How To Control Welded Pipe
|
|
|
- Horatio Miles
- 3 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 INTEGRATED SYSTEM FOR PROCESS CONTROL OF HIGH FREQUENCY ELECTRIC RESISTANCE WELDED STEEL PIPE Esteban Baralla Siat S.A. Tenaris Group Guatemala 3400, (B1822AXZ) Valentín Alsina, Buenos Aires, Argentina Claudio Tommasi Siat S.A. Tenaris Group Guatemala 3400, (B1822AXZ) Valentín Alsina, Buenos Aires, Argentina Abstract. A control system that integrates on-line multichannel ultrasonic inspection and welding parameter monitoring was implemented at Siat s high frequency electric resistance welded (HF-ERW) pipe facilities. The system was developed to correlate on real time basis the welding conditions (welding variables) and the ultrasonic weld indications in order to narrow the process control limits and improve the quality and reliability of the product. Most of Siat s HF-ERW pipes are produced according to API 5L standard plus supplementary client requirements and destined for conveying gas and oil at high pressures. During last years conditions of use of HF-ERW pipes have become increasingly severe: higher pressures, low temperature environments, offshore applications, sour service and high toughness requirements. Consequently customer specifications are more stringent regarding pipe production and quality and process control. The control system was conceived to satisfy client specifications and as a tool to establish relationships among weld ultrasonic indications and welding variables with the aid of metallographic examination. Some cases are shown where the integrated control system proves to be a powerful tool to prevent the occurrence of weld defects, to assist its early detection or to set up the optimum operative window. Keywords. ultrasonic test, high frequency welding, electric resistance welding, process control, steel pipes. 1. Introduction High frequency electric resistance welding (HF-ERW) is one of the most common methods for production of high quality welded carbon steel pipes for conveying gas and oil at high pressures. The widening of the field of application of HF-ERW pipes into more severe environments has been possible due to the progress in the areas of steel making, hot coil rolling and pipe making technology. To keep up with this evolution quality and process control equipment and procedures have also been updated. Most of these pipes are produced according to API 5L Standard plus client supplementary requirements. A typical quality plan shall conform to the following inspections and tests: - Chemical analyses. - Mechanical tests of weld seam and base metal (tensile test, Charpy V-Notch test, flattening test). - Metallographic examination. - Hydrostatic test. - Ultrasonic test of the weld area. - Visual inspection. - Dimensional control. - First day qualification tests. The results of these activities are always recorded pipe by pipe on a computerized system, but many times it is also required the monitoring of process variables in order to get full traceability. The new control system was developed to give an answer to the outstanding quality requirements for HF-ERW pipes. By correlating on real time the welding variables with the results of the on-line ultrasonic inspection it is possible to establish and maintain the optimum welding conditions to get a reliable product. This report describes the features of the integrated control system. 02 a 06 de Junho de 2003 / June 2 to Rio de Janeiro - RJ - Brasil
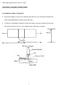
2 2. Description of the integrated control system 2.1. Production of high frequency electric resistance welded pipes Siat produces high frequency electric resistance welded pipes from 114 mm (4 ½ inch) to 610 mm (24 inch) outside diameter. Figure (1) illustrates the production sequence. Figure 1. Flowchart of high frequency electric resistance welding process. Hot rolled coils loaded into the mill are uncoiled and flattened by a leveler. The leading end of the strip, usually of irregular shape, is cut off. If required by the specification, the coil is inspected by ultrasonic test to detect laminations. As the coil proceeds down the line a rotary side trimmer shears the edges to get an accurate width. The skelp goes into the forming mill where it is gradually cold formed to an oval shape. In the forming process the attention is centered on the reduction of edge strains and prevention of edge fluctuation, since it is a key point to assure a stable weld. To make the weld the edges that converge to form a V are continuously heated by the pass of a high frequency current (300 to 400 KHz) and are immediately forged together by a squeeze roll assembly. The material extruded on the inside and outside weld surfaces is removed by scarfing while still hot. Afterwards, the weld seam and heat affected zone undergo a normalizing heat treatment to get a fine grain microstructure of similar characteristics to the base metal. The heat treatment consists in heating by induction the weld area to achieve complete austenization follow by air cooling until the temperature is below 350 C. Downstream, the welded coil goes through the sizing mill to obtain the proper round shape and straightness. After the pipe exits the sizing section 100 % of the weld area is inspected on-line by an automatic ultrasonic equipment. Then the pipes are cut to the required length by the flying cut off and continue to the finishing floor. Every joint is subjected to the following operations and inspections in accordance to the ruling specification: pipe ends beveling, hydrostatic test, bevel ultrasonic inspection to detect laminations, weld ends manual ultrasonic
3 inspection, final automatic ultrasonic inspection of the weld, visual and dimensional control, pipe marking and varnishing or coating depending on client requirements. Finally finished pipes are storage at the pipe yard. The high frequency welding, the weld heat treatment and the on-line weld ultrasonic inspection, highlighted in Fig. (1), are the processes linked by the integrated control system High frequency electric resistance welding process The high frequency current is transmitted by sliding contacts as seen in Fig. (2). The current travels up and down the Vee heating the edges. The squeeze rolls supply the mechanical pressure necessary to forge the edges and produce the weld. There is not addition of filler metal. Figure 2. High frequency electric resistance welding. Figure (3) shows macrographs of the weld area (a) immediately after the squeeze roll centerline: the white line in the center is the weld line, typical of high frequency welding, the sand clock shaped region is the heat affected zone and the black cavities on the outside and inside beads contains the oxides and non-metallic inclusions expelled by forging; (b) in the final condition, after the outside and inside beads have been trimmed and the weld and heat affected zone normalized. a b Figure 3. Macrographs of the weld area: a) Immediately after squeeze rolls, b) final condition after heat treatment. (Pipe size: outside diameter 610 mm, wall thickness 11.9 mm, steel grade API 5L X70) Process control methods for high frequency welding As explained below, different methods are being used by pipe manufacturers for process control purposes Manual control The welding power is adjusted manually by the operator, based on the brightness of the welding zone at the convergence Vee. The method is strongly dependant on the operator judgement and it is not possible to keep the welding variables within narrow limits.
4 Automatic control Several methods or combinations thereof are in use. All of them are based on the automatic adjustment of the welding power in order to keep a target parameter within the preset range. Next there is a brief description of the most common ones. - Heat input control: The heat input is defined as a function of the welding power, the welding speed and the material wall thickness. The target is to maintain the heat input within the desired limits. - Welding temperature control: The welding temperature, measured at the convergence Vee, is a function of the heat input and the electric impedance of the Vee. In this case the welding temperature must be kept within the preset range (Terada et al, 1981; Haga et al, 1985; Mihara et al, 1986). - Control of the welding current frequency: The optimum welding condition may be correlated to the variation of the electric frequency of the welding current. Therefore, the objective is to keep the variation of the welding current frequency within the specified limits (Haga et al, 1985; Watanabe et al, 1986). - Control of the shape of the outside weld bead: It is possible to determine the bead shapes associated to the optimum welding condition. Then the objective is to keep the actual bead shape within the allowable range (Mihara et al, 1986) Integrated control system To establish a control system two questions must be solved. The first one is to determine the optimum range for the welding variables, the second is to keep them within the optimum range. The heat input and the welding temperature control methods have been used successfully at Siat to deal with the second question since the early nineties. The objective of the integrated control system is to give an accurate answer to the first subject. Therefore the welding variables (causes) are related to the results of the ultrasonic inspection (effects) on real time basis as shown in Fig. (4). Welding Variables High Frequency Welding Process Ultrasonic Inspection Results Operative Window Optimization Figure 4. Schematic diagram of the integrated control system. Any indication of the ultrasonic equipment is analyzed against the welding parameters at that exact location. Furthermore, the type and size of the defect or indication may be determined with the aid of metallographic examination, using samples similar to that of Fig. (3.b). Through this feedback procedure it is possible to establish a narrow optimum working range for any of the welding variables On-line weld ultrasonic inspection Siat has been using the ultrasonic test for the weld seam since the middle sixties according to API 5L requirements. At the present time, the on-line ultrasonic equipment is located upstream of the flying cut off, as shown in Fig. (1). Thus 100 % of the weld is continuously inspected along the complete coil, before it is cut to the required joint lengths. The ultrasonic equipment is Krautkramer USIP 20 with 8 channels and 8 cycles. The weld inspection is performed with four 70 degree shear wave probes, or more if required, each of them dedicated to the detection of longitudinal defects by pulse echo mode. Additionally, coupling is controlled between opposite probes by through transmission mode. The amplitude signals from each of the four channels dedicated to defect detection are addressed to four analog outputs and recorded by the integrated control system as a function of the coil position. Whenever the amplitude signal of any of the channels exceeds the corresponding gate threshold an alarm is triggered, the pipe is automatically paint marked at the exact location of the indication an this event is also recorded by the integrated control system. The typical automatic ultrasonic procedure is summarized in Tab. (1).
5 Table 1. Procedure for on-line weld ultrasonic inspection. Item Specification Remarks Equipment Krautkramer USIP 20 8 channels / 8 cycles Probe type Krautkramer W70Z4N Probe frequency: 4 MHz Beam angle: 70 degree Probe arrangement 4 probes, 2 on each side of the weld. Distance (d) from the probe center to the weld centerline Weld Line is set according to the pipe diameter and wall thickness. d Cycle configuration Reference standard Cycle Probe A Mill speed 30 m/min maximum Pulse repetition frequency 1500 to 2000 Hz per cycle Reference signal Cycles 1 to 4: 80 % TSH Cycles 5 and 6: 100 % TSH Gate threshold B C D T R T R T R T R T - - R - - T - - R - - Cycles 1 to 4: 64 % TSH set for coincidence mode Cycles 5 and 6: 50 % TSH set for anticoincidence mode 4 cycles in Pulse / Echo mode for longitudinal defect detection. 2 cycles in Through Transmission mode for coupling control 3.2 mm drilled hole (one on the weld centerline and two 6 mm each side of the weld) and N10 notch (one external and one internal) Depending on distance d Based on 3.2 mm drilled hole. Gain control adjustable in 0.1 db steps. One gate for each cycle. The gate threshold is adjustable in 0.5 % increments and the amplitude evaluation resolution is 0.4 % TSH. The gate start and width are set with the 3.2 mm drilled holes at both sides of the weld. Defect alarm Automatic paint marking and visual alarm Triggered through power outputs. Loss of coupling alarm Visual alarm Triggered through digital outputs Record of signal amplitude For cycles 1 to 4 One analog output per cycle, linked to the integrated control system. The indications of the automatic equipment are checked by manual ultrasonic inspection, calibrated with the same reference standard, in order to evaluate whether they are within the acceptance limits of the applicable specifications or not. Whenever is necessary, samples containing defects are cut and sent to the metallographic laboratory for further analysis in order to diagnose the type and characteristics of the defects.
6 2.6. Examples The following examples correspond to the production of pipes of outside diameter 168 mm, wall thickness 7.1 mm, grade API 5L X42 and are brought out to give a brief overview of the capabilities and limitations of the integrated control system. They help to understand the relationships among the welding conditions, the ultrasonic test results and the type of defects. Example 1: Figure (5) is a photograph of a sample with a defect known as cold weld (API Standard 5T1, 1996), as it is seen after a nick break test. The darkest areas are zones with lack of fusion, while the adjacent metal presents brittle fracture due to inadequate bonding strength. Figure 5. Example 1. Nick break specimen with a cold weld. Figure (6) is a hardcopy of the on-screen presentation for the ultrasonic signal amplitudes and the welding variables for the coil section where the defect of Fig. (5) was found. Ultrasonic indication Signal amplitudes (% TSH) Coil length (m) Welding power (KW) Drop of welding variables Welding speed (m/min) Welding Voltage and Amperage (%) Figure 6. Example1. Records of ultrasonic test results and welding conditions.
7 The upper graph plots the signal amplitudes of each of the four channels used for ultrasonic inspection as a function of the coil length. The header includes information to assure the traceability to the final product, as the production order number, the coil number, the location of the pipe within the coil, the pipe length after being cut by the flying cut off, and the time. The lower graph presents the welding variables also related to the coil length. The cause of the defect is the low heat input condition that results from the sudden drop of the welding power, while the welding speed remains without any significant variation. The ultrasonic graph puts in evidence that the ultrasonic equipment picked up the defect, and triggered the paint marking alarm. This example shows a clearly defined correlation among the elements that form part of the integrated control system and it outlines the basis used for optimization of the working range for the welding variables for different pipe sizes and grades produced during last year since the integrated control system was put into operation. Example 2: Is illustrated by Fig. (7) and Fig. (8). Figure 7. Example 2. Nick break test specimen with lack of fusion. Figure 8. Example 2. Nick break test specimen with the presence of oxides. Both defects were detected by the ultrasonic inspection, but there were not significant variations of the welding parameters. Probably the frequency for data collection of the integrated control system is not enough to keep up with rapid changes in welding variables. The welding speed for this kind of pipe is 14 m/min (230 mm/sec) and the frequency for data collection is 10 Hz. This means an average of one sample every 23 mm, while the defects of Fig. (7) and Fig. (8) have an extension in the longitudinal direction of scarcely 2 mm. Otherwise the defects may arise from foreign causes to the electrical behavior. Further investigation is necessary to adequate the system. Example 3: Shows the results of an experience developed to evaluate the consequences of a poor edge preparation. One of the edges of the coil was intentionally damaged. As welding proceeded there was no change in the welding variables, but the ultrasonic inspection disclosed the defect of Fig. (9). Figure 9. Example 3. Nick break specimen of an edge damaged before welding. It comes out that this kind of defects and some others originated in intrinsic problems of the base material fall outside the scope of the integrated control system. Even though the system is powerful to correlate on real time basis welding conditions and ultrasonic test results, there is still work to do to improve its performance.
8 2.7. Conclusions The integrated control system has been working reliably for almost one year and allows to relate accurately the results of the ultrasonic inspection with the welding conditions. It has proved good efficiency for correlating welding variable deviations to ultrasonic indications being an useful tool to adjust the limits of the operative window for process control. The data acquisition frequency of the system seems not to be capable of recording rapid variations of the welding variables lasting few tenths of a second. This assumption is based in the existence of minor defects detected by ultrasonic inspection, without any significant variations in the welding conditions. Some types of defects are out of the scope the integrated control system like those caused by edge damages or problems inherent to base material, as non metallic inclusions. Finally, even though the integrated control system has been helpful to improve the welding conditions and consequently pipe quality, there is still work to do to extend its field of application Work to be done Investigate the causes of minor defects detected by the ultrasonic test and not explained by deviations in the welding conditions. To deal with this situation the following alternatives are being analyzed: - To increase the frequency for data collection from 10 samples per second that is being used to approximately 100 per second. - To add new variables to the system or combinations of the ones that are being used. - To analyze other causes not related to welding variables and that are out of the scope of the integrated control system. 3. References American Petroleum Institute, 1996, Standard on Imperfection Terminology, API Standard 5T1, Tenth Edition, November Haga, H., Mizuhashi, N., Tanaka, N., Yamada, M., Watanabe, Y. and Hosooka, A., 1985, Automatic Heat Input Control in Production Welding of Médium-Diameter ERW Pipe, Nippon Steel Technical Report N 26 July 1985, pp Mihara, Y., Suzuki, K., Ohkawa, T., Harada, N., Komine, I. and Ishiro, S., 1986, A New Automatic Heat Input Control for Production of Electric Resistance Welded Pipe, Transactions ISIJ, Vol. 26, 1986, pp Terada, T., Yutaka, H., Otano, T., Yoshimoto, Y., Takizawa, S., Fukai, M., Onishi, F. and Yokoyama, E., 1981, Manufacturing of New 26-inch ERW High-Test Line Pipe, Kawasaki Steel Technical Report N 4 December 1981, pp Watanabe, N., Funaki, M., Sanmiya, S., Kosuge, N., Haga, H. and Mizuhashi, N., 1986, An Automatic Power Input Control System in High Frequency Electric Resistance Welding, Transactions ISIJ, Vol. 26, 1986, pp
ASTM A860/A860M-09 Standard Specification for Wrought High Strength. Ferritic Steel Butt Welding Fittings. 1. Scope :- 2. Reference Documents :-
 Standard Specification for Wrought High Strength Ferritic Steel Butt Welding Fittings 1. Scope :- 1.1 This specification covers wrought high strength ferritic steel butt-welding fitting of seamless and
Standard Specification for Wrought High Strength Ferritic Steel Butt Welding Fittings 1. Scope :- 1.1 This specification covers wrought high strength ferritic steel butt-welding fitting of seamless and
JIS G3472 Electric Resistance Welded Carbon Steel Tubes for Automobile Structural Purposes
 JIS G3472 Electric Resistance Welded Carbon Steel Tubes for Automobile Structural Purposes 1. Scope This Japanese Industrial Standard specifies the electric resistance welded carbon steel tubes, hereinafter
JIS G3472 Electric Resistance Welded Carbon Steel Tubes for Automobile Structural Purposes 1. Scope This Japanese Industrial Standard specifies the electric resistance welded carbon steel tubes, hereinafter
Ultrasonic Wave Propagation Review
 Ultrasonic Wave Propagation Review Presented by: Sami El-Ali 1 1. Introduction Ultrasonic refers to any study or application of sound waves that are higher frequency than the human audible range. Ultrasonic
Ultrasonic Wave Propagation Review Presented by: Sami El-Ali 1 1. Introduction Ultrasonic refers to any study or application of sound waves that are higher frequency than the human audible range. Ultrasonic
Phased Array Ultrasonic Inspection Of 25%Cr Super Duplex Stainless Steel. On Subsea Manifold Piping Girth Welds In Lieu Of Radiography
 National Seminar & Exhibition on Non-Destructive Evaluation, NDE 2014, Pune, December 4-6, 2014 (NDE-India 2014) Vol.20 No.6 (June 2015) - The e-journal of Nondestructive Testing - ISSN 1435-4934 www.ndt.net/?id=17866
National Seminar & Exhibition on Non-Destructive Evaluation, NDE 2014, Pune, December 4-6, 2014 (NDE-India 2014) Vol.20 No.6 (June 2015) - The e-journal of Nondestructive Testing - ISSN 1435-4934 www.ndt.net/?id=17866
Application of Welding Standards in Hong Kong. S. K. Babu Laboratory Manager - Foundation Techniques Ltd
 Application of Welding Standards in Hong Kong S. K. Babu Laboratory Manager - Foundation Techniques Ltd Introduction: This paper summarizes the current welding standards practiced in Hong Kong & also outlines
Application of Welding Standards in Hong Kong S. K. Babu Laboratory Manager - Foundation Techniques Ltd Introduction: This paper summarizes the current welding standards practiced in Hong Kong & also outlines
Mechanical Property Changes in Steel during the Pipe Making Process Brent Keil 1
 381 Mechanical Property Changes in Steel during the Pipe Making Process Brent Keil 1 Abstract Welded Steel Pipe (WSP) is arguably the most widely utilized pipe material for the transmission of water throughout
381 Mechanical Property Changes in Steel during the Pipe Making Process Brent Keil 1 Abstract Welded Steel Pipe (WSP) is arguably the most widely utilized pipe material for the transmission of water throughout
Specification for Rotary Drill Stem Elements
 Addendum 1 March 2007 Effective Date: September 1, 2007 Specification for Rotary Drill Stem Elements ANSI/API SPECIFICATION 7-1 FIRST EDITION, MARCH 2006 EFFECTIVE DATE: SEPTEMBER 2006 ISO 10424-1:2004
Addendum 1 March 2007 Effective Date: September 1, 2007 Specification for Rotary Drill Stem Elements ANSI/API SPECIFICATION 7-1 FIRST EDITION, MARCH 2006 EFFECTIVE DATE: SEPTEMBER 2006 ISO 10424-1:2004
NON-DESTRUCTIVE TESTING OF DUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL
 NON-DESTRUCTIVE TESTING OF DUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL AUTHORS: Keith Doughten, District Manager, Magnetic Analysis Corporation, ASNT NDT Level III ET, UT David Bauer, Marketing and Training Manager, Magnetic
NON-DESTRUCTIVE TESTING OF DUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL AUTHORS: Keith Doughten, District Manager, Magnetic Analysis Corporation, ASNT NDT Level III ET, UT David Bauer, Marketing and Training Manager, Magnetic
Lecture slides on rolling By: Dr H N Dhakal Lecturer in Mechanical and Marine Engineering, School of Engineering, University of Plymouth
 Lecture slides on rolling By: Dr H N Dhakal Lecturer in Mechanical and Marine Engineering, School of Engineering, University of Plymouth Bulk deformation forming (rolling) Rolling is the process of reducing
Lecture slides on rolling By: Dr H N Dhakal Lecturer in Mechanical and Marine Engineering, School of Engineering, University of Plymouth Bulk deformation forming (rolling) Rolling is the process of reducing
Handbook on the Ultrasonic Examination. Austenitic Welds
 Handbook on the Ultrasonic Examination Austenitic Welds The International Institute of Welding Edition Handbook On the Ultrasonic Examination of Austenitic Welds Compiled by COMMISSION V Testing, Measurement,
Handbook on the Ultrasonic Examination Austenitic Welds The International Institute of Welding Edition Handbook On the Ultrasonic Examination of Austenitic Welds Compiled by COMMISSION V Testing, Measurement,
IHSS-N1 WELDED HONEYCOMB CORE SPECIFICATION. Generated: Sergiy Papyshev Engineering. Approved: Don Prysi Manufacturing. Approved: Merzuk Ramic Quality
 IHSS-N1 WELDED HONEYCOMB CORE SPECIFICATION Generated: Sergiy Papyshev Engineering Approved: Don Prysi Manufacturing Approved: Merzuk Ramic Quality Approved: Steven Barnett Administrative DATE DATE DATE
IHSS-N1 WELDED HONEYCOMB CORE SPECIFICATION Generated: Sergiy Papyshev Engineering Approved: Don Prysi Manufacturing Approved: Merzuk Ramic Quality Approved: Steven Barnett Administrative DATE DATE DATE
Salzgitter Industrial Supply Chain Concept for Offshore Wind Jackets
 Salzgitter Industrial Supply Chain Concept for Offshore Wind Jackets Cost Reduction Potentials in the Fabrication of Offshore Wind Jackets by Standardized Pipes and Pre-fabricated Components The facts
Salzgitter Industrial Supply Chain Concept for Offshore Wind Jackets Cost Reduction Potentials in the Fabrication of Offshore Wind Jackets by Standardized Pipes and Pre-fabricated Components The facts
TARIFF CODE and updates standard
 TARIFF CODE and updates standard No HS CODE AHTN CODE PRODUCT DESCRIPTION PRODUCT TYPE STANDARDS IDENTIFIED 7207 Semi finished products of iron or non alloy steel Containing by weight less than 0.25% of
TARIFF CODE and updates standard No HS CODE AHTN CODE PRODUCT DESCRIPTION PRODUCT TYPE STANDARDS IDENTIFIED 7207 Semi finished products of iron or non alloy steel Containing by weight less than 0.25% of
ROLLED STAINLESS STEEL PLATES, SECTIONS AND BARS
 STANDARD FOR CERTIFICATION No. 2.9 ROLLED STAINLESS STEEL PLATES, SECTIONS AND BARS OCTOBER 2008 Veritasveien 1, NO-1322 Høvik, Norway Tel.: +47 67 57 99 00 Fax: +47 67 57 99 11 FOREWORD (DNV) is an autonomous
STANDARD FOR CERTIFICATION No. 2.9 ROLLED STAINLESS STEEL PLATES, SECTIONS AND BARS OCTOBER 2008 Veritasveien 1, NO-1322 Høvik, Norway Tel.: +47 67 57 99 00 Fax: +47 67 57 99 11 FOREWORD (DNV) is an autonomous
ADDA FERreport JANUARY 2015
 ADDA FERreport JANUARY 2015 REPORT 2015 PREVIEW COMPLETE TUBE MILL TM8 FOR VIETNAM FABTECH & METAL EXPO 2014 JANUARY 2015 2015 PREVIEW The year 2014 has closed in a positive way for Adda Fer Meccanica,
ADDA FERreport JANUARY 2015 REPORT 2015 PREVIEW COMPLETE TUBE MILL TM8 FOR VIETNAM FABTECH & METAL EXPO 2014 JANUARY 2015 2015 PREVIEW The year 2014 has closed in a positive way for Adda Fer Meccanica,
JIS G3445 Carbon steel tubes for machine structural purposes
 JIS G3445 arbon steel tubes for machine structural purposes 1. Scope This Japanese Industrial Standard specifies the carbon steel tubes, hereinafter referred to as the "tubes", used for machinery, automobiles,
JIS G3445 arbon steel tubes for machine structural purposes 1. Scope This Japanese Industrial Standard specifies the carbon steel tubes, hereinafter referred to as the "tubes", used for machinery, automobiles,
Ultrasonic Reference Blocks
 Ultrasonic Reference Blocks Custom and Standard Test Blocks for Nondestructive Testing Introduction 3 IIW Type 1 Calibration Block 4 Miniature Angle Beam (ROMPAS) Calibration Block 4 Distance Calibration
Ultrasonic Reference Blocks Custom and Standard Test Blocks for Nondestructive Testing Introduction 3 IIW Type 1 Calibration Block 4 Miniature Angle Beam (ROMPAS) Calibration Block 4 Distance Calibration
ULTRASONIC THICKNESS GAUGE TT100/110/120/130
 ULTRASONIC THICKNESS GAUGE TT100/110/120/130 TT100 TT110 Portable size and easy operation Suitable for any metallic and non-metallic materials ultrasonic can go through Self-compensating of nonlinearity
ULTRASONIC THICKNESS GAUGE TT100/110/120/130 TT100 TT110 Portable size and easy operation Suitable for any metallic and non-metallic materials ultrasonic can go through Self-compensating of nonlinearity
PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
 1 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS 1.1 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS Different materials possess different properties in varying degree and therefore behave in different ways under given conditions. These properties
1 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS 1.1 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS Different materials possess different properties in varying degree and therefore behave in different ways under given conditions. These properties
AISI CHEMICAL COMPOSITION LIMITS: Nonresulphurized Carbon Steels
 AISI CHEMICAL COMPOSITION LIMITS: Nonresulphurized Carbon Steels AISI No. 1008 1010 1012 1015 1016 1017 1018 1019 1020 1021 1022 1023 1024 10 1026 1027 1029 10 1035 1036 1037 1038 1039 10 1041 1042 1043
AISI CHEMICAL COMPOSITION LIMITS: Nonresulphurized Carbon Steels AISI No. 1008 1010 1012 1015 1016 1017 1018 1019 1020 1021 1022 1023 1024 10 1026 1027 1029 10 1035 1036 1037 1038 1039 10 1041 1042 1043
JIS G3461 Carbon Steel Tubes for Boiler and Heat Exchanger
 JIS G3461 Carbon Steel Tubes for Boiler and Heat Exchanger 1. Scope This Japanese Industrial Standard specifies the carbon steel tubes, hereinafter referred to as the "tubes", used for exchanging heat
JIS G3461 Carbon Steel Tubes for Boiler and Heat Exchanger 1. Scope This Japanese Industrial Standard specifies the carbon steel tubes, hereinafter referred to as the "tubes", used for exchanging heat
TABLE OF CONTENTS 2 Heavy-Wall Seamless & Welded Carbon Steel Pipe. 4 Alloy Pipe & Tube. 6 Chrome-Moly Pipe. 7 Low-Temp Pipe
 PRODUCT CATALOG TABLE OF CONTENTS 2 Heavy-Wall Seamless & Welded Carbon Steel Pipe 4 Alloy Pipe & Tube 6 Chrome-Moly Pipe 7 Low-Temp Pipe 9 Services amerpipe.com 1.800.316.5737 sales@amerpipe.com 18333
PRODUCT CATALOG TABLE OF CONTENTS 2 Heavy-Wall Seamless & Welded Carbon Steel Pipe 4 Alloy Pipe & Tube 6 Chrome-Moly Pipe 7 Low-Temp Pipe 9 Services amerpipe.com 1.800.316.5737 sales@amerpipe.com 18333
PIPELINE INSPECTION UTILIZING ULTRASOUND TECHNOLOGY: ON THE ISSUE OF RESOLUTION By, M. Beller, NDT Systems & Services AG, Stutensee, Germany
 ABSTRACT: PIPELINE INSPECTION UTILIZING ULTRASOUND TECHNOLOGY: ON THE ISSUE OF RESOLUTION By, M. Beller, NDT Systems & Services AG, Stutensee, Germany Today, in-line inspection tools are used routinely
ABSTRACT: PIPELINE INSPECTION UTILIZING ULTRASOUND TECHNOLOGY: ON THE ISSUE OF RESOLUTION By, M. Beller, NDT Systems & Services AG, Stutensee, Germany Today, in-line inspection tools are used routinely
DIN 17172-78 STEEL PIPES FOR PIPE LINES FOR THE TRANSPORT OF COMBUSTIBLE FLUIDS AND GASES
 DIN 17172-78 STEEL PIPES FOR PIPE LINES FOR THE TRANSPORT OF COMBUSTIBLE FLUIDS AND GASES For connection with the International Draft Standards 3183 and 3845 published by the International Organization
DIN 17172-78 STEEL PIPES FOR PIPE LINES FOR THE TRANSPORT OF COMBUSTIBLE FLUIDS AND GASES For connection with the International Draft Standards 3183 and 3845 published by the International Organization
Structural welding is a process by which the parts that are to be connected are heated and
 CHAPTER 6. WELDED CONNECTIONS 6.1 INTRODUCTORY CONCEPTS Structural welding is a process by which the parts that are to be connected are heated and fused, with supplementary molten metal at the joint. A
CHAPTER 6. WELDED CONNECTIONS 6.1 INTRODUCTORY CONCEPTS Structural welding is a process by which the parts that are to be connected are heated and fused, with supplementary molten metal at the joint. A
NORSOK STANDARD M-650 Edition 4. Qualification of manufacturers of special materials
 Date: 2014-05-30 NORSOK STANDARD M-650 Edition 4 Qualification of manufacturers of special materials A: Frequently Asked Questions FAQ B: Clarification and Comment List NORSOK standard M650 Ed. 4 INTRODUCTION
Date: 2014-05-30 NORSOK STANDARD M-650 Edition 4 Qualification of manufacturers of special materials A: Frequently Asked Questions FAQ B: Clarification and Comment List NORSOK standard M650 Ed. 4 INTRODUCTION
Caps STANDARD WEIGHT Inches / Pounds
 Standard Caps you are here: Home > Weldbend Catalog > Fittings > Caps Caps STANDARD WEIGHT Inches / Pounds For Metric Units >Click Here Nominal Pipe Size Outside Inside Wall Thickness (T) Length (E) Pipe
Standard Caps you are here: Home > Weldbend Catalog > Fittings > Caps Caps STANDARD WEIGHT Inches / Pounds For Metric Units >Click Here Nominal Pipe Size Outside Inside Wall Thickness (T) Length (E) Pipe
GK Packing System Welding Instructions
 GK Packing System Welding Instructions Roxtec GmbH Neuer Höltigbaum 1-3, 22143 Hamburg GERMANY Tel +49 (040) 657398-0, Fax +49 (040) 657398-50 EMAIL info@de.roxtec.com, www.roxtec.de Welding instructions
GK Packing System Welding Instructions Roxtec GmbH Neuer Höltigbaum 1-3, 22143 Hamburg GERMANY Tel +49 (040) 657398-0, Fax +49 (040) 657398-50 EMAIL info@de.roxtec.com, www.roxtec.de Welding instructions
Unit 6: EXTRUSION. Difficult to form metals like stainless steels, nickel based alloys and high temperature metals can also be extruded.
 1 Unit 6: EXTRUSION Introduction: Extrusion is a metal working process in which cross section of metal is reduced by forcing the metal through a die orifice under high pressure. It is used to produce cylindrical
1 Unit 6: EXTRUSION Introduction: Extrusion is a metal working process in which cross section of metal is reduced by forcing the metal through a die orifice under high pressure. It is used to produce cylindrical
Choosing the Proper Nondestructive Testing Techniques
 Choosing the Proper Nondestructive Testing Techniques Donald N. Bugden Magnetic Analysis Corporation, Mt. Vernon, NY, USA Phone: (914) 699-9450, Fax: (914) 699-9837; e-mail: info@mac-ndt.com Abstract This
Choosing the Proper Nondestructive Testing Techniques Donald N. Bugden Magnetic Analysis Corporation, Mt. Vernon, NY, USA Phone: (914) 699-9450, Fax: (914) 699-9837; e-mail: info@mac-ndt.com Abstract This
Field Welding Inspection Guide
 Field Welding Inspection Guide Assistance in interpretation of any specification or questions concerning field welding issues can be obtained from the Office of Materials Management, Structural Welding
Field Welding Inspection Guide Assistance in interpretation of any specification or questions concerning field welding issues can be obtained from the Office of Materials Management, Structural Welding
Health Care for Pipelines From Cradle to Grave
 Health Care for Pipelines From Cradle to Grave By Jim Costain, GE Inspection Technologies Assuring the mechanical integrity of piping systems, whether they be in exploration, transmission, or process plants
Health Care for Pipelines From Cradle to Grave By Jim Costain, GE Inspection Technologies Assuring the mechanical integrity of piping systems, whether they be in exploration, transmission, or process plants
THE STRAIN GAGE PRESSURE TRANSDUCER
 THE STRAIN GAGE PRESSURE TRANSDUCER Pressure transducers use a variety of sensing devices to provide an electrical output proportional to applied pressure. The sensing device employed in the transducers
THE STRAIN GAGE PRESSURE TRANSDUCER Pressure transducers use a variety of sensing devices to provide an electrical output proportional to applied pressure. The sensing device employed in the transducers
APPLICATION NOTE ULTRASONIC CERAMIC TRANSDUCERS
 APPLICATION NOTE ULTRASONIC CERAMIC TRANSDUCERS Selection and use of Ultrasonic Ceramic Transducers The purpose of this application note is to aid the user in the selection and application of the Ultrasonic
APPLICATION NOTE ULTRASONIC CERAMIC TRANSDUCERS Selection and use of Ultrasonic Ceramic Transducers The purpose of this application note is to aid the user in the selection and application of the Ultrasonic
The promise of ultrasonic phased arrays and the role of modeling in specifying systems
 1 modeling in specifying systems ABSTRACT Guillaume Neau and Deborah Hopkins This article illustrates the advantages of phased-array systems and the value of modeling through several examples taken from
1 modeling in specifying systems ABSTRACT Guillaume Neau and Deborah Hopkins This article illustrates the advantages of phased-array systems and the value of modeling through several examples taken from
American Petroleum Institute Purchasing Guidelines Purchase API Spec 7K online at www.api.org/publications
 Purchase API Spec online at www.api.org/publications 7.9.3 Forgings and Castings All repair welding shall be performed in accordance with the manufacturer s written welding specifications. WPSs shall be
Purchase API Spec online at www.api.org/publications 7.9.3 Forgings and Castings All repair welding shall be performed in accordance with the manufacturer s written welding specifications. WPSs shall be
Detection of Pipe Leaks Connection of Pulse Monitoring System in Thermal Utilities
 ZPU MIĘDZYRZECZ PREINSULATED PIPE Detection of Pipe Leaks in Thermal Utilities Assembly Manual Principles of Assembly and Servicing ZAKŁAD PRODUKCYJNO USŁUGOWY Międzyrzecz Polskie Rury Preizolowane Sp.
ZPU MIĘDZYRZECZ PREINSULATED PIPE Detection of Pipe Leaks in Thermal Utilities Assembly Manual Principles of Assembly and Servicing ZAKŁAD PRODUKCYJNO USŁUGOWY Międzyrzecz Polskie Rury Preizolowane Sp.
Phased-Array ROWA-SPA: High-performance testing machine for combined, 100-percent automated testing of square and round bars
 11th European Conference on Non-Destructive Testing (ECNDT 2014), October 6-10, 2014, Prague, Czech Republic Phased-Array ROWA-SPA: High-performance testing machine for combined, 100-percent automated
11th European Conference on Non-Destructive Testing (ECNDT 2014), October 6-10, 2014, Prague, Czech Republic Phased-Array ROWA-SPA: High-performance testing machine for combined, 100-percent automated
SPECIFICATIONS FOR STEEL PIPE
 SPECIFICATIONS FOR STEEL PIPE Published pipe standards serve three functions. 1. They dictate manufacturing and testing requirements and prescribed methods of measuring the required mechanical and physical
SPECIFICATIONS FOR STEEL PIPE Published pipe standards serve three functions. 1. They dictate manufacturing and testing requirements and prescribed methods of measuring the required mechanical and physical
TITANIUM FABRICATION CORP.
 TITANIUM FABRICATION CORP. Titanium, Zirconium, and Tantalum Clad Construction General Considerations In many applications, particularly for large pressure vessels designed for high temperature and pressure,
TITANIUM FABRICATION CORP. Titanium, Zirconium, and Tantalum Clad Construction General Considerations In many applications, particularly for large pressure vessels designed for high temperature and pressure,
Typical TIG-plasma solutions
 Typical -plasma solutions 2228-005 2003-670 Boilers maker solutions 2004-257 1210-064 1210-067 64 3638-008 2008-400 1415-014 2000-169 2003-204 1467-003 2000-343 2000-160 Pipework solutions or plasma welded
Typical -plasma solutions 2228-005 2003-670 Boilers maker solutions 2004-257 1210-064 1210-067 64 3638-008 2008-400 1415-014 2000-169 2003-204 1467-003 2000-343 2000-160 Pipework solutions or plasma welded
High-strength and ultrahigh-strength. Cut sheet from hot-rolled steel strip and heavy plate. voestalpine Steel Division www.voestalpine.
 High-strength and ultrahigh-strength TM steels Cut sheet from hot-rolled steel strip and heavy plate Josef Elmer, Key account manager voestalpine Steel Division www.voestalpine.com/steel Weight savings
High-strength and ultrahigh-strength TM steels Cut sheet from hot-rolled steel strip and heavy plate Josef Elmer, Key account manager voestalpine Steel Division www.voestalpine.com/steel Weight savings
Reproduced with the permission of the American Welding Society (AWS), Miami, Florida - 09/15/2011. 7. Stud Welding
 7. Stud Welding 7.1 Scope Section 7 contains general requirements for welding steel studs to steel (see 7.2.7 and 1.2.2 for approved steels). In addition, it stipulates specific requirements for the following:
7. Stud Welding 7.1 Scope Section 7 contains general requirements for welding steel studs to steel (see 7.2.7 and 1.2.2 for approved steels). In addition, it stipulates specific requirements for the following:
Fundamentals of Extrusion
 CHAPTER1 Fundamentals of Extrusion The first chapter of this book discusses the fundamentals of extrusion technology, including extrusion principles, processes, mechanics, and variables and their effects
CHAPTER1 Fundamentals of Extrusion The first chapter of this book discusses the fundamentals of extrusion technology, including extrusion principles, processes, mechanics, and variables and their effects
Objective To conduct Charpy V-notch impact test and determine the ductile-brittle transition temperature of steels.
 IMPACT TESTING Objective To conduct Charpy V-notch impact test and determine the ductile-brittle transition temperature of steels. Equipment Coolants Standard Charpy V-Notched Test specimens Impact tester
IMPACT TESTING Objective To conduct Charpy V-notch impact test and determine the ductile-brittle transition temperature of steels. Equipment Coolants Standard Charpy V-Notched Test specimens Impact tester
The Suitability of CRA Lined Pipes for Flowlines Susceptible to Lateral Buckling SUT Global Pipeline Buckling Symposium, 23 24 February 2011
 The Suitability of CRA Lined Pipes for Flowlines Susceptible to Lateral Buckling SUT Global Pipeline Buckling Symposium, 23 24 February 2011 Duncan Wilmot, Technical Manager, Cladtek International, Australia
The Suitability of CRA Lined Pipes for Flowlines Susceptible to Lateral Buckling SUT Global Pipeline Buckling Symposium, 23 24 February 2011 Duncan Wilmot, Technical Manager, Cladtek International, Australia
Application Specification SIAMEZE * Standard and 114-13166 Fine Range Terminals 18 Mar 11 Rev C
 Application Specification SIAMEZE * Standard and 4-66 Fine Range Terminals 8 Mar Rev C NOTE i All numerical values are in metric units [with U.S. customary units in brackets]. Dimensions are in millimeters
Application Specification SIAMEZE * Standard and 4-66 Fine Range Terminals 8 Mar Rev C NOTE i All numerical values are in metric units [with U.S. customary units in brackets]. Dimensions are in millimeters
Ultrasonic Testing of Spot Welds in the Automotive Industry
 Ultrasonic Testing of Spot Welds in the Automotive Industry Werner Roye Krautkrämer GmbH & Co. ohg, Hürth Summary In the modern motorcar production, more than 300 deep-drawn sheet metal parts are joined
Ultrasonic Testing of Spot Welds in the Automotive Industry Werner Roye Krautkrämer GmbH & Co. ohg, Hürth Summary In the modern motorcar production, more than 300 deep-drawn sheet metal parts are joined
Introduction. ε 1 θ=55 ε 2. Localized necking Because ν=0.5 in plasticity, ε 1 =-2ε 2 =-2ε 3. ε 3,ε 2
 SHEET METALWORKING 1. Cutting Operation 2. Bending Operation 3. Drawing 4. Other Sheet-metal Forming 5. Dies and Presses 6. Sheet-metal Operation 7. Bending of Tube Stock 1 Introduction Cutting and forming
SHEET METALWORKING 1. Cutting Operation 2. Bending Operation 3. Drawing 4. Other Sheet-metal Forming 5. Dies and Presses 6. Sheet-metal Operation 7. Bending of Tube Stock 1 Introduction Cutting and forming
4 Installation Requirements
 4 Installation Requirements 9 4.1 Code Reference The authority having jurisdiction should be referenced to determine what law, ordinance or code shall apply in the use of flexible duct. Ducts conforming
4 Installation Requirements 9 4.1 Code Reference The authority having jurisdiction should be referenced to determine what law, ordinance or code shall apply in the use of flexible duct. Ducts conforming
Instruction Manual Service Program ULTRA-PROG-IR
 Instruction Manual Service Program ULTRA-PROG-IR Parameterizing Software for Ultrasonic Sensors with Infrared Interface Contents 1 Installation of the Software ULTRA-PROG-IR... 4 1.1 System Requirements...
Instruction Manual Service Program ULTRA-PROG-IR Parameterizing Software for Ultrasonic Sensors with Infrared Interface Contents 1 Installation of the Software ULTRA-PROG-IR... 4 1.1 System Requirements...
North American Stainless
 North American Stainless Flat Products Stainless Steel Grade Sheet 430 (S43000)/ EN 1.4016 Introduction: SS430 is a low-carbon plain chromium, ferritic stainless steel without any stabilization of carbon
North American Stainless Flat Products Stainless Steel Grade Sheet 430 (S43000)/ EN 1.4016 Introduction: SS430 is a low-carbon plain chromium, ferritic stainless steel without any stabilization of carbon
DSM http://www.dsmmfg.com 1 (800) 886-6376
 DESIGN GUIDE FOR BENT SHEET METAL This guide discusses how the bends are made, what thicknesses of sheet metal are commonly used, recommended bend radius to use when modeling the part, some practical limits
DESIGN GUIDE FOR BENT SHEET METAL This guide discusses how the bends are made, what thicknesses of sheet metal are commonly used, recommended bend radius to use when modeling the part, some practical limits
CONTRACT SPECIFICATIONS - SEISMIC ISOLATION BEARINGS
 CONTRACT SPECIFICATIONS - SEISMIC ISOLATION BEARINGS 1.0 DESIGN 1.1 Scope of Work 1.1.1 This work shall consist of furnishing Isolation Bearings and installing Isolation Bearing Assemblies at the locations
CONTRACT SPECIFICATIONS - SEISMIC ISOLATION BEARINGS 1.0 DESIGN 1.1 Scope of Work 1.1.1 This work shall consist of furnishing Isolation Bearings and installing Isolation Bearing Assemblies at the locations
CHAPTER 11: Flip Flops
 CHAPTER 11: Flip Flops In this chapter, you will be building the part of the circuit that controls the command sequencing. The required circuit must operate the counter and the memory chip. When the teach
CHAPTER 11: Flip Flops In this chapter, you will be building the part of the circuit that controls the command sequencing. The required circuit must operate the counter and the memory chip. When the teach
General Allowances for Insulation & Cladding
 TRADE OF Industrial Insulation PHASE 2 Module 1 Sheet Metal and Insulation Fundamentals UNIT: 4 General Allowances for Insulation & Cladding Produced by In cooperation with subject matter expert: Michael
TRADE OF Industrial Insulation PHASE 2 Module 1 Sheet Metal and Insulation Fundamentals UNIT: 4 General Allowances for Insulation & Cladding Produced by In cooperation with subject matter expert: Michael
Weld Cracking. An Excerpt from The Fabricators' and Erectors' Guide to Welded Steel Construction. The James F. Lincoln Arc Welding Foundation
 Weld Cracking An Excerpt from The Fabricators' and Erectors' Guide to Welded Steel Construction The James F. Lincoln Arc Welding Foundation Weld Cracking Several types of discontinuities may occur in welds
Weld Cracking An Excerpt from The Fabricators' and Erectors' Guide to Welded Steel Construction The James F. Lincoln Arc Welding Foundation Weld Cracking Several types of discontinuities may occur in welds
Ultrasonic Technique and Device for Residual Stress Measurement
 Ultrasonic Technique and Device for Residual Stress Measurement Y. Kudryavtsev, J. Kleiman Integrity Testing Laboratory Inc. 80 Esna Park Drive, Units 7-9, Markham, Ontario, L3R 2R7 Canada ykudryavtsev@itlinc.com
Ultrasonic Technique and Device for Residual Stress Measurement Y. Kudryavtsev, J. Kleiman Integrity Testing Laboratory Inc. 80 Esna Park Drive, Units 7-9, Markham, Ontario, L3R 2R7 Canada ykudryavtsev@itlinc.com
Ultrasonic Guided Waves Evaluation of Trials for Pipeline Inspection
 17th World Conference on Nondestructive Testing, 25-28 Oct 2008, Shanghai, China Ultrasonic Guided Waves Evaluation of Trials for Pipeline Inspection Francisco C. R. MARQUES 1, Alessandro DEMMA 2 1 E&P
17th World Conference on Nondestructive Testing, 25-28 Oct 2008, Shanghai, China Ultrasonic Guided Waves Evaluation of Trials for Pipeline Inspection Francisco C. R. MARQUES 1, Alessandro DEMMA 2 1 E&P
Specification for Pipe Coating Repairs Offshore
 Specification for Pipe Coating Repairs Offshore Specification for Pipe Coating Repairs Offshore 1 of 6 Table of Contents 1.0 SCOPE... 3 2.0 REFERENCE DOCUMENTS... 3 3.0 MATERIALS... 3 4.0 EQUIPMENT AND
Specification for Pipe Coating Repairs Offshore Specification for Pipe Coating Repairs Offshore 1 of 6 Table of Contents 1.0 SCOPE... 3 2.0 REFERENCE DOCUMENTS... 3 3.0 MATERIALS... 3 4.0 EQUIPMENT AND
Experiment 7: Familiarization with the Network Analyzer
 Experiment 7: Familiarization with the Network Analyzer Measurements to characterize networks at high frequencies (RF and microwave frequencies) are usually done in terms of scattering parameters (S parameters).
Experiment 7: Familiarization with the Network Analyzer Measurements to characterize networks at high frequencies (RF and microwave frequencies) are usually done in terms of scattering parameters (S parameters).
DDX 7000 & 8003. Digital Partial Discharge Detectors FEATURES APPLICATIONS
 DDX 7000 & 8003 Digital Partial Discharge Detectors The HAEFELY HIPOTRONICS DDX Digital Partial Discharge Detector offers the high accuracy and flexibility of digital technology, plus the real-time display
DDX 7000 & 8003 Digital Partial Discharge Detectors The HAEFELY HIPOTRONICS DDX Digital Partial Discharge Detector offers the high accuracy and flexibility of digital technology, plus the real-time display
APPLICATION NOTE AP050830
 APPLICATION NOTE AP050830 Selection and use of Ultrasonic Ceramic Transducers Pro-Wave Electronics Corp. E-mail: sales@pro-wave.com.tw URL: http://www.prowave.com.tw The purpose of this application note
APPLICATION NOTE AP050830 Selection and use of Ultrasonic Ceramic Transducers Pro-Wave Electronics Corp. E-mail: sales@pro-wave.com.tw URL: http://www.prowave.com.tw The purpose of this application note
11. NONDESTRUCTIVE TESTING
 11. NONDESTRUCTIVE TESTING Nondestructive testing includes magnetic particle testing (MT), Liquid Dye Penetrant testing (PT), Radiographic Testing (RT) and Ultrasonic Testing (UT). The purpose of nondestructive
11. NONDESTRUCTIVE TESTING Nondestructive testing includes magnetic particle testing (MT), Liquid Dye Penetrant testing (PT), Radiographic Testing (RT) and Ultrasonic Testing (UT). The purpose of nondestructive
2000 Series Ultrasonic Welding
 2000 Series Ultrasonic Welding Modular Standard Components Exclusively from BRANSON worldwide Second Generation Digital Power Supplies Branson Worldwide Best for Plastics BRANSON offers a wide range of
2000 Series Ultrasonic Welding Modular Standard Components Exclusively from BRANSON worldwide Second Generation Digital Power Supplies Branson Worldwide Best for Plastics BRANSON offers a wide range of
Tube Control Measurement, Sorting Modular System for Glass Tube
 Tube Control Measurement, Sorting Modular System for Glass Tube Tube Control is a modular designed system of settled instruments and modules. It comprises measuring instruments for the tube dimensions,
Tube Control Measurement, Sorting Modular System for Glass Tube Tube Control is a modular designed system of settled instruments and modules. It comprises measuring instruments for the tube dimensions,
American Petroleum Institute Purchasing Guidelines Purchase API Spec 5CT online at www.api.org/publications
 API Specification 5CT ISO 11960:2011 Petroleum and natural gas industries Steel pipes for use as casing or tubing for wells 9th Edition, June 2011 Table of Contents 1.0 Product 1.1 Products 1.2 Casing
API Specification 5CT ISO 11960:2011 Petroleum and natural gas industries Steel pipes for use as casing or tubing for wells 9th Edition, June 2011 Table of Contents 1.0 Product 1.1 Products 1.2 Casing
Offshore Application of HFI-Pipes Production and Properties
 Offshore Application of HFI-Pipes Production and Properties Hendrik Löbbe Mannesmann Fuchs Rohr Germany Abstract High Frequency Inductive (HFI) welding is a highly productive process for the fabrication
Offshore Application of HFI-Pipes Production and Properties Hendrik Löbbe Mannesmann Fuchs Rohr Germany Abstract High Frequency Inductive (HFI) welding is a highly productive process for the fabrication
PIPING SYSTEM - ABRASIVE SLURRIES Engineering Standard Specification. 96 B. Riutta
 PIPING SYSTEM - ABRASIVE SLURRIES Engineering Standard Specification Number: 3503-11.2.610 Rev. 2 Rubber Lined Steel Pipe and Fittings Mechanically Coupled Plain End Type System Issued Revised Approved
PIPING SYSTEM - ABRASIVE SLURRIES Engineering Standard Specification Number: 3503-11.2.610 Rev. 2 Rubber Lined Steel Pipe and Fittings Mechanically Coupled Plain End Type System Issued Revised Approved
ATI 2205 ATI 2205. Technical Data Sheet. Duplex Stainless Steel GENERAL PROPERTIES. (UNS S31803 and S32205)
 ATI 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel (UNS S31803 and S32205) GENERAL PROPERTIES ATI 2205 alloy (UNS S31803 and/or S32205) is a nitrogen-enhanced duplex stainless steel alloy. The nitrogen serves to significantly
ATI 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel (UNS S31803 and S32205) GENERAL PROPERTIES ATI 2205 alloy (UNS S31803 and/or S32205) is a nitrogen-enhanced duplex stainless steel alloy. The nitrogen serves to significantly
Claims Management Policy
 Claims Management Policy INTRODUCTION ARCELORMITTAL DOFASCO CLAIMS MANAGEMENT POLICY This general claims policy covers light flat rolled sheet products produced at all ArcelorMittal Dofasco flat rolled
Claims Management Policy INTRODUCTION ARCELORMITTAL DOFASCO CLAIMS MANAGEMENT POLICY This general claims policy covers light flat rolled sheet products produced at all ArcelorMittal Dofasco flat rolled
Environmental Stress Crack Resistance of Polyethylene Pipe Materials
 Environmental Stress Crack Resistance of Polyethylene Pipe Materials ROBERT B. TAMPA, Product Development and Service Engineer* Abstract Slow crack growth is a phenomenon that can occur in most plastics.
Environmental Stress Crack Resistance of Polyethylene Pipe Materials ROBERT B. TAMPA, Product Development and Service Engineer* Abstract Slow crack growth is a phenomenon that can occur in most plastics.
COMPAX SUPREME Mold Quality Tool Steel
 T OOL STEEL FACTS COMPAX Mold Quality Tool Steel Great Tooling Starts Here! 2 This information is based on our present state of knowledge and is intended to provide general notes on our products and their
T OOL STEEL FACTS COMPAX Mold Quality Tool Steel Great Tooling Starts Here! 2 This information is based on our present state of knowledge and is intended to provide general notes on our products and their
NEW METHOD TO DETECT COLD FUSION JOINTS IN HIGH DENSITY POLYETHYLENE PIPE
 NEW METHOD TO DETECT COLD FUSION JOINTS IN HIGH DENSITY POLYETHYLENE PIPE Robert Stakenborghs, General Manger, Evisive, Inc. Baton Rouge, LA Abstract This paper describes an innovative apparatus and method
NEW METHOD TO DETECT COLD FUSION JOINTS IN HIGH DENSITY POLYETHYLENE PIPE Robert Stakenborghs, General Manger, Evisive, Inc. Baton Rouge, LA Abstract This paper describes an innovative apparatus and method
Premium Tubular Solutions Super Duplex Welded Tubes for Umbilical Applications
 Premium Tubular Solutions Super Duplex Welded Tubes for Umbilical Applications Premium Tubular Solutions Innovative Tubes for Umbilical Applications Over 35 years of experience in Premium welded t ubular
Premium Tubular Solutions Super Duplex Welded Tubes for Umbilical Applications Premium Tubular Solutions Innovative Tubes for Umbilical Applications Over 35 years of experience in Premium welded t ubular
Auditing a Printed Circuit Board Fabrication Facility Greg Caswell
 Auditing a Printed Circuit Board Fabrication Facility Greg Caswell Introduction DfR is often requested to audit the PCB fabrication process of a customer s supplier. Understanding the process variations
Auditing a Printed Circuit Board Fabrication Facility Greg Caswell Introduction DfR is often requested to audit the PCB fabrication process of a customer s supplier. Understanding the process variations
mgr inż. Rafał Kaczmarek (MSc Eng.), dr inż. Ryszard Krawczyk (PhD (DSc) Eng.) Częstochowa University of Technology, Welding Technology Department
 Rafał Kaczmarek, Ryszard Krawczyk Analysis of dimensions of test joints in the process of technology qualification according to PN-EN ISO 15614-1 in the aspect of ultrasonic testing according to Abstract:
Rafał Kaczmarek, Ryszard Krawczyk Analysis of dimensions of test joints in the process of technology qualification according to PN-EN ISO 15614-1 in the aspect of ultrasonic testing according to Abstract:
It's large enough to handle most welding job shop projects, yet small enough to make it a worth while home-workshop tool
 It's large enough to handle most welding job shop projects, yet small enough to make it a worth while home-workshop tool H Craft Print Project No. 272 ERE'S a metal bender that will enable you to bend
It's large enough to handle most welding job shop projects, yet small enough to make it a worth while home-workshop tool H Craft Print Project No. 272 ERE'S a metal bender that will enable you to bend
WJM Technologies excellence in material joining
 Girish P. Kelkar, Ph.D. (562) 743-7576 girish@welding-consultant.com www.welding-consultant.com Weld Cracks An Engineer s Worst Nightmare There are a variety of physical defects such as undercut, insufficient
Girish P. Kelkar, Ph.D. (562) 743-7576 girish@welding-consultant.com www.welding-consultant.com Weld Cracks An Engineer s Worst Nightmare There are a variety of physical defects such as undercut, insufficient
TEST REPORT Pipe-abc Line Inspection Project
 TEST REPORT Pipe-abc Line Inspection Project Client YYYYYY / XX Facility Pipe-abc Cooling Spool Item Inspected General Pipe Inspection Method SLOFEC Date Commenced November 2007 Date Completed November
TEST REPORT Pipe-abc Line Inspection Project Client YYYYYY / XX Facility Pipe-abc Cooling Spool Item Inspected General Pipe Inspection Method SLOFEC Date Commenced November 2007 Date Completed November
DIESEL EFFECT PROBLEM SOLVING DURING INJECTION MOULDING
 RESEARCH PAPERS FACULTY OF MATERIALS SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY IN TRNAVA SLOVAK UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY IN BRATISLAVA 2014 Volume 22, Special Number DIESEL EFFECT PROBLEM SOLVING DURING INJECTION MOULDING
RESEARCH PAPERS FACULTY OF MATERIALS SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY IN TRNAVA SLOVAK UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY IN BRATISLAVA 2014 Volume 22, Special Number DIESEL EFFECT PROBLEM SOLVING DURING INJECTION MOULDING
1150 hp motor design, electromagnetic and thermal analysis
 115 hp motor design, electromagnetic and thermal analysis Qasim Al Akayshee 1, and David A Staton 2 1 Mawdsley s Ltd., The Perry Centre, Davey Close, Waterwells, Gloucester GL2 4AD phone: +44 1452 888311
115 hp motor design, electromagnetic and thermal analysis Qasim Al Akayshee 1, and David A Staton 2 1 Mawdsley s Ltd., The Perry Centre, Davey Close, Waterwells, Gloucester GL2 4AD phone: +44 1452 888311
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION FOR HIGH TENSION LINE HARDWARE AND ACCESSORIES FOR ACSR PANTHER & WOLF CONDUCTOR
 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION FOR HIGH TENSION LINE HARDWARE AND ACCESSORIES FOR ACSR PANTHER & WOLF CONDUCTOR 1.1.0 SCOPE : This specification covers design, manufacture, testing at manufacture s works before
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION FOR HIGH TENSION LINE HARDWARE AND ACCESSORIES FOR ACSR PANTHER & WOLF CONDUCTOR 1.1.0 SCOPE : This specification covers design, manufacture, testing at manufacture s works before
Disclosure to Promote the Right To Information
 इ टरन ट म नक Disclosure to Promote the Right To Information Whereas the Parliament of India has set out to provide a practical regime of right to information for citizens to secure access to information
इ टरन ट म नक Disclosure to Promote the Right To Information Whereas the Parliament of India has set out to provide a practical regime of right to information for citizens to secure access to information
PMCap Local Thin Area Repair and Restoration Component. for Pressure Retaining Items
 by Paul S. Manzon President and John K. Wiedemann Vice President, Engineering PMC Engineering Solutions, Inc. 272 Grubb Rd. Pottstown, PA 19465 ABSTRACT A common method of pressure boundary repair for
by Paul S. Manzon President and John K. Wiedemann Vice President, Engineering PMC Engineering Solutions, Inc. 272 Grubb Rd. Pottstown, PA 19465 ABSTRACT A common method of pressure boundary repair for
Standard Specification for Tool Steels Alloy 1
 Designation: A 68 8 Standard Specification for Tool Steels Alloy This standard is issued under the fixed designation A 68; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original
Designation: A 68 8 Standard Specification for Tool Steels Alloy This standard is issued under the fixed designation A 68; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original
Problems in Welding of High Strength Aluminium Alloys
 Singapore Welding Society Newsletter, September 1999 Problems in Welding of High Strength Aluminium Alloys Wei Zhou Nanyang Technological University, Singapore E-mail: WZhou@Cantab.Net Pure aluminium has
Singapore Welding Society Newsletter, September 1999 Problems in Welding of High Strength Aluminium Alloys Wei Zhou Nanyang Technological University, Singapore E-mail: WZhou@Cantab.Net Pure aluminium has
AMPSEAL* Automotive Plug Connector and Header Assembly
 AMPSEAL* Automotive Plug Connector and Header Assembly Application Specification 24 SEP 97 Rev E All dimensions are given in millimeters unless otherwise specified. All dimensional tolerances are +0.2
AMPSEAL* Automotive Plug Connector and Header Assembly Application Specification 24 SEP 97 Rev E All dimensions are given in millimeters unless otherwise specified. All dimensional tolerances are +0.2
LABORATORY EXPERIMENTS TESTING OF MATERIALS
 LABORATORY EXPERIMENTS TESTING OF MATERIALS 1. TENSION TEST: INTRODUCTION & THEORY The tension test is the most commonly used method to evaluate the mechanical properties of metals. Its main objective
LABORATORY EXPERIMENTS TESTING OF MATERIALS 1. TENSION TEST: INTRODUCTION & THEORY The tension test is the most commonly used method to evaluate the mechanical properties of metals. Its main objective
AISI O1 Cold work tool steel
 T OOL STEEL FACTS AISI O1 Cold work tool steel Great Tooling Starts Here! This information is based on our present state of knowledge and is intended to provide general notes on our products and their
T OOL STEEL FACTS AISI O1 Cold work tool steel Great Tooling Starts Here! This information is based on our present state of knowledge and is intended to provide general notes on our products and their
Cross-beam scanning system to detect slim objects. 100 mm 3.937 in
 891 Object Area Sensor General terms and conditions... F-17 Related Information Glossary of terms... P.1359~ Sensor selection guide...p.831~ General precautions... P.1405 PHOTO PHOTO Conforming to EMC
891 Object Area Sensor General terms and conditions... F-17 Related Information Glossary of terms... P.1359~ Sensor selection guide...p.831~ General precautions... P.1405 PHOTO PHOTO Conforming to EMC
How to reduce the cure time without damaging the rubber compound during injection molding?
 How to reduce the cure time without damaging the rubber compound during injection molding? 0Introduction This article aims at analyzing the rubber injection process and highlighting the limits that prevent
How to reduce the cure time without damaging the rubber compound during injection molding? 0Introduction This article aims at analyzing the rubber injection process and highlighting the limits that prevent
Verification Experiment on Cooling and Deformation Effects of Automatically Designed Cooling Channels for Block Laminated Molds
 International Journal of Engineering and Advanced Technology (IJEAT ISSN: 2249 8958 Volume-4 Issue-5 June 2015 Verification Experiment on Cooling and Deformation Effects of Automatically Designed Cooling
International Journal of Engineering and Advanced Technology (IJEAT ISSN: 2249 8958 Volume-4 Issue-5 June 2015 Verification Experiment on Cooling and Deformation Effects of Automatically Designed Cooling
US-Key New generation of High performances Ultrasonic device
 US-Key New generation of High performances Ultrasonic device US-Key connected to a laptop computer US-Key Ultrasound device single channel Features USB2 High Speed connection Ultralow noise preamplifier
US-Key New generation of High performances Ultrasonic device US-Key connected to a laptop computer US-Key Ultrasound device single channel Features USB2 High Speed connection Ultralow noise preamplifier
STAVAX SUPREME. Stainless tool steel
 STAVAX SUPREME Stainless tool steel General Demands placed on plastic mould tooling are increasing. Such conditions require mould steels that possess a unique combination of toughness, corrosion resistance
STAVAX SUPREME Stainless tool steel General Demands placed on plastic mould tooling are increasing. Such conditions require mould steels that possess a unique combination of toughness, corrosion resistance
PAAM COMMERCIAL PRIVATE LIMITED
 METAL PACKAGING We at Paam Group have been providing vast range of packaging products to our customers based on their preferences, needs and specifications. We provide all the materials required in metal
METAL PACKAGING We at Paam Group have been providing vast range of packaging products to our customers based on their preferences, needs and specifications. We provide all the materials required in metal
Construction of Quality Hot Mix Asphalt Pavements
 59 th Annual Asphalt Paving Conference Outline Best Practices for Pavement Construction Placement Best Practices Surface Prep Project planning Understanding the paver Factors affecting the screed Screed
59 th Annual Asphalt Paving Conference Outline Best Practices for Pavement Construction Placement Best Practices Surface Prep Project planning Understanding the paver Factors affecting the screed Screed
