Digestive Physiology
|
|
|
- Octavia Lyons
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Digestive Physiology We need food for cellular utilization: nutrients as building blocks for synthesis sugars, etc to break down for energy most food that we eat cannot be directly used by the body too large and complex to be absorbed chemical composition must be modified to be useable by cells digestive system functions to altered the chemical and physical composition of food so that it can be absorbed and used by the body; ie physical and chemical digestion absorption collect & eliminate nonuseable components lumen of GI tract is continuous with outside of body food being digested must be isolated from body cells since it s the same composition as rest of body digestion occurs OUTSIDE the internal environment of cells and tissues protects internal cells Movement of Materials as materials are being processed they are moved through alimentary canal by: swallowing reflex controlled by medulla pharynx to esophagus Digestion peristalsis sequential smooth muscle contractions in adjacent segments pushes food forward esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine segmentation alternating contractions and relaxations of adjoining portions of intestine food is moved backward and foreward helps to physically break up and mix contents for better digestion & absorption digestion = all food changes that occur in the alimentary canal Anatomy & Physiology: Digestive System, Ziser,
2 need to convert food into a form that can be absorbed and used by body cells two types of digestion: physical digestion breaking large pieces down into smaller pieces chemical digestion breaking large molecules (proteins, fats, starches, etc) into small molecules (amino acids, fatty acids, sugars, etc) 1. Mouth food entering mouth is physically broken down teeth mixed with saliva lubricant enzyme = amylase begins carbohydrate digestion most (60%) of starch digestion by amylase from saliva occurs in stomach after swallowing bolus at end of digestion in mouth food = bolus 2. Stomach physical digestion involves muscular contractions to separate and mix food particles in stomach bolus is mixed with gastric juices gastric juices low ph ~2 hydrochloric acid pepsin ideal for breaking proteins into smaller fragments body must be protected from harsh ph of gastric juices: a. thick coating of bicarbonate rich mucous b. tight junctions join epithelial cells to help prevent leakage c. stomach lining is rapidly replaced renewed every 3-6 days d. pepsin and HCl are secreted in inactive forms vomiting = medullary reflex: triggered by irritants in stomach closing nose and glottis relaxes cardiac sphincter spasm of diaphragm gastric ulcers: Helicobacter pylori part of normal flora of stomach can neutralize stomach acids excessive growth can irritate stomach lining to produce ulcers Anatomy & Physiology: Digestive System, Ziser,
3 physical digestion is completed in stomach once digestion in stomach is competed have a white milky liquid = chyme stomach takes about 2-6 hours to empty after a meal gastric emptying is controlled by enterogastric reflex: periodic opening/ closing of pyloric valve prevents overburdening smaller duodenum 3. Duodenum all physical digestion has been completed Completes chemical digestion of food most chemical digestion occurs here receives digestive juices from pancreas and gall bladder also produces its own set of enzymes intestinal and pancreatic juices are alkaline neutralize acidity of chyme: enzymes in duodenum work best at alkaline ph presence of chyme in duodenum triggers: a. release of bile from liver & gall bladder b. release of pancreatic secretions c. release of duodenal secretions a. Bile contains no enzymes contains bile salts bile pigments cholesterol made from cholesterol in liver (bilirubin, biliverdin) normally remains in solution may precipitate out as gall stones bile is a surfactant emulsifies fats into smaller fat droplets to speed their digestion b. Pancreatic Juices pancreas is an endocrine gland (insulin, glucagon) but 98% of its tissues make and secrete digestive juices through ducts to the duodenum Anatomy & Physiology: Digestive System, Ziser,
4 include: bicarbonates to neutralize gastric acids proteinases (esp trypsin and chymotrypsin) - breaks proteins into peptides and amino acids lipases fats to fatty acids and glycerol amylase starches to mono & disaccharides nucleases nucleic acids into nucleotides c. Duodenal Secretions include: peptidases breaks polypeptides into amino acids disaccharidases disaccharides into monosaccharides nucleosidases & phosphatases break nucleotides into component parts 4. Large Intestine some digestion occurs here due to bacteria esp in caecum esp herbivores large caecum carnivores small or no caecum Control of Digestive Secretions secretions from digestive glands is under nervous and hormonal control digestion begins as mainly an autonomic nervous reflex digestion is completed due mainly to hormonal controls 1. Saliva (~1500ml/day) strictly a nervous reflex reflex is triggered by: mechanical and chemical presence of food in mouth olfactory stimulation visual stimulation salivation can also be a learned response learned by association: eg. Pavlov s dog 2. Gastric Secretions (~1500ml/day) secretions occur in three separate phases: cephalic phase secretions first activated by sight, smell, taste and thoughts of food gastric phase Anatomy & Physiology: Digestive System, Ziser,
5 continued secretion is triggered by presence of polypeptides in pyloric region of stomach stimulates parietal cells to secrete hormone = gastrin gastrin circulates within capillaries of stomach and enhance secretions from gastric glands in stomach wall gastrin is secreted as long as there is food in stomach intestinal phase chyme is released into duodenum duodenum presence of chyme causes release of intestinal gastrin this further stimulates gastric secretions Enterogastric Reflex slows stomach emptying to once/~20 seconds signaled by stretch receptors in duodenum speed of reflex varies by a. types of foods eg. fats - slow; proteins fast b. fluidity solids slower; liquids quicker c. age infant fast; adult slower Presence of fatty chyme in duodenum (fats float last to leave stomach) stimulates release of GIP (gastric inhibitory peptide) shuts down gastric secretions 4. Bile (~1000ml/day) when chyme enters duodenum secretes cholecystokinin stimulates peristalsis of gall bladder 5. Pancreatic Juices (~1000ml/day) when chyme enters duodenum it causes the release of: cholecystokinin stimulates pancreas to release enzymes secretin stimulates pancreas to release bicarbonates 6. Duodenal Enzymes (~2000ml/day) may be another hormone that stimulates release of duodenal enzymes don t know now Anatomy & Physiology: Digestive System, Ziser,
6 Absorption ~9-10 liters (2.5 gallons) of food, liquids and GI secretions enter tract/day ~1000 ml reaches the large intestine 150 ml is expelled as feces ~half of that is bacteria from intestines 75 ml wastes/d absorption occurs throughout digestive tract ~90% occurs in small intestine; ~10% in large intestine and stomach Stomach some water alcohol a few drugs (eg. aspirin) Small Intestine absorb ~90% of materials absorbs virtually all foodstuffs absorbs 80% of electrolytes absorbs most water Jejunum all food stuffs most water most electrolytes Ileum reclaims some additional bile salts Large Intestine additional water if body needs it some Vit K and B s made by bacteria there Most nutrient absorption occurs in the small intestine Small intestine is greatly modified for absorption 1. epithelial cells are joined by tight junctions better control of what is absorbed substances can t move between cells materials must pass through cells to get to interstitial spaces (=transepithelial transport) Anatomy & Physiology: Digestive System, Ziser,
7 2. surface area is greatly increased for more efficient absorption of nutrients: a. 1 diameter x 10 long if smooth tube= 0.33 m 2 (3 sq ft) b. but: interior is folded increases area ~3 x s c. also: fingerlike projections = villi each ~1mm tall contain capillary beds & lacteals increases area another 10x s d. also: each epithelial cell of villus has microvilli up to 1700/cell =brush border increases area another 20x s Total Area = 200m 2 (1800 sq ft) Mechanisms of Absorption absorption can be an active or passive process essentially some kind of membrane transport In terms of transport processes involved: 1. most nutrients are absorbed by active transport eg. glucose amino acids some minerals 2. some lipids are absorbed by diffusion to lacteals eg. fats fat soluble vitamins 3. water is absorbed by osmosis 4. large molecules are absorbed by pinocytosis eg. a few large fats and proteins passed to lacteals with other fats Anatomy & Physiology: Digestive System, Ziser,
8 In terms of the Absorption of Specific Nutrients: 1. Carbohydrates mono facilitated diffusion capillaries 2. Proteins amino acids active transport capillaries each requires a specific carrier eg. genetic diseases 3. Lipids whole proteins endocytosis capillaries rarely absorbed, but more common in newborns results in food allergies may also be how IgA are absorbed from mothers milk bile salts are essential for absorption as well as digestion micelles = collections of fatty elements clustered together with bile salts polar on outside nonpolar core micelles are much smaller than emulsion droplets easily diffuse between microvilli to come in contact with cell surface fats, cholesterol, fat soluble vitamins then leave the micelles and move through the cell membrane by diffusion into epithelial cells of villi once inside epithelial cells: triglycerides are coated with proteins to produce chylomicrons golgi bodies process and secrete them most lipids enter lacteals in villi a few enter capillary beds micelles diffusion chylomicrons lacteals in absence of bile, (eg gall stones), most fat passes to large intestine Anatomy & Physiology: Digestive System, Ziser,
9 once in blood: fats are hydrolyzed back into free fatty acids that can be used by cells for energy production or converted to fat in adipose tissue 4. Nucleic Acids nucleotides active transport blood 5. Vitamins a. water soluble vitamins diffusion blood except B 12, very large, charged molecule binds to intrinsic factor produced by stomach taken in by endocytosis b. fat soluble micelles etc 6. Electrolytes most are actively absorbed throughout the length of intestine Fe and Ca ++ mainly in duodenum for most nutrients the amount reaching the intestine is the amount absorbed But absorption of Fe and Ca is closely tied to body s need: Fe Ca is actively transported into mucosal cells binds to protein ferritin stored until needed or lost as cells sloughed off women have 4x s more transport proteins than men in blood Fe binds to protein = transferrin, for transport regulated by Vitamin D acts as a cofactor to facilitate Ca absorption eg. <Bld Ca >PTH: >Ca release from bone >reabsorption of Ca by kidney renal activation of Vit D to increase Anatomy & Physiology: Digestive System, Ziser,
10 absorption in intestine Na + is coupled with active absorption of glucose and Amino acids K + moves in by simple diffusion most anions passively diffuse along a gradient but Cl - is actively transported 7. Water 9 L of water enters small intestine daily 95% is absorbed by small intestine (osmosis) coupled to solute uptake rest is absorbed by large intestine of ~ 500 ml of chyme entering large intestine ~150 ml of feces is produced Anatomy & Physiology: Digestive System, Ziser,
11 Processing of Absorbed Nutrients Liver is main organ for metabolic regulation in the body over 200 specific functions 1. stores carbohydrates, iron, vitamin A, B12 & D 2. synthesizes plasma proteins 3. releases nutrients (eg glucose) to maintain blood levels 4. phagocytes remove old/damaged blood cells and pathogens 5. detoxify blood from digestive system 6. is largest blood reservoir in body receives 25% of cardiac output 7. collects and removes metabolic wastes such as cholesterol, products of RBC destruction, etc 8. secrete bile to aid in digestion (~1pt /day) lobule is functional unit of liver each liver lobe is divided into millions of lobules tiny hexagonal cylinders (~2mm x 1mm) sinusoid spaces with small branch of hepatic vein extends through middle hepatic cells extend outward from hepatic vein branches around periphery of each lobule are branches of: hepatic portal vein hepatic artery hepatic bile ducts arterial blood brings oxygen to liver cells venous blood from hepatic portal vein passes through lobule for inspection within each lobule: a. phagocytic cells remove toxic compounds and convert them to nontoxic compounds b. some vitamins and nutrients are removed and stored c. synthesis of starches, lipids and proteins for storage d. cholesterol, bile pigments and bile salts are secreted into bile ducts for later use in digestion of fats Anatomy & Physiology: Digestive System, Ziser,
12 Hepatic Artery Hepatic Portal Vein sinusoids oxygen removes toxins stores vitamins stores nutrients Hepatic Vein Hepatic Bile Ducts Hepatic Duct Cystic Duct Common Bile Duct Gall Bladder stores and concentrates bile Pancreas can hold ml of bile gall stones jaundice = bile ducts obstructed body cant get rid of bile bile is absorbed into blood causes yellowing of skin composed of 2 kinds of glandular tissue: exocrine digestive function endocrine secretes hormones islets = 2% of total mass of pancreas their secretions pass into circulatory system secrete insulin and glucagon Anatomy & Physiology: Digestive System, Ziser,
13 Digestive Problems 1. Choking food in air passages usually meats, hot dogs, grapes, carrots, hard candy, popcorn, peanut butter may not be able to make a sound DON T hit on back 2. Vomiting symptom of many diseases waves of reverse peristalsis if severe may empty duodenum as well rest and drink small amounts of fluids guard against massive fluid loss 3. Bulemia self induced vomiting may cause damage and infection of esophagus, pharynx, or salivary glands erosion of teeth, more dental caries esophagus may rupture or tear 4. Diarrhea frequent loose watery stool intestinal contents moving too fast for fluid absorption to occur main danger is fluid loss also upsets acid/base balance 5. Constipation caused by: lifestyle inadequate water input lack of physical activity side effect of medication increase in fiber, prunes, laxatives attracts water softens stool Colonic Irrigation alternative medical practice potentially harmful unneccessary can rupture the intestine frequent use of laxatives and enemas: can lead to dependency upset body s fluid balance Anatomy & Physiology: Digestive System, Ziser,
14 mineral oil can interfere with absorption of fat soluble vitamins 6. Belching results from swallowed air carbonated drinks and chewing gums can contribute occasionally can be a sign of a more serious disorder: gall bladder pain, colonic distress eat slowly, chew thoroughly relax while eating 7. Hiccups repeated spasms of diaphragm may be triggered by eating or drinking too fast 8. Gas normally we expell several 100 ml of gas/day most is odorless 1% are volatile gasses high carb foods known to produce excess gas 9. Heartburn cardiac sphincter doesn t close properly eat or drink too much clothing too tight cure: eat small meals drink liquids 1 hr before or 1 hr after meal don t lie down or bend over lose weight if overweight don t smoke use antacids but sparingly 10. Ulcers caused by: bacterial infection use of some antiinflammatory drugs disorders that cause excessive gastric secretions diet therapy used to be main cure, now antibiotics Anatomy & Physiology: Digestive System, Ziser,
Digestion, Absorption. How & where?
 Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411
 10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
Digestive System Functions
 Digestive System Functions A. Gastrointestinal Processes 1. Ingestion: placing food in mouth (voluntary) 2. Propulsion: moving food through GI tract a. Peristalsis: alternating waves of contraction and
Digestive System Functions A. Gastrointestinal Processes 1. Ingestion: placing food in mouth (voluntary) 2. Propulsion: moving food through GI tract a. Peristalsis: alternating waves of contraction and
Digestive System Notes
 Digestive System Notes Structure Function Relation Mouth cavity Mechanical digestion by teeth; chemical digestion of starch by saliva. Salivary glands Three pairs of glands which secrete saliva containing
Digestive System Notes Structure Function Relation Mouth cavity Mechanical digestion by teeth; chemical digestion of starch by saliva. Salivary glands Three pairs of glands which secrete saliva containing
Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi
 Lec.13 Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Functions of the Digestive System The major functions of the digestive tract include the following six processes, summarized in Figure 1: 1. Ingestion Food must
Lec.13 Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Functions of the Digestive System The major functions of the digestive tract include the following six processes, summarized in Figure 1: 1. Ingestion Food must
The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System
 The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System Mouth - mastication, lubrication, digestion Pharynx and Esophagus - swallowing Stomach - some digestion Small intestine - most digestion and absorption Large
The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System Mouth - mastication, lubrication, digestion Pharynx and Esophagus - swallowing Stomach - some digestion Small intestine - most digestion and absorption Large
The Digestive System. You are what you eat!
 The Digestive System You are what you eat! Try to label the diagram (PENCIL!!) What is Digestion? Digestion: the breakdown of large macromolecules (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) into smaller molecules
The Digestive System You are what you eat! Try to label the diagram (PENCIL!!) What is Digestion? Digestion: the breakdown of large macromolecules (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) into smaller molecules
Digestion, Absorption. How & where?
 Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
GI TRACT ORGANS ACCESSORY ORGANS
 Digestive System GI TRACT ORGANS Oral cavity Oropharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large Intestine Anus ACCESSORY ORGANS Salivary glands Pancreas Liver Gall bladder GI TRACT LAYERS Mucosa Submucosa
Digestive System GI TRACT ORGANS Oral cavity Oropharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large Intestine Anus ACCESSORY ORGANS Salivary glands Pancreas Liver Gall bladder GI TRACT LAYERS Mucosa Submucosa
Chapter 17 Digestive System. Alimentary Canal. Movements of the Tube
 Chapter 17 Digestive System Functions of Digestive System ingestion mechanical digestion chemical digestion propulsion absorption defecation Consists of the alimentary canal and accessory organs 1 Alimentary
Chapter 17 Digestive System Functions of Digestive System ingestion mechanical digestion chemical digestion propulsion absorption defecation Consists of the alimentary canal and accessory organs 1 Alimentary
Special organ structures and functions conduct these tasks through the successive parts of the overall system.
 Chapter 5 Digestion, Absorption, and Metabolism Chapter 5 Lesson 5.1 Key Concepts Through a balanced system of mechanical and chemical digestion, food is broken down into smaller substances and the nutrients
Chapter 5 Digestion, Absorption, and Metabolism Chapter 5 Lesson 5.1 Key Concepts Through a balanced system of mechanical and chemical digestion, food is broken down into smaller substances and the nutrients
Chapter 48. Nutrients in Food. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids, continued
 Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Digestion. What we ll cover. Main stages of digestion. Digestion: A Closer Look. A Tour of the Human Digestive System. Mechanical digestion
 Digestion What we ll cover What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where does carbohydrate, protein and fat digestion and absorption occur? What are the 3 accessory organs of digestion?
Digestion What we ll cover What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where does carbohydrate, protein and fat digestion and absorption occur? What are the 3 accessory organs of digestion?
Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly)
 Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly) 6 basic nutrients - 4 food groups (milk, meat, fruit and vegetable,
Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly) 6 basic nutrients - 4 food groups (milk, meat, fruit and vegetable,
The Human Digestive System
 The Human Digestive System Name: Section: Date: Page 1 of 10 Page 2 of 10 Page 3 of 10 Page 4 of 10 Page 5 of 10 Page 6 of 10 Putting it All Together Digestive Enzymes Page 7 of 10 Page 8 of 10 Page 9
The Human Digestive System Name: Section: Date: Page 1 of 10 Page 2 of 10 Page 3 of 10 Page 4 of 10 Page 5 of 10 Page 6 of 10 Putting it All Together Digestive Enzymes Page 7 of 10 Page 8 of 10 Page 9
Digestive system Review
 Digestive system Review 1. Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion. The physical breakdown of food begins in the mouth with two types of processes. The mouth is a complex structure
Digestive system Review 1. Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion. The physical breakdown of food begins in the mouth with two types of processes. The mouth is a complex structure
5. Secretion: release of water, acids. Enzymes, buffers by digestive tract.
 Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
The Excretory and Digestive Systems
 The Excretory and Digestive Systems 38.2 The Process of Digestion Organs of the Digestive System The digestive system includes the: Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine. Other structures
The Excretory and Digestive Systems 38.2 The Process of Digestion Organs of the Digestive System The digestive system includes the: Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine. Other structures
SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS
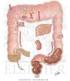 SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS Objectives At the end of lecture student should be able to know, Digestive system Digestive system secretions Small intestine Component of small intestine Intestinal
SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS Objectives At the end of lecture student should be able to know, Digestive system Digestive system secretions Small intestine Component of small intestine Intestinal
Outline Digestive System
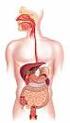 Outline Digestive System The Digestive System Digestive System Lecture Packet 19 Chapter 15 I. Function II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,
Outline Digestive System The Digestive System Digestive System Lecture Packet 19 Chapter 15 I. Function II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Histological Organization. Overview of Digestive System. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Functions of the GI Tract. Chapter 18. Functions of the GI Tract (continued)
 Functions of the GI Tract Chapter 18 The Digestive System Motility: Movement of of food through the GI tract. Ingestion: Taking food into the mouth. Mastication: Chewing the food and mixing it with saliva.
Functions of the GI Tract Chapter 18 The Digestive System Motility: Movement of of food through the GI tract. Ingestion: Taking food into the mouth. Mastication: Chewing the food and mixing it with saliva.
Chapter 15 Digestive System.
 Chapter 15 Digestive System. I. The Gastrointestinal Tract. a. The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaks down food into molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream or lymph. Residues
Chapter 15 Digestive System. I. The Gastrointestinal Tract. a. The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaks down food into molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream or lymph. Residues
Digestive System Why is digestion important? How is food digested? Physical Digestion and Movement
 Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49457 1 Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look Donna Browne Based on Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look by OpenStax This work is
OpenStax-CNX module: m49457 1 Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look Donna Browne Based on Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look by OpenStax This work is
1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption?
 Digestion Review 1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption? (a.) intestinal glands (b.) villi (c.) pseudopodia (d.) cilia (e.) flagella 2. The
Digestion Review 1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption? (a.) intestinal glands (b.) villi (c.) pseudopodia (d.) cilia (e.) flagella 2. The
Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition
 Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition THE CONTENTS OF FOOD Food contains nutrients: Nutrients include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nutrients must be small enough to enter our cells. If they are too large they must be digested
Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition THE CONTENTS OF FOOD Food contains nutrients: Nutrients include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nutrients must be small enough to enter our cells. If they are too large they must be digested
2) Digestion the breakdown of. There are two types of digestion: Mechanical and Chemical. 3) Absorption when the nutrients enter into the blood.
 The Digestive System Video on the digestive system (5 min) The digestive system is responsible for the breakdown of the we eat so that it can be absorbed into the. There are four main stages of the digestive
The Digestive System Video on the digestive system (5 min) The digestive system is responsible for the breakdown of the we eat so that it can be absorbed into the. There are four main stages of the digestive
I. The basic function of the digestive system is
 Chapter 15, Digestive System - ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. The basic function of the digestive system is. This process is called. II. List 2 other names for the digestive tract: A. B. III. The digestive
Chapter 15, Digestive System - ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. The basic function of the digestive system is. This process is called. II. List 2 other names for the digestive tract: A. B. III. The digestive
AP Biology. What do animals need to live? Animal Nutrition. Nutritional requirements. How do animals get their food? Different diets; different lives
 Animal Nutrition What do animals need to live? Animals make energy using: food food oxygen Animals build bodies using: food for raw materials amino acids, sugars, fats, nucleotides O 2 ATP energy for synthesis
Animal Nutrition What do animals need to live? Animals make energy using: food food oxygen Animals build bodies using: food for raw materials amino acids, sugars, fats, nucleotides O 2 ATP energy for synthesis
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Secretion Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.
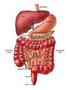 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Secretion Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1: Title Page Digestive system secretion involves
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Secretion Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1: Title Page Digestive system secretion involves
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM What is digestion? Digestion is the process of breaking down food so that it's small enough to be absorbed and used by the body for energy or in other bodily functions. Digestion involves
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM What is digestion? Digestion is the process of breaking down food so that it's small enough to be absorbed and used by the body for energy or in other bodily functions. Digestion involves
The Digestive System. Chapter 15
 The Digestive System Chapter 15 Introduction Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food so the nutrients can be absorbed by cells Carried out by the digestive system Consists of
The Digestive System Chapter 15 Introduction Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food so the nutrients can be absorbed by cells Carried out by the digestive system Consists of
The Digestive System. Chapter 14. The Digestive System and Body Metabolism. Metabolism. Organs of the Digestive System. Digestion.
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Digestion of ingested food of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of Constructive and degradative cellular activities
Chapter 14 The Digestive System The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Digestion of ingested food of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of Constructive and degradative cellular activities
Eating, pooping, and peeing THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients
 Jenny Kim Professor Rosario Nutrition: Macronutrients Project June 26, 2014 1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients Whenever we eat, the foods we ingest in our bodies undergo
Jenny Kim Professor Rosario Nutrition: Macronutrients Project June 26, 2014 1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients Whenever we eat, the foods we ingest in our bodies undergo
1. gustatory cells: Surface cells in the throat and on the taste buds in the mouth that transmit
 Chapter 3 Digestion and Absorption Key Terms 1. gustatory cells: Surface cells in the throat and on the taste buds in the mouth that transmit taste information. 2. absorption: The movement of substances
Chapter 3 Digestion and Absorption Key Terms 1. gustatory cells: Surface cells in the throat and on the taste buds in the mouth that transmit taste information. 2. absorption: The movement of substances
Digestive System AKA. GI System. Overview. GI Process Process Includes. G-I Tract Alimentary Canal
 Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Topic 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems
 Topic 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Organ Systems Organ systems must have the ability to to changes within and outside of your body to maintain life
Topic 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Organ Systems Organ systems must have the ability to to changes within and outside of your body to maintain life
Chapter 24: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 Chapter 24: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. OVERVIEW A. Gross anatomy (Fig. 24.1) and functions (Table 24.1) B. "You are what you eat." 1. The problem: Ingestion (eating) is not the same as absorption. 2. The solution:
Chapter 24: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. OVERVIEW A. Gross anatomy (Fig. 24.1) and functions (Table 24.1) B. "You are what you eat." 1. The problem: Ingestion (eating) is not the same as absorption. 2. The solution:
Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition
 Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition Digestive System: Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of foods so that nutrients can be absorbed by cells. Consists of the canal which is all of
Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition Digestive System: Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of foods so that nutrients can be absorbed by cells. Consists of the canal which is all of
Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption Chapter Outline
 Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption Chapter Outline I. Anatomy of the Digestive Tract A. The Digestive Organs 1. Mouth to the Esophagus 2. Esophagus to the Stomach 3. The Small Intestine 4. The Large Intestine
Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption Chapter Outline I. Anatomy of the Digestive Tract A. The Digestive Organs 1. Mouth to the Esophagus 2. Esophagus to the Stomach 3. The Small Intestine 4. The Large Intestine
Learning Objectives. Introduction to Medical Careers. Vocabulary: Chapter 16 FACTS. Functions. Organs. Digestive System Chapter 16
 Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Digestive Structures Mouth including teeth and tongue Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Accessory structures - salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, & pancreas Digestive
The Digestive System Digestive Structures Mouth including teeth and tongue Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Accessory structures - salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, & pancreas Digestive
8. Be able to label a diagram of an earthworm. Know the function of each of the major parts of the earthworm.
 Review for Unit Test: The Digestive System 1. Know the meaning of these terms: heterotrophs digestion peristalsis microvilli autotrophs chemical digestion chyme lacteal intracellular digestion mechanical
Review for Unit Test: The Digestive System 1. Know the meaning of these terms: heterotrophs digestion peristalsis microvilli autotrophs chemical digestion chyme lacteal intracellular digestion mechanical
Weds 5/20/15. Membranes - finish last lecture outline. Digestive System Nutrition Types of digestion & digestive systems Vertebrate digestive system
 Membranes - finish last lecture outline Weds 5/20/15 Digestive System Nutrition Types of digestion & digestive systems Vertebrate digestive system structures and functions // accessory organs mechanism
Membranes - finish last lecture outline Weds 5/20/15 Digestive System Nutrition Types of digestion & digestive systems Vertebrate digestive system structures and functions // accessory organs mechanism
Digestive System. Gross Anatomy and Physiology
 Digestive System Gross Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. Base Function: Working with the circulatory system the digestive system provides the body with fuel. B. Main players: 1. Digestive tract:
Digestive System Gross Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. Base Function: Working with the circulatory system the digestive system provides the body with fuel. B. Main players: 1. Digestive tract:
Absorption and Transport of Nutrients
 Page1 Digestion Food travels from mouth esophagus stomach small intestine colon rectum anus. Food mixes with digestive juices, moving it through the digestive tract Large molecules of food are broken into
Page1 Digestion Food travels from mouth esophagus stomach small intestine colon rectum anus. Food mixes with digestive juices, moving it through the digestive tract Large molecules of food are broken into
The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
 The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine The digestive organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Liver Gall bladder Pancreas
The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine The digestive organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Liver Gall bladder Pancreas
Each gland has at least one duct that takes saliva to the oral cavity.
 kufa university Physiology College of Nursing first year student Ass. Lect :- Hisham Qassem M. Lecture No :-3 The Digestive System Digestive system consists of: 1. Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT). 2. Accessory
kufa university Physiology College of Nursing first year student Ass. Lect :- Hisham Qassem M. Lecture No :-3 The Digestive System Digestive system consists of: 1. Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT). 2. Accessory
Digestion in the small and Large Intestines
 9.5 Digestion in the small and Large Intestines Do some foods keep you feeling full for a long time? Do you ever feel that after eating certain foods, you are hungry again in a short time? Some foods stay
9.5 Digestion in the small and Large Intestines Do some foods keep you feeling full for a long time? Do you ever feel that after eating certain foods, you are hungry again in a short time? Some foods stay
Digestive system. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College
 Digestive system Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College Functions Motility ingestion mastication deglutition peristalsis Secretion exocrine endocrine Digestion Absorption Tunics Innervation
Digestive system Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College Functions Motility ingestion mastication deglutition peristalsis Secretion exocrine endocrine Digestion Absorption Tunics Innervation
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Objectives Name and locate the digestive organs and the accessory organs of digestion. List the general function of the digestive system and the function of each organ. Define mechanical
The Digestive System Objectives Name and locate the digestive organs and the accessory organs of digestion. List the general function of the digestive system and the function of each organ. Define mechanical
26. Digestive System
 26. Digestive System Your body needs food for two primary purposes: growth and maintenance. Molecules and atoms in the food you eat are generally used to either build new molecules in your body or to provide
26. Digestive System Your body needs food for two primary purposes: growth and maintenance. Molecules and atoms in the food you eat are generally used to either build new molecules in your body or to provide
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System What do you know?? quiz-digestive-health Digestion Videos The Digestive System Inside-Dr-Ozs-Digestive-System-Video Now it is your turn to recreate the digestive system. How is food
The Digestive System What do you know?? quiz-digestive-health Digestion Videos The Digestive System Inside-Dr-Ozs-Digestive-System-Video Now it is your turn to recreate the digestive system. How is food
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems. Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion 1 Terms Absorption Amino acids Anus Avian Bile Cecum Chyme Crop Cud Digestion Digestive system Enzymes Eructated Feces Gizzard
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion 1 Terms Absorption Amino acids Anus Avian Bile Cecum Chyme Crop Cud Digestion Digestive system Enzymes Eructated Feces Gizzard
30.3 The Digestive System
 30.3 The Digestive System Lesson Objectives Describe the organs of the digestive system and explain their functions. Explain what happens during digestion. Describe how nutrients are absorbed into the
30.3 The Digestive System Lesson Objectives Describe the organs of the digestive system and explain their functions. Explain what happens during digestion. Describe how nutrients are absorbed into the
Digestive System Lecture 5 Winter 2014
 Digestive System Lecture 5 Winter 2014 This lecture tells the story of the Flow of Matter from Food to Cells. The pictures are only there to help you visualize structures don t worry about names of structures
Digestive System Lecture 5 Winter 2014 This lecture tells the story of the Flow of Matter from Food to Cells. The pictures are only there to help you visualize structures don t worry about names of structures
The Respiratory System
 Human Anatomy III: Respiratory, Urinary & Digestive Systems The Respiratory System Major functions include: Obtaining oxygen Removing carbon dioxide Maintenance of ph balance Respiration may be accomplished
Human Anatomy III: Respiratory, Urinary & Digestive Systems The Respiratory System Major functions include: Obtaining oxygen Removing carbon dioxide Maintenance of ph balance Respiration may be accomplished
The 6 th International Junior Science Olympiad Training Programme
 The 6 th International Junior Science Olympiad Training Programme KEEPING HEALTHY SECTION 2: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Notes to Teachers Learning Objectives: Processes of nutrition in human (0.25 hr) General plan
The 6 th International Junior Science Olympiad Training Programme KEEPING HEALTHY SECTION 2: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Notes to Teachers Learning Objectives: Processes of nutrition in human (0.25 hr) General plan
Biology 2402 Anatomy &Physiology II - Digestive system notes - Ch. 15
 Biology 2402 Anatomy &Physiology II - Digestive system notes - Ch. 15 Digestive system processes the food used as fuel and nutrients for the body. Composed of a tube through the body (digestive tract,
Biology 2402 Anatomy &Physiology II - Digestive system notes - Ch. 15 Digestive system processes the food used as fuel and nutrients for the body. Composed of a tube through the body (digestive tract,
Upper Gastrointestinal Tract KNH 406
 Upper Gastrointestinal Tract KNH 406 Upper GI A&P GI tract long tube ~ 15 ft. Upper GI mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach Accessory organs pancreas, biliary system, liver Four basic functions: motility,
Upper Gastrointestinal Tract KNH 406 Upper GI A&P GI tract long tube ~ 15 ft. Upper GI mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach Accessory organs pancreas, biliary system, liver Four basic functions: motility,
SEER Training Modules
 http://training.seer.cancer.gov/anatomy/digestive/ WiRED International wishes to thank the National Cancer Institute for use of this information. SEER Training Modules Introduction to the Digestive System
http://training.seer.cancer.gov/anatomy/digestive/ WiRED International wishes to thank the National Cancer Institute for use of this information. SEER Training Modules Introduction to the Digestive System
Divisions of Digestive System. Organs of the Alimentary Canal. Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal. CHAPTER 14 p.
 Divisions of Digestive System Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal CHAPTER 14 p. 412-423 1. Alimentary Canal or Gastrointestinal Tract (GI)-digests and absorbs food coiled hollow
Divisions of Digestive System Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal CHAPTER 14 p. 412-423 1. Alimentary Canal or Gastrointestinal Tract (GI)-digests and absorbs food coiled hollow
Physiology of Digestive system II
 Small Intestine Physiology of Digestive system II Motility of small intestine: Distention of the Small Intestine Elicits Mixing Contractions Called Segmentation Contractions. These are concentric contractions
Small Intestine Physiology of Digestive system II Motility of small intestine: Distention of the Small Intestine Elicits Mixing Contractions Called Segmentation Contractions. These are concentric contractions
NSW Higher School Certificate Senior Science 9.2 Lifestyle Chemistry
 NSW Higher School Certificate Senior Science 9.2 Lifestyle Chemistry Section 5 Drug Solubility 9.2 Lifestyle Chemistry Section 5 ::: Drug Solubility 9.2.5 The solubility of drugs has an effect on the way
NSW Higher School Certificate Senior Science 9.2 Lifestyle Chemistry Section 5 Drug Solubility 9.2 Lifestyle Chemistry Section 5 ::: Drug Solubility 9.2.5 The solubility of drugs has an effect on the way
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Five Basic Processes The Gastrointestinal tract (alimentary canal)
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Five Basic Processes 1. Ingestion - eating 2. Movement of the food along the G.I. tract. 3. Digestion- chemical and mechanical breakdown of food. 4. Absorption of the breakdown products
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Five Basic Processes 1. Ingestion - eating 2. Movement of the food along the G.I. tract. 3. Digestion- chemical and mechanical breakdown of food. 4. Absorption of the breakdown products
Horse Science: The Digestive System of the Horse Page 3
 Horse Science: The Digestive System of the Horse Page 3 The digestive system of the horse is different from that Mastication (chewing) is the mechanical reduction of of the other farm animals. Although
Horse Science: The Digestive System of the Horse Page 3 The digestive system of the horse is different from that Mastication (chewing) is the mechanical reduction of of the other farm animals. Although
Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System
 The Digestive System Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System 1 Functions of the Digestive System: 1. Break up food into smaller pieces 2. Absorbing nutrients into the blood 3. Excreting
The Digestive System Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System 1 Functions of the Digestive System: 1. Break up food into smaller pieces 2. Absorbing nutrients into the blood 3. Excreting
Alimentary canal (gastrointestinal or GI tract) continuous coiled hollow tube
 The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Gross Anatomy Function The Digestive System Functions Ingestion taking in food Digestion breaking food down both physically and chemically Absorption movement of
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Gross Anatomy Function The Digestive System Functions Ingestion taking in food Digestion breaking food down both physically and chemically Absorption movement of
II. General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal
 Human Anatomy & Physiology 17 Be sure to watch the Video: The Digestive System. Digestive System URLs http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/biobk/ BioBookDIGEST.html http://yahooligans.yahoo.com/reference/gray/244.html
Human Anatomy & Physiology 17 Be sure to watch the Video: The Digestive System. Digestive System URLs http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/biobk/ BioBookDIGEST.html http://yahooligans.yahoo.com/reference/gray/244.html
The digestive system, also called the gastrointestinal
 exercise 8 Chemical and Physical Processes of Digestion Objectives 1. To define digestive tract, accessory glands, digestion, hydrolases, salivary amylase, carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, bile salts,
exercise 8 Chemical and Physical Processes of Digestion Objectives 1. To define digestive tract, accessory glands, digestion, hydrolases, salivary amylase, carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, bile salts,
Mechanical digestion: physical breaking of food chewing by teeth churning by stomach segmentation by intestines (= mixing food) p.611/ Fig. 22.
 The Digestive System 1. Describe the general functions of the digestive system Ingestion: Taking food in Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal voluntary: swalloing involuntary: peristalsis
The Digestive System 1. Describe the general functions of the digestive system Ingestion: Taking food in Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal voluntary: swalloing involuntary: peristalsis
1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A on the diagram. 2. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled B on the diagram.
 2013 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Sample Tournament Station A: Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A on the diagram. 2. Give the name and functions
2013 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Sample Tournament Station A: Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A on the diagram. 2. Give the name and functions
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford
 By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
22 Digestive System. Taft College Human Physiology
 22 Digestive System Taft College Human Physiology Functions of the Digestive System (4 Basic Functions of Digestion) 1. Ingestion - food intake. 2. Digestion - process of reducing foods to their constituent
22 Digestive System Taft College Human Physiology Functions of the Digestive System (4 Basic Functions of Digestion) 1. Ingestion - food intake. 2. Digestion - process of reducing foods to their constituent
Functions of the digestive system
 Digestive system Functions of the digestive system Digestion-mechanical and chemical breakdown of material Motility-movement of material from the oral cavity to the anus-swallowing / peristalsis Secretion-exocrine
Digestive system Functions of the digestive system Digestion-mechanical and chemical breakdown of material Motility-movement of material from the oral cavity to the anus-swallowing / peristalsis Secretion-exocrine
Introduction. Digestive System. Physiology. Anatomy. Physiology. Alimentary Canal. Chapter 21
 Chapter 21 Digestive System Susan G. Salvo Introduction Digestive process is a disassembly line Digestive system provides processes in which proteins, carbohydrates, and fats are broken down and used a
Chapter 21 Digestive System Susan G. Salvo Introduction Digestive process is a disassembly line Digestive system provides processes in which proteins, carbohydrates, and fats are broken down and used a
LAB 3: DIGESTION OF ORGANIC MACROMOLECULES
 LAB 3: DIGESTION OF ORGANIC MACROMOLECULES INTRODUCTION Enzymes are a special class of proteins that lower the activation energy of biological reactions. These biological catalysts change the rate of chemical
LAB 3: DIGESTION OF ORGANIC MACROMOLECULES INTRODUCTION Enzymes are a special class of proteins that lower the activation energy of biological reactions. These biological catalysts change the rate of chemical
Care and Problems of the Digestive System. Chapter 18 Lesson 2
 Care and Problems of the Digestive System Chapter 18 Lesson 2 Care of the Digestive System Good eating habits are the best way to avoid or minimize digestive system problems. Eat a variety of foods Avoid
Care and Problems of the Digestive System Chapter 18 Lesson 2 Care of the Digestive System Good eating habits are the best way to avoid or minimize digestive system problems. Eat a variety of foods Avoid
CHAPTER 17: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. 2. Distinguish between mechanical digestion and chemical digestion.
 CHAPTER 17: SYSTEM OBJECTIVES 1. Define the term digestion and explain its significance. 2. Distinguish between mechanical digestion and chemical digestion. 3. Discuss the five digestive processes that
CHAPTER 17: SYSTEM OBJECTIVES 1. Define the term digestion and explain its significance. 2. Distinguish between mechanical digestion and chemical digestion. 3. Discuss the five digestive processes that
10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402
 10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402 Macromolecules and Living Systems The body is made up of more than 60 % water. The water is found in the cells cytoplasm, the interstitial fluid and the blood (5
10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402 Macromolecules and Living Systems The body is made up of more than 60 % water. The water is found in the cells cytoplasm, the interstitial fluid and the blood (5
Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition
 Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition Chapter Objectives INTRODUCTION 1. Generalize the way in which nutrients are processed through the three major metabolic fates in order to perform various energetic
Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition Chapter Objectives INTRODUCTION 1. Generalize the way in which nutrients are processed through the three major metabolic fates in order to perform various energetic
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley
 Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam III Name: Instructions This exam consists of 50 questions. You may write on the exam itself, but be sure to answer all your questions on a Scantron
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam III Name: Instructions This exam consists of 50 questions. You may write on the exam itself, but be sure to answer all your questions on a Scantron
Anatomy of the Digestive System. The Digestive System. We need food for cellular utilization:
 The Digestive System We need food for cellular utilization:!nutrients as building blocks for synthesis!sugars, etc to break down for energy most food that we eat cannot be directly used by the body!too
The Digestive System We need food for cellular utilization:!nutrients as building blocks for synthesis!sugars, etc to break down for energy most food that we eat cannot be directly used by the body!too
2012 Anatomy & Physiology C Division. National Competition-Science
 2012 Anatomy & Physiology C Division National Competition-Science Olympiad 1. The alimentary canal includes 8 different parts and 4 accessory organs. Name 5 parts from the alimentary canal and 3 accessory
2012 Anatomy & Physiology C Division National Competition-Science Olympiad 1. The alimentary canal includes 8 different parts and 4 accessory organs. Name 5 parts from the alimentary canal and 3 accessory
The Digestive System 24-1
 The Digestive System 24-1 Overview of GI tract Functions Mouth---bite, chew, swallow Pharynx and esophagus---- transport Stomach----mechanical disruption; absorption of water & alcohol Small intestine--chemical
The Digestive System 24-1 Overview of GI tract Functions Mouth---bite, chew, swallow Pharynx and esophagus---- transport Stomach----mechanical disruption; absorption of water & alcohol Small intestine--chemical
CHAPTER 23 DIGESTIVE
 CHAPTER 23 DIGESTIVE nutrition requires : getting nutrients digesting nutrients transporting nutrients Digestive System musculo-skeletal digestive circulatory Digestive System alimentary canal ~ gastrointestinal
CHAPTER 23 DIGESTIVE nutrition requires : getting nutrients digesting nutrients transporting nutrients Digestive System musculo-skeletal digestive circulatory Digestive System alimentary canal ~ gastrointestinal
Digestive System. Student Learning Objectives: Structures to be studied: Introduction
 Digestive System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the digestive system. Describe the use of various important nutrient materials in the body. Structures to be studied: Oral
Digestive System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the digestive system. Describe the use of various important nutrient materials in the body. Structures to be studied: Oral
The Digestive System
 16 The Digestive System FOCUS: The function of the digestive system is to take in food, break it down into smaller compounds, and absorb those compounds so that the body can use them. This process provides
16 The Digestive System FOCUS: The function of the digestive system is to take in food, break it down into smaller compounds, and absorb those compounds so that the body can use them. This process provides
A comparison of the different livestock systems. By: Kristy Baird
 A comparison of the different livestock systems By: Kristy Baird Describe the basic function of the primary components of the digestive system. Compare the function and location of the digestive organs
A comparison of the different livestock systems By: Kristy Baird Describe the basic function of the primary components of the digestive system. Compare the function and location of the digestive organs
Overview... 1 What is the Outreach Program?... 1 Concepts... 2 Objectives... 3 Arizona Science Standards... 3 College and Career Ready ELA
 Overview... 1 What is the Outreach Program?... 1 Concepts... 2 Objectives... 3 Arizona Science Standards... 3 College and Career Ready ELA Standards... 4 Next Generation Science Standards... 4 Learning
Overview... 1 What is the Outreach Program?... 1 Concepts... 2 Objectives... 3 Arizona Science Standards... 3 College and Career Ready ELA Standards... 4 Next Generation Science Standards... 4 Learning
Mammalian Physiology. Gastrointestinal System: Digestion and Absorption
 Mammalian Physiology Gastrointestinal System: Digestion and Absorption 1UNLV UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 33 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton Objectives Describe the digestive secretions
Mammalian Physiology Gastrointestinal System: Digestion and Absorption 1UNLV UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 33 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton Objectives Describe the digestive secretions
Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and Gallbladder
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46496 1 Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and Gallbladder OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution
OpenStax-CNX module: m46496 1 Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and Gallbladder OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution
1. The diagram below represents a biological process
 1. The diagram below represents a biological process 5. The chart below indicates the elements contained in four different molecules and the number of atoms of each element in those molecules. Which set
1. The diagram below represents a biological process 5. The chart below indicates the elements contained in four different molecules and the number of atoms of each element in those molecules. Which set
General Structure and Function of the Digestive System
 General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Do Now Why does food have to be digested before cells can use it? What are the typical four layers of the digestive tract wall? What is the name of
General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Do Now Why does food have to be digested before cells can use it? What are the typical four layers of the digestive tract wall? What is the name of
Integumentary System Digestive System. Outline. Integumentary System 11/4/2008. Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND
 Integumentary System Digestive System Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND Outline Integumentary system and body membranes Types of body membranes and their function General structure and main
Integumentary System Digestive System Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND Outline Integumentary system and body membranes Types of body membranes and their function General structure and main
DIGESTION is the physical and
 Digestion DIGESTION is the physical and chemical breakdown of feeds as they pass through the gastrointestinal tract. The structures of the gastrointestinal tract include the mouth, the esophagus, the stomach,
Digestion DIGESTION is the physical and chemical breakdown of feeds as they pass through the gastrointestinal tract. The structures of the gastrointestinal tract include the mouth, the esophagus, the stomach,
Digestive System. About the Digestive System. How Digestion Works
 Digestive System The first step in the digestive process happens before we even taste food. Just by smelling that homemade apple pie or thinking about how delicious that ripe tomato is going to be, you
Digestive System The first step in the digestive process happens before we even taste food. Just by smelling that homemade apple pie or thinking about how delicious that ripe tomato is going to be, you
Lab 18 The Digestive System
 Lab 18 The Digestive System Laboratory Objectives Identify on a diagram, model or cadaver the parts of the digestive system and accessory organs. Describe the general histology of the digestive system.
Lab 18 The Digestive System Laboratory Objectives Identify on a diagram, model or cadaver the parts of the digestive system and accessory organs. Describe the general histology of the digestive system.
