Security Enhancement Using Mutual Authentication in Existing CDMA Systems
|
|
|
- Francis Owens
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Security Enhancement Using Mutual Authentication in Existing CDMA Systems L. Krishna Bharathi 1, Department of ECE, Pondicherry Engineering College, Pondicherry, India. Gnanou Florence Sudha 2, Department of ECE, Pondicherry Engineering College, Pondicherry, India. Abstract Even though CDMA2000 wireless networks are being widely deployed as a cellular digital standard around the world, it has some hidden vulnerabilities concerned with security issues. The existing CDMA systems use authentication mechanism by CAVE (Cellular Authentication and Voice Encryption) algorithm. This authentication method has several disadvantages. Only one way authentication is provided, that is, only a base station authenticates a subscriber. And, CAVE algorithm is prone to cryptographic attacks. This work proposes to implement authentication method using ESA (Enhanced Subscriber Authentication) algorithm instead of CAVE algorithm in the existing CDMA systems. Authentication mechanism using ESA algorithm uses AKA (Authentication and Key Agreement) to enhance security strength and to provide mutual authentication between a base station and a mobile terminal. AKA with 128-bit key adopts the SHA1 hash algorithm to generate authentication value and message encryption keys. Performance analysis of the proposed work is done by calculating the autocorrelation, crosscorrelation of the transmitted voice signal and also the BER (Bit Error Rate) of the system. Thus the proposed work enhances the security strength of the system with increased key strength and bilateral authentication. The proposed scheme can readily be applied to the existing CDMA systems because only the algorithm is replaced but the input parameters remain the same. Keywords ESA, AKA, CAVE, CDMA, authentication I. INTRODUCTION As wireless services become increasingly prevalent, new possibilities and challenges continue to emerge. Security becomes vital to delivering solutions that meet today s demand for mobility. Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) mobile communication system starts from IS-95, called 2 nd generation system, to CDMA2000 1x, which is the 3 rd generation system. And now, CDMA2000 1x EV-DO system for high speed packet data is served in many countries. CDMA xRTT technology makes eavesdropping very complex. It uses 42-bit PN (Pseudo-Random Noise) Sequence called Long Code to scramble voice and data [1]. The existing CDMA systems uses Cellular Authentication and Voice Encryption (CAVE) algorithm. It provides only unilateral authentication which leads to false base station attacks and it is also prone to cryptographic attacks. These are the major challenges in the existing CDMA systems. This work proposes to apply ESA instead of CAVE in the authentication process of CDMA mobile communication systems. If ESA can be applied in the existing systems, demerits of CAVE algorithm can be improved. The rest of the paper is designed as follows. Section II discusses about the CAVE algorithm and its drawbacks. Section III and IV discuss about the proposed scheme in detail. Section V discusses the simulation results and section VI concludes the proposed work. Finally, section VII discuss about the future work. II. SECURITY IN EXISTING CDMA2000 NETWORKS Security has been a major concern for both service providers and subscribers, since the birth of the cellular industry. Service providers are primarily concerned with security to prevent fraudulent such as cloning, while subscribers are mainly concerned with privacy issues. CDMA2000 1xRTT network security protocols rely on a 64-bit Authentication Key (A-Key) and the ESN of the mobile. A random binary number called RANDSSD, which is generated at the Authentication Center (AC), is been used for authentication procedure. This section discusses about the generation of Shared Secret Data (SSD) and Authentication signature using CAVE algorithm and the drawbacks of CAVE algorithm. A. Cellular Authentication and Voice Encryption Algorithm Cellular Authentication and Voice Encryption (CAVE) is a set of cryptographic algorithms collectively referred to as the CAVE algorithm which is used during the authentication process. Based on the ISSN :
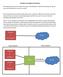
2 inputs used, the CAVE algorithm enables calculation of SSD and authentication signature during challenge/response procedure. 1) Authentication key: The Authentication Key (Akey) also known as master key, is the cornerstone of CAVE-based authentication. The A-key is provisioned in the home Authentication Center and the mobile station (MS).The purpose of the A-key in authentication is to generate Shared Secret Data. 2) Shared secret data: Shared Secret Data is a 128- bit value that is calculated using the CAVE algorithm. The SSD has two parts: SSD_A (64 bit) and SSD_B (64 bit) [2]. The mobile uses the SSD_A and the broadcast RAND as inputs to the CAVE algorithm to generate an 18-bit authentication signature and sends it to the base station. Figure 1 illustrates the generation of shared secret data in existing CDMA 2000 networks. This signature is then used by the base station to check that the subscriber is legitimate. The mobile uses the SSD_B and the CAVE algorithm to generate a Public Long Code Mask (PLCM), a Cellular Message Encryption Algorithm (CMEA) key (64 bits), and a data key (32 bits). The PLCM is utilized in both the mobile and the network to change the characteristics of a Long code. This modified Long code is used for voice encryption. Figure 1. Generation of shared secret data B. Drawbacks of CAVE Algorithm The CAVE algorithm is intended to authenticate a legitimate subscriber to the wireless network and protect the network and customers of mobile phones from the cloning fraud. The different attacks on CAVE algorithm namely false base station attacks and cryptographic attacks are described as follows. 1) False base station attacks: Authentication mechanism by CAVE algorithm provides only one way authentication, i.e. only a base station authenticates a subscriber and subscriber cannot authenticate the base station. This leads to base station impersonation or false base station attacks [3]. False base station attacks leads to eavesdropping of private identity information of the subscriber. 2) Cryptographic attacks: A hash function must be able to withstand all known types of cryptographic attacks. As a minimum, it must have the following properties: a) Pre-image resistance: Given a hash h, it should be difficult to find any message m such that h = hash(m). Functions which don t satisfy this property are vulnerable to pre-image attacks. b) Second pre-image resistance: Given an input message m1, it should be hard to find another input message m2 (not equal to m1) such that hash(m1) = hash(m2). Functions which don t satisfy this property are vulnerable to second pre-image attacks. c) Collison resistance: It should be difficult to find two different messages m1 and m2, such that hash(m1) = hash(m2). Functions which don t satisfy this property are vulnerable to collision attacks. d) Reconstruction attack : The reconstruction attack on CAVE shows that the security offered by CAVE- 4 is less than 12 bits as it computes a pre-image for a given hash value in around 2^11 hashing of the algorithm (around 2^13 for CAVE-8). This attack clearly reveals that, 4-round CAVE can be broken in average time equivalent to 1.3*2 ^10 and 8- round CAVE can be broken in 1.25*2^12 executions of the algorithm [4, 5]. Increasing number of rounds from 4 to 8 increases only the workload by 8 times. Hence, increasing the number of rounds of CAVE is not an effective way to increase security. e) List attack: The second approach to attack CAVE is List attack. In this attack, precomputation is done to establish look-up-tables that define the operation of a segment in CAVE [4, 5]. These experiments reveal that the resulting data sets can specify about half of the unknown LFSR (Linear Feedback Shift Register) bits. III. ENHANCED SUBSCRIBER AUTHENTICATION ALGORITHM Enhanced Subscriber Authentication refers to the 3 rd generation authentication, this new form of authentication is based on 3GPP Authentication and Key Agreement (AKA). Authentication mechanism by CAVE algorithm uses a symmetry key cryptosystem ISSN :
3 with Challenge-Response protocol between a base station and a mobile station. This authentication mechanism has several disadvantages. Only one way authentication is provided, that is, only a base station authenticates a subscriber and CAVE algorithm is also prone to cryptographic attacks. But, Authentication mechanism using ESA algorithm uses AKA to enhance security strength and to provide mutual authentication between a base station and a mobile terminal. This section discusses about the implementation of the ESA algorithm to the existing CDMA systems and also the generation of shared secret data, authentication signature value, voice privacy code and signaling message encryption key using ESA algorithm. 1) Construction of ESA input to produce SSD: Construction of ESA input to produce SSD involves the construction of Input 1 and Input 2. Figure 3 shows the construction of Input bit length Input 1 is comprised of 16 words and size of each word is 32 bits. First word is the value XORed Index into standard SHA1 constant value [6]. SHA1 constant value can be any value with 32-bit length. Second word is the value XORed ESN into SHA1 constant value. And, third and fourth words are each XORed first and second word of RANDSSD into SHA1 constant value. A. Implementation of the ESA Algorithm to the Existing CDMA Systems Implementation of the ESA algorithm to the existing CDMA systems involves the following three phases Generation of SSD from A_Key, Generation of Auth_Signature from SSD_A and Generation of PLCM from SSD_B. Figure 2 illustrates the ESA algorithm implementation in the existing CDMA systems. To reduce the simulation runtime the Long Code has been replaced by Short code in this proposed work. Figure 3. Construction of Input 1 Next is to construct 160-bit Input 2. Input 2 consists of 5 words. Figure 4 shows the construction of Input 2. First and second words are each XORed A_Key into first and second words of standard SHA1 Initial Vector. Figure 4. Construction of Input 2 Figure 2. ESA algorithm implementation in the existing CDMA systems B. Generation of SSD from A_Key Generation of SSD from A_Key, involves the generation of shared secret data for authentication, SSD_A and shared secret data for encryption, SSD_B, using ESA algorithm and subscriber s secret key A_key. As a preceding work to do this, construction of inputs of ESA algorithm is done. 2) Generation of SSD_A and SSD_B: Input 1 and Input 2 are used for the generation of SSD_A and SSD_B. Figure 5 shows the Generation of SSD_A and SSD_B by ESA algorithm. Input 1 and Input 2 are loaded into SHA1. Run SHA1 to produce 160-bit output [7]. And then, polynomial AX+BmodG is computed, where A and B are predetermined 160-bit random numbers and treated as polynomials with binary coefficients in the variable T. X is a 160-bits output from SHA1 operation. ISSN :
4 D. Generation of PLCM from SSD_B The generation of voice privacy code, PLCM, CMEAKEY, using ESA algorithm can be discussed as follows: 1) Construction of ESA Input to Produce PLCM : Construction of ESA input to produce PLCM is almost similar to the construction of Input 3 and Input 4. Besides, first word of Input 3 is the value XORed Index into SHA1 constant value to produce Input 5. And, SSD_A in Input 4 is replaced by SSD_B to produce Input 6. Figure 5. Generation of SSD_A and SSD_B by ESA algorithm C. Generation of Auth_Signature from SSD_A The generation of authentication signature value Auth_Signature, using ESA algorithm can be discussed as follows: 1) Construction of ESA input to produce auth_signature : Construction of ESA input to produce AUTH_SIGNATURE is almost similar to the construction of Input 1 and Input 2 besides some parameters are changed as follows. Figure 6 shows the construction of Input 3. Referring to the construction of Input 1, first word of Input 3 is filled with SHA1 constant value which is the same value used in Input1. Second word is the value XORed ESN into SHA1 constant value. The construction of Input 4 is identical with the construction of Input 2 besides A_key is replaced with SSD_A. 2) Generation of PLCM : Input 5 and Input 6 are used for the generation of PLCM and CMEAKEY. Most steps are similar to Figure 5, however, only least significant 15 bits is used for PLCM and 64 bits for CMEAKEY are extracted from the 160 bit output. E. Advantages of ESA over CAVE Algorithm ESA algorithm overcomes the false base station attacks using AKA mechanism. It also overcomes the cryptographic attacks. Table I shows the comparison of attacks in ESA and CAVE algorithm. Table I: Comparison of attacks in ESA and CAVE Types of attacks CAVE algorithm ESA algorithm Pre-image attack Second pre-image attack Collision attack Reconstruction attack List attack 2^128 hashing 2^128 hashing 2^16 hashing 2^91 hashing 2^72 hashing Nil Nil 2^52 hashing Nil Nil IV. AUTHENTICATION AND KEY AGREEMENT Figure 6. Construction of Input 3 2) Generation of auth_signature: Input 3 and Input 4 are used for the generation of Auth_Signature. Most steps are similar to Figure 5, however, only least significant 18 bits of final 160 bits is extracted as Auth_Signature. Authentication and Key Agreement relies on an authentication key associated with the MS and available only to the MS and its home AC. AKA involves a challenge process that allows the network to authenticate the MS. However, in AKA the information provided during this challenge also enables the MS to authenticate the network, providing for bilateral authentication [8]. Following the bilateral authentication, AKA also allows for the generation of new Cipher Key (CK) and Integrity Key (IK). These 128-bit keys enable a security association between the MS and the serving MSC for supporting security ISSN :
5 services such as data integrity and data encryption. This section discusses about the various phases involved in AKA process. A. Phases involved in AKA Process AKA process involves four major phases - Distribution of Authentication Vectors (AV), Authentication of the network by the MS, Authentication of the MS by the network, Establishment of security association between MS and MSC. Figure 7 illustrates the AKA mechanism. Figure 8. Information contained in an authentication vector C. Authentication of the Network by the MS To ensure synchronization between MS and network, a sequence number is provided by the network and compared against the sequence number maintained by the MS. To validate the authenticity of the message, a MAC_A (Message Authentication Code) is provided by the network and compared against an XMAC_A (Expected Message Authentication Code) computed by the MS. D. Authentication of the MS by the Network Authentication of the MS by the network in AKA is similar to a unique challenge without shared SSD in CAVE. The Authentication response (RES) received from the MS is verified against the Expected RES (XRES) received from the home system in the network authentication token (AUTN). Figure 7. Authentication and key agreement mechanism B. Distribution of Authentication Vectors An Authentication Vector (AV) is essentially a group of information used for one AKA attempt. Figure 8 illustrates the information contained in an authentication vector. AVs are generated by the home AC and distributed to the visited network [8]. Each AV contains all information required by the visited network to locally perform AKA with an AKA-enabled mobile station. To thwart replay attempts, each AV must be used for only one AKA attempt. E. Establishment of Security Association between MS and MSC The CK, IK and UIM authentication key (UAK) are generated by the MS in such a way that they are identical to the ones provided to the visited network in the AV. The security association between MS and MSC involves using these keys to support security services such as confidentiality and integrity. The last phase involves the establishment of a security association following bilateral authentication between MS and network. ISSN :
6 V. PERFORMANCE METRICS In this Section, the performance of the ESA algorithm has been evaluated by effective voice transmission and reception and also by calculating autocorrelation, cross-correlation and BER of the system in a CDMA environment. A. Speech Signal For the security analysis, the proposed method utilized speech signal of the type WAV (Waveform Audio File Format), which is sampled at 16 khz. The generated short PN-sequence is been XORed with the given voice signal to generate scrambled voice. The Figure 9 shows the speech waveform and Figure 10 shows the autocorrelation of short PN-sequence. The short PN-sequence generated using the LFSR has been used to scramble the given voice signal. All simulations are done using Matlab version software. Figure 10. Autocorrelation for short PN-sequence Figure 11. Cross-correlation between voice and scrambled-voice B. Authentication and Key Agreement Process Figure 9. Speech signal waveform 1) Cross-correlation between voice and scrambledvoice: Cross-correlation compares two sequences from different sources rather than a shifted copy of a sequence with itself. The cross-correlation between voice and scrambled voice is shown in Figure 11. From this figure, it is observed that the correlation between the voice and scrambled voice is zero, i.e. both the sequences are dissimilar. Implementation of the ESA algorithm to the existing CDMA system is followed by the authentication and key agreement process. In AKA, the MS authenticates the network, similarly, the network authenticates the MS and finally security association is established between MS and MSC. 1) Establishment of Bilateral Authentication between MS and Network: The establishment of security association between MS and the network leads to bilateral authentication between the MS and the network. The bilateral authentication between MS and network is shown in Figure 12. From this figure, it is observed that successful completion of AKA process ISSN :
7 leads to bilateral authentication between MS and network. for generation of short code, the generated short code is in turn used for voice encryption. The performance Figure 12. Establishment of bilateral authentication between MS and network analysis is done by calculating the BER of the system. C. Descrambling Process The scrambled voice which has been generated at the MS, after successful mutual authentication is transmitted to the MSC where the descrambling process takes place. If the mutual authentication fails, the descrambling of the voice signal does not takes place. 1) Cross-correlation between voice and descrambled-voice: Cross-correlation compares two sequences from different sources rather than a shifted copy of a sequence with itself. The cross-correlation between voice and descrambled voice is shown in Figure 13. From this figure, it is observed that the correlation between the original voice and descrambled voice is one, i.e. both the sequences are similar. D. Performance Analysis of ESA in CDMA Environment Performance analysis of the ESA algorithm is done after implementing the ESA algorithm in a CDMA. Using ESA, PLCM has been generated which is used Figure 13. Cross-correlation between original voice and descrambledvoice 1) BER comparison for ESA PLCM and RAND PLCM: The BER comparison for ESA PLCM and RAND PLCM is shown in Figure 14. Here, RAND PLCM is nothing but the PLCM which has been randomly generated without using ESA algorithm. From this figure, it is observed that the proposed ISSN :
8 algorithm shows better performance starts at low power. Consider the BER of 1/10000, the power utilized by the proposed algorithm is about 13db, while the power utilized by RAND PLCM is about 15db and the error rate is also less. This clearly implies that the performance of ESA algorithm is better than existing algorithm. BER BER Performance of ESA & RAND PLCM ESA PLCM RAND PLCM Authentication algorithm enhances the security of the CDMA systems. VII. SCOPE FOR FUTURE WORK Though the proposed method enhances the security of CDMA systems, it can be further enhanced by employing AES in the scrambling process, instead of pseudo-random scrambling. It enhances the physical layer built-in security of CDMA systems through secure scrambling. AES consumes less memory and also ease of implementation and flexibility. CDMA systems with secure scrambling improve the system performance and information privacy. Since, SHA1 algorithm is prone to collision attack, it can be overcome by using SHA2 algorithm instead of SHA1. In addition to that, the short PN-sequence can also be replaced by Gold codes to yield better system performance. ACKNOWLEDGMENT The authors would like to express their cordial thanks to Dr. E. Srinivasan for his valuable advice Eb/N0(db) Figure 14. BER performance of ESA and RAND PLCM VI. CONCLUSION Thus the proposed work enhances the built-in security of CDMA systems by applying the ESA algorithm instead of CAVE algorithm in the authentication process of existing CDMA mobile communication systems. The proposed method is also compatible to the existing CDMA systems because only the algorithm is replaced but the input parameters remain the same. This method utilizes the Authentication and Key Agreement which provides mutual authentication between a base station and mobile terminal with increased key size. Mutual authentication overcomes the problem of false base station attacks, thereby preventing the voice privacy or private identity information of the subscribers from being compromised. The ESA algorithm also dismantles the cryptographic attacks such as reconstruction attack and list attack, thereby enhancing the security of existing CDMA systems. The simulation results also clearly indicates that ESA based systems consumes less power and the error rate is also less when compared with CAVE based system. Thus, the Enhanced Subscriber REFERENCES [1] M.Naidu and C.Wingert, CDMA 1xRTT Security Overview, Qualcomm Inc., August [2] K.Chung, D.Hong and K.Kim, Application of ESA in the CAVE Mode Authentication, World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology, Vol.18, pp.92-96, June [3] Bellcore and S.Patel, Weakness of North American Wireless Authentication Protocol, IEEE Personal Communications Magazine, Vol.4, pp.40-44, June [4] P.Gauravaram and W.Millan, Cryptanalysis of the Cellular Authentication and Voice Encryption Algorithm, IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.1, No.15, pp , November [5] P.Gauravaram and W.Millan, Improved Attack on the Cellular Authentication and Voice Encryption Algorithm, Proceedings of International workshop on Cryptographic Algorithms and their Uses, Australia, pp.1-13, July [6] FIPS 180-2, Secure Hash Standard, NIST, August [7] 3GPP2 S.S0055, Enhanced Cryptographic Algorithms, January [8] 3GPP AKA: BIOGRAPHY Krishna Bharathi received the B.E degree in Electronics & Communication Engineering in 2007 from Anna University, Chennai, India. He is currently pursuing M.Tech in the Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering at Pondicherry Engineering College in the field of Wireless ISSN :
9 communication. His fields of interests include mobile and wireless network security. Gnanou Florence Sudha completed B.Tech in Electronics & Communication Engineering from Pondicherry Engineering College affiliated to Pondicherry University in Obtained M.Tech in Electronics & Communication Engineering from Pondicherry Engineering College in Completed PhD in Electronics & Communication Engg in She joined the Dept. of Electronics & Communication Engg, Pondicherry Engineering College as Lecturer in She worked as Senior Lecturer in the same institute from 2000 to Currently, she is Associate Professor in the same department. She has published more than 36 journals and conference papers and her fields of research interests are in Signal Processing and Bio-Medical engineering. ISSN :
WHITE PAPER. August, 2002. Contacts: Christopher Wingert Mullaguru Naidu
 C D M A 1 X R T T S E C U R I T Y WHITE PAPER O V E R V I E W August, 2002 Contacts: Christopher Wingert Mullaguru Naidu T A B L E O F C O N T E N T S 1. Executive Summary 2 2. Security CDMA Networks 3
C D M A 1 X R T T S E C U R I T Y WHITE PAPER O V E R V I E W August, 2002 Contacts: Christopher Wingert Mullaguru Naidu T A B L E O F C O N T E N T S 1. Executive Summary 2 2. Security CDMA Networks 3
Authentication and Security in Mobile Phones
 Authentication and Security in Mobile Phones Greg Rose QUALCOMM Australia ggr@qualcomm.com ABSTRACT Mobile telephone systems have a checkered reputation regarding security and authentication features after
Authentication and Security in Mobile Phones Greg Rose QUALCOMM Australia ggr@qualcomm.com ABSTRACT Mobile telephone systems have a checkered reputation regarding security and authentication features after
Security Evaluation of CDMA2000
 Security Evaluation of CDMA2000 L. Ertaul 1, S. Natte 2, and G. Saldamli 3 1 Mathematics and Computer Science, CSU East Bay, Hayward, CA, USA 2 Mathematics and Computer Science, CSU East Bay, Hayward,
Security Evaluation of CDMA2000 L. Ertaul 1, S. Natte 2, and G. Saldamli 3 1 Mathematics and Computer Science, CSU East Bay, Hayward, CA, USA 2 Mathematics and Computer Science, CSU East Bay, Hayward,
UMTS security. Helsinki University of Technology S-38.153 Security of Communication Protocols k-p.perttula@hut.fi 15.4.2003
 UMTS security Helsinki University of Technology S-38.153 Security of Communication Protocols k-p.perttula@hut.fi 15.4.2003 Contents UMTS Security objectives Problems with GSM security UMTS security mechanisms
UMTS security Helsinki University of Technology S-38.153 Security of Communication Protocols k-p.perttula@hut.fi 15.4.2003 Contents UMTS Security objectives Problems with GSM security UMTS security mechanisms
Single Sign-On Secure Authentication Password Mechanism
 Single Sign-On Secure Authentication Password Mechanism Deepali M. Devkate, N.D.Kale ME Student, Department of CE, PVPIT, Bavdhan, SavitribaiPhule University Pune, Maharashtra,India. Assistant Professor,
Single Sign-On Secure Authentication Password Mechanism Deepali M. Devkate, N.D.Kale ME Student, Department of CE, PVPIT, Bavdhan, SavitribaiPhule University Pune, Maharashtra,India. Assistant Professor,
Authentication in WLAN
 Authentication in WLAN Flaws in WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) Based on draft 3 of the IEEE 802.11i. Provides stronger data encryption and user authentication (largely missing
Authentication in WLAN Flaws in WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) Based on draft 3 of the IEEE 802.11i. Provides stronger data encryption and user authentication (largely missing
GSM and UMTS security
 2007 Levente Buttyán Why is security more of a concern in wireless? no inherent physical protection physical connections between devices are replaced by logical associations sending and receiving messages
2007 Levente Buttyán Why is security more of a concern in wireless? no inherent physical protection physical connections between devices are replaced by logical associations sending and receiving messages
SECURITY ANALYSIS OF PASSWORD BASED MUTUAL AUTHENTICATION METHOD FOR REMOTE USER
 SECURITY ANALYSIS OF PASSWORD BASED MUTUAL AUTHENTICATION METHOD FOR REMOTE USER Mrs. P.Venkateswari Assistant Professor / CSE Erode Sengunthar Engineering College, Thudupathi ABSTRACT Nowadays Communication
SECURITY ANALYSIS OF PASSWORD BASED MUTUAL AUTHENTICATION METHOD FOR REMOTE USER Mrs. P.Venkateswari Assistant Professor / CSE Erode Sengunthar Engineering College, Thudupathi ABSTRACT Nowadays Communication
Overview of Cryptographic Tools for Data Security. Murat Kantarcioglu
 UT DALLAS Erik Jonsson School of Engineering & Computer Science Overview of Cryptographic Tools for Data Security Murat Kantarcioglu Pag. 1 Purdue University Cryptographic Primitives We will discuss the
UT DALLAS Erik Jonsson School of Engineering & Computer Science Overview of Cryptographic Tools for Data Security Murat Kantarcioglu Pag. 1 Purdue University Cryptographic Primitives We will discuss the
Threats and Security Analysis for Enhanced Secure Neighbor Discovery Protocol (SEND) of IPv6 NDP Security
 Threats and Security Analysis for Enhanced Secure Neighbor Discovery Protocol (SEND) of IPv6 NDP Security Yvette E. Gelogo 1, Ronnie D. Caytiles 1 and Byungjoo Park 1 * 1Multimedia Engineering Department,
Threats and Security Analysis for Enhanced Secure Neighbor Discovery Protocol (SEND) of IPv6 NDP Security Yvette E. Gelogo 1, Ronnie D. Caytiles 1 and Byungjoo Park 1 * 1Multimedia Engineering Department,
Thwarting Selective Insider Jamming Attacks in Wireless Network by Delaying Real Time Packet Classification
 Thwarting Selective Insider Jamming Attacks in Wireless Network by Delaying Real Time Packet Classification LEKSHMI.M.R Department of Computer Science and Engineering, KCG College of Technology Chennai,
Thwarting Selective Insider Jamming Attacks in Wireless Network by Delaying Real Time Packet Classification LEKSHMI.M.R Department of Computer Science and Engineering, KCG College of Technology Chennai,
Formal Analysis of A Novel Mutual Authentication and Key Agreement Protocol
 Formal Analysis of A Novel Mutual Authentication and ey Agreement Protocol Ja'afer M. AL-Saraireh Applied Science University Amman 11961, Jordan Saleh S. Saraireh Philadelphia University Amman 11961, Jordan
Formal Analysis of A Novel Mutual Authentication and ey Agreement Protocol Ja'afer M. AL-Saraireh Applied Science University Amman 11961, Jordan Saleh S. Saraireh Philadelphia University Amman 11961, Jordan
Algorithms for Interference Sensing in Optical CDMA Networks
 Algorithms for Interference Sensing in Optical CDMA Networks Purushotham Kamath, Joseph D. Touch and Joseph A. Bannister {pkamath, touch, joseph}@isi.edu Information Sciences Institute, University of Southern
Algorithms for Interference Sensing in Optical CDMA Networks Purushotham Kamath, Joseph D. Touch and Joseph A. Bannister {pkamath, touch, joseph}@isi.edu Information Sciences Institute, University of Southern
Using an approximated One-Time Pad to Secure Short Messaging Service (SMS)
 Using an approximated One-Time Pad to Secure Short Messaging Service (SMS) N.J Croft and M.S Olivier Information and Computer Security Architectures (ICSA) Research Group Department of Computer Science
Using an approximated One-Time Pad to Secure Short Messaging Service (SMS) N.J Croft and M.S Olivier Information and Computer Security Architectures (ICSA) Research Group Department of Computer Science
Authentication and Authorization Applications in 4G Networks
 Authentication and Authorization Applications in 4G Networks Abstract Libor Dostálek dostalek@prf.jcu.cz Faculty of Science University of South Bohemia Ceske Budejovice, Czech Republic The principle of
Authentication and Authorization Applications in 4G Networks Abstract Libor Dostálek dostalek@prf.jcu.cz Faculty of Science University of South Bohemia Ceske Budejovice, Czech Republic The principle of
SecureMessageRecoveryandBatchVerificationusingDigitalSignature
 Global Journal of Computer Science and Technology: F Graphics & Vision Volume 14 Issue 4 Version 1.0 Year 2014 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Global Journal of Computer Science and Technology: F Graphics & Vision Volume 14 Issue 4 Version 1.0 Year 2014 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Authentication requirement Authentication function MAC Hash function Security of
 UNIT 3 AUTHENTICATION Authentication requirement Authentication function MAC Hash function Security of hash function and MAC SHA HMAC CMAC Digital signature and authentication protocols DSS Slides Courtesy
UNIT 3 AUTHENTICATION Authentication requirement Authentication function MAC Hash function Security of hash function and MAC SHA HMAC CMAC Digital signature and authentication protocols DSS Slides Courtesy
 6.857 Computer and Network Security Fall Term, 1997 Lecture 4 : 16 September 1997 Lecturer: Ron Rivest Scribe: Michelle Goldberg 1 Conditionally Secure Cryptography Conditionally (or computationally) secure
6.857 Computer and Network Security Fall Term, 1997 Lecture 4 : 16 September 1997 Lecturer: Ron Rivest Scribe: Michelle Goldberg 1 Conditionally Secure Cryptography Conditionally (or computationally) secure
Wireless Networks. Welcome to Wireless
 Wireless Networks 11/1/2010 Wireless Networks 1 Welcome to Wireless Radio waves No need to be physically plugged into the network Remote access Coverage Personal Area Network (PAN) Local Area Network (LAN)
Wireless Networks 11/1/2010 Wireless Networks 1 Welcome to Wireless Radio waves No need to be physically plugged into the network Remote access Coverage Personal Area Network (PAN) Local Area Network (LAN)
Lecture Objectives. Lecture 8 Mobile Networks: Security in Wireless LANs and Mobile Networks. Agenda. References
 Lecture Objectives Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems Lecture 8 Mobile Networks: Security in Wireless LANs and Mobile Networks Introduce security vulnerabilities and defenses Describe security functions
Lecture Objectives Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems Lecture 8 Mobile Networks: Security in Wireless LANs and Mobile Networks Introduce security vulnerabilities and defenses Describe security functions
CDMA TECHNOLOGY. Brief Working of CDMA
 CDMA TECHNOLOGY History of CDMA The Cellular Challenge The world's first cellular networks were introduced in the early 1980s, using analog radio transmission technologies such as AMPS (Advanced Mobile
CDMA TECHNOLOGY History of CDMA The Cellular Challenge The world's first cellular networks were introduced in the early 1980s, using analog radio transmission technologies such as AMPS (Advanced Mobile
IT Networks & Security CERT Luncheon Series: Cryptography
 IT Networks & Security CERT Luncheon Series: Cryptography Presented by Addam Schroll, IT Security & Privacy Analyst 1 Outline History Terms & Definitions Symmetric and Asymmetric Algorithms Hashing PKI
IT Networks & Security CERT Luncheon Series: Cryptography Presented by Addam Schroll, IT Security & Privacy Analyst 1 Outline History Terms & Definitions Symmetric and Asymmetric Algorithms Hashing PKI
Mobile Phone Security. Hoang Vo Billy Ngo
 Mobile Phone Security Hoang Vo Billy Ngo Table of Content 1. Introduction Page 2 1.1 Analog Network Page 2 1.2 Digital Network Page 2 2. Security Protocols Page 4 2.1 Analog Page 4 2.2 Digital Page 5 3.
Mobile Phone Security Hoang Vo Billy Ngo Table of Content 1. Introduction Page 2 1.1 Analog Network Page 2 1.2 Digital Network Page 2 2. Security Protocols Page 4 2.1 Analog Page 4 2.2 Digital Page 5 3.
Contactless Smart Cards vs. EPC Gen 2 RFID Tags: Frequently Asked Questions. July, 2006. Developed by: Smart Card Alliance Identity Council
 Contactless Smart Cards vs. EPC Gen 2 RFID Tags: Frequently Asked Questions July, 2006 Developed by: Smart Card Alliance Identity Council Contactless Smart Cards vs. EPC Gen 2 RFID Tags: Frequently Asked
Contactless Smart Cards vs. EPC Gen 2 RFID Tags: Frequently Asked Questions July, 2006 Developed by: Smart Card Alliance Identity Council Contactless Smart Cards vs. EPC Gen 2 RFID Tags: Frequently Asked
Cryptography and Network Security Chapter 11
 Cryptography and Network Security Chapter 11 Fifth Edition by William Stallings Lecture slides by Lawrie Brown (with edits by RHB) Chapter 11 Cryptographic Hash Functions Each of the messages, like each
Cryptography and Network Security Chapter 11 Fifth Edition by William Stallings Lecture slides by Lawrie Brown (with edits by RHB) Chapter 11 Cryptographic Hash Functions Each of the messages, like each
Secure Large-Scale Bingo
 Secure Large-Scale Bingo Antoni Martínez-Ballesté, Francesc Sebé and Josep Domingo-Ferrer Universitat Rovira i Virgili, Dept. of Computer Engineering and Maths, Av. Països Catalans 26, E-43007 Tarragona,
Secure Large-Scale Bingo Antoni Martínez-Ballesté, Francesc Sebé and Josep Domingo-Ferrer Universitat Rovira i Virgili, Dept. of Computer Engineering and Maths, Av. Països Catalans 26, E-43007 Tarragona,
CS 758: Cryptography / Network Security
 CS 758: Cryptography / Network Security offered in the Fall Semester, 2003, by Doug Stinson my office: DC 3122 my email address: dstinson@uwaterloo.ca my web page: http://cacr.math.uwaterloo.ca/~dstinson/index.html
CS 758: Cryptography / Network Security offered in the Fall Semester, 2003, by Doug Stinson my office: DC 3122 my email address: dstinson@uwaterloo.ca my web page: http://cacr.math.uwaterloo.ca/~dstinson/index.html
Estimation and Equalization of Fiber-Wireless Uplink for Multiuser CDMA 4g Networks
 Estimation and Equalization of Fiber-Wireless Uplink for Multiuser CDMA 4g Networks Vangala susmitha *1, Nagandla Bhavana* 2, Lankisetti Divya Sai Ratna *3, Bhuma Naresh *4 1,2,3,4 Dept. of Electronics
Estimation and Equalization of Fiber-Wireless Uplink for Multiuser CDMA 4g Networks Vangala susmitha *1, Nagandla Bhavana* 2, Lankisetti Divya Sai Ratna *3, Bhuma Naresh *4 1,2,3,4 Dept. of Electronics
A MELIORATED APPROACH TO TEXT STEGANOGRAPHY USING MARKUP LANGUAGES AND AES
 A MELIORATED APPROACH TO TEXT STEGANOGRAPHY USING MARKUP LANGUAGES AND AES K.Ramesh 1, P.Manivannan 2 1,2 Assistant Professor, Department of Information Technology, V.R.S. College of Engineering & Technology,
A MELIORATED APPROACH TO TEXT STEGANOGRAPHY USING MARKUP LANGUAGES AND AES K.Ramesh 1, P.Manivannan 2 1,2 Assistant Professor, Department of Information Technology, V.R.S. College of Engineering & Technology,
802.11 Security (WEP, WPA\WPA2) 19/05/2009. Giulio Rossetti Unipi Giulio.Rossetti@gmail.com
 802.11 Security (WEP, WPA\WPA2) 19/05/2009 Giulio Rossetti Unipi Giulio.Rossetti@gmail.com 802.11 Security Standard: WEP Wired Equivalent Privacy The packets are encrypted, before sent, with a Secret Key
802.11 Security (WEP, WPA\WPA2) 19/05/2009 Giulio Rossetti Unipi Giulio.Rossetti@gmail.com 802.11 Security Standard: WEP Wired Equivalent Privacy The packets are encrypted, before sent, with a Secret Key
Cryptosystems. Bob wants to send a message M to Alice. Symmetric ciphers: Bob and Alice both share a secret key, K.
 Cryptosystems Bob wants to send a message M to Alice. Symmetric ciphers: Bob and Alice both share a secret key, K. C= E(M, K), Bob sends C Alice receives C, M=D(C,K) Use the same key to decrypt. Public
Cryptosystems Bob wants to send a message M to Alice. Symmetric ciphers: Bob and Alice both share a secret key, K. C= E(M, K), Bob sends C Alice receives C, M=D(C,K) Use the same key to decrypt. Public
12/3/08. Security in Wireless LANs and Mobile Networks. Wireless Magnifies Exposure Vulnerability. Mobility Makes it Difficult to Establish Trust
 Security in Wireless LANs and Mobile Networks Wireless Magnifies Exposure Vulnerability Information going across the wireless link is exposed to anyone within radio range RF may extend beyond a room or
Security in Wireless LANs and Mobile Networks Wireless Magnifies Exposure Vulnerability Information going across the wireless link is exposed to anyone within radio range RF may extend beyond a room or
A Secure Software Implementation of Nonlinear Advanced Encryption Standard
 IOSR Journal of VLSI and Signal Processing (IOSR-JVSP) ISSN: 2319 4200, ISBN No. : 2319 4197 Volume 1, Issue 5 (Jan. - Feb 2013), PP 44-48 A Secure Software Implementation of Nonlinear Advanced Encryption
IOSR Journal of VLSI and Signal Processing (IOSR-JVSP) ISSN: 2319 4200, ISBN No. : 2319 4197 Volume 1, Issue 5 (Jan. - Feb 2013), PP 44-48 A Secure Software Implementation of Nonlinear Advanced Encryption
Security Requirements for Wireless Networking
 Security Requirements for Wireless Networking Developed by Copyright 2007 Rysavy Research TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 2 SECURITY REQUIREMENTS... 2 WIRELESS OPERATOR SECURITY LIMITATIONS... 3 END
Security Requirements for Wireless Networking Developed by Copyright 2007 Rysavy Research TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 2 SECURITY REQUIREMENTS... 2 WIRELESS OPERATOR SECURITY LIMITATIONS... 3 END
Monitoring Data Integrity while using TPA in Cloud Environment
 Monitoring Data Integrity while using TPA in Cloud Environment Jaspreet Kaur, Jasmeet Singh Abstract Cloud Computing is the arising technology that delivers software, platform and infrastructure as a service
Monitoring Data Integrity while using TPA in Cloud Environment Jaspreet Kaur, Jasmeet Singh Abstract Cloud Computing is the arising technology that delivers software, platform and infrastructure as a service
HASH CODE BASED SECURITY IN CLOUD COMPUTING
 ABSTRACT HASH CODE BASED SECURITY IN CLOUD COMPUTING Kaleem Ur Rehman M.Tech student (CSE), College of Engineering, TMU Moradabad (India) The Hash functions describe as a phenomenon of information security
ABSTRACT HASH CODE BASED SECURITY IN CLOUD COMPUTING Kaleem Ur Rehman M.Tech student (CSE), College of Engineering, TMU Moradabad (India) The Hash functions describe as a phenomenon of information security
Keeping SCADA Networks Open and Secure DNP3 Security
 Keeping SCADA Networks Open and Secure DNP3 Security June 2008 DNP3 Protocol DNP3 protocol has become widely accepted within water and electrical utilities worldwide for SCADA communications with field
Keeping SCADA Networks Open and Secure DNP3 Security June 2008 DNP3 Protocol DNP3 protocol has become widely accepted within water and electrical utilities worldwide for SCADA communications with field
Improving data integrity on cloud storage services
 International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6734, ISSN (Print): 2319 6726 Volume 2 Issue 2 ǁ February. 2013 ǁ PP.49-55 Improving data integrity on cloud storage services
International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6734, ISSN (Print): 2319 6726 Volume 2 Issue 2 ǁ February. 2013 ǁ PP.49-55 Improving data integrity on cloud storage services
StenoCast s Wireless Bluetooth Security. A StenoCast White Paper. 3949 Ruffin Road, Suite E. San Diego, CA 92123 858.279.5700. www.stenocast.
 A StenoCast White Paper 3949 Ruffin Road, Suite E San Diego, CA 92123 858.279.5700 www.stenocast.com StenoCast s Wireless Bluetooth Security Michael Appelman, President Contents Introduction 2 Introduction
A StenoCast White Paper 3949 Ruffin Road, Suite E San Diego, CA 92123 858.279.5700 www.stenocast.com StenoCast s Wireless Bluetooth Security Michael Appelman, President Contents Introduction 2 Introduction
Outline. Computer Science 418. Digital Signatures: Observations. Digital Signatures: Definition. Definition 1 (Digital signature) Digital Signatures
 Outline Computer Science 418 Digital Signatures Mike Jacobson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Week 12 1 Digital Signatures 2 Signatures via Public Key Cryptosystems 3 Provable 4 Mike
Outline Computer Science 418 Digital Signatures Mike Jacobson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Week 12 1 Digital Signatures 2 Signatures via Public Key Cryptosystems 3 Provable 4 Mike
Recommendation for Applications Using Approved Hash Algorithms
 NIST Special Publication 800-107 Recommendation for Applications Using Approved Hash Algorithms Quynh Dang Computer Security Division Information Technology Laboratory C O M P U T E R S E C U R I T Y February
NIST Special Publication 800-107 Recommendation for Applications Using Approved Hash Algorithms Quynh Dang Computer Security Division Information Technology Laboratory C O M P U T E R S E C U R I T Y February
Cryptographic Hash Functions Message Authentication Digital Signatures
 Cryptographic Hash Functions Message Authentication Digital Signatures Abstract We will discuss Cryptographic hash functions Message authentication codes HMAC and CBC-MAC Digital signatures 2 Encryption/Decryption
Cryptographic Hash Functions Message Authentication Digital Signatures Abstract We will discuss Cryptographic hash functions Message authentication codes HMAC and CBC-MAC Digital signatures 2 Encryption/Decryption
Wireless Encryption Protection
 Wireless Encryption Protection We re going to jump around a little here and go to something that I really find interesting, how do you secure yourself when you connect to a router. Now first and foremost
Wireless Encryption Protection We re going to jump around a little here and go to something that I really find interesting, how do you secure yourself when you connect to a router. Now first and foremost
Introduction to Cryptography CS 355
 Introduction to Cryptography CS 355 Lecture 30 Digital Signatures CS 355 Fall 2005 / Lecture 30 1 Announcements Wednesday s lecture cancelled Friday will be guest lecture by Prof. Cristina Nita- Rotaru
Introduction to Cryptography CS 355 Lecture 30 Digital Signatures CS 355 Fall 2005 / Lecture 30 1 Announcements Wednesday s lecture cancelled Friday will be guest lecture by Prof. Cristina Nita- Rotaru
Network Security. Computer Networking Lecture 08. March 19, 2012. HKU SPACE Community College. HKU SPACE CC CN Lecture 08 1/23
 Network Security Computer Networking Lecture 08 HKU SPACE Community College March 19, 2012 HKU SPACE CC CN Lecture 08 1/23 Outline Introduction Cryptography Algorithms Secret Key Algorithm Message Digest
Network Security Computer Networking Lecture 08 HKU SPACE Community College March 19, 2012 HKU SPACE CC CN Lecture 08 1/23 Outline Introduction Cryptography Algorithms Secret Key Algorithm Message Digest
The Misuse of RC4 in Microsoft Word and Excel
 The Misuse of RC4 in Microsoft Word and Excel Hongjun Wu Institute for Infocomm Research, Singapore hongjun@i2r.a-star.edu.sg Abstract. In this report, we point out a serious security flaw in Microsoft
The Misuse of RC4 in Microsoft Word and Excel Hongjun Wu Institute for Infocomm Research, Singapore hongjun@i2r.a-star.edu.sg Abstract. In this report, we point out a serious security flaw in Microsoft
A PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF COMMON ENCRYPTION TECHNIQUES WITH SECURE WATERMARK SYSTEM (SWS)
 A PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF COMMON ENCRYPTION TECHNIQUES WITH SECURE WATERMARK SYSTEM (SWS) Ashraf Odeh 1, Shadi R.Masadeh 2, Ahmad Azzazi 3 1 Computer Information Systems Department, Isra University,
A PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF COMMON ENCRYPTION TECHNIQUES WITH SECURE WATERMARK SYSTEM (SWS) Ashraf Odeh 1, Shadi R.Masadeh 2, Ahmad Azzazi 3 1 Computer Information Systems Department, Isra University,
Data Encryption WHITE PAPER ON. Prepared by Mohammed Samiuddin. www.itmr.ac.in
 01 0110 0001 01101 WHITE PAPER ON Data Encryption Prepared by Mohammed Samiuddin www.itmr.ac.in Contents INTRODUCTION... 2 NEED FOR DATA ENCRYPTION... 3 DUE CARE... 3 REPUTATIONAL RISK... 3 REGULATORY
01 0110 0001 01101 WHITE PAPER ON Data Encryption Prepared by Mohammed Samiuddin www.itmr.ac.in Contents INTRODUCTION... 2 NEED FOR DATA ENCRYPTION... 3 DUE CARE... 3 REPUTATIONAL RISK... 3 REGULATORY
Rfid Authentication Protocol for security and privacy Maintenance in Cloud Based Employee Management System
 Rfid Authentication Protocol for security and privacy Maintenance in Cloud Based Employee Management System ArchanaThange Post Graduate Student, DKGOI s COE, Swami Chincholi, Maharashtra, India archanathange7575@gmail.com,
Rfid Authentication Protocol for security and privacy Maintenance in Cloud Based Employee Management System ArchanaThange Post Graduate Student, DKGOI s COE, Swami Chincholi, Maharashtra, India archanathange7575@gmail.com,
TETRA Security. TETRA MoU Association Association House South Park Road Macclesfield Sk11 6SH England
 TETRA Security TETRA MoU Association Association House South Park Road Macclesfield Sk11 6SH England www.tetramou.com February 2006 TETRA Security Page 2 of 2 1 The TETRA security functions TETRA contains
TETRA Security TETRA MoU Association Association House South Park Road Macclesfield Sk11 6SH England www.tetramou.com February 2006 TETRA Security Page 2 of 2 1 The TETRA security functions TETRA contains
Computer Security: Principles and Practice
 Computer Security: Principles and Practice Chapter 20 Public-Key Cryptography and Message Authentication First Edition by William Stallings and Lawrie Brown Lecture slides by Lawrie Brown Public-Key Cryptography
Computer Security: Principles and Practice Chapter 20 Public-Key Cryptography and Message Authentication First Edition by William Stallings and Lawrie Brown Lecture slides by Lawrie Brown Public-Key Cryptography
Mobile Office Security Requirements for the Mobile Office
 Mobile Office Security Requirements for the Mobile Office S.Rupp@alcatel.de Alcatel SEL AG 20./21.06.2001 Overview Security Concepts in Mobile Networks Applications in Mobile Networks Mobile Terminal used
Mobile Office Security Requirements for the Mobile Office S.Rupp@alcatel.de Alcatel SEL AG 20./21.06.2001 Overview Security Concepts in Mobile Networks Applications in Mobile Networks Mobile Terminal used
Part I. Universität Klagenfurt - IWAS Multimedia Kommunikation (VK) M. Euchner; Mai 2001. Siemens AG 2001, ICN M NT
 Part I Contents Part I Introduction to Information Security Definition of Crypto Cryptographic Objectives Security Threats and Attacks The process Security Security Services Cryptography Cryptography (code
Part I Contents Part I Introduction to Information Security Definition of Crypto Cryptographic Objectives Security Threats and Attacks The process Security Security Services Cryptography Cryptography (code
CS 393 Network Security. Nasir Memon Polytechnic University Module 11 Secure Email
 CS 393 Network Security Nasir Memon Polytechnic University Module 11 Secure Email Course Logistics HW 5 due Thursday Graded exams returned and discussed. Read Chapter 5 of text 4/2/02 Module 11 - Secure
CS 393 Network Security Nasir Memon Polytechnic University Module 11 Secure Email Course Logistics HW 5 due Thursday Graded exams returned and discussed. Read Chapter 5 of text 4/2/02 Module 11 - Secure
Key Hopping A Security Enhancement Scheme for IEEE 802.11 WEP Standards
 White Paper Key Hopping A Security Enhancement Scheme for IEEE 802.11 WEP Standards By Dr. Wen-Ping Ying, Director of Software Development, February 2002 Introduction Wireless LAN networking allows the
White Paper Key Hopping A Security Enhancement Scheme for IEEE 802.11 WEP Standards By Dr. Wen-Ping Ying, Director of Software Development, February 2002 Introduction Wireless LAN networking allows the
Vulnerabilities in WEP Christopher Hoffman Cryptography 2 2011-3
 Vulnerabilities in WEP Christopher Hoffman Cryptography 2 2011-3 1. Abstract Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) was the first encryption scheme used for protecting wireless traffic. It consisted of a private
Vulnerabilities in WEP Christopher Hoffman Cryptography 2 2011-3 1. Abstract Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) was the first encryption scheme used for protecting wireless traffic. It consisted of a private
CS549: Cryptography and Network Security
 CS549: Cryptography and Network Security by Xiang-Yang Li Department of Computer Science, IIT Cryptography and Network Security 1 Notice This lecture note (Cryptography and Network Security) is prepared
CS549: Cryptography and Network Security by Xiang-Yang Li Department of Computer Science, IIT Cryptography and Network Security 1 Notice This lecture note (Cryptography and Network Security) is prepared
International Journal of Computing and Business Research (IJCBR)
 AN INVESTIGATION OF GSM ARCHITECTURE AND OVERLAYING WITH EFFICIENT SECURITY PROTOCOL Karun Madan, Surya World Institute of Engg. & Technology, Rajpura, Punjab ABSTRACT The Global System for Mobile Communications
AN INVESTIGATION OF GSM ARCHITECTURE AND OVERLAYING WITH EFFICIENT SECURITY PROTOCOL Karun Madan, Surya World Institute of Engg. & Technology, Rajpura, Punjab ABSTRACT The Global System for Mobile Communications
CSE/EE 461 Lecture 23
 CSE/EE 461 Lecture 23 Network Security David Wetherall djw@cs.washington.edu Last Time Naming Application Presentation How do we name hosts etc.? Session Transport Network Domain Name System (DNS) Data
CSE/EE 461 Lecture 23 Network Security David Wetherall djw@cs.washington.edu Last Time Naming Application Presentation How do we name hosts etc.? Session Transport Network Domain Name System (DNS) Data
Keywords Cloud Storage, Error Identification, Partitioning, Cloud Storage Integrity Checking, Digital Signature Extraction, Encryption, Decryption
 Partitioning Data and Domain Integrity Checking for Storage - Improving Cloud Storage Security Using Data Partitioning Technique Santosh Jogade *, Ravi Sharma, Prof. Rajani Kadam Department Of Computer
Partitioning Data and Domain Integrity Checking for Storage - Improving Cloud Storage Security Using Data Partitioning Technique Santosh Jogade *, Ravi Sharma, Prof. Rajani Kadam Department Of Computer
Cryptography and Network Security Chapter 12
 Cryptography and Network Security Chapter 12 Fifth Edition by William Stallings Lecture slides by Lawrie Brown (with edits by RHB) Chapter 12 Message Authentication Codes At cats' green on the Sunday he
Cryptography and Network Security Chapter 12 Fifth Edition by William Stallings Lecture slides by Lawrie Brown (with edits by RHB) Chapter 12 Message Authentication Codes At cats' green on the Sunday he
Keywords : audit, cloud, integrity, station to station protocol, SHA-2, third party auditor, XOR. GJCST-B Classification : C.2.4, H.2.
 Global Journal of Computer Science and Technology Cloud and Distributed Volume 13 Issue 3 Version 1.0 Year 2013 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Global Journal of Computer Science and Technology Cloud and Distributed Volume 13 Issue 3 Version 1.0 Year 2013 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
A NEW APPROACH FOR COMPLEX ENCRYPTING AND DECRYPTING DATA
 A NEW APPROACH FOR COMPLEX ENCRYPTING AND DECRYPTING DATA ABSTRACT Obaida Mohammad Awad Al-Hazaimeh Department of Information Technology, Al-balqa Applied University, AL-Huson University College, Irbid,
A NEW APPROACH FOR COMPLEX ENCRYPTING AND DECRYPTING DATA ABSTRACT Obaida Mohammad Awad Al-Hazaimeh Department of Information Technology, Al-balqa Applied University, AL-Huson University College, Irbid,
Chapter 14. Key management and Distribution. Symmetric Key Distribution Using Symmetric Encryption
 Chapter 14. Key management and Distribution Symmetric Key Distribution Using Symmetric Encryption For symmetric encryption to work, the two parties to an exchange must share the same key, and that key
Chapter 14. Key management and Distribution Symmetric Key Distribution Using Symmetric Encryption For symmetric encryption to work, the two parties to an exchange must share the same key, and that key
Security Architecture in UMTS Third Generation Cellular Networks Tomás Balderas-Contreras René A. Cumplido-Parra
 Security Architecture in UMTS Third Generation Cellular Networks Tomás Balderas-Contreras René A. Cumplido-Parra Reporte Técnico No. CCC-04-002 27 de febrero de 2004 Coordinación de Ciencias Computacionales
Security Architecture in UMTS Third Generation Cellular Networks Tomás Balderas-Contreras René A. Cumplido-Parra Reporte Técnico No. CCC-04-002 27 de febrero de 2004 Coordinación de Ciencias Computacionales
Privacy and Security in library RFID Issues, Practices and Architecture
 Privacy and Security in library RFID Issues, Practices and Architecture David Molnar and David Wagner University of California, Berkeley CCS '04 October 2004 Overview Motivation RFID Background Library
Privacy and Security in library RFID Issues, Practices and Architecture David Molnar and David Wagner University of California, Berkeley CCS '04 October 2004 Overview Motivation RFID Background Library
Enhancing Advanced Encryption Standard S-Box Generation Based on Round Key
 Enhancing Advanced Encryption Standard S-Box Generation Based on Round Key Julia Juremi Ramlan Mahmod Salasiah Sulaiman Jazrin Ramli Faculty of Computer Science and Information Technology, Universiti Putra
Enhancing Advanced Encryption Standard S-Box Generation Based on Round Key Julia Juremi Ramlan Mahmod Salasiah Sulaiman Jazrin Ramli Faculty of Computer Science and Information Technology, Universiti Putra
Public Auditing & Automatic Protocol Blocking with 3-D Password Authentication for Secure Cloud Storage
 Public Auditing & Automatic Protocol Blocking with 3-D Password Authentication for Secure Cloud Storage P. Selvigrija, Assistant Professor, Department of Computer Science & Engineering, Christ College
Public Auditing & Automatic Protocol Blocking with 3-D Password Authentication for Secure Cloud Storage P. Selvigrija, Assistant Professor, Department of Computer Science & Engineering, Christ College
The Feasibility and Application of using a Zero-knowledge Protocol Authentication Systems
 The Feasibility and Application of using a Zero-knowledge Protocol Authentication Systems Becky Cutler Rebecca.cutler@tufts.edu Mentor: Professor Chris Gregg Abstract Modern day authentication systems
The Feasibility and Application of using a Zero-knowledge Protocol Authentication Systems Becky Cutler Rebecca.cutler@tufts.edu Mentor: Professor Chris Gregg Abstract Modern day authentication systems
Encryption, Data Integrity, Digital Certificates, and SSL. Developed by. Jerry Scott. SSL Primer-1-1
 Encryption, Data Integrity, Digital Certificates, and SSL Developed by Jerry Scott 2002 SSL Primer-1-1 Ideas Behind Encryption When information is transmitted across intranets or the Internet, others can
Encryption, Data Integrity, Digital Certificates, and SSL Developed by Jerry Scott 2002 SSL Primer-1-1 Ideas Behind Encryption When information is transmitted across intranets or the Internet, others can
Security in Wireless Local Area Network
 Fourth LACCEI International Latin American and Caribbean Conference for Engineering and Technology (LACCET 2006) Breaking Frontiers and Barriers in Engineering: Education, Research and Practice 21-23 June
Fourth LACCEI International Latin American and Caribbean Conference for Engineering and Technology (LACCET 2006) Breaking Frontiers and Barriers in Engineering: Education, Research and Practice 21-23 June
Secure Sockets Layer
 SSL/TLS provides endpoint authentication and communications privacy over the Internet using cryptography. For web browsing, email, faxing, other data transmission. In typical use, only the server is authenticated
SSL/TLS provides endpoint authentication and communications privacy over the Internet using cryptography. For web browsing, email, faxing, other data transmission. In typical use, only the server is authenticated
DATA SECURITY IN CLOUD USING ADVANCED SECURE DE-DUPLICATION
 DATA SECURITY IN CLOUD USING ADVANCED SECURE DE-DUPLICATION Hasna.R 1, S.Sangeetha 2 1 PG Scholar, Dhanalakshmi Srinivasan College of Engineering, Coimbatore. 2 Assistant Professor, Dhanalakshmi Srinivasan
DATA SECURITY IN CLOUD USING ADVANCED SECURE DE-DUPLICATION Hasna.R 1, S.Sangeetha 2 1 PG Scholar, Dhanalakshmi Srinivasan College of Engineering, Coimbatore. 2 Assistant Professor, Dhanalakshmi Srinivasan
CLOUD COMPUTING SECURITY ARCHITECTURE - IMPLEMENTING DES ALGORITHM IN CLOUD FOR DATA SECURITY
 CLOUD COMPUTING SECURITY ARCHITECTURE - IMPLEMENTING DES ALGORITHM IN CLOUD FOR DATA SECURITY Varun Gandhi 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Dronacharya College of Engineering, Khentawas,
CLOUD COMPUTING SECURITY ARCHITECTURE - IMPLEMENTING DES ALGORITHM IN CLOUD FOR DATA SECURITY Varun Gandhi 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Dronacharya College of Engineering, Khentawas,
Security Analysis of PLAID
 Security Analysis of PLAID Dai Watanabe 1 Yokoyama Laboratory, Hitachi, Ltd., 292 Yoshida-cho, Totsuka-ku, Yokohama, 244-0817, Japan dai.watanabe.td@hitachi.com Abstract. PLAID is a mutual authentication
Security Analysis of PLAID Dai Watanabe 1 Yokoyama Laboratory, Hitachi, Ltd., 292 Yoshida-cho, Totsuka-ku, Yokohama, 244-0817, Japan dai.watanabe.td@hitachi.com Abstract. PLAID is a mutual authentication
Connected from everywhere. Cryptelo completely protects your data. Data transmitted to the server. Data sharing (both files and directory structure)
 Cryptelo Drive Cryptelo Drive is a virtual drive, where your most sensitive data can be stored. Protect documents, contracts, business know-how, or photographs - in short, anything that must be kept safe.
Cryptelo Drive Cryptelo Drive is a virtual drive, where your most sensitive data can be stored. Protect documents, contracts, business know-how, or photographs - in short, anything that must be kept safe.
MUTI-KEYWORD SEARCH WITH PRESERVING PRIVACY OVER ENCRYPTED DATA IN THE CLOUD
 MUTI-KEYWORD SEARCH WITH PRESERVING PRIVACY OVER ENCRYPTED DATA IN THE CLOUD A.Shanthi 1, M. Purushotham Reddy 2, G.Rama Subba Reddy 3 1 M.tech Scholar (CSE), 2 Asst.professor, Dept. of CSE, Vignana Bharathi
MUTI-KEYWORD SEARCH WITH PRESERVING PRIVACY OVER ENCRYPTED DATA IN THE CLOUD A.Shanthi 1, M. Purushotham Reddy 2, G.Rama Subba Reddy 3 1 M.tech Scholar (CSE), 2 Asst.professor, Dept. of CSE, Vignana Bharathi
Secret File Sharing Techniques using AES algorithm. C. Navya Latha 200201066 Garima Agarwal 200305032 Anila Kumar GVN 200305002
 Secret File Sharing Techniques using AES algorithm C. Navya Latha 200201066 Garima Agarwal 200305032 Anila Kumar GVN 200305002 1. Feature Overview The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) feature adds support
Secret File Sharing Techniques using AES algorithm C. Navya Latha 200201066 Garima Agarwal 200305032 Anila Kumar GVN 200305002 1. Feature Overview The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) feature adds support
Research Article Physical Layer Built-In Security Analysis and Enhancement Algorithms for CDMA Systems
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking Volume 2007, Article ID 83589, 7 pages doi:10.1155/2007/83589 Research Article Physical Layer Built-In Security
Hindawi Publishing Corporation EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking Volume 2007, Article ID 83589, 7 pages doi:10.1155/2007/83589 Research Article Physical Layer Built-In Security
Strengthen RFID Tags Security Using New Data Structure
 International Journal of Control and Automation 51 Strengthen RFID Tags Security Using New Data Structure Yan Liang and Chunming Rong Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, University
International Journal of Control and Automation 51 Strengthen RFID Tags Security Using New Data Structure Yan Liang and Chunming Rong Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, University
Authentication and Secure Communication in GSM, GPRS, and UMTS Using Asymmetric Cryptography
 ISSN (Online): 1694-0784 ISSN (Print): 1694-0814 10 Authentication and Secure Communication in GSM, GPRS, and UMTS Using Asymmetric Cryptography Wilayat Khan 1 and Habib Ullah 2 1 Department of Electrical
ISSN (Online): 1694-0784 ISSN (Print): 1694-0814 10 Authentication and Secure Communication in GSM, GPRS, and UMTS Using Asymmetric Cryptography Wilayat Khan 1 and Habib Ullah 2 1 Department of Electrical
SSL A discussion of the Secure Socket Layer
 www.harmonysecurity.com info@harmonysecurity.com SSL A discussion of the Secure Socket Layer By Stephen Fewer Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Encryption Techniques 3 3 Protocol Overview 3 3.1 The SSL Record
www.harmonysecurity.com info@harmonysecurity.com SSL A discussion of the Secure Socket Layer By Stephen Fewer Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Encryption Techniques 3 3 Protocol Overview 3 3.1 The SSL Record
III. Our Proposal ASOP ROUTING ALGORITHM. A.Position Management
 Secured On-Demand Position Based Private Routing Protocol for Ad-Hoc Networks Ramya.R, Shobana.K, Thangam.V.S ramya_88@yahoo.com, k shobsi@yahoo.co.in,thangam_85@yahoo.com Department of Computer Science,
Secured On-Demand Position Based Private Routing Protocol for Ad-Hoc Networks Ramya.R, Shobana.K, Thangam.V.S ramya_88@yahoo.com, k shobsi@yahoo.co.in,thangam_85@yahoo.com Department of Computer Science,
Chapter 6 CDMA/802.11i
 Chapter 6 CDMA/802.11i IC322 Fall 2014 Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 6 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley March 2012 Some material copyright 1996-2012 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross,
Chapter 6 CDMA/802.11i IC322 Fall 2014 Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 6 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley March 2012 Some material copyright 1996-2012 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross,
A PPENDIX H RITERIA FOR AES E VALUATION C RITERIA FOR
 A PPENDIX H RITERIA FOR AES E VALUATION C RITERIA FOR William Stallings Copyright 20010 H.1 THE ORIGINS OF AES...2 H.2 AES EVALUATION...3 Supplement to Cryptography and Network Security, Fifth Edition
A PPENDIX H RITERIA FOR AES E VALUATION C RITERIA FOR William Stallings Copyright 20010 H.1 THE ORIGINS OF AES...2 H.2 AES EVALUATION...3 Supplement to Cryptography and Network Security, Fifth Edition
Design and Analysis of Methods for Signing Electronic Documents Using Mobile Phones
 Design and Analysis of Methods for Signing Electronic Documents Using Mobile Phones Pramote Kuacharoen School of Applied Statistics National Institute of Development Administration 118 Serithai Rd. Bangkapi,
Design and Analysis of Methods for Signing Electronic Documents Using Mobile Phones Pramote Kuacharoen School of Applied Statistics National Institute of Development Administration 118 Serithai Rd. Bangkapi,
Roaming authentication September 2006. Page 1. Roaming Authentication. Student Guide Book 1. 80-W0984-1 Rev A
 Roaming authentication Page 1 Roaming Authentication Student Guide Book 1 Export of this technology may be controlled by the United States Government. Diversion contrary to U.S. law prohibited. CDG is
Roaming authentication Page 1 Roaming Authentication Student Guide Book 1 Export of this technology may be controlled by the United States Government. Diversion contrary to U.S. law prohibited. CDG is
HLA BASED PUBLIC AUDITING ARCHITECTURE TO FIND MALICIOUS NODE IN AD HOC NETWORK - A REVIEW
 HLA BASED PUBLIC AUDITING ARCHITECTURE TO FIND MALICIOUS NODE IN AD HOC NETWORK - A REVIEW Aejaz Ahmed 1, H C Sateesh Kumar 2 1 M.Tech student, Department of Telecommunication Engineering, DSCE, aejazkmlpr@gmail.com
HLA BASED PUBLIC AUDITING ARCHITECTURE TO FIND MALICIOUS NODE IN AD HOC NETWORK - A REVIEW Aejaz Ahmed 1, H C Sateesh Kumar 2 1 M.Tech student, Department of Telecommunication Engineering, DSCE, aejazkmlpr@gmail.com
Network Security Technology Network Management
 COMPUTER NETWORKS Network Security Technology Network Management Source Encryption E(K,P) Decryption D(K,C) Destination The author of these slides is Dr. Mark Pullen of George Mason University. Permission
COMPUTER NETWORKS Network Security Technology Network Management Source Encryption E(K,P) Decryption D(K,C) Destination The author of these slides is Dr. Mark Pullen of George Mason University. Permission
Research Article. Research of network payment system based on multi-factor authentication
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(7):437-441 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Research of network payment system based on multi-factor
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(7):437-441 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Research of network payment system based on multi-factor
Side Channel Analysis and Embedded Systems Impact and Countermeasures
 Side Channel Analysis and Embedded Systems Impact and Countermeasures Job de Haas Agenda Advances in Embedded Systems Security From USB stick to game console Current attacks Cryptographic devices Side
Side Channel Analysis and Embedded Systems Impact and Countermeasures Job de Haas Agenda Advances in Embedded Systems Security From USB stick to game console Current attacks Cryptographic devices Side
Secure Collaborative Privacy In Cloud Data With Advanced Symmetric Key Block Algorithm
 Secure Collaborative Privacy In Cloud Data With Advanced Symmetric Key Block Algorithm Twinkle Graf.F 1, Mrs.Prema.P 2 1 (M.E- CSE, Dhanalakshmi College of Engineering, Chennai, India) 2 (Asst. Professor
Secure Collaborative Privacy In Cloud Data With Advanced Symmetric Key Block Algorithm Twinkle Graf.F 1, Mrs.Prema.P 2 1 (M.E- CSE, Dhanalakshmi College of Engineering, Chennai, India) 2 (Asst. Professor
AStudyofEncryptionAlgorithmsAESDESandRSAforSecurity
 Global Journal of Computer Science and Technology Network, Web & Security Volume 13 Issue 15 Version 1.0 Year 2013 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Global Journal of Computer Science and Technology Network, Web & Security Volume 13 Issue 15 Version 1.0 Year 2013 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Problems of Security in Ad Hoc Sensor Network
 Problems of Security in Ad Hoc Sensor Network Petr Hanáček * hanacek@fit.vutbr.cz Abstract: The paper deals with a problem of secure communication between autonomous agents that form an ad hoc sensor wireless
Problems of Security in Ad Hoc Sensor Network Petr Hanáček * hanacek@fit.vutbr.cz Abstract: The paper deals with a problem of secure communication between autonomous agents that form an ad hoc sensor wireless
159.334 Computer Networks. Network Security 1. Professor Richard Harris School of Engineering and Advanced Technology
 Network Security 1 Professor Richard Harris School of Engineering and Advanced Technology Presentation Outline Overview of Identification and Authentication The importance of identification and Authentication
Network Security 1 Professor Richard Harris School of Engineering and Advanced Technology Presentation Outline Overview of Identification and Authentication The importance of identification and Authentication
Message Authentication Codes
 2 MAC Message Authentication Codes : and Cryptography Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University Prepared by Steven Gordon on 28 October 2013 css322y13s2l08, Steve/Courses/2013/s2/css322/lectures/mac.tex,
2 MAC Message Authentication Codes : and Cryptography Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University Prepared by Steven Gordon on 28 October 2013 css322y13s2l08, Steve/Courses/2013/s2/css322/lectures/mac.tex,
CCMP Advanced Encryption Standard Cipher For Wireless Local Area Network (IEEE 802.11i): A Comparison with DES and RSA
 Journal of Computer Science Original Research Paper CCMP Advanced Encryption Standard Cipher For Wireless Local Area Network (IEEE 802.11i): A Comparison with DES and RSA 1 Velayutham, R. and 2 D. Manimegalai
Journal of Computer Science Original Research Paper CCMP Advanced Encryption Standard Cipher For Wireless Local Area Network (IEEE 802.11i): A Comparison with DES and RSA 1 Velayutham, R. and 2 D. Manimegalai
Implementing Enhanced AES for Cloud based Biometric SaaS on Raspberry Pi as a Remote Authentication Node
 Implementing Enhanced AES for Cloud based Biometric SaaS on Raspberry Pi as a Remote Authentication Node Dhvani. K. Shah Information Technology Thakur College of Engineering and Technology. Vinayak Bharadi,
Implementing Enhanced AES for Cloud based Biometric SaaS on Raspberry Pi as a Remote Authentication Node Dhvani. K. Shah Information Technology Thakur College of Engineering and Technology. Vinayak Bharadi,
Secure Navigation and Authentication. Sherman Lo November 2008
 Secure Navigation and Authentication Sherman Lo November 2008 1 Outline Motivating Authentication Proposed techniques for authentication Source authentication Cross checking My research 2 GNSS: Position,
Secure Navigation and Authentication Sherman Lo November 2008 1 Outline Motivating Authentication Proposed techniques for authentication Source authentication Cross checking My research 2 GNSS: Position,
CIS 6930 Emerging Topics in Network Security. Topic 2. Network Security Primitives
 CIS 6930 Emerging Topics in Network Security Topic 2. Network Security Primitives 1 Outline Absolute basics Encryption/Decryption; Digital signatures; D-H key exchange; Hash functions; Application of hash
CIS 6930 Emerging Topics in Network Security Topic 2. Network Security Primitives 1 Outline Absolute basics Encryption/Decryption; Digital signatures; D-H key exchange; Hash functions; Application of hash
