The goal of endodontic therapy is the removal of all vital or necrotic tissue, microorganisms,
|
|
|
- Lee Rich
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A High-resolution Computed Tomographic Study of Changes in Root Canal Isthmus Area by Instrumentation and Root Filling Unni Endal, DDS,* Ya Shen, DDS, PhD, Arving Knut, DDS,* Yuan Gao, DDS, PhD, and Markus Haapasalo, DDS, PhD Abstract Introduction: The aim of this study was to obtain a three-dimensional analysis of the isthmus area of the mesiobuccal root canal system in mandibular molars using high-resolution micro computed tomography (m-ct) scanning and to measure the amount of debris and root filling material in the isthmus after instrumentation/irrigation and root filling. Methods: Mandibular molars with two separated mesial root canals (10 teeth) were scanned by using the Skyscan 1172 m-ct system (Skyscan, Aartselaar, Belgium) before and after instrumentation and after filling using the Thermafil root filling technique. An isthmus was defined as the ribbon-shaped or thin connecting structure between two root canals after instrumentation. The characteristics of the isthmuses were quantitatively monitored during the whole treatment. The images were segmented and quantified. The surface area of the isthmus, volume of debris after rotary instrumentation, and volume of the filled space in the isthmus after obturation were evaluated. Results: Of the seven mesial roots, two had isthmus/anastomoses somewhere along its length in the apical 5 mm, and five had an isthmus that was continuous all the way from the coronal part to the apical part. The average percentage of isthmus surface area and isthmus volume after instrumentation was 21.4% and 9.4% of the whole root canal system, respectively. About 35.2% of the isthmus volume was filled with apparent hard tissue debris after instrumentation/irrigation. The average percentage of volume of filling material in the isthmus areas was significantly lower (57.5%) than in the main root canals (98.5%, p < 0.001). Conclusions: A considerable amount of dentin debris is produced and packed into the isthmus area during rotary instrumentation of mesial canals of lower molars despite continuous irrigation during and after instrumentation. The debris may partly prevent penetration of the filling material and sealer into the isthmus area. (J Endod 2011;37: ) Key Words Debris, isthmus, instrumentation, micro computed tomography scanning, root filling The goal of endodontic therapy is the removal of all vital or necrotic tissue, microorganisms, and microbial byproducts from the root canal system. Although this may be achieved through chemomechanical debridement (1), it is difficult to predictably reach this goal (2 4) because of the intricate nature of root canal anatomy (5 7). Isthmuses, fins, webs, and other irregularities within the root canal often harbor tissue, microbes, and debris after instrumentation (8). Instrumentation of the root canal system must always be supported by an irrigation capable of removing pulp tissue remnants and other loose material. The efficacy of an irrigation delivery system is dependent not only on its ability to deliver the irrigant to the apical and noninstrumented regions of the canal space and to create a current strong enough to carry the debris away from the canal systems (9 13) but also on the ability of the irrigating solutions to dissolve both organic and inorganic matter. The effervescence created by conventional irrigation with syringes has been used to remove debris from the root canal although without tissue dissolving ability of the solutions this alone is not effective. Irrigation also is essential for eliminating or reducing the number of bacteria in an infected root canal. There has been increased interest in recent years in the effect of instrumentation and irrigation on the isthmus area. Comparative studies with traditional needle irrigation and irrigation facilitated by ultrasound indicated that complete softtissue removal requires effective ultrasonic agitation of sodium hypochlorite (14). High-resolution micro computed tomography (m-ct) scanning is an emerging technology with several promising applications in different fields of dentistry. In endodontic research, m-ct technology is frequently used for the study of root canal anatomy and for the assessment of changes in root canal morphology by instrumentation (7, 15 21). The quality of root canal obturation has also been investigated by m-ct (22 26), and a few studies have focused on filling of the isthmus area by obturation. Recently, Paque etal(8) showed that dentin debris is formed and packed into the isthmus area during rotary instrumentation. However, no irrigation was used in this study, leaving the question of the role of irrigation in debris retention unanswered. The aim of this study was therefore (1) to examine if dentin debris is packed into the isthmus area of mesial roots of lower molars during rotary instrumentation and vigorous irrigation using high-resolution m-ct scanning; (2) to measure the amount of dentin debris, if any, in the isthmus after instrumentation/irrigation; and (3) to measure the percentage of the volume of the isthmus area filled by gutta-percha coated solid core thermoplastic root filling. From the *Department of Endodontics, University of Oslo, Oslo, Norway; Division of Endodontics, Department of Oral Biological & Medical Sciences, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada; and State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases, West China College & Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China. Address requests for reprints to Markus Haapasalo, Division of Endodontics, Oral Biological & Medical Sciences, UBC Faculty of Dentistry, 2199 Wesbrook Mall, Vancouver, BC, Canada V6T 1Z3. address: markush@interchange.ubc.ca /$ - see front matter Copyright ª 2011 American Association of Endodontists. doi: /j.joen JOE Volume 37, Number 2, February 2011 m-ct Study of Changes in Root Canal Isthmus Area 223
2 Materials and Methods Root Specimens Ten extracted mandibular molars were externally cleaned with pumice and then stored in 0.001% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) before use. The pulp chambers and mesial root canals were accessed conventionally. Size 10 K-type files were inserted through both the mesiobuccal and mesiolingual canals 1 mm beyond the apical foramen (two separated canals all the way to the apex) to establish apical patency. The working length was established 1 mm shorter than the length of the root. The tooth specimens were embedded in acryl, which was then polymerized. Scanning of the embedded teeth was performed with the Skyscan 1172 m-ct system (Skyscan, Aartselaar, Belgium). The canals were prepared with six ProTaper Universal rotary instruments (Dentsply Tulsa Dental Specialties, OK) in the sequence recommended by the manufacturer (S1, S2, F1-F4). Apical enlargement of the root canal was carried out to size F4 (#40, 06 taper); 5% NaOCl was used as the first irrigating solution delivered with a 30-G Max-i- Probe needle (Dentsply-Rinn, Elgin, IL) placed to 1 mm short of working length. Each canal was filled with irrigant during instrumentation. Two milliliters of 5% NaOCl was used to irrigate the canal between each instrument. After completed instrumentation, the canal was irrigated with 10 ml 5% NaOCl for 5 minutes followed by 17% EDTA (5 ml) for 3 min. The tooth specimens were scanned for the second time with the m-ct. Root Filling All canals (14 canals) were fitted with Thermafil ProTaper point (Dentsply Maillefer, Ballaigues, Switzerland) size F4. A Thermaprep oven (Dentsply, Maillefer) was used to soften the gutta-percha on the Thermafil points as recommended by the manufacturer. A thin layer of sealer (AH Plus, Tulsa Dental) was applied to the canal walls with a size 35 paper point (taper.02; Maillefer, Ballaigues, Switzerland) before filling with a size F4 Thermafil point following the manufacturer s instructions. Excess coronal gutta-percha and the plastic handle were removed with a Thermacut bur without water cooling, and the guttapercha was vertically condensed with root canal pluggers (model LM XSi; LM-Dental, Naantali, Finland). Access cavities were sealed with intermediate restorative material (Dentsply Caulk, Milford, DE) and the teeth were stored at 37 C in 100% humidity until being scanned for the third time by the m-ct scanner. m-ct Measurements and Evaluations A commercially available high-resolution Skyscan 1172 m-ct system was used to scan the specimens before and after instrumentation and after obturation. The x-ray tube was operated at 75 kv and 100 ma (0.5 mm Al filter), and the scanning was performed by 360 rotation around the vertical axis and with rotation step of 0.3. The crosssectional pixel size and intersection distance were 11 mm. Subsequently, the cross-section image was reconstructed from the projection image with beam-hardening compensation of 45%. The cross-section images were segmented, registered, visualized, and quantified by using image software from Mevislab (Germany) (available from www. mevislab.de/) (27). The isthmus was defined as the ribbon-shaped or thin structure between the two mesial root canals after preparation. Accordingly, the isthmus was segmented with Mevislab software and the volume and the surface area of the isthmus were calculated. In addition, the following parameters were measured: the volume of debris and the volume of the filled space (by Thermafil and sealer) in the isthmus after instrumentation and obturation, respectively. Three teeth were excluded because of technical errors in scanning (because the samples mounted on stubs were slightly moved during scanning process). The debris in the isthmus after instrumentation was identified and calculated as follows: voxels with black color were identified as soft tissue, liquid, or air (black color) in the preoperative scan; in the second scan, voxels that had changed from black to opaque were assumed to be dentin debris. The unfilled space of the isthmus after filling was identified and calculated as follows: voxels in the isthmus that were identified as soft tissue, liquid, or air (black color) in the preoperative scan and that were not occupied with debris or filling material (bright, opaque color) in the postobturation scan were considered to be the unfilled space of the isthmus. Three-dimensional images of the three stages were generated for visualization. Data were analyzed using a nonparametric test (Mann-Whitney rank sum test). Results Of the seven mesial roots, two had isthmus or anastomoses somewhere in the apical 5 mm of the root, and five had an isthmus that was continuous all the way from the coronal part to the apical part (Figs. 1 and 2). The percentage of isthmus surface area and volume were 21.4% (12%-27%) and 9.4% (3%-15%) of the whole root canal system after instrumentation, respectively (Table 1); 35.2% (13%-56%) of the volume of the isthmus was filled with apparent hard tissue debris after instrumentation/irrigation. The average percentage of the volume of filling material in the isthmus areas was significantly lower (57.5%: 45%-68%) than in the main root canals (98.5%: 97%-99%) (p < 0.001). Discussion The present research used a model that allows for the assessment of changes of the root canal isthmus area caused by instrumentation/ irrigation and root filling. In recent years, the resolution of m-ct has improved considerably from 81 mm (18) and values between 34 and 68 mm (7, 20, 23) to 25 mm (28). At present, axial scanning steps of 14 mm are possible (25, 29). The SkyScan 1172 system could provide nondestructive three-dimensional microscopy of the internal structures of small objects with high spatial resolution and unprecedented speed. The advantage of such a high resolution is a greater accuracy of the rendered images. The main morphologic characteristic of isthmuses in molars is the presence of a fin, web, or ribbon connecting the main root canals. In the present study, the isthmus was defined as a narrow, often ribbon-shaped communication between two root canals after instrumentation. Instrumentation created a round bulge in the main canal, leaving unprepared area(s) between the two mesial canals. Therefore, the consistent definition of boundaries of the isthmus area from m-ct images was possible after instrumentation. A limitation in the present and similar studies is the fact that only hard-tissue debris and filling material can be viewed; the remaining soft tissue is invisible. This is because m-ct scanning is based on radiographic images. Theoretically, it could be possible to obtain indirect evidence of the presence of residual organic/soft tissue in the root canal (eg, a thin line between an opaque root filling material and mineralized dentin might be an indication of soft-tissue debris [or predentin] that remains in the canal space after instrumentation/irrigation and filling). To our knowledge, this is the first study in which accumulation of dentin debris in the isthmus area during rotary instrumentation/irrigation and its relationship to subsequent penetration of filling material have been quantitatively monitored in human teeth. The only previous micro-ct study in which packing of dentin debris by rotary instruments into isthmus and other noninstrumented areas was examined was done without irrigation (8). The main goals of these two studies are different; in the previous study, the goal obviously was to answer a baseline question: do rotary NiTi instruments create debris when cutting dentin and to 224 Endal et al. JOE Volume 37, Number 2, February 2011
3 Figure 1. Three-dimensional reconstruction m-ct scans of the mesial root canal system of the mandibular molar under investigation. (A) The initial canal configuration with the complex isthmus area from its coronal part to the apical part. (B) Corresponding three-dimensional m-ct reconstruction after instrumentation. Prepared canal areas are indicated in green, and untouched areas indicated in red. (C) Superimposition of the apparent accumulated hard-tissue debris areas indicates with silver color. The canal space and empty space in isthmus after instrumentation are indicated in green. (D) Root filling material is indicated in brown, and the nonfilling material area on the ribbon-shaped isthmus is indicated in blue, which includes debris and void. (E-G) A cross-section of mesial root at the (top) middle part and (bottom) apical part: (E) before instrumentation, (F) after instrumentation, and (G) after obturation. discover what happens to this debris in the first place. In order to clarify this basic question, irrigation would have been a confounding factor. In the present study, a step further was taken, and copious amounts of irrigating solutions (NaOCl and EDTA) were used during and after instrumentation before the second scanning was performed. Finally, a thermoplastic root filling method, Thermafil, with recognized, excellent capability to penetrate laterally during compaction into the fine details of the root canal system (ie, lateral canals, fins, and isthmuses) was used to examine the spatial relationship of the original isthmus space and space occupied by the mineral debris and the root filling material. It has been recommended that once canal preparation is completed, the canal should be flushed by means of a small-diameter irrigation needle with a safety tip (side vented), and the tip should be placed in the apical third of the canal (12, 13, 30, 31). The results of the present study show that even copious irrigation during and after instrumentation with solutions dissolving both organic and inorganic matter was not able to prevent or remove the debris packed into the isthmus area between the main root canals. Recently, computational fluid dynamics model (31) recently showed that the fastest flow was found in the turbulent boundary, whereas the minimum velocity was observed on the wall in all root canal irrigations. Fluid stagnation makes adequate irrigant replacement difficult, resulting in gross debris retention especially in apical third area. Hence, it is perhaps not surprising that in the present study irrigation was ineffective in removing debris from the isthmus using syringe irrigation. Despite the current progress in endodontic treatment, cleaning the isthmus with JOE Volume 37, Number 2, February 2011 m-ct Study of Changes in Root Canal Isthmus Area 225
4 Figure 2. Three-dimensional reconstruction m-ct scans of the mesial root canal system of another mandibular molar examined. Legends to images A through G as in Figure 1. nonsurgical methods is still problematic (32). Studies using a new type of ultrasonic device showed that although the addition of 1 minute of ultrasonically activated irrigation after hand/rotary instrumentation significantly increased the isthmus cleanliness values, complete debridement of the isthmuses was not always achieved (33, 34). However, in these studies, the emphasis was on soft-tissue retention and analysis was based on histological sections. Despite obvious difficulties to predictably obtain complete cleanliness, the management of the isthmus area is considered a potentially important factor that may have an impact on the long-term prognosis of nonsurgical endodontic treatment or periapical surgery. A recent case report (35) showed that a complex, variable, multispecies biofilm was present at the entire length of the isthmus in which the tooth had been initially treated 10 years earlier and then retreated 2 years ago. Both gram-positive and gram-negative organisms were detected surviving in an extremely harsh and nutrient-deficient environment that had existed for more than a decade after root canal treatment. Further work using various methods, including m-ct, is required to examine the effect of contemporary irrigant delivery and agitation on cleaning the isthmus and anastomoses between root canals. TABLE 1. The Relative Proportions (expressed as volume %) of Isthmus, Dentin Debris, and Root Filling Material after Instrumentation and Root Filling Isthmus volume of the entire Amount of debris Root filling volume in Root filling material N root canal systems in isthmus isthmus/entire isthmus volume main root canals % * * *There was significant between root filling material in isthmus versus main root canal area (p < 0.001). 226 Endal et al. JOE Volume 37, Number 2, February 2011
5 The incidence of canal isthmuses varies depending on the type of tooth (36), root level (6), and age (37). The incidence of canal isthmuses in first molars ranges from 54% to 89% in mesial roots of mandibular first molars (36, 37). Mannocci et al (38) reported that the prevalence of isthmuses ranged from 17% to 50% in the apical 5 mm of the mesial root of mandibular first molars, with the highest prevalence at the 3-mm level. A recent study (37) showed that the highest prevalence of isthmus is 4 to 6 mm from the apex in mandibular first molars using m-ct scanning. Despite the low number of teeth examined in the present study, these findings are consistent with our results. Complete elimination of microbes from the root canal system is regarded as the prerequisite for optimal long-term prognosis of endodontic treatment. Instrumentation is supposed to create an effective channel for the delivery of irrigating solutions and root filling material. Irrigants play a key role in disinfection of the canal space, and the root filling continues bacterial killing and is supposed to prevent reinfection. Dentin debris formed during instrumentation and soft-tissue remnants, both remaining in the isthmus area and canal anastomoses, prevent root filling material to fully occupy this space and may allow bacteria/biofilm survival. Nutrient deprivation or exhaustion stimulates a starvation response, which allows bacterial long-term persistence in a nongrowing but culturable state (39). Bacteria in the multispecies anaerobic biofilm can be returned to normal physiological state by reestablishing their access to nutrients while still in biofilm (40). Modern understanding of the complexities of the root canal anatomy has made it easier to comprehend that bacteria in such biofilms may well have or later establish a communication with periradicular tissues and compromise healing. With further improvement in m-ct hardware and software, it might be possible in the future to directly determine the amount of biofilm in peripheral parts of the root canal system before and after endodontic treatment (17). Within the limitations of this in vitro study, isthmuses and canal anastomoses had not been completely cleaned and obturated. The accumulation of dentin debris, despite much irrigation, into these areas may play an important role in their incomplete cleaning and filling. Further research is necessary to determine optimal ways to obtain better cleanliness in all parts of the root canal system. References 1. Sj ogren U, Hagglund B, Sundqvist G, et al. Factors affecting the long-term results of endodontic treatment. J Endod 1990;16: Shuping GB, Østravik D, Sigurdsson A, et al. Reduction of intracanal bacteria using nickel-titanium rotary instrumentation and various medications. J Endod 2000;26: Card SJ, Sigurdsson A, Østravik D, et al. The effectiveness of increased apical enlargement in reducing intracanal bacteria. J Endod 2002;28: Fariniuk LF, Baratto-Filho F, da Cruz-Filho AM, et al. Histologic analysis of the cleaning capacity of mechanical endodontic instruments activated by the ENDOflash system. J Endod 2003;29: Skidmore AE, Bjorndal AM. Root canal morphology of the human mandibular first molar. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1971;32: Vertucci FJ. Root canal anatomy of the human permanent teeth. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1984;58: Peters OA, Laib A, R uegsegger P, et al. Three dimensional analysis of root canal geometry using high resolution computed tomography. J Dent Res 2000;79: Paque F, Laib A, Gautschi H, et al. Hard-tissue debris accumulation analysis by highresolution computed tomography scans. J Endod 2009;35: Moser JB, Heuer MA. Forces and efficacy in endodontic irrigation systems. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1982;53: Chow TW. Mechanical effectiveness of root canal irrigation. J Endod 1983;9: Sedgley CM, Nagel AC, Hall D, et al. Influence of irrigant needle depth in removing bioluminescent bacteria inoculated into instrumented root canals using real-time imaging in vitro. Int Endod J 2005;38: Boutsioukis C, Lambrianidis T, Kastrinakis E. Irrigant flow within a prepared root canal using various flow rates: a computational fluid dynamics study. Int Endod J 2009;42: Tay FR, Gu LS, Schoeffel GJ, et al. Effect of vapor lock on root canal debridement by using a side-vented needle for positive-pressure irrigant delivery. J Endod 2010;36: Burleson A, Nusstein J, Reader A, et al. The in vivo evaluation of hand/rotary/ultrasound instrumentation in necrotic, human mandibular molars. J Endod 2007;33: Peters OA, Laib A, Gohring T, et al. Changes in root canal geometry after preparation assessed by high-resolution computed tomography. J Endod 2001;27: Peters OA, Peters CI, Sch unenberger K, et al. ProTaper rotary root canal preparation: effects of canal anatomy on final shape analysed by micro CT. Int Endod J 2003;36: Peters OA, Boessler C, Paque F. Root canal preparation with a novel nickel-titanium instrument evaluated with micro-computed tomography: canal surface preparation over time. J Endod 2010;36: Rhodes JS, Ford TR, Lynch JA, et al. A comparison of two nickel-titanium instrumentation techniques in teeth using microcomputed tomography. Int Endod J 2000;33: Bergmans L, Van Cleynenbreugel J, Beullens M, et al. Progressive versus constant tapered shaft design using NiTi rotary instruments. Int Endod J 2003;36: Gluskin AH, Brown DC, Buchanan LS. A reconstructed computerized tomographic comparison of Ni-Ti rotary GT files versus traditional instruments in canals shaped by novice operators. Int Endodc J 2001;34: Paque F, Balmer M, Attin T, et al. Preparation of oval-shaped root canals in mandibular molars using nickel-titanium rotary instruments: a micro-computed tomography study. J Endod 2010;36: Nielsen RB, Alyassin AM, Peters DD. Microcomputed tomography: an advanced system for detailed endodontic research. J Endod 1995;21: Dowker SE, Davis GR, Elliott JC. X-ray microtomography: nondestructive threedimensional imaging for in vitro endodontic studies. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 1997;83: Jung M, Lommel D, Klimek J. The imaging of root canal obturation using micro-ct. Int Endod J 2005;38: Hammad M, Qualtrough A, Silikas N. Evaluation of root canal obturation: a threedimensional in vitro study. J Endod 2009;35: Mirfendereski M, Roth K, Fan B, et al. Technique acquisition in the use of two thermoplasticized root filling methods by inexperienced dental students: a microcomputed tomography analysis. J Endod 2009;35: Gao Y, Peters OA, Wu H, et al. An application framework of three-dimensional reconstruction and measurement for endodontic research. J Endod 2009;35: Verdonschot N, Fennis WM, Kuijs RH, et al. Generation of 3-D finite element models of restored human teeth using micro-ct techniques. Int J Prosthodont 2001;14: Hammad M, Qualtrough A, Silikas N. Three-dimensional evaluation of effectiveness of hand and rotary instrumentation for retreatment of canals filled with different materials. J Endod 2008;34: Haapasalo M, Shen Y, Qian W, et al. Irrigation in endodontics. Dent Clin North Am 2010;54: Shen Y, Gao Y, Qian W, et al. Three-dimensional numeric simulation of root canal irrigant flow with different irrigation needles. J Endod 2010;36: Kim S, Pecora G, Rubinstein RA. The resected root surface and isthmus. In: Kim S, Pecora G, Rubinstein RA, eds. Color Atlas of Microsurgery in Endodontics. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2001: Gutarts R, Nusstein J, Reader A, et al. In vivo debridement efficacy of ultrasonic irrigation following hand-rotary instrumentation in human mandibular molars. J Endod 2005;31: Burleson A, Nusstein J, Reader A, et al. The in vivo evaluation of hand/rotary/ultrasound instrumentation in necrotic, human mandibular molars. J Endod 2007;33: Carr GB, Schwartz RS, Schaudinn C, et al. Ultrastructural examination of failed molar retreatment with secondary apical periodontitis: an examination of endodontic biofilms in an endodontic retreatment failure. J Endod 2009;35: von Arx T. Frequency and type of canal isthmuses in first molars detected by endoscopic inspection during periradicular surgery. Int Endod J 2005;38: Gu L, Wei X, Ling J, et al. A microcomputed tomographic study of canal isthmuses in the mesial root of mandibular first molars in a Chinese population. J Endod 2009; 35: Mannocci F, Peru M, Sherriff M, et al. The isthmuses of the mesial root of mandibular molars: a micro-computed tomographic study. Int Endod J 2005;38: Oliver JD. The viable but nonculturable state in bacteria. J Microbiol 2005;43: Shen Y, Stojicic S, Haapasalo M. Bacterial viability in starved and revitalized biofilms: comparison of viability staining and direct culture. J Endod 2010;36: JOE Volume 37, Number 2, February 2011 m-ct Study of Changes in Root Canal Isthmus Area 227
The main goal of endodontic therapy is to eradicate all vital and necrotic tissue, microorganisms,
 Efficacy and Safety of Various Active Irrigation Devices When Used with Either Positive or Negative Pressure: An In Vitro Study Augusto Malentacca, MD, DDS,* Umberto Uccioli, DDS, Dario Zangari, DDS,*
Efficacy and Safety of Various Active Irrigation Devices When Used with Either Positive or Negative Pressure: An In Vitro Study Augusto Malentacca, MD, DDS,* Umberto Uccioli, DDS, Dario Zangari, DDS,*
BioRace NiTi system: biologically desirable apical sizes safely and efficiently
 BioRace NiTi system: biologically desirable apical sizes safely and efficiently Dr Martin Trope and Dr Gilberto Debelian explore the BioRace NiTi system, designed to achieve an apical preparation that
BioRace NiTi system: biologically desirable apical sizes safely and efficiently Dr Martin Trope and Dr Gilberto Debelian explore the BioRace NiTi system, designed to achieve an apical preparation that
Removal of a fractured instrument with a new extractor: clinical cases
 Clinical Removal of a fractured instrument with a new extractor: clinical cases Dominique Martin 1 Introduction The fracture of a root canal instrument during endodontic treatment is a surgical accident
Clinical Removal of a fractured instrument with a new extractor: clinical cases Dominique Martin 1 Introduction The fracture of a root canal instrument during endodontic treatment is a surgical accident
EndoActivator from Tulsa Dental
 EndoActivator from Tulsa Dental Irrigation-EndoActivator http://endoactivator.com/video3.html EndoActivator System did not enhance the removal of smear layer as compared with conventional Max-I-Probe irrigation
EndoActivator from Tulsa Dental Irrigation-EndoActivator http://endoactivator.com/video3.html EndoActivator System did not enhance the removal of smear layer as compared with conventional Max-I-Probe irrigation
C-shaped root canal system in mandibular second molars in a Chinese population evaluated by cone-beam computed tomography
 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2011.01896.x C-shaped root canal system in mandibular second molars in a Chinese population evaluated by cone-beam computed tomography Q. Zheng 1, L. Zhang 1, X. Zhou 2, Q. Wang
doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2011.01896.x C-shaped root canal system in mandibular second molars in a Chinese population evaluated by cone-beam computed tomography Q. Zheng 1, L. Zhang 1, X. Zhou 2, Q. Wang
Tooth anatomy risk factors influencing root canal working length accessibility
 Int J Oral Sci (2011) 3: 135-140. www.ijos.org.cn ORIGINAL ARTICLE Tooth anatomy risk factors influencing root canal working length accessibility Lu Tang 1,2, Tuo-qi Sun 1,2, Xiao-jie Gao 1, Xue-dong Zhou
Int J Oral Sci (2011) 3: 135-140. www.ijos.org.cn ORIGINAL ARTICLE Tooth anatomy risk factors influencing root canal working length accessibility Lu Tang 1,2, Tuo-qi Sun 1,2, Xiao-jie Gao 1, Xue-dong Zhou
Introduction. Abstract
 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01108.x The influence of volume, type of irrigant and flushing method on removing artificially placed dentine debris from the apical root canal during passive ultrasonic irrigation
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01108.x The influence of volume, type of irrigant and flushing method on removing artificially placed dentine debris from the apical root canal during passive ultrasonic irrigation
Root Canal Retreatment: 2. Practical Solutions T.R. PITT FORD AND J.S. RHODES
 E N D O D O N T I CE SN D O D O N T I C S Root Canal Retreatment: 2. Practical Solutions T.R. PITT FORD AND J.S. RHODES Abstract: Root canal retreatment is often the preferred method of treating a tooth
E N D O D O N T I CE SN D O D O N T I C S Root Canal Retreatment: 2. Practical Solutions T.R. PITT FORD AND J.S. RHODES Abstract: Root canal retreatment is often the preferred method of treating a tooth
The efficacy of gutta-percha removal using ProFiles
 Blackwell Science, Ltd The efficacy of gutta-percha removal using ProFiles J. J. Ferreira, J. S. Rhodes & T. R. Pitt Ford Department of Conservative Dentistry, Guy s, King s and St. Thomas Dental Institute,
Blackwell Science, Ltd The efficacy of gutta-percha removal using ProFiles J. J. Ferreira, J. S. Rhodes & T. R. Pitt Ford Department of Conservative Dentistry, Guy s, King s and St. Thomas Dental Institute,
Instruction manual. Safe and efficient NiTi rotary system. Fulfilling the biological requirement for successful endodontics
 Instruction manual Safe and efficient NiTi rotary system Fulfilling the biological requirement for successful endodontics FKG REF. - 99.7AA.50.04B.AN - 06/2010 BioRaCe kit 1 Educational CD 1 Endo Stand
Instruction manual Safe and efficient NiTi rotary system Fulfilling the biological requirement for successful endodontics FKG REF. - 99.7AA.50.04B.AN - 06/2010 BioRaCe kit 1 Educational CD 1 Endo Stand
C. Research Proposal 1. Introduction and Specific Aims of the Project 2. Previous Work and Background of the Project
 C. Research Proposal 1. Introduction and Specific Aims of the Project Endodontic success relies on thorough chemomechanical preparation of the root canal system (1-3). Adequate canal debridement is necessary
C. Research Proposal 1. Introduction and Specific Aims of the Project Endodontic success relies on thorough chemomechanical preparation of the root canal system (1-3). Adequate canal debridement is necessary
Location of the apical foramen and its relationship with foraminal file size
 original article Location of the apical foramen and its relationship with foraminal file size Ronaldo Araújo Souza, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 José Antônio Poli de Figueiredo, DDS, MSc, PhD 2 Suely Colombo, DDS 1
original article Location of the apical foramen and its relationship with foraminal file size Ronaldo Araújo Souza, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 José Antônio Poli de Figueiredo, DDS, MSc, PhD 2 Suely Colombo, DDS 1
Analysis of forces developed during root canal filling by different operators
 original article Analysis of forces developed during root canal filling by different operators Maria Rosa Felix de Sousa G. GUIMARÃES, DDS, MSc 1 Henner Alberto GOMIDE, DDS, MSc, PhD 2 Maria Antonieta
original article Analysis of forces developed during root canal filling by different operators Maria Rosa Felix de Sousa G. GUIMARÃES, DDS, MSc 1 Henner Alberto GOMIDE, DDS, MSc, PhD 2 Maria Antonieta
The WaveOne single-file reciprocating system
 I clinical technique _ WaveOne The WaveOne single-file reciprocating system Authors_ Dr Julian Webber, UK; Drs Pierre Machtou & Wilhelm Pertot, France; Drs Sergio Kuttler, Clifford Ruddle & John West,
I clinical technique _ WaveOne The WaveOne single-file reciprocating system Authors_ Dr Julian Webber, UK; Drs Pierre Machtou & Wilhelm Pertot, France; Drs Sergio Kuttler, Clifford Ruddle & John West,
Removal of a silver cone by using clinical microscope and ultrasound: Case report
 original article Removal of a silver cone by using clinical microscope and ultrasound: Case report Maíra do Prado 1 Marcos Cesar Pimenta de Araújo 2 Heloísa Carla Gusman 3 abstract Introduction: The retreatment
original article Removal of a silver cone by using clinical microscope and ultrasound: Case report Maíra do Prado 1 Marcos Cesar Pimenta de Araújo 2 Heloísa Carla Gusman 3 abstract Introduction: The retreatment
Oftentimes, as implant surgeons, we are
 CLINICAL AVOIDING INJURY TO THE INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE BY ROUTINE USE OF INTRAOPERATIVE RADIOGRAPHS DURING IMPLANT PLACEMENT Jeffrey Burstein, DDS, MD; Chris Mastin, DMD; Bach Le, DDS, MD Injury to the
CLINICAL AVOIDING INJURY TO THE INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE BY ROUTINE USE OF INTRAOPERATIVE RADIOGRAPHS DURING IMPLANT PLACEMENT Jeffrey Burstein, DDS, MD; Chris Mastin, DMD; Bach Le, DDS, MD Injury to the
Endodontic treatment with MTA apical plugs: a case report
 325 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 325-329, 2007 Case Report Endodontic treatment with MTA apical plugs: a case report Pari Ghaziani 1), Navid Aghasizadeh 2) and Mahshid Sheikh-Nezami 1) 1) Department
325 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 325-329, 2007 Case Report Endodontic treatment with MTA apical plugs: a case report Pari Ghaziani 1), Navid Aghasizadeh 2) and Mahshid Sheikh-Nezami 1) 1) Department
Jamia Millia Islamia: Performa for CV of Faculty/ Staff Members
 Curriculum Vitae Brief Profile: 1-2 paragraphs (not exceeding 500 words) 1. Name: Vivek Aggarwal 2. Designation: Assistant Professor 3. Office Address: Department of Conservative Dentistry & Endodontics,
Curriculum Vitae Brief Profile: 1-2 paragraphs (not exceeding 500 words) 1. Name: Vivek Aggarwal 2. Designation: Assistant Professor 3. Office Address: Department of Conservative Dentistry & Endodontics,
Review of ultrasonic irrigation in endodontics: increasing action of irrigating solutions
 Journal section: Endodontics Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.17621 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.17621 Review of ultrasonic irrigation in endodontics: increasing action of irrigating
Journal section: Endodontics Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.17621 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.17621 Review of ultrasonic irrigation in endodontics: increasing action of irrigating
Endodontics. Colleagues for Excellence. Access Opening and Canal Location
 Endodontics Colleagues for Excellence Spring 2010 Access Opening and Canal Location Published for the Dental Professional Community by the American Association of Endodontists Cover artwork: Rusty Jones,
Endodontics Colleagues for Excellence Spring 2010 Access Opening and Canal Location Published for the Dental Professional Community by the American Association of Endodontists Cover artwork: Rusty Jones,
ULTRASONIC TREATMENT ENDODONTICE
 ULTRASONIC TREATMENT ENDODONTICE Prof.Dr.Eng.Gheorghe AMZA, Dr. Eng. Oana Elena AMZA, Dr.Eng.Zoia APOSTOLESCU Department of Materials Technology and Welding - University Politehnica of Bucharest Abstract:
ULTRASONIC TREATMENT ENDODONTICE Prof.Dr.Eng.Gheorghe AMZA, Dr. Eng. Oana Elena AMZA, Dr.Eng.Zoia APOSTOLESCU Department of Materials Technology and Welding - University Politehnica of Bucharest Abstract:
Develop a specialist who is capable of correlation of basic sciences and clinical sciences, and challenge the requirements for certification.
 Course Specification Faculty : Dentistry Department : Endodontics Program Specification: Diploma Degree A-Basic Information 1-Programme Title: Diploma in Endodontics 2-Departments (s): Endodontics 4-Coordinator:
Course Specification Faculty : Dentistry Department : Endodontics Program Specification: Diploma Degree A-Basic Information 1-Programme Title: Diploma in Endodontics 2-Departments (s): Endodontics 4-Coordinator:
We gratefully acknowledge our colleagues from ROOTS (www.rxroots.com) Dr. Simon Bender and Dr. Gary Henkel for their help with the text in english.
 1 We gratefully acknowledge our colleagues from ROOTS (www.rxroots.com) Dr. Simon Bender and Dr. Gary Henkel for their help with the text in english., Dr. Roberto Cristescu for your translation into Romanian
1 We gratefully acknowledge our colleagues from ROOTS (www.rxroots.com) Dr. Simon Bender and Dr. Gary Henkel for their help with the text in english., Dr. Roberto Cristescu for your translation into Romanian
Contributions regarding FEM for an ultrasonic endodontic device and his appliance in the root canal treatments
 Contributions regarding FEM for an ultrasonic endodontic device and his appliance in the root canal treatments GHEORGHE AMZA, ROXANA YOLANDA ONEA, OANA ELENA AMZA, VICTOR CARP Department of Materials Technology
Contributions regarding FEM for an ultrasonic endodontic device and his appliance in the root canal treatments GHEORGHE AMZA, ROXANA YOLANDA ONEA, OANA ELENA AMZA, VICTOR CARP Department of Materials Technology
Case Report(s): Uncomplicated Crown Fractures
 Case Report(s): Uncomplicated Crown Fractures Tooth fractures can be classified as follows: Uncomplicated crown fracture = fracture limited to the crown of the tooth with dentin exposure but no pulp exposure.
Case Report(s): Uncomplicated Crown Fractures Tooth fractures can be classified as follows: Uncomplicated crown fracture = fracture limited to the crown of the tooth with dentin exposure but no pulp exposure.
Clinical Efficacy of Three Different Electronic Apex Locators in Comparison with Radiographic Working Length Determination
 Research Article Clinical Efficacy of Three Different Electronic Apex Locators in Comparison with Radiographic Working Length Determination Ayca Yilmaz, (contact author) aycasimsek@gmail.com Selçuk Gokyay
Research Article Clinical Efficacy of Three Different Electronic Apex Locators in Comparison with Radiographic Working Length Determination Ayca Yilmaz, (contact author) aycasimsek@gmail.com Selçuk Gokyay
Universal Endo System Directions for Use. ProTaper
 ProTaper Universal Endo System Directions for Use An instructional DVD is included with your system purchase. Please view this DVD, in addition to reading this booklet, to gain a complete understanding
ProTaper Universal Endo System Directions for Use An instructional DVD is included with your system purchase. Please view this DVD, in addition to reading this booklet, to gain a complete understanding
Cleaning of Oval Canals Using Ultrasonic or Sonic Instrumentation
 0099-2399/93/1909-0453/$03.00/0 JOURNAL OF ENOOOONTICS Copyright 1993 by The American Association of Endoclontists Printed in U.S.A. VOL. 19, No. 9, SEPTEMBER 1993 Cleaning of Oval Canals Using Ultrasonic
0099-2399/93/1909-0453/$03.00/0 JOURNAL OF ENOOOONTICS Copyright 1993 by The American Association of Endoclontists Printed in U.S.A. VOL. 19, No. 9, SEPTEMBER 1993 Cleaning of Oval Canals Using Ultrasonic
Telescopes or loupes have been readily available in
 THE USE OF MAGNIFICATION IN ENDODONTIC THERAPY: THE OPERATING MICROSCOPE Bertrand G. Khayat, DDS, MSD* KHAYAT Clinicians have recognized that the use of magnification can improve the performance of dental
THE USE OF MAGNIFICATION IN ENDODONTIC THERAPY: THE OPERATING MICROSCOPE Bertrand G. Khayat, DDS, MSD* KHAYAT Clinicians have recognized that the use of magnification can improve the performance of dental
Micro-CT for SEM Non-destructive Measurement and Volume Visualization of Specimens Internal Microstructure in SEM Micro-CT Innovation with Integrity
 Micro-CT for SEM Non-destructive Measurement and Volume Visualization of Specimens Internal Microstructure in SEM Innovation with Integrity Micro-CT 3D Microscopy Using Micro-CT for SEM Micro-CT for SEM
Micro-CT for SEM Non-destructive Measurement and Volume Visualization of Specimens Internal Microstructure in SEM Innovation with Integrity Micro-CT 3D Microscopy Using Micro-CT for SEM Micro-CT for SEM
ENDODONTICS. Colleagues for Excellence. The Standard of Practice in Contemporary Endodontics. www.aae.org/colleagues
 ENDODONTICS Colleagues for Excellence Fall 2014 The Standard of Practice in Contemporary Endodontics Published for the Dental Professional Community by the American Association of Endodontists and the
ENDODONTICS Colleagues for Excellence Fall 2014 The Standard of Practice in Contemporary Endodontics Published for the Dental Professional Community by the American Association of Endodontists and the
Rebilda DC. Rebilda Post System. Rebilda
 Rebilda DC Rebilda Post System Rebilda Rebilda DC Systematic coronal build-up reconstruction Nowadays, modern composite and adhesive systems enable the reconstruction of severely damaged teeth, even if
Rebilda DC Rebilda Post System Rebilda Rebilda DC Systematic coronal build-up reconstruction Nowadays, modern composite and adhesive systems enable the reconstruction of severely damaged teeth, even if
The use of ultrasonics (US) or ultrasonic instrumentation was first introduced to
 Ultrasonics in Endodontics: A Review of the Literature Gianluca Plotino, DDS,* Cornelis H. Pameijer, DMD, DSc, PhD, Nicola Maria Grande, DDS,* and Francesco Somma, MD, DDS* Abstract During the past few
Ultrasonics in Endodontics: A Review of the Literature Gianluca Plotino, DDS,* Cornelis H. Pameijer, DMD, DSc, PhD, Nicola Maria Grande, DDS,* and Francesco Somma, MD, DDS* Abstract During the past few
Non-surgical management of a large periapical lesion using a simple aspiration technique: a case report
 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2010.01719.x CASE REPORT Non-surgical management of a large periapical lesion using a simple aspiration technique: a case report M. Fernandes & I. De Ataide Goa Dental College &
doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2010.01719.x CASE REPORT Non-surgical management of a large periapical lesion using a simple aspiration technique: a case report M. Fernandes & I. De Ataide Goa Dental College &
Endodontic treatment outcome is related to treatment expectations of the operator
 Endodontic Treatment Outcome: Survey of Oral Health Care Professionals Ilan Rotstein, DDS,* Robert Salehrabi, DDS,* and Jane L. Forrest, BSDH, MS, EdD Abstract This study assessed the opinion of oral health
Endodontic Treatment Outcome: Survey of Oral Health Care Professionals Ilan Rotstein, DDS,* Robert Salehrabi, DDS,* and Jane L. Forrest, BSDH, MS, EdD Abstract This study assessed the opinion of oral health
A new cone beam computerized tomography system for use in endodontic surgery
 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01198.x CASE REPORT A new cone beam computerized tomography system for use in endodontic surgery T. Tsurumachi 1 & K. Honda 2 1 Department of Endodontics, Division of Advanced
doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01198.x CASE REPORT A new cone beam computerized tomography system for use in endodontic surgery T. Tsurumachi 1 & K. Honda 2 1 Department of Endodontics, Division of Advanced
4-1-2005. Dental Clinical Criteria and Documentation Requirements
 4-1-2005 Dental Clinical Criteria and Documentation Requirements Table of Contents Dental Clinical Criteria Cast Restorations and Veneer Procedures... Pages 1-3 Crown Repair... Page 3 Endodontic Procedures...
4-1-2005 Dental Clinical Criteria and Documentation Requirements Table of Contents Dental Clinical Criteria Cast Restorations and Veneer Procedures... Pages 1-3 Crown Repair... Page 3 Endodontic Procedures...
RICHMOND CROWN - FOR RESTORATION OF BADLY MUTILATED POSTERIOR TEETH - A CASE REPORT
 RICHMOND CROWN - FOR RESTORATION OF BADLY MUTILATED POSTERIOR TEETH - A CASE REPORT 1. Dr. Yadav Chakravarthy, MDS* Professor and Head of The Department. Department of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics
RICHMOND CROWN - FOR RESTORATION OF BADLY MUTILATED POSTERIOR TEETH - A CASE REPORT 1. Dr. Yadav Chakravarthy, MDS* Professor and Head of The Department. Department of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics
BioPure MTAD Antibacterial Root Canal Cleanser Research
 BioPure MTAD Antibacterial Root Canal Cleanser Research ANTIBACTERIAL 1. Torabinejad M, Shabahang S, Aprecio RM, Kettering JD. The antimicrobial effect of MTAD: An in vitro investigation. J Endodon 2003;
BioPure MTAD Antibacterial Root Canal Cleanser Research ANTIBACTERIAL 1. Torabinejad M, Shabahang S, Aprecio RM, Kettering JD. The antimicrobial effect of MTAD: An in vitro investigation. J Endodon 2003;
The Treatment of Traumatic Dental Injuries
 The Recommended Guidelines of the American Association of Endodontists for The Treatment of Traumatic Dental Injuries 2013 American Association of Endodontists Revised 9/13 The Recommended Guidelines of
The Recommended Guidelines of the American Association of Endodontists for The Treatment of Traumatic Dental Injuries 2013 American Association of Endodontists Revised 9/13 The Recommended Guidelines of
Precision Endodontic System. Precision Obturation System. So sophisticated, it s simple
 Precision Endodontic System Precision Obturation System So sophisticated, it s simple The EndoSequence File System and Brasseler USA Obturation Systems Work in Unison to Deliver What You ve Always Wanted
Precision Endodontic System Precision Obturation System So sophisticated, it s simple The EndoSequence File System and Brasseler USA Obturation Systems Work in Unison to Deliver What You ve Always Wanted
Clinical Accuracy of Ipex Apex Locator for Measurement of Root Canal Length of Primary Molars
 Original Article Clinical Accuracy of Ipex Apex Locator for Measurement of Root Canal Length of Primary Molars M. Karami Nogorani 1, M. Zare Jahromi 2, Z. Dehghan 3, R. Talaei 4. 1 Associate Professor,
Original Article Clinical Accuracy of Ipex Apex Locator for Measurement of Root Canal Length of Primary Molars M. Karami Nogorani 1, M. Zare Jahromi 2, Z. Dehghan 3, R. Talaei 4. 1 Associate Professor,
Ando A., Nakamura Y., Kanbara R., Kumano H., Miyata T., Masuda T., Ohno Y. and Tanaka Y.
 11. The Effect of Abutment Tooth Connection with Extracoronal Attachment using the Three Dimensional Finite Element Method - Part 2. The Construction of Finite Element Model from CT Data - Ando A., Nakamura
11. The Effect of Abutment Tooth Connection with Extracoronal Attachment using the Three Dimensional Finite Element Method - Part 2. The Construction of Finite Element Model from CT Data - Ando A., Nakamura
Endo Easy Efficient Sonic Powered Endo Irrigation
 Endo Easy Efficient Sonic Powered Endo Irrigation www.vdw-dental.com Naturally fascinating: gentle, yet powerful In our goal to provide easy and safe products and systems for endodontics which fulfil
Endo Easy Efficient Sonic Powered Endo Irrigation www.vdw-dental.com Naturally fascinating: gentle, yet powerful In our goal to provide easy and safe products and systems for endodontics which fulfil
Perforations are unfortunate complications that occur in the course of endodontic
 Management of Perforations: Four Cases from Two Private Practices with Medium- to Long-term Recalls Marga Ree, DDS, MSc,* and Richard Schwartz, DDS Abstract Introduction: Perforation repair is a fairly
Management of Perforations: Four Cases from Two Private Practices with Medium- to Long-term Recalls Marga Ree, DDS, MSc,* and Richard Schwartz, DDS Abstract Introduction: Perforation repair is a fairly
The Benefits of Using Arap Locator in Root Canal Treatment
 UNSURPASSED ACCURACY UNRIVALED RELIABILITY 1 1. Data on file. Unsurpassed accuracy 1 with convenient, easy-to-read display Fully automatic multifrequency measurements Compact design with small footprint
UNSURPASSED ACCURACY UNRIVALED RELIABILITY 1 1. Data on file. Unsurpassed accuracy 1 with convenient, easy-to-read display Fully automatic multifrequency measurements Compact design with small footprint
Current developments in rotary root canal instrument technology and clinical use: A review
 Current developments in rotary root canal instrument technology and clinical use: A review Ove A. Peters, DMD, MS, PhD 1 /Frank Paqué, Dr Med Dent 2 Rotary root canal instruments manufactured from nickel-titanium
Current developments in rotary root canal instrument technology and clinical use: A review Ove A. Peters, DMD, MS, PhD 1 /Frank Paqué, Dr Med Dent 2 Rotary root canal instruments manufactured from nickel-titanium
MEDICAID DENTAL PROGRAMS CODING, POLICY AND RELATED FEE REVISION INFORMATION
 MEDICAID DENTAL PROGRAMS CODING, POLICY AND RELATED FEE REVISION INFORMATION Effective for dates of service on and after November 1, 2005, the following dental coding, policy and related fee revisions
MEDICAID DENTAL PROGRAMS CODING, POLICY AND RELATED FEE REVISION INFORMATION Effective for dates of service on and after November 1, 2005, the following dental coding, policy and related fee revisions
Revascularization of Immature Permanent Teeth With Apical Periodontitis: New Treatment Protocol?
 JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2004 by The American Association of Endodontists VOL. 30, NO. 4, APRIL 2004 CLINICAL RESEARCH Revascularization of Immature Permanent Teeth With Apical
JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2004 by The American Association of Endodontists VOL. 30, NO. 4, APRIL 2004 CLINICAL RESEARCH Revascularization of Immature Permanent Teeth With Apical
Complications Associated with Tooth Extraction
 1 Complications Associated with Tooth Extraction Mark M. Smith, VMD, DACVS, DAVDC Center for Veterinary Dentistry and Oral Surgery 9041 Gaither Road Gaithersburg, MD 20877 Introduction Tooth extraction
1 Complications Associated with Tooth Extraction Mark M. Smith, VMD, DACVS, DAVDC Center for Veterinary Dentistry and Oral Surgery 9041 Gaither Road Gaithersburg, MD 20877 Introduction Tooth extraction
Root canal treatment by means of electronic conductometry without radiographic transoperative verification: a report of five cases
 original article Root canal treatment by means of electronic conductometry without radiographic transoperative verification: a report of five cases Norberto J. BROON 1 Alvaro CRUZ 2 Claudia A. PALAFOX-SÁNCHEZ
original article Root canal treatment by means of electronic conductometry without radiographic transoperative verification: a report of five cases Norberto J. BROON 1 Alvaro CRUZ 2 Claudia A. PALAFOX-SÁNCHEZ
The present study reports on the application of silver anode in root canals for disinfection of
 Murat AYDIN *, The antibacterial effect of silver anode in root canals Oral Microbiol Immunol Abstract The present study reports on the application of silver anode in root canals for disinfection of infected
Murat AYDIN *, The antibacterial effect of silver anode in root canals Oral Microbiol Immunol Abstract The present study reports on the application of silver anode in root canals for disinfection of infected
Feel the Safety and Control
 e n d o d o n t i c f i l e s L i b e r a t o r N i t i r o t a r y f i l e s Liberator rotary nickel-titanium endodontic files are the result of years of research and development as well as feedback from
e n d o d o n t i c f i l e s L i b e r a t o r N i t i r o t a r y f i l e s Liberator rotary nickel-titanium endodontic files are the result of years of research and development as well as feedback from
Maxillary sinusitis of odontogenic origin: cone-beam volumetric computerized tomography aided diagnosis
 Maxillary sinusitis of odontogenic origin: cone-beam volumetric computerized tomography aided diagnosis Umadevi P. Nair, DMD, MDS, a and Madhu K. Nair, DMD, MS, PhD, b Gainesville, Florida UNIVERSITY OF
Maxillary sinusitis of odontogenic origin: cone-beam volumetric computerized tomography aided diagnosis Umadevi P. Nair, DMD, MDS, a and Madhu K. Nair, DMD, MS, PhD, b Gainesville, Florida UNIVERSITY OF
Mani Silk: A new and novel means of predictable canal shaping
 technique_ instrumentation I Mani Silk: A new and novel means of predictable canal shaping Author_Rich Mounce, DDS _Introduction Irrespective of how a root canal is shaped, the goals of canal shaping remain
technique_ instrumentation I Mani Silk: A new and novel means of predictable canal shaping Author_Rich Mounce, DDS _Introduction Irrespective of how a root canal is shaped, the goals of canal shaping remain
THE VOICE OF TECHNO-CLINICAL DENTISTRY
 May 2009 Vol. 3, No. 2 THE VOICE OF TECHNO-CLINICAL DENTISTRY The Enhanced Restoration of Removables Jim Collis, CDT Patients with existing full or partial dentures often report that they would like to
May 2009 Vol. 3, No. 2 THE VOICE OF TECHNO-CLINICAL DENTISTRY The Enhanced Restoration of Removables Jim Collis, CDT Patients with existing full or partial dentures often report that they would like to
Endodontics. Colleagues for Excellence. Root Canal Irrigants and Disinfectants
 Endodontics Colleagues for Excellence Winter 2011 Winter 2011 Root Canal Irrigants and Disinfectants Published for the Dental Professional Community by the American Association of Endodontists Cover artwork:
Endodontics Colleagues for Excellence Winter 2011 Winter 2011 Root Canal Irrigants and Disinfectants Published for the Dental Professional Community by the American Association of Endodontists Cover artwork:
Straumann Dental Implant System. Implant Selection Guide.
 Straumann Dental Implant System. Implant Selection Guide. STRAUMANN's IMPLANT PORTFOLIO The Straumann Dental Implant System offers two implant lines with diverse body and neck designs ranging from the
Straumann Dental Implant System. Implant Selection Guide. STRAUMANN's IMPLANT PORTFOLIO The Straumann Dental Implant System offers two implant lines with diverse body and neck designs ranging from the
Powertome Assisted Atraumatic Tooth Extraction
 Powertome Assisted Atraumatic Tooth Extraction White et al Jason White, DDS 1 2 3 Abstract Background: While traditional dental extraction techniques encourage minimal trauma, luxated elevation and forceps
Powertome Assisted Atraumatic Tooth Extraction White et al Jason White, DDS 1 2 3 Abstract Background: While traditional dental extraction techniques encourage minimal trauma, luxated elevation and forceps
Micro-CT evaluation of residual material in canals filled with Activ GP or GuttaFlow following removal with NiTi instruments
 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2009.01659.x Micro-CT evaluation of residual material in canals filled with Activ GP or GuttaFlow following removal with NiTi instruments M. J. Roggendorf 1, M. Legner 2, J. Ebert
doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2009.01659.x Micro-CT evaluation of residual material in canals filled with Activ GP or GuttaFlow following removal with NiTi instruments M. J. Roggendorf 1, M. Legner 2, J. Ebert
Eliminating effect of Er, Cr: YSGG laser irradiation on the smear layer of dentin
 Eliminating effect of Er, Cr: YSGG laser irradiation on the smear layer of dentin Jingtao Yu, MD, DDS, and Lu Yan, MD, DDS College of Stomatology, China Medical University, Shenyang, P. R. China Purpose:
Eliminating effect of Er, Cr: YSGG laser irradiation on the smear layer of dentin Jingtao Yu, MD, DDS, and Lu Yan, MD, DDS College of Stomatology, China Medical University, Shenyang, P. R. China Purpose:
Dental Radiography Core Subject. Digital Radiography
 Dental Radiography Core Subject Digital Radiography Aims: To develop an understanding of the history of digital radiography, the different types of digital x-rays and the advantages and disadvantages of
Dental Radiography Core Subject Digital Radiography Aims: To develop an understanding of the history of digital radiography, the different types of digital x-rays and the advantages and disadvantages of
TITLE: Metal-Ceramic and Porcelain Dental Crowns: A Review of Clinical and Cost- Effectiveness
 TITLE: Metal-Ceramic and Porcelain Dental Crowns: A Review of Clinical and Cost- Effectiveness DATE: 23 June 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES: Dental ceramics are widely used to repair damaged teeth and
TITLE: Metal-Ceramic and Porcelain Dental Crowns: A Review of Clinical and Cost- Effectiveness DATE: 23 June 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES: Dental ceramics are widely used to repair damaged teeth and
Postendodontic Tooth Restoration - Part I: The Aim and the Plan of. the procedure.
 Postendodontic Tooth Restoration - Part I: The Aim and the Plan of the Procedure Sanja egoviê 1 Nada GaliÊ 1 Ana Davanzo 2 Boæidar PaveliÊ 1 1 Department of Dental Pathology School of Dental Medicine University
Postendodontic Tooth Restoration - Part I: The Aim and the Plan of the Procedure Sanja egoviê 1 Nada GaliÊ 1 Ana Davanzo 2 Boæidar PaveliÊ 1 1 Department of Dental Pathology School of Dental Medicine University
Dental Services. Dental Centre. HKSH Healthcare Medical Centre Dental Centre. For enquiries and appointments, please contact us
 Dental Services For enquiries and appointments, please contact us HKSH Healthcare Medical Centre Dental Centre Level 22, One Pacific Place 88 Queensway, Hong Kong (852) 2855 6666 (852) 2892 7589 dentalcentre@hksh.com
Dental Services For enquiries and appointments, please contact us HKSH Healthcare Medical Centre Dental Centre Level 22, One Pacific Place 88 Queensway, Hong Kong (852) 2855 6666 (852) 2892 7589 dentalcentre@hksh.com
original article Keywords: Sodium hypochlorite. Chlorhexidine. Calcium hydroxide. Endodontic infection. Root canal medication.
 original article Efficacy of chemo-mechanical preparation with different substances and the use of a root canal medication in dog s teeth with induced periapical lesion Frederico C. Martinho, DDS, MSc
original article Efficacy of chemo-mechanical preparation with different substances and the use of a root canal medication in dog s teeth with induced periapical lesion Frederico C. Martinho, DDS, MSc
Atraumatic Restorative Treatment - ART
 Atraumatic Restorative Treatment - ART Full Summary Description and Use: Atraumatic restorative treatment (ART) is an alternative treatment for dental caries used to emove demineralized and insensitive
Atraumatic Restorative Treatment - ART Full Summary Description and Use: Atraumatic restorative treatment (ART) is an alternative treatment for dental caries used to emove demineralized and insensitive
EFFECT OF PASSIVE ULTRASONIC IRRIGATION ON THE REMOVAL OF ROOT CANAL FILLING DURING RETREATMENT PROCEDURES
 Article Scientifique Scientific Article EFFECT OF PASSIVE ULTRASONIC IRRIGATION ON THE REMOVAL OF ROOT CANAL FILLING DURING RETREATMENT PROCEDURES Khaldoun AL-Naal* Mohammad Rekab** Abstract The aim of
Article Scientifique Scientific Article EFFECT OF PASSIVE ULTRASONIC IRRIGATION ON THE REMOVAL OF ROOT CANAL FILLING DURING RETREATMENT PROCEDURES Khaldoun AL-Naal* Mohammad Rekab** Abstract The aim of
Key words maxillary sinus, posterior teeth roots. Introduction. Tikrit Journal for Dental Sciences 1(2012)81-88
 Tikrit Journal for Dental Sciences 1(2012)81-88 The Relation of Maxillary Posterior Teeth Roots to the Maxillary Sinus Floor Using Panoramic and Computed Tomography Imaging in a Sample of Kurdish People
Tikrit Journal for Dental Sciences 1(2012)81-88 The Relation of Maxillary Posterior Teeth Roots to the Maxillary Sinus Floor Using Panoramic and Computed Tomography Imaging in a Sample of Kurdish People
Classification of dental cements
 Classification of dental cements Type I: Luting agents* that include temporary cements Class 1: powder-liquid -> harden Class 2: paste-paste -> remain soft Type II: Luting agents for permanent applications
Classification of dental cements Type I: Luting agents* that include temporary cements Class 1: powder-liquid -> harden Class 2: paste-paste -> remain soft Type II: Luting agents for permanent applications
Restoring the Endodontically Treated Tooth:Post and Core Design and Material 根 管 治 療 後 牙 齒 的 修 復 :Post and Core 的 設 計 與 材 料
 劉 俊 麟 高 雄 醫 學 大 學 牙 醫 學 系 31 屆 美 國 賓 州 大 學 牙 周 病 學 研 究 所 畢 業 美 國 賓 州 大 學 牙 周 - 補 綴 學 研 究 所 畢 業 美 國 賓 州 大 學 臨 床 副 教 授 美 國 賓 州 大 學 人 工 植 牙 課 程 主 任 Restoring the Endodontically Treated Tooth:Post and Core
劉 俊 麟 高 雄 醫 學 大 學 牙 醫 學 系 31 屆 美 國 賓 州 大 學 牙 周 病 學 研 究 所 畢 業 美 國 賓 州 大 學 牙 周 - 補 綴 學 研 究 所 畢 業 美 國 賓 州 大 學 臨 床 副 教 授 美 國 賓 州 大 學 人 工 植 牙 課 程 主 任 Restoring the Endodontically Treated Tooth:Post and Core
ULTRASONIC and SONIC INSTRUMENTATION FALL SEMESTER 2012
 ULTRASONIC and SONIC INSTRUMENTATION FALL SEMESTER 2012 PRINICPLES OF POWER- DRIVEN INSTRUMENTATION Ultrasonic/sonic and hand instrumentation are both utilized in initial and supportive periodontal therapy
ULTRASONIC and SONIC INSTRUMENTATION FALL SEMESTER 2012 PRINICPLES OF POWER- DRIVEN INSTRUMENTATION Ultrasonic/sonic and hand instrumentation are both utilized in initial and supportive periodontal therapy
Persistent infection in root-filled tooth: an SEM morphological analysis after apical microsurgery
 ISSN: Printed version: 1806-7727 Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2012 Oct-Dec;9(4):463-7 Case Report Article Persistent infection in root-filled tooth: an SEM morphological analysis after apical microsurgery
ISSN: Printed version: 1806-7727 Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2012 Oct-Dec;9(4):463-7 Case Report Article Persistent infection in root-filled tooth: an SEM morphological analysis after apical microsurgery
ACADEMY OF LASER DENTISTRY COMMITTEE ON REGULATORY AFFAIRS TABLE OF CONTENTS
 ACADEMY OF LASER DENTISTRY COMMITTEE ON REGULATORY AFFAIRS INFORMATION PACKET FOR STATE BOARDS OF DENTISTRY May 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Mission Statement of the Academy... 1 2. Position Statement on
ACADEMY OF LASER DENTISTRY COMMITTEE ON REGULATORY AFFAIRS INFORMATION PACKET FOR STATE BOARDS OF DENTISTRY May 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Mission Statement of the Academy... 1 2. Position Statement on
SuperEndo B&L-alpha II Cordless Heat Carrier Operation & Maintenance Instruction Manual
 SuperEndo B&L-alpha II Cordless Heat Carrier Operation & Maintenance Instruction Manual PLEASE READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS PROVIDED FOR THIS DEVICE BEFORE USING IT. Caution: This product should only be used
SuperEndo B&L-alpha II Cordless Heat Carrier Operation & Maintenance Instruction Manual PLEASE READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS PROVIDED FOR THIS DEVICE BEFORE USING IT. Caution: This product should only be used
Full Crown Module: Learner Level 1
 Full Crown Module Restoration / Tooth # Full Gold Crown (FGC) / 30 Extensions: Porcelain Fused to Metal (PFM) / 12 All Ceramic / 8 Learner Level 1 Mastery of Tooth Preparation Estimated Set Up Time: 30
Full Crown Module Restoration / Tooth # Full Gold Crown (FGC) / 30 Extensions: Porcelain Fused to Metal (PFM) / 12 All Ceramic / 8 Learner Level 1 Mastery of Tooth Preparation Estimated Set Up Time: 30
Teeth and Dental Implants: When to save, and when to extract.
 Teeth and Dental Implants: When to save, and when to extract. One of the most difficult decisions a restorative dentist has to make is when to refer a patient for extraction and placement of dental implants.
Teeth and Dental Implants: When to save, and when to extract. One of the most difficult decisions a restorative dentist has to make is when to refer a patient for extraction and placement of dental implants.
CRACKED TOOTH SYNDROME
 CRACKED TOOTH SYNDROME Dr Vijay Salvi We all come across apparently healthy teeth eliciting complex and often bizarre symptoms. The patient will give a long history of undiagnosed but severe pain, and
CRACKED TOOTH SYNDROME Dr Vijay Salvi We all come across apparently healthy teeth eliciting complex and often bizarre symptoms. The patient will give a long history of undiagnosed but severe pain, and
The prevention or healing of endodontic pathology depends on a thorough chemomechanical
 The Radix Entomolaris and Paramolaris: Clinical Approach in Endodontics Filip L. Calberson, DDS, MMS, Roeland J. De Moor, DDS, MMS, PhD, and Christophe A. Deroose, DDS, MMS Abstract Mandibular molars can
The Radix Entomolaris and Paramolaris: Clinical Approach in Endodontics Filip L. Calberson, DDS, MMS, Roeland J. De Moor, DDS, MMS, PhD, and Christophe A. Deroose, DDS, MMS Abstract Mandibular molars can
anatomage table Interactive anatomy study table
 anatomage table Interactive anatomy study table Anatomage offers a unique, life-size interactive anatomy visualization table for the medical community. Anatomage Table offers an unprecedented realistic
anatomage table Interactive anatomy study table Anatomage offers a unique, life-size interactive anatomy visualization table for the medical community. Anatomage Table offers an unprecedented realistic
The use of confocal laser scanning microscopy for the study of dentin infection
 The use of confocal laser scanning microscopy for the study of dentin infection R. Ordinola-Zapata 1, C. Monteiro Bramante 1, I. Gomes de Moraes 1, N. Bernardineli 1, V. Carvalho Porto 2, AP. Campanelli
The use of confocal laser scanning microscopy for the study of dentin infection R. Ordinola-Zapata 1, C. Monteiro Bramante 1, I. Gomes de Moraes 1, N. Bernardineli 1, V. Carvalho Porto 2, AP. Campanelli
Diagnosis, Treatment and Prognosis of Cracked Teeth Iowa Dental Association Annual Session May 6, 2011 Dr. Bruce C. Justman
 Diagnosis, Treatment and Prognosis of Cracked Teeth Iowa Dental Association Annual Session May 6, 2011 Dr. Bruce C. Justman Longitudinal Fractures Types of Longitudinal Fractures Craze Lines Cusp Fracture
Diagnosis, Treatment and Prognosis of Cracked Teeth Iowa Dental Association Annual Session May 6, 2011 Dr. Bruce C. Justman Longitudinal Fractures Types of Longitudinal Fractures Craze Lines Cusp Fracture
ENDODONTOLOGY INTRODUCTION. Original Research ABSTRACT
 Original Research Radiovisiography and ultrasound real time imaging in the differential diagnosis of periapical lesions of endodontic origin A comparative in vivo study SHILPA H. BHANDI * SUBHASH T.S.
Original Research Radiovisiography and ultrasound real time imaging in the differential diagnosis of periapical lesions of endodontic origin A comparative in vivo study SHILPA H. BHANDI * SUBHASH T.S.
DENTAL TRAUMATIC INJURIES
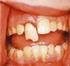 DENTAL TRAUMATIC INJURIES Nitrous Oxide Not Contraindicated Predisposing Factors > 90% of All Injuries Protrusion of Anterior Teeth Poor Lip Coverage Mouthguards Girls as Well as Boys Off - the - Shelf
DENTAL TRAUMATIC INJURIES Nitrous Oxide Not Contraindicated Predisposing Factors > 90% of All Injuries Protrusion of Anterior Teeth Poor Lip Coverage Mouthguards Girls as Well as Boys Off - the - Shelf
Endodontic Treatment Failure Consecutive to Unsystematic Radiographic Examination
 Endodontic Treatment Failure Consecutive to Unsystematic Radiographic Examination Oscar Alonso-Ezpeleta DDS 1, Jenifer Martín-González DDS 2, Milagros Martín-Jiménez DDS 2, Juan J Segura-Egea MD, PhD,
Endodontic Treatment Failure Consecutive to Unsystematic Radiographic Examination Oscar Alonso-Ezpeleta DDS 1, Jenifer Martín-González DDS 2, Milagros Martín-Jiménez DDS 2, Juan J Segura-Egea MD, PhD,
Molar Uprighting Dr. Margherita Santoro Division of Orthodontics School of Dental and Oral surgery. Consequences of tooth loss.
 Molar Uprighting Dr. Margherita Santoro Division of Orthodontics School of Dental and Oral surgery Molars The wide occlusal surface is designed for food grinding. The surface needs to be aligned with the
Molar Uprighting Dr. Margherita Santoro Division of Orthodontics School of Dental and Oral surgery Molars The wide occlusal surface is designed for food grinding. The surface needs to be aligned with the
We make a point of ensuring safety.
 CAD/CAM SYSTEMS INSTRUMENTES HYGIENE SYSTEMS TREATMENT CENTERS IMAGING SYSTEMS INSTRUMENTS FOR EFFICIENT ROOT CANAL TREATMENT We make a point of ensuring safety. T h e D e n t a l C o m p a n y ENDODONTIC
CAD/CAM SYSTEMS INSTRUMENTES HYGIENE SYSTEMS TREATMENT CENTERS IMAGING SYSTEMS INSTRUMENTS FOR EFFICIENT ROOT CANAL TREATMENT We make a point of ensuring safety. T h e D e n t a l C o m p a n y ENDODONTIC
PIPELINE INSPECTION UTILIZING ULTRASOUND TECHNOLOGY: ON THE ISSUE OF RESOLUTION By, M. Beller, NDT Systems & Services AG, Stutensee, Germany
 ABSTRACT: PIPELINE INSPECTION UTILIZING ULTRASOUND TECHNOLOGY: ON THE ISSUE OF RESOLUTION By, M. Beller, NDT Systems & Services AG, Stutensee, Germany Today, in-line inspection tools are used routinely
ABSTRACT: PIPELINE INSPECTION UTILIZING ULTRASOUND TECHNOLOGY: ON THE ISSUE OF RESOLUTION By, M. Beller, NDT Systems & Services AG, Stutensee, Germany Today, in-line inspection tools are used routinely
Universal Crown and Bridge Preparation
 Universal Crown and Bridge Preparation The All-Ceramic Crown Preparation Technique for Predictable Success According to Dr. Ronald E. Goldstein Expect the Best. Buy Direct. The Universal * Crown and Bridge
Universal Crown and Bridge Preparation The All-Ceramic Crown Preparation Technique for Predictable Success According to Dr. Ronald E. Goldstein Expect the Best. Buy Direct. The Universal * Crown and Bridge
Forensic Science: The Basics. Microscopy
 Forensic Science: The Basics Microscopy Chapter 6 Jay A. Siegel,Ph.D. Power point presentation by Greg Galardi, Peru State College, Peru Nebraska Presentation by Greg Galardi, Peru State College CRC Press,
Forensic Science: The Basics Microscopy Chapter 6 Jay A. Siegel,Ph.D. Power point presentation by Greg Galardi, Peru State College, Peru Nebraska Presentation by Greg Galardi, Peru State College CRC Press,
Communication Task - Scenario 1 CANDIDATE COPY
 Communication Task - Scenario 1 Your patient is 30 years old, and has presented today complaining of pain from the lower right posterior side. The tooth had been cold sensitive for several weeks, but the
Communication Task - Scenario 1 Your patient is 30 years old, and has presented today complaining of pain from the lower right posterior side. The tooth had been cold sensitive for several weeks, but the
The Obvious and the Obscure:Diagnostic Steps for Crack Confirmation
 Cracking the Cracked Tooth Code In response to your requests... At the end of each issue of ENDODONTICS: Colleagues for Excellence, the American Association of Endodontists (AAE) asks readers to send in
Cracking the Cracked Tooth Code In response to your requests... At the end of each issue of ENDODONTICS: Colleagues for Excellence, the American Association of Endodontists (AAE) asks readers to send in
INTRAOSSEOUS ANESTHESIA
 ENDODONTICS: Colleagues for Excellence Winter 2009 Bonus Material F INTRAOSSEOUS ANESTHESIA Intraosseous Anesthesia With the Stabident and X Tip Systems The intraosseous injection allows placement of a
ENDODONTICS: Colleagues for Excellence Winter 2009 Bonus Material F INTRAOSSEOUS ANESTHESIA Intraosseous Anesthesia With the Stabident and X Tip Systems The intraosseous injection allows placement of a
Fractional Distillation and Gas Chromatography
 Fractional Distillation and Gas Chromatography Background Distillation The previous lab used distillation to separate a mixture of hexane and toluene based on a difference in boiling points. Hexane boils
Fractional Distillation and Gas Chromatography Background Distillation The previous lab used distillation to separate a mixture of hexane and toluene based on a difference in boiling points. Hexane boils
Air. Air and light. Light
 Air Air and light Light Light and Premiering The best quality light: Excellent visibility even in posterior areas, Cold light (6 000 7 000 K) for better tissue recognition, Ideal for working with loupes,
Air Air and light Light Light and Premiering The best quality light: Excellent visibility even in posterior areas, Cold light (6 000 7 000 K) for better tissue recognition, Ideal for working with loupes,
Ultrasonic Wave Propagation Review
 Ultrasonic Wave Propagation Review Presented by: Sami El-Ali 1 1. Introduction Ultrasonic refers to any study or application of sound waves that are higher frequency than the human audible range. Ultrasonic
Ultrasonic Wave Propagation Review Presented by: Sami El-Ali 1 1. Introduction Ultrasonic refers to any study or application of sound waves that are higher frequency than the human audible range. Ultrasonic
Rochester Regional Health. Dental Plan
 Rochester Regional Health Dental Plan TABLE OF CONTENTS EXPLANATION OF TERMS... 2 INTRODUCTION... 4 DENTAL BENEFITS... 5 DEDUCTIBLES AND COINSURANCE... 7 PRE-TREATMENT ESTIMATES... 8 LIMITATIONS... 8
Rochester Regional Health Dental Plan TABLE OF CONTENTS EXPLANATION OF TERMS... 2 INTRODUCTION... 4 DENTAL BENEFITS... 5 DEDUCTIBLES AND COINSURANCE... 7 PRE-TREATMENT ESTIMATES... 8 LIMITATIONS... 8
Residency Competency and Proficiency Statements
 Residency Competency and Proficiency Statements 1. REQUEST AND RESPOND TO REQUESTS FOR CONSULTATIONS Identify needs and make referrals to appropriate health care providers for the treatment of physiologic,
Residency Competency and Proficiency Statements 1. REQUEST AND RESPOND TO REQUESTS FOR CONSULTATIONS Identify needs and make referrals to appropriate health care providers for the treatment of physiologic,
Instructions and User Guide. Select Series: Vascular Access Ultrasound Training Models BPO100, BPBV110, BPP120, BPNB150. June 8, 2011 Rev 2.
 Instructions and User Guide Select Series: Vascular Access Ultrasound Training Models BPO100, BPBV110, BPP120, BPNB150 June 8, 2011 Rev 2.1 Contents 3 Chapter 1: Overview 3 Giving you the confidence only
Instructions and User Guide Select Series: Vascular Access Ultrasound Training Models BPO100, BPBV110, BPP120, BPNB150 June 8, 2011 Rev 2.1 Contents 3 Chapter 1: Overview 3 Giving you the confidence only
Electronic Apex Locators
 Electronic Apex Locators This material is provided for information and education purposes only. No doctor/patient relationship has been established by the use of this site. No diagnosis or treatment is
Electronic Apex Locators This material is provided for information and education purposes only. No doctor/patient relationship has been established by the use of this site. No diagnosis or treatment is
