RPW Shockwave Therapy Clinical Guide
|
|
|
- Jonas Porter
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RPW Shockwave Therapy Clinical Guide
2 1
3 2 Clinical Guide Chattanooga RPW Dear customer! In your hands you have the Clinical Guide for the Chattanooga line of Radial Pressure Wave units. This practical guide provides specific information on the scientific background, methodology and applications of radial pressure wave therapy, it also includes treatment protocols for every program offered by our RPW devices. In this guide, you will find the most common indications that can be treated with the Chattanooga RPW devices, with images showing the hand piece placement as well as advice for treatment dosage and information regarding the different applications. The information is easy to read with the purpose of providing extra support in your daily work to help you achieve optimal treatment outcomes for your patients. RPW Introduction
4 3 Chattanooga & DJO Global Chattanooga is the world s largest manufacturer of rehabilitation equipment for treating musculoskeletal, neurological and soft tissue disorders. For over six decades, Chattanooga has set a benchmark for leadership, reliability and excellence. Our products contribute to better treatment outcomes in hospitals, clinics and home settings worldwide. We lead the physiotherapy industry by example and, through continuous innovation, provide real world solutions for clinicians and their patients. As the world s leading brand in rehabilitation, Chattanooga is sold in over 80 countries worldwide. Chattanooga is directly represented in our key markets but also has long lasting relationships with dedicated distributors in the USA, Canada, Latin America, EMEA and Asia Pacific. Our Chattanooga distributors and customers are supported for order placement, training, product delivery and after sales service by a dedicated team of highly skilled DJO employees based all over the world. Chattanooga is a brand of DJO Global Inc. DJO Global provides solutions for musculoskeletal health, vascular health and pain management. Our products help prevent injuries or rehabilitate after surgery, injury or from degenerative disease, enabling patients to regain or maintain their natural motion. Visit
5 4 Table of Contents Chapter Content Page Chapter Content Page RPW Introduction Background 10 Physical Effects of Shockwaves 12 Indications 13 Contraindications / Side Effects 14 How to Perform an RPW 15 General Muscle Activation / Coupling 16 / Ramp Functionality 17 Preset Program Levels / Transmitters 18 Transmitter Chart 19 V-ACTOR / Scientific Background 20 Foot Plantar Fasciitis with Heel Spur - Muscular Plantar Fasciitis with Heel Spur I 24 Plantar Fasciitis with Heel Spur II Foot (Cont.) Lower Leg & Ankle Plantar Fasciitis without Heel Spur - Muscular Plantar Fasciitis without Heel Spur I 27 Plantar Fasciitis without Heel Spur II 28 Achillodynia - Muscular 31 Achillodynia I 32 Achillodynia II 33 Shin Splint - Muscular 34 Shin Splint I 35 Shin Splint II 36 Massage, Vibration * 37 General Muscle Sprain, Calf Muscles 38 Muscular Cramps/Spasm, Calf Muscles 39 Trigger Point Therapy *Not offered on Mobile RPW RPW Introduction
6 5 Table of Contents Chapter Content Page Thigh & Knee Jumpers Knee - Muscular 43 Jumpers Knee I 44 Jumpers Knee II 45 Runners Knee - Muscular 46 Runners Knee I 47 Runners Knee II 48 Massage, Vibration 49 General Muscle Sprain, Thigh Muscles 50 Trigger Point Therapy 51 Pelvis & Hip Trochanteric Insertional Tendonitis - Muscular 54 Trochanteric Insertional Tendonitis I 55 Trochanteric Insertional Tendonitis II 56 Bursitis - Muscular 57 Chapter Content Page Pelvis & Hip (Cont.) Piriformis Syndrome - Muscular 58 Massage, Vibration 59 Cellulite 60 Trigger Point Therapy 62 Lower Back Lower Back - Muscular 65 Lower Back I 66 Lower Back II 67 Massage, Vibration * 68 Lumbalgia - Activation of Muscles and Connective Tissue Trigger Point Therapy 70 Upper Back Thoracic Back Pain - Muscular 73 Thoracic Back Pain I 74 Thoracic Back Pain II 75 Massage, Vibration *Not offered on Mobile RPW
7 6 Table of Contents Chapter Content Page Upper Back (Cont.) Dorsalgia - Activation of Muscles and Connective Tissue Trigger Point Therapy 78 Neck Cervicobrachial Neuralgia - Muscular 81 Cervicobrachial Neuralgia I 82 Cervicobrachial Neuralgia II 83 Massage, Vibration * 84 Trapezius Tension - Muscular 85 Tension Headache - Muscular 86 Trigger Point Therapy 87 Shoulder Calcified Tendonitis Shoulder - Muscular Calcified Tendonitis Shoulder I 91 Calcified Tendonitis Shoulder II 92 Shoulder Pain - Muscular Chapter Content Page Shoulder (Cont.) Shoulder Pain I 94 Upper Arm & Elbow Shoulder Pain II 95 Frozen Shoulder - Muscular 96 Frozen Shoulder I 97 Frozen Shoulder II 98 Massage, Vibration 99 Bursitis - Muscular 100 Trigger Point Therapy 101 Ulnar / Medial Epicondylitis (Golfer's Elbow) - Muscular 104 Ulnar / Medial Epicondylitis (Golfer's Elbow) I 105 Ulnar / Medial Epicondylitis (Golfer's Elbow) II 106 Radial / Lateral Epicondylitis (Tennis Elbow) - Muscular 107 Radial / Lateral Epicondylitis (Tennis Elbow) I 108 *Not offered on Mobile RPW RPW Introduction
8 7 Table of Contents Chapter Content Page Upper Arm & Elbow (Cont.) Radial / Lateral Epicondylitis (Tennis Elbow) II 109 Massage, Vibration * 110 Trigger Point Therapy 111 Forearm, Wrist & Hand Finger Tendonitis - Muscular 114 Finger Tendonitis I 115 Finger Tendonitis II 116 Dupuytren s Contracture 117 Dupuytren's Contracture - Muscular 118 De Quervain Syndrome 119 De Quervain Syndrome - Muscular 120 *Not offered on Mobile RPW
9 RPW Introduction 8 RPW Introduction
10 9 RPW Introduction Background... Physical Effects of Shockwaves... Indications... Contraindications / Side Effects... How to Perform an RPW... General Muscle Activation / Coupling... / Ramp Functionality*... Preset Program Levels* / Transmitters... Transmitter Chart... V-ACTOR * / Scientific Background *Not offered on Mobile RPW
11 PRESSURE PRESSURE 10 Background Therapeutic shockwaves were introduced as a medical treatment for eliminating kidney stones 20 years ago. One of the side effects discovered during treatment, was the effect on bone healing (bone density increase), as well as accelerated tissue healing in the area. In nature, shockwaves are caused by a high energy wave. This wave has an extremely short build up time and high amplitude, similar to an explosion. When we talk about shockwave treatment there are basically two different methods: FOCUSED SHW (Electromagnetic) RADIAL PW (Kinetic->accoustic) - Focused Shockwave: Can be Electromagnetically generated, high energy, deep penetration, and precise focus on a very small area. - Radial Shockwave: Radial shockwaves are often referred to as TIME TIME Radial Pressure Waves (RPW). In physical terms this is the correct definition. RPW Introduction
12 11 Radial Pressure Waves Radial pressure waves are pulses generated by compressed air. The compressed air is used to drive a projectile in a cylinder, located inside the hand piece, to a shock transmitter. The kinetic energy generated by the motion and weight of the projectile, converts into acoustic energy when the projectile hits the shock transmitter. The acoustic pulses then spread into the underlying tissue, treating a larger area than the focused shockwave shown on the previous page. The highest energy level of the pressure waves will be at the tip of the transmitter (max 0, 63 mj/mm² at 5 Bar) right on the skin over the treatment point and 4 Bar on the Mobile RPW. The energy level will then gradually decrease as the penetration depth increases. The penetration depths are normally 0-6 cm (0-2.3 ). Apart from providing focused shockwaves, a treatment with radial pressure waves needs no additional pre examinations or treatments such as ultrasound imaging, local anesthesia, MRT or X-ray. With a correct handling, RPW is an excellent non invasive treatment method with very few negative side effects, for indications that normally are very difficult to treat. For these indications we now know that radial pressure waves is a treatment method that reduces pain as well as improves function and quality of life.
13 12 Physical Effects of Shockwaves Radial pressure waves offer a non invasive treatment solution to long term insertion and soft tissue pathologies. Local treatment in the affected area will support and reset the healing pattern. Today there are several working hypothesis for the physical effects of radial pressure waves: Pain reduction: The patient experiences a reduction of pain, explained by the Gate Control Theory. Intensive pulses from the transmitter into the tissues create a strong nociceptor activation of the A-β fibers, which affect interneurons that inhibit the transmission of the pain signals. Increased metabolism: Shockwaves influence the tissues on a cellular level. The chemical environment of the cells is affected by free radicals promoting the release of pain and inflammatory inhibiting substances. Revascularization: Repeated shockwaves to the affected area create a revascularization effect, with the new blood flow in the area promoting tissue healing and regeneration. Reduced muscle tone: The vicious circle, as well as the strong pathological association between pain and muscle tone, will be broken and lead to restoring a normalized muscular tone. RPW Introduction
14 13 Indications In the Intelect RPW, you will find preset programs for several indications. The majority of the treatment programs are for what we commonly refer to as insertional tendinopathies. Soft/connective tissue/muscles with trigger points or / and increased tension are also targets for treatment. In many cases shockwave treatment gives excellent results in order to dissolve calcifications. Example of indications for the preset programs*: Plantar fasciitis Achillodynia Shin splint Muscle sprain Jumpers knee Runners knee Trigger point therapy Trochanteric insertion tendonitis Piriformis syndrome Low back/thoracic pain Calcified shoulder tendonitis Frozen Shoulder Cervicobrachial neuralgia Trapezius tension Radial/medial epicondylitis Finger tendonitis Muscular cramps/spasm Cellulite treatment Massage, vibration therapy *Not offered on Mobile RPW
15 14 Contraindications / Side Effects Contraindications NOTE: Read the full list of contraindications, precautions and the safety instructions in the Chattanooga RPW User Manual prior to treatment! Before a treatment with radial pressure wave, a correct examination and diagnosis should be performed. A correct diagnosis is the best way to ensure an optimal effect of the treatment. Please make sure that you are aware of the latest developments and medical publications on Radial Pressure Wave therapy for details on contraindications and side effects not known at the time of manufacturing. Side Effects Side effects could occur after treatment with radial pressure wave therapy. Side effects - if any - usually appear within 2 days of the treatment having been performed, they usually fade and disappear after 3-5 days. Do not repeat a treatment if previous side effects have not diminished. The most common side effects include: reddening, swelling, pain, worsening conditions, hematoma and petechiae (red spots). RPW Introduction
16 15 How to Perform a Radial Pressure Wave RPW treatment, given in the right dose and for the correct indications, is an excellent treatment for many chronic conditions that other treatment methods can t improve or heal. Radial pressure therapy is very well perceived among therapists thanks to its positive outcomes and its relatively short treatment period. Let your patient rest in a relaxing position during a treatment session. Localise the painful points you plan to treat. Sometimes it s a good idea to mark up the points with a felt tip pen. Apply gel on the skin of the treatment area. A treatment with radial pressure waves requires a hand piece with a transmitter tip especially designed for the treatment (read more about the transmitters below). Point the hand piece on the painful area or on the surrounding muscles. Warn the patient about the sound the projectile makes when hitting the transmitter during the treatment. The painful spots are localised by palpation following the patient s indications. Radial pressure wave therapy is a powerful treatment and it can be perceived very differently from patient to patient. It is important to observe, communicate and keep in close contact with the patient throughout the treatment.
17 16 General Muscle Activation / Coupling General Muscle Activation There are two different ways in which to start a treatment. The important thing to take into account is that both pain point stimulation and muscle activation/muscular treatment/vibration treatment are included in a full treatment. If you prefer to use a preset program you will find these programs under Muscular or Vibration in the Intelect RPW*. Some therapists find it most convenient to start up with activation and smoothing of the surrounding muscles and connective tissue to get the muscles relaxed before treating the painful points. More commonly, some therapists start with the painful points in order to eliminate the pain radiating from the spots, and then finalize the treatment by activation and smoothing of the surrounding muscles. Coupling To ensure efficiency and optimal effect of the treatment, make sure that there is a good contact between the transmitter and the patient s skin. Always apply a sufficient amount of gel on the treatment area, and be sure that the transmitter surface is in contact with the skin, throughout the treatment. NOTE: If you prefer to use the CERAma-x R-15 transmitter, the unique feature of this transmitter allows you to work without any gel as coupling. CERAma-x is equal to the R-15 (regular) transmitter, and can replace it in the preset programs. *Not offered on Mobile RPW RPW Introduction
18 BAR 17 / Ramp Functionality Depending on the indication, a total of 3-6 sessions with 5-10 days interval, is the most common treatment frequency. Initial success of the treatment can generally be evaluated after 3-4 sessions, but additional improvement can be seen within 2 weeks and up to 3 months after the treatment period is completed. NO RAMP RAMP ON RAMP ON BUT STOP 3 BAR Ramp Functionality* The Intelect RPW has a unique system for increasing the intensity gradually during a treatment session. Instead of starting treatment on a low level, you can manually interrupt the treatment and readjust the intensity (Bar), the ramp on functionality allows you to have an automatic and smooth increase in intensity in tune with your patient. If you prefer to stop the stimulation due to the intensity, just turn off the hand piece. Then, you can choose if you want to go on at the same intensity level, or continue ramping up. *Not offered on Mobile RPW TREATMENT 2000 PULSES The ramp allows a smooth intensity increase, and if the treatment is stopped before the full ramp up, you have the choice of continuing ramping up or of using the new lower intensity level.
19 18 Preset Program Levels / Transmitters Preset Program Levels Many of the preset programs you ll find in the Intelect RPW are available in level I and II. The first level is a lighter version recommended if the patient is very sensitive or the injury fairly recent. Level II of the programs can be used for patients with a higher tolerance, later on in the treatment process or for patients with a longer lasting, more chronic disorder. The preset programs are not available on the Mobile RPW. Transmitters The hand pieces can be used with a variety of transmitters, all exclusive and especially developed for optimal results. Each transmitter has its own characteristic effect and area of use. In the software of the Intelect RPW you will find specific information for each transmitter. The majority of the transmitters generate the shockwaves (R 15, DI 15, F 15, Cera 15). The D-transmitters (D 20 and D 35) generate a combination of shockwaves and vibrations, and the V-transmitters* (V 25 and V 40) generate vibrations only. Always use a sufficient amount of gel on the treatment area in order to ensure contact between the skin and the transmitter throughout the treatment session. Depending on the size of the treatment area and the pressure you want to keep to the tissue, there are different ways of holding the hand piece (ex: one or two hands). Please see the hand piece placement images for the preset programs. During treatment, keep contact with the tissue and move the hand piece with small circular movements. *Not offered on Mobile RPW RPW Introduction
20 19 Transmitters Transmitter Data Indications Energy Flux Density/ Penetration Depth Transmitter Data Indications Energy Flux Density/ Penetration Depth C 15, 15 mm, CERAma-x ESWT Transmitter, Elastic pressure waves R 15, 15 mm, EWST Transmitter, Radial spreading D 20-S, 20 mm, D-ACTOR Transmitter, Radial pressure waves and vibration pulses Gel free, elastic pressure wave therapy for all tendinopathies Radial pressure wave therapy, all tendinopathies Myofascial trigger therapy, muscle and connective tissue, dissolution of fibrosis, treatment of deep-seated muscles 0.45 mj/mm mm 0.38 mj/mm mm 0.48 mj/mm mm D 35, 35 mm, D-ACTOR Transmitter, Radial pressure waves and vibration pulses DI 15, 15 mm, Deep Impact Transmitter, Energy focused beam F 15, 15 mm, Focus-Lens Transmitter, Energy focused area Myofascial trigger therapy, muscle and connective tissue back muscles, skin elasticity, trigger-diagnosis, dissolution of fibrosis, treatment of deep-seated muscles Deep-seated diseases, trigger, chronic diseases, high energy requirements Close to surface pain areas, facial muscles, neck, head, individual triggers 0.46 mj/mm mm 0.63 mj/mm mm 0.16 mj/mm mm
21 20 V-ACTOR / Scientific Background V-ACTOR * The V-ACTOR hand piece is used as a complement to the radial shockwave therapy. The V-ACTOR hand piece is an optional accessory and the kit includes two different sizes of transmitters (V-25 and V-40), which allow soft tissue treatment with high frequency vibrations. With the V-ACTOR hand piece and V-transmitters only vibrations are generated. It is ideally suited to reduce muscular strain and increase local blood circulation. Scientific Background Radial shockwave therapy is a modality which is successfully used by doctors, practitioners and physiotherapists in both sport medicine and rehabilitation. Radial shockwave therapy has recently been the subject of clinical evidence in several medical papers. The research is progressing continuously with a steadily increasing volume of publications. For references regarding radial shockwave therapy, please visit our research library: and complete your DJO registration. *Not offered on Mobile RPW RPW Introduction
22 21 Foot
23 22 Foot Plantar Fasciitis with Heel Spur - Muscular... Plantar Fasciitis with Heel Spur I... Plantar Fasciitis with Heel Spur II... Plantar Fasciitis without Heel Spur - Muscular... Plantar Fasciitis without Heel Spur I... Plantar Fasciitis without Heel Spur II Foot
24 23 Plantar Fasciitis with Heel Spur Muscular Intensity Plantar fasciitis is a painful disorder due to inflammatory/degenerative process of the fascia originating on the calcaneus. The heel spur is a bony calcification on the calcaneus, which can be an incidental finding associated with plantar fasciitis. Overpronators, high weight bearers and people with tight calf muscles are often affected by this indication. General activation and smoothing of surrounding muscles and connective tissue in order to get a muscular relaxation. Calf muscles, Gastrocnemius, Soleus and Intrinsic muscles of the foot sole. Apply over muscles and soft tissue, the treatment may feel uncomfortable in bony areas. 3-6 treatments with 5-10 days interval. Combine this treatment with a RPW treatment of the painful points. 2,0 Bar - 3,0 Bar Pulses 2000 Frequency 15 Hz / 14Hz Mobile RPW Transmitter D mj/mm mm
25 24 Plantar Fasciitis with Heel Spur I Plantar fasciitis is a painful disorder due to inflammatory/degenerative process of the fascia originating on the calcaneus. The heel spur is a bony calcification on the calcaneus, which can be an incidental finding associated with plantar fasciitis. Overpronators, high weight bearers and people with tight calf muscles are often affected by this indication. Work with the applicator on the pain points with very small circular movements. Localise the painful points on the foot sole. 3-6 treatments with 5-10 days interval. Combine this treatment with a general activation of surrounding muscles. Alternative 1 Alternative 2 Intensity 1,6 Bar - 3,2 Bar 1,8 Bar - 3,5 Bar Pulses Frequency 10 Hz 15 Hz / 10 Hz Mobile RPW Transmittert DI 15 R mj/mm mj/mm mm 0-40 mm Foot
26 25 Plantar Fasciitis with Heel Spur II Plantar fasciitis is a painful disorder due to inflammatory/degenerative process of the fascia originating on the calcaneus. The heel spur is a bony calcification on the calcaneus, which can be an incidental finding associated with plantar fasciitis. Overpronators, high weight bearers and people with tight calf muscles are often affected by this indication. Work with the applicator on the pain points with very small circular movements. Localise the painful points on the foot sole. 3-6 treatments with 5-10 days interval. Combine this treatment with a general activation of surrounding muscles. Alternative 1 Alternative 2 Intensity 1,8 Bar - 4,0 Bar 2,0 Bar - 4,5 Bar Pulses Frequency 10 Hz / 8 Hz Mobile RPW 15 Hz / This protocol not available on Mobile RPW Transmitter DI 15 R mj/mm mj/mm mm 0-40 mm
27 26 Plantar Fasciitis without Heel Spur Muscular Intensity Plantar fasciitis is a painful disorder due to inflammatory/degenerative process of the fascia originating on the calcaneus. Overpronators, high weight bearers and people with tight calf muscles are often affected by this indication. General activation and smoothing of surrounding muscles and connective tissue in order to get a muscular relaxation. Calf muscles, Gastrocnemius, Soleus and Intrinsic muscles of the foot sole. Apply over muscles and soft tissue, the treatment may feel uncomfortable in bony areas. 3-6 treatments with 5-10 days interval. Combine this treatment with a RPW treatment of the painful points. 2,0 Bar - 3,0 Bar Pulses 2000 Frequency 15 Hz / 14 Hz Mobile RPW Transmitter D mj/mm mm Foot
28 27 Plantar Fasciitis without Heel Spur I Plantar fasciitis is a painful disorder due to inflammatory/degenerative process of the fascia originating on the calcaneus. Overpronators, high weight bearers and people with tight calf muscles are often affected by this indication. Work with the applicator on the pain points with very small circular movements. Localise the painful points on the foot sole. 3-6 treatments with 5-10 days interval. Combine this treatment with a general activation of surrounding muscles. Alternative 1 Alternative 2 Intensity 1,8 Bar - 2,8 Bar 1,6 Bar - 3,2 Bar Pulses Frequency 15 Hz / 14 Hz mobile RPW 10 Hz / 12 Hz Mobile RPW Transmitter R 15 DI mj/mm mj/mm mm 0-60 mm
29 28 Plantar Fasciitis without Heel Spur II Plantar fasciitis is a painful disorder due to inflammatory/degenerative process of the fascia originating on the calcaneus. Overpronators, high weight bearers and people with tight calf muscles are often affected by this indication. Work with the applicator on the pain points with very small circular movements. Localise the painful points on the foot sole. 3-6 treatments with 5-10 days interval. Combine this treatment with a general activation of surrounding muscles. Alternative 1 Alternative 2 Intensity 2,0 Bar - 3,2 Bar 1,8 Bar - 4,0 Bar Pulses Frequency 15 Hz / 12 Hz Mobile RPW 10 Hz / 8 Hz Mobile RPW Transmitter R 15 DI mj/mm mj/mm mm 0-60 mm Foot
30 29 Lower Leg & Ankle
31 30 Lower Leg & Ankle Achillodynia - Muscular... Achillodynia I... Achillodynia II... Shin Splint - Muscular... Shin Splint I... Shin Splint II... Massage, Vibration... General Muscle Sprain, Calf Muscles... Muscular Cramps/Spasm, Calf Muscles... Trigger Point Therapy Lower Leg & Ankle
32 31 Achillodynia Muscular Intensity Chronic achillodynia is mostly due to either an injury of the tendon itself (tendinosis) or to an inflammatory process occurring inside the surrounding tissues (bursitis or peritendinitis). The condition can be either at the attachment point of the heel or in the mid-portion of the tendon (typically around 4 cm above the heel). Healing of the achilles tendon is often slow, due to its poor blood supply. General activation and smoothing of surrounding muscles and connective tissue in order to get a muscular relaxation. Calf muscles, Gastrocnemius, Soleus and Intrinsic muscles of the foot sole. Apply over muscles and soft tissue, the treatment may feel uncomfortable in bony areas. 3-6 treatments with 5-10 days interval. Combine this treatment with a RPW treatment of the painful points. 2,0 Bar - 3,0 Bar Pulses 2000 Frequency 15 Hz / 14 Hz Mobile RPW Transmitter D mj/mm mm
33 32 Achillodynia I Chronic achillodynia is mostly due to either an injury of the tendon itself (tendinosis) or to an inflammatory process occurring inside the surrounding tissues (bursitis or peritendinitis). The condition can be either at the attachment point of the heel or in the mid-portion of the tendon (typically around 4 cm above the heel). Healing of the achilles tendon is often slow, due to its poor blood supply. Work with the applicator on the pain points with very small circular movements. Localise the painful points on the tendon. Treat over the Achilles tendon in fiber direction but give the majority of the pulses from lateral or medial side of the tendon. 3-6 treatments with 5-10 days interval. Combine this treatment with a general activation of surrounding muscles. Alternative 1 Alternative 2 Intensity 1,6 Bar - 3,0 Bar 1,6 Bar - 2,8 Bar Pulses Frequency 10 Hz / 14 Hz Mobile RPW 15 Hz Transmitter DI 15 R mj/mm mj/mm mm 0-40 mm Lower Leg & Ankle
34 33 Achillodynia II Intensity Chronic achillodynia is mostly due to either an injury of the tendon itself (tendinosis) or to an inflammatory process occurring inside the surrounding tissues (bursitis or peritendinitis). The condition can be either at the attachment point of the heel or in the mid-portion of the tendon (typically around 4 cm above the heel). Healing of the achilles tendon is often slow, due to its poor blood supply. Work with the applicator on the pain points with very small circular movements. Localise the painful points on the tendon. Treat over the Achilles tendon in fiber direction but give the majority of the pulses from lateral or medial side of the tendon. 3-6 treatments with 5-10 days interval. Combine this treatment with a general activation of surrounding muscles. 1,6 Bar - 3,0 Bar Pulses 2000 Frequency 15 Hz / 14 Hz Mobile RPW Transmitter R mj/mm mm
35 34 Shin Splints Muscular Intensity Shin splints is simply the name given to pain over the front of the lower leg and can be caused by several conditions, most commonly a medial tibial stress syndrome, or an exercise induced compartment syndrome. A tibial stress syndrome is due to overuse and results in an irritation and inflammation in the tibial periost. Tight calf muscles are often associated with this condition. General activation and smoothing of surrounding muscles and connective tissue in order to get a muscular relaxation. Gastrocnemius, Soleus, Tibialis Anterior and Peroneal muscles. Apply over muscles and soft tissue, the treatment may feel uncomfortable in bony areas. 3-6 treatments with 5-10 days interval. Combine this treatment with a RPW treatment of the painful points. 2,0 Bar - 2,8 Bar Pulses 2000 Frequency 15 Hz Transmitter D mj/mm mm Lower Leg & Ankle
36 35 Shin Splints I Shin splints is simply the name given to pain over the front of the lower leg and can be caused by several conditions, most commonly a medial tibial stress syndrome, or an exercise induced compartment syndrome. A tibial stress syndrome is due to overuse and results in an irritation and inflammation in the tibial periost. Work with the applicator on the pain points with very small circular movements. Localise the most painful points and treat along both sides of the shin bone 3-6 treatments with 5-10 days interval. Combine this treatment with a general activation of surrounding muscles. Alternative 1 Alternative 2 Intensity 1,6 Bar - 2,8 Bar 1,6 Bar - 2,8 Bar Pulses Frequency 10 Hz 15 Hz Transmitter DI 15 R mj/mm mj/mm mm 0-40 mm
37 36 Shin Splints II Shin splints is simply the name given to pain over the front of the lower leg and can be caused by several conditions, most commonly a medial tibial stress syndrome, or an exercise induced compartment syndrome. A tibial stress syndrome is due to overuse and results in an irritation and inflammation in the tibial periost. Work with the applicator on the pain points with very small circular movements. Localise the most painful points and treat along both sides of the shin bone 3-6 treatments with 5-10 days interval. Combine this treatment with a general activation of surrounding muscles. Alternative 1 Alternative 2 Intensity 1,8 Bar - 3,0 Bar 1,8 Bar - 3,0 Bar Pulses Frequency 10 Hz / 14 Hz Mobile RPW 15 Hz Transmitter DI 15 R mj/mm mj/mm mm 0-40 mm Lower Leg & Ankle
38 37 Massage Vibration Intensity Pulses Frequency Transmitter Vibration therapy feels very comfortable and is very well accepted by the patients. The vibrations affect the fluid in- and out flow within the tissue. Circulation increases locally and muscular relaxation is enhanced. The treatment can also be used to improve drainage, to treat post injury/ operative oedemas, or to improve lymphatic drainage*. Apply the treatment in the fiber direction over muscle or soft tissue areas. Cover large areas with broader movements and stay longer over integrated trigger points. To improve drainage, move the V-ACTOR in the same direction as the lymphatic drainage system. Gastrocnemius, Soleus, Tibialis Anterior and Peroneal muscles. 3-6 treatments, 3-10 days interval 2,4 Bar - 3,4 Bar Could vary between depending on treatment area 30 Hz V 25 for smaller muscle groups and more integrated trigger points. For larger areas and larger muscle groups, V 40 is recommended. *Not offered on Mobile RPW
39 38 General Muscle Sprain/Strain, Calf Muscles Intensity Sprains and strains are among the most common orthopaedic injuries. Sprains describe an injury to a ligament and strains describe an injury to muscle. A calf strain is a very common sport injury, and is more likely to occur if the calf muscles are tight. General activation and smoothing of surrounding muscles and connective tissue in order to get a muscular relaxation. Do not treat in the acute phase or if there is ongoing bleeding or hemorrhage. Gastrocnemius, Soleus, Tibialis Anterior and Peroneal muscles. Apply over muscles and soft tissue, the treatment may feel uncomfortable in bony areas. 3-6 treatments with 5-10 days interval 1,8 Bar - 2,6 Bar Pulses 2000 Frequency 15 Hz Transmitter D mj/mm mm Lower Leg & Ankle
40 39 Muscular Cramps/Spasm, Calf Muscles Leg cramps are painful contractions of the muscle that happen involuntarily. A common site for leg cramps are the calf muscles. Severe leg cramp may cause damage to the muscle. Fibres of the muscle may be torn due to the shear strength of the muscle contraction. If this happens the muscle will be painful for some time afterwards. General activation and smoothing of surrounding muscles and connective tissue in order to increase circulation locally, and get a muscular relaxation. Do not treat in the acute phase or if there is ongoing bleeding or hemorrhage. Muscles in the affected area. Gastrocnemius, Soleus, Tibialis Anterior and Peroneal muscles. Apply over muscles and soft tissue, the treatment may feel uncomfortable in bony areas. 3-6 treatments with 5-10 days interval Alternative 1 Alternative 2 Intensity 1,8 Bar - 3,0 Bar 1,8 Bar - 3,2 Bar Pulses Frequency 15 Hz / 14 Hz Mobile RPW 12 Hz / 12 Hz Mobile RPW Transmitter D 20 D mj/mm mj/mm mm 0-50 mm
41 40 Trigger Point Therapy A trigger point is a tender nodule located in a taut band of muscles in the tissue, which affects not only the muscle where the trigger point is located, but also causes "referred pain" in tissues supplied by nerves. A passive trigger point causes the referred pain if it is pressed, the active trigger point causes the referred pain constantly. Work with the applicator on the trigger points with very small circular movements. Localise the trigger points by duplicating the perceived pain pattern. The taut band is often recognizable when you move the transmitter over the point. 3-8 treatments with 5-10 days interval. Combine this treatment with a general activation of surrounding muscles. Stretch after treatment. Use between pulses on the same trigger point, higher values on a passive trigger point, lower values on an active trigger point. Alternative 1 Alternative 2 Intensity 1,8 Bar - 2,6 Bar 1,6 Bar - 2,4 Bar Pulses Frequency 15 Hz 15 Hz Transmitter D 20 R mj/mm mj/mm mm 0-40 mm Lower Leg & Ankle
42 41 Thigh & Knee
43 42 Thigh & Knee Jumpers Knee - Muscular... Jumpers Knee I... Jumpers Knee II... Runners Knee - Muscular... Runners Knee I... Runners Knee II... Massage, Vibration... General Muscle Sprain, Thigh Muscles... Trigger Point Therapy Thigh & Knee
44 43 Jumpers Knee Muscular Intensity Known as patellar tendinopathy or Jumpers Knee. With repeated strain like jumping movements, or overuse, micro-tears as well as collagen degeneration may occur in the patellar tendon insertion below the knee cap. Pressing the tendon in the affected area normally causes pain. General activation and smoothing of surrounding muscles and connective tissue in order to get a muscular relaxation. Quadriceps, Tensor Fascia Latae (Iliotib tract), Anterior Tibialis, Peroneal muscles. Apply over muscles and soft tissue, the treatment may feel uncomfortable in bony areas. 3-6 treatments with 5-10 days interval. Combine this treatment with a RPW treatment of the painful points. 2,0 Bar - 3,0 Bar Pulses 2500 Frequency 15 Hz / 14 Hz Mobile RPW Transmitter D mj/mm mm
45 44 Jumpers Knee I Intensity Known as patellar tendinopathy or Jumpers Knee. With repeated strain like jumping movements, or overuse, micro-tears as well as collagen degeneration may occur in the patellar tendon insertion below the knee cap. Pressing the tendon in the affected area normally causes pain. Work with the applicator on the pain points with very small circular movements. In extension, lift apex patella by pressing and pushing Patella from cranial direction. Localise the painful points on the tendon. 3-6 treatments with 5-10 days interval. Combine this treatment with a general activation of surrounding muscles. 1,6 Bar - 2,6 Bar Pulses 2000 Frequency 15 Hz Transmitter R mj/mm mm Thigh & Knee
46 45 Jumpers Knee II Intensity Known as patellar tendinopathy or Jumpers Knee. With repeated strain like jumping movements, or overuse, micro-tears as well as collagen degeneration may occur in the patellar tendon insertion below the knee cap. Pressing the tendon in the affected area normally causes pain. Work with the applicator on the pain points with very small circular movements. In extension, lift apex patella by pressing and pushing Patella from cranial direction. Localise the painful points on the tendon. 3-6 treatments with 5-10 days interval. Combine this treatment with a general activation of surrounding muscles. 1,6 Bar - 3,0 Bar Pulses 2000 Frequency 15 Hz / 14 Hz Mobile RPW Transmitter R mj/mm mm
47 46 Runners Knee Muscular Intensity The Ilio Tibial Band (ITB) is a fibrous connective tissue which attaches at the top of both the Iliac and the Tensor. It then inserts into the outer surface of the Tibia. As the ITB passes over the lateral epicondyle of the Femur it is prone to friction. For people who run regularly, the friction can create a painful condition where this sensitive area of the ITB causes pain if palpated. General activation and smoothing of surrounding muscles and connective tissue in order to get a muscular relaxation. Tensor Fascia Latae (Iliotib tract), Quadriceps vastus lateral, Anterior Tibial. Apply over muscles and soft tissue, the treatment may feel uncomfortable in bony areas. 3-6 treatments with 5-10 days interval. Combine this treatment with a RPW treatment of the painful points. 2,0 Bar - 3,0 Bar Pulses 2500 Frequency 15 Hz / 14 Hz Mobile RPW Transmitter D mj/mm mm Thigh & Knee
48 47 Runners Knee I Intensity The Ilio Tibial Band (ITB) is a fibrous connective tissue which attaches at the top of both the Iliac and the Tensor. It then inserts into the outer surface of the Tibia. As the ITB passes over the lateral epicondyle of the Femur it is prone to friction. For people who run regularly, the friction can create a painful condition where this sensitive area of the ITB causes pain if palpated. Work with the applicator on the pain points with very small circular movements. Localise the painful points on the tendon. 3-6 treatments with 5-10 days interval. Combine this treatment with a general activation of surrounding muscles. 1,6 Bar - 2,6 Bar Pulses 2000 Frequency 15 Hz Transmitter R mj/mm mm
49 48 Runners Knee II Intensity The Ilio Tibial Band (ITB) is a fibrous connective tissue which attaches at the top of both the Iliac and the Tensor. It then inserts into the outer surface of the Tibia. As the ITB passes over the lateral epicondyle of the Femur it is prone to friction. For people who run regularly, the friction can create a painful condition where this sensitive area of the ITB causes pain if palpated. Work with the applicator on the pain points with very small circular movements. Localise the painful points on the tendon. 3-6 treatments with 5-10 days interval. Combine this treatment with a general activation of surrounding muscles. 1,6 Bar - 3,0 Bar Pulses 2000 Frequency 15 Hz / 14 Hz Mobile RPW Transmitter R mj/mm mm Thigh & Knee
50 49 Massage Vibration Intensity Pulses Frequency Transmitter Vibration therapy feels very comfortable and is very well accepted by the patients. The vibrations affect the fluid in- and out flow within the tissue. Circulation increases locally and muscular relaxation is enhanced. The treatment can also be used to improve drainage, to treat post injury/ operative oedemas, or to improve lymphatic drainage*. Apply the treatment in the fiber direction over muscle or soft tissue areas. Cover large areas with broader movements and stay longer over integrated trigger points. To improve drainage, move the V-ACTOR in the same direction as the lymphatic drainage system. Quadriceps and Hamstrings muscles 3-6 treatments, 3-10 days interval 2,4 Bar - 3,6 Bar Could vary between depending on treatment area 35 Hz V 40 is recommended for larger areas and larger muscle groups, V 25 for smaller muscle groups and more integrated trigger points. *Not offered on Mobile RPW
51 50 General Muscle Sprain/Strain, Thigh Muscles Intensity Sprains and strains are among the most common orthopaedic injuries. Sprains describe an injury to a ligament and strains describe an injury to muscle. Strains can range in severity, from a very small tear to a complete rupture. Hamstring strains are common in sprinters and hurdle jumpers, and in the Quadriceps, the Rectus Femoris is most susceptible to injury. General activation and smoothing of surrounding muscles and connective tissue in order to get a muscular relaxation. Do not treat in the acute phase or if there is ongoing bleeding or hemorrhage. Quadriceps, Hamstrings and Tensor Fasciae Latae. Apply over muscles and soft tissue, the treatment may feel uncomfortable in bony areas. 3-6 treatments with 5-10 days interval 2,0 Bar - 3,0 Bar Pulses 2000 Frequency 15 Hz / 14 Hz Mobile RPW Transmitter D mj/mm mm Thigh & Knee
52 51 Trigger Point Therapy A trigger point is a tender nodule located in a taut band of muscles in the tissue, which affects not only the muscle where the trigger point is located, but also causes "referred pain" in tissues supplied by nerves. A passive trigger point causes the referred pain if it is pressed, the active trigger point causes the referred pain constantly. Work with the applicator on the trigger points with very small circular movements. Localise the trigger points by duplicating the perceived pain pattern. The taut band is often recognizable when you move the transmitter over the point. 3-8 treatments with 5-10 days interval. Combine this treatment with a general activation of surrounding muscles. Stretch after treatment. Use between pulses on the same trigger point, higher values on a passive trigger point, lower values on an active trigger point. Alternative 1 Alternative 2 Intensity 1,8 Bar - 2,6 Bar 1,6 Bar - 2,4 Bar Pulses Frequency 15 Hz 15 Hz Transmitter D 20 R mj/mm mj/mm mm 0-40 mm
53 52 Pelvis & Hip Pelvis & Hip
54 53 Pelvis & Hip Trochanteric Insertional Tendonitis - Muscular... Trochanteric Insertional Tendonitis I... Trochanteric Insertional Tendonitis II... Bursitis - Muscular... Piriformis Syndrome - Muscular... Massage, Vibration... Cellulite... Trigger Point Therapy
55 54 Trochanteric Insertional Tendonitis Muscular Intensity Tendonitis can occur in any of the tendons that surround the hip joint. The most frequently encountered tendonitis around the hip is the Iliotibial (IT) band. Pressing the tendon in the affected area normally causes pain. General activation and smoothing of surrounding muscles and connective tissue in order to get a muscular relaxation. Tensor Fascia Latae (Iliotib tract), Quadriceps (Vastus lateralis), Gluteal muscles. Apply over muscles and soft tissue, the treatment may feel uncomfortable in bony areas. 3-6 treatments with 5-10 days interval. Combine this treatment with a RPW treatment of the painful points. 2,0 Bar - 3,0 Bar Pulses 2500 Frequency 15 Hz / 14 Hz Mobile RPW Transmitter D mj/mm mm Pelvis & Hip
56 55 Trochanteric Insertional Tendonitis I Tendonitis can occur in any of the tendons that surround the hip joint. The most frequently encountered tendonitis around the hip is the Iliotibial (IT) band. Pressing the tendon in the affected area normally causes pain. Work with the applicator on the pain points with very small circular movements. Localise and treat the most painful points. 3-6 treatments with 5-10 days interval. Combine this treatment with a general activation of surrounding muscles. Alternative 1 Alternative 2 Intensity 1,8 Bar - 3,2 Bar 2,0 Bar - 4,0 Bar Pulses Frequency 20 Hz / 12 Hz Mobile RPW 15 Hz Transmitter DI 15 R mj/mm mj/mm mm 0-40 mm
57 56 Trochanteric Insertional Tendonitis II Tendonitis can occur in any of the tendons that surround the hip joint. The most frequently encountered tendonitis around the hip is the Iliotibial (IT) band. Pressing the tendon in the affected area normally causes pain. Work with the applicator on the pain points with very small circular movements. Localise and treat the most painful points. 3-6 treatments with 5-10 days interval. Combine this treatment with a general activation of surrounding muscles. Alternative 1 Alternative 2 Intensity 2,0 Bar - 3,6 Bar 2,0 Bar - 4,5 Bar Pulses Frequency 20 Hz / 10 Hz Mobile RPW 15 Hz Transmitter DI 15 R mj/mm mj/mm mm 0-40 mm Pelvis & Hip
58 57 Bursitis Muscular Intensity The trochanteric bursa rests between the Trochanter major and the Iliotibial band. The bursal sac becomes inflamed, or irritated from trauma or repetitive friction. Each time the tendon has to move over the bone, pain results. Pressing the tendon in the affected area normally causes pain. General activation and smoothing of surrounding muscles and connective tissue in order to get a muscular relaxation. Do not treat in the acute phase when there is an active inflammation, ongoing bleeding or hemorrhage. Tensor Fascia Latae (Iliotib tract), Quadriceps (Vastus lateralis), Gluteal muscles. Apply over muscles and soft tissue, the treatment may feel uncomfortable in bony areas. 3-6 treatments with 5-10 days interval 2,0 Bar - 3,4 Bar Pulses 2000 Frequency 15 Hz / 11 Hz Mobile RPW Transmitter D mj/mm mm
59 58 Piriformis Syndrome Muscular Intensity The Piriformis muscle is a deep buttock muscle that rotates the leg outwards. The sciatic nerve runs very close to it, and a tight Piriformis put pressure on, or irritates the nerve, causing pain (sometimes radiating) as a result. Tight adductor muscles is common among these patients, combine treatment with stretching. General activation and smoothing of surrounding muscles and connective tissue in order to get a muscular relaxation. Do not treat in the acute phase when there is an active inflammation, ongoing bleeding or hemorrhage. Gluteal muscles (Medius and Maximus), Piriformis, Hamstrings, Tensor Fasciae Latae. Apply over muscles and soft tissue, the treatment may feel uncomfortable in bony areas. 3-6 treatments with 5-10 days interval 2,0 Bar - 3,4 Bar Pulses 2000 Frequency 15 Hz / 11 Hz Mobile RPW Transmitter D mj/mm mm Pelvis & Hip
60 59 Massage Vibration Intensity Pulses Frequency Transmitter Vibration therapy feels very comfortable and is very well accepted by the patients. The vibrations affect the fluid in- and out flow within the tissue. Circulation increases locally and muscular relaxation is enhanced. The treatment can also be used to improve drainage, to treat post injury/ operative oedemas, or to improve lymphatic drainage*. Apply the treatment in the fiber direction over muscle or soft tissue areas. Cover large areas with broader movements and stay longer over integrated trigger points. For improving drainage, move the V-ACTOR in the same direction as the lymphatic drainage system. Gluteal muscles, Hamstrings and Tensor Fasciae Latae 3-6 treatments, 3-10 days interval 2,4 Bar - 3,6 Bar Could vary between depending on treatment area 35 Hz V 40 is recommended for larger areas and larger muscle groups, V 25 for smaller muscle groups and more integrated trigger points. *Not offered on Mobile RPW
61 60 Cellulite Despite the fact that cellulite is not considered a disease, but purely a cosmetic problem, it is very common among post pubertal women. It is a non inflammatory, degenerative condition where the adipose tissue and microcirculation in the hypodermis alters and causes fibrosclerosis in the connective tissue. The skin gets an orange peel appearance. Cellulite appears in 3 stages: Stage I : Orange peel appearance on pinching the skin Stage II : Orange peel appearance visible when standing Stage III: Orange peel skin while standing and lying down Use enough coupling gel in the area to ensure good transmission. Always move the hand piece in the direction of the lymph flow. A 3-5 minute session with V-ACTOR massage after a treatment, is recommended*. Treat the affected areas like buttocks and thighs. Use more pulses and higher energy levels for more severe stages of cellulite, but be sure that a session never is painful for the client treatment sessions in total, 1-2 times a week. Always let the body rest 2-3 days between treatments. Continued over... *Not offered on Mobile RPW Pelvis & Hip
62 61 Cellulite (Cont.) Alternative 1 Deeper penetration Alternative 2 Intensity 2,0 Bar - 3,2 Bar 2,6 Bar - 4,2 Bar Pulses 2000 (Stage III ) 1500 (Stage II) 1000 (Stage I) 3000 (Stage III) 2500 (Stage I and II) Frequency 12 Hz 12 Hz Transmitter DI 15 D mj/mm mj/mm mm 0-50 mm
63 62 Trigger Point Therapy A trigger point is a tender nodule located in a taut band of muscles in the tissue, which affects not only the muscle where the trigger point is located, but also causes "referred pain" in tissues supplied by nerves. A passive trigger point causes the referred pain if it is pressed, the active trigger point causes the referred pain constantly. Work with the applicator on the trigger points with very small circular movements. Localise the trigger points by duplicating the perceived pain pattern. The taut band is often recognizable when you move the transmitter over the point. 3-8 treatments with 5-10 days interval. Combine this treatment with a general activation of surrounding muscles. Stretch after treatment. Use between pulses on the same trigger point, higher values on a passive trigger point, lower values on an active trigger point. Alternative 1 Alternative 2 Intensity 1,8 Bar - 2,6 Bar 1,6 Bar - 2,4 Bar Pulses Frequency 15 Hz 15 Hz Transmitter D 20 R mj/mm mj/mm mm 0-40 mm Pelvis & Hip
64 63 Lower Back
65 64 Lower Back Lower Back - Muscular... Lower Back I... Lower Back II... Massage, Vibration... Lumbalgia - Activation of Muscles and Connective Tissue... Trigger Point Therapy Lower Back
66 65 Lower Back Muscular Intensity Muscle strains are one of the most common causes of lower back pain. Most lumbar muscle strains and sprains cause symptoms isolated to the lower back, usually they do not cause radiating pain in the legs like some other spine conditions. The most common symptoms of a lumbar strain or sprain are muscle spasm and pain around the lower back and upper buttocks. General activation and smoothing of surrounding muscles and connective tissue in order to get a muscular relaxation. Gluteal muscles (Medius and Maximus). Along the Pelvic rim, Piriformis, Longissimus dorsi, Quadratus lumborum. Apply over muscles and soft tissue, the treatment may feel uncomfortable in bony areas. 3-6 treatments with 5-10 days interval 2,2 Bar - 3,2 Bar Pulses 2500 Frequency 15 Hz / 12 Hz Mobile RPW Transmitter D mj/mm mm
Most Common Running Injuries
 Most Common Running Injuries 1. Achilles Tendonitis 2. Chrondomalacia Runner s Knee 3. Iliotibial Band (ITB) syndrome 4. Plantar Fasciitis 5. Shin Splints Achilles Tendonitis inflammation of the Achilles
Most Common Running Injuries 1. Achilles Tendonitis 2. Chrondomalacia Runner s Knee 3. Iliotibial Band (ITB) syndrome 4. Plantar Fasciitis 5. Shin Splints Achilles Tendonitis inflammation of the Achilles
.org. Achilles Tendinitis. Description. Cause. Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel.
 Achilles Tendinitis Page ( 1 ) Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your
Achilles Tendinitis Page ( 1 ) Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your
Elbow Injuries and Disorders
 Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
Integrated Manual Therapy & Orthopedic Massage For Low Back Pain, Hip Pain, and Sciatica
 Integrated Manual Therapy & Orthopedic Massage For Low Back Pain, Hip Pain, and Sciatica Assessment Protocols Treatment Protocols Treatment Protocols Corrective Exercises By Author & International Lecturer
Integrated Manual Therapy & Orthopedic Massage For Low Back Pain, Hip Pain, and Sciatica Assessment Protocols Treatment Protocols Treatment Protocols Corrective Exercises By Author & International Lecturer
KINESIOLOGY TAPING GUIDE
 KINESIOLOGY TAPING GUIDE What is Kinesiology tape and how does Kinesiology tape work? How to apply Kinesiology tape Examples of application of UP Kinesiology tape for common injuries and conditions Introduction
KINESIOLOGY TAPING GUIDE What is Kinesiology tape and how does Kinesiology tape work? How to apply Kinesiology tape Examples of application of UP Kinesiology tape for common injuries and conditions Introduction
Sports Injury Treatment
 Sports Injury Treatment Participating in a variety of sports is fun and healthy for children and adults. However, it's critical that before you participate in any sport, you are aware of the precautions
Sports Injury Treatment Participating in a variety of sports is fun and healthy for children and adults. However, it's critical that before you participate in any sport, you are aware of the precautions
.org. Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs. Anatomy. Cause
 Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Page ( 1 ) Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition
Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Page ( 1 ) Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition
o Understand the anatomy of the covered areas. This includes bony, muscular and ligamentous anatomy.
 COURSE TITLE Kin 505 Activities, Injuries Disease in the Larger Society On-Line offering Instructor Dr. John Miller John.Miller@unh.edu Course Description. Sports and exercise are a part of American society
COURSE TITLE Kin 505 Activities, Injuries Disease in the Larger Society On-Line offering Instructor Dr. John Miller John.Miller@unh.edu Course Description. Sports and exercise are a part of American society
By Agnes Tan (PT) I-Sports Rehab Centre Island Hospital
 By Agnes Tan (PT) I-Sports Rehab Centre Island Hospital Physiotherapy Provides aids to people Deals with abrasion and dysfunction (muscles, joints, bones) To control and repair maximum movement potentials
By Agnes Tan (PT) I-Sports Rehab Centre Island Hospital Physiotherapy Provides aids to people Deals with abrasion and dysfunction (muscles, joints, bones) To control and repair maximum movement potentials
RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION
 RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION Topics of Tonight s s Lecture Common Injuries and Treatments Causes of Common Injuries Measures to Avoid Injury Most Common Running Injuries Plantar Fascitis
RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION Topics of Tonight s s Lecture Common Injuries and Treatments Causes of Common Injuries Measures to Avoid Injury Most Common Running Injuries Plantar Fascitis
What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis?
 Bursitis and tendinitis are both common conditions that cause swelling around muscles and bones. They occur most often in the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, or ankle. A bursa is a small, fluid-filled
Bursitis and tendinitis are both common conditions that cause swelling around muscles and bones. They occur most often in the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, or ankle. A bursa is a small, fluid-filled
THE PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION OF SPORTS INJURIES THE PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION OF SPORTS INJURIES. NO, there isn t.
 THE PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION OF SPORTS INJURIES VILMOS DANI M.D. Department of Family Medicine Faculty of Medicine, Semmelweis University Budapest, Hungay GIZELLA PERÉNYI M.D. Department of Rehabilitation
THE PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION OF SPORTS INJURIES VILMOS DANI M.D. Department of Family Medicine Faculty of Medicine, Semmelweis University Budapest, Hungay GIZELLA PERÉNYI M.D. Department of Rehabilitation
Plantar Fasciitis. Plantar Fascia
 Plantar Fasciitis Introduction Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the thick band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. This thick band of tissue is called the plantar fascia. Plantar
Plantar Fasciitis Introduction Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the thick band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. This thick band of tissue is called the plantar fascia. Plantar
Screening Examination of the Lower Extremities BUY THIS BOOK! Lower Extremity Screening Exam
 Screening Examination of the Lower Extremities Melvyn Harrington, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Loyola University Medical Center BUY THIS BOOK! Essentials of Musculoskeletal Care
Screening Examination of the Lower Extremities Melvyn Harrington, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Loyola University Medical Center BUY THIS BOOK! Essentials of Musculoskeletal Care
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon
Runner's Injury Prevention
 JEN DAVIS DPT Runner's Injury Prevention Jen Davis DPT Orthopedic Physical Therapy Foot Traffic 7718 SE 13th Ave Portland, OR 97202 (503) 482-7232 Jen@runfastpt.com www.runfastpt.com!1 THE AMAZING RUNNER
JEN DAVIS DPT Runner's Injury Prevention Jen Davis DPT Orthopedic Physical Therapy Foot Traffic 7718 SE 13th Ave Portland, OR 97202 (503) 482-7232 Jen@runfastpt.com www.runfastpt.com!1 THE AMAZING RUNNER
KNEES A Physical Therapist s Perspective American Physical Therapy Association
 Taking Care of Your KNEES A Physical Therapist s Perspective American Physical Therapy Association Taking Care of Your Knees When the mother of the hero Achilles dipped him in the river Styx, she held
Taking Care of Your KNEES A Physical Therapist s Perspective American Physical Therapy Association Taking Care of Your Knees When the mother of the hero Achilles dipped him in the river Styx, she held
Self-Myofascial Release Foam Roller Massage
 How it works. Self-Myofascial Release Foam Roller Massage Traditional stretching techniques simply cause increases in muscle length and can actually increase your chances of injury. Self-myofascial release
How it works. Self-Myofascial Release Foam Roller Massage Traditional stretching techniques simply cause increases in muscle length and can actually increase your chances of injury. Self-myofascial release
BP MS 150 lunch and learn: Stretching and injury prevention. Dr. Bart Kennedy (Sports Chiropractor) and Josh Thompson February 04, 2015
 BP MS 150 lunch and learn: Stretching and injury prevention Dr. Bart Kennedy (Sports Chiropractor) and Josh Thompson February 04, 2015 Epidemiology Overuse injuries most common, traumatic event second
BP MS 150 lunch and learn: Stretching and injury prevention Dr. Bart Kennedy (Sports Chiropractor) and Josh Thompson February 04, 2015 Epidemiology Overuse injuries most common, traumatic event second
HIGH INTENSITY LASER A REVOLUTION IN THERAPEUTIC LASER TECHNOLOGY
 HIGH INTENSITY LASER A REVOLUTION IN THERAPEUTIC LASER TECHNOLOGY sales@btlnet.com www.btlnet.com All rights reserved. Although every care has been taken to provide accurate and up-to-date information,
HIGH INTENSITY LASER A REVOLUTION IN THERAPEUTIC LASER TECHNOLOGY sales@btlnet.com www.btlnet.com All rights reserved. Although every care has been taken to provide accurate and up-to-date information,
A Guide to Heel Pain
 The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists A Guide to Heel Pain The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists Heel pain may be caused by a number of different problems; for effective treatment you need
The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists A Guide to Heel Pain The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists Heel pain may be caused by a number of different problems; for effective treatment you need
Heel pain and Plantar fasciitis
 A patient s guide Heel pain and Plantar fasciitis Fred Robinson BSc FRCS FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon Alex Wee BSc FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon. What causes
A patient s guide Heel pain and Plantar fasciitis Fred Robinson BSc FRCS FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon Alex Wee BSc FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon. What causes
Shoulder Tendonitis. Brett Sanders, MD Center For Sports Medicine and Orthopaedic 2415 McCallie Ave. Chattanooga, TN (423) 624-2696
 Shoulder Tendonitis Brett Sanders, MD Center For Sports Medicine and Orthopaedic 2415 McCallie Ave. Chattanooga, TN (423) 624-2696 Shoulder tendinitis is a common overuse injury in sports (such as swimming,
Shoulder Tendonitis Brett Sanders, MD Center For Sports Medicine and Orthopaedic 2415 McCallie Ave. Chattanooga, TN (423) 624-2696 Shoulder tendinitis is a common overuse injury in sports (such as swimming,
MUSCLE PAIN RELIEF CLINIC
 MUSCLE PAIN RELIEF CLINIC LONG GRAIGUE Revolutionary Muscle Pain Relief Clinic All Injuries Treated Including Back Pain Shoulders Necks Hips Knees Ankles Complete Evaluation Postural Alignment Sports Injuries
MUSCLE PAIN RELIEF CLINIC LONG GRAIGUE Revolutionary Muscle Pain Relief Clinic All Injuries Treated Including Back Pain Shoulders Necks Hips Knees Ankles Complete Evaluation Postural Alignment Sports Injuries
Plantar Fasciitis Information Leaflet. Maneesh Bhatia. Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon
 Plantar Fasciitis Information Leaflet Maneesh Bhatia Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon What is plantar fasciitis? The plantar fascia is a strong band of tissue that stretches from the heel to the toes. It
Plantar Fasciitis Information Leaflet Maneesh Bhatia Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon What is plantar fasciitis? The plantar fascia is a strong band of tissue that stretches from the heel to the toes. It
COMPUTER-RELATED MUSCLE, TENDON, AND JOINT INJURIES
 CHAPTER ELEVEN COMPUTER-RELATED MUSCLE, TENDON, AND JOINT INJURIES To reduce the risk of pain in your neck and shoulders, stay within these recommended ranges of movement: Neck Flexion: 0 o -15 o (bending
CHAPTER ELEVEN COMPUTER-RELATED MUSCLE, TENDON, AND JOINT INJURIES To reduce the risk of pain in your neck and shoulders, stay within these recommended ranges of movement: Neck Flexion: 0 o -15 o (bending
MET: Posterior (backward) Rotation of the Innominate Bone.
 MET: Posterior (backward) Rotation of the Innominate Bone. Purpose: To reduce an anterior rotation of the innominate bone at the SI joint. To increase posterior (backward) rotation of the SI joint. Precautions:
MET: Posterior (backward) Rotation of the Innominate Bone. Purpose: To reduce an anterior rotation of the innominate bone at the SI joint. To increase posterior (backward) rotation of the SI joint. Precautions:
DSM Spine+Sport - Mobility
 To set yourself up for success, practice keeping a neutral spine throughout all of these movements. This will ensure the tissue mobilization is being applied to the correct area, and make the techniques
To set yourself up for success, practice keeping a neutral spine throughout all of these movements. This will ensure the tissue mobilization is being applied to the correct area, and make the techniques
CONSTRUCTION WORK and CUMULATIVE TRAUMA DISORDERS
 Connecticut Department of Public Health Environmental and Occupational Health Assessment Program 410 Capitol Avenue MS # 11OSP, PO Box 340308 Hartford, CT 06134-0308 (860) 509-7740 http://www.ct.gov/dph
Connecticut Department of Public Health Environmental and Occupational Health Assessment Program 410 Capitol Avenue MS # 11OSP, PO Box 340308 Hartford, CT 06134-0308 (860) 509-7740 http://www.ct.gov/dph
Plantar Fascia Release
 Plantar Fascia Release Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. If other treatments are unsuccessful,
Plantar Fascia Release Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. If other treatments are unsuccessful,
Trochanteric Bursitis Self Management for Patients
 Trochanteric Bursitis Self Management for Patients Updated May 2010 What is the Trochanteric Bursa? The trochanteric bursa is a fluid-filled sac that functions as a gliding surface to reduce friction between
Trochanteric Bursitis Self Management for Patients Updated May 2010 What is the Trochanteric Bursa? The trochanteric bursa is a fluid-filled sac that functions as a gliding surface to reduce friction between
Overuse injuries. 1. Main types of injuries
 OVERUSE INJURIES Mr. Sansouci is an ardent runner and swimmer. To train for an upcoming 10-km race, he has decided to increase the intensity of his training. Lately, however, his shoulder and Achilles
OVERUSE INJURIES Mr. Sansouci is an ardent runner and swimmer. To train for an upcoming 10-km race, he has decided to increase the intensity of his training. Lately, however, his shoulder and Achilles
BALANCED BODYWORKS LA Rejuvenate. Heal. Restore.
 Tools For Myofascial Self Massage and Stretching Foam Roller Lacrosse Ball (Hard) Stretch Strap What is Foam Rolling? Foam Rolling or Self Myofascial Release, is a form of soft tissue massage. Similar
Tools For Myofascial Self Massage and Stretching Foam Roller Lacrosse Ball (Hard) Stretch Strap What is Foam Rolling? Foam Rolling or Self Myofascial Release, is a form of soft tissue massage. Similar
Pain Management Top Diagnosis Codes (Crosswalk)
 Pain Management Top s (Crosswalk) 274.00 Gout arthropathy, M1000 Idiopathic gout, unspecified site unspecified M10011 Idiopathic gout, right shoulder M10012 Idiopathic gout, left shoulder M10019 Idiopathic
Pain Management Top s (Crosswalk) 274.00 Gout arthropathy, M1000 Idiopathic gout, unspecified site unspecified M10011 Idiopathic gout, right shoulder M10012 Idiopathic gout, left shoulder M10019 Idiopathic
Understanding. Heel Pain
 Understanding Heel Pain What Causes Heel Pain? Heel pain is a common problem that occurs when the heel is placed under too much stress. Heel pain is most often caused by walking in ways that irritate tissues
Understanding Heel Pain What Causes Heel Pain? Heel pain is a common problem that occurs when the heel is placed under too much stress. Heel pain is most often caused by walking in ways that irritate tissues
Pre - Operative Rehabilitation Program for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction
 Pre - Operative Rehabilitation Program for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction This protocol is designed to assist you with your preparation for surgery and should be followed under the direction
Pre - Operative Rehabilitation Program for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction This protocol is designed to assist you with your preparation for surgery and should be followed under the direction
A small roller with a big effect. The mini roller for massaging, strengthening, stretching and warming up
 A small roller with a big effect The mini roller for massaging, strengthening, stretching and warming up Suva Preventative products P. O Box, 6002 Lucerne Enquiries Tel. 041 419 58 51 Orders www.suva.ch/waswo
A small roller with a big effect The mini roller for massaging, strengthening, stretching and warming up Suva Preventative products P. O Box, 6002 Lucerne Enquiries Tel. 041 419 58 51 Orders www.suva.ch/waswo
PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome)
 PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome) R. Amadeus Mason MD Description Plantar fascitis is characterized by stiffness and inflammation of the main fascia (fibrous connective [ligament-like] tissue) on the
PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome) R. Amadeus Mason MD Description Plantar fascitis is characterized by stiffness and inflammation of the main fascia (fibrous connective [ligament-like] tissue) on the
Back & Neck Pain Survival Guide
 Back & Neck Pain Survival Guide www.kleinpeterpt.com Zachary - 225-658-7751 Baton Rouge - 225-768-7676 Kleinpeter Physical Therapy - Spine Care Program Finally! A Proven Assessment & Treatment Program
Back & Neck Pain Survival Guide www.kleinpeterpt.com Zachary - 225-658-7751 Baton Rouge - 225-768-7676 Kleinpeter Physical Therapy - Spine Care Program Finally! A Proven Assessment & Treatment Program
How To Treat Heel Pain
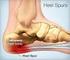 Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Heel Pain The Plantar Fasciitis Organization is dedicated to the understanding of Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, and all other forms of Heel Pain. Welcome to the Plantar
Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Heel Pain The Plantar Fasciitis Organization is dedicated to the understanding of Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, and all other forms of Heel Pain. Welcome to the Plantar
Imagine LIFE WITHOUT PAIN
 Imagine LIFE WITHOUT PAIN High Dosage Laser Therapy (HDLT) What does it do? High Dosage Laser Therapy (HDLT) from Diowave offers a powerful new solution for numerous painful conditions previously refractive
Imagine LIFE WITHOUT PAIN High Dosage Laser Therapy (HDLT) What does it do? High Dosage Laser Therapy (HDLT) from Diowave offers a powerful new solution for numerous painful conditions previously refractive
Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries
 Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries Symptoms Related to Abnormal Foot Biomechanics & their Differential Diagnosis Daniel Pang BSc (Hon) P&O, Cped Certified Pedorthist (USA) Only 10% of foot having structure
Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries Symptoms Related to Abnormal Foot Biomechanics & their Differential Diagnosis Daniel Pang BSc (Hon) P&O, Cped Certified Pedorthist (USA) Only 10% of foot having structure
Stretching the Major Muscle Groups of the Lower Limb
 2 Stretching the Major Muscle Groups of the Lower Limb In this chapter, we present appropriate stretching exercises for the major muscle groups of the lower limb. All four methods (3S, yoga, slow/static,
2 Stretching the Major Muscle Groups of the Lower Limb In this chapter, we present appropriate stretching exercises for the major muscle groups of the lower limb. All four methods (3S, yoga, slow/static,
Flat foot and lower back pain
 Flat foot and lower back pain Dr James Tang, MBA, BDS, LDS RCS General Dental Practitioner, NASM Corrective Exercise Specialist with special interest in postural dysfunction & lower back problems, Level
Flat foot and lower back pain Dr James Tang, MBA, BDS, LDS RCS General Dental Practitioner, NASM Corrective Exercise Specialist with special interest in postural dysfunction & lower back problems, Level
Integrated Manual Therapy & Orthopedic Massage For Complicated Knee Conditions
 Integrated Manual Therapy & Orthopedic Massage For Complicated Knee Conditions Assessment Protocols Treatment Protocols Treatment Protocols Corrective Exercises Artwork and slides taken from the book Clinical
Integrated Manual Therapy & Orthopedic Massage For Complicated Knee Conditions Assessment Protocols Treatment Protocols Treatment Protocols Corrective Exercises Artwork and slides taken from the book Clinical
Neck Pain Overview Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment Options
 Neck Pain Overview Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment Options Neck pain is one of the most common forms of pain for which people seek treatment. Most individuals experience neck pain at some point during
Neck Pain Overview Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment Options Neck pain is one of the most common forms of pain for which people seek treatment. Most individuals experience neck pain at some point during
Plantar fascia. Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot)
 ! Plantar fascia Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot) Plantar Fasciitis is the most common foot problem seen in runners and is often associated with an increase in running mileage. Typically
! Plantar fascia Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot) Plantar Fasciitis is the most common foot problem seen in runners and is often associated with an increase in running mileage. Typically
.org. Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction. Anatomy. Cause. Symptoms
 Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy
 Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain centralized around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. Health care providers
Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain centralized around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. Health care providers
Flexibility Assessment and Improvement Compiled and Adapted by Josh Thompson
 Flexibility Assessment and Improvement Compiled and Adapted by Josh Thompson Muscles must have a full and normal range of motion in order for joints and skeletal structure to function properly. Flexibility
Flexibility Assessment and Improvement Compiled and Adapted by Josh Thompson Muscles must have a full and normal range of motion in order for joints and skeletal structure to function properly. Flexibility
Keeping the Aging Worker Productive and Injury Free
 Keeping the Aging Worker Productive and Injury Free Peter Goyert PT CCPE Senior Ergonomist WorkSafeBC Aging Some say aging is > 30 years. Everybody is aging. Generally aging workers refer to those in last
Keeping the Aging Worker Productive and Injury Free Peter Goyert PT CCPE Senior Ergonomist WorkSafeBC Aging Some say aging is > 30 years. Everybody is aging. Generally aging workers refer to those in last
Page 2 of 6 plantar fascia. This is called the windlass mechanism. Later, we'll discuss how this mechanism is used to treat plantar fasciitis with str
 Page 1 of 6 Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain) Plantar fasciitis is a painful condition affecting the bottom of the foot. It is a common cause of heel pain and is sometimes called a heel spur. Plantar fasciitis
Page 1 of 6 Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain) Plantar fasciitis is a painful condition affecting the bottom of the foot. It is a common cause of heel pain and is sometimes called a heel spur. Plantar fasciitis
McMaster Spikeyball Therapy Drills
 BODY BLOCKS In sequencing Breathing and Tempo Flexibility / Mobility and Proprioception (feel) Upper body segment Middle body segment Lower body segment Extension / Static Posture Office / Computer Travel
BODY BLOCKS In sequencing Breathing and Tempo Flexibility / Mobility and Proprioception (feel) Upper body segment Middle body segment Lower body segment Extension / Static Posture Office / Computer Travel
Chapter 4 Physiological Therapeutics. 3 Therapeutic Ultrasound
 Chapter 4 Physiological Therapeutics 3 Therapeutic Ultrasound Therapeutic Ultrasound PHYSIOLOGIC EFFECTS OF ULTRASOUND 1. Increased collagen extensibility 5. Increased nerve conduction velocities 2. Increased
Chapter 4 Physiological Therapeutics 3 Therapeutic Ultrasound Therapeutic Ultrasound PHYSIOLOGIC EFFECTS OF ULTRASOUND 1. Increased collagen extensibility 5. Increased nerve conduction velocities 2. Increased
Knowledgable Doctors & Caring Staff
 Knowledgable Doctors & Caring Staff Better Technology = Better Results = Patient Satisfaction Hello and thank you for visiting our website. We hope you find the information here helpful. We REGULARLY travel,
Knowledgable Doctors & Caring Staff Better Technology = Better Results = Patient Satisfaction Hello and thank you for visiting our website. We hope you find the information here helpful. We REGULARLY travel,
Hip Bursitis/Tendinitis
 Hip Bursitis/Tendinitis Anatomy and Biomechanics The hip is a ball and socket joint that occurs between the head of the femur (ball) and the acetabulum of the pelvis (socket). It is protected by several
Hip Bursitis/Tendinitis Anatomy and Biomechanics The hip is a ball and socket joint that occurs between the head of the femur (ball) and the acetabulum of the pelvis (socket). It is protected by several
PERFORMANCE RUNNING. Piriformis Syndrome
 Piriformis Syndrome Have you started to experience pain in your hip or down your leg while beginning or advancing your fitness program? This pain may be stemming from the piriformis muscle in your hip.
Piriformis Syndrome Have you started to experience pain in your hip or down your leg while beginning or advancing your fitness program? This pain may be stemming from the piriformis muscle in your hip.
How To Roll Out
 THE GUIDE: ROLLING OUT WHAT IS THE MYOFASCIAL SYSTEM? The Myofascial System is a superficial fascia (a thin sheath of silvery tissue) that wraps around the outer surface of muscles and individual muscle
THE GUIDE: ROLLING OUT WHAT IS THE MYOFASCIAL SYSTEM? The Myofascial System is a superficial fascia (a thin sheath of silvery tissue) that wraps around the outer surface of muscles and individual muscle
Massage and Movement
 Massage and Movement Incorporating Movement into Massage Part One: Theory and Technique in Prone With Lee Stang, LMT NCBTMB #450217-06 1850 West Street Southington, CT 06489 860.747.6388 www.bridgestohealthseminars.com
Massage and Movement Incorporating Movement into Massage Part One: Theory and Technique in Prone With Lee Stang, LMT NCBTMB #450217-06 1850 West Street Southington, CT 06489 860.747.6388 www.bridgestohealthseminars.com
Get Rid of Elbow Pain
 Get Rid of Elbow Pain Self Regional Healthcare Optimum Life Center 115 Academy Avenue Greenwood, SC 29646 Office: (864) 725-7088 Self Regional Healthcare Physical Therapy Savannah Lakes 207 Holiday Road
Get Rid of Elbow Pain Self Regional Healthcare Optimum Life Center 115 Academy Avenue Greenwood, SC 29646 Office: (864) 725-7088 Self Regional Healthcare Physical Therapy Savannah Lakes 207 Holiday Road
Athletic/Sports Massage
 CHAPTER18 Athletic/Sports Massage COMPLETION: In the space(s) provided, write the word(s) that correctly complete(s) each statement. 1. The 1972 Olympic gold medalist who was known as the flying Finn and
CHAPTER18 Athletic/Sports Massage COMPLETION: In the space(s) provided, write the word(s) that correctly complete(s) each statement. 1. The 1972 Olympic gold medalist who was known as the flying Finn and
Dr. O Meara s. Anterior Knee Pain (PatelloFemoral Syndrome) Rehabilitation Protocol www.palomarortho.com
 Dr. O Meara s Anterior Knee Pain (PatelloFemoral Syndrome) Rehabilitation Protocol www.palomarortho.com Anterior Knee Pain (PatelloFemoral Syndrome) Rehabilitation Protocol Hamstring Stretching & Strengthening
Dr. O Meara s Anterior Knee Pain (PatelloFemoral Syndrome) Rehabilitation Protocol www.palomarortho.com Anterior Knee Pain (PatelloFemoral Syndrome) Rehabilitation Protocol Hamstring Stretching & Strengthening
THE BENJAMIN INSTITUTE PRESENTS. Excerpt from Listen To Your Pain. Assessment & Treatment of. Low Back Pain. Ben E. Benjamin, Ph.D.
 THE BENJAMIN INSTITUTE PRESENTS Excerpt from Listen To Your Pain Assessment & Treatment of Low Back Pain A B E N J A M I N I N S T I T U T E E B O O K Ben E. Benjamin, Ph.D. 2 THERAPIST/CLIENT MANUAL The
THE BENJAMIN INSTITUTE PRESENTS Excerpt from Listen To Your Pain Assessment & Treatment of Low Back Pain A B E N J A M I N I N S T I T U T E E B O O K Ben E. Benjamin, Ph.D. 2 THERAPIST/CLIENT MANUAL The
Treatment Guide Understanding Elbow Pain. Using this Guide. Choosing Your Care. Table of Contents:
 Treatment Guide Understanding Elbow Pain Elbow pain is extremely common whether due to aging, overuse, trauma or a sports injury. When elbow pain interferes with carrying the groceries, participating in
Treatment Guide Understanding Elbow Pain Elbow pain is extremely common whether due to aging, overuse, trauma or a sports injury. When elbow pain interferes with carrying the groceries, participating in
Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body
 Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Patellar Tendon and Quadriceps Tendon Repair
 UW Health Sports Rehabilitation Rehabilitation Guidelines for Patellar Tendon and Quadriceps Tendon Repair The knee consists of four bones that form three joints. The femur is the large bone in the thigh
UW Health Sports Rehabilitation Rehabilitation Guidelines for Patellar Tendon and Quadriceps Tendon Repair The knee consists of four bones that form three joints. The femur is the large bone in the thigh
High Dose Laser Therapy Revolutionizing Pain Management
 High Dose Laser Therapy Revolutionizing Pain Management The Best New Profit Center In Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation TECHNOLOGICAL MEDICAL ADVANCEMENTS, LLC High Dosage Laser Therapy (HDLT) Common
High Dose Laser Therapy Revolutionizing Pain Management The Best New Profit Center In Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation TECHNOLOGICAL MEDICAL ADVANCEMENTS, LLC High Dosage Laser Therapy (HDLT) Common
Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933
 Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933 www.grhsonline.org Important Notice The information contained in this document is for informational
Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933 www.grhsonline.org Important Notice The information contained in this document is for informational
.org. Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems. Anatomy. Cause
 Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems Page ( 1 ) What most people call the shoulder is really several joints that combine with tendons and muscles to allow a wide range of motion in the arm from scratching
Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems Page ( 1 ) What most people call the shoulder is really several joints that combine with tendons and muscles to allow a wide range of motion in the arm from scratching
CUMMULATIVE DISORDERS OF UPPER EXTIMITY DR HABIBOLLAHI
 CUMMULATIVE DISORDERS OF UPPER EXTIMITY DR HABIBOLLAHI Definition Musculoskeletal disorder (MSD) is an injury or disorder of the muscles, nerves, tendons, joints, cartilage,ligament and spinal discs. It
CUMMULATIVE DISORDERS OF UPPER EXTIMITY DR HABIBOLLAHI Definition Musculoskeletal disorder (MSD) is an injury or disorder of the muscles, nerves, tendons, joints, cartilage,ligament and spinal discs. It
Myofit Massage Therapy Stretches for Cycling
 Guidelines for Stretching Always assume the stretch start position and comfortably apply the stretch as directed. Think Yoga - gently and slowly, no ballistic actions or bouncing at joint end range. Once
Guidelines for Stretching Always assume the stretch start position and comfortably apply the stretch as directed. Think Yoga - gently and slowly, no ballistic actions or bouncing at joint end range. Once
Muscular System. Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body
 Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Healing your pain changing your life.
 Healing your pain changing your life. About K-Laser What is Laser Therapy? Laser Therapy, or photobiomodulation, is the use of specific wavelengths of light (red and nearinfrared) to create therapeutic
Healing your pain changing your life. About K-Laser What is Laser Therapy? Laser Therapy, or photobiomodulation, is the use of specific wavelengths of light (red and nearinfrared) to create therapeutic
Anterior Superior Iliac Spine. Anterior Inferior Iliac Spine. head neck greater trochanter intertrochanteric line lesser trochanter
 Ilium Bones The Skeleton Ischium Pubis Sacro-iliac Joint Iliac Crest Anterior Superior Superior Pubic Ramus Anterior Inferior Acetabulum Obturator Foramen Ischio-pubic ramus Ischial tuberosity Pubic Crest
Ilium Bones The Skeleton Ischium Pubis Sacro-iliac Joint Iliac Crest Anterior Superior Superior Pubic Ramus Anterior Inferior Acetabulum Obturator Foramen Ischio-pubic ramus Ischial tuberosity Pubic Crest
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
ICD-10 Cheat Sheet Frequently Used ICD-10 Codes for Musculoskeletal Conditions *
 ICD-10 Cheat Sheet Frequently Used ICD-10 Codes for Musculoskeletal Conditions * Finding the ICD-10 equivalent for an ICD-9 code can be a challenge. This resource of frequently used codes can help when
ICD-10 Cheat Sheet Frequently Used ICD-10 Codes for Musculoskeletal Conditions * Finding the ICD-10 equivalent for an ICD-9 code can be a challenge. This resource of frequently used codes can help when
helping patients thrive Physical Therapy
 helping patients thrive Physical Therapy in Hemophilia Care 8402 Harcourt Road, Suite 500, Indianapolis, IN 46260 Tel: 317-871-0000 Toll Free: 1-877-256-8837 Fax: 317-871-0010 www.ihtc.org Rev 12/12 The
helping patients thrive Physical Therapy in Hemophilia Care 8402 Harcourt Road, Suite 500, Indianapolis, IN 46260 Tel: 317-871-0000 Toll Free: 1-877-256-8837 Fax: 317-871-0010 www.ihtc.org Rev 12/12 The
Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology. treatment program that will effectively treat it. The tricky part about the shoulder is that it is a ball and
 Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology Shoulder injuries occur to most people at least once in their life. This highly mobile and versatile joint is one of the most common reasons people visit their health care
Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology Shoulder injuries occur to most people at least once in their life. This highly mobile and versatile joint is one of the most common reasons people visit their health care
Ergonomics Monitor Training Manual
 Table of contents I. Introduction Ergonomics Monitor Training Manual II. Definition of Common Injuries Common Hand & Wrist Injuries Common Neck & Back Injuries Common Shoulder & Elbow Injuries III. Ergonomics
Table of contents I. Introduction Ergonomics Monitor Training Manual II. Definition of Common Injuries Common Hand & Wrist Injuries Common Neck & Back Injuries Common Shoulder & Elbow Injuries III. Ergonomics
Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understa
 Plantar Fasciitis Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understand why it occurs. Recognize the injury
Plantar Fasciitis Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understand why it occurs. Recognize the injury
What is a Sports Physician?
 What is a Sports Physician? Dr Mike Bundy MBBS MRCGP Dip Sports Med FFSEM Consultant in Sport and Exercise Medicine Medical Director at Pure Sports Medicine Ex-England Rugby senior team Doctor www.puresportsmed.com
What is a Sports Physician? Dr Mike Bundy MBBS MRCGP Dip Sports Med FFSEM Consultant in Sport and Exercise Medicine Medical Director at Pure Sports Medicine Ex-England Rugby senior team Doctor www.puresportsmed.com
Muscular System. Principles of Health Science Dr. Wood
 Muscular System Principles of Health Science Dr. Wood Characteristics of muscles Excitability: : irritability or ability to respond to stimulus Contractibility: : ability to contract (become short and
Muscular System Principles of Health Science Dr. Wood Characteristics of muscles Excitability: : irritability or ability to respond to stimulus Contractibility: : ability to contract (become short and
.org. Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) Anatomy. Cause
 Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) Page ( 1 ) Tennis elbow, or lateral epicondylitis, is a painful condition of the elbow caused by overuse. Not surprisingly, playing tennis or other racquet sports can
Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) Page ( 1 ) Tennis elbow, or lateral epicondylitis, is a painful condition of the elbow caused by overuse. Not surprisingly, playing tennis or other racquet sports can
For Deep Pressure Massage
 T H E R A C A N E O W N E R S M A N U A L For Deep Pressure Massage Thera Cane is a self massager used to apply pressure to sore muscles. The unique design of the Thera Cane lets you apply deep pressure
T H E R A C A N E O W N E R S M A N U A L For Deep Pressure Massage Thera Cane is a self massager used to apply pressure to sore muscles. The unique design of the Thera Cane lets you apply deep pressure
Common Foot Pathologies
 Common Foot Pathologies Chondromalacia Patella (patellofemoral pain syndrome) Chondromalacia Patella (patellofemoral pain syndrome) What is it? Chondromalacia (of Greek origin meaning softening of the
Common Foot Pathologies Chondromalacia Patella (patellofemoral pain syndrome) Chondromalacia Patella (patellofemoral pain syndrome) What is it? Chondromalacia (of Greek origin meaning softening of the
TheraCane. Owner's Manual
 TheraCane Owner's Manual THERA CANE 411 Thera Cane is a therapeutic massager that allows you to apply pressure to treat muscle dysfunction. Benefits of using the Thera Cane Eliminate painful knots in your
TheraCane Owner's Manual THERA CANE 411 Thera Cane is a therapeutic massager that allows you to apply pressure to treat muscle dysfunction. Benefits of using the Thera Cane Eliminate painful knots in your
What are Core Muscles?... 2. A Healthy Lumbar Spine...3. What is Low Back Pain?...4. Rehabilitation...6. Stages of Rehabilitation...
 Table of Contents What are Core Muscles?... 2 A Healthy Lumbar Spine...3 What is Low Back Pain?...4 Rehabilitation...6 Stages of Rehabilitation...7 Pain Management....................... 8 Heat/Ice What
Table of Contents What are Core Muscles?... 2 A Healthy Lumbar Spine...3 What is Low Back Pain?...4 Rehabilitation...6 Stages of Rehabilitation...7 Pain Management....................... 8 Heat/Ice What
Knee Conditioning Program. Purpose of Program
 Prepared for: Prepared by: OrthoInfo Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle.
Prepared for: Prepared by: OrthoInfo Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle.
SELF-MASSAGE HANDOUTS
 SELF-MASSAGE HANDOUTS Self-Massage for the Head and Face Self-Massage for the Low Back and Buttocks Self-Massage for Runners Self-Massage for the Neck Self-Massage for the Feet Self-Massage for the Arms
SELF-MASSAGE HANDOUTS Self-Massage for the Head and Face Self-Massage for the Low Back and Buttocks Self-Massage for Runners Self-Massage for the Neck Self-Massage for the Feet Self-Massage for the Arms
A Patient s Guide to Plantar Fasciitis. Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, P.C.
 A Patient s Guide to Plantar Fasciitis Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
A Patient s Guide to Plantar Fasciitis Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
Hip Conditioning Program. Purpose of Program
 Prepared for: Prepared by: OrthoInfo Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle.
Prepared for: Prepared by: OrthoInfo Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle.
This is caused by muscle strain to the Achilles tendon in the heel of the foot.
 Foot Facts Our feet were designed to move across uneven earthy surfaces. The hard, inflexible surfaces that we regularly walk on today, such as concrete, tile or wood, leave our feet wanting in terms of
Foot Facts Our feet were designed to move across uneven earthy surfaces. The hard, inflexible surfaces that we regularly walk on today, such as concrete, tile or wood, leave our feet wanting in terms of
ACL Reconstruction Physiotherapy advice for patients
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust ACL Reconstruction Physiotherapy advice for patients Introduction This booklet is designed to provide you with advice and guidance on your rehabilitation after reconstruction
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust ACL Reconstruction Physiotherapy advice for patients Introduction This booklet is designed to provide you with advice and guidance on your rehabilitation after reconstruction
Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis
 Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints
Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints
UTILIZING STRAPPING AND TAPING CODES FOR HEALTH CARE REIMBURSEMENT:
 UTILIZING STRAPPING AND TAPING CODES FOR HEALTH CARE REIMBURSEMENT: A GUIDE TO BILLING FOR SPIDERTECH PRE-CUT APPLICATIONS AND TAPE Billing and coding taping and strapping services can be a complex issue.
UTILIZING STRAPPING AND TAPING CODES FOR HEALTH CARE REIMBURSEMENT: A GUIDE TO BILLING FOR SPIDERTECH PRE-CUT APPLICATIONS AND TAPE Billing and coding taping and strapping services can be a complex issue.
Therapeutic Canine Massage
 Meet our Certified Canine Massage Therapist, Stevi Quick After years of competitive grooming and handling several breeds in conformation, I became interested in training and competing with my dogs in the
Meet our Certified Canine Massage Therapist, Stevi Quick After years of competitive grooming and handling several breeds in conformation, I became interested in training and competing with my dogs in the
SCRIPT NUMBER 82 SPRAINED ANKLE (TWO SPEAKERS)
 SCRIPT NUMBER 82 SPRAINED ANKLE (TWO SPEAKERS) PROGRAM NAME: HEALTH NUGGETS PROGRAM TITLE: SPRAINED ANKLE PROGRAM NUMBER: 82 SUBJECT: PATHOLOGY, CAUSES, DIAGNOSIS, TREATMENT, PREVENTION OF SPRAINED ANKLES
SCRIPT NUMBER 82 SPRAINED ANKLE (TWO SPEAKERS) PROGRAM NAME: HEALTH NUGGETS PROGRAM TITLE: SPRAINED ANKLE PROGRAM NUMBER: 82 SUBJECT: PATHOLOGY, CAUSES, DIAGNOSIS, TREATMENT, PREVENTION OF SPRAINED ANKLES
Lower Back Pain An Educational Guide
 Lower Back Pain An Educational Guide A publication from the Center of Pain Medicine and Physiatric Rehabilitation 2002 Medical Parkway Ste 150 1630 Main St Ste 215 Annapolis, MD 21401 Chester, MD 21619
Lower Back Pain An Educational Guide A publication from the Center of Pain Medicine and Physiatric Rehabilitation 2002 Medical Parkway Ste 150 1630 Main St Ste 215 Annapolis, MD 21401 Chester, MD 21619
SECTION II General Osteopathic Techniques
 SECTION II General Osteopathic Techniques Chapter Four The Lower Extremities 40 Ligamentous Articular Strain The lower extremities are among the most important structures of the body and yet are often
SECTION II General Osteopathic Techniques Chapter Four The Lower Extremities 40 Ligamentous Articular Strain The lower extremities are among the most important structures of the body and yet are often

 More information >>> HERE
More information >>> HERE