Thermodynamics: First Law, Calorimetry, Enthalpy. Calorimetry. Calorimetry: constant volume. Monday, January 23 CHEM 102H T.
|
|
|
- Marjorie Tate
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Thermodynamics: First Law, Calorimetry, Enthalpy Monday, January 23 CHEM 102H T. Hughbanks Calorimetry Reactions are usually done at either constant V (in a closed container) or constant P (open to the atmosphere). In either case, we can measure q by measuring a change in T (assuming we know heat capacities). Calorimetry: constant volume U = q + w and w = -P ex ΔV If V is constant, then ΔV = 0, and w = 0. This leaves U = q v, again, subscript v indicates const. volume. Measure ΔU by measuring heat released or taken up at constant volume.
2 Calorimetry Problem When g of quinone (C 6 H 4 O 2 ) is burned with excess oxygen in a bomb (constant volume) calorimeter, the temperature of the calorimeter increases by 3.26 C. The heat capacity of the calorimeter is known to be 1.56 kj/ C. Find ΔU for the combustion of 1 mole of quinone. Calorimetry: Constant Pressure Reactions run in an open container will occur at constant P. Calorimetry done at constant pressure will measure heat: q p. How does this relate to U, etc.? q P & ΔU U = q + w = q - PΔV At constant V, PΔV term was zero, giving U = q v. If P is constant and ΔT 0, then ΔV 0. In particular, if gases are involved, PV = nrt w p 0, so U q p
3 Enthalpy: A New State Function It would be nice to have a state function which is directly related to q p : (?) = q p We could then measure this function by calorimetry at constant pressure. Call this function enthalpy, H, defined by: H = U + PV Enthalpy Enthalpy: H = U + PV U, P, V all state functions, so H must also be a state function. ΔH = q p? Do some algebra, assuming that P is constant: H = U + (PV) = U + P V ΔH = q P But w = -PΔV, so: ΔH = ΔU + PΔV = (q + w) + PΔV ΔH = (q - PΔV) + PΔV = q And since we used constant P, this is ΔH = q p
4 Compare U & H H = U + P V (const. P) PΔV term due to expansion or compression. For solids & liquids, PΔV is small. Therefore, ΔH ΔU for condensed phase systems. For systems involving gases, ΔH and ΔU may differ considerably H for Physical Processes H = U + P V (const. P) If heat must be put in to the system to bring about a physical change, then ΔH > 0 for that process. For changes involving only condensed phases (solids & liquids), PΔV contribution is small. ΔH for physical processes can be qualitatively understood by thinking about intermolecular forces. Compare ΔU & ΔH; Examples A heat input of kj is required to melt one mole of ice at 1 atm. pressure. What is H? What is U? A heat input of kj is required to boil one mole of water at 1 atm. pressure. What is H? What is U?
5 Conclusion from example If volume changes are large, the difference between H and U can be significant. Volume changes are large when the number of moles of gas changes from the initial and final states. Since gases usually are approximately ideal, (PV) (nrt) = ( n)rt, so H = U + (PV) U + ( n)rt Heating curves (H 2 O shown) Melting and Boiling constitute jumps in the heating of a substance their sizes reflect strength of intermolecular forces overcome in the processes. All phase transitions occur at constant temperatures H solid!h fus = 6.01 kj mol 1 liquid!h vap = 40.7 kj mol kj mol 1 vapor T(K) Again, Heat Capacities For one mole of an ideal gas: U = 3 / 2 RT We ve seen that U = q v, therefore since C V = q V!T, C =!U! V!T = du $ in the limit " # dt % & C V = 3 R for an ideal gas 2 We ve seen that H = q P, and H = (U + PV) since C P = q P!T, C =! H! P!T = dh $ in the limit " # dt % & C P = 3 2 R + d(pv ) dt = 3 2 R + d(rt ) dt = 5 R for an ideal gas 2
6 Enthalpy & Chemistry Many reactions occur at constant P, so ΔH is a useful quantity. ΔH < 0 heat is released, so reaction is exothermic ΔH > 0 heat is absorbed, so reaction is endothermic ΔH is related to the amount of energy we might get out of a reaction. H vs. H We always talk about H, never H itself. (Same is true for U & U) Why? H is an energy, so we need some reference point. Absolute energy is not readily defined. Reaction Enthalpies Enthalpies don t just apply to changes in physical state, but to reactions too. Example: Fe(s) + 2S(s) > FeS 2 (s) H = kj If these chemicals constitute the system, then when the reaction occurs, kj of heat will be released into the surroundings if 1.0 mol of FeS 2 is formed. Note: this says nothing about the rate of the reaction or the conditions under which it would be practical to carry it out.
7 Reaction Enthalpy If H reaction is negative, energy is given off. Exothermic If H reaction is positive, energy is absorbed. Endothermic We can NOT predict whether a reaction will occur based only on H! Energy Diagram activated complex Enthalpy reactants ΔH rxn E a products Thermodynamic Quantity Reaction Coordinate Using Bond Enthalpies Imagine running the reaction as follows: break every bond in reactants, giving a collection of atoms make new bonds among these atoms to form products reactants free atoms products Will each step cost energy, or release energy?
8 Standard States Define a standard state: The enthalpy of an element in its most stable physical form at 1 atm and 25 C is equal to zero. Gives a reference for each element, since they are not interconverted in chemical processes This definition fixes all ΔH values, since H is a state function. Tabulating & Using ΔH Exhaustive tabulation of ΔH s (for all possible reactions) is not feasible. Exploit the fact that ΔH is a state function to get maximum useful information from a more reasonable amount of data. Standard Enthalpy of Formation, ΔH f Formation Reactions For any compound we can write a formation reaction in which: Elements in 1 mole of standard states compound ΔH for such a reaction is called the standard enthalpy of formation, ΔH f, for the compound. Also called heat of formation
9 Formation Reactions Elements in 1 mole of standard states compound C (s, graphite) + 2 H 2 (g) CH 4 (g) 1/2 N 2 (g) + 3/2 H 2 (g) NH 3 (g) Always one mole of product, so often need to use fractional coefficients. Many such reactions can not actually be carried out. (But values can be found indirectly & tabulated.) Using ΔH f s ΔH =? C 6 H 12 O O 2 6 CO H 2 O Since H is a state function, we can create any # of intermediate states. Use ΔH for these steps to find the ΔH we want. Path Independence ΔH = H products - H reactants This does not specify what might exist between reactants and products. ΔU is path independent. We can imagine any set of steps that get us from the reactants to the products. Because it is path independent, we say ΔH is a state function.
10 H is a state function! C 6 H 12 O O 2 6 CO H 2 O ΔH 1 ΔH ΔH 2 ΔH 4 3 A B C Because H is a state function: ΔH rxn = ΔH 1 + ΔH 2 + ΔH 3 + ΔH 4 ΔH 1, ΔH 2, etc. refer to the individual steps Using ΔH f s to find ΔH rxn Choose a useful path for the reaction. Reactants ΔH f, reactants Elements in standard states ΔH f, products Products ΔH rxn = ΔH f, products - ΔH f, reactants Problem Given the ΔH f s below, find ΔH for the combustion of one mole of glucose at 298 K. glucose(c 6 H 12 O 6, s) ΔH f = kj/mol CO 2 (g) ΔH f = kj/mol H 2 O(l) ΔH f = kj/mol (Data are from Appendix 2 in your book.)
11 Hess s Law For any reaction, we can write: ΔH rxn = Σ nδh f (products) - Σ nδh f (reactants) n s are the stoichiometric coefficients from the balanced chemical equation. This lets us find ΔH for any reaction from a table of ΔH f s. Another Problem - Hess s Law Acetylene torches are used in welding. Chemical reaction involved is: C 2 H 2 (g) + 5/2 O 2 (g) 2 CO 2 (g) + H 2 O (g) Find ΔH for this reaction. Estimate the maximum temperature which could be obtained in an acetylene flame. Some useful data are on the next slide. Data For Problem Heat of formation (ΔH f ) C 2 H 2 (g) kj/mol CO 2 (g) H 2 O(g) Heat capacities (C p ) C 2 H 2 (g) 44 J/mol K CO 2 (g) 37 H 2 O(g) 36
12 Thermochemical (Born-Haber) Cycle M(g) + X(g) I(M) E X M + (g) + X (g) S M + ( 1 / 2 )D X2!H L M(s) + ( 1 / 2 )X 2 (g)!h f MX(s) S M : sublimation Enthalpy of Metal (298 K) 108 D X2 : dissociation Energy of X 2 bond (298 K) 242 I(M) : Ionization Enthalpy of Metal M 496 E X : electron attachment Enthalpy of X atom 349 H L : Enthalpy for separation of salt to ions theory Values for (kj/mol) Thermochemical (Born-Haber) Cycle M(g) + X(g) I(M) E X M + (g) + X (g) S M + ( 1 / 2 )D X2!H L M(s) + ( 1 / 2 )X 2 (g)!h f MX(s) H L = V min = N A (e 2 /r min )[Z+ Z ](1 - r*/r min )A for, r min = Å (5.162 a.u.) 776kJ/mol Experiment (Born-Haber cycle): H f = S M + ( 1 / 2 ) D X2 + I(M) E M H L for, measured value of H f is -411kJ/mol -411 = (242/2) H L H L = 787 (- 2 for C p correction) = 785 kj/mol Rocksalt () type: ccp stacked ; all octahedral holes filled
13 Ionic Bonding; Lattice Energies Energy Lattice Energies - Details V = VCoulomb + Vrepulsion r = cation-anion distance ion - ion Coulomb interactions repulsions between ion cores eg., -type: (cgs units - a factor of 1/4!!0 must be included to convert to SI) V Coulomb = + 6 (e 2 / r )Z + Z + 12 (e 2 /!2r )(Z + ) (e 2 /!3r )Z + Z + 6 (e 2 / 2r )(Z + ) type: V Coulomb = N A (e 2 /r)[z + Z ]! A A = [ /!2 8 /!3 + 6 / 2 24 /!5 +...]!2!3 The Madelung constant: a geometrical parameter that is the same for all compounds of a given structure type Ion core Ion core repulsions Vrepulsion = + N A C exp{-(r/r*)} estimated from compressibilities, r* is always much smaller than a typical internuclear distance (~ Å). V = N A (e 2 /r)[z+ Z ]A + N A C exp{-(r/r*)} Minimize (set (dv/dr) = 0) to obtain: C exp{-(r min /r*)} = - e 2 [Z+ Z ] A r*/(r min ) 2 Alternative: Vrep = + N A (B/r n ) ion core n He 5 Ne 7 Ar 9 Kr 10 Xe 12 V min = N A (e 2 /r min )[Z+ Z ](1 r*/r min )A V min = N A (e 2 /r min ) [Z+ Z ](1 1 / n )A Bond Enthalpies and Reactions We can measure the strength and length of chemical bonds. (some easily, some with great difficulty) Energy of a particular type of bond (carbon - hydrogen, etc.) approximately (but not exactly) the same in different molecules. This is because bonds are often mainly localized and because orbitals used to make bonds are similar in different molecules.
14 Using Bond Enthalpies: Reaction Energy Average bond enthalpies are tabulated. We can use these to estimate the enthalpy change for any chemical reaction for which bond enthalpies are known. Decide whether the reaction was likely to succeed, evaluate possible fuels, etc. Reaction Enthalpy Reactants Products Reaction Enthalpy: Enthalpy taken in or given off during reaction H = H products H reactants Using Bond Energies Can use bond energies to find the energy required or released in these imaginary steps. Get H by combining these. H reaction = Σ BE reactants - Σ BE products ( Σ means summation ) NOTE: Because bond energies are defined relative to ATOM energies, this has a reactants minus products - not usual!
15 Acrylonitrile Synthesis 2 C 3 H NH 3 +3 O 2 6 H 2 O + 2 H 2 C=CH C N Use bond enthalpies to estimate ΔH for this reaction. Some data are on next slide. Some Bond Enthalpies (kj/mol) Diatomic molecules (actual values) H H O=O C O 1071 Other bonds (avg. values) C C 348 C=C 612 C C 837 C H 412 C=N 615 C N 890 N H 388 N=O 630 O H 463 Thermodynamics & Chemistry Study of the energy changes associated with chemical or physical processes. Chemical applications of principles you will study in physics & engineering reaction energy, fuels, etc. Goal - to be able to predict whether or not a given reaction can occur, using simple tabulated data.
16 Thermodynamics vs. Kinetics Thermodynamics tells us things about the eventual outcome of a chemical reaction, but NOT about how fast the reaction might be. To know if something will happen fast, we need to consider kinetics. Need both thermodynamics and kinetics to assess practical usefulness of a reaction.
Bomb Calorimetry. Example 4. Energy and Enthalpy
 Bomb Calorimetry constant volume often used for combustion reactions heat released by reaction is absorbed by calorimeter contents need heat capacity of calorimeter q cal = q rxn = q bomb + q water Example
Bomb Calorimetry constant volume often used for combustion reactions heat released by reaction is absorbed by calorimeter contents need heat capacity of calorimeter q cal = q rxn = q bomb + q water Example
Chapter 6 Thermodynamics: The First Law
 Key Concepts 6.1 Systems Chapter 6 Thermodynamics: The First Law Systems, States, and Energy (Sections 6.1 6.8) thermodynamics, statistical thermodynamics, system, surroundings, open system, closed system,
Key Concepts 6.1 Systems Chapter 6 Thermodynamics: The First Law Systems, States, and Energy (Sections 6.1 6.8) thermodynamics, statistical thermodynamics, system, surroundings, open system, closed system,
1. Thermite reaction 2. Enthalpy of reaction, H 3. Heating/cooling curves and changes in state 4. More thermite thermodynamics
 Chem 105 Fri 10-23-09 1. Thermite reaction 2. Enthalpy of reaction, H 3. Heating/cooling curves and changes in state 4. More thermite thermodynamics 10/23/2009 1 Please PICK UP your graded EXAM in front.
Chem 105 Fri 10-23-09 1. Thermite reaction 2. Enthalpy of reaction, H 3. Heating/cooling curves and changes in state 4. More thermite thermodynamics 10/23/2009 1 Please PICK UP your graded EXAM in front.
Thermochemical equations allow stoichiometric calculations.
 CHEM 1105 THERMOCHEMISTRY 1. Change in Enthalpy ( H) Heat is evolved or absorbed in all chemical reactions. Exothermic reaction: heat evolved - heat flows from reaction mixture to surroundings; products
CHEM 1105 THERMOCHEMISTRY 1. Change in Enthalpy ( H) Heat is evolved or absorbed in all chemical reactions. Exothermic reaction: heat evolved - heat flows from reaction mixture to surroundings; products
The first law: transformation of energy into heat and work. Chemical reactions can be used to provide heat and for doing work.
 The first law: transformation of energy into heat and work Chemical reactions can be used to provide heat and for doing work. Compare fuel value of different compounds. What drives these reactions to proceed
The first law: transformation of energy into heat and work Chemical reactions can be used to provide heat and for doing work. Compare fuel value of different compounds. What drives these reactions to proceed
Standard Free Energies of Formation at 298 K. Average Bond Dissociation Energies at 298 K
 1 Thermodynamics There always seems to be at least one free response question that involves thermodynamics. These types of question also show up in the multiple choice questions. G, S, and H. Know what
1 Thermodynamics There always seems to be at least one free response question that involves thermodynamics. These types of question also show up in the multiple choice questions. G, S, and H. Know what
SUGGESTION ANSWER SCHEME CHAPTER 8: THERMOCHEMISTRY. 1 (a) Use the data in the table below to answer the following questions:
 SUGGESTION ANSWER SCHEME CHAPTER 8: THERMOCHEMISTRY ANSWER SCHEME UPS 2004/2005 SK027 1 (a) Use the data in the table below to answer the following questions: Enthalpy change ΔH (kj/mol) Atomization energy
SUGGESTION ANSWER SCHEME CHAPTER 8: THERMOCHEMISTRY ANSWER SCHEME UPS 2004/2005 SK027 1 (a) Use the data in the table below to answer the following questions: Enthalpy change ΔH (kj/mol) Atomization energy
Energy and Chemical Reactions. Characterizing Energy:
 Energy and Chemical Reactions Energy: Critical for virtually all aspects of chemistry Defined as: We focus on energy transfer. We observe energy changes in: Heat Transfer: How much energy can a material
Energy and Chemical Reactions Energy: Critical for virtually all aspects of chemistry Defined as: We focus on energy transfer. We observe energy changes in: Heat Transfer: How much energy can a material
UNIT 1 THERMOCHEMISTRY
 UNIT 1 THERMOCHEMISTRY THERMOCHEMISTRY LEARNING OUTCOMES Students will be expected to: THERMOCHEMISTRY STSE analyse why scientific and technological activities take place in a variety individual and group
UNIT 1 THERMOCHEMISTRY THERMOCHEMISTRY LEARNING OUTCOMES Students will be expected to: THERMOCHEMISTRY STSE analyse why scientific and technological activities take place in a variety individual and group
Thermochemistry. r2 d:\files\courses\1110-20\99heat&thermorans.doc. Ron Robertson
 Thermochemistry r2 d:\files\courses\1110-20\99heat&thermorans.doc Ron Robertson I. What is Energy? A. Energy is a property of matter that allows work to be done B. Potential and Kinetic Potential energy
Thermochemistry r2 d:\files\courses\1110-20\99heat&thermorans.doc Ron Robertson I. What is Energy? A. Energy is a property of matter that allows work to be done B. Potential and Kinetic Potential energy
Name Class Date. In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question.
 Assessment Chapter Test A Chapter: States of Matter In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. 1. The kinetic-molecular
Assessment Chapter Test A Chapter: States of Matter In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. 1. The kinetic-molecular
Enthalpy of Reaction and Calorimetry worksheet
 Enthalpy of Reaction and Calorimetry worksheet 1. Calcium carbonate decomposes at high temperature to form carbon dioxide and calcium oxide, calculate the enthalpy of reaction. CaCO 3 CO 2 + CaO 2. Carbon
Enthalpy of Reaction and Calorimetry worksheet 1. Calcium carbonate decomposes at high temperature to form carbon dioxide and calcium oxide, calculate the enthalpy of reaction. CaCO 3 CO 2 + CaO 2. Carbon
DETERMINING THE ENTHALPY OF FORMATION OF CaCO 3
 DETERMINING THE ENTHALPY OF FORMATION OF CaCO 3 Standard Enthalpy Change Standard Enthalpy Change for a reaction, symbolized as H 0 298, is defined as The enthalpy change when the molar quantities of reactants
DETERMINING THE ENTHALPY OF FORMATION OF CaCO 3 Standard Enthalpy Change Standard Enthalpy Change for a reaction, symbolized as H 0 298, is defined as The enthalpy change when the molar quantities of reactants
Thermodynamics. Thermodynamics 1
 Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamics Some Important Topics First Law of Thermodynamics Internal Energy U ( or E) Enthalpy H Second Law of Thermodynamics Entropy S Third law of Thermodynamics Absolute Entropy
Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamics Some Important Topics First Law of Thermodynamics Internal Energy U ( or E) Enthalpy H Second Law of Thermodynamics Entropy S Third law of Thermodynamics Absolute Entropy
Chem 1A Exam 2 Review Problems
 Chem 1A Exam 2 Review Problems 1. At 0.967 atm, the height of mercury in a barometer is 0.735 m. If the mercury were replaced with water, what height of water (in meters) would be supported at this pressure?
Chem 1A Exam 2 Review Problems 1. At 0.967 atm, the height of mercury in a barometer is 0.735 m. If the mercury were replaced with water, what height of water (in meters) would be supported at this pressure?
1 Exercise 2.19a pg 86
 In this solution set, an underline is used to show the last significant digit of numbers. For instance in x = 2.51693 the 2,5,1, and 6 are all significant. Digits to the right of the underlined digit,
In this solution set, an underline is used to show the last significant digit of numbers. For instance in x = 2.51693 the 2,5,1, and 6 are all significant. Digits to the right of the underlined digit,
Reading: Moore chapter 18, sections 18.6-18.11 Questions for Review and Thought: 62, 69, 71, 73, 78, 83, 99, 102.
 Thermodynamics 2: Gibbs Free Energy and Equilibrium Reading: Moore chapter 18, sections 18.6-18.11 Questions for Review and Thought: 62, 69, 71, 73, 78, 83, 99, 102. Key Concepts and skills: definitions
Thermodynamics 2: Gibbs Free Energy and Equilibrium Reading: Moore chapter 18, sections 18.6-18.11 Questions for Review and Thought: 62, 69, 71, 73, 78, 83, 99, 102. Key Concepts and skills: definitions
Module 5: Combustion Technology. Lecture 34: Calculation of calorific value of fuels
 1 P age Module 5: Combustion Technology Lecture 34: Calculation of calorific value of fuels 2 P age Keywords : Gross calorific value, Net calorific value, enthalpy change, bomb calorimeter 5.3 Calculation
1 P age Module 5: Combustion Technology Lecture 34: Calculation of calorific value of fuels 2 P age Keywords : Gross calorific value, Net calorific value, enthalpy change, bomb calorimeter 5.3 Calculation
Chemistry B11 Chapter 4 Chemical reactions
 Chemistry B11 Chapter 4 Chemical reactions Chemical reactions are classified into five groups: A + B AB Synthesis reactions (Combination) H + O H O AB A + B Decomposition reactions (Analysis) NaCl Na +Cl
Chemistry B11 Chapter 4 Chemical reactions Chemical reactions are classified into five groups: A + B AB Synthesis reactions (Combination) H + O H O AB A + B Decomposition reactions (Analysis) NaCl Na +Cl
States of Matter CHAPTER 10 REVIEW SECTION 1. Name Date Class. Answer the following questions in the space provided.
 CHAPTER 10 REVIEW States of Matter SECTION 1 SHORT ANSWER Answer the following questions in the space provided. 1. Identify whether the descriptions below describe an ideal gas or a real gas. ideal gas
CHAPTER 10 REVIEW States of Matter SECTION 1 SHORT ANSWER Answer the following questions in the space provided. 1. Identify whether the descriptions below describe an ideal gas or a real gas. ideal gas
ENTHALPY CHANGES FOR A CHEMICAL REACTION scaling a rxn up or down (proportionality) quantity 1 from rxn heat 1 from Δ r H. = 32.
 CHEMISTRY 103 Help Sheet #10 Chapter 4 (Part II); Sections 4.6-4.10 Do the topics appropriate for your lecture Prepared by Dr. Tony Jacob http://www.chem.wisc.edu/areas/clc (Resource page) Nuggets: Enthalpy
CHEMISTRY 103 Help Sheet #10 Chapter 4 (Part II); Sections 4.6-4.10 Do the topics appropriate for your lecture Prepared by Dr. Tony Jacob http://www.chem.wisc.edu/areas/clc (Resource page) Nuggets: Enthalpy
Chemistry 13: States of Matter
 Chemistry 13: States of Matter Name: Period: Date: Chemistry Content Standard: Gases and Their Properties The kinetic molecular theory describes the motion of atoms and molecules and explains the properties
Chemistry 13: States of Matter Name: Period: Date: Chemistry Content Standard: Gases and Their Properties The kinetic molecular theory describes the motion of atoms and molecules and explains the properties
Why? Intermolecular Forces. Intermolecular Forces. Chapter 12 IM Forces and Liquids. Covalent Bonding Forces for Comparison of Magnitude
 1 Why? Chapter 1 Intermolecular Forces and Liquids Why is water usually a liquid and not a gas? Why does liquid water boil at such a high temperature for such a small molecule? Why does ice float on water?
1 Why? Chapter 1 Intermolecular Forces and Liquids Why is water usually a liquid and not a gas? Why does liquid water boil at such a high temperature for such a small molecule? Why does ice float on water?
AP Chemistry A. Allan Chapter 8 Notes - Bonding: General Concepts
 AP Chemistry A. Allan Chapter 8 Notes - Bonding: General Concepts 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds A. Ionic Bonding 1. Electrons are transferred 2. Metals react with nonmetals 3. Ions paired have lower energy
AP Chemistry A. Allan Chapter 8 Notes - Bonding: General Concepts 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds A. Ionic Bonding 1. Electrons are transferred 2. Metals react with nonmetals 3. Ions paired have lower energy
Chemistry 151 Final Exam
 Chemistry 151 Final Exam Name: SSN: Exam Rules & Guidelines Show your work. No credit will be given for an answer unless your work is shown. Indicate your answer with a box or a circle. All paperwork must
Chemistry 151 Final Exam Name: SSN: Exam Rules & Guidelines Show your work. No credit will be given for an answer unless your work is shown. Indicate your answer with a box or a circle. All paperwork must
11 Thermodynamics and Thermochemistry
 Copyright ç 1996 Richard Hochstim. All rights reserved. Terms of use.» 37 11 Thermodynamics and Thermochemistry Thermodynamics is the study of heat, and how heat can be interconverted into other energy
Copyright ç 1996 Richard Hochstim. All rights reserved. Terms of use.» 37 11 Thermodynamics and Thermochemistry Thermodynamics is the study of heat, and how heat can be interconverted into other energy
Mr. Bracken. Multiple Choice Review: Thermochemistry
 Mr. Bracken AP Chemistry Name Period Multiple Choice Review: Thermochemistry 1. If this has a negative value for a process, then the process occurs spontaneously. 2. This is a measure of how the disorder
Mr. Bracken AP Chemistry Name Period Multiple Choice Review: Thermochemistry 1. If this has a negative value for a process, then the process occurs spontaneously. 2. This is a measure of how the disorder
SUPPLEMENTARY TOPIC 3 ENERGY AND CHEMICAL REACTIONS
 SUPPLEMENTARY TOPIC 3 ENERGY AND CHEMICAL REACTIONS Rearranging atoms. In a chemical reaction, bonds between atoms in one or more molecules (reactants) break and new bonds are formed with other atoms to
SUPPLEMENTARY TOPIC 3 ENERGY AND CHEMICAL REACTIONS Rearranging atoms. In a chemical reaction, bonds between atoms in one or more molecules (reactants) break and new bonds are formed with other atoms to
Thermodynamics of Crystal Formation
 Thermodynamics of Crystal Formation! All stable ionic crystals have negative standard enthalpies of formation, ΔH o f, and negative standard free energies of formation, ΔG o f. Na(s) + ½ Cl 2 (g) NaCl(s)
Thermodynamics of Crystal Formation! All stable ionic crystals have negative standard enthalpies of formation, ΔH o f, and negative standard free energies of formation, ΔG o f. Na(s) + ½ Cl 2 (g) NaCl(s)
CHEM 36 General Chemistry EXAM #1 February 13, 2002
 CHEM 36 General Chemistry EXAM #1 February 13, 2002 Name: Serkey, Anne INSTRUCTIONS: Read through the entire exam before you begin. Answer all of the questions. For questions involving calculations, show
CHEM 36 General Chemistry EXAM #1 February 13, 2002 Name: Serkey, Anne INSTRUCTIONS: Read through the entire exam before you begin. Answer all of the questions. For questions involving calculations, show
Chapter 8 Concepts of Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 8 Concepts of Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonds Three types: Ionic Electrostatic attraction between ions Covalent Sharing of electrons Metallic Metal atoms bonded to several other atoms Ionic Bonding
Chapter 8 Concepts of Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonds Three types: Ionic Electrostatic attraction between ions Covalent Sharing of electrons Metallic Metal atoms bonded to several other atoms Ionic Bonding
87 16 70 20 58 24 44 32 35 40 29 48 (a) graph Y versus X (b) graph Y versus 1/X
 HOMEWORK 5A Barometer; Boyle s Law 1. The pressure of the first two gases below is determined with a manometer that is filled with mercury (density = 13.6 g/ml). The pressure of the last two gases below
HOMEWORK 5A Barometer; Boyle s Law 1. The pressure of the first two gases below is determined with a manometer that is filled with mercury (density = 13.6 g/ml). The pressure of the last two gases below
Introductory Chemistry, 3 rd Edition Nivaldo Tro. Roy Kennedy Massachusetts Bay Community College Wellesley Hills, Maqqwertd ygoijpk[l
 Introductory Chemistry, 3 rd Edition Nivaldo Tro Quantities in Car an octane and oxygen molecules and carbon dioxide and water Chemical Reactions Roy Kennedy Massachusetts Bay Community College Wellesley
Introductory Chemistry, 3 rd Edition Nivaldo Tro Quantities in Car an octane and oxygen molecules and carbon dioxide and water Chemical Reactions Roy Kennedy Massachusetts Bay Community College Wellesley
Unit 5 Practice Test. Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Class: Date: Unit 5 Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The internal energy of a system is always increased by. A) adding
Name: Class: Date: Unit 5 Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The internal energy of a system is always increased by. A) adding
Gibbs Free Energy and Chemical Potential. NC State University
 Chemistry 433 Lecture 14 Gibbs Free Energy and Chemical Potential NC State University The internal energy expressed in terms of its natural variables We can use the combination of the first and second
Chemistry 433 Lecture 14 Gibbs Free Energy and Chemical Potential NC State University The internal energy expressed in terms of its natural variables We can use the combination of the first and second
Test Review # 9. Chemistry R: Form TR9.13A
 Chemistry R: Form TR9.13A TEST 9 REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 9 Collision theory. In order for a reaction to occur, particles of the reactant must collide. Not all collisions cause reactions.
Chemistry R: Form TR9.13A TEST 9 REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 9 Collision theory. In order for a reaction to occur, particles of the reactant must collide. Not all collisions cause reactions.
CHEMISTRY. Matter and Change. Section 13.1 Section 13.2 Section 13.3. The Gas Laws The Ideal Gas Law Gas Stoichiometry
 CHEMISTRY Matter and Change 13 Table Of Contents Chapter 13: Gases Section 13.1 Section 13.2 Section 13.3 The Gas Laws The Ideal Gas Law Gas Stoichiometry State the relationships among pressure, temperature,
CHEMISTRY Matter and Change 13 Table Of Contents Chapter 13: Gases Section 13.1 Section 13.2 Section 13.3 The Gas Laws The Ideal Gas Law Gas Stoichiometry State the relationships among pressure, temperature,
AP CHEMISTRY 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES. Question 2
 AP CHEMISTRY 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 2 N 2 (g) + 3 F 2 (g) 2 NF 3 (g) ΔH 298 = 264 kj mol 1 ; ΔS 298 = 278 J K 1 mol 1 The following questions relate to the synthesis reaction represented by the
AP CHEMISTRY 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 2 N 2 (g) + 3 F 2 (g) 2 NF 3 (g) ΔH 298 = 264 kj mol 1 ; ΔS 298 = 278 J K 1 mol 1 The following questions relate to the synthesis reaction represented by the
Questions on Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding
 Questions on Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding Circle the Correct Answer: 1) Which ion below has a noble gas electron configuration? A) Li 2+ B) Be 2+ C) B2+ D) C2+ E) N 2-2) Of the ions below,
Questions on Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding Circle the Correct Answer: 1) Which ion below has a noble gas electron configuration? A) Li 2+ B) Be 2+ C) B2+ D) C2+ E) N 2-2) Of the ions below,
CHEM 105 HOUR EXAM III 28-OCT-99. = -163 kj/mole determine H f 0 for Ni(CO) 4 (g) = -260 kj/mole determine H f 0 for Cr(CO) 6 (g)
 CHEM 15 HOUR EXAM III 28-OCT-99 NAME (please print) 1. a. given: Ni (s) + 4 CO (g) = Ni(CO) 4 (g) H Rxn = -163 k/mole determine H f for Ni(CO) 4 (g) b. given: Cr (s) + 6 CO (g) = Cr(CO) 6 (g) H Rxn = -26
CHEM 15 HOUR EXAM III 28-OCT-99 NAME (please print) 1. a. given: Ni (s) + 4 CO (g) = Ni(CO) 4 (g) H Rxn = -163 k/mole determine H f for Ni(CO) 4 (g) b. given: Cr (s) + 6 CO (g) = Cr(CO) 6 (g) H Rxn = -26
Final Exam Review. I normalize your final exam score out of 70 to a score out of 150. This score out of 150 is included in your final course total.
 Final Exam Review Information Your ACS standardized final exam is a comprehensive, 70 question multiple choice (a d) test featuring material from BOTH the CHM 101 and 102 syllabi. Questions are graded
Final Exam Review Information Your ACS standardized final exam is a comprehensive, 70 question multiple choice (a d) test featuring material from BOTH the CHM 101 and 102 syllabi. Questions are graded
www.chemsheets.co.uk 17-Jul-12 Chemsheets A2 033 1
 www.chemsheets.co.uk 17-Jul-12 Chemsheets A2 033 1 AS THERMODYNAMICS REVISION What is enthalpy? It is a measure of the heat content of a substance Enthalpy change ( H) = Change in heat content at constant
www.chemsheets.co.uk 17-Jul-12 Chemsheets A2 033 1 AS THERMODYNAMICS REVISION What is enthalpy? It is a measure of the heat content of a substance Enthalpy change ( H) = Change in heat content at constant
Transfer of heat energy often occurs during chemical reactions. A reaction
 Chemistry 111 Lab: Thermochemistry Page I-3 THERMOCHEMISTRY Heats of Reaction The Enthalpy of Formation of Magnesium Oxide Transfer of heat energy often occurs during chemical reactions. A reaction may
Chemistry 111 Lab: Thermochemistry Page I-3 THERMOCHEMISTRY Heats of Reaction The Enthalpy of Formation of Magnesium Oxide Transfer of heat energy often occurs during chemical reactions. A reaction may
Chapter 3. Chemical Reactions and Reaction Stoichiometry. Lecture Presentation. James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 3 Chemical Reactions and Reaction James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT The study of the mass relationships in chemistry Based on the Law of Conservation of Mass
Lecture Presentation Chapter 3 Chemical Reactions and Reaction James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT The study of the mass relationships in chemistry Based on the Law of Conservation of Mass
Chemistry 1050 Chapter 13 LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS 1. Exercises: 25, 27, 33, 39, 41, 43, 51, 53, 57, 61, 63, 67, 69, 71(a), 73, 75, 79
 Chemistry 1050 Chapter 13 LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS 1 Text: Petrucci, Harwood, Herring 8 th Edition Suggest text problems Review questions: 1, 5!11, 13!17, 19!23 Exercises: 25, 27, 33, 39, 41, 43, 51, 53, 57,
Chemistry 1050 Chapter 13 LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS 1 Text: Petrucci, Harwood, Herring 8 th Edition Suggest text problems Review questions: 1, 5!11, 13!17, 19!23 Exercises: 25, 27, 33, 39, 41, 43, 51, 53, 57,
Gas Laws. The kinetic theory of matter states that particles which make up all types of matter are in constant motion.
 Name Period Gas Laws Kinetic energy is the energy of motion of molecules. Gas state of matter made up of tiny particles (atoms or molecules). Each atom or molecule is very far from other atoms or molecules.
Name Period Gas Laws Kinetic energy is the energy of motion of molecules. Gas state of matter made up of tiny particles (atoms or molecules). Each atom or molecule is very far from other atoms or molecules.
Problem Set 3 Solutions
 Chemistry 360 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 3 Solutions 1 (a) One mole of an ideal gas at 98 K is expanded reversibly and isothermally from 10 L to 10 L Determine the amount of work in Joules We start
Chemistry 360 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 3 Solutions 1 (a) One mole of an ideal gas at 98 K is expanded reversibly and isothermally from 10 L to 10 L Determine the amount of work in Joules We start
CHEMISTRY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND BONDING
 CHEMISTRY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND BONDING Essential Standard: STUDENTS WILL UNDERSTAND THAT THE PROPERTIES OF MATTER AND THEIR INTERACTIONS ARE A CONSEQUENCE OF THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER,
CHEMISTRY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND BONDING Essential Standard: STUDENTS WILL UNDERSTAND THAT THE PROPERTIES OF MATTER AND THEIR INTERACTIONS ARE A CONSEQUENCE OF THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER,
CHEMISTRY 113 EXAM 4(A)
 Summer 2003 1. The molecular geometry of PF 4 + ion is: A. bent B. trigonal planar C. tetrahedral D. octahedral CHEMISTRY 113 EXAM 4(A) 2. The Cl-C-Cl bond angle in CCl 2 O molecule (C is the central atom)
Summer 2003 1. The molecular geometry of PF 4 + ion is: A. bent B. trigonal planar C. tetrahedral D. octahedral CHEMISTRY 113 EXAM 4(A) 2. The Cl-C-Cl bond angle in CCl 2 O molecule (C is the central atom)
Chemistry 11 Some Study Materials for the Final Exam
 Chemistry 11 Some Study Materials for the Final Exam Prefix Abbreviation Exponent giga G 10 9 mega M 10 6 kilo k 10 3 hecto h 10 2 deca da 10 1 deci d 10-1 centi c 10-2 milli m 10-3 micro µ 10-6 nano n
Chemistry 11 Some Study Materials for the Final Exam Prefix Abbreviation Exponent giga G 10 9 mega M 10 6 kilo k 10 3 hecto h 10 2 deca da 10 1 deci d 10-1 centi c 10-2 milli m 10-3 micro µ 10-6 nano n
CHEM 120 Online Chapter 7
 CHEM 120 Online Chapter 7 Date: 1. Which of the following statements is not a part of kinetic molecular theory? A) Matter is composed of particles that are in constant motion. B) Particle velocity increases
CHEM 120 Online Chapter 7 Date: 1. Which of the following statements is not a part of kinetic molecular theory? A) Matter is composed of particles that are in constant motion. B) Particle velocity increases
Test 5 Review questions. 1. As ice cools from 273 K to 263 K, the average kinetic energy of its molecules will
 Name: Thursday, December 13, 2007 Test 5 Review questions 1. As ice cools from 273 K to 263 K, the average kinetic energy of its molecules will 1. decrease 2. increase 3. remain the same 2. The graph below
Name: Thursday, December 13, 2007 Test 5 Review questions 1. As ice cools from 273 K to 263 K, the average kinetic energy of its molecules will 1. decrease 2. increase 3. remain the same 2. The graph below
Chemistry 110 Lecture Unit 5 Chapter 11-GASES
 Chemistry 110 Lecture Unit 5 Chapter 11-GASES I. PROPERITIES OF GASES A. Gases have an indefinite shape. B. Gases have a low density C. Gases are very compressible D. Gases exert pressure equally in all
Chemistry 110 Lecture Unit 5 Chapter 11-GASES I. PROPERITIES OF GASES A. Gases have an indefinite shape. B. Gases have a low density C. Gases are very compressible D. Gases exert pressure equally in all
Thermodynamics Worksheet I also highly recommend Worksheets 13 and 14 in the Lab Manual
 Thermodynamics Worksheet I also highly recommend Worksheets 13 and 14 in the Lab Manual 1. Predict the sign of entropy change in the following processes a) The process of carbonating water to make a soda
Thermodynamics Worksheet I also highly recommend Worksheets 13 and 14 in the Lab Manual 1. Predict the sign of entropy change in the following processes a) The process of carbonating water to make a soda
Determination of the enthalpy of combustion using a bomb calorimeter TEC
 Determination of the enthalpy of TEC Related concepts First law of thermodynamics, Hess s law of constant heat summation, enthalpy of combustion, enthalpy of formation, heat capacity. Principle The bomb
Determination of the enthalpy of TEC Related concepts First law of thermodynamics, Hess s law of constant heat summation, enthalpy of combustion, enthalpy of formation, heat capacity. Principle The bomb
Exam 4 Practice Problems false false
 Exam 4 Practice Problems 1 1. Which of the following statements is false? a. Condensed states have much higher densities than gases. b. Molecules are very far apart in gases and closer together in liquids
Exam 4 Practice Problems 1 1. Which of the following statements is false? a. Condensed states have much higher densities than gases. b. Molecules are very far apart in gases and closer together in liquids
Final Exam CHM 3410, Dr. Mebel, Fall 2005
 Final Exam CHM 3410, Dr. Mebel, Fall 2005 1. At -31.2 C, pure propane and n-butane have vapor pressures of 1200 and 200 Torr, respectively. (a) Calculate the mole fraction of propane in the liquid mixture
Final Exam CHM 3410, Dr. Mebel, Fall 2005 1. At -31.2 C, pure propane and n-butane have vapor pressures of 1200 and 200 Torr, respectively. (a) Calculate the mole fraction of propane in the liquid mixture
A pure covalent bond is an equal sharing of shared electron pair(s) in a bond. A polar covalent bond is an unequal sharing.
 CHAPTER EIGHT BNDING: GENERAL CNCEPT or Review 1. Electronegativity is the ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself. Electronegativity is a bonding term. Electron affinity is the
CHAPTER EIGHT BNDING: GENERAL CNCEPT or Review 1. Electronegativity is the ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself. Electronegativity is a bonding term. Electron affinity is the
Chemical Reactions Practice Test
 Chemical Reactions Practice Test Chapter 2 Name Date Hour _ Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The only sure evidence for a chemical reaction
Chemical Reactions Practice Test Chapter 2 Name Date Hour _ Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The only sure evidence for a chemical reaction
Problem Set 4 Solutions
 Chemistry 360 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 4 Solutions 1 Two moles of an ideal gas are compressed isothermally and reversibly at 98 K from 1 atm to 00 atm Calculate q, w, ΔU, and ΔH For an isothermal
Chemistry 360 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 4 Solutions 1 Two moles of an ideal gas are compressed isothermally and reversibly at 98 K from 1 atm to 00 atm Calculate q, w, ΔU, and ΔH For an isothermal
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK COURSE OUTLINE CHEM 150 - COLLEGE CHEMISTRY I
 STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK COURSE OUTLINE CHEM 150 - COLLEGE CHEMISTRY I PREPARED BY: NICOLE HELDT SCHOOL OF SCIENCE, HEALTH, AND PROFESSIONAL STUDIES SCIENCE DEPARTMENT
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK COURSE OUTLINE CHEM 150 - COLLEGE CHEMISTRY I PREPARED BY: NICOLE HELDT SCHOOL OF SCIENCE, HEALTH, AND PROFESSIONAL STUDIES SCIENCE DEPARTMENT
7. 1.00 atm = 760 torr = 760 mm Hg = 101.325 kpa = 14.70 psi. = 0.446 atm. = 0.993 atm. = 107 kpa 760 torr 1 atm 760 mm Hg = 790.
 CHATER 3. The atmosphere is a homogeneous mixture (a solution) of gases.. Solids and liquids have essentially fixed volumes and are not able to be compressed easily. have volumes that depend on their conditions,
CHATER 3. The atmosphere is a homogeneous mixture (a solution) of gases.. Solids and liquids have essentially fixed volumes and are not able to be compressed easily. have volumes that depend on their conditions,
Sample Exercise 8.1 Magnitudes of Lattice Energies
 Sample Exercise 8.1 Magnitudes of Lattice Energies Without consulting Table 8.2, arrange the following ionic compounds in order of increasing lattice energy: NaF, CsI, and CaO. Analyze: From the formulas
Sample Exercise 8.1 Magnitudes of Lattice Energies Without consulting Table 8.2, arrange the following ionic compounds in order of increasing lattice energy: NaF, CsI, and CaO. Analyze: From the formulas
Study the following diagrams of the States of Matter. Label the names of the Changes of State between the different states.
 Describe the strength of attractive forces between particles. Describe the amount of space between particles. Can the particles in this state be compressed? Do the particles in this state have a definite
Describe the strength of attractive forces between particles. Describe the amount of space between particles. Can the particles in this state be compressed? Do the particles in this state have a definite
4. Using the data from Handout 5, what is the standard enthalpy of formation of BaO (s)? What does this mean?
 HOMEWORK 3A 1. In each of the following pairs, tell which has the higher entropy. (a) One mole of liquid water or one mole of water vapor (b) One mole of dry ice or one mole of carbon dioxide at 1 atm
HOMEWORK 3A 1. In each of the following pairs, tell which has the higher entropy. (a) One mole of liquid water or one mole of water vapor (b) One mole of dry ice or one mole of carbon dioxide at 1 atm
CHEM 1211K Test IV. MULTIPLE CHOICE (3 points each)
 CEM 1211K Test IV MULTIPLE COICE (3 points each) 1) ow many single covalent bonds must a silicon atom form to have a complete octet in its valence shell? A) 4 B) 3 C) 1 D) 2 E) 0 2) What is the maximum
CEM 1211K Test IV MULTIPLE COICE (3 points each) 1) ow many single covalent bonds must a silicon atom form to have a complete octet in its valence shell? A) 4 B) 3 C) 1 D) 2 E) 0 2) What is the maximum
Adiabatic Bomb Calorimetry
 CHEM 366 II-1 Adiabatic Bomb Calorimetry Introduction Obtaining energy in the form of heat from the combustion or oxidation of thermodynamically unstable (and often kinetically inert) hydrocarbons and
CHEM 366 II-1 Adiabatic Bomb Calorimetry Introduction Obtaining energy in the form of heat from the combustion or oxidation of thermodynamically unstable (and often kinetically inert) hydrocarbons and
Intermolecular Forces
 Intermolecular Forces: Introduction Intermolecular Forces Forces between separate molecules and dissolved ions (not bonds) Van der Waals Forces 15% as strong as covalent or ionic bonds Chapter 11 Intermolecular
Intermolecular Forces: Introduction Intermolecular Forces Forces between separate molecules and dissolved ions (not bonds) Van der Waals Forces 15% as strong as covalent or ionic bonds Chapter 11 Intermolecular
IB Chemistry 1 Mole. One atom of C-12 has a mass of 12 amu. One mole of C-12 has a mass of 12 g. Grams we can use more easily.
 The Mole Atomic mass units and atoms are not convenient units to work with. The concept of the mole was invented. This was the number of atoms of carbon-12 that were needed to make 12 g of carbon. 1 mole
The Mole Atomic mass units and atoms are not convenient units to work with. The concept of the mole was invented. This was the number of atoms of carbon-12 that were needed to make 12 g of carbon. 1 mole
Determination of the enthalpy of combustion using a bomb calorimeter TEC. Safety precautions
 Safety precautions Naphthalene is harmful if swallowed. May cause cancer. Is further very toxic to aquatic organisms and can have long-term harmful effects in bodies of water. Equipment 1 Bomb calorimeter
Safety precautions Naphthalene is harmful if swallowed. May cause cancer. Is further very toxic to aquatic organisms and can have long-term harmful effects in bodies of water. Equipment 1 Bomb calorimeter
Bomb Calorimetry. Electrical leads. Stirrer
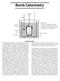 Bomb Calorimetry Stirrer Electrical leads Oxygen inlet valve Bomb Fuse Calorimeter Outer jacket Not shown: heating and cooling system for outer jacket, and controls that keep the outer jacket at the same
Bomb Calorimetry Stirrer Electrical leads Oxygen inlet valve Bomb Fuse Calorimeter Outer jacket Not shown: heating and cooling system for outer jacket, and controls that keep the outer jacket at the same
1. The Kinetic Theory of Matter states that all matter is composed of atoms and molecules that are in a constant state of constant random motion
 Physical Science Period: Name: ANSWER KEY Date: Practice Test for Unit 3: Ch. 3, and some of 15 and 16: Kinetic Theory of Matter, States of matter, and and thermodynamics, and gas laws. 1. The Kinetic
Physical Science Period: Name: ANSWER KEY Date: Practice Test for Unit 3: Ch. 3, and some of 15 and 16: Kinetic Theory of Matter, States of matter, and and thermodynamics, and gas laws. 1. The Kinetic
FUNDAMENTALS OF ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS
 FUNDAMENTALS OF ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS System: Quantity of matter (constant mass) or region in space (constant volume) chosen for study. Closed system: Can exchange energy but not mass; mass is constant
FUNDAMENTALS OF ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS System: Quantity of matter (constant mass) or region in space (constant volume) chosen for study. Closed system: Can exchange energy but not mass; mass is constant
Thermodynamics. Chapter 13 Phase Diagrams. NC State University
 Thermodynamics Chapter 13 Phase Diagrams NC State University Pressure (atm) Definition of a phase diagram A phase diagram is a representation of the states of matter, solid, liquid, or gas as a function
Thermodynamics Chapter 13 Phase Diagrams NC State University Pressure (atm) Definition of a phase diagram A phase diagram is a representation of the states of matter, solid, liquid, or gas as a function
Chapter 6 Chemical Calculations
 Chapter 6 Chemical Calculations 1 Submicroscopic Macroscopic 2 Chapter Outline 1. Formula Masses (Ch 6.1) 2. Percent Composition (supplemental material) 3. The Mole & Avogadro s Number (Ch 6.2) 4. Molar
Chapter 6 Chemical Calculations 1 Submicroscopic Macroscopic 2 Chapter Outline 1. Formula Masses (Ch 6.1) 2. Percent Composition (supplemental material) 3. The Mole & Avogadro s Number (Ch 6.2) 4. Molar
FORMA is EXAM I, VERSION 1 (v1) Name
 FORMA is EXAM I, VERSION 1 (v1) Name 1. DO NOT TURN THIS PAGE UNTIL DIRECTED TO DO SO. 2. These tests are machine graded; therefore, be sure to use a No. 1 or 2 pencil for marking the answer sheets. 3.
FORMA is EXAM I, VERSION 1 (v1) Name 1. DO NOT TURN THIS PAGE UNTIL DIRECTED TO DO SO. 2. These tests are machine graded; therefore, be sure to use a No. 1 or 2 pencil for marking the answer sheets. 3.
Thermodynamics AP Physics B. Multiple Choice Questions
 Thermodynamics AP Physics B Name Multiple Choice Questions 1. What is the name of the following statement: When two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, then they are in thermal equilibrium
Thermodynamics AP Physics B Name Multiple Choice Questions 1. What is the name of the following statement: When two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, then they are in thermal equilibrium
Chapter 18 Homework Answers
 Chapter 18 Homework Answers 18.22. 18.24. 18.26. a. Since G RT lnk, as long as the temperature remains constant, the value of G also remains constant. b. In this case, G G + RT lnq. Since the reaction
Chapter 18 Homework Answers 18.22. 18.24. 18.26. a. Since G RT lnk, as long as the temperature remains constant, the value of G also remains constant. b. In this case, G G + RT lnq. Since the reaction
KINETIC THEORY OF MATTER - molecules in matter are always in motion - speed of molecules is proportional to the temperature
 1 KINETIC TERY F MATTER - molecules in matter are always in motion - speed of molecules is proportional to the temperature TE STATES F MATTER 1. Gas a) ideal gas - molecules move freely - molecules have
1 KINETIC TERY F MATTER - molecules in matter are always in motion - speed of molecules is proportional to the temperature TE STATES F MATTER 1. Gas a) ideal gas - molecules move freely - molecules have
Thermodynamics and Equilibrium
 Chapter 19 Thermodynamics and Equilibrium Concept Check 19.1 You have a sample of 1.0 mg of solid iodine at room temperature. Later, you notice that the iodine has sublimed (passed into the vapor state).
Chapter 19 Thermodynamics and Equilibrium Concept Check 19.1 You have a sample of 1.0 mg of solid iodine at room temperature. Later, you notice that the iodine has sublimed (passed into the vapor state).
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 General Chemistry PHS 1015 Practice Exam 4 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements about pressure
General Chemistry PHS 1015 Practice Exam 4 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements about pressure
Chapter 8 - Chemical Equations and Reactions
 Chapter 8 - Chemical Equations and Reactions 8-1 Describing Chemical Reactions I. Introduction A. Reactants 1. Original substances entering into a chemical rxn B. Products 1. The resulting substances from
Chapter 8 - Chemical Equations and Reactions 8-1 Describing Chemical Reactions I. Introduction A. Reactants 1. Original substances entering into a chemical rxn B. Products 1. The resulting substances from
Read the sections on Allotropy and Allotropes in your text (pages 464, 475, 871-2, 882-3) and answer the following:
 Descriptive Chemistry Assignment 5 Thermodynamics and Allotropes Read the sections on Allotropy and Allotropes in your text (pages 464, 475, 871-2, 882-3) and answer the following: 1. Define the word allotrope
Descriptive Chemistry Assignment 5 Thermodynamics and Allotropes Read the sections on Allotropy and Allotropes in your text (pages 464, 475, 871-2, 882-3) and answer the following: 1. Define the word allotrope
Chapter 4 Practice Quiz
 Chapter 4 Practice Quiz 1. Label each box with the appropriate state of matter. A) I: Gas II: Liquid III: Solid B) I: Liquid II: Solid III: Gas C) I: Solid II: Liquid III: Gas D) I: Gas II: Solid III:
Chapter 4 Practice Quiz 1. Label each box with the appropriate state of matter. A) I: Gas II: Liquid III: Solid B) I: Liquid II: Solid III: Gas C) I: Solid II: Liquid III: Gas D) I: Gas II: Solid III:
REVIEW QUESTIONS Chapter 8
 Chemistry 101 ANSWER KEY REVIEW QUESTIONS Chapter 8 Use only a periodic table to answer the following questions. 1. Write complete electron configuration for each of the following elements: a) Aluminum
Chemistry 101 ANSWER KEY REVIEW QUESTIONS Chapter 8 Use only a periodic table to answer the following questions. 1. Write complete electron configuration for each of the following elements: a) Aluminum
AAHS-CHEMISTRY FINAL EXAM PREP-REVIEW GUIDE MAY-JUNE 2014 DR. GRAY CLASS OF 2016
 AAHS-CHEMISTRY FINAL EXAM PREP-REVIEW GUIDE MAY-JUNE 2014 DR. GRAY CLASS OF 2016 UNIT I: (CHAPTER 1-Zumdahl text) The Nature of Science and Chemistry 1. Explain why knowledge of chemistry is central to
AAHS-CHEMISTRY FINAL EXAM PREP-REVIEW GUIDE MAY-JUNE 2014 DR. GRAY CLASS OF 2016 UNIT I: (CHAPTER 1-Zumdahl text) The Nature of Science and Chemistry 1. Explain why knowledge of chemistry is central to
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Given: 4 NO2(g) + O2(g) 2 N2O5(g) ΔH = -110.2 kj find ΔH for N2O5(g) 2 NO2(g) + 1/2 O2(g).
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Given: 4 NO2(g) + O2(g) 2 N2O5(g) ΔH = -110.2 kj find ΔH for N2O5(g) 2 NO2(g) + 1/2 O2(g).
AP Chemistry 2005 Scoring Guidelines Form B
 AP Chemistry 2005 Scoring Guidelines Form B The College Board: Connecting Students to College Success The College Board is a not-for-profit membership association whose mission is to connect students to
AP Chemistry 2005 Scoring Guidelines Form B The College Board: Connecting Students to College Success The College Board is a not-for-profit membership association whose mission is to connect students to
Chem 112 Intermolecular Forces Chang From the book (10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20,84,92,94,102,104, 108, 112, 114, 118 and 134)
 Chem 112 Intermolecular Forces Chang From the book (10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20,84,92,94,102,104, 108, 112, 114, 118 and 134) 1. Helium atoms do not combine to form He 2 molecules, What is the strongest attractive
Chem 112 Intermolecular Forces Chang From the book (10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20,84,92,94,102,104, 108, 112, 114, 118 and 134) 1. Helium atoms do not combine to form He 2 molecules, What is the strongest attractive
= 1.038 atm. 760 mm Hg. = 0.989 atm. d. 767 torr = 767 mm Hg. = 1.01 atm
 Chapter 13 Gases 1. Solids and liquids have essentially fixed volumes and are not able to be compressed easily. Gases have volumes that depend on their conditions, and can be compressed or expanded by
Chapter 13 Gases 1. Solids and liquids have essentially fixed volumes and are not able to be compressed easily. Gases have volumes that depend on their conditions, and can be compressed or expanded by
Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
 Chapter 3 Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations Concept Check 3.1 You have 1.5 moles of tricycles. a. How many moles of seats do you have? b. How many moles of tires do you have? c. How could
Chapter 3 Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations Concept Check 3.1 You have 1.5 moles of tricycles. a. How many moles of seats do you have? b. How many moles of tires do you have? c. How could
Order of Filling Subshells
 Bonding: General Concepts Ionic Bonds Sections 13.2-13.6 Covalent Bonds Section 13.7 Covalent Bond Energy & Chemical Reactions Section 13.8-13.9 Lewis Structures Sections 13.10-13.12 VSEPR Theory Section
Bonding: General Concepts Ionic Bonds Sections 13.2-13.6 Covalent Bonds Section 13.7 Covalent Bond Energy & Chemical Reactions Section 13.8-13.9 Lewis Structures Sections 13.10-13.12 VSEPR Theory Section
48 Practice Problems for Ch. 17 - Chem 1C - Joseph
 48 Practice Problems for Ch. 17 - Chem 1C - Joseph 1. Which of the following concentration measures will change in value as the temperature of a solution changes? A) mass percent B) mole fraction C) molality
48 Practice Problems for Ch. 17 - Chem 1C - Joseph 1. Which of the following concentration measures will change in value as the temperature of a solution changes? A) mass percent B) mole fraction C) molality
Unit 19 Practice. Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Class: Date: Unit 19 Practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The first law of thermodynamics can be given as. A) E = q + w B) =
Name: Class: Date: Unit 19 Practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The first law of thermodynamics can be given as. A) E = q + w B) =
Chem 115 POGIL Worksheet - Week 4 Moles & Stoichiometry
 Chem 115 POGIL Worksheet - Week 4 Moles & Stoichiometry Why? Chemists are concerned with mass relationships in chemical reactions, usually run on a macroscopic scale (grams, kilograms, etc.). To deal with
Chem 115 POGIL Worksheet - Week 4 Moles & Stoichiometry Why? Chemists are concerned with mass relationships in chemical reactions, usually run on a macroscopic scale (grams, kilograms, etc.). To deal with
Enthalpy of Combustion via Calorimetry
 Enthalpy of Combustion via Calorimetry Introduction This experiment measures the enthalpy change when a system consisting of a known amount of a substance in the presence of excess oxygen is quantitatively
Enthalpy of Combustion via Calorimetry Introduction This experiment measures the enthalpy change when a system consisting of a known amount of a substance in the presence of excess oxygen is quantitatively
CHEMISTRY 1710 - Practice Exam #5 - SPRING 2014 (KATZ)
 CHEMISTRY 1710 - Practice Exam #5 - SPRING 2014 (KATZ) Name: Score: This is a multiple choice exam. Choose the BEST answer from the choices which are given and write the letter for your choice in the space
CHEMISTRY 1710 - Practice Exam #5 - SPRING 2014 (KATZ) Name: Score: This is a multiple choice exam. Choose the BEST answer from the choices which are given and write the letter for your choice in the space
Paper 1 (7405/1): Inorganic and Physical Chemistry Mark scheme
 AQA Qualifications A-level Chemistry Paper (7405/): Inorganic and Physical Chemistry Mark scheme 7405 Specimen paper Version 0.5 MARK SCHEME A-level Chemistry Specimen paper 0. This question is marked
AQA Qualifications A-level Chemistry Paper (7405/): Inorganic and Physical Chemistry Mark scheme 7405 Specimen paper Version 0.5 MARK SCHEME A-level Chemistry Specimen paper 0. This question is marked
Answer, Key Homework 6 David McIntyre 1
 Answer, Key Homework 6 David McIntyre 1 This print-out should have 0 questions, check that it is complete. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page: find all choices before making
Answer, Key Homework 6 David McIntyre 1 This print-out should have 0 questions, check that it is complete. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page: find all choices before making
CHAPTER 12. Gases and the Kinetic-Molecular Theory
 CHAPTER 12 Gases and the Kinetic-Molecular Theory 1 Gases vs. Liquids & Solids Gases Weak interactions between molecules Molecules move rapidly Fast diffusion rates Low densities Easy to compress Liquids
CHAPTER 12 Gases and the Kinetic-Molecular Theory 1 Gases vs. Liquids & Solids Gases Weak interactions between molecules Molecules move rapidly Fast diffusion rates Low densities Easy to compress Liquids
