Guidelines for Patients having a. Total Knee Replacement
|
|
|
- Amie McCarthy
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Guidelines for Patients having a Total Knee Replacement
2 contents introduction Introduction 3 What is a Total Knee Replacement? 4 Preparing for Admission Checklist 5 Pain Management 6 Physiotherapy & Exercises 9 Walking 14 Stairs Technique 16 Rehabilitation Goals 17 General Recommendations (Sleeping, Driving etc.) 21 Discharge Instructions 27 Conclusion 31 This information booklet has been written to give you and your family a basic understanding of what is involved when you require a total knee replacement. In this booklet we provide information, including things you should know before and after your operation, as well as information regarding your discharge from the hospital. It is important for you to understand the benefits but also the possible problems that may occur after this form of surgery. Throughout your stay in UPMC Beacon Hospital, you will receive continuous advice and support from all members of the orthopaedic team. 2 Exercise Diary 32 Appendix: Potential Complications 34 Individual Patient Notes 38 3
3 What is a Total Knee Replacement? A total knee replacement is designed to replace a knee joint that has been damaged by arthritis. Replacing the painful and arthritic joint with an artificial one gives the joint a new surface that moves smoothly and painlessly. This is a surgical procedure in which the injured or damaged parts are replaced with artificial parts. will have better motion after a total knee replacement. Please refer to the Physiotherapy section for more information on these activities. Preparing for Admission Checklist Smoking: It is advisable to give up smoking, or at least to reduce the number of cigarettes you smoke a day, as smoking interferes with wound healing. It also impairs bone growth and repair and will delay or even prevent healing of the joint after surgery. 4 The procedure is performed by separating the muscles and ligaments around the knee to expose the knee capsule (the tough, gristle-like tissue surrounding the knee joint). The ends of the thigh bone (femur) and the shin bone (tibia) are removed and sometimes the underside of the kneecap (patella) is removed. The new knee consists of a metal shell on the end of the femur and a metal and plastic cover on the tibia. The parts are sometimes held in place with special cement. The operation normally lasts about 90 minutes. What can I expect from an artificial knee? An artificial knee is not a normal knee, nor is it as good as a normal knee. The operation will provide pain relief for ten years or more. Activities that overload the artificial knee must be avoided. About 90 percent of patients with stiff knees before surgery Clothing: Loose comfortable clothing is advised e.g. long shorts, tracksuit bottoms or loose three-quarter length trousers. Footwear: Comfortable lace up or slip on shoes with a low heel are recommended. Please ensure there is a back to these shoes. Valuables: Please leave all valuables and jewellery at home. Dentist: It is important that your teeth and gums are healthy before your operation as bad teeth can be the source of infection. Please make sure that you have had a dental check up in the last six months. Skin preparation: Your skin around the area to be operated 5
4 on will have to be prepared for surgery. This will involve washing the area with a disinfectant agent the night before and the morning of surgery as well as using special anti-microbial wipes on the area. More information on this is provided to you when you attend the pre-operative meeting with the nurse. The pre-operative meeting is a time for you to speak with the orthopaedic nurses and physiotherapists and ask any questions you may have regarding your surgery and rehabilitation. Patients who are being admitted the day before their surgery will receive information on skin preparation at this time. Planning your Discharge: If there is ANY possibility that you may require convalescence or additional help at home, now is the time to start planning and arranging it. It can be extremely difficult to get a bed in a convalescence centre at short notice. If you require further information regarding this, we have an information pack to help you plan your convalescence. Convalescence is the term we use to describe where you will go to recover after your surgery. This may be your home setting or you may require a short stay in a nursing home. special pain management devices and ice. The pain will naturally reduce as your wound heals and with regular use of analgesics (painkillers). It is imperative to keep your pain well controlled so you can mobilise comfortably, perform your physiotherapy exercises and resume normal activities after your surgery. You will be required to rate or score your pain regularly after your surgery. You will be asked to give a number between 0 and 10, where 0 represents no pain and 10 represents the worst pain you can imagine. Your score will depend on how intense your pain is. The nurses will administer appropriate treatments/ medications depending on your pain score. The nurse will reassess your pain score after the treatment to make sure it has worked to reduce your pain. 0 = No pain, 10 = Worst pain imaginable no pain mild pain moderate pain severe pain very severe pain worst pain imaginable 6 Pain Management Pain is a common occurrence following any surgical procedure. It can be well managed with medications, 7
5 8 Analgesics are painkillers and can include tablets, suppositories and injections into your veins or skin. You will receive analgesics at regular intervals throughout your recovery to maintain pain control. You can ask your nurse for extra painkillers if you need them for soreness or before your exercises. People using analgesia to manage pain are extremely unlikely to become addicted. If you have any medication allergies, please tell your nurse and doctor. If you have had unpleasant experiences taking analgesia in the past or are concerned about taking painkillers, please discuss this with your nurse or doctor. Side effects are very easily treated; they can include constipation, nausea, vomiting, itchiness, drowsiness and urinary retention. The special pain management devices can include a Patient Controlled Analgesic (PCA) pump or an Epidural Infusion/ Patient Controlled Epidural Analgesia (PCEA) pump. A PCA allows you to administer a small amount of analgesic into a tube (cannula) in your arm. You press a special button to activate the pump if you feel pain. This pump can be used for 1-2 days after your surgery. The epidural infusion/pcea involves inserting a tiny plastic tube into your back to administer analgesia and local anaesthetics to numb your joint area so you do not feel pain. This pump can stay in place for up to 2 days after surgery. The medications infuse every hour and you may have a special button (PCEA) to give yourself extra analgesia if you feel pain. Physiotherapy When muscles are not used, they become weak and do not perform well in supporting and moving the body. Your leg muscles are probably weak because you may not have used them very much due to your knee pain. The surgery can correct the knee problem, but the muscles will remain weak and will only be strengthened through regular exercise. You will be assisted and advised how to do this, but the responsibility for exercising is yours. Exercise Programme Exercise is very important following knee replacement surgery. Frequency: You will need to exercise at least three times a day to ensure you reach your rehabilitation goals. Please be sure to read the exercises carefully and ask your physiotherapist any questions that you may have before you leave the hospital. 9
6 The following exercises start on day one. You may feel uncomfortable at first, but these exercises will speed up your recovery. 1 Ankle Pumps With your legs straight, bend your ankles up and down, towards and away from your face. Repeat 15 times Continue this exercise until you are fully recovered and all ankle and lower-leg swelling has subsided. 3 Quadriceps Contraction With your leg straight out in front of you, tighten the muscles at the front of your thigh, pushing the back of your knee down into the bed. The result should be straightening of the knee. Hold the contraction for 5 seconds. Repeat 15 times. 2 Knee Flexion Lie on your back with your legs straight Slowly bend your knee by sliding your foot up towards your buttocks as far as you can. Hold for the count of 5. Relax and repeat 15 times. Every day you should be able to bend it a little further. Your therapist will measure the amount of bending. 4 Inner Range Quadriceps Place a towel in at the back of the knee of the operated leg. Push the back of the knee into the towel and lift the heel up off the bed. Hold the contraction for 5 seconds. Slowly return to your starting position. Repeat 15 times
7 5 Knee Extension Heel Prop It is critical that you are able to straighten your knee fully, for normal knee function. Place a small rolled towel under your heel. Tighten your thigh muscles trying to push your knee downwards fully straightening your knee. Hold for 5 seconds. Repeat 15 times. You are also encouraged to put your foot on a foot stool when sitting out for long periods both to reduce swelling and to maintain knee extension. 6 7 Straight Leg Raising Start by tightening the muscles at the top of your leg. Keeping your operated leg straight, raise the leg about 6 to 10 inches off the bed. Hold for 5 seconds. Lower the leg slowly to the bed. Repeat 15 times. Sitting Knee Flexion Practice knee bends sitting on the bedside or in a chair. Cross unoperated (good) leg over the operated leg at the ankle. Using your unoperated leg to assist, bend your operated knee as far as possible. Straighten and repeat. Repeat 15 times
8 8 Standing Knee Extension While holding on to a supportive surface, bend your operated knee slightly. Gently pull back your knee by tightening your thigh muscles, straightening your knee. Hold for 5 seconds. Repeat 15 times. on how to proceed. Walking pattern with crutches: 1. Stand in the middle of your crutches. 2. Place crutches in front of you. They should be a comfortable arm s length away. 3. Push down on the hand grips. Step forward to the crutches with your operated (weaker) leg. 4. Step past the crutches with your unoperated (good) leg. 5. Repeat the same sequence. 14 Walking In most cases after an uncomplicated first knee replacement (primary total knee replacement) you will be encouraged, when using crutches for support, to put your full weight through the operated leg. Your consultant will advise you when you can reduce your support to one crutch or progress to a stick in the opposite hand. If you have a complicated primary total knee replacement or a revision total knee replacement, you will be instructed to reduce the amount of weight bearing on your leg. In such a case you will be given specific instructions Tips for walking with crutches: Carry items in a backpack. Maintain good posture when walking. Wear shoes that fit well, support your feet, and are comfortable. Be careful when walking on uneven or wet surfaces. Walk at a safe comfortable pace. 15
9 Going upstairs Going downstairs Stairs Technique and banister for support. Going upstairs Maintain crutches/walking stick on the step below. Lead with the unoperated (good) leg up onto the step above. Follow with the unoperated (good) leg onto the same step. Hint: The good leg goes up the stairs first and the bad leg goes down the stairs first. 16 Take your weight onto the unoperated leg by pushing on crutches/walking stick and banister. Follow with the crutch/walking stick onto the same step. Going downstairs Put crutch/walking stick down onto the step below. Follow with the operated leg. Take weight onto the operated leg using the crutches Rehabilitation Goals Knee Replacement Goals of Care These goals have been developed to assist you in understanding your patient journey and also to outline your physiotherapy goals as a patient in UPMC Beacon Hospital. Your goals are divided into two areas, Nursing and Physiotherapy, and these start right after your surgery. Therefore you have some goals that remain the same from day one, with new goals added each day. 17
10 Knee Replacement Goals of Care Nursing Goals Your Physiotherapy Goals Nursing Goals Your Physiotherapy Goals Day of Procedure Day One You will: receive adequate pain relief be started on intravenous (IV) antibiotics depending on the time of day you return from theatre, you will be given something light to eat and drink commence use of your cryocuff (ice therapy) may have an x-ray of your new joint completed on this day or on day one anti-dvt medication will commence this day or on day one. You will: receive adequate pain relief be started on medications to prevent clots and be given IV antibiotics have bloods taken to check your iron levels after surgery have a wash and get dressed with assistance have cryotherapy applied to your knee using the cryocuff, a minimum of three times per day be encouraged to drink plenty of fluids A continuous passive motion (CPM) machine will be applied three times daily for one and a half hours each day. The flexion (bending) range is increased as high as is comfortable (aim for 85 degree bend by day three). If your consultant has requested a continuous passive motion (CPM) machine, the nurse or physiotherapist will apply this machine to your knee. Complete knee exercises under the supervision of the physiotherapist Get out of bed with the help of the physiotherapist Mobilise a short distance with a frame Sit out for a short period of time Ensure CPM progression Practise exercises independently Participate in a second physiotherapy treatment session with exercises and walking practice. Day Two Day Three You will: receive adequate pain relief be given medication to prevent clots have the wound dressing checked to ensure it is intact have a wash and get dressed with assistance have the cryocuff applied to your knee at least three times per day have the CPM machine applied mobilise with the appropriate aid (Zimmer frame or crutches) under the supervision of the nurse or healthcare assistant. You will: receive adequate pain relief be given medications to prevent clots be checked by your nurse to ensure your bowels have returned to normal function have your wound checked to ensure it is clean and dressing intact have resumed a normal diet have your Discharge Plan reviewed by your nurse have the CPM applied again, and range is increased if required until 85 degrees is reached. be encouraged to mobilise with appropriate aid Complete exercises with the physiotherapist Mobilise outside of your room with the frame Be able to get in and out of bed on your own Progress to 2 elbow crutches, if able Complete exercises independently throughout the day Have achieved a minimum of degrees knee bend on the CPM Sit out for a longer period of time. Mobilise for longer distances outside of your patient room with a frame or crutches (your physiotherapist will advise you on how far to walk). Learn how to climb stairs with the physiotherapist. Complete exercises independently throughout the day Have achieved a minimum of degrees knee bend on the CPM Sit out during the day
11 20 Day Four Day Five Nursing Goals You will: receive adequate pain relief be given medications to prevent clots be checked by your nurse to ensure your bowels have returned to normal function have your wound checked to ensure it is clean and dressing intact have your Discharge Plan reviewed with your nurse and implement any discharge arrangements continue with CPM and cryotherapy be encouraged to mobilise. You will: be given oral pain medication be given medications to prevent clots have your wound checked to ensure it is clean and dressing intact be checked by your nurse to ensure your bowels have returned to normal function implement discharge arrangements be provided with written discharge instructions. Your Physiotherapy Goals Mobilise with elbow crutches at ward level independently Climb a flight of stairs with the physiotherapist Have achieved degree knee bend on the CPM Complete exercise independently throughout the day Sit out during the day. Mobilise safely and independently Independent in completion of your exercise programme Have achieved a minimum of 90 degree knee bend Understand the importance of rehabilitation and follow up outpatient physiotherapy Ensure you have the necessary equipment for your rehabilitation. General Recommendations Sleeping While in hospital some patients find it harder to sleep for various reasons, e.g. different bed and environment. If you find that you are having this problem please let the nursing staff know as you may require something to help you sleep. After the day of the procedure you can sleep on your side or back unless otherwise indicated by the consultant. If you decide to lie on your side then a pillow between the knees may provide additional comfort. Nausea Some of the medications you may be prescribed can cause nausea. Please inform the nursing staff if you feel sick or are getting sick. Your medications may need to be changed/adjusted and the nursing staff can also get medication prescribed to help relieve this nausea. Pain Medication On discharge from hospital you will be prescribed some medications. At least one of the medications will be for pain. Plan to take your pain medication 30 minutes before your exercises. Preventing pain is easier than chasing pain. If pain control continues to be a problem, contact your general practitioner. 21
12 Guidelines for Patients Having a Total Knee Replacement Nutrition your hospital stay. Aim to follow a well balanced diet which includes protein, fats and carbohydrates. It is important to be well nourished to promote wound healing, so eat well and do not attempt to lose weight at this time. The following nutrients are particularly important to promote wound healing: Protein found in meat, fish, eggs, milk, cheese, yoghurt, beans and pulses. Vitamin A found in liver, fortified milk, carrots, turnips, and leafy green vegetables. Vitamin C found in citrus fruits, potatoes and leafy green vegetables. Iron found in liver, red meat and leafy green vegetables. Zinc found in fortified breakfast cereals, red meat and leafy green vegetables. If you are on a special diet or have any queries, please discuss with your doctor, nurse or dietician. Swelling and Bruising Most patients experience swelling and bruising in the knee after surgery. This is a normal part of the recovery phase after a total knee replacement. The swelling can cause pain in your knee and may restrict the amount of movement you have in the joint. To reduce this, take the medications that are prescribed for you, and ice your knee. Use of Ice Your knee may be hot, red and swollen after surgery. Ice may therefore be used during your hospital stay and at home, to help reduce the pain and swelling in your knee. A cryocuff may be placed on your knee for minutes. Your sensation may be decreased after surgery, so use extra care. You shall continue to ice regularly during the day both as an in-patient and on discharge home in order to help control swelling and any pain and also to encourage healing. This should be done at least 3 times a day for the first 6 weeks after surgery and as required after that. Bowel Care Driving 22 A high fibre diet is recommended after surgery. You may also be prescribed laxatives (eg. Lactalose, Senokot) during Your consultant will tell you when you are allowed to drive again after your operation. In order to be safe driving 23
13 a motor vehicle, you must be in control of the pedals effectively. It is recommended that you do not drive a motor vehicle until you have complete control over your leg. This does not normally occur until at least 6 weeks after your surgery. When you feel capable of driving, it is recommended to complete a trial period in an empty car park to accustom yourself to your new knee. Please check with your motor insurer prior to your return to driving. There may be additional requirements or restrictions to follow after your surgery. Car Transfers When travelling in the car you should sit in the front passenger seat. It is important that you avoid long journeys if possible. Before getting into the car, make sure you are standing on level ground and not on a kerb. Your driver should move the seat back as far as it will go and recline the seat slightly. swing your legs into the footwell of the car. When getting out of the car, reverse the above procedure and ensure the operated leg is out in front of you before standing up. Travel Prolonged periods of sitting on airlines may predispose you to leg swelling and deep venous thrombosis, and it is recommended that you avoid this until 6 weeks after your surgery. If you must travel, wear your elasticated stockings and keep your leg elevated as much as possible. Please discuss any imminent travel arrangements with your consultant. General Safety Advice for the Home: Please be aware of the hazards in your home as this will make your recovery easier and safer. Move electrical cords, phone lines and ensure clear pathways. 24 When getting into the car, stand with your back to the car and lower yourself down slowly onto the seat, keeping your operated leg slightly out in front of you. Slide back into the centre of the passenger seat allowing your operated leg to come onto the seat with slightly knee bent. Keep leaning backwards, twist your bottom and Store items within easy reach specifically in the kitchen and bathroom areas. Remove rugs including bath mats and entrance mats. Be careful with pets and young children. Be aware of water spills, slipper floors and always think 25
14 26 before you move. Pace yourself and take your time. Showering/Bathing A shower usually has a small step in and care should be taken getting in and out. A shower chair, non-slip mat and grab rail will maximise your safety if you choose to use the shower. If you only have a bath then transfers should only be completed with assistance of family member/carers and with the use of assistive equipment eg. bath board. Sitting while washing at a sink or using a family member s shower might be helpful alternatives. The website is a useful resource for information and local suppliers of assistive equipment for showering/ bathing. If you require more specific advice in relation to bathing the Occupational Therapist can assist you. Sexual Activity Resumption of sexual activity is possible on discharge. However, care should be taken to avoid excessive force on the knee and the wound should be protected. Stockings Your consultant may wish for you to go home with elasticated stockings. These can be an important part of preventing the development of deep vein thrombosis (blood clots in the legs). It is recommended to wear these for 6 weeks after surgery. Antibiotics Following knee replacement surgery there can be a greater risk of developing an infection in the knee with some procedures. Antibiotics to prevent the development of an infection in the knee should be taken when having a bladder catheter inserted, urinary surgery (e.g. prostatectomy) or when having infected teeth removed. Always tell your dentist that you have had a total knee replacement. Discharge Instructions Assuming no complications arise after your operation, and once your physiotherapist considers you independently mobile, you will be discharged from hospital. This is usually about day four or day five of your stay. Some people go straight home, while others require some time in a convalescent home. When you leave the hospital you will be given an appointment to see your consultant, usually around 6 weeks after the operation. This is for a routine check-up which will make sure you are progressing satisfactorily and x-rays may be taken. It is important to still bring your old x-rays with you at this time. 27
15 Subsequent appointments may be at 6 months, 1 year, or 2 years after surgery. You will be advised to attend outpatient physiotherapy within two weeks of discharge. You can either attend a physiotherapist in the hospital or one more local to your home. If you would prefer to exercise in a group setting, UPMC Beacon Hospital provides weekly group exercise classes for total knee replacement patients. Your physiotherapist will provide you with the details of these classes. You will need to continue your physiotherapy for a minimum of three months after your surgery. Your physiotherapists will advise you after your surgery regarding your requirements. Wound Care You will leave the hospital with a simple surgical wound. Before leaving your dressing will be changed and the wound site checked. Keep the wound dressing clean and dry. The nurse looking after you will advise you on when the dressings need to be changed. You may then remove the dressing after showering and apply a fresh dressing. Please check with your nurse prior to discharge regarding your consultant s specific wound care instructions, and instructions regarding removal of clips or stitches. the symptoms below occur then you will need to see your GP or liaise with the centre for orthopaedics for advice and possibly antibiotics. Signs of Infection If you develop any of the following signs of infection, it is important to report them to your doctor. The signs of infection include: Redness around the wound site Increased pain in the wound Swelling around the wound Heat at the wound site Discharge of fluid may be green or yellow Odour or smell from the wound Feeling of being generally unwell Fever or temperature Most people will have sutures (stitches) that will need to be removed approximately days after surgery. This may be done by the GP, Centre for Orthopaedics, consultant or in the convalescence centre. Make sure you receive a copy of the Patient Wound Care Discharge Instructions prior to your discharge. 28 Infection may occur despite your very best efforts. If any of 29
16 Activities at Home During the first 6 weeks after your surgery, we recommend limiting your activities to walking with support, or when the dressing has been removed, to swimming in the shallow end. We recommend that you refrain from more strenuous activities such as golf and social tennis for a period of 3 months. The following are some of our recommendations: Not Recommended after Surgery Jogging or running Contact sports and high impact aerobics Vigorous walking or hiking Skiing Tennis Repetitive lifting exceeding 50lbs Ballroom dancing Normal stair climbing Conclusion We hope that you have found this booklet useful and that it has helped to relieve some of your fears and anxieties regarding your surgery. During your hospital stay, your medical team will be available to discuss anything mentioned in this booklet or to answer any other queries you may have. We look forward to meeting you soon. Expected Activity after Surgery Recreational walking Golf Driving Light hiking Recreational biking 30 31
17 Exercise Diary Following Total Knee Replacement Surgery Day Post Operation: Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4 Day 5 Time of Day: Morning Afternoon Evening Morning Afternoon Evening Morning Afternoon Evening Morning Afternoon Evening Morning Afternoon Evening Target Volume (Repetitions x Sets) 1. Ankle Pumps 2. Knee Flexion 3. Quads Contraction 4. Inner Range Quads 5. Knee Extension Heel Prop 6. Straight Leg Raising 7. Sitting Knee Flexion 8. Standing Knee Extension Instructions: The exercise programme will begin the first day after your surgery and the physiotherapist will teach you the exercises the first time you perform them. From then on you should record the number of repetitions of each exercise that you complete in the boxes in the table above. The aim is to perform three exercise sets per day (morning, afternoon and evening)
18 Appendix Potential Complications of Knee Replacement Surgery Incidence: THE MAJORITY OF PATIENTS WHO UNDERGO KNEE REPLACEMENT SURGERY HAVE A PLEASANT EXPERIENCE WITHOUT ANY COMPLICATIONS. OF ALL PATIENTS WHO UNDERGO TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENTS, MORE THAN 96% HAVE NO COMPLICATIONS. THE FOLLOWING IS A COMPREHENSIVE LIST OF ALL PROBLEMS THAT COULD POTENTIALLY OCCUR. FOR INFORMED CONSENT IT IS IMPORTANT THAT YOU KNOW OF THESE PROBLEMS BUT PLEASE BE REASSURED THAT THE VAST MAJORITY OF PATIENTS SUFFER NO COMPLICATIONS. medication to try to limit the risk of a DVT forming. Starting to walk and mobilising is one of the best ways to prevent clots from forming. However despite all these precautions, some patients still develop clots and may require treatment with further medication. Knee Stiffness Knee stiffness may occur after the operation, especially if the knee is stiff before the surgery. Manipulation of the joint (under general anaesthetic) may be necessary. Pain The knee area will be sore after the operation. If I am in pain, I understand that it is important to tell staff so that medications can be given. Pain will decrease with time. Rarely, pain will be a chronic problem and may be due to any of the other complications listed below, or, for no obvious reason. Some replaced knees can remain painful; however this is rare. Prosthesis Wear and Loosening With modern techniques and new implants, knee replacements last many years. In some cases however, they fail sooner. The reason is often unknown. Wear may contribute to loosening. Loosening may cause pain and if loosening is significant, a second joint replacement may be required. This operation is significantly more complicated than the original joint replacement. 34 Bleeding This is usually small, which is controlled during the operation. A blood transfusion or iron tablets may occasionally be required. Rarely, the bleeding may form a blood clot or large bruise within the knee, which may become painful and require an operation to remove it. Blood Clot (DVT)/Phlebitis A DVT (deep venous thrombosis) is a blood clot in the vein. This may present as red, painful and swollen legs (usually). The risk of a DVT is greater after any surgery (and especially bone surgery). A DVT may pass in the blood stream and be deposited in the lungs (a pulmonary embolism/pe). This is a serious and rare condition, which affects your breathing. The consultant will prescribe Infection Antibiotics are given just before and after the operation, and the procedure will be performed in an operating theatre with sterile equipment. Despite this, postoperative infection may still occur. The wound site may become red, hot and painful. There may also be a discharge of fluid or pus. This is usually treated with antibiotics, but an operation to wash out the joint may be necessary. In rare cases, the implants may be removed and replaced at a later date. The infection can sometimes lead to sepsis (blood infection) and strong antibiotics may be required. Infection is now a rare complication occurring in less than 1% of patients. Strict protocols in the operating theatre, intra-operative antibiotics, special surgical gowns and meticulous attention to surgical detail have helped achieve this low number, but for the unlucky 1% it is a catastrophic outcome. Spread of infection from another part of the 35
19 body to a joint replacement can occur, sometimes years after the operation. To prevent such infections, persons with a joint replacement are generally given antibiotics with extensive dental procedures, urinary tract infections or surgery as well as before other types of surgery. If an infection occurs anywhere in the body it must be treated promptly with antibiotics. Blood/Fat Embolism (PE) A PE (pulmonary embolism) is a consequence of DVT (deep vein thrombosis). PE may occur if the clot detaches from the vein and travels to the lung and can make breathing difficult. A PE can be treated with blood thinning medication, but can also be fatal. Joint Dislocation If this occurs, the joint can usually be put back into place without the need for surgery. Sometimes this is not possible, and an operation is required followed by application of a knee brace. Nerve Damage Rarely, nerves in the vicinity of the knee joint are stretched or damaged during the operation (a neuropraxia). This is often only noticed upon returning to the ward where the patient may complain of altered sensation in the foot or, in more severe cases, inability to move their foot outwards. Changes in sensation to the outer half of the knee may be normal. Every effort is made to prevent this; however damage to the small nerves of the knee is a risk. This may cause temporary or permanent altered sensation around the knee. Total knee replacement surgery is done under tourniquet (where a blood pressure cuff is applied to your leg) and occasionally a nerve by the side of the knee can get damaged (the peroneal nerve), which may cause temporary or permanent weakness or altered sensation of the lower leg. Fortunately, the majority of these neuropraxias resolve over a period of time, sometimes months. In a very small minority the damage may be permanent. Bone Damage A bone may be broken when the prosthesis (replaced knee joint) is inserted. This may require fixation, either at the time or at a later operation. Periprosthetic Fracture This complication can occur after a knee replacement if the bone is weak, especially in the first two months after surgery. Sometimes it is caused by a fall or stumble. Periprosthetic femoral fracture causes thigh pain with weight bearing and may cause shortening and rotation of the limb. Heterotropic Ossification There is a small risk of developing ossification or calcification in the muscle tissue around the knee after surgery. In the majority of cases, this involves small islands of bone that do not cause any functional restriction and are only noticeable on x-rays. Rarely, in less than 1% of cases there may be more extensive ossification that may cause stiffness and pain. This can be corrected by surgical removal but only after 12 months have passed since the surgery. Blood Vessel Damage The vessels at the back of the knee may rarely be damaged and may require further surgery. Stroke (CVA)/ Sudden Death This is a very rare complication that can occur after any major surgery and from any of the above
20 Individual Patient Notes Notes: Consultant Name: Date of Surgery: Weight Bearing Status: Walking Device: Date for Removal of Sutures (Stitches): Other Recommendations: 38 39
21 UPMC Beacon Centre for Orthopaedics UPMC Beacon Hospital Sandyford Dublin 18 Tel: UPMC Beacon Physiotherapy Department Tel: Scan with your smartphone to visit our website to download our free app Version 2
Guidelines for Patients having a. Total Knee Replacement
 Guidelines for Patients having a Total Knee Replacement contents introduction Introduction 3 What is a Total Knee Replacement? 4 Potential Complications 5 Preparing for Admission Checklist 7 Manage Your
Guidelines for Patients having a Total Knee Replacement contents introduction Introduction 3 What is a Total Knee Replacement? 4 Potential Complications 5 Preparing for Admission Checklist 7 Manage Your
Total Hip Replacement
 NOTES Total Hip Replacement QUESTIONS DATES PHONE NOS. Compiled by Mr John F Nolan FRCS for The British Hip Society 2009. A patient s information booklet 16 1 Introduction This booklet has been produced
NOTES Total Hip Replacement QUESTIONS DATES PHONE NOS. Compiled by Mr John F Nolan FRCS for The British Hip Society 2009. A patient s information booklet 16 1 Introduction This booklet has been produced
Wrist Fracture. Please stick addressograph here
 ORTHOPAEDIC UNIT: 01-293 8687 /01-293 6602 UPMC BEACON CENTRE FOR ORTHOPAEDICS: 01-2937575 PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT: 01-2936692 GUIDELINES FOR PATIENTS FOLLOWING WRIST FRACTURE Please stick addressograph
ORTHOPAEDIC UNIT: 01-293 8687 /01-293 6602 UPMC BEACON CENTRE FOR ORTHOPAEDICS: 01-2937575 PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT: 01-2936692 GUIDELINES FOR PATIENTS FOLLOWING WRIST FRACTURE Please stick addressograph
Total knee replacement
 Patient Information to be retained by patient What is a total knee replacement? In a total knee replacement the cartilage surfaces of the thigh bone (femur) and leg bone (tibia) are replaced. The cartilage
Patient Information to be retained by patient What is a total knee replacement? In a total knee replacement the cartilage surfaces of the thigh bone (femur) and leg bone (tibia) are replaced. The cartilage
Knee Microfracture Surgery Patient Information Leaflet
 ORTHOPAEDIC UNIT: 01-293 8687 /01-293 6602 BEACON CENTRE FOR ORTHOPAEDICS: 01-2937575 PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT: 01-2936692 Knee Microfracture Surgery Patient Information Leaflet Table of Contents 1. Introduction
ORTHOPAEDIC UNIT: 01-293 8687 /01-293 6602 BEACON CENTRE FOR ORTHOPAEDICS: 01-2937575 PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT: 01-2936692 Knee Microfracture Surgery Patient Information Leaflet Table of Contents 1. Introduction
Information and exercises following dynamic hip screw
 Physiotherapy Department Information and exercises following dynamic hip screw Introduction A dynamic hip screw is performed where the neck of femur has been fractured and where there is a good chance
Physiotherapy Department Information and exercises following dynamic hip screw Introduction A dynamic hip screw is performed where the neck of femur has been fractured and where there is a good chance
Total hip replacement
 Patient Information to be retained by patient What is a total hip replacement? In a total hip replacement both the ball (femoral or thigh bone) side of the hip joint and the socket (acetabular or pelvic
Patient Information to be retained by patient What is a total hip replacement? In a total hip replacement both the ball (femoral or thigh bone) side of the hip joint and the socket (acetabular or pelvic
Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft)
 Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft) Why do I need the operation? You have a blockage or narrowing of the arteries supplying blood to your leg. This reduces the blood flow to
Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft) Why do I need the operation? You have a blockage or narrowing of the arteries supplying blood to your leg. This reduces the blood flow to
Guidelines for patients having a Lumbar. Discectomy. Lumbar Discectomy
 ORTHOPAEDIC UNIT: 01-293 8687 /01-293 6602 BEACON CENTRE FOR ORTHOPAEDICS: 01-2937575 PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT: 01-2936692 Guidelines for patients having a Lumbar Discectomy Please stick addressograph
ORTHOPAEDIC UNIT: 01-293 8687 /01-293 6602 BEACON CENTRE FOR ORTHOPAEDICS: 01-2937575 PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT: 01-2936692 Guidelines for patients having a Lumbar Discectomy Please stick addressograph
Hip Replacement. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Tel: 01473 702107
 Information for Patients Hip Replacement Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Tel: 01473 702107 DMI ref: 0134-08.indd(RP) Issue 3: February 2008 The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust, 2005-2008. All rights reserved.
Information for Patients Hip Replacement Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Tel: 01473 702107 DMI ref: 0134-08.indd(RP) Issue 3: February 2008 The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust, 2005-2008. All rights reserved.
Total Knee Replacement
 Total Knee Replacement Contents Introduction Total Knee Replacement Preparing for surgery Pre-op visit Day of surgery After surgery (In Hospital) After surgery (In Rehab) Exercise Program and Physical
Total Knee Replacement Contents Introduction Total Knee Replacement Preparing for surgery Pre-op visit Day of surgery After surgery (In Hospital) After surgery (In Rehab) Exercise Program and Physical
Total knee replacement: The enhanced recovery programme
 INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Total knee replacement: The enhanced recovery programme Aim This leaflet aims to explain the enhanced recovery programme after total knee replacement surgery, and outline what
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Total knee replacement: The enhanced recovery programme Aim This leaflet aims to explain the enhanced recovery programme after total knee replacement surgery, and outline what
OPERATION:... Proximal tibial osteotomy Distal femoral osteotomy
 AFFIX PATIENT DETAIL STICKER HERE Forename.. Surname NHS Organisation. Responsible surgeon. Job Title Hospital Number... D.O.B.././ No special requirements OPERATION:..... Proximal tibial osteotomy Distal
AFFIX PATIENT DETAIL STICKER HERE Forename.. Surname NHS Organisation. Responsible surgeon. Job Title Hospital Number... D.O.B.././ No special requirements OPERATION:..... Proximal tibial osteotomy Distal
SHOULDER ACROMIOPLASTY/ SHOULDER DECOMPRESSION
 ORTHOPAEDIC WARD: 01-293 8687 /01-293 6602 BEACON CENTRE FOR ORTHOPAEDICS: 01-2937575 PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT: 01-2936692 GUIDELINES FOR PATIENTS HAVING A SHOULDER ACROMIOPLASTY/ SHOULDER DECOMPRESSION
ORTHOPAEDIC WARD: 01-293 8687 /01-293 6602 BEACON CENTRE FOR ORTHOPAEDICS: 01-2937575 PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT: 01-2936692 GUIDELINES FOR PATIENTS HAVING A SHOULDER ACROMIOPLASTY/ SHOULDER DECOMPRESSION
Knee arthroscopy advice sheet
 Knee arthroscopy advice sheet During an arthroscopy, a camera is inserted into the knee through two or three small puncture wounds. It allows the surgeon to look at the joint surfaces, cartilage and the
Knee arthroscopy advice sheet During an arthroscopy, a camera is inserted into the knee through two or three small puncture wounds. It allows the surgeon to look at the joint surfaces, cartilage and the
Premier Orthopaedic Pathway. Physiotherapy after dynamic hip screw (DHS)
 Premier Orthopaedic Pathway Physiotherapy after dynamic hip screw (DHS) The surgery After a fractured hip a dynamic hip screw (DHS) is used to hold the bones in place while the fracture heals. It allows
Premier Orthopaedic Pathway Physiotherapy after dynamic hip screw (DHS) The surgery After a fractured hip a dynamic hip screw (DHS) is used to hold the bones in place while the fracture heals. It allows
Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865
 Write questions or notes here: Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865 Document Title: Revision Total Hip Replacement Further Information and Feedback: Tell us how
Write questions or notes here: Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865 Document Title: Revision Total Hip Replacement Further Information and Feedback: Tell us how
Tibial Intramedullary Nailing
 Tibial Intramedullary Nailing Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4898 All Rights Reserved 2015. Document for issue as handout. Procedure The tibia is the long shin bone in the lower leg. It is a weight
Tibial Intramedullary Nailing Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4898 All Rights Reserved 2015. Document for issue as handout. Procedure The tibia is the long shin bone in the lower leg. It is a weight
PHYSIOTHERAPY OF HIP AND KNEE AFTER SURGERY AND INJURY BY RACHEL GEVELL PHYSIOTHERAPIST
 PHYSIOTHERAPY OF HIP AND KNEE AFTER SURGERY AND INJURY BY RACHEL GEVELL PHYSIOTHERAPIST AIMS AND OBJECTIVES To demonstrate the use of physiotherapy assessment and treatment following: Hip Arthroplasty
PHYSIOTHERAPY OF HIP AND KNEE AFTER SURGERY AND INJURY BY RACHEL GEVELL PHYSIOTHERAPIST AIMS AND OBJECTIVES To demonstrate the use of physiotherapy assessment and treatment following: Hip Arthroplasty
Rehabilitation. Rehabilitation. Walking after Total Knee Replacement. Continuous Passive Motion Device
 Walking after Total Knee Replacement After your TKR, continue using your walker or crutches until your surgeons tells you it is okay to stop using them. When turning with a walker or crutches DO NOT PIVOT
Walking after Total Knee Replacement After your TKR, continue using your walker or crutches until your surgeons tells you it is okay to stop using them. When turning with a walker or crutches DO NOT PIVOT
Knee Arthroscopy Post-operative Instructions
 Amon T. Ferry, MD Orthopedic Surgery Sports Medicine Knee Arthroscopy Post-operative Instructions PLEASE READ ALL OF THESE INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY. THEY WILL ANSWER MOST OF YOUR QUESTIONS. 1. You may walk
Amon T. Ferry, MD Orthopedic Surgery Sports Medicine Knee Arthroscopy Post-operative Instructions PLEASE READ ALL OF THESE INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY. THEY WILL ANSWER MOST OF YOUR QUESTIONS. 1. You may walk
Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865
 Write questions or notes here: Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865 Document Title: Total Knee Replacement Further Information and Feedback: Tell us how useful
Write questions or notes here: Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865 Document Title: Total Knee Replacement Further Information and Feedback: Tell us how useful
Total Hip Replacement Surgery Home Care Instructions
 Total Hip Replacement Surgery Home Care Instructions Surgery: Date: Doctor: This handout will review the care you need to follow once you are home. If you have any questions or concerns, please ask your
Total Hip Replacement Surgery Home Care Instructions Surgery: Date: Doctor: This handout will review the care you need to follow once you are home. If you have any questions or concerns, please ask your
Arthritis of the hip. Normal hip In an x-ray of a normal hip, the articular cartilage (the area labeled normal joint space ) is clearly visible.
 Arthritis of the hip Arthritis of the hip is a condition in which the smooth gliding surfaces of your hip joint (articular cartilage) have become damaged. This usually results in pain, stiffness, and reduced
Arthritis of the hip Arthritis of the hip is a condition in which the smooth gliding surfaces of your hip joint (articular cartilage) have become damaged. This usually results in pain, stiffness, and reduced
A Patient s Guide to Post-Operative Physiotherapy. Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction of the Knee
 A Patient s Guide to Post-Operative Physiotherapy Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction of the Knee Introduction The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the main supporting ligaments
A Patient s Guide to Post-Operative Physiotherapy Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction of the Knee Introduction The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the main supporting ligaments
ADVICE TO PATIENT DUE TO HAVE MICRODISCECTOMY / SPINAL STENOSIS DECOMPRESSION. Under the Care of Mr M Paterson - 11 -
 ADVICE TO PATIENT DUE TO HAVE MICRODISCECTOMY / SPINAL STENOSIS DECOMPRESSION Under the Care of Mr M Paterson Acknowledgement: Drawings by Jean Paterson Perth Australia 2006 Brochure: R. Grubb Amended:
ADVICE TO PATIENT DUE TO HAVE MICRODISCECTOMY / SPINAL STENOSIS DECOMPRESSION Under the Care of Mr M Paterson Acknowledgement: Drawings by Jean Paterson Perth Australia 2006 Brochure: R. Grubb Amended:
Physical & Occupational Therapy
 In this section you will find our recommendations for exercises and everyday activities around your home. We hope that by following our guidelines your healing process will go faster and there will be
In this section you will find our recommendations for exercises and everyday activities around your home. We hope that by following our guidelines your healing process will go faster and there will be
Procedure Information Guide
 Procedure Information Guide Total hip replacement Brought to you in association with EIDO and endorsed by the The Royal College of Surgeons of England Discovery has made every effort to ensure that the
Procedure Information Guide Total hip replacement Brought to you in association with EIDO and endorsed by the The Royal College of Surgeons of England Discovery has made every effort to ensure that the
Knee Replacement: Information for Patients and Carers
 Directorate of Surgical Care Department of Orthopaedics Knee Replacement: Information for Patients and Carers This information is for patients who are considering having a knee replacement. What is a Knee
Directorate of Surgical Care Department of Orthopaedics Knee Replacement: Information for Patients and Carers This information is for patients who are considering having a knee replacement. What is a Knee
Enhanced recovery after laparoscopic surgery (ERALS) programme: patient information and advice 2
 This booklet is funded by, and developed in collaboration between University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust and Pfizer Limited. NPKAM0198 March 2014 Enhanced recovery after laparoscopic surgery
This booklet is funded by, and developed in collaboration between University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust and Pfizer Limited. NPKAM0198 March 2014 Enhanced recovery after laparoscopic surgery
Total knee replacement Uni-compartmental knee replacement
 Your Knee Replacement at the Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre A patient s guide to: Total knee replacement Uni-compartmental knee replacement Welcome to Team Two at the NOC. Together you and your surgeon have
Your Knee Replacement at the Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre A patient s guide to: Total knee replacement Uni-compartmental knee replacement Welcome to Team Two at the NOC. Together you and your surgeon have
Rehabilitation. Rehabilitation. Walkers, Crutches, Canes
 Walkers, Crutches, Canes These devices provide support through your arms to limit the amount of weight on your operated hip. Initially, after a total hip replacement you will use a walker to get around.
Walkers, Crutches, Canes These devices provide support through your arms to limit the amount of weight on your operated hip. Initially, after a total hip replacement you will use a walker to get around.
AFTER TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT. Living with Your New Knee
 AFTER TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Living with Your New Knee Stepping into Recovery Before knee replacement surgery, your painful knee may have limited your activity. Movements that you once took for granted
AFTER TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Living with Your New Knee Stepping into Recovery Before knee replacement surgery, your painful knee may have limited your activity. Movements that you once took for granted
TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT
 TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 9 What is a hip replacement? A hip replacement is an operation in which the damaged surfaces of the hip joint are removed
TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 9 What is a hip replacement? A hip replacement is an operation in which the damaged surfaces of the hip joint are removed
Knee Arthroscopy Exercise Programme
 Chester Knee Clinic & Cartilage Repair Centre Nuffield Health, The Grosvenor Hospital Chester Wrexham Road Chester CH4 7QP Hospital Telephone: 01244 680 444 CKC Website: www.kneeclinic.info Email: office@kneeclinic.info
Chester Knee Clinic & Cartilage Repair Centre Nuffield Health, The Grosvenor Hospital Chester Wrexham Road Chester CH4 7QP Hospital Telephone: 01244 680 444 CKC Website: www.kneeclinic.info Email: office@kneeclinic.info
TIPS and EXERCISES for your knee stiffness. and pain
 TIPS and EXERCISES for your knee stiffness and pain KNEE EXERCISES Range of motion exercise 3 Knee bending exercises 3 Knee straightening exercises 5 STRENGTHENING EXERCISES 6 AEROBIC EXERCISE 10 ADDITIONAL
TIPS and EXERCISES for your knee stiffness and pain KNEE EXERCISES Range of motion exercise 3 Knee bending exercises 3 Knee straightening exercises 5 STRENGTHENING EXERCISES 6 AEROBIC EXERCISE 10 ADDITIONAL
Procedure Information Guide
 Procedure Information Guide Resurfacing hip replacement Brought to you in association with EIDO and endorsed by the The Royal College of Surgeons of England Discovery has made every effort to ensure that
Procedure Information Guide Resurfacing hip replacement Brought to you in association with EIDO and endorsed by the The Royal College of Surgeons of England Discovery has made every effort to ensure that
X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary
 X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary Introduction Severe arthritis in the hip can lead to severe pain and inability to walk. To relieve the pain and improve
X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary Introduction Severe arthritis in the hip can lead to severe pain and inability to walk. To relieve the pain and improve
Further information You can get more information and share your experience at www.aboutmyhealth.org
 OS01 Total Hip Replacement Further information You can get more information and share your experience at www.aboutmyhealth.org Local information You can get information locally from: Taunton and Somerset
OS01 Total Hip Replacement Further information You can get more information and share your experience at www.aboutmyhealth.org Local information You can get information locally from: Taunton and Somerset
Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients This leaflet has been developed to answer any questions you may have regarding
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients This leaflet has been developed to answer any questions you may have regarding
Broström Lateral Ligament Reconstruction of Ankle
 Broström Lateral Ligament Reconstruction of Ankle This leaflet aims to answer your questions about having a broström lateral ligament reconstruction of ankle under the care of Mr Sam Singh. It explains
Broström Lateral Ligament Reconstruction of Ankle This leaflet aims to answer your questions about having a broström lateral ligament reconstruction of ankle under the care of Mr Sam Singh. It explains
Delivering Excellence. Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre NHS Trust. Information for Patients. Hip and Knee service. Total Knee Replacement NHS
 www.noc.nhs.uk/hipandknee/default.aspx Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre NHS Trust www.noc.nhs.uk NHS Total Knee Replacement Information for Patients Hip and Knee service Delivering Excellence Contents Page
www.noc.nhs.uk/hipandknee/default.aspx Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre NHS Trust www.noc.nhs.uk NHS Total Knee Replacement Information for Patients Hip and Knee service Delivering Excellence Contents Page
Total Knee Replacement
 Manchester Royal Infirmary Total Knee Replacement Department of Orthopaedic Surgery 2 What is a Total Knee Replacement? Total knee replacement is one of the most commonly performed orthopaedic operations
Manchester Royal Infirmary Total Knee Replacement Department of Orthopaedic Surgery 2 What is a Total Knee Replacement? Total knee replacement is one of the most commonly performed orthopaedic operations
total hip replacement
 total hip replacement EXCERCISE BOOKLET patient s name: date of surgery: physical therapist: www.jointpain.md Get Up and Go Joint Program Philosophy: With the development of newer and more sophisticated
total hip replacement EXCERCISE BOOKLET patient s name: date of surgery: physical therapist: www.jointpain.md Get Up and Go Joint Program Philosophy: With the development of newer and more sophisticated
Hip Replacement Surgery Understanding the Risks
 Hip Replacement Surgery Understanding the Risks Understanding the Risks of Hip Replacement Surgery Introduction This booklet is designed to help your doctor talk to you about the most common risks you
Hip Replacement Surgery Understanding the Risks Understanding the Risks of Hip Replacement Surgery Introduction This booklet is designed to help your doctor talk to you about the most common risks you
Epidural Continuous Infusion. Patient information Leaflet
 Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
TOTAL KNEE JOINT REPLACEMENT. Journey through your new knee
 TOTAL KNEE JOINT REPLACEMENT Journey through your new knee CONTENTS... 1 What is a Total Knee Joint Replacement (TKJR)? 2 What you can do to prepare for surgery? 3 The operation and your stay in hospital
TOTAL KNEE JOINT REPLACEMENT Journey through your new knee CONTENTS... 1 What is a Total Knee Joint Replacement (TKJR)? 2 What you can do to prepare for surgery? 3 The operation and your stay in hospital
YOUR GUIDE TO TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT
 A Partnership for Better Healthcare A Partnership for Better Healthcare YOUR GUIDE TO TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT PEI Limited M50 Business Park Ballymount Road Upper Ballymount Dublin 12 Tel: 01-419 6900 Fax:
A Partnership for Better Healthcare A Partnership for Better Healthcare YOUR GUIDE TO TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT PEI Limited M50 Business Park Ballymount Road Upper Ballymount Dublin 12 Tel: 01-419 6900 Fax:
HIP JOINT REPLACEMENT
 HIP JOINT REPLACEMENT Information for Patients WHAT IS HIP JOINT REPLACEMENT? The hip joint is a ball-and-socket joint formed by the upper part of the thigh bone (femoral head) and a part of the pelvis
HIP JOINT REPLACEMENT Information for Patients WHAT IS HIP JOINT REPLACEMENT? The hip joint is a ball-and-socket joint formed by the upper part of the thigh bone (femoral head) and a part of the pelvis
Enhanced recovery programme (ERP) for patients undergoing bowel surgery
 Enhanced recovery programme (ERP) for patients undergoing bowel surgery Information for patients, relatives and carers An enhanced recovery programme (ERP) has been established at Imperial College Healthcare
Enhanced recovery programme (ERP) for patients undergoing bowel surgery Information for patients, relatives and carers An enhanced recovery programme (ERP) has been established at Imperial College Healthcare
Elbow Joint Replacement A guide for patients
 Elbow Joint Replacement A guide for patients GATESHEAD UPPER LIMB UNIT Mr Andreas Hinsche Mr John Harrison Mr Jagannath Chakravarthy Page 1 of 7 The elbow joint The elbow consists of three bones; the humerus
Elbow Joint Replacement A guide for patients GATESHEAD UPPER LIMB UNIT Mr Andreas Hinsche Mr John Harrison Mr Jagannath Chakravarthy Page 1 of 7 The elbow joint The elbow consists of three bones; the humerus
Recovering from Hip or Knee Joint Replacement Surgery. How to Care for Yourself at Home
 Recovering from Hip or Knee Joint Replacement Surgery How to Care for Yourself at Home 2 For more detailed information refer to the Before, during and after joint replacement surgery booklet. If there
Recovering from Hip or Knee Joint Replacement Surgery How to Care for Yourself at Home 2 For more detailed information refer to the Before, during and after joint replacement surgery booklet. If there
Physical & Occupational Therapy
 In this section you will find our recommendations for exercises and everyday activities around your home. We hope that by following our guidelines your healing process will go faster and there will be
In this section you will find our recommendations for exercises and everyday activities around your home. We hope that by following our guidelines your healing process will go faster and there will be
Recovering from a broken hip
 Recovering from a broken hip Information for patients, relatives and carers Who will will look look after after me me during during my hospital my hospital stay? stay? A multidisciplinary team of healthcare
Recovering from a broken hip Information for patients, relatives and carers Who will will look look after after me me during during my hospital my hospital stay? stay? A multidisciplinary team of healthcare
Treating your abdominal aortic aneurysm by open repair (surgery)
 Patient information Abdominal aortic aneurysm open surgery Treating your abdominal aortic aneurysm by open repair (surgery) Introduction This leaflet tells you about open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm,
Patient information Abdominal aortic aneurysm open surgery Treating your abdominal aortic aneurysm by open repair (surgery) Introduction This leaflet tells you about open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm,
Patient Information for Lumbar Spinal Fusion. What is a lumbar spinal fusion? Page 1 of 5
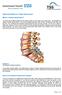 Patient Information for Lumbar Spinal Fusion What is a lumbar spinal fusion? You have been offered surgery to the lumbar region of your spine, your lower back. The operation is called a lumbar spinal fusion.
Patient Information for Lumbar Spinal Fusion What is a lumbar spinal fusion? You have been offered surgery to the lumbar region of your spine, your lower back. The operation is called a lumbar spinal fusion.
TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT
 PENN ORTHOPAEDICS TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Home Exercise Program PENN ORTHOPAEDICS TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT HOME EXERCISE PROGRAM To get the best results from your surgery, it is important that you do your
PENN ORTHOPAEDICS TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Home Exercise Program PENN ORTHOPAEDICS TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT HOME EXERCISE PROGRAM To get the best results from your surgery, it is important that you do your
Arthroscopic subacromial decompression and rotator cuff repair
 Further sources of information http://www.patient.co.uk/showdoc/553/ http://www.shoulderdoc.co.uk/article.asp?section=11 http://www.medic8.com/healthguide/articles/painfulshoulder.html http://www.cks.nhs.uk/patientinformationleaflet/shoulderpainarc/st
Further sources of information http://www.patient.co.uk/showdoc/553/ http://www.shoulderdoc.co.uk/article.asp?section=11 http://www.medic8.com/healthguide/articles/painfulshoulder.html http://www.cks.nhs.uk/patientinformationleaflet/shoulderpainarc/st
Total Knee Replacement
 Total Knee Replacement Patient Information Author ID: AW Leaflet Number: Musc 012 Name of Leaflet: Total Knee Replacement Date Produced: April 2014 Review Date: April 2016 Total Knee Replacement Page 1
Total Knee Replacement Patient Information Author ID: AW Leaflet Number: Musc 012 Name of Leaflet: Total Knee Replacement Date Produced: April 2014 Review Date: April 2016 Total Knee Replacement Page 1
TOTAL HIP JOINT REPLACEMENT
 TOTAL HIP JOINT REPLACEMENT Journey through your new HIP JOINT CONTENTS... 1 What is a Total Hip Joint Replacement (THJR)? 2 What you can do to prepare for surgery? 3 The operation and your stay in hospital
TOTAL HIP JOINT REPLACEMENT Journey through your new HIP JOINT CONTENTS... 1 What is a Total Hip Joint Replacement (THJR)? 2 What you can do to prepare for surgery? 3 The operation and your stay in hospital
KNEE ARTHROSCOPY. Dr C.S. Waller. Orthopaedic Surgeon
 KNEE ARTHROSCOPY Dr C.S. Waller Orthopaedic Surgeon Specializing in surgery of the hip and knee 83826199 What is Arthroscopy? Arthroscopy involves the inspection of the inside of the knee joint with a
KNEE ARTHROSCOPY Dr C.S. Waller Orthopaedic Surgeon Specializing in surgery of the hip and knee 83826199 What is Arthroscopy? Arthroscopy involves the inspection of the inside of the knee joint with a
Ankle Fractures: A Guide to Recovery
 Ankle fractures (breaks) are very common injuries that usually happen from a fall where the ankle is twisted or rolled or there is high energy trauma, like a car accident. There are two long bones in the
Ankle fractures (breaks) are very common injuries that usually happen from a fall where the ankle is twisted or rolled or there is high energy trauma, like a car accident. There are two long bones in the
Total Hip Replacement
 Please contactmethroughthegoldcoasthospitaswityouhaveanyproblemsafteryoursurgery. Dr. Benjamin Hewitt Orthopaedic Surgeon Total Hip Replacement The hip joint is a ball and socket joint that connects the
Please contactmethroughthegoldcoasthospitaswityouhaveanyproblemsafteryoursurgery. Dr. Benjamin Hewitt Orthopaedic Surgeon Total Hip Replacement The hip joint is a ball and socket joint that connects the
==Knee replacement surgery and your recovery programme
 40 Publication date: Apr 2006 Date last reviewed: May 2011 Date next review due: May 2013 Leaflet code: UCLH/S&C//SUR/ORTHO/TKR/3 University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Main switchboard:
40 Publication date: Apr 2006 Date last reviewed: May 2011 Date next review due: May 2013 Leaflet code: UCLH/S&C//SUR/ORTHO/TKR/3 University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Main switchboard:
Elective Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
 General Surgery Elective Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy This information aims to explain what will happen before, during and after your surgery to remove your gallbladder. It includes information about the
General Surgery Elective Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy This information aims to explain what will happen before, during and after your surgery to remove your gallbladder. It includes information about the
TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT
 PENN ORTHOPAEDICS TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Home Exercise Program Maintain Your 3 HIP PRECAUTIONS! The purpose of your hip precautions is to allow for the best healing and the most successful outcomes from
PENN ORTHOPAEDICS TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Home Exercise Program Maintain Your 3 HIP PRECAUTIONS! The purpose of your hip precautions is to allow for the best healing and the most successful outcomes from
REHABILITATION AFTER REPAIR OF THE PATELLAR AND QUADRICEPS TENDON
 175 Cambridge Street, 4 th floor Boston, MA 02114 617-726-7500 REHABILITATION AFTER REPAIR OF THE PATELLAR AND QUADRICEPS TENDON The patellar tendon attaches to the tibial tubercle on the front of the
175 Cambridge Street, 4 th floor Boston, MA 02114 617-726-7500 REHABILITATION AFTER REPAIR OF THE PATELLAR AND QUADRICEPS TENDON The patellar tendon attaches to the tibial tubercle on the front of the
A Patient s Guide to Lateral Ligament Reconstruction of the Ankle
 A Patient s Guide to Lateral Ligament Reconstruction of the Ankle The Foot and Ankle unit at the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital (RNOH) is a multi-disciplinary team. The team consists of three specialist
A Patient s Guide to Lateral Ligament Reconstruction of the Ankle The Foot and Ankle unit at the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital (RNOH) is a multi-disciplinary team. The team consists of three specialist
Before Surgery You will likely be asked to see your family physician or an internal medicine doctor for a thorough medical evaluation.
 Anterior Hip Replacement - Before and After Surgery Your Hip Evaluation An orthopaedic surgeon specializes in problems affecting bones and joints. The surgeon will ask you many questions about your hip
Anterior Hip Replacement - Before and After Surgery Your Hip Evaluation An orthopaedic surgeon specializes in problems affecting bones and joints. The surgeon will ask you many questions about your hip
A Guide. To Revision Total Knee Replacement. Patient Information Leaflet
 A Guide This leaflet is available in large print, Braille and on tape. Please contact Geoff Pennock on 0151 604 7289. To Revision Total Knee Replacement Wirral University Teaching Hospital NHS Foundation
A Guide This leaflet is available in large print, Braille and on tape. Please contact Geoff Pennock on 0151 604 7289. To Revision Total Knee Replacement Wirral University Teaching Hospital NHS Foundation
Total Knee Arthroplasty (Knee Replacement) PROCEDURAL CONSENT FORM. A. Interpreter / cultural needs. B. Condition and treatment
 The State of Queensland (Queensland Health), 2011 Permission to reproduce should be sought from ip_officer@health.qld.gov.au DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BINDING MARGIN v4.00-04/2011 SW9337 Total Knee Arthroplasty
The State of Queensland (Queensland Health), 2011 Permission to reproduce should be sought from ip_officer@health.qld.gov.au DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BINDING MARGIN v4.00-04/2011 SW9337 Total Knee Arthroplasty
This is my information booklet: Introduction
 Hip arthroscopy is a relatively new procedure which allows the surgeon to diagnose and treat hip disorders by providing a clear view of the inside of the hip with very small incisions. This is a more complicated
Hip arthroscopy is a relatively new procedure which allows the surgeon to diagnose and treat hip disorders by providing a clear view of the inside of the hip with very small incisions. This is a more complicated
Contents. Overview. Removing the womb (hysterectomy) Overview
 This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding womb (endometrial) cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 9. Overview Contents Overview Removing
This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding womb (endometrial) cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 9. Overview Contents Overview Removing
ACL RECONSTRUCTION POST-OPERATIVE REHABILITATION PROGRAMME
 ACL RECONSTRUCTION POST-OPERATIVE REHABILITATION PROGRAMME ABOUT THE OPERATION The aim of your operation is to reconstruct the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) to restore knee joint stability. A graft,
ACL RECONSTRUCTION POST-OPERATIVE REHABILITATION PROGRAMME ABOUT THE OPERATION The aim of your operation is to reconstruct the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) to restore knee joint stability. A graft,
Enhancing your recovery after cardiac surgery
 Enhancing your recovery after cardiac surgery Steps you can take to get better sooner Patient s name:... Consultant s name:... Admission date:... Planned discharge date:... Type of operation:... Date of
Enhancing your recovery after cardiac surgery Steps you can take to get better sooner Patient s name:... Consultant s name:... Admission date:... Planned discharge date:... Type of operation:... Date of
Epidurals for pain relief after surgery
 Epidurals for pain relief after surgery This information leaflet is for anyone who may benefit from an epidural for pain relief after surgery. We hope it will help you to ask questions and direct you to
Epidurals for pain relief after surgery This information leaflet is for anyone who may benefit from an epidural for pain relief after surgery. We hope it will help you to ask questions and direct you to
Total Abdominal Hysterectomy
 What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
Shoulder Dislocation or Instability Surgery: A Guide to Recovery After Surgery
 What is Shoulder Instability? What is a Shoulder Dislocation? The shoulder joint is a ball in socket joint and is the most mobile joint in the human body. The socket, however, is quite shallow which means
What is Shoulder Instability? What is a Shoulder Dislocation? The shoulder joint is a ball in socket joint and is the most mobile joint in the human body. The socket, however, is quite shallow which means
Cast removal what to expect #3 Patient Information Leaflet
 Cast removal what to expect #3 Patient Information Leaflet SM466 Now your cast is off, self help is the key! Follow the advice given to you by your doctor and the staff in the clinic. Your skin will be
Cast removal what to expect #3 Patient Information Leaflet SM466 Now your cast is off, self help is the key! Follow the advice given to you by your doctor and the staff in the clinic. Your skin will be
PATIENTS GUIDE TO SPINAL SURGERY
 Mr Paul S. D Urso MBBS(Hons), PhD, FRACS Neurosurgeon Provider Nº: 081161DY PATIENTS GUIDE TO SPINAL SURGERY The Epworth Centre Suite 6.1 32 Erin Street Richmond 3121 Tel: 03 9421 5844 Fax: 03 9421 4186
Mr Paul S. D Urso MBBS(Hons), PhD, FRACS Neurosurgeon Provider Nº: 081161DY PATIENTS GUIDE TO SPINAL SURGERY The Epworth Centre Suite 6.1 32 Erin Street Richmond 3121 Tel: 03 9421 5844 Fax: 03 9421 4186
Recovery plan: radical cystectomy Information for patients
 Recovery plan: radical cystectomy Information for patients Help for you following a bereavement 5 This leaflet will help you know what to expect during your time with us. Please take some time to read
Recovery plan: radical cystectomy Information for patients Help for you following a bereavement 5 This leaflet will help you know what to expect during your time with us. Please take some time to read
Varicose Veins Operation. Patient information Leaflet
 Varicose Veins Operation Patient information Leaflet 22 nd August 2014 WHAT IS VARICOSE VEIN SURGERY (HIGH LIGATION AND MULTIPLE AVULSIONS) The operation varies from case to case, depending on where the
Varicose Veins Operation Patient information Leaflet 22 nd August 2014 WHAT IS VARICOSE VEIN SURGERY (HIGH LIGATION AND MULTIPLE AVULSIONS) The operation varies from case to case, depending on where the
Achilles Tendon Repair Surgery Post-operative Instructions Phase One: The First Week After Surgery
 Amon T. Ferry, MD Orthopedic Surgery Sports Medicine Achilles Tendon Repair Surgery Post-operative Instructions Phase One: The First Week After Surgery Amon T. Ferry, MD Orthopedic Surgery / Sports Medicine
Amon T. Ferry, MD Orthopedic Surgery Sports Medicine Achilles Tendon Repair Surgery Post-operative Instructions Phase One: The First Week After Surgery Amon T. Ferry, MD Orthopedic Surgery / Sports Medicine
Wrightington Total Hip Replacement Programme
 Wrightington Total Hip Replacement Programme Patient Information Author ID: AW Leaflet Number: Musc 011 Name of Leaflet: Wrightington Total Hip Replacement Programme Date Produced: April 2014 Review Date:
Wrightington Total Hip Replacement Programme Patient Information Author ID: AW Leaflet Number: Musc 011 Name of Leaflet: Wrightington Total Hip Replacement Programme Date Produced: April 2014 Review Date:
Low Back Surgery. Remember to bring this handout to the hospital with you.
 Remember to bring this handout to the hospital with you. Table of contents Page Why do I need low back surgery?... 1 What kinds of low back surgeries are there?... 2 Before your surgery... 3 After your
Remember to bring this handout to the hospital with you. Table of contents Page Why do I need low back surgery?... 1 What kinds of low back surgeries are there?... 2 Before your surgery... 3 After your
Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients page 2 What is the Carpal Tunnel? The carpal tunnel is made up of the bones
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients page 2 What is the Carpal Tunnel? The carpal tunnel is made up of the bones
Baker Rehab Group HomeCare Rehab and Nursing LLC
 Baker Rehab Group HomeCare Rehab and Nursing LLC Introduction So it s time for a joint replacement... Are you worried about the surgery? Are you wondering about the pre and post surgical process? Do you
Baker Rehab Group HomeCare Rehab and Nursing LLC Introduction So it s time for a joint replacement... Are you worried about the surgery? Are you wondering about the pre and post surgical process? Do you
University College Hospital
 University College Hospital Total hip joint replacement and your recovery programme UCLH Trauma and Orthopaedic Team Please bring this booklet with you when attending your pre-assessment appointment and
University College Hospital Total hip joint replacement and your recovery programme UCLH Trauma and Orthopaedic Team Please bring this booklet with you when attending your pre-assessment appointment and
Laparoscopic Nephrectomy
 Laparoscopic Nephrectomy Information for Patients This leaflet explains: What is a Nephrectomy?... 2 Why do I need a nephrectomy?... 3 What are the risks and side effects of laparoscopic nephrectomy?...
Laparoscopic Nephrectomy Information for Patients This leaflet explains: What is a Nephrectomy?... 2 Why do I need a nephrectomy?... 3 What are the risks and side effects of laparoscopic nephrectomy?...
Having denervation of the renal arteries for treatment of high blood pressure
 Having denervation of the renal arteries for treatment of high blood pressure The aim of this information sheet is to help answer some of the questions you may have about having denervation of the renal
Having denervation of the renal arteries for treatment of high blood pressure The aim of this information sheet is to help answer some of the questions you may have about having denervation of the renal
Having a Trans-Arterial Embolisation
 Having a Trans-Arterial Embolisation Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Having a Trans-Arterial Embolisation Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
ARTHROSCOPIC HIP SURGERY
 ARTHROSCOPIC HIP SURGERY Hip Arthroscopy is a relatively simple procedure whereby common disorders of the hip can be diagnosed and treated using keyhole surgery. Some conditions, which previously were
ARTHROSCOPIC HIP SURGERY Hip Arthroscopy is a relatively simple procedure whereby common disorders of the hip can be diagnosed and treated using keyhole surgery. Some conditions, which previously were
Posterior Lumbar Decompression for Spinal Stenosis
 Posterior Lumbar Decompression for Spinal Stenosis Issue 6: March 2016 Review date: February 2019 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon you have been diagnosed with
Posterior Lumbar Decompression for Spinal Stenosis Issue 6: March 2016 Review date: February 2019 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon you have been diagnosed with
Total Knee Replacement Surgery
 Total Knee Replacement Surgery On this page: Overview Reasons for Surgery Evaluation Preparing for Surgery Your Surgery Risks Expectations after Surgery Convalescence Also: Partial Knee Replacement Overview
Total Knee Replacement Surgery On this page: Overview Reasons for Surgery Evaluation Preparing for Surgery Your Surgery Risks Expectations after Surgery Convalescence Also: Partial Knee Replacement Overview
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery. Managing Spasticity. Spasticity Service
 National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Managing Spasticity Spasticity Service If you would like this document in another language or format, or require the services of an interpreter please contact
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Managing Spasticity Spasticity Service If you would like this document in another language or format, or require the services of an interpreter please contact
Removal of Haemorrhoids (Haemorrhoidectomy) Information for patients
 Removal of Haemorrhoids (Haemorrhoidectomy) Information for patients What are Haemorrhoids? Haemorrhoids (piles) are enlarged blood vessels around the anus (back passage). There are two types of haemorrhoids:
Removal of Haemorrhoids (Haemorrhoidectomy) Information for patients What are Haemorrhoids? Haemorrhoids (piles) are enlarged blood vessels around the anus (back passage). There are two types of haemorrhoids:
Rehabilitation guidelines for patients undergoing knee arthroscopy
 Rehabilitation guidelines for patients undergoing knee arthroscopy At the RNOH, our emphasis is patient specific, which encourages recognition of those who may progress slower then others. We also want
Rehabilitation guidelines for patients undergoing knee arthroscopy At the RNOH, our emphasis is patient specific, which encourages recognition of those who may progress slower then others. We also want
Colon Cancer Surgery and Recovery. A Guide for Patients and Families
 Colon Cancer Surgery and Recovery A Guide for Patients and Families This Booklet You are receiving this booklet because you will be having surgery shortly. This booklet tells you what to do before, during,
Colon Cancer Surgery and Recovery A Guide for Patients and Families This Booklet You are receiving this booklet because you will be having surgery shortly. This booklet tells you what to do before, during,
Elbow arthroscopy. Key points
 Patient information Elbow arthroscopy This information has been produced to help you gain the maximum benefit and understanding of your operation. It includes the following information: Key points About
Patient information Elbow arthroscopy This information has been produced to help you gain the maximum benefit and understanding of your operation. It includes the following information: Key points About
ACL Reconstruction Physiotherapy advice for patients
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust ACL Reconstruction Physiotherapy advice for patients Introduction This booklet is designed to provide you with advice and guidance on your rehabilitation after reconstruction
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust ACL Reconstruction Physiotherapy advice for patients Introduction This booklet is designed to provide you with advice and guidance on your rehabilitation after reconstruction
