Venous duplex imaging follow-up of acute symptomatic deep vein thrombosis of the leg
|
|
|
- Cecilia Gibbs
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Venous duplex imaging follow-up of acute symptomatic deep vein thrombosis of the leg Joseph A. Caprini, MD, Juan I. Arcelus, MD, PhD, Kevin N. Hoffman, BA, Gail Size, RVT, Maureen Laubach, RVT, Clara I. Traverso, MD, PhD, Robert Coats, BS, Nicole Finke, BA, mad Jose J. Reyna, MD, Glenview, Ill., and MAlaga, Spain Purpose: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the rate of resolution of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in the leg, by means of duplex imaging, in patients with symptoms during a 6-month period after initial diagnosis. Methods: Seventy-three limbs in 69 patients with acute DVT diagnosed by duplex imaging received conventional heparin and warfarin treatment and underwent subsequent duplex studies 1, 4, 12, and 24 weeks after the initial diagnosis. The objectives of the study were to document (1) the rate or complete resolution of DVT, (2) the proportion of unstable, floating thrombi, and (3) the development of chronic damage as a result of vessel wall scarring. Results: The rate of normalization of DVT 6 months after diagnosis was 78% in the common femoral vein, 70% in the superficial femoral vein, 75% in the popliteal vein, and 70% in the calf veins examined at the scheduled intervals. Twenty-six percent of thrombi were considered unstable on the baseline examination. The average number of days necessary for these thrombi to become stable was 10.7 days. Damage to the vessel wall or valves was documented in 44% of the patients. Conclusions: Rates of resolution of DVT were similar for the different veins of the leg studied. There was a high proportion of unstable thrombi, which present a high potential risk of embolization. Serial duplex scanning after DVT renders important information with regard to thrombus resolution, propagation, and attachment to the vein wall. (J VASC SURG 1995;21:472-6.) During the past few years, real-time B-Mode ultrasonography combined with pulsed Doppler echocardiography (duplex imaging) has become one of the most reliable diagnostic techniques for the evaluation of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) of the legs. 1-s Because of its noninvasive nature, venous duplex imaging is repeatable, allowing for continued follow-up after DVT is diagnosed, at no risk to the patient. In addition, duplex imaging can assess the echogenic characteristics of the thrombus and its degree of adherence to the vein wall s This test also provides important information regarding valve mo- From the Departments of Surgery, the Glenbrook Hospital and Hospital de la Axarquia, Vdlez-M~ilaga. Presented at the Sixth Annual Meeting of the American Venous Forum, Wailea Maui, Hawaii, Feb , Reprint requests: Joseph A. Caprini, MD, Department of Surgery, the Glenbrook Hospital, 2100 Pfingsten Rd., Glenview, IL Copyright 1995 by The Society for Vascular Surgery and International Society for Cardiovascular Surgery, North American Chapter /95/$ /6/61339 tion and reflux in the superficial and deep venous systems. 3,6 Initial therapy of acute DVT is based primarily on objective diagnosis, usually ascending venography or, more recently, duplex imaging, whereas secondary prevention of recurrences relies on protocols recommending at least 3 months of treatment with oral anticoagulants. 7,8 The recent European Consensus Statement on the prevention of venous thromboembolism recognizes that the optimal duration of secondary prophylaxis is not known. 9 Only a small number of studies have prospectively assessed the outcome of acute DVT by means of serial duplex scanning. 71 This study was undertaken to assess the rate of normalization of duplex imaging within 6 months after the diagnosis of acute DVT in various vein segments and to estimate prospectively the frequency of presentation of unstable, floating thrombi. METHODS During a 3-year period, 69 patients (42 men and 27 women) aged 35 to 85 years (mean 67.6 years), 472
2 Volume 21, Number 3 Caprini et al. 473 diagnosed with acute DVT of the legs by duplex scanning, were scheduled to repeat duplex scanning 1, 4, 12, and 24 weeks after the initial diagnosis. M1 patients had been referred by their attending physicians to the vascular laboratory of the Glenbrook Hospital, Glenview, Ill. There were four patients with bilateral DVT; accordingly, 73 limbs were evaluated prospectively. Duplex imaging studies were performed with an Ultrasonix 750 SDX scanner, with a 7.5 MHz linear transducer and, later on, an Ultramark 9 HDI color scanner (Advanced Technology Laboratories, Bothell, Wash.). Pulsed Doppler signals were obtained with a 5 MHz probe. All veins were examined in the transverse and longitudinal views. For every leg, four vein segments were evaluated prospectively: common femoral, superficial femoral, popliteal, and calf. All tests were performed by vascular technologists, recorded on videotape, and interpreted by one senior attending physician. Abnormal examination criteria diagnostic of DVT included absence of Doppler signal noted with respiration or augmentation maneuvers, echogenicfilled vein lumen occluding the vessel partially or completely, inability to compress the vein with gentle pressure of the probe, and the presence of an area of dilation of the vein, usually distal to the level of the thrombus. Often vein compression will reveal intraluminal echogenicity when a thrombus is present. The outcome of DVT, according to duplex scan follow-up findings, was divided into four categories: no change, worsening, improvement, or complete resolution. No change was reported when the thrombus remained confined to the same vein segment, without recanalization, and appeared to be the same size. Worsening was reported if the clot extended to other previously unaffected vein segments. A thrombus was considered to improve if the clot inside the vein lumen had undergone evidence of recanalization, with persistence of incomplete compression of the vein segment with the probe. An overall decrease in size or volume of the clot was also a criterion indicating improvement. Criteria to consider that resolution of the DVT process had occurred included return of phasic Doppler signals with respiration and augmentation maneuvers, disappearance of the echogenic filling defect, and ability to compress the vein fully in the transverse position by gentle pressure of the probe. If all these criteria were met but there were findings such as abnormal thickening and increased echogenicity of the vessel wall, abnormal valve motion, or reflux, the DVT process was considered resolved but the patient was considered at high risk for postphlebitic syndrome and elastic compression therapy was encouraged. Chronic damage included thickening of the vein wall, reflux, and abnormal valves. A vein wall was considered thickened when it was twice the thickness of a normal venous wall segment, with increased echogenicity brighter than the normal vessel wall. Reflux was assessed in the supine and reverse Trendelenburg position with the transducer placed over the vein segment. The patient was asked to perform the Valsalva maneuver, and reflux was present if retrograde flow lasted for more than 2 seconds. Proximal or distal hand compression of the leg was done when the Valsalva maneuver was inadequate or could not be performed. Valves were considered abnormal if they were grossly distorted or immobile or the cusps failed to oppose with the Valsalva maneuver. Under the above circumstances, although the DVT process was considered resolved, the patient was encouraged to wear therapeutic compression hose to decrease the risk ofpostphlebitic syndrome. Recurrence of file DVT process was diagnosed when the aforementioned criteria for DVT reappeared in a vein segment that had previously been considered resolved. A thrombus was considered floating at presentation if at least one third of the clot was not adhered to the vein wall. These clots were examined every 24 to 48 hours until there was not any remaining "floating" component. These patients were kept in bed until the clot was completely attached to the vessel wall, and warfarin and compression hose were also withheld until the clot was fully attached to the vein wall. Data were analyzed by use of the SPSS-PC program run on a 486 DX2 IBM-compatible computer (Packard-Bell, Kenoga Park, Calif.). Comparisons between groups were made by means of Fisher's exact test. Statistical significance was defined as p < RESULTS Apart from the initial 73 examinations, there were another 214 follow-up studies. This represents an average of 2.93 follow-up examinations per patient (range 2 to 5). There were 198 segments with DVT on the baseline examinations, which represents 67% of the 292 vein segments studied (four per leg). The distribution of thrombi among the different vein segments at diagnosis was as follows: 46 in the common femoral, 48 in the superficial femoral, 50 in the popliteal, and 54 in at least one of the calf veins.
3 474 Caprini et al. March 1995 Table I. Outcome of DVT in the common femoral vein (n = 46) Time(w~ n Nochange (%) Worse (%) Improved( /o) Resoled(%) Table II. Outcome of DVT in the superficial femoral vein (n = 48) Time (wk) n No change (%) Worse(%) Improved(%) Resoled(%) Table III. Outcome of DVT in the popliteal vein (n = 50) Time (wk) n Nochange(%) Worse (%) Improved (%) Resoled(%) Table IV. Outcome of DVT in the calf veins (n = 54) Time (wk) n No change (%) Worse (%) Improved (%) Resoled (%) The percentage of thrombi completely occluding the vein lumen among the different vein segments was 70% (32/46) in the common femoral, 81% (39/48) in the superficial femoral, 59% (29/50) in the popliteal, and 69% (37/54) in the calf veins. The results of the follow-up duplex examinations regarding the normalization of the examination in the four vein segments evaluated are detailed in Tables I to IV. The percentages shown in the tables indicate the number of segments with resolution, improvement, worsening, or no change of the DVT process divided by the number of segments with thrombosis at presentation examined at that specific interval. There were no statistical differences in the rates of resolution among the four vein segments at the four intervals. There were 18 vein segments with floating thrombi at diagnosis, as defined above, which represents 24.5% of all thrombi. Most of these thrombi were located in the common femoral vein segment (n = 13), whereas there were three and two in the superficial femoral and popliteal veins, respectively. The average number of days for clot stabilization was 10.7, with a range between 2 and 33 days. One thrombus showed dramatic reduction in size in the follow-up study performed 48 hours after diagnosis, suggesting that a part of the clot had embolized. This was confirmed by a ventilation/perfusion lung scan. There were no other cases of suspected pulmonary embolism in this group. Chronic damage, as defined by alteration of valve motion, reflux of venous flow, and thickened vein wall, developed in 31 (44%) of the 69 limbs during the study. Throughout the 6-month study period, there were six cases (8.2%) of recurrence of DVT in previously normalized segments. DISCUSSION The natural history of DVT is not well understood. A significant number of patients have clinical evidence of chronic venous insufficiency months or years after an acute DVT, which is sometimes
4 Volume 21, Number 3 Caprini et al. 475 difficult to differentiate from a recurrent DVT. With experimental models, several authors have documented that organization and recanalization of venous thrombi proceed at a constant yet variable rate. n~4 The organization of the thrombus appears to depend initially on circulatory cells, and later on there is cellular proliferation and migration from the vessel wall. u A few studies have prospectively assessed the evolution of DVT for several weeks after diagnosis, according to noninvasive objective diagnostic methods such as duplex ultrasound scanning s-a or impedance plethysmography, is Another study has retrospectively reviewed the normalization rates of duplex scans within 6 months after DVT diagnosis and compared the results obtained in patients with symptoms versus those without. 16 The results of this study revealed that the total normalization rate at 6 months was 77% in symptom-free patients and 53% in patients with symptoms. Our results are similar to those of Jay et al., is who found normalization of impedance plethysmography in 60% of the patients 3 months after diagnosis of DVT. At that time, we found that 54% of common femoral and 38% of superficial femoral thrombi had resolved. On the other hand, Krupski et al.9 reported improved duplex scans in 62% of cases within 1 week. Our results reveal that approximately 60% of cases of DVT had improved or resolved 1 week after diagnosis, irrespective of the vein segment in which they were located (Tables I to IV). Whereas some studies have reported that thrombi located distal to the knee undergo faster resolution than those above the knee, 17 others have shown better recanalization in proximal veins, is There were no statistically significant differences in the outcome among the different vein segments examined in our study. This is coincident with another recent prospective study, in which the rate of regression of thrombus was similar over time among the deep vein segments, s Of particular interest was the high proportion of "floating" thrombi (25%), which is above the 16% reported by Berry et al. 19 in a retrospective review of 400 cases of DVT diagnosed by duplex scanning. The mean time to stabilization of thrombus and attachment to the vein wall in our series is similar to that of Berry et al., who reported 9.2 days. We had only one documented pulmonary embolism in this group (6%), whereas they reported 17 cases (26%). We do agree with Berry et al. when they recommend serial duplex scanning every second or third day to monitor the floating thrombus for attachment, propagation, or embolization. It is our routine clinical practice to avoid patient ambulation until the thrombus is attached to the vessel wall. Although most patients in our study showed dramatic improvement of the DVT process within the 6-month follow-up period, it is important to notice that 44% had ultrasound findings suggesting a high risk for the development of postphlebitic syndrome. Similar results have been reported by Markel et al., 2 who found that 52% and 69% of limbs with venous thrombosis had reflux 3 and 6 months after diagnosis, respectively. Another similar study has documented the development of valxatlar incompetence in 62% of patients during a 9-month follow-up period. 1 A major contribution of that study is their finding that vein valves became incompetent both above and below the segment where the clot was located. Lindner et al. 2I have reported that 80% of patients had documented postphlebitic syndrome 5 to 10 years after leg DVT. A long-term follow-up of patients diagnosed with DVT is required to correlate the development of clinically evident postphlebitic syndrome with the duplex scan findings over time. In conclusion, duplex scanning represents a valid clinical tool, not only for the initial diagnosis of DVT but also to assess long-term outcome of thrombus. This test can guide initial patient management, providing information about clot attachment to the vein wall and resolution. In addition, duplex scanning can identify those patients with a potential high risk for postphlebitic syndrome. Finally, duplex scans may be used to compare and evaluate the results of different regimens of anticoagulant and fibrinolytic drug therapy on the long-term outcome of venous thrombi in the lower extremity. REFERENCES 1. White RH, McGahan ]P, Daschbach MM, Harding RP. Diagnosis of deep-vein thrombosis using duplex ultrasound. Ann Intern Med 1989;111: Hobson RW, Mintz BL, Jamil Z, Breitbar G. Current status of duplex ultrasonography in the diagnosis of acute deep venous thrombosis. In: Bergan JJ, Yao JST, eds. Venous disorders. Philadelphia: WB Sannders, 1991: Rollins DL, Semrow C, Friedell M, Buchbinder D. Use of ultrasonic venography in the evaluation of venous valve fimction. Am J Surg 1987;154: Lensing AWA, Marcel ML, Buller HR, et al. Diagnosis of deep-vein thrombosis using an objective Doppler method. Ann Intern Med 1990;113: Semrow C, Friedell M, Buchbinder D, Rollins DL. Characterization of lower extremity venous disease using real-time B-mode ultrasonic imaging. J Vase Technol 1987; 11:
5 476 Caprini et al. March Szendro G, Nicolaides AN, Zukowski Aj', et al. Duplex scanning in the assessment of deep venous incompetence. J VASC SURG 1986;4: Killewich LA, Bedford GR, Beach KW, Strandness DE. Spontaneous lysis of deep venous thrombi. I VASC SURG 1989;9: Murphy TP, Cronan JJ. Evolution of deep venous thrombosis: a prospective evaluation with US. Radiology 1990; 177: Krupski WC, Bass A, DiUey RB, Bernstein EF, Otis SM. Propagation of deep venous thrombosis identified by duplex ultrasonography. J VASC SURG 1990;12: Ramhorst B, Bemmelen PS, Hoeneveld H, Faber JAJ, Eikelboom BC. Thrombus regression of spontaneous thrombolysis with duplex scanning. Circulation 1992;86: Cox JST. The maturation and canalization of thrombi. Surg Gynecol Obstet 1963;116: Moser ICVI, Guisan M, Bartimmo EE, Longo AM, Harsanyi PG, Chorazzi N. In vivo and postmortem dissolutiofi rates of pulmonary emboli and venous thrombi in the dog. Circulation 1973;48: Flanc C. An experimental study ofthe recanalization of arterial and venous thrombi. Br J Surg 1968; Sevitt S. The mechanism of canalization in deep vein thrombosis. J Pathol 1973;110: lay R, Hull R, Carter C, et al. Outcome of abnormal impedance plethysmography results in patients with proximal vein thrombosis: frequency of return to normal. Thromb Res 1984;36: Siragusa S, Carbone S, Vicentini L, Barone M, Piovella FA. Retrospective study to evaluate the normalization rate of real-time B-mode compression ultrasonography in symptomatic and asymptomatic patients with acute deep vein thrombosis of the lower limbs. Thromb Haemost 1993;69: Lea-Thomas M, McAlfister V. The radiological progression of deep vein thrombus. Radiology 1971;99: Bergvall U, Hjelmstedt A. Recanalization of deep venous thrombosis of the lower leg and thigh. Acta Chir Scand 1968;134: Berry RE, George JE, Shaver WA. Free-floating venous thrombosis: a retrospective analysis. Ann Surg 1990;211: Markel A, Manzo RA, Bergelin RO, Strandness DE. Valvular reflux after deep vein thrombosis: incidence and time of occurrence. J VASC SUR~ 1992;15: Lindner DJ, Edwards JM, Phinney ES, Taylor LM, Potter JM. Long-term hemodynamic and clinical sequelae of lower extremity deep vein thrombosis. J VASC SURe 1986;4: Submitted March 2, 1994; accepted Oct. 17, 1994.
Deep vein thrombosis outcome and the level of oral anticoagulation therapy
 Deep vein thrombosis outcome and the level of oral anticoagulation therapy Joseph A. Caprini, MD, Juan I. Arcelus, MD, PhD, José J. Reyna, MD, Gary D. Motykie, MD, David Mohktee, BS, Lukas P. Zebala, BS,
Deep vein thrombosis outcome and the level of oral anticoagulation therapy Joseph A. Caprini, MD, Juan I. Arcelus, MD, PhD, José J. Reyna, MD, Gary D. Motykie, MD, David Mohktee, BS, Lukas P. Zebala, BS,
SCREENING COMPRESSION ULTRASOUND FOR LOWER EXTREMITY DVT
 SCREENING COMPRESSION ULTRASOUND FOR LOWER EXTREMITY DVT R. Eugene Zierler, M.D. The D. E. Strandness, Jr. Vascular Laboratory University of Washington Medical Center Division of Vascular Surgery University
SCREENING COMPRESSION ULTRASOUND FOR LOWER EXTREMITY DVT R. Eugene Zierler, M.D. The D. E. Strandness, Jr. Vascular Laboratory University of Washington Medical Center Division of Vascular Surgery University
Clinically Important Pulmonary Emboli: Does Calf Vein US Alter Outcomes? 1
 Ultrasonography Ronald H. Gottlieb, MD Jani Widjaja, MD Sonu Mehra, MD William B. Robinette, MS, RDMS, RVT Clinically Important Pulmonary Emboli: Does Calf Vein US Alter Outcomes? 1 Index terms: Embolism,
Ultrasonography Ronald H. Gottlieb, MD Jani Widjaja, MD Sonu Mehra, MD William B. Robinette, MS, RDMS, RVT Clinically Important Pulmonary Emboli: Does Calf Vein US Alter Outcomes? 1 Index terms: Embolism,
Lower Extremity Venous Duplex Evaluation
 VASCULAR TECHNOLOGY PROFESSIONAL PERFORMANCE GUIDELINES Lower Extremity Venous Duplex Evaluation This Guideline was prepared by the Professional Guidelines Subcommittee of the Society for Vascular Ultrasound
VASCULAR TECHNOLOGY PROFESSIONAL PERFORMANCE GUIDELINES Lower Extremity Venous Duplex Evaluation This Guideline was prepared by the Professional Guidelines Subcommittee of the Society for Vascular Ultrasound
Upper Extremity Vein Mapping for Placement of a Dialysis Access
 VASCULAR TECHNOLOGY PROFESSIONAL PERFORMANCE GUIDELINES Upper Extremity Vein Mapping for Placement of a Dialysis Access This Guideline was prepared by the Professional Guidelines Subcommittee of the Society
VASCULAR TECHNOLOGY PROFESSIONAL PERFORMANCE GUIDELINES Upper Extremity Vein Mapping for Placement of a Dialysis Access This Guideline was prepared by the Professional Guidelines Subcommittee of the Society
Provided by the American Venous Forum: veinforum.org
 CHAPTER 17 SURGICAL THERAPY FOR DEEP VALVE INCOMPETENCE Original author: Seshadri Raju Abstracted by Gary W. Lemmon Introduction Deep vein valvular incompetence happens when the valves in the veins (tubes
CHAPTER 17 SURGICAL THERAPY FOR DEEP VALVE INCOMPETENCE Original author: Seshadri Raju Abstracted by Gary W. Lemmon Introduction Deep vein valvular incompetence happens when the valves in the veins (tubes
Venous Reflux Disease and Current Treatments VN20-87-A 01/06
 Venous Reflux Disease and Current Treatments Leg Vein Anatomy Your legs are made up of a network of veins and vessels that carry blood back to the heart The venous system is comprised of: Deep veins Veins
Venous Reflux Disease and Current Treatments Leg Vein Anatomy Your legs are made up of a network of veins and vessels that carry blood back to the heart The venous system is comprised of: Deep veins Veins
LOWER EXTREMITY VENOUS DUPLEX ULTRASOUND:
 LOWER EXTREMITY VENOUS DUPLEX ULTRASOUND: Chronic Venous Insufficiency Phillip J Bendick, PhD William Beaumont Hospital Royal Oak, Michigan Prevalence: Carotid ASO ~ 3M Peripheral Arterial Dz ~ 5M + CAD
LOWER EXTREMITY VENOUS DUPLEX ULTRASOUND: Chronic Venous Insufficiency Phillip J Bendick, PhD William Beaumont Hospital Royal Oak, Michigan Prevalence: Carotid ASO ~ 3M Peripheral Arterial Dz ~ 5M + CAD
Paul G. Lee. 2 ND YEAR RESEARCH ELECTIVE RESIDENT S JOURNAL Volume III, 1998-1999. A. Objective
 A comparison of six months of anticoagulation with extended anticoagulation for a first episode of venous thromboembolism in patients with thrombophilia Paul G. Lee A. Objective a. To evaluate the risk
A comparison of six months of anticoagulation with extended anticoagulation for a first episode of venous thromboembolism in patients with thrombophilia Paul G. Lee A. Objective a. To evaluate the risk
Surgical Options for Venous Disease. Sandra C Carr MD Vascular Surgery Meriter Wisconsin Heart
 Surgical Options for Venous Disease Sandra C Carr MD Vascular Surgery Meriter Wisconsin Heart Chronic Venous Disease Approximately 23% of adults in the US have varicose veins Estimated 22 million women
Surgical Options for Venous Disease Sandra C Carr MD Vascular Surgery Meriter Wisconsin Heart Chronic Venous Disease Approximately 23% of adults in the US have varicose veins Estimated 22 million women
UHS CLINICAL CARE COLLABORATION: Outpatient & Inpatient
 Guidelines for Anticoagulation Initiation and Management Y2014 UHS CLINICAL CARE COLLABORATION: Outpatient & Inpatient Topic Page Number MEDICATION FLOW AND PATIENT FLOW... 2 AND 3 PARENTERAL ANTICOAGULANTS...
Guidelines for Anticoagulation Initiation and Management Y2014 UHS CLINICAL CARE COLLABORATION: Outpatient & Inpatient Topic Page Number MEDICATION FLOW AND PATIENT FLOW... 2 AND 3 PARENTERAL ANTICOAGULANTS...
Prior Authorization Guideline
 Guideline Guideline Name Formulary Xarelto (rivaroxaban) UnitedHealthcare Community & State Approval Date 0/0/203 Revision Date 8//204 Technician Note: CPS Approval Date: /5/20; CPS Revision Date: 8/20/204
Guideline Guideline Name Formulary Xarelto (rivaroxaban) UnitedHealthcare Community & State Approval Date 0/0/203 Revision Date 8//204 Technician Note: CPS Approval Date: /5/20; CPS Revision Date: 8/20/204
Position Statement: The Use of VTED Prophylaxis in Foot and Ankle Surgery
 Position Statement: The Use of VTED Prophylaxis in Foot and Ankle Surgery Position Statement There is currently insufficient data for the (AOFAS) to recommend for or against routine VTED prophylaxis for
Position Statement: The Use of VTED Prophylaxis in Foot and Ankle Surgery Position Statement There is currently insufficient data for the (AOFAS) to recommend for or against routine VTED prophylaxis for
Importance and Advantages of Intermittent External Pneumatic Compression Therapy in Venous Stasis Ulceration
 Angiology Volume 56, Number 1, 2005 19 Importance and Advantages of Intermittent External Pneumatic Compression Therapy in Venous Stasis Ulceration Ufuk Alpagut, MD and Enver Dayioglu, MD, Istanbul, Turkey
Angiology Volume 56, Number 1, 2005 19 Importance and Advantages of Intermittent External Pneumatic Compression Therapy in Venous Stasis Ulceration Ufuk Alpagut, MD and Enver Dayioglu, MD, Istanbul, Turkey
Confirmed Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
 Confirmed Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Information for patients What is deep vein thrombosis? Blood clotting provides us with essential protection against severe loss of blood from an injury to a vein or
Confirmed Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Information for patients What is deep vein thrombosis? Blood clotting provides us with essential protection against severe loss of blood from an injury to a vein or
Chronic Thromboembolic Disease. Chronic Thromboembolic Disease Definition. Diagnosis Prevention Treatment Surgical Nonsurgical
 Chronic Thromboembolic Disease Diagnosis Prevention Treatment Surgical Nonsurgical Chronic Thromboembolic Disease Definition Pulmonary Hypertension due to chronic thromboembolism 6 months post acute PE:
Chronic Thromboembolic Disease Diagnosis Prevention Treatment Surgical Nonsurgical Chronic Thromboembolic Disease Definition Pulmonary Hypertension due to chronic thromboembolism 6 months post acute PE:
Yes when meets criteria below
 Vein Disease Treatment MP9241 Covered Service: Prior Authorization Required: Additional Information: Medicare Policy: BadgerCare Plus Policy: Yes when meets criteria below Yes None Dean Health Plan covers
Vein Disease Treatment MP9241 Covered Service: Prior Authorization Required: Additional Information: Medicare Policy: BadgerCare Plus Policy: Yes when meets criteria below Yes None Dean Health Plan covers
Ultrasound in Vascular Surgery. Torbjørn Dahl
 Ultrasound in Vascular Surgery Torbjørn Dahl 1 The field of vascular surgery Veins dilatation and obstruction (varicose veins and valve dysfunction) Arteries dilatation and narrowing (aneurysms and atherosclerosis)
Ultrasound in Vascular Surgery Torbjørn Dahl 1 The field of vascular surgery Veins dilatation and obstruction (varicose veins and valve dysfunction) Arteries dilatation and narrowing (aneurysms and atherosclerosis)
CHAPTER 4 QUALITY ASSURANCE AND TEST VALIDATION
 CHAPTER 4 QUALITY ASSURANCE AND TEST VALIDATION CINDY WEILAND AND SANDRA L. KATANICK Continued innovations in noninvasive testing equipment provide skilled sonographers and physicians with the technology
CHAPTER 4 QUALITY ASSURANCE AND TEST VALIDATION CINDY WEILAND AND SANDRA L. KATANICK Continued innovations in noninvasive testing equipment provide skilled sonographers and physicians with the technology
LONG TERM FOLLOW-UP AFTER ENDOVENOUS LASER ABLATION
 LONG TERM FOLLOW-UP AFTER ENDOVENOUS LASER ABLATION Giorgio Spreafico Centro Multidisciplinare Day Surgery Azienda Ospedaliera Università Padova - Italy Faculty Disclosure I have no financial relationships
LONG TERM FOLLOW-UP AFTER ENDOVENOUS LASER ABLATION Giorgio Spreafico Centro Multidisciplinare Day Surgery Azienda Ospedaliera Università Padova - Italy Faculty Disclosure I have no financial relationships
Medicare C/D Medical Coverage Policy
 Varicose Vein Treatment Medicare C/D Medical Coverage Policy Origination Date: June 1, 1993 Review Date: September 16, 2015 Next Review: September, 2017 DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE OR SERVICE Varicose veins
Varicose Vein Treatment Medicare C/D Medical Coverage Policy Origination Date: June 1, 1993 Review Date: September 16, 2015 Next Review: September, 2017 DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE OR SERVICE Varicose veins
Venous Thromboembolic Treatment Guidelines
 Venous Thromboembolic Treatment Guidelines About the NYU Venous Thromboembolic Center (VTEC) The center s mission is to deliver advanced screening, detection, care, and management services for patients
Venous Thromboembolic Treatment Guidelines About the NYU Venous Thromboembolic Center (VTEC) The center s mission is to deliver advanced screening, detection, care, and management services for patients
Vascular Technology (VT) Content Outline Anatomy & physiology 20% Cerebrovascular Cerebrovascular normal anatomy Evaluate the cerebrovascular vessels
 Vascular Technology (VT) Content Outline Anatomy & physiology 20% normal anatomy Evaluate the cerebrovascular vessels hemodynamics Evaluate the cerebrovascular vessels for normal perfusion normal anatomy
Vascular Technology (VT) Content Outline Anatomy & physiology 20% normal anatomy Evaluate the cerebrovascular vessels hemodynamics Evaluate the cerebrovascular vessels for normal perfusion normal anatomy
EFSUMB EUROPEAN FEDERATION OF SOCIETIES FOR ULTRASOUND IN MEDICINE AND BIOLOGY Building a European Ultrasound Community
 MINIMUM TRAINING REQUIREMENTS FOR THE PRACTICE OF MEDICAL ULTRASOUND IN EUROPE Appendix 8: Vascular Ultrasound Level 1 Training and Practice Practical training should involve at least two half day ultrasound
MINIMUM TRAINING REQUIREMENTS FOR THE PRACTICE OF MEDICAL ULTRASOUND IN EUROPE Appendix 8: Vascular Ultrasound Level 1 Training and Practice Practical training should involve at least two half day ultrasound
New Anticoagulants for the Treatment of Thromboembolism With a little subplot on superficial thrombophlebitis. Mark Crowther
 New Anticoagulants for the Treatment of Thromboembolism With a little subplot on superficial thrombophlebitis Mark Crowther 1 Disclosures Advisory Boards in last 24 months Pfizer, Alexion, Bayer, CSL Behring,
New Anticoagulants for the Treatment of Thromboembolism With a little subplot on superficial thrombophlebitis Mark Crowther 1 Disclosures Advisory Boards in last 24 months Pfizer, Alexion, Bayer, CSL Behring,
Guidelines for the Management of Patients Following Endoluminal Vein Dilation Procedures for the Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis
 Guidelines for the Management of Patients Following Endoluminal Vein Dilation Procedures for the Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis Report Submitted to the Minister of Health and Long-Term Care By the Ontario
Guidelines for the Management of Patients Following Endoluminal Vein Dilation Procedures for the Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis Report Submitted to the Minister of Health and Long-Term Care By the Ontario
2. Background This indication of rivaroxaban had not previously been considered by the PBAC.
 PUBLIC SUMMARY DOCUMENT Product: Rivaroxaban, tablets, 15mg and 20mg, Xarelto Sponsor: Bayer Australia Ltd Date of PBAC Consideration: March 2013 1. Purpose of Application The application requested the
PUBLIC SUMMARY DOCUMENT Product: Rivaroxaban, tablets, 15mg and 20mg, Xarelto Sponsor: Bayer Australia Ltd Date of PBAC Consideration: March 2013 1. Purpose of Application The application requested the
Dabigatran etexilate for the treatment and secondary prevention of deep vein thrombosis and/or pulmonary embolism ERRATUM
 Dabigatran etexilate for the treatment and secondary prevention of deep vein thrombosis and/or pulmonary embolism ERRATUM This report was commissioned by the NIHR HTA Programme as project number 12/78
Dabigatran etexilate for the treatment and secondary prevention of deep vein thrombosis and/or pulmonary embolism ERRATUM This report was commissioned by the NIHR HTA Programme as project number 12/78
PROVIDER POLICIES & PROCEDURES
 PROVIDER POLICIES & PROCEDURES SCLEROTHERAPY TREATMENT OF SUPERFICIAL VARICOSE VEINS OF THE LEGS The purpose of this document is to provide guidance to providers enrolled in the Connecticut Medical Assistance
PROVIDER POLICIES & PROCEDURES SCLEROTHERAPY TREATMENT OF SUPERFICIAL VARICOSE VEINS OF THE LEGS The purpose of this document is to provide guidance to providers enrolled in the Connecticut Medical Assistance
MEDICAL COVERAGE POLICY. SERVICE: Varicose Veins of the Lower Extremities. PRIOR AUTHORIZATION: Required.
 Page 1 of 5 MEDICAL COVERAGE POLICY Important note Even though this policy may indicate that a particular service or supply may be considered covered, this conclusion is not based upon the terms of your
Page 1 of 5 MEDICAL COVERAGE POLICY Important note Even though this policy may indicate that a particular service or supply may be considered covered, this conclusion is not based upon the terms of your
PARTICULAR ASPECTS OF ANTI-THROMBOTIC TREATMENT IN HIP ARTHROPLASTY
 1 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA PARTICULAR ASPECTS OF ANTI-THROMBOTIC TREATMENT IN HIP ARTHROPLASTY ABSTRACT Ph.D student DR. TRUŞCĂ PAUL TIBERIU SCIENTIFIC COORDONATOR PROF. DR.VALENTIN
1 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA PARTICULAR ASPECTS OF ANTI-THROMBOTIC TREATMENT IN HIP ARTHROPLASTY ABSTRACT Ph.D student DR. TRUŞCĂ PAUL TIBERIU SCIENTIFIC COORDONATOR PROF. DR.VALENTIN
Provided by the American Venous Forum: veinforum.org
 CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
XARELTO (rivaroxaban tablets) in Knee and Hip Replacement Surgery
 XARELTO (rivaroxaban tablets) in Knee and Hip Replacement Surgery Fast Facts: XARELTO is a novel, once-daily, oral anticoagulant recently approved in the United States for the prevention (prophylaxis)
XARELTO (rivaroxaban tablets) in Knee and Hip Replacement Surgery Fast Facts: XARELTO is a novel, once-daily, oral anticoagulant recently approved in the United States for the prevention (prophylaxis)
Prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in adult patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation (AF) with one or more risk factors
 News Release For use outside the US and UK only Bayer Pharma AG 13342 Berlin Germany Tel. +49 30 468-1111 www.bayerpharma.com Bayer s Xarelto Approved in the EU for the Prevention of Stroke in Patients
News Release For use outside the US and UK only Bayer Pharma AG 13342 Berlin Germany Tel. +49 30 468-1111 www.bayerpharma.com Bayer s Xarelto Approved in the EU for the Prevention of Stroke in Patients
Lower Extremity Arterial Segmental Physiologic Evaluation
 VASCULAR TECHNOLOGY PROFESSIONAL PERFORMANCE GUIDELINES Lower Extremity Arterial Segmental Physiologic Evaluation This Guideline was prepared by the Professional Guidelines Subcommittee of the Society
VASCULAR TECHNOLOGY PROFESSIONAL PERFORMANCE GUIDELINES Lower Extremity Arterial Segmental Physiologic Evaluation This Guideline was prepared by the Professional Guidelines Subcommittee of the Society
Tired, Aching Legs? Swollen Ankles? Varicose Veins? An informative guide for patients
 Tired, Aching Legs? Swollen Ankles? Varicose Veins? An informative guide for patients Are You at Risk? Leg problems are widespread throughout the world, but what most people don t know is that approximately
Tired, Aching Legs? Swollen Ankles? Varicose Veins? An informative guide for patients Are You at Risk? Leg problems are widespread throughout the world, but what most people don t know is that approximately
Evaluation of d-dimer in the Diagnosis of Suspected Deep-Vein Thrombosis
 original article Evaluation of d-dimer in the Diagnosis of Suspected Deep-Vein Thrombosis Philip S. Wells, M.D., David R. Anderson, M.D., Marc Rodger, M.D., Melissa Forgie, M.D., Clive Kearon, M.D., Ph.D.,
original article Evaluation of d-dimer in the Diagnosis of Suspected Deep-Vein Thrombosis Philip S. Wells, M.D., David R. Anderson, M.D., Marc Rodger, M.D., Melissa Forgie, M.D., Clive Kearon, M.D., Ph.D.,
Anticoagulant therapy
 Anticoagulation: The risks Anticoagulant therapy 1990 2002: 600 incidents reported 120 resulted in death of patient 92 deaths related to warfarin usage 28 reports related to heparin usage Incidents in
Anticoagulation: The risks Anticoagulant therapy 1990 2002: 600 incidents reported 120 resulted in death of patient 92 deaths related to warfarin usage 28 reports related to heparin usage Incidents in
Ultrasound - Vascular
 Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Vascular Vascular ultrasound uses sound waves to evaluate the body s circulatory system and help identify blockages and detect blood clots. A Doppler ultrasound study
Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Vascular Vascular ultrasound uses sound waves to evaluate the body s circulatory system and help identify blockages and detect blood clots. A Doppler ultrasound study
THE INTERNET STROKE CENTER PRESENTATIONS AND DISCUSSIONS ON STROKE MANAGEMENT
 THE INTERNET STROKE CENTER PRESENTATIONS AND DISCUSSIONS ON STROKE MANAGEMENT Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Gregory Albers, M.D. Director Stanford Stroke Center Professor of Neurology and Neurological
THE INTERNET STROKE CENTER PRESENTATIONS AND DISCUSSIONS ON STROKE MANAGEMENT Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Gregory Albers, M.D. Director Stanford Stroke Center Professor of Neurology and Neurological
Thrombosis and Hemostasis
 Thrombosis and Hemostasis Wendy Lim, MD, MSc, FRCPC Associate Professor, Department of Medicine McMaster University, Hamilton, ON Overview To review the important developments in venous thromboembolism
Thrombosis and Hemostasis Wendy Lim, MD, MSc, FRCPC Associate Professor, Department of Medicine McMaster University, Hamilton, ON Overview To review the important developments in venous thromboembolism
Horton General Hospital Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Information for patients
 Horton General Hospital Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Information for patients What is a Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)? A DVT is a blood clot which forms in a deep vein, usually in
Horton General Hospital Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Information for patients What is a Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)? A DVT is a blood clot which forms in a deep vein, usually in
Thrombophilia. Steven R. Lentz, M.D. Ph.D. Carver College of Medicine The University of Iowa May 2003
 Thrombophilia Steven R. Lentz, M.D. Ph.D. Carver College of Medicine The University of Iowa May 2003 Thrombophilia Hereditary and acquired risk factors for thrombosis Venous thromboembolism Arterial thromboembolism
Thrombophilia Steven R. Lentz, M.D. Ph.D. Carver College of Medicine The University of Iowa May 2003 Thrombophilia Hereditary and acquired risk factors for thrombosis Venous thromboembolism Arterial thromboembolism
How To Use An Ekosonic Endovascular System
 EkoSonic Endovascular System Nursing Presentation Imagine where we can go. Imagine where we can go. Forward-looking statement This presentation and information communicated verbally to you may contain
EkoSonic Endovascular System Nursing Presentation Imagine where we can go. Imagine where we can go. Forward-looking statement This presentation and information communicated verbally to you may contain
What Does Pregnancy Have to Do With Blood Clots in a Woman s Legs?
 Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning A Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning Drugs to Prevent Abnormal Blood
Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning A Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning Drugs to Prevent Abnormal Blood
Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations. CardioCase presentation. Ethel s Case. Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC
 Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC CardioCase presentation Ethel s Case Ethel, 73, presents with rapid heart beating and mild chest discomfort. In the ED, ECG
Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC CardioCase presentation Ethel s Case Ethel, 73, presents with rapid heart beating and mild chest discomfort. In the ED, ECG
ABOUT XARELTO CLINICAL STUDIES
 ABOUT XARELTO CLINICAL STUDIES FAST FACTS Xarelto (rivaroxaban) is a novel, oral direct Factor Xa inhibitor. On September 30, 2008, the European Commission granted marketing approval for Xarelto for the
ABOUT XARELTO CLINICAL STUDIES FAST FACTS Xarelto (rivaroxaban) is a novel, oral direct Factor Xa inhibitor. On September 30, 2008, the European Commission granted marketing approval for Xarelto for the
Extracranial Cerebrovascular Duplex Ultrasound Evaluation
 VASCULAR TECHNOLOGY PROFESSIONAL PERFORMANCE GUIDELINES Extracranial Cerebrovascular Duplex Ultrasound Evaluation This Guideline was prepared by the Professional Guidelines Subcommittee of the Society
VASCULAR TECHNOLOGY PROFESSIONAL PERFORMANCE GUIDELINES Extracranial Cerebrovascular Duplex Ultrasound Evaluation This Guideline was prepared by the Professional Guidelines Subcommittee of the Society
Tired, Aching Legs? Swollen Ankles? Varicose Veins?
 Tired, Aching Legs? Swollen Ankles? Varicose Veins? Healthy Legs 2006 http://healthylegs.com Page 1 Venous disorders are widespread Leg problems are widespread throughout the world, but what most people
Tired, Aching Legs? Swollen Ankles? Varicose Veins? Healthy Legs 2006 http://healthylegs.com Page 1 Venous disorders are widespread Leg problems are widespread throughout the world, but what most people
VARICOSE VEINS. Information Leaflet. Your Health. Our Priority. VTE Ambulatory Clinic Stepping Hill Hospital
 VARICOSE VEINS Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 7 Varicose Veins There are no accurate figures for the number of people with varicose veins. Some studies suggest that 3 in 100 people
VARICOSE VEINS Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 7 Varicose Veins There are no accurate figures for the number of people with varicose veins. Some studies suggest that 3 in 100 people
CHAPTER 15 SCLEROTHERAPY FOR VENOUS DISEASE
 Introduction CHAPTER 15 SCLEROTHERAPY FOR VENOUS DISEASE Original authors: Niren Angle, John J. Bergan, Joshua I. Greenberg, and J. Leonel Villavicencio Abstracted by Teresa L. Carman New technology has
Introduction CHAPTER 15 SCLEROTHERAPY FOR VENOUS DISEASE Original authors: Niren Angle, John J. Bergan, Joshua I. Greenberg, and J. Leonel Villavicencio Abstracted by Teresa L. Carman New technology has
Predictive Value of the Rapid Whole Blood Agglutination D-Dimer Assay (AGEN SimpliRED) in Community Outpatients with Suspected Deep Venous Thrombosis
 CME clinical contributions Predictive Value of the Rapid Whole Blood Agglutination D-Dimer Assay (AGEN SimpliRED) in Community Outpatients with Suspected Deep Venous Thrombosis By Julieta E Hayag, MD Prem
CME clinical contributions Predictive Value of the Rapid Whole Blood Agglutination D-Dimer Assay (AGEN SimpliRED) in Community Outpatients with Suspected Deep Venous Thrombosis By Julieta E Hayag, MD Prem
Vascular Laboratory Education and Training
 Vascular Laboratory Education and Training David L. Dawson, MD, RVT, RPVI Vascular laboratory professionals technologists and physicians have specific knowledge and expertise in the use of non- invasive
Vascular Laboratory Education and Training David L. Dawson, MD, RVT, RPVI Vascular laboratory professionals technologists and physicians have specific knowledge and expertise in the use of non- invasive
Clinical Study Synopsis
 Clinical Study Synopsis This Clinical Study Synopsis is provided for patients and healthcare professionals to increase the transparency of Bayer's clinical research. This document is not intended to replace
Clinical Study Synopsis This Clinical Study Synopsis is provided for patients and healthcare professionals to increase the transparency of Bayer's clinical research. This document is not intended to replace
National Guidance and New Protocols
 National Guidance and New Protocols Dr Jane Strong Consultant Haematologist DVT clinical lead Acute VTE chair DAWN AC Twentieth User Group Meeting 8 th October 2012 Autumn dawn Restless geese take flight
National Guidance and New Protocols Dr Jane Strong Consultant Haematologist DVT clinical lead Acute VTE chair DAWN AC Twentieth User Group Meeting 8 th October 2012 Autumn dawn Restless geese take flight
Title Use of rivaroxaban in suspected DVT in the Emergency Department Standard Operating Procedure. Author s job title. Pharmacist.
 Document Control Title Use of rivaroxaban in suspected DVT in the Emergency Department Author Pharmacist Directorate Clinical Support Services Version Date Issued Status 0.1 Oct Draft 2015 1.0 Dec Final
Document Control Title Use of rivaroxaban in suspected DVT in the Emergency Department Author Pharmacist Directorate Clinical Support Services Version Date Issued Status 0.1 Oct Draft 2015 1.0 Dec Final
A Patient s Guide to Primary and Secondary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Using Blood-Thinning (Anticoagulant) Drugs
 A Patient s Guide to Primary and Secondary Prevention of PATIENT EDUCATION GUIDE What Is Cardiovascular Disease? Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a broad term that covers any disease of the heart and circulatory
A Patient s Guide to Primary and Secondary Prevention of PATIENT EDUCATION GUIDE What Is Cardiovascular Disease? Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a broad term that covers any disease of the heart and circulatory
Recurrent Varicose Veins
 Information for patients Recurrent Varicose Veins Sheffield Vascular Institute Northern General Hospital You have been diagnosed as having Varicose Veins that have recurred (come back). This leaflet explains
Information for patients Recurrent Varicose Veins Sheffield Vascular Institute Northern General Hospital You have been diagnosed as having Varicose Veins that have recurred (come back). This leaflet explains
Cost Effectiveness of Apixaban (Eliquis ) for the Prevention of Venous Thromboembolic Events in Adult Patients who have Undergone Elective Total Hip
 Cost Effectiveness of Apixaban (Eliquis ) for the Prevention of Venous Thromboembolic Events in Adult Patients who have Undergone Elective Total Hip Replacement or Total Knee Replacement National Centre
Cost Effectiveness of Apixaban (Eliquis ) for the Prevention of Venous Thromboembolic Events in Adult Patients who have Undergone Elective Total Hip Replacement or Total Knee Replacement National Centre
CDEC FINAL RECOMMENDATION
 CDEC FINAL RECOMMENDATION RIVAROXABAN (Xarelto Bayer Inc.) New Indication: Pulmonary Embolism Note: The Canadian Drug Expert Committee (CDEC) previously reviewed rivaroxaban for the treatment of deep vein
CDEC FINAL RECOMMENDATION RIVAROXABAN (Xarelto Bayer Inc.) New Indication: Pulmonary Embolism Note: The Canadian Drug Expert Committee (CDEC) previously reviewed rivaroxaban for the treatment of deep vein
Inpatient Anticoagulation Safety. To provide safe and effective anticoagulation therapy through a collaborative approach.
 Inpatient Anticoagulation Safety Purpose: Policy: To provide safe and effective anticoagulation therapy through a collaborative approach. Upon the written order of a physician, Heparin, Low Molecular Weight
Inpatient Anticoagulation Safety Purpose: Policy: To provide safe and effective anticoagulation therapy through a collaborative approach. Upon the written order of a physician, Heparin, Low Molecular Weight
Non-surgical treatment of severe varicose veins
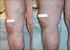 Non-surgical treatment of severe varicose veins Yasu Harasaki UCHSC Department of Surgery General Surgery Grand Rounds March 19, 2007 Definition Dilated, palpable, subcutaneous veins generally >3mm in
Non-surgical treatment of severe varicose veins Yasu Harasaki UCHSC Department of Surgery General Surgery Grand Rounds March 19, 2007 Definition Dilated, palpable, subcutaneous veins generally >3mm in
The importance of adherence and persistence: The advantages of once-daily dosing
 The importance of adherence and persistence: The advantages of once-daily dosing Craig I. Coleman, PharmD Professor, University of Connecticut School of Pharmacy Storrs, CT, USA Conflicts of interest Dr
The importance of adherence and persistence: The advantages of once-daily dosing Craig I. Coleman, PharmD Professor, University of Connecticut School of Pharmacy Storrs, CT, USA Conflicts of interest Dr
National Guidance and New Protocols
 National Guidance and New Protocols Dr Jane Strong Consultant Haematologist DVT clinical lead Acute VTE chair DAWN AC Twentieth User Group Meeting 8 th October 2012 DVT patient pathway Assessment Diagnosis
National Guidance and New Protocols Dr Jane Strong Consultant Haematologist DVT clinical lead Acute VTE chair DAWN AC Twentieth User Group Meeting 8 th October 2012 DVT patient pathway Assessment Diagnosis
How To Get A Dose Of Bayer Healthcare'S Oral Anticoagulant, Xarelto
 News Release FOR UK HEALTHCARE MEDIA ONLY Bayer HealthCare Bayer plc Bayer House Strawberry Hill Newbury Berkshire, RG14 1JA www.bayer.co.uk Bayer s Xarelto (rivaroxaban) Recommended by CHMP for EU Approval
News Release FOR UK HEALTHCARE MEDIA ONLY Bayer HealthCare Bayer plc Bayer House Strawberry Hill Newbury Berkshire, RG14 1JA www.bayer.co.uk Bayer s Xarelto (rivaroxaban) Recommended by CHMP for EU Approval
Preventing Blood Clots in Adult Patients. Information For Patients
 Preventing Blood Clots in Adult Patients Information For Patients 1 This leaflet will give you information on how to reduce the risk of developing blood clots during and after your stay in hospital. If
Preventing Blood Clots in Adult Patients Information For Patients 1 This leaflet will give you information on how to reduce the risk of developing blood clots during and after your stay in hospital. If
Joseph A. Caprini, MD, MS, FACS, RVT
 Joseph A. Caprini, MD, MS, FACS, RVT Louis W. Biegler Chair of Surgery NorthShore University HealthSystem, Evanston, IL Clinical Professor of Surgery University of Chicago Pritzker School of Medicine,
Joseph A. Caprini, MD, MS, FACS, RVT Louis W. Biegler Chair of Surgery NorthShore University HealthSystem, Evanston, IL Clinical Professor of Surgery University of Chicago Pritzker School of Medicine,
Spotlight Series: Interventional Radiology. Varicose Veins and Venous Insufficiency
 Spotlight Series: Interventional Radiology Varicose Veins and Venous Insufficiency What is venous insufficiency? Spectrum of Disease Spider veins and telangiectasias Small reddish and purple veins near
Spotlight Series: Interventional Radiology Varicose Veins and Venous Insufficiency What is venous insufficiency? Spectrum of Disease Spider veins and telangiectasias Small reddish and purple veins near
APSR RESPIRATORY UPDATES
 APSR RESPIRATORY UPDATES Volume 6, Issue 1 Newsletter Date: January 2014 APSR EDUCATION PUBLICATION Inside this issue: Venous thromboembolism Pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis. 2 Outpatient versus
APSR RESPIRATORY UPDATES Volume 6, Issue 1 Newsletter Date: January 2014 APSR EDUCATION PUBLICATION Inside this issue: Venous thromboembolism Pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis. 2 Outpatient versus
ENTITLEMENT ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINES VARICOSE VEINS AND SUPERFICIAL THROMBOPHLEBITIS
 ENTITLEMENT ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINES VARICOSE VEINS AND SUPERFICIAL THROMBOPHLEBITIS 1. VARICOSE VEINS MPC 00727 ICD-9 454 DEFINITION Varicose Veins of the lower extremities are a dilatation, lengthening
ENTITLEMENT ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINES VARICOSE VEINS AND SUPERFICIAL THROMBOPHLEBITIS 1. VARICOSE VEINS MPC 00727 ICD-9 454 DEFINITION Varicose Veins of the lower extremities are a dilatation, lengthening
To provide an evidenced-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis.
 DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS: TREATMENT TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidenced-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis.
DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS: TREATMENT TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidenced-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis.
ACUTE DVT MANAGEMENT Richard J. DeMasi, MD April 26, 2014
 ACUTE DVT MANAGEMENT Richard J. DeMasi, MD April 26, 2014 Thromboembolism epidemiology 5 million DVT s 900,000 PE s 290,000 fatalities Heit J. Blood. 2005;106:910. 10 VTE events Since this talk began DVT
ACUTE DVT MANAGEMENT Richard J. DeMasi, MD April 26, 2014 Thromboembolism epidemiology 5 million DVT s 900,000 PE s 290,000 fatalities Heit J. Blood. 2005;106:910. 10 VTE events Since this talk began DVT
Varicose Veins Backgrounder
 What Are Varicose Veins? Varicose veins are a clinical presentation of superficial venous insufficiency a condition in which veins are inefficient in returning blood to the heart due to venous hypertension.
What Are Varicose Veins? Varicose veins are a clinical presentation of superficial venous insufficiency a condition in which veins are inefficient in returning blood to the heart due to venous hypertension.
Investor News. Not intended for U.S. and UK media
 Investor News Not intended for U.S. and UK media Bayer AG Investor Relations 51368 Leverkusen Germany www.investor.bayer.com Bayer s Xarelto (Rivaroxaban) Approved for the Treatment of Pulmonary Embolism
Investor News Not intended for U.S. and UK media Bayer AG Investor Relations 51368 Leverkusen Germany www.investor.bayer.com Bayer s Xarelto (Rivaroxaban) Approved for the Treatment of Pulmonary Embolism
Dr. Linde is an international beauty expert and an acclaimed keynote speaker at conferences all over the world. He is specialized in the treatment of
 VEINS Dr. Linde is an international beauty expert and an acclaimed keynote speaker at conferences all over the world. He is specialized in the treatment of fat pads, wrinkles and transformations of the
VEINS Dr. Linde is an international beauty expert and an acclaimed keynote speaker at conferences all over the world. He is specialized in the treatment of fat pads, wrinkles and transformations of the
Varicose Veins: Causes, Symptoms and Management. Andrew C. Stanley MD Section of Vascular Surgery
 Varicose Veins: Causes, Symptoms and Management Andrew C. Stanley MD Section of Vascular Surgery Circulation Heart (Pump)-MI, Sudden Death Arteries (Stroke, Aneurysms, Walking dysfunction, Limb loss) Veins
Varicose Veins: Causes, Symptoms and Management Andrew C. Stanley MD Section of Vascular Surgery Circulation Heart (Pump)-MI, Sudden Death Arteries (Stroke, Aneurysms, Walking dysfunction, Limb loss) Veins
Recurrent Varicose Veins. Vineet Mishra, MD Director of Mohs Surgery and Procedural Dermatology University of Texas Health Science Center San Antonio
 Recurrent Varicose Veins Vineet Mishra, MD Director of Mohs Surgery and Procedural Dermatology University of Texas Health Science Center San Antonio Disclosures None Possible Causes of Recurrence DNA:
Recurrent Varicose Veins Vineet Mishra, MD Director of Mohs Surgery and Procedural Dermatology University of Texas Health Science Center San Antonio Disclosures None Possible Causes of Recurrence DNA:
Medicare C/D Medical Coverage Policy
 Varicose Vein Treatment Origination Date: June 1, 1993 Review Date: July 20, 2016 Next Review: July, 2018 Medicare C/D Medical Coverage Policy DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE OR SERVICE Varicose veins of the
Varicose Vein Treatment Origination Date: June 1, 1993 Review Date: July 20, 2016 Next Review: July, 2018 Medicare C/D Medical Coverage Policy DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE OR SERVICE Varicose veins of the
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE: MOBILITY WITH A DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT) Page 1 of 10
 Page 1 of 10 1.0 FOCUS: Mobilization with a Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT). The purpose of this clinical practice guideline (CPG) is to ensure that new knowledge is integrated across Fraser Health and to standardize
Page 1 of 10 1.0 FOCUS: Mobilization with a Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT). The purpose of this clinical practice guideline (CPG) is to ensure that new knowledge is integrated across Fraser Health and to standardize
Chapter: Deep Vein Thrombosis and Stroke. 1 Contact Hour. Learning objectives. Introduction. Types of venous thrombosis.
 Chapter: Deep Vein Thrombosis and Stroke 1 Contact Hour Learning objectives Differentiate among the different types of venous thrombosis. Describe the pathophysiology of thrombus formation. Identify risk
Chapter: Deep Vein Thrombosis and Stroke 1 Contact Hour Learning objectives Differentiate among the different types of venous thrombosis. Describe the pathophysiology of thrombus formation. Identify risk
HERTFORDSHIRE MEDICINES MANAGEMENT COMMITTEE (HMMC) RIVAROXABAN RECOMMENDED see specific recommendations for licensed indications below
 Name: generic (trade) Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) HERTFORDSHIRE MEDICINES MANAGEMENT COMMITTEE (HMMC) RIVAROXABAN RECOMMENDED see specific recommendations for licensed indications below What it is Indications
Name: generic (trade) Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) HERTFORDSHIRE MEDICINES MANAGEMENT COMMITTEE (HMMC) RIVAROXABAN RECOMMENDED see specific recommendations for licensed indications below What it is Indications
Duplex Carotid Sonography in Distinguishing Acute Unilateral Atherothrombotic from Cardioembolic Carotid Artery Occlusion
 Duplex Carotid Sonography in Distinguishing Acute Unilateral Atherothrombotic from Cardioembolic Carotid Artery Occlusion Kazumi Kimura, Kiminobu Yonemura, Tadashi Terasaki, Yoichiro Hashimoto, and Makoto
Duplex Carotid Sonography in Distinguishing Acute Unilateral Atherothrombotic from Cardioembolic Carotid Artery Occlusion Kazumi Kimura, Kiminobu Yonemura, Tadashi Terasaki, Yoichiro Hashimoto, and Makoto
Baby Your Legs! Get relief for: Heavy, tired or aching legs Swollen ankles and feet Varicose or spider veins. Managing leg health during pregnancy
 Baby Your Legs! Get relief for: Heavy, tired or aching legs Swollen ankles and feet Varicose or spider veins Managing leg health during pregnancy Common leg health problems during pregnancy Venous disorders
Baby Your Legs! Get relief for: Heavy, tired or aching legs Swollen ankles and feet Varicose or spider veins Managing leg health during pregnancy Common leg health problems during pregnancy Venous disorders
Subclavian Steal Syndrome By Marta Thorup
 Subclavian Steal Syndrome By Marta Thorup Definition Subclavian steal syndrome (SSS), is a constellation of signs and symptoms that arise from retrograde flow of blood in the vertebral artery, due to proximal
Subclavian Steal Syndrome By Marta Thorup Definition Subclavian steal syndrome (SSS), is a constellation of signs and symptoms that arise from retrograde flow of blood in the vertebral artery, due to proximal
Effective Date: March 2, 2016
 Medical Review Criteria Varicose Vein Procedures Effective Date: March 2, 2016 Treatmetn Subject: Varicose Vein Procedures VeinTreatment of Varicose Policy: Veins HPHC covers specific non-experimental
Medical Review Criteria Varicose Vein Procedures Effective Date: March 2, 2016 Treatmetn Subject: Varicose Vein Procedures VeinTreatment of Varicose Policy: Veins HPHC covers specific non-experimental
Model Answer: Australasian College of Phlebology > Ultrasound in Phlebology > Advanced Course > Topic 4
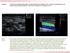 Ques?on 1: Compression sonography (lee image) is the gold standard for the diagnosis of DVT. Are there any advantages of color Doppler ultrasound (right image) over compression sonography in the diagnosis
Ques?on 1: Compression sonography (lee image) is the gold standard for the diagnosis of DVT. Are there any advantages of color Doppler ultrasound (right image) over compression sonography in the diagnosis
Bayer Initiates Rivaroxaban Phase III Study to Support Dose Selection According to Individual Benefit-Risk Profile in Long- Term VTE Prevention
 Investor News Not intended for U.S. and UK Media Bayer AG Investor Relations 51368 Leverkusen Germany www.investor.bayer.com Long-term prevention of venous blood clots (VTE): Bayer Initiates Rivaroxaban
Investor News Not intended for U.S. and UK Media Bayer AG Investor Relations 51368 Leverkusen Germany www.investor.bayer.com Long-term prevention of venous blood clots (VTE): Bayer Initiates Rivaroxaban
Updates to the Alberta Drug Benefit List. Effective January 1, 2016
 Updates to the Alberta Drug Benefit List Effective January 1, 2016 Inquiries should be directed to: Pharmacy Services Alberta Blue Cross 10009 108 Street NW Edmonton AB T5J 3C5 Telephone Number: (780)
Updates to the Alberta Drug Benefit List Effective January 1, 2016 Inquiries should be directed to: Pharmacy Services Alberta Blue Cross 10009 108 Street NW Edmonton AB T5J 3C5 Telephone Number: (780)
New Oral Anticoagulants. How safe are they outside the trials?
 New Oral Anticoagulants How safe are they outside the trials? Objectives The need for anticoagulant therapy Indications for anticoagulation Traditional anticoagulant therapies Properties of new oral anticoagulants
New Oral Anticoagulants How safe are they outside the trials? Objectives The need for anticoagulant therapy Indications for anticoagulation Traditional anticoagulant therapies Properties of new oral anticoagulants
CDEC RECORD OF ADVICE
 CDEC RECORD OF ADVICE RIVAROXABAN (Xarelto Bayer Inc.) Indication: Deep Vein Thrombosis Without Symptomatic Pulmonary Embolism This document summarizes the Canadian Drug Expert Committee (CDEC) response
CDEC RECORD OF ADVICE RIVAROXABAN (Xarelto Bayer Inc.) Indication: Deep Vein Thrombosis Without Symptomatic Pulmonary Embolism This document summarizes the Canadian Drug Expert Committee (CDEC) response
Varicose veins - 1 -
 Varicose veins - 1 - Varicose Veins About 3 in 10 adults develop varicose veins at some time in their life. Most people with varicose veins do not have an underlying disease and they usually occur for
Varicose veins - 1 - Varicose Veins About 3 in 10 adults develop varicose veins at some time in their life. Most people with varicose veins do not have an underlying disease and they usually occur for
X-Plain Varicose Veins Reference Summary
 X-Plain Varicose Veins Reference Summary Introduction Varicose veins are very common, in both women and men. Varicose veins can be painful and unattractive. Vein doctors use non-invasive ultrasound imaging
X-Plain Varicose Veins Reference Summary Introduction Varicose veins are very common, in both women and men. Varicose veins can be painful and unattractive. Vein doctors use non-invasive ultrasound imaging
Oxford Anticoagulation & Thrombosis Service Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Oxford Anticoagulation & Thrombosis Service Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Information for people with a blood clot (thrombus) What is this
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Oxford Anticoagulation & Thrombosis Service Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Information for people with a blood clot (thrombus) What is this
Information for you Treatment of venous thrombosis in pregnancy and after birth. What are the symptoms of a DVT during pregnancy?
 Information for you Treatment of venous thrombosis in pregnancy and after birth Published in September 2011 What is venous thrombosis? Thrombosis is a blood clot in a blood vessel (a vein or an artery).
Information for you Treatment of venous thrombosis in pregnancy and after birth Published in September 2011 What is venous thrombosis? Thrombosis is a blood clot in a blood vessel (a vein or an artery).
VFI Technology to Change the Way You Work
 Technology to Change the Way You Work Vascular Ultrasound Made Easier Vector Flow Imaging VFI VFI is a ground-breaking technology that can revolutionize the workflow for many Doppler ultrasound applications.
Technology to Change the Way You Work Vascular Ultrasound Made Easier Vector Flow Imaging VFI VFI is a ground-breaking technology that can revolutionize the workflow for many Doppler ultrasound applications.
Clinical Study Synopsis
 Clinical Study Synopsis This Clinical Study Synopsis is provided for patients and healthcare professionals to increase the transparency of Bayer's clinical research. This document is not intended to replace
Clinical Study Synopsis This Clinical Study Synopsis is provided for patients and healthcare professionals to increase the transparency of Bayer's clinical research. This document is not intended to replace
DVT/PE Management with Rivaroxaban (Xarelto)
 DVT/PE Management with Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) Rivaroxaban is FDA approved for the acute treatment of DVT and PE and reduction in risk of recurrence of DVT and PE. FDA approved indications: Non valvular
DVT/PE Management with Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) Rivaroxaban is FDA approved for the acute treatment of DVT and PE and reduction in risk of recurrence of DVT and PE. FDA approved indications: Non valvular
Venous and Lymphatic Disorders
 Venous and Lymphatic Disorders. ก. Venous and Lymphatic Disorders Varicose Veins Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Lymphedema What Is Varicose Veins? Latin: Varicose = Varix = twisted Abnormal venous dilatation
Venous and Lymphatic Disorders. ก. Venous and Lymphatic Disorders Varicose Veins Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Lymphedema What Is Varicose Veins? Latin: Varicose = Varix = twisted Abnormal venous dilatation
How To Take Xarelto
 A patient's guide Your clinic's contact details are: Name: Contact number: Contents 2 Why have I been prescribed Xarelto? 2 What is Xarelto? 3 How do I take Xarelto? 3 What should I do if I miss a dose
A patient's guide Your clinic's contact details are: Name: Contact number: Contents 2 Why have I been prescribed Xarelto? 2 What is Xarelto? 3 How do I take Xarelto? 3 What should I do if I miss a dose
Using CDS (Clinical Decision Support) for Quality Initiatives at a Community Hospital
 Using CDS (Clinical Decision Support) for Quality Initiatives at a Community Hospital Jonathan Sykes MD, CMIO Jacalyn Liebowitz RN, MBA,NEA-BCFACHE VP Care Continuum Allegiance Health - Jackson, MI DISCLAIMER:
Using CDS (Clinical Decision Support) for Quality Initiatives at a Community Hospital Jonathan Sykes MD, CMIO Jacalyn Liebowitz RN, MBA,NEA-BCFACHE VP Care Continuum Allegiance Health - Jackson, MI DISCLAIMER:
