Real-time earthquake monitoring at the Indian Tsunami Early Warning System for tsunami advisories in the Indian Ocean
|
|
|
- Beatrice Allen
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 623164OCS / The International Journal of Ocean and Climate Systems X(X)Devi et al. research-article2016 Original Article Real-time earthquake monitoring at the Indian Tsunami Early Warning System for tsunami advisories in the Indian Ocean The International Journal of Ocean and Climate Systems January-April 2016: The Author(s) 2016 Reprints and permissions: sagepub.co.uk/journalspermissions.nav DOI: / ocs.sagepub.com E Uma Devi, MV Sunanda, B Ajay Kumar, Ch Patanjali Kumar and T Srinivasa Kumar Abstract The Indian Tsunami Early Warning System situated at Indian National Center for Ocean Information Services, Hyderabad, India, monitors real-time earthquake activity throughout the Indian Ocean to evaluate potential tsunamigenic earthquakes. The functions of the Indian Tsunami Early Warning System earthquake monitoring system include detection, location and determination of the magnitude of potentially tsunamigenic earthquakes occurring in the Indian Ocean. The real-time seismic monitoring network comprises 17 broadband Indian seismic stations transmitting real-time earthquake data through VSAT communication to the central receiving stations located at the Indian Meteorological Department, New Delhi, and the Indian National Center for Ocean Information Services, Hyderabad, simultaneously for processing and interpretation. In addition to this, earthquake data from around 300 global seismic stations are also received at the Indian National Center for Ocean Information Services in near-real-time. Most of these data are provided by IRIS Global Seismographic Network and GEOFON Extended Virtual Network through Internet. The Indian National Center for Ocean Information Services uses SeisComP3 software for auto-location of earthquake parameters (location, magnitude, focal depth and origin time). All earthquakes of Mw >5.0 are auto-located within 5 10 minutes of the occurrence of the earthquake. Since its inception in October 2007 to date, the warning centre has monitored and reported 55 tsunamigenic earthquakes (under-sea and near coast earthquakes of magnitude 6.5) in the Indian Ocean region. Comparison of the earthquake parameters (elapsed time, magnitude, focal depth and location) estimated by the Indian Tsunami Early Warning System with the US Geological Survey suggests that the Indian Tsunami Early Warning System is performing well and has achieved the target set up by the Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission. Keywords Earthquake, tsunami, seismic network Date received: 7 August 2015; accepted: 15 October 2015 Introduction Tsunamis are infrequent high-impact events that can cause a considerable number of fatalities, inflict major damage and cause significant economic loss to large sections of the coastlines. Under-sea earthquakes account for nearly 85% of the world s tsunamis (Whitmore et al., 2008), and tsunamis are less commonly caused by submarine landslides, infrequently by submarine volcanic eruptions and very rarely by a large meteorite impact in the ocean (Nayak and Kumar, 2011). The Indian Ocean tsunami of 26 December 2004 killed over 230,000 people and displaced more than 1 million people. In India, the tsunami devastated the coastal communities in Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Puducherry, and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands claiming nearly 18,000 lives (National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA), 2010). In response to this great tragedy, the Government Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS), Hyderabad, India Corresponding author: E Uma Devi, Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS), Ocean Valley, Nizampet BO, Pragathi Nagar SO, Hyderabad , India. umadevi@incois.gov.in Creative Commons Non Commercial CC-BY-NC: This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 License ( which permits non-commercial use, reproduction and distribution of the work without further permission provided the original work is attributed as specified on the SAGE and Open Access pages (
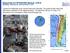
2 Devi et al. 21 Figure 1. Historical seismicity indicating the tsunamigenic source regions in the Indian Ocean. of India established the Indian Tsunami Early Warning System (ITEWS) at the Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS), Hyderabad (Gupta, 2005). The ITEWS comprises a real-time network of seismic stations, tsunami buoys, tide gauges and a 24 7 operational tsunami warning centre to detect tsunamigenic earthquakes, to monitor tsunamis and to provide timely advisories with back-end support of scenario database, vulnerability modelling and decision support system (Kumar et al., 2010). The concept Within any tsunami early warning concept, but mainly for a warning system for near-field tsunamis, the earthquake monitoring system plays a central role (Hanka et al., 2006). The time available to warn the population in the near-field regions like the Andaman and Nicobar Islands after a tsunami has been generated by a large earthquake is extremely short since the expected tsunami travel times are only of the order of min or even less. Therefore, tsunami watch or warning bulletins should be issued preferably within min in order to be able to initiate timely civil protection measures. These bulletins will initially be based primarily on rapidly determined earthquake parameters and on selected precalculated tsunami scenarios which fit the initial seismic parameters (Behrens et al., 2010). The sea level sensor data will be used in the later bulletins to warn the far field regions like the Indian mainland. These sea level data will also be used to validate the model results and also help in giving the final ALL Clear advisory. The seismic network Observation of the historical earthquake data sets in the Indian Ocean region indicates two potential source regions, namely, the Andaman Nicobar Sumatra island arc and the Makran subduction zone north of the Arabian Sea (Nayak and Kumar, 2008). The east and west coasts of India and the island regions are likely to be affected by tsunamis generated mainly by subduction zone related
3 22 The International Journal of Ocean and Climate Systems 7(1) earthquakes occurring in these zones (Figure 1). In order to monitor earthquakes occurring in these regions and to estimate earthquake parameters with reasonable accuracy in the shortest possible time, a well-distributed network of broadband seismic stations communicating data in real-time is vital for the tsunami early warning system. INCOIS has established a land-based network of 17 seismic stations (Figure 2) in collaboration with the Indian Meteorological Department (IMD), New Delhi. All these stations transmit real-time data through VSAT Figure 2. Location map of the Indian seismic stations for tsunami early warning. communication to the central receiving stations (CRSs) located at IMD, New Delhi, and INCOIS, Hyderabad, simultaneously for processing and interpretation. The stations are listed in Table 1. In order to have good azimuthal coverage of stations for quick and precise estimation of the earthquake parameters, the ITEWS has also configured stations from internationally coordinated networks like the IRIS, GEOFON and GSN networks, where real-time data are received through the Internet. Station configuration Each field station is equipped with Trillium 240 broadband seismometer, Taurus seismograph, and necessary power and communication facilities. The seismometer is well covered with thermal insulation and kept on pier for direct contact with hard rock on the ground and shielded perfectly to avoid the thermal and pressure fluctuations and to protect it from other atmospheric effects. The seismometer continuously records ground motion with 100 samples/s in the frequency range of Hz with constant frequency response. The recorded data are stored in the Taurus seismograph and transmitted continuously in automatic mode to the CRS through VSAT communication. The CRSs are equipped with state-of-the-art computing hardware, communication, data processing, visualisation and dissemination facilities. The field equipment can be accessed from the CRS remotely at any point of time and perform functions such as calibration of sensors including centring of mass, inspecting the state of health and downloading the seismic data from field stations. The schematic diagram at each station is given in Figure 3. Table 1. Station list of the Indian seismic stations established for tsunami early warning. S. No. Station name (code) Latitude (N) Longitude (E) 1 Shillong (SHL) Visakhapatnam (VSKP) Bokaro (BOKO) Madras (MDRS) Hyderabad (HYB) Trivandrum (TRVM) Goa (GOA) Pune (POO) Bhuj (BHUJ) Bhopal (BHPL) Simla (SMLA) Dharmsala (DHRM) Dehradun (DDN) Minicoy (MNC) Portblair (PBA) Diglipur (DGPR) Campbell Bay (CMBY)
4 Devi et al. 23 Figure 3. Schematic diagram of broadband sensor set-up at each field station. Figure 4. Earthquake summary display in the SeisComP3 software. Real-time data processing The real-time seismic data received at the ITEWS have to be quickly processed for the estimation of the earthquake parameters. SeisComP3 software is configured for real-time data reception, archiving, processing and auto-location using the national and international stations. Any earthquake of magnitude >5.0 occurring on the globe is auto-located within 5 10 min using this software. The earthquake parameters are displayed (Figure 4) with an alarm notification to alert the warning centre operators. The system can compute almost all types of magnitudes such as the local magnitude (ML), body wave magnitude (mb), broadband body wave magnitude (mb), broadband p-wave magnitude (Mwp), surface wave magnitude (MS) and moment magnitude (Mw). After the auto-location is given by the system, the operators can review the earthquake waveforms to refine
5 24 The International Journal of Ocean and Climate Systems 7(1) Table 2. Summary of the performance levels achieved by the ITEWS as criteria given by the IOC. Parameter Target Achievement Indian Ocean Elapse time from earthquake origin time to initial earthquake 10/15 min 8.3 information issuance (local/distant) Probability of detection of Indian Ocean earthquakes with Mw % 100% Accuracy of epicentre location (with respect to USGS) Within 30 km 24.5 Accuracy of hypocentre depth (with respect to USGS) Within 25 km 19.8 km Accuracy of earthquake Mw magnitude (with respect to USGS) ITEWS: Indian Tsunami Early Warning System; IOC: Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission; USGS: US Geological Survey. the auto-located parameters and the focal mechanism can be computed to know the tsunamigenic potential of the under-sea earthquake. The ITEWS has been recognised as one of the Regional Tsunami advisory Service Providers (TSP) for the Indian Ocean region on 12 October 2011 by the Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC) of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). As part of its regional services, the ITEWS compares its estimated earthquake parameters (elapsed time, magnitude, focal depth and location) with those of the US Geological Survey (USGS) to maintain its regional performance (targets set by IOC-ICG/IOTWS-V/13, 2008). Since its inception in October 2007 till 31 May 2015, ITEWS has monitored 475 earthquakes of magnitude 6.5 all over the globe (both land and ocean). Out of these earthquakes, 55 are in the Indian Ocean region (both Ocean and near coast). A summary of the performance of the warning centre against key performance indicators since it attained regional status, that is, since 12 October 2011 (22 earthquakes), is given in Table 2. It is evident from Table 2 that the parameters estimated by the ITEWS seismic network are very well within the target set up by IOC-ICG/IOTWS-V/13. Elapsed time is the time span between origin time of the earthquake and initial earthquake information issuance. It is observed that the average elapsed time of the ITEWS is 8.3 min, which is within the target of 10/15 min, while the USGS has an elapsed time of 10 min. The average difference in magnitude of the ITEWS estimate with the USGS is 0.30, which also achieves the target of 0.3. The average focal depth difference with the USGS is 19.8 km (Figure 5(a)), which is within the target value of 25 km. A comparison of earthquake location estimated by the ITEWS with the USGS indicates that the average difference in location is within the target of 30 km (Figure 5(b)). As a case study, we will discuss the ITEWS performance during the large strike-slip earthquakes of magnitude Mw (mb) 8.5 and 8.2 that occurred on 11 April 2012 in the Indian Ocean region. The former earthquake generated a small ocean-wide tsunami that has been recorded by various tide gauges and tsunami buoys located in the Indian Ocean region. The ITEWS detected this earthquake within 3 min 52 seconds and located it within 7 min from its occurrence with the help of SeisComP3 auto-location software. The initial magnitude of this earthquake was estimated as Mw (mb) 8.7 with a focal depth of 10 km. Both the national and regional earthquake information bulletins were issued after 8 min of the occurrence of the earthquake which is within the target of 10/15 min prescribed by the IOC. The earthquake parameters were reviewed, and considering the tsunami model results, the second bulletin was issued at 12 min with the revised earthquake magnitude as Mw (mb) 8.5 with threat information considering the earthquake as thrust fault as it occurred in the subduction zone. Furthermore, the realtime waveforms were analysed and noted that the earthquake occurred with strike-slip faulting and concluded there was no threat of an ocean-wide tsunami. But considering the tsunami model results and the real-time sea level observations, only a few parts of Andaman and Nicobar Islands were advised to evacuate. The ITEWS issued further bulletins according to its Standard Operating Procedure and avoided unnecessary evacuations to the mainland. This event once again proved the efficiency of the ITEWS. Summary The ITEWS established at the INCOIS with all the necessary computational and communication infrastructure is performing satisfactorily since its inception in October The real-time seismic monitoring network is continuously providing data and achieved its design goals. The earthquake monitoring capability of the ITEWS is significantly improved with the real-time seismic network, in particular with respect to the potential tsunamigenic earthquake generating regions.
6 Devi et al. 25 Figure 5. Plot of the ITEWS earthquake parameters with the USGS estimated values: (a) focal depth and (b) epicentre location. Acknowledgements We would like to express our sincere thanks to the Director, INCOIS, for his constant support. We thank the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES), New Delhi, for support and encouragement and our colleagues at IMD, SOI, NIOT, INCOIS and MoES for support in developing and operating this state-of-theart system. Some of the figures have been generated using GMT freeware developed by Paul Wessel and Walter H.F. Smith. Declaration of conflicting interests The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship and/or publication of this article. Funding The author(s) received no financial support for the research, authorship and/or publication of this article. References Behrens J, Androsov A, Babeyko AY, et al. (2010) A new multisensor approach to simulation assisted tsunami early warning. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences 10: Gupta H (2005) Mega-tsunami of 26th December, 2004: Indian initiatives for early warning system and mitigation of oceanic hazards. Episodes 28(1): 2 5. Hanka W and Lauterjung J; GITEWS Team (2006) GEOFON and the German Indian Ocean tsunami warning system. IRIS Newsletter, issue 2, pp IOC-ICG/IOTWS-V/13 (2008) Implementation plan for Regional Tsunami Watch Providers (RTWP). In: Fifth session of the intergovernmental coordination group for the Indian Ocean Tsunami Warning and Mitigation System, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 8 10 April. Srinivasa Kumar T, Patanjali Kumar Ch and Nayak S (2010) Performance of the Indian Tsunami Early Warning System.
7 26 The International Journal of Ocean and Climate Systems 7(1) In: International archives of the photogrammetry. Remote sensing and spatial information science, vol. XXXVIII, part 8, Kyoto, Japan. National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) (2010) National disaster management guidelines: Management of tsunamis, August. Available at: Nayak S and Srinivasa Kumar T (2008) Addressing the risk of tsunami in the Indian Ocean. Journal of South Asia Disaster Studies 1(1): Nayak S and Srinivasa Kumar T (2011) Tsunami watch and warning centers. In: Gupta Harsh K (ed.) Encyclopedia of Solid Earth Geophysics, vol. 2. Dordrecht: Springer, pp Whitmore P, Benz H, Bolton M, et al. (2008) NOAA/West Coast and Alaska Tsunami Warning Center Pacific Ocean response criteria. Science of Tsunami Hazards 27(2): Author biographies E Uma Devi is a Scientist and In-Charge for the Operational Activities of the Indian Tsunami Early Warning Centre with ESSO-Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (ESSO-INCOIS), Ministry of Earth Sciences, Government of India, Hyderabad, India. Currently, she works in the fields of Seismology & Tsunami Sciences. She has authored 11 papers in the national/international peer-reviewed journals. M V Sunanda is a Scientist at the Indian Tsunami Early Warning Centre with ESSO-Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (ESSO-INCOIS), Ministry of Earth Sciences, Government of India, Hyderabad, India. Her research interests include Seismology, Tsunami Sciences and GPS studies. She has authored 3 papers in the national/international peer-reviewed journals. B Ajay Kumar is a Scientist at the Indian Tsunami Early Warning Centre with ESSO-Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (ESSO-INCOIS), Ministry of Earth Sciences, Government of India, Hyderabad, India. His research interests include Seismology, Tsunami Sciences. He has authored 6 papers in the national/international peer-reviewed journals. Ch Patanjali Kumar is a Scientist at the Indian Tsunami Early Warning Centre with ESSO-Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (ESSO-INCOIS), Ministry of Earth Sciences, Government of India, Hyderabad, India. His research interests include Tsunami Modelling and Coastal Vulnerability Studies. He has authored 6 papers in the national/international peer-reviewed journals. T Srinivasa Kumar is heading the Advisory Services and Satellite Oceanography Group at ESSO-Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (ESSO-INCOIS), Ministry of Earth Sciences, Government of India, Hyderabad, India. He is also the In-charge of the Indian Tsunami Early Warning System at ESSO- INCOIS. He has authored 37 scientific papers in reputed national and international journals and 19 in conference/symposium proceedings. He has also contributed 3 chapters for various books.
Real time earthquake monitoring for early warning of tsunamis
 Real time earthquake monitoring for early warning of tsunamis 2 nd R.S.Dattatrayam India Meteorological Department Ministry of Earth Sciences New Delhi-110003 nd India Disaster Management Congress 4-6
Real time earthquake monitoring for early warning of tsunamis 2 nd R.S.Dattatrayam India Meteorological Department Ministry of Earth Sciences New Delhi-110003 nd India Disaster Management Congress 4-6
Lessons learned from the tsunami disaster caused by the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake and improvements in JMA's tsunami warning system
 Lessons learned from the tsunami disaster caused by the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake and improvements in JMA's tsunami warning system October 2013 Japan Meteorological Agency Lessons learned from the
Lessons learned from the tsunami disaster caused by the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake and improvements in JMA's tsunami warning system October 2013 Japan Meteorological Agency Lessons learned from the
The earthquake source
 Global seismology: The earthquake source Reading: Fowler p111-140 and Bolt Appendix G Earthquake location Earthquake focus: Latitude, longitude, depth Earthquake epicenter: Latitude, longitude Earthquakes
Global seismology: The earthquake source Reading: Fowler p111-140 and Bolt Appendix G Earthquake location Earthquake focus: Latitude, longitude, depth Earthquake epicenter: Latitude, longitude Earthquakes
HAZARD MAPPING, RISK ASSESSMENT, AND INSURANCE COVERAGE OF NATURAL CATASTROPHE RISK
 SESSION III HAZARD MAPPING, RISK ASSESSMENT, AND INSURANCE COVERAGE OF NATURAL CATASTROPHE RISK Mr. Sumarjono Insurance Bureau of The Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Indonesia Geological Position
SESSION III HAZARD MAPPING, RISK ASSESSMENT, AND INSURANCE COVERAGE OF NATURAL CATASTROPHE RISK Mr. Sumarjono Insurance Bureau of The Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Indonesia Geological Position
DRAFT TSUNAMI WARNING INFORMATION DISSEMINATION PROTOCOL FOR TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO (CDEMA PARTICIPATING STATE)
 DRAFT TSUNAMI WARNING INFORMATION DISSEMINATION PROTOCOL FOR TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO (CDEMA PARTICIPATING STATE) ODPM 6/3/2011 CONTENTS 1. Acronyms 2. Standard operating procedures A: (SOP A): 3. Standard
DRAFT TSUNAMI WARNING INFORMATION DISSEMINATION PROTOCOL FOR TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO (CDEMA PARTICIPATING STATE) ODPM 6/3/2011 CONTENTS 1. Acronyms 2. Standard operating procedures A: (SOP A): 3. Standard
THE 2004 SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE AND INDIAN OCEAN TSUNAMI: WHAT HAPPENED AND WHY
 Page 6 The Earth Scientist THE 2004 SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE AND INDIAN OCEAN TSUNAMI: WHAT HAPPENED AND WHY Seth Stein and Emile A. Okal Dept of Geological Sciences, Northwestern University, Evanston Illinois
Page 6 The Earth Scientist THE 2004 SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE AND INDIAN OCEAN TSUNAMI: WHAT HAPPENED AND WHY Seth Stein and Emile A. Okal Dept of Geological Sciences, Northwestern University, Evanston Illinois
GITEWS The German-Indonesian Tsunami Early-Warning System
 GITEWS The German-Indonesian Tsunami Early-Warning System GITEWS-Partner National Helmholtz-Gemeinschaft deutscher Forschungszentren (HGF) GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam (GFZ) Deutsches Zentrum für Luft-
GITEWS The German-Indonesian Tsunami Early-Warning System GITEWS-Partner National Helmholtz-Gemeinschaft deutscher Forschungszentren (HGF) GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam (GFZ) Deutsches Zentrum für Luft-
Chapter 5: Earthquakes
 Chapter 5: Earthquakes 1. Experiencing an Earthquake firsthand 2. The Science of Ghost Forests and Megaearthquakes 3. Faults, Earthquakes, and Plate Tectonics 4. Seismic Waves and Earthquake Detection
Chapter 5: Earthquakes 1. Experiencing an Earthquake firsthand 2. The Science of Ghost Forests and Megaearthquakes 3. Faults, Earthquakes, and Plate Tectonics 4. Seismic Waves and Earthquake Detection
Magnitude 7.2 GUERRERO, MEXICO
 A powerful magnitude-7.2 earthquake shook central and southern Mexico on Friday. The earthquake occurred at a depth of 24 km (15 miles). Its epicenter was in the western state of Guerrero, near the seaside
A powerful magnitude-7.2 earthquake shook central and southern Mexico on Friday. The earthquake occurred at a depth of 24 km (15 miles). Its epicenter was in the western state of Guerrero, near the seaside
DYNAMIC CRUST: Unit 4 Exam Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes
 DYNAMIC CRUST: Unit 4 Exam Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes NAME: BLOCK: DATE: 1. Base your answer to the following question on The block diagram below shows the boundary between two tectonic plates. Which
DYNAMIC CRUST: Unit 4 Exam Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes NAME: BLOCK: DATE: 1. Base your answer to the following question on The block diagram below shows the boundary between two tectonic plates. Which
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY FOR DISASTER MANAGEMENT Tulsi Vyas t4tulsi@gmail.com Aneri Desai ans_987@yahoo.co.in
 Computing for Nation Development, February 23 24, 2007 Bharati Vidyapeeth University Institute of Computer Applications and Management, New Delhi. INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY FOR DISASTER MANAGEMENT Tulsi Vyas
Computing for Nation Development, February 23 24, 2007 Bharati Vidyapeeth University Institute of Computer Applications and Management, New Delhi. INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY FOR DISASTER MANAGEMENT Tulsi Vyas
Earthquake Magnitude Calculator for the AS-1 Seismograph 1
 Magnitude calculator for the AS-1 Page 1 of 23 Earthquake Magnitude Calculator for the AS-1 Seismograph 1 Lawrence W. Braile and Saptarshi Dasgupta, Purdue University SKIP TO CALCULATORS Introduction:
Magnitude calculator for the AS-1 Page 1 of 23 Earthquake Magnitude Calculator for the AS-1 Seismograph 1 Lawrence W. Braile and Saptarshi Dasgupta, Purdue University SKIP TO CALCULATORS Introduction:
Interactive Plate Tectonics
 Interactive Plate Tectonics Directions: Go to the following website and complete the questions below. http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/index.html How do scientists learn about the interior
Interactive Plate Tectonics Directions: Go to the following website and complete the questions below. http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/index.html How do scientists learn about the interior
UNIT I INTRODUCTION. This unit deals with Location space relations and India s place in the world
 UNIT I INTRODUCTION This unit deals with Location space relations and India s place in the world CHAPTER INDIA LOCATION You have already seen the map of India in the previous classes. Now you closely examine
UNIT I INTRODUCTION This unit deals with Location space relations and India s place in the world CHAPTER INDIA LOCATION You have already seen the map of India in the previous classes. Now you closely examine
Regents Questions: Plate Tectonics
 Earth Science Regents Questions: Plate Tectonics Name: Date: Period: August 2013 Due Date: 17 Compared to the oceanic crust, the continental crust is (1) less dense and more basaltic (3) more dense and
Earth Science Regents Questions: Plate Tectonics Name: Date: Period: August 2013 Due Date: 17 Compared to the oceanic crust, the continental crust is (1) less dense and more basaltic (3) more dense and
Magnitude 8.8 OFFSHORE MAULE, CHILE
 A great 8.8-magnitude struck central Chile early Saturday. The quake hit 200 miles (325 kilometers) southwest of the capital Santiago. The epicenter was just 70 miles (115 kilometers) from Concepcion,
A great 8.8-magnitude struck central Chile early Saturday. The quake hit 200 miles (325 kilometers) southwest of the capital Santiago. The epicenter was just 70 miles (115 kilometers) from Concepcion,
ABSG Consulting, Tokyo, Japan Email: tkubo@absconsulting.co.jp 2. Professor, Kogakuin University, Tokyo, Japan 3
 Application of Earthquake Early Warning System and Real-time Strong-motion Monitoring System to Earthquake Disaster Mitigation of a High-Rise Building in Tokyo, Japan Tomohiro Kubo 1, Yoshiaki Hisada 2,
Application of Earthquake Early Warning System and Real-time Strong-motion Monitoring System to Earthquake Disaster Mitigation of a High-Rise Building in Tokyo, Japan Tomohiro Kubo 1, Yoshiaki Hisada 2,
Glossary. continental crust: the sections of crust, the outermost layer of the earth, that include the continents
 aftershock: an earthquake that follows a larger earthquake or main shock and originates in or near the rupture zone of the larger earthquake. Generally, major earthquakes are followed by a number of aftershocks
aftershock: an earthquake that follows a larger earthquake or main shock and originates in or near the rupture zone of the larger earthquake. Generally, major earthquakes are followed by a number of aftershocks
Improved Warnings for Natural Hazards: A Prototype System for Southern California
 Improved Warnings for Natural Hazards: A Prototype System for Southern California Yehuda Bock Research Geodesist Scripps Institution of Oceanography University of California San Diego, La Jolla, Calif.
Improved Warnings for Natural Hazards: A Prototype System for Southern California Yehuda Bock Research Geodesist Scripps Institution of Oceanography University of California San Diego, La Jolla, Calif.
EARTHQUAKES. Compressional Tensional Slip-strike
 Earthquakes-page 1 EARTHQUAKES Earthquakes occur along faults, planes of weakness in the crustal rocks. Although earthquakes can occur anywhere, they are most likely along crustal plate boundaries, such
Earthquakes-page 1 EARTHQUAKES Earthquakes occur along faults, planes of weakness in the crustal rocks. Although earthquakes can occur anywhere, they are most likely along crustal plate boundaries, such
A disaster occurs at the point of contact between social activities and a natural phenomenon of unusual scale.
 Hazard Mapping and Vulnerability Assessment Mr. Toshiaki Udono Senior Project Manager, Kansai Division, PASCO Corporation, Japan Mr. Awadh Kishor Sah Project Manager, Project Implementation Department,
Hazard Mapping and Vulnerability Assessment Mr. Toshiaki Udono Senior Project Manager, Kansai Division, PASCO Corporation, Japan Mr. Awadh Kishor Sah Project Manager, Project Implementation Department,
Assessment of Impact of the December 26, 2004 Tsunami In Aceh Province Indonesia
 Assessment of Impact of the December 26, 2004 Tsunami In Aceh Province Indonesia Jay H. Samek, David L. Skole, and Walter Chomentowski December 30, 2004 Center for Global Change and Earth Observations
Assessment of Impact of the December 26, 2004 Tsunami In Aceh Province Indonesia Jay H. Samek, David L. Skole, and Walter Chomentowski December 30, 2004 Center for Global Change and Earth Observations
PACIFIC TSUNAMI: CONTINUING RESEARCH AND FORMATION OF A MUSEUM EXHIBIT
 PACIFIC TSUNAMI: CONTINUING RESEARCH AND FORMATION OF A MUSEUM EXHIBIT Melissa Ann Meiner Geology/Marine Science Department University of Hawai i at Hilo Hilo, HI 96720 ABSTRACT The Sumatran tsunami was
PACIFIC TSUNAMI: CONTINUING RESEARCH AND FORMATION OF A MUSEUM EXHIBIT Melissa Ann Meiner Geology/Marine Science Department University of Hawai i at Hilo Hilo, HI 96720 ABSTRACT The Sumatran tsunami was
Disaster Risk Reduction through people centered National Multi-hazard Early Warning System in the context of Maldives
 Disaster Risk Reduction through people centered National Multi-hazard Early Warning System in the context of Maldives Abdul Muhusin, Deputy Director Department of Meteorology, Maldives Fourth Technical
Disaster Risk Reduction through people centered National Multi-hazard Early Warning System in the context of Maldives Abdul Muhusin, Deputy Director Department of Meteorology, Maldives Fourth Technical
Technical Documentation
 Technical Documentation Tsunami Hazard Maps for Bali Multi-scenario Tsunami Hazard Maps for Bali, 1:100,000 Multi-scenario Tsunami Hazard Maps for Southern Bali, 1:25,000 with zoning based on wave height
Technical Documentation Tsunami Hazard Maps for Bali Multi-scenario Tsunami Hazard Maps for Bali, 1:100,000 Multi-scenario Tsunami Hazard Maps for Southern Bali, 1:25,000 with zoning based on wave height
Earthquakes. Earthquakes: Big Ideas. Earthquakes
 Earthquakes Earthquakes: Big Ideas Humans cannot eliminate natural hazards but can engage in activities that reduce their impacts by identifying high-risk locations, improving construction methods, and
Earthquakes Earthquakes: Big Ideas Humans cannot eliminate natural hazards but can engage in activities that reduce their impacts by identifying high-risk locations, improving construction methods, and
Natural Disaster Impact on Business and Communities in Taiwan. Dr. Chung-Sheng Lee. NCDR Chinese Taipei
 Natural Disaster Impact on Business and Communities in Taiwan Dr. Chung-Sheng Lee NCDR Chinese Taipei 1 Brief Introduction of NCDR 2 Organizational Chart of NCDR NDPPC: National Disaster Preparation and
Natural Disaster Impact on Business and Communities in Taiwan Dr. Chung-Sheng Lee NCDR Chinese Taipei 1 Brief Introduction of NCDR 2 Organizational Chart of NCDR NDPPC: National Disaster Preparation and
SIXTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 SIXTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SIXTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing the structure of different types of volcanoes. LAB: Plotting
SIXTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SIXTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing the structure of different types of volcanoes. LAB: Plotting
Head 168 HONG KONG OBSERVATORY
 Controlling officer: the Director of the Hong Kong Observatory will account for expenditure under this Head. Estimate... $203.4m Establishment ceiling (notional annual mid-point salary value) representing
Controlling officer: the Director of the Hong Kong Observatory will account for expenditure under this Head. Estimate... $203.4m Establishment ceiling (notional annual mid-point salary value) representing
Plotting Earthquake Epicenters an activity for seismic discovery
 Plotting Earthquake Epicenters an activity for seismic discovery Tammy K Bravo Anne M Ortiz Plotting Activity adapted from: Larry Braile and Sheryl Braile Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Purdue
Plotting Earthquake Epicenters an activity for seismic discovery Tammy K Bravo Anne M Ortiz Plotting Activity adapted from: Larry Braile and Sheryl Braile Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Purdue
Chapter 2. Plate Tectonics. Plate Tectonics: Learning Goals
 Plate Tectonics Chapter 2 Interactions at depend on the direction of relative plate motion and the type of crust. Which kind of plate boundary is associated with Earthquake activity? A. Divergent Boundary
Plate Tectonics Chapter 2 Interactions at depend on the direction of relative plate motion and the type of crust. Which kind of plate boundary is associated with Earthquake activity? A. Divergent Boundary
TsunamiReady Program Definitions
 TsunamiReady Program Definitions 24-Hour Warning Point (WP): A communication facility at a state or local level, operating 24 hours a day, which has the capability to receive NWS alerts and warnings, plus
TsunamiReady Program Definitions 24-Hour Warning Point (WP): A communication facility at a state or local level, operating 24 hours a day, which has the capability to receive NWS alerts and warnings, plus
FIFTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FIFTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIFTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Exploring the rocks produced by volcanoes. LAB: Comparing igneous rocks.
FIFTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIFTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Exploring the rocks produced by volcanoes. LAB: Comparing igneous rocks.
Communications Systems Used in the USA TARNS. Chris Hill, Meteorologist in Charge (ret) National Weather Service Seattle, Washington, USA
 Communications Systems Used in the USA TARNS Chris Hill, Meteorologist in Charge (ret) National Weather Service Seattle, Washington, USA Washington Faces Many Non-Weather Hazards Earthquakes Tsunamis Terrorism
Communications Systems Used in the USA TARNS Chris Hill, Meteorologist in Charge (ret) National Weather Service Seattle, Washington, USA Washington Faces Many Non-Weather Hazards Earthquakes Tsunamis Terrorism
Geology 112 Earthquakes. Activity 1 Worksheet Introduction to the Course. What is a Fault? What is an Earthquake?
 Geology 112 Earthquakes Name Activity 1 Worksheet Introduction to the Course. What is a Fault? What is an Earthquake? Activity 1 Objectives: Introduce student to the topics, requirements and format of
Geology 112 Earthquakes Name Activity 1 Worksheet Introduction to the Course. What is a Fault? What is an Earthquake? Activity 1 Objectives: Introduce student to the topics, requirements and format of
Georgia Performance Standards Framework for Natural Disasters 6 th Grade
 The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
Determination of source parameters from seismic spectra
 Topic Determination of source parameters from seismic spectra Authors Michael Baumbach, and Peter Bormann (formerly GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam, Telegrafenberg, D-14473 Potsdam, Germany); E-mail: pb65@gmx.net
Topic Determination of source parameters from seismic spectra Authors Michael Baumbach, and Peter Bormann (formerly GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam, Telegrafenberg, D-14473 Potsdam, Germany); E-mail: pb65@gmx.net
Possible Inundation Map of Coastal Areas of Gujarat with a Tsunamigenic Earthquake
 Indian Minerals, Vol.61(3-4) & 62 (1-4), (July, 2007 - December, 2008); pp. 59-64 Possible Inundation Map of Coastal Areas of Gujarat with a Tsunamigenic Earthquake A. P. Singh 1*, U. Bhonde 1, B. K. Rastogi
Indian Minerals, Vol.61(3-4) & 62 (1-4), (July, 2007 - December, 2008); pp. 59-64 Possible Inundation Map of Coastal Areas of Gujarat with a Tsunamigenic Earthquake A. P. Singh 1*, U. Bhonde 1, B. K. Rastogi
Japan Meteorological Business Support Center (JMBSC)
 Japan Meteorological Business Support Center (JMBSC) The Japan Meteorological Business Support Center (JMBSC) is a general incorporated foundation* inaugurated in 1994, in accordance with the Meteorological
Japan Meteorological Business Support Center (JMBSC) The Japan Meteorological Business Support Center (JMBSC) is a general incorporated foundation* inaugurated in 1994, in accordance with the Meteorological
Government of India Earth System Science Organization Ministry of Earth Sciences India Meteorological Department
 Government of India Earth System Science Organization Ministry of Earth Sciences India Meteorological Department Press Release Dated: 1 October, 2015 Subject: Current status of southwest monsoon 2015 and
Government of India Earth System Science Organization Ministry of Earth Sciences India Meteorological Department Press Release Dated: 1 October, 2015 Subject: Current status of southwest monsoon 2015 and
Geosciences - Programme subject in programme for Specialization in General Studies
 Geosciences - Programme subject in programme for Specialization in General Studies Dette er en oversettelse av den fastsatte læreplanteksten. Læreplanen er fastsatt på Bokmål Laid down as a regulation
Geosciences - Programme subject in programme for Specialization in General Studies Dette er en oversettelse av den fastsatte læreplanteksten. Læreplanen er fastsatt på Bokmål Laid down as a regulation
UrEDAS, URGENT EARTHQUAKE DETECTION AND ALARM SYSTEM, NOW AND FUTURE
 3 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August -6, 24 Paper No. 98 UrEDAS, URGENT EARTHQUAKE DETECTION AND ALARM SYSTEM, NOW AND FUTURE Yutaka NAKAMURA SUMMARY UrEDAS, Urgent
3 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August -6, 24 Paper No. 98 UrEDAS, URGENT EARTHQUAKE DETECTION AND ALARM SYSTEM, NOW AND FUTURE Yutaka NAKAMURA SUMMARY UrEDAS, Urgent
SYLLABUS OF DIPLOMA IN DISASTER MANAGEMENT (DDM) Semester-I. Semester-II
 SYLLABUS OF DIPLOMA IN DISASTER MANAGEMENT (DDM) For Academic Session 2016-17 Duration: 1 Year Total Credit: 32 Semester-I DDM 01 Introduction to Disaster Management 6 Credit DDM 02 GIS and ICT in Disaster
SYLLABUS OF DIPLOMA IN DISASTER MANAGEMENT (DDM) For Academic Session 2016-17 Duration: 1 Year Total Credit: 32 Semester-I DDM 01 Introduction to Disaster Management 6 Credit DDM 02 GIS and ICT in Disaster
Presentations. Session 1. Slide 1. Earthquake Risk Reduction. 1- Concepts & Terminology
 Earthquake Risk Reduction Presentations Session 1 Slide 1 Earthquake Risk Reduction 1- Concepts & Terminology Welcome to the World Bank Institute s (WBI) Distance Learning (DL) course on Earthquake Risk
Earthquake Risk Reduction Presentations Session 1 Slide 1 Earthquake Risk Reduction 1- Concepts & Terminology Welcome to the World Bank Institute s (WBI) Distance Learning (DL) course on Earthquake Risk
TERMS OF REFERENCE OF CONSULTANT- GIS AND VULNERABILITY ANALYSIS & RISK ASSESSMENT
 TERMS OF REFERENCE OF CONSULTANT- GIS AND VULNERABILITY ANALYSIS & RISK ASSESSMENT Educational Qualifications and Experience: For Senior Consultant (GIS & Risk and Vulnerability Analysis) - Master of Engineering
TERMS OF REFERENCE OF CONSULTANT- GIS AND VULNERABILITY ANALYSIS & RISK ASSESSMENT Educational Qualifications and Experience: For Senior Consultant (GIS & Risk and Vulnerability Analysis) - Master of Engineering
Where in the World Are All the Earthquakes?
 Curry School of Education, University of Virginia www.teacherlink.org/content/science/ Where in the World Are All the Earthquakes? In this activity, students go to the United States Geological Survey (USGS)
Curry School of Education, University of Virginia www.teacherlink.org/content/science/ Where in the World Are All the Earthquakes? In this activity, students go to the United States Geological Survey (USGS)
Plate Tectonics: Ridges, Transform Faults and Subduction Zones
 Plate Tectonics: Ridges, Transform Faults and Subduction Zones Goals of this exercise: 1. review the major physiographic features of the ocean basins 2. investigate the creation of oceanic crust at mid-ocean
Plate Tectonics: Ridges, Transform Faults and Subduction Zones Goals of this exercise: 1. review the major physiographic features of the ocean basins 2. investigate the creation of oceanic crust at mid-ocean
1 Introduction. External Grant Award Number: 04HQGR0038. Title: Retrieval of high-resolution kinematic source parameters for large earthquakes
 External Grant Award Number: 04HQGR0038 Title: Retrieval of high-resolution kinematic source parameters for large earthquakes Author: Hong Kie Thio URS Group Inc. 566 El Dorado Street, 2 nd floor Pasadena,
External Grant Award Number: 04HQGR0038 Title: Retrieval of high-resolution kinematic source parameters for large earthquakes Author: Hong Kie Thio URS Group Inc. 566 El Dorado Street, 2 nd floor Pasadena,
Name: Date: Class: Finding Epicenters and Measuring Magnitudes Worksheet
 Example Answers Name: Date: Class: Finding Epicenters and Measuring Magnitudes Worksheet Objective: To use seismic data and an interactive simulation to triangulate the location and measure the magnitude
Example Answers Name: Date: Class: Finding Epicenters and Measuring Magnitudes Worksheet Objective: To use seismic data and an interactive simulation to triangulate the location and measure the magnitude
Institute for Risk and Disaster Reduction University College London
 Institute for Risk and Disaster Reduction University College London Wilkins Building South Wing, UCL, Gower Street London, England, WC1E 6BT www.ucl.ac.uk/rdr Outline Reducing the impact of disasters globally
Institute for Risk and Disaster Reduction University College London Wilkins Building South Wing, UCL, Gower Street London, England, WC1E 6BT www.ucl.ac.uk/rdr Outline Reducing the impact of disasters globally
How can we defend ourselves from the hazard of Nature in the modern society?
 How can we defend ourselves from the hazard of Nature in the modern society?, University of Bologna President of the EGU Division of Natural Hazards Email: stefano.tinti@unibo.it nh@egu.eu GIFT 2013 Natural
How can we defend ourselves from the hazard of Nature in the modern society?, University of Bologna President of the EGU Division of Natural Hazards Email: stefano.tinti@unibo.it nh@egu.eu GIFT 2013 Natural
Tsunami Practice Questions and Answers Revised November 2008
 Tsunami Practice Questions and Answers Revised November 2008 1. What happened on 26 December 2004 off the west coast of Sumatra? 2. What is the final estimate of the magnitude of the Sumatra 26 December
Tsunami Practice Questions and Answers Revised November 2008 1. What happened on 26 December 2004 off the west coast of Sumatra? 2. What is the final estimate of the magnitude of the Sumatra 26 December
TECTONICS ASSESSMENT
 Tectonics Assessment / 1 TECTONICS ASSESSMENT 1. Movement along plate boundaries produces A. tides. B. fronts. C. hurricanes. D. earthquakes. 2. Which of the following is TRUE about the movement of continents?
Tectonics Assessment / 1 TECTONICS ASSESSMENT 1. Movement along plate boundaries produces A. tides. B. fronts. C. hurricanes. D. earthquakes. 2. Which of the following is TRUE about the movement of continents?
Data in seismology: networks, instruments, current problems
 Data in seismology: networks, instruments, current problems Seismic networks, data centres, instruments Seismic Observables and their interrelations Seismic data acquisition parameters (sampling rates,
Data in seismology: networks, instruments, current problems Seismic networks, data centres, instruments Seismic Observables and their interrelations Seismic data acquisition parameters (sampling rates,
2015 Global Risk Assessment. Sahar Safaie Program Officer, UNISDR Risk Knowledge Section
 2015 Global Risk Assessment Sahar Safaie Program Officer, UNISDR Risk Knowledge Section Outline Global Assessment Report (GAR) evolution Global Risk Assessment for GAR15 Objective Scope Audience/Users
2015 Global Risk Assessment Sahar Safaie Program Officer, UNISDR Risk Knowledge Section Outline Global Assessment Report (GAR) evolution Global Risk Assessment for GAR15 Objective Scope Audience/Users
Natural Disasters & Assessing Hazards and Risk. Natural Hazards and Natural Disasters
 Page 1 of 9 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Natural Disasters & Assessing Hazards and Risk This page last updated on 19-Aug-2014 Natural Hazards and Natural Disasters
Page 1 of 9 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Natural Disasters & Assessing Hazards and Risk This page last updated on 19-Aug-2014 Natural Hazards and Natural Disasters
WELCOMES ALL THE ATTENDEES WATER UTILISATION, MEASUREMENT AND METHODOLOGIES
 SUTRON india WELCOMES ALL THE ATTENDEES WATER UTILISATION, MEASUREMENT AND ABOUT SUTRON USA Strong Corporation was founded in 1975 Sutron Operates in : Hydrological Meteorological Oceanic Aviation Real-Time
SUTRON india WELCOMES ALL THE ATTENDEES WATER UTILISATION, MEASUREMENT AND ABOUT SUTRON USA Strong Corporation was founded in 1975 Sutron Operates in : Hydrological Meteorological Oceanic Aviation Real-Time
Comparison of the P-wave Earthquake Alarm by Multi-Station and Single Station Detection System
 Comparison of the P-wave Earthquake Alarm by Multi-Station and Single Station Detection System Tsutomu Sato, Y. Nakamura System and Data Research Co., Ltd., Japan SUMMARY: The earthquake motion of the
Comparison of the P-wave Earthquake Alarm by Multi-Station and Single Station Detection System Tsutomu Sato, Y. Nakamura System and Data Research Co., Ltd., Japan SUMMARY: The earthquake motion of the
Coral Bleaching Alert System
 Coral Bleaching Alert System Technical Document Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS) Hyderabad 2011 Contents Page No. 1. Introduction...1 1. Objective...2 2. Study Area...2 3.
Coral Bleaching Alert System Technical Document Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS) Hyderabad 2011 Contents Page No. 1. Introduction...1 1. Objective...2 2. Study Area...2 3.
Building 1D reference velocity model of the Irpinia region (Southern Apennines): microearthquakes locations and focal mechanism
 Building 1D reference velocity model of the Irpinia region (Southern Apennines): microearthquakes locations and focal mechanism Tutor Prof. Raffaella De Matteis PhD student Emanuela Matrullo Geophisics
Building 1D reference velocity model of the Irpinia region (Southern Apennines): microearthquakes locations and focal mechanism Tutor Prof. Raffaella De Matteis PhD student Emanuela Matrullo Geophisics
Risks of future Earthquake- and extreme hydrological Disasters in Southeast Asia with a Focus on Thailand
 Risks of future Earthquake- and extreme hydrological Disasters in Southeast Asia with a Focus on Thailand Manfred Koch Department of Geohydraulics and Engineering Hydrology University of Kassel Germany
Risks of future Earthquake- and extreme hydrological Disasters in Southeast Asia with a Focus on Thailand Manfred Koch Department of Geohydraulics and Engineering Hydrology University of Kassel Germany
Earthquakes. www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk
 Earthquakes www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk Introduction Earthquakes are among the most deadly natural hazards. There are around 100 earthquakes each year of a size that could cause serious damage. They strike
Earthquakes www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk Introduction Earthquakes are among the most deadly natural hazards. There are around 100 earthquakes each year of a size that could cause serious damage. They strike
DENSITY OF POPULATION. Figures Map Table/Statements Notes
 7 DENSITY OF POPULATION Figures Map Table/Statements Notes 7 Density of population Experience shows that a very populous city can rarely, if ever, be well governed. To the size of states there is a limit,
7 DENSITY OF POPULATION Figures Map Table/Statements Notes 7 Density of population Experience shows that a very populous city can rarely, if ever, be well governed. To the size of states there is a limit,
THE NEED TO IMPLEMENT CONSTRUCTION DEFORMATION SPATIAL MONITORING SYSTEMS IN ROMANIA
 THE NEED TO IMPLEMENT CONSTRUCTION DEFORMATION SPATIAL MONITORING SYSTEMS IN ROMANIA Cristian ONU, Lecturer PhD. Eng., Technical University Gheorghe Asachi of Iasi, Romania, e-mail: cristi_onu@yahoo.com
THE NEED TO IMPLEMENT CONSTRUCTION DEFORMATION SPATIAL MONITORING SYSTEMS IN ROMANIA Cristian ONU, Lecturer PhD. Eng., Technical University Gheorghe Asachi of Iasi, Romania, e-mail: cristi_onu@yahoo.com
The Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) Correlation to. EarthComm, Second Edition. Project-Based Space and Earth System Science
 The Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) Achieve, Inc. on behalf of the twenty-six states and partners that collaborated on the NGSS Copyright 2013 Achieve, Inc. All rights reserved. Correlation to,
The Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) Achieve, Inc. on behalf of the twenty-six states and partners that collaborated on the NGSS Copyright 2013 Achieve, Inc. All rights reserved. Correlation to,
Seismic Networks in Canada
 Seismic Networks in Canada Tim Côté Canadian Hazards Information Service Geological Survey of Canada (GSC) Natural Resources Canada (NRCan) Antelope Users Group meeting San Diego, CA January 14-16, 2015
Seismic Networks in Canada Tim Côté Canadian Hazards Information Service Geological Survey of Canada (GSC) Natural Resources Canada (NRCan) Antelope Users Group meeting San Diego, CA January 14-16, 2015
A Real Time Tracking and Alerting System Using LabVIEW
 A Real Time Tracking and Alerting System Using LabVIEW J Jyothirmai Joshi Assistant Professor, Dept. of EIE, VNR Vignan Jyothi Institute of Engineering and Technology, Hyderabad, Telangana, India ABSTRACT:
A Real Time Tracking and Alerting System Using LabVIEW J Jyothirmai Joshi Assistant Professor, Dept. of EIE, VNR Vignan Jyothi Institute of Engineering and Technology, Hyderabad, Telangana, India ABSTRACT:
Chapter 7 Earthquake Hazards Practice Exam and Study Guide
 Chapter 7 Earthquake Hazards Practice Exam and Study Guide 1. Select from the following list, all of the factors that affect the intensity of ground shaking. a. The magnitude of the earthquake b. Rather
Chapter 7 Earthquake Hazards Practice Exam and Study Guide 1. Select from the following list, all of the factors that affect the intensity of ground shaking. a. The magnitude of the earthquake b. Rather
Tsunami Inundation Maps
 1946 1964 Today Tomorrow Tsunami Inundation Maps For Emergency Response Planning Available at www.tsunami.ca.gov Multi-year project covers all low-lying populated coastal areas 20 counties and over 75
1946 1964 Today Tomorrow Tsunami Inundation Maps For Emergency Response Planning Available at www.tsunami.ca.gov Multi-year project covers all low-lying populated coastal areas 20 counties and over 75
February 28 Earthquake: We got off easy
 February 28 Earthquake: We got off easy State Geologist John Beaulieu Lucky may not be the first word that comes to mind after an earthquake that injured more than 200 and caused more than $1 billion damage,
February 28 Earthquake: We got off easy State Geologist John Beaulieu Lucky may not be the first word that comes to mind after an earthquake that injured more than 200 and caused more than $1 billion damage,
German Earth Observation Systems and Programs Capacities for nation building
 German Earth Observation Systems and Programs Capacities for nation building German Aerospace Center, DLR, Earth Observation Center, EOC German Remote Sensing Data Center, DFD Gunter Schreier Deputy Director
German Earth Observation Systems and Programs Capacities for nation building German Aerospace Center, DLR, Earth Observation Center, EOC German Remote Sensing Data Center, DFD Gunter Schreier Deputy Director
ROLE OF REMOTE SENSING AND ITS APPLICATIONS IN DISASTER MANAGEMENT LIKE EARTHQUAKE, FLOOD AND TSUNAMIS. Rajeev 1, Tanuja 2,
 ROLE OF REMOTE SENSING AND ITS APPLICATIONS IN DISASTER MANAGEMENT LIKE EARTHQUAKE, FLOOD AND TSUNAMIS. Rajeev 1, Tanuja 2, Abstract: This study highlights the use of remote sensing technologies in disaster
ROLE OF REMOTE SENSING AND ITS APPLICATIONS IN DISASTER MANAGEMENT LIKE EARTHQUAKE, FLOOD AND TSUNAMIS. Rajeev 1, Tanuja 2, Abstract: This study highlights the use of remote sensing technologies in disaster
Lecture 12 Earthquake Magnitude
 Lecture 12 Earthquake Magnitude Locating Earthquakes Last time, we learned that we could obtain a rough estimate of the distance in miles to an earthquake epicenter by multiplying the S - P time interval
Lecture 12 Earthquake Magnitude Locating Earthquakes Last time, we learned that we could obtain a rough estimate of the distance in miles to an earthquake epicenter by multiplying the S - P time interval
Earthquakes. www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk. Seismograph stations operated by the British Geological Survey
 Seismograph stations operated by the British Geological Survey Earthquakes Photograph supplied by Andy Thompson, Arup Advanced Technology, EEFIT Mission www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk Introduction Earthquakes
Seismograph stations operated by the British Geological Survey Earthquakes Photograph supplied by Andy Thompson, Arup Advanced Technology, EEFIT Mission www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk Introduction Earthquakes
Development of Emergent Alarm System using the Earthquake Early Warning by Japan Meteorological Agencyed from Microtremor Records
 Development of Emergent Alarm System using the Earthquake Early Warning by Japan Meteorological Agencyed from Microtremor Records K. Masaki Department of Urban Environment, Aichi Institute of Technology,
Development of Emergent Alarm System using the Earthquake Early Warning by Japan Meteorological Agencyed from Microtremor Records K. Masaki Department of Urban Environment, Aichi Institute of Technology,
TSUNAMI RISK ASSESSMENT
 Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission Manuals and Guides 52 TSUNAMI RISK ASSESSMENT ANDMITIGATION FOR THE INDIAN OCEAN KNOWING YOUR TSUNAMI RISK AND WHAT
Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission Manuals and Guides 52 TSUNAMI RISK ASSESSMENT ANDMITIGATION FOR THE INDIAN OCEAN KNOWING YOUR TSUNAMI RISK AND WHAT
FOURTH GRADE EARTHQUAKES 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FOURTH GRADE EARTHQUAKES 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. DURING: Modeling three types
FOURTH GRADE EARTHQUAKES 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. DURING: Modeling three types
Workflows and Decision Tables for Flexible Early Warning Systems
 Workflows and Decision Tables for Flexible Early Warning Systems Felix Riedel Fraunhofer IOSB felix.riedel@iosb.fraunhofer.de Fernando Chaves Fraunhofer IOSB fernando.chaves-salamanca@iosb.fraunhofer.de
Workflows and Decision Tables for Flexible Early Warning Systems Felix Riedel Fraunhofer IOSB felix.riedel@iosb.fraunhofer.de Fernando Chaves Fraunhofer IOSB fernando.chaves-salamanca@iosb.fraunhofer.de
SUMMARY OF MAGNITUDE WORKING GROUP RECOMMENDATIONS ON DETERMINING EARTHQUAKE MAGNITUDES FROM DIGITAL DATA
 B SUMMARY OF MAGNITUDE WORKING GROUP RECOMMENDATIONS ON DETERMINING EARTHQUAKE MAGNITUDES FROM DIGITAL DATA The Working Group on Magnitudes (Magnitude WG) of the International Association of Seismology
B SUMMARY OF MAGNITUDE WORKING GROUP RECOMMENDATIONS ON DETERMINING EARTHQUAKE MAGNITUDES FROM DIGITAL DATA The Working Group on Magnitudes (Magnitude WG) of the International Association of Seismology
Introduction. Large amounts of seismic data are currently being collected and generated at a rate of approximately 3.3 Gbytes/year.
 Utilizing Large Integrated Data Sets for Regional Seismic Research in Asia Aaron A. Velasco, Julio Aguilar-Chang, Hans E. Hartse Geophysics Group (EES-3), Los Alamos National Laboratory LA-UR-00-342 Introduction
Utilizing Large Integrated Data Sets for Regional Seismic Research in Asia Aaron A. Velasco, Julio Aguilar-Chang, Hans E. Hartse Geophysics Group (EES-3), Los Alamos National Laboratory LA-UR-00-342 Introduction
OECD RECOMMENDATION CONCERNING GUIDELINES ON EARTHQUAKE SAFETY IN SCHOOLS
 OECD RECOMMENDATION CONCERNING GUIDELINES ON EARTHQUAKE SAFETY IN SCHOOLS THE COUNCIL Having regard to article 5b) of the Convention establishing the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
OECD RECOMMENDATION CONCERNING GUIDELINES ON EARTHQUAKE SAFETY IN SCHOOLS THE COUNCIL Having regard to article 5b) of the Convention establishing the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
CONFEDERATION OF ASIA-PACIFIC CHAMBERS OF COMMERCE AND INDUSTRY (CACCI)
 CONFEDERATION OF ASIA-PACIFIC CHAMBERS OF COMMERCE AND INDUSTRY (CACCI) Policy Paper on Flexible Responses to Environmental Uncertainty and Infrastructure Resolved as of 3 rd October,. A. BACKGROUND 1.
CONFEDERATION OF ASIA-PACIFIC CHAMBERS OF COMMERCE AND INDUSTRY (CACCI) Policy Paper on Flexible Responses to Environmental Uncertainty and Infrastructure Resolved as of 3 rd October,. A. BACKGROUND 1.
Plate Tectonics. Introduction. Boundaries between crustal plates
 Plate Tectonics KEY WORDS: continental drift, seafloor spreading, plate tectonics, mid ocean ridge (MOR) system, spreading center, rise, divergent plate boundary, subduction zone, convergent plate boundary,
Plate Tectonics KEY WORDS: continental drift, seafloor spreading, plate tectonics, mid ocean ridge (MOR) system, spreading center, rise, divergent plate boundary, subduction zone, convergent plate boundary,
GEO4180. Strategies for Mitigation of Risk Associated with Geohazards
 GEO4180 Geohazard Mitigation Strategies for Mitigation of Risk Associated with Geohazards Classification of geohazard mitigation strategies (1) land use plans, (2) enforcement of building codes and good
GEO4180 Geohazard Mitigation Strategies for Mitigation of Risk Associated with Geohazards Classification of geohazard mitigation strategies (1) land use plans, (2) enforcement of building codes and good
Seismic Waves Practice
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which shows models of two types of earthquake waves. Model A best represents the motion of earthquake waves called 1) P-waves (compressional
1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which shows models of two types of earthquake waves. Model A best represents the motion of earthquake waves called 1) P-waves (compressional
EARTH SCIENCE ACTIVITY #1 Tsunami in a Bottle
 EARTH SCIENCE ACTIVITY #1 Tsunami in a Bottle Grades 3 and Up This activity is one of several in a basic curriculum designed to increase student knowledge about earthquake science and preparedness. The
EARTH SCIENCE ACTIVITY #1 Tsunami in a Bottle Grades 3 and Up This activity is one of several in a basic curriculum designed to increase student knowledge about earthquake science and preparedness. The
Insurance B.C. Construction Round Table Seminar. Order of Presentation. June 23, 2011. Lindsay Olson Vice-President BC, SK, MB
 Earthquake Risk and Insurance B.C. Construction Round Table Seminar June 23, 2011 Lindsay Olson Vice-President BC, SK, MB Order of Presentation Canada s P&C Insurance Industry Canadian Earthquake Risk
Earthquake Risk and Insurance B.C. Construction Round Table Seminar June 23, 2011 Lindsay Olson Vice-President BC, SK, MB Order of Presentation Canada s P&C Insurance Industry Canadian Earthquake Risk
Emergency Management Audit For Businesses
 Emergency Management Audit For Businesses Sponsor Acknowledgement: This manual is sponsored by NZ Safety Limited and produced for the Ministry of Civil Defence Public Education Advisory Committee by Auckland
Emergency Management Audit For Businesses Sponsor Acknowledgement: This manual is sponsored by NZ Safety Limited and produced for the Ministry of Civil Defence Public Education Advisory Committee by Auckland
ES Chapter 10 Review. Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Class: Date: ES Chapter 10 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Scientists used the pattern of alternating normal and reversed
Name: Class: Date: ES Chapter 10 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Scientists used the pattern of alternating normal and reversed
Geohazards: Minimizing Risk, Maximizing Awareness The Role of the Insurance Industry
 Geohazards: Minimizing Risk, Maximizing Awareness The Role of the Insurance Industry Prof. Dr. Peter Hoeppe Head of Geo Risks Research Munich Re International Year of Planet Earth, Paris, 13 February 2008
Geohazards: Minimizing Risk, Maximizing Awareness The Role of the Insurance Industry Prof. Dr. Peter Hoeppe Head of Geo Risks Research Munich Re International Year of Planet Earth, Paris, 13 February 2008
View. A New. Into Earth
 View A New Into Earth EarthScope is a bold undertaking to apply modern observational, analytical and telecommunications technologies to investigate the structure and evolution of the North American continent
View A New Into Earth EarthScope is a bold undertaking to apply modern observational, analytical and telecommunications technologies to investigate the structure and evolution of the North American continent
Earth Science & Environmental Science SOL
 Earth Science & Environmental Science SOL THE SOL FOR GRADE 6 The Virginia Science SOL for Grades K 6 are organized according to a set of strands, with the SOL in each strand developed progressively through
Earth Science & Environmental Science SOL THE SOL FOR GRADE 6 The Virginia Science SOL for Grades K 6 are organized according to a set of strands, with the SOL in each strand developed progressively through
Leica Monitoring Solutions. Leica Monitoring Solutions Certainty builds confidence.
 Leica Monitoring Solutions Leica Monitoring Solutions Certainty builds confidence. Risk and Cost Reduction Proven Solutions Facing new challenges Engineering companies and contractors are facing challenges
Leica Monitoring Solutions Leica Monitoring Solutions Certainty builds confidence. Risk and Cost Reduction Proven Solutions Facing new challenges Engineering companies and contractors are facing challenges
Earthquake Magnitude
 Earthquake Magnitude Earthquake magnitude scales: Logarithmic measure of earthquake size amplitude of biggest wave: Magnitude 6 quake 10 * Magnitude 5 energy: Magnitude 6 quake is about 32 * Magnitude
Earthquake Magnitude Earthquake magnitude scales: Logarithmic measure of earthquake size amplitude of biggest wave: Magnitude 6 quake 10 * Magnitude 5 energy: Magnitude 6 quake is about 32 * Magnitude
Monitoring of High Rise Building using Real-Time Differential GPS
 Monitoring of High Rise Building using Real-Time Differential GPS Victor H.S. KHOO, Yam Khoon TOR and Gerry ONG, Singapore Key words: Global Positioning System (GPS), Differential GPS (DGPS), Structural
Monitoring of High Rise Building using Real-Time Differential GPS Victor H.S. KHOO, Yam Khoon TOR and Gerry ONG, Singapore Key words: Global Positioning System (GPS), Differential GPS (DGPS), Structural
Chapter Overview. Bathymetry. Measuring Bathymetry. Echo Sounding Record. Measuring Bathymetry. CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces
 Chapter Overview CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces The study of bathymetry charts ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools. Most ocean floor features
Chapter Overview CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces The study of bathymetry charts ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools. Most ocean floor features
Third United Nations World Conference on Disaster Risk Reduction Working Session 2: Risk Identification and Assessment. Speakers
 Third United Nations World Conference on Disaster Risk Reduction Working Session 2: Risk Identification and Assessment Speakers Chair: Ms. Florika Fink-Hooijer, Director for Strategy, Policy and International
Third United Nations World Conference on Disaster Risk Reduction Working Session 2: Risk Identification and Assessment Speakers Chair: Ms. Florika Fink-Hooijer, Director for Strategy, Policy and International
SUPERCOMPUTING FACILITY INAUGURATED AT BARC
 SUPERCOMPUTING FACILITY INAUGURATED AT BARC The Honourable Prime Minister of India, Dr Manmohan Singh, inaugurated a new Supercomputing Facility at Bhabha Atomic Research Centre, Mumbai, on November 15,
SUPERCOMPUTING FACILITY INAUGURATED AT BARC The Honourable Prime Minister of India, Dr Manmohan Singh, inaugurated a new Supercomputing Facility at Bhabha Atomic Research Centre, Mumbai, on November 15,
Climate Change Impacts in the Asia/Pacific Region
 Climate Change Impacts in the Asia/Pacific Region Global CC threat CC in the A/P region The Stern Review and IPCC 4 th Assessment Report both state that climate change will have adverse impact on people
Climate Change Impacts in the Asia/Pacific Region Global CC threat CC in the A/P region The Stern Review and IPCC 4 th Assessment Report both state that climate change will have adverse impact on people
Waves disturbances caused by the movement of energy from a source through some medium.
 Oceanography Chapter 10 Waves disturbances caused by the movement of energy from a source through some medium. Floating Gull- Figure 10.1 water is not moving only the energy is moving through the water.
Oceanography Chapter 10 Waves disturbances caused by the movement of energy from a source through some medium. Floating Gull- Figure 10.1 water is not moving only the energy is moving through the water.
