Certified Pedorthist. A. Peritendonitis B. Plantar Fasciitis C. Heel Spurs D. Sever s Disease. Achilles Tendonitis
|
|
|
- Emory Riley
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 30 Common & Not So Common Foot Pathologies, Conditions & Observations Rick E. Sevier, BS Ed., C.Ped, ROPA, COF CFS Allied Health Education Certified Pedorthist Pedorthics is the design, manufacture, modification and/or fit of footwear, including shoes, orthoses and foot devices, to prevent or alleviate foot problems caused by disease, congenital defect, overuse or injury. CEO - CFS Allied Health Education Board Member International Alliance for the Advancement of Pedorthic Education Adjunct Oklahoma State University Adjunct Robert M. Palmer MD Institute of Biomechanics Adjunct Eneslow Pedorthic Institute 30 Common Foot Pathologies Question Answer Etiology (Cause) Epidemiology (Incidence) Symptoms Effects on gait Your patient is a 40 year old male. He complains of pain in the left heel when walking or running. You observe that the tendon is painful to touch and the skin over the tendon is swollen and warm. You suspect: A. Peritendonitis B. Plantar Fasciitis C. Heel Spurs D. Sever s Disease Your patient is a 40 year old male. He complains of pain in the left heel when walking or running. You observe that the tendon is painful to touch and the skin over the tendon is swollen and warm. You suspect: A. Peritendonitis B. Plantar Fasciitis C. Heel Spurs D. Sever s Disease Achilles Tendonitis AKA Peritendonitis Insertional Achilles Tendonitis Non-insertional Achilles Tendonitis Achilles Tendonitis Achilles tendon can become inflamed, most commonly as a result of overuse or arthritis, although inflammation can also be associated with trauma and infection Achilles Tendonitis More common in patients over age 35 1
2 Achilles Tendonitis: Symptoms Pain in the affected heel when walking or running The tendon is usually painful to touch and the skin over the tendon may be swollen and warm Achilles Tendonitis: Symptoms Achilles tendonitis may predispose the patient to achilles rupture Patients who experience this usually describe the injury as a sharp pain, like someone hit them in the back of the heel with a stick Achilles Tendonitis: Effects On Gait Decreased propulsion in toeoff on affected side Pain on heel strike Hallux Valgus is most often associated with what pathology? A. Callouses B. Bunions C. Diabetes D. Arthritis Hallux Valgus is most often associated with what pathology? A. Callouses B. Bunions C. Diabetes D. Arthritis Bunions / Hallux Valgus Bunions can be a result of narrow-toed, highheeled shoes Bunions / Hallux Valgus The condition may become painful as extra bone and a fluid-filled bursa grow where the base of the Hallux meets the foot and the overlying skin Bunions / Hallux Valgus Associated with Hallux Valgus. Estimated as the third most common foot problem in the United States Bunions: Symptoms Reddened skin over the base of the great toe. Pain over the joint where the great toe joins the foot (MTP joint), aggravated by pressure from shoes 2
3 Bunions: Effects on Gait Overpronation due to 1st ray instability Degraded toe-off Your patient is a 6 year old female. Upon examination you notice excess calcaneal eversion during the contact phase of gait followed by slap-foot gait from heel-strike to foot-flat. You suspect: A. Cerebral Palsy B. Charcot-Marie-Tooth C. Calcaneovalgus D. None of the above. Your patient is a 6 year old female. Upon examination you notice excess calcaneal eversion during the contact phase of gait followed by slap-foot gait from heel-strike to foot-flat. You suspect: A. Cerebral Palsy B. Charcot-Marie-Tooth C. Calcaneovalgus D. None of the above. AKA Congenital Flat Foot, Talipes Calcaneovalgus Congenital Calcaneovalgus Calcaneovalgus A congenital deformity of the foot characterized by extreme dorsiflexion It may be a uni- or bilateral finding Calcaneovalgus The prognosis for talipes calcaneovalgus is usually very good Calcaneovalgus Calcaneovalgus: Symptoms The foot is pointing upwards and outwards Calcaneovalgus: Effects on Gait Excess calcaneal eversion during the contact phase of gait Slap-foot gait from heel-strike to foot-flat Your patient is an 80 year old non-diabetic male. He states that he has Charcot- Marie-Tooth disease. You observe that he has a foot deformity typical to CMT. How would you best describe it? A. Pes Planus B. Severe Pronation C. Severe Supination D. Ankle rigidity 3
4 Your patient is an 80 year old non-diabetic male. He states that he has Charcot- Marie-Tooth disease. You observe that he has a foot deformity typical to CMT. How would you best describe it? A. Pes Planus B. Severe Pronation C. Severe Supination D. Ankle rigidity Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease CMT patients slowly lose normal use of their feet/legs and hands/arms as nerves to the extremities degenerate The muscles in the extremities become weakened because of the loss of stimulation by the affected nerves Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease Additionally, there is a loss of sensory nerve function Unlike muscular dystrophy in which the defect is in the muscles, CMT is a disorder in which the defect is in the nerves that control the muscles CMT: Symptoms A high arched foot is one of the first signs of this disorder As the disease progresses, structural foot deformities take place The patient develops a pes cavus foot with hammer toes Foot drop and ankle sprains are frequent manifestations CMT: Symptoms The progressive muscle wasting leads to problems with walking, running, and balance To avoid tripping, patients with foot drop raise their knees unusually high resulting in high steppage gait In some patients, muscle weakness may also occur in the upper legs CMT: Effects on Gait High Steppage gait Loss of balance Upon patient examination, you observe areas of white moist skin between the fourth and fifth toes. This is most likely: A. Clavus mollis B. Heloma molle C. Soft Corn D. All of the above. Upon patient examination, you observe areas of white moist skin between the fourth and fifth toes. This is most likely: A. Clavus mollis B. Heloma molle C. Soft Corn D. All of the above. AKA Soft Corns Heloma molle Interdigital Corns Clavus mollis 4
5 Caused by pressure from a bony prominence on the next toe, they are often brought on by shoes that squeeze the toes together Clavus mollis Clavus mollis: Symptoms Soft corns are areas of white moist skin between the toes They most commonly occur between the fourth and fifth toes Clavus mollis: Symptoms They can be very painful and if not treated can form small ulcerations or sinus tracts that can become infected Clavus mollis: Effects on Gait Pain can substantially effect gait A hard corns are also known as. A. Dorsal Callouses B. Interdigital Corns C. Heloma durum D. All of the above. A hard corns are also known as. A. Dorsal Callouses B. Interdigital Corns C. Heloma durum D. All of the above. AKA Hard Corn heloma durum Clavus durus Corns are thickened layers of skin caused by repeated pressure or friction They are well circumscribed and have a central conical keratin core Clavus durus Clavus durus: Symptoms Typical sites include the dorsolateral aspect of fifth toe and the dorsum of interphalangeal joints of lateral toes 5
6 Clavus durus: Symptoms They tend to develop over a bony prominence Thick Hardened May be flaky and dry Clavus durus: Effects on Gait An abnormal gait pattern is a common cause of corns Your patient is a 12 year old female with cerebral palsy. The patient "toe walks". You observe a bouncy gait with early heel lift. Upon examination, you find that the foot is unable to fully dorsiflex against the ground. This condition is called: A. Equinus B. Sciatica C. Pes Cavus D. Kohler s Disease Your patient is a 12 year old female with cerebral palsy. The patient "toe walks". You observe a bouncy gait with early heel lift. Upon examination, you find that the foot is unable to fully dorsiflex against the ground. This condition is called: A. Equinus B. Sciatica C. Pes Cavus D. Kohler s Disease Equinus A spastic equinus may develop in patients with a neuromuscular disease. If the muscles in the back of the leg overpower the muscles in the front of the leg then equinus may develop Equinus Non-spastic equinus can be hereditarily acquired when one is born with a shorter achilles tendon Commonly following trauma, arthritis or cerebral palsy Equinus: Symptoms Less than 10 of available dorsiflexion at the ankle joint, when the Subtalar joint is in its neutral position and the midtarsal joint is fully locked. Equinus: Effects on Gait Typically this is seen in patients that tend to walk more on there toes, or have a bouncy gait If the foot is unable to fully dorsiflex against the ground there may be early heel off giving this bouncy gait pattern Your patient is a 22 year old diabetic female. She complains of pinpoint pain and swelling localized to the 2nd metatarsal head. She states that pain increases with weight bearing and typically becomes worse with the duration of time spent on the feet. Upon examination, you observe limited ability to flex the 2nd toe. You suspect: A. Diabetic Neuropathy B. Freiberg s Infraction C. Morton s Neuroma D. Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease 6
7 Your patient is a 22 year old diabetic female. She complains of pinpoint pain and swelling localized to the 2nd metatarsal head. She states that pain increases with weight bearing and typically becomes worse with the duration of time spent on the feet. Upon examination, you observe limited ability to flex the 2nd toe. You suspect: A. Diabetic Neuropathy B. Freiberg s Infraction C. Morton s Neuroma D. Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease Freiberg's Infraction AKA avascular necrosis AVN Freiberg's Infraction A condition specific to the lesser metatarsal heads, most commonly the second metatarsal This condition results in a focal loss of blood supply to the metatarsal head Freiberg's Infraction: Symptoms Freiberg's Infraction is most commonly seen in women and has an onset during the second decade of life Pain and swelling localized to the metatarsal head are the most specific symptoms Freiberg's Infraction: Symptoms Pain may be increased with weight bearing and typically becomes worse with the duration of time spent on the feet Patients may have only pinpoint tenderness or may have difficulty walking Limited ability to bend the toe Freiberg's Infraction: Effects on Gait Pain may be increased with weight bearing or may have difficulty walking Need to reduce pressure off the 2nd Met head is a condition of pain and discomfort on the posterior aspect of the heel at the area of the insertion of the Achilles tendon. A. Haglund's Deformity B. Haglund's Syndrome C. Pump Bump D. All of the above. is a condition of pain and discomfort on the posterior aspect of the heel at the area of the insertion of the Achilles tendon. A. Haglund's Deformity B. Haglund's Syndrome C. Pump Bump D. All of the above. Haglund's Syndrome AKA Haglund's Heel Haglund's Syndrome Pump Bump 7
8 Haglund's Syndrome The friction may cause an inflamed bursa known as an Achilles Bursitis The typical patient with Haglund's Deformity that is symptomatic is usually a female who wears highheeled shoes Haglund's Syndrome: Symptoms A noticeably enlarged bone prominence on the back of the heel, commonly seen at the area where the Achilles tendon attaches Haglund's Syndrome: Symptoms The bump may be painful especially when tight shoes are worn against the area. It may be red and swollen, It may form a bursa which can become inflamed Haglund's Syndrome: Effects on Gait Pain on heel strike and toe off is a condition, where the navicular bone in the foot undergoes avascular necrosis. A. Haglund s Syndrome B. Tarsal Coalition C. Freiberg s Infraction D. Kohler's disease is a condition, where the navicular bone in the foot undergoes avascular necrosis. A. Haglund s Syndrome B. Tarsal Coalition C. Freiberg s Infraction D. Kohler's disease Kohler's Disease Kohler's disease is a condition, where the navicular bone in the foot undergoes avascular necrosis For some unknown reason, typically in a child, the navicular bone in the foot loses its blood supply for a while Kohler's Disease The affected foot usually has typical findings of a dense flattened navicular bone, compared to the normal foot Can be unilateral or bilateral Kohler's Disease: Symptoms Usually male approximately 5 yrs old Pain at the apex of the medial longitudinal arch 8
9 Kohler's Disease: Symptoms Talonavicular joint is tender Some swelling my be evident Kohler's Disease: Effects on Gait Pain on weightbearing and antalgic gait Metatarsalgia is a general term used to denote a painful foot condition in the metatarsal region of the foot. Metatarsalgia is often. A. located under the 1st Metatarsal Head B. located under the 2nd, 3rd and 4th Metatarsal Heads C. diagnosed in patients with rheumatoid arthritis D. All of the above. Metatarsalgia is a general term used to denote a painful foot condition in the metatarsal region of the foot. Metatarsalgia is often. A. located under the 1st Metatarsal Head B. located under the 2nd, 3rd and 4th Metatarsal Heads C. diagnosed in patients with rheumatoid arthritis D. All of the above. Metatarsalgia Metatarsalgia is a general term used to denote a painful foot condition in the metatarsal region of the foot Metatarsalgia Metatarsalgia is often located under the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th metatarsal heads, or more isolated at the first metatarsal head Metatarsalgia: Symptoms Diagnosis is common for patients with rheumatoid arthritis Discomfort in the planter aspect of the metatarsal area caused by a variety of disorders Metatarsalgia: Effects on Gait Person tries to avoid pain associated with the ambulation Often quick, short and soft foot steps Your patient is an 18 year old female. She complains of a burning sensation on the dorsal aspect of her foot between the third and fourth digits. Upon examination you find that she wears tight fitting footwear and works as a cashier. You suspect: A. Plantar Fasciitis B. Morton's Neuroma C. Metatarsalgia D. Sesamoiditis 9
10 Your patient is an 18 year old female. She complains of a burning sensation on the dorsal aspect of her foot between the third and fourth digits. Upon examination you find that she wears tight fitting footwear and works as a cashier. You suspect: A. Plantar Fasciitis B. Morton's Neuroma C. Metatarsalgia D. Sesamoiditis Morton's Neuroma AKA Interdigital Neuroma Morton's Neuroma When two bones repeatedly rub together, it will usually cause the outer coating of a nerve in your foot to swell which is called a neuroma or a Morton's neuroma. It is most commonly affected between the metatarsal heads of the third and fourth toe Morton's Neuroma The exact etiology of Morton's Neuroma is still somewhat unclear, however, there are a number of precipitation factors that can cause a localized irritation to the nerve and thus may contribute to the development of a neuroma. These precipitating factors are: Morton's Neuroma FOOTGEAR: Any shoe that is high-heeled or is constricting may place the individual at higher risk for developing a neuroma. Morton's Neuroma are commonly found in women who have worn high heeled shoes for many years or men who's occupation require excessive stress of the forefoot such as kneeling or climbing ladders or are required to wear constricting shoegear. Morton's Neuroma BIOMECHANICAL ABNORMALITIES: An unstable (pronated) foot can predispose the foot to the development of a neuroma. The excessive pulling on the common digital nerve against the deep transverse intermetatarsal ligament results in irritation and eventually the development of the neuroma. Morton's Neuroma TRAUMA: Repetitive trauma that results from certain activities such as basketball, tennis, aerobics, running, etc., may precipitate the development of a neuroma. Trauma resulting from an injury such as fractures, sprains, dislocations, and crushing injuries may cause a neuroma. Morton's Neuroma Almost 90% of all Neuroma's are found in females between the ages of year old. Single Neuroma's are most common, however, instances of multiple neuromas in the same foot have been reported. Morton's Neuroma: Symptoms The pain from the neuroma may start gradually but may become a severe and persistent pain Burning, cramping, or aching sensation but may cause tingling or numbness Usually occurs after walking or standing on your feet for a long period of time 10
11 Morton's Neuroma: Symptoms Commonly found in people who wear tightfitting shoes Pain is usually relieved by removing the shoe and massaging the affected area Morton's Neuroma: Effects on Gait Person tries to avoid pain associated with the ambulation Often quick, short and soft foot steps is a common forefoot disorder where the second digit is longer than the Hallux. A. Oblique Forefoot B. Marie s Disease C. Digitorum Longus D. Morton's Toe is a common forefoot disorder where the second digit is longer than the Hallux. A. Oblique Forefoot B. Marie s Disease C. Digitorum Longus D. Morton's Toe Morton's Toe Morton's Toe is a common forefoot disorder where the second toe is longer than the Hallux Morton's Toe Morton's toe leads to excessive pressure on the second metatarsal head resulting in pain similar to the discomfort associated with metatarsalgia Morton's Toe The constant pressure placed on the longer second toe while walking or standing can lead to callus formation under the second metatarsal head due to this excessive pressure Morton's Toe: Symptoms Pain similar to the discomfort associated with metatarsalgia Callus formation under the second metatarsal head Morton's Toe: Effects on Gait Protective gait to avoid pressure and pain 11
12 Plantar Warts. A. are contagious. B. can spread to genitalia C. never resolve without treatment D. All of the above. Plantar Warts. A. are contagious. B. can spread to genitalia C. never resolve without treatment D. All of the above. Plantar Warts AKA Verruca Wart Plantar warts are hyperkeratotic lesions on the plantar surface They tend to develop over areas of pressure such as the heel and ball of the foot Plantar Warts Plantar warts are often endophytic (ie, they grow into the deeper layers of skin because of pressure) Although they are generally self-limited, plantar warts should be treated to lessen symptomatology, decrease duration, and reduce transmission. Plantar Warts Plantar warts are caused by direct exposure of HPV to the epidermis. This occurs through breaks in the stratum corneum of the epidermis. Such exposure frequently is associated with using public showers Plantar Warts Plantar warts are widespread; 7-10% of the population have warts Commonly found in patients who have warts elsewhere or who have a history of previous warts Plantar Warts Plantar warts affect females slightly more often than males Plantar warts may occur at any age, although they are more common in children and teenagers Plantar Warts: Symptoms Plantar warts may cause pain, particularly when walking. They may spread to other sites but not to histologically dissimilar areas (ie, plantar warts do not spread to genitalia). Most resolve spontaneously. Firm, hyperkeratotic lesions Plantar Warts: Symptoms Smooth surface with a gray-yellow color Usually occur over areas of pressure or bony prominence such as the heel and ball of the foot Usually flat because of pressure Several warts may fuse to form mosaic warts 12
13 Plantar Warts: Effects on Gait Person tries to avoid pain associated with the ambulation. Often quick, short and soft foot steps. Resembles stepping on a stone in the shoe "Too many toes" sign may be an indication of. A. adult acquired flatfoot B. severe pronation C. posterior tibialis dysfunction D. All of the above. "Too many toes" sign may be an indication of. A. adult acquired flatfoot B. severe pronation C. posterior tibialis dysfunction D. All of the above. Posterior Tibial Dysfunction AKA Acquired Flatfoot / Too Many Toes Posterior Tibial Dysfunction A damaged posterior tibial can be caused by trauma, a degenerative tear (simple deterioration over time), muscle dysfunction or tenosynovitis (inflammation of the tendon). Posterior Tibial Dysfunction: Symptoms Mainly affects women over 40 years of age. Pain and swelling at the inner ankle when weight is put on the foot. Too Many Toes Sign Posterior Tibial Dysfunction: Symptoms There will also be tenderness of the tendon itself. Patients will usually have trouble walking on their tiptoes Posterior Tibial Dysfunction: Effects on Gait The mid tarsal joint becomes locked and the subtalar joint pronates There will also be increase abduction of the forefoot in stance phase Your patient is an eleven year old male. He complains of heel pain on exercise, especially running and jumping. He states that the pain is often worse before and after activity and increased on deceleration or when landing from a jump. You observe that the patient is tip toeing and limping. After a complete exam and assessment you suspect. A. Reiter's Syndrome B. Kohler s Disease C. Sever's Disease D. Haglund's Deformity 13
14 Your patient is an eleven year old male. He complains of heel pain on exercise, especially running and jumping. He states that the pain is often worse before and after activity and increased on deceleration or when landing from a jump. You observe that the patient is tip toeing and limping. After a complete exam and assessment you suspect. A. Reiter's Syndrome B. Kohler s Disease C. Sever's Disease D. Haglund's Deformity Sever's Disease AKA Calcaneal Apophysitis Sever's Disease Sever's disease is a traction apophysitis of the Achilles tendon insertion at the calcaneus It is the most common cause of heel pain in the growing athlete and the second most common osteochondroses of both sexes Sever's Disease: Symptoms The condition occurs in both sexes usually between the age of 8 and 12 years and resolves upon cessation of growth. Patients suffering from Sever's disease complain of heel pain on exercise, especially running and jumping. Sever's Disease: Effects on Gait Patient may be tip toeing or limping Your patient is a 15 year old male complaining of chronic hind foot pain and peroneal spasm. Upon examination you observe rigid flat feet, and a rigid talocalcaneal joint. The patient walks with quick, short and soft foot steps. You suspect: A. Calcaneal Apophysitis B. Metatarsalgia C. Tarsal Coalition D. None of the above. Your patient is a 15 year old male complaining of chronic hind foot pain and peroneal spasm. Upon examination you observe rigid flat feet, and a rigid talocalcaneal joint. The patient walks with quick, short and soft foot steps. You suspect: A. Calcaneal Apophysitis B. Metatarsalgia C. Tarsal Coalition D. None of the above. Tarsal Coalition AKA Tarsal Union, Tarsal fusion Calcaneous Talar fusion Calcaneous Navicular fusion Cartilaginous coalition begins to ossify with resultant loss of inversion and eversion. Tarsal Coalition Ossification generally occurs between 8 12 years of age for calcaneonavicular coalition years of age for talocalcaneal coalition. The condition may be uni- or bilateral, is often familial 14
15 Tarsal Coalition: Symptoms Pain upon standing or with prolonged activity Tarsal Coalition: Effects on Gait Person tries to avoid pain associated with the ambulation. Often quick, short and soft foot steps Your patient is a 47 year old female. The patient complains of numbness over the bottom of the foot, as well as pain, burning, and tingling over the base of the foot and heel. The patient has a history of trauma to the medial malleolus. You suspect: A. Exostosis B. Plantar Fasciitis C. Charcot-Marie-Tooth D. Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Your patient is a 47 year old female. The patient complains of numbness over the bottom of the foot, as well as pain, burning, and tingling over the base of the foot and heel. The patient has a history of trauma to the medial malleolus. You suspect: A. Exostosis B. Plantar Fasciitis C. Charcot-Marie-Tooth D. Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Tarsal Tunnel AKA Posterior tibial nerve entrapment The tarsal tunnel is a structure in the foot formed between bones of the foot and overlying fibrous tissue. Tarsal Tunnel Within this tunnel lies a nerve called the posterior tibial nerve Tarsal tunnel syndrome results when the posterior tibial nerve is compressed within the tarsal tunnel Tarsal Tunnel Tarsal Tunnel: Symptoms Affects patients with an average onset of 47 Slight female preponderance Flat feet, cyst or trauma Pain, burning, and tingling on the sole of the foot Tarsal Tunnel: Symptoms Pain, burning, and tingling on the sole of the foot This pain can usually be relieved by rest, elevation, or massage Usually worsens as the day progresses 15
16 Tarsal Tunnel: Effects on Gait Person tries to avoid pain associated with the ambulation Often quick, short and soft foot steps Turf toe is. A. a torsion injury to the 5th digit B. rupture of the hallux longus extensor C. hyperextension of the 1st MTPJ D. fracture of the hallux Turf toe is. A. a torsion injury to the 5th digit B. rupture of the hallux longus extensor C. hyperextension of the 1st MTPJ D. fracture of the hallux Turf toe is an injury to the joint capsule and ligaments that connect the foot to the Hallux. Hyperextension of the 1st metatarsal phalangeal joint. Traumatic hyperextension of 1st MTPJ. Turf Toe Turf Toe: Symptoms Pain and tenderness in the ball of the foot and the big toe Swelling and bruising of the ball of the foot and the big toe Turf Toe: Symptoms Inability to bear weight on the ball of the injured foot Inability to push off on the big toe Reduced range of motion in the big toe Turf Toe: Effects on Gait Varies from an inability to bear weight to an antalgic gait followed by beer drinking and swearing Plantar Fasciitis is may be caused by: A. Heel spurs B. Obesity C. Overuse D. All of the above Plantar Fasciitis is may be caused by: A. Heel spurs B. Obesity C. Overuse D. All of the above 16
17 Plantar Fasciitis, an irritation and swelling with presence of extra immune cells of the fascia on the plantar surface of the foot. Plantar Fasciitis Some risk factors for development of this problem include a cavus arch, a planus arch, obesity, sudden weight gain, running and a tight Achilles tendon Plantar Fasciitis Plantar Fasciitis Plantar fasciitis is commonly though of as being caused by a heel spur, but research has found that this is not the case. On X-ray, heel spurs are seen commonly both in people with and without plantar fasciitis. Plantar Fasciitis: Symptoms Characteristic: dull tooth-ache or burning pain Stiffness may also be present Pain Location: Posterior and medial aspect of heel Medial tubercle of calcaneus Medial longitudinal arch Both heels often affected Pain worse with first few steps in morning Pain may be worse at days end in severe cases Pain worse with first steps of run Pain worse with prolonged standing (weight bearing) Plantar Fasciitis: Effects on Gait Person tries to avoid pain associated with the ambulation. Often quick, short and soft foot steps. Painful first step in the morning Heel Spurs are most often the result of: A. Stress on the muscles and fascia B. Increased intake of calcium C. Diabetes D. All of the above Heel Spurs are most often the result of: A. Stress on the muscles and fascia B. Increased intake of calcium C. Diabetes D. All of the above Heel Spurs Heel Spurs or heel spur syndrome are most often the result of stress on the muscles and fascia of the foot. This stress may form a spur on the bottom of the heel. While many spurs are painless others may produce chronic pain. Heel Spurs: Symptoms Bony heel growth Foot pain Heel pain Heel pain when walking Heel pain under weight bearing 17
18 Heel Spurs: Effects on Gait Pain throughout the stance phase of the gait cycle Painful first step in the morning Your patient is a 19 year old male. His diagnosis is Acute Ankle Sprain. Upon examination you notice moderate pain and swelling, mild to moderate ecchymosis, tenderness over involved structures, some loss of motion and function and mild to moderate instability. How would you classify this sprain? A. Class I B. Class II C. Class III D. Class IV Your patient is a 19 year old male. His diagnosis is Acute Ankle Sprain. Upon examination you notice moderate pain and swelling, mild to moderate ecchymosis, tenderness over involved structures, some loss of motion and function and mild to moderate instability. How would you classify this sprain? A. Class I B. Class II C. Class III D. Class IV Acute Ankle Sprain Acute trauma or injury usually results in an acute ankle sprain, a lateral twisting of the ankle that can cause ankle pain and cause damage to the stabilizing ligaments of the lateral ankle. Acute Ankle Sprain Ankle sprains remain one of the most frequent injuries in sports, comprising 45% of all sports injuries. The recurrence rate after an Ankle Sprain has been estimated to be as high as 80%. Acute Ankle Sprain: Symptoms Class I: Partial tear of a ligament Mild tenderness and swelling Slight or no functional loss No mechanical instability Acute Ankle Sprain: Symptoms Class II: Incomplete tear of a ligament, with moderate functional impairment Moderate pain and swelling Mild to moderate ecchymosis Tenderness over involved structures Some loss of motion and function Mild to moderate instability Acute Ankle Sprain: Symptoms Class III: complete tear and loss of integrity of a ligament Severe swelling Severe ecchymosis Loss of function and motion Mechanical instability Acute Ankle Sprain: Effects on Gait Varies from ability to bear weight and ambulate with minimal pain to total loss of ambulation 18
19 Your patient is a 63 year old female 6 months post ankle arthrodesis surgery. During gait you notice: A. Increased sagittal ROM B. Difficult toe clearance in the swing phase C. Increased stride length D. All of the above Your patient is a 63 year old female 6 months post ankle arthrodesis surgery. During gait you notice: A. Increased sagittal ROM B. Difficult toe clearance in the swing phase C. Increased stride length D. All of the above Ankle Arthrodesis Arthrodesis procedures are the removal of cartilage and any diseased bone from a joint to produce a fusion of at least two bones to create one bone. This removal of cartilage exposes the underlying bone on both sides of the joint. These joints surfaces are then compressed together with some form of fixation to create the fusion. Ankle Arthrodesis In an ankle arthrodesis, typically the tibial position is fused to the talus. In some cases the fibula is part of arthrodesis, but this is the surgeon s preference. Ankle Arthrodesis: Symptoms Post Arthrodesis Surgery Ankle Arthrodesis: Effects on Gait Decreased Sagittal ROM Decreased Plantarflexion at toe off Decreased stride length Hyperextension of the knee after foot-flat is achieved as the body moves forward without compensatory ankle dorsiflexion resulting in excess strain on the knee Ankle Arthrodesis: Effects on Gait Early heel-off, with prolonged weight bearing in the forefoot and associated pain of the metatarsals Difficult toe clearance in the swing phase, resulting in toe drag, compensatory increased hip and knee flexion, or circumduction of the lower limb Ankle Arthrodesis: Shoes Elevations for leg length discrepancy toe is a contracture of MTP joint, dorsiflexed PIP, and plantarflexed MTP. A. Claw B. Hammer C. Mallet D. Turf 19
20 toe is a contracture of MTP joint, dorsiflexed PIP, and plantarflexed MTP. A. Claw B. Hammer C. Mallet D. Turf Claw, Hammer & Mallet Toe Claw toe can be congenital or acquired. Claw toes may result from a problem with the peripheral nerves in the leg or from a spinal cord problem. Many cases have an unknown cause. Claw toes in and of themselves are not usually dangerous, but sometimes they are the first symptoms of a more serious disease of the nervous system. Claw toe is a dorsiflexed PIP, flexed MTP, and flexed DIP. Claw, Hammer & Mallet Toe Hammer toe is a deformity of the toe in which the end of the toe is bent downward. Hammer toe usually affects the second toe, although it can also affect the other toes. The toe assumes a claw-like position. The condition may occur as a result of pressure from a bunion. A high arch may also develop. Hammer toe is a contracture of MTP joint, dorsiflexed PIP, and plantarflexed MTP. Claw, Hammer & Mallet Toe Mallet toe occurs when the joint at the end of the toe cannot straighten up. The tip of the toe is often turned down against the shoe causing pressure and discomfort. Development of mallet toes is often caused by bone and muscle imbalances. People who are constantly on their feet or participate in athletic activities are more likely to develop mallet toes. Mallet toe is a variation of hammer toe in which DIP is plantarflexed. Claw, Hammer & Mallet Toe This condition can result from a jamming injury to a toe. As the second toe is the longest, it is the most commonly affected. Mallet toe can also result from wearing shoes that are too tight. Other causes include: Bone and muscle imbalances Arthritic condition Restrictive or poorly fitting shoes Prevalence in the age group is 1:15 with a 2.5:1 female predominance. In the 60+ age group there is a 1:10 incidence with a 3:1 predominance. Claw, Hammer & Mallet Toe: Symptoms Besides pain and an obvious deformity to the toe, symptoms may include: Changes in gait and balance Redness and swelling on and around the affected toe Corns or calluses where the toe bends and rubs An infection may develop Ulcers sometimes develop in patients with diabetes, who have decreased sensitivity in the foot It may be difficult to find shoes that accommodate the deformity Claw, Hammer & Mallet Toe: Effects on Gait Motion of the foot inside the shoe during gait can also cause intermittent, repetitive crowding of toes with painful gait. Early symptoms of a diabetic foot ulcer include: A. drainage B. pain C. blistering D. infection Early symptoms of a diabetic foot ulcer include: A. drainage B. pain C. blistering D. infection 20
21 Microvascular disease is a significant problem for diabetics and can lead to ulcerations. It is well known that diabetes is called a small vessel disease. Diabetic Ulcers Diabetic Ulcers Diabetics are prone to foot ulcerations due to both neurologic and vascular complications It is critical that diabetics maintain close control on their glucose level, maintain a good body weight and avoid smoking in an attempt to reduce the onset of small vessel disease. Diabetic Ulcers: Symptoms Early symptoms of a diabetic foot ulcer include redness of the skin, blistering, and other signs of irritation. In later stages, the person may have an open wound that drains fluid onto socks or bedding. The open wound can then become infected and develop swelling, redness, and drainage of pus. The person may have a fever, and blood sugar levels may be higher than usual. Diabetic Ulcers: Effects on Gait Shorter stride with wider stance Diabetic Ulcers: Shoes Long medial counters to control the heel and medial arch and decrease shear Blucher openings to allow easy entry into the shoe Shock-absorbing soles to reduce impact shock Low heels to decrease pressure on the metatarsal heads and the toes and decrease shear. Diabetic Ulcers: Shoes An appropriate rocker sole may be prescribed to help reduce overall pressure and impact shock, limit motion of the joints, and improve the transfer of weight. Extended steel shank may be added to enhance the effects of the rocker sole. Your patient is a 48 year old male. The patients foot spins in the toe off phase of gait. Upon examination you notice smooth skin under the 1st met head and callusing under the 2 nd through 5 th. You suspect: A. Calcaneal Eversion B. Hallux Rigidus C. Morton's Toe D. Achilles Tendonitis Your patient is a 48 year old male. The patients foot spins in the toe off phase of gait. Upon examination you notice smooth skin under the 1st met head and callusing under the 2 nd through 5 th. You suspect: A. Calcaneal Eversion B. Hallux Rigidus C. Morton's Toe D. Achilles Tendonitis Hallux Limitus/Rigidus Hallux Limitus is diminished motion in the first metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint Hallux rigidus is a continuation of the Hallux Limitus deformity. Both are often due to traumatic arthritis of first metatarsophalangeal joint. Motion ceases to occur in the joint, the first ray becomes fixed or rigid. 21
22 Hallux Limitus/Rigidus Hallux Limitus can also result from trauma or bunion surgery in which the first metatarsal is elevated during an osteotomy. Occurs secondary to repeated dorsiflexion stress; Results in restricted range of motion of great toe. Hallux Limitus/Rigidus: Symptoms Gradually increasing great toe pain and stiffness Precipitated by minor injury Provocative Ambulation / Dorsiflexion Smooth skin condition under the 1st met heads. This is an indication of hallux Rigidus / Limitus Hallux Limitus/Rigidus: Effects on Gait Spinning of the foot in the toe off phase of gait. The best way to detect limb length discrepancy is: A. X-Ray B. CT Scan C. Measuring Tape D. Physical Exam The best way to detect limb length discrepancy is: A. X-Ray B. CT Scan C. Measuring Tape D. Physical Exam Limb Length Discrepancy A limb length discrepancy may be due to a normal variation Differences of 3 1/2 to 4 percent of the total length of the lower extremity (4 cm or 1 2/3 inches in an average adult), including the thigh, lower leg and foot, may cause noticeable abnormalities while walking and require more effort to walk. Common with total hip arthroplasty 27-50% of cases. 32% of general population has minimal LLD. Limb Length Discrepancy: Symptoms Neck pain Change in structure of the lumbar vertebrae Sciatica Arthritis of hip or knee Patellar tendonitis Shin splints Limb Length Discrepancy: Effects on Gait A patient with a significant shortening of one leg will walk with an apparent lateral lurch to the affected side - somewhat like a Trendelenburg gait. However, if you watch his head, it bobs down during stance phase on the short leg, whereas in a Trendelenburg or coxalgic gait the head merely sways laterally Your patient is a 26 year old female. She complains of pain focused under the great toe on the ball of the foot. Upon examination you find no swelling. There is difficulty flexing the Hallux. You suspect: A. Turf Toe B. Morton s Toe C. Kohler s Disease D. Sesamoiditis 22
23 Your patient is a 26 year old female. She complains of pain focused under the great toe on the ball of the foot. Upon examination you find no swelling. There is difficulty flexing the Hallux. You suspect: A. Turf Toe B. Morton s Toe C. Kohler s Disease D. Sesamoiditis Sesamoiditis With a first-ray deformity such as hallux valgus, the sesamoids are no longer in their correct anatomic position because of the change in the musculotendinous balance around the joint. The tendons surrounding the sesamoids can become irritated or inflamed. This is called sesamoiditis and is a form of tendinitis. Sesamoid injuries include simple inflammation, Avascular necrosis, and fracture. Sesamoiditis: Symptoms Common among ballet dancers, runners and baseball catchers Pain is focused under the great toe on the ball of the foot. With sesamoiditis, pain may develop gradually; with a fracture, pain will be immediate Swelling and bruising may or may not be present. Difficulty and pain in bending and straightening the great toe Sesamoiditis: Effects on Gait Person tries to avoid pain associated with the ambulation. Often quick, short and soft foot steps. Torsional Deformities Your patient is a 58 year old male with diabetes. He has had an amputation across the 1 st ray. What is this type of amputation called? A. Chopart B. Ray Disarticulation C. Ray Amputation D. Lisfranc Your patient is a 58 year old male with diabetes. He has had an amputation across the 1 st ray. What is this type of amputation called? A. Chopart B. Ray Disarticulation C. Ray Amputation D. Lisfranc Amputations Amputations can fall into two different categories depending upon the location of amputation. A disarticulation is an amputation at a joint, leaving the proximal bone(s) intact. A "trans" amputation is an amputation done by cutting through the bone. Amputations TOE DISARTICULATIONS Interphalangeal disarticulation of the great toe Interphalangeal disarticulation of the lesser toes MTP joint disarticulation of the great toe Disarticulation at lesser toe MTP joints RAY AMPUTATIONS First ray amputation Lesser toe ray amputation Amputations 23
24 TRANSMETATARSAL AMPUTATION Amputation perpendicular to the metatarsals Amputations LISFRANC DISARTICULATION Amputation at the base of the metatarsals Amputations MIDTARSAL (CHOPART) DISARTICULATION Amputation at the talonavicular and calcanealcuboid joints Amputations Amputations: Effect on Gait Toe Amputation - Little effect unless Hallux is involved, then decreased toe-off and stability Ray Amputation - Little effect unless 1st ray is involved, then greatly decreased toe-off stability in stance phase Transmetatarsal Amputation - Poor gait with little propulsion Lisfranc Amputation - Poor barefoot gait. Chopart Amputation - Allows direct end bearing, but no roll over function. Because heel pad is stable and because preservation of full leg length, no prosthesis is needed for walking, but gait is apropulsive. The Torsional deformity most commonly seen in females that causes a pigeontoed appearance is: A. Internal Tibial Torsion B. Femoral Anteversion C. Metatarsus Adductus D. Forefoot Adductus The Torsional deformity most commonly seen in females that causes a pigeontoed appearance is: A. Internal Tibial Torsion B. Femoral Anteversion C. Metatarsus Adductus D. Forefoot Adductus Torsional Deformities There are three major pathologies involved with Torsional Deformities: Internal Tibial Torsion Femoral anteversion Metatarsus Adductus Torsional Deformities: Internal Tibial Torsion Internal Tibial Torsion (ITT) is a condition in early childhood in which the tibia (leg bone) is twisted inwards axially, causing the child to intoe as he walks. ITT is universal in infants and toddlers, and when the child takes his first steps, intoeing is the norm. With walking, the ITT resolves, and disappears by 18 to 24 months of age. ITT is a normal phase of skeletal development in the first 2 years of life. Torsional Deformities: Internal Tibial Torsion The tibia derotates itself over time, and the intoeing improves. During this phase, walking causes the ITT to correct itself. In a small proportion of children, however, the ITT does not resolve completely, or improves partially only. Even in these cases, the ITT can still improve spontaneously beyond age 2. 24
25 Torsional Deformities: Internal Tibial Torsion Internal Tibial Torsion is a very common condition Considered normal unless it does not resolve beyond 18 to 24 months of age Torsional Deformities: Femoral anteversion The normal femoral head and neck are rotated anteriorly with respect to the femoral condyles. Femoral anteversion decreases from an average of 40 at birth to 15 at skeletal maturity (25 change). The Dermal tibia is externally rotated 5 at birth and 15 at skeletal maturity. Total for femur and tibia = 35 of external rotation Femoral anteversion causes the child's knees and feet to turn inward, or have what is also known as a pigeon-toed appearance. Torsional Deformities: Femoral anteversion It is twice as likely to be seen in girls and most typically occurs among toddlers. Femoral anteversion can be the result of stiff hip muscles due to the position of the baby in the uterus. It also has a tendency to run in families. Typically, a child's walking style looks like that of his/her parents. Torsional Deformities: Femoral anteversion Femoral anteversion is most common cause for Toeing-In More common in girls (2:1) Most common onset ages 3-5 years Torsional Deformities: Metatarsus Adductus Forefoot is adducted at the tarsal-metatarsal joint. Usually seen shortly after birth and usually resolves with in the first year of life. It may be associated with hip dysplasia (10-15%). 85% resolve spontaneously. Feet that can be actively corrected to neutral do not need any treatment. Torsional Deformities: Metatarsus Adductus Usually seen shortly after birth Usually resolves with in the first year of life Torsional Deformities: Effects on Gait Child trips frequently Arms out for balance Torsional Deformities: Orthosis Functional Orthosis Dennis Browne Bar Fillauer Clamp Counter Rotational System Torsional Deformities: Shoes High top shoe Spinner wedge Reverse Thomas Heel Rocker Sole Lateral Wedging Lateral Counter reinforcements 25
26 Thank You! Please visit 26
This is caused by muscle strain to the Achilles tendon in the heel of the foot.
 Foot Facts Our feet were designed to move across uneven earthy surfaces. The hard, inflexible surfaces that we regularly walk on today, such as concrete, tile or wood, leave our feet wanting in terms of
Foot Facts Our feet were designed to move across uneven earthy surfaces. The hard, inflexible surfaces that we regularly walk on today, such as concrete, tile or wood, leave our feet wanting in terms of
Clinical Analysis of Foot Problems
 Clinical Analysis of Foot Problems by Karen S. Seale, M.D. Introduction Orthotists are vital members of the foot care team. Their expertise and special interests in materials and biomechanics add a unique
Clinical Analysis of Foot Problems by Karen S. Seale, M.D. Introduction Orthotists are vital members of the foot care team. Their expertise and special interests in materials and biomechanics add a unique
Common Foot Pathologies
 Common Foot Pathologies Chondromalacia Patella (patellofemoral pain syndrome) Chondromalacia Patella (patellofemoral pain syndrome) What is it? Chondromalacia (of Greek origin meaning softening of the
Common Foot Pathologies Chondromalacia Patella (patellofemoral pain syndrome) Chondromalacia Patella (patellofemoral pain syndrome) What is it? Chondromalacia (of Greek origin meaning softening of the
The Five Most Common Pathomechanical Foot Types (Rearfoot varus, forefoot varus, equinus, plantarflexed first ray, forefoot valgus)
 The Five Most Common Pathomechanical Foot Types (Rearfoot varus, forefoot varus, equinus, plantarflexed first ray, forefoot valgus) Pathomechanical foot types usually refer to structural deformities that
The Five Most Common Pathomechanical Foot Types (Rearfoot varus, forefoot varus, equinus, plantarflexed first ray, forefoot valgus) Pathomechanical foot types usually refer to structural deformities that
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE
 PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE Presenter Dr. Richard Coughlin AOFAS Lecture Series OBJECTIVES 1. ASSESS 2. DIAGNOSE 3. TREAT HISTORY TAKING Take a HISTORY What is the patient s chief complaint?
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE Presenter Dr. Richard Coughlin AOFAS Lecture Series OBJECTIVES 1. ASSESS 2. DIAGNOSE 3. TREAT HISTORY TAKING Take a HISTORY What is the patient s chief complaint?
Predislocation syndrome
 Predislocation syndrome Sky Ridge Medical Center, Aspen Building Pre-dislocation syndrome, capsulitis, and metatarsalgia are all similar problems usually at the ball of the foot near the second and third
Predislocation syndrome Sky Ridge Medical Center, Aspen Building Pre-dislocation syndrome, capsulitis, and metatarsalgia are all similar problems usually at the ball of the foot near the second and third
Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries
 Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries Symptoms Related to Abnormal Foot Biomechanics & their Differential Diagnosis Daniel Pang BSc (Hon) P&O, Cped Certified Pedorthist (USA) Only 10% of foot having structure
Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries Symptoms Related to Abnormal Foot Biomechanics & their Differential Diagnosis Daniel Pang BSc (Hon) P&O, Cped Certified Pedorthist (USA) Only 10% of foot having structure
.org. Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction. Anatomy. Cause. Symptoms
 Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies
 Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies David Lee, D.P.M., D. A.B.P.S. Purpose Identification of mechanical foot and ankle conditions Base treatments Knowing when to refer to a podiatrist
Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies David Lee, D.P.M., D. A.B.P.S. Purpose Identification of mechanical foot and ankle conditions Base treatments Knowing when to refer to a podiatrist
Outline. The Agony of the Foot: Disclosure. Plantar Fasciitis. Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care. Daniel Thuillier, M.D.
 The Agony of the Foot: Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care Daniel Thuillier, M.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Orthopaedics University of California San Francisco Plantar Fasciitis Achilles
The Agony of the Foot: Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care Daniel Thuillier, M.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Orthopaedics University of California San Francisco Plantar Fasciitis Achilles
RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION
 RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION Topics of Tonight s s Lecture Common Injuries and Treatments Causes of Common Injuries Measures to Avoid Injury Most Common Running Injuries Plantar Fascitis
RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION Topics of Tonight s s Lecture Common Injuries and Treatments Causes of Common Injuries Measures to Avoid Injury Most Common Running Injuries Plantar Fascitis
Elbow Injuries and Disorders
 Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
Plantar fascia. Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot)
 ! Plantar fascia Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot) Plantar Fasciitis is the most common foot problem seen in runners and is often associated with an increase in running mileage. Typically
! Plantar fascia Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot) Plantar Fasciitis is the most common foot problem seen in runners and is often associated with an increase in running mileage. Typically
PATHOLOGIC GAIT -- MUSCULOSKELETAL. Focal Weakness. Ankle Dorsiflexion Weakness COMMON GAIT ABNORMALITIES
 Pathological Gait I: Musculoskeletal - 1 PATHOLOGIC GAIT -- MUSCULOSKELETAL Normal walking is the standard against which pathology is measured Efficiency is often reduced in pathology COMMON GAIT ABNORMALITIES
Pathological Gait I: Musculoskeletal - 1 PATHOLOGIC GAIT -- MUSCULOSKELETAL Normal walking is the standard against which pathology is measured Efficiency is often reduced in pathology COMMON GAIT ABNORMALITIES
Glossary of Foot & Ankle Terminology
 Glossary of Foot & Ankle Terminology Achilles Tendon One of the longer tendons in the body, stretching from the bones of the heel to the calf muscles. Abrasion An injury in which superficial layers of
Glossary of Foot & Ankle Terminology Achilles Tendon One of the longer tendons in the body, stretching from the bones of the heel to the calf muscles. Abrasion An injury in which superficial layers of
Deformities. Assessment of Foot. The majority of foot deformities occur in otherwise healthy infants. However most generalized.
 Assessment of Foot Deformities in the Infant By Maureen Baxter, MDCM, FRCS The majority of foot deformities occur in otherwise healthy infants. However most generalized neurologic disorders (spina bifida,
Assessment of Foot Deformities in the Infant By Maureen Baxter, MDCM, FRCS The majority of foot deformities occur in otherwise healthy infants. However most generalized neurologic disorders (spina bifida,
WHEN TO BE CONCERNED: Leg Bowing, Intoeing and Flat Feet.
 WHEN TO BE CONCERNED: Leg Bowing, Intoeing and Flat Feet. Understanding normal childhood development and recognizing signs of pathology WHAT IS NORMAL? Very important: the average and normal are not the
WHEN TO BE CONCERNED: Leg Bowing, Intoeing and Flat Feet. Understanding normal childhood development and recognizing signs of pathology WHAT IS NORMAL? Very important: the average and normal are not the
GET A HANDLE ON YOUR HEEL PAIN GUIDE
 GET A HANDLE ON YOUR HEEL PAIN GUIDE American Podiatric Medical Association www.apma.org/heelpain Take a Moment to Focus in on Your Feet. Does one (or even both) of your heels hurt? If so, you aren t alone.
GET A HANDLE ON YOUR HEEL PAIN GUIDE American Podiatric Medical Association www.apma.org/heelpain Take a Moment to Focus in on Your Feet. Does one (or even both) of your heels hurt? If so, you aren t alone.
Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle
 Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease that attacks multiple joints throughout the body. It most often
Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease that attacks multiple joints throughout the body. It most often
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon
PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome)
 PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome) R. Amadeus Mason MD Description Plantar fascitis is characterized by stiffness and inflammation of the main fascia (fibrous connective [ligament-like] tissue) on the
PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome) R. Amadeus Mason MD Description Plantar fascitis is characterized by stiffness and inflammation of the main fascia (fibrous connective [ligament-like] tissue) on the
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle. Dr. Travis Kieckbusch August 7, 2014
 Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Dr. Travis Kieckbusch August 7, 2014 Foot and Ankle Injuries in Athletes Lateral ankle sprains Syndesmosis sprains high ankle sprain Achilles tendon injuries Lisfranc
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Dr. Travis Kieckbusch August 7, 2014 Foot and Ankle Injuries in Athletes Lateral ankle sprains Syndesmosis sprains high ankle sprain Achilles tendon injuries Lisfranc
.org. Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs. Anatomy. Cause
 Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Page ( 1 ) Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition
Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Page ( 1 ) Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition
Osteoarthritis progresses slowly and the pain and stiffness it causes worsens over time.
 Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States. It can occur at any age, and literally means "pain within a joint." As a result, arthritis is a term used
Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States. It can occur at any age, and literally means "pain within a joint." As a result, arthritis is a term used
November 2012 Case Study. Authors: Kyle Nagle, MD, MPH; Karl Fry, PT, DPT, OCS; David Bernhardt, MD
 CC: Right foot pain November 2012 Case Study Authors: Kyle Nagle, MD, MPH; Karl Fry, PT, DPT, OCS; David Bernhardt, MD HPI: A 17 year old female cross country runner presents with right foot pain. At a
CC: Right foot pain November 2012 Case Study Authors: Kyle Nagle, MD, MPH; Karl Fry, PT, DPT, OCS; David Bernhardt, MD HPI: A 17 year old female cross country runner presents with right foot pain. At a
Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures
 Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures Fractures of the heel bone, or calcaneus, can be disabling injuries. They most often occur during high-energy collisions
Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures Fractures of the heel bone, or calcaneus, can be disabling injuries. They most often occur during high-energy collisions
Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933
 Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933 www.grhsonline.org Important Notice The information contained in this document is for informational
Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933 www.grhsonline.org Important Notice The information contained in this document is for informational
Plantar Fasciitis. Plantar Fascia
 Plantar Fasciitis Introduction Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the thick band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. This thick band of tissue is called the plantar fascia. Plantar
Plantar Fasciitis Introduction Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the thick band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. This thick band of tissue is called the plantar fascia. Plantar
How To Treat Heel Pain
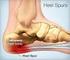 Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Heel Pain The Plantar Fasciitis Organization is dedicated to the understanding of Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, and all other forms of Heel Pain. Welcome to the Plantar
Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Heel Pain The Plantar Fasciitis Organization is dedicated to the understanding of Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, and all other forms of Heel Pain. Welcome to the Plantar
Chapter 5. Objectives. Normal Ankle Range of Motion. Lateral Ankle Sprains. Lateral Ankle Sprains. Assessment of Lateral Ankle Sprains
 Objectives Chapter 5 Assessment of Ankle & Lower Leg Injuries Review the following components of injury assessment related to the ankle and lower leg Stress tests Special tests Normal Ankle Range of Motion
Objectives Chapter 5 Assessment of Ankle & Lower Leg Injuries Review the following components of injury assessment related to the ankle and lower leg Stress tests Special tests Normal Ankle Range of Motion
Arches. Foot Injuries. Medial Longitudinal Arch. Lateral Longitudinal Arch. Transverse Arch. Arch Strains
 Arches Foot Injuries Three arches in the foot: 1) Lateral longitudinal arch 2) Medial longitudinal arch 3) Transverse arch These arches are maintained and supported by the wedging of the interlocking tarsal
Arches Foot Injuries Three arches in the foot: 1) Lateral longitudinal arch 2) Medial longitudinal arch 3) Transverse arch These arches are maintained and supported by the wedging of the interlocking tarsal
Screening Examination of the Lower Extremities BUY THIS BOOK! Lower Extremity Screening Exam
 Screening Examination of the Lower Extremities Melvyn Harrington, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Loyola University Medical Center BUY THIS BOOK! Essentials of Musculoskeletal Care
Screening Examination of the Lower Extremities Melvyn Harrington, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Loyola University Medical Center BUY THIS BOOK! Essentials of Musculoskeletal Care
University of South Florida
 University of South Florida Foot & Ankle Orthopaedics PGY 2 Competency Based Goals & Objectives Competency 1- Patient Care: Provide patient care that is compassionate, appropriate and effective for the
University of South Florida Foot & Ankle Orthopaedics PGY 2 Competency Based Goals & Objectives Competency 1- Patient Care: Provide patient care that is compassionate, appropriate and effective for the
Heel pain and Plantar fasciitis
 A patient s guide Heel pain and Plantar fasciitis Fred Robinson BSc FRCS FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon Alex Wee BSc FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon. What causes
A patient s guide Heel pain and Plantar fasciitis Fred Robinson BSc FRCS FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon Alex Wee BSc FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon. What causes
The Forefoot Valgus Foot-Type Joe Fox, MS, LAT June 10, 2014
 The Forefoot Valgus Foot-Type Joe Fox, MS, LAT June 10, 2014 Introduction BS Kinesiology Exercise Science and Athletic Training, University of Wisconsin-Madison MS in Exercise Science Athletic Training,
The Forefoot Valgus Foot-Type Joe Fox, MS, LAT June 10, 2014 Introduction BS Kinesiology Exercise Science and Athletic Training, University of Wisconsin-Madison MS in Exercise Science Athletic Training,
Foot and Ankle Complaints
 Foot and Ankle Complaints INTRODUCTION Anatomy and Function Foot Ankle Common complaints Common diagnoses FOOT AND ANKLE ANATOMY 26 bones and 2 sesamoids Forefoot Metatarsals phalanges Midfoot 5 tarsals
Foot and Ankle Complaints INTRODUCTION Anatomy and Function Foot Ankle Common complaints Common diagnoses FOOT AND ANKLE ANATOMY 26 bones and 2 sesamoids Forefoot Metatarsals phalanges Midfoot 5 tarsals
.org. Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems. Anatomy. Cause
 Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems Page ( 1 ) What most people call the shoulder is really several joints that combine with tendons and muscles to allow a wide range of motion in the arm from scratching
Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems Page ( 1 ) What most people call the shoulder is really several joints that combine with tendons and muscles to allow a wide range of motion in the arm from scratching
.org. Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury. Anatomy. Description
 Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury Page ( 1 ) Lisfranc (midfoot) injuries result if bones in the midfoot are broken or ligaments that support the midfoot are torn. The severity of the injury can vary from simple
Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury Page ( 1 ) Lisfranc (midfoot) injuries result if bones in the midfoot are broken or ligaments that support the midfoot are torn. The severity of the injury can vary from simple
The Knee Internal derangement of the knee (IDK) The Knee. The Knee Anatomy of the anteromedial aspect. The Knee
 Orthopedics and Neurology James J. Lehman, DC, MBA, FACO University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Internal derangement of the knee (IDK) This a common provisional diagnosis for any patient with
Orthopedics and Neurology James J. Lehman, DC, MBA, FACO University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Internal derangement of the knee (IDK) This a common provisional diagnosis for any patient with
Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understa
 Plantar Fasciitis Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understand why it occurs. Recognize the injury
Plantar Fasciitis Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understand why it occurs. Recognize the injury
A Guide to Heel Pain
 The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists A Guide to Heel Pain The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists Heel pain may be caused by a number of different problems; for effective treatment you need
The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists A Guide to Heel Pain The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists Heel pain may be caused by a number of different problems; for effective treatment you need
What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis?
 Bursitis and tendinitis are both common conditions that cause swelling around muscles and bones. They occur most often in the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, or ankle. A bursa is a small, fluid-filled
Bursitis and tendinitis are both common conditions that cause swelling around muscles and bones. They occur most often in the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, or ankle. A bursa is a small, fluid-filled
.org. Achilles Tendinitis. Description. Cause. Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel.
 Achilles Tendinitis Page ( 1 ) Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your
Achilles Tendinitis Page ( 1 ) Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your
The Land of Os: Accessory Ossicles of the Foot
 The Land of Os: Accessory Ossicles of the Foot Susan Cross, Anshul Rastogi, Rosy Jalan; Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK Contact: susan.cross@bartshealth.nhs.uk Pictorial review Abstract
The Land of Os: Accessory Ossicles of the Foot Susan Cross, Anshul Rastogi, Rosy Jalan; Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK Contact: susan.cross@bartshealth.nhs.uk Pictorial review Abstract
Lower Back Spinal Fusion & Exercise
 & Exercise with Rick Kaselj, MS More FREE Information on Exercise & Injuries $299 Fitness Education Returning the Shoulder Back to Optimal Function Seminar Exercise Modification for the Sensitive Shoulder
& Exercise with Rick Kaselj, MS More FREE Information on Exercise & Injuries $299 Fitness Education Returning the Shoulder Back to Optimal Function Seminar Exercise Modification for the Sensitive Shoulder
Runner's Injury Prevention
 JEN DAVIS DPT Runner's Injury Prevention Jen Davis DPT Orthopedic Physical Therapy Foot Traffic 7718 SE 13th Ave Portland, OR 97202 (503) 482-7232 Jen@runfastpt.com www.runfastpt.com!1 THE AMAZING RUNNER
JEN DAVIS DPT Runner's Injury Prevention Jen Davis DPT Orthopedic Physical Therapy Foot Traffic 7718 SE 13th Ave Portland, OR 97202 (503) 482-7232 Jen@runfastpt.com www.runfastpt.com!1 THE AMAZING RUNNER
Understanding. Heel Pain
 Understanding Heel Pain What Causes Heel Pain? Heel pain is a common problem that occurs when the heel is placed under too much stress. Heel pain is most often caused by walking in ways that irritate tissues
Understanding Heel Pain What Causes Heel Pain? Heel pain is a common problem that occurs when the heel is placed under too much stress. Heel pain is most often caused by walking in ways that irritate tissues
Hand Injuries and Disorders
 Hand Injuries and Disorders Introduction Each of your hands has 27 bones, 15 joints and approximately 20 muscles. There are many common problems that can affect your hands. Hand problems can be caused
Hand Injuries and Disorders Introduction Each of your hands has 27 bones, 15 joints and approximately 20 muscles. There are many common problems that can affect your hands. Hand problems can be caused
BACK PAIN: WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW
 BACK PAIN: WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW Diane Metzer LOWER BACK PAIN Nearly everyone at some point has back pain that interferes with work, recreation and routine daily activities. Four out of five adults experience
BACK PAIN: WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW Diane Metzer LOWER BACK PAIN Nearly everyone at some point has back pain that interferes with work, recreation and routine daily activities. Four out of five adults experience
Lower Extremity Orthopedic Surgery in Cerebral Palsy. Hank Chambers, MD Rady Children s Hospital - San Diego
 Lower Extremity Orthopedic Surgery in Cerebral Palsy Hank Chambers, MD Rady Children s Hospital - San Diego Indications Fixed contracture Joint dislocations Shoe wear problems Pain Perineal hygiene problems
Lower Extremity Orthopedic Surgery in Cerebral Palsy Hank Chambers, MD Rady Children s Hospital - San Diego Indications Fixed contracture Joint dislocations Shoe wear problems Pain Perineal hygiene problems
Plantar Fasciitis Information Leaflet. Maneesh Bhatia. Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon
 Plantar Fasciitis Information Leaflet Maneesh Bhatia Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon What is plantar fasciitis? The plantar fascia is a strong band of tissue that stretches from the heel to the toes. It
Plantar Fasciitis Information Leaflet Maneesh Bhatia Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon What is plantar fasciitis? The plantar fascia is a strong band of tissue that stretches from the heel to the toes. It
Sports Injury Treatment
 Sports Injury Treatment Participating in a variety of sports is fun and healthy for children and adults. However, it's critical that before you participate in any sport, you are aware of the precautions
Sports Injury Treatment Participating in a variety of sports is fun and healthy for children and adults. However, it's critical that before you participate in any sport, you are aware of the precautions
Self Management Program. Ankle Sprains. Improving Care. Improving Business.
 Ankle Sprains Improving Care. Improving Business. What is an ankle sprain? Ligaments attach to the ankle bones and allow for normal movement and help prevent too much motion within the joint. Ankle sprains
Ankle Sprains Improving Care. Improving Business. What is an ankle sprain? Ligaments attach to the ankle bones and allow for normal movement and help prevent too much motion within the joint. Ankle sprains
LATERAL PAIN SYNDROMES OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE
 C H A P T E R 3 LATERAL PAIN SYNDROMES OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE William D. Fishco, DPM The majority of patient encounters with the podiatrist are secondary to pain in the foot and/or ankle. If we draw an
C H A P T E R 3 LATERAL PAIN SYNDROMES OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE William D. Fishco, DPM The majority of patient encounters with the podiatrist are secondary to pain in the foot and/or ankle. If we draw an
Dr Rick Robinson, DPM Director of Podiatric Services USPHS Hospital at Whiteriver, AZ 2015 IHS National Combined Council Winter Meeting Friday,
 Dr Rick Robinson, DPM Director of Podiatric Services USPHS Hospital at Whiteriver, AZ 2015 IHS National Combined Council Winter Meeting Friday, January 30, 2015 1 We are all athletes, the difference is
Dr Rick Robinson, DPM Director of Podiatric Services USPHS Hospital at Whiteriver, AZ 2015 IHS National Combined Council Winter Meeting Friday, January 30, 2015 1 We are all athletes, the difference is
RX: Custom Thermoplastic AFO Compliance Documentation
 RX: Custom Thermoplastic AFO Compliance Documentation Doctor Name: Phone: Patient Name: HICN: DOB: Indicate Quality ARIZONA THERMOPLASTIC ARTICULATED AFO, DORSI-ASSIST CROW L4631 A bivalved custom molded
RX: Custom Thermoplastic AFO Compliance Documentation Doctor Name: Phone: Patient Name: HICN: DOB: Indicate Quality ARIZONA THERMOPLASTIC ARTICULATED AFO, DORSI-ASSIST CROW L4631 A bivalved custom molded
Structure & Function of the Ankle and Foot. A complicated model of simplicity that you really think little about until you have a problem with one.
 Structure & Function of the Ankle and Foot A complicated model of simplicity that you really think little about until you have a problem with one. The Foot and Ankle Terminology Plantar flexion Dorsi flexion
Structure & Function of the Ankle and Foot A complicated model of simplicity that you really think little about until you have a problem with one. The Foot and Ankle Terminology Plantar flexion Dorsi flexion
Flat foot and lower back pain
 Flat foot and lower back pain Dr James Tang, MBA, BDS, LDS RCS General Dental Practitioner, NASM Corrective Exercise Specialist with special interest in postural dysfunction & lower back problems, Level
Flat foot and lower back pain Dr James Tang, MBA, BDS, LDS RCS General Dental Practitioner, NASM Corrective Exercise Specialist with special interest in postural dysfunction & lower back problems, Level
Podiatric Medicine. What is a Podiatrist?
 Page 3 Podiatric Medicine Podiatric Medicine is the profession that strives to improve the overall health and wellbeing of patients by focusing on preventing, diagnosing, and treating conditions associated
Page 3 Podiatric Medicine Podiatric Medicine is the profession that strives to improve the overall health and wellbeing of patients by focusing on preventing, diagnosing, and treating conditions associated
Most Common Running Injuries
 Most Common Running Injuries 1. Achilles Tendonitis 2. Chrondomalacia Runner s Knee 3. Iliotibial Band (ITB) syndrome 4. Plantar Fasciitis 5. Shin Splints Achilles Tendonitis inflammation of the Achilles
Most Common Running Injuries 1. Achilles Tendonitis 2. Chrondomalacia Runner s Knee 3. Iliotibial Band (ITB) syndrome 4. Plantar Fasciitis 5. Shin Splints Achilles Tendonitis inflammation of the Achilles
International Standards for the Classification of Spinal Cord Injury Motor Exam Guide
 C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
Page 2 of 6 plantar fascia. This is called the windlass mechanism. Later, we'll discuss how this mechanism is used to treat plantar fasciitis with str
 Page 1 of 6 Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain) Plantar fasciitis is a painful condition affecting the bottom of the foot. It is a common cause of heel pain and is sometimes called a heel spur. Plantar fasciitis
Page 1 of 6 Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain) Plantar fasciitis is a painful condition affecting the bottom of the foot. It is a common cause of heel pain and is sometimes called a heel spur. Plantar fasciitis
FORGET ME NOT: The Triple Arthrodesis
 C H A P T E R 1 5 FORGET ME NOT: The Triple Arthrodesis Andrea D. Cass, DPM INTRODUCTION The triple arthrodesis is a procedure that is performed much less commonly for the same conditions as it was 20
C H A P T E R 1 5 FORGET ME NOT: The Triple Arthrodesis Andrea D. Cass, DPM INTRODUCTION The triple arthrodesis is a procedure that is performed much less commonly for the same conditions as it was 20
Functional Anatomy and Lower Extremity Biomechanics
 Functional Anatomy and Lower Extremity Biomechanics Eric Folmar, MPT, OCS Functional Lower Extremity Biomechanics The science of foot, ankle, knee and hip biomechanics and their relationships and interactions
Functional Anatomy and Lower Extremity Biomechanics Eric Folmar, MPT, OCS Functional Lower Extremity Biomechanics The science of foot, ankle, knee and hip biomechanics and their relationships and interactions
Plantar Heel Pain. By: Kevin Kleiner, M.B.S. New York College of Podiatric Medicine
 Plantar Heel Pain By: Kevin Kleiner, M.B.S. New York College of Podiatric Medicine Plantar Heel Pain: - Many Etiologies but few solutions Plantar heel pain more specifically: Heel pain felt in ones rear-foot
Plantar Heel Pain By: Kevin Kleiner, M.B.S. New York College of Podiatric Medicine Plantar Heel Pain: - Many Etiologies but few solutions Plantar heel pain more specifically: Heel pain felt in ones rear-foot
How To Treat Turf Toe Injuries
 How To Treat Turf Toe Injuries Turf toe injuries can have a significant impact upon the playing time of professional athletes. Accordingly, this author reviews the etiology of these injuries and assesses
How To Treat Turf Toe Injuries Turf toe injuries can have a significant impact upon the playing time of professional athletes. Accordingly, this author reviews the etiology of these injuries and assesses
HEEL PAIN. Differential diagnosis. 1. Insertional Plantar fascitis. 2. Enthesis. 3. Heel pad atrophy. 4. Tarsal tunnel syndrome
 HEEL PAIN Differential diagnosis 1. Insertional Plantar fascitis 2. Enthesis 3. Heel pad atrophy 4. Tarsal tunnel syndrome 5. Calcaneal stress fracture 6. Haglund s syndrome 7. Posterior ankle impingement
HEEL PAIN Differential diagnosis 1. Insertional Plantar fascitis 2. Enthesis 3. Heel pad atrophy 4. Tarsal tunnel syndrome 5. Calcaneal stress fracture 6. Haglund s syndrome 7. Posterior ankle impingement
Y O U R S U R G E O N S. choice of. implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y
 Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Your Surgeon Has Chosen the C 2 a-taper Acetabular System The
Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Your Surgeon Has Chosen the C 2 a-taper Acetabular System The
Adult Advisor: Plantar Fasciitis. Plantar Fasciitis
 Adult Advisor: Plantar Fasciitis Page 1 of 3 Plantar Fasciitis What is plantar fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is a painful inflammation of the bottom of the foot between the ball of the foot and the heel.
Adult Advisor: Plantar Fasciitis Page 1 of 3 Plantar Fasciitis What is plantar fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is a painful inflammation of the bottom of the foot between the ball of the foot and the heel.
.org. Arthritis of the Hand. Description
 Arthritis of the Hand Page ( 1 ) The hand and wrist have multiple small joints that work together to produce motion, including the fine motion needed to thread a needle or tie a shoelace. When the joints
Arthritis of the Hand Page ( 1 ) The hand and wrist have multiple small joints that work together to produce motion, including the fine motion needed to thread a needle or tie a shoelace. When the joints
Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities. John A. Schneider, M.D.
 Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities John A. Schneider, M.D. Biographical Sketch Dr. Schneider is an orthopedic surgeon that specializes in the treatment of hand and upper extremity
Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities John A. Schneider, M.D. Biographical Sketch Dr. Schneider is an orthopedic surgeon that specializes in the treatment of hand and upper extremity
.org. Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Anatomy. Cause
 Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Page ( 1 ) Neck pain can be caused by many things but is most often related to getting older. Like the rest of the body, the disks and joints in the neck (cervical
Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Page ( 1 ) Neck pain can be caused by many things but is most often related to getting older. Like the rest of the body, the disks and joints in the neck (cervical
Neck Injuries and Disorders
 Neck Injuries and Disorders Introduction Any part of your neck can be affected by neck problems. These affect the muscles, bones, joints, tendons, ligaments or nerves in the neck. There are many common
Neck Injuries and Disorders Introduction Any part of your neck can be affected by neck problems. These affect the muscles, bones, joints, tendons, ligaments or nerves in the neck. There are many common
DROP FOOT AND TREATMENTS YOUNGMEE PARK
 DROP FOOT AND TREATMENTS YOUNGMEE PARK WHAT IS FOOT DROP Foot drop / Drop foot the inability to lift the front part of the foot not a disease a symptom of some other medical problems a sign of an underlying
DROP FOOT AND TREATMENTS YOUNGMEE PARK WHAT IS FOOT DROP Foot drop / Drop foot the inability to lift the front part of the foot not a disease a symptom of some other medical problems a sign of an underlying
Posttraumatic medial ankle instability
 Posttraumatic medial ankle instability Alexej Barg, Markus Knupp, Beat Hintermann Orthopaedic Department University Hospital of Basel, Switzerland Clinic of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kantonsspital Baselland
Posttraumatic medial ankle instability Alexej Barg, Markus Knupp, Beat Hintermann Orthopaedic Department University Hospital of Basel, Switzerland Clinic of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kantonsspital Baselland
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments of Rheumatoid Foot and Ankle
 Rheumatoid arthritis is the most common form of inflammatory arthritis, affecting about two to three million Americans. Rheumatoid arthritis is a symmetric disease, meaning that it will usually involve
Rheumatoid arthritis is the most common form of inflammatory arthritis, affecting about two to three million Americans. Rheumatoid arthritis is a symmetric disease, meaning that it will usually involve
A compressive dressing that you apply around your ankle, and
 Ankle Injuries & Treatment The easiest way to remember this is: R.I.C.E. Each of these letters stands for: Rest. Rest your ankle. Do not place weight on it if it is very tender. Avoid walking long distances.
Ankle Injuries & Treatment The easiest way to remember this is: R.I.C.E. Each of these letters stands for: Rest. Rest your ankle. Do not place weight on it if it is very tender. Avoid walking long distances.
JOINT PAIN IN THE ADOLESCENT
 JOINT PAIN IN THE ADOLESCENT HOW SERIOUS CAN THAT BE? ROBERT A. KELLY, M.D. RESURGENS ORTHOPAEDICS JOINT PAIN IN THE ADOLESCENT INJURIES ABOUT JOINTS CAN BE CLASSIFIED AS EITHER: ACUTE/TRAUMATIC OR REPETITIVE/OVERUSE
JOINT PAIN IN THE ADOLESCENT HOW SERIOUS CAN THAT BE? ROBERT A. KELLY, M.D. RESURGENS ORTHOPAEDICS JOINT PAIN IN THE ADOLESCENT INJURIES ABOUT JOINTS CAN BE CLASSIFIED AS EITHER: ACUTE/TRAUMATIC OR REPETITIVE/OVERUSE
Pathology-Designed Custom Molded Foot Orthoses
 Pathology-Designed Custom Molded Foot Orthoses Kevin B. Rosenbloom, CPed KEYWORDS Foot orthoses Custom orthoses Orthotic devices Pathology-designed orthoses Orthosis design Treating patients with custom
Pathology-Designed Custom Molded Foot Orthoses Kevin B. Rosenbloom, CPed KEYWORDS Foot orthoses Custom orthoses Orthotic devices Pathology-designed orthoses Orthosis design Treating patients with custom
Ankle-Foot Injury Injuries
 Ankle-Foot Injury Injuries Ed Mulligan, PT, DPT, OCS, SCS, ATC Clinical Orthopedic Rehabilitation Education What are the possible imposters to orthopedic foot/ankle injuries? 1. Lumbar Radiculopathy 2.
Ankle-Foot Injury Injuries Ed Mulligan, PT, DPT, OCS, SCS, ATC Clinical Orthopedic Rehabilitation Education What are the possible imposters to orthopedic foot/ankle injuries? 1. Lumbar Radiculopathy 2.
INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D.
 05/05/2007 INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D. Hand injuries, especially the fractures of metacarpals and phalanges, are the most common fractures in the skeletal system. Hand injuries
05/05/2007 INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D. Hand injuries, especially the fractures of metacarpals and phalanges, are the most common fractures in the skeletal system. Hand injuries
A Patient's Guide to Arthritis of the Finger Joints
 Introduction A Patient's Guide to Arthritis of the Finger Joints When you stop to think about how much you use your hands, it's easy to see why the joints of the fingers are so important. Arthritis of
Introduction A Patient's Guide to Arthritis of the Finger Joints When you stop to think about how much you use your hands, it's easy to see why the joints of the fingers are so important. Arthritis of
A Patient s Guide to Arthritis of the Big Toe (Hallux Rigidus) With Discussion on Cheilectomy and Fusion
 A Patient s Guide to Arthritis of the Big Toe (Hallux Rigidus) With Discussion on Cheilectomy and Fusion The foot and ankle unit at the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital (RNOH) is a multi-disciplinary
A Patient s Guide to Arthritis of the Big Toe (Hallux Rigidus) With Discussion on Cheilectomy and Fusion The foot and ankle unit at the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital (RNOH) is a multi-disciplinary
A Patient s Guide to Plantar Fasciitis. Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, P.C.
 A Patient s Guide to Plantar Fasciitis Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
A Patient s Guide to Plantar Fasciitis Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
Biomechanical Explanations for Selective Sport Injuries of the Lower Extremity
 Biomechanical Explanations for Selective Sport Injuries of the Lower Extremity DR. LEE S. COHEN Podiatric Consultant: Philadelphia Eagles Philadelphia 76ers Philadelphia Wings Understanding Normalcy What
Biomechanical Explanations for Selective Sport Injuries of the Lower Extremity DR. LEE S. COHEN Podiatric Consultant: Philadelphia Eagles Philadelphia 76ers Philadelphia Wings Understanding Normalcy What
.org. Herniated Disk in the Lower Back. Anatomy. Description
 Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
Semmelweis University Department of Traumatology Dr. Gál Tamás
 Semmelweis University Department of Traumatology Dr. Gál Tamás Anatomy Ankle injuries DIRECT INDIRECT Vertical Compression (Tibia plafond Pilon) AO 43-A,B,C Suppination (adduction + inversion) AO 44-A
Semmelweis University Department of Traumatology Dr. Gál Tamás Anatomy Ankle injuries DIRECT INDIRECT Vertical Compression (Tibia plafond Pilon) AO 43-A,B,C Suppination (adduction + inversion) AO 44-A
Achilles Tendon Repair Surgery Post-operative Instructions Phase One: The First Week After Surgery
 Amon T. Ferry, MD Orthopedic Surgery Sports Medicine Achilles Tendon Repair Surgery Post-operative Instructions Phase One: The First Week After Surgery Amon T. Ferry, MD Orthopedic Surgery / Sports Medicine
Amon T. Ferry, MD Orthopedic Surgery Sports Medicine Achilles Tendon Repair Surgery Post-operative Instructions Phase One: The First Week After Surgery Amon T. Ferry, MD Orthopedic Surgery / Sports Medicine
KINESIOLOGY TAPING GUIDE
 KINESIOLOGY TAPING GUIDE What is Kinesiology tape and how does Kinesiology tape work? How to apply Kinesiology tape Examples of application of UP Kinesiology tape for common injuries and conditions Introduction
KINESIOLOGY TAPING GUIDE What is Kinesiology tape and how does Kinesiology tape work? How to apply Kinesiology tape Examples of application of UP Kinesiology tape for common injuries and conditions Introduction
.org. Osteochondroma. Solitary Osteochondroma
 Osteochondroma Page ( 1 ) An osteochondroma is a benign (noncancerous) tumor that develops during childhood or adolescence. It is an abnormal growth that forms on the surface of a bone near the growth
Osteochondroma Page ( 1 ) An osteochondroma is a benign (noncancerous) tumor that develops during childhood or adolescence. It is an abnormal growth that forms on the surface of a bone near the growth
Plantar Fascia Release
 Plantar Fascia Release Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. If other treatments are unsuccessful,
Plantar Fascia Release Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. If other treatments are unsuccessful,
Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System
 Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Pathomechanics, Gait Deviations, and Treatment of the Rheumatoid Foot
 Pathomechanics, Gait Deviations, and Treatment of the Rheumatoid Foot A Clinical Report PHYLLIS DIMONTE and HOLLIS LIGHT This article describes the five major foot deformities or problems often seen in
Pathomechanics, Gait Deviations, and Treatment of the Rheumatoid Foot A Clinical Report PHYLLIS DIMONTE and HOLLIS LIGHT This article describes the five major foot deformities or problems often seen in
Gait. Maturation of Gait Beginning ambulation ( Infant s gait ) Upper Limb. Lower Limb
 Gait Terminology Gait Cycle : from foot strike to foot strike Gait Phase : stance (60%) : swing (40%) Velocity : horizontal speed along progression Cadence : no. of steps per unit time Step length : distance
Gait Terminology Gait Cycle : from foot strike to foot strike Gait Phase : stance (60%) : swing (40%) Velocity : horizontal speed along progression Cadence : no. of steps per unit time Step length : distance
John M. Sigle, DPM, FACFAS Foot & Ankle Center of Illinois (217) 787-2700 www.myfootandanklecenter.com
 The MiToe implant is manufactured by Wright Medical, the recognized leader of surgical solutions for foot and ankle. Wright has been in business for more than 60 years and markets products in over 60 countries,
The MiToe implant is manufactured by Wright Medical, the recognized leader of surgical solutions for foot and ankle. Wright has been in business for more than 60 years and markets products in over 60 countries,
Musculoskeletal System
 CHAPTER 3 Impact of SCI on the Musculoskeletal System Voluntary movement of the body is dependent on a number of systems. These include: The brain initiates the movement and receives feedback to assess
CHAPTER 3 Impact of SCI on the Musculoskeletal System Voluntary movement of the body is dependent on a number of systems. These include: The brain initiates the movement and receives feedback to assess
THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK)
 THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK) At a glance Chronic back pain, especially in the area of the lumbar spine (lower back), is a widespread condition. It can be assumed that 75 % of all people have it sometimes or
THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK) At a glance Chronic back pain, especially in the area of the lumbar spine (lower back), is a widespread condition. It can be assumed that 75 % of all people have it sometimes or
.org. Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Anatomy
 Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Page ( 1 ) A broken ankle is also known as an ankle fracture. This means that one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint are broken. A fractured ankle can range
Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Page ( 1 ) A broken ankle is also known as an ankle fracture. This means that one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint are broken. A fractured ankle can range
THE WRIST. At a glance. 1. Introduction
 THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
