SOPHOMORE DENTAL/OPTOMETRY MICROBIOLOGY SECTION: IMMUNOLOGY
|
|
|
- Phillip Neal
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SOPHOMORE DENTAL/OPTOMETRY MICROBIOLOGY SECTION: IMMUNOLOGY LYMPHOCYTE ACTIVATION Lecturer: Louis B. Justement, Ph.D Objectives: To review the structure of the T and B cell antigen receptor complexes, what they recognize and the nature of the signals that are transduced leading to lymphocyte activation. To become familiar with the additional receptors and ligands involved in promoting lymphocyte activation and differentiation. Reading Assignment: Kuby Immunology 6 th edition Chapter 10, pp and 11, pp LYMPHOCYTE ACTIVATION The activation of lymphocytes requires two distinct signals the first signal is provided by binding of antigen to the antigen receptor and the second signal is provided through costimulatory or accessory receptors this ensures specificity and selectivity of the immune response against foreign antigens The response of lymphocytes to antigens and second signals consists of several steps: Synthesis of new proteins: shortly after the encounter with antigen, lymphocytes transcribe genes that were previously silent, which synthesize proteins including cytokines and their receptors, costimulatory molecules and proteins involved in cell division Cellular proliferation: in response to antigen and other factors, antigen-specific lymphocytes enter the cell cycle and begin to proliferate to expand the number of antigen-specific cells (i.e. clonal expansion) Differentiation into effector cells: Progeny of the antigen-stimulated lymphocytes differentiate into effector cells that are responsible for elimination of foreign antigen. Homeostasis decline of immune response: after the immune response has run its course, the system returns to its basal state due to death of most of the antigenspecific lymphocyte progeny via apoptosis or programmed cell death decline occurs in conjunction with the clearance of foreign antigen
2 Differentiation into memory cells: some of the progeny of antigen-stimulated cells do not differentiate into effector cells but become functionally quiescent memory cells that are capable of surviving for an extended period of time LYMPHOCYTE ANTIGEN RECEPTORS B Cell Antigen Receptor (BCR): The BCR consists of two heavy chains and two light chains that are disulfide bonded to form a heterotetrameric structure Both the heavy and light chains contain variable domains at the amino terminus that exhibit sequence hypervariability within three CDRs The pairing of heavy and light chain variable domains forms the antigen binding site and each BCR molecule has the ability to bind two antigenic molecules All antibody molecules produced by a particular B cell have identical VH and VL regions and thus the same antigen specificity Antibody molecules can be displayed on the surface of the B cell or secreted into the surrounding environment or both The membrane-bound form of antibody is referred to as membrane immunoglobulin or the B cell antigen receptor (BCR) Mature, resting B cells express two isoforms of membrane immunoglobulin - membrane IgM and membrane IgD both isoforms of mig have the same VH and VL regions and therefore recognize the same antigen Importantly, the BCR can recognize many forms of antigen and antigen recognition is NOT restricted by other lymphoid surface molecules such as MHC Class I or II The membrane-bound forms of IgM and IgD possess a hydrophobic transmembrane domain, which contains charged amino acids, and a cytoplasmic tail that is only 3 amino acids long BCR Complex (CD79a/b): The BCR is non-covalently associated with one heterodimeric complexe - the heterodimer consists of one Igα (CD79a) subunit disulfide bonded to one Igβ (CD79b) subunit The Igα/Igβ heterodimer serves both a transport as well as a signal transducer function The cytoplasmic domains of both Igα and Igβ contain ITAMs that are important for signal transduction in response to binding of antigen to the BCR The Igα/Igβ heterodimer serves to recruit PTKs to the BCR complex - association of PTKs with the ITAMs of Igα and Igβ promotes activation of multiple signaling pathways that regulate the B cell response to antigen
3 T Cell Antigen Receptor (TCR): The TCR complex is comprised of an antigen recognition structure and a transport/transducer component The antigen recognition structure or TCR is comprised of either a disulfide-linked αβ or γδ heterodimer Each chain has two immunoglobulin domains containing an intrachain disulfide bond The amino-terminal domain in both chains exhibits marked sequence variation and is termed that variable domain whereas the membrane-proximal domain in more conserved and is therefore called the constant domain TCR variable domains contain three hypervariable domains or complimentarity determining regions (CDRs) The TCR exhibits dual specificity recognizing both polymorphic regions of either MHC class I or II as well as peptides that are bound to either class I or class II thus it is important to understand that the TCR recognizes antigen in the context of a particular self MHC class I or II molecule The transmembrane domain of the TCR polypeptides contain positively charged amino acids that mediate non-covalent interactions with associated transport/transducer elements TCR Complex (CD3): The TCR is non-covalently associated with the CD3 complex, which serves both a transport and signal transduction function CD3 is a complex of 5 invariant polypeptide chains that associate to form three dimers: a heterodimer of gamma and epsilon a heterodimer of epsilon and delta a homodimer of two zeta chains or occasionally a zeta/eta heterodimer The zeta and eta polypeptides are encoded by the same gene and differ at the carboxyterminal end due to alternative RNA splicing The cytoplasmic tails of the CD3 complex proteins contain one (γ, δ, ε) or more (ζ, π) motifs called the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM), which has the consensus sequence D/E-X 7 -D/E-X 2 -Y-X 2 -L/I-X 7 -Y-X 2 -L/I The ITAMs are important for recruitment and activation of protein tyrosine kinases (PTK) that initiate signal transduction in response to binding of antigen TCR Accessory Molecules (CD4 and CD8): T cells can be divided into two subpopulations based on their expression of CD4 or CD8
4 CD4+ T cells recognize antigen that is bound to MHC Class II molecules and function primarily as helper T cells CD8+ T cells recognize antigen that is bound to MHC Class I and function primarily as cytotoxic T cells The extracellular domains of CD4 and CD8 exhibit the ability to bind to non-polymorphic regions in the membrane-proximal domains of MHC Class II (β2 domain) and Class I (α3 domain), respectively Binding of CD4 and CD8 is thought to increase the avidity of the TCR interaction with MHC/peptide and thus provide a stronger signal to the T cell CD4 and CD8 also serve an important signal transduction role during T cell activation as they are associated with the Src family protein tyrosine kinase Lck, which phosphorylates the ITAM motifs on the CD3 complex polypeptides Adhesion Molecules: The affinity of TCRs for peptide-mhc is low to moderate (K d 10-4 to 10-7 ) unlike the BCR, which binds to antigen with moderate to strong affinity (K d 10-6 to ) Additional molecules strengthen the interaction between T cells and antigen-presenting cells or target cells including CD2, and LFA-1, which bind to LFA-3 and ICAM-1, respectively Adhesion receptor-dependent contact between a T cell and APC allows the T cell to scan the APC for peptide-mhc complexes TCR-mediated activation also results in upregulation of adhesion molecules expression to promote further T cell activation via cytokines and other co-stimulatory receptors TCR AND BCR MEDIATED SIGNALING Compartmentalization of Function Within Receptor Subunits: Both the T and B cell express multimeric receptor complexes that contain antigen recognition polypeptides (migm or migd on the B cell, or αβ, γδ on the T cell) as well as polypeptides that transduce signal to the interior of the cell (CD3 on the T cell, Igα/Igβ on the B cell) Dephosphorylation of Key Src Protein Tyrosine Kinases by CD45: The transmembrane protein tyrosine phosphatase CD45 functions to maintain Src family PTKs in an active state so that they can initiate signal transduction in response to antigen binding and cross-linking of either the TCR or BCR Initiation of Signal Transduction by Membrane-Associated Src PTKs:
5 The Src PTKs Lck and Fyn in the T cell and Lyn in the B cell mediate phosphorylation of the ITAMs in signal transducer subunits thereby promoting their ability to recruit intracellular signaling proteins Assembly of Large Signaling Complexes Based on Protein Tyrosine Phosphorylation: Phosphorylation of the ITAMs in CD3 and Iga/Igb promotes recruitment of the PTKs (ZAP 70 in the T cell and Syk in the B cell) that phosphorylate adapter proteins and downstream enzymes thereby propagating the signal initiated in response to antigen binding Activation of Specific downstream Signaling Pathways: The initial activation of PTKs leads to the subsequent production of second messengers and the activation of serine-threonine kinases and phosphatases. Activation of Syk and ZAP-70 leads to activation of PLCgamma, which hydrolyzes PIP2 to produce the second messengers IP3 and DAG. IP3 causes Ca2+ levels in the cell to rise leading to activation of the serine phosphatase calcineurin. DAG activates the serine protein kinase PKC. Additional small molecular weight G proteins are activated by Syk and ZAP-70 which mediate activation of the serine-threonine MAP kinases (Erk, Jnk and P38). Changes in gene expression: The activation of intermediate serine-threonine kinases and phosphatases promotes activation of transcriptional regulators that translocate to the nucleus and promote gene transcription. Calcineurin promotes activation of NF-AT, PKC promotes activation of NF-kB and the MAP kinases mediate activation of Fos and Jun which comprise the AP-1 complex. These transcription factors work in concert to regulate gene transcription most importantly upregulation of IL-2 and IL-2R expression BCR Coreceptors: Signals transduced via the BCR complex are modulated by coreceptors, which either potentiate or attenuate the signal Coreceptors provide contextual information to the B cell concerning its location, the type of antigen and the state of the immune response In general, coreceptors are transmembrane glycoproteins that are phosphorylated on cytoplasmic tyrosine residues in response to BCR-dependent signaling Tyrosine phosphorylation of coreceptors creates phosphotyrosine motifs that function as docking sites for intracellular effector proteins that contain SH2 or PTB domains When coreceptors are brought into close proximity to the BCR complex, their associated
6 intracellular effector proteins have the ability to modulate signal transduction via the BCR complex CD19: Present in the membrane as part of a multimeric complex including CD21, CD81 and Leu-13 CD19 is recruited to the BCR via CD21 CD21 binds to the C3d complement component thus complement-coated antigen is bound by the BCR and CD21, the physical bridge between the BCR and CD21 serves to recruit CD19 to the BCR complex Tyrosine phosphorylation of CD19 promotes the recruitment of effector proteins that enhance BCR signal transduction CD19 increases the initial B cell response to bacterial pathogens CD22: Constitutively associated with the BCR complex is resting B cells Phosphorylation of CD22 promotes the recruitment of inhibitory effector proteins (the SHP-1 protein tyrosine phosphatase), which attenuate BCR-dependent signaling CD22 may be physically removed from the B cell surface or sequestered in lymphoid-rich regions thereby allowing the B cell to respond more effectively to antigenic stimulation CD22 therefore, may be important for preventing B cells from responding to antigen unless they are located in the appropriate immunological environment Other Coreceptors: FcγRIIb, PIR-B CO-STIMULATORY SIGNALS T Cell Co-stimulation: Optimal T cell activation is dependent on two distinct signals that promote proliferation and differentiation into effector cells: The initial signal is generated by the interaction between peptide-mhc and the TCR The second antigen-nonspecific co-stimulatory signal is provided primarily by the interaction between CD28 on the T cell with members of the B7 family on the APC There are two related forms of B7, B7-1 and B7-2 both are members of the Ig superfamily Both B7-1 and B7-2 are constitutively expressed on dendritic cells and are inducibly expressed on macrophages and B cells. The ligands are CD28 and CTLA-4 (CD152) and are expressed on T cells CD28 and CTLA-4 act antagonistically whereas CD28 is expressed on both resting and
7 activated T cells, CTLA-4 is inducibly expressed in response to T cell activation Signals delivered through CD28 promote T cell proliferation and differentiation they also prevent the development of clonal anergy a state of antigen-specific nonresponsiveness CTLA-4 is required to maintain homeostasis of the immune response and to promote resolution of the immune response Only professional APC (i.e. dendritic cells, macrophages and B cells) are able to present antigen in the context of MHC Class II and to deliver the co-stimulatory signal because dendritic cells constitutively express high levels of MHC class I and II as well as high levels of B7-1 and B7-2 they are very potent activators of naïve, memory and effector T cells B Cell Co-stimulation: The response to T-dependent soluble antigens requires two signals to induce full activation of the B cell: The first signal is delivered by binding of antigen to the BCR The second signal is delivered by CD40 ligand expressed on the T cell, which interacts with CD40 on the B cell Binding of antigen to the BCR is followed by internalization, processing and presentation in the context of MHC Class II Signals delivered via the BCR complex lead to upregulation of MHC Class II expression as well as B7 expression to enhance presentation of antigen to T cells Once a TH cell recognizes processed antigenic peptide in the context of MHC Class II on the B cell, the two cells form a T-B conjugate The formation of the T-B conjugate promotes upregulation of CD40L on the T cell, which then binds CD40 on the B cell thereby providing to co-stimulatory signal additionally, the T-B conjugate promotes the directional release of cytokines from the TH cell to the B cell CD40-dependent signals are essential for B cell proliferation, isotype switching, somatic mutation and memory cell formation
B Cell Generation, Activation & Differentiation. B cell maturation
 B Cell Generation, Activation & Differentiation Naïve B cells- have not encountered Ag. Have IgM and IgD on cell surface : have same binding VDJ regions but different constant region leaves bone marrow
B Cell Generation, Activation & Differentiation Naïve B cells- have not encountered Ag. Have IgM and IgD on cell surface : have same binding VDJ regions but different constant region leaves bone marrow
T Cell Maturation,Activation and Differentiation
 T Cell Maturation,Activation and Differentiation Positive Selection- In thymus, permits survival of only those T cells whose TCRs recognize self- MHC molecules (self-mhc restriction) Negative Selection-
T Cell Maturation,Activation and Differentiation Positive Selection- In thymus, permits survival of only those T cells whose TCRs recognize self- MHC molecules (self-mhc restriction) Negative Selection-
HUMORAL IMMUNE RE- SPONSES: ACTIVATION OF B CELLS AND ANTIBODIES JASON CYSTER SECTION 13
 SECTION 13 HUMORAL IMMUNE RE- SPONSES: ACTIVATION OF B CELLS AND ANTIBODIES CONTACT INFORMATION Jason Cyster, PhD (Email) READING Basic Immunology: Functions and Disorders of the Immune System. Abbas,
SECTION 13 HUMORAL IMMUNE RE- SPONSES: ACTIVATION OF B CELLS AND ANTIBODIES CONTACT INFORMATION Jason Cyster, PhD (Email) READING Basic Immunology: Functions and Disorders of the Immune System. Abbas,
B cell activation and Humoral Immunity
 B cell activation and Humoral Immunity Humoral immunity is mediated by secreted antibodies and its physiological function is defense against extracellular microbes (including viruses) and microbial exotoxins.
B cell activation and Humoral Immunity Humoral immunity is mediated by secreted antibodies and its physiological function is defense against extracellular microbes (including viruses) and microbial exotoxins.
LESSON 3: ANTIBODIES/BCR/B-CELL RESPONSES
 Introduction to immunology. LESSON 3: ANTIBODIES/BCR/B-CELL RESPONSES Today we will get to know: The antibodies How antibodies are produced, their classes and their maturation processes Antigen recognition
Introduction to immunology. LESSON 3: ANTIBODIES/BCR/B-CELL RESPONSES Today we will get to know: The antibodies How antibodies are produced, their classes and their maturation processes Antigen recognition
TEMA 10. REACCIONES INMUNITARIAS MEDIADAS POR CÉLULAS.
 TEMA 10. REACCIONES INMUNITARIAS MEDIADAS POR CÉLULAS. The nomenclature of cytokines partly reflects their first-described function and also the order of their discovery. There is no single unified nomenclature,
TEMA 10. REACCIONES INMUNITARIAS MEDIADAS POR CÉLULAS. The nomenclature of cytokines partly reflects their first-described function and also the order of their discovery. There is no single unified nomenclature,
B Cells and Antibodies
 B Cells and Antibodies Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture outline Functions of antibodies B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production
B Cells and Antibodies Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture outline Functions of antibodies B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production
Module 2: Antibodies and Antigens
 Module 2: Antibodies and Antigens Lecture 7: Antibodies and Antigens (part I) Antibodies may be defined as the proteins that recognize and neutralize any microbial toxin or foreign substance such as bacteria
Module 2: Antibodies and Antigens Lecture 7: Antibodies and Antigens (part I) Antibodies may be defined as the proteins that recognize and neutralize any microbial toxin or foreign substance such as bacteria
specific B cells Humoral immunity lymphocytes antibodies B cells bone marrow Cell-mediated immunity: T cells antibodies proteins
 Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
2) Macrophages function to engulf and present antigen to other immune cells.
 Immunology The immune system has specificity and memory. It specifically recognizes different antigens and has memory for these same antigens the next time they are encountered. The Cellular Components
Immunology The immune system has specificity and memory. It specifically recognizes different antigens and has memory for these same antigens the next time they are encountered. The Cellular Components
CHAPTER 9 IMMUNOGLOBULIN BIOSYNTHESIS
 CHAPTER 9 IMMUNOGLOBULIN BIOSYNTHESIS Although the process by which a functional gene for immunoglobulin HEAVY and LIGHT CHAINS is formed is highly unusual, the SYNTHESIS, POST- TRANSLATIONAL PROCESSING
CHAPTER 9 IMMUNOGLOBULIN BIOSYNTHESIS Although the process by which a functional gene for immunoglobulin HEAVY and LIGHT CHAINS is formed is highly unusual, the SYNTHESIS, POST- TRANSLATIONAL PROCESSING
Some terms: An antigen is a molecule or pathogen capable of eliciting an immune response
 Overview of the immune system We continue our discussion of protein structure by considering the structure of antibodies. All organisms are continually subject to attack by microorganisms and viruses.
Overview of the immune system We continue our discussion of protein structure by considering the structure of antibodies. All organisms are continually subject to attack by microorganisms and viruses.
Name (print) Name (signature) Period. (Total 30 points)
 AP Biology Worksheet Chapter 43 The Immune System Lambdin April 4, 2011 Due Date: Thurs. April 7, 2011 You may use the following: Text Notes Power point Internet One other person in class "On my honor,
AP Biology Worksheet Chapter 43 The Immune System Lambdin April 4, 2011 Due Date: Thurs. April 7, 2011 You may use the following: Text Notes Power point Internet One other person in class "On my honor,
Antibody Function & Structure
 Antibody Function & Structure Specifically bind to antigens in both the recognition phase (cellular receptors) and during the effector phase (synthesis and secretion) of humoral immunity Serology: the
Antibody Function & Structure Specifically bind to antigens in both the recognition phase (cellular receptors) and during the effector phase (synthesis and secretion) of humoral immunity Serology: the
B Lymphocyte (B cell)
 B Lymphocyte (B cell) B cells: Develop from stem cells in the bone marrow and differentiate into antibody-producing plasma cells in the blood Are capable of making a vast number of antibody specificities
B Lymphocyte (B cell) B cells: Develop from stem cells in the bone marrow and differentiate into antibody-producing plasma cells in the blood Are capable of making a vast number of antibody specificities
Activation and effector functions of HMI
 Activation and effector functions of HMI Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 August 2015 ว ตถ ประสงค หล งจากช วโมงบรรยายน แล วน กศ กษาสามารถ
Activation and effector functions of HMI Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 August 2015 ว ตถ ประสงค หล งจากช วโมงบรรยายน แล วน กศ กษาสามารถ
Making the switch to a safer CAR-T cell therapy
 Making the switch to a safer CAR-T cell therapy HaemaLogiX 2015 Technical Journal Club May 24 th 2016 Christina Müller - chimeric antigen receptor = CAR - CAR T cells are generated by lentiviral transduction
Making the switch to a safer CAR-T cell therapy HaemaLogiX 2015 Technical Journal Club May 24 th 2016 Christina Müller - chimeric antigen receptor = CAR - CAR T cells are generated by lentiviral transduction
Antibody Structure, and the Generation of B-cell Diversity CHAPTER 4 04/05/15. Different Immunoglobulins
 Antibody Structure, and the Generation of B-cell Diversity B cells recognize their antigen without needing an antigen presenting cell CHAPTER 4 Structure of Immunoglobulin G Different Immunoglobulins Differences
Antibody Structure, and the Generation of B-cell Diversity B cells recognize their antigen without needing an antigen presenting cell CHAPTER 4 Structure of Immunoglobulin G Different Immunoglobulins Differences
Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTLs) and NK Cells. Effector T cells. After activation, naïve T cells differentiate into effector and memory T cells
 After activation, naïve T cells differentiate into effector and memory T cells Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTLs) and NK Cells After activation, T cells remain in lymph nodes for 5-6 days Effector T cells
After activation, naïve T cells differentiate into effector and memory T cells Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTLs) and NK Cells After activation, T cells remain in lymph nodes for 5-6 days Effector T cells
MHC (MAJOR HISTOCOMPATIBILITY COMPLEX)
 MHC (MAJOR HISTOCOMPATIBILITY COMPLEX) MHC complex is group of genes on a single chromosome that codes the MHC antigens. Major as well as minor histocompatibility antigens (also called transplantation
MHC (MAJOR HISTOCOMPATIBILITY COMPLEX) MHC complex is group of genes on a single chromosome that codes the MHC antigens. Major as well as minor histocompatibility antigens (also called transplantation
3) There are different types of extracellular signaling molecules. 4) most signaling molecules are secreted by exocytosis
 XIV) Signaling. A) The need for Signaling in multicellular organisms B) yeast need to signal to respond to various factors C) Extracellular signaling molecules bind to receptors 1) most bind to receptors
XIV) Signaling. A) The need for Signaling in multicellular organisms B) yeast need to signal to respond to various factors C) Extracellular signaling molecules bind to receptors 1) most bind to receptors
Guidance for Industry
 Guidance for Industry Interpreting Sameness of Monoclonal Antibody Products Under the Orphan Drug Regulations U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation
Guidance for Industry Interpreting Sameness of Monoclonal Antibody Products Under the Orphan Drug Regulations U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation
The immune system. Bone marrow. Thymus. Spleen. Bone marrow. NK cell. B-cell. T-cell. Basophil Neutrophil. Eosinophil. Myeloid progenitor
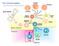 The immune system Basophil Neutrophil Bone marrow Eosinophil Myeloid progenitor Dendritic cell Pluripotent Stem cell Lymphoid progenitor Platelets Bone marrow Thymus NK cell T-cell B-cell Spleen Cancer
The immune system Basophil Neutrophil Bone marrow Eosinophil Myeloid progenitor Dendritic cell Pluripotent Stem cell Lymphoid progenitor Platelets Bone marrow Thymus NK cell T-cell B-cell Spleen Cancer
The Immune System: A Tutorial
 The Immune System: A Tutorial Modeling and Simulation of Biological Systems 21-366B Shlomo Ta asan Images taken from http://rex.nci.nih.gov/behindthenews/uis/uisframe.htm http://copewithcytokines.de/ The
The Immune System: A Tutorial Modeling and Simulation of Biological Systems 21-366B Shlomo Ta asan Images taken from http://rex.nci.nih.gov/behindthenews/uis/uisframe.htm http://copewithcytokines.de/ The
Dendritic Cells: A Basic Review *last updated May 2003
 *last updated May 2003 Prepared by: Eric Wieder, PhD MD Anderson Cancer Center Houston, TX USA What is a dendritic cell? Dendritic cells are antigen-presenting cells (APCs) which play a critical role in
*last updated May 2003 Prepared by: Eric Wieder, PhD MD Anderson Cancer Center Houston, TX USA What is a dendritic cell? Dendritic cells are antigen-presenting cells (APCs) which play a critical role in
Chapter 5: Organization and Expression of Immunoglobulin Genes
 Chapter 5: Organization and Expression of Immunoglobulin Genes I. Genetic Model Compatible with Ig Structure A. Two models for Ab structure diversity 1. Germ-line theory: maintained that the genome contributed
Chapter 5: Organization and Expression of Immunoglobulin Genes I. Genetic Model Compatible with Ig Structure A. Two models for Ab structure diversity 1. Germ-line theory: maintained that the genome contributed
Overview. Transcriptional cascades. Amazing aspects of lineage plasticity. Conventional (B2) B cell development
 Overview B cell development Transcriptional cascades Amazing aspects of lineage plasticity Conventional (B2) B cell development What happens to an autoreactive B cell? B1 vs B2 cells Key anatomical sites
Overview B cell development Transcriptional cascades Amazing aspects of lineage plasticity Conventional (B2) B cell development What happens to an autoreactive B cell? B1 vs B2 cells Key anatomical sites
Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION
 TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
Chapter 43: The Immune System
 Name Period Our students consider this chapter to be a particularly challenging and important one. Expect to work your way slowly through the first three concepts. Take particular care with Concepts 43.2
Name Period Our students consider this chapter to be a particularly challenging and important one. Expect to work your way slowly through the first three concepts. Take particular care with Concepts 43.2
Immunology. B lymphocytes & Antibodies. 20.10.2014, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, marcus.peters@rub.de
 Immunology B lymphocytes & Antibodies 20.10.2014, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, marcus.peters@rub.de What is an antibody? An antibody is a glycoprotein, which specifically binds to a substance,
Immunology B lymphocytes & Antibodies 20.10.2014, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, marcus.peters@rub.de What is an antibody? An antibody is a glycoprotein, which specifically binds to a substance,
Actions of Hormones on Target Cells Page 1. Actions of Hormones on Target Cells Page 2. Goals/ What You Need to Know Goals What You Need to Know
 Actions of Hormones on Target Cells Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Actions of Hormones on Target Cells Hormones
Actions of Hormones on Target Cells Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Actions of Hormones on Target Cells Hormones
FARMACOLOGIA DEL SISTEMA INMUNE
 FARMACOLOGIA DEL SISTEMA INMUNE Inmunosupresión Inmunoestimulación Medicina Molecular. JM,2008 Las dos caras de Janus INMUNOSUPRESIÓN CICLOSPORINA Jean Francois Borel Scanning electron micrograph of
FARMACOLOGIA DEL SISTEMA INMUNE Inmunosupresión Inmunoestimulación Medicina Molecular. JM,2008 Las dos caras de Janus INMUNOSUPRESIÓN CICLOSPORINA Jean Francois Borel Scanning electron micrograph of
Types, production of antibodies and Antibody/antigen interaction
 Types, production of antibodies and Antibody/antigen interaction Antibodies Secreted by B lymphocytes Great diversity and specificity: >109 different antibodies; can distinguish between very similar molecules
Types, production of antibodies and Antibody/antigen interaction Antibodies Secreted by B lymphocytes Great diversity and specificity: >109 different antibodies; can distinguish between very similar molecules
The immune response Antibodies Antigens Epitopes (antigenic determinants) the part of a protein antigen recognized by an antibody Haptens small
 The immune response Antibodies Antigens Epitopes (antigenic determinants) the part of a protein antigen recognized by an antibody Haptens small molecules that can elicit an immune response when linked
The immune response Antibodies Antigens Epitopes (antigenic determinants) the part of a protein antigen recognized by an antibody Haptens small molecules that can elicit an immune response when linked
Lecture 8. Protein Trafficking/Targeting. Protein targeting is necessary for proteins that are destined to work outside the cytoplasm.
 Protein Trafficking/Targeting (8.1) Lecture 8 Protein Trafficking/Targeting Protein targeting is necessary for proteins that are destined to work outside the cytoplasm. Protein targeting is more complex
Protein Trafficking/Targeting (8.1) Lecture 8 Protein Trafficking/Targeting Protein targeting is necessary for proteins that are destined to work outside the cytoplasm. Protein targeting is more complex
Hapten - a small molecule that is antigenic but not (by itself) immunogenic.
 Chapter 3. Antigens Terminology: Antigen: Substances that can be recognized by the surface antibody (B cells) or by the TCR (T cells) when associated with MHC molecules Immunogenicity VS Antigenicity:
Chapter 3. Antigens Terminology: Antigen: Substances that can be recognized by the surface antibody (B cells) or by the TCR (T cells) when associated with MHC molecules Immunogenicity VS Antigenicity:
2006 7.012 Problem Set 6 KEY
 2006 7.012 Problem Set 6 KEY ** Due before 5 PM on WEDNESDAY, November 22, 2006. ** Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. You create an artificial
2006 7.012 Problem Set 6 KEY ** Due before 5 PM on WEDNESDAY, November 22, 2006. ** Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. You create an artificial
Recognition of T cell epitopes (Abbas Chapter 6)
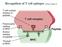 Recognition of T cell epitopes (Abbas Chapter 6) Functions of different APCs (Abbas Chapter 6)!!! Directon Routes of antigen entry (Abbas Chapter 6) Flow of Information Barrier APCs LNs Sequence of Events
Recognition of T cell epitopes (Abbas Chapter 6) Functions of different APCs (Abbas Chapter 6)!!! Directon Routes of antigen entry (Abbas Chapter 6) Flow of Information Barrier APCs LNs Sequence of Events
Mechanism of hormone action
 Mechanism of hormone action ผศ.ดร.พญ.ส ว ฒณ ค ปต ว ฒ ภาคว ชาสร รว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล Aims What is hormone receptor Type of hormone receptors - cell surface receptor - intracellular receptor
Mechanism of hormone action ผศ.ดร.พญ.ส ว ฒณ ค ปต ว ฒ ภาคว ชาสร รว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล Aims What is hormone receptor Type of hormone receptors - cell surface receptor - intracellular receptor
Basics of Immunology
 Basics of Immunology 2 Basics of Immunology What is the immune system? Biological mechanism for identifying and destroying pathogens within a larger organism. Pathogens: agents that cause disease Bacteria,
Basics of Immunology 2 Basics of Immunology What is the immune system? Biological mechanism for identifying and destroying pathogens within a larger organism. Pathogens: agents that cause disease Bacteria,
Autoimmunity and immunemediated. FOCiS. Lecture outline
 1 Autoimmunity and immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails Genetics of autoimmune diseases Therapeutic
1 Autoimmunity and immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails Genetics of autoimmune diseases Therapeutic
Mechanisms of Hormonal Action Bryant Miles
 Mechanisms of ormonal Action Bryant Miles Multicellular organisms need to coordinate metabolic activities. Complex signaling systems have evolved using chemicals called hormones to regulate cellular activities.
Mechanisms of ormonal Action Bryant Miles Multicellular organisms need to coordinate metabolic activities. Complex signaling systems have evolved using chemicals called hormones to regulate cellular activities.
Helices From Readily in Biological Structures
 The α Helix and the β Sheet Are Common Folding Patterns Although the overall conformation each protein is unique, there are only two different folding patterns are present in all proteins, which are α
The α Helix and the β Sheet Are Common Folding Patterns Although the overall conformation each protein is unique, there are only two different folding patterns are present in all proteins, which are α
Control of Gene Expression
 Control of Gene Expression What is Gene Expression? Gene expression is the process by which informa9on from a gene is used in the synthesis of a func9onal gene product. What is Gene Expression? Figure
Control of Gene Expression What is Gene Expression? Gene expression is the process by which informa9on from a gene is used in the synthesis of a func9onal gene product. What is Gene Expression? Figure
Hormones & Chemical Signaling
 Hormones & Chemical Signaling Part 2 modulation of signal pathways and hormone classification & function How are these pathways controlled? Receptors are proteins! Subject to Specificity of binding Competition
Hormones & Chemical Signaling Part 2 modulation of signal pathways and hormone classification & function How are these pathways controlled? Receptors are proteins! Subject to Specificity of binding Competition
Activity 7.21 Transcription factors
 Purpose To consolidate understanding of protein synthesis. To explain the role of transcription factors and hormones in switching genes on and off. Play the transcription initiation complex game Regulation
Purpose To consolidate understanding of protein synthesis. To explain the role of transcription factors and hormones in switching genes on and off. Play the transcription initiation complex game Regulation
Chapter-21b: Hormones and Receptors
 1 hapter-21b: Hormones and Receptors Hormone classes Hormones are classified according to the distance over which they act. 1. Autocrine hormones --- act on the same cell that released them. Interleukin-2
1 hapter-21b: Hormones and Receptors Hormone classes Hormones are classified according to the distance over which they act. 1. Autocrine hormones --- act on the same cell that released them. Interleukin-2
Control of Gene Expression
 Control of Gene Expression (Learning Objectives) Explain the role of gene expression is differentiation of function of cells which leads to the emergence of different tissues, organs, and organ systems
Control of Gene Expression (Learning Objectives) Explain the role of gene expression is differentiation of function of cells which leads to the emergence of different tissues, organs, and organ systems
Final Review. Aptamers. Making Aptamers: SELEX 6/3/2011. sirna and mirna. Central Dogma. RNAi: A translation regulation mechanism.
 Central Dogma Final Review Section Week 10 DNA RNA Protein DNA DNA replication DNA RNA transcription RNA Protein translation **RNA DNA reverse transcription http://bass.bio.uci.edu/~hudel/bs99a/lecture20/lecture1_1.html
Central Dogma Final Review Section Week 10 DNA RNA Protein DNA DNA replication DNA RNA transcription RNA Protein translation **RNA DNA reverse transcription http://bass.bio.uci.edu/~hudel/bs99a/lecture20/lecture1_1.html
THE HUMORAL IMMUNE SYSTEM
 MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology - Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert A. Weinberg, Dr. Claudette Gardel HUMORAL IMMUNOLOGY We are surrounded by a sea of microorganisms
MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology - Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert A. Weinberg, Dr. Claudette Gardel HUMORAL IMMUNOLOGY We are surrounded by a sea of microorganisms
Diabetes and Insulin Signaling
 Diabetes and Insulin Signaling NATIONAL CENTER FOR CASE STUDY TEACHING IN SCIENCE by Kristy J. Wilson School of Mathematics and Sciences Marian University, Indianapolis, IN Part I Research Orientation
Diabetes and Insulin Signaling NATIONAL CENTER FOR CASE STUDY TEACHING IN SCIENCE by Kristy J. Wilson School of Mathematics and Sciences Marian University, Indianapolis, IN Part I Research Orientation
O ρόλος της ακετυλοχολίνης στη σύσπαση και τον πολλαπλασιασµό των ΛΜΚ (του αναπνευστικού) Απ. Χατζηευθυµίου 2015
 O ρόλος της ακετυλοχολίνης στη σύσπαση και τον πολλαπλασιασµό των ΛΜΚ (του αναπνευστικού) Απ. Χατζηευθυµίου 2015 Σύσπαση ΛΜΙ An increase in free intracellular calcium can result from either increased flux
O ρόλος της ακετυλοχολίνης στη σύσπαση και τον πολλαπλασιασµό των ΛΜΚ (του αναπνευστικού) Απ. Χατζηευθυµίου 2015 Σύσπαση ΛΜΙ An increase in free intracellular calcium can result from either increased flux
Corso di Immunologia A.A. 2011-12. Immunoglobuline. Struttura e Funzione
 Corso di Immunologia A.A. 2011-12 Immunoglobuline Struttura e Funzione 1 Definitions Immunoglobulins (Ig) - Glycoprotein molecules which are produced by plasma cells in response to an immunogen and which
Corso di Immunologia A.A. 2011-12 Immunoglobuline Struttura e Funzione 1 Definitions Immunoglobulins (Ig) - Glycoprotein molecules which are produced by plasma cells in response to an immunogen and which
The Use of Antibodies in Immunoassays
 TECHNICAL NOTE The Use of Antibodies in Immunoassays Introduction Structure of an IgG Antibody Immunological reagents are the backbone of every immunoassay system. Immunoassays can be utilized to quantitatively
TECHNICAL NOTE The Use of Antibodies in Immunoassays Introduction Structure of an IgG Antibody Immunological reagents are the backbone of every immunoassay system. Immunoassays can be utilized to quantitatively
Copyright 2000-2003 Mark Brandt, Ph.D. 54
 Pyruvate Oxidation Overview of pyruvate metabolism Pyruvate can be produced in a variety of ways. It is an end product of glycolysis, and can be derived from lactate taken up from the environment (or,
Pyruvate Oxidation Overview of pyruvate metabolism Pyruvate can be produced in a variety of ways. It is an end product of glycolysis, and can be derived from lactate taken up from the environment (or,
Understanding the immune response to bacterial infections
 Understanding the immune response to bacterial infections A Ph.D. (SCIENCE) DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO JADAVPUR UNIVERSITY SUSHIL KUMAR PATHAK DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY BOSE INSTITUTE 2008 CONTENTS Page SUMMARY
Understanding the immune response to bacterial infections A Ph.D. (SCIENCE) DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO JADAVPUR UNIVERSITY SUSHIL KUMAR PATHAK DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY BOSE INSTITUTE 2008 CONTENTS Page SUMMARY
Myoglobin and Hemoglobin
 Myoglobin and Hemoglobin Myoglobin and hemoglobin are hemeproteins whose physiological importance is principally related to their ability to bind molecular oxygen. Myoglobin (Mb) The oxygen storage protein
Myoglobin and Hemoglobin Myoglobin and hemoglobin are hemeproteins whose physiological importance is principally related to their ability to bind molecular oxygen. Myoglobin (Mb) The oxygen storage protein
Module 3 Questions. 7. Chemotaxis is an example of signal transduction. Explain, with the use of diagrams.
 Module 3 Questions Section 1. Essay and Short Answers. Use diagrams wherever possible 1. With the use of a diagram, provide an overview of the general regulation strategies available to a bacterial cell.
Module 3 Questions Section 1. Essay and Short Answers. Use diagrams wherever possible 1. With the use of a diagram, provide an overview of the general regulation strategies available to a bacterial cell.
Lecture Series 7. From DNA to Protein. Genotype to Phenotype. Reading Assignments. A. Genes and the Synthesis of Polypeptides
 Lecture Series 7 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype Reading Assignments Read Chapter 7 From DNA to Protein A. Genes and the Synthesis of Polypeptides Genes are made up of DNA and are expressed
Lecture Series 7 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype Reading Assignments Read Chapter 7 From DNA to Protein A. Genes and the Synthesis of Polypeptides Genes are made up of DNA and are expressed
DNA Replication & Protein Synthesis. This isn t a baaaaaaaddd chapter!!!
 DNA Replication & Protein Synthesis This isn t a baaaaaaaddd chapter!!! The Discovery of DNA s Structure Watson and Crick s discovery of DNA s structure was based on almost fifty years of research by other
DNA Replication & Protein Synthesis This isn t a baaaaaaaddd chapter!!! The Discovery of DNA s Structure Watson and Crick s discovery of DNA s structure was based on almost fifty years of research by other
Chem 465 Biochemistry II
 Chem 465 Biochemistry II Name: 2 points Multiple choice (4 points apiece): 1. Formation of the ribosomal initiation complex for bacterial protein synthesis does not require: A) EF-Tu. B) formylmethionyl
Chem 465 Biochemistry II Name: 2 points Multiple choice (4 points apiece): 1. Formation of the ribosomal initiation complex for bacterial protein synthesis does not require: A) EF-Tu. B) formylmethionyl
INTRODUCTION TO HORMONES
 INTRODUCTION TO HORMONES UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL MBBS II SEMINAR VJ Temple What are hormones? Cells in multi-cellular
INTRODUCTION TO HORMONES UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL MBBS II SEMINAR VJ Temple What are hormones? Cells in multi-cellular
13.2 Ribosomes & Protein Synthesis
 13.2 Ribosomes & Protein Synthesis Introduction: *A specific sequence of bases in DNA carries the directions for forming a polypeptide, a chain of amino acids (there are 20 different types of amino acid).
13.2 Ribosomes & Protein Synthesis Introduction: *A specific sequence of bases in DNA carries the directions for forming a polypeptide, a chain of amino acids (there are 20 different types of amino acid).
Analyzing antibody sequence for recombinant antibody expression. Hangxing Yu, Ph.D Senior Scientist, GenScript May 20, 2015
 Analyzing antibody sequence for recombinant antibody expression Hangxing Yu, Ph.D Senior Scientist, GenScript May 20, 2015 Presentation Outline 1 2 3 4 Antibody basics, structure and function Antibody
Analyzing antibody sequence for recombinant antibody expression Hangxing Yu, Ph.D Senior Scientist, GenScript May 20, 2015 Presentation Outline 1 2 3 4 Antibody basics, structure and function Antibody
From DNA to Protein. Proteins. Chapter 13. Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes. The Path From Genes to Proteins. All proteins consist of polypeptide chains
 Proteins From DNA to Protein Chapter 13 All proteins consist of polypeptide chains A linear sequence of amino acids Each chain corresponds to the nucleotide base sequence of a gene The Path From Genes
Proteins From DNA to Protein Chapter 13 All proteins consist of polypeptide chains A linear sequence of amino acids Each chain corresponds to the nucleotide base sequence of a gene The Path From Genes
Translation Study Guide
 Translation Study Guide This study guide is a written version of the material you have seen presented in the replication unit. In translation, the cell uses the genetic information contained in mrna to
Translation Study Guide This study guide is a written version of the material you have seen presented in the replication unit. In translation, the cell uses the genetic information contained in mrna to
Molecular Genetics. RNA, Transcription, & Protein Synthesis
 Molecular Genetics RNA, Transcription, & Protein Synthesis Section 1 RNA AND TRANSCRIPTION Objectives Describe the primary functions of RNA Identify how RNA differs from DNA Describe the structure and
Molecular Genetics RNA, Transcription, & Protein Synthesis Section 1 RNA AND TRANSCRIPTION Objectives Describe the primary functions of RNA Identify how RNA differs from DNA Describe the structure and
CONTENT. Chapter 1 Review of Literature. List of figures. List of tables
 Abstract Abbreviations List of figures CONTENT I-VI VII-VIII IX-XII List of tables XIII Chapter 1 Review of Literature 1. Vaccination against intracellular pathogens 1-34 1.1 Role of different immune responses
Abstract Abbreviations List of figures CONTENT I-VI VII-VIII IX-XII List of tables XIII Chapter 1 Review of Literature 1. Vaccination against intracellular pathogens 1-34 1.1 Role of different immune responses
Student name ID # 2. (4 pts) What is the terminal electron acceptor in respiration? In photosynthesis? O2, NADP+
 1. Membrane transport. A. (4 pts) What ion couples primary and secondary active transport in animal cells? What ion serves the same function in plant cells? Na+, H+ 2. (4 pts) What is the terminal electron
1. Membrane transport. A. (4 pts) What ion couples primary and secondary active transport in animal cells? What ion serves the same function in plant cells? Na+, H+ 2. (4 pts) What is the terminal electron
ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1. Immunity and Disease
 ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1 Immunity and Disease Introduction The principal role of the mammalian immune response is to contain infectious disease agents. This response is mediated by several cellular and molecular
ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1 Immunity and Disease Introduction The principal role of the mammalian immune response is to contain infectious disease agents. This response is mediated by several cellular and molecular
Ms. Campbell Protein Synthesis Practice Questions Regents L.E.
 Name Student # Ms. Campbell Protein Synthesis Practice Questions Regents L.E. 1. A sequence of three nitrogenous bases in a messenger-rna molecule is known as a 1) codon 2) gene 3) polypeptide 4) nucleotide
Name Student # Ms. Campbell Protein Synthesis Practice Questions Regents L.E. 1. A sequence of three nitrogenous bases in a messenger-rna molecule is known as a 1) codon 2) gene 3) polypeptide 4) nucleotide
The role of IBV proteins in protection: cellular immune responses. COST meeting WG2 + WG3 Budapest, Hungary, 2015
 The role of IBV proteins in protection: cellular immune responses COST meeting WG2 + WG3 Budapest, Hungary, 2015 1 Presentation include: Laboratory results Literature summary Role of T cells in response
The role of IBV proteins in protection: cellular immune responses COST meeting WG2 + WG3 Budapest, Hungary, 2015 1 Presentation include: Laboratory results Literature summary Role of T cells in response
CELL MEMBRANES, TRANSPORT, and COMMUNICATION. Teacher Packet
 AP * BIOLOGY CELL MEMBRANES, TRANSPORT, and COMMUNICATION Teacher Packet AP* is a trademark of the College Entrance Examination Board. The College Entrance Examination Board was not involved in the production
AP * BIOLOGY CELL MEMBRANES, TRANSPORT, and COMMUNICATION Teacher Packet AP* is a trademark of the College Entrance Examination Board. The College Entrance Examination Board was not involved in the production
BSC 2010 - Exam I Lectures and Text Pages. The Plasma Membrane Structure and Function. Phospholipids. I. Intro to Biology (2-29) II.
 BSC 2010 - Exam I Lectures and Text Pages I. Intro to Biology (2-29) II. Chemistry of Life Chemistry review (30-46) Water (47-57) Carbon (58-67) Macromolecules (68-91) III. Cells and Membranes Cell structure
BSC 2010 - Exam I Lectures and Text Pages I. Intro to Biology (2-29) II. Chemistry of Life Chemistry review (30-46) Water (47-57) Carbon (58-67) Macromolecules (68-91) III. Cells and Membranes Cell structure
Modelling and analysis of T-cell epitope screening data.
 Modelling and analysis of T-cell epitope screening data. Tim Beißbarth 2, Jason A. Tye-Din 1, Gordon K. Smyth 1, Robert P. Anderson 1 and Terence P. Speed 1 1 WEHI, 1G Royal Parade, Parkville, VIC 3050,
Modelling and analysis of T-cell epitope screening data. Tim Beißbarth 2, Jason A. Tye-Din 1, Gordon K. Smyth 1, Robert P. Anderson 1 and Terence P. Speed 1 1 WEHI, 1G Royal Parade, Parkville, VIC 3050,
Specific problems. The genetic code. The genetic code. Adaptor molecules match amino acids to mrna codons
 Tutorial II Gene expression: mrna translation and protein synthesis Piergiorgio Percipalle, PhD Program Control of gene transcription and RNA processing mrna translation and protein synthesis KAROLINSKA
Tutorial II Gene expression: mrna translation and protein synthesis Piergiorgio Percipalle, PhD Program Control of gene transcription and RNA processing mrna translation and protein synthesis KAROLINSKA
2007 7.013 Problem Set 1 KEY
 2007 7.013 Problem Set 1 KEY Due before 5 PM on FRIDAY, February 16, 2007. Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. Where in a eukaryotic cell do you
2007 7.013 Problem Set 1 KEY Due before 5 PM on FRIDAY, February 16, 2007. Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. Where in a eukaryotic cell do you
Identification of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients by transcriptome-based rule set generation
 Identification of rheumatoid arthritis and osterthritis patients by transcriptome-based rule set generation Bering Limited Report generated on September 19, 2014 Contents 1 Dataset summary 2 1.1 Project
Identification of rheumatoid arthritis and osterthritis patients by transcriptome-based rule set generation Bering Limited Report generated on September 19, 2014 Contents 1 Dataset summary 2 1.1 Project
B Cells and Antibodies
 LECTURE 3 B Cells and Antibodies REVIEW Let s quickly review the material we covered in the last lecture. We talked about the complement system of proteins, and how complement fragments can function as
LECTURE 3 B Cells and Antibodies REVIEW Let s quickly review the material we covered in the last lecture. We talked about the complement system of proteins, and how complement fragments can function as
AP BIOLOGY 2008 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP BIOLOGY 2008 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 1 1. The physical structure of a protein often reflects and affects its function. (a) Describe THREE types of chemical bonds/interactions found in proteins.
AP BIOLOGY 2008 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 1 1. The physical structure of a protein often reflects and affects its function. (a) Describe THREE types of chemical bonds/interactions found in proteins.
RNA & Protein Synthesis
 RNA & Protein Synthesis Genes send messages to cellular machinery RNA Plays a major role in process Process has three phases (Genetic) Transcription (Genetic) Translation Protein Synthesis RNA Synthesis
RNA & Protein Synthesis Genes send messages to cellular machinery RNA Plays a major role in process Process has three phases (Genetic) Transcription (Genetic) Translation Protein Synthesis RNA Synthesis
Viral Infection: Receptors
 Viral Infection: Receptors Receptors: Identification of receptors has come from expressing the gene for the receptor in a cell to which a virus does not normally bind -OR- By blocking virus attachment
Viral Infection: Receptors Receptors: Identification of receptors has come from expressing the gene for the receptor in a cell to which a virus does not normally bind -OR- By blocking virus attachment
Chapter 3. Protein Structure and Function
 Chapter 3 Protein Structure and Function Broad functional classes So Proteins have structure and function... Fine! -Why do we care to know more???? Understanding functional architechture gives us POWER
Chapter 3 Protein Structure and Function Broad functional classes So Proteins have structure and function... Fine! -Why do we care to know more???? Understanding functional architechture gives us POWER
FAK phospho S732 Antibody, Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
 GenWay Biotech, Inc. 6777 Nancy Ridge Drive San Diego, CA 92121 Tel: (858)458-0866 Fax: (858)458-0833 sales@genwaybio.com FAK phospho S732 Antibody, Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody Catalog Number: 18-272-197354
GenWay Biotech, Inc. 6777 Nancy Ridge Drive San Diego, CA 92121 Tel: (858)458-0866 Fax: (858)458-0833 sales@genwaybio.com FAK phospho S732 Antibody, Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody Catalog Number: 18-272-197354
The Body s Defenses CHAPTER 24
 CHAPTER 24 The Body s Defenses PowerPoint Lectures for Essential Biology, Third Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece, and Eric Simon Essential Biology with Physiology, Second Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece,
CHAPTER 24 The Body s Defenses PowerPoint Lectures for Essential Biology, Third Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece, and Eric Simon Essential Biology with Physiology, Second Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece,
Structure and Function of DNA
 Structure and Function of DNA DNA and RNA Structure DNA and RNA are nucleic acids. They consist of chemical units called nucleotides. The nucleotides are joined by a sugar-phosphate backbone. The four
Structure and Function of DNA DNA and RNA Structure DNA and RNA are nucleic acids. They consist of chemical units called nucleotides. The nucleotides are joined by a sugar-phosphate backbone. The four
BIOM 255 - Firestein, Winter 2009. Rheumatoid arthritis. Page 1
 Rheumatoid arthritis Page 1 Vascular events in RA Synovium in rheumatoid arthritis Non-extra articular RA Extra articular RA Turesson, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007;66:60 Normal Rheumatoid Arthritis Major
Rheumatoid arthritis Page 1 Vascular events in RA Synovium in rheumatoid arthritis Non-extra articular RA Extra articular RA Turesson, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007;66:60 Normal Rheumatoid Arthritis Major
BIO315HF HUMAN CELL BIOLOGY Midterm Test October 26, 2009 100marks 90 minutes Professor Danton H. O Day
 BIO315HF HUMAN CELL BIOLOGY Midterm Test October 26, 2009 100marks 90 minutes Professor Danton H. O Day Part A. Use short, complete phrases to answer the questions (10 marks). 1. As simply and accurately
BIO315HF HUMAN CELL BIOLOGY Midterm Test October 26, 2009 100marks 90 minutes Professor Danton H. O Day Part A. Use short, complete phrases to answer the questions (10 marks). 1. As simply and accurately
Amino Acids. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. All AA s have the same basic structure: Side Chain. Alpha Carbon. Carboxyl. Group.
 Protein Structure Amino Acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. All AA s have the same basic structure: Side Chain Alpha Carbon Amino Group Carboxyl Group Amino Acid Properties There are
Protein Structure Amino Acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. All AA s have the same basic structure: Side Chain Alpha Carbon Amino Group Carboxyl Group Amino Acid Properties There are
Applications of Ab Molecules. Chapter 4 Monoclonal Ab (p.99) Chapter 5 Ab genes and Ab Engineering (p.128)
 Applications of Ab Molecules Chapter 4 Monoclonal Ab (p.99) Chapter 5 Ab genes and Ab Engineering (p.128) Monoclonal Antibodies Clonal Selection of B Lymphocytes Hybridoma Köhler and Milsten (1975) - continuous
Applications of Ab Molecules Chapter 4 Monoclonal Ab (p.99) Chapter 5 Ab genes and Ab Engineering (p.128) Monoclonal Antibodies Clonal Selection of B Lymphocytes Hybridoma Köhler and Milsten (1975) - continuous
The Costimulatory Molecule CD27 Maintains Clonally
 Immunity, Volume 35 Supplemental Information The Costimulatory Molecule CD7 Maintains Clonally Diverse CD8 + T Cell Responses of Low Antigen Affinity to Protect against Viral Variants Klaas P.J.M. van
Immunity, Volume 35 Supplemental Information The Costimulatory Molecule CD7 Maintains Clonally Diverse CD8 + T Cell Responses of Low Antigen Affinity to Protect against Viral Variants Klaas P.J.M. van
NO CALCULATORS OR CELL PHONES ALLOWED
 Biol 205 Exam 1 TEST FORM A Spring 2008 NAME Fill out both sides of the Scantron Sheet. On Side 2 be sure to indicate that you have TEST FORM A The answers to Part I should be placed on the SCANTRON SHEET.
Biol 205 Exam 1 TEST FORM A Spring 2008 NAME Fill out both sides of the Scantron Sheet. On Side 2 be sure to indicate that you have TEST FORM A The answers to Part I should be placed on the SCANTRON SHEET.
T Cell Immunotherapy for Cancer
 T Cell Immunotherapy for Cancer Chimeric Antigen Receptors Targeting Tag-72 Glycoprotein for Colorectal Cancer Mitchell H. Finer Ph.D Genetix Pharmaceuticals Inc Work Completed at Cell Genesys Inc T Cell
T Cell Immunotherapy for Cancer Chimeric Antigen Receptors Targeting Tag-72 Glycoprotein for Colorectal Cancer Mitchell H. Finer Ph.D Genetix Pharmaceuticals Inc Work Completed at Cell Genesys Inc T Cell
Transcription in prokaryotes. Elongation and termination
 Transcription in prokaryotes Elongation and termination After initiation the σ factor leaves the scene. Core polymerase is conducting the elongation of the chain. The core polymerase contains main nucleotide
Transcription in prokaryotes Elongation and termination After initiation the σ factor leaves the scene. Core polymerase is conducting the elongation of the chain. The core polymerase contains main nucleotide
Copyright 2000-2003 Mark Brandt, Ph.D. 93
 Signal transduction In order to interact properly with their environment, cells need to allow information as well as molecules to cross their cell membranes. Information in many single-celled and all multicellular
Signal transduction In order to interact properly with their environment, cells need to allow information as well as molecules to cross their cell membranes. Information in many single-celled and all multicellular
Protein Synthesis How Genes Become Constituent Molecules
 Protein Synthesis Protein Synthesis How Genes Become Constituent Molecules Mendel and The Idea of Gene What is a Chromosome? A chromosome is a molecule of DNA 50% 50% 1. True 2. False True False Protein
Protein Synthesis Protein Synthesis How Genes Become Constituent Molecules Mendel and The Idea of Gene What is a Chromosome? A chromosome is a molecule of DNA 50% 50% 1. True 2. False True False Protein
Idiotypes. Introduction. Structure and Expression of Idiotypes. Advanced article
 Aysegul Uner, Hacettepe University, Ankara, Turkey Jerrie Gavalchin, SUNY Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, New York, USA Idiotypes, the unique and characteristic determinants of an immunoglobulin
Aysegul Uner, Hacettepe University, Ankara, Turkey Jerrie Gavalchin, SUNY Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, New York, USA Idiotypes, the unique and characteristic determinants of an immunoglobulin
Regulation of enzyme activity
 1 Regulation of enzyme activity Regulation of enzyme activity is important to coordinate the different metabolic processes. It is also important for homeostasis i.e. to maintain the internal environment
1 Regulation of enzyme activity Regulation of enzyme activity is important to coordinate the different metabolic processes. It is also important for homeostasis i.e. to maintain the internal environment
Publikationsliste Claudia Götz
 Publikationsliste Claudia Götz 1. Reinhard,B., Götz, C., and Faillard, H.: Synthesis of N-Acetyl-9-Oacetylneuraminic acid α-p-aminophenylthioketoside and its application as ligand in the affinity chromatography
Publikationsliste Claudia Götz 1. Reinhard,B., Götz, C., and Faillard, H.: Synthesis of N-Acetyl-9-Oacetylneuraminic acid α-p-aminophenylthioketoside and its application as ligand in the affinity chromatography
Molecular Cell Biology. Prof. D. Karunagaran. Department of Biotechnology. Indian Institute of Technology Madras. Module 7 Cell Signaling Mechanisms
 Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madras Module 7 Cell Signaling Mechanisms Lecture 2 GPCR Signaling Receptors - G protein coupled receptors
Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madras Module 7 Cell Signaling Mechanisms Lecture 2 GPCR Signaling Receptors - G protein coupled receptors
