the Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Clinical Pathway Health Quality Ontario s integrated episode of care for COPD Dr. Charlie Chan Health Quality Ontario Expert Panel Co-Chair May/June
David J. Lederer, MD, MS
 COPD: Definition Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Chronic airflow obstruction due to chronic bronchitis and/or pulmonary emphysema David J. Lederer, MD, MS Associate Medical Director, Lung Transplant
COPD: Definition Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Chronic airflow obstruction due to chronic bronchitis and/or pulmonary emphysema David J. Lederer, MD, MS Associate Medical Director, Lung Transplant
Ventilation Perfusion Relationships
 Ventilation Perfusion Relationships VENTILATION PERFUSION RATIO Ideally, each alveolus in the lungs would receive the same amount of ventilation and pulmonary capillary blood flow (perfusion). In reality,
Ventilation Perfusion Relationships VENTILATION PERFUSION RATIO Ideally, each alveolus in the lungs would receive the same amount of ventilation and pulmonary capillary blood flow (perfusion). In reality,
Documenting & Coding. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Presented by: David S. Brigner, MLA, CPC
 Documenting & Coding Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Presented by: David S. Brigner, MLA, CPC Sr. Provider Training & Development Consultant Professional Profile David Brigner currently performs
Documenting & Coding Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Presented by: David S. Brigner, MLA, CPC Sr. Provider Training & Development Consultant Professional Profile David Brigner currently performs
James F. Kravec, M.D., F.A.C.P
 James F. Kravec, M.D., F.A.C.P Chairman, Department of Internal Medicine, St. Elizabeth Health Center Chair, General Internal Medicine, Northeast Ohio Medical University Associate Medical Director, Hospice
James F. Kravec, M.D., F.A.C.P Chairman, Department of Internal Medicine, St. Elizabeth Health Center Chair, General Internal Medicine, Northeast Ohio Medical University Associate Medical Director, Hospice
EMPHYSEMA THERAPY. Information brochure for valve therapy in the treatment of emphysema.
 EMPHYSEMA THERAPY Information brochure for valve therapy in the treatment of emphysema. PATIENTS WITH EMPHYSEMA With every breath, lungs deliver oxygen to the rest of the body to perform essential life
EMPHYSEMA THERAPY Information brochure for valve therapy in the treatment of emphysema. PATIENTS WITH EMPHYSEMA With every breath, lungs deliver oxygen to the rest of the body to perform essential life
Asthma COPD and Asthma - COPD Overlap Syndrome (ACOS)
 Diagnosis of Diseases of Chronic Airflow Limitation: Asthma COPD and Asthma - COPD Overlap Syndrome (ACOS) Based on the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention and the Global Strategy for
Diagnosis of Diseases of Chronic Airflow Limitation: Asthma COPD and Asthma - COPD Overlap Syndrome (ACOS) Based on the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention and the Global Strategy for
Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency
 CORAM S VOLUME 5 Coram LLC is a leading national provider of home infusion services, including alternate site of care and specialty pharmacy distribution. 12450 East Arapahoe Road, Suite A, Centennial,
CORAM S VOLUME 5 Coram LLC is a leading national provider of home infusion services, including alternate site of care and specialty pharmacy distribution. 12450 East Arapahoe Road, Suite A, Centennial,
COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org
 written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org What Is COPD? COPD stands for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. There are 2 major diseases included in COPD:
written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org What Is COPD? COPD stands for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. There are 2 major diseases included in COPD:
Pulmonary Diseases. Lung Disease: Pathophysiology, Medical and Exercise Programming. Overview of Pathophysiology
 Lung Disease: Pathophysiology, Medical and Exercise Programming Overview of Pathophysiology Ventilatory Impairments Increased airway resistance Reduced compliance Increased work of breathing Ventilatory
Lung Disease: Pathophysiology, Medical and Exercise Programming Overview of Pathophysiology Ventilatory Impairments Increased airway resistance Reduced compliance Increased work of breathing Ventilatory
How to use FENO-guided asthma control in routine clinical practice
 How to use FENO-guided asthma control in routine clinical practice Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways. This has implications for the diagnosis, management and potential prevention
How to use FENO-guided asthma control in routine clinical practice Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways. This has implications for the diagnosis, management and potential prevention
Original Article COPD and Hospital Stay Pak Armed Forces Med J 2014; 64 (1): 46-50. Ahmed Raza, Mahmood Iqbal Malik*, Yousaf Jamal**
 Original Article COPD and Hospital Stay Pak Armed Forces Med J 2014; 64 (1): 46-50 COMPARISON OF NIPPV WITH STANDARD TREATMENT IN PATIENTS WITH ACUTE EXACERBATIONS OF COPD IN TERMS OF IMPROVEMENT IN ABGS
Original Article COPD and Hospital Stay Pak Armed Forces Med J 2014; 64 (1): 46-50 COMPARISON OF NIPPV WITH STANDARD TREATMENT IN PATIENTS WITH ACUTE EXACERBATIONS OF COPD IN TERMS OF IMPROVEMENT IN ABGS
2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system
 2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system 2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system Essential questions What are the functions of the respiratory
2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system 2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system Essential questions What are the functions of the respiratory
Marilyn Borkgren-Okonek, APN, CCNS, RN, MS Suburban Lung Associates, S.C. Elk Grove Village, IL
 Marilyn Borkgren-Okonek, APN, CCNS, RN, MS Suburban Lung Associates, S.C. Elk Grove Village, IL www.goldcopd.com GLOBAL INITIATIVE FOR CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE LUNG DISEASE GLOBAL STRATEGY FOR DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT
Marilyn Borkgren-Okonek, APN, CCNS, RN, MS Suburban Lung Associates, S.C. Elk Grove Village, IL www.goldcopd.com GLOBAL INITIATIVE FOR CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE LUNG DISEASE GLOBAL STRATEGY FOR DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Developing Drugs for Treatment Guidance for Industry
 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Developing Drugs for Treatment Guidance for Industry DRAFT GUIDANCE This guidance document is being distributed for comment purposes only. Comments and suggestions
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Developing Drugs for Treatment Guidance for Industry DRAFT GUIDANCE This guidance document is being distributed for comment purposes only. Comments and suggestions
How To Treat Acute Bronchitis
 Bronchitis in Adults and Children Kristen Lewis, MD Acute Bronchitis Cough, with or without phlegm Lasting less than 3 weeks Frequently associated with or preceded d by other upper respiratory symptoms
Bronchitis in Adults and Children Kristen Lewis, MD Acute Bronchitis Cough, with or without phlegm Lasting less than 3 weeks Frequently associated with or preceded d by other upper respiratory symptoms
written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org/copd
 written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org/copd What Is COPD? COPD stands for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. There are two major diseases included in
written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org/copd What Is COPD? COPD stands for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. There are two major diseases included in
Exploratory data: COPD and blood eosinophils. David Price: 9.23-9.35am
 Exploratory data: COPD and blood eosinophils David Price: 9.23-9.35am Blood Eosinophilia in COPD The reliability and utility of blood eosinophils as a marker of disease burden, healthcare resource utilisation
Exploratory data: COPD and blood eosinophils David Price: 9.23-9.35am Blood Eosinophilia in COPD The reliability and utility of blood eosinophils as a marker of disease burden, healthcare resource utilisation
9/16/2014. Anti-Immunoglobulin E (IgE) Omalizumab (Xolair ) Dosing Guidance
 Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest New Therapies for Asthma Including Omalizumab and Anti-Cytokine Therapies Marsha Dangler, PharmD, BCACP Clinical Pharmacy Specialist James H. Quillen VA Medical
Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest New Therapies for Asthma Including Omalizumab and Anti-Cytokine Therapies Marsha Dangler, PharmD, BCACP Clinical Pharmacy Specialist James H. Quillen VA Medical
Before prescribing for COPD management, the patient should have had appropriate assessment, including spirometry, as per NICE guidelines.
 Formulary Guidance for Management of COPD patients Before prescribing for COPD management, the patient should have had appropriate assessment, including spirometry, as per NICE guidelines. For inhaler
Formulary Guidance for Management of COPD patients Before prescribing for COPD management, the patient should have had appropriate assessment, including spirometry, as per NICE guidelines. For inhaler
Asthma COPD and Asthma - COPD Overlap Syndrome (ACOS)
 Diagnosis of Diseases of Chronic Airflow Limitation: Asthma COPD and Asthma - COPD Overlap Syndrome (ACOS) Based on the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention and the Global Strategy for
Diagnosis of Diseases of Chronic Airflow Limitation: Asthma COPD and Asthma - COPD Overlap Syndrome (ACOS) Based on the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention and the Global Strategy for
is working on is about nutrition, specifically as it pertains to Alpha- continued on page 2
 Alpha-1 Canada Update May 2010 It has been very busy here over the last few months. Well it always seems to be busy, but lately exceptionally so. As this newsletter goes to press we are only days away
Alpha-1 Canada Update May 2010 It has been very busy here over the last few months. Well it always seems to be busy, but lately exceptionally so. As this newsletter goes to press we are only days away
AECOPD: Management and Prevention
 AECOPD: Management and Prevention Neil MacIntyre MD Duke University Medical Center Durham NC AECOPD: Management and Prevention AECOPD: Definitions and impact Acute management of AECOPD Preventing AECOPD.
AECOPD: Management and Prevention Neil MacIntyre MD Duke University Medical Center Durham NC AECOPD: Management and Prevention AECOPD: Definitions and impact Acute management of AECOPD Preventing AECOPD.
RESPIRATORY VENTILATION Page 1
 Page 1 VENTILATION PARAMETERS A. Lung Volumes 1. Basic volumes: elements a. Tidal Volume (V T, TV): volume of gas exchanged each breath; can change as ventilation pattern changes b. Inspiratory Reserve
Page 1 VENTILATION PARAMETERS A. Lung Volumes 1. Basic volumes: elements a. Tidal Volume (V T, TV): volume of gas exchanged each breath; can change as ventilation pattern changes b. Inspiratory Reserve
COPD. Information brochure for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
 COPD Information brochure for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. CONTENTS What does COPD mean?...04 What are the symptoms of COPD?...06 What causes COPD?...09 Treating COPD...10 Valve therapy in COPD...12
COPD Information brochure for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. CONTENTS What does COPD mean?...04 What are the symptoms of COPD?...06 What causes COPD?...09 Treating COPD...10 Valve therapy in COPD...12
Clinical guideline Published: 23 June 2010 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg101
 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in over 16s: diagnosis and management Clinical guideline Published: 23 June 2010 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg101 NICE 2010. All rights reserved. Your responsibility The
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in over 16s: diagnosis and management Clinical guideline Published: 23 June 2010 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg101 NICE 2010. All rights reserved. Your responsibility The
Asthma (With a little SCID to start) Disclosures Outline Starting with the Immune System The Innate Immune System The Adaptive Immune System
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Asthma (With a little SCID to start) Lauren Smith, MD CHKD Pediatric Allergy/Immunology Disclosures None Will be discussing some medications that are not yet FDA approved Outline SCID
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Asthma (With a little SCID to start) Lauren Smith, MD CHKD Pediatric Allergy/Immunology Disclosures None Will be discussing some medications that are not yet FDA approved Outline SCID
PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS A Workshop on Simple Spirometry & Flow Volume Loops
 PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS A Workshop on Simple Spirometry & Flow Volume Loops YOU SHOULD READ THE FOLLOWING MATERIAL BEFORE Tuesday March 30 Interpretation of PFTs Learning Objectives 1. Specify the indications
PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS A Workshop on Simple Spirometry & Flow Volume Loops YOU SHOULD READ THE FOLLOWING MATERIAL BEFORE Tuesday March 30 Interpretation of PFTs Learning Objectives 1. Specify the indications
This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data.
 abcd Clinical Study for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis which is part of the clinical
abcd Clinical Study for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis which is part of the clinical
Hospital-at-Home Programs for Patients With Acute Exacerbations of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): An Evidence-Based Analysis
 Hospital-at-Home Programs for Patients With Acute Exacerbations of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): An Evidence-Based Analysis BR McCurdy March 2012 Ontario Health Technology Assessment Series;
Hospital-at-Home Programs for Patients With Acute Exacerbations of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): An Evidence-Based Analysis BR McCurdy March 2012 Ontario Health Technology Assessment Series;
Medications for Managing COPD in Hospice Patients. Jim Joyner, PharmD, CGP Director of Clinical Operations Outcome Resources
 Medications for Managing COPD in Hospice Patients Jim Joyner, PharmD, CGP Director of Clinical Operations Outcome Resources Goal of medications in COPD Decrease symptoms and/or complications Reduce frequency
Medications for Managing COPD in Hospice Patients Jim Joyner, PharmD, CGP Director of Clinical Operations Outcome Resources Goal of medications in COPD Decrease symptoms and/or complications Reduce frequency
COPD Prescribing Guidelines
 South Staffordshire Area Prescribing Group COPD Prescribing Guidelines Inhaler choices in this guideline are different from previous versions produced by the APG. It is not expected patients controlled
South Staffordshire Area Prescribing Group COPD Prescribing Guidelines Inhaler choices in this guideline are different from previous versions produced by the APG. It is not expected patients controlled
Management of Asthma
 Federal Bureau of Prisons Clinical Practice Guidelines May 2013 Clinical guidelines are made available to the public for informational purposes only. The Federal Bureau of Prisons (BOP) does not warrant
Federal Bureau of Prisons Clinical Practice Guidelines May 2013 Clinical guidelines are made available to the public for informational purposes only. The Federal Bureau of Prisons (BOP) does not warrant
Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
 Page 1 of 67 AJRCCM Articles in Press. Published on August 9, 2012 as doi:10.1164/rccm.201204-0596pp GOLD Executive Summary Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive
Page 1 of 67 AJRCCM Articles in Press. Published on August 9, 2012 as doi:10.1164/rccm.201204-0596pp GOLD Executive Summary Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive
AECOPD. Guideline for. The Management of Acute Exacerbations of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (AECOPD) 2006 Update
 Guideline for Administered by the Alberta Medical Association 2006 Update The Management of Acute Exacerbations of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (AECOPD) AECOPD This clinical practice guideline
Guideline for Administered by the Alberta Medical Association 2006 Update The Management of Acute Exacerbations of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (AECOPD) AECOPD This clinical practice guideline
Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease
 Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease POCKET GUIDE TO COPD DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT, AND PREVENTION A Guide for Health Care Professionals REVISED 2011 Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive
Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease POCKET GUIDE TO COPD DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT, AND PREVENTION A Guide for Health Care Professionals REVISED 2011 Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive
IN-HOME QUALITY IMPROVEMENT. BEST PRACTICE: DISEASE MANAGEMENT Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease NURSE TRACK
 IN-HOME QUALITY IMPROVEMENT BEST PRACTICE: DISEASE MANAGEMENT Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease NURSE TRACK Best Practice Intervention Packages were designed for use by any In-Home Provider Agency
IN-HOME QUALITY IMPROVEMENT BEST PRACTICE: DISEASE MANAGEMENT Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease NURSE TRACK Best Practice Intervention Packages were designed for use by any In-Home Provider Agency
Guideline on the clinical investigation of medicinal products for the treatment of asthma
 22 October 2015 CHMP/EWP/2922/01 Rev.1 Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) Guideline on the clinical investigation of medicinal products for the treatment of Draft Agreed by Respiratory
22 October 2015 CHMP/EWP/2922/01 Rev.1 Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) Guideline on the clinical investigation of medicinal products for the treatment of Draft Agreed by Respiratory
DRUG UTILISATION STUDY IN BRONCHIAL ASTHMA IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL
 International Journal of Pharmaceutical Applications ISSN 0976-2639, Online ISSN 2278 6023 Vol 3, Issue 2, 2012, pp 297-305 http://www.bipublication.com DRUG UTILISATION STUDY IN BRONCHIAL ASTHMA IN A
International Journal of Pharmaceutical Applications ISSN 0976-2639, Online ISSN 2278 6023 Vol 3, Issue 2, 2012, pp 297-305 http://www.bipublication.com DRUG UTILISATION STUDY IN BRONCHIAL ASTHMA IN A
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 12 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Anna Murphy Case study and questions Day 1 Mr LT, a 68-year-old man, attended his general practitioner s (GP s) surgery for a routine check-up. He had been diagnosed
12 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Anna Murphy Case study and questions Day 1 Mr LT, a 68-year-old man, attended his general practitioner s (GP s) surgery for a routine check-up. He had been diagnosed
Understanding Pulmonary Function Testing. PFTs, Blood Gases and Oximetry Skinny Little Reference Guide
 Understanding Pulmonary Function Testing PFTs, Blood Gases and Oximetry Skinny Little Reference Guide INTRODUCTION This brochure is intended to help you understand the meaning of Pulmonary Function Testing,
Understanding Pulmonary Function Testing PFTs, Blood Gases and Oximetry Skinny Little Reference Guide INTRODUCTION This brochure is intended to help you understand the meaning of Pulmonary Function Testing,
5. Treatment of Asthma in Children
 Treatment of sthma in hildren 5. Treatment of sthma in hildren 5.1 Maintenance Treatment 5.1.1 rugs Inhaled Glucocorticoids. Persistent wheezing in children under the age of three can be controlled with
Treatment of sthma in hildren 5. Treatment of sthma in hildren 5.1 Maintenance Treatment 5.1.1 rugs Inhaled Glucocorticoids. Persistent wheezing in children under the age of three can be controlled with
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency
 Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_alpha_1_antitrypsin_deficiency 5/2012
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_alpha_1_antitrypsin_deficiency 5/2012
Pulmonary Rehabilitation in Newark and Sherwood
 Pulmonary Rehabilitation in Newark and Sherwood With exception of smoking cessation pulmonary rehabilitation is the single most effective intervention for any patient with COPD. A Cochrane review published
Pulmonary Rehabilitation in Newark and Sherwood With exception of smoking cessation pulmonary rehabilitation is the single most effective intervention for any patient with COPD. A Cochrane review published
COPD MANAGEMENT PROTOCOL STANFORD COORDINATED CARE
 I. PURPOSE To establish guidelines f the collabative management of patients with a diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) who are not adequately controlled and to define the roles and
I. PURPOSE To establish guidelines f the collabative management of patients with a diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) who are not adequately controlled and to define the roles and
COPD Intervention. Components:
 COPD Intervention 1. Primary disease education Member will have an increased understanding of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, the causes, risks and complications. Explain COPD Explain how COPD is
COPD Intervention 1. Primary disease education Member will have an increased understanding of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, the causes, risks and complications. Explain COPD Explain how COPD is
Asthma in Infancy, Childhood and Adolescence. Presented by Frederick Lloyd, MD Palo Alto Medical Foundation Palo Alto, California
 Asthma in Infancy, Childhood and Adolescence Presented by Frederick Lloyd, MD Palo Alto Medical Foundation Palo Alto, California Major Health Problem in Childhood Afflicts 2.7 million children in the USA
Asthma in Infancy, Childhood and Adolescence Presented by Frederick Lloyd, MD Palo Alto Medical Foundation Palo Alto, California Major Health Problem in Childhood Afflicts 2.7 million children in the USA
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
 COPD Guideline Team Team Leader Davoren A Chick, MD General Medicine Team Members Paul J Grant, MD General Medicine Meilan K Han, MD, MS Pulmonary Medicine R Van Harrison, PhD Medical Education Elisa B
COPD Guideline Team Team Leader Davoren A Chick, MD General Medicine Team Members Paul J Grant, MD General Medicine Meilan K Han, MD, MS Pulmonary Medicine R Van Harrison, PhD Medical Education Elisa B
COPD. (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) (Emphysema) (Chronic Bronchitis) Education For Our Community
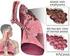 COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) (Emphysema) (Chronic Bronchitis) Education For Our Community Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Definition Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) (Emphysema) (Chronic Bronchitis) Education For Our Community Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Definition Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
1 ALPHA-1. What is Alpha-1? A family history... of lung disease? of liver disease? FOUNDATION
 What is Alpha-1? A family history... of lung disease? of liver disease? What you need to know about Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency 1 ALPHA-1 FOUNDATION What is Alpha-1? Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (Alpha-1)
What is Alpha-1? A family history... of lung disease? of liver disease? What you need to know about Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency 1 ALPHA-1 FOUNDATION What is Alpha-1? Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (Alpha-1)
NEWS NP S. Inside. Defining COPD. Is it COPD? National Prescribing Service Newsletter
 NP S NEWS National Prescribing Service Newsletter 5 1999 ISSN 1441-7421 Aug 99 Inside Bronchodilators and corticosteroids: Their use in COPD Give it up the best advice for COPD patients: NRT can help This
NP S NEWS National Prescribing Service Newsletter 5 1999 ISSN 1441-7421 Aug 99 Inside Bronchodilators and corticosteroids: Their use in COPD Give it up the best advice for COPD patients: NRT can help This
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) Research
 Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF): Why Early Referral is Critical Even if Your Patient is Not Eligible for a Clinical Trial Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) Research Management of IPF requires a confident
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF): Why Early Referral is Critical Even if Your Patient is Not Eligible for a Clinical Trial Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) Research Management of IPF requires a confident
Pulmonary Hypertension in Sickle Cell Disease. Jorge Ramos Hematology Fellows Conference June 28, 2013
 Pulmonary Hypertension in Sickle Cell Disease Jorge Ramos Hematology Fellows Conference June 28, 2013 Patient Presentation 28F with SCD, genotype SS. Presented to UWMC ER with 1 month progressive DOE and
Pulmonary Hypertension in Sickle Cell Disease Jorge Ramos Hematology Fellows Conference June 28, 2013 Patient Presentation 28F with SCD, genotype SS. Presented to UWMC ER with 1 month progressive DOE and
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
 Page 1 of 10 View this article online at: patient.info/health/chronic-obstructive-pulmonary-disease-leaflet Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is an umbrella
Page 1 of 10 View this article online at: patient.info/health/chronic-obstructive-pulmonary-disease-leaflet Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is an umbrella
Guideline on clinical investigation of medicinal products in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
 21 June 2012 EMA/CHMP/483572/2012 -corr 1 Respiratory Drafting Group Guideline on clinical investigation of medicinal products in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Draft Agreed
21 June 2012 EMA/CHMP/483572/2012 -corr 1 Respiratory Drafting Group Guideline on clinical investigation of medicinal products in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Draft Agreed
Emphysema. Introduction Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD. COPD affects about 64 million people worldwide.
 Emphysema Introduction Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD. COPD affects about 64 million people worldwide. Emphysema involves damage to the air sacs in the lungs. This
Emphysema Introduction Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD. COPD affects about 64 million people worldwide. Emphysema involves damage to the air sacs in the lungs. This
inability to take a deep breath)
 Algorithm for the diagnosis and management of asthma: a practice parameter update These parameters were developed by the Joint Task Force on Practice Parameters, representing the American Academy of Allergy,
Algorithm for the diagnosis and management of asthma: a practice parameter update These parameters were developed by the Joint Task Force on Practice Parameters, representing the American Academy of Allergy,
Inpatient Strategies. Hataya Kristy Poonyagariyagorn, MD Oregon Pulmonary Associates
 Inpatient Strategies Hataya Kristy Poonyagariyagorn, MD Oregon Pulmonary Associates Medical Director Intensive Care Unit and Respiratory Therapy Department Providence Newberg Medical Center Associate Program
Inpatient Strategies Hataya Kristy Poonyagariyagorn, MD Oregon Pulmonary Associates Medical Director Intensive Care Unit and Respiratory Therapy Department Providence Newberg Medical Center Associate Program
Asthma. Micah Long, MD
 Asthma Micah Long, MD Goals Define the two components of asthma. Describe the method of action and uses for: Steroids (inhaled and IV) Quick Beta Agonists (Nebs and MDIs) The "Others" Magnesium, Epi IM,
Asthma Micah Long, MD Goals Define the two components of asthma. Describe the method of action and uses for: Steroids (inhaled and IV) Quick Beta Agonists (Nebs and MDIs) The "Others" Magnesium, Epi IM,
Renovascular Hypertension
 Renovascular Hypertension Philip Stockwell, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine (Clinical) Warren Alpert School of Medicine Cardiology for the Primary Care Provider September 28, 201 Renovascular Hypertension
Renovascular Hypertension Philip Stockwell, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine (Clinical) Warren Alpert School of Medicine Cardiology for the Primary Care Provider September 28, 201 Renovascular Hypertension
