Memory in SystemVerilog
|
|
|
- Rudolph Cook
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Memory in SystemVerilog Prof. Stephen A. Edwards Columbia University Spring 2015
2 Implementing Memory
3 Memory = Storage Element Array + Addressing Bits are expensive They should dumb, cheap, small, and tighly packed Bits are numerous Can t just connect a long wire to each one
4 Williams Tube CRT-based random access memory, Used on the Manchester Mark I bits.
5 Mercury acoustic delay line Used in the EDASC, bits
6 Selectron Tube RCA, bits Four-dimensional addressing A four-input AND gate at each bit for selection
7 Magnetic Core IBM, 1952.
8 Magnetic Drum Memory 1950s & 60s. Secondary storage.
9 Modern Memory Choices Family Programmed Persistence Mask ROM at fabrication PROM once EPROM 1000s, UV 10 years FLASH 1000s, block 10 years EEPROM 1000s, byte 10 years NVRAM 5 years SRAM while powered DRAM 64 ms
10 Implementing ROMs 0 0/1 Z: not connected Bitline 2 Bitline 1 Bitline Wordline Wordline A 1 A 0 2-to-4 Decoder Wordline 2 Add. Data 3 Wordline D 2 D 1 D 0
11 Implementing ROMs 0 0/1 Z: not connected 0 0 Bitline 2 Bitline 1 Bitline 0 Wordline Wordline A 1 0 A 0 2-to-4 Decoder Wordline 2 Add. Data 0 3 Wordline D 2 D 1 D 0
12 Implementing ROMs 0 0/1 Z: not connected A 1 A 0 2-to-4 Decoder 2 Add. Data D 2 D 1 D 0
13 Implementing ROMs 0 0/1 1 Z: not connected A 1 A 0 2-to-4 Decoder 0 2 Add. Data D 2 D 1 D 0
14 Mask ROM Die Photo
15 A Floating Gate MOSFET Cross section of a NOR FLASH transistor. Kawai et al., ISSCC 2008 (Renesas)
16 Floating Gate n-channel MOSFET SiO 2 Control Gate Drain Floating Gate Channel Source Floating gate uncharged; Control gate at 0V: Off
17 Floating Gate n-channel MOSFET Control Gate SiO Drain Floating Gate Channel Source Floating gate uncharged; Control gate positive: On
18 Floating Gate n-channel MOSFET SiO 2 Drain Control Gate ++++ Floating Gate ++++ Channel Source Floating gate negative; Control gate at 0V: Off
19 Floating Gate n-channel MOSFET Control Gate SiO Drain Floating Gate ++ Channel Source Floating gate negative; Control gate positive: Off
20 EPROMs and FLASH use Floating-Gate MOSFETs
21 Static Random-Access Memory Cell Bit line Bit line Word line
22 Layout of a 6T SRAM Cell Weste and Harris. Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design. Addison-Wesley, 2010.
23 Intel s 2102 SRAM, bit, 1972
24 2102 Block Diagram
25 SRAM Timing A12 A11. A2 A1 A0 CS1 CS2 WE OE K 8 SRAM D7 D6. D1 D0 CS1 CS2 WE OE Addr 1 2 Data write 1 read 2
26 6264 SRAM Block Diagram INPUT BUFFER I/O 0 I/O 1 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 A 6 A 7 A x 32 x 8 ARRAY I/O 2 I/O 3 I/O 4 I/O 5 I/O 6 CE 1 CE 2 WE COLUMN DECODER POWER DOWN I/O 7 OE CY6264-1
27 Toshiba TC55V16256J 256K 16 A17 A16 A2. A1 A0 UB LB WE OE CE 256K 16 SRAM D15 D14. D1 D0
28 Dynamic RAM Cell Column Row
29 Ancient (c. 1982) DRAM: K 1 A7 A6 A2. A1 A0 Din WE CAS RAS K 1 DRAM Dout
30 Basic DRAM read and write cycles RAS CAS Addr Row Col Row Col WE Din Dout to write read
31 Page Mode DRAM read cycle RAS CAS Addr Row Col Col Col WE Din Dout read read read
32 Samsung 8M 16 SDRAM BA1 BA0 A11 A10. A2 A1 A0 8M 16 SDRAM UDQM LDQM WE CAS RAS CS CKE CLK DQ15 DQ14. DQ1 DQ0 CLK ADD LCKE Address Register Data Input Register Bank Select Row Buffer Refresh Counter LCBR LRAS Row Decoder Col. Buffer 8M x 4 / 4M x 8 / 2M x 16 8M x 4 / 4M x 8 / 2M x 16 8M x 4 / 4M x 8 / 2M x 16 8M x 4 / 4M x 8 / 2M x 16 Column Decoder Latency & Burst Length Programming Register I/O Control Output Buffer Sense AMP LRAS LCBR LWE LCAS LWCBR LDQM Timing Register CLK CKE CS RAS CAS WE L(U)DQM LWE LDQM DQi
33 SDRAM: Control Signals RAS CAS WE Action NOP Load mode register Active (select row) Read (select column, start burst) Write (select column, start burst) Terminate Burst Precharge (deselect row) Auto Refresh Mode register: selects 1/2/4/8-word bursts, CAS latency, burst on write
34 SDRAM: Timing with 2-word bursts Load Active Write Read Refresh Clk RAS CAS WE Addr Op R C C BA B B B DQ W W R R
35 Using Memory in SystemVerilog
36 Basic Memory Model Clock Address Data In Write Clock Memory Data Out Address A0 A1 A1 Read A0 Data In Write D1 Data Out D0 old D1 D1
37 Basic Memory Model Clock Address Data In Write Clock Memory Data Out Address A0 A1 A1 Write A1 Data In Write D1 Data Out D0 old D1 D1
38 Basic Memory Model Clock Address Data In Write Clock Memory Data Out Address A0 A1 A1 Read A1 Data In Write D1 Data Out D0 old D1 D1
39 Memory Is Fundamentally a Bottleneck Plenty of bits, but You can only see a small window each clock cycle Using memory = scheduling memory accesses Software hides this from you: sequential programs naturally schedule accesses You must schedule memory accesses in a hardware design
40 Modeling Synchronous Memory in SystemVerilog module memory( input logic clk, input logic write, input logic [3:0] address, input logic [7:0] data_in, output logic [7:0] data_out); logic [7:0] mem [15:0]; clk) begin if (write) mem[address] <= data_in; data_out <= mem[address]; end endmodule Write enable 4-bit address 8-bit input bus 8-bit output bus The memory array: 16 8-bit bytes Clocked Write to array when asked Always read (old) value from array
41 M10K Blocks in the Cyclone V 10 kilobits (10240 bits) per block Dual ported: two addresses, write enable signals Data busses can be 1 20 bits wide Our Cyclone V 5CSXFC6 has 557 of these blocks (696 KB)
42 Memory in Quartus: the Megafunction Wizard
43 Memory: Single- or Dual-Ported
44 Memory: Select Port Widths
45 Memory: One or Two Clocks
46 Memory: Output Ports Need Not Be Registered
47 Memory: Wizard-Generated Verilog Module This generates the following SystemVerilog module: module memory ( // Port A: input logic [12:0] address_a, // bit words input logic clock_a, input logic [0:0] data_a, input logic wren_a, // Write enable output logic [0:0] q_a, // Port B: input logic [8:0] address_b, // bit words input logic clock_b, input logic [15:0] data_b, input logic wren_b, // Write enable output logic [15:0] q_b); Instantiate like any module; Quartus treats specially
48 Two Ways to Ask for Memory 1. Use the Megafunction Wizard + Warns you in advance about resource usage Awkward to change 2. Let Quartus infer memory from your code + Better integrated with your code Easy to inadvertantly ask for garbage
49 The Perils of Memory Inference module twoport( input logic clk, input logic [8:0] aa, ab, input logic [19:0] da, db, input logic wa, wb, output logic [19:0] qa, qb); logic [19:0] mem [511:0]; clk) begin if (wa) mem[aa] <= da; qa <= mem[aa]; if (wb) mem[ab] <= db; qb <= mem[ab]; end endmodule Failure: Exploded! Synthesized to an 854-page schematic with registers (no M10K blocks) Page 1 looked like this:
50 The Perils of Memory Inference module twoport2( input logic clk, input logic [8:0] aa, ab, input logic [19:0] da, db, input logic wa, wb, output logic [19:0] qa, qb); logic [19:0] mem [511:0]; clk) begin if (wa) mem[aa] <= da; qa <= mem[aa]; end clk) begin if (wb) mem[ab] <= db; qb <= mem[ab]; end endmodule Failure Still didn t work: RAM logic mem is uninferred due to unsupported read-during-write behavior
51 The Perils of Memory Inference module twoport3( input logic clk, input logic [8:0] aa, ab, input logic [19:0] da, db, input logic wa, wb, output logic [19:0] qa, qb); logic [19:0] mem [511:0]; clk) begin if (wa) begin mem[aa] <= da; qa <= da; end else qa <= mem[aa]; end clk) begin if (wb) begin mem[ab] <= db; qb <= db; end else qb <= mem[ab]; end endmodule Finally! Took this structure from a template: Edit Insert Template Verilog HDL Full Designs RAMs and ROMs True Dual-Port RAM (single clock) clk da[19..0] db[19..0] ab[8..0] wb aa[8..0] wa CLK0 DATAIN[19..0] PORTBCLK0 PORTBDATAIN[19..0] PORTBRADDR[8..0] PORTBWADDR[8..0] PORTBWE RADDR[8..0] WADDR[8..0] WE mem SYNC_RAM DATAOUT[19..0] PORTBDATAOUT[0] PORTBDATAOUT[1] PORTBDATAOUT[2] PORTBDATAOUT[3] PORTBDATAOUT[4] PORTBDATAOUT[5] PORTBDATAOUT[6] PORTBDATAOUT[7] PORTBDATAOUT[8] PORTBDATAOUT[9] PORTBDATAOUT[10] PORTBDATAOUT[11] PORTBDATAOUT[12] PORTBDATAOUT[13] PORTBDATAOUT[14] PORTBDATAOUT[15] PORTBDATAOUT[16] PORTBDATAOUT[17] PORTBDATAOUT[18] PORTBDATAOUT[19] qa[0]~reg[19..0] D CLK Q qb[0]~reg[19..0] D CLK Q qa[19..0] qb[19..0]
52 The Perils of Memory Inference module twoport4( input logic clk, input logic [8:0] ra, wa, input logic write, input logic [19:0] d, output logic [19:0] q); logic [19:0] mem [511:0]; Also works: separate read and write addresses clk d[19..0] ra[8..0] wa[8..0] write CLK0 DATAIN[19..0] RADDR[8..0] WADDR[8..0] WE mem SYNC_RAM DATAOUT[19..0] q[0]~reg[19..0] D CLK Q q[19..0] clk) begin if (write) mem[wa] <= d; q <= mem[ra]; end endmodule Conclusion: Inference is fine for single port or one read and one write port. Use the Megafunction Wizard for anything else.
Chapter 5 :: Memory and Logic Arrays
 Chapter 5 :: Memory and Logic Arrays Digital Design and Computer Architecture David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris Copyright 2007 Elsevier 5- ROM Storage Copyright 2007 Elsevier 5- ROM Logic Data
Chapter 5 :: Memory and Logic Arrays Digital Design and Computer Architecture David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris Copyright 2007 Elsevier 5- ROM Storage Copyright 2007 Elsevier 5- ROM Logic Data
A N. O N Output/Input-output connection
 Memory Types Two basic types: ROM: Read-only memory RAM: Read-Write memory Four commonly used memories: ROM Flash, EEPROM Static RAM (SRAM) Dynamic RAM (DRAM), SDRAM, RAMBUS, DDR RAM Generic pin configuration:
Memory Types Two basic types: ROM: Read-only memory RAM: Read-Write memory Four commonly used memories: ROM Flash, EEPROM Static RAM (SRAM) Dynamic RAM (DRAM), SDRAM, RAMBUS, DDR RAM Generic pin configuration:
Memory Basics. SRAM/DRAM Basics
 Memory Basics RAM: Random Access Memory historically defined as memory array with individual bit access refers to memory with both Read and Write capabilities ROM: Read Only Memory no capabilities for
Memory Basics RAM: Random Access Memory historically defined as memory array with individual bit access refers to memory with both Read and Write capabilities ROM: Read Only Memory no capabilities for
Module 2. Embedded Processors and Memory. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 2 Embedded Processors and Memory Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 5 Memory-I Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would Pre-Requisite
Module 2 Embedded Processors and Memory Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 5 Memory-I Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would Pre-Requisite
RAM & ROM Based Digital Design. ECE 152A Winter 2012
 RAM & ROM Based Digital Design ECE 152A Winter 212 Reading Assignment Brown and Vranesic 1 Digital System Design 1.1 Building Block Circuits 1.1.3 Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) 1.1.4 SRAM Blocks in
RAM & ROM Based Digital Design ECE 152A Winter 212 Reading Assignment Brown and Vranesic 1 Digital System Design 1.1 Building Block Circuits 1.1.3 Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) 1.1.4 SRAM Blocks in
Memory. The memory types currently in common usage are:
 ory ory is the third key component of a microprocessor-based system (besides the CPU and I/O devices). More specifically, the primary storage directly addressed by the CPU is referred to as main memory
ory ory is the third key component of a microprocessor-based system (besides the CPU and I/O devices). More specifically, the primary storage directly addressed by the CPU is referred to as main memory
Table 1: Address Table
 DDR SDRAM DIMM D32PB12C 512MB D32PB1GJ 1GB For the latest data sheet, please visit the Super Talent Electronics web site: www.supertalentmemory.com Features 184-pin, dual in-line memory module (DIMM) Fast
DDR SDRAM DIMM D32PB12C 512MB D32PB1GJ 1GB For the latest data sheet, please visit the Super Talent Electronics web site: www.supertalentmemory.com Features 184-pin, dual in-line memory module (DIMM) Fast
Modeling Sequential Elements with Verilog. Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: jimmy@ee.ncu.edu.tw. Sequential Circuit
 Modeling Sequential Elements with Verilog Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: jimmy@ee.ncu.edu.tw 4-1 Sequential Circuit Outputs are functions of inputs and present states of storage elements
Modeling Sequential Elements with Verilog Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: jimmy@ee.ncu.edu.tw 4-1 Sequential Circuit Outputs are functions of inputs and present states of storage elements
Internal Memory (RAM and ROM) User Guide
 Internal Memory (RAM and ROM) Internal Memory (RAM and ROM) 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com UG-01068-4.3 Feedback Subscribe 2013 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. ALTERA,
Internal Memory (RAM and ROM) Internal Memory (RAM and ROM) 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com UG-01068-4.3 Feedback Subscribe 2013 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. ALTERA,
1. Memory technology & Hierarchy
 1. Memory technology & Hierarchy RAM types Advances in Computer Architecture Andy D. Pimentel Memory wall Memory wall = divergence between CPU and RAM speed We can increase bandwidth by introducing concurrency
1. Memory technology & Hierarchy RAM types Advances in Computer Architecture Andy D. Pimentel Memory wall Memory wall = divergence between CPU and RAM speed We can increase bandwidth by introducing concurrency
Homework # 2. Solutions. 4.1 What are the differences among sequential access, direct access, and random access?
 ECE337 / CS341, Fall 2005 Introduction to Computer Architecture and Organization Instructor: Victor Manuel Murray Herrera Date assigned: 09/19/05, 05:00 PM Due back: 09/30/05, 8:00 AM Homework # 2 Solutions
ECE337 / CS341, Fall 2005 Introduction to Computer Architecture and Organization Instructor: Victor Manuel Murray Herrera Date assigned: 09/19/05, 05:00 PM Due back: 09/30/05, 8:00 AM Homework # 2 Solutions
Chapter 9 Semiconductor Memories. Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan
 Chapter 9 Semiconductor Memories Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 2 Outline Introduction
Chapter 9 Semiconductor Memories Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 2 Outline Introduction
3. Memory Blocks in Arria II Devices
 3. Memory Blocks in Arria II Devices December 2011 AIIGX51003-3.2 AIIGX51003-3.2 This chapter describes the Arria II device memory blocks that include 640-bit memory logic array blocks (MLABs), 9-Kbit
3. Memory Blocks in Arria II Devices December 2011 AIIGX51003-3.2 AIIGX51003-3.2 This chapter describes the Arria II device memory blocks that include 640-bit memory logic array blocks (MLABs), 9-Kbit
Internal Memory (RAM and ROM) User Guide
 Internal Memory (RAM and ROM) Internal Memory (RAM and ROM) 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com UG-01068-5.0 Feedback Subscribe 2014 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. ALTERA,
Internal Memory (RAM and ROM) Internal Memory (RAM and ROM) 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com UG-01068-5.0 Feedback Subscribe 2014 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. ALTERA,
GR2DR4B-EXXX/YYY/LP 1GB & 2GB DDR2 REGISTERED DIMMs (LOW PROFILE)
 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The Gigaram is a 128M/256M bit x 72 DDDR2 SDRAM high density JEDEC standard ECC Registered memory module. The Gigaram consists of eighteen CMOS 128MX4 DDR2 for 1GB and thirty-six CMOS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION The Gigaram is a 128M/256M bit x 72 DDDR2 SDRAM high density JEDEC standard ECC Registered memory module. The Gigaram consists of eighteen CMOS 128MX4 DDR2 for 1GB and thirty-six CMOS
Computer Architecture
 Computer Architecture Random Access Memory Technologies 2015. április 2. Budapest Gábor Horváth associate professor BUTE Dept. Of Networked Systems and Services ghorvath@hit.bme.hu 2 Storing data Possible
Computer Architecture Random Access Memory Technologies 2015. április 2. Budapest Gábor Horváth associate professor BUTE Dept. Of Networked Systems and Services ghorvath@hit.bme.hu 2 Storing data Possible
ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-17: Memory organisation, and types of memory
 ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-17: Memory organisation, and types of memory 1 1. Memory Organisation 2 Random access model A memory-, a data byte, or a word, or a double
ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-17: Memory organisation, and types of memory 1 1. Memory Organisation 2 Random access model A memory-, a data byte, or a word, or a double
Memory unit. 2 k words. n bits per word
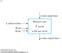 9- k address lines Read n data input lines Memory unit 2 k words n bits per word n data output lines 24 Pearson Education, Inc M Morris Mano & Charles R Kime 9-2 Memory address Binary Decimal Memory contents
9- k address lines Read n data input lines Memory unit 2 k words n bits per word n data output lines 24 Pearson Education, Inc M Morris Mano & Charles R Kime 9-2 Memory address Binary Decimal Memory contents
Features. DDR SODIMM Product Datasheet. Rev. 1.0 Oct. 2011
 Features 200pin, unbuffered small outline dual in-line memory module (SODIMM) Fast data transfer rates: PC-2100, PC-2700, PC3-3200 Single or Dual rank 256MB(32Megx64), 512MB (64Meg x 64), 1GB(128 Meg x
Features 200pin, unbuffered small outline dual in-line memory module (SODIMM) Fast data transfer rates: PC-2100, PC-2700, PC3-3200 Single or Dual rank 256MB(32Megx64), 512MB (64Meg x 64), 1GB(128 Meg x
ECE 451 Verilog Exercises. Sept 14, 2007. James Barnes (James.Barnes@colostate.edu)
 ECE 451 Verilog Exercises Sept 14, 2007 James Barnes (James.Barnes@colostate.edu) Organization These slides give a series of self-paced exercises. Read the specification of each exercise and write your
ECE 451 Verilog Exercises Sept 14, 2007 James Barnes (James.Barnes@colostate.edu) Organization These slides give a series of self-paced exercises. Read the specification of each exercise and write your
Mobile SDRAM. MT48H16M16LF 4 Meg x 16 x 4 banks MT48H8M32LF 2 Meg x 32 x 4 banks
 Features Mobile SDRAM MT48H6M6LF 4 Meg x 6 x 4 banks MT48H8M32LF 2 Meg x 32 x 4 banks Features Fully synchronous; all signals registered on positive edge of system clock V DD /V D =.7.95V Internal, pipelined
Features Mobile SDRAM MT48H6M6LF 4 Meg x 6 x 4 banks MT48H8M32LF 2 Meg x 32 x 4 banks Features Fully synchronous; all signals registered on positive edge of system clock V DD /V D =.7.95V Internal, pipelined
Internal Memory (RAM and ROM) User Guide
 Internal Memory (RAM and ROM) User Guide November 2009 UG-01068-1.0 Introduction Altera provides various internal memory (RAM and ROM) features to address the memory requirements of today's system-on-a-programmable-chip
Internal Memory (RAM and ROM) User Guide November 2009 UG-01068-1.0 Introduction Altera provides various internal memory (RAM and ROM) features to address the memory requirements of today's system-on-a-programmable-chip
ADQYF1A08. DDR2-1066G(CL6) 240-Pin O.C. U-DIMM 1GB (128M x 64-bits)
 General Description ADQYF1A08 DDR2-1066G(CL6) 240-Pin O.C. U-DIMM 1GB (128M x 64-bits) The ADATA s ADQYF1A08 is a 128Mx64 bits 1GB DDR2-1066(CL6) SDRAM over clocking memory module, The SPD is programmed
General Description ADQYF1A08 DDR2-1066G(CL6) 240-Pin O.C. U-DIMM 1GB (128M x 64-bits) The ADATA s ADQYF1A08 is a 128Mx64 bits 1GB DDR2-1066(CL6) SDRAM over clocking memory module, The SPD is programmed
Semiconductor Memories
 Semiconductor Memories Semiconductor memories array capable of storing large quantities of digital information are essential to all digital systems Maximum realizable data storage capacity of a single
Semiconductor Memories Semiconductor memories array capable of storing large quantities of digital information are essential to all digital systems Maximum realizable data storage capacity of a single
1 / 25. CS 137: File Systems. Persistent Solid-State Storage
 1 / 25 CS 137: File Systems Persistent Solid-State Storage Technology Change is Coming Introduction Disks are cheaper than any solid-state memory Likely to be true for many years But SSDs are now cheap
1 / 25 CS 137: File Systems Persistent Solid-State Storage Technology Change is Coming Introduction Disks are cheaper than any solid-state memory Likely to be true for many years But SSDs are now cheap
ECE410 Design Project Spring 2008 Design and Characterization of a CMOS 8-bit Microprocessor Data Path
 ECE410 Design Project Spring 2008 Design and Characterization of a CMOS 8-bit Microprocessor Data Path Project Summary This project involves the schematic and layout design of an 8-bit microprocessor data
ECE410 Design Project Spring 2008 Design and Characterization of a CMOS 8-bit Microprocessor Data Path Project Summary This project involves the schematic and layout design of an 8-bit microprocessor data
Computer Architecture
 Computer Architecture Slide Sets WS 2013/2014 Prof. Dr. Uwe Brinkschulte M.Sc. Benjamin Betting Part 11 Memory Management Computer Architecture Part 11 page 1 of 44 Prof. Dr. Uwe Brinkschulte, M.Sc. Benjamin
Computer Architecture Slide Sets WS 2013/2014 Prof. Dr. Uwe Brinkschulte M.Sc. Benjamin Betting Part 11 Memory Management Computer Architecture Part 11 page 1 of 44 Prof. Dr. Uwe Brinkschulte, M.Sc. Benjamin
Chapter 7 Memory and Programmable Logic
 NCNU_2013_DD_7_1 Chapter 7 Memory and Programmable Logic 71I 7.1 Introduction ti 7.2 Random Access Memory 7.3 Memory Decoding 7.5 Read Only Memory 7.6 Programmable Logic Array 77P 7.7 Programmable Array
NCNU_2013_DD_7_1 Chapter 7 Memory and Programmable Logic 71I 7.1 Introduction ti 7.2 Random Access Memory 7.3 Memory Decoding 7.5 Read Only Memory 7.6 Programmable Logic Array 77P 7.7 Programmable Array
CHAPTER 16 MEMORY CIRCUITS
 CHPTER 6 MEMORY CIRCUITS Chapter Outline 6. atches and Flip-Flops 6. Semiconductor Memories: Types and rchitectures 6.3 Random-ccess Memory RM Cells 6.4 Sense-mplifier and ddress Decoders 6.5 Read-Only
CHPTER 6 MEMORY CIRCUITS Chapter Outline 6. atches and Flip-Flops 6. Semiconductor Memories: Types and rchitectures 6.3 Random-ccess Memory RM Cells 6.4 Sense-mplifier and ddress Decoders 6.5 Read-Only
Technical Note. Initialization Sequence for DDR SDRAM. Introduction. Initializing DDR SDRAM
 TN-46-8: Initialization Sequence for DDR SDRAM Introduction Technical Note Initialization Sequence for DDR SDRAM Introduction The double data rate DDR synchronous dynamic random access memory SDRAM device
TN-46-8: Initialization Sequence for DDR SDRAM Introduction Technical Note Initialization Sequence for DDR SDRAM Introduction The double data rate DDR synchronous dynamic random access memory SDRAM device
Features. DDR3 SODIMM Product Specification. Rev. 1.7 Feb. 2016
 Features DDR3 functionality and operations supported as defined in the component data sheet 204pin, small-outline dual in-line memory module (SODIMM) Fast data transfer rates: DDR3-1066(PC3-8500) DDR3-1333(PC3-10600)
Features DDR3 functionality and operations supported as defined in the component data sheet 204pin, small-outline dual in-line memory module (SODIMM) Fast data transfer rates: DDR3-1066(PC3-8500) DDR3-1333(PC3-10600)
The 104 Duke_ACC Machine
 The 104 Duke_ACC Machine The goal of the next two lessons is to design and simulate a simple accumulator-based processor. The specifications for this processor and some of the QuartusII design components
The 104 Duke_ACC Machine The goal of the next two lessons is to design and simulate a simple accumulator-based processor. The specifications for this processor and some of the QuartusII design components
Qsys and IP Core Integration
 Qsys and IP Core Integration Prof. David Lariviere Columbia University Spring 2014 Overview What are IP Cores? Altera Design Tools for using and integrating IP Cores Overview of various IP Core Interconnect
Qsys and IP Core Integration Prof. David Lariviere Columbia University Spring 2014 Overview What are IP Cores? Altera Design Tools for using and integrating IP Cores Overview of various IP Core Interconnect
Contents. Overview... 5-1 Memory Compilers Selection Guide... 5-2
 Memory Compilers 5 Contents Overview... 5-1 Memory Compilers Selection Guide... 5-2 CROM Gen... 5-3 DROM Gen... 5-9 SPSRM Gen... 5-15 SPSRM Gen... 5-22 SPRM Gen... 5-31 DPSRM Gen... 5-38 DPSRM Gen... 5-47
Memory Compilers 5 Contents Overview... 5-1 Memory Compilers Selection Guide... 5-2 CROM Gen... 5-3 DROM Gen... 5-9 SPSRM Gen... 5-15 SPSRM Gen... 5-22 SPRM Gen... 5-31 DPSRM Gen... 5-38 DPSRM Gen... 5-47
DDR SDRAM SODIMM. MT9VDDT1672H 128MB 1 MT9VDDT3272H 256MB MT9VDDT6472H 512MB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.
 Features DDR SDRAM SODIMM MT9VDDT1672H 128MB 1 MT9VDDT3272H 256MB MT9VDDT6472H 512MB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com Features 200-pin, small-outline dual in-line memory
Features DDR SDRAM SODIMM MT9VDDT1672H 128MB 1 MT9VDDT3272H 256MB MT9VDDT6472H 512MB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com Features 200-pin, small-outline dual in-line memory
With respect to the way of data access we can classify memories as:
 Memory Classification With respect to the way of data access we can classify memories as: - random access memories (RAM), - sequentially accessible memory (SAM), - direct access memory (DAM), - contents
Memory Classification With respect to the way of data access we can classify memories as: - random access memories (RAM), - sequentially accessible memory (SAM), - direct access memory (DAM), - contents
DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM MT16HTF12864H 1GB MT16HTF25664H 2GB
 Features DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM MT16HTF12864H 1GB MT16HTF25664H 2GB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com Features 200-pin, small outline dual in-line memory module (SODIMM)
Features DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM MT16HTF12864H 1GB MT16HTF25664H 2GB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com Features 200-pin, small outline dual in-line memory module (SODIMM)
Table 1 SDR to DDR Quick Reference
 TECHNICAL NOTE TN-6-05 GENERAL DDR SDRAM FUNCTIONALITY INTRODUCTION The migration from single rate synchronous DRAM (SDR) to double rate synchronous DRAM (DDR) memory is upon us. Although there are many
TECHNICAL NOTE TN-6-05 GENERAL DDR SDRAM FUNCTIONALITY INTRODUCTION The migration from single rate synchronous DRAM (SDR) to double rate synchronous DRAM (DDR) memory is upon us. Although there are many
Computer Systems Structure Main Memory Organization
 Computer Systems Structure Main Memory Organization Peripherals Computer Central Processing Unit Main Memory Computer Systems Interconnection Communication lines Input Output Ward 1 Ward 2 Storage/Memory
Computer Systems Structure Main Memory Organization Peripherals Computer Central Processing Unit Main Memory Computer Systems Interconnection Communication lines Input Output Ward 1 Ward 2 Storage/Memory
CS250 VLSI Systems Design Lecture 8: Memory
 CS250 VLSI Systems esign Lecture 8: Memory John Wawrzynek, Krste Asanovic, with John Lazzaro and Yunsup Lee (TA) UC Berkeley Fall 2010 CMOS Bistable 1 0 Flip State 0 1 Cross-coupled inverters used to hold
CS250 VLSI Systems esign Lecture 8: Memory John Wawrzynek, Krste Asanovic, with John Lazzaro and Yunsup Lee (TA) UC Berkeley Fall 2010 CMOS Bistable 1 0 Flip State 0 1 Cross-coupled inverters used to hold
DDR SDRAM SODIMM. MT8VDDT3264H 256MB 1 MT8VDDT6464H 512MB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com
 SODIMM MT8VDDT3264H 256MB 1 MT8VDDT6464H 512MB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com 256MB, 512MB (x64, SR) 200-Pin SODIMM Features Features 200-pin, small-outline dual
SODIMM MT8VDDT3264H 256MB 1 MT8VDDT6464H 512MB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com 256MB, 512MB (x64, SR) 200-Pin SODIMM Features Features 200-pin, small-outline dual
Flash Memories. João Pela (52270), João Santos (55295) December 22, 2008 IST
 Flash Memories João Pela (52270), João Santos (55295) IST December 22, 2008 João Pela (52270), João Santos (55295) (IST) Flash Memories December 22, 2008 1 / 41 Layout 1 Introduction 2 How they work 3
Flash Memories João Pela (52270), João Santos (55295) IST December 22, 2008 João Pela (52270), João Santos (55295) (IST) Flash Memories December 22, 2008 1 / 41 Layout 1 Introduction 2 How they work 3
Lab #5: Design Example: Keypad Scanner and Encoder - Part 1 (120 pts)
 Dr. Greg Tumbush, gtumbush@uccs.edu Lab #5: Design Example: Keypad Scanner and Encoder - Part 1 (120 pts) Objective The objective of lab assignments 5 through 9 are to systematically design and implement
Dr. Greg Tumbush, gtumbush@uccs.edu Lab #5: Design Example: Keypad Scanner and Encoder - Part 1 (120 pts) Objective The objective of lab assignments 5 through 9 are to systematically design and implement
SOLVING HIGH-SPEED MEMORY INTERFACE CHALLENGES WITH LOW-COST FPGAS
 SOLVING HIGH-SPEED MEMORY INTERFACE CHALLENGES WITH LOW-COST FPGAS A Lattice Semiconductor White Paper May 2005 Lattice Semiconductor 5555 Northeast Moore Ct. Hillsboro, Oregon 97124 USA Telephone: (503)
SOLVING HIGH-SPEED MEMORY INTERFACE CHALLENGES WITH LOW-COST FPGAS A Lattice Semiconductor White Paper May 2005 Lattice Semiconductor 5555 Northeast Moore Ct. Hillsboro, Oregon 97124 USA Telephone: (503)
Algorithms and Methods for Distributed Storage Networks 3. Solid State Disks Christian Schindelhauer
 Algorithms and Methods for Distributed Storage Networks 3. Solid State Disks Institut für Informatik Wintersemester 2007/08 Solid State Disks Motivation 2 10 5 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 PRODUCTION
Algorithms and Methods for Distributed Storage Networks 3. Solid State Disks Institut für Informatik Wintersemester 2007/08 Solid State Disks Motivation 2 10 5 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 PRODUCTION
Computers. Hardware. The Central Processing Unit (CPU) CMPT 125: Lecture 1: Understanding the Computer
 Computers CMPT 125: Lecture 1: Understanding the Computer Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 3, 2009 A computer performs 2 basic functions: 1.
Computers CMPT 125: Lecture 1: Understanding the Computer Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 3, 2009 A computer performs 2 basic functions: 1.
Registers & Counters
 Objectives This section deals with some simple and useful sequential circuits. Its objectives are to: Introduce registers as multi-bit storage devices. Introduce counters by adding logic to registers implementing
Objectives This section deals with some simple and useful sequential circuits. Its objectives are to: Introduce registers as multi-bit storage devices. Introduce counters by adding logic to registers implementing
V58C2512(804/404/164)SB HIGH PERFORMANCE 512 Mbit DDR SDRAM 4 BANKS X 16Mbit X 8 (804) 4 BANKS X 32Mbit X 4 (404) 4 BANKS X 8Mbit X 16 (164)
 V58C2512804/404/164SB HIGH PERFORMAE 512 Mbit DDR SDRAM 4 BANKS X 16Mbit X 8 804 4 BANKS X 32Mbit X 4 404 4 BANKS X 8Mbit X 16 164 5 6 75 DDR400 DDR333 DDR266 Clock Cycle Time t CK2.5 6ns 6ns 7.5ns Clock
V58C2512804/404/164SB HIGH PERFORMAE 512 Mbit DDR SDRAM 4 BANKS X 16Mbit X 8 804 4 BANKS X 32Mbit X 4 404 4 BANKS X 8Mbit X 16 164 5 6 75 DDR400 DDR333 DDR266 Clock Cycle Time t CK2.5 6ns 6ns 7.5ns Clock
1.55V DDR2 SDRAM FBDIMM
 1.55V DDR2 SDRAM FBDIMM MT18RTF25672FDZ 2GB 2GB (x72, DR) 240-Pin DDR2 SDRAM FBDIMM Features Features 240-pin, fully buffered DIMM (FBDIMM) Very low-power DDR2 operation Component configuration: 256 Meg
1.55V DDR2 SDRAM FBDIMM MT18RTF25672FDZ 2GB 2GB (x72, DR) 240-Pin DDR2 SDRAM FBDIMM Features Features 240-pin, fully buffered DIMM (FBDIMM) Very low-power DDR2 operation Component configuration: 256 Meg
DDR SDRAM UDIMM MT16VDDT6464A 512MB MT16VDDT12864A 1GB MT16VDDT25664A 2GB
 DDR SDRAM UDIMM MT16VDDT6464A 512MB MT16VDDT12864A 1GB MT16VDDT25664A 2GB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com 512MB, 1GB, 2GB (x64, DR) 184-Pin DDR SDRAM UDIMM Features
DDR SDRAM UDIMM MT16VDDT6464A 512MB MT16VDDT12864A 1GB MT16VDDT25664A 2GB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com 512MB, 1GB, 2GB (x64, DR) 184-Pin DDR SDRAM UDIMM Features
Memory Hierarchy. Arquitectura de Computadoras. Centro de Investigación n y de Estudios Avanzados del IPN. adiaz@cinvestav.mx. MemoryHierarchy- 1
 Hierarchy Arturo Díaz D PérezP Centro de Investigación n y de Estudios Avanzados del IPN adiaz@cinvestav.mx Hierarchy- 1 The Big Picture: Where are We Now? The Five Classic Components of a Computer Processor
Hierarchy Arturo Díaz D PérezP Centro de Investigación n y de Estudios Avanzados del IPN adiaz@cinvestav.mx Hierarchy- 1 The Big Picture: Where are We Now? The Five Classic Components of a Computer Processor
NAND Flash FAQ. Eureka Technology. apn5_87. NAND Flash FAQ
 What is NAND Flash? What is the major difference between NAND Flash and other Memory? Structural differences between NAND Flash and NOR Flash What does NAND Flash controller do? How to send command to
What is NAND Flash? What is the major difference between NAND Flash and other Memory? Structural differences between NAND Flash and NOR Flash What does NAND Flash controller do? How to send command to
User s Manual HOW TO USE DDR SDRAM
 User s Manual HOW TO USE DDR SDRAM Document No. E0234E30 (Ver.3.0) Date Published April 2002 (K) Japan URL: http://www.elpida.com Elpida Memory, Inc. 2002 INTRODUCTION This manual is intended for users
User s Manual HOW TO USE DDR SDRAM Document No. E0234E30 (Ver.3.0) Date Published April 2002 (K) Japan URL: http://www.elpida.com Elpida Memory, Inc. 2002 INTRODUCTION This manual is intended for users
1 Gbit, 2 Gbit, 4 Gbit, 3 V SLC NAND Flash For Embedded
 1 Gbit, 2 Gbit, 4 Gbit, 3 V SLC NAND Flash For Embedded Distinctive Characteristics Density 1 Gbit / 2 Gbit / 4 Gbit Architecture Input / Output Bus Width: 8-bits / 16-bits Page Size: x8 = 2112 (2048 +
1 Gbit, 2 Gbit, 4 Gbit, 3 V SLC NAND Flash For Embedded Distinctive Characteristics Density 1 Gbit / 2 Gbit / 4 Gbit Architecture Input / Output Bus Width: 8-bits / 16-bits Page Size: x8 = 2112 (2048 +
Technical Note DDR2 Offers New Features and Functionality
 Technical Note DDR2 Offers New Features and Functionality TN-47-2 DDR2 Offers New Features/Functionality Introduction Introduction DDR2 SDRAM introduces features and functions that go beyond the DDR SDRAM
Technical Note DDR2 Offers New Features and Functionality TN-47-2 DDR2 Offers New Features/Functionality Introduction Introduction DDR2 SDRAM introduces features and functions that go beyond the DDR SDRAM
Slide Set 8. for ENCM 369 Winter 2015 Lecture Section 01. Steve Norman, PhD, PEng
 Slide Set 8 for ENCM 369 Winter 2015 Lecture Section 01 Steve Norman, PhD, PEng Electrical & Computer Engineering Schulich School of Engineering University of Calgary Winter Term, 2015 ENCM 369 W15 Section
Slide Set 8 for ENCM 369 Winter 2015 Lecture Section 01 Steve Norman, PhD, PEng Electrical & Computer Engineering Schulich School of Engineering University of Calgary Winter Term, 2015 ENCM 369 W15 Section
CHAPTER 7: The CPU and Memory
 CHAPTER 7: The CPU and Memory The Architecture of Computer Hardware, Systems Software & Networking: An Information Technology Approach 4th Edition, Irv Englander John Wiley and Sons 2010 PowerPoint slides
CHAPTER 7: The CPU and Memory The Architecture of Computer Hardware, Systems Software & Networking: An Information Technology Approach 4th Edition, Irv Englander John Wiley and Sons 2010 PowerPoint slides
MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCOMPUTER BASICS
 Introduction MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCOMPUTER BASICS At present there are many types and sizes of computers available. These computers are designed and constructed based on digital and Integrated Circuit
Introduction MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCOMPUTER BASICS At present there are many types and sizes of computers available. These computers are designed and constructed based on digital and Integrated Circuit
Memory Testing. Memory testing.1
 Memory Testing Introduction Memory Architecture & Fault Models Test Algorithms DC / AC / Dynamic Tests Built-in Self Testing Schemes Built-in Self Repair Schemes Memory testing.1 Memory Market Share in
Memory Testing Introduction Memory Architecture & Fault Models Test Algorithms DC / AC / Dynamic Tests Built-in Self Testing Schemes Built-in Self Repair Schemes Memory testing.1 Memory Market Share in
DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM MT8HTF6464HDZ 512MB MT8HTF12864HDZ 1GB. Features. 512MB, 1GB (x64, DR) 200-Pin DDR2 SODIMM. Features
 DDR SDRAM SODIMM MT8HTF6464HDZ 5MB MT8HTF864HDZ GB 5MB, GB (x64, DR) 00-Pin DDR SODIMM Features Features 00-pin, small-outline dual in-line memory module (SODIMM) Fast data transfer rates: PC-300, PC-400,
DDR SDRAM SODIMM MT8HTF6464HDZ 5MB MT8HTF864HDZ GB 5MB, GB (x64, DR) 00-Pin DDR SODIMM Features Features 00-pin, small-outline dual in-line memory module (SODIMM) Fast data transfer rates: PC-300, PC-400,
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design. Part 3: Verilog Tutorial. http://www.ecs.umass.edu/ece/ece232/ Basic Verilog
 ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Part 3: Verilog Tutorial http://www.ecs.umass.edu/ece/ece232/ Basic Verilog module ();
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Part 3: Verilog Tutorial http://www.ecs.umass.edu/ece/ece232/ Basic Verilog module ();
Memory ICS 233. Computer Architecture and Assembly Language Prof. Muhamed Mudawar
 Memory ICS 233 Computer Architecture and Assembly Language Prof. Muhamed Mudawar College of Computer Sciences and Engineering King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Presentation Outline Random
Memory ICS 233 Computer Architecture and Assembly Language Prof. Muhamed Mudawar College of Computer Sciences and Engineering King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Presentation Outline Random
2. Link and Memory Architectures and Technologies
 2. Link and Memory Architectures and Technologies 2.1 Links, Thruput/Buffering, Multi-Access Ovrhds 2.2 Memories: On-chip / Off-chip SRAM, DRAM 2.A Appendix: Elastic Buffers for Cross-Clock Commun. Manolis
2. Link and Memory Architectures and Technologies 2.1 Links, Thruput/Buffering, Multi-Access Ovrhds 2.2 Memories: On-chip / Off-chip SRAM, DRAM 2.A Appendix: Elastic Buffers for Cross-Clock Commun. Manolis
4M x 16Bits x 4Banks Mobile Synchronous DRAM
 4M x 16Bits x 4Banks Mobile Synchronous DRAM Description These IS42/45SM/RM/VM16160K are mobile 268,435,456 bits CMOS Synchronous DRAM organized as 4 banks of 4,194,304 words x 16 bits. These products
4M x 16Bits x 4Banks Mobile Synchronous DRAM Description These IS42/45SM/RM/VM16160K are mobile 268,435,456 bits CMOS Synchronous DRAM organized as 4 banks of 4,194,304 words x 16 bits. These products
MAX II ISP Update with I/O Control & Register Data Retention
 MAX II ISP Update with I/O Control & Register Data Retention March 2006, ver 1.0 Application Note 410 Introduction MAX II devices support the real-time in-system mability (ISP) feature that allows you
MAX II ISP Update with I/O Control & Register Data Retention March 2006, ver 1.0 Application Note 410 Introduction MAX II devices support the real-time in-system mability (ISP) feature that allows you
Modeling Registers and Counters
 Lab Workbook Introduction When several flip-flops are grouped together, with a common clock, to hold related information the resulting circuit is called a register. Just like flip-flops, registers may
Lab Workbook Introduction When several flip-flops are grouped together, with a common clock, to hold related information the resulting circuit is called a register. Just like flip-flops, registers may
Arria 10 Core Fabric and General Purpose I/Os Handbook
 Arria 10 Core Fabric and General Purpose I/Os Handbook Subscribe A10-HANDBOOK 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Logic Array Blocks and Adaptive Logic Modules in Arria 10 Devices
Arria 10 Core Fabric and General Purpose I/Os Handbook Subscribe A10-HANDBOOK 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Logic Array Blocks and Adaptive Logic Modules in Arria 10 Devices
Tuning DDR4 for Power and Performance. Mike Micheletti Product Manager Teledyne LeCroy
 Tuning DDR4 for Power and Performance Mike Micheletti Product Manager Teledyne LeCroy Agenda Introduction DDR4 Technology Expanded role of MRS Power Features Examined Reliability Features Examined Performance
Tuning DDR4 for Power and Performance Mike Micheletti Product Manager Teledyne LeCroy Agenda Introduction DDR4 Technology Expanded role of MRS Power Features Examined Reliability Features Examined Performance
DDR SDRAM SODIMM MT16VDDF6464H 512MB MT16VDDF12864H 1GB
 SODIMM MT16VDDF6464H 512MB MT16VDDF12864H 1GB 512MB, 1GB (x64, DR) 200-Pin DDR SODIMM Features For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com Features 200-pin, small-outline dual
SODIMM MT16VDDF6464H 512MB MT16VDDF12864H 1GB 512MB, 1GB (x64, DR) 200-Pin DDR SODIMM Features For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com Features 200-pin, small-outline dual
DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM MT4HTF6464HZ 512MB. Features. 512MB (x64, SR) 200-Pin DDR2 SODIMM. Features. Figure 1: 200-Pin SODIMM (MO-224 R/C C)
 DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM MT4HTF6464HZ 512MB 512MB (x64, SR) 200-Pin DDR2 SODIMM Features Features 200-pin, small-outline dual in-line memory module (SODIMM) Fast data transfer rates: PC2-3200, PC2-4200, PC2-5300,
DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM MT4HTF6464HZ 512MB 512MB (x64, SR) 200-Pin DDR2 SODIMM Features Features 200-pin, small-outline dual in-line memory module (SODIMM) Fast data transfer rates: PC2-3200, PC2-4200, PC2-5300,
A New Paradigm for Synchronous State Machine Design in Verilog
 A New Paradigm for Synchronous State Machine Design in Verilog Randy Nuss Copyright 1999 Idea Consulting Introduction Synchronous State Machines are one of the most common building blocks in modern digital
A New Paradigm for Synchronous State Machine Design in Verilog Randy Nuss Copyright 1999 Idea Consulting Introduction Synchronous State Machines are one of the most common building blocks in modern digital
Objectives. Units of Memory Capacity. CMPE328 Microprocessors (Spring 2007-08) Memory and I/O address Decoders. By Dr.
 CMPE328 Microprocessors (Spring 27-8) Memory and I/O address ecoders By r. Mehmet Bodur You will be able to: Objectives efine the capacity, organization and types of the semiconductor memory devices Calculate
CMPE328 Microprocessors (Spring 27-8) Memory and I/O address ecoders By r. Mehmet Bodur You will be able to: Objectives efine the capacity, organization and types of the semiconductor memory devices Calculate
Lecture 9: Memory and Storage Technologies
 CS61: Systems Programming and Machine Organization Harvard University, Fall 2009 Lecture 9: Memory and Storage Technologies October 1, 2009 Announcements Lab 3 has been released! You are welcome to switch
CS61: Systems Programming and Machine Organization Harvard University, Fall 2009 Lecture 9: Memory and Storage Technologies October 1, 2009 Announcements Lab 3 has been released! You are welcome to switch
are un-buffered 200-Pin Double Data Rate (DDR) Synchronous DRAM Small Outline Dual In-Line Memory Module (SO-DIMM). All devices
 PC2700 200 pin Unbuffered DDR SO-DIMM Based on DDR333 512Mb bit B Die device Features 200-Pin Small Outline Dual In-Line Memory Module (SO-DIMM) Unbuffered DDR SO-DIMM based on 110nm 512M bit die B device,
PC2700 200 pin Unbuffered DDR SO-DIMM Based on DDR333 512Mb bit B Die device Features 200-Pin Small Outline Dual In-Line Memory Module (SO-DIMM) Unbuffered DDR SO-DIMM based on 110nm 512M bit die B device,
Switch Fabric Implementation Using Shared Memory
 Order this document by /D Switch Fabric Implementation Using Shared Memory Prepared by: Lakshmi Mandyam and B. Kinney INTRODUCTION Whether it be for the World Wide Web or for an intra office network, today
Order this document by /D Switch Fabric Implementation Using Shared Memory Prepared by: Lakshmi Mandyam and B. Kinney INTRODUCTION Whether it be for the World Wide Web or for an intra office network, today
Tuning DDR4 for Power and Performance. Mike Micheletti Product Manager Teledyne LeCroy
 Tuning DDR4 for Power and Performance Mike Micheletti Product Manager Teledyne LeCroy Agenda Introduction DDR4 Technology Expanded role of MRS Power Features Examined Reliability Features Examined Performance
Tuning DDR4 for Power and Performance Mike Micheletti Product Manager Teledyne LeCroy Agenda Introduction DDR4 Technology Expanded role of MRS Power Features Examined Reliability Features Examined Performance
AN1837. Non-Volatile Memory Technology Overview By Stephen Ledford Non-Volatile Memory Technology Center Austin, Texas.
 Order this document by /D Non-Volatile Memory Technology Overview By Stephen Ledford Non-Volatile Memory Technology Center Austin, Texas Introduction Today s microcontroller applications are more sophisticated
Order this document by /D Non-Volatile Memory Technology Overview By Stephen Ledford Non-Volatile Memory Technology Center Austin, Texas Introduction Today s microcontroller applications are more sophisticated
Handout 17. by Dr Sheikh Sharif Iqbal. Memory Unit and Read Only Memories
 Handout 17 by Dr Sheikh Sharif Iqbal Memory Unit and Read Only Memories Objective: - To discuss different types of memories used in 80x86 systems for storing digital information. - To learn the electronic
Handout 17 by Dr Sheikh Sharif Iqbal Memory Unit and Read Only Memories Objective: - To discuss different types of memories used in 80x86 systems for storing digital information. - To learn the electronic
-80E PC2-6400 800 800 533 400 12.5 12.5 55-667 PC2-5300 667 533 400 15 15 55-53E PC2-4200 533 400 15 15 55
 SDRAM FBDIMM MT18HTF12872FDZ 1GB MT18HTF25672FDZ 2GB 1GB, 2GB (x72, DR) 240-Pin SDRAM FBDIMM Features Features 240-pin, fully buffered dual in-line memory module (FBDIMM) Fast data transfer rates: PC2-4200,
SDRAM FBDIMM MT18HTF12872FDZ 1GB MT18HTF25672FDZ 2GB 1GB, 2GB (x72, DR) 240-Pin SDRAM FBDIMM Features Features 240-pin, fully buffered dual in-line memory module (FBDIMM) Fast data transfer rates: PC2-4200,
GETTING STARTED WITH PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC DEVICES, THE 16V8 AND 20V8
 GETTING STARTED WITH PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC DEVICES, THE 16V8 AND 20V8 Robert G. Brown All Rights Reserved August 25, 2000 Alta Engineering 58 Cedar Lane New Hartford, CT 06057-2905 (860) 489-8003 www.alta-engineering.com
GETTING STARTED WITH PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC DEVICES, THE 16V8 AND 20V8 Robert G. Brown All Rights Reserved August 25, 2000 Alta Engineering 58 Cedar Lane New Hartford, CT 06057-2905 (860) 489-8003 www.alta-engineering.com
AN10935 Using SDR/DDR SDRAM memories with LPC32xx
 Rev. 2 11 October 2010 Application note Document information Info Keywords Abstract Content LPC32x0, LPC32xx, LPC3220, LPC3230, LPC3240, LPC3250, SDR, SDRAM, DDR This application note covers hardware related
Rev. 2 11 October 2010 Application note Document information Info Keywords Abstract Content LPC32x0, LPC32xx, LPC3220, LPC3230, LPC3240, LPC3250, SDR, SDRAM, DDR This application note covers hardware related
Introduction to Programmable Logic Devices. John Coughlan RAL Technology Department Detector & Electronics Division
 Introduction to Programmable Logic Devices John Coughlan RAL Technology Department Detector & Electronics Division PPD Lectures Programmable Logic is Key Underlying Technology. First-Level and High-Level
Introduction to Programmable Logic Devices John Coughlan RAL Technology Department Detector & Electronics Division PPD Lectures Programmable Logic is Key Underlying Technology. First-Level and High-Level
DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM MT8HTF12864HZ 1GB MT8HTF25664HZ 2GB. Features. 1GB, 2GB (x64, SR) 200-Pin DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM. Features
 DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM MT8HTF12864HZ 1GB MT8HTF25664HZ 2GB 1GB, 2GB (x64, SR) 200-Pin DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM Features Features 200-pin, small-outline dual in-line memory module (SODIMM) Fast data transfer rates:
DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM MT8HTF12864HZ 1GB MT8HTF25664HZ 2GB 1GB, 2GB (x64, SR) 200-Pin DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM Features Features 200-pin, small-outline dual in-line memory module (SODIMM) Fast data transfer rates:
Memory Module Specifications KVR667D2D8F5/2GI. 2GB 256M x 72-Bit PC2-5300 CL5 ECC 240-Pin FBDIMM DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATIONS
 Memory Module Specifications KVR667DD8F5/GI GB 56M x 7-Bit PC-5300 CL5 ECC 40- FBDIMM DESCRIPTION This document describes s GB (56M x 7-bit) PC-5300 CL5 (Synchronous DRAM) fully buffered ECC dual rank,
Memory Module Specifications KVR667DD8F5/GI GB 56M x 7-Bit PC-5300 CL5 ECC 40- FBDIMM DESCRIPTION This document describes s GB (56M x 7-bit) PC-5300 CL5 (Synchronous DRAM) fully buffered ECC dual rank,
DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM MT8HTF3264HD 256MB MT8HTF6464HD 512MB MT8HTF12864HD 1GB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.
 DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM MT8HTF3264HD 256MB MT8HTF6464HD 512MB MT8HTF12864HD 1GB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com 256MB, 512MB, 1GB (x64, DR): 200-Pin DDR2 SODIMM Features
DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM MT8HTF3264HD 256MB MT8HTF6464HD 512MB MT8HTF12864HD 1GB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com 256MB, 512MB, 1GB (x64, DR): 200-Pin DDR2 SODIMM Features
Chapter 7: Advanced Modeling Techniques
 Chapter 7: Advanced Modeling Techniques Prof. Ming-Bo Lin Department of Electronic Engineering National Taiwan University of Science and Technology Digital System Designs and Practices Using Verilog HDL
Chapter 7: Advanced Modeling Techniques Prof. Ming-Bo Lin Department of Electronic Engineering National Taiwan University of Science and Technology Digital System Designs and Practices Using Verilog HDL
A Dual-Mode NAND Flash Memory: 1-Gb Multilevel and High-Performance 512-Mb Single-Level Modes
 1700 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 36, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 2001 A Dual-Mode NAND Flash Memory: 1-Gb Multilevel and High-Performance 512-Mb Single-Level Modes Taehee Cho, Yeong-Taek Lee, Eun-Cheol
1700 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 36, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 2001 A Dual-Mode NAND Flash Memory: 1-Gb Multilevel and High-Performance 512-Mb Single-Level Modes Taehee Cho, Yeong-Taek Lee, Eun-Cheol
Microprocessor or Microcontroller?
 Microprocessor or Microcontroller? A little History What is a computer? [Merriam-Webster Dictionary] one that computes; specifically : programmable electronic device that can store, retrieve, and process
Microprocessor or Microcontroller? A little History What is a computer? [Merriam-Webster Dictionary] one that computes; specifically : programmable electronic device that can store, retrieve, and process
MICROPROCESSOR BCA IV Sem MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 MICROPROCESSOR BCA IV Sem MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1) Which is the microprocessor comprises: a. Register section b. One or more ALU c. Control unit 2) What is the store by register? a. data b. operands
MICROPROCESSOR BCA IV Sem MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1) Which is the microprocessor comprises: a. Register section b. One or more ALU c. Control unit 2) What is the store by register? a. data b. operands
Random-Access Memory (RAM) The Memory Hierarchy. SRAM vs DRAM Summary. Conventional DRAM Organization. Page 1
 Random-ccess Memor (RM) The Memor Hierarch Topics Storage technologies and trends Localit of reference Caching in the hierarch Ke features RM is packaged as a chip. Basic storage unit is a cell (one bit
Random-ccess Memor (RM) The Memor Hierarch Topics Storage technologies and trends Localit of reference Caching in the hierarch Ke features RM is packaged as a chip. Basic storage unit is a cell (one bit
Memory Systems. Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) Cell
 Memory Systems This chapter begins the discussion of memory systems from the implementation of a single bit. The architecture of memory chips is then constructed using arrays of bit implementations coupled
Memory Systems This chapter begins the discussion of memory systems from the implementation of a single bit. The architecture of memory chips is then constructed using arrays of bit implementations coupled
DDR3 DIMM Slot Interposer
 DDR3 DIMM Slot Interposer DDR3-1867 Digital Validation High Speed DDR3 Digital Validation Passive 240-pin DIMM Slot Interposer Custom Designed for Agilent Logic Analyzers Compatible with Agilent Software
DDR3 DIMM Slot Interposer DDR3-1867 Digital Validation High Speed DDR3 Digital Validation Passive 240-pin DIMM Slot Interposer Custom Designed for Agilent Logic Analyzers Compatible with Agilent Software
Features. DDR3 Unbuffered DIMM Spec Sheet
 Features DDR3 functionality and operations supported as defined in the component data sheet 240-pin, unbuffered dual in-line memory module (UDIMM) Fast data transfer rates: PC3-8500, PC3-10600, PC3-12800
Features DDR3 functionality and operations supported as defined in the component data sheet 240-pin, unbuffered dual in-line memory module (UDIMM) Fast data transfer rates: PC3-8500, PC3-10600, PC3-12800
DDR2 SDRAM FBDIMM MT18HTF12872FD 1GB MT18HTF25672FD 2GB. Features. 1GB, 2GB (x72, DR) 240-Pin DDR2 SDRAM FBDIMM. Features
 SDRAM FBDIMM MT18HTF12872FD 1GB MT18HTF25672FD 2GB 1GB, 2GB (x72, DR) 240-Pin SDRAM FBDIMM Features Features 240-pin, fully buffered dual in-line memory module (FBDIMM) Fast data transfer rates: PC2-4200,
SDRAM FBDIMM MT18HTF12872FD 1GB MT18HTF25672FD 2GB 1GB, 2GB (x72, DR) 240-Pin SDRAM FBDIMM Features Features 240-pin, fully buffered dual in-line memory module (FBDIMM) Fast data transfer rates: PC2-4200,
DS1225Y 64k Nonvolatile SRAM
 DS1225Y 64k Nonvolatile SRAM www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES years minimum data retention in the absence of external power Data is automatically protected during power loss Directly replaces 2k x 8 volatile
DS1225Y 64k Nonvolatile SRAM www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES years minimum data retention in the absence of external power Data is automatically protected during power loss Directly replaces 2k x 8 volatile
Ingar Fredriksen AVR Applications Manager. Tromsø August 12, 2005
 Ingar Fredriksen AVR Applications Manager Tromsø August 12, 2005 Atmel Norway 2005 Atmel Norway 2005 The history of computers Foundation for modern computing 3 An automatic computing machine must have:
Ingar Fredriksen AVR Applications Manager Tromsø August 12, 2005 Atmel Norway 2005 Atmel Norway 2005 The history of computers Foundation for modern computing 3 An automatic computing machine must have:
FLASH TECHNOLOGY DRAM/EPROM. Flash. 1980 1982 1984 1986 1988 1990 1992 1994 1996 Year Source: Intel/ICE, "Memory 1996"
 10 FLASH TECHNOLOGY Overview Flash memory technology is a mix of EPROM and EEPROM technologies. The term flash was chosen because a large chunk of memory could be erased at one time. The name, therefore,
10 FLASH TECHNOLOGY Overview Flash memory technology is a mix of EPROM and EEPROM technologies. The term flash was chosen because a large chunk of memory could be erased at one time. The name, therefore,
Vcc DQ1 DQ2 DQ3 DQ4 Vcc DQ5 DQ6 DQ7 DQ8 NC. NC NC WE# RAS# NC NC A0 A1 A2 A3 Vcc
 TECHNOLOGY INC. MEG x 6 DRAM MT4CM6E5 MT4LCM6E5 FEATURES JEDEC- and industry-standard x6 timing functions pinouts and packages High-performance CMOS silicon-gate process Single power supply (+3.3 ±.3 or
TECHNOLOGY INC. MEG x 6 DRAM MT4CM6E5 MT4LCM6E5 FEATURES JEDEC- and industry-standard x6 timing functions pinouts and packages High-performance CMOS silicon-gate process Single power supply (+3.3 ±.3 or
Fairchild Solutions for 133MHz Buffered Memory Modules
 AN-5009 Fairchild Semiconductor Application Note April 1999 Revised December 2000 Fairchild Solutions for 133MHz Buffered Memory Modules Fairchild Semiconductor provides several products that are compatible
AN-5009 Fairchild Semiconductor Application Note April 1999 Revised December 2000 Fairchild Solutions for 133MHz Buffered Memory Modules Fairchild Semiconductor provides several products that are compatible
Programming NAND devices
 Technical Guide Programming NAND devices Kelly Hirsch, Director of Advanced Technology, Data I/O Corporation Recent Design Trends In the past, embedded system designs have used NAND devices for storing
Technical Guide Programming NAND devices Kelly Hirsch, Director of Advanced Technology, Data I/O Corporation Recent Design Trends In the past, embedded system designs have used NAND devices for storing
