Defining the quality of surgical breast cancer care. Margriet van der Heiden - van der Loo
|
|
|
- Baldwin Dixon
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Defining the quality of surgical breast cancer care Margriet van der Heiden - van der Loo
2 Defining the quality of surgical breast cancer care Margriet van der Heiden - van der Loo
3 Defining the quality of surgical breast cancer care Thesis, Utrecht University, the Netherlands, 2013 Margriet van der Heiden-van der Loo ISBN: Cover design and layout: Marja van Vliet Printed by: Ridderprint, Ridderkerk
4 Defining the quality of surgical breast cancer care Kwaliteit van de chirurgische borstkankerzorg (met een samenvatting in het Nederlands) Proefschrift ter verkrijging van de graad van doctor aan de Universiteit Utrecht op gezag van de rector magnificus, prof.dr. G.J. van der Zwaan, ingevolge het besluit van het college voor promoties in het openbaar te verdedigen op donderdag 14 februari 2013 des middags te 2.30 uur door Margriet van der Heiden-van der Loo geboren op 21 augustus 1974 te Waddinxveen
5 Promotoren: Prof.dr. P.H.M. Peeters Prof.dr. E.J.Th. Rutgers Dit proefschrift werd mede mogelijk gemaakt met financiële steun van IKNL.
6
7
8 Contents 1 General introduction 9 Part 1 Implementation of sentinel node biopsy 2 Implementation of sentinel node biopsy in breast cancer patients in the Netherlands 3 Axillary recurrence rate after tumour negative and micrometastatic positive sentinel node procedures in breast cancer patients, a population based multicenter study Introduction of sentinel node biopsy and stage migration of breast cancer 49 5 Outcomes of a population based series of early breast cancer patients with micrometastases and isolated tumour cells in axillary lymph nodes 59 Part 2 Comparing quality of surgical breast cancer care between hospitals 6 Weinig lokaal recidieven na mammachirurgie: goede kwaliteit van de Nederlandse borstkankerzorg 7 Measuring the quality of breast cancer care in the Netherlands: hospital variation in ipsilateral breast tumour recurrence rates 8 Variation between hospitals in surgical margins after first breast-conserving surgery in the Netherlands General discussion 117 Summary 128 Samenvatting 131 Dankwoord 135 Curriculum Vitae 139 Publications 141
9
10 Chapter 1 General introduction
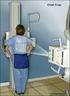
11 General introduction A total of 13,257 primary breast cancers and 1,996 carcinoma in situ were diagnosed in the Netherlands in The 10-year overall survival for breast cancer is 76% but is largely defined by the stage at diagnosis. It is estimated that on January 1st, 2011, 99,372 women in The Netherlands were alive who had breast cancer diagnosed in the past ten years. 1 These numbers make the quality of breast cancer care a major healthcare issue; for patients, physicians and the health care system in general. Surgical breast cancer care Breast cancer diagnosis and treatment focus on three basic elements: optimal local control, examining lymph node involvement and assessment of the risk of potential distant metastases. Optimal local control Adequate removal of the primary tumour is the basis for treatment of breast cancer. Breast conserving surgery (BCS) was introduced as an alternative to mastectomy. Major benefit of BCS is a better cosmetic outcome, resulting in higher patient satisfaction. BCS became commonly used in the 1980s for patients with tumours up to 2 cm. 2,3 Efficacy in tumours up to 5 cm was later demonstrated and led to further implementation of BCS. 4 7 To obtain the same cosmetic results for patients with larger tumours, neo-adjuvant systemic therapy before surgery is increasingly used to reduce the size of the lesion. BCS has become a treatment option for even more patients. In 2011, 63% of patients with early breast cancer (pt1-2, any N, M0) underwent BCS (non published data NCR). Radiotherapy is standard after BCS. To optimise local control, adequate removal of the tumour is assessed through meticulous examination of tumour margins. In case of positive margins, re-excision or additional radiotherapy on the tumour bed is required. Lymph node involvement Examination of the axilla is of major importance in staging breast cancer, for nodal involvement is associated with poorer prognosis. Staging entails removal of all axillary lymph nodes for pathological examination. A major change in lymph node staging was the introduction of the sentinel node biopsy (SNB) in the late 1990s SNB replaces the complete axillary lymph node dissection, which can lead to substantial morbidity, such as lymphedema. SNB builds on the hypothesis of an orderly pattern of lymphogenic tumour cell dissemination; if the sentinel node is free of tumour, remaining axillary nodes are also likely to be tumour negative. Sentinel nodes are identified through lymphatic mapping with radioactive colloid and intra-operative patent blue dye injection (Figure 1). The surgeon locates and removes the sentinel node(s) for histopathological examination by the pathologist. Based on results of the SNB, additional axillary clearance is considered. 10
12 Chapter 1 Chapter 1 Figure 1. Sentinel node biopsy Risk assessment of distant metastases Adjuvant systemic therapies, such as chemotherapy and hormonal treatment, aim to prevent distant metastases. Given the therapy side effects and costs, accurate patient selection is essential. Decisions are based on data on the primary tumour, axillary status and patient characteristics. Thorough deliberation by a multidisciplinary breast cancer team is required. Quality of care Quality of care is often defined as the degree to which health services for individuals and populations increase the likelihood of desired health outcomes and are consistent with current professional knowledge. 11 The desired health outcomes can be characterised by several dimensions, e.g. safe care, effective care, appropriate care, patient-centred care, timely care and equitable care (accessible to all). 12 Conclusions on the quality of care are based on the perspective chosen. During the past decade, measuring the quality of care gained growing interest. Various reports were made public, in some cases even with contradicting conclusions on the quality of care in the same hospital. 13 This reflects the complexity of the concept as was already stated by Donabedian in 1966 by saying: the quality of care is a remarkably difficult notion to define. 14 However, as stated in the fore mentioned definition, care has to be consistent with current professional knowledge. Tools to measure quality of care are called performance indicators. Many performance indicators are derived from professional knowledge. Clinical practice guidelines Current professional knowledge is readily available in clinical practice guidelines that support physicians treating breast cancer patients. The Dutch breast cancer guideline is developed by the National Breast cancer Organization Netherlands (NABON), a multidisciplinary working group facilitated by Comprehensive Cancer Centre the Netherlands (CCCNL). 15 The guideline includes all important aspects of breast cancer care, i.e. screening, diagnosis, treatment 11
13 General introduction (surgery, radiotherapy and systemic treatment), rehabilitation and follow up. The most recent guideline was published on February 13, Complementary to the diagnosis and treatment guideline is the so-called NABON nota ; a manual about the organisation of breast cancer care. 16 The NABON nota is based on the European standard and the Dutch breast cancer guideline. 15,17 It describes the basic elements to enable adequate care by health care providers and sets basic standards to be achieved by all breast cancer teams. Performance indicators in breast cancer care Currently, a number of indicators in breast cancer care are obligatory for all hospitals in the Netherlands (Table 1). Results are monitored and made public by the Dutch health care inspectorate. The health care inspectorate uses these data to identify hospitals with potential risks to the quality of care. Others use these data after publication for their own purposes, e.g. insurance companies for debating the contracts with the hospitals which care will be reimbursed and patient groups to inform patients about the quality of care of different hospitals. Table 1. Breast cancer indicators Dutch health care inspectorate 2012 Number of patients operated with primary breast cancer (or DCIS) Percentage of patients with more than focal tumour residue after first breast conserving surgery for invasive breast cancer Percentage of patients with unknown tumour residue after first breast conserving surgery for invasive breast cancer Percentage of patients with focal or more than focal tumour residue after first breast conserving surgery for DCIS Percentage of patients with unknown tumour residue after first breast conserving surgery for DCIS Percentage of patients who undergo first surgery within 5 weeks after diagnosis Percentage of patients who received first neo adjuvant treatment within 5 weeks after diagnosis Percentage of patients discussed in a multidisciplinary team before treatment started Percentage of patients discussed in a multidisciplinary team after surgery Percentage of local recurrences within 5 year after diagnoses for patients with breast conserving surgery as final surgery Percentage of local recurrences within 5 year after diagnoses for patients with mastectomy as final surgery Outline of this thesis In Part 1 of this thesis, we focus on various aspects of the implementation of SNB as an innovative method in axillary staging. The Dutch national guideline on SNB was released in Chapter 2 provides an overview of SNB implementation over the period in the Netherlands. Patient and tumour characteristics that are associated with the procedure of SNB are described, and region-specific patterns of introduction are visualised. To aid the implementation, seven hospitals in the Utrecht region (formerly known as CCCMN) jointly developed local sentinel node protocols. Not all hospitals had a nuclear department 12
14 Chapter 1 and pathology laboratory on site, so tailored procedures were needed. Treatment results for all hospitals were monitored through a registration study coordinated by CCCMN. The results are presented in Chapter 3. Sentinel nodes generally are more thoroughly examined than lymph nodes from a complete axillary dissection. As pathologists receive only a few lymph nodes for investigation, standard dissection of nodes evolved into serial sectioning with immunohistochemistry staining, with potential increase of diagnosing small deposits of tumour metastases (between 0.2 and 2 mm) or even isolated tumour cells (single cells or small clusters of cells <0.2 mm). In Chapter 4, we examine whether the introduction of the sentinel node biopsy led to more patients being diagnosed with tumour positive lymph nodes. With the possible detection of more and smaller nodal metastases, the relevance of minimal lymph node involvement in breast cancer becomes increasingly important. Chapter 5 examines the prognosis of breast cancer patients with minimal lymph node involvement and studies the effect of adjuvant systemic therapy in these patients. Chapter 1 In Part 2 of this thesis, we present studies in which performance indicators are used to provide insight in the quality of care and variations between hospitals. The most important outcomes in breast cancer care are disease free and overall survival. Since 2009, hospitals are obliged to report the 5-year local recurrence rate after breast cancer surgery. The Netherlands Cancer Registry (NCR) aided in uniform and complete registration of this indicator. Chapter 6 describes the results of the local recurrence rates of patients diagnosed in 2003 of all Dutch hospitals. The value of the indicator is discussed and recommendations are made for future use. Chapter 7 reports on the same indicator of local recurrences, but combines data on four consecutive years. This study aims to determine whether extra data can add to the value of the indicator. A more timely indicator used by the Dutch health care inspectorate is on the adequate surgical removal of tumour tissue during the first BCS. Chapter 8 describes the variation between hospitals in surgical margins after first breast conserving surgery. In the general discussion (Chapter 9) we focus on the process of improving the quality of care and on the measurement of this concept. We also discuss opportunities and pitfalls in comparing hospitals based on performance indicators. 13
15 General introduction References 1. www. cijfersoverkanker.nl; accessed 17th July, Veronesi U, Saccozzi R, Del Vecchio M, Banfi A, Clemente C, De Lena M, et al. Comparing radical mastectomy with quadrantectomy, axillary dissection, and radiotherapy in patients with small cancers of the breast. N Engl J Med 1981; 305(1): Fisher B, Bauer M, Margolese R, Poisson R, Pilch Y, Redmond C, et al. Five-year results of a randomized clinical trial comparing total mastectomy and segmental mastectomy with or without radiation in the treatment of breast cancer. N Engl J Med 1985; 312(11): Effects of radiotherapy and surgery in early breast cancer. An overview of the randomized trials. Early Breast Cancer Trialists Collaborative Group. N Engl J Med 1995; 333(22): Fisher B, Anderson S, Redmond CK, Wolmark N, Wickerham DL, Cronin WM. Reanalysis and results after 12 years of follow-up in a randomized clinical trial comparing total mastectomy with lumpectomy with or without irradiation in the treatment of breast cancer. N Engl J Med 1995; 333(22): Jacobson JA, Danforth DN, Cowan KH, d Angelo T, Steinberg SM, Pierce L, et al. Ten-year results of a comparison of conservation with mastectomy in the treatment of stage I and II breast cancer. N Engl J Med 1995; 332(14): van Dongen JA, Voogd AC, Fentiman IS, Legrand C, Sylvester RJ, Tong D, et al. Long-term results of a randomized trial comparing breast-conserving therapy with mastectomy: European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer trial. J Natl Cancer Inst 2000; 92(14): Roumen RM, Pijpers HJ, Thunnissen FB, Ruers TJ. Summary of the guideline Sentinel node biopsy in breast cancer. Dutch Work Group Sentinel Node Biopsy for Breast Cancer. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd 2000; 144(39): Giuliano AE, Kirgan DM, Guenther JM, Morton DL. Lymphatic mapping and sentinel lymphadenectomy for breast cancer. Ann Surg 1994; 220(3): 391,8; discussion Krag DN, Weaver DL, Alex JC, Fairbank JT. Surgical resection and radiolocalization of the sentinel lymph node in breast cancer using a gamma probe. Surg Oncol 1993; 2(6): 335,9; discussion Committee on Quality of Health Care in America. Crossing the quality chasm: the IOM Health Care Quality Initiative. 1998;. 12. Brien SE, Dixon E, Ghali WA. Measuring and reporting on quality in health care: a framework and road map for improving care. J Surg Oncol 2009; 99(8): van Dishoeck AM, Steyerberg EW. Hospital top 100: changing rankings, changing reputations. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd 2007; 151(4): Donabedian A. Evaluating the quality of medical care. Milbank Q 1966; 83(4): National Breast cancer Organization Netherlands, NABON. Guideline breast cancer diagnosis and treatment. 2012; accessed 12th July, NABON nota. 2008; at php&richtlijn_id=608; accessed 17th July, Del Turco MR, Ponti A, Bick U, Biganzoli L, Cserni G, Cutuli B, et al. Quality indicators in breast cancer care. Eur J Cancer 2010; 46(13):
16
17
18 Part 1 Implementation of sentinel node biopsy
19
20 Chapter 2 Implementation of sentinel node biopsy in breast cancer patients in the Netherlands V.K.Y. Ho M. van der Heiden-van der Loo E. J. Th. Rutgers P.J. van Diest M.G. Hobbelink V.C.G. Tjan-Heijnen M.J.M. Dirx A.M.J. Reedijk J.A.A.M. van Dijck L.V. van de Poll-Franse M. Schaapveld P.H.M. Peeters Eur J Cancer 2008; 44(5):
21 Implementation of sentinel node biopsy in the Netherlands Abstract Background This population-based study describes the implementation of the sentinel node biopsy (SNB) in breast cancer patients in The Netherlands. We examined the extent of use over time of SNB in women who were considered eligible for SNB on the basis of their clinical status. Methods The study included a total of 35,465 breast cancer patients who were diagnosed with T1 2 tumours ( 5.0 cm), negative axillary lymph node status and no distant metastases upon clinical examination between January 1, 1998, and December 31, 2003 in six Comprehensive Cancer Centre regions in The Netherlands. Information on axillary surgery was classified as SNB alone, SNB + axillary lymph node dissection (ALND), ALND alone, or none. Patterns of use of axillary surgery were summarized as the proportion of patients receiving each surgery type. Results Overall, 25.7% of patients underwent SNB alone, 19.1% underwent SNB + ALND, 50.0% had ALND alone, and 5.2% did not have axillary surgery. SNB was more common in women who had breast-conserving surgery: 50.5% of patients who received breast-conserving surgery underwent SNB compared to 40.7% of patients who had mastectomy (p<0.0001). Among patients receiving breast-conserving treatment, 31.7% had SNB as final axillary surgery, while 20.5% of patients who had mastectomy had SNB alone (p<0.0001). The proportion of women who underwent a SNB alone or in combination with ALND increased over the period 1998 to 2003, from 2.1% to 45.8% and from 6.7% to 24.8%, respectively. There were marked differences in patterns of dissemination of the use of SNB between regions: by 2003, the difference between the regions with the highest and lowest proportion of use was 25%. Conclusions SNB has become standard-of-care for the treatment of breast cancer patients clinically diagnosed with T1 2 tumours, clinically negative lymph nodes and without distant metastases. In 2003, 70.6% of patients with early breast cancer in The Netherlands received SNB, and within this group, 64.9% of patients had SNB as final axillary treatment. Implementation of SNB may depend on factors associated with regional organization of care. 20
22 Chapter 2 Introduction The sentinel node biopsy (SNB) was introduced almost 15 years ago as an intraoperative lymph node staging method for breast cancer patients. 1,2 The SNB had already been described as a staging method for patients with penile cancer in , and the procedure was then further developed for detection of non palpable lymph node metastases of melanoma. 4 SNB may also be applied in other solid malignancies. 5 Axillary lymph node status is the most important prognostic factor for breast cancer, and it affects the choice of adjuvant systemic therapy and radiotherapy. Histopathologic examination of lymph nodes requires axillary-specific surgery as a critical component of breast cancer care. Until recently, axillary surgery consisted of axillary lymph node dissection (ALND). Although ALND is considered a safe procedure resulting in optimal regional control after local treatment and additional prognostic information, dissection of all lymph nodes lacks clinical value if the nodes are tumour negative, as is the case in about 70% of breast cancer patients in countries with mammographic screening programs. Moreover, post-alnd morbidity, which include upper arm paresthesias, shoulder and arm pain, restriction of shoulder mobility and permanent and potentially disabling lymph oedema, have a significant impact on patients quality of life The technique of SNB allows for a selective method of staging, thus enabling lymph node assessment without the use of ALND: as a result, use of ALND should be restricted to patients with lymph node metastases. Indeed, the risks of short-term morbidity and lymph oedema are markedly lower with SNB Also, SNB shows a similar sensitivity for detecting patients with positive lymph nodes. 15 Chapter 2 SNB is based on the by now confirmed hypothesis of an orderly pattern of lymphogenic tumour cell dissemination. Sentinel lymph nodes should be at the greatest risk of bearing cancer metastases, and if these nodes prove to be negative, the remaining axillary lymph nodes are also likely to be negative. The sentinel nodes are located by lymphatic mapping with preoperative lymphoscintigraphy alone or the most frequently used combined technique, lymphoscintigraphy with 99m technetium-labeled nanocolloid and patent blue dye. As the colloidal material accumulates in the draining sentinel lymph nodes, the nodes may be identified at surgery, visually and by gamma probe if required, and removed for histopathologic examination. Ideally, sentinel nodes are examined during breast surgery, and if the pathologist then identifies cancer metastases, e.g. by frozen section analysis 16, ALND may be performed in the same surgery. SNBs require adequate cooperation between departments of surgery, nuclear medicine, and pathology. Since community hospitals may not be equipped with a pathology laboratory, SNBs often require cooperation between hospitals as well. SNBs are suitable for breast cancer patients with primary tumours with a maximum size of 5 cm or less (T1 2), with no multiple lesions, no previous breast surgery or axillary surgery, and no signs of malignancy in axillary lymph nodes. 17 The reliability of the procedure in these patients is considered adequately tested after several studies of SNB with concomitant ALND: experienced surgeons are able to locate sentinel nodes in more than 90% of cases, while 21
23 Implementation of sentinel node biopsy in the Netherlands the prediction of lymph node status assessed by SNB is accurate in 95% (range %) of cases. 18,19 The false-negative rate has been estimated at 3.2% (range 0 15%), but follow-up of patients with a negative sentinel lymph node seldom detected axillary metastases A recent study showed a false-negative rate of 9.8%, with higher percentages for patients who had excisional biopsy and patients with a tumour in the upper outer quadrant of the breast. 24 In The Netherlands, the procedure for SNB was first described in Dutch national guidelines for staging of breast cancer in , but regional implementation had by then already started. This study examines the implementation of SNB in The Netherlands from 1998 through 2003, a time period during which SNB entered clinical practice. Patients and Methods Data sources Information on women with newly diagnosed breast cancer was extracted from the regional cancer registries of six out of nine Dutch Comprehensive Cancer Centres (CCCs, Figure 1). A. CCC East B. CCC Limburg C. CCC Middle Netherlands D. CCC North Netherlands E. CCC Rotterdam F. CCC South Figure 1. The regions of six Dutch Comprehensive Cancer Centres (in dark grey) These six registries cover around 10,350,000 inhabitants in 2006, or approximately 60% of the total Dutch population. The CCCs form a network of health care professionals and institutions for cancer care and palliative care in The Netherlands. The CCC regions cover between five and twenty hospitals. The CCCs do not treat patients, but foster expertise and multidisciplinary cohesion in (regional) cancer care. Among other activities, they host the Netherlands Cancer 22
24 Chapter 2 Registry (NCR), a nationwide population-based cancer registry established in The NCR provides incidence data on a national level. It is composed of the Regional Cancer Registries (RCRs) of the nine CCCs in The Netherlands. PALGA, the Dutch network and registry of histo- and cytopathology, notifies the RCRs of all newly diagnosed malignancies. Following this notification, trained registry personnel from the RCRs collect data on diagnosis, staging, and treatment from hospital records, including pathology and surgery reports. Primary treatment is coded in sequence of administration, and patients are staged according to the TNM system of the International Union Against Cancer (UICC). 26,27 Case ascertainment is provided by the national hospital discharge database, which receives discharge diagnoses of patients admitted from all hospitals in The Netherlands. The study design, data abstraction process and storage protocols have been approved by the national supervisory committee of the NCR. Chapter 2 Study population and eligibility criteria The data of the NCR distinguishes clinical tumour stages (ctnm) from pathologic stages (ptnm), which enabled us to accurately identify the larger part of patients who should have undergone SNB on the basis of their clinical tumour status (ctnm) according to the Dutch guideline for the treatment of breast cancer. 17 The clinical status of patients was based on physical examination, biopsies, imaging techniques and other diagnostic information retrieved prior to therapeutic intervention; this information was supplemented with post-surgical histopathological examination to determine the pathological tumour status (ptnm). In case the clinical extent of the primary tumour was unknown (ctx), patient information was supplemented by the pathologic extent of the tumour (pt); this was the case for 19.2% of the population. Patients were eligible for this study if they were clinically diagnosed with T1 2 tumours ( 5.0 cm), negative axillary lymph node status and no (signs of) distant metastases. Patients had to be presented in one of the six regions participating in the study between January 1, 1998, and December 31, For the study period, the data from the remaining three CCCs could not be used to identify SNB implementation patterns as these centres only register the most extensive axillary surgery for each patient. In these regions, SNB was not registered if the procedure was followed by ALND. Classification of axillary and definitive breast surgery The type of axillary surgery was classified into one of four categories for each patient: no axillary surgery (None); SNB without further axillary surgery (SNB alone); SNB followed by complete ALND (SNB + ALND); or ALND without SNB (ALND alone). Patients were considered as lymph node positive if any axillary lymph node contained histologically proven metastases (whether assessed by SNB or otherwise). Axillary surgery was coded as SNB alone if SNB was performed and the patient had no other axillary surgery at any time during initial treatment of the primary cancer. Axillary surgery was classified as ALND alone if axillary dissection was performed and the patient had no prior or concomitant SNB. 23
25 Implementation of sentinel node biopsy in the Netherlands The type of definitive breast surgery was classified into one of three categories for each patient: no breast surgery (None); breast-conserving surgery; and mastectomy. Patients who were initially treated with breast-conserving surgery but had subsequent mastectomy were included in the latter category. Statistical analysis Descriptive statistics were used to describe the patient population. We summarized the patterns of use of definitive breast surgery as the proportion of patients receiving each surgery type (i.e., None, Breast-conserving surgery, or Mastectomy). The same was done for patterns of use of axillary surgery (i.e., None, SNB alone, SNB + ALND, or ALND alone). The type of axillary surgery was also linked with type of definitive breast surgery. Since our study population consisted mainly of breast cancer patients with small primary tumours, we expected to observe a large group of women who underwent breast-conserving therapy, especially when a SNB had indicated a negative axillary lymph node status in these patients. The chi-square test was applied to test associations of axillary surgery with type of breast surgery. The type of axillary surgery was also analyzed according to patient age, clinical and pathological tumour size, and pathological tumour stage. A p-value below 0.05 (two-sided) was considered statistically significant. To describe the implementation of SNB during the study period, we examined the time trends of axillary surgery among women who may be considered eligible for SNB on the basis of their clinical status from January 1998 through December Time trends were also studied for the separate regions. Results Patient characteristics Between January 1, 1998, and December 31, 2003, 35,904 women were diagnosed with clinically small breast tumours ( 5.0 cm), clinically negative axillary lymph node status and no signs of distant metastases in the six CCC regions under study. Of these patients, we excluded 439 (1.2%) for lack of reliable and unambiguous information on definitive breast surgery, leaving 35,465 women (98.8%) in our study. 4,825 (13.6%) Patients were diagnosed or treated in the region of CCC East (Figure 1: A); 3,141 (8.9%) in CCC Limburg (B); 4,122 (11.6%) in CCC Middle Netherlands (C); 7,888 (22.2%) in CCC North Netherlands (D); 7,652 (21.6%) in CCC Rotterdam (E); and 7,837 (22.1%) in CCC South (F). The median age of patients was 59 years (Table 1); 27.1% of all patients was aged 50 years or younger. The clinical tumour size was 2 cm or less for 68.6% of patients, and 52.7% of these patients received breast-conserving surgery. Overall, 48.8% of patients underwent breastconserving surgery, 49.1% had mastectomy, and 2.1% did not have definitive breast surgery. With respect to axillary surgery, 25.7% of all patients had SNB alone, 19.1% had SNB with concomitant ALND, and 50.0% had ALND alone; 5.2% of the patients did not have axillary surgery performed. The patient selection concerns a population which would be considered eligible for SNB on 24
26 Chapter 2 the basis of clinical tumour status (ctnm). As for the pathological staging of patients (ptnm), which is determined postoperatively and therefore does not affect the indication for SNB, 48.5% of patients were diagnosed with stage I breast cancer, 33.9% with stage IIA, and 14.5% with IIB. Furthermore, 2.9% of the patients were diagnosed with stage III and 0.2% with stage IV breast cancer. Four (<0.0%) patients had unknown stage, and five (<0.0%) patients were pathologically diagnosed with in situ breast malignancy. Table 1. Patient characteristics for 35,465 patients with breast cancer who presented with a clinical T1 2 tumour (tumour size 5.0 cm), clinically negative lymph nodes and without distant metastases in six Dutch Comprehensive Cancer Centre regions in N % Age at diagnosis (years) Median (interquartile range) 59 (50-71) < 40 2, % , % , % , % , % 80 3, % Tumour size (ct), cm , % > , % Type of definitive surgery None % Breast-conserving surgery 17, % Mastectomy 17, % Breast-conserving surgery within tumour size, cm (n = 24,326) 12, % > (n = 11,139) 4, % Type of axillary surgery None 1, % SNB alone 9, % SNB + ALND 6, % ALND alone 17, % Chapter 2 a SNB: sentinel node biopsy, ALND: axillary lymph node dissection Patterns of axillary surgery according to definitive surgery type Use of SNB (SNB alone or with concomitant ALND) was statistically significantly associated with breast-conserving surgery (Table 2). Among patients who received breast-conserving surgical treatment 50.6% had SNB, while this proportion was 40.7% for patients who underwent mastectomy (p<0.0001). Also, SNB was more often the only axillary surgery in women who were treated with breast-conserving surgery than in women who had mastectomy: 31.7% vs. 20.5%, respectively (p<0.0001). 25
Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma
 Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma Medical Expert: Breast Rotation Specific Competencies/Objectives 1.0 Medical History
Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma Medical Expert: Breast Rotation Specific Competencies/Objectives 1.0 Medical History
Management of Postmenopausal Women with T1 ER+ Tumors: Options and Tradeoffs. Case Study. Surgery. Lumpectomy and Radiation
 Management of Postmenopausal Women with T1 ER+ Tumors: Options and Tradeoffs Michael Alvarado, MD Associate Professor of Surgery University of California San Francisco Case Study 59 yo woman with new palpable
Management of Postmenopausal Women with T1 ER+ Tumors: Options and Tradeoffs Michael Alvarado, MD Associate Professor of Surgery University of California San Francisco Case Study 59 yo woman with new palpable
Chapter 2 Staging of Breast Cancer
 Chapter 2 Staging of Breast Cancer Zeynep Ozsaran and Senem Demirci Alanyalı 2.1 Introduction Five decades ago, Denoix et al. proposed classification system (tumor node metastasis [TNM]) based on the dissemination
Chapter 2 Staging of Breast Cancer Zeynep Ozsaran and Senem Demirci Alanyalı 2.1 Introduction Five decades ago, Denoix et al. proposed classification system (tumor node metastasis [TNM]) based on the dissemination
Sentinel Lymph Node Mapping for Endometrial Cancer. Locke Uppendahl, MD Grand Rounds
 Sentinel Lymph Node Mapping for Endometrial Cancer Locke Uppendahl, MD Grand Rounds Endometrial Cancer Most common gynecologic malignancy in US estimated 52,630 new cases in 2014 estimated 8,590 deaths
Sentinel Lymph Node Mapping for Endometrial Cancer Locke Uppendahl, MD Grand Rounds Endometrial Cancer Most common gynecologic malignancy in US estimated 52,630 new cases in 2014 estimated 8,590 deaths
Pathologic Assessment Of The Breast And Axilla After Preoperative Therapy
 Pathologic Assessment Of The Breast And Axilla After Preoperative Therapy W. Fraser Symmans, M.D. Associate Professor of Pathology UT M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Pathologic Complete Response (pcr) Proof
Pathologic Assessment Of The Breast And Axilla After Preoperative Therapy W. Fraser Symmans, M.D. Associate Professor of Pathology UT M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Pathologic Complete Response (pcr) Proof
Surgical guidelines for the management of breast cancer
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com EJSO xx (2009) S1eS22 www.ejso.com Guidelines Surgical guidelines for the management of breast cancer Contents Association of Breast Surgery at BASO 2009 Introduction...
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com EJSO xx (2009) S1eS22 www.ejso.com Guidelines Surgical guidelines for the management of breast cancer Contents Association of Breast Surgery at BASO 2009 Introduction...
Understanding ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and deciding about treatment
 Understanding ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and deciding about treatment Developed by National Breast and Ovarian Cancer Centre Funded by the Australian Government Department of Health and Ageing Understanding
Understanding ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and deciding about treatment Developed by National Breast and Ovarian Cancer Centre Funded by the Australian Government Department of Health and Ageing Understanding
HAVE YOU BEEN NEWLY DIAGNOSED with DCIS?
 HAVE YOU BEEN NEWLY DIAGNOSED with DCIS? Jen D. Mother and volunteer. Diagnosed with DCIS breast cancer in 2012. An educational guide prepared by Genomic Health This guide is designed to educate women
HAVE YOU BEEN NEWLY DIAGNOSED with DCIS? Jen D. Mother and volunteer. Diagnosed with DCIS breast cancer in 2012. An educational guide prepared by Genomic Health This guide is designed to educate women
Understanding Your Surgical Options For Breast Cancer
 RADIATION THERAPY SYMPTOM MANAGEMENT CANCER INFORMATION Understanding Your Surgical Options For Breast Cancer In this booklet you will learn about: Role of surgery in breast cancer diagnosis and treatment
RADIATION THERAPY SYMPTOM MANAGEMENT CANCER INFORMATION Understanding Your Surgical Options For Breast Cancer In this booklet you will learn about: Role of surgery in breast cancer diagnosis and treatment
Current Status and Perspectives of Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer
 Breast Cancer Current Status and Perspectives of Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer JMAJ 45(10): 434 439, 2002 Masahiro HIRAOKA, Masaki KOKUBO, Chikako YAMAMOTO and Michihide MITSUMORI Department of Therapeutic
Breast Cancer Current Status and Perspectives of Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer JMAJ 45(10): 434 439, 2002 Masahiro HIRAOKA, Masaki KOKUBO, Chikako YAMAMOTO and Michihide MITSUMORI Department of Therapeutic
Loco-regional Recurrence
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer AGO AGO e. e. V. V. Loco-regional Recurrence Loco-regional Recurrence Version 2002: Brunnert / Simon Versions 2003 2012: Audretsch
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer AGO AGO e. e. V. V. Loco-regional Recurrence Loco-regional Recurrence Version 2002: Brunnert / Simon Versions 2003 2012: Audretsch
Axillary Ultrasonography in Breast Cancer Patients Helps in Identifying Patients Preoperatively with Limited Disease of the Axilla
 Ann Surg Oncol DOI 10.1245/s10434-014-3674-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE BREAST ONCOLOGY Axillary Ultrasonography in Breast Cancer Patients Helps in Identifying Patients Preoperatively with Limited Disease of the
Ann Surg Oncol DOI 10.1245/s10434-014-3674-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE BREAST ONCOLOGY Axillary Ultrasonography in Breast Cancer Patients Helps in Identifying Patients Preoperatively with Limited Disease of the
ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
 Understanding ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and deciding about treatment Understanding ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and deciding about treatment Developed by National Breast and Ovarian Cancer Centre
Understanding ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and deciding about treatment Understanding ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and deciding about treatment Developed by National Breast and Ovarian Cancer Centre
Local control in ductal carcinoma in situ treated by excision alone: incremental benefit of larger margins
 The American Journal of Surgery 190 (2005) 521 525 George Peter s Award Winner Local control in ductal carcinoma in situ treated by excision alone: incremental benefit of larger margins Heather R. MacDonald,
The American Journal of Surgery 190 (2005) 521 525 George Peter s Award Winner Local control in ductal carcinoma in situ treated by excision alone: incremental benefit of larger margins Heather R. MacDonald,
Understanding your pathology report
 Understanding your pathology report 2 Contents Contents Introduction 3 What is a pathology report? 3 Waiting for your results 4 What s in a pathology report? 4 Information about your breast cancer 5 What
Understanding your pathology report 2 Contents Contents Introduction 3 What is a pathology report? 3 Waiting for your results 4 What s in a pathology report? 4 Information about your breast cancer 5 What
TITLE: Comparison of the dosimetric planning of partial breast irradiation with and without the aid of 3D virtual reality simulation (VRS) software.
 SAMPLE CLINICAL RESEARCH APPLICATION ABSTRACT: TITLE: Comparison of the dosimetric planning of partial breast irradiation with and without the aid of 3D virtual reality simulation (VRS) software. Hypothesis:
SAMPLE CLINICAL RESEARCH APPLICATION ABSTRACT: TITLE: Comparison of the dosimetric planning of partial breast irradiation with and without the aid of 3D virtual reality simulation (VRS) software. Hypothesis:
Goals and Objectives: Breast Cancer Service Department of Radiation Oncology
 Goals and Objectives: Breast Cancer Service Department of Radiation Oncology The breast cancer service provides training in the diagnosis, management, treatment, and follow-up of breast malignancies, including
Goals and Objectives: Breast Cancer Service Department of Radiation Oncology The breast cancer service provides training in the diagnosis, management, treatment, and follow-up of breast malignancies, including
How TARGIT Intra-operative Radiotherapy can help Older Patients with Breast cancer
 How TARGIT Intra-operative Radiotherapy can help Older Patients with Breast cancer Jeffrey S Tobias, Jayant S Vaidya, Frederik Wenz and Michael Baum, University College Hospital, London, UK - on behalf
How TARGIT Intra-operative Radiotherapy can help Older Patients with Breast cancer Jeffrey S Tobias, Jayant S Vaidya, Frederik Wenz and Michael Baum, University College Hospital, London, UK - on behalf
Wisconsin Cancer Data Bulletin Wisconsin Department of Health Services Division of Public Health Office of Health Informatics
 Wisconsin Cancer Data Bulletin Wisconsin Department of Health Services Division of Public Health Office of Health Informatics In Situ Breast Cancer in Wisconsin INTRODUCTION This bulletin provides information
Wisconsin Cancer Data Bulletin Wisconsin Department of Health Services Division of Public Health Office of Health Informatics In Situ Breast Cancer in Wisconsin INTRODUCTION This bulletin provides information
Adiuwantowe i neoadiuwantowe leczenie chorych na zaawansowanego raka żołądka
 Adiuwantowe i neoadiuwantowe leczenie chorych na zaawansowanego raka żołądka Neoadiuvant and adiuvant therapy for advanced gastric cancer Franco Roviello, IT Neoadjuvant and adjuvant therapy for advanced
Adiuwantowe i neoadiuwantowe leczenie chorych na zaawansowanego raka żołądka Neoadiuvant and adiuvant therapy for advanced gastric cancer Franco Roviello, IT Neoadjuvant and adjuvant therapy for advanced
Guidelines for the treatment of breast cancer with radiotherapy
 London Cancer Guidelines for the treatment of breast cancer with radiotherapy March 2013 Review March 2014 Version 1.0 Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Indications and dosing schedules... 3 2.1. Ductal
London Cancer Guidelines for the treatment of breast cancer with radiotherapy March 2013 Review March 2014 Version 1.0 Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Indications and dosing schedules... 3 2.1. Ductal
Lymphatic Mapping Techniques and Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Breast Cancer
 Surg Clin N Am 87 (2007) 353 364 Lymphatic Mapping Techniques and Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Breast Cancer Erika A. Newman, MD a, Lisa A. Newman, MD, MPH, FACS b, * a Department of Surgery, University
Surg Clin N Am 87 (2007) 353 364 Lymphatic Mapping Techniques and Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Breast Cancer Erika A. Newman, MD a, Lisa A. Newman, MD, MPH, FACS b, * a Department of Surgery, University
Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition
 www.rcr.ac.uk Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition Breast cancer Faculty of Clinical Radiology www.rcr.ac.uk Contents Breast cancer 2 Clinical background 2 Who
www.rcr.ac.uk Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition Breast cancer Faculty of Clinical Radiology www.rcr.ac.uk Contents Breast cancer 2 Clinical background 2 Who
Survival and axillary recurrence following sentinel nodepositive breast cancer without completion axillary lymph node dissection the SENOMAC trial.
 Survival and axillary recurrence following sentinel nodepositive breast cancer without completion axillary lymph node dissection the SENOMAC trial. A randomized study of patients with sentinel node macrometastasis
Survival and axillary recurrence following sentinel nodepositive breast cancer without completion axillary lymph node dissection the SENOMAC trial. A randomized study of patients with sentinel node macrometastasis
SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER
 Protocol for Planning and Treatment The process to be followed in the management of: SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Patient information given at each stage following agreed information pathway 1. DIAGNOSIS New
Protocol for Planning and Treatment The process to be followed in the management of: SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Patient information given at each stage following agreed information pathway 1. DIAGNOSIS New
Breast Cancer: from bedside and grossing room to diagnoses and beyond. Adriana Corben, M.D.
 Breast Cancer: from bedside and grossing room to diagnoses and beyond Adriana Corben, M.D. About breast anatomy Breasts are special organs that develop in women during puberty when female hormones are
Breast Cancer: from bedside and grossing room to diagnoses and beyond Adriana Corben, M.D. About breast anatomy Breasts are special organs that develop in women during puberty when female hormones are
Breast cancer close to the nipple: Does this carry a higher risk ofaxillary node metastasesupon diagnosis?
 Breast cancer close to the nipple: Does this carry a higher risk ofaxillary node metastasesupon diagnosis? Erin I. Lewis, BUSM 2010 Cheri Nguyen, BUSM 2008 Priscilla Slanetz, M.D., MPH Al Ozonoff, Ph.d.
Breast cancer close to the nipple: Does this carry a higher risk ofaxillary node metastasesupon diagnosis? Erin I. Lewis, BUSM 2010 Cheri Nguyen, BUSM 2008 Priscilla Slanetz, M.D., MPH Al Ozonoff, Ph.d.
Prognostic and Predictive Factors in Breast Cancer Kyle T. Bradley, MD, MS CAP Cancer Committee
 Prognostic and Predictive Factors in Breast Cancer Kyle T. Bradley, MD, MS CAP Cancer Committee Breast cancer is the most common malignant tumor in American women and is second only to lung cancer as a
Prognostic and Predictive Factors in Breast Cancer Kyle T. Bradley, MD, MS CAP Cancer Committee Breast cancer is the most common malignant tumor in American women and is second only to lung cancer as a
Report series: General cancer information
 Fighting cancer with information Report series: General cancer information Eastern Cancer Registration and Information Centre ECRIC report series: General cancer information Cancer is a general term for
Fighting cancer with information Report series: General cancer information Eastern Cancer Registration and Information Centre ECRIC report series: General cancer information Cancer is a general term for
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Treated With Breast-Conserving Surgery and Radiotherapy: A Comparison With ECOG Study 5194
 Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Treated With Breast-Conserving Surgery and Radiotherapy: A Comparison With ECOG Study 5194 Sabin B. Motwani, MD 1 ; Sharad Goyal, MD 1 ; Meena S. Moran, MD 2 ; Arpit Chhabra, BS
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Treated With Breast-Conserving Surgery and Radiotherapy: A Comparison With ECOG Study 5194 Sabin B. Motwani, MD 1 ; Sharad Goyal, MD 1 ; Meena S. Moran, MD 2 ; Arpit Chhabra, BS
Effects of Herceptin on circulating tumor cells in HER2 positive early breast cancer
 Effects of Herceptin on circulating tumor cells in HER2 positive early breast cancer J.-L. Zhang, Q. Yao, J.-H. Chen,Y. Wang, H. Wang, Q. Fan, R. Ling, J. Yi and L. Wang Xijing Hospital Vascular Endocrine
Effects of Herceptin on circulating tumor cells in HER2 positive early breast cancer J.-L. Zhang, Q. Yao, J.-H. Chen,Y. Wang, H. Wang, Q. Fan, R. Ling, J. Yi and L. Wang Xijing Hospital Vascular Endocrine
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Early-stage Breast Cancer
 -Based Series 17-5 A Quality Initiative of the Program in -Based Care (PEBC, Cancer Care Ontario (CCO) Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Early-stage Breast Cancer R. George, M. L. Quan, D. McCready, R. McLeod,
-Based Series 17-5 A Quality Initiative of the Program in -Based Care (PEBC, Cancer Care Ontario (CCO) Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Early-stage Breast Cancer R. George, M. L. Quan, D. McCready, R. McLeod,
CLINICAL NEGLIGENCE ARTICLE: THE DETECTION & TREATMENT OF BREAST CANCER & CLAIMS FOR LOSS OF LIFE EXPECTANCY IN CLINICAL NEGLIGENCE CASES
 CLINICAL NEGLIGENCE ARTICLE: THE DETECTION & TREATMENT OF BREAST CANCER & CLAIMS FOR LOSS OF LIFE EXPECTANCY IN CLINICAL NEGLIGENCE CASES Reports relating to the detection and treatment of breast cancer
CLINICAL NEGLIGENCE ARTICLE: THE DETECTION & TREATMENT OF BREAST CANCER & CLAIMS FOR LOSS OF LIFE EXPECTANCY IN CLINICAL NEGLIGENCE CASES Reports relating to the detection and treatment of breast cancer
Articles. Early Breast Cancer Trialists Collaborative Group (EBCTCG)* www.thelancet.com Vol 366 December 17/24/31, 2005 2087
 Effects of radiotherapy and of differences in the extent of surgery for early breast cancer on local recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials Early Breast Cancer Trialists
Effects of radiotherapy and of differences in the extent of surgery for early breast cancer on local recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials Early Breast Cancer Trialists
Protein kinase C alpha expression and resistance to neo-adjuvant gemcitabine-containing chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
 Protein kinase C alpha expression and resistance to neo-adjuvant gemcitabine-containing chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer Dan Vogl Lay Abstract Early stage non-small cell lung cancer can be cured
Protein kinase C alpha expression and resistance to neo-adjuvant gemcitabine-containing chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer Dan Vogl Lay Abstract Early stage non-small cell lung cancer can be cured
Integrating Chemotherapy and Liver Surgery for the Management of Colorectal Metastases
 I Congresso de Oncologia D Or July 5-6, 2013 Integrating Chemotherapy and Liver Surgery for the Management of Colorectal Metastases Michael A. Choti, MD, MBA, FACS Department of Surgery Johns Hopkins University
I Congresso de Oncologia D Or July 5-6, 2013 Integrating Chemotherapy and Liver Surgery for the Management of Colorectal Metastases Michael A. Choti, MD, MBA, FACS Department of Surgery Johns Hopkins University
Second Axillary Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy for Breast Tumor Recurrence: Experience of the European Institute of Oncology
 Ann Surg Oncol (2015) 22:2372 2377 DOI 10.1245/s10434-014-4282-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE BREAST ONCOLOGY Second Axillary Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy for Breast Tumor Recurrence: Experience of the European Institute
Ann Surg Oncol (2015) 22:2372 2377 DOI 10.1245/s10434-014-4282-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE BREAST ONCOLOGY Second Axillary Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy for Breast Tumor Recurrence: Experience of the European Institute
RESEARCH EDUCATE ADVOCATE. Just Diagnosed with Melanoma Now What?
 RESEARCH EDUCATE ADVOCATE Just Diagnosed with Melanoma Now What? INTRODUCTION If you are reading this, you have undergone a biopsy (either of a skin lesion or a lymph node) or have had other tests in which
RESEARCH EDUCATE ADVOCATE Just Diagnosed with Melanoma Now What? INTRODUCTION If you are reading this, you have undergone a biopsy (either of a skin lesion or a lymph node) or have had other tests in which
Mesothelioma. 1. Introduction. 1.1 General Information and Aetiology
 Mesothelioma 1. Introduction 1.1 General Information and Aetiology Mesotheliomas are tumours that arise from the mesothelial cells of the pleura, peritoneum, pericardium or tunica vaginalis [1]. Most are
Mesothelioma 1. Introduction 1.1 General Information and Aetiology Mesotheliomas are tumours that arise from the mesothelial cells of the pleura, peritoneum, pericardium or tunica vaginalis [1]. Most are
General Rules SEER Summary Stage 2000. Objectives. What is Staging? 5/8/2014
 General Rules SEER Summary Stage 2000 Linda Mulvihill Public Health Advisor NCRA Annual Meeting May 2014 National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion Division of Cancer Prevention
General Rules SEER Summary Stage 2000 Linda Mulvihill Public Health Advisor NCRA Annual Meeting May 2014 National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion Division of Cancer Prevention
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment Comparison to NCCN Guidelines
 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment Comparison to NCCN Guidelines April 2008 (presented at 6/12/08 cancer committee meeting) By Shelly Smits, RHIT, CCS, CTR Conclusions by Dr. Ian Thompson, MD Dr. James
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment Comparison to NCCN Guidelines April 2008 (presented at 6/12/08 cancer committee meeting) By Shelly Smits, RHIT, CCS, CTR Conclusions by Dr. Ian Thompson, MD Dr. James
Helen Joseph Breast Care Clinic - Johannesburg, South Africa
 - Johannesburg, South Africa General Information New breast cancer cases treated per year 360 Breast multidisciplinarity team members 12 Radiologists, surgeons, pathologists, medical oncologists, radiotherapists
- Johannesburg, South Africa General Information New breast cancer cases treated per year 360 Breast multidisciplinarity team members 12 Radiologists, surgeons, pathologists, medical oncologists, radiotherapists
Audit. Process for managing outliers in breast cancer surgery. March 2005
 Process for managing outliers in breast cancer surgery Audit March 2005 Prepared by: Australian Safety & Efficacy Register of New Interventional Procedures Surgical On behalf of: The Section of Breast
Process for managing outliers in breast cancer surgery Audit March 2005 Prepared by: Australian Safety & Efficacy Register of New Interventional Procedures Surgical On behalf of: The Section of Breast
Breast Cancer & Treatment in ACT and Surrounding Regions QUALITY ASSURANCE PROJECT. Five-year report
 Breast Cancer & Treatment in ACT and Surrounding Regions QUALITY ASSURANCE PROJECT Five-year report Community Health Pathology Southern Area Health Service ACT Health General Practitioners Nurses Social
Breast Cancer & Treatment in ACT and Surrounding Regions QUALITY ASSURANCE PROJECT Five-year report Community Health Pathology Southern Area Health Service ACT Health General Practitioners Nurses Social
Corporate Medical Policy Brachytherapy Treatment of Breast Cancer
 Corporate Medical Policy Brachytherapy Treatment of Breast Cancer File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: brachytherapy_treatment_of_breast_cancer 7/1996 5/2015 5/2016 5/2015
Corporate Medical Policy Brachytherapy Treatment of Breast Cancer File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: brachytherapy_treatment_of_breast_cancer 7/1996 5/2015 5/2016 5/2015
BRACHYTHERAPY FOR TREATMENT OF BREAST CANCER
 BRACHYTHERAPY FOR TREATMENT OF BREAST CANCER Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This
BRACHYTHERAPY FOR TREATMENT OF BREAST CANCER Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This
BREAST CANCER PATHOLOGY
 BREAST CANCER PATHOLOGY FACT SHEET Version 4, Aug 2013 This fact sheet was produced by Breast Cancer Network Australia with input from The Royal College of Pathologists of Australasia I m a nurse and know
BREAST CANCER PATHOLOGY FACT SHEET Version 4, Aug 2013 This fact sheet was produced by Breast Cancer Network Australia with input from The Royal College of Pathologists of Australasia I m a nurse and know
Breast Cancer Treatment Guidelines
 Breast Cancer Treatment Guidelines DCIS Stage 0 TisN0M0 Tamoxifen for 5 years for patients with ER positive tumors treated with: -Breast conservative therapy (lumpectomy) and radiation therapy -Excision
Breast Cancer Treatment Guidelines DCIS Stage 0 TisN0M0 Tamoxifen for 5 years for patients with ER positive tumors treated with: -Breast conservative therapy (lumpectomy) and radiation therapy -Excision
Postoperative radiotherapy after conservative surgery for early breast cancer: 5-year results
 Original article UDC: 618.19-006:849.1:616-089.8 Arch Oncol 2004;12(1):29-33. Postoperative radiotherapy after conservative surgery for early breast cancer: 5-year results Jasmina MLADENOVIÆ Marko DO IÆ
Original article UDC: 618.19-006:849.1:616-089.8 Arch Oncol 2004;12(1):29-33. Postoperative radiotherapy after conservative surgery for early breast cancer: 5-year results Jasmina MLADENOVIÆ Marko DO IÆ
PROPERTY OF ELSEVIER SAMPLE CONTENT - NOT FINAL
 Oncoplastic breast conservation surgery Melvin J Silverstein C H A P T E R 5 Introduction Oncoplastic breast conservation surgery combines oncologic principles with plastic surgical techniques. But it
Oncoplastic breast conservation surgery Melvin J Silverstein C H A P T E R 5 Introduction Oncoplastic breast conservation surgery combines oncologic principles with plastic surgical techniques. But it
Early-stage Breast Cancer Treatment: A Patient and Doctor Dialogue
 page 1 Early-stage Breast Cancer Treatment: A Patient and Doctor Dialogue Q: What is breast cancer, and what type do I have? A: Cancer is a disease in which cells become abnormal and form more cells in
page 1 Early-stage Breast Cancer Treatment: A Patient and Doctor Dialogue Q: What is breast cancer, and what type do I have? A: Cancer is a disease in which cells become abnormal and form more cells in
SUNY DOWNSTATE MEDICAL CENTER SURGERY GRAND ROUNDS February 28, 2013 VERENA LIU, MD ROSEANNA LEE, MD
 SUNY DOWNSTATE MEDICAL CENTER SURGERY GRAND ROUNDS February 28, 2013 VERENA LIU, MD ROSEANNA LEE, MD Case Presentation 35 year old male referred from PMD with an asymptomatic palpable right neck mass PMH/PSH:
SUNY DOWNSTATE MEDICAL CENTER SURGERY GRAND ROUNDS February 28, 2013 VERENA LIU, MD ROSEANNA LEE, MD Case Presentation 35 year old male referred from PMD with an asymptomatic palpable right neck mass PMH/PSH:
KIDNEY FUNCTION RELATION TO SIZE OF THE TUMOR IN RENAL CELL CANCINOMA
 KIDNEY FUNCTION RELATION TO SIZE OF THE TUMOR IN RENAL CELL CANCINOMA O.E. Stakhvoskyi, E.O. Stakhovsky, Y.V. Vitruk, O.A. Voylenko, P.S. Vukalovich, V.A. Kotov, O.M. Gavriluk National Canсer Institute,
KIDNEY FUNCTION RELATION TO SIZE OF THE TUMOR IN RENAL CELL CANCINOMA O.E. Stakhvoskyi, E.O. Stakhovsky, Y.V. Vitruk, O.A. Voylenko, P.S. Vukalovich, V.A. Kotov, O.M. Gavriluk National Canсer Institute,
7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse
 7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse A patient with prostate cancer in PSA relapse is one who, having received a primary treatment with intent to cure, has a raised PSA (prostate-specific antigen) level defined
7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse A patient with prostate cancer in PSA relapse is one who, having received a primary treatment with intent to cure, has a raised PSA (prostate-specific antigen) level defined
Breast cancer in women diagnosis, treatment and follow-up
 Breast cancer in women diagnosis, treatment and follow-up H. WILDIERS, S. STORDEUR, J. VLAYEN, R. SCHOLTEN, F. VAN DE WETERING, C. BOURGAIN, B. CARLY, MR. CHRISTIAENS, V. COCQUYT, E. LIFRANGE, JC. SCHOBBENS,
Breast cancer in women diagnosis, treatment and follow-up H. WILDIERS, S. STORDEUR, J. VLAYEN, R. SCHOLTEN, F. VAN DE WETERING, C. BOURGAIN, B. CARLY, MR. CHRISTIAENS, V. COCQUYT, E. LIFRANGE, JC. SCHOBBENS,
Principles of Radiation Therapy A Bapsi Chakravarthy, MD Associate e P rofessor Professor Radiation Oncology
 Principles of Radiation Therapy A Bapsi Chakravarthy, MD Associate Professor Radiation Oncology Disclosure Information I have no financial relationships to disclose relevant to the conten of this presentation.
Principles of Radiation Therapy A Bapsi Chakravarthy, MD Associate Professor Radiation Oncology Disclosure Information I have no financial relationships to disclose relevant to the conten of this presentation.
Victims Compensation Claim Status of All Pending Claims and Claims Decided Within the Last Three Years
 Claim#:021914-174 Initials: J.T. Last4SSN: 6996 DOB: 5/3/1970 Crime Date: 4/30/2013 Status: Claim is currently under review. Decision expected within 7 days Claim#:041715-334 Initials: M.S. Last4SSN: 2957
Claim#:021914-174 Initials: J.T. Last4SSN: 6996 DOB: 5/3/1970 Crime Date: 4/30/2013 Status: Claim is currently under review. Decision expected within 7 days Claim#:041715-334 Initials: M.S. Last4SSN: 2957
Appendix One. HER2-positive early breast cancer, its treatment and prognosis
 Appendix One. HER2-positive early breast cancer, its treatment and prognosis Breast cancer and HER2/neu over-expression Health need is one of PHARMAC s nine decision criteria (http://www.pharmac.govt.nz/pdf/231205.pdf
Appendix One. HER2-positive early breast cancer, its treatment and prognosis Breast cancer and HER2/neu over-expression Health need is one of PHARMAC s nine decision criteria (http://www.pharmac.govt.nz/pdf/231205.pdf
Analysis of Prostate Cancer at Easter Connecticut Health Network Using Cancer Registry Data
 The 2014 Cancer Program Annual Public Reporting of Outcomes/Annual Site Analysis Statistical Data from 2013 More than 70 percent of all newly diagnosed cancer patients are treated in the more than 1,500
The 2014 Cancer Program Annual Public Reporting of Outcomes/Annual Site Analysis Statistical Data from 2013 More than 70 percent of all newly diagnosed cancer patients are treated in the more than 1,500
Chapter 13. The hospital-based cancer registry
 Chapter 13. The hospital-based cancer registry J.L. Young California Tumor Registry, 1812 14th Street, Suite 200, Sacramento, CA 95814, USA Introduction The purposes of a hospital-based cancer registry
Chapter 13. The hospital-based cancer registry J.L. Young California Tumor Registry, 1812 14th Street, Suite 200, Sacramento, CA 95814, USA Introduction The purposes of a hospital-based cancer registry
Post-recurrence survival in completely resected stage I non-small cell lung cancer with local recurrence
 Post- survival in completely resected stage I non-small cell lung cancer with local J-J Hung, 1,2,3 W-H Hsu, 3 C-C Hsieh, 3 B-S Huang, 3 M-H Huang, 3 J-S Liu, 2 Y-C Wu 3 See Editorial, p 185 c A supplementary
Post- survival in completely resected stage I non-small cell lung cancer with local J-J Hung, 1,2,3 W-H Hsu, 3 C-C Hsieh, 3 B-S Huang, 3 M-H Huang, 3 J-S Liu, 2 Y-C Wu 3 See Editorial, p 185 c A supplementary
Management of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ of the Breast
 Evidence-based Series 1-10 Version 2.2006 IN REVIEW A Quality Initiative of the Program in Evidence-Based Care (PEBC), Cancer Care Ontario (CCO) Management of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ of the Breast W.
Evidence-based Series 1-10 Version 2.2006 IN REVIEW A Quality Initiative of the Program in Evidence-Based Care (PEBC), Cancer Care Ontario (CCO) Management of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ of the Breast W.
www.downstatesurgery.org
 Male Breast Cancer Rabih Nemr MD Kings County Hospital August 2008 ACGME Core Competencies 1 Patient t Care Medical Knowledge 2 g 3 4 Practice Based Learning/Improvement Interpersonal Communication Skills
Male Breast Cancer Rabih Nemr MD Kings County Hospital August 2008 ACGME Core Competencies 1 Patient t Care Medical Knowledge 2 g 3 4 Practice Based Learning/Improvement Interpersonal Communication Skills
Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation (APBI) for Breast Cancer [Preauthorization Required]
![Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation (APBI) for Breast Cancer [Preauthorization Required] Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation (APBI) for Breast Cancer [Preauthorization Required]](/thumbs/33/16383903.jpg) Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation (APBI) for Breast Cancer [Preauthorization Required] Medical Policy: MP-SU-01-11 Original Effective Date: February 24, 2011 Reviewed: Revised: This policy applies
Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation (APBI) for Breast Cancer [Preauthorization Required] Medical Policy: MP-SU-01-11 Original Effective Date: February 24, 2011 Reviewed: Revised: This policy applies
Ipsilateral In-Breast Tumor Relapse after Breast Conservation Therapy: True Recurrence Versus New Primary Tumor
 Journal of the Egyptian Nat. Cancer Inst., Vol. 18, No., September: 18-19, 6 Ipsilateral In-Breast Tumor Relapse after Breast Conservation Therapy: True Recurrence Versus New Primary Tumor HASSAN M. ABD-ALLA,
Journal of the Egyptian Nat. Cancer Inst., Vol. 18, No., September: 18-19, 6 Ipsilateral In-Breast Tumor Relapse after Breast Conservation Therapy: True Recurrence Versus New Primary Tumor HASSAN M. ABD-ALLA,
Breast Cancer. Sometimes cells keep dividing and growing without normal controls, causing an abnormal growth called a tumor.
 Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
Guidelines for Management of Renal Cancer
 Guidelines for Management of Renal Cancer Date Approved by Network Governance July 2012 Date for Review July 2015 Changes Between Versions 2 and 3 Section 5 updated bullets 5.3 and 5.4 Section 6 updated
Guidelines for Management of Renal Cancer Date Approved by Network Governance July 2012 Date for Review July 2015 Changes Between Versions 2 and 3 Section 5 updated bullets 5.3 and 5.4 Section 6 updated
Description of Procedure or Service. assays_of_genetic_expression_to_determine_prognosis_of_breast_cancer 11/2004 3/2015 3/2016 3/2015
 Corporate Medical Policy Assays of Genetic Expression to Determine Prognosis of Breast File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: assays_of_genetic_expression_to_determine_prognosis_of_breast_cancer
Corporate Medical Policy Assays of Genetic Expression to Determine Prognosis of Breast File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: assays_of_genetic_expression_to_determine_prognosis_of_breast_cancer
Historical Basis for Concern
 Androgens After : Are We Ready? Mohit Khera, MD, MBA Assistant Professor of Urology Division of Male Reproductive Medicine and Surgery Scott Department of Urology Baylor College of Medicine Historical
Androgens After : Are We Ready? Mohit Khera, MD, MBA Assistant Professor of Urology Division of Male Reproductive Medicine and Surgery Scott Department of Urology Baylor College of Medicine Historical
Outcome analysis of breast cancer patients who declined evidence-based treatment
 Joseph et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2012, 10:118 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY RESEARCH Open Access Outcome analysis of breast cancer patients who declined evidence-based treatment Kurian
Joseph et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2012, 10:118 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY RESEARCH Open Access Outcome analysis of breast cancer patients who declined evidence-based treatment Kurian
Breast Cancer. CSC Cancer Experience Registry Member, breast cancer
 ESSENTIALS Breast Cancer Take things one step at a time. Try not to be overwhelmed by the tidal wave of technical information coming your way. Finally you know your body best; you have to be your own advocate.
ESSENTIALS Breast Cancer Take things one step at a time. Try not to be overwhelmed by the tidal wave of technical information coming your way. Finally you know your body best; you have to be your own advocate.
Cancer research in the Midland Region the prostate and bowel cancer projects
 Cancer research in the Midland Region the prostate and bowel cancer projects Ross Lawrenson Waikato Clinical School University of Auckland MoH/HRC Cancer Research agenda Lung cancer Palliative care Prostate
Cancer research in the Midland Region the prostate and bowel cancer projects Ross Lawrenson Waikato Clinical School University of Auckland MoH/HRC Cancer Research agenda Lung cancer Palliative care Prostate
Surgery Choices. National Cancer Institute. For Women with DCIS or Breast Cancer. National Institutes of Health
 National Cancer Institute Surgery Choices For Women with DCIS or Breast Cancer U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health The National Cancer Institute is grateful for our
National Cancer Institute Surgery Choices For Women with DCIS or Breast Cancer U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health The National Cancer Institute is grateful for our
Significance of Sentinel Lymph Node Micrometastases in Human Breast Cancer
 Significance of Sentinel Lymph Node Micrometastases in Human Breast Cancer Charles E Cox, MD, FACS, John V Kiluk, MD, Adam I Riker, MD, FACS,JohnMCox,MD, Nathon Allred, BA, Daniel C Ramos, BS, Elisabeth
Significance of Sentinel Lymph Node Micrometastases in Human Breast Cancer Charles E Cox, MD, FACS, John V Kiluk, MD, Adam I Riker, MD, FACS,JohnMCox,MD, Nathon Allred, BA, Daniel C Ramos, BS, Elisabeth
INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of radical laparoscopic hysterectomy for early stage cervical cancer Introduction This overview
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of radical laparoscopic hysterectomy for early stage cervical cancer Introduction This overview
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a heterogeneous disease that currently accounts for approximately 20% of all
 Predictors of Invasive Breast Cancer in Patients with an Initial Diagnosis of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ: A Guide to Selective Use of Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Management of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ
Predictors of Invasive Breast Cancer in Patients with an Initial Diagnosis of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ: A Guide to Selective Use of Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Management of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ
This vision does not represent government policy but provides useful insight into how breast cancer services might develop over the next 5 years
 Breast Cancer 2015 Annex C Background 1. Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women in England with (not including cases of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) 1 ) 39,681 new cases diagnosed in 2008
Breast Cancer 2015 Annex C Background 1. Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women in England with (not including cases of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) 1 ) 39,681 new cases diagnosed in 2008
PATIENT SUBSETS WITH T1-T2, NODE-NEGATIVE BREAST CANCER AT HIGH LOCOREGIONAL RECURRENCE RISK AFTER MASTECTOMY
 doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2004.09.013 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 62, No. 1, pp. 175 182, 2005 Copyright 2005 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/05/$ see front
doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2004.09.013 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 62, No. 1, pp. 175 182, 2005 Copyright 2005 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/05/$ see front
GUIDELINES ADJUVANT SYSTEMIC BREAST CANCER
 GUIDELINES ADJUVANT SYSTEMIC BREAST CANCER Author: Dr Susan O Reilly On behalf of the Breast CNG Written: December 2008 Agreed at CNG: June 2009 & June 2010 Review due: June 2011 Guidelines Adjuvant Systemic
GUIDELINES ADJUVANT SYSTEMIC BREAST CANCER Author: Dr Susan O Reilly On behalf of the Breast CNG Written: December 2008 Agreed at CNG: June 2009 & June 2010 Review due: June 2011 Guidelines Adjuvant Systemic
Azienda Ospedale Annunziata Cosenza - Cosenza, Italy
 - Cosenza, Italy General Information New breast cancer cases treated per year 180 Breast multidisciplinarity team members 9 Radiologists, surgeons, pathologists, medical oncologists, radiotherapists and
- Cosenza, Italy General Information New breast cancer cases treated per year 180 Breast multidisciplinarity team members 9 Radiologists, surgeons, pathologists, medical oncologists, radiotherapists and
Changes in Breast Cancer Reports After Second Opinion. Dr. Vicente Marco Department of Pathology Hospital Quiron Barcelona. Spain
 Changes in Breast Cancer Reports After Second Opinion Dr. Vicente Marco Department of Pathology Hospital Quiron Barcelona. Spain Second Opinion in Breast Pathology Usually requested when a patient is referred
Changes in Breast Cancer Reports After Second Opinion Dr. Vicente Marco Department of Pathology Hospital Quiron Barcelona. Spain Second Opinion in Breast Pathology Usually requested when a patient is referred
Adjuvant Therapy for Breast Cancer: Questions and Answers
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Adjuvant Therapy for Breast
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Adjuvant Therapy for Breast
The Di Bella Method (DBM) improves Survival, Objective Response and Performance Status in Breast Cancer
 BIT's 4th World Cancer Congress 2011 People s Republic of China Dalian The Di Bella Method (DBM) improves Survival, Objective Response and Performance Status in treated with DBM therapy Retrospective observational
BIT's 4th World Cancer Congress 2011 People s Republic of China Dalian The Di Bella Method (DBM) improves Survival, Objective Response and Performance Status in treated with DBM therapy Retrospective observational
Cancer of the Cardia/GE Junction: Surgical Options
 Cancer of the Cardia/GE Junction: Surgical Options Michael A Smith, MD Associate Chief Thoracic Surgery Center for Thoracic Disease St Joseph s Hospital and Medical Center Phoenix, AZ Michael Smith, MD
Cancer of the Cardia/GE Junction: Surgical Options Michael A Smith, MD Associate Chief Thoracic Surgery Center for Thoracic Disease St Joseph s Hospital and Medical Center Phoenix, AZ Michael Smith, MD
ADJUVANT RADIATION THERAPY FOR INVASIVE BREAST CANCER
 ADJUVANT RADIATION THERAPY FOR INVASIVE BREAST CANCER Effective Date: May 2015 The recommendations contained in this guideline are a consensus of the Alberta Provincial Breast Tumour Team and are a synthesis
ADJUVANT RADIATION THERAPY FOR INVASIVE BREAST CANCER Effective Date: May 2015 The recommendations contained in this guideline are a consensus of the Alberta Provincial Breast Tumour Team and are a synthesis
OBJECTIVES By the end of this segment, the community participant will be able to:
 Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
A Practical Guide to Advances in Staging and Treatment of NSCLC
 A Practical Guide to Advances in Staging and Treatment of NSCLC Robert J. Korst, M.D. Director, Thoracic Surgery Medical Director, The Blumenthal Cancer Center The Valley Hospital Objectives Revised staging
A Practical Guide to Advances in Staging and Treatment of NSCLC Robert J. Korst, M.D. Director, Thoracic Surgery Medical Director, The Blumenthal Cancer Center The Valley Hospital Objectives Revised staging
The University of Southern California/Van Nuys prognostic index for ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast
 The American Journal of Surgery 186 (2003) 337 343 Scientific paper The University of Southern California/Van Nuys prognostic index for ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast Melvin J. Silverstein, M.D.*
The American Journal of Surgery 186 (2003) 337 343 Scientific paper The University of Southern California/Van Nuys prognostic index for ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast Melvin J. Silverstein, M.D.*
ElioTanaka, MD, Medical Oncology, Audit Medical in Health Service, Curitiba s Health Institute, Paraná, Brazil. www.isaebrasil.com.
 IP2: The cost-effectiveness of breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to detect a locoregional recurrence in patients with breast conserving therapy. Is it feasible in Latin America? www.isaebrasil.com.br
IP2: The cost-effectiveness of breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to detect a locoregional recurrence in patients with breast conserving therapy. Is it feasible in Latin America? www.isaebrasil.com.br
Understanding INTRABEAM Intraoperative Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer A patient guide
 Understanding INTRABEAM Intraoperative Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer A patient guide A diagnosis of breast cancer is never easy, but today there are more treatment options than ever before. A breast
Understanding INTRABEAM Intraoperative Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer A patient guide A diagnosis of breast cancer is never easy, but today there are more treatment options than ever before. A breast
Florida Breast Health Specialists Breast Cancer Information and Facts
 Definition Breast cancer is a cancer that starts in the tissues of the breast. There are two main types of breast cancer: Ductal carcinoma starts in the tubes (ducts) that move milk from the breast to
Definition Breast cancer is a cancer that starts in the tissues of the breast. There are two main types of breast cancer: Ductal carcinoma starts in the tubes (ducts) that move milk from the breast to
The Whipple Operation for Pancreatic Cancer: Optimism vs. Reality. Franklin Wright UCHSC Department of Surgery Grand Rounds September 11, 2006
 The Whipple Operation for Pancreatic Cancer: Optimism vs. Reality Franklin Wright UCHSC Department of Surgery Grand Rounds September 11, 2006 Overview Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma Pancreaticoduodenectomy
The Whipple Operation for Pancreatic Cancer: Optimism vs. Reality Franklin Wright UCHSC Department of Surgery Grand Rounds September 11, 2006 Overview Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma Pancreaticoduodenectomy
Disparities in Stage at Diagnosis, Survival, and Quality of Cancer Care in California by Source of Health Insurance
 Disparities in Stage at Diagnosis, Survival, and Quality of Cancer Care in California by Source of Health Insurance Acknowledgements and Disclaimer The collection of cancer incidence data used in this
Disparities in Stage at Diagnosis, Survival, and Quality of Cancer Care in California by Source of Health Insurance Acknowledgements and Disclaimer The collection of cancer incidence data used in this
Detection and staging of recurrent prostate cancer is still one of the important clinical problems in prostate cancer. A rise in PSA or biochemical
 Summary. 111 Detection and staging of recurrent prostate cancer is still one of the important clinical problems in prostate cancer. A rise in PSA or biochemical recurrence (BCR) is the first sign of recurrent
Summary. 111 Detection and staging of recurrent prostate cancer is still one of the important clinical problems in prostate cancer. A rise in PSA or biochemical recurrence (BCR) is the first sign of recurrent
National Breast and Ovarian Cancer Centre and Royal Australasian College of Surgeons
 National Breast and Ovarian Cancer Centre and Royal Australasian College of Surgeons National Breast Cancer Audit Public Health Monitoring Series 2008 Data Published August 2010 National Breast and Ovarian
National Breast and Ovarian Cancer Centre and Royal Australasian College of Surgeons National Breast Cancer Audit Public Health Monitoring Series 2008 Data Published August 2010 National Breast and Ovarian
Male breast cancer - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 pagina 1 van 5 Male breast cancer From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Male breast cancer is a relatively rare cancer in men that originates from the breast. As it presents a similar pathology as female
pagina 1 van 5 Male breast cancer From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Male breast cancer is a relatively rare cancer in men that originates from the breast. As it presents a similar pathology as female
Chapter 2. Impact of the number of histologically examined lymph nodes on prognosis in colon cancer: a population-based study in the Netherlands.
 Chapter 2 Impact of the number of histologically examined lymph nodes on prognosis in colon cancer: a population-based study in the Netherlands. Wendy Kelder 1,2, Bas Inberg 2, Michael Schaapveld 3, Arend
Chapter 2 Impact of the number of histologically examined lymph nodes on prognosis in colon cancer: a population-based study in the Netherlands. Wendy Kelder 1,2, Bas Inberg 2, Michael Schaapveld 3, Arend
Local Recurrences After Conservative Treatment of Ductal Carcinoma-In-Situ of the Breast Without Radiotherapy: The Effect of Age
 Annals of Surgical Oncology (Ó 2006) DOI: 10.1245/ASO.2006.05.044 Local Recurrences After Conservative Treatment of Ductal Carcinoma-In-Situ of the Breast Without Radiotherapy: The Effect of Age Arjan
Annals of Surgical Oncology (Ó 2006) DOI: 10.1245/ASO.2006.05.044 Local Recurrences After Conservative Treatment of Ductal Carcinoma-In-Situ of the Breast Without Radiotherapy: The Effect of Age Arjan
Are Patients Diagnosed With Breast Cancer Before Age 50 Years Ever Cured? Hermann Brenner and Timo Hakulinen
 VOLUME 22 NUMBER 3 FEBRUARY 1 2004 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY O R I G I N A L R E P O R T Are Patients Diagnosed With Breast Cancer Before Age 50 Years Ever Cured? Hermann Brenner and Timo Hakulinen
VOLUME 22 NUMBER 3 FEBRUARY 1 2004 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY O R I G I N A L R E P O R T Are Patients Diagnosed With Breast Cancer Before Age 50 Years Ever Cured? Hermann Brenner and Timo Hakulinen
Santa Maria Annunziata Hospital / Azienda Sanitaria di Firenze
 - Firenze, Italy General Information New breast cancer cases treated per year 350 Breast multidisciplinarity team members 12 Radiologists, surgeons, pathologists, medical oncologists, radiotherapists and
- Firenze, Italy General Information New breast cancer cases treated per year 350 Breast multidisciplinarity team members 12 Radiologists, surgeons, pathologists, medical oncologists, radiotherapists and
