Changes in European Society
|
|
|
- Dortha Casey
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Changes in European Society 1. Monarchs of Europe Enlightenment and Revolution The French Revolution and Napoleon
2 The Monarchs of Europe The Powers of Spain Absolute Monarchy of France Monarch in England Rules of Russia and Central Europe Throughout the 1500 s, global discoveries and exploration brought new wealth and prestige to Europe s monarchs. Kings, queens, and emperors ruled with few limits on their power. Over the next three centuries, their power was challenged by internal problems, rebellions, and wars.
3 New Monarchies of Europe Spain unification by marriage. France consolidation of power. England stability under the Tudors Holy Roman Empire different model: the cost of decentralization.
4 Characteristics of the New Monarchies 1. They offered the institution of monarchy as a guarantee of law and order. 2. They proclaimed that hereditary monarchy was the legitimate form of public power all should accept this without resistance. 3. They enlisted the support of the middle class in the towns tired of the local power of feudal nobles. 4. They would have to get their monarchies sufficiently organized & their finances into reliable order. 5. They would break down the mass of feudal, inherited, customary, or common law in which the rights of the feudal classes were entrenched. 6. The kings would MAKE law, enact it by his own authority, regardless of previous custom or historic liberties What pleases the prince has the force of law!
5 1. Kingdoms of Spain: 1492 What are the major kingdoms of Spain?
6 The Power of Spain Ferdinand & Isabella of Spain Spain experienced a golden age during the 1500 s, but economic problems and military struggles decreased. King Ferdinand of Aragon and Queen Isabella of Castile married a formed a powerful empire on the Iberian Peninsula. For most of the fifteenth century, the Spanish Armada controlled the seas. The Madonna of the Monarchs
7 The King Becomes Emperor King Charles I of Spain In 1516, the teenaged Charles became King Charles I of Spain. Absolute Monarch a ruler whose power was not limited by having to consult with the nobles, common people, or their representatives. Divine right held that the monarchs received their power from God and therefore must not be challenged.
8 Charles V and the Empire When Charles became king, his territory included the Low Counties of Belgium and the Netherlands, along with colonies in the Americas throne of the Holy Roman Empire became vacant Charles I of Spain became Holy Roman Emperor Charles V. Empire included Italy, Austria, and various German states.
9 Peace of Augsburg As Holy Roman Emperor, Charles wanted Europe to be Roman Catholic. Despite Charles efforts, Protestantism under Luther still spread and led to a compromise. Peace of Augsburg 1555 gave each German prince the right to decide whether his state would be Catholic or Protestant.
10 The Empire of Philip II 1556 Charles V gave up his throne and divided his empire between his son, Phillip II ruled the Netherlands, Spain, Sicily, and Spanish colonies in America and his brother ruled Austria
11 Religion and Revolt Spain reached the peak of its grandeur during the reign of Phillip II. To spread Catholicism, Phillip married Queen Mary I of England. (she died before giving birth) The Court of Blood spread of Catholicism in the Benelux Countries failed and led to the Duke of Alba torturing and executing thousands of people suspected of being rebels. Led to the Dutch rebellion and revolt throughout Europe The Court of Blood
12 Spain and England Rivalry develops between Spain and England. Catholic Spain Protestant England helps the Dutch against the Spanish. Queen Elizabeth I of England was allowing her sea dogs Sir Francis Drake attack the Spanish treasure ships. As a result, King Phillip II decided to attack England. Queen Elizabeth Sir Francis Drake
13 War with England The Spanish Armada, 130 ships and 20, 000 sailors sailed into the English Channel in Despite their efforts, the Invincible Spanish navy was sent back to Spain in defeat. Although the Spanish navy did recover, the traditional agricultural economy of Spain helped lead to the decline of the empire in the 1600s.
14 Artistic Achievements Golden Century in Art and Literature El Greco Greek Domenicos Theotocopoulos and Diego Velazquez reflected Spain s central role in the Counter Reformation. Miquel de Cervantes Don Quixote de la Mancha and Sister Juana Ines de la Cruz two writers of the Golden Age of Spain
15 2. Absolute Monarchy in France Henry IV, Louis XIII, and Louis XIV strengthened the French Monarchy, with Louis XIV setting the example of an absolute monarchy for the rest of Europe.
16 Religious War and Henry IV The Protestant Reformation began in Germany and also spread to France. By 1560 s, one in ten French men were Huguenot, or French Calvinist Protestant. Noble Protestants threatened the life of Catholic French monarchy. one king, one law, one religion
17 Conflict and a New King Saint Bartholomew s Day Massacre fighting between Huguenots and the Catholic queen. Nobles who were attending a Huguenot wedding of Henry of Navarre in Paris were assassinated and from there the violence spread to other parts of France. Death toll 10,000 t0 70,000 Henry, who escaped eventually became King Henry IV and converted to Catholicism.
18 Compromise and Progress King Henry in 1598 to restore peace issued the Edict of Nantes that gave Huguenots limited freedom of worship. Right to hold office and rule 200 towns Henry also eliminated France s debt and even built up a surplus. New industries, drained swamps, built canals and roads and stimulated trade and agriculture. He became one of France s more respected monarchs.
19 Louis XIII and Richelieu 1610 a fanatic Catholic stabbed Henry while his carriage was stopped in traffic Louis XIII, a very young man, who for a while depended upon his mother to serve as regent, that is to govern France. Cardinal Richelieu Catholic churchman became his chief minister and most trusted advisor He and King Louis XIII wanted to reduce the power of the Huguenots La Rochelle Huguenot port city was captured and converted to Catholic
20 Monarchy of Louis XIV Both Richelieu and Louis XIII died within one year of another ( ) Louis XIV, history s best example of a monarch, Louis led France during a time of great power, prosperity, and glory. His reign had a lasting impact on France both negative and positive
21 Rise of the Sun King Louis XIV just like his father, became king at a young age. His mother and Cardinal Mazarin provided advice. When Cardinal Mazarin died, King Louis declared that at age 18 he would govern France. He chose the sun as his personal symbol, implying that the world revolved around him.
22 Absolutism at Versailles Retained Absolute power in charge of the military, political and economic interest All his subjects under his direct control At the same time that he became absolute, he deprived the nobles of their rights and powers. The Palace at Versailles Louis enormous palace home to 10,000 officials, servants, and nobles making it a city
23 Louis and Protestantism Put an end to Huguenot control throughout France. He revoked the Edict of Nantes and outlawed Protestantism in France. Over 200 Huguenots fled France, causing a financial crisis.
24 Money and the Military Louis s finances were also a concern for France. His grand lifestyle demanded a great deal of money. He needed cash to increase the size of his army and expanding French territory 70,000 to 200,000 soldiers.
25 War over a Throne Louis XIV wanted to increase his power beyond the borders of France. War of the Spanish Succession Spain had no heir Three rulers claim heir Louis was one of them; the other two feared French control and Holy Roman Empire, England, and the Netherlands went to war against France. (known as the French and Indian War in America) Treaty of Utrecht 1713, Said that France and Spain would never be ruled by the same monarch. The war benefited England in many ways dominated North America
26 3. Monarchy in England In contrast to the absolute monarchies of Spain and France, the English monarchy was limited by Parliament; following a civil war, Parliament became even more powerful.
27 The Tudors and Parliament Two prominent Tudors Henry VIII and his daughter Elizabeth I, ruled during the time when absolutism was common in Europe. In England, however, Parliament limited their power. Henry VIII created the Protestant Church of England so he could divorce his first wife. Henry had Parliament pass laws ending the pope s power in England and establishing the king as the head of the Church of England. Edward short reign Bloody Mary (Catholic) Queen Elizabeth (Protestant)
28 The Stuarts and Parliament When the Virgin Queen Elizabeth died, a relative of the Tudor family from Scotland, King James I, became King James VI of Great Britain. He was the first member of the Stuart family and caused conflict with Parliament.
29 James I Clashes with Parliament He wanted to rule as an absolute monarch divine right. He was considered an outsider (Scotland). Had difficulty getting along with Parliament. Puritans a group of strict Calvinists, demanded that the Church of England be reformed. Also take away power of the church officials who supported the king One reform the King James Bible
30 Charles I Defies Parliament Son of James, King Charles I was crowned king when James died in Popular at first; however asked Parliament for money for overseas adventures and Parliament refused unless... Petition of Right place limits on the king s power (could not levy taxes without Parliamentary approval) Direct challenged to absolutism and in response Charles taxed his citizens without Parliament approval and decided to rule without Parliament control.
31 The English Civil War Conflict intensified between King Charles I and the English Parliament. The conflict became so severe that it led to the king s death.
32 Parliament Reconvenes King Charles in debt needed to ask Parliament for money He reconvened Parliament known as the Long Parliament took the opportunity to further limit the king s power Demanded that Parliament must be called at least every three years, and the king could no longer dismiss the Parliament. King Charles gave in!
33 War with Parliament King Charles, waiting for the right moment, arrested Puritan leaders for treason. Parliament in response decided to rise up against the king and in 1642, the English Civil war had begun. Royalists loyal to the king of England Roundheads Puritans in Parliament led by Oliver Cromwell 1646 the king outnumbered surrendered
34 Trial and Execution The king was charged with treason and on January 30, 1649, Charles I was publically beheaded in front of his own palace the first European monarch to be formally tried and sentenced to death by a court of law.
35 England under Oliver Cromwell The monarchy was completely outlawed. England became a commonwealth republican government based on the good of all the people. Cromwell established as Lord Protector of England, Scotland, and Ireland.
36 A Defender of Absolutism Cromwell, the king s death, and the war, troubled many of the English people. Thomas Hobbes Royalist who fled to France Levianthan political science humans are naturally selfish and fearful. Need an all powerful monarch to tell them how to live.
37 The Monarchy Returns Hobbes ideas reflected that many people were unhappy with Cromwell, and wanted a return to the monarchy.
38 The Restoration When Cromwell died in 1658, his son Richard Cromwell became Lord Protector and lacked the leadership skills of his father. The Parliament was reconvened and the monarch was brought back RESTORATION
39 The Reign of Charles II The son of the dead Charles I, Charles II became king. (Knew he had to watch his step) Positives reopened theaters, Habeas Corpus- someone accused of a crime must have a chance in court Negative another bubonic plague The Great Fire of London
40 James II When Charles II died, his brother, James II, who was Catholic, was next in line and became king of England. He was not popular. He wanted to rule as an absolute monarch, but Englishmen would no longer tolerate such a belief.
41 The Glorious Revolution 1688 a group of nobles invited James daughter Mary and her husband William, who were Protestants to become king and queen. James, knowing it was pointless to fight, fled to France. Glorious Revolution peaceful transfer of power to William and Mary.
42 Changes in Government The English Bill of Rights had to be signed by William and Mary Prevented the monarchy from levying taxes without the consent of Parliament. Constitutional Monarchy monarchy limited by law
43 4. Rulers of Russia and Central Europe The czars of Russia struggled with the westernization of their empire, while powerful families battled for control of central Europe.
44 The Monarch of Ivan IV In the 1500 s, Russia was far behind western Europe in technology and centralized governments. Russia was ruled by Boyars church officials, or landowners, usually with conservative view points. Czar 1546 a young prince took the title of czar (Latin Caesar, or emperor) That new czar, was Ivan IV.
45 Reforms of Ivan IV During his early years, he made many reforms. A General Council that included merchants and lowered-level nobles. Promoted military officers based on merit. He expanded Russia s borders and trade. Ivan s Good Period
46 Ivan the Terrible During the 1560 s, Ivan changed. Strict policies and violent actions sealed his reputation as Ivan the Terrible. Started with the death of his wife, Anastasia suspicious of closest advisors and killed them or sent them away. Climax of his insanity 1581, he killed his own son, who was next in line to be czar.
47 Peter the Great The death of Ivan s son left Russia without an heir and as a result, succession, economic problems, and foreign invasions added up to period known as the Time of Troubles Michael, a relative of Ivan s first wife, was crowned czar. (Romanov Dynasty ruled Russia until 1917) s Peter the Great transformed Russia into a modern state. Regained absolute power for the Russian monarchy. One of his first acts gain control of the Turkish port of Azov on the Black Sea. (disaster at first, but eventually the Turks surrendered)
48 Modernization and Reform Westernization Peters attempt to catch up Russia with the rest of western Europe. Reforms modernized the army and navy, brought the church under state control, built up the Russian industry, started the first Russian newspaper and sponsored new schools. Wanted Russia to adopt European styles boyars often rejected and resisted his actions Considered founder of modern Russia
49 Founding of St. Petersburg In addition to his reforms, he also founded a new city s St. Petersburg Russia s government was moved to the new city. Featured Western-style architecture rather than traditional Russian styles
50 Catherine the Great Russia s next important ruler was actually a German princess who came to Russia to marry a grandson of Peter the Great. She was known as Catherine the Great. After her husband became Czar Peter III in 1761 Catherine and many Russian nobles grew angry at his incompetent rule. Czar Peter III was murdered and Catherine became czarina. Reforms influenced by Western Europe, reformed Russian legal and educational systems and removed restrictions on trade
51 Challenges to Catherine s Rule Shortly after she received power she was soon distracted by a war in modern day Poland. Poland wanted freedom from Russia. Russia, however, won the war with Poland. Catherine also faced a uprising by a man named Yemelyan Pugachec. He claimed that he was Peter III. He served the same fate and was eventually found and beheaded.
52 Monarchy and Conflict in Central Europe Rulers in Central Europe never became absolute monarchs. The Holy Roman Empire was headed by a single emperor, but did not have total authority. Series of families known as the Hapsburgs. One of the Hapsburgs launched a terrible conflict that resulted in the thirty years war.
53 The Thirty Years War Began as a religious dispute in modern day Czech Republic. Protestants threw the Holy Roman Emperor s representative out of the window of a church. He was unharmed. Holy Roman Empire, Spain (Catholic countries) France, German states of Bavaria, Denmark, Sweden (Protestant countries) Devastated Germany millions died Treaty of Westphalia ended the war reduced the power of the Holy Roman Empire and strengthened the rulers of the states within it.
54 Austria and Prussia Among the leaders who gained from the treaty were the rulers of Austria and Prussia (Hapsburg) Emperor Charles VI died without a male heir and daughter, Maria Theresa took the throne of Austria. Prussia s ruler, (Hohenzollerns) Frederick the Great offered a truce with Maria Theresa and she declined. Started the War of the Austrian Secession. The Hapsburgs and the Hohenzollerns
55 Continued Rivalry In 1756, the Seven Years War began. One side Prussia, Great Britain Other side Austria, France, Russia Fighting occurred in Europe and North America (French and Indian War) Rivalry between Austria and Prussia (Hapsburgs and the Hohenzollerns) struggle to control Central Europe for many more years.
The failure of the Spanish Armada in 1588 permanently crippled the Spanish navy.
 AP European History Mr. Mercado Name Chapter 15B Politics, Religion, and War (Note: only do the sections Politics, Religion, and War ; Changing Attitudes ; and Literature and Art ) A. True or False Where
AP European History Mr. Mercado Name Chapter 15B Politics, Religion, and War (Note: only do the sections Politics, Religion, and War ; Changing Attitudes ; and Literature and Art ) A. True or False Where
World History Course Summary Department: Social Studies. Semester 1
 World History Course Summary Department: Social Studies All World History courses (Honors or otherwise) utilize the same targets and indicators for student performance. However, students enrolled in Honors
World History Course Summary Department: Social Studies All World History courses (Honors or otherwise) utilize the same targets and indicators for student performance. However, students enrolled in Honors
I N V E S T I C E D O R O Z V O J E V Z D Ě L Á V Á N Í ABSOLUTE MONARCHIES
 ABSOLUTE MONARCHIES Absolutism: Louis XIV of France born in 1638, ruled 1643-1715 as a child, he had to face the Frondes Revolt when the French high nobles rebelled against him he managed to take control
ABSOLUTE MONARCHIES Absolutism: Louis XIV of France born in 1638, ruled 1643-1715 as a child, he had to face the Frondes Revolt when the French high nobles rebelled against him he managed to take control
Renaissance and Reformation Study Guide and Notebook Checklist. **Use your notes and pages 34-57 and 146-148. Answers in Italics
 Renaissance and Reformation Study Guide and Notebook Checklist **Use your notes and pages 34-57 and 146-148 Answers in Italics 1. What is the Renaissance Movement the rebirth of? Art and learning 2. Where
Renaissance and Reformation Study Guide and Notebook Checklist **Use your notes and pages 34-57 and 146-148 Answers in Italics 1. What is the Renaissance Movement the rebirth of? Art and learning 2. Where
The Protestant Reformation
 The Protestant Reformation Mr. Montreuil April 2015 1 The Big Picture I can explain how the Protestant Reformation impacted Europe religiously, politically, & socially. This Lesson I can identify Reformation
The Protestant Reformation Mr. Montreuil April 2015 1 The Big Picture I can explain how the Protestant Reformation impacted Europe religiously, politically, & socially. This Lesson I can identify Reformation
Late Medieval Period (WHI.12)
 Name Late Medieval Period (WHI.12) Label on Map: England, France, Spain, Russia, Holly Roman Empire, Paris, Rome, Mediterranean Sea, English Channel, Atlantic Ocean Term: Nation-state Describe: Draw: 1
Name Late Medieval Period (WHI.12) Label on Map: England, France, Spain, Russia, Holly Roman Empire, Paris, Rome, Mediterranean Sea, English Channel, Atlantic Ocean Term: Nation-state Describe: Draw: 1
YEAR 1: Kings, Queens and Leaders (6 lessons)
 YEAR 1: Kings, Queens and Leaders (6 lessons) Contents Include: The United Kingdom and the Union Jack Kings and Queens The Magna Carta Charles I Parliament The Prime Minister Suggested Teacher Resources:
YEAR 1: Kings, Queens and Leaders (6 lessons) Contents Include: The United Kingdom and the Union Jack Kings and Queens The Magna Carta Charles I Parliament The Prime Minister Suggested Teacher Resources:
Napoleonic France, 1799 1815. Napoleon Bonaparte as a young Officer
 Napoleonic France, 1799 1815 Napoleon Bonaparte as a young Officer 1 2 1796 Napoleon crossed the Alps & drove the Austrians out of Northern Italy. He then turned N. Italy into the Cisalpine Republic and
Napoleonic France, 1799 1815 Napoleon Bonaparte as a young Officer 1 2 1796 Napoleon crossed the Alps & drove the Austrians out of Northern Italy. He then turned N. Italy into the Cisalpine Republic and
The Tudor Myth. and the Place of the Stage
 The Tudor Myth and the Place of the Stage Shakespeare s History Plays Two tetralogies (series of four plays): First Tetralogy (1590-93): Henry VI, parts 1,2 and 3 Richard III Second Tetralogy (1595-1599):
The Tudor Myth and the Place of the Stage Shakespeare s History Plays Two tetralogies (series of four plays): First Tetralogy (1590-93): Henry VI, parts 1,2 and 3 Richard III Second Tetralogy (1595-1599):
Hobbes, Locke, Montesquieu, and Rousseau on Government
 CONSTITUTIONAL RIGHTS FOUNDATION Bill of Rights in Action 20:2 Hobbes, Locke, Montesquieu, and Rousseau on Government Starting in the 1600s, European philosophers began debating the question of who should
CONSTITUTIONAL RIGHTS FOUNDATION Bill of Rights in Action 20:2 Hobbes, Locke, Montesquieu, and Rousseau on Government Starting in the 1600s, European philosophers began debating the question of who should
Chapter 3: The English Colonies
 Chapter 3: The English Colonies Section 1: The Southern Colonies Settlement in Jamestown In 1605 a company of English merchants asked King James I for the right to found, or establish, a settlement. In
Chapter 3: The English Colonies Section 1: The Southern Colonies Settlement in Jamestown In 1605 a company of English merchants asked King James I for the right to found, or establish, a settlement. In
Mary Queen of Scots Family Tree
 Mary Queen of Scots Family Tree Mary Queen of Scots is a complex historical persona. She has a significant place in Scottish, English and British history and is a required character to study for the Scottish
Mary Queen of Scots Family Tree Mary Queen of Scots is a complex historical persona. She has a significant place in Scottish, English and British history and is a required character to study for the Scottish
Unit 9 Lesson 5 Popes, Kings and Challenges to the Church
 Unit 9 Lesson 5 Popes, Kings and Challenges to the Church Lesson 5 Popes, Kings and Challenges to the Church Directions Read each False statement below. Replace each underlined word with one from the word
Unit 9 Lesson 5 Popes, Kings and Challenges to the Church Lesson 5 Popes, Kings and Challenges to the Church Directions Read each False statement below. Replace each underlined word with one from the word
Note Taking Study Guide PHILOSOPHY IN THE AGE OF REASON
 SECTION 1 Note Taking Study Guide PHILOSOPHY IN THE AGE OF REASON Focus Question: What effects did Enlightenment philosophers have on government and society? As you read this section in your textbook,
SECTION 1 Note Taking Study Guide PHILOSOPHY IN THE AGE OF REASON Focus Question: What effects did Enlightenment philosophers have on government and society? As you read this section in your textbook,
Note Taking Study Guide THE BYZANTINE EMPIRE
 SECTION 1 Note Taking Study Guide THE BYZANTINE EMPIRE Focus Question: What made the Byzantine empire rich and successful for so long, and why did it finally crumble? As you read this section in your textbook,
SECTION 1 Note Taking Study Guide THE BYZANTINE EMPIRE Focus Question: What made the Byzantine empire rich and successful for so long, and why did it finally crumble? As you read this section in your textbook,
 Penguin Readers Factsheets Teacher s Notes A History of Britain By Fiona Beddall Summary More than 2,000 years of times past are brought to life in this lively and interesting account of Britain s history.
Penguin Readers Factsheets Teacher s Notes A History of Britain By Fiona Beddall Summary More than 2,000 years of times past are brought to life in this lively and interesting account of Britain s history.
GEORGIA AMERICAN REVOLUTION
 GEORGIA in the AMERICAN REVOLUTION AMERICA HEADS TOWARD INDEPENDENCE: Until 1763, independence was unthinkable!!! Great Britain was the greatest, most powerful nation on earth, and the American colonists
GEORGIA in the AMERICAN REVOLUTION AMERICA HEADS TOWARD INDEPENDENCE: Until 1763, independence was unthinkable!!! Great Britain was the greatest, most powerful nation on earth, and the American colonists
Napoleon Bonaparte Rise & Reform
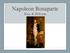 Napoleon Bonaparte Rise & Reform Personal Life Born into a noble family on the French island of Corsica Quickly rose through the military, fighting for the Revolutionary army Supported the Jacobins Self-proclaimed
Napoleon Bonaparte Rise & Reform Personal Life Born into a noble family on the French island of Corsica Quickly rose through the military, fighting for the Revolutionary army Supported the Jacobins Self-proclaimed
Name: Class: Global Studies Date: Mr. Wallace. The Enlightenment & The American Revolution Test Review
 Name: Class: Global Studies Date: Mr Wallace The Enlightenment & The American Revolution Test Review 1) The United States "founding fathers" were not influenced by the ideas of Enlightenment thinkers 2)
Name: Class: Global Studies Date: Mr Wallace The Enlightenment & The American Revolution Test Review 1) The United States "founding fathers" were not influenced by the ideas of Enlightenment thinkers 2)
General Certificate of Education History
 General Certificate of Education History Unit HIS3D Report on the Examination (Specification 2040) June 2013 Version: 1.0 Further copies of this Report are available from aqa.org.uk Copyright 2013 AQA
General Certificate of Education History Unit HIS3D Report on the Examination (Specification 2040) June 2013 Version: 1.0 Further copies of this Report are available from aqa.org.uk Copyright 2013 AQA
France (Monarchs of France)
 TUDOR FOREIGN POLICY: TIMELINE Year 1450 1451 1452 1453 1454 1455 1456 1457 1458 1459 1460 1461 1462 1463 1464 1465 1466 1467 1468 1469 1470 1471 1472 1473 1474 1475 1476 1477 England (Monarchs of England)
TUDOR FOREIGN POLICY: TIMELINE Year 1450 1451 1452 1453 1454 1455 1456 1457 1458 1459 1460 1461 1462 1463 1464 1465 1466 1467 1468 1469 1470 1471 1472 1473 1474 1475 1476 1477 England (Monarchs of England)
ROLE OF KING WILLIAM I IN THE UNIFICATION OF GERMANY STATES
 History S5 AOlution ROLE OF KING WILLIAM I IN THE UNIFICATION OF GERMANY STATES Lesson 40 Developed by (Maxon J. Kasumba) Subtopic ROLE OF KING WILLIAM I IN THE UNIFICATION OF GERMANY STATES Overview/general
History S5 AOlution ROLE OF KING WILLIAM I IN THE UNIFICATION OF GERMANY STATES Lesson 40 Developed by (Maxon J. Kasumba) Subtopic ROLE OF KING WILLIAM I IN THE UNIFICATION OF GERMANY STATES Overview/general
AP EUROPEAN HISTORY 2010 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP EUROPEAN HISTORY 2010 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 3 Analyze the various Protestant views of the relationship between church and state in the period circa 1500 1700. 9 8 Points The thesis is explicit
AP EUROPEAN HISTORY 2010 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 3 Analyze the various Protestant views of the relationship between church and state in the period circa 1500 1700. 9 8 Points The thesis is explicit
Use space below for notes
 AP European History: Unit 2.2 HistorySage.com Wars of Religion: 1559-1648 I. Hapsburg-Valois Wars (c. 1519-1559) A. Treaty of Cateau-Cambrèsis, 1559 1. Ended the Habsburg-Valois Wars (last purely dynastic
AP European History: Unit 2.2 HistorySage.com Wars of Religion: 1559-1648 I. Hapsburg-Valois Wars (c. 1519-1559) A. Treaty of Cateau-Cambrèsis, 1559 1. Ended the Habsburg-Valois Wars (last purely dynastic
10/3/2015. Habsburg Family Crest. Holy Roman Empire: 1750. Louis XIV ruled France for 72 years.
 TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Louis XIV ruled France for 72 years. His court
TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Louis XIV ruled France for 72 years. His court
Table of Contents. Part One: Social Studies Curriculum
 Table of Contents Part One: Social Studies Curriculum Chapter I: Social Studies Essay Questions and Prewriting Activities 1. Western Political Thought 1 2. The Age of Revolution 6 3. The Age of Napoleon
Table of Contents Part One: Social Studies Curriculum Chapter I: Social Studies Essay Questions and Prewriting Activities 1. Western Political Thought 1 2. The Age of Revolution 6 3. The Age of Napoleon
Reformation Lesson Plan. Central Historical Question: Why did Luther challenge the Catholic Church?
 Reformation Lesson Plan Central Historical Question: Why did Luther challenge the Catholic Church? Materials: Reformation PowerPoint Copies of Documents A and B Copies of Reformation: Guiding Questions
Reformation Lesson Plan Central Historical Question: Why did Luther challenge the Catholic Church? Materials: Reformation PowerPoint Copies of Documents A and B Copies of Reformation: Guiding Questions
The Hanoverian Dynasty. Queen Anne was the last of the Scottish Stuart dynasty
 The Hanoverian Dynasty The present British Royal Family is called the House of Windsor. Until 1917, this House was called the House of Hanover or Saxe-Coberg-Gotta. Saxe-Coberg-Gotta was added when Queen
The Hanoverian Dynasty The present British Royal Family is called the House of Windsor. Until 1917, this House was called the House of Hanover or Saxe-Coberg-Gotta. Saxe-Coberg-Gotta was added when Queen
AP EUROPEAN HISTORY 2014 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP EUROPEAN HISTORY 2014 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 3 Analyze the similarities in the methods that various absolute monarchs used in the 1600s and 1700s to consolidate and increase their power. 9 8 Points
AP EUROPEAN HISTORY 2014 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 3 Analyze the similarities in the methods that various absolute monarchs used in the 1600s and 1700s to consolidate and increase their power. 9 8 Points
Tudor Resource Box. Introduction
 Introduction Tudor Resource Box Welcome to the Tudor box. This resource is for teachers and group leaders working with Special Educational Needs groups. This box contains resources to support your self-directed
Introduction Tudor Resource Box Welcome to the Tudor box. This resource is for teachers and group leaders working with Special Educational Needs groups. This box contains resources to support your self-directed
www.gale.cengage.co.uk/statepapers
 King Henry VIII National Portrait Gallery, London Queen Anne National Portrait Gallery, London www.gale.cengage.co.uk/statepapers State Papers Online, 1509-1714, published in four seamless Parts, offers
King Henry VIII National Portrait Gallery, London Queen Anne National Portrait Gallery, London www.gale.cengage.co.uk/statepapers State Papers Online, 1509-1714, published in four seamless Parts, offers
4. After all groups have finished, have the groups share and explain their answers.
 Title: Patriot, Loyalist, or Neutral? You Decide By Lynne Fuller, Carusi Middle School Historical Background: During the American Revolution, the American colonists had to decide to support the War for
Title: Patriot, Loyalist, or Neutral? You Decide By Lynne Fuller, Carusi Middle School Historical Background: During the American Revolution, the American colonists had to decide to support the War for
History programmes of study: key stage 3
 History programmes of study: key stage 3 National curriculum in England Purpose of study A high-quality history education will help pupils gain a coherent knowledge and understanding of Britain s past
History programmes of study: key stage 3 National curriculum in England Purpose of study A high-quality history education will help pupils gain a coherent knowledge and understanding of Britain s past
The Frankish Empire. The Franks and the Origins of the Frankish Empire
 The Frankish Empire The Germanic tribe known as the Franks established and ruled the Frankish Empire, in the ancient territory of Gaul (largely encompassing modern-day France and parts of modern-day Germany),
The Frankish Empire The Germanic tribe known as the Franks established and ruled the Frankish Empire, in the ancient territory of Gaul (largely encompassing modern-day France and parts of modern-day Germany),
Notes on Friedrich Schiller s Mary Stuart.
 Notes on Friedrich Schiller s Mary Stuart. Introduction. Mary Stuart was first performed in 1800 and the real life historical figure it is based on, Mary Queen Of Scots, was executed in 1587 so it s a
Notes on Friedrich Schiller s Mary Stuart. Introduction. Mary Stuart was first performed in 1800 and the real life historical figure it is based on, Mary Queen Of Scots, was executed in 1587 so it s a
Remember the Alamo. The Changing Border of the Southwest
 Remember the Alamo The Changing Border of the Southwest Interact: What do you think this picture shows? In the year 1820, the new country of the United States and the newer country of Mexico had a lot
Remember the Alamo The Changing Border of the Southwest Interact: What do you think this picture shows? In the year 1820, the new country of the United States and the newer country of Mexico had a lot
An Outline of British History. By Steven L. Rosen, Ph.D.
 An Outline of British History By Steven L. Rosen, Ph.D. 1 MAIN PERIODS IN BRITISH HISTORY STONE AGE BRITAIN (5000 BC- 55BC) THE CELTS (800-600 BC- Roman occupation) ROMAN BRITAIN (55BC- AD 440) ANGLO-SAXON
An Outline of British History By Steven L. Rosen, Ph.D. 1 MAIN PERIODS IN BRITISH HISTORY STONE AGE BRITAIN (5000 BC- 55BC) THE CELTS (800-600 BC- Roman occupation) ROMAN BRITAIN (55BC- AD 440) ANGLO-SAXON
Unit 4 Lesson 8 The Qin and Han Dynasties
 Unit 4 Lesson 8 The Qin and Han Dynasties Directions Read the False statements below. Replace each underlined word with one from the word bank that makes each sentence True. Word Bank Ying Zheng army copper
Unit 4 Lesson 8 The Qin and Han Dynasties Directions Read the False statements below. Replace each underlined word with one from the word bank that makes each sentence True. Word Bank Ying Zheng army copper
No Taxation Without Representation!! Actions that led to the Revolutionary War
 No Taxation Without Representation!! Actions that led to the Revolutionary War Raising Taxes The French and Indian War had caused the British to be in a great deal of debt. They decided to keep a standing
No Taxation Without Representation!! Actions that led to the Revolutionary War Raising Taxes The French and Indian War had caused the British to be in a great deal of debt. They decided to keep a standing
History of Law in Society
 History of Law in Society Laws in Canada Our legal system has its origins in many cultures including aspects of Mosaic Law, Greek Law, Roman Law, French Law, and British Laws. In Canada, we are also influenced
History of Law in Society Laws in Canada Our legal system has its origins in many cultures including aspects of Mosaic Law, Greek Law, Roman Law, French Law, and British Laws. In Canada, we are also influenced
Summarize how Portugal built a trading empire
 Objectives Summarize how Portugal built a trading empire in. Analyze the rise of Dutch and Spanish dominance in the region. Understand how the decline of Mughal India affected European traders in the region.
Objectives Summarize how Portugal built a trading empire in. Analyze the rise of Dutch and Spanish dominance in the region. Understand how the decline of Mughal India affected European traders in the region.
5- Why did the Shogun rule Japan?
 Global History and Geography I The Rise of Feudalism in Japan Name: The emperor was an important political and religious figure in Japan. However, by the 1100s, the emperor s power was so weakened that
Global History and Geography I The Rise of Feudalism in Japan Name: The emperor was an important political and religious figure in Japan. However, by the 1100s, the emperor s power was so weakened that
Becoming a World Power. The Imperialist Vision. Imperialism (cont) 1872-1912. Americans wanted to develop overseas markets
 Becoming a World Power 1872-1912 The Imperialist Vision Imperialism economic and political domination of a strong nation over a weaker one Became popular with countries in Europe Imperialism (cont) Protectorates
Becoming a World Power 1872-1912 The Imperialist Vision Imperialism economic and political domination of a strong nation over a weaker one Became popular with countries in Europe Imperialism (cont) Protectorates
Chapter 22: World War I. Four most powerful European nations in the early 1900s were Great Britain, France, Germany, Russia.
 Chapter 22: World War I The Beginnings of World War I World War I was fought from 1914-1918. United States entered World War I in 1917. The Origins of Europe s Great War Nationalism Four most powerful
Chapter 22: World War I The Beginnings of World War I World War I was fought from 1914-1918. United States entered World War I in 1917. The Origins of Europe s Great War Nationalism Four most powerful
EXAMPLE: "Reading Passages" from: EDU108 - "Alamo Chocolate Pot" Art InHistory's Lesson Plans all feature thematic reading passages which contain
 EXAMPLE: "Reading Passages" from: EDU108 - "Alamo Chocolate Pot" Art InHistory's Lesson Plans all feature thematic reading passages which contain content on the time period, key people, historical events,
EXAMPLE: "Reading Passages" from: EDU108 - "Alamo Chocolate Pot" Art InHistory's Lesson Plans all feature thematic reading passages which contain content on the time period, key people, historical events,
World History Middle Ages Test
 World History Middle Ages Test 1. Europe became a feudal society because a. Europeans needed to defend themselves against constant raids and invasions. b. overpopulation required that a more efficient
World History Middle Ages Test 1. Europe became a feudal society because a. Europeans needed to defend themselves against constant raids and invasions. b. overpopulation required that a more efficient
1996 DBQ: Dutch Republic & Rival States1
 AP European History! Mr. Walters 1996 DBQ: Dutch Republic & Rival States1 Task: Identify and analyze the challenges to the security, unity and prosperity of the Dutch Republic, 1650-1713. Take into account
AP European History! Mr. Walters 1996 DBQ: Dutch Republic & Rival States1 Task: Identify and analyze the challenges to the security, unity and prosperity of the Dutch Republic, 1650-1713. Take into account
TEACHER S KEY SESSION 1. THE WORLD BEFORE THE GREAT WAR. PRETASK. 3. Pre- listening.
 TEACHER S KEY SESSION 1. THE WORLD BEFORE THE GREAT WAR. PRETASK 3. Pre- listening. 1. Before 1914, the nations of Europe were involved in a race to obtain overseas colonies all over the world, mainly
TEACHER S KEY SESSION 1. THE WORLD BEFORE THE GREAT WAR. PRETASK 3. Pre- listening. 1. Before 1914, the nations of Europe were involved in a race to obtain overseas colonies all over the world, mainly
The French Revolution A Brief Outline
 FOUR STAGES Moderate (1789-1792) Reign of Terror (1793-94) Reaction (1794-98) Napoleonic (1799-1815) The French Revolution A Brief Outline Why? A fed up people revolt against old ways, economic injustice,
FOUR STAGES Moderate (1789-1792) Reign of Terror (1793-94) Reaction (1794-98) Napoleonic (1799-1815) The French Revolution A Brief Outline Why? A fed up people revolt against old ways, economic injustice,
THE EXECUTIVE AND LEGISLATIVE BRANCHES OF GOVERNMENT
 THE EXECUTIVE AND LEGISLATIVE BRANCHES OF GOVERNMENT The political institutions of the United Kingdom are divided into the legislative, the executive and the judiciary. The last of these will be developed
THE EXECUTIVE AND LEGISLATIVE BRANCHES OF GOVERNMENT The political institutions of the United Kingdom are divided into the legislative, the executive and the judiciary. The last of these will be developed
The French Revolution Begins Close Read
 The French Revolution Begins Close Read Standards Alignment Text with Close Read instructions for students Intended to be the initial read in which students annotate the text as they read. Students may
The French Revolution Begins Close Read Standards Alignment Text with Close Read instructions for students Intended to be the initial read in which students annotate the text as they read. Students may
Home work. Fill in the Blanks Use your study sheet to find the correct answers. BETWEEN ANCIENT AND MODERN
 Date: 1 BETWEEN ANCIENT AND MODERN The Middle Ages is the period between a and m history. The early period of the Middle Ages is known as the D Ages because the great c of G and R had fallen. Life during
Date: 1 BETWEEN ANCIENT AND MODERN The Middle Ages is the period between a and m history. The early period of the Middle Ages is known as the D Ages because the great c of G and R had fallen. Life during
UNIT Y213: THE FRENCH REVOLUTION AND THE RULE OF NAPOLEON
 UNIT Y213: THE FRENCH REVOLUTION AND THE RULE OF NAPOLEON NOTE: BASED ON 2X 50 MINUTE LESSONS PER WEEK TERMS BASED ON 6 TERM YEAR. Key Topic Term Week Number Indicative Content Extended Content Resources
UNIT Y213: THE FRENCH REVOLUTION AND THE RULE OF NAPOLEON NOTE: BASED ON 2X 50 MINUTE LESSONS PER WEEK TERMS BASED ON 6 TERM YEAR. Key Topic Term Week Number Indicative Content Extended Content Resources
WORLD WARS (1914 to 1918 and 1939 to 1945) First World War (1914 to 1918) I. One mark questions (Answer in one sentence each)
 WORLD WARS (1914 to 1918 and 1939 to 1945) First World War (1914 to 1918) I. One mark questions (Answer in one sentence each) 1. When did the First World War begin? First World War began on 28 th July
WORLD WARS (1914 to 1918 and 1939 to 1945) First World War (1914 to 1918) I. One mark questions (Answer in one sentence each) 1. When did the First World War begin? First World War began on 28 th July
Egyptian History 101 By Vickie Chao
 Egyptian History 101 By Vickie Chao 1 A long time ago, before Egypt was a united country, there were two kingdoms -- Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. Upper Egypt was in the south. It controlled the areas along
Egyptian History 101 By Vickie Chao 1 A long time ago, before Egypt was a united country, there were two kingdoms -- Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. Upper Egypt was in the south. It controlled the areas along
Rome: Rise and Fall Of An Empire: Julius Caesar (Disc 1.3)
 1 Name Date 1. What was the condition of Rome when Julius Caesar was born in 100 B.C.E.? 2. Why was Young Caesar kidnapped? 3. What kind of captor was Caesar? 4. How and why did Caesar enter politics in
1 Name Date 1. What was the condition of Rome when Julius Caesar was born in 100 B.C.E.? 2. Why was Young Caesar kidnapped? 3. What kind of captor was Caesar? 4. How and why did Caesar enter politics in
Sample Test: Colonialism and Foundations of America. Use the following map and your knowledge of Social Studies to answer question 1.
 Sample Test: Colonialism and Foundations of America Use the following map and your knowledge of Social Studies to answer question 1. 1. What key activity does this map depict? A Middle Passage B Trans-Saharan
Sample Test: Colonialism and Foundations of America Use the following map and your knowledge of Social Studies to answer question 1. 1. What key activity does this map depict? A Middle Passage B Trans-Saharan
Colonial Massachusetts, 1607-1750. Colonial Massachusetts, 1607-1750. Colonial Massachusetts, 1607-1750. Topics of Discussion
 Topics of Discussion I. Virginia Company of Plymouth Fails, 1607-09 II. Puritans still interested in North America. III. Why were the Puritans interested in North America? IV. Pilgrims and the movement
Topics of Discussion I. Virginia Company of Plymouth Fails, 1607-09 II. Puritans still interested in North America. III. Why were the Puritans interested in North America? IV. Pilgrims and the movement
THE AGE OF ENLIGHTENMENT
 THE AGE OF ENLIGHTENMENT To view this PDF as a projectable presentation, save the file, click View in the top menu bar of the file, and select Full Screen Mode To request an editable PPT version of this
THE AGE OF ENLIGHTENMENT To view this PDF as a projectable presentation, save the file, click View in the top menu bar of the file, and select Full Screen Mode To request an editable PPT version of this
A Century of War and Wonder, 1550 1650
 CHAPTER 15 A Century of War and Wonder, 1550 1650 CHAPTER OUTLINE I. Europe s Economy and Society A. Europe s Continuing Overseas Expansion 1. Portuguese and Spanish overseas empires faced challenges from
CHAPTER 15 A Century of War and Wonder, 1550 1650 CHAPTER OUTLINE I. Europe s Economy and Society A. Europe s Continuing Overseas Expansion 1. Portuguese and Spanish overseas empires faced challenges from
How useful is the Diary of Samuel Pepys to a Historian studying Restoration England? 1,962 words
 How useful is the Diary of Samuel Pepys to a Historian studying Restoration England? 1,962 words 1 1 http://www.mylearning.org/learning/samuel-pepys-and-the-great-fire-of-london/pepys.jpg 1 Content Page
How useful is the Diary of Samuel Pepys to a Historian studying Restoration England? 1,962 words 1 1 http://www.mylearning.org/learning/samuel-pepys-and-the-great-fire-of-london/pepys.jpg 1 Content Page
Historical Background (Columbia Encyclopaedia)
 Historical Background (Columbia Encyclopaedia) Queen Anne half brother rose and fell in Great Britain, the question of succession continued after the Act of Settlement and after Anne s accession. The last
Historical Background (Columbia Encyclopaedia) Queen Anne half brother rose and fell in Great Britain, the question of succession continued after the Act of Settlement and after Anne s accession. The last
My Magna Carta. an international creative writing competition for 11-18 year olds.
 My Magna Carta an international creative writing competition for 11-18 year olds. About the Competition The English-Speaking Union is delighted to present My Magna Carta an international creative writing
My Magna Carta an international creative writing competition for 11-18 year olds. About the Competition The English-Speaking Union is delighted to present My Magna Carta an international creative writing
Chapter 5 The Enlightenment and the American Revolution I. Philosophy in the Age of Reason (5-1) A. Scientific Revolution Sparks the Enlightenment 1.
 Chapter 5 The Enlightenment and the American Revolution I. Philosophy in the Age of Reason (5-1) A. Scientific Revolution Sparks the Enlightenment 1. Natural Law: Rules or discoveries made by reason B.
Chapter 5 The Enlightenment and the American Revolution I. Philosophy in the Age of Reason (5-1) A. Scientific Revolution Sparks the Enlightenment 1. Natural Law: Rules or discoveries made by reason B.
Effects of the Enlightenment Grade Nine
 History Ohio Standards Connection: Benchmark A Explain connections between the ideas of the Enlightenment and changes in the relationships between citizens and their governments. Indicator 1 Explain how
History Ohio Standards Connection: Benchmark A Explain connections between the ideas of the Enlightenment and changes in the relationships between citizens and their governments. Indicator 1 Explain how
AP EUROPEAN HISTORY 2012 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP EUROPEAN HISTORY 2012 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 4 Analyze various ways in which government policies during the Revolutionary and Napoleonic era contributed to a greater sense of French national identity
AP EUROPEAN HISTORY 2012 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 4 Analyze various ways in which government policies during the Revolutionary and Napoleonic era contributed to a greater sense of French national identity
1914-1918: WORLD WAR I CFE 3201V
 1914-1918: WORLD WAR I CFE 3201V OPEN CAPTIONED NATIONAL GEOGRAPHIC SOCIETY 1992 Grade Levels: 10-13+ 25 minutes 1 Instructional Graphic Enclosed DESCRIPTION The forces of nationalism, imperialism, and
1914-1918: WORLD WAR I CFE 3201V OPEN CAPTIONED NATIONAL GEOGRAPHIC SOCIETY 1992 Grade Levels: 10-13+ 25 minutes 1 Instructional Graphic Enclosed DESCRIPTION The forces of nationalism, imperialism, and
No Taxation without Representation
 No Taxation without Representation After the French and Indian War, England was broke. They had spent a lot of money to protect the colonists in America. England thought that America should help to pay
No Taxation without Representation After the French and Indian War, England was broke. They had spent a lot of money to protect the colonists in America. England thought that America should help to pay
Here is the list of history courses with cross listings and how they fit in each of the sections of the History Major.
 Here is the list of history courses with cross listings and how they fit in each of the sections of the History Major. Note: if you take a History course that is cross listed and you take it under the
Here is the list of history courses with cross listings and how they fit in each of the sections of the History Major. Note: if you take a History course that is cross listed and you take it under the
YEAR 3: WARS OF THE ROSES (5 lessons)
 YEAR 3: WARS OF THE ROSES (5 lessons) Contents Include: Henry VI Edward IV The Princes in the Tower Richard III The Battle of Bosworth Field Suggested Teacher Resources: The Young Oxford History of Britain
YEAR 3: WARS OF THE ROSES (5 lessons) Contents Include: Henry VI Edward IV The Princes in the Tower Richard III The Battle of Bosworth Field Suggested Teacher Resources: The Young Oxford History of Britain
Phillis Wheatley, 1753-1784: Early African- American Poet
 17 December 2011 voaspecialenglish.com Phillis Wheatley, 1753-1784: Early African- American Poet A rare signed edition of Phillis Wheatley s poetry from 1773 (Download an MP3 of this story at voaspecialenglish.com)
17 December 2011 voaspecialenglish.com Phillis Wheatley, 1753-1784: Early African- American Poet A rare signed edition of Phillis Wheatley s poetry from 1773 (Download an MP3 of this story at voaspecialenglish.com)
Poster 5 - This is a primary source ; a poster ordered by the British government during the first world war. It was addressed to the English.
 Poster 1 ordered by the British government during the first world war. It was addressed to English men to incite them to enlist in the British army. - A military leader, Lord Kitchener, is drawn and painted
Poster 1 ordered by the British government during the first world war. It was addressed to English men to incite them to enlist in the British army. - A military leader, Lord Kitchener, is drawn and painted
Men from the British Empire in the First World War
 In 1914, Britain ruled over one quarter of the world s surface area and 434 million people. This was known as the British Empire. When war broke out, Britain was desperate for men to fight. Unlike France,
In 1914, Britain ruled over one quarter of the world s surface area and 434 million people. This was known as the British Empire. When war broke out, Britain was desperate for men to fight. Unlike France,
There are ten mistakes in this account. Underline them and correct them. were dead. Aramis told him that his mother was alive.
 1The Bastille, Paris There are ten mistakes in this account. Underline them and correct them. It was a cool autumn night in 1660. Aramis went to the Bastille prison and told the guard of the prison that
1The Bastille, Paris There are ten mistakes in this account. Underline them and correct them. It was a cool autumn night in 1660. Aramis went to the Bastille prison and told the guard of the prison that
The History of Early Modern Britain from 1485-1603. Henry VII (1485-1509) James VI of Scotland (1567-1625) and I of England (1603-1625)
 The History of Early Modern Britain from 1485-1603 Kings of England Tudor Stuart Henry VII (1485-1509) James VI of Scotland (1567-1625) and I of England (1603-1625) Henry VIII (1509-1547) Charles I (1625-1649),
The History of Early Modern Britain from 1485-1603 Kings of England Tudor Stuart Henry VII (1485-1509) James VI of Scotland (1567-1625) and I of England (1603-1625) Henry VIII (1509-1547) Charles I (1625-1649),
Chapter 2 Democracy in the colonies
 Chapter 2 Democracy in the colonies Learning Objectives Explain how self-government got its start in the colonies Explain the purpose of the Mayflower Compact. Describe the ways the Pilgrims practiced
Chapter 2 Democracy in the colonies Learning Objectives Explain how self-government got its start in the colonies Explain the purpose of the Mayflower Compact. Describe the ways the Pilgrims practiced
Ninth Grade History & Social Science World History I
 SEPTEMBER WHI.1 Historical Research and Geographical Analysis *(ongoing throughout year) identify, analyze, and interpret primary and secondary sources use maps, globes, artifacts, pictures identify major
SEPTEMBER WHI.1 Historical Research and Geographical Analysis *(ongoing throughout year) identify, analyze, and interpret primary and secondary sources use maps, globes, artifacts, pictures identify major
Macbeth. by William Shakespeare -1-
 Macbeth by William Shakespeare witches also told Banquo that he would be the father of kings. Macbeth, who was already Thane of Glamis, asked the witches why they called him Thane of Cawdor and king; but
Macbeth by William Shakespeare witches also told Banquo that he would be the father of kings. Macbeth, who was already Thane of Glamis, asked the witches why they called him Thane of Cawdor and king; but
TEST BOOK AND ANSWER KEY
 The Story of the World TEST BOOK AND ANSWER KEY Volume 1: Ancient Times Peace Hill Press Charles City, Virginia www.peacehillpress.com How to Use These Tests and Answer Key These Tests and their accompanying
The Story of the World TEST BOOK AND ANSWER KEY Volume 1: Ancient Times Peace Hill Press Charles City, Virginia www.peacehillpress.com How to Use These Tests and Answer Key These Tests and their accompanying
Images of the French Revolution and Napoleon. Review A little information about Napoleon Map Work and the Congress of Vienna Reading
 Images of the French Revolution and Napoleon Review A little information about Napoleon Map Work and the Congress of Vienna Reading Who are these people? What do these images represent? What in the World
Images of the French Revolution and Napoleon Review A little information about Napoleon Map Work and the Congress of Vienna Reading Who are these people? What do these images represent? What in the World
WORLD HISTORY: SCIENTIFIC REVOLUTION AND ENLIGHTENMENT. Jeopardy Version Watch out Alex Trebek
 WORLD HISTORY: SCIENTIFIC REVOLUTION AND ENLIGHTENMENT Jeopardy Version Watch out Alex Trebek Scientists Philosophes Enlightenment Spreads Terms Thnkers 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300
WORLD HISTORY: SCIENTIFIC REVOLUTION AND ENLIGHTENMENT Jeopardy Version Watch out Alex Trebek Scientists Philosophes Enlightenment Spreads Terms Thnkers 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300
Kings of Poland. Boleslaw The Brave 992 1025. Kazimierz The Restorer 1039 1058. Mieszko II 1025 1034. Wladyslaw Herman 1079 1102
 Kings of Poland Christianity, patriotism and a passionate love of freedom are the dominant trends of the ten centuries of Poland's turbulent history. Few nations have suffered as much and faced so many
Kings of Poland Christianity, patriotism and a passionate love of freedom are the dominant trends of the ten centuries of Poland's turbulent history. Few nations have suffered as much and faced so many
Paper 2 Shaping the nation 2B Britain: power and the people: c1170 to the present day with British depth studies
 SPECIMEN MATERIAL GCSE HISTORY Paper 2 Shaping the nation 2B Britain: power and the people: c1170 to the present day with British depth studies Specimen 2018 Morning Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials
SPECIMEN MATERIAL GCSE HISTORY Paper 2 Shaping the nation 2B Britain: power and the people: c1170 to the present day with British depth studies Specimen 2018 Morning Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials
The Downfall of the Dutch Republic
 Western Michigan University ScholarWorks at WMU Best Midwestern High School Writing 2014 Winners Best Midwestern High School Writing: A Celebration and Recognition of Outstanding Prose 5-2014 The Downfall
Western Michigan University ScholarWorks at WMU Best Midwestern High School Writing 2014 Winners Best Midwestern High School Writing: A Celebration and Recognition of Outstanding Prose 5-2014 The Downfall
Note Taking Study Guide ON THE EVE OF REVOLUTION
 SECTION 1 ON THE EVE OF REVOLUTION Focus Question: What led to the storming of the Bastille, and therefore, to the start of the French Revolution? As you read this section in your textbook, complete the
SECTION 1 ON THE EVE OF REVOLUTION Focus Question: What led to the storming of the Bastille, and therefore, to the start of the French Revolution? As you read this section in your textbook, complete the
Adolf Hitler. The man that did the unthinkable
 Adolf Hitler The man that did the unthinkable Hitler s Childhood Born on April 20 th 1889 His hometown is the Austrian town of Braunau His Mother was a housemaid while his father was an Austrian Custom
Adolf Hitler The man that did the unthinkable Hitler s Childhood Born on April 20 th 1889 His hometown is the Austrian town of Braunau His Mother was a housemaid while his father was an Austrian Custom
The French Revolution and Napoleon
 The French Revolution and Napoleon Chapter 23 Marie Antoinette King Louis XVI Napoleon French Revolution Homework Schedule Wed 10/22 Thurs 10/23 Fri 10/24 Homework Schedule No Written HW Read p.215-216
The French Revolution and Napoleon Chapter 23 Marie Antoinette King Louis XVI Napoleon French Revolution Homework Schedule Wed 10/22 Thurs 10/23 Fri 10/24 Homework Schedule No Written HW Read p.215-216
Modern European History courses, fall 2008 B226 Mafia and other Italian mysteries Carl Ipsen T, Th 2:30-3:45
 Modern European History courses, fall 2008 B226 Mafia and other Italian mysteries Carl Ipsen T, Th 2:30-3:45 B323 The Holocaust Mark Roseman M, W 1:25-2:15; plus discussion B357 Modern France Rebecca Spang
Modern European History courses, fall 2008 B226 Mafia and other Italian mysteries Carl Ipsen T, Th 2:30-3:45 B323 The Holocaust Mark Roseman M, W 1:25-2:15; plus discussion B357 Modern France Rebecca Spang
Inheritance: Laws of Inheritance & Unfair Gifts
 Inheritance: Laws of Inheritance & Unfair Gifts A woman gifted her house to her niece only two weeks before her death, thus depriving her heirs, two sisters and a brother, from their shares of inheritance.
Inheritance: Laws of Inheritance & Unfair Gifts A woman gifted her house to her niece only two weeks before her death, thus depriving her heirs, two sisters and a brother, from their shares of inheritance.
Great Britain Raises Taxes
 BUILDING BACKGROUND As the British colonies grew and became prosperous, the colonists got used to running their own lives. Britain began to seem very far away. At the same time, officials in Britain still
BUILDING BACKGROUND As the British colonies grew and became prosperous, the colonists got used to running their own lives. Britain began to seem very far away. At the same time, officials in Britain still
Devotion NT347 CHILDREN S DEVOTIONS FOR THE WEEK OF: LESSON TITLE: The Hall of Faith. THEME: God wants us to trust Him. SCRIPTURE: Hebrews 11:1-40
 Devotion NT347 CHILDREN S DEVOTIONS FOR THE WEEK OF: LESSON TITLE: The Hall of Faith THEME: God wants us to trust Him. SCRIPTURE: Hebrews 11:1-40 Dear Parents Welcome to Bible Time for Kids! This is a
Devotion NT347 CHILDREN S DEVOTIONS FOR THE WEEK OF: LESSON TITLE: The Hall of Faith THEME: God wants us to trust Him. SCRIPTURE: Hebrews 11:1-40 Dear Parents Welcome to Bible Time for Kids! This is a
Chapter 8, Section 2 The Louisiana Purchase. Pages 272-277
 Chapter 8, Section 2 The Louisiana Purchase Pages 272-277 American Settlers Move West By the early 1800s, thousands of Americans settle in the area between the Appalachians and the Mississippi River. Kentucky,
Chapter 8, Section 2 The Louisiana Purchase Pages 272-277 American Settlers Move West By the early 1800s, thousands of Americans settle in the area between the Appalachians and the Mississippi River. Kentucky,
Social Studies. Directions: Complete the following questions using the link listed below.
 Social Studies Name: Directions: Complete the following questions using the link listed below. Questions 1-8: http://www.biography.com/people/adolf-hitler-9340144 (Pages 1-2) Questions 9-17: http://www.history.com/topics/world-war-ii/adolf-hitler
Social Studies Name: Directions: Complete the following questions using the link listed below. Questions 1-8: http://www.biography.com/people/adolf-hitler-9340144 (Pages 1-2) Questions 9-17: http://www.history.com/topics/world-war-ii/adolf-hitler
Chapter 3: European Exploration and Colonization
 Chapter 3: European Exploration and Colonization Trade Route to Asia in the 1400s European Trade With Asia Traders - people who get wealth by buying items from a group of people at a low price and selling
Chapter 3: European Exploration and Colonization Trade Route to Asia in the 1400s European Trade With Asia Traders - people who get wealth by buying items from a group of people at a low price and selling
Chapter 9: The Policies of Alexander Hamilton and Thomas Jefferson
 Chapter 9: The Policies of Alexander Hamilton and Thomas Jefferson Department of State, Department of Treasury, Department of War, Attorney General, Postmaster General : 5 government departments established
Chapter 9: The Policies of Alexander Hamilton and Thomas Jefferson Department of State, Department of Treasury, Department of War, Attorney General, Postmaster General : 5 government departments established
Causes of the Revolution War Test. (Do not write on this Test)
 Causes of the Revolution War Test (Do not write on this Test) 1) Which group supported Patrick Henry, a famous American colonist who said, Give me liberty or give me death? a) Loyalist b) Patriots c) Tories
Causes of the Revolution War Test (Do not write on this Test) 1) Which group supported Patrick Henry, a famous American colonist who said, Give me liberty or give me death? a) Loyalist b) Patriots c) Tories
Shays Rebellion. Central Historical Question: How did Americans react to Shays rebellion?
 Central Historical Question: How did Americans react to Shays rebellion? Materials: PowerPoint on Articles of Confederation Copies of Textbook Excerpt on Copies of Thomas Jefferson Letter Copies of Guiding
Central Historical Question: How did Americans react to Shays rebellion? Materials: PowerPoint on Articles of Confederation Copies of Textbook Excerpt on Copies of Thomas Jefferson Letter Copies of Guiding
Second Grade The War of 1812 Assessment
 Second Grade The War of 1812 Assessment 1a. Who was president during the War of 1812? a. George Washington b. James Madison 1b. Who was president during the War of 1812? a. George Washington b. James Madison
Second Grade The War of 1812 Assessment 1a. Who was president during the War of 1812? a. George Washington b. James Madison 1b. Who was president during the War of 1812? a. George Washington b. James Madison
