The Cell Cycle TEACHER NOTES MIDDLE GRADES SCIENCE NSPIRED. Science Objectives. Vocabulary. About the Lesson. TI-Nspire Navigator. Activity Materials
|
|
|
- Kristopher Joseph
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Science Objectives Students will identify the changes that occur in cells during each phase of mitosis. Students will correlate these changes to the duration of time cells spend in each phase. While looking at a section of an onion root tip, students will count the number of cells observed in each phase of the cell cycle. They will then estimate the amount of time that a cell spends in each of the phases of the cell cycle. Students will watch a simulation of the process of mitosis and answer accompanying questions. Vocabulary anaphase interphase nucleus cell cycle metaphase prophase chromosomes mitosis telophase About the Lesson In this lesson students investigate the cell cycle, which includes interphase and mitosis. Students will: Identify the major changes that occur in a cell during each phase of mitosis by watching a simulation. Correlate the time a cell spends in each phase with the number of cells in a rapidly dividing region of an onion root tip undergoing each phase. Understand the implications of the differences between cells that have long or short cell cycles. TI-Nspire Navigator Send out the The_Cell_Cycle.tns file. Monitor student progress using Class Capture. Use Live Presenter to spotlight student answers. Activity Materials Compatible TI Technologies: TI-Nspire CX Handhelds, TI-Nspire Apps for ipad, TI-Nspire Software Tech Tips: This activity includes class Nspire CX handheld. It is also appropriate for use with the TI-Nspire family of products including TI-Nspire software and TI-Nspire App. Slight variations to these directions may be required if using other technologies besides the handheld. Watch for additional Tech Tips throughout the activity for the specific technology you are using. Access free tutorials at captures taken from the TI- calculators/pd/us/online- Learning/Tutorials Lesson Files: Student Activity The_Cell_Cycle_ Student.doc The_Cell_Cycle_ Student.pdf TI-Nspire document The_Cell_Cycle.tns 2014 Texas Instruments Incorporated 1 education.ti.com
2 Discussion Points and Possible Answers Allow students to read the background information stated on their activity sheet and then in the.tns file on pages 1.2 and 1.3. Move to pages 1.4 and 1.5. Have students answer questions 1-10 on their activity sheet. 1. When the students analyze the pie charts of the cell cycles of kidney and skin cells, remind them that the mitosis portion of the cell cycle generally lasts for the same amount of time for each type of cell. The variation in the lengths of the cell cycle occurs in the interphase. For example, some cells may have a cell-cycle duration of 48 hours, half of which is in interphase and half is in mitosis. Liver cells, on the other hand, may divide only once a year, even though the mitosis portion may last only 24 hours, just as with a skin cell. Students should use proportions to answer the following questions. ipad Tip: To see the number of cells in the sample that are in a particular phase, students can tap on each phase in the pie chart. Q1. Select each phase in the Kidney Cell Cycle pie chart. You will see the number of cells in the sample that are in each of the different phases. Record the number of cells in each phase in the table that follows. Add the number of cells in prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase to find the total number of cells in mitosis. Then do the same for the Skin Cell Cycle pie chart. Answers: Phase Kidney Skin Prophase Metaphase 6 6 Anaphase 4 4 Telophase 5 5 Total in Mitosis Interphase Texas Instruments Incorporated 2 education.ti.com
3 Q2. Suppose the mitosis portion of the cell cycle lasts for 24 hours in both kidney cells and skin cells. Estimate how long interphase lasts in each cell by solving the proportion for x, the number of hours of interphase. # of cells in mitosis 24 # of cells in interphase x Note: Remember your answer is in hours. Divide it by 24 to also see how many days it lasts. Answers: Kidney Cell: 25 24, approx. 216 hours or 9 days 225 x Skin Cell: 25 24, approx. 33 to 34 hours or about a day and a half 35 x Q3. Mitosis includes 4 mitotic phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Estimate how long each of the 4 mitotic phases lasts in skin cell mitosis. Use the formula below. # of cells in phase 24 total # of cells in mitosis Answer: Prophase: 10 hours Metaphase: 6 hours Anaphase: 4 hours Telophase: 5 hours Q4. How long is each of the 4 phases in kidney cell mitosis? Answer: Prophase: 10 hours Metaphase: 6 hours Anaphase: 4 hours Telophase: 5 hours Q5. Estimate the length of one entire cell cycle (mitosis and interphase combined) in each of the cell types in the activity. Answer: Kidney Cell: approx. 10 days Skin Cell: approx. 55 hours Q6. You re looking in a microscope at a tissue sample of living cells. In which stage of the cell cycle would you expect to find the most cells? In which stage would you expect to find the fewest cells? Answer: Most: Interphase Fewest: Anaphase 2014 Texas Instruments Incorporated 3 education.ti.com
4 Q7. Which of the two types of cells, kidney or skin, divides more often? Explain. Possible Answer: Skin cells divide more often. The cell cycle is shorter, which means that they go through mitosis more frequently. This is so because skin cells need to be replaced more frequently than kidney cells do. Q8. The process of mitosis produces new body cells for you. What are two reasons your body needs to produce new cells? Possible Answers: growth, repair, replacing dead cells Q9. When, (at what stages), during a human's lifetime, would you expect to find lots and lots of cells undergoing mitosis? When would you expect to find fewer? Explain both of your answers. Possible Answer: Find lots in a developing fetus, in an infant, during the growth spurt years. Find fewer in middle-age and beyond. Q10. Interphase is an equally important part of the cell cycle. It is when the cell really does its regular job, such as filtering blood for kidney cells or digesting food in the stomach. During this time, the cell can consume energy and can perform cell functions. Based on what you now know about the cell cycle, what might happen if interphase did not have enough time before mitosis? Possible Answer: Cells that don t have enough time in interphase may not have the energy resources to make it through mitosis. Some cell types stay in interphase for a long time because they don t die often, too much mitosis could lead to unchecked cell growth (including cancer), or failure to divide properly. Teacher Tip: Students often get confused about the point of interphase, and wonder why it takes so long to divide. Be sure to point out that cell division is not the only purpose of a cell; the other important functions can happen during interphase Texas Instruments Incorporated 4 education.ti.com
5 Move to pages 2.1 and In this part of the activity, students will interact with the.tns document. The spreadsheet on page 2.2 contains arbitrary data collected from an imaginary biology student. The student looked at a prepared microscope slide with a longitudinal section of actively dividing onion root tip tissue and counted the number of cells that she observed in each phase of the cell cycle. The numbers have been recorded in Column 2 of the spreadsheet, and then displayed in the adjacent pie chart. In order for your students to interact with this page, you may choose one of three possible options : A) Have students examine their own onion root tip slides and count the number of cells in each phase. The protocol for that process will not be included here, but can be found on several websites. If this is what you wish to do, have the students count cells while looking at the section on either medium or high power, and have them look in the area just above the tip of the root. If time permits, have them do cell counts from 3-4 different areas on the same slide, or on different slides and enter the total number of cells from all of the counts. The more cells they count, the more accurate their results may be. B) Many biological supply companies sell flash cards with pictures of onion root tip sections on them. This is a quick, easy, and accurate way to count the cells, although the students will not be given the opportunity to use the microscope. C) Have the students simply change the numbers in the spreadsheet to their liking. However, ask them to be realistic, as cell cycles always include more interphase than mitosis. You may wish to challenge them to change the numbers to generate pie charts that look identical to the pie charts included in Part 1. ipad Tip: To modify the spreadsheet, students can double-tap on the appropriate cell and enter the value. Students can observe the changes in the pie chart as they enter new values Texas Instruments Incorporated 5 education.ti.com
6 Q11. The entire cell cycle in an onion root tip cell lasts for about 24 hours. Based on your cell counts (or the student s cell count on page 2.2), how long does each of the 5 phases of the cell cycle last? How long does the entire process of mitosis last? Explain how you determined your answers. Answer: Answers will vary depending on the student cell counts. The student should add the number of cells in each phase to find the total number of cells. To find the length of each phase, students should divide the number of cells in the phase by the total number of cells and then multiply by 24 (the length of the cycle). Students can add the lengths of the 4 phases in mitosis to find the total length of mitosis. 100 Using the original counts on page 2.2: Interphase = hours; Prophase = 24 2 hours; Metaphase = 24 1 hour; Anaphase = hour or 45 minutes; Telophase = 24 1 hour Mitosis last about 4-5 hours. Move to pages 3.1 and 3.2. Have students answer questions on either the device, on the activity sheet, or both. 3. Students should move to page 3.1, read the information on that page, and then proceed to page 3.2 for the mitosis simulation. After may pause and reset as many times as they d like; they can also watch the simulation as many times as needed.. Discussion points: Students often get confused about why each of these phases is important or distinct. The cell has control mechanisms called checkpoints that prevent the initiation of each mitotic phase until the previous phase is complete. For example, if spindles pulled apart DNA that was not condensed into chromatids, it would break. Q12. Which important event does NOT happen during mitosis? Answer: B. DNA is copied. Q13. During which phase does the nuclear membrane disappear? Answer: A. prophase Q14. In the cell shown, how many PAIRS of chromosomes are present? Answer: A Texas Instruments Incorporated 6 education.ti.com
7 Q15. One round of the cell cycle makes two new cells. How many cells do you have after 5 rounds of the cell cycle? Answer: C. 64 Q16. During which phase do the chromatids separate from one another? Answer: C. anaphase Q17. At the end of the cell cycle shown, how many chromosomes are present in each new cell? Answer: A. 2 Q18. If you had been watching a simulation of a human cell undergoing mitosis, how many chromosomes would have been present in each new cell? Answer: C. 46 Q19. What might be the outcome for a cell that doesn't properly finish anaphase? Answer: B. Chromosomes are not evenly divided into new cells. TI-Nspire Navigator Opportunities Use TI-Nspire Navigator to capture screen shots of student progress and to retrieve the file from each student at the end of the class period. The student questions can be electronically graded and added to the student portfolio. Make several students Live Presenters while doing Problem 2. Cell counts will be different from student to student, and it is interesting to see how these differences show up in the pie charts. Additionally, the class screen capture feature allows you to see all (or at least most) of the students handheld screens at one time. This is also a good way to compare the results that students get. In Problem 3, student answers may be collected and analyzed using TI-Nspire Navigator, if desired Texas Instruments Incorporated 7 education.ti.com
8 Extension A possible extension would be to pool the class data from Part 2 if the students are doing actual cell counts. This will make the numbers in the spreadsheet much larger, and it is interesting to observe whether the increased numbers of cells appreciably changes the distribution shown in the pie chart. Wrap Up When students are finished with the activity, retrieve the.tns file using TI-Nspire Navigator. Save grades to Portfolio. Discuss activity questions using Slide Show. Assessment Formative assessment will consist of questions embedded in the.tns file. The questions will be graded when the.tns file is retrieved by TI-Nspire Navigator. The TI-Nspire Navigator Slide Show can be utilized to give students immediate feedback on their assessment Texas Instruments Incorporated 8 education.ti.com
Addition by Division TEACHER NOTES SCIENCE NSPIRED
 Science Objectives Students will identify the changes that occur in cells during each phase of the cell cycle. Students will correlate these changes to the duration of time cells spend in each phase. While
Science Objectives Students will identify the changes that occur in cells during each phase of the cell cycle. Students will correlate these changes to the duration of time cells spend in each phase. While
Transformations: Rotations
 Math Objectives Students will identify a rotation as an isometry, also called a congruence transformation. Students will identify which properties (side length, angle measure, perimeter, area, and orientation)
Math Objectives Students will identify a rotation as an isometry, also called a congruence transformation. Students will identify which properties (side length, angle measure, perimeter, area, and orientation)
Time For Mitosis. Materials. Procedure. Name
 Time For Mitosis Name Do all phases of mitosis require the same amount of time for completion? This question can be answered by counting the number of onion root tip cells in the four phases of mitosis
Time For Mitosis Name Do all phases of mitosis require the same amount of time for completion? This question can be answered by counting the number of onion root tip cells in the four phases of mitosis
Rotational Motion and Torque
 Science Objectives Students will describe how different forces can be balanced. Students will relate the balance of a lever to torque on a wrench. Students will develop an understanding of torques as they
Science Objectives Students will describe how different forces can be balanced. Students will relate the balance of a lever to torque on a wrench. Students will develop an understanding of torques as they
TEACHER NOTES MATH NSPIRED
 Math Objectives Students will understand that normal distributions can be used to approximate binomial distributions whenever both np and n(1 p) are sufficiently large. Students will understand that when
Math Objectives Students will understand that normal distributions can be used to approximate binomial distributions whenever both np and n(1 p) are sufficiently large. Students will understand that when
Cell Division Simulation: Bacteria Activity One
 Cell Division Simulation: Bacteria Activity One Introduction All living things are made of cells. Some living things, like plants and animals, are made of millions of cells. But some living things are
Cell Division Simulation: Bacteria Activity One Introduction All living things are made of cells. Some living things, like plants and animals, are made of millions of cells. But some living things are
The Cell Cycle: A series of modeling activities
 The Cell Cycle: A series of modeling activities Cancer Education Project University of Rochester Premise: Students learn best when exposed to a variety of activities Overview 1. Information Gathering:
The Cell Cycle: A series of modeling activities Cancer Education Project University of Rochester Premise: Students learn best when exposed to a variety of activities Overview 1. Information Gathering:
Meiosis is a special form of cell division.
 Page 1 of 6 KEY CONCEPT Meiosis is a special form of cell division. BEFORE, you learned Mitosis produces two genetically identical cells In sexual reproduction, offspring inherit traits from both parents
Page 1 of 6 KEY CONCEPT Meiosis is a special form of cell division. BEFORE, you learned Mitosis produces two genetically identical cells In sexual reproduction, offspring inherit traits from both parents
Biology 3A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction
 Biology 3A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction OBJECTIVE To study the cell cycle and understand how, when and why cells divide. To study and identify the major stages of cell division. To relate the
Biology 3A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction OBJECTIVE To study the cell cycle and understand how, when and why cells divide. To study and identify the major stages of cell division. To relate the
MITOSIS IN ONION ROOT TIP CELLS: AN INTRODUCTION TO LIGHT MICROSCOPY
 MITOSIS IN ONION ROOT TIP CELLS: AN INTRODUCTION TO LIGHT MICROSCOPY Adapted from Foundations of Biology I; Lab 6 Introduction to Microscopy Dr. John Robertson, Westminster College Biology Department,
MITOSIS IN ONION ROOT TIP CELLS: AN INTRODUCTION TO LIGHT MICROSCOPY Adapted from Foundations of Biology I; Lab 6 Introduction to Microscopy Dr. John Robertson, Westminster College Biology Department,
Lab 3: Testing Hypotheses about Mitosis
 Lab 3: Testing Hypotheses about Mitosis Why do cells divide? Lab today focuses on cellular division, also known as cellular reproduction. To become more familiar with why cells divide, the types of cell
Lab 3: Testing Hypotheses about Mitosis Why do cells divide? Lab today focuses on cellular division, also known as cellular reproduction. To become more familiar with why cells divide, the types of cell
The Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens
 The Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Rooting for Mitosis Overview Students will fix, stain, and make slides of onion root tips. These slides will be examined for the presence
The Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Rooting for Mitosis Overview Students will fix, stain, and make slides of onion root tips. These slides will be examined for the presence
Building Concepts: Dividing a Fraction by a Whole Number
 Lesson Overview This TI-Nspire lesson uses a unit square to explore division of a unit fraction and a fraction in general by a whole number. The concept of dividing a quantity by a whole number, n, can
Lesson Overview This TI-Nspire lesson uses a unit square to explore division of a unit fraction and a fraction in general by a whole number. The concept of dividing a quantity by a whole number, n, can
Cell Growth and Reproduction Module B, Anchor 1
 Cell Growth and Reproduction Module B, Anchor 1 Key Concepts: - The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, a larger cell is less efficient in moving nutrients
Cell Growth and Reproduction Module B, Anchor 1 Key Concepts: - The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, a larger cell is less efficient in moving nutrients
Type 1 Diabetes - Managing a Critical Ratio
 Objectives Students will learn about how ratios and proportions are a key part of managing Type 1 Diabetes Students will learn about the regulation of blood glucose through insulin (hormone) binding with
Objectives Students will learn about how ratios and proportions are a key part of managing Type 1 Diabetes Students will learn about the regulation of blood glucose through insulin (hormone) binding with
LABORATORY 2 THE CELL CYCLE AND THE STAGES OF MITOSIS LEARNING OBJECTIVES AFTER COMPLETING THIS LABORATORY, YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO:
 LABORATORY 2 THE CELL CYCLE AND THE STAGES OF MITOSIS LEARNING OBJECTIVES AFTER COMPLETING THIS LABORATORY, YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Describe the cell cycle. 2. Identify stages of mitosis from prepared
LABORATORY 2 THE CELL CYCLE AND THE STAGES OF MITOSIS LEARNING OBJECTIVES AFTER COMPLETING THIS LABORATORY, YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Describe the cell cycle. 2. Identify stages of mitosis from prepared
Laboratory Observing the Cell Cycle of Onion Root Tip Cells
 Laboratory Observing the Cell Cycle of Onion Root Tip Cells Background: Because of their rapid growth, the cells of the root tips of plants undergo rapid cell division. Ornamental onion root tips cells
Laboratory Observing the Cell Cycle of Onion Root Tip Cells Background: Because of their rapid growth, the cells of the root tips of plants undergo rapid cell division. Ornamental onion root tips cells
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells
 Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Cell Division Mitosis and the Cell Cycle
 Cell Division Mitosis and the Cell Cycle A Chromosome and Sister Chromatids Key Points About Chromosome Structure A chromosome consists of DNA that is wrapped around proteins (histones) and condensed Each
Cell Division Mitosis and the Cell Cycle A Chromosome and Sister Chromatids Key Points About Chromosome Structure A chromosome consists of DNA that is wrapped around proteins (histones) and condensed Each
List, describe, diagram, and identify the stages of meiosis.
 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles In this topic we will examine a second type of cell division used by eukaryotic cells: meiosis. In addition, we will see how the 2 types of eukaryotic cell division, mitosis
Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles In this topic we will examine a second type of cell division used by eukaryotic cells: meiosis. In addition, we will see how the 2 types of eukaryotic cell division, mitosis
Chapter 3. Cell Division. Laboratory Activities Activity 3.1: Mock Mitosis Activity 3.2: Mitosis in Onion Cells Activity 3.
 Chapter 3 Cell Division Laboratory Activities Activity 3.1: Mock Mitosis Activity 3.2: Mitosis in Onion Cells Activity 3.3: Mock Meiosis Goals Following this exercise students should be able to Recognize
Chapter 3 Cell Division Laboratory Activities Activity 3.1: Mock Mitosis Activity 3.2: Mitosis in Onion Cells Activity 3.3: Mock Meiosis Goals Following this exercise students should be able to Recognize
Appendix C DNA Replication & Mitosis
 K.Muma Bio 6 Appendix C DNA Replication & Mitosis Study Objectives: Appendix C: DNA replication and Mitosis 1. Describe the structure of DNA and where it is found. 2. Explain complimentary base pairing:
K.Muma Bio 6 Appendix C DNA Replication & Mitosis Study Objectives: Appendix C: DNA replication and Mitosis 1. Describe the structure of DNA and where it is found. 2. Explain complimentary base pairing:
The illustrations below reflect other scientists results in identifying and counting the stages of the onion root tip and the whitefish blastula.
 Abstract: The purpose of this laboratory experiment was to identify in what stage of mitosis viewed cells were in. The stages of mitosis include prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Although the
Abstract: The purpose of this laboratory experiment was to identify in what stage of mitosis viewed cells were in. The stages of mitosis include prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Although the
1. Identify each phase of mitosis on the onion root tip and the whitefish blastula. 3. Explain differences in mitosis between plant and animal cells.
 Mitosis Objectives Having completed the lab on mitosis, you should be able to: 1. Identify each phase of mitosis on the onion root tip and the whitefish blastula. 2. Describe the events during each phase
Mitosis Objectives Having completed the lab on mitosis, you should be able to: 1. Identify each phase of mitosis on the onion root tip and the whitefish blastula. 2. Describe the events during each phase
www.njctl.org PSI Biology Mitosis & Meiosis
 Mitosis and Meiosis Mitosis Classwork 1. Identify two differences between meiosis and mitosis. 2. Provide an example of a type of cell in the human body that would undergo mitosis. 3. Does cell division
Mitosis and Meiosis Mitosis Classwork 1. Identify two differences between meiosis and mitosis. 2. Provide an example of a type of cell in the human body that would undergo mitosis. 3. Does cell division
LAB 8 EUKARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS
 LAB 8 EUKARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS Los Angeles Mission College Biology 3 Name: Date: INTRODUCTION BINARY FISSION: Prokaryotic cells (bacteria) reproduce asexually by binary fission. Bacterial
LAB 8 EUKARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS Los Angeles Mission College Biology 3 Name: Date: INTRODUCTION BINARY FISSION: Prokaryotic cells (bacteria) reproduce asexually by binary fission. Bacterial
Body of Evidence Using clues from a decomposing body to solve a mystery
 Objectives Students will analyze forensic clues in a story to infer the identity of a decomposing body. Students will interpret histogram plots to deduce the correct missing person. Students will understand
Objectives Students will analyze forensic clues in a story to infer the identity of a decomposing body. Students will interpret histogram plots to deduce the correct missing person. Students will understand
CHAPTER 9 CELLULAR REPRODUCTION P. 243-257
 CHAPTER 9 CELLULAR REPRODUCTION P. 243-257 SECTION 9-1 CELLULAR GROWTH Page 244 ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why is it beneficial for cells to remain small? MAIN IDEA Cells grow until they reach their size limit,
CHAPTER 9 CELLULAR REPRODUCTION P. 243-257 SECTION 9-1 CELLULAR GROWTH Page 244 ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why is it beneficial for cells to remain small? MAIN IDEA Cells grow until they reach their size limit,
The River of Life TEACHER NOTES SCIENCE NSPIRED. Science Objectives. Math Objectives. Materials Needed. Vocabulary.
 Science Objectives Students will calculate the volume of blood in their own bodies. Students will analyze and quantify some of the components of their blood. Math Objectives Students will use tabular data
Science Objectives Students will calculate the volume of blood in their own bodies. Students will analyze and quantify some of the components of their blood. Math Objectives Students will use tabular data
LAB 09 Cell Division
 LAB 09 Cell Division Introduction: One of the characteristics of living things is the ability to replicate and pass on genetic information to the next generation. Cell division in individual bacteria and
LAB 09 Cell Division Introduction: One of the characteristics of living things is the ability to replicate and pass on genetic information to the next generation. Cell division in individual bacteria and
Cell Division CELL DIVISION. Mitosis. Designation of Number of Chromosomes. Homologous Chromosomes. Meiosis
 Cell Division CELL DIVISION Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial purpose.
Cell Division CELL DIVISION Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial purpose.
From DNA to Protein
 Nucleus Control center of the cell contains the genetic library encoded in the sequences of nucleotides in molecules of DNA code for the amino acid sequences of all proteins determines which specific proteins
Nucleus Control center of the cell contains the genetic library encoded in the sequences of nucleotides in molecules of DNA code for the amino acid sequences of all proteins determines which specific proteins
Cell Cycle in Onion Root Tip Cells (IB)
 Cell Cycle in Onion Root Tip Cells (IB) A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules,
Cell Cycle in Onion Root Tip Cells (IB) A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules,
Sexual Reproduction. The specialized cells that are required for sexual reproduction are known as. And come from the process of: GAMETES
 Sexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction We know all about asexual reproduction 1. Only one parent required. 2. Offspring are identical to parents. 3. The cells that produce the offspring are not usually
Sexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction We know all about asexual reproduction 1. Only one parent required. 2. Offspring are identical to parents. 3. The cells that produce the offspring are not usually
1. When new cells are formed through the process of mitosis, the number of chromosomes in the new cells
 Cell Growth and Reproduction 1. When new cells are formed through the process of mitosis, the number of chromosomes in the new cells A. is half of that of the parent cell. B. remains the same as in the
Cell Growth and Reproduction 1. When new cells are formed through the process of mitosis, the number of chromosomes in the new cells A. is half of that of the parent cell. B. remains the same as in the
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Name Period Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know. Define: gene locus gamete male gamete female
Name Period Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know. Define: gene locus gamete male gamete female
Where is Mitosis Most Common in the Onion Root?
 Where is Mitosis Most Common in the Onion Root? Faith Loyd Biology Miss Carpenter February 20, 2013 Problem, Hypothesis, and Prediction The problem in this lab is: To analyze data to see whether mitosis
Where is Mitosis Most Common in the Onion Root? Faith Loyd Biology Miss Carpenter February 20, 2013 Problem, Hypothesis, and Prediction The problem in this lab is: To analyze data to see whether mitosis
The cell cycle, mitosis and meiosis
 The cell cycle, mitosis and meiosis Learning objective This learning material is about the life cycle of a cell and the series of stages by which genetic materials are duplicated and partitioned to produce
The cell cycle, mitosis and meiosis Learning objective This learning material is about the life cycle of a cell and the series of stages by which genetic materials are duplicated and partitioned to produce
CCR Biology - Chapter 5 Practice Test - Summer 2012
 Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 5 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. If a cell cannot move enough material
Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 5 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. If a cell cannot move enough material
Sexual Reproduction. and Meiosis. Sexual Reproduction
 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Describe the stages of meiosis and how sex cells are produced. Explain why meiosis is needed for sexual reproduction. Name the cells that are involved in fertilization.
Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Describe the stages of meiosis and how sex cells are produced. Explain why meiosis is needed for sexual reproduction. Name the cells that are involved in fertilization.
1. Why is mitosis alone insufficient for the life cycle of sexually reproducing eukaryotes?
 Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles 1. Why is mitosis alone insufficient for the life cycle of sexually reproducing eukaryotes? 2. Define: gamete zygote meiosis homologous chromosomes diploid haploid
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles 1. Why is mitosis alone insufficient for the life cycle of sexually reproducing eukaryotes? 2. Define: gamete zygote meiosis homologous chromosomes diploid haploid
5. The cells of a multicellular organism, other than gametes and the germ cells from which it develops, are known as
 1. True or false? The chi square statistical test is used to determine how well the observed genetic data agree with the expectations derived from a hypothesis. True 2. True or false? Chromosomes in prokaryotic
1. True or false? The chi square statistical test is used to determine how well the observed genetic data agree with the expectations derived from a hypothesis. True 2. True or false? Chromosomes in prokaryotic
High School Science Lesson Plan: Biology
 High School Science Lesson Plan: Biology Introduction Each lesson in the Adolescent Literacy Toolkit is designed to support students through the reading/learning process by providing instruction before,
High School Science Lesson Plan: Biology Introduction Each lesson in the Adolescent Literacy Toolkit is designed to support students through the reading/learning process by providing instruction before,
The Somatic Cell Cycle
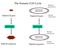 The Somatic Cell Cycle Maternal chromosome Diploid Zygote Diploid Zygote Paternal chromosome MITOSIS MITOSIS Maternal chromosome Diploid organism Diploid organism Paternal chromosome Int terpha ase The
The Somatic Cell Cycle Maternal chromosome Diploid Zygote Diploid Zygote Paternal chromosome MITOSIS MITOSIS Maternal chromosome Diploid organism Diploid organism Paternal chromosome Int terpha ase The
Lecture 7 Mitosis & Meiosis
 Lecture 7 Mitosis & Meiosis Cell Division Essential for body growth and tissue repair Interphase G 1 phase Primary cell growth phase S phase DNA replication G 2 phase Microtubule synthesis Mitosis Nuclear
Lecture 7 Mitosis & Meiosis Cell Division Essential for body growth and tissue repair Interphase G 1 phase Primary cell growth phase S phase DNA replication G 2 phase Microtubule synthesis Mitosis Nuclear
Area Formulas TEACHER NOTES MATH NSPIRED. Math Objectives. Vocabulary. About the Lesson. TI-Nspire Navigator System
 Math Objectives Students will be able to describe how the area of a parallelogram relates to the area of a rectangle with the same base and height. Students will be able to describe how the area of a triangle
Math Objectives Students will be able to describe how the area of a parallelogram relates to the area of a rectangle with the same base and height. Students will be able to describe how the area of a triangle
Trigonometric Ratios TEACHER NOTES. About the Lesson. Vocabulary. Teacher Preparation and Notes. Activity Materials
 About the Lesson In this activity, students discover the trigonometric ratios through measuring the side lengths of similar triangles and calculating their ratios. The formal definitions of the sine, cosine,
About the Lesson In this activity, students discover the trigonometric ratios through measuring the side lengths of similar triangles and calculating their ratios. The formal definitions of the sine, cosine,
CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE CHROMOSOME NUMBERS
 CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE 1. During nuclear division, the DNA (as chromatin) in a Eukaryotic cell's nucleus is coiled into very tight compact structures called chromosomes. These are rod-shaped structures made
CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE 1. During nuclear division, the DNA (as chromatin) in a Eukaryotic cell's nucleus is coiled into very tight compact structures called chromosomes. These are rod-shaped structures made
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Bio EOC Questions for Cell Reproduction:
 Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Name Period Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know.
Name Period Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know.
CELL DIVISION. STAGES OF MITOTIC DIVISION (Diag. C1)
 1 CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which cells replicate in order to replace cell loss, repair tissue damage and reproduce the organism. Two types of cell division are encountered in the Eukaryotic
1 CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which cells replicate in order to replace cell loss, repair tissue damage and reproduce the organism. Two types of cell division are encountered in the Eukaryotic
Lecture 11 The Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 Lecture 11 The Cell Cycle and Mitosis In this lecture Cell division Chromosomes The cell cycle Mitosis PPMAT Apoptosis What is cell division? Cells divide in order to reproduce themselves The cell cycle
Lecture 11 The Cell Cycle and Mitosis In this lecture Cell division Chromosomes The cell cycle Mitosis PPMAT Apoptosis What is cell division? Cells divide in order to reproduce themselves The cell cycle
Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle
 Name Period Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle Overview: 1. What are the three key roles of cell division? State each role, and give an example. Key Role Example 2. What is meant by the cell cycle? Concept 12.1
Name Period Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle Overview: 1. What are the three key roles of cell division? State each role, and give an example. Key Role Example 2. What is meant by the cell cycle? Concept 12.1
CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION
 CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION Cell division is an inherent property of living organisms. It is a process in which cells reproduce their own kind. The growth, differentiation, reproduction and
CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION Cell division is an inherent property of living organisms. It is a process in which cells reproduce their own kind. The growth, differentiation, reproduction and
Genetic material of all living organisms. Biology - 100
 Genetic material of all living organisms. Biology - 100 This antibiotic is made from a fungus that was first discovered growing on an orange and it became the first antibiotic to treat infection. Biology
Genetic material of all living organisms. Biology - 100 This antibiotic is made from a fungus that was first discovered growing on an orange and it became the first antibiotic to treat infection. Biology
Biology Behind the Crime Scene Week 4: Lab #4 Genetics Exercise (Meiosis) and RFLP Analysis of DNA
 Page 1 of 5 Biology Behind the Crime Scene Week 4: Lab #4 Genetics Exercise (Meiosis) and RFLP Analysis of DNA Genetics Exercise: Understanding how meiosis affects genetic inheritance and DNA patterns
Page 1 of 5 Biology Behind the Crime Scene Week 4: Lab #4 Genetics Exercise (Meiosis) and RFLP Analysis of DNA Genetics Exercise: Understanding how meiosis affects genetic inheritance and DNA patterns
Application of Function Composition
 Math Objectives Given functions f and g, the student will be able to determine the domain and range of each as well as the composite functions defined by f ( g( x )) and g( f ( x )). Students will interpret
Math Objectives Given functions f and g, the student will be able to determine the domain and range of each as well as the composite functions defined by f ( g( x )) and g( f ( x )). Students will interpret
Name of Lesson: Properties of Equality A Review. Mathematical Topic: The Four Properties of Equality. Course: Algebra I
 Name of Lesson: Properties of Equality A Review Mathematical Topic: The Four Properties of Equality Course: Algebra I Time Allocation: One (1) 56 minute period Pre-requisite Knowledge: The students will
Name of Lesson: Properties of Equality A Review Mathematical Topic: The Four Properties of Equality Course: Algebra I Time Allocation: One (1) 56 minute period Pre-requisite Knowledge: The students will
Cellular Reproduction
 9 Cellular Reproduction section 1 Cellular Growth Before You Read Think about the life cycle of a human. On the lines below, write some of the stages that occur in the life cycle of a human. In this section,
9 Cellular Reproduction section 1 Cellular Growth Before You Read Think about the life cycle of a human. On the lines below, write some of the stages that occur in the life cycle of a human. In this section,
4.2 Meiosis. Meiosis is a reduction division. Assessment statements. The process of meiosis
 4.2 Meiosis Assessment statements State that meiosis is a reduction division of a diploid nucleus to form haploid nuclei. Define homologous chromosomes. Outline the process of meiosis, including pairing
4.2 Meiosis Assessment statements State that meiosis is a reduction division of a diploid nucleus to form haploid nuclei. Define homologous chromosomes. Outline the process of meiosis, including pairing
Balancing Chemical Equations Practice
 Science Objectives Students will describe what reactants and products in a chemical equation mean. Students will explain the difference between coefficients and subscripts in chemical equations. Students
Science Objectives Students will describe what reactants and products in a chemical equation mean. Students will explain the difference between coefficients and subscripts in chemical equations. Students
How Well Do You Know Your Cells?
 How Well Do You Know Your Cells? Complete each sentence below with words from the box. One word will not be used. cells cell membrane cell walls chloroplasts cytoplasm Hooke Leeuwenhoek mitochondria nucleus
How Well Do You Know Your Cells? Complete each sentence below with words from the box. One word will not be used. cells cell membrane cell walls chloroplasts cytoplasm Hooke Leeuwenhoek mitochondria nucleus
Cell Division and Mitosis DNA. Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis. 2. Meiosis occurs in the reproductive organs, producing four haploid sex cells.
 ell Division and Mitosis 1. he life cycle of a cell has two parts growth and development, and cell division. 2. In mitosis, the nucleus divides to form two identical nuclei. Mitosis occurs in four continuous
ell Division and Mitosis 1. he life cycle of a cell has two parts growth and development, and cell division. 2. In mitosis, the nucleus divides to form two identical nuclei. Mitosis occurs in four continuous
BioSci 2200 General Genetics Problem Set 1 Answer Key Introduction and Mitosis/ Meiosis
 BioSci 2200 General Genetics Problem Set 1 Answer Key Introduction and Mitosis/ Meiosis Introduction - Fields of Genetics To answer the following question, review the three traditional subdivisions of
BioSci 2200 General Genetics Problem Set 1 Answer Key Introduction and Mitosis/ Meiosis Introduction - Fields of Genetics To answer the following question, review the three traditional subdivisions of
Triangle Trigonometry and Circles
 Math Objectives Students will understand that trigonometric functions of an angle do not depend on the size of the triangle within which the angle is contained, but rather on the ratios of the sides of
Math Objectives Students will understand that trigonometric functions of an angle do not depend on the size of the triangle within which the angle is contained, but rather on the ratios of the sides of
Use of the Microscope and Cytology
 Use of the Microscope and Cytology Introduction: A true study of anatomy not only considers the large, visible structures of an organism, but also the small structures that provide the organism its form
Use of the Microscope and Cytology Introduction: A true study of anatomy not only considers the large, visible structures of an organism, but also the small structures that provide the organism its form
Lecture 2: Mitosis and meiosis
 Lecture 2: Mitosis and meiosis 1. Chromosomes 2. Diploid life cycle 3. Cell cycle 4. Mitosis 5. Meiosis 6. Parallel behavior of genes and chromosomes Basic morphology of chromosomes telomere short arm
Lecture 2: Mitosis and meiosis 1. Chromosomes 2. Diploid life cycle 3. Cell cycle 4. Mitosis 5. Meiosis 6. Parallel behavior of genes and chromosomes Basic morphology of chromosomes telomere short arm
Look for these related items from Learning Resources :
 Look for these related items from Learning Resources : LER 1901 Cross Section Plant Cell LER 1902 Cross Section Heart Model LER 1903 Cross Section Brain Model LER 2437 Cross Section Earth Model For a dealer
Look for these related items from Learning Resources : LER 1901 Cross Section Plant Cell LER 1902 Cross Section Heart Model LER 1903 Cross Section Brain Model LER 2437 Cross Section Earth Model For a dealer
Transforming Bivariate Data
 Math Objectives Students will recognize that bivariate data can be transformed to reduce the curvature in the graph of a relationship between two variables. Students will use scatterplots, residual plots,
Math Objectives Students will recognize that bivariate data can be transformed to reduce the curvature in the graph of a relationship between two variables. Students will use scatterplots, residual plots,
Graphic Designing with Transformed Functions
 Math Objectives Students will be able to identify a restricted domain interval and use function translations and dilations to choose and position a portion of the graph accurately in the plane to match
Math Objectives Students will be able to identify a restricted domain interval and use function translations and dilations to choose and position a portion of the graph accurately in the plane to match
Factors Galore C: Prime Factorization
 Concept Number sense Activity 4 Factors Galore C: Prime Factorization Students will use the TI-73 calculator s ability to simplify fractions to find the prime factorization of a number. Skills Simplifying
Concept Number sense Activity 4 Factors Galore C: Prime Factorization Students will use the TI-73 calculator s ability to simplify fractions to find the prime factorization of a number. Skills Simplifying
Mitosis, Meiosis and Fertilization 1
 Mitosis, Meiosis and Fertilization 1 I. Introduction When you fall and scrape the skin off your hands or knees, how does your body make new skin cells to replace the skin cells that were scraped off? How
Mitosis, Meiosis and Fertilization 1 I. Introduction When you fall and scrape the skin off your hands or knees, how does your body make new skin cells to replace the skin cells that were scraped off? How
If and when cancer cells stop dividing, they do so at random points, not at the normal checkpoints in the cell cycle.
 Cancer cells have escaped from cell cycle controls Cancer cells divide excessively and invade other tissues because they are free of the body s control mechanisms. Cancer cells do not stop dividing when
Cancer cells have escaped from cell cycle controls Cancer cells divide excessively and invade other tissues because they are free of the body s control mechanisms. Cancer cells do not stop dividing when
3.1 Cells and cell function
 BTEC s own resources 3.1 Cells and cell function In this section: P1 How you are made Key terms Tissue a group of similar cells acting together to perform a particular function. Epithelial cells one of
BTEC s own resources 3.1 Cells and cell function In this section: P1 How you are made Key terms Tissue a group of similar cells acting together to perform a particular function. Epithelial cells one of
Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle
 Name Period Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle Overview: 1. What are the three key roles of cell division? State each role, and give an example. Key Role Reproduction Growth and development Tissue removal Example
Name Period Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle Overview: 1. What are the three key roles of cell division? State each role, and give an example. Key Role Reproduction Growth and development Tissue removal Example
Materials and Methods. Ribonuclease.--Removal of ribonucleic acid from meristematic onion cells did not show any qualitative differences
 B~U~ Noz~s 129 Alterations in Nuclear Ribonucleic Acid Metabolism Induced by l~inetin.* BY RUTH GUNMAN. From the Department of Genetics, University of California, Be, kezey.~ Kinetin, a substance recently
B~U~ Noz~s 129 Alterations in Nuclear Ribonucleic Acid Metabolism Induced by l~inetin.* BY RUTH GUNMAN. From the Department of Genetics, University of California, Be, kezey.~ Kinetin, a substance recently
What qualities are employers looking for in teen workers? How can you prove your own skills?
 Sell Yourself 4 Finding a job The BIG Idea What qualities are employers looking for in teen workers? How can you prove your own skills? AGENDA Approx. 45 minutes I. Warm Up: Employer Survey Review (15
Sell Yourself 4 Finding a job The BIG Idea What qualities are employers looking for in teen workers? How can you prove your own skills? AGENDA Approx. 45 minutes I. Warm Up: Employer Survey Review (15
1 Mutation and Genetic Change
 CHAPTER 14 1 Mutation and Genetic Change SECTION Genes in Action KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What is the origin of genetic differences among organisms? What kinds
CHAPTER 14 1 Mutation and Genetic Change SECTION Genes in Action KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What is the origin of genetic differences among organisms? What kinds
Teacher s Guide. Mitosis. Grades 5-9 MTTV
 Teacher s Guide Mitosis Grades 5-9 MTTV CREDITS Program Production Sunburst Visual Media Teacher s Guide Terry Gates Print Material Design Cecile Foshee 2004 Sunburst Visual Media, a division of Global
Teacher s Guide Mitosis Grades 5-9 MTTV CREDITS Program Production Sunburst Visual Media Teacher s Guide Terry Gates Print Material Design Cecile Foshee 2004 Sunburst Visual Media, a division of Global
GRADE 7: Life science 1. UNIT 7L.1 7 hours. Specialised cells. Resources. About this unit. Previous learning. Key vocabulary and technical terms
 GRADE 7: Life science 1 Specialised cells UNIT 7L.1 7 hours About this unit This unit is the first of six units on life science for Grade 7. This unit is designed to guide your planning and teaching of
GRADE 7: Life science 1 Specialised cells UNIT 7L.1 7 hours About this unit This unit is the first of six units on life science for Grade 7. This unit is designed to guide your planning and teaching of
Students will identify these animal cell structures: Students should properly answer the pre-activity cell membrane, nucleus. questions.
 WHAT DO PLANT & ANIMAL CELLS LOOK LIKE? Grade Levels: 10-12 Time Frame: 2 periods Big Idea: Students will compare various plant epithelial cells (onion and elodea) with human epithelial cells (cheek lining
WHAT DO PLANT & ANIMAL CELLS LOOK LIKE? Grade Levels: 10-12 Time Frame: 2 periods Big Idea: Students will compare various plant epithelial cells (onion and elodea) with human epithelial cells (cheek lining
Lesson 13: The Formulas for Volume
 Student Outcomes Students develop, understand, and apply formulas for finding the volume of right rectangular prisms and cubes. Lesson Notes This lesson is a continuation of Lessons 11, 12, and Module
Student Outcomes Students develop, understand, and apply formulas for finding the volume of right rectangular prisms and cubes. Lesson Notes This lesson is a continuation of Lessons 11, 12, and Module
Living things: Cells Living things:
 unit 1 The cell is the smallest unit capable of living an independent existence. Most cells contain a nucleus which controls the way they work; the only cells in the human body with no nuclei are the red
unit 1 The cell is the smallest unit capable of living an independent existence. Most cells contain a nucleus which controls the way they work; the only cells in the human body with no nuclei are the red
Guided Notes: Chapter 9 Cellular Reproduction
 Guided Notes: Cellular Reproduction When do cells divide? Cells grow and function normally until they become too. Cell size is because increases faster than This means that there is not enough area on
Guided Notes: Cellular Reproduction When do cells divide? Cells grow and function normally until they become too. Cell size is because increases faster than This means that there is not enough area on
Sample Questions for Exam 3
 Sample Questions for Exam 3 1. All of the following occur during prometaphase of mitosis in animal cells except a. the centrioles move toward opposite poles. b. the nucleolus can no longer be seen. c.
Sample Questions for Exam 3 1. All of the following occur during prometaphase of mitosis in animal cells except a. the centrioles move toward opposite poles. b. the nucleolus can no longer be seen. c.
AS Biology Unit 2 Key Terms and Definitions. Make sure you use these terms when answering exam questions!
 AS Biology Unit 2 Key Terms and Definitions Make sure you use these terms when answering exam questions! Chapter 7 Variation 7.1 Random Sampling Sampling a population to eliminate bias e.g. grid square
AS Biology Unit 2 Key Terms and Definitions Make sure you use these terms when answering exam questions! Chapter 7 Variation 7.1 Random Sampling Sampling a population to eliminate bias e.g. grid square
Perpendicular and Angle Bisectors
 Perpendicular and Angle Bisectors Mathematics Objectives Students will investigate and define perpendicular bisector and angle bisector. Students will discover and describe the property that any point
Perpendicular and Angle Bisectors Mathematics Objectives Students will investigate and define perpendicular bisector and angle bisector. Students will discover and describe the property that any point
Christian Dietz M.Sc. University of Konstanz
 Quantification of dynamic recruitment of repair factors to DNA-Damage and Automated localization, tracking and classification of dividing cells in live cell movies Christian Dietz M.Sc. University of Konstanz
Quantification of dynamic recruitment of repair factors to DNA-Damage and Automated localization, tracking and classification of dividing cells in live cell movies Christian Dietz M.Sc. University of Konstanz
Human Chromosomes lab 5
 Human Chromosomes lab 5 Objectives Upon completion of this activity, you should be able to: describe the structure of human chromosomes with reference to size, centromere position, and presence or absence
Human Chromosomes lab 5 Objectives Upon completion of this activity, you should be able to: describe the structure of human chromosomes with reference to size, centromere position, and presence or absence
Fifth Grade, Cells: Structures and Processes 2005 Colorado Summer Writing Institute 1
 Cells: Structures and Processes Grade Level or Special Area: Fifth Grade Written by: Ellie Luyombya, The Academy, Denver, CO Length of Unit: Nine lessons (approximately nine to eleven days 45 minutes each
Cells: Structures and Processes Grade Level or Special Area: Fifth Grade Written by: Ellie Luyombya, The Academy, Denver, CO Length of Unit: Nine lessons (approximately nine to eleven days 45 minutes each
Introduction to the TI-Nspire CX
 Introduction to the TI-Nspire CX Activity Overview: In this activity, you will become familiar with the layout of the TI-Nspire CX. Step 1: Locate the Touchpad. The Touchpad is used to navigate the cursor
Introduction to the TI-Nspire CX Activity Overview: In this activity, you will become familiar with the layout of the TI-Nspire CX. Step 1: Locate the Touchpad. The Touchpad is used to navigate the cursor
How Cancer Begins???????? Chithra Manikandan Nov 2009
 Cancer Cancer is one of the most common diseases in the developed world: 1 in 4 deaths are due to cancer 1 in 17 deaths are due to lung cancer Lung cancer is the most common cancer in men Breast cancer
Cancer Cancer is one of the most common diseases in the developed world: 1 in 4 deaths are due to cancer 1 in 17 deaths are due to lung cancer Lung cancer is the most common cancer in men Breast cancer
Concepts Sectors, arcs, circumference, areas of circles and properties of cones.
 Making Witches Hats from Cones ID: XXXX Time required 45 minutes Activity Overview In this activity, students make cones from circles, exploring the relationship between the size of the sector cut from
Making Witches Hats from Cones ID: XXXX Time required 45 minutes Activity Overview In this activity, students make cones from circles, exploring the relationship between the size of the sector cut from
Objective: On a team of no more than (2). Build to illustrate a 3D model of a PLANT or ANIMAL cell. 10 pts.
 THE CELL model: Activity 4.1 Science / Biology Objective: On a team of no more than (2). Build to illustrate a 3D model of a PLANT or ANIMAL cell. - Your models should clearly demonstrate the following
THE CELL model: Activity 4.1 Science / Biology Objective: On a team of no more than (2). Build to illustrate a 3D model of a PLANT or ANIMAL cell. - Your models should clearly demonstrate the following
1.1 Introduction. 1.2 Cells CHAPTER. 1.2.1 Prokaryotic Cells. 1.2.2 Eukaryotic Cells
 C HAPTER 1CELLS AND CELL DIVISION CHAPTER 1.1 Introduction In genetics, we view cells as vessels for the genetic material. Our main interest is in the chromosomes and their environment. This being said,
C HAPTER 1CELLS AND CELL DIVISION CHAPTER 1.1 Introduction In genetics, we view cells as vessels for the genetic material. Our main interest is in the chromosomes and their environment. This being said,
Biology 1406 Exam 4 Notes Cell Division and Genetics Ch. 8, 9
 Biology 1406 Exam 4 Notes Cell Division and Genetics Ch. 8, 9 Ch. 8 Cell Division Cells divide to produce new cells must pass genetic information to new cells - What process of DNA allows this? Two types
Biology 1406 Exam 4 Notes Cell Division and Genetics Ch. 8, 9 Ch. 8 Cell Division Cells divide to produce new cells must pass genetic information to new cells - What process of DNA allows this? Two types
Grade 6: Module 1: Unit 2: Lesson 19 Peer Critique and Pronoun Mini-Lesson: Revising Draft Literary Analysis
 Grade 6: Module 1: Unit 2: Lesson 19 Revising Draft Literary Analysis This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. Exempt third-party content
Grade 6: Module 1: Unit 2: Lesson 19 Revising Draft Literary Analysis This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. Exempt third-party content
Excel 2003 PivotTables Summarizing, Analyzing, and Presenting Your Data
 The Company Rocks Excel 2003 PivotTables Summarizing, Analyzing, and Presenting Step-by-step instructions to accompany video lessons Danny Rocks 5/19/2011 Creating PivotTables in Excel 2003 PivotTables
The Company Rocks Excel 2003 PivotTables Summarizing, Analyzing, and Presenting Step-by-step instructions to accompany video lessons Danny Rocks 5/19/2011 Creating PivotTables in Excel 2003 PivotTables
DNA. Discovery of the DNA double helix
 DNA Replication DNA Discovery of the DNA double helix A. 1950 s B. Rosalind Franklin - X-ray photo of DNA. C. Watson and Crick - described the DNA molecule from Franklin s X-ray. What is DNA? Question:
DNA Replication DNA Discovery of the DNA double helix A. 1950 s B. Rosalind Franklin - X-ray photo of DNA. C. Watson and Crick - described the DNA molecule from Franklin s X-ray. What is DNA? Question:
Unit 1 Number Sense. In this unit, students will study repeating decimals, percents, fractions, decimals, and proportions.
 Unit 1 Number Sense In this unit, students will study repeating decimals, percents, fractions, decimals, and proportions. BLM Three Types of Percent Problems (p L-34) is a summary BLM for the material
Unit 1 Number Sense In this unit, students will study repeating decimals, percents, fractions, decimals, and proportions. BLM Three Types of Percent Problems (p L-34) is a summary BLM for the material
