RADICAL CYSTECTOMY. Procedure Guide
|
|
|
- Sandra McGee
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RADICAL CYSTECTOMY Procedure Guide
2
3 RADICAL CYSTECTOMY Procedure Guide
4 Disclaimer The following material has been reviewed and approved by the following independent surgeons, who are not Intuitive Surgical employees: Raj S. Pruthi, M.D. Associate Professor of Surgery/Urology Director of Urologic Oncology University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Chapel Hill, NC, USA Khurshid A. Guru, M.D. Director, Robotic Surgery, Clinical Assistant Professor of Surgical Oncology, Roswell Park Cancer Institute Clinical Assistant Professor of Urology, University at Buffalo Buffalo, NY, USA Eric M. Wallen, M.D. Associate Professor of Surgery/Urology Director of Urologic Laparoscopy University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Chapel Hill, NC, USA This procedure guide is provided for general information only and is not provided as formal medical training or certification. Intuitive Surgical trains only on the use of the da Vinci Surgical System. Intuitive Surgical does not provide clinical training nor does it provide or evaluate surgical credentialing or train in surgical procedures or techniques. This material presents the opinions of and techniques used by the above surgeons and not those of Intuitive Surgical. Before performing any clinical procedure utilizing the System, physicians are responsible for receiving sufficient training and proctoring to ensure that they have the requisite training, skill and experience necessary to protect the health and safety of the patient. For technical information, including full cautions and warnings on using the da Vinci System, please refer to the System User Manual. Read all instructions carefully. Failure to properly follow instructions, notes, cautions, warnings and danger messages associated with this equipment may lead to serious injury or complications for the patient. While clinical studies support the use of the da Vinci Surgical System as an effective tool for minimally invasive surgery, outcomes cannot be guaranteed, as surgery is patient and procedure specific Intuitive Surgical. All rights reserved. Intuitive, Intuitive Surgical, da Vinci, da Vinci S, da Vinci Si, InSite, TilePro and EndoWrist are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intuitive Surgical. All other product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders. PN Rev. C 4/10
5 da Vinci Radical Cystectomy Procedure Guide Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION 1a. Patient Benefits 1b. Surgical Benefits 2. INSTRUMENTS AND ACCESSORIES 2a. Recommended EndoWrist Instrumentation 2b. Additional EndoWrist Options 2c. Additional da Vinci Supplies 2d. Recommended Laparoscopic Instrumentation and Accessories 2e. Recommended Sutures/Clips 3. PATIENT SELECTION AND PREPARATION 3a. Patient Selection 3b. Experience of Surgical Teams 3c. Patient Preparation 3d. Operating Room Configuration 4. POSITIONING, PORT PLACEMENT AND DOCKING 4a. Patient Positioning 4b. Port Placement 4c. Docking 5. PROCEDURE STEPS - MALE RADICAL CYSTECTOMY 5a. Isolate Ureters 5b. Posterior Dissection 5c. Lateral Dissection 5d. Securing Bladder Pedicles 5e. Anterior Dissection 5f. Ligation of Dorsal Venous Complex (DVC) 5g. Prostatic Dissection/Nerve-Sparing 5h. Specimen Retrieval 5i. Pelvic Lymphadenectomy Page 2 of 25 da Vinci Radical Cystectomy Procedure Guide PN Rev. C 4/10
6 5j. Tagging the Ureters 5k. Pre-Placing Anastomotic Stitches for Orthotopic Neobladder (Option 1) 5l. Urinary Diversion 5m. Urethra-Neobladder Anastomosis (Option 2) 6. PROCEDURE STEPS - FEMALE RADICAL CYSTECTOMY 6a. Divide Ovarian Pedicles 6b. Isolate Ureters 6c. Dissection of Uterine Support 6d. Secure Bladder Pedicles 6e. Vaginal Dissection 6f. Anterior Dissection 6g. Ligation of Dorsal Venous Complex (DVC) 6h. Completion of Hysterectomy and Bi-Lateral Salpingo-Oophorectomy 6i. Reconstruction of the Vagina 6j. Pelvic Lymphadenectomy 6k. Tagging the Ureters 6l. Pre-Placing Anastomotic Stitches for Orthotopic Neobladder 6m. Urinary Diversion 6n. Urethra-Neobladder Anastomosis 7. POST-OPERATIVE CARE APPENDIX A Cannula Remote Center da Vinci Radical Cystectomy Procedure Guide PN Rev. C 4/10 Page 3 of 25
7 1. INTRODUCTION 1a. Patient Benefits da Vinci Radical Cystectomy offers patients numerous potential benefits, including: Significantly less pain medication 1,2 Less blood loss 2,3 Fewer transfusions 3 Fewer major complications 4 Improved cosmesis Shorter hospital stay 3,4 Fast recovery time 1b. Surgical Benefits da Vinci Radical Cystectomy maintains the oncologic principles of open radical cystectomy while also providing the potential benefits of a minimally invasive approach. The unsurpassed visualization, precision, dexterity and control provided by the da Vinci System offers the potential for: Favorable operative, pathologic and short-term oncologic outcomes 2,4,5 Meticulous dissection for standard and/or extended lymphadenectomy Complete and anatomic bladder removal with minimal blood loss 6 Precise suturing of the DVC and creation of watertight urethra-neobladder anastomosis 5 Enhanced ability to preserve the neurovascular bundles in appropriately selected patients 7 A more rapid return of bowel function 2,5 1 Guru, K.A., et al., Robot-assisted radical cystectomy versus open radical cystectomy; assessment of postoperative pain. Can J Urol, (6); p Nix. J., et al., Prospective randomized controlled trial of robotic versus open radical cystectomy for bladder cancer; Perioperative and pathologic results. Eur Uol, Wang, G.J., et al., Robotic vs open radical cystectomy; prospective comparison of perioperative outcomes and pathological measures of early oncological efficacy. BJU Int, (1); p Ng, C.K., et al,. A comparison of postoperative complications in open versus robotic cystectomy. Eur Urol, Pruthi, R.S. and Wallen, E.M., Robotic assisted laparoscopic radical cystoprostatectomy; Operative and pathological outcomes. J Urol, Menon, M., et al., Robot-assisted radical cystectomy and urinary diversion in female patients; Technique with preservation of the uterus and vagina. J Am Coll Surg, (3); p Menon, M., et al., Nerve-sparing robot-assisted radical cystoprostatectomy and urinary diversion. BJU Int, (3); p Page 4 of 25 da Vinci Radical Cystectomy Procedure Guide PN Rev. C 4/10
8 2. INSTRUMENTS AND ACCESSORIES 2a. Recommended EndoWrist Instrumentation HotShears (Monopolar Curved Scissors) (400179/420179) Maryland Bipolar Forceps (400172/420172) 2 Large Needle Drivers (400006/420006) or 1 Large Needle Driver (400006/420006) and 1 SutureCut Needle Driver (400309/420309) Fenestrated Bipolar Grasper (400205/420205) EndoWrist Hem-o-lok Clip Applier, Large (400230/420230) 2b. Additional EndoWrist Options PK Dissecting Forceps (400227/420227) Permanent Cautery Hook (400183/420183) Cobra Grasper (400190/420190) Round Tip Scissors (400007/420007) ProGrasp Forceps (400093/420093) 2c. Additional da Vinci Supplies Basic accessory kit and drapes Intuitive Surgical camera head Intuitive Surgical 0º and 30º endoscopes 2d. Recommended Laparoscopic Instrumentation and Accessories 5 mm endoscopic long suction irrigator (45 mm) 5 mm endoscopic scissors 5 mm endoscopic locking grasper 5 mm endoscopic needle driver (for passing suture) 10 mm endoscopic Babcock forceps 10 mm specimen retrieval bag 2e. Recommended Sutures/Clips Dorsal vein stitch o 0 Vicryl on CT-2 or CT-1 (6) o Alternate: Stapler with vascular load Backbleeding/retraction stitch o 0 Vicryl on CT-1 (6) Ureteral and terminal ileum tags o 3-0 Vicryl on SH (full length) Anastomosis stitch (for orthotopic diversion) o 3-0 Vicryl (or Monocryl ) suture on RB-1 or SH Hem-o-lok (Weck Closure Systems, RTP, NC) Large Clips Hem-o-lok (Weck Closure Systems, RTP, NC) Extra Large Clips/Endoscopic Applier Clamshell closure stitch (for vaginal reconstruction/female patients) o 2-0 Vicryl (or Monocryl) suture on CT-2 da Vinci Radical Cystectomy Procedure Guide PN Rev. C 4/10 Page 5 of 25
9 3. PATIENT SELECTION AND PREPARATION 3a. Patient Selection Ideal Patient Selection Criteria for Early Cases Good performance status Non-obese patients (BMI < 30) Healthy: age < 70, few co-morbidities No previous intra-abdominal or pelvic surgery No prior chemotherapy or pelvic radiotherapy Low volume disease (non-bulky tumors) Avoid patients with moderate to severe cardiopulmonary compromise, a common co-morbidity due to tobacco abuse. Prolonged operative times and steep Trendelenburg positioning may be poorly tolerated by patients with cardiopulmonary disease. 3b. Experience of Surgical Team Teams should be experienced in robotic surgical approaches. It is recommended that teams be proficient performing da Vinci Prostatectomy before embarking upon a robotic radical cystectomy. 3c. Patient Preparation Pre-Operative Patient Preparation Bowel preparation is dependent on surgeon s preference and is identical to that of the open radical cystectomy. Intra-Operative Patient Preparation Intra-operative preparation includes shaving the patient from the costal margin to the pubic bone. The abdomen, pelvis, perineum, upper thighs and peri-anal area are prepped and draped in the usual sterile fashion. A Foley catheter and a rectal bougie are inserted. Intra-operative fluids are restricted to 500 ml per hour as tolerated by the patient. This minimizes the risk of edema of the face and neck which can occur due to fluids and the steep Trendelenburg position. A nasogastric or orogastric tube is inserted at the start of the procedure and removed at the end of the case. Page 6 of 25 da Vinci Radical Cystectomy Procedure Guide PN Rev. C 4/10
10 3d. Operating Room (OR) Configuration The following figure shows an overhead view of the recommended OR configuration for a da Vinci Radical Cystectomy (Figure 1). Figure 1: Operating room set-up NOTE: Configuration of the operating suite is dependent on the room dimensions as well as the preference and experience of the surgeon. The assistant can also be placed on the other side of the table, mirroring what is shown above. da Vinci Radical Cystectomy Procedure Guide PN Rev. C 4/10 Page 7 of 25
11 4. POSITIONING, PORT PLACEMENT AND DOCKING 4a. Patient Positioning After positioning, padding, securing and preparing the patient in the supine position, the table is then placed in a steep Trendelenburg (>20) position identical to the position used for da Vinci Prostatectomy. Place table in Trendelenburg position before rolling in the patient cart (Figure 2). A split-leg table with mild leg separation and slight hip extension is used. Stirrups or leg boards may be employed (Figure 3). Great care is taken to adequately pad and support the patient to avoid neuromuscular injury. Sequential compression devices are applied to the legs for DVT prophylaxis. Carefully secure patient to the table to avoid any shifting with the Trendelenburg position (Figure 4). Figure 2: Trendelenburg position Figure 3: Patient positioning Figure 4: Patient positioning Page 8 of 25 da Vinci Radical Cystectomy Procedure Guide PN Rev. C 4/10
12 4b. Port Placement The port placement is similar to da Vinci Prostatectomy with the addition of a 12 mm port on the side opposite of the assistant. Figure 5 demonstrates port placement based on a left-sided assistant. Preparing for Port Placement Veress insufflation is achieved through a vertical skin incision above the umbilicus, 20 cm above the symphysis pubis on the deflated abdomen where the camera port is placed. Perform initial assessment of anatomy once the camera port is inserted and place remaining ports under direct vision. da Vinci Camera Port, 12 mm (Blue): Place the port near the umbilicus, 20 cm above the symphysis pubis. A2 A3 da Vinci Instrument Arm Port, 8 mm ( YYeel lll llooww): Place the port 8 cm from the camera port, along the line from the umbilicus to the right anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS). Camera A1 da Vinci Instrument Arm Port, 8 mm (Green): Place the port 8 cm from the camera port, along the line from the umbilicus to the left ASIS. da Vinci Instrument Arm Port, 8 mm (Red): Place the port 8 cm directly lateral to the instrument arm port. Assistant Port (A1), 12 mm ( ): Place the port two finger-breadths medial and superior to the ASIS on the left and at least 8 cm from the instrument arm port. Figure 5: 4-arm port placement NOTE: Following port placement, the patient is then placed in the steep Trendelenburg position and the patient cart is docked. Assistant Port (A2), 12 mm ( ): Place the port for retraction and stapling 10 cm superior to the instrument arm port. Assistant Port (A3), 5 mm (Black): Place the port 12 cm superior to the instrument arm port. da Vinci Radical Cystectomy Procedure Guide PN Rev. C 4/10 Page 9 of 25
13 4c. Docking Positioning the Patient Cart Step 1- Adjust the camera arm set-up joint to side opposite of the 3 rd da Vinci instrument arm Step 2 - Determine sweet spot Step 3 - Align the camera arm Step 4 - Roll in the patient cart Step 5 - Dock the patient cart Step 1: Adjust the Camera Arm Set-Up Joint When using all three da Vinci instrument arms, position the camera arm set-up joint towards the patient's side with just one instrument arm, as seen in (Figure 6). Figure 6: Positioning of camera set-up joint for 4-arm approach Step 2: Determining the "Sweet Spot The sweet spot maximizes the range of motion for the instrument arms. Confirm sweet spot prior to docking. da Vinci S System - The blue arrow should align within the blue marker on the 2 nd joint (Figure 7a) or there should be ~90 angle between the 1 st and 3 rd joint on the camera arm (Figure 7b). da Vinci Surgical System - There should be a ~10 cm distance from the 1 st and 3 rd joints on the camera arm set-up joint (Figure 8). A B Figures 7a-b: Sweet Spot on da Vinci S Figure 8: Sweet Spot on da Vinci Standard Page 10 of 25 da Vinci Radical Cystectomy Procedure Guide PN Rev. C 4/10
14 Step 3: Align the Camera Arm Align the camera arm, camera arm set-up joint, column and target anatomy. A straight line should be achieved by aligning the clutch button, the 3 rd joint of the camera arm and the gray dot in da Vinci on the center column (Figure 9). Step 4: Roll in the Patient Cart Patient is placed in steep Trendelenburg position before rolling in patient cart. Patient cart is positioned directly between the legs and locked (Figure 10). The base of the cart will straddle the base of the operating table (Figure 11). Push aside overhead lights and equipment to maintain sterility of the patient cart. The arms of the patient cart should be positioned high enough to clear the height of the patient's legs. Figure 9: Align camera arm Figure 10: Overhead view of docked patient cart Figure 11: Side view of docked patient cart Step 5: Dock the Arms Ensure camera port, target anatomy and patient cart center column are aligned Position camera cannula mount over the camera port and dock Use port and arm clutch maneuvers to dock remaining instrument arms Maximize spacing between arms Keep instruments in the center of their range of motion da Vinci Radical Cystectomy Procedure Guide PN Rev. C 4/10 Page 11 of 25
15 5. PROCEDURE STEPS - Male Radical Cystectomy Instruments: 1 Monopolar Instrument 1 Bipolar Forceps Grasper for 3 rd Instrument Arm (Fenestrated Bipolar, Cobra Grasper, ProGrasp Forceps) Additional Option: EndoWrist Hem-o-lok Clip Applier, Large Anatomy Overview: Medial Umbilical Ligament Urachus Medial Umbilical Ligament Vas Deferens Ureter Spermatic Cord Iliac Vessels Bladder Rectum Figure 12: Pelvic anatomy overview Procedure Overview: Male Radical Cystectomy (Cystoprostatectomy) Surgery to remove the bladder, prostate, seminal vesicles and lymph nodes Bladder Pubic Bone Seminal Vesicle Urethra Rectum Prostate Figure 13: Lateral view before surgery Figure 14: Lateral view after surgery Page 12 of 25 da Vinci Radical Cystectomy Procedure Guide PN Rev. C 4/10
16 5a. Isolate the Ureters - Step 1 The goal of this step is to first dissect the ureters distally to the level of the bladder, then to ligate and transect them. Bladder bladder V 1-Isolate Ureters 1 1 U Rectum Figure 15a: Diagram of ureteral incision Figure 15b: Intra-operative image of ureteral incision Identify the Ureters Sharply release sigmoid adhesions on the left side of the bladder to mobilize the sigmoid colon. The posterior peritoneum is incised to identify the ureters bilaterally (Figures 15a and 15b). The ureters are frequently identified just medial to the spermatic vessels or they may be found crossing over the iliac vessels. Ureteral Dissection and Ligation Ureteral dissection is carried out proximally as far as possible and distally to the level of the bladder (Figure 16). Ligate the ureters using clips and transect (Figure 17). After transection the ureters are released proximally and tucked into the upper quadrants, away from the pelvic dissection. Bladder Figure 16: Dissect ureter distally to level of bladder Figure 17: Ligate ureters using EndoWrist Large Clip Applier Caveats & Considerations: Laparoscopic Babcock forceps can be used to encircle the ureter to assist with dissection. Use 3D HD vision and magnification to help preserve the healthy tissue around the ureters. Avoid grasping the ureters to prevent crush injury and devascularization. da Vinci Radical Cystectomy Procedure Guide PN Rev. C 4/10 Page 13 of 25
17 5b. Posterior Dissection - Step 2 The aim of this dissection is to mobilize the bladder and base of the prostate off the rectum. Bladder 2 - Posterior Dissection 2 Rectum Figure 18a: Diagram of posterior incision Figure 18b: Intra-operative image of posterior incision Incise the Posterior Peritoneum The posterior peritoneum is incised just above its reflection over the rectum, connecting the incisions previously made for the ureteral dissection (Figures 18a and 18b). A grasper may be used in the 3 rd instrument arm to retract the bladder anteriorly and/or to give lateral traction to the redundant sigmoid colon. Develop the Rectovesical Space Use blunt dissection to develop the rectovesical cul-de-sac. Mobilize the bladder and the base of the prostate off the rectum (Figure 19). Caveats & Considerations: If necessary, the 30 up scope can be used for adequate posterior visualization; the 0 scope is adequate in most cases. Figure 19: Posterior dissection Page 14 of 25 da Vinci Radical Cystectomy Procedure Guide PN Rev. C 4/10
18 5c. Lateral Dissection - Step 3 During this step, the goal is to develop the space between the bladder and lateral pelvic sidewalls. This will facilitate exposure and isolation of the bladder pedicles. 3 3 Bladder 3 - Lateral Dissection SC Figure 20a: Diagram of lateral incision Figure 20b: Intra-operative image of lateral incision Lateral incisions in the peritoneum are made bilaterally to develop the perivesical space. Incisions are made from the medial umbilical ligaments and connect the posterior peritoneal incisions made with the initial ureteral dissection (Figures 20a and 20b). The line of incision travels parallel to the spermatic cord. It is important not to drop the bladder at this point. The urachal and medial umbilical attachments are left intact, in order to suspend the bladder. The perivesical space is developed distally to the level of the endopelvic fascia (Figure 21) and continues posteriorly to the bladder pedicles. At this point the lateral vascular pedicles of the bladder are readily visualized. Caveats & Considerations: Care should be taken to avoid aggressive lateral dissection as the iliac vessels are located here. It is important not to drop the bladder at this point, since the bladder s suspension will facilitate additional posterior dissection which may be needed to secure the bladder pedicles. Figure 21: Dissect to the level of endopelvic fascia da Vinci Radical Cystectomy Procedure Guide PN Rev. C 4/10 Page 15 of 25
19 5d. Securing Bladder Pedicles - Step 4 A laparoscopic endovascular linear stapler/cutter is used to ligate and transect vascular pedicles to the bladder. Bladder 4 4 Pedicle Pedicle 4 - Secure Bladder Pedicles Figure 22a: Diagram of bladder pedicles Figure 22b: Intra-operative image of bladder pedicles Identify bladder pedicles (Figures 22a and 22b) and isolate them (Figure 23). A laparoscopic endovascular stapler is used to ligate and transect the vascular pedicles to the bladder (Figure 24). Usually, a single fire 60 mm stapler/cutter is sufficient to secure the bladder pedicles. The console surgeon may aid in retraction while the assistant positions and fires the stapler. In a nerve-sparing procedure, the surgeon should not be overly aggressive with the distal dissection and pedicle ligation as this may injure the neurovascular bundles. However, intact endopelvic fascia helps prevent the stapler tips from closing too far distally. Alternatively, clips and bipolar forceps may also be used to secure the vascular pedicles. Pedicle Pedicle Figure 23: Isolate bladder pedicle Figure 24: Secure bladder pedicle using an endovascular stapler Caveats & Considerations: A grasper in the 3 rd instrument arm may be used to retract redundant bladder. Page 16 of 25 da Vinci Radical Cystectomy Procedure Guide PN Rev. C 4/10
20 5e. Anterior Dissection - Step 5 The aim of this dissection is to drop the bladder posteriorly as is done in da Vinci Prostatectomy in order to access the space of Retzius. M UR M Anterior Dissection 2 4 Figure 25a: Diagram of anterior incision Figure 25b: Intra-operative image of anterior incision Incise Anterior Peritoneum The peritoneum is incised anteriorly through the medial umbilical ligaments and the urachus (Figures 25a and 25b). The bladder is dropped as is done in da Vinci Prostatectomy (Figure 26). The endopelvic fascia is identified and incised bilaterally. Figure 26: Incising anterior peritoneum da Vinci Radical Cystectomy Procedure Guide PN Rev. C 4/10 Page 17 of 25
21 5f. Ligating the Dorsal Venous Complex (DVC) - Step 6 During this step, the goal is to control the dorsal venous complex and prostatic apex. The DVC is secured just as is done in da Vinci Prostatectomy. o The DVC is ligated with a 6 inch 0 Vicryl on a CT-2 needle (Figure 27). o A backbleeding stitch is placed for retraction and exposure of the prostatic apex. This is a 6 inch 0 Vicryl on a CT-1 needle (Figure 28). When an orthotopic neobladder is planned, care is taken to maintain adequate urethral length during the apical dissection. For other types of diversions, a long urethral margin is left on the specimen. At this point the Foley catheter is left in place. Figure 27: Ligating dorsal venous complex Figure 28: Placing "backbleeding" stitch 5g. Prostatic Dissection/Nerve-Sparing - Step 7 In this step, the remaining lateral tissue and prostatic pedicles are taken with clips and bipolar cautery. In select patients a nerve-sparing technique may be performed. Prostatic Dissection In a non-nerve-sparing procedure the remainder of the lateral tissue and prostatic pedicles are taken with clips or bipolar cautery, freeing up the entire specimen. Athermal Bilateral Nerve-Sparing Technique Nerve-sparing in da Vinci Radical Cystectomy is undertaken in the same fashion as in da Vinci Prostatectomy. Care must be taken to avoid thermal energy and traction injury to the neurovascular bundles. The prostate and bladder are retracted laterally and superiorly to expose the contralateral prostatic pedicle. The pedicle is secured with clips and sharply divided with cold scissors. The contralateral pedicle is secured and nerve preservation is performed in a similar manner. Transection of the Urethra The posterior urethra is transected and any remaining prostatic attachments are freed. A clip may be applied proximally to the Foley catheter to prevent urine spillage prior to transection of the urethra. Page 18 of 25 da Vinci Radical Cystectomy Procedure Guide PN Rev. C 4/10
22 5h. Specimen Retrieval - Step 8 Once the cystoprostatectomy specimen is free, it should be placed into a retrieval bag. Bag Specimen With the specimen completely free, a clip is applied to the Foley catheter and it is transected to avoid urinary spillage and contamination. The catheter is cut outside of the patient and the cut end is brought into the pelvis. The specimen is then placed in a retrieval bag which is moved out of the pelvis. The pelvis is irrigated, the rectal surface inspected and hemostasis is ensured. A urethral margin is sent for frozen section evaluation. 5i. Pelvic Lymphadenectomy - Step 9 The goal of this step is to perform a complete lymphadenectomy. Lymph Node Dissection Lymphadenectomy is carried out utilizing sharp and blunt dissection (Figures 29a and 29b). Clips may be used for hemostasis and lymphastasis. Margins of lymphadenectomy vary according to the discretion of the surgeon, and generally include the obturator nodes, the external iliac nodes and the common iliac nodes up to the aortic bifurcation. Para-aortic lymphadenectomy is also possible, particularly with the use of the da Vinci S System which allows for more range of motion of the robotic arms. Figure 29a: Pelvic anatomy guide Figure 29b: Pelvic anatomy intra-operative image Caveats & Considerations: During dissection over the iliac vessels, care should be taken to avoid inadvertent injury to the vein. During this procedure, the patient is placed in the steep Trendelenburg position and maintained relatively hypovolemic. Consequently, the iliac vein can be decompressed and thereby prone to grasping or sharp injury. Decreasing the insufflation pressure to mmhg during this portion of the procedure may allow for distension of the vein and better visualization. Pelvic lymph node dissection is typically performed after the cystectomy since absence of the bladder and prostate from the pelvis facilitates room and exposure for the lymphadenectomy. The nodal packet can be placed in a specimen bag and removed through the 12 mm assistant port or placed in a specimen bag for later removal. da Vinci Radical Cystectomy Procedure Guide PN Rev. C 4/10 Page 19 of 25
23 5j. Tagging the Ureters - Step 10 The goal of this step is to tag the ureters in order to allow for ready identification during the urinary diversion. Before undocking the da Vinci System, the ureters are returned to the pelvis. At the distal end of each ureter, a full-length 3-0 Vicryl suture on a SH needle is placed as a tag, and the ends are brought out through the assistant ports on each side (Figure 30). A 3-0 Vicryl stitch may also be placed in the terminal ileum to allow for its ready identification during the urinary diversion. Figure 30: Tagging the ureters 5k. Pre-Placing the Anastomotic Stitches for the Orthotopic Neobladder (Option 1) - Step 11 For an orthotopic neobladder the posterior anastomotic stitches can be pre-placed in the urethra if the urethra-neobladder anastomosis will be performed extracorporally. Another option is to perform the anastomosis robotically following urinary diversion (Option 2). Placing Posterior Sutures 3-0 Vicryl sutures (on RB-1 needles) are placed at the 5 and 7 o clock positions in the urethra prior to undocking the da Vinci System for urinary diversion. These posterior sutures are sometimes the most difficult to place in an open fashion and pre-placement under robotic guidance is easier. The da Vinci System is then undocked. Upon completion of the urinary diversion, the urethra-neobladder anastomosis is completed through the open incision. Page 20 of 25 da Vinci Radical Cystectomy Procedure Guide PN Rev. C 4/10
24 5l. Urinary Diversion - Step 12 During this step, a urinary diversion is created extracorporally. Prepare Field and Perform Diversion Undock the da Vinci System. The ureteral sutures are kept through their corresponding port sites and tagged. It is important to keep the patient in the Trendelenburg position initially in order to prevent the intestines from descending into the pelvis. A 6 to 8 cm infraumbilical midline incision is made to perform the urinary diversion. Through this incision any further mobilization of the ureters can be carried out if needed. For an ileal conduit, the left ureter is tunneled under the sigmoid mesentery. In the case of an orthotopic neobladder where the afferent limb lies on the left side, the right ureter is tunneled underneath the sigmoid mesentery. The terminal ileum may be identified with the assistance of the replaced stitch, and a segment of bowel is harvested. The planned urinary diversion is then performed extracorporeally and the ureteroenteric anastomosis is completed. Complete the Urethra-Neobladder Anastomosis (Option 1) For an orthotopic neobladder, the pre-placed posterior urethral stitches are placed in their proper position in the neobladder neck. Anterior anastomotic sutures are placed and the anastomosis is completed. 5m. Perform the Urethra-Neobladder Anastomosis (Option 2) - Step 13 The goal of this step is to perform a watertight urethra-neobladder anastomosis using the same principles required to perform an urethrovesical anastomosis in da Vinci Prostatectomy. The neobladder specimen is returned to the pelvis and the abdominal incision is closed, except for the upper most portion through which the camera port is inserted. The abdomen is insufflated and all robotic arms are docked. Create an opening in the neobladder in the most dependent portion. The running anastomosis is constructed using a double-armed 3-0 Vicryl or Moncryl on either an RB-1 or SH needle as is done for the urethrovesical anastomosis in a da Vinci Prostatectomy (Figure 28). Sew outside to inside on the neobladder and inside to outside on the urethra starting near the 6 o'clock position. Irrigate to confirm a watertight urethra-neobladder anastomosis. Figure 31: Creating urethra-neobladder anastomosis da Vinci Radical Cystectomy Procedure Guide PN Rev. C 4/10 Page 21 of 25
25 6. PROCEDURE STEPS - Female Radical Cystectomy Instruments: 1 Monopolar Instrument 1 Bipolar Forceps Grasper for 3 rd Instrument Arm (Cobra Grasper, Fenestrated Bipolar, ProGrasp Forceps) Additional Option: EndoWrist Hem-o-lok Clip Applier, Large Procedure Overview: Female Radical Cystectomy (Anterior Pelvic Exenteration) Surgery to remove the bladder, uterus, cervix, ovaries, anterior wall of the vagina* and lymph nodes Uterus Bladder Rectum Pubic Bone Urethra Vagina Figure: 32 Lateral view before surgery Figure: 33 Lateral view after surgery * The vagina may be spared in select cases. NOTE: Several steps for performing a da Vinci Radical Cystectomy on a female patient are the same as the steps presented in the Male Radical Cystectomy (Section 5). Steps unique for a female patient are presented here. Page 22 of 25 da Vinci Radical Cystectomy Procedure Guide PN Rev. C 4/10
26 6a. Divide Ovarian Pedicles - Step 1 Prior to identification of the ureters, the ovarian pedicles are identified and divided between clips. 6b. Isolate Ureters - Step 2 Follow steps in Section 5a in order to isolate ureters. 6c. Dissection of Uterine Support - Step 3 After ureters are isolated, the uterus is anteverted and retracted using the 3 rd instrument arm. The cardinal and uterosacral ligaments should be divided bilaterally. The uterus is dropped and retracted proximally for the retrovesical dissection. 6d. Secure Bladder Pedicles - Step 4 Once the bladder pedicles are isolated, they are secured using the technique presented in Section 5d. 6e. Vaginal Dissection - Step 5 Visually identify the junction of the vagina and the bladder. This step may be facilitated by filling the bladder with approximately 100 ml of saline. A transverse incision opens the junction until the uterine manipulator or sponge stick is visible within the vagina. The vaginal incision is carried laterally past the urethra to ensure that a strip of the anterior vaginal wall is removed en bloc with the bladder. In the case of a vaginal sparing procedure, the plane between the bladder and vagina can be developed. 6f. Anterior Dissection - Step 6 Follow steps presented in Section 5e to drop the bladder. 6g. Ligation of Dorsal Venous Complex (DVC) - Step 7 The DVC is ligated and the urethra is transected using the technique presented in Section 5f. 6h. Completion of Hysterectomy and Bi-Lateral Salpingo-Oophorectomy - Step 8 After the bladder is removed, the uterus is retracted superiorly using the 3 rd instrument arm and the uterus and cervix are excised. In cases where the anterior vaginal wall is resected, the specimen may be delivered through the introitus. In vaginal sparing cases, the specimen may be placed in a specimen bag and removed through the abdominal incision made for the urinary diversion. 6i. Reconstruction of the Vagina (if necessary) - Step 9 The vagina is reconstructed using the clam-shell technique. 5 The edges of the vagina are closed using a running interlock suture. The pneumoperitoneum is decreased to evaluate homeostatus prior to proceeding to pelvic lymph-node dissection. 5 Guru KA, et al. Robot-Assisted Anterior Exenteration: Technique and Initial Series. J of Endourology. Jun (6); da Vinci Radical Cystectomy Procedure Guide PN Rev. C 4/10 Page 23 of 25
27 NOTE: The remaining procedure steps follow the same steps that are used for performing a da Vinci Radical Cystectomy on a male patient. 6j. Pelvic Lymphadenectomy - Step 10 Follow steps in Section 5i. 6k. Tagging the Ureters - Step 11 Follow steps in Section 5j. 6l. Pre-Placing Anastomotic Stitches for Orthotopic Neobladder (Option1) - Step 12 Follow steps in Section 5k. 6m. Urinary Diversion - Step 13 Follow steps in Section 5l. 6n. Urethra-Neobladder Anastomosis (Option 2) - Step 14 Follow steps in Section 5m. 7. POST-OPERATIVE CARE Post-operative considerations should be based on surgeon s experience and preference. Page 24 of 25 da Vinci Radical Cystectomy Procedure Guide PN Rev. C 4/10
28 APPENDIX A Cannula Remote Center Set-Up To correctly place the remote center, the thick black line on the da Vinci cannula (which indicates the remote center) should be inserted within the boundaries of the patient s body wall. Correct placement will allow the robotic instrumentation to pivot through the incision with the least friction and highest precision, which will minimize tissue trauma (Figure A1 a, below). Correct placement of the cannula should be verified by looking at the cannula tip with the endoscopic camera (cannulas should always be placed under endoscopic camera view). Only the first thin line at the distal cannula tip should be visible. This indicates that the remote center is placed correctly within the boundaries of the patient s body wall (Figure A1 b, below). If the thick black line on the cannula is seen in the endoscopic view, this means that the remote center is set incorrectly (inserted too deeply). Setting the remote center incorrectly will increase friction, reduce precision and increase tissue trauma at the port site (Figure A1 c, below). a b c Figure A1: Proper placement of the instrument s cannula remote center da Vinci Radical Cystectomy Procedure Guide PN Rev. C 4/10 Page 25 of 25
RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY IN ROBOTIC SURGERY
 RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY IN ROBOTIC SURGERY FLORENCE BOCHU CENTRE OSCAR LAMBRET LILLE PATRICIA VARUMBEKE CENTRE OSCAR LAMBRET LILLE MELANIE FLAMENT CENTRE OSCAR LAMBRET LILLE More and more centers across the
RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY IN ROBOTIC SURGERY FLORENCE BOCHU CENTRE OSCAR LAMBRET LILLE PATRICIA VARUMBEKE CENTRE OSCAR LAMBRET LILLE MELANIE FLAMENT CENTRE OSCAR LAMBRET LILLE More and more centers across the
da Vinci Prostatectomy Information Guide (Robotically-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy)
 da Vinci Prostatectomy Information Guide (Robotically-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy) Prostate Cancer Overview Prostate cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the
da Vinci Prostatectomy Information Guide (Robotically-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy) Prostate Cancer Overview Prostate cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the
Laparoscopic Anatomy of the Pelvis
 2 Laparoscopic Anatomy of the Pelvis Intra-Abdominal Anatomy of the Male Pelvic Region Bladder Medial Umbilical Ligaments Lateral Umbilical Ligaments Spermatic Cords Iliac Vessels Ureters Seminal Vesicular
2 Laparoscopic Anatomy of the Pelvis Intra-Abdominal Anatomy of the Male Pelvic Region Bladder Medial Umbilical Ligaments Lateral Umbilical Ligaments Spermatic Cords Iliac Vessels Ureters Seminal Vesicular
Robotic versus total laparoscopic radical hysterectomy with pelvic lymphadenectomy for the treatment of early cervical cancer
 International Journal of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics and Gynecology Goud JG et al. Int J Reprod Contracept Obstet Gynecol. 2014 Mar;3(1):34-39 www.ijrcog.org pissn 2320-1770 eissn 2320-1789
International Journal of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics and Gynecology Goud JG et al. Int J Reprod Contracept Obstet Gynecol. 2014 Mar;3(1):34-39 www.ijrcog.org pissn 2320-1770 eissn 2320-1789
HOW I DO IT. Introduction. The surgical procedure
 HOW I DO IT Robot assisted radical prostatectomy: how I do it. Part II: surgical technique Roger F. Valdivieso, MD, Pierre-Alain Hueber, MD, Kevin C. Zorn, MD University of Montreal Hospital Center (CHUM)
HOW I DO IT Robot assisted radical prostatectomy: how I do it. Part II: surgical technique Roger F. Valdivieso, MD, Pierre-Alain Hueber, MD, Kevin C. Zorn, MD University of Montreal Hospital Center (CHUM)
Laparoscopic extended right hemicolectomy for transverse colon
 Laparoscopic extended right hemicolectomy for transverse colon cancer Elsa B. Valsdottir, MD Department of General Surgery University Hospital of Iceland Hringbraut 101 Reykjavik Iceland Phone +354 543
Laparoscopic extended right hemicolectomy for transverse colon cancer Elsa B. Valsdottir, MD Department of General Surgery University Hospital of Iceland Hringbraut 101 Reykjavik Iceland Phone +354 543
Laparoscopic Assisted Vaginal Hysterectomy
 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital at ChiaYi 嘉 義 長 庚 紀 念 醫 院 婦 產 科 Clinical Guideline Laparoscopic Assisted Vaginal Hysterectomy By Dr. CJ Tseng Laparoscopic assisted
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital at ChiaYi 嘉 義 長 庚 紀 念 醫 院 婦 產 科 Clinical Guideline Laparoscopic Assisted Vaginal Hysterectomy By Dr. CJ Tseng Laparoscopic assisted
How To Perform Da Vinci Surgery
 Facing a Hysterectomy? If you ve been diagnosed with early stage gynecologic cancer, learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Early Stage Gynecologic Cancer A variety of gynecologic
Facing a Hysterectomy? If you ve been diagnosed with early stage gynecologic cancer, learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Early Stage Gynecologic Cancer A variety of gynecologic
Facing a Hysterectomy? If you ve been diagnosed with early stage gynecologic cancer, learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery
 Facing a Hysterectomy? If you ve been diagnosed with early stage gynecologic cancer, learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Early Stage Gynecologic Cancer A variety of gynecologic
Facing a Hysterectomy? If you ve been diagnosed with early stage gynecologic cancer, learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Early Stage Gynecologic Cancer A variety of gynecologic
INSTRUMENT & ACCESSORY CATALOG
 INSTRUMENT & ACCESSORY CATALOG MAY 205 For more information, call Intuitive Surgical +800.082.2020 (toll-free) / +4.2.82.2020 or visit www.intuitivesurgical.com Some products in the catalog may not be
INSTRUMENT & ACCESSORY CATALOG MAY 205 For more information, call Intuitive Surgical +800.082.2020 (toll-free) / +4.2.82.2020 or visit www.intuitivesurgical.com Some products in the catalog may not be
Surgical techniques: robot-assisted laparoscopic hysterectomy with the da Vinci surgical system
 THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MEDICAL ROBOTICS AND COMPUTER ASSISTED SURGERY Int J Med Robotics Comput Assist Surg 2006; 2: 305 311. Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com)..111
THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MEDICAL ROBOTICS AND COMPUTER ASSISTED SURGERY Int J Med Robotics Comput Assist Surg 2006; 2: 305 311. Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com)..111
The main surgical options for treating early stage cervical cancer are:
 INFORMATION LEAFLET ON TOTAL LAPAROSCOPIC RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY (TLRH) FOR EARLY STAGE CERVICAL CANCER (TREATING EARLY STAGE CERVICAL CANCER BY RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY THROUGH KEYHOLE SURGERY) Aim of the leaflet
INFORMATION LEAFLET ON TOTAL LAPAROSCOPIC RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY (TLRH) FOR EARLY STAGE CERVICAL CANCER (TREATING EARLY STAGE CERVICAL CANCER BY RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY THROUGH KEYHOLE SURGERY) Aim of the leaflet
Laparoscopic Trainer Product Catalog
 Laparoscopic Trainer Product Catalog Laparoscopic Trainer Product Catalog Simsei Table of Contents Laparoscopic Trainers 6 Organ Models 8 Skill Exercises 11 Accessories 12 Additional Information About
Laparoscopic Trainer Product Catalog Laparoscopic Trainer Product Catalog Simsei Table of Contents Laparoscopic Trainers 6 Organ Models 8 Skill Exercises 11 Accessories 12 Additional Information About
Considering a Hysterectomy?
 Considering a Hysterectomy? Learn more about virtually scarless surgery using da Vinci Single-Site technology { {Symptoms & Conditions: Chronic Pain, Heavy Bleeding, Fibroids, Endometriosis, Pelvic Prolapse
Considering a Hysterectomy? Learn more about virtually scarless surgery using da Vinci Single-Site technology { {Symptoms & Conditions: Chronic Pain, Heavy Bleeding, Fibroids, Endometriosis, Pelvic Prolapse
DA VINCI ROBOTIC HYSTERECTOMY
 DA VINCI ROBOTIC HYSTERECTOMY Until recently, surgery for most gynecologic conditions was performed using a large abdominal incision. This is because while conventional laparoscopic surgery is effective
DA VINCI ROBOTIC HYSTERECTOMY Until recently, surgery for most gynecologic conditions was performed using a large abdominal incision. This is because while conventional laparoscopic surgery is effective
Facing Prostate Cancer Surgery? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery
 Facing Prostate Cancer Surgery? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Prostate Cancer Your prostate is a walnut-sized gland that is part of the male reproductive system. The prostate
Facing Prostate Cancer Surgery? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Prostate Cancer Your prostate is a walnut-sized gland that is part of the male reproductive system. The prostate
Considering a Hysterectomy?
 Considering a Hysterectomy? Learn more about virtually scarless surgery using da Vinci Single-Site technology { {Symptoms & Conditions: Chronic Pain, Heavy Bleeding, Fibroids, Endometriosis, Adenomyosis,
Considering a Hysterectomy? Learn more about virtually scarless surgery using da Vinci Single-Site technology { {Symptoms & Conditions: Chronic Pain, Heavy Bleeding, Fibroids, Endometriosis, Adenomyosis,
da Vinci and Beyond Simon DiMaio, Ph.D. Intuitive Surgical 21 July 2014
 da Vinci and Beyond Simon DiMaio, Ph.D. Intuitive Surgical 21 July 2014 Medical Robots as Products Radio- Therapy Robots Robotic Assistants Tele- Robots MEDICAL ROBOTICS Imaging Robots Image- Guided Robots
da Vinci and Beyond Simon DiMaio, Ph.D. Intuitive Surgical 21 July 2014 Medical Robots as Products Radio- Therapy Robots Robotic Assistants Tele- Robots MEDICAL ROBOTICS Imaging Robots Image- Guided Robots
Facing Hysterectomy? Learn why da Vinci Surgery may be your best treatment option for early stage gynecologic cancer
 Facing Hysterectomy? Learn why da Vinci Surgery may be your best treatment option for early stage gynecologic cancer The Condition: Early Stage Gynecologic Cancer A wide variety of gynecologic cancers
Facing Hysterectomy? Learn why da Vinci Surgery may be your best treatment option for early stage gynecologic cancer The Condition: Early Stage Gynecologic Cancer A wide variety of gynecologic cancers
9/26/14. Joel E. Rand, MPAS, PA-C DMU Luncheon May 1, 2014
 Joel E. Rand, MPAS, PA-C DMU Luncheon May 1, 2014 No financial relationship or commercial interest in any of the technologies discussed Not supporting any non-fda off label uses of any product or service
Joel E. Rand, MPAS, PA-C DMU Luncheon May 1, 2014 No financial relationship or commercial interest in any of the technologies discussed Not supporting any non-fda off label uses of any product or service
How To Treat Cervical Cancer
 Total Laparoscopic Radical Hysterectomy in Cervical Cancer K Jardon, B. Rabischong, M, Canis, R Botchorishvili, C. Pomel, A. Wattiez, J.L Pouly G. Le Bouedec, J.L Achard, J. Dauplat, Mage G Polyclinique
Total Laparoscopic Radical Hysterectomy in Cervical Cancer K Jardon, B. Rabischong, M, Canis, R Botchorishvili, C. Pomel, A. Wattiez, J.L Pouly G. Le Bouedec, J.L Achard, J. Dauplat, Mage G Polyclinique
Robotic Radical Prostatectomy: What s s the Advantage? Matthew T. Gettman, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Urology
 Robotic Radical Prostatectomy: What s s the Advantage? Matthew T. Gettman, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Urology Prostate Cancer Epidemiology: 2009 Estimated new cases: 230,000 Estimated deaths:
Robotic Radical Prostatectomy: What s s the Advantage? Matthew T. Gettman, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Urology Prostate Cancer Epidemiology: 2009 Estimated new cases: 230,000 Estimated deaths:
DISCUSSION ABOUT OPEN, LAPAROSCOPIC, AND ROBOTIC PROSTATECTOMIES MOUNT SINAI MEDICAL CENTER NEW YORK CITY, NEW YORK August 13, 2008
 DISCUSSION ABOUT OPEN, LAPAROSCOPIC, AND ROBOTIC PROSTATECTOMIES MOUNT SINAI MEDICAL CENTER NEW YORK CITY, NEW YORK August 13, 2008 00:00:08 ANNOUNCER: Today, Mount Sinai Medical Center s leading urological
DISCUSSION ABOUT OPEN, LAPAROSCOPIC, AND ROBOTIC PROSTATECTOMIES MOUNT SINAI MEDICAL CENTER NEW YORK CITY, NEW YORK August 13, 2008 00:00:08 ANNOUNCER: Today, Mount Sinai Medical Center s leading urological
Summa Health System. A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy
 Summa Health System A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy Hysterectomy A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove a woman s uterus (womb). The uterus is the organ which shelters and nourishes a baby during
Summa Health System A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy Hysterectomy A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove a woman s uterus (womb). The uterus is the organ which shelters and nourishes a baby during
2. Does the patient have one of the following appropriate indications for placing indwelling urinary catheters?
 A. Decision to Insert a Urinary Catheter: 1. Before placing an indwelling catheter, please consider if these alternatives would be more appropriate: Bladder scanner: to assess and confirm urinary retention,
A. Decision to Insert a Urinary Catheter: 1. Before placing an indwelling catheter, please consider if these alternatives would be more appropriate: Bladder scanner: to assess and confirm urinary retention,
ANTERIOR LUMBAR INTERBODY FUSION (ALIF) Basic Anatomical Landmarks: Anterior Lumbar Spine
 (ALIF) Anterior In human anatomy, referring to the front surface of the body or the position of one structure relative to another Lumbar Relating to the loins or the section of the back and sides between
(ALIF) Anterior In human anatomy, referring to the front surface of the body or the position of one structure relative to another Lumbar Relating to the loins or the section of the back and sides between
Urinary Incontinence. Anatomy and Terminology Overview. Moeen Abu-Sitta, MD, FACOG, FACS
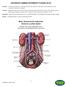
 Urinary Incontinence Anatomy and Terminology Overview Moeen Abu-Sitta, MD, FACOG, FACS Purpose Locate and describe the anatomy of the Female Urinary System Define terminology related to Incontinence Describe
Urinary Incontinence Anatomy and Terminology Overview Moeen Abu-Sitta, MD, FACOG, FACS Purpose Locate and describe the anatomy of the Female Urinary System Define terminology related to Incontinence Describe
The percentage of women 21-64 years of age who received one or more Pap tests to screen for cervical cancer.
 Measure Name: Cervical Cancer Screen Owner: NCQA (CCS) Measure Code: CER Lab Data: Y Rule Description: General Criteria Summary The percentage of women 21-64 years of age who received one or more Pap tests
Measure Name: Cervical Cancer Screen Owner: NCQA (CCS) Measure Code: CER Lab Data: Y Rule Description: General Criteria Summary The percentage of women 21-64 years of age who received one or more Pap tests
2016 Hysterectomy Reimbursement Fact Sheet
 2016 Hysterectomy Reimbursement Fact Sheet The information contained in this document is provided for informational purposes only and represents no statement, promise, or guarantee by Ethicon concerning
2016 Hysterectomy Reimbursement Fact Sheet The information contained in this document is provided for informational purposes only and represents no statement, promise, or guarantee by Ethicon concerning
MINIMALLY INVASIVE SURGERY FOR WOMEN Back to Life. Faster.
 MINIMALLY INVASIVE SURGERY FOR WOMEN Back to Life. Faster. Pictured above: UF gynecologists Sharon Byun, MD, Shireen Madani Sims, MD, and Michael Lukowski, MD, with the robotic surgery equipment. Make
MINIMALLY INVASIVE SURGERY FOR WOMEN Back to Life. Faster. Pictured above: UF gynecologists Sharon Byun, MD, Shireen Madani Sims, MD, and Michael Lukowski, MD, with the robotic surgery equipment. Make
Integumentary System Individual Exercises
 Integumentary System Individual Exercises 1. A physician performs an incision and drainage of a subcutaneous abscess in his office for a particularly uncooperative established patient. How should this
Integumentary System Individual Exercises 1. A physician performs an incision and drainage of a subcutaneous abscess in his office for a particularly uncooperative established patient. How should this
da Vinci Myomectomy Changing the Experience of Surgery Are you a candidate for the latest treatment option for uterine fibroids?
 da Vinci Myomectomy Changing the Experience of Surgery Are you a candidate for the latest treatment option for uterine fibroids? Your doctor may be able to offer you a new, minimally invasive surgical
da Vinci Myomectomy Changing the Experience of Surgery Are you a candidate for the latest treatment option for uterine fibroids? Your doctor may be able to offer you a new, minimally invasive surgical
Role of Robotic Surgery in Obese Women with Endometrial Cancer
 Role of Robotic Surgery in Obese Women with Endometrial Cancer Anil Tailor Consultant Gynaecological Oncologist Royal Surrey County Hospital Guildford, Surrey, UK St Peters Hospital Chertsey, Surrey, UK
Role of Robotic Surgery in Obese Women with Endometrial Cancer Anil Tailor Consultant Gynaecological Oncologist Royal Surrey County Hospital Guildford, Surrey, UK St Peters Hospital Chertsey, Surrey, UK
FEMALE ANATOMY. the Functions of the Female Organs
 FEMALE ANATOMY the Functions of the Female Organs An educational video for every woman who is told she needs pelvic surgery, including exploratory surgery or removal of the uterus, fallopian tubes, or
FEMALE ANATOMY the Functions of the Female Organs An educational video for every woman who is told she needs pelvic surgery, including exploratory surgery or removal of the uterus, fallopian tubes, or
Get the Facts, Be Informed, Make YOUR Best Decision. Pelvic Organ Prolapse
 Pelvic Organ Prolapse ETHICON Women s Health & Urology, a division of ETHICON, INC., a Johnson & Johnson company, is dedicated to providing innovative solutions for common women s health problems and to
Pelvic Organ Prolapse ETHICON Women s Health & Urology, a division of ETHICON, INC., a Johnson & Johnson company, is dedicated to providing innovative solutions for common women s health problems and to
Total Vaginal Hysterectomy with an Anterior and Posterior Repair
 Total Vaginal Hysterectomy with an Anterior and Posterior Repair What is a total vaginal hysterectomy with an anterior and posterior repair? Total vaginal hysterectomy is the removal of the uterus and
Total Vaginal Hysterectomy with an Anterior and Posterior Repair What is a total vaginal hysterectomy with an anterior and posterior repair? Total vaginal hysterectomy is the removal of the uterus and
Placement of an indwelling urinary catheter in female dogs
 Female Dog Urinary Catheterization 1 of 6 Placement of an indwelling urinary catheter in female dogs Bernie Hansen DVM MS North Carolina State University College of Veterinary Medicine Materials Needed
Female Dog Urinary Catheterization 1 of 6 Placement of an indwelling urinary catheter in female dogs Bernie Hansen DVM MS North Carolina State University College of Veterinary Medicine Materials Needed
Hysterectomy. What is a hysterectomy? Why is hysterectomy done? Are there alternatives to hysterectomy?
 ROBERT LEVITT, MD JESSICA BERGER-WEISS, MD ADRIENNE POTTS, MD HARTAJ POWELL, MD, MPH COURTNEY LEVENSON, MD LAUREN BURNS, MSN, RN, WHNP OBGYNCWC.COM What is a hysterectomy? Hysterectomy Hysterectomy is
ROBERT LEVITT, MD JESSICA BERGER-WEISS, MD ADRIENNE POTTS, MD HARTAJ POWELL, MD, MPH COURTNEY LEVENSON, MD LAUREN BURNS, MSN, RN, WHNP OBGYNCWC.COM What is a hysterectomy? Hysterectomy Hysterectomy is
Urinary Diversion: Ileovesicostomy/Ileal Loop/Colon Loop
 Urinary Diversion: Ileovesicostomy/Ileal Loop/Colon Loop Why do I need this surgery? A urinary diversion is a surgical procedure that is performed to allow urine to safely pass from the kidneys into a
Urinary Diversion: Ileovesicostomy/Ileal Loop/Colon Loop Why do I need this surgery? A urinary diversion is a surgical procedure that is performed to allow urine to safely pass from the kidneys into a
Less Invasive is Best
 Less Invasive is Best June 22, 2011 By OBGYN.net Staff [1] Laparoscopic hysterectomy (LH) is an optimum approach to the second most common surgical procedure in the United States. There are close to 600,000
Less Invasive is Best June 22, 2011 By OBGYN.net Staff [1] Laparoscopic hysterectomy (LH) is an optimum approach to the second most common surgical procedure in the United States. There are close to 600,000
Surgeon perception is not a good predictor of peri-operative outcomes in robot-assisted radical prostatectomy
 DOI 10.1007/s11701-011-0293-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Surgeon perception is not a good predictor of peri-operative outcomes in robot-assisted radical prostatectomy Joshua Stern Saurabh Sharma Pierre Mendoza Mary
DOI 10.1007/s11701-011-0293-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Surgeon perception is not a good predictor of peri-operative outcomes in robot-assisted radical prostatectomy Joshua Stern Saurabh Sharma Pierre Mendoza Mary
PHaSES: Practical Hands-on Surgical Education System
 U.S. Toll Free 866-GOLIMBS PHaSES Range PHaSES: Practical Hands-on Surgical Education System Limbs & Things is pleased to introduce the PHaSES Range. The range is based upon our well known basic & general
U.S. Toll Free 866-GOLIMBS PHaSES Range PHaSES: Practical Hands-on Surgical Education System Limbs & Things is pleased to introduce the PHaSES Range. The range is based upon our well known basic & general
Considering Endometriosis Surgery? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery
 Considering Endometriosis Surgery? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Endometriosis Endometriosis is a condition in which the tissue that lines your uterus (the endometrium)
Considering Endometriosis Surgery? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Endometriosis Endometriosis is a condition in which the tissue that lines your uterus (the endometrium)
EndoWrist /Single-Site Instrument & Accessory Catalog
 EndoWrist /Single-Site Instrument & Accessory Catalog May 2014 Not all products are available in all countries. Please see your local Intuitive Surgical representative for product availability in your
EndoWrist /Single-Site Instrument & Accessory Catalog May 2014 Not all products are available in all countries. Please see your local Intuitive Surgical representative for product availability in your
Minimally Invasive Hip Replacement through the Direct Lateral Approach
 Surgical Technique INNOVATIONS IN MINIMALLY INVASIVE JOINT SURGERY Minimally Invasive Hip Replacement through the Direct Lateral Approach *smith&nephew Introduction Prosthetic replacement of the hip joint
Surgical Technique INNOVATIONS IN MINIMALLY INVASIVE JOINT SURGERY Minimally Invasive Hip Replacement through the Direct Lateral Approach *smith&nephew Introduction Prosthetic replacement of the hip joint
Facing a Hernia Repair? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery
 Facing a Hernia Repair? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Hernia A hernia happens when part of an internal organ or tissue bulges through a hole or weak area in the belly wall
Facing a Hernia Repair? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Hernia A hernia happens when part of an internal organ or tissue bulges through a hole or weak area in the belly wall
Target Volumes for Anal Carcinoma For RTOG 0529
 Target Volumes for Anal Carcinoma For RTOG 0529 Robert Myerson, M.D. Ph.D.*, Lisa Kachnic, M.D.**, Jacqueline Esthappan, Ph.D.*,Parag Parikh M.D.*William Straube M.S.*, John Willins, Ph.D.** *Washington
Target Volumes for Anal Carcinoma For RTOG 0529 Robert Myerson, M.D. Ph.D.*, Lisa Kachnic, M.D.**, Jacqueline Esthappan, Ph.D.*,Parag Parikh M.D.*William Straube M.S.*, John Willins, Ph.D.** *Washington
VATTIKUTI INSTITUTE PROSTATECTOMY (VIP) AND CURRENT RESULTS.
 UROLOGY ROBOTIC SURGERY Arch. Esp. Urol., 60, 4 (397-407), 2007 VATTIKUTI INSTITUTE PROSTATECTOMY (VIP) AND CURRENT RESULTS. Mahendra Bhandari and Mani Menon. Vattikuti Urology Institute. Henry Ford Health
UROLOGY ROBOTIC SURGERY Arch. Esp. Urol., 60, 4 (397-407), 2007 VATTIKUTI INSTITUTE PROSTATECTOMY (VIP) AND CURRENT RESULTS. Mahendra Bhandari and Mani Menon. Vattikuti Urology Institute. Henry Ford Health
Foley Catheter Placement
 Foley Catheter Placement Indications for a Foley Catheter Retention of urine leading to urinary hesitancy, straining to urinate, decrease in size and force of the urinary stream, interruption of urinary
Foley Catheter Placement Indications for a Foley Catheter Retention of urine leading to urinary hesitancy, straining to urinate, decrease in size and force of the urinary stream, interruption of urinary
Therapies for Prostate Cancer and Treatment Selection
 Prostatic Diseases Therapies for Prostate Cancer and Treatment Selection JMAJ 47(12): 555 560, 2004 Yoichi ARAI Professor and Chairman, Department of Urology, Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine
Prostatic Diseases Therapies for Prostate Cancer and Treatment Selection JMAJ 47(12): 555 560, 2004 Yoichi ARAI Professor and Chairman, Department of Urology, Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine
Oncological and functional outcomes of laparoscopic radical prostatectomy following fellowship training.
 Oncological and functional outcomes of laparoscopic radical prostatectomy following fellowship training. Journal: BJU International Manuscript ID: Draft Manuscript Type: Original Article Date Submitted
Oncological and functional outcomes of laparoscopic radical prostatectomy following fellowship training. Journal: BJU International Manuscript ID: Draft Manuscript Type: Original Article Date Submitted
Women s Health Laparoscopy Information for patients
 Women s Health Laparoscopy Information for patients This leaflet is for women who have been advised to have a laparoscopy. It outlines the common reasons doctors recommend this operation, what will happen
Women s Health Laparoscopy Information for patients This leaflet is for women who have been advised to have a laparoscopy. It outlines the common reasons doctors recommend this operation, what will happen
Consumer summary Minimally invasive techniques for the relief of stress urinary incontinence
 ASERNIP S Australian Safety and Efficacy Register of New Interventional Procedures Surgical Consumer summary Minimally invasive techniques for the relief of stress urinary incontinence (Adapted from the
ASERNIP S Australian Safety and Efficacy Register of New Interventional Procedures Surgical Consumer summary Minimally invasive techniques for the relief of stress urinary incontinence (Adapted from the
Surgical scissors and forceps Product List
 Surgical scissors and forceps Product List Sr. No Items Picture of Product Product specification 1 Grasping forceps-- 5 MM Grasping forceps are used to remove stones and retrieve foreign objects under
Surgical scissors and forceps Product List Sr. No Items Picture of Product Product specification 1 Grasping forceps-- 5 MM Grasping forceps are used to remove stones and retrieve foreign objects under
SECTION 1 General Principles
 SECTION 1 General Principles Pierre-Alain Clavien Michael G. Sarr Introduction Pierre A. Clavien, Michael G. Sarr A competent surgeon must be aware of all the general aspects of a surgical procedure to
SECTION 1 General Principles Pierre-Alain Clavien Michael G. Sarr Introduction Pierre A. Clavien, Michael G. Sarr A competent surgeon must be aware of all the general aspects of a surgical procedure to
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Contents. Overview. Removing the womb (hysterectomy) Overview
 This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding womb (endometrial) cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 9. Overview Contents Overview Removing
This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding womb (endometrial) cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 9. Overview Contents Overview Removing
Lesions, and Masses, and Tumors Oh My!!
 Lesions, and Masses, and Tumors Oh My!! Presented by: Susan Ward, CPC, CPC-H, CPC-I, CPCD, CEMC, CPRC 1 1 CPT GUIDELINES Agenda CPT DEFINITIONS OP REPORT CASES 2 Definitions Cyst - a closed sac having
Lesions, and Masses, and Tumors Oh My!! Presented by: Susan Ward, CPC, CPC-H, CPC-I, CPCD, CEMC, CPRC 1 1 CPT GUIDELINES Agenda CPT DEFINITIONS OP REPORT CASES 2 Definitions Cyst - a closed sac having
About the Uterus. Hysterectomy may be done to treat conditions that affect the uterus. Some reasons a hysterectomy may be needed include:
 Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
SILS. Port Insertion By Homero Rivas, MD, MBA, FACS. Single incision. Single port. Simple choice.
 SILS Port Insertion By Homero Rivas, MD, MBA, FACS Single incision. Single port. Simple choice. SILS Port Insertion By Homero Rivas, MD, MBA, FACS For the last 20 years, there has given surgical procedure.
SILS Port Insertion By Homero Rivas, MD, MBA, FACS Single incision. Single port. Simple choice. SILS Port Insertion By Homero Rivas, MD, MBA, FACS For the last 20 years, there has given surgical procedure.
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery
 Chapter 1 Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery 1 H.M. Mayer Primum non nocere First do no harm In the long history of surgery it always has been a basic principle to restrict the iatrogenic trauma done to
Chapter 1 Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery 1 H.M. Mayer Primum non nocere First do no harm In the long history of surgery it always has been a basic principle to restrict the iatrogenic trauma done to
Pelvic Anatomy. Robert E. Gutman, MD
 Pelvic Anatomy Robert E. Gutman, MD Objectives Understand pelvic anatomy Organs and structures of the female pelvis Vascular Supply Neurologic supply Pelvic and retroperitoneal contents and spaces Bony
Pelvic Anatomy Robert E. Gutman, MD Objectives Understand pelvic anatomy Organs and structures of the female pelvis Vascular Supply Neurologic supply Pelvic and retroperitoneal contents and spaces Bony
URINARY CATHETER INSERTION - STRAIGHT OR INDWELLING CATHETER
 URINARY CATHETER INSERTION - STRAIGHT OR INDWELLING CATHETER PURPOSE To obtain a sterile urine specimen. To facilitate emptying bladder. To relieve bladder distention. To irrigate bladder. To measure residual
URINARY CATHETER INSERTION - STRAIGHT OR INDWELLING CATHETER PURPOSE To obtain a sterile urine specimen. To facilitate emptying bladder. To relieve bladder distention. To irrigate bladder. To measure residual
Acute abdominal conditions Key Points
 7 Acute abdominal conditions Key Points 7.1 ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS Referred abdominal pain Fore gut pain (stomach, duodenum, gall bladder) is referred to the upper abdomen Mid gut pain (small intestine,
7 Acute abdominal conditions Key Points 7.1 ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS Referred abdominal pain Fore gut pain (stomach, duodenum, gall bladder) is referred to the upper abdomen Mid gut pain (small intestine,
PRESENTATION OF NOVEL GYNECOLOGIC ONCOLOGY PROCEDURES M.D. ANDERSON CANCER CENTER, UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS November 15, 2006
 PRESENTATION OF NOVEL GYNECOLOGIC ONCOLOGY PROCEDURES M.D. ANDERSON CANCER CENTER, UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS November 15, 2006 00:00:11 ANNOUNCER: This program is made possible through an educational grant from
PRESENTATION OF NOVEL GYNECOLOGIC ONCOLOGY PROCEDURES M.D. ANDERSON CANCER CENTER, UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS November 15, 2006 00:00:11 ANNOUNCER: This program is made possible through an educational grant from
Bankart Repair using the Smith & Nephew BIORAPTOR 2.9 Suture Anchor
 Shoulder Series Technique Guide *smith&nephew BIORAPTOR 2.9 Suture Anchor Bankart Repair using the Smith & Nephew BIORAPTOR 2.9 Suture Anchor Gary M. Gartsman, M.D. Introduction Arthroscopic studies of
Shoulder Series Technique Guide *smith&nephew BIORAPTOR 2.9 Suture Anchor Bankart Repair using the Smith & Nephew BIORAPTOR 2.9 Suture Anchor Gary M. Gartsman, M.D. Introduction Arthroscopic studies of
Total Abdominal Hysterectomy
 What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
The lungs What is lung cancer? How common is it? Risks & symptoms Diagnosis & treatment options
 Why We re Here The lungs What is lung cancer? How common is it? Risks & symptoms Diagnosis & treatment options What Are Lungs? What Do They Do? 1 Located in the chest Allow you to breathe Provide oxygen
Why We re Here The lungs What is lung cancer? How common is it? Risks & symptoms Diagnosis & treatment options What Are Lungs? What Do They Do? 1 Located in the chest Allow you to breathe Provide oxygen
Laparoscopic Sleeve gastrectomy
 Restrictive procedure Laparoscopic Sleeve gastrectomy Dr. R. Peterli Professional Education 1 2 Introduction Gastric sleeve resection is the restrictive part of the biliopancreatic diversion duodenal switch,
Restrictive procedure Laparoscopic Sleeve gastrectomy Dr. R. Peterli Professional Education 1 2 Introduction Gastric sleeve resection is the restrictive part of the biliopancreatic diversion duodenal switch,
BLUNT TORSO INJURY FROM IMPACT OR DECELERATION HAS ABDOMINAL SOLID ORGAN TRAUMA UNTIL PROVEN OTHERWISE
 Abdominal and Pelvic Trauma In the primary survey, the circulation part includes thinking about the abdomen as a source of occult hemorrhage The OBVIOUS THING is a penetrating abdominal injury Generally
Abdominal and Pelvic Trauma In the primary survey, the circulation part includes thinking about the abdomen as a source of occult hemorrhage The OBVIOUS THING is a penetrating abdominal injury Generally
X-Plain Inguinal Hernia Repair Reference Summary
 X-Plain Inguinal Hernia Repair Reference Summary Introduction Hernias are common conditions that affect men and women of all ages. Your doctor may recommend a hernia operation. The decision whether or
X-Plain Inguinal Hernia Repair Reference Summary Introduction Hernias are common conditions that affect men and women of all ages. Your doctor may recommend a hernia operation. The decision whether or
Total Vaginal Hysterectomy
 What is a total vaginal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through the vagina. Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient. Why is this surgery used? To treat disease of
What is a total vaginal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through the vagina. Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient. Why is this surgery used? To treat disease of
Thomas A. Kollmorgen, M.D. Oregon Urology Institute
 Thomas A. Kollmorgen, M.D. Oregon Urology Institute None 240,000 new diagnosis per year, and an estimated 28,100 deaths (2012) 2 nd leading cause of death from cancer in U.S.A. Approximately 1 in 6 men
Thomas A. Kollmorgen, M.D. Oregon Urology Institute None 240,000 new diagnosis per year, and an estimated 28,100 deaths (2012) 2 nd leading cause of death from cancer in U.S.A. Approximately 1 in 6 men
Instructions for Use
 Pleural Effusion Shunt with External Pump Chamber Catalog No. 42-9005 Instructions for Use Denver Biomedical, Inc. Table of Contents Description 2 Indications 2 Contraindications 2 Warnings 4 Cautions
Pleural Effusion Shunt with External Pump Chamber Catalog No. 42-9005 Instructions for Use Denver Biomedical, Inc. Table of Contents Description 2 Indications 2 Contraindications 2 Warnings 4 Cautions
X-Plain Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Vascular Surgery Reference Summary
 X-Plain Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Vascular Surgery Reference Summary Ballooning of the aorta, also known as an "abdominal aortic aneurysm," can lead to life threatening bleeding. Doctors may recommend
X-Plain Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Vascular Surgery Reference Summary Ballooning of the aorta, also known as an "abdominal aortic aneurysm," can lead to life threatening bleeding. Doctors may recommend
HAND INSTRUMENTS. HiQ+ Monopolar Hand Instruments Needle Holders Suction and Irrigation Monopolar HF Electrodes. THE HiQ+ SERIES
 HAND INSTRUMENTS HiQ+ Monopolar Hand Instruments Needle Holders Suction and Irrigation Monopolar HF Electrodes THE HiQ+ SERIES CONTENTS FORM FOLLOWS FUNCTION FOLLOWS YOUR NEEDS HiQ+ Monopolar and Standard...4
HAND INSTRUMENTS HiQ+ Monopolar Hand Instruments Needle Holders Suction and Irrigation Monopolar HF Electrodes THE HiQ+ SERIES CONTENTS FORM FOLLOWS FUNCTION FOLLOWS YOUR NEEDS HiQ+ Monopolar and Standard...4
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Endometriosis
 Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
67273 EN V40/14 NOUVAG AG, all rights reserved Subject to change. Laparoscopic Hysterectomy Morcellator
 67273 EN V40/14 NOUVAG AG, all rights reserved Subject to change Laparoscopic Hysterectomy Morcellator Laparoscopic Hysterectomy Nowadays newly developed medical devices make hysterectomy possible by a
67273 EN V40/14 NOUVAG AG, all rights reserved Subject to change Laparoscopic Hysterectomy Morcellator Laparoscopic Hysterectomy Nowadays newly developed medical devices make hysterectomy possible by a
The Abdominal Wall And Hernias. Stanley Kurek, DO, FACS Associate Professor of Surgery UTMCK
 The Abdominal Wall And Hernias Stanley Kurek, DO, FACS Associate Professor of Surgery UTMCK The Abdominal Wall The structure of the abdominal wall is similar in principle to the thoracic wall. There are
The Abdominal Wall And Hernias Stanley Kurek, DO, FACS Associate Professor of Surgery UTMCK The Abdominal Wall The structure of the abdominal wall is similar in principle to the thoracic wall. There are
Achilles Tendon Repair, Operative Technique
 *smith&nephew ANKLE TECHNIQUE GUIDE Achilles Tendon Repair, Operative Technique Prepared in Consultation with: C. Niek van Dijk, MD, PhD KNEE HIP SHOULDER EXTREMITIES Achilles Tendon Repair, Operative
*smith&nephew ANKLE TECHNIQUE GUIDE Achilles Tendon Repair, Operative Technique Prepared in Consultation with: C. Niek van Dijk, MD, PhD KNEE HIP SHOULDER EXTREMITIES Achilles Tendon Repair, Operative
Considering Surgery for Fibroids? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery
 Considering Surgery for Fibroids? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Uterine Fibroid (Fibroid Tumor) A uterine fibroid is a benign (non-cancerous) tumor that grows in the uterine
Considering Surgery for Fibroids? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Uterine Fibroid (Fibroid Tumor) A uterine fibroid is a benign (non-cancerous) tumor that grows in the uterine
Innovation for optimized outcomes
 Innovation for optimized outcomes VASOVIEW Endoscopic Vessel Harvesting Systems MAQUET MAQUET Medical Systems Medical USA Systems VASOVIEW USA PRODUCT EVH SYSTEMS NAME 31 Minimally invasive endoscopic
Innovation for optimized outcomes VASOVIEW Endoscopic Vessel Harvesting Systems MAQUET MAQUET Medical Systems Medical USA Systems VASOVIEW USA PRODUCT EVH SYSTEMS NAME 31 Minimally invasive endoscopic
Dept. of Medical Imaging University of Ottawa
 ED Visits Related to Bariatric Surgery: Review of Normal Post-Surgical Anatomy as Well as Complications Dept. of Medical Imaging University of Ottawa Disclosures Background Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Surgery
ED Visits Related to Bariatric Surgery: Review of Normal Post-Surgical Anatomy as Well as Complications Dept. of Medical Imaging University of Ottawa Disclosures Background Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Surgery
Hysteroscopy. What is a hysteroscopy? When is this surgery used? How do I prepare for surgery?
 What is a hysteroscopy? This is a procedure where a doctor uses a thin tube with a tiny camera to look inside the uterus. There are no incisions. Saline solution is used to expand the uterus in order to
What is a hysteroscopy? This is a procedure where a doctor uses a thin tube with a tiny camera to look inside the uterus. There are no incisions. Saline solution is used to expand the uterus in order to
Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place.
 What is an abdominal myomectomy? Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place. When is this surgery used? Treatment
What is an abdominal myomectomy? Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place. When is this surgery used? Treatment
KnifeLight. Carpal Tunnel Ligament Release. Operative Technique
 KnifeLight Carpal Tunnel Ligament Release Operative Technique Contents Page 1. Features & Benefits 3 Intended Use and Indications 3 Contraindications 3 Features & Benefits 3 2. Operative Technique 4 Antegrade
KnifeLight Carpal Tunnel Ligament Release Operative Technique Contents Page 1. Features & Benefits 3 Intended Use and Indications 3 Contraindications 3 Features & Benefits 3 2. Operative Technique 4 Antegrade
Abdomen X-Ray (AXR) Collimation is ideally from diaphragms to lower border of the symphysis pubis and the lateral skin margins.
 Abdomen X-Ray (AXR) Collimation is ideally from diaphragms to lower border of the symphysis pubis and the lateral skin margins. LMP of child-bearing age female patients should be checked. 1. Acute abdomen
Abdomen X-Ray (AXR) Collimation is ideally from diaphragms to lower border of the symphysis pubis and the lateral skin margins. LMP of child-bearing age female patients should be checked. 1. Acute abdomen
Facing Pancreatic Surgery? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery
 Facing Pancreatic Surgery? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Pancreatitis/Pancreatic Cancer The pancreas is an organ that produces enzymes and hormones to help your body digest
Facing Pancreatic Surgery? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Pancreatitis/Pancreatic Cancer The pancreas is an organ that produces enzymes and hormones to help your body digest
Understanding Laparoscopic Colorectal Surgery
 Understanding Laparoscopic Colorectal Surgery University Colon & Rectal Surgery A Problem with Your Colon Your doctor has told you that you have a colon problem. Now you ve learned that surgery is needed
Understanding Laparoscopic Colorectal Surgery University Colon & Rectal Surgery A Problem with Your Colon Your doctor has told you that you have a colon problem. Now you ve learned that surgery is needed
AMS Sphincter 800 Urinary Prosthesis
 AMS Sphincter 800 Urinary Prosthesis AMS Sphincter 800 AMS Sphincter 800 AMS Sphincter 800 The device is implanted in the body and cannot be seen. The cuff can be placed at the bulbous urethra or at the
AMS Sphincter 800 Urinary Prosthesis AMS Sphincter 800 AMS Sphincter 800 AMS Sphincter 800 The device is implanted in the body and cannot be seen. The cuff can be placed at the bulbous urethra or at the
Clinical Practice Assessment Robotic surgery
 Clinical Practice Assessment Robotic surgery Background: Surgery is by nature invasive. Efforts have been made over time to reduce complications and the trauma inherently associated with surgery through
Clinical Practice Assessment Robotic surgery Background: Surgery is by nature invasive. Efforts have been made over time to reduce complications and the trauma inherently associated with surgery through
Why Robotic Surgery Is Changing the Impacts of Medical Field
 Volume Article.13-08 Publish Date: 25th March 2013 Author(s): MPUH - CRS Team Why Robotic Surgery Is Changing the Impacts of Medical Field ARTICLE hhh Muljibhai Patel Urological Hospital (MPUH) Centre
Volume Article.13-08 Publish Date: 25th March 2013 Author(s): MPUH - CRS Team Why Robotic Surgery Is Changing the Impacts of Medical Field ARTICLE hhh Muljibhai Patel Urological Hospital (MPUH) Centre
13 Adductor Muscle Group Excision
 Malawer Chapter 13 21/02/2001 15:36 Page 243 13 Adductor Muscle Group Excision Martin Malawer and Paul Sugarbaker OVERVIEW The adductor muscle group is the second most common site for high- and low-grade
Malawer Chapter 13 21/02/2001 15:36 Page 243 13 Adductor Muscle Group Excision Martin Malawer and Paul Sugarbaker OVERVIEW The adductor muscle group is the second most common site for high- and low-grade
Common Surgical Procedures Gyn/Oncology
 Malignancy Description Codes wrvu Comments Cervical Typical Open Cone biopsy 57520 4.11 Leep conization 57522 3.67 Colposcopy/Leep 57461 3.43 TAH +/- BSO 58150 17.31 Radical hysterectomy +/- BSO (Total,
Malignancy Description Codes wrvu Comments Cervical Typical Open Cone biopsy 57520 4.11 Leep conization 57522 3.67 Colposcopy/Leep 57461 3.43 TAH +/- BSO 58150 17.31 Radical hysterectomy +/- BSO (Total,
Legally Speaking: Malpractice suit revolves around damaged ureter
 Legally Speaking: Malpractice suit revolves around damaged ureter By Andrew I. Kaplan, Esq. Aug 1, 2008 In an effort to defend medical care, there is a risk of adhering too closely to an initial, and often
Legally Speaking: Malpractice suit revolves around damaged ureter By Andrew I. Kaplan, Esq. Aug 1, 2008 In an effort to defend medical care, there is a risk of adhering too closely to an initial, and often
Spinal Arthrodesis Group Exercises
 Spinal Arthrodesis Group Exercises 1. Two surgeons work together to perform an arthrodesis. Dr. Bonet, a general surgeon, makes the anterior incision to gain access to the spine for the arthrodesis procedure.
Spinal Arthrodesis Group Exercises 1. Two surgeons work together to perform an arthrodesis. Dr. Bonet, a general surgeon, makes the anterior incision to gain access to the spine for the arthrodesis procedure.
INTERDISCIPLINARY CLINICAL MANUAL Practice Guideline
 INTERDISCIPLINARY CLINICAL MANUAL Practice Guideline TITLE: Insertion of a curved tip Urinary Catheter (Coude/Tiemann) NUMBER: CC 50-013 Effective Date: August 2015 Page 1 of 5 Applies To: All Preamble:
INTERDISCIPLINARY CLINICAL MANUAL Practice Guideline TITLE: Insertion of a curved tip Urinary Catheter (Coude/Tiemann) NUMBER: CC 50-013 Effective Date: August 2015 Page 1 of 5 Applies To: All Preamble:
Facing Hysterectomy? Learn why da Vinci Surgery may be your best treatment option for a benign gynecologic condition
 Facing Hysterectomy? Learn why da Vinci Surgery may be your best treatment option for a benign gynecologic condition The Condition(s): Chronic Pain, Heavy Bleeding, Fibroids, Endometriosis and/or Prolapse
Facing Hysterectomy? Learn why da Vinci Surgery may be your best treatment option for a benign gynecologic condition The Condition(s): Chronic Pain, Heavy Bleeding, Fibroids, Endometriosis and/or Prolapse
Laparoscopic Colectomy. What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery?
 Laparoscopic Colectomy What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery? Traditionally, colon & rectal surgery requires a large, abdominal and/or pelvic incision, which often requires a
Laparoscopic Colectomy What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery? Traditionally, colon & rectal surgery requires a large, abdominal and/or pelvic incision, which often requires a
