Hypertensive Encephalopathy in Children
|
|
|
- Marcia Walton
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hypertensive Encephalopathy in Children Blaise V. Jones, John C. Egelhoff, and Richard J. Patterson Summary: We present five cases of hypertensive encephalopathy in children, three with MR imaging findings and two with CT findings alone. One of the five patients had MR perfusion imaging, which showed perfusion abnormalities that support the concept of vasodilatation as the major contributor to the syndrome. Hypertensive encephalopathy is rarely reported in children, and its true prevalence may be underestimated. Characteristic lesions in the severely hypertensive child should be recognized as manifestations of hypertensive encephalopathy, and subsequent clinical management should focus on treatment of the hypertension and/or its underlying causes. Index terms: Brain, diseases; Children, diseases; Hypertension Hypertensive encephalopathy is a condition characterized by varying degrees of headache, nausea, vomiting, visual disturbances, focal neurologic deficit, and seizures in the setting of severe systemic hypertension that is relatively acute in onset. The degree of hypertension varies, but systolic pressure greater than 250 mm Hg and diastolic pressure greater than 150 mm Hg are commonly encountered. It can be seen in patients with acute elevation of blood pressure related to nephritis or eclampsia; alternatively, it may be superimposed on chronic, untreated, or inadequately treated essential hypertension (1, 2). Clinical findings typically resolve with adequate treatment of the hypertension; permanent deficits are seen in those cases complicated by frank infarction or hemorrhage. We are aware of two previously reported cases of nonobstetric hypertensive encephalopathy in children (3, 4). Case Reports Case 1 A 10-year-old boy had a generalized tonicoclonic seizure preceded by a severe headache. Blood pressure was 140/108 mm Hg. Findings at neurologic examination were normal. Findings on computed tomographic (CT) scans obtained at the time of presentation with and without intravenous contrast material were also normal. Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging performed approximately 8 hours later showed regions of abnormal hyperintense signal on T2-weighted images in the cortex and subcortical white matter of the high occipital lobes (Fig 1). There was minimal associated hypointense signal on T1-weighted images; no enhancement was seen after administration of contrast material. During a second MR examination performed 18 hours later, gradient-echo (24/15/1 [repetition time/echo time/excitations]) images with a 10 flip angle were obtained every 1.8 seconds at the level of the region of abnormal signal during bolus infusion of contrast material. This study showed mildly increased perfusion in the regions of abnormal signal. No cause of the hypertension was found, despite an extensive imaging and metabolic workup. The patient was treated medically, with good blood pressure control and no further seizure activity or neurologic symptoms. Case 2 An 11-year-old girl had headache, mental status changes, and hypertension of 240/180 mm Hg. Abdominal sonographic and CT studies showed a chronically shrunken kidney. MR examination of the brain showed regions of abnormal hyperintense signal throughout the occipital lobes on T2-weighted images. Additional foci of abnormal T2 prolongation were seen in the medulla oblongata, pons, and cerebellar hemispheres (Fig 2A). There was no enhancement after administration of contrast material in any of the lesions. Embolization of the atrophic kidney was performed, with resolution of the systemic hypertension and neurologic symptoms. Follow-up MR imaging showed resolution of the lesions (Fig 2B). Case 3 A 15-year-old boy with Addison disease was admitted with a new onset of generalized seizures and with blood pressure of 185/125 mm Hg. MR imaging at the Received December 4, 1995; accepted after revision March 4, Presented in part at the annual meeting of the American Society of Neuroradiology, Chicago, Ill, April From the Department Radiology, Children s Hospital Medical Center, Cincinnati, Ohio. Address reprint requests to Blaise V. Jones, MD, Department of Radiology, Room CG533B, M. S. Hershey Medical Center, PO Box 850, Hershey, PA AJNR 18: , Jan /97/ American Society of Neuroradiology 101
2 102 JONES AJNR: 18, January 1997 Fig 1. Case 1: 10-year-old boy with idiopathic hypertension and seizures. A, Axial T2-weighted (2500/110) MR image through the parietooccipital junction shows abnormal hyperintense signal in the subcortical white matter bilaterally (arrows), extending into the overlying cortex. B, Axial gradient-echo (24/15) MR images with a 10 flip angle, obtained at 1.8- second intervals during bolus injection of contrast material, show mildly increased perfusion in the left occipital pole at the site of greatest signal abnormality on T2- weighted imaging (arrows). time of presentation showed patchy foci of hyperintense signal on T2-weighted images at the parietooccipital junction bilaterally. These lesions were hypointense on T1-weighted images, with local mass effect. There was mild gyral enhancement after administration of contrast material. Repeat contrast-enhanced MR imaging performed 1 week after treatment of the hypertension showed marked decrease in T1 and T2 signal abnormalities and resolution of the abnormal enhancement (Fig 3). Case 4 An 11-year-old girl had a seizure preceded by severe headache. She also had increasing abdominal girth over a period of several weeks. Blood pressure on admission was 165/117 mm Hg. A CT scan of the abdomen revealed a large primitive neuroectodermal tumor with abundant malignant ascites. A contrast-enhanced CT scan of the head showed regions of abnormal decreased attenuation in the high occipital lobes, with some cortical enhancement after contrast administration (Fig 4). Neurologic findings re-
3 AJNR: 18, January 1997 HYPERTENSIVE ENCEPHALOPATHY 103 Fig 2. Case 2: 11-year-old girl with renovascular hypertension and headache. A, Axial T2-weighted image (2500/90) through the posterior fossa shows abnormal hyperintense signal in the olives (black arrows) and the periphery of the cerebellar hemispheres (white arrow). B, MR image obtained after treatment of hypertension shows resolution of the signal abnormalities. Fig 3. Case 3: 15-year-old boy with hypertension caused by Addison disease. A, Coronal postcontrast T1-weighted image (550/15) through the posterior parietal lobes shows abnormal cortical enhancement with mild associated mass effect and surrounding low signal intensity (arrows). B, MR image obtained after treatment of hypertension shows resolution of the abnormal enhancement and mass effect and only minimal residual hypointense signal. Fig 4. Case 4: 11-year-old girl with hypertension caused by a pelvic primitive neuroectodermal tumor. Axial CT scans before (A) and after (B) contrast administration show abnormal cortical enhancement and surrounding low attenuation.
4 104 JONES AJNR: 18, January 1997 turned to normal with treatment of the hypertension; follow-up imaging was not performed. Case 5 A 9-year-old boy with a recent renal transplant had seizures in the hospital associated with subacute graft rejection and a blood pressure of 180/110 mm Hg. A contrast-enhanced CT scan of the head showed bilateral and symmetric regions of decreased attenuation centered in the subcortical white matter of the parietooccipital junctions and the cerebellar hemispheres with extension into the overlying cortex. A less prominent region of decreased attenuation was seen in the right frontal lobe. There was no enhancement with contrast administration. Neurologic symptoms resolved with control of the hypertension, and follow-up imaging was not performed. Discussion The lesions of hypertensive encephalopathy were initially thought to be ischemic in nature. Autoregulatory vasoconstriction in the cerebral vasculature is seen in response to systemic hypertension. It has been theorized that in hypertensive encephalopathy this responsive vasoconstriction is severe enough to cause ischemia in the affected vascular territory, and that the symptoms and imaging findings are a reflection of the ischemia (5 7). This theory is supported by cases of angiographically demonstrated vasospasm in patients with eclampsia and neurologic symptoms (7, 8). More recent investigators have implicated vasodilatation rather than vasoconstriction as the major component of hypertensive encephalopathy. Animal studies have shown that severe and acute increases in cerebral blood pressure result in overdistention of arterioles, accompanied by hydrostatic edema and increased pinocytosis, resulting in extravasation of proteins and fluid into the interstitium (9 11). Cerebral perfusion is actually increased in affected regions (12). These changes may be mediated by increased prostaglandin synthesis (9). They are reversible up to a point; more severe and permanent endothelial damage occurs with higher pressures (9, 11). Arterioles situated a short distance from the cortical surface are most affected, and sympathetic nervous activity affords protection from these effects. The posterior circulation has significantly less sympathetic innervation than the carotid circulation (10, 13), which may explain why the majority of lesions in hypertensive encephalopathy are found in the vascular territory of the posterior circulation. Previous authors have detailed the imaging findings in adults with hypertensive encephalopathy (4 6, 14, 15). The most commonly described abnormalities consist of foci of hyperintense signal on T2-weighted MR images in the subcortical white matter of the occipital lobes. These lesions frequently have associated hypointensity on T1-weighted MR images and decreased attenuation on CT scans. Focal or diffuse brain swelling and gray matter involvement are usually evident. Associated contrast enhancement has been reported in a small number of cases. Lesions are less often seen in other brain locations, including the cerebellum, brain stem, parietooccipital junction, basal ganglia, and frontal lobes. While hemorrhagic foci are commonly encountered in autopsy studies (16), they are infrequently seen at imaging, except in patients with chronic hypertension (4, 14, 15). The five cases reported here showed a characteristic distribution of imaging abnormalities, with the majority of lesions occurring in the vascular distribution of the posterior circulation. All cases had involvement of both subcortical white matter and adjacent gray matter, and all had lesions in the occipital lobes or at the parietooccipital junction. Focal swelling/edema was seen in all cases. Enhancement was seen in two cases, and two children had lesions in the cerebellar hemispheres. No lesions were seen in the basal ganglia, and only one patient had frontal lobe involvement. No hemorrhagic foci were seen. The child with the most lesions (case 2) had the greatest level of hypertension. All symptoms resolved in these five patients, and in all cases in which follow-up imaging was performed there was either resolution of or marked improvement in the abnormal findings. T2 * -weighted gradient-echo imaging during bolus infusion of gadopentetate dimeglumine is a useful technique for assessing regional cerebral perfusion. This method takes advantage of the sensitivity of gradient-recalled imaging to the susceptibility effects of contrast agent within the vascular bed, reflecting perfusion at the arteriolar level. The effect is seen during bolus infusion, necessitating rapid acquisition of multiple images at a single level to map out the dynamics of arteriolar perfusion (17). In our case 1, perfusion imaging was performed approximately 18 hours after the initial diagnostic examination. The child s symptoms had resolved by this time, and there was some decrease in the signal abnormality of the previ-
5 AJNR: 18, January 1997 HYPERTENSIVE ENCEPHALOPATHY 105 ously identified lesions on spin-echo images. The increased perfusion to these lesions seen on the gradient-echo images was mild in degree, but is consistent with the theory of vasodilatation with blood-brain barrier disturbance and extravasation of proteins as the primary event in hypertensive encephalopathy. These findings correspond well to those of Schwartz et al (15), who reported results of 99m Tc-hexamethylpropyleneamine oxime (HMPAO) singlephoton emission CT (SPECT) studies in two patients with hypertensive encephalopathy. In the one patient who was symptomatic during imaging, increased perfusion to regions of abnormal signal was clearly demonstrated on MR examination. In their second patient, who was studied 1 day after resolution of acute signs and symptoms, only mild perfusion abnormalities were seen. Perfusion imaging may provide a greater insight into the mechanism of hypertensive encephalopathy, but this will require further investigation of additional cases. It has been observed that previously normotensive persons develop hypertensive encephalopathy at lower blood pressures than do chronically hypertensive persons (1). In the adult, cerebral blood flow is maintained by autoregulation over a range of systemic mean arterial pressures from 60 to 150 mm Hg. This range is shifted to higher pressures in untreated hypertensive patients. Normal systemic arterial pressures are lower in children than adults, with systolic measurements ranging from 105 mm Hg or less at 1 year of age to 135 mm Hg or less at age 18 (90th percentile) (18). It is reasonable to assume that the pressure range of cerebral blood flow autoregulation is accordingly lower in children as well. The five patients in this study had an average systolic pressure of 182 mm Hg and an average diastolic pressure of 128 mm Hg, somewhat lower than the values typically reported in adults. We postulate that children develop hypertensive encephalopathy at lower absolute pressures than adults owing to the relative left shift of their range of cerebral blood flow autoregulation. Hypertension is uncommon in children, and is often seen in conjunction with systemic disease. Three of the five children in this report had systemic illnesses that directly contributed to their hypertension; a fourth had renovascular hypertension. Of two previously reported cases of hypertension in children, one occurred in a child with hypertension associated with Wilms tumor and the other was in a teenager with renovascular hypertension. Given the infrequency of hypertension in the pediatric population and the nonspecific and reversible nature of the findings in hypertensive encephalopathy, it is not surprising that the diagnosis has rarely been reported in children. The actual prevalence may be underestimated. More aggressive and effective treatment of hypertension in the obstetric population appears to have decreased the frequency of hypertensive encephalopathy (1). The infrequent identification of infarct or hemorrhage in recent reports as compared with earlier imaging and autopsy studies suggests that these are complications seen in the more severe cases of hypertensive encephalopathy. Such cases are expected to be less common in children, as they are more likely to present with symptoms at lower absolute levels of systemic pressure, and they generally respond well to antihypertensive therapy. The characteristic intracranial lesions of hypertensive encephalopathy should be recognized in the hypertensive child, and subsequent clinical management should focus on treatment of the hypertension and/or its underlying causes. It is our experience that in uncomplicated cases follow-up imaging is not necessary. References 1. Dinsdale HB. Hypertensive encephalopathy. Stroke 1982;13: Gifford RW. Management of hypertensive crises. JAMA 1991;266: Shanley DJ, Sisler CL. MR demonstration of reversible cerebral lesions in a child with hypertensive encephalopathy caused by Wilms tumor. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1992;158: Weingarten K, Barbut D, Filippi C, Zimmerman RD. Acute hypertensive encephalopathy: findings on spin-echo and gradient-echo MR imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1994;162: Coughlin WF, McMurdo SK, Reeves T. MR imaging of postpartum cortical blindness. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1989;13: Waldron RL, Abbott DC, Vellody D. Computed tomography in preeclampsia-eclampsia syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1985;6: Will AD, Lewis KL, Hinshaw DB Jr, et al. Cerebral vasoconstriction in toxemia. Neurology 1987;37: Trommer BL, Homer D, Mikhael MA. Cerebral vasospasm and eclampsia. Stroke 1988;19: Kontos HA, Wei EP, Deitrich D, et al. Mechanism of cerebral arteriolar abnormalities after acute hypertension. Am J Physiol 1981;240: MacKenzie ET, Strandgaard S, Graham DI, Jones JV, Harper AM,
6 106 JONES AJNR: 18, January 1997 Farrar JK. Effects of acutely induced hypertension in cats on pial arteriolar caliber, local cerebral blood flow, and the blood-brain barrier. Circ Res 1976;39: Nag S, Robertson DM, Dinsdale HB. Cerebral cortical changes in acute experimental hypertension. Lab Invest 1977;36: Skinhøj E, Strangaard S. Pathogenesis of hypertensive encephalopathy. Lancet 1973;1: Beausang-Linder M, Bill A. Cerebral circulation in acute arterial hypertension: protective effects of sympathetic nervous activity. Acta Physiol Scand 1981;111: Sanders TG, Clayman DA, Sanchez-Ramos L, Vines FS, Russo L. Brain in eclampsia: MR imaging with clinical correlation. Radiology 1991;80: Schwartz RB, Jones KM, Kalina P, et al. Hypertensive encephalopathy: findings on CT, MR imaging, and SPECT imaging in 14 cases. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1992;159: Richards A, Graham D, Bullock R. Clinicopathological study of neurological complications due to hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1988;51: Tzika AA, Massoth RJ, Ball WS Jr, Majumdar S, Dunn RS, Kirks DR. Cerebral perfusion in children: detection with dynamic contrast-enhanced T2 * -weighted MR images. Radiology 1993;187: Report of the Task Force on Blood Pressure in Children. Pediatrics 1977;59:797
Hemorrhagic venous infarction Heather Borders, MD
 Hemorrhagic venous infarction Heather Borders, MD 12/13/2010 History 16 year old female with four day history of headache and acute change in mental status. History of two days of oral contraceptive use
Hemorrhagic venous infarction Heather Borders, MD 12/13/2010 History 16 year old female with four day history of headache and acute change in mental status. History of two days of oral contraceptive use
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)?
 What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
Case Report. Central Neurocytoma. Fotis Souslian, MD; Dino Terzic, MD; Ramachandra Tummala, MD. Department of Neurosurgery, University of Minnesota
 1 Case Report Central Neurocytoma Fotis, MD; Dino Terzic, MD; Ramachandra Tummala, MD Department of Neurosurgery, University of Minnesota Case This is a previously healthy 20 year old female, with 3 months
1 Case Report Central Neurocytoma Fotis, MD; Dino Terzic, MD; Ramachandra Tummala, MD Department of Neurosurgery, University of Minnesota Case This is a previously healthy 20 year old female, with 3 months
Short Communications. Alcoholic Intracerebral Hemorrhage
 Short Communications 1565 Alcoholic Intracerebral Hemorrhage Leon A. Weisberg, MD Six alcoholic patients developed extensive cerebral hemispheric hemorrhages with both intraventricular and subarachnoid
Short Communications 1565 Alcoholic Intracerebral Hemorrhage Leon A. Weisberg, MD Six alcoholic patients developed extensive cerebral hemispheric hemorrhages with both intraventricular and subarachnoid
Reversibility of Acute Demyelinating Lesions in relapsingremitting
 Reversibility of Acute Demyelinating Lesions in relapsingremitting Multiple Sclerosis Omar A. Khan ( Division of Neuroimmunology, Department of Neurology, Neurology and Research Services. Veterans Affairs
Reversibility of Acute Demyelinating Lesions in relapsingremitting Multiple Sclerosis Omar A. Khan ( Division of Neuroimmunology, Department of Neurology, Neurology and Research Services. Veterans Affairs
Diabetic Ketoacidosis: When Sugar Isn t Sweet!!!
 Diabetic Ketoacidosis: When Sugar Isn t Sweet!!! W Ricks Hanna Jr MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics University of Tennessee Health Science Center LeBonheur Children s Hospital Introduction Diabetes
Diabetic Ketoacidosis: When Sugar Isn t Sweet!!! W Ricks Hanna Jr MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics University of Tennessee Health Science Center LeBonheur Children s Hospital Introduction Diabetes
PE finding: Left side extremities mild weakness No traumatic wound No bloody otorrhea, nor rhinorrhea
 Case report A 82-year-old man was suffered from sudden onset spasm of extremities then he fell down to the ground with loss of consciousness. He recovered his consciousness 7-8 mins later but his conscious
Case report A 82-year-old man was suffered from sudden onset spasm of extremities then he fell down to the ground with loss of consciousness. He recovered his consciousness 7-8 mins later but his conscious
NEUROIMAGING in Parkinsonian Syndromes
 NEUROIMAGING in Parkinsonian Syndromes (Focus on Structural Techniques: CT and MRI) Dr. Roberto Cilia Parkinson Institute, ICP, Milan, Italy OUTLINE Primary Parkinsonism Idiopathic Parkinson s Disease
NEUROIMAGING in Parkinsonian Syndromes (Focus on Structural Techniques: CT and MRI) Dr. Roberto Cilia Parkinson Institute, ICP, Milan, Italy OUTLINE Primary Parkinsonism Idiopathic Parkinson s Disease
Steps to getting a diagnosis: Finding out if it s Alzheimer s Disease.
 Steps to getting a diagnosis: Finding out if it s Alzheimer s Disease. Memory loss and changes in mood and behavior are some signs that you or a family member may have Alzheimer s disease. If you have
Steps to getting a diagnosis: Finding out if it s Alzheimer s Disease. Memory loss and changes in mood and behavior are some signs that you or a family member may have Alzheimer s disease. If you have
Intracranial Tuberculoma: Comparison of MR with Pathologic Findings
 Intracranial Tuberculoma: Comparison of MR with Pathologic Findings Tae Kyoung Kim, Kee Hyun Chang, Chong Jai Kim, Jin Mo Goo, Myeong Cherl Kook, and Moon Hee Han PURPOSE: To compare the MR signal intensity
Intracranial Tuberculoma: Comparison of MR with Pathologic Findings Tae Kyoung Kim, Kee Hyun Chang, Chong Jai Kim, Jin Mo Goo, Myeong Cherl Kook, and Moon Hee Han PURPOSE: To compare the MR signal intensity
Imaging of Acute Stroke. Noam Eshkar, M.D New Jersey Neuroscience Institute JFK Medical Center Edison Radiology Group
 Imaging of Acute Stroke Noam Eshkar, M.D New Jersey Neuroscience Institute JFK Medical Center Edison Radiology Group Modalities Non Contrast CT (NCCT) Contrast CT Angiography MRI MR Angiography Perfusion
Imaging of Acute Stroke Noam Eshkar, M.D New Jersey Neuroscience Institute JFK Medical Center Edison Radiology Group Modalities Non Contrast CT (NCCT) Contrast CT Angiography MRI MR Angiography Perfusion
Stroke Coding Issues Presentation to: NorthEast Cerebrovascular Consortium
 Stroke Coding Issues Presentation to: NorthEast Cerebrovascular Consortium October 30, 2008 Barry Libman, RHIA, CCS, CCS-P President, Barry Libman Inc. Stroke Coding Issues Outline Medical record documentation
Stroke Coding Issues Presentation to: NorthEast Cerebrovascular Consortium October 30, 2008 Barry Libman, RHIA, CCS, CCS-P President, Barry Libman Inc. Stroke Coding Issues Outline Medical record documentation
Do We Need a New Definition of Stroke & TIA as Proposed by the AHA? Stroke & TIA need to Remain Clinical Diagnoses: to Change Would be Bonkers!
 Do We Need a New Definition of Stroke & TIA as Proposed by the AHA? No Stroke & TIA need to Remain Clinical Diagnoses: to Change Would be Bonkers! A/Prof Anne L. Abbott Neurologist School of Public Health
Do We Need a New Definition of Stroke & TIA as Proposed by the AHA? No Stroke & TIA need to Remain Clinical Diagnoses: to Change Would be Bonkers! A/Prof Anne L. Abbott Neurologist School of Public Health
CHAPTER 9 DISEASES OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM (I00-I99)
 CHAPTER 9 DISEASES OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM (I00-I99) March 2014 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc. CHAPTER 9 CHAPTER SPECIFIC CATEGORY CODE BLOCKS I00-I02 Acute rheumatic fever I05-I09 Chronic rheumatic heart
CHAPTER 9 DISEASES OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM (I00-I99) March 2014 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc. CHAPTER 9 CHAPTER SPECIFIC CATEGORY CODE BLOCKS I00-I02 Acute rheumatic fever I05-I09 Chronic rheumatic heart
Disruption of the Blood-Brain Barrier in Open and Closed Cranial Window Preparations in Rats. William G. Mayhan, PhD
 1059 Disruption of the Blood-Brain Barrier in Open and Closed Cranial Window Preparations in Rats William G. Mayhan, PhD The goal of this study was to determine whether the severity of disruption of the
1059 Disruption of the Blood-Brain Barrier in Open and Closed Cranial Window Preparations in Rats William G. Mayhan, PhD The goal of this study was to determine whether the severity of disruption of the
Cerebral Cortical and White Matter Lesions in Chronic Hepatic Encephalopathy: MR-Pathologic Correlations
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:347 351, February 2005 Case Report Cerebral Cortical and White Matter Lesions in Chronic Hepatic Encephalopathy: MR-Pathologic Correlations Eiji Matsusue, Toshibumi Kinoshita,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:347 351, February 2005 Case Report Cerebral Cortical and White Matter Lesions in Chronic Hepatic Encephalopathy: MR-Pathologic Correlations Eiji Matsusue, Toshibumi Kinoshita,
Brain Spots on Imaging Tests
 Brain Spots on Imaging Tests To Be or Not to Be Concerned Metropolitan Underwriting Discussion Group 1/29/13 Charles Levy, MD Aviva USA CT and MRI 2 most common forms of brain imaging today As with any
Brain Spots on Imaging Tests To Be or Not to Be Concerned Metropolitan Underwriting Discussion Group 1/29/13 Charles Levy, MD Aviva USA CT and MRI 2 most common forms of brain imaging today As with any
What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms
 What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Interventions Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Radiology Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D.,
What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Interventions Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Radiology Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D.,
Guidance for evaluation of new neurological symptoms in patients receiving TYSABRI
 Guidance for evaluation of new neurological symptoms in patients receiving TYSABRI Background information Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) PML is a demyelinating disease that attacks the
Guidance for evaluation of new neurological symptoms in patients receiving TYSABRI Background information Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) PML is a demyelinating disease that attacks the
Vertebrobasilar Disease
 The Vascular Surgery team at the University of Michigan is dedicated to providing exceptional treatments for in the U-M Cardiovascular Center (CVC), our new state-of-the-art clinical facility. Treatment
The Vascular Surgery team at the University of Michigan is dedicated to providing exceptional treatments for in the U-M Cardiovascular Center (CVC), our new state-of-the-art clinical facility. Treatment
Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure Diagnoses
 Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : to 402.01 Hypertensive heart disease, malignant, with heart failure 402.11 Hypertensive heart disease, benign, with heart failure 402.91 Hypertensive heart disease, unspecified,
Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : to 402.01 Hypertensive heart disease, malignant, with heart failure 402.11 Hypertensive heart disease, benign, with heart failure 402.91 Hypertensive heart disease, unspecified,
Stuart B Black MD, FAAN Chief of Neurology Co-Medical Director: Neuroscience Center Baylor University Medical Center at Dallas
 Billing and Coding in Neurology and Headache Stuart B Black MD, FAAN Chief of Neurology Co-Medical Director: Neuroscience Center Baylor University Medical Center at Dallas CPT Codes vs. ICD Codes Category
Billing and Coding in Neurology and Headache Stuart B Black MD, FAAN Chief of Neurology Co-Medical Director: Neuroscience Center Baylor University Medical Center at Dallas CPT Codes vs. ICD Codes Category
MEDICAL POLICY No. 91104-R7 DETOXIFICATION I. POLICY/CRITERIA
 DETOXIFICATION MEDICAL POLICY Effective Date: January 7, 2013 Review Dates: 1/93, 2/97, 4/99, 2/01, 12/01, 2/02, 2/03, 1/04, 1/05, 12/05, 12/06, 12/07, 12/08, 12/09, 12/10, 12/11, 12/12, 12/13, 11/14 Date
DETOXIFICATION MEDICAL POLICY Effective Date: January 7, 2013 Review Dates: 1/93, 2/97, 4/99, 2/01, 12/01, 2/02, 2/03, 1/04, 1/05, 12/05, 12/06, 12/07, 12/08, 12/09, 12/10, 12/11, 12/12, 12/13, 11/14 Date
Headache: Differential diagnosis and Evaluation. Raymond Rios PGY-1 Pediatrics
 Headache: Differential diagnosis and Evaluation Raymond Rios PGY-1 Pediatrics You are evaluating a 9 year old male patient at the ED brought by his mother, who says that her son has had a fever, cough,
Headache: Differential diagnosis and Evaluation Raymond Rios PGY-1 Pediatrics You are evaluating a 9 year old male patient at the ED brought by his mother, who says that her son has had a fever, cough,
DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA OF STROKE
 DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA OF STROKE Diagnostic criteria are used to validate clinical diagnoses. Here below MONICA diagnostic criteria are reported. MONICA - MONItoring trends and determinants of CArdiovascular
DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA OF STROKE Diagnostic criteria are used to validate clinical diagnoses. Here below MONICA diagnostic criteria are reported. MONICA - MONItoring trends and determinants of CArdiovascular
Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide
 Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide Figure 1: Right Hemisphere of Sheep s Brain Figure 2: Underside of Sheep s Brain Figure 3: Saggital cut of Sheep s Brain to reveal subcortical structures Figure 4:
Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide Figure 1: Right Hemisphere of Sheep s Brain Figure 2: Underside of Sheep s Brain Figure 3: Saggital cut of Sheep s Brain to reveal subcortical structures Figure 4:
CT scans and IV contrast (radiographic iodinated contrast) utilization in adults
 CT scans and IV contrast (radiographic iodinated contrast) utilization in adults At United Radiology Group, a majority of CT exams are performed either with IV contrast or without while just a few exams
CT scans and IV contrast (radiographic iodinated contrast) utilization in adults At United Radiology Group, a majority of CT exams are performed either with IV contrast or without while just a few exams
Neurological System Best Practice Documentation
 Neurological System Best Practice Documentation Click on the desired Diagnoses link or press Enter to view all information. Diagnoses: Dementia Delirium/Encephalopathy Parkinson s Epilepsy /Seizure Migraines
Neurological System Best Practice Documentation Click on the desired Diagnoses link or press Enter to view all information. Diagnoses: Dementia Delirium/Encephalopathy Parkinson s Epilepsy /Seizure Migraines
Case Report: Whole-body Oncologic Imaging with syngo TimCT
 Case Report: Whole-body Oncologic Imaging with syngo TimCT Eric Hatfield, M.D. 1 ; Agus Priatna, Ph.D. 2 ; John Kotyk, Ph.D. 1 ; Benjamin Tan, M.D. 1 ; Alto Stemmer 3 ; Stephan Kannengiesser, Ph.D. 3 ;
Case Report: Whole-body Oncologic Imaging with syngo TimCT Eric Hatfield, M.D. 1 ; Agus Priatna, Ph.D. 2 ; John Kotyk, Ph.D. 1 ; Benjamin Tan, M.D. 1 ; Alto Stemmer 3 ; Stephan Kannengiesser, Ph.D. 3 ;
Discovery of an Aneurysm Following a Motorcycle Accident. Maya Babu, MSIII Gillian Lieberman, M.D.
 Discovery of an Aneurysm Following a Motorcycle Accident Maya Babu, MSIII Gillian Lieberman, M.D. Patient CC: July 2004 65 yo male transferred to the BI from an OSH s/p motorcycle crash w/o a helmet CC
Discovery of an Aneurysm Following a Motorcycle Accident Maya Babu, MSIII Gillian Lieberman, M.D. Patient CC: July 2004 65 yo male transferred to the BI from an OSH s/p motorcycle crash w/o a helmet CC
Computed Tomography, Head Or Brain; Without Contrast Material, Followed By Contrast Material(S) And Further Sections
 1199SEIU BENEFIT AND PENSION FUNDS High Tech Diagnostic Radiology and s # 1 70336 Magnetic Resonance (Eg, Proton) Imaging, Temporomandibular Joint(S) 2 70450 Computed Tomography, Head Or Brain; Without
1199SEIU BENEFIT AND PENSION FUNDS High Tech Diagnostic Radiology and s # 1 70336 Magnetic Resonance (Eg, Proton) Imaging, Temporomandibular Joint(S) 2 70450 Computed Tomography, Head Or Brain; Without
 Approximately 70-80% of all strokes are ischemic and 20-30% are hemorrhagic Hemorrhagic stroke is defined as an acute neurologic injury resulting from bleeding in the brain There are two distinct types
Approximately 70-80% of all strokes are ischemic and 20-30% are hemorrhagic Hemorrhagic stroke is defined as an acute neurologic injury resulting from bleeding in the brain There are two distinct types
AI CPT Codes. x x. 70336 MRI Magnetic resonance (eg, proton) imaging, temporomandibular joint(s)
 Code Category Description Auth Required Medicaid Medicare 0126T IMT Testing Common carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) study for evaluation of atherosclerotic burden or coronary heart disease risk factor
Code Category Description Auth Required Medicaid Medicare 0126T IMT Testing Common carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) study for evaluation of atherosclerotic burden or coronary heart disease risk factor
STATEMENT OF STANDARD
 OHSU HEALTH CARE SYSTEM PRACTICE STANDARD Acute Stroke Practice Standard for the Emergency Department (includes ischemic stroke, TIAs, intracerebral hemorrhage, and non-subarachnoid hemorrhage), PS 01.11
OHSU HEALTH CARE SYSTEM PRACTICE STANDARD Acute Stroke Practice Standard for the Emergency Department (includes ischemic stroke, TIAs, intracerebral hemorrhage, and non-subarachnoid hemorrhage), PS 01.11
Head Injury. Dr Sally McCarthy Medical Director ECI
 Head Injury Dr Sally McCarthy Medical Director ECI Head injury in the emergency department A common presentation 80% Mild Head Injury = GCS 14 15 10% Moderate Head Injury = GCS 9 13 10% Severe Head Injury
Head Injury Dr Sally McCarthy Medical Director ECI Head injury in the emergency department A common presentation 80% Mild Head Injury = GCS 14 15 10% Moderate Head Injury = GCS 9 13 10% Severe Head Injury
Renovascular Hypertension
 Renovascular Hypertension Philip Stockwell, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine (Clinical) Warren Alpert School of Medicine Cardiology for the Primary Care Provider September 28, 201 Renovascular Hypertension
Renovascular Hypertension Philip Stockwell, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine (Clinical) Warren Alpert School of Medicine Cardiology for the Primary Care Provider September 28, 201 Renovascular Hypertension
Subclavian Steal Syndrome By Marta Thorup
 Subclavian Steal Syndrome By Marta Thorup Definition Subclavian steal syndrome (SSS), is a constellation of signs and symptoms that arise from retrograde flow of blood in the vertebral artery, due to proximal
Subclavian Steal Syndrome By Marta Thorup Definition Subclavian steal syndrome (SSS), is a constellation of signs and symptoms that arise from retrograde flow of blood in the vertebral artery, due to proximal
NEURO M203 & BIOMED M263 WINTER 2014
 NEURO M203 & BIOMED M263 WINTER 2014 MRI Lab 1: Structural and Functional Anatomy During today s lab, you will work with and view the structural and functional imaging data collected from the scanning
NEURO M203 & BIOMED M263 WINTER 2014 MRI Lab 1: Structural and Functional Anatomy During today s lab, you will work with and view the structural and functional imaging data collected from the scanning
Therapeutic Management Options for. Acute Ischemic Stroke Anna Rosenbaum, MD
 Therapeutic Management Options for Acute Ischemic Stroke Anna Rosenbaum, MD Epidemiology Epidemiology 4 th leading cause of death in the United States 1 Leading cause of disability Increase in projected
Therapeutic Management Options for Acute Ischemic Stroke Anna Rosenbaum, MD Epidemiology Epidemiology 4 th leading cause of death in the United States 1 Leading cause of disability Increase in projected
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones. Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke
 Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
LIPID PANEL CHOLESTEROL LIPOPROTEIN, ELECTROPHORETIC SEPARATION LIPOPROTEIN, DIRECT MEASUREMENT (HDL) LDL DIRECT TRIGLYCERIDES
 Test Code Test Name CPT CHOL Cholesterol, Serum 82465 HDL HDL, (High Density Lipoprotein) 83718 TRIG Triglycerides, Serum 84478 FTRIG Triglycerides (Fluid) 84478 LIPID Lipid Panel 80061 LDL LDL (Low Density
Test Code Test Name CPT CHOL Cholesterol, Serum 82465 HDL HDL, (High Density Lipoprotein) 83718 TRIG Triglycerides, Serum 84478 FTRIG Triglycerides (Fluid) 84478 LIPID Lipid Panel 80061 LDL LDL (Low Density
Renovascular Disease. Renal Artery and Arteriosclerosis
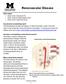 Other names: Renal Artery Stenosis (RAS) Renal Vascular Hypertension (RVH) Renal Artery Aneurysm (RAA) How does the normal kidney work? The blood passes through the kidneys to remove the body s waste.
Other names: Renal Artery Stenosis (RAS) Renal Vascular Hypertension (RVH) Renal Artery Aneurysm (RAA) How does the normal kidney work? The blood passes through the kidneys to remove the body s waste.
Metronidazole-induced Encephalopathy: Case Report and Review Literature
 Case Reports 74 Metronidazole-induced Encephalopathy: Case Report and Review Literature Ying-Ting Huang, Lu-An Chen, Shin-Jung Cheng Abstract- Purpose: Neurotoxicities resulting from various medications
Case Reports 74 Metronidazole-induced Encephalopathy: Case Report and Review Literature Ying-Ting Huang, Lu-An Chen, Shin-Jung Cheng Abstract- Purpose: Neurotoxicities resulting from various medications
Social Security Disability Insurance and young onset dementia: A guide for employers and employees
 Social Security Disability Insurance and young onset dementia: A guide for employers and employees What is Social Security Disability Insurance? Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) is a payroll
Social Security Disability Insurance and young onset dementia: A guide for employers and employees What is Social Security Disability Insurance? Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) is a payroll
In conjunction with clinical history, structural
 A QUICK GUIDE FOR NEUROIMAGING OF COMMON DEMENTIAS SEEN IN CLINICAL PRACTICE PRINT THIS ARTICLE David F. Tang-Wai, MDCM, FRCPC, assistant professor of neurology and geriatric medicine at the University
A QUICK GUIDE FOR NEUROIMAGING OF COMMON DEMENTIAS SEEN IN CLINICAL PRACTICE PRINT THIS ARTICLE David F. Tang-Wai, MDCM, FRCPC, assistant professor of neurology and geriatric medicine at the University
Hospital-based SNF Coding Tip Sheet: Top 25 codes and ICD-10 Chapter Overview
 Hospital-based SNF Coding Tip Sheet: Top 25 codes and Chapter Overview Chapter 5 - Mental, Behavioral and Neurodevelopmental Disorders (F00-F99) Classification improvements (different categories) expansions:
Hospital-based SNF Coding Tip Sheet: Top 25 codes and Chapter Overview Chapter 5 - Mental, Behavioral and Neurodevelopmental Disorders (F00-F99) Classification improvements (different categories) expansions:
Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD
 Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD With the widespread use of cross-sectional imaging, many renal masses are incidentally found. These need to be accurately
Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD With the widespread use of cross-sectional imaging, many renal masses are incidentally found. These need to be accurately
The Treatment of Brain Ischemia With Vasopressor Drugs
 The Treatment of Brain Ischemia With Vasopressor Drugs BY GARY WISE, M.D., ROBERT SUTTER, M.D., AND JAMES BURKHOLDER, M.D. Abstract: The Treat me nl of Brain Ischemia With Vasopressor Drugs Vasopressor
The Treatment of Brain Ischemia With Vasopressor Drugs BY GARY WISE, M.D., ROBERT SUTTER, M.D., AND JAMES BURKHOLDER, M.D. Abstract: The Treat me nl of Brain Ischemia With Vasopressor Drugs Vasopressor
APPENDIX A NEUROLOGIST S GUIDE TO USING ICD-9-CM CODES FOR CEREBROVASCULAR DISEASES INTRODUCTION
 APPENDIX A NEUROLOGIST S GUIDE TO USING ICD-9-CM CODES FOR CEREBROVASCULAR DISEASES INTRODUCTION ICD-9-CM codes for cerebrovascular diseases is not user friendly. This presentation is designed to assist
APPENDIX A NEUROLOGIST S GUIDE TO USING ICD-9-CM CODES FOR CEREBROVASCULAR DISEASES INTRODUCTION ICD-9-CM codes for cerebrovascular diseases is not user friendly. This presentation is designed to assist
Test Request Tip Sheet
 With/Without Contrast CT, MRI Studies should NOT be ordered simultaneously as dual studies (i.e., with and without contrast). Radiation exposure is doubled and both views are rarely necessary. The study
With/Without Contrast CT, MRI Studies should NOT be ordered simultaneously as dual studies (i.e., with and without contrast). Radiation exposure is doubled and both views are rarely necessary. The study
MR Imaging of the Postoperative Lumbar Spine: Assessment with Gadopentetate Dimeglumine
 771 MR Imaging of the Postoperative Lumbar Spine: Assessment with Gadopentetate Dimeglumine Jeffrey S. Ross 1.2 Thomas J. Masaryk 1 2 Mauricio Schrader 1 Amilcare Gentili 1 Henry Bohlman 3 Michael T. Modic
771 MR Imaging of the Postoperative Lumbar Spine: Assessment with Gadopentetate Dimeglumine Jeffrey S. Ross 1.2 Thomas J. Masaryk 1 2 Mauricio Schrader 1 Amilcare Gentili 1 Henry Bohlman 3 Michael T. Modic
Level III Stroke Center Data Collection Requirements
 Who? Level III Stroke Center Data Collection Requirements All LERN Level III Stroke Centers. LERN Level I and II Stroke Centers have reporting requirements to The Joint Commission or other Board approved
Who? Level III Stroke Center Data Collection Requirements All LERN Level III Stroke Centers. LERN Level I and II Stroke Centers have reporting requirements to The Joint Commission or other Board approved
Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation
 J Clin Ultrasound 17:327-332, June 1989 Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation Mark A. Helvie, MD,* and Terry M. Silver, MDI Abstract: The sonographic and clinical findings of 13 patients with surgically
J Clin Ultrasound 17:327-332, June 1989 Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation Mark A. Helvie, MD,* and Terry M. Silver, MDI Abstract: The sonographic and clinical findings of 13 patients with surgically
How are Parts of the Brain Related to Brain Function?
 How are Parts of the Brain Related to Brain Function? Scientists have found That the basic anatomical components of brain function are related to brain size and shape. The brain is composed of two hemispheres.
How are Parts of the Brain Related to Brain Function? Scientists have found That the basic anatomical components of brain function are related to brain size and shape. The brain is composed of two hemispheres.
CERTIFICATE OF NEED AND ACUTE CARE LICENSURE PROGRAM. Hospital Licensing Standards: Emergency Department and Trauma Services:
 HEALTH AND SENIOR SERVICES HEALTH CARE QUALITY AND OVERSIGHT BRANCH HEALTH CARE QUALITY AND OVERSIGHT DIVISION ACUTE CARE FACILITY OVERSIGHT CERTIFICATE OF NEED AND ACUTE CARE LICENSURE PROGRAM Hospital
HEALTH AND SENIOR SERVICES HEALTH CARE QUALITY AND OVERSIGHT BRANCH HEALTH CARE QUALITY AND OVERSIGHT DIVISION ACUTE CARE FACILITY OVERSIGHT CERTIFICATE OF NEED AND ACUTE CARE LICENSURE PROGRAM Hospital
MRI of Bone Marrow Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 MRI of Bone Marrow Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel, M.D. Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University School of Medicine St. Louis, MO and Visiting Scientist, AFIP, Washington,
MRI of Bone Marrow Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel, M.D. Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University School of Medicine St. Louis, MO and Visiting Scientist, AFIP, Washington,
Table 11: Pros and Cons of 1.5 T MRI vs. 3.0 T MRI; Safety and Technical Issues, and Clinical Applications
 Safety Issue 3.0 T MRI Pro 3.0 T MRI Con Immediate fringe field surrounding magnet A ferromagnetic object inadvertently brought into the scan room will experience a sharp increase in attraction toward
Safety Issue 3.0 T MRI Pro 3.0 T MRI Con Immediate fringe field surrounding magnet A ferromagnetic object inadvertently brought into the scan room will experience a sharp increase in attraction toward
Anoxic Brain Injury and Neural Damage: Three Case Reports
 Anoxic Brain Injury and Neural Damage: Three Case Reports Abstract Anoxic brain injury (ABI) is common and can occur in a wide variety of disorders. This neural injury is associated with significant and
Anoxic Brain Injury and Neural Damage: Three Case Reports Abstract Anoxic brain injury (ABI) is common and can occur in a wide variety of disorders. This neural injury is associated with significant and
Duplex Carotid Sonography in Distinguishing Acute Unilateral Atherothrombotic from Cardioembolic Carotid Artery Occlusion
 Duplex Carotid Sonography in Distinguishing Acute Unilateral Atherothrombotic from Cardioembolic Carotid Artery Occlusion Kazumi Kimura, Kiminobu Yonemura, Tadashi Terasaki, Yoichiro Hashimoto, and Makoto
Duplex Carotid Sonography in Distinguishing Acute Unilateral Atherothrombotic from Cardioembolic Carotid Artery Occlusion Kazumi Kimura, Kiminobu Yonemura, Tadashi Terasaki, Yoichiro Hashimoto, and Makoto
Headaches and Kids. Jennifer Bickel, MD Assistant Professor of Neurology Co-Director of Headache Clinic Children s Mercy Hospital
 Headaches and Kids Jennifer Bickel, MD Assistant Professor of Neurology Co-Director of Headache Clinic Children s Mercy Hospital Overview Headache classifications and diagnosis Address common headache
Headaches and Kids Jennifer Bickel, MD Assistant Professor of Neurology Co-Director of Headache Clinic Children s Mercy Hospital Overview Headache classifications and diagnosis Address common headache
Parts of the Brain. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Apparent Diffusion Coefficients in the Evaluation of High-grade Cerebral Gliomas
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:60 64, January 2001 Apparent Diffusion Coefficients in the Evaluation of High-grade Cerebral Gliomas Mauricio Castillo, J. Keith Smith, Lester Kwock, and Kathy Wilber BACKGROUND
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:60 64, January 2001 Apparent Diffusion Coefficients in the Evaluation of High-grade Cerebral Gliomas Mauricio Castillo, J. Keith Smith, Lester Kwock, and Kathy Wilber BACKGROUND
New Onset Seizure Clinic
 New Onset Seizure Clinic Timely Care from the Region s Experts The New Onset Seizure Clinic at UH Rainbow Babies & Children s Hospital provides expert diagnostic services, referrals, treatment and follow-up
New Onset Seizure Clinic Timely Care from the Region s Experts The New Onset Seizure Clinic at UH Rainbow Babies & Children s Hospital provides expert diagnostic services, referrals, treatment and follow-up
Pathology ICD-10-CM Coding Tip Sheet Overview of Key Chapter Updates for Pathology and Top 25 codes
 Pathology ICD-10-CM Coding Tip Sheet Overview of Key Chapter Updates for Pathology and Top 25 codes Chapter 2 Neoplasms (C00-D49) Classification improvements Code expansions Significant expansions or revisions
Pathology ICD-10-CM Coding Tip Sheet Overview of Key Chapter Updates for Pathology and Top 25 codes Chapter 2 Neoplasms (C00-D49) Classification improvements Code expansions Significant expansions or revisions
Traumatic brain injury (TBI)
 Traumatic brain injury (TBI) A topic in the Alzheimer s Association series on understanding dementia. About dementia Dementia is a condition in which a person has significant difficulty with daily functioning
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) A topic in the Alzheimer s Association series on understanding dementia. About dementia Dementia is a condition in which a person has significant difficulty with daily functioning
New Approaches to Neuroimaging of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy. Alexandra Binnie, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, M.D.
 New Approaches to Neuroimaging of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy Alexandra Binnie, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, M.D. What is Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML)? A demyelinating
New Approaches to Neuroimaging of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy Alexandra Binnie, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, M.D. What is Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML)? A demyelinating
1. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF METABOLIC SYNDROME
 1. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF METABOLIC SYNDROME Izet Aganović, Tina Dušek Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Endocrinology, University Hospital Center Zagreb, Croatia 1 Introduction The metabolic syndrome
1. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF METABOLIC SYNDROME Izet Aganović, Tina Dušek Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Endocrinology, University Hospital Center Zagreb, Croatia 1 Introduction The metabolic syndrome
13. Volume-pressure infusion tests: Typical patterns of infusion studies in different forms of CSF circulatory disorders.
 13. Volume-pressure infusion tests: Typical patterns of infusion studies in different forms of CSF circulatory disorders. Hydrocephalus is far more complex than disorder of CSF circulation CSF circulation
13. Volume-pressure infusion tests: Typical patterns of infusion studies in different forms of CSF circulatory disorders. Hydrocephalus is far more complex than disorder of CSF circulation CSF circulation
Acute Myocardial Infarction (the formulary thrombolytic for AMI at AAMC is TNK, please see the TNK monograph in this manual for information)
 ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Alteplase (Tissue Plasminogen Activator (t-pa)), Activase in the Treatment
ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Alteplase (Tissue Plasminogen Activator (t-pa)), Activase in the Treatment
Local Coverage Article: NCD Coding Article for Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scans Used for Non- Oncologic Conditions (A53134)
 Local Coverage Article: NCD Coding Article for Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scans Used for Non- Oncologic Conditions (A53134) Contractor Information Contractor Name Novitas Solutions, Inc. Article
Local Coverage Article: NCD Coding Article for Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scans Used for Non- Oncologic Conditions (A53134) Contractor Information Contractor Name Novitas Solutions, Inc. Article
Brain Tumor Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumor Treatment Brain Tumors Overview A brain tumor is a group of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. Tumors can directly destroy healthy brain cells. They can
Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumor Treatment Brain Tumors Overview A brain tumor is a group of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. Tumors can directly destroy healthy brain cells. They can
NCD for Lipids Testing
 Applicable CPT Code(s): NCD for Lipids Testing 80061 Lipid panel 82465 Cholesterol, serum or whole blood, total 83700 Lipoprotein, blood; electrophoretic separation and quantitation 83701 Lipoprotein blood;
Applicable CPT Code(s): NCD for Lipids Testing 80061 Lipid panel 82465 Cholesterol, serum or whole blood, total 83700 Lipoprotein, blood; electrophoretic separation and quantitation 83701 Lipoprotein blood;
Endovascular Repair of an Axillary Artery Aneurysm: A Novel Approach
 Endovascular Repair of an Axillary Artery Aneurysm: A Novel Approach Bao- Thuy D. Hoang, MD 1, Jonathan- Hien Vu, MD 2, Jerry Matteo, MD 3 1 Department of Surgery, University of Florida College of Medicine,
Endovascular Repair of an Axillary Artery Aneurysm: A Novel Approach Bao- Thuy D. Hoang, MD 1, Jonathan- Hien Vu, MD 2, Jerry Matteo, MD 3 1 Department of Surgery, University of Florida College of Medicine,
CRITERIA FOR AD DEMENTIA June 11, 2010
 CRITERIA F AD DEMENTIA June 11, 2010 Alzheimer s Disease Dementia Workgroup Guy McKhann, Johns Hopkins University (Chair) Bradley Hyman, Massachusetts General Hospital Clifford Jack, Mayo Clinic Rochester
CRITERIA F AD DEMENTIA June 11, 2010 Alzheimer s Disease Dementia Workgroup Guy McKhann, Johns Hopkins University (Chair) Bradley Hyman, Massachusetts General Hospital Clifford Jack, Mayo Clinic Rochester
Cardiac Masses and Tumors
 Cardiac Masses and Tumors Question: What is the diagnosis? A. Aortic valve myxoma B. Papillary fibroelastoma C. Vegetation from Infective endocarditis D. Thrombus in transit E. None of the above Answer:
Cardiac Masses and Tumors Question: What is the diagnosis? A. Aortic valve myxoma B. Papillary fibroelastoma C. Vegetation from Infective endocarditis D. Thrombus in transit E. None of the above Answer:
6/3/2011. High Prevalence and Incidence. Low back pain is 5 th most common reason for all physician office visits in the U.S.
 High Prevalence and Incidence Prevalence 85% of Americans will experience low back pain at some time in their life. Incidence 5% annual Timothy C. Shen, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sub-specialty
High Prevalence and Incidence Prevalence 85% of Americans will experience low back pain at some time in their life. Incidence 5% annual Timothy C. Shen, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sub-specialty
THEORIES OF NEUROLOGICAL AGING AND DEMENTIA
 THEORIES OF NEUROLOGICAL AGING AND DEMENTIA Aging Overview The primary care physician must advise middle-age and older patients about ways to age successfully. Dementia is a common disabling illness that
THEORIES OF NEUROLOGICAL AGING AND DEMENTIA Aging Overview The primary care physician must advise middle-age and older patients about ways to age successfully. Dementia is a common disabling illness that
Medicare Risk Adjustment and You. Health Plan of San Mateo Spring 2009
 Medicare Risk Adjustment and You Health Plan of San Mateo Spring 2009 Background CMS reimburses health plans on a risk-adjusted basis: The sicker a member is expected to be, the more CMS pays a plan, which
Medicare Risk Adjustment and You Health Plan of San Mateo Spring 2009 Background CMS reimburses health plans on a risk-adjusted basis: The sicker a member is expected to be, the more CMS pays a plan, which
Exchange solutes and water with cells of the body
 Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
HEALTH MANAGEMENT PLAN PROGRAMME
 HEALTH MANAGEMENT PLAN PROGRAMME Medical Controls for Referees and Candidates The FIVB believes that Referees and Referees Candidates health is very important therefore in accordance with the Medical and
HEALTH MANAGEMENT PLAN PROGRAMME Medical Controls for Referees and Candidates The FIVB believes that Referees and Referees Candidates health is very important therefore in accordance with the Medical and
3. The neuron has many branch-like extensions called that receive input from other neurons. a. glia b. dendrites c. axons d.
 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer: A difficulty: 1 factual
Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer: A difficulty: 1 factual
Cavernous Angioma. Cerebral Cavernous Malformation ...
 Cavernous Angioma... Cerebral Cavernous Malformation Information For Patients And Loved Ones 107 Quaker Meeting House Road Williamsburg, Virginia 23188 USA 1-866-HEAL-CCM 1-757-258-3355 www.angiomaalliance.org
Cavernous Angioma... Cerebral Cavernous Malformation Information For Patients And Loved Ones 107 Quaker Meeting House Road Williamsburg, Virginia 23188 USA 1-866-HEAL-CCM 1-757-258-3355 www.angiomaalliance.org
Guidelines Most Significantly Affected Under ICD-10-CM. May 29, 2013
 Guidelines Most Significantly Affected Under ICD-10-CM May 29, 2013 Guidelines Most Significantly Affected Under ICD-10-CM A look at the new system and how it compares to ICD-9-CM Presented by Therese
Guidelines Most Significantly Affected Under ICD-10-CM May 29, 2013 Guidelines Most Significantly Affected Under ICD-10-CM A look at the new system and how it compares to ICD-9-CM Presented by Therese
CLINICAL NEUROPHYSIOLOGY
 CLINICAL NEUROPHYSIOLOGY Barry S. Oken, MD, Carter D. Wray MD Objectives: 1. Know the role of EMG/NCS in evaluating nerve and muscle function 2. Recognize common EEG findings and their significance 3.
CLINICAL NEUROPHYSIOLOGY Barry S. Oken, MD, Carter D. Wray MD Objectives: 1. Know the role of EMG/NCS in evaluating nerve and muscle function 2. Recognize common EEG findings and their significance 3.
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back
 Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS, REGISTRY
 Measure #317: Preventive Care and Screening: Screening for High Blood Pressure and Follow-Up Documented National Quality Strategy Domain: Community / Population Health 2016 PQRS OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
Measure #317: Preventive Care and Screening: Screening for High Blood Pressure and Follow-Up Documented National Quality Strategy Domain: Community / Population Health 2016 PQRS OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
ICD-9-CM coding for patients with Traumatic Brain Injury*
 ICD-9-CM coding for patients with Traumatic Brain Injury* The diagnostic code for sequelae of traumatic brain injury is: 907.0 Late effect of intracranial injury without mention of skull fracture (Late
ICD-9-CM coding for patients with Traumatic Brain Injury* The diagnostic code for sequelae of traumatic brain injury is: 907.0 Late effect of intracranial injury without mention of skull fracture (Late
NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY
 NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY Jared B. Galle, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) Dogwood Veterinary Referral Center 4920 Ann Arbor-Saline Road Ann Arbor, MI 48103 Localizing a neurologic problem to an anatomical
NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY Jared B. Galle, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) Dogwood Veterinary Referral Center 4920 Ann Arbor-Saline Road Ann Arbor, MI 48103 Localizing a neurologic problem to an anatomical
MR Imaging of Perinatal Brain Damage: Comparison of Clinical Outcome with Initial and Follow-up MR Findings
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:1909 1921, November 1998 MR Imaging of Perinatal Brain Damage: Comparison of Clinical Outcome with Initial and Follow-up MR Findings Noriko Aida, Gen Nishimura, Yuriko Hachiya,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:1909 1921, November 1998 MR Imaging of Perinatal Brain Damage: Comparison of Clinical Outcome with Initial and Follow-up MR Findings Noriko Aida, Gen Nishimura, Yuriko Hachiya,
Childhood Cancer in the Primary Care Setting
 Childhood Cancer in the Primary Care Setting Mohamed Radhi, M.D. Associate Professor, UMKC Pediatric Hematology/Oncology/BMT Children s Mercy Hospital I will discuss: Overview of childhood cancer Presentation
Childhood Cancer in the Primary Care Setting Mohamed Radhi, M.D. Associate Professor, UMKC Pediatric Hematology/Oncology/BMT Children s Mercy Hospital I will discuss: Overview of childhood cancer Presentation
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
CPT * Codes Included in AIM Preauthorization Program for 2013 With Grouper Numbers
 CPT * Codes Included in AIM Preauthorization Program for 2013 With Grouper Numbers Computerized Tomography (CT) CPT Description Abdomen 74150 CT abdomen; w/o contrast 6 74160 CT abdomen; with contrast
CPT * Codes Included in AIM Preauthorization Program for 2013 With Grouper Numbers Computerized Tomography (CT) CPT Description Abdomen 74150 CT abdomen; w/o contrast 6 74160 CT abdomen; with contrast
Zika Virus. Fred A. Lopez, MD, MACP Richard Vial Professor Department of Medicine Section of Infectious Diseases
 Zika Virus Fred A. Lopez, MD, MACP Richard Vial Professor Department of Medicine Section of Infectious Diseases What is the incubation period for Zika virus infection? Unknown but likely to be several
Zika Virus Fred A. Lopez, MD, MACP Richard Vial Professor Department of Medicine Section of Infectious Diseases What is the incubation period for Zika virus infection? Unknown but likely to be several
A case of labyrinthitis diagnosed with MRI
 A case of labyrinthitis diagnosed with MRI Saiz-Mendiguren R, García-Lallana A, Simon I, Slon P, Etxano J, Dominguez PD, Zubieta JL, García-Eulate R. Radiology Service. Clínica Universidad de Navarra,
A case of labyrinthitis diagnosed with MRI Saiz-Mendiguren R, García-Lallana A, Simon I, Slon P, Etxano J, Dominguez PD, Zubieta JL, García-Eulate R. Radiology Service. Clínica Universidad de Navarra,
DRAFT. ICD-10 Clinical Modification Code Sets
 NOTE: The tables provided below are for reference only and should not be programmed or submitted. Table 8.1 Ischemic Stroke ICD-10 Code I6300 I63011 I63012 I63019 I6302 I63031 I63032 I63039 I6309 I6310
NOTE: The tables provided below are for reference only and should not be programmed or submitted. Table 8.1 Ischemic Stroke ICD-10 Code I6300 I63011 I63012 I63019 I6302 I63031 I63032 I63039 I6309 I6310
2016 CODING FOR FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS
 2016 CODING FOR FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS Listed below are the most commonly used codes applicable to FASD patient care. Code Description ICD-10-CM Primary Diagnosis P04.3 Newborn (suspected to
2016 CODING FOR FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS Listed below are the most commonly used codes applicable to FASD patient care. Code Description ICD-10-CM Primary Diagnosis P04.3 Newborn (suspected to
CHAPTER 2. Neoplasms (C00-D49) March 2014. 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc.
 Neoplasms (C00-D49) March 2014 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc. CHAPTER SPECIFIC CATEGORY CODE BLOCKS C00-C14 Malignant neoplasms of lip, oral cavity and pharynx C15-C26 Malignant neoplasms of digestive organs
Neoplasms (C00-D49) March 2014 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc. CHAPTER SPECIFIC CATEGORY CODE BLOCKS C00-C14 Malignant neoplasms of lip, oral cavity and pharynx C15-C26 Malignant neoplasms of digestive organs
Long term care coding issues for ICD-10-CM
 Long term care coding issues for ICD-10-CM Coding Clinic, Fourth Quarter 2012 Pages: 90-98 Effective with discharges: October 1, 2012 Related Information Long Term Care Coding Issues for ICD-10-CM Coding
Long term care coding issues for ICD-10-CM Coding Clinic, Fourth Quarter 2012 Pages: 90-98 Effective with discharges: October 1, 2012 Related Information Long Term Care Coding Issues for ICD-10-CM Coding
CPT Radiology Codes Requiring Review by AIM Effective 01/01/2016
 CPT Radiology Codes Requiring Review by AIM Effective 01/01/2016 When a service is authorized only one test per group is payable. *Secondary codes or add-on codes do not require preauthorization or separate
CPT Radiology Codes Requiring Review by AIM Effective 01/01/2016 When a service is authorized only one test per group is payable. *Secondary codes or add-on codes do not require preauthorization or separate
The Nuts and Bolts of Multiple Sclerosis. Rebecca Milholland, M.D., Ph.D. Center for Neurosciences
 The Nuts and Bolts of Multiple Sclerosis Rebecca Milholland, M.D., Ph.D. Center for Neurosciences Objectives Discuss which patients are at risk for Multiple Sclerosis Discuss the diagnostic criteria for
The Nuts and Bolts of Multiple Sclerosis Rebecca Milholland, M.D., Ph.D. Center for Neurosciences Objectives Discuss which patients are at risk for Multiple Sclerosis Discuss the diagnostic criteria for
