DETECTION OF ANTI-GLUTAMATE RECEPTOR (NMDA) (REFERENCE )
|
|
|
- Madison Parrish
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DETECTION OF ANTI-GLUTAMATE RECEPTOR (NMDA) (REFERENCE ) Notice of Assessment December 2014 DISCLAIMER: This document was originally drafted in French by the Institut national d'excellence en santé et en services sociaux (INESSS), and that version can be consulted at alyses_bio_med_dec_2014_3.pdf. It was translated into English by the Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health (CADTH) with INESSS s permission. INESSS assumes no responsibility with regard to the quality or accuracy of the translation. While CADTH has taken care in the translation of the document to ensure it accurately represents the content of the original document, CADTH does not make any guarantee to that effect. CADTH is not responsible for any errors or omissions or injury, loss, or damage arising from or relating to the use (or misuse) of any information, statements, or conclusions contained in or implied by the information in this document, the original document, or in any of the source documentation.
2 1. GENERAL INFORMATION 1.1. Requester: CHU Sainte-Justine 1.2. Application for Review Submitted to MSSS: May 1, Application Received by INESSS: July 10, Notice Issued: October 31, 2014 Note: This notice is based on the scientific and commercial information submitted by the requester and on a complementary review of the literature according to the data available at the time that this test was assessed by INESSS. 2. TECHNOLOGY, COMPANY, AND LICENCE(S) 2.1 Name of the Technology Detection of anti-glutamate receptor NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) using indirect immunofluorescence in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) or in serum 2.2 Brief Description of the Technology, and Clinical and Technical Specifications The test is designed to detect, in CSF or serum, the presence of autoantibodies directed against membrane antigens of the central nervous system, the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor, 1 or the anti-glutamate receptor 2 [Dalmau et al., 2008]. The test is carried out using indirect immunofluorescence on various substrates, rat hippocampal and cerebellar tissue (tissue-based assay), and cell cultures expressing recombinant NMDA receptors (transfected 3 HEK cells). Non-transfected cells are used as controls. Tissuebased assays allow the detection of anti-nmda receptor antibodies as well as other antibodies (e.g., anti-vgkc 5 and anti-ampa 6 receptors). Parallel testing on HEK293 cells (cell-based assay or CBA) provides sensitive, monospecific detection of anti-nmda receptor antibodies [EUROIMMUN, 2014]. Various kits are available, depending on the substrates used, including a microplate with four biochips combining all the substrates, described below, and a microplate with two biochips with transfected and non-transfected cells as substrates. 1. The NMDA receptor, comprising four postsynaptic transmembrane proteins (tetramers), is generally composed of two RN1 subunits and RN2. It is present in large quantities in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus and is involved in numerous pathophysiological mechanisms such as locomotion, pain perception, memory, and learning. The four proteins form a channel that allows the flow of calcium, sodium, and potassium ions and is normally blocked by magnesium ions, which have binding sites inside the channel. Several molecules, particularly NMDA, can bind to the receptor. When glutamate is released into the synaptic cleft, it can open NMDA receptors, thus allowing calcium molecules to enter postsynaptic dendrites [Lafaix, 2013]. 2. Glutamate is the brain s primary excitatory neurotransmitter, acting on three types of receptors: NMDA, kainate, and AMPA [Monier and Fabien, 2006]. 3. Transfection is the process of introducing a fragment of foreign DNA into a eukaryotic cell so that the cell may express a given gene (Futura- Santé. Transfection [website], available at: Human embryonic kidney cells (HEK293) were transfected with plasmids expressing rodent NR1, NR2A, or NR2B subunits of the NMDAR [Dalmau et al., 2007]. Plasmid: an extrachromosomal self-replicating structure found in bacterial cells that carries genes for a variety of functions not essential for cell growth (Dorland s Illustreated Medical Dictionary, 32nd edition, Elsevier). 4. HEK: human embryonic kidney. 5. VGKC: voltage-gated potassium channel. 6. AMPA: alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid. 1
3 Technique The test samples (serum diluted to 1:10 in PBS 7 -Tween or undiluted CSF) are applied to the reagent support using the TITERPLANE TM technique. The biochip slide with the various substrates is then placed on this same support so that it comes into contact with the liquids and allows the individual samples to react simultaneously. The incubation step at room temperature lasts 30 minutes. If a sample is positive, specific IgA, IgG, and IgM antibodies bind to the antigens coupled to the solid phase (biochips). After each incubation step, the biochip slides are washed with PBS-Tween to remove any unbound antibodies or fluorescein-labelled reagents. Bound antibodies are detected with fluorescein-labelled antihuman IgG antibodies and made visible under a fluorescence microscope. Anti-NMDA receptor antibodies show a smooth to fine-granular fluorescence in the cytoplasm of transfected HEK293 cells Company or Developer The company EUROIMMUN (Medizinische Labordiagnostika AG) (Germany). 2.4 Licence(s): Not applicable. 2.5 Patent, If Any: Not applicable. 2.6 Approval Status (Health Canada, FDA, other countries) The Anti-Glutamate Receptor (Type NMDA) IIFT kit (which uses the CBA method) from the company EUROIMMUN is approved by Health Canada (No ). The FDA has approved EUROIMMUN s Anti-Glutamate Receptor (Type NMDA) IIFT kit, which uses a CBA with semi-quantitative indirect immunofluorescence technique (k ). 2.7 Weighted Value Value of , including the cost of two slides for each type of sample: serum and CSF ($ per slide). 7. PBS: phosphate-buffered saline. 8. EUROIMMUN. Autoantibodies against neuronal antigens [website]. Available at: 9. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 510(k) Substantial equivalence determination: Decision summary. 510(k) Number: k Available at: 2
4 3. CLINICAL INDICATIONS, PRACTICE SETTINGS, AND TESTING PROCEDURES 3.1 Targeted Patient Group Patients with autoimmune encephalitis with no known common infectious cause (HSV, 10 VZV, 11 enterovirus). 3.2 Targeted Disease(s) Clinical signs combining ovarian teratoma with episodes of memory deficits, psychiatric symptoms, decreased level of consciousness or hypersomnia, and signs of central hypoventilation were reported in four women examined by the authors of a study published in 2005 and in five other previously described cases reported in the same study [Vitaliani et al., 2005]. Since then, approximately 419 other patients with this syndrome have been identified, including children and young adults with or without the associated tumour. The exact incidence of the disease is unknown, but it appears to be increasingly common, occurring predominantly in women (80% of cases) [Dalmau et al., 2011]. Most patients with anti-nmda receptor (anti-nmdar) encephalitis have intrathecal synthesis of anti-nmdar antibodies. The main epitope targeted by these antibodies is in the extracellular N-terminal domain of the NR1 subunit [Dalmau et al., 2008]. NMDAR antibodies cause a decrease in the number of NMDA receptors and affect the interneuronal transmission of information. This disorder is most recently called anti-nmdar encephalitis [Peery et al., 2012; Dalmau et al., 2011 et 2007]. Early clinical signs of the disease, as described by Dalmau et al. [2008], include headaches, fever, or symptoms of nonspecific viral infection. Psychiatric symptoms follow, such as anxiety, restlessness, behaviour problems, paranoid delusions, and visual and auditory hallucinations. Some patients suffer from short-term memory loss or from seizures,which may be associated with psychiatric symptoms. Patient prognosis depends on early diagnosis, appropriate immunomodulatory treatment, and resection of a teratoma, if relevant [Wandinger et al., 2011]. 3.3 Number of Patients Targeted The CHU Sainte-Justine sends 20 to 30 samples each year to Dr. Dalmau s research laboratory in Spain. The requester estimates that 100 tests will be conducted locally each year. 3.4 Medical Specialties and Other Professions Involved Neurology, psychiatry, neuro-oncology, microbiology. 3.5 Testing Procedure CSF samples obtained by lumbar puncture or serum samples obtained by venipuncture. 10. HSV: herpes simplex virus. 11. VZV: varicella-zoster virus. 3
5 4. TECHNOLOGY BACKGROUND 4.1 Nature of the Diagnostic Technology This test would replace tests being sent outside Quebec. According to the data provided by the MSSS, during the year , 26 tests were sent outside Quebec, either to the United States (Athena Diagnostics or Mayo Medical Laboratories) or to Alberta (Mitogen Advanced Diagnostics in Calgary). The unit cost of the test ranges from $85 to $ This new test was developed in collaboration with the company EUROIMMUN and Dr. Joseph Dalmau s research laboratory in Spain. 4.2 Brief Description of the Current Technological Context Several diagnostic tests help establish a diagnosis of anti-nmdar encephalitis [Dalmau et al., 2011]: electroencephalogram (EEG): abnormal in most patients, with reduced, unfocused and disorganized activity; magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): abnormal in 50% of cases, most commonly with hyperintensities in T2-weighted sequences in the hippocampus and cerebral cortex; abnormal CSF in 80% of cases at the time of diagnosis, including moderate lymphocytic pleocytosis, 12 normal or slightly elevated protein concentration, and specific oligoclonal bands, present in 60% of patients; screening for anti-nmdar antibodies in the CSF or serum using the method developed by Dalmau et al. [2007]. These are tissue-based assays and cell-based assays (CBA) using HEK293 cells overexpressing NR1/NR2B heteromers of NMDAR. The presence of antibodies was initially determined by the reactivity of the patient s serum and CSF. Some authors test for antibodies using cell-based indirect immunofluorescence assays using serum only. Given the qualitative nature of the result, its interpretation depends on the researcher s experience. Moreover, the serum is often used at low dilutions (< 1:100), which can increase the number of false-positive results despite rigorous controls [Lancaster and Dalmau, 2012]. Therefore, as serum screening has limitations, it is necessary to include screening of CSF to establish the diagnosis of anti-nmdar encephalitis [Gresa-Arribas et al., 2014; Dalmau et al., 2011]. 4.3 Brief Description of the Advantages Cited for the New Technology Tissue-based indirect immunofluorescence assays have the advantage of detecting new antibodies, but this technique can have limitations when several autoantibodies coexist in a single patient [Lancaster et Dalmau, 2012]. When it is performed on CBA, it enables the monospecific detection of anti-nmdar overexpressing the heteromers of the NMDA receptor NR1 subunit [EUROIMMUN, 2011a]. 4.4 Cost of Technology and Options: Not assessed. 12. Lymphocytic pleocytosis: increase in the number of white blood cells, with a predominance of lymphocytes in the CSF. 4
6 5. EVIDENCE 5.1 Clinical Relevance Other Tests Replaced This new test would replace tests sent outside Quebec Diagnostic or Prognostic Value Screening for anti-nmdar antibodies helps confirm the diagnosis of anti-nmdar encephalitis and monitor concentrations of these antibodies as the disease progresses. When results are positive, a more extensive clinical investigation, mainly to detect ovarian teratomas or testicular germ cell tumours, is recommended [Wandinger et al., 2011]. Moreover, early diagnosis of anti-nmdar encephalitis is crucial, as patients treated in the early stages of the disease make a full recovery or show a mild neurological deficit (75% of cases) [Kayser et Dalmau, 2011]. If the outcome is poor (25% of cases), patients may be permanently disabled with severe neurological deficits, or they may die. Based on data for 360 patients who had a clinical follow-up of longer than 6 months, the mortality rate is estimated at 4% (15/360) with a median time of 3.5 months (from 1 to 8 months) between disease onset and death. The majority of deaths occurred in intensive care units as a result of septic shock, cardiac arrest, acute respiratory distress, refractory status epilepticus, or tumour progression [Dalmau et al., 2011]. Mortality was very high for three patients in a case series [Day et al., 2011]. The three patients died after developing complications associated with prolonged hospitalization in intensive care units. The authors agree on the importance of early diagnosis and treatment. The determination of anti-nmdar titres is complementary to clinical assessments, since high antibody titres in CSF and serum are associated with poor outcome or the presence of a teratoma, or both. In cases of both good and poor outcome, changes in antibody titres were observed more often in CSF test results than they were in serum test results (p = 0.037) [Gresa-Arribas et al., 2014]. Moreover, the study by Suh-Lailam et al. [2013] showed that, despite the rapid decrease of anti-nmdar titres in CSF, and despite clinical response to treatment, anti-nmdar serum titres remained high Therapeutic Value The detection of anti-nmdar is useful in providing the appropriate immunomodulatory therapy and in assessing the effect of treatment, particularly on the central nervous system [Dalmau et al., 2011]. Irani et al. [2010] reported that a decrease in antibody titres is associated with the administration of immunotherapy less than 40 days after the onset of symptoms in patients without an associated tumour, compared with patients who were not treated or who received treatment after 40 days (p < ); antibody titres may also decrease with early tumor resection in the case of an associated tumour. 5.2 Clinical Validity Few studies examined clinical performance in terms of the sensitivity and specificity of tissue-based and cell-based indirect immunofluorescence assays. The only available data were taken from four studies and from data from EUROIMMUN. The literature did not report any direct comparisons of indirect immunofluorescence performance on different substrates (tissue or CBA). 5
7 The sensitivity of anti-nmdar detection in serum and CSF using indirect immunofluorescence on tissue sections and CBA in patients diagnosed with anti-nmdar encephalitis was tested in two studies 13 [Wandinger et al., 2010; Dalmau et al., 2008]. Dalmau et al. [2008] reported that subunit NR1 (target of anti-nmdar) was identified, in CSF or serum (100%), by the antibodies of all the patients (n = 100). In the second study, the sensitivity also was 100% (n = 66) regardless of the substrate used [Wandinger et al., 2010]. Table 1 presents the performance results of cell-based indirect immunofluorescence assays for the detection of anti-nmdar in a selected patient population diagnosed with anti-nmdar encephalitis (Studies 1, 3, and 4) and in 6 patients with clinical symptoms of encephalitis of unknown origin selected from a large population of 2,990 patients (Study 2). These data were taken from the manufacturer's monograph [EUROIMMUN, 2011a]. The capacity of cell-based indirect immunofluorescence assays to detect anti-nmdar in the serum of these patients was 100% for Studies 1, 3, and 4. Five of the six serum samples (83.3%) of patients fulfilling the diagnostic criteria for anti-nmdar encephalitis were positive for this type of antibody (Study 2). The specificity of the methods of analysis (tissue-based and CBA) tested on groups of healthy volunteers or patients in whom suspected autoimmune encephalitis was another type (e.g., anti-vgkc 14 receptor and anti-ampa 15 receptor) or in patients with other autoimmune diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus or multiple sclerosis) is 100%, regardless of the type of sample used (CSF or serum) [Gresa-Arribas et al., 2014; Suh-Lailam et al., ; EUROIMMUN, 2011a; Wandinger et al., 2010]. Table 1: Results of anti-nmdar detection in serum using cell-based indirect immunofluorescence assay (EUROIMMUN) Study Number of cases CONTROLS (N) N positive (%) Confidence interval of 95% Diagnosis of anti-nmdar encephalitis Study HV 18 other AE * 29 (100) 88.1% to 100.0% Study (100) 63.1% to 100.0% Study (100) 66.4% to 100.0% Total other AE 46 (100) Clinical symptoms of encephalitis of unknown origin Study (83.3) 35.9% to 99.6% Abbreviations: AE = autoimmune encephalitis; CBA = cell-based assay; HV = healthy volunteers. * Anti-VGKC (voltage-gated potassium channels) and anti-ampa (alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4 isoxazole propionic acid) receptor encephalitis. 13. The authors of these studies have a stake in the company EUROIMMUN [Wandinger et al., 2010; Dalmau et al., 2008]. 14. VGKC: voltage-gated potassium channels. 15. AMPA: alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid. 16. The test kits used in the study by Suh-Lailam et al. [2013] were provide free of charge by the company EUROIMMUN. 6
8 Other data on the screening of serum samples (235 patients) and CSF samples(216 patients) from patients with anti-nmdar encephalitis are available on the website of the company EUROIMMUN. Results show that cell-based indirect immunofluorescence assays have a greater capacity to detect anti-nmdar in CSF (99.5%) than in serum (85.5%). A positive result was reported in serological tests from a group of 200 healthy volunteers and in CSF tests from a group of 60 patients without neurological abnormalities [EUROIMMUN, 2011b]. 5.3 Analytical (or Technical) Validity Repeatability COMPONENT PRESENCE ABSENCE NOT APPLICABLE Reproducibility Analytical sensitivity Analytical specificity X X X Matrix effect Concordance Correlation between test and comparator X Other, depending on type of test Reproducibility/Precision The manufacturer's monograph indicates that six different serum samples were used to test the intra-assay (10 parallel tests) and inter-assay reproducibility of cell-based indirect immunofluorescence assay on 5 series (tested in duplicate). Interlot reproducibility was tested on three different serum samples and three different lots. The intensity of the specific fluorescence is expressed as a numeric value. All serum samples were tested according to fluorescence intensity levels of 0 (no specific fluorescence), 1 (very weak positive reaction visible), 2 (weak positive reaction visible), and 3 (specific positive reaction very visible). In all cases, the deviation in fluorescence intensity level did not exceed ± 1 level for all samples tested [EUROIMMUN, 2011a]. Sensitivity of Measurement in Paired Samples of Serum and CSF Results for the sensitivity of CSF for the detection of anti-nmdar using indirect immunofluorescence vary from those of serum. Gresa-Arribas et al. [2014] tested the sensitivity of tissue-based and cell-based indirect immunofluorescence assays on paired samples (serum and CSF) from 250 patients. The samples were taken the same day from patients randomly selected from a cohort of 577 cases of anti-nmdar encephalitis from around the world. Test results had been positive for anti-nmdar in CSF and serum in a previous study [Titulaer et al., 2013]. Results of the test conducted by Gresa-Arribas et al. [2014] show a sensitivity of the method on CSF of 100% (98.5 to 100%) compared with that of serum (91.6% [87.5 to 94.7%] for tissue-based immunofluorescence and 86.8% [82 to 90.7%] for cell-based immunofluorescence). The difference in sensitivity of the test in both types of samples is significant (p < ). These results confirm the importance of detecting anti-nmdar in CSF; serum sample tests are not sufficient. As reported by Dalmau et al. [2008], antibody titres are higher in CSF than in serum for 53 paired samples. 7
9 Suh-Lailam et al. [2013] reported the results of their observations for 20 paired samples (CSF and serum) tested with a cell-based indirect immunofluorescence assay over a period of 24 hours. They obtained 14 positive results (paired CSF and sera) and 6 discordant results (4 positive CSF and negative sera and 2 negative CSF and positive sera). Serum antibody levels were significantly higher than in CSF (p = 0.02). Reference Range Anti-NMDAR (IgG) serum levels were analyzed using a cell-based indirect immunofluorescence assay on 120 serum samples from healthy adult donors. All serum samples were negative. The reference range was determined to be an antibody titre equivalent to 1: < 10 [EUROIMMUN, 2011a]. Cross-Reactivity Cross-reactivity was tested on 29 serum samples from patients with autoimmune encephalitis, 1 sample from a patient with cerebellar degeneration, and 1 sample from a patient with retinopathy. The method used was a cell-based indirect immunofluorescence assay. Samples that were positive for anti-glur2, anti-vgkc, and anti-zic4 (cerebellar degeneration) were negative for the glutamate receptor (type NMDA) [EUROIMMUN, 2011a]. Interference Results of tests using cell-based indirect immunofluorescence assays were not affected by concentrations of up to 500 mg/dl of hemoglobin, 2000 mg/dl of triglycerides, and 40 mg/dl of bilirubin [EUROIMMUN, 2011a]. Correlation Correlation between cell-based indirect immunofluorescence assays and the immunoprecipitation method (Spearman s rank correlation: r = 0.86; p < ) [Irani et al., 2010]. 5.4 Recommendations from Other Organizations Recommendations from official organizations are not yet available. However, a panel of three international experts (Austria, Spain, United States) proposed a decision algorithm for the diagnosis of anti-neuronal antibodies, including anti-nmdar [Höftberger et al., 2012]. The diagnostic approach includes tissue-based indirect immunofluorescence assays on CSF or serum for the detection of these antibodies. Based on the results obtained, there are three possible scenarios: If the results are positive, confirmation of the presence of anti-nmdar using cell-based indirect immunofluorescence assays is indicated. When the clinical presentation is strongly suggestive of anti-nmdar encephalitis, or in cases of uncertain results in serum samples using tissue-based indirect immunofluorescence assays, diagnostic confirmation must be obtained by a repeated measurement with this same method on CSF or with a cell-based indirect immunofluorescence assay. If the cell-based indirect immunofluorescence assay is used to detect these antibodies without the use of the tissue-based method, results must be interpreted with caution and according to the clinical context. The European Autoimmunity Standardisation Initiative (EASI) published a general practice 8
10 guideline based on expert opinion rather than on recommendations. The guideline was created to provide family physicians with the necessary information regarding various autoimmune diseases, such as autoimmune encephalitis, to ensure better care for patients with the disease, including refer patients to medical specialists. The authors indicate that the cell-based indirect immunofluorescence assay is the best diagnostic method for anti- NMDAR encephalitis, and that these antibodies may be present in CSF when serum screens are negative [Shoenfeld and Meroni, 2012]. 6. ANTICIPATED OUTCOMES OF INTRODUCING THE TEST 6.1 Impact on Material and Human Resources Not assessed. 6.2 Economic Consequences of Introducing Test Into Quebec's Health Care and Social Services System Not assessed. 6.3 Main Organizational, Ethical, and Other (Social, Legal, Political) Issues 7. IN BRIEF Not assessed. 7.1 Clinical Relevance The clinical relevance of anti-nmdar encephalitis is recent. Screening for anti-nmdar should be considered if signs of encephalitis develop (neuropsychiatric symptoms, seizures, abnormal movements, dysautonomia) with sudden onset, which occurs mainly at a young age and primarily in women. Tests for anti-nmdar antibodies with indirect immunofluorescence on serum and CSF are useful to: confirm the clinical diagnosis of anti-nmdar encephalitis and the autoimmune origin of neurologic disorders; help detect a tumour syndrome, if relevant. CSF is more informative than serum for the detection of anti-nmdar in paraneoplastic autoimmune encephalitis; monitor the concentrations of these antibodies as the disease progresses, and assess the effects of treatment; determine antibody titres, which complement clinical and biological assessments. 7.2 Clinical Validity Available results show good clinical performance of tissue-based and cell-based indirect immunofluorescence assays for the detection of anti-nmdar antibodies. However, according to the evidence found in the literature, no direct comparisons were made of the performance of indirect immunofluorescence on different substrates (tissue-based and cellbased assay) or with any other technique. 9
11 7.3 Analytical Validity Data from the company EUROIMMUN and from several validation studies suggest good analytical performance of cell-based indirect immunofluorescence assay for the detection of anti-nmdar antibodies in serum. The analytical validity of indirect immunofluorescence has not been assessed, either for cell-based assays on CSF or for tissue-based assays on CSF or serum. 7.4 Recommendations from Other Organizations No official organization has produced recommendations on the clinical relevance of screening for anti-nmdar antibodies in serum and CSF using indirect immunofluorescence. According to a decision algorithm developed by a group of experts, tissue-based assays are the most appropriate method for the diagnosis of anti-nmdar, followed by CBA to confirm the presence of these antibodies [Höftberger et al., 2012]. Cell-based assays may be used as first-line tests, and the results must be interpreted according to clinical context. 10
12 8. INESSS NOTICE IN BRIEF Detection of anti-glutamate receptor (NMDA) Status of the Diagnostic Technology: Established Innovative Experimental (for research purposes only) Replacement for technology:, which becomes obsolete INESSS Recommendation: Include test in the Index Do not include test in the Index Reassess test Additional Recommendation: Draw connection with listing of drugs, if companion test Produce an optimal use manual Identify indicators, when monitoring is required Note This test has several advantages. It enables: the diagnosis of a rare disease; more effective monitoring of the disease; appropriate therapy. Making the test available in Quebec would provide a faster turnaround time than sending the samples outside Quebec. 11
13 REFERENCES Dalmau J, Gleichman AJ, Hughes EG, Rossi JE, Peng X, Lai M, et al. Anti-NMDA-receptor encephalitis: Case series and analysis of the effects of antibodies. Lancet Neurol 2008;7(12): Dalmau J, Lancaster E, Martinez-Hernandez E, Rosenfeld MR, Balice-Gordon R. Clinical experience and laboratory investigations in patients with anti-nmdar encephalitis. Lancet Neurol 2011;10(1): Dalmau J, Tüzün E, Wu HY, Masjuan J, Rossi JE, Voloschin A, et al. Paraneoplastic anti-n-methyl- D-aspartate receptor encephalitis associated with ovarian teratoma. Ann Neurol 2007;61(1): Day GS, High SM, Cot B, Tang-Wai DF. Anti-NMDA-receptor encephalitis: Case report and literature review of an under-recognized condition. J Gen Intern Med 2011;26(7): EUROIMMUN. Product catalogue Lübeck, Allemagne : EUROIMMUN Medizinische Labordiagnostika AG; Available at: EUROIMMUN. Anti-glutamate receptor (type NMDA) IFA. Test instructions. Lübeck, Allemagne : EUROIMMUN Medizinische Labordiagnostika AG; 2011a. Available at: 51_A_US_D03.pdf. EUROIMMUN. Test characteristics. IIFT: Autoimmune encephalitis mosaic 1. Lübeck, Allemagne : EUROIMMUN Medizinische Labordiagnostika AG; 2011b. Available at: phalitis_en.pdf. Gresa-Arribas N, Titulaer MJ, Torrents A, Aguilar E, McCracken L, Leypoldt F, et al. Antibody titres at diagnosis and during follow-up of anti-nmda receptor encephalitis: A retrospective study. Lancet Neurol 2014;13(2): Höftberger R, Dalmau J, Graus F. Clinical neuropathology practice guide : Updated guideline for the diagnosis of antineuronal antibodies. Clin Neuropathol 2012;31(5): Irani SR, Bera K, Waters P, Zuliani L, Maxwell S, Zandi MS, et al. N-methyl-D-aspartate antibody encephalitis: Temporal progression of clinical and paraclinical observations in a predominantly non-paraneoplastic disorder of both sexes. Brain 2010;133(Pt 6): Kayser MS et Dalmau J. Anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis in psychiatry. Curr Psychiatry Rev 2011;7(3): Lafaix O. Implication du récepteur au NMDA dans le vieillissement, l apprentissage et la mémorisation : approche expérimentale par sur-régulation de la sous-unité GluN2B du récepteur au NMDA dans l hippocampe de souris. Thesis in veterinary medicine. Toulouse, France : Ecole nationale vétérinaire de Toulouse (ENVT); Available at: Lancaster E and Dalmau J. Neuronal autoantigens Pathogenesis, associated disorders and antibody testing. Nat Rev Neurol 2012;8(7):
14 Monier JC and Fabien N. VI. Autoanticorps anti-récepteurs ionotropiques du glutamate. GEAI L'info 2006;8:23-4. Peery HE, Day GS, Dunn S, Fritzler MJ, Pruss H, De Souza C, et al. Anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis. The disorder, the diagnosis and the immunobiology. Autoimmun Rev 2012;11(12): Shoenfeld Y and Meroni PL. The general practice guide to autoimmune diseases. Lengerich, Allemagne : Pabst Science Publishers; Suh-Lailam BB, Haven TR, Copple SS, Knapp D, Jaskowski TD, Tebo AE. Anti-NMDA-receptor antibody encephalitis: performance evaluation and laboratory experience with the anti- NMDA-receptor IgG assay. Clin Chim Acta 2013;421:1-6. Titulaer MJ, McCracken L, Gabilondo I, Armangue T, Glaser C, Iizuka T, et al. Treatment and prognostic factors for long-term outcome in patients with anti-nmda receptor encephalitis: an observational cohort study. Lancet Neurol 2013;12(2): Vitaliani R, Mason W, Ances B, Zwerdling T, Jiang Z, Dalmau J. Paraneoplastic encephalitis, psychiatric symptoms, and hypoventilation in ovarian teratoma. Ann Neurol 2005;58(4): Wandinger KP, Saschenbrecker S, Stoecker W, Dalmau J. Anti-NMDA-receptor encephalitis: A severe, multistage, treatable disorder presenting with psychosis. J Neuroimmunol 2011;231(1-2): Wandinger KP, Dalmau J, Borowski K, Probst C, Rosemann A, Fechner K, Stoecker W. Laboratory diagnosis and follow-up in patients with anti-nmda-receptor encephalitis. Scientific presentation at the 7th International Congress on Autoimmunity, Ljubljana, Slovenia, May Available at: 13
Brains on Fire Autoimmune causes of psychosis. Dr Belinda Lennox Department of Psychiatry, University of Oxford Belinda.lennox@psych.ox.ac.
 Brains on Fire Autoimmune causes of psychosis Dr Belinda Lennox Department of Psychiatry, University of Oxford Belinda.lennox@psych.ox.ac.uk RCPsych Brighton 16 th October 2014 Overview The new disorders
Brains on Fire Autoimmune causes of psychosis Dr Belinda Lennox Department of Psychiatry, University of Oxford Belinda.lennox@psych.ox.ac.uk RCPsych Brighton 16 th October 2014 Overview The new disorders
By Dr Sarosh R Irani, Dr Camilla Buckley and Prof Angela Vincent
 Limbic Encephalitis By Dr Sarosh R Irani, Dr Camilla Buckley and Prof Angela Vincent This factsheet aims to provide people affected by Encephalitis, their families, friends and carers with a better undertstanding
Limbic Encephalitis By Dr Sarosh R Irani, Dr Camilla Buckley and Prof Angela Vincent This factsheet aims to provide people affected by Encephalitis, their families, friends and carers with a better undertstanding
Treatment and prognostic factors for long-term outcome in patients with anti-nmda receptor encephalitis: an observational cohort study
 Treatment and prognostic factors for long-term outcome in patients with anti-nmda receptor encephalitis: an observational cohort study Maarten J Titulaer, Lindsey McCracken, Iñigo Gabilondo, Thaís Armangué,
Treatment and prognostic factors for long-term outcome in patients with anti-nmda receptor encephalitis: an observational cohort study Maarten J Titulaer, Lindsey McCracken, Iñigo Gabilondo, Thaís Armangué,
L E A D I N G C N S A N T I B O D Y T E S T I N G S E R V I C E S
 L E A D I N G C N S A N T I B O D Y T E S T I N G S E R V I C E S Paraneoplastic Autoimmune Neurological Disorder Testing Services New Tests Now Available. Why Athena Diagnostics? Faster, More Relevant
L E A D I N G C N S A N T I B O D Y T E S T I N G S E R V I C E S Paraneoplastic Autoimmune Neurological Disorder Testing Services New Tests Now Available. Why Athena Diagnostics? Faster, More Relevant
Lyme (IgG and IgM) Antibody Confirmation
 Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Lyme (IgG and IgM) Antibody Confirmation TEST UPDATE: New Test Notification Date: 1/9/2013 Effective Date: 1/7/2013 CONTACT INFO Call 802-847-5121 800-991-2799 email labmarketing@vtmednet.org
Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Lyme (IgG and IgM) Antibody Confirmation TEST UPDATE: New Test Notification Date: 1/9/2013 Effective Date: 1/7/2013 CONTACT INFO Call 802-847-5121 800-991-2799 email labmarketing@vtmednet.org
INTERPRETATION INFORMATION SHEET
 Creative Testing Solutions 2424 West Erie Dr. 2205 Highway 121 10100 Martin Luther King Jr. St. No. Tempe, AZ 85282 Bedford, TX 76021 St. Petersburg, FL 33716 INTERPRETATION INFORMATION SHEET Human Immunodeficiency
Creative Testing Solutions 2424 West Erie Dr. 2205 Highway 121 10100 Martin Luther King Jr. St. No. Tempe, AZ 85282 Bedford, TX 76021 St. Petersburg, FL 33716 INTERPRETATION INFORMATION SHEET Human Immunodeficiency
Zika Virus. Fred A. Lopez, MD, MACP Richard Vial Professor Department of Medicine Section of Infectious Diseases
 Zika Virus Fred A. Lopez, MD, MACP Richard Vial Professor Department of Medicine Section of Infectious Diseases What is the incubation period for Zika virus infection? Unknown but likely to be several
Zika Virus Fred A. Lopez, MD, MACP Richard Vial Professor Department of Medicine Section of Infectious Diseases What is the incubation period for Zika virus infection? Unknown but likely to be several
Young women with psychosis, seizures, and ovarian teratoma
 Young women with psychosis, seizures, and ovarian teratoma A review on anti-nmdar encephalitis 1 PAULA DE ROBLES, MD CLINICAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR CLINICAL NEUROSCIENCES AND ONCOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY
Young women with psychosis, seizures, and ovarian teratoma A review on anti-nmdar encephalitis 1 PAULA DE ROBLES, MD CLINICAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR CLINICAL NEUROSCIENCES AND ONCOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY
Appendix B: Provincial Case Definitions for Reportable Diseases
 Infectious Diseases Protocol Appendix B: Provincial Case Definitions for Reportable Diseases Disease: West Nile Virus Illness Revised December 2014 West Nile Virus Illness 1.0 Provincial Reporting Confirmed
Infectious Diseases Protocol Appendix B: Provincial Case Definitions for Reportable Diseases Disease: West Nile Virus Illness Revised December 2014 West Nile Virus Illness 1.0 Provincial Reporting Confirmed
PATHOLOGY. HercepTestTM. Product Information
 PATHOLOGY HercepTestTM Product Information CLINICAL TRIALS HercepTest The First and Foremost Dako s pharmdx HercepTest was the first FDA-approved assay developed exclusively to aid physicians in identifying
PATHOLOGY HercepTestTM Product Information CLINICAL TRIALS HercepTest The First and Foremost Dako s pharmdx HercepTest was the first FDA-approved assay developed exclusively to aid physicians in identifying
High Resolution Epitope Mapping of Human Autoimmune Sera against Antigens CENPA and KDM6B. PEPperPRINT GmbH Heidelberg, 06/2014
 High Resolution Epitope Mapping of Human Autoimmune Sera against Antigens CENPA and KDM6B PEPperPRINT GmbH Heidelberg, 06/2014 Introduction This report describes the epitope mapping of autoimmune sera
High Resolution Epitope Mapping of Human Autoimmune Sera against Antigens CENPA and KDM6B PEPperPRINT GmbH Heidelberg, 06/2014 Introduction This report describes the epitope mapping of autoimmune sera
SOGC recommendation on ZIKA virus exposure for clinicians caring for pregnant women and those who intend to get pregnant
 SOGC recommendation on ZIKA virus exposure for clinicians caring for pregnant women and those who intend to get pregnant Foreword The rapid emergence of Zika virus as a potential causative agent for fetal
SOGC recommendation on ZIKA virus exposure for clinicians caring for pregnant women and those who intend to get pregnant Foreword The rapid emergence of Zika virus as a potential causative agent for fetal
1.5 Function of analyte For albumin, see separate entry. The immunoglobulins are components of the humoral arm of the immune system.
 Total protein (serum, plasma) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Total protein 1.2 Alternative names None 1.3 NMLC code 1.4 Description of analyte This is a quantitative measurement
Total protein (serum, plasma) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Total protein 1.2 Alternative names None 1.3 NMLC code 1.4 Description of analyte This is a quantitative measurement
510(k) SUBSTANTIAL EQUIVALENCE DETERMINATION DECISION SUMMARY
 A. 510(k) Number: K092353 510(k) SUBSTANTIAL EQUIVALENCE DETERMINATION DECISION SUMMARY B. Purpose for Submission: This is a new 510k application for a new indication for the MONOLISA Anti-HAV IgM EIA
A. 510(k) Number: K092353 510(k) SUBSTANTIAL EQUIVALENCE DETERMINATION DECISION SUMMARY B. Purpose for Submission: This is a new 510k application for a new indication for the MONOLISA Anti-HAV IgM EIA
LAB 1 - Direct agglutination. Serology-the study of the in vitro reactions between antibody and antigen
 LAB 1 - Direct agglutination Serology-the study of the in vitro reactions between antibody and antigen Serological reaction: - quantitative (weight/volume) - qualitative Agglutination - the aggregation
LAB 1 - Direct agglutination Serology-the study of the in vitro reactions between antibody and antigen Serological reaction: - quantitative (weight/volume) - qualitative Agglutination - the aggregation
Diagnosis of HIV-1 Infection. Estelle Piwowar-Manning HPTN Central Laboratory The Johns Hopkins University
 Diagnosis of HIV-1 Infection Estelle Piwowar-Manning HPTN Central Laboratory The Johns Hopkins University Tests Used to Diagnose HIV-1 Infection HIV antibody (today s topic) HIV p24 antigen HIV DNA HIV
Diagnosis of HIV-1 Infection Estelle Piwowar-Manning HPTN Central Laboratory The Johns Hopkins University Tests Used to Diagnose HIV-1 Infection HIV antibody (today s topic) HIV p24 antigen HIV DNA HIV
Hepatitis and Retrovirus. LIAISON XL Accurate detection of HIV infection. HIV Ab/Ag FOR OUTSIDE THE US AND CANADA ONLY
 Hepatitis and Retrovirus LIAISON XL Accurate detection of HIV infection HIV Ab/Ag FOR OUTSIDE THE US AND CANADA ONLY LIAISON XL HIV Ab/Ag is Your solution LIAISON XL murex HIV Ab/Ag main features The LIAISON
Hepatitis and Retrovirus LIAISON XL Accurate detection of HIV infection HIV Ab/Ag FOR OUTSIDE THE US AND CANADA ONLY LIAISON XL HIV Ab/Ag is Your solution LIAISON XL murex HIV Ab/Ag main features The LIAISON
Steps to getting a diagnosis: Finding out if it s Alzheimer s Disease.
 Steps to getting a diagnosis: Finding out if it s Alzheimer s Disease. Memory loss and changes in mood and behavior are some signs that you or a family member may have Alzheimer s disease. If you have
Steps to getting a diagnosis: Finding out if it s Alzheimer s Disease. Memory loss and changes in mood and behavior are some signs that you or a family member may have Alzheimer s disease. If you have
CANADIAN RULE BASED CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM (IVDD) Life Sciences British Columbia NRC-Industry Research Assistance Program
 CANADIAN RULE BASED CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM (IVDD) Life Sciences British Columbia NRC-Industry Research Assistance Program Health Canada Regulations on Medical Devices Vancouver, B.C. October 29, 2007 Nancy
CANADIAN RULE BASED CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM (IVDD) Life Sciences British Columbia NRC-Industry Research Assistance Program Health Canada Regulations on Medical Devices Vancouver, B.C. October 29, 2007 Nancy
Cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine use for Alzheimer s disease TOPIC REVIEW
 Cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine use for Alzheimer s disease TOPIC REVIEW Diagnosis of Dementia : DSM-IV criteria Loss of memory and one or more other cognitive abilities Aphasia Apraxia Agnosia
Cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine use for Alzheimer s disease TOPIC REVIEW Diagnosis of Dementia : DSM-IV criteria Loss of memory and one or more other cognitive abilities Aphasia Apraxia Agnosia
F r e q u e n t l y A s k e d Q u e s t i o n s
 Myasthenia Gravis Q: What is myasthenia gravis (MG)? A: Myasthenia gravis (meye-uhss- THEEN-ee-uh GRAV uhss) (MG) is an autoimmune disease that weakens the muscles. The name comes from Greek and Latin
Myasthenia Gravis Q: What is myasthenia gravis (MG)? A: Myasthenia gravis (meye-uhss- THEEN-ee-uh GRAV uhss) (MG) is an autoimmune disease that weakens the muscles. The name comes from Greek and Latin
Standardization and Evaluation of IgA and IgM Gel Column Agglutination for Direct Antiglobulin Testing
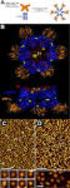 Standardization and Evaluation of IgA and IgM Gel Column Agglutination for Direct Antiglobulin Testing ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Diagnosis of autoimmune hemolytic anemia is commonly confirmed with a positive
Standardization and Evaluation of IgA and IgM Gel Column Agglutination for Direct Antiglobulin Testing ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Diagnosis of autoimmune hemolytic anemia is commonly confirmed with a positive
Development and Validation of In Vitro Diagnostic Tests. YC Lee, Ph.D. CEO
 Development and Validation of In Vitro Diagnostic Tests YC Lee, Ph.D. CEO 1 Validation of In Vitro Diagnostic Tests Validated d Diagnostic Test should: Provides test results that identify if positive i
Development and Validation of In Vitro Diagnostic Tests YC Lee, Ph.D. CEO 1 Validation of In Vitro Diagnostic Tests Validated d Diagnostic Test should: Provides test results that identify if positive i
Some Immunological Test. Presented by Alaa Faeiz Ashwaaq Dyaa Aseel Abd AL-Razaq Supervised by D.Feras
 Some Immunological Test Presented by Alaa Faeiz Ashwaaq Dyaa Aseel Abd AL-Razaq Supervised by D.Feras Alaa Faeiz Antigen -Antibody Reactions. Antigen antibody reactions are performed to determine the presence
Some Immunological Test Presented by Alaa Faeiz Ashwaaq Dyaa Aseel Abd AL-Razaq Supervised by D.Feras Alaa Faeiz Antigen -Antibody Reactions. Antigen antibody reactions are performed to determine the presence
Topic: Serological reactions: the purpose and a principle of reactions. Agglutination test. Precipitation test. CFT, IFT, ELISA, RIA.
 Topic: Serological reactions: the purpose and a principle of reactions. Agglutination test. Precipitation test. CFT, IFT, ELISA, RIA. Serology is the study and use of immunological tests to diagnose and
Topic: Serological reactions: the purpose and a principle of reactions. Agglutination test. Precipitation test. CFT, IFT, ELISA, RIA. Serology is the study and use of immunological tests to diagnose and
Algorithm for detecting Zika virus (ZIKV) 1
 Algorithm for detecting Zika virus (ZIKV) 1 This algorithm is addressed to laboratories with established capacity (molecular, antigenic and/or serological) to detect dengue (DENV), Zika (ZIKV) 2, and chikungunya
Algorithm for detecting Zika virus (ZIKV) 1 This algorithm is addressed to laboratories with established capacity (molecular, antigenic and/or serological) to detect dengue (DENV), Zika (ZIKV) 2, and chikungunya
LYME DISEASE. 2.5M specimen tests per year. 97% accuracy with Rockland tools
 LYME DISEASE The current situation & our solutions Lateral Flow Data Proof of Concept Studies Core Technology Sequence Analysis & Protein Expression The most common vector-borne illness in the United States
LYME DISEASE The current situation & our solutions Lateral Flow Data Proof of Concept Studies Core Technology Sequence Analysis & Protein Expression The most common vector-borne illness in the United States
LIAISON XL HCV Ab Accurate diagnosis of the early stage of HCV infection
 Hepatitis and Retrovirus LIAISON XL HCV Ab Accurate diagnosis of the early stage of HCV infection FOR OUTSIDE THE US AND CANADA ONLY LIAISON XL HCV Ab is Your solution LIAISON XL murex HCV Ab main features
Hepatitis and Retrovirus LIAISON XL HCV Ab Accurate diagnosis of the early stage of HCV infection FOR OUTSIDE THE US AND CANADA ONLY LIAISON XL HCV Ab is Your solution LIAISON XL murex HCV Ab main features
Testing for Tick Borne Diseases: How and When?
 Testing for Tick Borne Diseases: How and When? Rick Alleman, DVM, PhD University of Florida C. Guillermo Couto, DVM The Ohio State University Tick borne diseases (TBDs) used to be quite common in Greyhounds,
Testing for Tick Borne Diseases: How and When? Rick Alleman, DVM, PhD University of Florida C. Guillermo Couto, DVM The Ohio State University Tick borne diseases (TBDs) used to be quite common in Greyhounds,
HuCAL Custom Monoclonal Antibodies
 HuCAL Custom Monoclonal Antibodies Highly Specific Monoclonal Antibodies in just 8 Weeks PROVEN, HIGHLY SPECIFIC, HIGH AFFINITY ANTIBODIES IN 8 WEEKS WITHOUT HuCAL PLATINUM IMMUNIZATION (Human Combinatorial
HuCAL Custom Monoclonal Antibodies Highly Specific Monoclonal Antibodies in just 8 Weeks PROVEN, HIGHLY SPECIFIC, HIGH AFFINITY ANTIBODIES IN 8 WEEKS WITHOUT HuCAL PLATINUM IMMUNIZATION (Human Combinatorial
2.1 Who first described NMO?
 History & Discovery 54 2 History & Discovery 2.1 Who first described NMO? 2.2 What is the difference between NMO and Multiple Sclerosis? 2.3 How common is NMO? 2.4 Who is affected by NMO? 2.1 Who first
History & Discovery 54 2 History & Discovery 2.1 Who first described NMO? 2.2 What is the difference between NMO and Multiple Sclerosis? 2.3 How common is NMO? 2.4 Who is affected by NMO? 2.1 Who first
A clinical approach to diagnosis of autoimmune encephalitis
 A clinical approach to diagnosis of autoimmune encephalitis Francesc Graus, Maarten J Titulaer, Ramani Balu, Susanne Benseler, Christian G Bien, Tania Cellucci, Irene Cortese, Russell C Dale, Jeffrey M
A clinical approach to diagnosis of autoimmune encephalitis Francesc Graus, Maarten J Titulaer, Ramani Balu, Susanne Benseler, Christian G Bien, Tania Cellucci, Irene Cortese, Russell C Dale, Jeffrey M
How Does a Doctor Test for AIDS?
 Edvo-Kit #S-70 How Does a Doctor Test for AIDS? S-70 Experiment Objective: The Human Immunodefi ciency Virus (HIV) is an infectious agent that causes Acquired Immunodefi ciency Syndrome (AIDS) in humans.
Edvo-Kit #S-70 How Does a Doctor Test for AIDS? S-70 Experiment Objective: The Human Immunodefi ciency Virus (HIV) is an infectious agent that causes Acquired Immunodefi ciency Syndrome (AIDS) in humans.
Defining Normal Cerebrospinal Fluid White Blood Cell Counts in Neonates and Young Infants: A Scholarly Pursuit
 Defining Normal Cerebrospinal Fluid White Blood Cell Counts in Neonates and Young Infants: A Scholarly Pursuit Lori A. Kestenbaum, Jessica L. Ebberson, Joseph J. Zorc, Caitlin LaRussa, Richard L. Hodinka
Defining Normal Cerebrospinal Fluid White Blood Cell Counts in Neonates and Young Infants: A Scholarly Pursuit Lori A. Kestenbaum, Jessica L. Ebberson, Joseph J. Zorc, Caitlin LaRussa, Richard L. Hodinka
A: Nursing Knowledge. Alberta Licensed Practical Nurses Competency Profile 1
 A: Nursing Knowledge Alberta Licensed Practical Nurses Competency Profile 1 Competency: A-1 Anatomy and Physiology A-1-1 A-1-2 A-1-3 A-1-4 A-1-5 A-1-6 A-1-7 A-1-8 Identify the normal structures and functions
A: Nursing Knowledge Alberta Licensed Practical Nurses Competency Profile 1 Competency: A-1 Anatomy and Physiology A-1-1 A-1-2 A-1-3 A-1-4 A-1-5 A-1-6 A-1-7 A-1-8 Identify the normal structures and functions
Effective Treatment of Lyme Borreliosis with Pentacyclic Alkaloid Uncaria tomentosa (TOA-free Cat s Claw)
 Effective Treatment of Lyme Borreliosis with Pentacyclic Alkaloid Uncaria tomentosa (TOA-free Cat s Claw) Executive Summary Introduction In a six-month prospective cohort study designed to compare the
Effective Treatment of Lyme Borreliosis with Pentacyclic Alkaloid Uncaria tomentosa (TOA-free Cat s Claw) Executive Summary Introduction In a six-month prospective cohort study designed to compare the
2006 7.012 Problem Set 6 KEY
 2006 7.012 Problem Set 6 KEY ** Due before 5 PM on WEDNESDAY, November 22, 2006. ** Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. You create an artificial
2006 7.012 Problem Set 6 KEY ** Due before 5 PM on WEDNESDAY, November 22, 2006. ** Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. You create an artificial
ALS and Lyme Disease Questions from Patient and Families Responses from Medical Experts
 ALS and Lyme Disease Questions from Patient and Families Responses from Medical Experts Introduction: When anyone receives a diagnosis of ALS, it is normal and understandable to ask why you ve developed
ALS and Lyme Disease Questions from Patient and Families Responses from Medical Experts Introduction: When anyone receives a diagnosis of ALS, it is normal and understandable to ask why you ve developed
ANTIBODIES AGAINST CITRULLINATED PEPTIDES IN EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: DIAGNOSTIC AND PROGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE
 ANTIBODIES AGAINST CITRULLINATED PEPTIDES IN EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: DIAGNOSTIC AND PROGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE Principal investigators: Dr Raimon Sanmartí Sala Hospital Clínic i Provincial de Barcelona
ANTIBODIES AGAINST CITRULLINATED PEPTIDES IN EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: DIAGNOSTIC AND PROGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE Principal investigators: Dr Raimon Sanmartí Sala Hospital Clínic i Provincial de Barcelona
ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1. Immunity and Disease
 ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1 Immunity and Disease Introduction The principal role of the mammalian immune response is to contain infectious disease agents. This response is mediated by several cellular and molecular
ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1 Immunity and Disease Introduction The principal role of the mammalian immune response is to contain infectious disease agents. This response is mediated by several cellular and molecular
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.021: Musculoskeletal Pathophysiology, IAP 2006 Course Director: Dr. Dwight R. Robinson Systemic Lupus Erythematosus A multi-system autoimmune
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.021: Musculoskeletal Pathophysiology, IAP 2006 Course Director: Dr. Dwight R. Robinson Systemic Lupus Erythematosus A multi-system autoimmune
LAB 14 ENZYME LINKED IMMUNOSORBENT ASSAY (ELISA)
 STUDENT GUIDE LAB 14 ENZYME LINKED IMMUNOSORBENT ASSAY (ELISA) GOAL The goal of this laboratory lesson is to explain the concepts and technique of enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). OBJECTIVES
STUDENT GUIDE LAB 14 ENZYME LINKED IMMUNOSORBENT ASSAY (ELISA) GOAL The goal of this laboratory lesson is to explain the concepts and technique of enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). OBJECTIVES
Accuracy in Space and Time: Diagnosing Multiple Sclerosis. 2012 Genzyme Corporation, a Sanofi company.
 Accuracy in Space and Time: Diagnosing Multiple Sclerosis 2012 Genzyme Corporation, a Sanofi company. Brought All rights to reserved. you by www.msatrium.com, MS.US.PO876.1012 your gateway to MS knowledge.
Accuracy in Space and Time: Diagnosing Multiple Sclerosis 2012 Genzyme Corporation, a Sanofi company. Brought All rights to reserved. you by www.msatrium.com, MS.US.PO876.1012 your gateway to MS knowledge.
HuCAL Custom Monoclonal Antibodies
 HuCAL Custom Monoclonal HuCAL Custom Monoclonal Antibodies Highly Specific, Recombinant Antibodies in 8 Weeks Highly Specific Monoclonal Antibodies in Just 8 Weeks HuCAL PLATINUM (Human Combinatorial Antibody
HuCAL Custom Monoclonal HuCAL Custom Monoclonal Antibodies Highly Specific, Recombinant Antibodies in 8 Weeks Highly Specific Monoclonal Antibodies in Just 8 Weeks HuCAL PLATINUM (Human Combinatorial Antibody
New HLA class I epitopes defined by murine monoclonal antibodies
 Human Immunology 71 (2010) 456 461 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect New HLA class I epitopes defined by murine monoclonal antibodies Nadim El-Awar a, *, Paul I. Terasaki b, Anh Nguyen a, Mamie
Human Immunology 71 (2010) 456 461 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect New HLA class I epitopes defined by murine monoclonal antibodies Nadim El-Awar a, *, Paul I. Terasaki b, Anh Nguyen a, Mamie
Antibody Function & Structure
 Antibody Function & Structure Specifically bind to antigens in both the recognition phase (cellular receptors) and during the effector phase (synthesis and secretion) of humoral immunity Serology: the
Antibody Function & Structure Specifically bind to antigens in both the recognition phase (cellular receptors) and during the effector phase (synthesis and secretion) of humoral immunity Serology: the
IKDT Laboratory. IKDT as Service Lab (CRO) for Molecular Diagnostics
 Page 1 IKDT Laboratory IKDT as Service Lab (CRO) for Molecular Diagnostics IKDT lab offer is complete diagnostic service to all external customers. We could perform as well single procedures or complex
Page 1 IKDT Laboratory IKDT as Service Lab (CRO) for Molecular Diagnostics IKDT lab offer is complete diagnostic service to all external customers. We could perform as well single procedures or complex
Summary Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Cerebrospinal Venous Insufficiency (CCSVI) in People with Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
 ETMIS 2012; Vol. 8: N o 7 Summary Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Cerebrospinal Venous Insufficiency (CCSVI) in People with Multiple Sclerosis (MS) March 2012 A production of the Institut national d
ETMIS 2012; Vol. 8: N o 7 Summary Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Cerebrospinal Venous Insufficiency (CCSVI) in People with Multiple Sclerosis (MS) March 2012 A production of the Institut national d
Serology: Fluorescent antibody tests and other tests employing conjugated antibodies
 Serology: Fluorescent antibody tests and other tests employing conjugated antibodies Authors: Adapted by Prof M van Vuuren. Originally compiled by Dr RW Worthington. (Retired) Licensed under a Creative
Serology: Fluorescent antibody tests and other tests employing conjugated antibodies Authors: Adapted by Prof M van Vuuren. Originally compiled by Dr RW Worthington. (Retired) Licensed under a Creative
Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT)
 Exercise 8 Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT) Objectives: 1. State the purpose for performing the DAT. 2. State what a positive DAT indicates. 3. List the reagents which are used for performing the DAT. 4.
Exercise 8 Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT) Objectives: 1. State the purpose for performing the DAT. 2. State what a positive DAT indicates. 3. List the reagents which are used for performing the DAT. 4.
Objectives. Immunologic Methods. Objectives. Immunology vs. Serology. Cross Reactivity. Sensitivity and Specificity. Definitions
 Immunologic Methods Part One Definitions Part Two Antigen-Antibody Reactions CLS 420 Clinical Immunology and Molecular Diagnostics Kathy Trudell MLS (ASCP) CM SBB CM ktrudell@nebraskamed.com Discuss the
Immunologic Methods Part One Definitions Part Two Antigen-Antibody Reactions CLS 420 Clinical Immunology and Molecular Diagnostics Kathy Trudell MLS (ASCP) CM SBB CM ktrudell@nebraskamed.com Discuss the
Selective IgA deficiency (slgad) hello@piduk.org 0800 987 8986 www.piduk.org
 Selective IgA deficiency (slgad) hello@piduk.org 0800 987 8986 www.piduk.org About this booklet This booklet provides information on selective IgA deficiency (sigad). It has been produced by the PID UK
Selective IgA deficiency (slgad) hello@piduk.org 0800 987 8986 www.piduk.org About this booklet This booklet provides information on selective IgA deficiency (sigad). It has been produced by the PID UK
NovaLisa (ZVM0790) Performance Characteristics
 NovaLisa Zika Virus IgM µ-capture ELISA (ZVM0790) Performance Characteristics Table of Contents 1 Introduction... 3 2 Intended Use... 4 3 Principle of the Assay... 4 4 Performance Characteristics... 4
NovaLisa Zika Virus IgM µ-capture ELISA (ZVM0790) Performance Characteristics Table of Contents 1 Introduction... 3 2 Intended Use... 4 3 Principle of the Assay... 4 4 Performance Characteristics... 4
HiPer RA Test Teaching Kit
 HiPer RA Test Teaching Kit Product Code: HTI019 Number of experiments that can be performed: 20 Duration of Experiment: 1hour Storage Instructions: The kit is stable for 6 months from the date of receipt
HiPer RA Test Teaching Kit Product Code: HTI019 Number of experiments that can be performed: 20 Duration of Experiment: 1hour Storage Instructions: The kit is stable for 6 months from the date of receipt
Chapter 6: Antigen-Antibody Interactions
 Chapter 6: Antigen-Antibody Interactions I. Strength of Ag-Ab interactions A. Antibody Affinity - strength of total noncovalent interactions between single Ag-binding site on an Ab and a single epitope
Chapter 6: Antigen-Antibody Interactions I. Strength of Ag-Ab interactions A. Antibody Affinity - strength of total noncovalent interactions between single Ag-binding site on an Ab and a single epitope
4A. Types of Laboratory Tests Available and Specimens Required. Three main types of laboratory tests are used for diagnosing CHIK: virus
 4. LABORATORY 4A. Types of Laboratory Tests Available and Specimens Required Three main types of laboratory tests are used for diagnosing CHIK: virus isolation, reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction
4. LABORATORY 4A. Types of Laboratory Tests Available and Specimens Required Three main types of laboratory tests are used for diagnosing CHIK: virus isolation, reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction
LIAISON XL HBsAg Quant
 Hepatitis and Retrovirus LIAISON XL HBsAg Quant Reliable detection of HBsAg mutants and genotypes for accurate differential diagnosis of the stage of infection FOR OUTSIDE THE US AND CANADA ONLY LIAISON
Hepatitis and Retrovirus LIAISON XL HBsAg Quant Reliable detection of HBsAg mutants and genotypes for accurate differential diagnosis of the stage of infection FOR OUTSIDE THE US AND CANADA ONLY LIAISON
THE His Tag Antibody, mab, Mouse
 THE His Tag Antibody, mab, Mouse Cat. No. A00186 Technical Manual No. TM0243 Update date 01052011 I Description.... 1 II Key Features. 2 III Storage 2 IV Applications.... 2 V Examples - ELISA..... 2 VI
THE His Tag Antibody, mab, Mouse Cat. No. A00186 Technical Manual No. TM0243 Update date 01052011 I Description.... 1 II Key Features. 2 III Storage 2 IV Applications.... 2 V Examples - ELISA..... 2 VI
MRI in Differential Diagnosis
 MRI in Differential Diagnosis Jill Conway, MD, MA, MSCE Director, Carolinas MS Center Clerkship Director, UNCSOM-Charlotte Campus Charlotte, NC DISCLOSURES Speaking, consulting, and/or advisory boards
MRI in Differential Diagnosis Jill Conway, MD, MA, MSCE Director, Carolinas MS Center Clerkship Director, UNCSOM-Charlotte Campus Charlotte, NC DISCLOSURES Speaking, consulting, and/or advisory boards
Cold Agglutination Titer detecting Cold Reacting Antibodies
 Objectives: Cold Agglutination Titer detecting Cold Reacting Antibodies 1. Perform a serial dilution to determine the amount of cold reacting antibody present in a patient specimen with the results obtained
Objectives: Cold Agglutination Titer detecting Cold Reacting Antibodies 1. Perform a serial dilution to determine the amount of cold reacting antibody present in a patient specimen with the results obtained
UPMCREHAB GRAND ROUNDS
 UPMCREHAB GRAND ROUNDS WINTER 2013 Accreditation Statement The University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education (ACCME) to provide
UPMCREHAB GRAND ROUNDS WINTER 2013 Accreditation Statement The University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education (ACCME) to provide
Cytomegalovirus (HHV5/CMV) Roseolovirus (HHV6 & 7)
 Betaherpesvirinae Cytomegalovirus (HHV5/CMV) Roseolovirus (HHV6 & 7) CYTOMEGALOVIRUS CMV is thought to be amongst the oldest type of herpesvirus in evolutionary terms. CMV is the prototype of beta-herpesviruses
Betaherpesvirinae Cytomegalovirus (HHV5/CMV) Roseolovirus (HHV6 & 7) CYTOMEGALOVIRUS CMV is thought to be amongst the oldest type of herpesvirus in evolutionary terms. CMV is the prototype of beta-herpesviruses
Core Topic 2. The immune system and how vaccines work
 Core Topic 2 The immune system and how vaccines work Learning outcome To be able to describe in outline the immune system and how vaccines work in individuals and populations Learning objectives Explain
Core Topic 2 The immune system and how vaccines work Learning outcome To be able to describe in outline the immune system and how vaccines work in individuals and populations Learning objectives Explain
New Onset Seizure Clinic
 New Onset Seizure Clinic Timely Care from the Region s Experts The New Onset Seizure Clinic at UH Rainbow Babies & Children s Hospital provides expert diagnostic services, referrals, treatment and follow-up
New Onset Seizure Clinic Timely Care from the Region s Experts The New Onset Seizure Clinic at UH Rainbow Babies & Children s Hospital provides expert diagnostic services, referrals, treatment and follow-up
The Nuts and Bolts of Multiple Sclerosis. Rebecca Milholland, M.D., Ph.D. Center for Neurosciences
 The Nuts and Bolts of Multiple Sclerosis Rebecca Milholland, M.D., Ph.D. Center for Neurosciences Objectives Discuss which patients are at risk for Multiple Sclerosis Discuss the diagnostic criteria for
The Nuts and Bolts of Multiple Sclerosis Rebecca Milholland, M.D., Ph.D. Center for Neurosciences Objectives Discuss which patients are at risk for Multiple Sclerosis Discuss the diagnostic criteria for
Alzheimer s disease. What is Alzheimer s disease?
 Alzheimer s disease What is Alzheimer s disease? What we know about dementia and Alzheimer s disease Alzheimer s disease is the most common of a large group of disorders known as dementias. It is an irreversible
Alzheimer s disease What is Alzheimer s disease? What we know about dementia and Alzheimer s disease Alzheimer s disease is the most common of a large group of disorders known as dementias. It is an irreversible
acquired chronic immune-mediated inflammatory condition of CNS. MS in children: 10% +secondary progressive MS: rare +primary progressive MS: rare
 Immunomodulatory Therapies in Pediatric MS Vuong Chinh Quyen Neurology Department Medscape Mar 8, 2013 Multiple Sclerosis in Children. Iran J Child Neurol. 2013 Spring Introduction acquired chronic immune-mediated
Immunomodulatory Therapies in Pediatric MS Vuong Chinh Quyen Neurology Department Medscape Mar 8, 2013 Multiple Sclerosis in Children. Iran J Child Neurol. 2013 Spring Introduction acquired chronic immune-mediated
GENOMICS: REINVIGORATING THE FIELD OF PSYCHIATRIC RESEARCH
 Office of Communications www.broadinstitute.org T 617-714-7151 communications@broadinstitute.org 7 Cambridge Center, Cambridge, MA 02142 GENOMICS: REINVIGORATING THE FIELD OF PSYCHIATRIC RESEARCH For decades,
Office of Communications www.broadinstitute.org T 617-714-7151 communications@broadinstitute.org 7 Cambridge Center, Cambridge, MA 02142 GENOMICS: REINVIGORATING THE FIELD OF PSYCHIATRIC RESEARCH For decades,
Homework 5: Differential Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis
 Homework 5: Differential Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis Due Wednesday, 3/3/99 1.0 Background Multiple Sclerosis affects approximately 350 K Americans and is the leading nontraumatic source of neurologic
Homework 5: Differential Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis Due Wednesday, 3/3/99 1.0 Background Multiple Sclerosis affects approximately 350 K Americans and is the leading nontraumatic source of neurologic
IgM ANTIBODY CAPTURE ENZYME-LINKED IMMUNOSORBENT ASSAY PROTOCOL
 Appendix C. IgM and IgG Serologic Assay Protocols IgM ANTIBODY CAPTURE ENZYME-LINKED IMMUNOSORBENT ASSAY PROTOCOL Introduction Principle Safety Assays that detect viral specific immunoglobulin M (IgM)
Appendix C. IgM and IgG Serologic Assay Protocols IgM ANTIBODY CAPTURE ENZYME-LINKED IMMUNOSORBENT ASSAY PROTOCOL Introduction Principle Safety Assays that detect viral specific immunoglobulin M (IgM)
Rheumatology Labs for Primary Care Providers. Robert Monger, M.D., F.A.C.P. 2015 Frontiers in Medicine
 Rheumatology Labs for Primary Care Providers Robert Monger, M.D., F.A.C.P. 2015 Frontiers in Medicine Objectives Review the Indications for and Interpretation of lab testing for the following diseases:
Rheumatology Labs for Primary Care Providers Robert Monger, M.D., F.A.C.P. 2015 Frontiers in Medicine Objectives Review the Indications for and Interpretation of lab testing for the following diseases:
Diabetic Ketoacidosis: When Sugar Isn t Sweet!!!
 Diabetic Ketoacidosis: When Sugar Isn t Sweet!!! W Ricks Hanna Jr MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics University of Tennessee Health Science Center LeBonheur Children s Hospital Introduction Diabetes
Diabetic Ketoacidosis: When Sugar Isn t Sweet!!! W Ricks Hanna Jr MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics University of Tennessee Health Science Center LeBonheur Children s Hospital Introduction Diabetes
Medical Laboratory Technology Program. Student Learning Outcomes & Course Descriptions with Learning Objectives
 Medical Laboratory Technology Program Student Learning Outcomes & Course Descriptions with Learning Objectives Medical Laboratory Technology Student Learning Outcomes All Colorado Mesa University associate
Medical Laboratory Technology Program Student Learning Outcomes & Course Descriptions with Learning Objectives Medical Laboratory Technology Student Learning Outcomes All Colorado Mesa University associate
Disease Surveillance in New Jersey Spring 2006
 Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease Surveillance in New Jersey Spring 2006 Shereen Brynildsen, MS Epidemiologist, Infectious & Zoonotic Disease Program New Jersey Department of Health & Senior Services Phone: 609-588
Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease Surveillance in New Jersey Spring 2006 Shereen Brynildsen, MS Epidemiologist, Infectious & Zoonotic Disease Program New Jersey Department of Health & Senior Services Phone: 609-588
Autoimmunity and immunemediated. FOCiS. Lecture outline
 1 Autoimmunity and immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails Genetics of autoimmune diseases Therapeutic
1 Autoimmunity and immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails Genetics of autoimmune diseases Therapeutic
Fact Sheet for Health Care Providers: Interpreting Results from the Aptima Zika Virus Assay. June 17, 2016
 Dear Health Care Provider: Fact Sheet for Health Care Providers: Interpreting Results from the Aptima Zika Virus Assay June 17, 2016 The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has issued an Emergency
Dear Health Care Provider: Fact Sheet for Health Care Providers: Interpreting Results from the Aptima Zika Virus Assay June 17, 2016 The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has issued an Emergency
Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT)
 Exercise 8 Exercise 9 Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT) Elution Study Task Aim Introduction To perform the DAT and elution procedure with correct interpretation of results. To perform with 100% accuracy the
Exercise 8 Exercise 9 Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT) Elution Study Task Aim Introduction To perform the DAT and elution procedure with correct interpretation of results. To perform with 100% accuracy the
Brain Cancer. This reference summary will help you understand how brain tumors are diagnosed and what options are available to treat them.
 Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
CNS DEMYLINATING DISORDERS
 CNS DEMYLINATING DISORDERS Multiple sclerosis A Dutch saint named Lidwina, who died in 1433, may have been one of the first known MS patients. After she fell while ice skating, she developed symptoms such
CNS DEMYLINATING DISORDERS Multiple sclerosis A Dutch saint named Lidwina, who died in 1433, may have been one of the first known MS patients. After she fell while ice skating, she developed symptoms such
Measles (Rubeola) IgM ELISA Catalog No. CB40-101-325099 (96 Tests)
 For Research Use Only. Not for use in Diagnostic Procedures. INTENDED USE Measles test is an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for the detection of IgG class antibodies to Measles (Rubeola) in
For Research Use Only. Not for use in Diagnostic Procedures. INTENDED USE Measles test is an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for the detection of IgG class antibodies to Measles (Rubeola) in
Natalizumab (Tysabri) and PMLthe current figures. Paul-Ehrlich-Institut Brigitte Keller Stanislawski Paul-Ehrlich-Str. 51-59 63225 Langen GERMANY
 Natalizumab (Tysabri) and PMLthe current figures Paul-Ehrlich-Institut Brigitte Keller Stanislawski Paul-Ehrlich-Str. 51-59 63225 Langen GERMANY Humanised MAB Natalizumab Specific binding to a4-integrin
Natalizumab (Tysabri) and PMLthe current figures Paul-Ehrlich-Institut Brigitte Keller Stanislawski Paul-Ehrlich-Str. 51-59 63225 Langen GERMANY Humanised MAB Natalizumab Specific binding to a4-integrin
Amylase and Lipase Tests
 Amylase and Lipase Tests Also known as: Amy Formal name: Amylase Related tests: Lipase The Test The blood amylase test is ordered, often along with a lipase test, to help diagnose and monitor acute or
Amylase and Lipase Tests Also known as: Amy Formal name: Amylase Related tests: Lipase The Test The blood amylase test is ordered, often along with a lipase test, to help diagnose and monitor acute or
METHODS OF VITAMIN ANALYSIS
 METHODS OF VITAMIN ANALYSIS Specimen requirements; Fasting plasma or serum Lithium Heparin is the anticoagulant of choice for vitamins such as; thiamine, riboflavin, retinol, tocopherols & cholecalciferol
METHODS OF VITAMIN ANALYSIS Specimen requirements; Fasting plasma or serum Lithium Heparin is the anticoagulant of choice for vitamins such as; thiamine, riboflavin, retinol, tocopherols & cholecalciferol
The Immune System and Disease
 Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1029 1033) This section describes the causes of disease and explains how infectious diseases are transmitted Introduction
Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1029 1033) This section describes the causes of disease and explains how infectious diseases are transmitted Introduction
One of the more complex systems we re looking at. An immune response (a response to a pathogen) can be of two types:
 Immune system. One of the more complex systems we re looking at. An immune response (a response to a pathogen) can be of two types: (pathogen - disease causing organism) 1) Non specific. Anything foreign
Immune system. One of the more complex systems we re looking at. An immune response (a response to a pathogen) can be of two types: (pathogen - disease causing organism) 1) Non specific. Anything foreign
Molecular Diagnosis of Hepatitis B and Hepatitis D infections
 Molecular Diagnosis of Hepatitis B and Hepatitis D infections Acute infection Detection of HBsAg in serum is a fundamental diagnostic marker of HBV infection HBsAg shows a strong correlation with HBV replication
Molecular Diagnosis of Hepatitis B and Hepatitis D infections Acute infection Detection of HBsAg in serum is a fundamental diagnostic marker of HBV infection HBsAg shows a strong correlation with HBV replication
Direct Testing Systems and Serology
 Direct Testing Systems and Serology Rapid Manual Tests 6-2 Serology Diagnostics 6-6 BD Diagnostics Diagnostic Systems Catalog 2005/2006 6-1 Rapid Manual Tests Meningitis Test Systems 252360 Directigen
Direct Testing Systems and Serology Rapid Manual Tests 6-2 Serology Diagnostics 6-6 BD Diagnostics Diagnostic Systems Catalog 2005/2006 6-1 Rapid Manual Tests Meningitis Test Systems 252360 Directigen
REVIEW SHEET EXERCISE 3 Neurophysiology of Nerve Impulses Name Lab Time/Date. The Resting Membrane Potential
 REVIEW SHEET EXERCISE 3 Neurophysiology of Nerve Impulses Name Lab Time/Date ACTIVITY 1 The Resting Membrane Potential 1. Explain why increasing extracellular K + reduces the net diffusion of K + out of
REVIEW SHEET EXERCISE 3 Neurophysiology of Nerve Impulses Name Lab Time/Date ACTIVITY 1 The Resting Membrane Potential 1. Explain why increasing extracellular K + reduces the net diffusion of K + out of
Borrelia burgdorferi IgG, IgM Fully automated chemiluminescence assays for quantitative determination of Borrelia antibodies in serum and CSF
 Borrelia burgdorferi IgG, IgM Fully automated chemiluminescence assays for quantitative determination of Borrelia antibodies in serum and FOR OUTSIDE THE US AND CANADA ONLY Borrelia burgdorferi IgG, IgM
Borrelia burgdorferi IgG, IgM Fully automated chemiluminescence assays for quantitative determination of Borrelia antibodies in serum and FOR OUTSIDE THE US AND CANADA ONLY Borrelia burgdorferi IgG, IgM
Diagnostic Scoring System for LQTS
 Medical Coverage Policy Genetic Testing: Congenital Long QT Syndrome Device/Equipment Drug Medical Surgery Test Other Effective Date: 2/15/2011 Policy Last Updated: 2/21/2012 Prospective review is recommended/required.
Medical Coverage Policy Genetic Testing: Congenital Long QT Syndrome Device/Equipment Drug Medical Surgery Test Other Effective Date: 2/15/2011 Policy Last Updated: 2/21/2012 Prospective review is recommended/required.
BIOPHYSICS OF NERVE CELLS & NETWORKS
 UNIVERSITY OF LONDON MSci EXAMINATION May 2007 for Internal Students of Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine This paper is also taken for the relevant Examination for the Associateship
UNIVERSITY OF LONDON MSci EXAMINATION May 2007 for Internal Students of Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine This paper is also taken for the relevant Examination for the Associateship
Uses of Flow Cytometry
 Uses of Flow Cytometry 1. Multicolour analysis... 2 2. Cell Cycle and Proliferation... 3 a. Analysis of Cellular DNA Content... 4 b. Cell Proliferation Assays... 5 3. Immunology... 6 4. Apoptosis... 7
Uses of Flow Cytometry 1. Multicolour analysis... 2 2. Cell Cycle and Proliferation... 3 a. Analysis of Cellular DNA Content... 4 b. Cell Proliferation Assays... 5 3. Immunology... 6 4. Apoptosis... 7
Clinically isolated syndrome (CIS)
 Clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) Spirella Building, Letchworth, SG6 4ET 01462 476700 www.mstrust.org.uk reg charity no. 1088353 We hope you find the information in this factsheet helpful. If you would
Clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) Spirella Building, Letchworth, SG6 4ET 01462 476700 www.mstrust.org.uk reg charity no. 1088353 We hope you find the information in this factsheet helpful. If you would
Management in the pre-hospital setting
 Management in the pre-hospital setting Inflammation of the joints Two main types: Osteoarthritis - cartilage loss from wear and tear Rheumatoid arthritis - autoimmune disorder Affects all age groups,
Management in the pre-hospital setting Inflammation of the joints Two main types: Osteoarthritis - cartilage loss from wear and tear Rheumatoid arthritis - autoimmune disorder Affects all age groups,
Blood Transfusion. There are three types of blood cells: Red blood cells. White blood cells. Platelets.
 Blood Transfusion Introduction Blood transfusions can save lives. Every second, someone in the world needs a blood transfusion. Blood transfusions can replace the blood lost from a serious injury or surgery.
Blood Transfusion Introduction Blood transfusions can save lives. Every second, someone in the world needs a blood transfusion. Blood transfusions can replace the blood lost from a serious injury or surgery.
AIR FORCE REPORTABLE EVENTS GUIDELINES & CASE DEFINITIONS
 AIR FORCE REPORTABLE EVENTS GUIDELINES & CASE DEFINITIONS An Air Force addendum to the TRI-SERVICE REPORTABLE EVENTS GUIDELINES & CASE DEFINITIONS Prepared by: Air Force Institute for Operational Health
AIR FORCE REPORTABLE EVENTS GUIDELINES & CASE DEFINITIONS An Air Force addendum to the TRI-SERVICE REPORTABLE EVENTS GUIDELINES & CASE DEFINITIONS Prepared by: Air Force Institute for Operational Health
Test Request Tip Sheet
 With/Without Contrast CT, MRI Studies should NOT be ordered simultaneously as dual studies (i.e., with and without contrast). Radiation exposure is doubled and both views are rarely necessary. The study
With/Without Contrast CT, MRI Studies should NOT be ordered simultaneously as dual studies (i.e., with and without contrast). Radiation exposure is doubled and both views are rarely necessary. The study
Chapter 10. Summary & Future perspectives
 Summary & Future perspectives 123 Multiple sclerosis is a chronic disorder of the central nervous system, characterized by inflammation and axonal degeneration. All current therapies modulate the peripheral
Summary & Future perspectives 123 Multiple sclerosis is a chronic disorder of the central nervous system, characterized by inflammation and axonal degeneration. All current therapies modulate the peripheral
Blood-Based Cancer Diagnostics
 The Biotechnology Education Company Blood-Based Cancer Diagnostics EDVO-Kit 141 Store entire experiment at room temperature. EXPERIMENT OBJECTIVE: The objective of this experiment is to learn and understand
The Biotechnology Education Company Blood-Based Cancer Diagnostics EDVO-Kit 141 Store entire experiment at room temperature. EXPERIMENT OBJECTIVE: The objective of this experiment is to learn and understand
Resting membrane potential ~ -70mV - Membrane is polarized
 Resting membrane potential ~ -70mV - Membrane is polarized (ie) Electrical charge on the outside of the membrane is positive while the electrical charge on the inside of the membrane is negative Changes
Resting membrane potential ~ -70mV - Membrane is polarized (ie) Electrical charge on the outside of the membrane is positive while the electrical charge on the inside of the membrane is negative Changes
