P517/617 Lec3, P1 R-L-C AC Circuits
|
|
|
- Agatha Hawkins
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 P517/617 Lec3, P1 R-L-C AC Circuits What does AC stand for? AC stands for "Alternating Current". Most of the time however, we are interested in the voltage at a point in the circuit, so we'll concentrate on voltages here rather than currents. We encounter AC circuits whenever a periodic voltage is applied to a circuit. The most common periodic voltage is in the form of a sine (or cosine) wave: V(t) V 0 coswt or V (t) V 0 sinwt Vo amplitude Volts -Vo period In this notation V 0 is the amplitude: V 0 Peak Voltage (V P ) V 0 1/2 Peak-to-Peak Voltage (V PP ) V 0 2 V RMS 1.41 V RMS Note: V PP is easiest to read off scope. V RMS is usually what multimeters read. In this notation w is the angular frequency: w 2pf, with f frequency of the waveform. The frequency (f) and period (T) are related by: T (sec) 1/f (sec -1 ) Household line voltage is usually V RMS ( V P ), f 60 Hz. It is extremely important to be able to analyze circuits (systems) with sine or cosine inputs since (almost) any waveform can be constructed from a sum of sines and cosines. This is the "heart" of Fourier analysis (Simpson, Chapter 3). The response of a circuit to a complicated waveform (e.g. a square wave) can be understood by analyzing each of the individual sine or cosine components that make up the complicated waveform. Usually only a few of these components are important in determining the circuit's response to the input waveform.
2 P517/617 Lec3, P2 R-C Circuits and AC waveforms There are many different techniques for solving AC circuits, all of them are based on Kirchhoff's laws. When we solve for the voltage and/or current in an AC circuit we are really solving a differential equation. The different circuit techniques are really just different ways of solving the same differential equation. brute force solution to differential equation complex numbers (algebra) Laplace transforms (integrals) We will solve the following RC circuit using the brute force method and complex numbers method. Let the input (driving) voltage be V(t) V 0 coswt and we want to find V R (t) and V C (t). V ( t ) R C Brute Force Method: Start with Kirchhoff's loop law: V(t) V R (t) + V C (t) V 0 coswt IR + Q / C RdQ(t ) / dt + Q(t) / C We have to solve an inhomogeneous D.E. The usual way to solve such a D.E. is to assume the solution has the same form as the input: Q(t) a sinwt + b coswt Plug our trial solution Q(t) back into the differential equation: V 0 coswt arw coswt - brw sinwt + (a / C)sinwt + (b / C)coswt (arw +b / C)coswt +(a / C - brw )sin wt V 0 arw +b / C a / C brw a RC 2 wv 0 1+ ( RCw ) 2 CV b 0 1+ ( RCw ) 2 We can now write the solution for V C (t): V C (t) Q / C (asinwt + b coswt) / C RCwV 0 1+ (RCw ) 2 sinwt + V (RCw ) 2 coswt
3 P517/617 Lec3, P3 We would like to rewrite the above solution in such a way that only a cosine term appears. In this form we can compare it to the input voltage. From the previous page we have: RCwV V C (t) 0 1+ (RCw ) 2 sinwt + V (RCw ) 2 coswt V È 0 RCw 1+ (RCw) 2 1+ (RCw ) sinwt (RCw ) coswt Í Î 2 We get the above equation in terms of cosine only using the following dirty trick from basic trig: cos(q 1 - q 2 ) sin q 1 sinq 2 + cosq 1 cosq 2 We can now define an angle such that: 1 cosf 1 + (RCw ) 2, sinf RCw, tan f RCw (RCw) Finally (!) we can write the desired expression for V C (t): V V C (t) 0 1+ (RCw) 2 cos(wt - f ) From the above expression we see that V C (t) and V 0 (t) are out of phase. Using the above expression for V C (t), we obtain: V R (t) IR R dq dt RC dv C dt -RCwV o 1+ (RCw ) sin(wt - f ) 2 Again, we would like to have cosines instead of sines. We do this using: -sin q cos(q + p / 2) Finally (!!) we have: RCwV V R (t) o 1+ (RCw ) 2 cos(wt - f + 2 p ) Some things to note: V C (t), V R (t), and I(t) are all out of phase with the applied voltage. I(t) and V R (t) are in phase with each other. V C (t) and V R (t) are out of phase by The amplitude of V C (t) and V R (t) depend on w.
4 Example: RC Circuit R1 1E3Ω P517/617 Lec3, P4 60 Hz Vp 1 V VSIN0 + SIN + C2 1E-5F - V out in out Solving circuits with complex numbers: PROS: don't explicitly solve differential equations (lots of algebra). can find magnitude and phase of voltage separately. CONS: have to use complex numbers! No "physics" in complex numbers. What's a complex number? (see Simpson, Appendix E, P835) Start with j -1 (solution to x ). A complex number can be written in two forms: X A + jb, with A and B real numbers or X R e jf, with R ( A 2 + B 2 ) 1/ 2, and tan f B / A (remember e jf cosf + j sin f )
5 Define the complex conjugate of X as: X* A - jb or X* R e - jf The magnitude of X can be found from: X ( XX*) 1/2 (X * X) 1/ 2 (A 2 + B 2 ) 1/2 Suppose we have 2 complex numbers, X and Y with phases a and b respectively, Z X Y X e ja Y e jb X j(a -b) e Y The magnitude of Z is just X / Y, while the phase of Z is a - b. So why is this useful? Consider the case of the capacitor and AC voltage: V(t) V 0 coswt ( ) Re al V 0 e jwt I(t) C dv dt -CwV 0 sin wt ( ) Re al jwcv 0 e jwt Re alá 0 e jwt ˆ Ë 1 jwc Re alá ˆ Ë X C with V and X C complex We now have Ohm's law for capacitors using the capacitive reactance X C. X C 1 jwc We can make a similar case for the inductor (V LdI / dt ): Ú I(t) 1 L V 0 coswt dt V 0sin wt Lw Re alá 0 e jwt ˆ Ë jwl Re alá ˆ Ë X L with V and X L complex We now have Ohm s law for inductors using the inductive reactance X L : X L jwl P517/617 Lec3, P5
6 P517/617 Lec3, P6 X C and X L act like frequency dependent resistors. However they also have a phase associated with them due to their complex nature. X L fi 0 as w fi 0 (short circuit, DC) X L fi as w fi (open circuit) X C fi 0 as w fi (short circuit) X C fi as w fi 0 (open circuit, DC) Back to the RC circuit. Allow voltages, currents, and charge to be complex V in V 0 coswt ( ) Re al V 0 e jwt ( ) Re al V R + V C We can write an expression for the charge (Q) taking into account the phase difference (f) between applied voltage and the voltage across the capacitor (V C ). Q(t) CV C (t) Ae j (wt-f ) where Q and V C are complex, A and C real. We can find the complex current by differentiating the above: I(t) dq(t) / dt j(w t- f ) jwae jwq(t ) jwcv C (t) V in V C + V R V C + IR V C V C + jwcv C R V in 1 + jwrc V in 1 jwc R + 1 jwc V in X C The above looks like a voltage divider equation!!!!!
7 We can easily find the magnitude of V C V C V in X C V 0 1 wc R 2 + (1 wc) 2 P517/617 Lec3, P7 V 0 1+ ( RCw ) 2 which is the same as the result on page 3. Is this solution the same as what we had when we solved by brute force? V C RealÁ in ˆ Ë 1 + jwrc RealÁ 0 e jwt ˆ Ë 1 + jwrc Ê RealÁ Ë V 0 e jwt ˆ 1 + (wrc) 2 e jf where f is given by tan f wrc. Ê j( wt-f ) V V C Real 0 e ˆ Á Ë 1 + (wrc) 2 V 0 cos(wt - f ) 1 + (wrc) 2 YES the solutions are identical. We can now solve for the voltage across the resistor. Start with the voltage divider equation in complex form: V R V in R V R V in R V 0 R R 2 + (1 wc) 2 V 0 wrc 1 + (wrc) 2 This amplitude is the same as the brute force differential equation case!
8 Important note: P517/617 Lec3, P8 When we add complex voltages together we must take into account the phase difference between them. Thus, the sum of the voltages at a given time satisfy: V 0 2 V R 2 + V C 2 and not V 0 V R + V C R-C Filters Filters: Allow us to select (reject) wanted (unwanted) signals on the basis of their frequency structure. Allow us to change the phase of the voltage or current in a circuit. Define the gain (G) or transfer (H) function of a circuit: G( jw ) H( jw ) V out / V in (jw is often denoted by s). G is independent of time, but can depend on w, R, L, C. For an RC circuit we can define G R and G C : V ( t ) R C G R V R V in G C V C V in R X C R R + 1/j wc 1/j wc R + 1/j wc We can categorize the G's as follows: High Frequencies ª 1, no phase shift ª 1/jwCR ª 0, phase shift high pass filter Low Frequencies ª jwcr ª 0, phase shift ª 1, no phase shift low pass filter G R G C
9 P517/617 Lec3, P9 V(t) R C G R V R R R V in V(t) R + 1/j G C V C V in X C 1/j wc R + 1/j Vout wc wc V(t) Vout
10 P517/617 Lec3, P10 Phase vs frequency for capacitor V(t) Decibels and Bode Plots: Decibel (db) describes voltage or power gain: db 20 log(v out / V in ) 10 log(p out / P in ) Bode Plot is a log-log plot with db on the Y axis and log(w) or log(f) on the X axis. 3 db point or 3 db frequency: (also called break frequency, corner frequency, 1/2 power point) At the 3 db point: V out 1 since 3 20 log(v V in 2 out / V in ) P out P in 1 2 since 3 10log(P out / P in ) wrc 1 for high or low pass filter
Phasors. Phasors. by Prof. Dr. Osman SEVAİOĞLU Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department. ^ V cos (wt + θ) ^ V sin (wt + θ)
 V cos (wt θ) V sin (wt θ) by Prof. Dr. Osman SEVAİOĞLU Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department EE 209 Fundamentals of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Prof. Dr. O. SEVAİOĞLU, Page 1 Vector
V cos (wt θ) V sin (wt θ) by Prof. Dr. Osman SEVAİOĞLU Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department EE 209 Fundamentals of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Prof. Dr. O. SEVAİOĞLU, Page 1 Vector
Unit2: Resistor/Capacitor-Filters
 Unit2: Resistor/Capacitor-Filters Physics335 Student October 3, 27 Physics 335-Section Professor J. Hobbs Partner: Physics335 Student2 Abstract Basic RC-filters were constructed and properties such as
Unit2: Resistor/Capacitor-Filters Physics335 Student October 3, 27 Physics 335-Section Professor J. Hobbs Partner: Physics335 Student2 Abstract Basic RC-filters were constructed and properties such as
ε: Voltage output of Signal Generator (also called the Source voltage or Applied
 Experiment #10: LR & RC Circuits Frequency Response EQUIPMENT NEEDED Science Workshop Interface Power Amplifier (2) Voltage Sensor graph paper (optional) (3) Patch Cords Decade resistor, capacitor, and
Experiment #10: LR & RC Circuits Frequency Response EQUIPMENT NEEDED Science Workshop Interface Power Amplifier (2) Voltage Sensor graph paper (optional) (3) Patch Cords Decade resistor, capacitor, and
Inductors in AC Circuits
 Inductors in AC Circuits Name Section Resistors, inductors, and capacitors all have the effect of modifying the size of the current in an AC circuit and the time at which the current reaches its maximum
Inductors in AC Circuits Name Section Resistors, inductors, and capacitors all have the effect of modifying the size of the current in an AC circuit and the time at which the current reaches its maximum
CIRCUITS LABORATORY EXPERIMENT 3. AC Circuit Analysis
 CIRCUITS LABORATORY EXPERIMENT 3 AC Circuit Analysis 3.1 Introduction The steady-state behavior of circuits energized by sinusoidal sources is an important area of study for several reasons. First, the
CIRCUITS LABORATORY EXPERIMENT 3 AC Circuit Analysis 3.1 Introduction The steady-state behavior of circuits energized by sinusoidal sources is an important area of study for several reasons. First, the
= V peak 2 = 0.707V peak
 BASIC ELECTRONICS - RECTIFICATION AND FILTERING PURPOSE Suppose that you wanted to build a simple DC electronic power supply, which operated off of an AC input (e.g., something you might plug into a standard
BASIC ELECTRONICS - RECTIFICATION AND FILTERING PURPOSE Suppose that you wanted to build a simple DC electronic power supply, which operated off of an AC input (e.g., something you might plug into a standard
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 4 - ALTERNATING CURRENT
 EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 4 - ALTERNATING CURRENT 4 Understand single-phase alternating current (ac) theory Single phase AC
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 4 - ALTERNATING CURRENT 4 Understand single-phase alternating current (ac) theory Single phase AC
Properties of electrical signals
 DC Voltage Component (Average voltage) Properties of electrical signals v(t) = V DC + v ac (t) V DC is the voltage value displayed on a DC voltmeter Triangular waveform DC component Half-wave rectifier
DC Voltage Component (Average voltage) Properties of electrical signals v(t) = V DC + v ac (t) V DC is the voltage value displayed on a DC voltmeter Triangular waveform DC component Half-wave rectifier
AC Power. by Prof. Dr. Osman SEVAİOĞLU Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department
 by Prof. Dr. Osman SEVAİOĞLU Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department EE 209 Fundamentals of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Prof. Dr. O. SEVAİOĞLU, Page 1 Voltage Waveform Consider the
by Prof. Dr. Osman SEVAİOĞLU Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department EE 209 Fundamentals of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Prof. Dr. O. SEVAİOĞLU, Page 1 Voltage Waveform Consider the
EXPERIMENT NUMBER 8 CAPACITOR CURRENT-VOLTAGE RELATIONSHIP
 1 EXPERIMENT NUMBER 8 CAPACITOR CURRENT-VOLTAGE RELATIONSHIP Purpose: To demonstrate the relationship between the voltage and current of a capacitor. Theory: A capacitor is a linear circuit element whose
1 EXPERIMENT NUMBER 8 CAPACITOR CURRENT-VOLTAGE RELATIONSHIP Purpose: To demonstrate the relationship between the voltage and current of a capacitor. Theory: A capacitor is a linear circuit element whose
Problem Solving 8: RC and LR Circuits
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Problem Solving 8: RC and LR Circuits Section Table and Group (e.g. L04 3C ) Names Hand in one copy per group at the end of the Friday Problem
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Problem Solving 8: RC and LR Circuits Section Table and Group (e.g. L04 3C ) Names Hand in one copy per group at the end of the Friday Problem
Experiment #11: LRC Circuit (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor)
 Experiment #11: LRC Circuit (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor) Concept: circuits Time: 30 m SW Interface: 750 Windows file: RLC.SWS EQUIPMENT NEEDED Science Workshop Interface Power Amplifier (2) Voltage
Experiment #11: LRC Circuit (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor) Concept: circuits Time: 30 m SW Interface: 750 Windows file: RLC.SWS EQUIPMENT NEEDED Science Workshop Interface Power Amplifier (2) Voltage
Introduction to Complex Numbers in Physics/Engineering
 Introduction to Complex Numbers in Physics/Engineering ference: Mary L. Boas, Mathematical Methods in the Physical Sciences Chapter 2 & 14 George Arfken, Mathematical Methods for Physicists Chapter 6 The
Introduction to Complex Numbers in Physics/Engineering ference: Mary L. Boas, Mathematical Methods in the Physical Sciences Chapter 2 & 14 George Arfken, Mathematical Methods for Physicists Chapter 6 The
RLC Series Resonance
 RLC Series Resonance 11EM Object: The purpose of this laboratory activity is to study resonance in a resistor-inductor-capacitor (RLC) circuit by examining the current through the circuit as a function
RLC Series Resonance 11EM Object: The purpose of this laboratory activity is to study resonance in a resistor-inductor-capacitor (RLC) circuit by examining the current through the circuit as a function
Using the Impedance Method
 Using the Impedance Method The impedance method allows us to completely eliminate the differential equation approach for the determination of the response of circuits. In fact the impedance method even
Using the Impedance Method The impedance method allows us to completely eliminate the differential equation approach for the determination of the response of circuits. In fact the impedance method even
Chapter 12 Driven RLC Circuits
 hapter Driven ircuits. A Sources... -. A ircuits with a Source and One ircuit Element... -3.. Purely esistive oad... -3.. Purely Inductive oad... -6..3 Purely apacitive oad... -8.3 The Series ircuit...
hapter Driven ircuits. A Sources... -. A ircuits with a Source and One ircuit Element... -3.. Purely esistive oad... -3.. Purely Inductive oad... -6..3 Purely apacitive oad... -8.3 The Series ircuit...
ANALYTICAL METHODS FOR ENGINEERS
 UNIT 1: Unit code: QCF Level: 4 Credit value: 15 ANALYTICAL METHODS FOR ENGINEERS A/601/1401 OUTCOME - TRIGONOMETRIC METHODS TUTORIAL 1 SINUSOIDAL FUNCTION Be able to analyse and model engineering situations
UNIT 1: Unit code: QCF Level: 4 Credit value: 15 ANALYTICAL METHODS FOR ENGINEERS A/601/1401 OUTCOME - TRIGONOMETRIC METHODS TUTORIAL 1 SINUSOIDAL FUNCTION Be able to analyse and model engineering situations
Electrical Resonance
 Electrical Resonance (R-L-C series circuit) APPARATUS 1. R-L-C Circuit board 2. Signal generator 3. Oscilloscope Tektronix TDS1002 with two sets of leads (see Introduction to the Oscilloscope ) INTRODUCTION
Electrical Resonance (R-L-C series circuit) APPARATUS 1. R-L-C Circuit board 2. Signal generator 3. Oscilloscope Tektronix TDS1002 with two sets of leads (see Introduction to the Oscilloscope ) INTRODUCTION
Circuits with inductors and alternating currents. Chapter 20 #45, 46, 47, 49
 Circuits with inductors and alternating currents Chapter 20 #45, 46, 47, 49 RL circuits Ch. 20 (last section) Symbol for inductor looks like a spring. An inductor is a circuit element that has a large
Circuits with inductors and alternating currents Chapter 20 #45, 46, 47, 49 RL circuits Ch. 20 (last section) Symbol for inductor looks like a spring. An inductor is a circuit element that has a large
Low Pass Filter Rise Time vs Bandwidth
 AN121 Dataforth Corporation Page 1 of 7 DID YOU KNOW? The number googol is ten raised to the hundredth power or 1 followed by 100 zeros. Edward Kasner (1878-1955) a noted mathematician is best remembered
AN121 Dataforth Corporation Page 1 of 7 DID YOU KNOW? The number googol is ten raised to the hundredth power or 1 followed by 100 zeros. Edward Kasner (1878-1955) a noted mathematician is best remembered
Circuits. The light bulbs in the circuits below are identical. Which configuration produces more light? (a) circuit I (b) circuit II (c) both the same
 Circuits The light bulbs in the circuits below are identical. Which configuration produces more light? (a) circuit I (b) circuit II (c) both the same Circuit II has ½ current of each branch of circuit
Circuits The light bulbs in the circuits below are identical. Which configuration produces more light? (a) circuit I (b) circuit II (c) both the same Circuit II has ½ current of each branch of circuit
The Time Constant of an RC Circuit
 The Time Constant of an RC Circuit 1 Objectives 1. To determine the time constant of an RC Circuit, and 2. To determine the capacitance of an unknown capacitor. 2 Introduction What the heck is a capacitor?
The Time Constant of an RC Circuit 1 Objectives 1. To determine the time constant of an RC Circuit, and 2. To determine the capacitance of an unknown capacitor. 2 Introduction What the heck is a capacitor?
Alternating-Current Circuits
 hapter 1 Alternating-urrent ircuits 1.1 A Sources... 1-1. Simple A circuits... 1-3 1..1 Purely esistive load... 1-3 1.. Purely Inductive oad... 1-5 1..3 Purely apacitive oad... 1-7 1.3 The Series ircuit...
hapter 1 Alternating-urrent ircuits 1.1 A Sources... 1-1. Simple A circuits... 1-3 1..1 Purely esistive load... 1-3 1.. Purely Inductive oad... 1-5 1..3 Purely apacitive oad... 1-7 1.3 The Series ircuit...
S-Parameters and Related Quantities Sam Wetterlin 10/20/09
 S-Parameters and Related Quantities Sam Wetterlin 10/20/09 Basic Concept of S-Parameters S-Parameters are a type of network parameter, based on the concept of scattering. The more familiar network parameters
S-Parameters and Related Quantities Sam Wetterlin 10/20/09 Basic Concept of S-Parameters S-Parameters are a type of network parameter, based on the concept of scattering. The more familiar network parameters
Chapter 29 Alternating-Current Circuits
 hapter 9 Alternating-urrent ircuits onceptual Problems A coil in an ac generator rotates at 6 Hz. How much time elapses between successive emf values of the coil? Determine the oncept Successive s are
hapter 9 Alternating-urrent ircuits onceptual Problems A coil in an ac generator rotates at 6 Hz. How much time elapses between successive emf values of the coil? Determine the oncept Successive s are
Step response of an RLC series circuit
 School of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:224 Principles of Electrical Engineering II Laboratory Experiment 5 Step response of an RLC series circuit 1 Introduction Objectives
School of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:224 Principles of Electrical Engineering II Laboratory Experiment 5 Step response of an RLC series circuit 1 Introduction Objectives
SERIES-PARALLEL DC CIRCUITS
 Name: Date: Course and Section: Instructor: EXPERIMENT 1 SERIES-PARALLEL DC CIRCUITS OBJECTIVES 1. Test the theoretical analysis of series-parallel networks through direct measurements. 2. Improve skills
Name: Date: Course and Section: Instructor: EXPERIMENT 1 SERIES-PARALLEL DC CIRCUITS OBJECTIVES 1. Test the theoretical analysis of series-parallel networks through direct measurements. 2. Improve skills
Lab #9: AC Steady State Analysis
 Theory & Introduction Lab #9: AC Steady State Analysis Goals for Lab #9 The main goal for lab 9 is to make the students familar with AC steady state analysis, db scale and the NI ELVIS frequency analyzer.
Theory & Introduction Lab #9: AC Steady State Analysis Goals for Lab #9 The main goal for lab 9 is to make the students familar with AC steady state analysis, db scale and the NI ELVIS frequency analyzer.
Let s examine the response of the circuit shown on Figure 1. The form of the source voltage Vs is shown on Figure 2. R. Figure 1.
 Examples of Transient and RL Circuits. The Series RLC Circuit Impulse response of Circuit. Let s examine the response of the circuit shown on Figure 1. The form of the source voltage Vs is shown on Figure.
Examples of Transient and RL Circuits. The Series RLC Circuit Impulse response of Circuit. Let s examine the response of the circuit shown on Figure 1. The form of the source voltage Vs is shown on Figure.
BASIC ELECTRONICS AC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS. December 2011
 AM 5-202 BASIC ELECTRONICS AC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS December 2011 DISTRIBUTION RESTRICTION: Approved for Pubic Release. Distribution is unlimited. DEPARTMENT OF THE ARMY MILITARY AUXILIARY RADIO SYSTEM FORT
AM 5-202 BASIC ELECTRONICS AC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS December 2011 DISTRIBUTION RESTRICTION: Approved for Pubic Release. Distribution is unlimited. DEPARTMENT OF THE ARMY MILITARY AUXILIARY RADIO SYSTEM FORT
EE 1202 Experiment #4 Capacitors, Inductors, and Transient Circuits
 EE 1202 Experiment #4 Capacitors, Inductors, and Transient Circuits 1. Introduction and Goal: Exploring transient behavior due to inductors and capacitors in DC circuits; gaining experience with lab instruments.
EE 1202 Experiment #4 Capacitors, Inductors, and Transient Circuits 1. Introduction and Goal: Exploring transient behavior due to inductors and capacitors in DC circuits; gaining experience with lab instruments.
Experiment 2 Diode Applications: Rectifiers
 ECE 3550 - Practicum Fall 2007 Experiment 2 Diode Applications: Rectifiers Objectives 1. To investigate the characteristics of half-wave and full-wave rectifier circuits. 2. To recognize the usefulness
ECE 3550 - Practicum Fall 2007 Experiment 2 Diode Applications: Rectifiers Objectives 1. To investigate the characteristics of half-wave and full-wave rectifier circuits. 2. To recognize the usefulness
Chapter 4: Passive Analog Signal Processing
 hapter 4: Passive Analog Signal Processing In this chapter we introduce filters and signal transmission theory. Filters are essential components of most analog circuits and are used to remove unwanted
hapter 4: Passive Analog Signal Processing In this chapter we introduce filters and signal transmission theory. Filters are essential components of most analog circuits and are used to remove unwanted
Homework Assignment 03
 Question 1 (2 points each unless noted otherwise) Homework Assignment 03 1. A 9-V dc power supply generates 10 W in a resistor. What peak-to-peak amplitude should an ac source have to generate the same
Question 1 (2 points each unless noted otherwise) Homework Assignment 03 1. A 9-V dc power supply generates 10 W in a resistor. What peak-to-peak amplitude should an ac source have to generate the same
PHYSICS 360 - LAB #2 Passive Low-pass and High-pass Filter Circuits and Integrator and Differentiator Circuits
 PHYSICS 360 - LAB #2 Passie Low-pass and High-pass Filter Circuits and Integrator and Differentiator Circuits Objectie: Study the behaior of low-pass and high-pass filters. Study the differentiator and
PHYSICS 360 - LAB #2 Passie Low-pass and High-pass Filter Circuits and Integrator and Differentiator Circuits Objectie: Study the behaior of low-pass and high-pass filters. Study the differentiator and
Rectifier circuits & DC power supplies
 Rectifier circuits & DC power supplies Goal: Generate the DC voltages needed for most electronics starting with the AC power that comes through the power line? 120 V RMS f = 60 Hz T = 1667 ms) = )sin How
Rectifier circuits & DC power supplies Goal: Generate the DC voltages needed for most electronics starting with the AC power that comes through the power line? 120 V RMS f = 60 Hz T = 1667 ms) = )sin How
The full wave rectifier consists of two diodes and a resister as shown in Figure
 The Full-Wave Rectifier The full wave rectifier consists of two diodes and a resister as shown in Figure The transformer has a centre-tapped secondary winding. This secondary winding has a lead attached
The Full-Wave Rectifier The full wave rectifier consists of two diodes and a resister as shown in Figure The transformer has a centre-tapped secondary winding. This secondary winding has a lead attached
Chapter 10. RC Circuits ISU EE. C.Y. Lee
 Chapter 10 RC Circuits Objectives Describe the relationship between current and voltage in an RC circuit Determine impedance and phase angle in a series RC circuit Analyze a series RC circuit Determine
Chapter 10 RC Circuits Objectives Describe the relationship between current and voltage in an RC circuit Determine impedance and phase angle in a series RC circuit Analyze a series RC circuit Determine
EE362L, Power Electronics Triac Light Dimmer
 1 EE362L, Power Electronics Triac Light Dimmer Rochelle Stortz and Brian Taraba, Team 277 2/2/05 Abstract - This document presents the construction of a light dimmer circuit that utilizes the current-regulating
1 EE362L, Power Electronics Triac Light Dimmer Rochelle Stortz and Brian Taraba, Team 277 2/2/05 Abstract - This document presents the construction of a light dimmer circuit that utilizes the current-regulating
A few words about imaginary numbers (and electronics) Mark Cohen mscohen@g.ucla.edu
 A few words about imaginary numbers (and electronics) Mark Cohen mscohen@guclaedu While most of us have seen imaginary numbers in high school algebra, the topic is ordinarily taught in abstraction without
A few words about imaginary numbers (and electronics) Mark Cohen mscohen@guclaedu While most of us have seen imaginary numbers in high school algebra, the topic is ordinarily taught in abstraction without
DOE FUNDAMENTALS HANDBOOK ELECTRICAL SCIENCE Volume 3 of 4
 DOE-HDBK-1011/3-92 JUNE 1992 DOE FUNDAMENTALS HANDBOOK ELECTRICAL SCIENCE Volume 3 of 4 U.S. Department of Energy Washington, D.C. 20585 FSC-6910 Distribution Statement A. Approved for public release;
DOE-HDBK-1011/3-92 JUNE 1992 DOE FUNDAMENTALS HANDBOOK ELECTRICAL SCIENCE Volume 3 of 4 U.S. Department of Energy Washington, D.C. 20585 FSC-6910 Distribution Statement A. Approved for public release;
The W5JCK Guide to the Mathematic Equations Required for the Amateur Extra Class Exam
 The W5JCK Guide to the Mathematic Equations Required for the Amateur Extra Class Exam This document contains every question from the Extra Class (Element 4) Question Pool* that requires one or more mathematical
The W5JCK Guide to the Mathematic Equations Required for the Amateur Extra Class Exam This document contains every question from the Extra Class (Element 4) Question Pool* that requires one or more mathematical
PHASOR DIAGRAMS HANDS-ON RELAY SCHOOL WSU PULLMAN, WA. RON ALEXANDER - BPA
 PHASOR DIAGRAMS HANDS-ON RELAY SCHOOL WSU PULLMAN, WA. RON ALEXANDER - BPA What are phasors??? In normal practice, the phasor represents the rms maximum value of the positive half cycle of the sinusoid
PHASOR DIAGRAMS HANDS-ON RELAY SCHOOL WSU PULLMAN, WA. RON ALEXANDER - BPA What are phasors??? In normal practice, the phasor represents the rms maximum value of the positive half cycle of the sinusoid
AC CIRCUITS - CAPACITORS AND INDUCTORS
 EXPRIMENT#8 AC CIRCUITS - CAPACITORS AND INDUCTORS NOTE: Two weeks are allocated for this experiment. Before performing this experiment, review the Proper Oscilloscope Use section of Experiment #7. Objective
EXPRIMENT#8 AC CIRCUITS - CAPACITORS AND INDUCTORS NOTE: Two weeks are allocated for this experiment. Before performing this experiment, review the Proper Oscilloscope Use section of Experiment #7. Objective
Bode Diagrams of Transfer Functions and Impedances ECEN 2260 Supplementary Notes R. W. Erickson
 Bode Diagrams of Transfer Functions and Impedances ECEN 2260 Supplementary Notes. W. Erickson In the design of a signal processing network, control system, or other analog system, it is usually necessary
Bode Diagrams of Transfer Functions and Impedances ECEN 2260 Supplementary Notes. W. Erickson In the design of a signal processing network, control system, or other analog system, it is usually necessary
Lock - in Amplifier and Applications
 Lock - in Amplifier and Applications What is a Lock in Amplifier? In a nut shell, what a lock-in amplifier does is measure the amplitude V o of a sinusoidal voltage, V in (t) = V o cos(ω o t) where ω o
Lock - in Amplifier and Applications What is a Lock in Amplifier? In a nut shell, what a lock-in amplifier does is measure the amplitude V o of a sinusoidal voltage, V in (t) = V o cos(ω o t) where ω o
Lecturer: James Grimbleby URL: http://www.personal.rdg.ac.uk/~stsgrimb/ email: j.b.grimbleby reading.ac.uk
 AC Circuit Analysis Module: SEEA5 Systems and Circuits Lecturer: UL: http://www.personal.rdg.ac.uk/~stsgrimb/ email:.b.grimbleby reading.ac.uk Number of Lectures: ecommended text book: David Irwin and
AC Circuit Analysis Module: SEEA5 Systems and Circuits Lecturer: UL: http://www.personal.rdg.ac.uk/~stsgrimb/ email:.b.grimbleby reading.ac.uk Number of Lectures: ecommended text book: David Irwin and
Since any real component also has loss due to the resistive component, the average power dissipated is 2 2R
 Quality factor, Q Reactive components such as capacitors and inductors are often described with a figure of merit called Q. While it can be defined in many ways, it s most fundamental description is: Q
Quality factor, Q Reactive components such as capacitors and inductors are often described with a figure of merit called Q. While it can be defined in many ways, it s most fundamental description is: Q
30. Bode Plots. Introduction
 0. Bode Plots Introduction Each of the circuits in this problem set is represented by a magnitude Bode plot. The network function provides a connection between the Bode plot and the circuit. To solve these
0. Bode Plots Introduction Each of the circuits in this problem set is represented by a magnitude Bode plot. The network function provides a connection between the Bode plot and the circuit. To solve these
L and C connected together. To be able: To analyse some basic circuits.
 circuits: Sinusoidal Voltages and urrents Aims: To appreciate: Similarities between oscillation in circuit and mechanical pendulum. Role of energy loss mechanisms in damping. Why we study sinusoidal signals
circuits: Sinusoidal Voltages and urrents Aims: To appreciate: Similarities between oscillation in circuit and mechanical pendulum. Role of energy loss mechanisms in damping. Why we study sinusoidal signals
Curcuits and Differential Equaitons
 Objective: Curcuits and Differential Equaitons Given a circuit, find the differential equation which describes that circuit. Solve that differential equation numerically (with SPICE, MATAB, or ISSIM) Ciruits
Objective: Curcuits and Differential Equaitons Given a circuit, find the differential equation which describes that circuit. Solve that differential equation numerically (with SPICE, MATAB, or ISSIM) Ciruits
Basic Electrical Technology Dr. L. Umanand Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore. Lecture - 33 3 phase System 4
 Basic Electrical Technology Dr. L. Umanand Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture - 33 3 phase System 4 Hello everybody. So, in the last class we have been
Basic Electrical Technology Dr. L. Umanand Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture - 33 3 phase System 4 Hello everybody. So, in the last class we have been
Positive Feedback and Oscillators
 Physics 3330 Experiment #6 Fall 1999 Positive Feedback and Oscillators Purpose In this experiment we will study how spontaneous oscillations may be caused by positive feedback. You will construct an active
Physics 3330 Experiment #6 Fall 1999 Positive Feedback and Oscillators Purpose In this experiment we will study how spontaneous oscillations may be caused by positive feedback. You will construct an active
Step Response of RC Circuits
 Step Response of RC Circuits 1. OBJECTIVES...2 2. REFERENCE...2 3. CIRCUITS...2 4. COMPONENTS AND SPECIFICATIONS...3 QUANTITY...3 DESCRIPTION...3 COMMENTS...3 5. DISCUSSION...3 5.1 SOURCE RESISTANCE...3
Step Response of RC Circuits 1. OBJECTIVES...2 2. REFERENCE...2 3. CIRCUITS...2 4. COMPONENTS AND SPECIFICATIONS...3 QUANTITY...3 DESCRIPTION...3 COMMENTS...3 5. DISCUSSION...3 5.1 SOURCE RESISTANCE...3
2. A conductor of length 2m moves at 4m/s at 30 to a uniform magnetic field of 0.1T. Which one of the following gives the e.m.f. generated?
 Extra Questions - 2 1. A straight length of wire moves through a uniform magnetic field. The e.m.f. produced across the ends of the wire will be maximum if it moves: a) along the lines of magnetic flux
Extra Questions - 2 1. A straight length of wire moves through a uniform magnetic field. The e.m.f. produced across the ends of the wire will be maximum if it moves: a) along the lines of magnetic flux
VCO Phase noise. Characterizing Phase Noise
 VCO Phase noise Characterizing Phase Noise The term phase noise is widely used for describing short term random frequency fluctuations of a signal. Frequency stability is a measure of the degree to which
VCO Phase noise Characterizing Phase Noise The term phase noise is widely used for describing short term random frequency fluctuations of a signal. Frequency stability is a measure of the degree to which
Diode Applications. As we have already seen the diode can act as a switch Forward biased or reverse biased - On or Off.
 Diode Applications Diode Switching As we have already seen the diode can act as a switch Forward biased or reverse biased - On or Off. Voltage Rectifier A voltage rectifier is a circuit that converts an
Diode Applications Diode Switching As we have already seen the diode can act as a switch Forward biased or reverse biased - On or Off. Voltage Rectifier A voltage rectifier is a circuit that converts an
Lecture 24. Inductance and Switching Power Supplies (how your solar charger voltage converter works)
 Lecture 24 Inductance and Switching Power Supplies (how your solar charger voltage converter works) Copyright 2014 by Mark Horowitz 1 Roadmap: How Does This Work? 2 Processor Board 3 More Detailed Roadmap
Lecture 24 Inductance and Switching Power Supplies (how your solar charger voltage converter works) Copyright 2014 by Mark Horowitz 1 Roadmap: How Does This Work? 2 Processor Board 3 More Detailed Roadmap
Current and Temperature Ratings
 Document 361-1 Current and Temperature Ratings Introduction This application note describes: How to interpret Coilcraft inductor current and temperature ratings Our current ratings measurement method and
Document 361-1 Current and Temperature Ratings Introduction This application note describes: How to interpret Coilcraft inductor current and temperature ratings Our current ratings measurement method and
Physics 15b Lab 4: Responses to Time Dependent Voltages
 Physics 15b Lab 4: Responses to Time Dependent Voltages Chapter 8 in Purcell covers AC circuit. The chapter focuses on the response to sinusoidal signals V = Vo cos(wt). If a circuit containing only resistors,
Physics 15b Lab 4: Responses to Time Dependent Voltages Chapter 8 in Purcell covers AC circuit. The chapter focuses on the response to sinusoidal signals V = Vo cos(wt). If a circuit containing only resistors,
RC Circuits and The Oscilloscope Physics Lab X
 Objective RC Circuits and The Oscilloscope Physics Lab X In this series of experiments, the time constant of an RC circuit will be measured experimentally and compared with the theoretical expression for
Objective RC Circuits and The Oscilloscope Physics Lab X In this series of experiments, the time constant of an RC circuit will be measured experimentally and compared with the theoretical expression for
RLC Resonant Circuits
 C esonant Circuits Andrew McHutchon April 20, 203 Capacitors and Inductors There is a lot of inconsistency when it comes to dealing with reactances of complex components. The format followed in this document
C esonant Circuits Andrew McHutchon April 20, 203 Capacitors and Inductors There is a lot of inconsistency when it comes to dealing with reactances of complex components. The format followed in this document
Measuring Impedance and Frequency Response of Guitar Pickups
 Measuring Impedance and Frequency Response of Guitar Pickups Peter D. Hiscocks Syscomp Electronic Design Limited phiscock@ee.ryerson.ca www.syscompdesign.com April 30, 2011 Introduction The CircuitGear
Measuring Impedance and Frequency Response of Guitar Pickups Peter D. Hiscocks Syscomp Electronic Design Limited phiscock@ee.ryerson.ca www.syscompdesign.com April 30, 2011 Introduction The CircuitGear
Three phase circuits
 Three phase circuits THREE PHASE CIRCUITS THREE-PHASE ADVANTAGES 1. The horsepower rating of three-phase motors and the kva rating of three-phase transformers are 150% greater than single-phase motors
Three phase circuits THREE PHASE CIRCUITS THREE-PHASE ADVANTAGES 1. The horsepower rating of three-phase motors and the kva rating of three-phase transformers are 150% greater than single-phase motors
Chapter 30 Inductance, Electromagnetic Oscillations, and AC Circuits. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 30 Inductance, Electromagnetic Oscillations, and AC Circuits 30-1 Mutual Inductance Mutual inductance: a changing current in one coil will induce a current in a second coil: Coil 1 produces a flux
Chapter 30 Inductance, Electromagnetic Oscillations, and AC Circuits 30-1 Mutual Inductance Mutual inductance: a changing current in one coil will induce a current in a second coil: Coil 1 produces a flux
Technical Note #3. Error Amplifier Design and Applications. Introduction
 Technical Note #3 Error Amplifier Design and Applications Introduction All regulating power supplies require some sort of closed-loop control to force the output to match the desired value. Both digital
Technical Note #3 Error Amplifier Design and Applications Introduction All regulating power supplies require some sort of closed-loop control to force the output to match the desired value. Both digital
See Horenstein 4.3 and 4.4
 EE 462: Laboratory # 4 DC Power Supply Circuits Using Diodes by Drs. A.V. Radun and K.D. Donohue (2/14/07) Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Kentucky Lexington, KY 40506 Updated
EE 462: Laboratory # 4 DC Power Supply Circuits Using Diodes by Drs. A.V. Radun and K.D. Donohue (2/14/07) Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Kentucky Lexington, KY 40506 Updated
electronics fundamentals
 electronics fundamentals circuits, devices, and applications THOMAS L. FLOYD DAVID M. BUCHLA Lesson 1: Diodes and Applications Center-Tapped Full-wave Rectifier The center-tapped (CT) full-wave rectifier
electronics fundamentals circuits, devices, and applications THOMAS L. FLOYD DAVID M. BUCHLA Lesson 1: Diodes and Applications Center-Tapped Full-wave Rectifier The center-tapped (CT) full-wave rectifier
First Order Circuits. EENG223 Circuit Theory I
 First Order Circuits EENG223 Circuit Theory I First Order Circuits A first-order circuit can only contain one energy storage element (a capacitor or an inductor). The circuit will also contain resistance.
First Order Circuits EENG223 Circuit Theory I First Order Circuits A first-order circuit can only contain one energy storage element (a capacitor or an inductor). The circuit will also contain resistance.
Power Supplies. 1.0 Power Supply Basics. www.learnabout-electronics.org. Module
 Module 1 www.learnabout-electronics.org Power Supplies 1.0 Power Supply Basics What you ll learn in Module 1 Section 1.0 Power Supply Basics. Basic functions of a power supply. Safety aspects of working
Module 1 www.learnabout-electronics.org Power Supplies 1.0 Power Supply Basics What you ll learn in Module 1 Section 1.0 Power Supply Basics. Basic functions of a power supply. Safety aspects of working
LM 358 Op Amp. If you have small signals and need a more useful reading we could amplify it using the op amp, this is commonly used in sensors.
 LM 358 Op Amp S k i l l L e v e l : I n t e r m e d i a t e OVERVIEW The LM 358 is a duel single supply operational amplifier. As it is a single supply it eliminates the need for a duel power supply, thus
LM 358 Op Amp S k i l l L e v e l : I n t e r m e d i a t e OVERVIEW The LM 358 is a duel single supply operational amplifier. As it is a single supply it eliminates the need for a duel power supply, thus
Reading: HH Sections 4.11 4.13, 4.19 4.20 (pgs. 189-212, 222 224)
 6 OP AMPS II 6 Op Amps II In the previous lab, you explored several applications of op amps. In this exercise, you will look at some of their limitations. You will also examine the op amp integrator and
6 OP AMPS II 6 Op Amps II In the previous lab, you explored several applications of op amps. In this exercise, you will look at some of their limitations. You will also examine the op amp integrator and
First Year (Electrical & Electronics Engineering)
 Z PRACTICAL WORK BOOK For The Course EE-113 Basic Electrical Engineering For First Year (Electrical & Electronics Engineering) Name of Student: Class: Batch : Discipline: Class Roll No.: Examination Seat
Z PRACTICAL WORK BOOK For The Course EE-113 Basic Electrical Engineering For First Year (Electrical & Electronics Engineering) Name of Student: Class: Batch : Discipline: Class Roll No.: Examination Seat
Chapter 12: The Operational Amplifier
 Chapter 12: The Operational Amplifier 12.1: Introduction to Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp) Operational amplifiers (op-amps) are very high gain dc coupled amplifiers with differential inputs; they are used
Chapter 12: The Operational Amplifier 12.1: Introduction to Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp) Operational amplifiers (op-amps) are very high gain dc coupled amplifiers with differential inputs; they are used
7-41 POWER FACTOR CORRECTION
 POWER FTOR CORRECTION INTRODUCTION Modern electronic equipment can create noise that will cause problems with other equipment on the same supply system. To reduce system disturbances it is therefore essential
POWER FTOR CORRECTION INTRODUCTION Modern electronic equipment can create noise that will cause problems with other equipment on the same supply system. To reduce system disturbances it is therefore essential
Using an Oscilloscope
 Using an Oscilloscope The oscilloscope is used to measure a voltage that changes in time. It has two probes, like a voltmeter. You put these probes on either side of the thing that you want to measure
Using an Oscilloscope The oscilloscope is used to measure a voltage that changes in time. It has two probes, like a voltmeter. You put these probes on either side of the thing that you want to measure
Network Theory Question Bank
 Network Theory Question Bank Unit-I JNTU SYLLABUS: Three Phase Circuits Three phase circuits: Phase sequence Star and delta connection Relation between line and phase voltages and currents in balanced
Network Theory Question Bank Unit-I JNTU SYLLABUS: Three Phase Circuits Three phase circuits: Phase sequence Star and delta connection Relation between line and phase voltages and currents in balanced
Laboratory 4: Feedback and Compensation
 Laboratory 4: Feedback and Compensation To be performed during Week 9 (Oct. 20-24) and Week 10 (Oct. 27-31) Due Week 11 (Nov. 3-7) 1 Pre-Lab This Pre-Lab should be completed before attending your regular
Laboratory 4: Feedback and Compensation To be performed during Week 9 (Oct. 20-24) and Week 10 (Oct. 27-31) Due Week 11 (Nov. 3-7) 1 Pre-Lab This Pre-Lab should be completed before attending your regular
The Importance of the X/R Ratio in Low-Voltage Short Circuit Studies
 The Importance of the X/R Ratio in Low-Voltage Short Circuit Studies DATE: November 17, 1999 REVISION: AUTHOR: John Merrell Introduction In some short circuit studies, the X/R ratio is ignored when comparing
The Importance of the X/R Ratio in Low-Voltage Short Circuit Studies DATE: November 17, 1999 REVISION: AUTHOR: John Merrell Introduction In some short circuit studies, the X/R ratio is ignored when comparing
Eðlisfræði 2, vor 2007
 [ Assignment View ] [ Print ] Eðlisfræði 2, vor 2007 30. Inductance Assignment is due at 2:00am on Wednesday, March 14, 2007 Credit for problems submitted late will decrease to 0% after the deadline has
[ Assignment View ] [ Print ] Eðlisfræði 2, vor 2007 30. Inductance Assignment is due at 2:00am on Wednesday, March 14, 2007 Credit for problems submitted late will decrease to 0% after the deadline has
Unit/Standard Number. High School Graduation Years 2010, 2011 and 2012
 1 Secondary Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Demonstrate an understanding of State and School safety regulations. 102 Practice safety techniques for electronics work. 103 Demonstrate an understanding of proper
1 Secondary Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Demonstrate an understanding of State and School safety regulations. 102 Practice safety techniques for electronics work. 103 Demonstrate an understanding of proper
Apprentice Telecommunications Technician Test (CTT) Study Guide
 Apprentice Telecommunications Technician Test (CTT) Study Guide 1 05/2014 Study Guide for Pacific Gas & Electric Company Apprentice Telecommunications Technician Qualifying Test (CTT) About the Test The
Apprentice Telecommunications Technician Test (CTT) Study Guide 1 05/2014 Study Guide for Pacific Gas & Electric Company Apprentice Telecommunications Technician Qualifying Test (CTT) About the Test The
EXPERIMENT NUMBER 5 BASIC OSCILLOSCOPE OPERATIONS
 1 EXPERIMENT NUMBER 5 BASIC OSCILLOSCOPE OPERATIONS The oscilloscope is the most versatile and most important tool in this lab and is probably the best tool an electrical engineer uses. This outline guides
1 EXPERIMENT NUMBER 5 BASIC OSCILLOSCOPE OPERATIONS The oscilloscope is the most versatile and most important tool in this lab and is probably the best tool an electrical engineer uses. This outline guides
LABORATORY 10 TIME AVERAGES, RMS VALUES AND THE BRIDGE RECTIFIER. Bridge Rectifier
 LABORATORY 10 TIME AVERAGES, RMS VALUES AND THE BRIDGE RECTIFIER Full-wave Rectification: Bridge Rectifier For many electronic circuits, DC supply voltages are required but only AC voltages are available.
LABORATORY 10 TIME AVERAGES, RMS VALUES AND THE BRIDGE RECTIFIER Full-wave Rectification: Bridge Rectifier For many electronic circuits, DC supply voltages are required but only AC voltages are available.
DRIVING LOOOONG CABLES
 DRIVING LOOOONG CABLES INTRODUCTION Microphone or line level cables may appear to be foolproof compared to loudspeaker cables. However, they are not. In particular you can easily encounter high frequency
DRIVING LOOOONG CABLES INTRODUCTION Microphone or line level cables may appear to be foolproof compared to loudspeaker cables. However, they are not. In particular you can easily encounter high frequency
Reading assignment: All students should read the Appendix about using oscilloscopes.
 10. A ircuits* Objective: To learn how to analyze current and voltage relationships in alternating current (a.c.) circuits. You will use the method of phasors, or the vector addition of rotating vectors
10. A ircuits* Objective: To learn how to analyze current and voltage relationships in alternating current (a.c.) circuits. You will use the method of phasors, or the vector addition of rotating vectors
Lab 3 Rectifier Circuits
 ECET 242 Electronic Circuits Lab 3 Rectifier Circuits Page 1 of 5 Name: Objective: Students successfully completing this lab exercise will accomplish the following objectives: 1. Learn how to construct
ECET 242 Electronic Circuits Lab 3 Rectifier Circuits Page 1 of 5 Name: Objective: Students successfully completing this lab exercise will accomplish the following objectives: 1. Learn how to construct
Precision Diode Rectifiers
 by Kenneth A. Kuhn March 21, 2013 Precision half-wave rectifiers An operational amplifier can be used to linearize a non-linear function such as the transfer function of a semiconductor diode. The classic
by Kenneth A. Kuhn March 21, 2013 Precision half-wave rectifiers An operational amplifier can be used to linearize a non-linear function such as the transfer function of a semiconductor diode. The classic
Lecture - 4 Diode Rectifier Circuits
 Basic Electronics (Module 1 Semiconductor Diodes) Dr. Chitralekha Mahanta Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Lecture - 4 Diode Rectifier Circuits
Basic Electronics (Module 1 Semiconductor Diodes) Dr. Chitralekha Mahanta Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Lecture - 4 Diode Rectifier Circuits
Ver 3537 E1.1 Analysis of Circuits (2014) E1.1 Circuit Analysis. Problem Sheet 1 (Lectures 1 & 2)
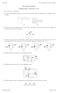 Ver 3537 E. Analysis of Circuits () Key: [A]= easy... [E]=hard E. Circuit Analysis Problem Sheet (Lectures & ). [A] One of the following circuits is a series circuit and the other is a parallel circuit.
Ver 3537 E. Analysis of Circuits () Key: [A]= easy... [E]=hard E. Circuit Analysis Problem Sheet (Lectures & ). [A] One of the following circuits is a series circuit and the other is a parallel circuit.
PHYSICAL METHODS, INSTRUMENTS AND MEASUREMENTS - Measurements Of Electrical Quantities - Ján Šaliga MEASUREMENTS OF ELECTRICAL QUANTITIES
 MEASUREMENTS OF ELECTRICAL QUANTITIES Ján Šaliga Department of Electronics and Multimedia Telecommunication, Technical University of Košice, Košice, Slovak Republic Keywords: basic electrical quantities,
MEASUREMENTS OF ELECTRICAL QUANTITIES Ján Šaliga Department of Electronics and Multimedia Telecommunication, Technical University of Košice, Košice, Slovak Republic Keywords: basic electrical quantities,
TESTS OF 1 MHZ SIGNAL SOURCE FOR SPECTRUM ANALYZER CALIBRATION 7/8/08 Sam Wetterlin
 TESTS OF 1 MHZ SIGNAL SOURCE FOR SPECTRUM ANALYZER CALIBRATION 7/8/08 Sam Wetterlin (Updated 7/19/08 to delete sine wave output) I constructed the 1 MHz square wave generator shown in the Appendix. This
TESTS OF 1 MHZ SIGNAL SOURCE FOR SPECTRUM ANALYZER CALIBRATION 7/8/08 Sam Wetterlin (Updated 7/19/08 to delete sine wave output) I constructed the 1 MHz square wave generator shown in the Appendix. This
45. The peak value of an alternating current in a 1500-W device is 5.4 A. What is the rms voltage across?
 PHYS Practice Problems hapters 8- hapter 8. 45. The peak value of an alternating current in a 5-W device is 5.4 A. What is the rms voltage across? The power and current can be used to find the peak voltage,
PHYS Practice Problems hapters 8- hapter 8. 45. The peak value of an alternating current in a 5-W device is 5.4 A. What is the rms voltage across? The power and current can be used to find the peak voltage,
Fundamentals of Signature Analysis
 Fundamentals of Signature Analysis An In-depth Overview of Power-off Testing Using Analog Signature Analysis www.huntron.com 1 www.huntron.com 2 Table of Contents SECTION 1. INTRODUCTION... 7 PURPOSE...
Fundamentals of Signature Analysis An In-depth Overview of Power-off Testing Using Analog Signature Analysis www.huntron.com 1 www.huntron.com 2 Table of Contents SECTION 1. INTRODUCTION... 7 PURPOSE...
The Calculation of G rms
 The Calculation of G rms QualMark Corp. Neill Doertenbach The metric of G rms is typically used to specify and compare the energy in repetitive shock vibration systems. However, the method of arriving
The Calculation of G rms QualMark Corp. Neill Doertenbach The metric of G rms is typically used to specify and compare the energy in repetitive shock vibration systems. However, the method of arriving
The Membrane Equation
 The Membrane Equation Professor David Heeger September 5, 2000 RC Circuits Figure 1A shows an RC (resistor, capacitor) equivalent circuit model for a patch of passive neural membrane. The capacitor represents
The Membrane Equation Professor David Heeger September 5, 2000 RC Circuits Figure 1A shows an RC (resistor, capacitor) equivalent circuit model for a patch of passive neural membrane. The capacitor represents
Laboratory Manual for AC Electrical Circuits
 AC Electrical Circuits Laboratory Manual James M. Fiore 2 Laboratory Manual for AC Electrical Circuits Laboratory Manual for AC Electrical Circuits by James M. Fiore Version 1.3.1, 01 March 2016 Laboratory
AC Electrical Circuits Laboratory Manual James M. Fiore 2 Laboratory Manual for AC Electrical Circuits Laboratory Manual for AC Electrical Circuits by James M. Fiore Version 1.3.1, 01 March 2016 Laboratory
Oscilloscope, Function Generator, and Voltage Division
 1. Introduction Oscilloscope, Function Generator, and Voltage Division In this lab the student will learn to use the oscilloscope and function generator. The student will also verify the concept of voltage
1. Introduction Oscilloscope, Function Generator, and Voltage Division In this lab the student will learn to use the oscilloscope and function generator. The student will also verify the concept of voltage
ECE 212 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY II
 ECE 212 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY II For use in ECE 212 Electrical Engineering Laboratory II a companion laboratory for ECE 262, Electric Circuits II January 2010 Dr. J. E. Harriss Revision History
ECE 212 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY II For use in ECE 212 Electrical Engineering Laboratory II a companion laboratory for ECE 262, Electric Circuits II January 2010 Dr. J. E. Harriss Revision History
