Prevalence and treatment of post partum urinary incontinence
|
|
|
- Philippa Bates
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Norsk Epidemiologi 1997; 7 (1): Prevalence and treatment of post partum urinary incontinence Siv Mørkved, MSc, PT 1,3, and Kari Bø, PhD, PT, PE 2 1. Sør-Trøndelag College, School of Health Education, Nursing and Social Work, Physiotherapy Department, Ranheimsveien 10, 7005 Trondheim, Norway 2. Norwegian Centre for Physiotherapy Research, Box 7009 Majorstua, 0306 Oslo, Norway 3. Correspondence to: Siv Mørkved, College of Sør-Trøndelag, Physiotherapy Department, Ranheimsveien 10, 7005 Trondheim, Norway Telephone Telefax siv.morkved@ahs.hist.no The article is based on a lecture given by the first author at the workshop on "Pelvic Floor and Physiotherapy for Urinary Incontinence" at the International Continence Society's Annual Meeting in Athens, Greece, SUMMARY Childbirth is often considered the main etiological factor in the development of female urinary incontinence (UI). For that reason women in the western countries have been encouraged to engage in post partum pelvic floor muscle (PFM) exercise in order to strengthen the pelvic floor. However, the effect of post partum PFM exercise has been sparsely documented. The aim of this article is to review and discuss literature related to prevalence of post partum UI and effect of post partum PFM exercise in the treatment of UI. The reported prevalence of UI post partum varies from 0.7% to 44%. The variation may be explained by different definitions of UI used in the questionnaires and that the registration of incontinence was done at different intervals after delivery. A few studies have tried to evaluate the effect of post natal PFM exercise. Some have evaluated PFM strength, others the frequency of UI. PFM strength is difficult to measure and the reliability and validity of the methods used is open to question. Another flaw in some of the previous studies is the training protocol applied to improve PFM strength. Mørkved and Bø tried to take into account the above mentioned methodological considerations, in a study aiming to evaluate the effect of post partum PFM exercise. The results demonstrate that post partum PFM exercise is effective in strengthening the PFM and in the treatment of UI. However, success of PFM exercise is dependent upon both the training frequency and intensity. This requires a closer follow up of the post partum women, than the written information that usually serves this purpose at the present time. Key words: physiotherapy, pelvic floor muscles, urinary incontinence, post partum exercise, prevalence INTRODUCTION Female urinary incontinence (UI) is often considered a problem primarily occuring after childbirth. However, Bø et al. (1) and Jolleys (2) have found a prevalence of 31% in young nulliparous women. The prevalence of UI is twice as high in women as in men (3). Prevalence studies of female stress urinary incontinence show a variation from 8% (4) to 52% (5). The variation may be explained by different populations investigated and the use of different definitions of incontinence in the questionnaires. Stress urinary incontinence (SUI) is the type of incontinence most frequently affecting women (6,7). The definition of SUI is involuntary loss of urine occuring during physical exertion (coughing, laughing, exercise) (8). Genuine stress incontinence (GSI) is defined as the involuntary loss of urine which occurs when, in the absence of a detrusor contraction, the intravesical pressure exceeds the maximum uretral pressure (8). Enhørning (9) explained the mechanism behind GSI as descent of the bladder and the urethra during an abrupt rise in intra-abdominal pressure. Normally the ligaments and the pelvic floor muscles (PFM) keep the bladder and the urethra within the intraabdominal cavity. If these supporting tissues are too elastic the urethra may descend. The hypothesis is that hypermobility is caused by weak connective tissue within the pubourethral ligaments (10). Such movement of bladder and urethra has been visualized in incontinent women by ultrasonography (11,12). For a
2 124 S. MØRKVED AND K. BØ short period of time the bladder pressure is higher than the urethral pressure, and leakage may occur. Etiology Age, menopause, connective tissue disorders and overweight is mentioned as etiological factors in the development of SUI (13). However, childbirth is often considered the main etiological factor. SUI after childbirth has been explained as a consequence of peripheral nerve damage (14-16). Snooks et al. (17) followed patients for 5 years and found persistent and impaired pudendal nerve damage. Rupture of muscle fibers and connective tissue and overstretching of supporting ligaments are other risk factors (18,19). Postpartum PFM exercise in the treatment of urinary incontinence As early as 1948 the american gynecologist Arnold Kegel emphasized the value of PFM exercise in restoring function after childbirth (20). Since that time women in the western countries have been encouraged to engage in post partum PFM exercise in order to strengthen the pelvic floor (21). Specialists in women's health care have focused on the role of the PFM in maintaining adequate pelvic support; for example maintaining the position and function of the bladder, uterus and rectum (22). DeLancey (23), Constantinou (24) and Koelbl et al. (11) have all emphazised the important role of the pelvic floor in maintenance of urinary continence. The theory behind PFM exercise in the treatment of SUI is that a strong and fast reflex contraction will clamp the urethra, thereby increasing urethral pressure during an abrupt increase in intra-abdominal pressure. DeLancey (23) has suggested that during PFM contraction the urethra will be pressed against the pubic symphysis, producing a mechanical pressure rise. There is some evidence that the PFM reflex contraction is an anticipatory control mechanism (24). Pre- and postnatal care are fields in which physiotherapists have been engaged both in preventive care and in treatment, in hospitals as well as in the community health service. Instructing women to conduct PFM exercise to rehabilitate the pelvic floor after delivery is one important part of postnatal care. However, the effect of post partum PFM exercise has been sparsely documented. The aim of this article is to review and discuss literature concerning prevalence of post partum UI and effect of post partum PFM exercise in the treatment of UI. METHODS The article is based on papers written in English compiled from computerized searches on Medline from 1983 to 1996, manual searches for articles found in references from this litterature, and a manual search of the proceedings of the International Continence Society. RESULTS Prevalence A higher prevalence of SUI has been demonstrated in parous than in nulliparous women (25-27). Prevalence of urinary incontinence post partum varies from 0.7% (28) to 44% (29). The variation may be explained by different definitions of incontinence used in the questionnaires and that the registration of incontinence was done at different intervals after delivery. The lowest prevalence is reported in studies where incontinence is defined according to the International Continence Society's definition: a condition in which involuntary loss of urine is a social or hygienic problem and is objectively demonstrated (8). Both Stanton et al. (30), Allen & Warell (15) and Sampselle et al. (31) found that the prevalence of SUI rose during pregnancy and then declined after childbirth, indicating that the increased pressure from the growing uterus on the bladder may temporarily cause leakage during pregnancy. When the increased weight disappear after delivery, incontinence may disappear in some women. However, Allen and Warell (15) demonstrated a higher prevalence after delivery than before gestation. Nygaard et al. (25) and Jolleys (2) found a higher prevalence with higher parity and Beck & Hsu (32) reported that the incontinence was progressively worse with successive pregnancies. On the other hand, Thomas et al. (33) could not demonstrate any differences within parity ranges of 1 to 3. However, the prevalence was increased in women having 4 or more children. No longitudinal studies have been conducted. Iosif (34) concluded that onset of incontinence is more often found during the first pregnancy than during subsequent pregnancies. Demonstrating a prevalence of 9% in women delivering with cesarean section, Iosif et al. (35) concluded that the pregnancy itself and hereditary factors may predispose more than parturition trauma in some women. Wilson et al. (36) showed that the mode of delivery, parity, pre-pregnancy BMI and antenatal PFM exercise are significantly related to the prevalence of urinary incontinence three months after delivery. They found that UI appeared to be a very common problem, affecting just over 34% of the women sampled. Effect of post partum PFM exercise In two retrospective studies Spence (37) and Bredsel et al. (38) found the strongest PFM in women performing PFM exercise during pregnancy and after delivery. Gordon and Lounge (39) measured vaginal pressure in 70 women months after delivery. Significant difference between three groups was
3 POST PARTUM URINARY INCONTINENCE 125 found. The group of women performing PFM exercise at the hospital and general physical activity afterwards, showed higher vaginal pressure measurements than women performing PFM at hospital and no following training. The lowest vaginal pressure was found in women not exercising at all. In a prospective study Sleep and Grant (29) used a questionnaire to evaluate prevalence of UI in 1800 women. During a 4 week period, one group had performed intensive PFM exercise and another group had performed the customary PFM training program. The prevalence of UI was similar in both groups 3 months post partum. The training protocols were not standardized in any of the above mentioned studies. Comparing two training groups and a control group, Dougherty et al. (40) found higher improvement in PFM strength in the training groups, than in the control group (N=15). Vaginal palpation and vaginal pressure readings was conducted before (6-17 weeks p.p.) and after (12-32 weeks p.p.) a 6 week training period. However, the difference was not statistically significant. The sample size was small and the standard deviation in vaginal pressure was large. In a prospective study of 83 women, Jonasson et al. (41) used vaginal cones to measure PFM strength in two postnatal groups before and after a training period. The training program was carried out by the women at home for 12 weeks, starting 8 weeks after spontaneous uneventful delivery. A group performing PFM exercise with vaginal cones improved significantly more than a group performing without. However, according to Hahn (42) and Bø (43) the validity of PFM strength measurements by vaginal cones, can be questioned. Neither Dougherty nor Jonasson registered UI. Dumolin et al. (44) assessed PFM strength and reduction of UI in eight women, both before and after attending a physical therapy program. The program consisted of pelvic floor neuromuscular electrostimulation combined with exercises. A 92% increase in vaginal pressure and a significant reduction of UI were measured in the population. A major limitation of the study was the lack of a control group. PFM strength is difficult to measure and the reliability and validity of the methods used is open to question. Bø et al. (45) concluded that an inward movement of the perineum must be visually observable during PFM contraction, in order that the vaginal pressure measurement be considered valid. This criterion has not been applied in previous studies. Another flaw in some of the previous studies is the training protocol applied to improve PFM strength. The general recommendation for strength training is 3 to 4 sets of 8-12 high resistant, close to maximum, slow velocity contractions three times per week (46). In some rehabilitation situations, however, maximum contraction or overload is not possible and more frequent training sessions need to be utilized and are often more desirable. Restoring function after childbirth might be considered such a rehabilitation situation. The results of strength training are specific to the type of contractions being trained. This means that the training situation should reflect the function in which the effect is wanted. The PFM are regular skeletal muscles, consisting of both slow and fast twitch fibers, which also reflects the function of the PFM: Namely to keep the bladder and the urethra within the intraabdominal cavity (11,12) and also to support the bladder and urethra during increased abdominal pressure (24). Aiming to study increase in PFM strength after postpartum PFM exercise, Mørkved and Bø tried to take into account the above mentioned methodological considerations (47). The study group consisted of 66 matched pairs of women. Matching criteria were age, parity and type of delivery. Eight weeks after delivery all women were individually instructed in pelvic floor anatomy and how to contract the PFM correctly. The ability to contract the PFM was controlled by vaginal palpation and observation of the movement of a vaginal balloon catheter during PFM contraction. No observable synergistic contraction of other muscles was accepted. Feedback knowledge of results and performance was provided by the physiotherapist. The training group (TG) followed a specially designed PFM exercise course, based on strength training principles in exercise physiology: The women were training with a physiotherapist in groups of 5-10 participants for 45 minutes once a week for a period of 8 weeks. The physiotherapist encouraged the participants to contract the PFM as hard as possible and to hold each contraction for 6-8 seconds. At the end of each contraction following Bø et al. (49) 3-4 fast contractions were added. In addition they were asked to perform 8 to 12 maximum PFM contractions twice a day at home. Frequency of exercise was recorded in a training diary. Participant motivation was strongly emphasized by the physiotherapist. The control group (CG) received, from the hospital, the customary written postnatal instructions, which included encouragement to perform daily contractions of the PFM. They were not discouraged from performing PFM exercise on their own. PFM strength was measured in both groups the 8th week and the 16th week after delivery. The results demonstrate a significantly greater improvement in PFM strength measured by vaginal pressure, in the TG compared to the CG. The results also indicate that the success of post partum PFM exercise is dependent upon the training frequency and intensity. Thorough instruction and measurement of improvement might be important key factors in motivation and adherence to training. Written or verbal instructions with no clinical assessment seems to have little effect. Mørkved and Bø also evaluated the effect of postpartum PFM exercise in prevention and treatment of UI. Preliminary results demonstrate a significantly greater reduction in prevalence of UI in a training group compared to a control group (49).
4 126 S. MØRKVED AND K. BØ CONCLUSION Prevalence of UI is higher among parous than nulliparous women and vaginal delivery is considered a main factor in the etiology of UI. Nevertheless, further work needs to be done enquiring about the onset and duration of incontinence. The effect of post partum PFM exercise in prevention and treatment of UI has been sparsely documented. However, a recent Norwegian study shows that post partum PFM exercise is effective in strengthening the PFM and in treatment of UI. Success of PFM exercise is dependent upon both the training frequency and intensity. This requires a closer follow up of the post partum women, than the written information which usually serves this purpose at the present time. It is essential that future services for women after childbirth should be organized according to results from controlled clinical trials. REFERENCES 1. Bø K, Mæhlum S, Oseid S, Larsen S. Prevalence of stress urinary incontinence among physically active and sedentary female students. Scand J Sports Sci 1989; 11 (3): Jolleys JV. Reported prevalence of uinary incontinence among women in a general practice. Br Med J 1988; 296: National Institutes of Health. Urinary incontinence in adults. Washington, DC: Medical Applications of Research. National Institutes of Health 1988: 7: Iosif S, Henriksson L, Ulmsten U. The frequency of disorders of the lower urinary tract, urinary incontinence in particular, as evaluated by a questionnaire survey in a gynaecological health control population. Acta Obstet Gynecol 1981; 60: Nemir A, Middleton RP. Stress incontinence in young nulliparous women. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1954; 68: Fall M, Frankenberg S, Frisen M, Larson B, Petren M svenskar kan ha urininkontinens. Endast var fjärde söker hjälp för besvären. Läkartidningen 1985: 82: Hørding U, Pederssen KH, Sidenius K, Hedegaard L. Urinary incontinence in 45-year-old women. Scand J Urol Nephrol 1986: 20: Abrams P, Blavias JG, Stanton SL, Andersen JT. The standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function. Scand J Urol Nephrol 1988: Suppl 114: Enhørning G. Simultaneous recording of intravesical and intra-urethral pressure. Acta Chir Scand 1961: 276 (Suppl): Ulmsten U, Ekman G, Giertz G, Malmstrøm A. Different biochemical composition of connective tissue in continent and stress incontinent women. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1987; 66: Koelbl H, Bernascheck G, Wolf G. A comparative study of perineal ultrasound scanning and urethrocystography in patients with genuine stress incontinence. Arch Gynecol Obstet 1988; 244: Hanzal E, Berger E, Koelbl H. Levator ani muscle morphology and recurrent genuine stress incontinence. Obstet Gynecol 1993; 81: Bø K. Stress urinary incontinence, physical activity and pelvic floor muscle strength training. Scand J Med Sci Sports 1992; 2: Snooks SJ, Setchell M, Swash M, Henry MM. Injury to innervation of pelvic floor sphincter musculature in childbirth. Lancet 1984 (Sept 8): Allen RE, Warell D. The role of pregnancy and childbirth in partial denervation of the pelvic floor. Neurourol Urodyn 1987; 6: Allen RE, Hosker GL, Smith ARB, Warell DW. Pelvic floor damage and childbirth: a neurophysiological study. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1990; 97: Snooks SJ, Swash M, Mathers SE, Henry MM. Effect of vaginal delivery on the pelvic floor: a five year follow up. Br J Surg 1990; 77: Sayer TR, Dixon JS, Hosker GL, Warell DW. A study of periurethral connective tissue in women with stress incontinence of urine. Neurourol Urodyn 1990; 9: Landon CR, Crofts CE, Smith ARB, Trowbridge EA. Mechanical properties of facia during pregnancy: a possible factor in the development of stress incontinence of urine. Contemp Rev Obstet Gynaecol 1990; 2: Kegel AH. Progressive resistance exercise in the functional restoration of the perineal muscles. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1948; 56: Polden M, Mantle J. Physiotherapy in Obstetrics and Gynaecology. Butterworth & Heinemann, Nichols DH, Milley PS. Functional pelvic anatomy: the soft tissue supports and spaces of the female pelvic organs. Reprod Med 1978; 2:
5 POST PARTUM URINARY INCONTINENCE DeLancey JOL. Anatomy and mechanics of structures around the vesical neck: how vesical neck position might affect its closure. Neurourol Urodyn 1988; 7 (3): Constantinou CE, Govan DE. Contribution and timing of transmitted and generated pressure components in the female urethra. In: Female Incontinence. New York: Allan R. Liss, 1981: Nygaard I, DeLancey JOL, Arnsdorf L, Murphy E. Exercise and incontinence. Obstet Gynecol 1990: 75: Thomas TM, Plymath KT, Blannin J, Meade TW. Prevalence of urinary incontinence. Br Med J 1980: 281: Sommer P, Bauer T, Nielsen KK, Kristensen ES, Hermann GG, Steven K, Nordling J. Voiding patterns and prevalence of incontinence in women. A questionnaire survey. Br J Urol 1990: 66: Viktrup L, Lose G, Rolf M, Barfoed K. The frequency of urinary symptoms during pregnancy and puerperium in the primipara. Int Urogynecol J 1993; 4: Sleep J, Grant A. Pelvic floor exercises in postnatal care. Midwifery 1987; 3: Stanton SL, Kerr-Wilson R, Harris VG. The incidence of urological symptoms in normal pregnancy. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1980; 87: Sampselle CM, DeLancey JOL, Ashton-Miller J. Neurourol Urodyn 1996; 15 (4): Beck KP, Hsu N. Pregnancy, childbirth, and the menopause related to the development of stress incontinence. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1965; 91: Thomas TM, Plymath KT, Blannin J, Meade TW. Prevalence of urinary incontinence. Br Med J 1980; 281: Iosif S. Stress incontinence during pregnancy and puerperium. Int J Gynecol Obstet 1981; 19: Iosif S, Ingemarsson I. Prevalence of stress incontinence among women delivered by elective cesarean section. Int J Gynecol Obstet 1983; 20: Wilson PD, Herbison RM, Herbison GP. Obstetric practice and the prevalence of urinary incontinence three months after delivery. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1996; 103: Spence M. Postnatal survey. Aust J Physiother 1978; 3: Brendsel C, Peterson G, Mehl LE. Routine epistiotomi and pelvic symptomatology. Women & Health 1980; 5 (4): Gordon H, Lounge M. Perineal muscle function after childbirth. Lancet 1985; ii: Dougherty M, Bishop KR, Abrams RM, Batich CD, Gimotty PA. The effect of exercise on the circumvaginal muscles in postpartum women. J Nurse Midwifery 1989; 34 (1): Jonasson A, Larsson B, Pschera H. Testing and training of the pelvic floor muscles after childbirth. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1989; 68: Hahn I. Pelvic floor training for genuine stress incontinence. Evaluation and long term results. Doctoral Thesis, Departement of Surgery and Departement of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Gothenburg, Gothenburg, Sweden, Bø K. Vaginal weight cones. Theoretical framework, effect on pelvic floor muscle strength and female stress urinary incontinence. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1995; 74: Dumoulin C, Seaborne DE, Quirion-DeGirardi C, Sullivan SJ. Pelvic-floor rehabilitation, Part 2. Phys Ther 1995; 75 (12): Bø K, Hagen RH, Kvarstein B, Larsen S. Pelvic floor muscle exercise for the treatment of female stress urinary incontinence II. Validity of vaginal pressure measurements of pelvic floor muscle strength. The necessity of supplementary methods for control of correct contraction. Neurourol Urodyn 1990; 9: DiNubile NA. Strength training. Clin Sports Med 1991; 10 (1): Mørkved S, Bø K. The effect of post-natal exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1996; 76: Bø K, Hagen RH, Kvarstein B, Jørgensen J, Larsen S. Pelvic floor muscle exercise for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence III. Effects on two different degrees of pelvic floor muscle exercises. Nerourol Urodyn 1990; 9: Mørkved S, Bø K. The effect of post-natal exercises in the treatment of urinary incontinence. Neurourol Urodyn 1996; 15:
Effects of Pregnancy & Delivery on Pelvic Floor
 Effects of Pregnancy & Delivery on Pelvic Floor 吳 銘 斌 M.D., Ph.D. 財 團 法 人 奇 美 醫 院 婦 產 部 婦 女 泌 尿 暨 骨 盆 醫 學 科 ; 台 北 醫 學 大 學 醫 學 院 婦 產 學 科 ; 古 都 府 城 台 南 Introduction Pelvic floor disorders (PFDs) include
Effects of Pregnancy & Delivery on Pelvic Floor 吳 銘 斌 M.D., Ph.D. 財 團 法 人 奇 美 醫 院 婦 產 部 婦 女 泌 尿 暨 骨 盆 醫 學 科 ; 台 北 醫 學 大 學 醫 學 院 婦 產 學 科 ; 古 都 府 城 台 南 Introduction Pelvic floor disorders (PFDs) include
Urinary incontinence symptoms during and after pregnancy in continent and incontinent primiparas
 Int Urogynecol J DOI 10.1007/s00192-006-0124-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Angela D. Thomason. Janis M. Miller. John OL DeLancey Urinary incontinence symptoms during and after pregnancy in continent and incontinent
Int Urogynecol J DOI 10.1007/s00192-006-0124-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Angela D. Thomason. Janis M. Miller. John OL DeLancey Urinary incontinence symptoms during and after pregnancy in continent and incontinent
CHAPTER 7. Summary and conclusions
 CHAPTER 7 Summary and conclusions 88 Summary 7.1 SUMMARY 7.1.1 Introduction 7.1.1.1 Incontinence in pregnancy and after childbirth Pelvic floor dysfunction in women is a major health problem. Symptoms
CHAPTER 7 Summary and conclusions 88 Summary 7.1 SUMMARY 7.1.1 Introduction 7.1.1.1 Incontinence in pregnancy and after childbirth Pelvic floor dysfunction in women is a major health problem. Symptoms
UNREPORTED URINARY AND ANAL INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN
 Original Article UNREPORTED URINARY AND ANAL INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN Humera Ansar, Fauzia Adil and Aftab A. Munir ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE: To know the occurrence of unreported urinary and anal incontinence in
Original Article UNREPORTED URINARY AND ANAL INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN Humera Ansar, Fauzia Adil and Aftab A. Munir ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE: To know the occurrence of unreported urinary and anal incontinence in
Women suffer in silence
 Women suffer in silence Stress urinary incontinence is the involuntary loss of urine resulting from increased intra-abdominal pressure. In people who suffer with this condition, forms of exertion such
Women suffer in silence Stress urinary incontinence is the involuntary loss of urine resulting from increased intra-abdominal pressure. In people who suffer with this condition, forms of exertion such
Title Page Stress incontinence 4 years postdelivery 1
 Title Page Stress incontinence 4 years postdelivery 1 Stress a Authors: retrospective urinary incontinence cohort Arnaud Xavier survey Fritel, Fauconnier, four MD years after the first delivery: Institution:
Title Page Stress incontinence 4 years postdelivery 1 Stress a Authors: retrospective urinary incontinence cohort Arnaud Xavier survey Fritel, Fauconnier, four MD years after the first delivery: Institution:
symptoms of Incontinence
 Types, causes and symptoms of Urinary Incontinence Aims and Objectives Aim: To have an understanding of the types and causes of urinary incontinence. Objectives: To be aware of the incidence and prevalence
Types, causes and symptoms of Urinary Incontinence Aims and Objectives Aim: To have an understanding of the types and causes of urinary incontinence. Objectives: To be aware of the incidence and prevalence
Does vaginal closure force differ in the supine and standing positions?
 American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology (2005) 192, 1722 8 www.ajog.org Does vaginal closure force differ in the supine and standing positions? Daniel M. Morgan, MD, a, * Gurpreet Kaur, BS, a Yvonne
American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology (2005) 192, 1722 8 www.ajog.org Does vaginal closure force differ in the supine and standing positions? Daniel M. Morgan, MD, a, * Gurpreet Kaur, BS, a Yvonne
URINARY INCONTINENCE CASE PRESENTATION #1. Urinary Incontinence - History 2014/10/07. Structure of the Female Lower Urinary Tract
 Bladder pressure 2014/10/07 Structure of the Female Lower Urinary Tract Ureter URINARY INCONTINENCE Clinical Clerkship Lecture Series Outer peritoneal coat Detrusor smooth muscle Mucosa Trigone Proximal
Bladder pressure 2014/10/07 Structure of the Female Lower Urinary Tract Ureter URINARY INCONTINENCE Clinical Clerkship Lecture Series Outer peritoneal coat Detrusor smooth muscle Mucosa Trigone Proximal
Stress Urinary Incontinence
 Saint Mary s Hospital Gynaecology Service Warrell Unit Stress Urinary Incontinence Information for patients What is Stress Incontinence? Stress incontinence is a leakage of urine occurring on physical
Saint Mary s Hospital Gynaecology Service Warrell Unit Stress Urinary Incontinence Information for patients What is Stress Incontinence? Stress incontinence is a leakage of urine occurring on physical
Urinary Incontinence after Vaginal Delivery or Cesarean Section
 The new england journal of medicine original article Urinary after Vaginal Delivery or Cesarean Section Guri Rortveit, M.D., Anne Kjersti Daltveit, Ph.D., Yngvild S. Hannestad, M.D., and Steinar Hunskaar,
The new england journal of medicine original article Urinary after Vaginal Delivery or Cesarean Section Guri Rortveit, M.D., Anne Kjersti Daltveit, Ph.D., Yngvild S. Hannestad, M.D., and Steinar Hunskaar,
A Physical Therapist s Perspective
 You Can Do Something About INCONTINENCE A Physical Therapist s Perspective American Physical Therapy Association 1 You Can Do Something About Urinary Incontinence Incontinence, involuntary loss of bladder
You Can Do Something About INCONTINENCE A Physical Therapist s Perspective American Physical Therapy Association 1 You Can Do Something About Urinary Incontinence Incontinence, involuntary loss of bladder
Urinary Incontinence (Involuntary Loss of Urine) A Patient Guide
 Urinary Incontinence (Involuntary Loss of Urine) A Patient Guide Urinary Incontinence (Urine Loss) This booklet is intended to give you some facts on urinary incontinence - what it is, and is not, and
Urinary Incontinence (Involuntary Loss of Urine) A Patient Guide Urinary Incontinence (Urine Loss) This booklet is intended to give you some facts on urinary incontinence - what it is, and is not, and
1 in 3 women experience Stress Urinary Incontinence.
 A PATIENT S GUIDE 1 in 3 women experience Stress Urinary Incontinence. It s time to talk about SUI Get the facts. This Patient s Guide is intended as a public resource on the issue of Stress Urinary Incontinence
A PATIENT S GUIDE 1 in 3 women experience Stress Urinary Incontinence. It s time to talk about SUI Get the facts. This Patient s Guide is intended as a public resource on the issue of Stress Urinary Incontinence
GENUINE STRESS AND URGE INCONTINENCE PROTOCOL
 GENUINE STRESS AND URGE INCONTINENCE PROTOCOL Using the NeuroTrac ETSTM in combination of electrostimulation and EMG Biofeedback in the treatment of female urinary incontinence. Anna Pawlaczyk Specialist
GENUINE STRESS AND URGE INCONTINENCE PROTOCOL Using the NeuroTrac ETSTM in combination of electrostimulation and EMG Biofeedback in the treatment of female urinary incontinence. Anna Pawlaczyk Specialist
Female Urinary Disorders and Pelvic Organ Prolapse
 Female Urinary Disorders and Pelvic Organ Prolapse Richard S. Bercik, M.D. Director, Division of Urogynecology & Reconstruction Pelvic Surgery Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive Sciences
Female Urinary Disorders and Pelvic Organ Prolapse Richard S. Bercik, M.D. Director, Division of Urogynecology & Reconstruction Pelvic Surgery Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive Sciences
Mixed urinary incontinence - sling or not sling
 Mixed urinary incontinence - sling or not sling 吳 銘 斌 Ming-Ping Wu, M.D.,Ph.D. Director, Div. Urogynecology & Pelvic Floor Reconstruction, Chi Mei Foundation Hospital, Tainan, Taiwan Assistant Professor,
Mixed urinary incontinence - sling or not sling 吳 銘 斌 Ming-Ping Wu, M.D.,Ph.D. Director, Div. Urogynecology & Pelvic Floor Reconstruction, Chi Mei Foundation Hospital, Tainan, Taiwan Assistant Professor,
Urinary incontinence during pregnancy
 Urinary incontinence during pregnancy Stian Langeland Wesnes 1,2 MD, Guri Rortveit 2,3 MD PhD, Kari Bø 4 PT PhD, Steinar Hunskaar 2 MD PhD Bergen, Norway From 1 Department of medicine, Haugesund Hospital,
Urinary incontinence during pregnancy Stian Langeland Wesnes 1,2 MD, Guri Rortveit 2,3 MD PhD, Kari Bø 4 PT PhD, Steinar Hunskaar 2 MD PhD Bergen, Norway From 1 Department of medicine, Haugesund Hospital,
Urinary incontinence poses major medical
 ONE SIZE DOES NOT FIT ALL: MANAGEMENT OF THE DIFFICULT PATIENT * Karl J. Kreder, Jr, MD ABSTRACT Although the prevalence of urinary incontinence varies greatly depending on the criteria used to define
ONE SIZE DOES NOT FIT ALL: MANAGEMENT OF THE DIFFICULT PATIENT * Karl J. Kreder, Jr, MD ABSTRACT Although the prevalence of urinary incontinence varies greatly depending on the criteria used to define
Urinary incontinence during sexual intercourse: a common, but rarely volunteered, symptom
 British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology April 1988, Vol. 95, pp. 77-81 Urinary incontinence during sexual intercourse: a common, but rarely volunteered, symptom PAUL HILTON Summary. A total of 4
British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology April 1988, Vol. 95, pp. 77-81 Urinary incontinence during sexual intercourse: a common, but rarely volunteered, symptom PAUL HILTON Summary. A total of 4
VAGINAL TAPE PROCEDURES FOR THE TREATMENT OF STRESS INCONTINENCE
 VAGINAL TAPE PROCEDURES FOR THE TREATMENT OF STRESS INCONTINENCE AN INFORMATION LEAFLET Written by: Department of Urology May 2011 Stockport: 0161 419 5698 Website: w w w. s t o c k p o r t. n h s. u k
VAGINAL TAPE PROCEDURES FOR THE TREATMENT OF STRESS INCONTINENCE AN INFORMATION LEAFLET Written by: Department of Urology May 2011 Stockport: 0161 419 5698 Website: w w w. s t o c k p o r t. n h s. u k
Classification of Mixed Incontinence
 european urology supplements 5 (2006) 837 841 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Classification of Mixed Incontinence Christopher Chapple * Sheffield Hallam University,
european urology supplements 5 (2006) 837 841 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Classification of Mixed Incontinence Christopher Chapple * Sheffield Hallam University,
URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN
 URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN Definition Urinary incontinence (UI) is defined as involuntary loss of urine that is a social or hygienic problem (International Continence Society, 1973) Magnitude of the
URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN Definition Urinary incontinence (UI) is defined as involuntary loss of urine that is a social or hygienic problem (International Continence Society, 1973) Magnitude of the
Stress incontinence. Supported by an unrestricted grant from
 Stress incontinence As a health care provider you can make a significant difference to the quality of life of patients like these by addressing urinary incontinence, introducing conservative therapies
Stress incontinence As a health care provider you can make a significant difference to the quality of life of patients like these by addressing urinary incontinence, introducing conservative therapies
Clinical audit of the use of tension-free vaginal tape as a surgical treatment for urinary stress incontinence, set against NICE guidelines
 GYNAECOLOGY Clinical audit of the use of tension-free vaginal tape as a surgical treatment for urinary stress incontinence, set against NICE guidelines NATALIA PRICE and SIMON R JACKSON The John Radcliffe
GYNAECOLOGY Clinical audit of the use of tension-free vaginal tape as a surgical treatment for urinary stress incontinence, set against NICE guidelines NATALIA PRICE and SIMON R JACKSON The John Radcliffe
Physiotherapy for Persistent Postnatal Stress Urinary Incontinence: A Randomized Controlled Trial
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Physiotherapy for Persistent Postnatal Stress Urinary Incontinence: A Randomized Controlled Trial Chantale Dumoulin, PhD, PT, Marie-Claude Lemieux, MD, FRCSC, Daniel Bourbonnais, PhD,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Physiotherapy for Persistent Postnatal Stress Urinary Incontinence: A Randomized Controlled Trial Chantale Dumoulin, PhD, PT, Marie-Claude Lemieux, MD, FRCSC, Daniel Bourbonnais, PhD,
ARTICLE IN PRESS Maturitas xxx (2010) xxx xxx
 Maturitas xxx (2010) xxx xxx Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Maturitas journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/maturitas Review Pelvic floor exercise for urinary incontinence: A systematic
Maturitas xxx (2010) xxx xxx Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Maturitas journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/maturitas Review Pelvic floor exercise for urinary incontinence: A systematic
Bard: Continence Therapy. Stress Urinary Incontinence. Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle.
 Bard: Continence Therapy Stress Urinary Incontinence Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle. Stress Urinary Incontinence Becoming knowledgeable about urinary incontinence Uterus Normal Pelvic Anatomy
Bard: Continence Therapy Stress Urinary Incontinence Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle. Stress Urinary Incontinence Becoming knowledgeable about urinary incontinence Uterus Normal Pelvic Anatomy
Low Back Pain and Urinary Incontinence. Mary Ka Mei LEUNG Physiotherapist Kwong Wah Hospital Hong Kong SAR, China
 Low Back Pain and Urinary Incontinence Mary Ka Mei LEUNG Physiotherapist Kwong Wah Hospital Hong Kong SAR, China Hong Kong Background Prevalence of LBP in HK 39%: LBP at some time 21%: LBP in the past
Low Back Pain and Urinary Incontinence Mary Ka Mei LEUNG Physiotherapist Kwong Wah Hospital Hong Kong SAR, China Hong Kong Background Prevalence of LBP in HK 39%: LBP at some time 21%: LBP in the past
Beverly E Hashimoto, M.D. Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA
 Pelvic Floor Relaxation Beverly E Hashimoto, M.D. Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA Disclosures Beverly Hashimoto: GE Medical Systems: research support and consultant (all fees given to Virginia
Pelvic Floor Relaxation Beverly E Hashimoto, M.D. Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA Disclosures Beverly Hashimoto: GE Medical Systems: research support and consultant (all fees given to Virginia
Stress Urinary Incontinence & The Pelvis
 Stress Urinary Incontinence & The Pelvis Updated January 2011 by Diane Lee Introduction The research in the last decade has led to a clearer understanding of how load is transferred through the low back
Stress Urinary Incontinence & The Pelvis Updated January 2011 by Diane Lee Introduction The research in the last decade has led to a clearer understanding of how load is transferred through the low back
The effect of home biofeedback training on stress incontinence
 Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2004: 83: 973 977 Copyright # Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2004 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica ORIGINAL ARTICLE The effect
Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2004: 83: 973 977 Copyright # Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2004 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica ORIGINAL ARTICLE The effect
Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet
 Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet Are you reluctant to talk to your doctor about your bladder control problem? Don t be. There is help. Loss of bladder control is called urinary incontinence. It can happen
Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet Are you reluctant to talk to your doctor about your bladder control problem? Don t be. There is help. Loss of bladder control is called urinary incontinence. It can happen
Patient. Frequently Asked Questions. Transvaginal Surgical Mesh for Pelvic Organ Prolapse
 Patient Frequently Asked Questions Transvaginal Surgical Mesh for Pelvic Organ Prolapse Frequently Asked Questions WHAT IS PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE AND HOW IS IT TREATED? Q: What is pelvic organ prolapse
Patient Frequently Asked Questions Transvaginal Surgical Mesh for Pelvic Organ Prolapse Frequently Asked Questions WHAT IS PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE AND HOW IS IT TREATED? Q: What is pelvic organ prolapse
PROCEEDINGS INCIDENCE AND PREVALENCE OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE * Ananias C. Diokno, MD ABSTRACT
 INCIDENCE AND PREVALENCE OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE * Ananias C. Diokno, MD ABSTRACT Urinary incontinence is a worldwide problem that affects millions of women, although the magnitude of the problem
INCIDENCE AND PREVALENCE OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE * Ananias C. Diokno, MD ABSTRACT Urinary incontinence is a worldwide problem that affects millions of women, although the magnitude of the problem
What you should know about Stress Urinary Incontinence
 Gynecare TVT Stop coping. Start living. What you should know about Stress Urinary Incontinence Have you ever leaked urine when you laughed, coughed or sneezed? You are not alone. Many women suffer from
Gynecare TVT Stop coping. Start living. What you should know about Stress Urinary Incontinence Have you ever leaked urine when you laughed, coughed or sneezed? You are not alone. Many women suffer from
Bladder Injury during Cesarean Section: A Case Control Study for 10 Years
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol., No., September Bladder Injury during Cesarean Section: A Case Control Study for Years Mesfer Al-Shahrani, MD, FRCSC* Objective: To determine the incidence, risk factors
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol., No., September Bladder Injury during Cesarean Section: A Case Control Study for Years Mesfer Al-Shahrani, MD, FRCSC* Objective: To determine the incidence, risk factors
Can the Preoperative Value of VLPP and MUCP Predict the Postoperative Quality of Life?
 42) Can the Preoperative Value of VLPP and MUCP Predict the Postoperative Quality of Life? Drahorádová P. 1, Mašata J. 1, Martan A. 1, Švabík K. 1, Pavlíková M. 2 1 Charles University in Prague, 1st Medical
42) Can the Preoperative Value of VLPP and MUCP Predict the Postoperative Quality of Life? Drahorádová P. 1, Mašata J. 1, Martan A. 1, Švabík K. 1, Pavlíková M. 2 1 Charles University in Prague, 1st Medical
Urinary Incontinence. Anatomy and Terminology Overview. Moeen Abu-Sitta, MD, FACOG, FACS
 Urinary Incontinence Anatomy and Terminology Overview Moeen Abu-Sitta, MD, FACOG, FACS Purpose Locate and describe the anatomy of the Female Urinary System Define terminology related to Incontinence Describe
Urinary Incontinence Anatomy and Terminology Overview Moeen Abu-Sitta, MD, FACOG, FACS Purpose Locate and describe the anatomy of the Female Urinary System Define terminology related to Incontinence Describe
Normal bladder function requires a coordinated effort between the brain, spinal cord, and the bladder.
 .. Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is not an inevitable part of aging, and it is not a disease. The loss of bladder control - called urinary incontinence - affects between 13 and 17 million adult
.. Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is not an inevitable part of aging, and it is not a disease. The loss of bladder control - called urinary incontinence - affects between 13 and 17 million adult
Urinary Continence. Second edition FAST FACTS. by Julian Shah and Gary Leach. Anatomy and physiology 7. Investigations and diagnosis 11
 FAST FACTS Urinary Continence Second edition Indispensable Guides to by Julian Shah and Gary Leach Clinical Practice Anatomy and physiology 7 Investigations and diagnosis 11 Detrusor instability 28 Primary
FAST FACTS Urinary Continence Second edition Indispensable Guides to by Julian Shah and Gary Leach Clinical Practice Anatomy and physiology 7 Investigations and diagnosis 11 Detrusor instability 28 Primary
Urinary Incontinence Dr. Leffler
 Urinary Incontinence Dr. Leffler The involuntary loss of urine at socially unacceptable times occurs in both women and men, but more commonly in women. It has multiple, far-reaching effects on daily activities,
Urinary Incontinence Dr. Leffler The involuntary loss of urine at socially unacceptable times occurs in both women and men, but more commonly in women. It has multiple, far-reaching effects on daily activities,
Transobturator tape sling Female sling system
 Transobturator tape sling Female sling system Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Transobturator tape sling Female sling system Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Urinary Incontinence in Women. Susan Hingle, M.D. Department of Medicine
 Urinary Incontinence in Women Susan Hingle, M.D. Department of Medicine Background Estimated 13 million Americans with urinary incontinence Women are affected twice as frequently as men Only 25% will seek
Urinary Incontinence in Women Susan Hingle, M.D. Department of Medicine Background Estimated 13 million Americans with urinary incontinence Women are affected twice as frequently as men Only 25% will seek
Prevalence of Stress Urinary Incontinence in Elite Female Endurance Athletes
 Journal of Human Kinetics volume 44/2014, 91-96 DOI: 10.2478/hukin-2014-0114 91 Section II Exercise Physiology & Sports Medicine Prevalence of Stress Urinary Incontinence in Elite Female Endurance Athletes
Journal of Human Kinetics volume 44/2014, 91-96 DOI: 10.2478/hukin-2014-0114 91 Section II Exercise Physiology & Sports Medicine Prevalence of Stress Urinary Incontinence in Elite Female Endurance Athletes
Case Based Urology Learning Program
 Case Based Urology Learning Program Resident s Corner: UROLOGY Case Number 21 CBULP 2011 068 Case Based Urology Learning Program Editor: Associate Editors: Manager: Case Contributors: Steven C. Campbell,
Case Based Urology Learning Program Resident s Corner: UROLOGY Case Number 21 CBULP 2011 068 Case Based Urology Learning Program Editor: Associate Editors: Manager: Case Contributors: Steven C. Campbell,
The Effect Of PAFMT On Uterine Incontinence In Antenatal Training
 Pelvic floor muscle training for prevention and treatment of urinary and faecal incontinence in antenatal and postnatal women (Review) Hay-Smith J, Mørkved S, Fairbrother KA, Herbison GP This is a reprint
Pelvic floor muscle training for prevention and treatment of urinary and faecal incontinence in antenatal and postnatal women (Review) Hay-Smith J, Mørkved S, Fairbrother KA, Herbison GP This is a reprint
Stress Urinary Incontinence & Sexual Function
 Stress Urinary Incontinence & Sexual Function Lior Lowenstein, MD, MS Associate Professor Deputy Chairman of Obstetrics and Gynecology Department Rambam Health Care Campus Haifa Israel No Disclosures Disclosures
Stress Urinary Incontinence & Sexual Function Lior Lowenstein, MD, MS Associate Professor Deputy Chairman of Obstetrics and Gynecology Department Rambam Health Care Campus Haifa Israel No Disclosures Disclosures
previous surgery for incontinence.
 Predictive Title page Authors procedure value for of urinary urethra stress mobility incontinence before sub-urethra in women tape Xavier Khalid Alain Fabien Jean-Louis Pigné, Demaria, Zabak, Fritel, MD
Predictive Title page Authors procedure value for of urinary urethra stress mobility incontinence before sub-urethra in women tape Xavier Khalid Alain Fabien Jean-Louis Pigné, Demaria, Zabak, Fritel, MD
Consumer summary Minimally invasive techniques for the relief of stress urinary incontinence
 ASERNIP S Australian Safety and Efficacy Register of New Interventional Procedures Surgical Consumer summary Minimally invasive techniques for the relief of stress urinary incontinence (Adapted from the
ASERNIP S Australian Safety and Efficacy Register of New Interventional Procedures Surgical Consumer summary Minimally invasive techniques for the relief of stress urinary incontinence (Adapted from the
NHS Professionals. CG8 Guidelines for Continence and Catheter Care. Introduction
 NHS Professionals CG8 Guidelines for Continence and Catheter Care Introduction Continence has been defined as control of bladder and bowel function and continence care is the name given to the total care
NHS Professionals CG8 Guidelines for Continence and Catheter Care Introduction Continence has been defined as control of bladder and bowel function and continence care is the name given to the total care
Urinary incontinence is a common condition in. Pathophysiology of Adult Urinary Incontinence. The Stress Continence Control System
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2004;126:S23 S32 Pathophysiology of Adult Urinary Incontinence JOHN O. L. DELANCEY* and JAMES A. ASHTON MILLER *Departments of Obstetrics and Gynecology and Mechanical Engineering, Biomedical
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2004;126:S23 S32 Pathophysiology of Adult Urinary Incontinence JOHN O. L. DELANCEY* and JAMES A. ASHTON MILLER *Departments of Obstetrics and Gynecology and Mechanical Engineering, Biomedical
Korean Women - Study Proves That Syndrome Does Not Effect on Sexual Life
 (25) 17, 158 163 & 25 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 955-993/5 $3. www.nature.com/ijir The effect of overactive bladder syndrome on the sexual quality of life in Korean young and middle aged
(25) 17, 158 163 & 25 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 955-993/5 $3. www.nature.com/ijir The effect of overactive bladder syndrome on the sexual quality of life in Korean young and middle aged
Urinary Incontinence
 Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary incontinence (UI)? A: UI is also known as loss of bladder control or urinary leakage. UI is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have UI,
Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary incontinence (UI)? A: UI is also known as loss of bladder control or urinary leakage. UI is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have UI,
Incontinence. What is incontinence?
 Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
Longitudinal Changes in Overactive Bladder and Stress Incontinence Among Parous Women
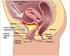 Neurourology and Urodynamics Longitudinal Changes in Overactive Bladder and Stress Incontinence Among Parous Women Victoria L. Handa, 1 * Christopher B. Pierce, 2 Alvaro Mu~noz, 2 and Joan L. Blomquist
Neurourology and Urodynamics Longitudinal Changes in Overactive Bladder and Stress Incontinence Among Parous Women Victoria L. Handa, 1 * Christopher B. Pierce, 2 Alvaro Mu~noz, 2 and Joan L. Blomquist
Prevention of Childbirth Injuries to the Pelvic Floor
 Prevention of Childbirth Injuries to the Pelvic Floor Michael Heit, MD, MSPH, Kelly Mudd, MD, and Patrick Culligan, MD Address University of Louisville Health Science Center, Department of Obstetrics and
Prevention of Childbirth Injuries to the Pelvic Floor Michael Heit, MD, MSPH, Kelly Mudd, MD, and Patrick Culligan, MD Address University of Louisville Health Science Center, Department of Obstetrics and
Refer to Coaptite Injectable Implant Instructions for Use provided with product for complete instructions for use.
 Questions for my Doctor Refer to Coaptite Injectable Implant Instructions for Use provided with product for complete instructions for use. INDICATIONS: Coaptite Injectable Implant is indicated for soft
Questions for my Doctor Refer to Coaptite Injectable Implant Instructions for Use provided with product for complete instructions for use. INDICATIONS: Coaptite Injectable Implant is indicated for soft
Topic review: Clinical presentation and diagnosis of urinary incontinence in the elderly. Prapa Pattrapornpisut 7 June 2012
 1 Topic review: Clinical presentation and diagnosis of urinary incontinence in the elderly Prapa Pattrapornpisut 7 June 2012 2 Urinary incontinence Definition the complaint of any involuntary leakage of
1 Topic review: Clinical presentation and diagnosis of urinary incontinence in the elderly Prapa Pattrapornpisut 7 June 2012 2 Urinary incontinence Definition the complaint of any involuntary leakage of
Bladder Health Promotion
 Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation Content contributions provided by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence (NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence
Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation Content contributions provided by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence (NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence
Twelve-year follow-up of conservative management of postnatal urinary and faecal incontinence and prolapse outcomes: randomised controlled trial
 DOI: 10.1111/1471-0528.12473 www.bjog.org Urogynaecology Twelve-year follow-up of conservative management of postnatal urinary and faecal incontinence and prolapse outcomes: randomised controlled trial
DOI: 10.1111/1471-0528.12473 www.bjog.org Urogynaecology Twelve-year follow-up of conservative management of postnatal urinary and faecal incontinence and prolapse outcomes: randomised controlled trial
PHYSICIAN / HEALTH CARE PROVIDER POCKET GUIDE. Stress Urinary Incontinence
 PHYSICIAN / HEALTH CARE PROVIDER POCKET GUIDE Stress Urinary Incontinence 1 in 3 women experience Stress Urinary Incontinence. This pocket guide is intended as a resource for physicians on the complex
PHYSICIAN / HEALTH CARE PROVIDER POCKET GUIDE Stress Urinary Incontinence 1 in 3 women experience Stress Urinary Incontinence. This pocket guide is intended as a resource for physicians on the complex
Overview of Urinary Incontinence in the Long Term Care Setting
 Overview of Urinary Incontinence in the Long Term Care Setting Management Strategies for the Nursing Assistant Ann M. Spenard RN, C, MSN Courtney Lyder ND, GNP Learning Objectives Describe common types
Overview of Urinary Incontinence in the Long Term Care Setting Management Strategies for the Nursing Assistant Ann M. Spenard RN, C, MSN Courtney Lyder ND, GNP Learning Objectives Describe common types
URINARY INCONTINENCE Information for Patients and Families Author: Chantale Dumoulin, PhD PT
 URINARY INCONTINENCE Information for Patients and Families Author: Chantale Dumoulin, PhD PT What is urinary incontinence? Urinary incontinence (UI) is the loss of the ability to hold in urine. This can
URINARY INCONTINENCE Information for Patients and Families Author: Chantale Dumoulin, PhD PT What is urinary incontinence? Urinary incontinence (UI) is the loss of the ability to hold in urine. This can
Tape Functionality: Sonographic Tape Characteristics and Outcome After TVT Incontinence Surgery
 Neurourology and Urodynamics Tape Functionality: Sonographic Tape Characteristics and Outcome After TVT Incontinence Surgery Jacek Kociszewski, 1 Oliver Rautenberg, 2 Daniele Perucchini, 3 Jakob Eberhard,
Neurourology and Urodynamics Tape Functionality: Sonographic Tape Characteristics and Outcome After TVT Incontinence Surgery Jacek Kociszewski, 1 Oliver Rautenberg, 2 Daniele Perucchini, 3 Jakob Eberhard,
Which women with stress incontinence require urodynamic evaluation?
 Which women with stress incontinence require urodynamic evaluation? Alison C. Weidner, MD, Evan R. Myers, MD, MPH, Anthony G. Visco, MD, Geoffrey W. Cundiff, MD, and Richard C. Bump, MD Durham, North Carolina
Which women with stress incontinence require urodynamic evaluation? Alison C. Weidner, MD, Evan R. Myers, MD, MPH, Anthony G. Visco, MD, Geoffrey W. Cundiff, MD, and Richard C. Bump, MD Durham, North Carolina
Urinary Incontinence
 Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary Urinary (YOOR-in-air-ee) incontinence (in-kahn-tih-nens) is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have urinary incontinence, you re not alone.
Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary Urinary (YOOR-in-air-ee) incontinence (in-kahn-tih-nens) is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have urinary incontinence, you re not alone.
Prevention & Treatment of De Novo Stress Incontinence after POP. Andy Vu, DO, FACOG UNT Health Science Center Fort Worth, TX.
 Prevention & Treatment of De Novo Stress Incontinence after POP Andy Vu, DO, FACOG UNT Health Science Center Fort Worth, TX Surgery Presenter Disclosure No Conflict of Interest to disclose No Financial
Prevention & Treatment of De Novo Stress Incontinence after POP Andy Vu, DO, FACOG UNT Health Science Center Fort Worth, TX Surgery Presenter Disclosure No Conflict of Interest to disclose No Financial
Stress Urinary Incontinence in Female Athletes Kelly I. Daly, Jennifer Doherty-Restrepo Florida International University, Miami, FL
 Stress Urinary Incontinence in Female Athletes Kelly I. Daly, Jennifer Doherty-Restrepo Florida International University, Miami, FL Objective: The purpose of this study is to educate allied health professionals
Stress Urinary Incontinence in Female Athletes Kelly I. Daly, Jennifer Doherty-Restrepo Florida International University, Miami, FL Objective: The purpose of this study is to educate allied health professionals
Quality of Life Impact of Using Tension-free Vaginal Tape for Stress Urinary Incontinence
 Original Article Quality of Life Impact of Using Tension-free Vaginal Tape for Stress Urinary Incontinence Shi-Wei Huang, Hong-Jeng Yu, Wai-Yan Wong, Jun Chen Department of Urology, National Taiwan University
Original Article Quality of Life Impact of Using Tension-free Vaginal Tape for Stress Urinary Incontinence Shi-Wei Huang, Hong-Jeng Yu, Wai-Yan Wong, Jun Chen Department of Urology, National Taiwan University
Registered Charity No. 5365
 THE MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS SOCIETY OF IRELAND Dartmouth House, Grand Parade, Dublin 6. Telephone: (01) 269 4599. Fax: (01) 269 3746 MS Helpline: 1850 233 233 E-mail: mscontact@ms-society.ie www.ms-society.ie
THE MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS SOCIETY OF IRELAND Dartmouth House, Grand Parade, Dublin 6. Telephone: (01) 269 4599. Fax: (01) 269 3746 MS Helpline: 1850 233 233 E-mail: mscontact@ms-society.ie www.ms-society.ie
Learning Resource Guide. Understanding Incontinence. 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved
 Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved ElderCare Online s Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence Table of Contents Introduction
Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved ElderCare Online s Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence Table of Contents Introduction
A Stress Urinary Incontinence fact sheet for
 A Stress Urinary Incontinence fact sheet for women and teenagers What is Stress Urinary Incontinence? Get to know your gusset - the science bit Stress urinary incontinence (SUI) is defined as a sudden
A Stress Urinary Incontinence fact sheet for women and teenagers What is Stress Urinary Incontinence? Get to know your gusset - the science bit Stress urinary incontinence (SUI) is defined as a sudden
Surgery for stress incontinence:
 Surgery for stress incontinence: information for you Published February 2005 by the RCOG Contents Page number Key points 1 About this information 2 What is stress incontinence? 2 Do I need an operation?
Surgery for stress incontinence: information for you Published February 2005 by the RCOG Contents Page number Key points 1 About this information 2 What is stress incontinence? 2 Do I need an operation?
Las Vegas Urogynecology
 Las Vegas Urogynecology 7500 Smoke Ranch Road - #200 Las Vegas, NV 89128 Telephone: (702) 233-0727 Fax: (702) 233-4799 Urinary Incontinence in Women Urinary incontinence is an inability to hold your urine
Las Vegas Urogynecology 7500 Smoke Ranch Road - #200 Las Vegas, NV 89128 Telephone: (702) 233-0727 Fax: (702) 233-4799 Urinary Incontinence in Women Urinary incontinence is an inability to hold your urine
SOGC Recommendations for Urinary Incontinence
 The quality of evidence is rated, and recommendations are made using the criteria described by the Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care. Clinical Practice Guidelines: The Evaluation of Stress
The quality of evidence is rated, and recommendations are made using the criteria described by the Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care. Clinical Practice Guidelines: The Evaluation of Stress
LOSS OF BLADDER CONTROL IS TREATABLE TAKE CONTROL AND RESTORE YOUR LIFESTYLE
 LOSS OF BLADDER CONTROL IS TREATABLE TAKE CONTROL AND RESTORE YOUR LIFESTYLE TALKING ABOUT STRESS INCONTINENCE (SUI) Millions of women suffer from stress incontinence (SUI). This condition results in accidental
LOSS OF BLADDER CONTROL IS TREATABLE TAKE CONTROL AND RESTORE YOUR LIFESTYLE TALKING ABOUT STRESS INCONTINENCE (SUI) Millions of women suffer from stress incontinence (SUI). This condition results in accidental
Treatment for Stress Incontinence Patient Decision Aid
 Treatment for Stress Incontinence Patient Decision Aid Patient Information Author ID: JD/NS Leaflet Number: Gyn 056 Version: 1 Name of Leaflet: Treatment for stress incontinence - Patient decision aid
Treatment for Stress Incontinence Patient Decision Aid Patient Information Author ID: JD/NS Leaflet Number: Gyn 056 Version: 1 Name of Leaflet: Treatment for stress incontinence - Patient decision aid
Urinary Incontinence 9/17/2015. Conflict of Interest. Objectives. None
 Urinary Incontinence Karla Reinhart DNP, FNP-C, ARNP October, 2015 Conflict of Interest None Objectives Acquire knowledge of A & P of micturition, as well as pertinent pathologies for male and female incontinence
Urinary Incontinence Karla Reinhart DNP, FNP-C, ARNP October, 2015 Conflict of Interest None Objectives Acquire knowledge of A & P of micturition, as well as pertinent pathologies for male and female incontinence
Tension-Free Vaginal Tape: Outcomes Among Women With Primary Versus Recurrent Stress Urinary Incontinence
 Tension-Free Vaginal Tape: Outcomes Among Women With Versus Stress Urinary Incontinence C. R. Rardin, MD, N. Kohli, MD, P. L. Rosenblatt, MD, J. R. Miklos, MD, R. Moore, MD, and W. C. Strohsnitter, MS
Tension-Free Vaginal Tape: Outcomes Among Women With Versus Stress Urinary Incontinence C. R. Rardin, MD, N. Kohli, MD, P. L. Rosenblatt, MD, J. R. Miklos, MD, R. Moore, MD, and W. C. Strohsnitter, MS
PFM Rehabilitation for Physical Therapists and Nurses The Northeastern Section of the American Urological Association November 1, 2013
 PFM Rehabilitation for Physical Therapists and Nurses The Northeastern Section of the American Urological Association November 1, 2013 Dr Description - This 15 minutes lecture will provide information
PFM Rehabilitation for Physical Therapists and Nurses The Northeastern Section of the American Urological Association November 1, 2013 Dr Description - This 15 minutes lecture will provide information
Tone Up Your Pelvic Floor. A regular pelvic floor exercise ( Kegel ) routine can prevent symptoms before, during, and after childbirth.
 Will Breastfeeding Affect Incontinence and Pelvic Symptoms? Yes, often for as long as you re nursing. Many breastfeeding women are unaware that a natural drop in estrogen which persists for as long as
Will Breastfeeding Affect Incontinence and Pelvic Symptoms? Yes, often for as long as you re nursing. Many breastfeeding women are unaware that a natural drop in estrogen which persists for as long as
Urodynamic study (UDS) is used to determine the
 Original Article 596 The Prevalence of Urinary Incontinence and Associated Risk Factors in Taiwanese Women with Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Ling-Hong Tseng 1,2, MD; Ching-Chung Liang 1,2, MD; Han-Po Lo
Original Article 596 The Prevalence of Urinary Incontinence and Associated Risk Factors in Taiwanese Women with Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Ling-Hong Tseng 1,2, MD; Ching-Chung Liang 1,2, MD; Han-Po Lo
Primary Care Management Guidelines Female Urinary Incontinence. Overview of Lecture
 Primary Care Management Guidelines Female Urinary Incontinence Professor Don Wilson Department of Women s and Children s Health Dunedin School of Medicine University of Otago GP Teaching for Roy Morris,
Primary Care Management Guidelines Female Urinary Incontinence Professor Don Wilson Department of Women s and Children s Health Dunedin School of Medicine University of Otago GP Teaching for Roy Morris,
Urinary incontinence
 Urinary incontinence Factsheet March 2013 Urinary incontinence Introduction Women and girls with cystic fibrosis (CF) are more likely to experience urinary incontinence (UI) than the healthy population.
Urinary incontinence Factsheet March 2013 Urinary incontinence Introduction Women and girls with cystic fibrosis (CF) are more likely to experience urinary incontinence (UI) than the healthy population.
Bladder Health Promotion
 Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation endorsed by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence( NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence This presentation
Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation endorsed by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence( NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence This presentation
FEMALE INCONTINENCE REVIEW
 200 S. Wenona Suite 298 Steven L. Jensen, M.D. 5400 Mackinaw, Suite 4302 Bay City, MI 48706 Frank H. Kim, M.D. Saginaw, MI 48604 Telephone (989) 895-2634 Adult & Pediatric Urologists (989) 791-4020 Fax
200 S. Wenona Suite 298 Steven L. Jensen, M.D. 5400 Mackinaw, Suite 4302 Bay City, MI 48706 Frank H. Kim, M.D. Saginaw, MI 48604 Telephone (989) 895-2634 Adult & Pediatric Urologists (989) 791-4020 Fax
Tension-free vaginal tape sling for recurrent stress incontinence after transobturator tape sling failure
 Int Urogynecol J (2007) 18:309 313 DOI 10.1007/s00192-006-0149-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE Tension-free vaginal tape sling for recurrent stress incontinence after transobturator tape sling failure Robert D. Moore
Int Urogynecol J (2007) 18:309 313 DOI 10.1007/s00192-006-0149-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE Tension-free vaginal tape sling for recurrent stress incontinence after transobturator tape sling failure Robert D. Moore
Impact of Early Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation After Transurethral Resection of the Prostate
 Neurourology and Urodynamics 20:53 59 (2001) Impact of Early Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation After Transurethral Resection of the Prostate Daniele Porru, 1 * Giuliana Campus, 2 Alessandro Caria, 2 Giuliana
Neurourology and Urodynamics 20:53 59 (2001) Impact of Early Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation After Transurethral Resection of the Prostate Daniele Porru, 1 * Giuliana Campus, 2 Alessandro Caria, 2 Giuliana
Stress Urinary Incontinence: Treatment Manisha Patel, MD April 10, 2006
 Stress Urinary Incontinence: Treatment Manisha Patel, MD April 10, 2006 What treatment options are available for a woman with stress urinary incontinence (SUI)? Behavioral therapy, medication, pessary,
Stress Urinary Incontinence: Treatment Manisha Patel, MD April 10, 2006 What treatment options are available for a woman with stress urinary incontinence (SUI)? Behavioral therapy, medication, pessary,
Get the Facts, Be Informed, Make YOUR Best Decision. Pelvic Organ Prolapse
 Pelvic Organ Prolapse ETHICON Women s Health & Urology, a division of ETHICON, INC., a Johnson & Johnson company, is dedicated to providing innovative solutions for common women s health problems and to
Pelvic Organ Prolapse ETHICON Women s Health & Urology, a division of ETHICON, INC., a Johnson & Johnson company, is dedicated to providing innovative solutions for common women s health problems and to
Prolapse Repair Systems. a guide To correcting PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE
 Anterior PROLAPSE & Posterior REPAIR SYSTEM Prolapse Repair Systems a guide To correcting PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE Restore Your Body Pelvic organ prolapse occurs when pelvic structures, like the bladder or
Anterior PROLAPSE & Posterior REPAIR SYSTEM Prolapse Repair Systems a guide To correcting PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE Restore Your Body Pelvic organ prolapse occurs when pelvic structures, like the bladder or
URINARY INCONTINENCE
 URINARY INCONTINENCE What is urinary incontinence? Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only a few drops when you cough or sneeze to entirely
URINARY INCONTINENCE What is urinary incontinence? Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only a few drops when you cough or sneeze to entirely
Overactive Bladder (OAB)
 Overactive Bladder (OAB) Overactive bladder is a problem with bladder storage function that causes a sudden urge to urinate. The urge may be difficult to suppress, and overactive bladder can lead to the
Overactive Bladder (OAB) Overactive bladder is a problem with bladder storage function that causes a sudden urge to urinate. The urge may be difficult to suppress, and overactive bladder can lead to the
EVALUATION OF URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN
 Urological Neurology Brazilian Journal of Urology Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology Vol. 27 (2): 165-170, March - April, 2001 EVALUATION OF URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN STEVEN P. PETROU,
Urological Neurology Brazilian Journal of Urology Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology Vol. 27 (2): 165-170, March - April, 2001 EVALUATION OF URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN STEVEN P. PETROU,
Bladder Wall Thickness on Ultrasonographic Cystourethrography
 Article Bladder Wall Thickness on Ultrasonographic Cystourethrography Affecting Factors and Their Implications Jenn-Ming Yang, MD, Wen-Chen Huang, MD Objective. To explore factors affecting bladder wall
Article Bladder Wall Thickness on Ultrasonographic Cystourethrography Affecting Factors and Their Implications Jenn-Ming Yang, MD, Wen-Chen Huang, MD Objective. To explore factors affecting bladder wall
Managing Urinary Incontinence
 Patient & Family Guide 2016 Managing Urinary Incontinence www.nshealth.ca Managing Urinary Incontinence What is the urinary system? Urine (pee) is made in the kidneys. It flows through tubes called ureters.
Patient & Family Guide 2016 Managing Urinary Incontinence www.nshealth.ca Managing Urinary Incontinence What is the urinary system? Urine (pee) is made in the kidneys. It flows through tubes called ureters.
Liberty Pelvic Floor Stimulation
 Liberty Pelvic Floor Stimulation A logical first choice for treatment of urinary incontinence Liberty s simplified design exercises the correct muscles and is easy to use, therefore helping increase patient
Liberty Pelvic Floor Stimulation A logical first choice for treatment of urinary incontinence Liberty s simplified design exercises the correct muscles and is easy to use, therefore helping increase patient
THE MANAGEMENT OF URINARY INCONTINENCE WITHIN A STROKE UNIT POPULATION REENA DHAMI STROKE CNS EPSOM & ST.HELIER UNIVERSITY HOSPITALS
 THE MANAGEMENT OF URINARY INCONTINENCE WITHIN A STROKE UNIT POPULATION REENA DHAMI STROKE CNS EPSOM & ST.HELIER UNIVERSITY HOSPITALS Definition Urinary Incontinence is AN INABILITY TO HOLD URINE until
THE MANAGEMENT OF URINARY INCONTINENCE WITHIN A STROKE UNIT POPULATION REENA DHAMI STROKE CNS EPSOM & ST.HELIER UNIVERSITY HOSPITALS Definition Urinary Incontinence is AN INABILITY TO HOLD URINE until
Sonographic Evaluation of Anatomic Results After the Pubovaginal Sling Procedure for Stress Urinary Incontinence
 Article Sonographic Evaluation of Anatomic Results After the Pubovaginal Sling Procedure for Stress Urinary Incontinence Hann-Chorng Kuo, MD Objective. To investigate the anatomic changes after the pubovaginal
Article Sonographic Evaluation of Anatomic Results After the Pubovaginal Sling Procedure for Stress Urinary Incontinence Hann-Chorng Kuo, MD Objective. To investigate the anatomic changes after the pubovaginal
