AN EVIDENCED BASED ASSESSMENT OF OPEN VS. ROBOTIC RADICAL PROSTATECTOMY
|
|
|
- Wilfrid Holland
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AN EVIDENCED BASED ASSESSMENT OF OPEN VS. ROBOTIC RADICAL PROSTATECTOMY Herbert Lepor, M.D. Professor and Martin Spatz Chairman Department of Urology NYU School of Medicine 1
2 INTRODUCTION The three approaches for the management of localized prostate cancer includes: radical prostatectomy, radiation therapy and active surveillance. There is general agreement that radical prostatectomy is the most definitive approach for curing localized prostate cancer. The curative advantage of radical prostatectomy is likely to translate into a survival advantage for younger men and for those individuals with more aggressive cancers. When radical prostatectomy is performed by experienced surgeons, the complications rates are comparable to those of radiation therapy. Radical prostatectomy is most commonly performed through an open incision or laparoscopically with robotic assistance. It is imperative that you select treatment for your localized prostate cancer based on credible medical evidence and not information that you gather from unfiltered websites which are often developed by the manufacturer of the robot. I am confident when you base your decision on factual information, you will conclude that the robotic approach offers no significant advantages over an open approach. The best way to ensure that you achieve the best surgical result possible is to seek out an experienced surgeon, make certain the expert surgeon is doing your surgery, demand that the surgeon provides you with credible statistics regarding their outcomes, and finally, make sure the surgeon is committed not only to the removal of your prostate, but also outlines a postoperative pathway for maximizing recovery of continence and potency. I am often invited to lecture on issues related to localized prostate cancer at medical meetings and academic institutions throughout the world. I am frequently invited to debate the pros and cons of open vs. robotic approaches to radical prostatectomy. I have included my powerpoint presentation titled Radical Prostatectomy for Localized Prostate Cancer: Technique, Outcomes, Future and a recent article I wrote for Reviews in Urology titled Open vs. Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy. Also, included in this information package is a recent editorial comment by the Editor-in-Chief of the Canadian Urological Association Journal. QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ABOUT OPEN VS. ROBOTIC RADICAL PROSTATECTOMY: AN EVIDENCED BASED ASSESSMENT DOES ROBOTIC PROSTATECTOMY COMPROMISE CANCER CONTROL? The most important outcome following radical prostatectomy is to cure the disease. The biggest disadvantage of robotic prostatectomy is the inability to feel the prostate and surrounding tissues during the dissection of the malignant gland. There is great concern amongst open surgeons that this lack of proprioception may compromise local cancer control. The positive surgical margin rates were recently summarized from major centers performing robotic radical prostatectomy. Positive surgical margins were stratified according to whether the cancer was pathologically localized to the gland (pt 2 ) or whether there was pathological evidence of extracapsular extension (pt 3 ). 2
3 SUMMARY OF POSITIVE SURGICAL MARGINS FOLLOWING ROBOTIC RADICAL PROSTATECTOMY Author Year # Case s Pathologic stage Overall PSM rate (%) PSM rate (%) pt2 pt3a pt3b pt2 pt3a pt3b Menon a [52] % 5% 9% 15% 10.5% 40% 40% Wolfram [54] % 31.5% 22% 12.7% 42% Bentas [46] % 22% 15% 30% 8% 67% Ahlering b [43] % 36% 36% 27% 50% Ahlering b [43] % 27% 16.7% 4.7% 44% Chatelineau [50] % 29% 22% 11.7% 43% Patel [48] % 14% 8% 10.5% 5.7% 26.2% 33% Joseph [45] % 14% 5% 13% 9.9% 37.1% 27.3% I have recently reported my positive surgical margins rates following open radical prostatectomy in an article published in the Journal of Urology titled The New York University Nerve Sparing Algorithm Decreases the Rate of Positive Surgical Margins Following Radical Retropubic Prostatectomy J. Urol, 169: , Table 2 and Figure 2 from this article summarizes my positive surgical margins rates for pt 2 and pt 3 disease p Value No. pts. Preop. PSA: Mean (ng./mi.) No ng./ml. (%) 243 (89) 233 (89) 0.78 No. greater than ng/ml. (%) 29 (11) 30 (11) No. clinical stage (%): 0.07 Tla 3 (11 0 Tlc ) 219 (83) T2a 25 (9) 30 (11) T2b 24 (9) 10 (4) T2c 4 ( 1) 3 (1) T3a ) No. preop. Gleason score (%): l1 1(0.4) (72) 186 (71) 7 66)24) 65 (25) (2) 11 (4) No. pathological stage (%): 0.76 Organ confined 218(80) 208 (79) 3
4 Extraprostatic extension 54 (20) 55 (21) No. tumor percentage of surgical specimen (%): Less than 10% 108 (45) 133 (51) % 96 (40) 97 (37) % 26 (11) 30 (11) 50% or Greater 8 (3) 3 (1) No. surgical margins (%): Neg. 234(86) 242 (92) Pos. 38 (14) 21 (8) Neurovascular bundle spared: No. bi/at. (%) 208 (76) 226 (86) No. unilat. (%) 49 (18) 31 (12) No. none (%) 15 (16) 6 (2) % Spared My overall positive surgical margin rate using the NYU algorithm to guide decisions regarding nerve sparing in 2001 was only 8%. Of 460 sides of the prostate with no extracapsular extension (pt 2 disease), the positive surgical margin rate was 2.2%. Of the 66 sides with extracapsular extension (pt 3 disease), my positive surgical margin rates was 24%. Overall, my positive surgical margin rate following open radical prostatectomy is considerably lower than the robotic series reported in the literature. The composite published literature suggests a higher positive surgical margin rate following robotic radical prostatectomy. We will not know definitely whether this apparent higher positive margin rates associated with robotic radical prostatectomy compromises cancer control until longer follow up is available. 4
5 DOES ROBOTIC PROSTATECTOMY ENHANCE POTENCY RATES? Prior to 1992, no one knew the anatomic location of the nerves controlling erections. Working under the direction of Patrick C. Walsh, I discovered the precise pathway of these microscopic nerves. These nerves are so small that it is ludicrous to state that magnification provided by the robot enhances the ability to see and preserve these nerves. One of the disadvantages of the robotic approach is that the dissection of the nerves off the prostate is performed with electrocautery. The heat associated with the cautery may destroy these fragile nerves. Dr. John Mulhull, one of the worlds leading experts in erectile dysfunction, presented a paper at the national meeting of the American Urological Association in May 2007 titled Sexual Health Misinformation on Robotic Prostatectomy Websites The following is the abstract from this presentation. Sexual Function/Dysfunction/Andrology: Evaluation (Ii) Podium Monday, May 21, :00 Pm - 3:00 Pm, 1034 Sexual Health Misinformation On Robotic Prostatectomy Websites Cesar Rojas-Cruz* and John P Mulhall. New York, NY. Introduction and Objective: Robot assisted radical prostatectomy (RARP) has become a wellestablished approach to the management of localized prostate cancer. Much of the marketing surrounding RARP is associated with advantages of this technique as it pertains to erectile function (EF) recovery. To date, there does not exist a comparative analysis of outcomes with RARP versus open radical prostatectomy (ORP). This analysis was conducted to define what the consumers are reading on the premier source of RARP information, the websites of the robotic prostatectomists. Methods: From October 19-26, 2006 we surveyed the website links posted on the Intuitive Surgical web page ( to hospitals and doctors that offer robot assisted radical prostatectomy (RARP). We reviewed the information related to EF outcomes posted on the center's web pages for accuracy and data support, specifically did the center mention that RARP was advantageous over ORP and was any scientific data presented to support these claims. Results: 116 hospital web pages were reviewed. 75 of them had information regarding the DaVinci surgical system, surgery technique and outcomes. 40 (54%) were university hospitals, the remainder community based urologic practices. 42% contained text that that was explicitly copied from the DaVinci prostatectomy website. 40% (30) had a link to the Intuitive Surgical site. 61% had information related to erectile function (EF) being associated with RARP, however 39% had no sexual health information 5
6 whatsoever. 78% of those that mentioned EF, stated that RARP is associated with a better EF outcome compared with ORP. 52% of the sites stated that RARP is better at preserving EF than OS, 26% stated that EF recovery with the RARP may be better than OS. 15% pages stated that the erectile dysfunction risk associated with RARP may be similar to OS. Only 7 sites (15%) had any specific EF data and only 2 had data pertaining to their own center, the others citing published series. No differences were noted in EF information between university and community centers. Conclusions: More than one third of the robotic prostatectomy websites had zero information regarding erectile function recovery. The majority stated that RARP had better EF outcomes compared to open prostatectomy, despite the absence of scientific data in support of these claims. This misinformation is giving patients who are considering radical prostatectomy unrealistic expectations. Source of Funding: None The take home message from this abstract is don t obtain your information from Intuitive Surgical since their goal is to sell robots and not to provide credible information. So, what is the credible medical evidence comparing open vs. robotic approaches. A multicenter study from several major centers in the United States compared potency data for those men undergoing open, laparoscopic, and robotic assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy using the identical outcomes instruments. The data analysis from this large study was presented at the national meeting of the American Urological Association in May Interestingly, this study demonstrated that the open approach was associated with the highest recovery of sexual quality of life scores. Prostate Cancer: Localized (II) Moderated Poster Sunday, May 20, :30 PM - 5:30 PM 552 Patient-Reported Outcomes After Retropubic, Laparoscopic, Or Robot- Assisted Prostatectomy: Results From A Prospective, Multi-Center Study. Andrew A Wagner*, John T Wei, Rodney L Dunn, Brent K Hollenbeck, Gerald L Andriole, Jr, David P Wood, Douglas M Dahl, Jim C Hu, Larry Hembroff, Mark S. Litwin, Christopher S Saigal, Eric A Klein, Adam S Kibel, Louis L Pisters, James E. Montie, Martin G Sanda. Boston, MA, Ann Arbor, MI, St Louis, MO, East Lansing, MI, Los Angeles, CA, Cleveland, OH, Houston, TX. Introduction and Objective: The comparative performance of retropubic (RP), laparoscopic (LAP), and robot-assisted prostatectomy (RAP) in quality of life (QOL) outcome has not yet been established in prospective, multi-center studies. 6
7 Methods: 602 prostate cancer patients were enrolled pre-prostatectomy (375 RP, 110 LAP, 117 RAP) at 8 academic centers. QOL was measured by the EPIC at baseline and 2,6,12, and 24 months after treatment. Although RP was associated with better sexual recovery than LAP and marginally better than RAP, there was also a significant difference in overall surgeon expertise with each procedure at start of study, hence learning curves may have influenced the findings. Continued evaluation of LAP and RAP outcomes is indicated. Source of Funding: NIH RO1-CA95662 Another paper presented at the national meeting of the American Urological Association in May 2007 compared outcomes from a single institution for open, laparoscopic and robotic prostatectomy at 18 months following surgery. Once again, this large study demonstrated that potency was better following open compared to robotic radical prostatectomy. General & Epidemiological Trends & Socioeconomics: Outcomes Analysis Moderated Poster Saturday, May 19, :00 PM - 3:00 PM 19 Prospective Longitudinal Comparison Of Health Related Quality Of Life In Patients Undergoing Treatment For Localized Prostate Cancer: An Evaluation Of Three Surgical Treatment Modalities From A Single Institution. C William Schwab, II*, Michael D Fabrizio, Robert W Given, Donald F Lynch, Raymond Lance, Bethany Barrone, Paul F Schellhammer. Norfolk, VA. Introduction and Objective: With multiple treatment options currently available for the treatment of clinically localized prostate cancer, quality of life (QOL) issues play an important role in the selection process of patients and the evaluation of 7
8 outcomes. We maintain a prospective, longitudinal study using validated instruments to evaluate QOL changes in patients treated with one of three surgical treatment options at a single institution: open radical prostatectomy (ORP), laparoscopic radical prostatectomy (LRP), or da Vinci Robotic prostatectomy (dvp). We now report outcomes with a minimum 18 months follow up Methods: An IRB approved questionnaire comprised of validated QOL instruments (UCLA-PCI and AUA symptom index) was sent to preoperatively to patients scheduled to undergo one of the three treatment modalities and again at 1, 3, 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, and 36 months following therapy. Comparisons of the change from baseline were made for disease specific domains. Patients with baseline scores of less than 30 were removed from analysis for that domain. Comparisons were made between the groups to evaluate differences in QOL Results: 575 patients undergoing surgical treatment for localized prostate cancer completed baseline questionnaires with 498 (86.6%) completing one or more post operative surveys. There was no statistical difference between the demographics or baseline values of the three groups. Patients undergoing extirpative treatments experienced adverse effects on all disease-specific QOL domains and trended back towards normal over the subsequent 18 months. Patients undergoing bilateral nerve sparing procedures had similar percent return to baseline of sexual function irrespective of surgical modality. A subgroup comparison by age decade suggested that sexual function was recovered better by younger patients though the groups were too small for statistical comparison. At 18 months the mean percent return to baseline urinary function was 79% for ORP, 76% for LRP, and 73% for dvp. The mean percent return to baseline sexual function was 45% for ORP, 36% for LRP, 38% for dvp. There was no statistically significant difference. Conclusions: All surgical treatment modalities for prostate cancer significantly impact disease specific QOL domains. Our early reuslts with LRP and dvp, has revealed no significant difference in HRQOL outcomes for patients compared to ORP. Source of Funding: None IS ROBOTIC RADIAL PROSTATECTOMY A MORE PRECISE TECHNIQUE FOR PERFORMING RADICAL PROSTATECTOMY? It is important to recognize that the robotic surgeon does not program the robot to perform the surgery. Rather, the robotic surgeon manually controls the robotic arm. Would you ever think your penmanship would be improved by putting your pen into a robotic arm and then manually moving the pen by physically moving the robotic arm? 8
9 The clinical relevance of precision should be based on outcomes such as complications, continence, and potency. No robotic series has ever matched the low complications rates that I have published following open radical prostatectomy. IS THE ROBOT MORE MINIMALLY INVASIVE? The factors that should define minimally invasiveness include: length of incision, operative time, length of hospital stay, severity of pain, and return to activities. Length of Incision I perform open radical prostatectomy through a four inch lower midline incision that is made in between the muscles. Robotic prostatectomy is performed by making four one inch incisions to allow placement of the robotic instruments and another incision under the umbilicus (bellybutton) for removal of the prostate. In cases with large prostates, the cumulative length of the incision for robotic prostatectomy is considerably longer than for the open procedure. Operative Time The mean time for me to perform the radical prostatectomy is approximately 60 minutes. Operative times are increased when I perform simultaneous pelvic lymphadenectomy, hernia repairs, or other secondary procedures. My total mean anesthesia time is less than 2 hours. The anesthesia time for robotic prostatectomy performed by the foremost experts is significantly greater. Length of Hospital of Stay The length of stay is determined by how fast the patient recovers and the criteria for hospital discharge. The overwhelming majority of my patients travel a great distance to NYU Medical Center for their surgery. While many of these patients could safely be discharged the following day after surgery, many individuals feel more secure staying in the hospital a second day. I am happy to accommodate one s preference to stay a second day. Therefore, my published mean length of hospital stay is two days. The surgeons at Vanderbilt are skilled at performing both open and robotic radical prostatectomy. They have recently published that the length of stay following open and robotic prostatectomy are identical. The following is the abstract from the Vanderbilt s recent publication. Comparison of Length of Hospital Stay Between Radical Retropubic Prostatectomy and Robotic Assisted Laparoscopic Prostatectomy Bradford Nelson, Melissa Kaufman, Gregory Broughton, Michael S. Cookson, Sam S. Chang, S. Duke Herrell, Roxelyn G. Baumgartner, Joseph A. Smith Jr. Received 2 May
10 Purpose: Minimally invasive surgery has been shown to decrease postoperative morbidity and length of stay for a number of surgical procedures. Furthermore, length of stay after open radical prostatectomy has decreased dramatically during the last decade. We examined differences in length of stay between a prospectively evaluated cohort of patients who underwent radical retropubic prostatectomy and robot assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy. Materials and Methods: Between January 2003 and March 2006, 1,003 radical prostatectomies were performed at our hospital. Data were collected in prospective fashion and a comparison was made between 374 patients who underwent radical retropubic prostatectomy and 629 who underwent robot assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy. Length of stay, factors influencing length of stay, readmission rates and unscheduled clinic or emergency room visits were evaluated. Patients in the 2 groups were treated using the same clinical care pathway. Results: Overall 94.3% of patients in the radical retropubic prostatectomy group and 97.5% in the robot assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy group were discharged home on or before postoperative day 1. Mean length of stay in the radical retropubic and robot assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy groups was 1.25 (median 1.09) and 1.17 days (median 1.03), which was similar and not statistically different (p = 0.27). Readmission rates were similar in robot assisted laparoscopic and radical retropubic prostatectomy patients (7% and 5%, respectively, p = 0.12). Unscheduled clinic or emergency room visits were the same in the robot assisted laparoscopic and radical retropubic prostatectomy groups (10%, p = 0.95). Conclusions: Patients who underwent radical retropubic prostatectomy or robot assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy can be treated on the same clinical pathway. A targeted hospital discharge date of postoperative day 1 can be achieved in the majority of patients who underwent radical prostatectomy. Readmission rates or unscheduled hospital visits are necessary in a small percent of patients treated with an early discharge program, of which the majority is caused by ileus. 10
11 Prostatectomy Robotic Open p Value LOS (days): Mean Median /629 (10) 37/374 (10) 0.95 No. unscheduled clinic + ER visits/total No. (%) No. hospital readmissions/ total No. (%) 45/629 (7) 18/374 (5) 0.12 Pain control Radical prostatectomy is performed through a four inch incision between the muscles. Robotic prostatectomy is performed via five incisions that are typically larger than 4 cm. Robotic prostatectomy distends the abdominal cavity with air which in some cases has a negative effect on return of bowl activity. The technique for removing the prostate is virtually identical between the approaches. Therefore, common sense would dictate that there should be little or no difference in the degree of pain. Once again, the Vanderbilt group compared pain following open and robotic radical prostatectomy using the same assessment instrument. As one would predict, the degree of pain was identical. Robotic Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy Versus Retropubic Radical Prostatectomy: A Prospective Assessment Of Postoperative Pain Todd M. Webster, S. Duke Herrell*, Sam S. Chang, Michael S. Cookson, Roxelyn G. Baumgartner, Laura W. Anderson, Joseph A. Smith Jr Purpose: Laparoscopic prostatectomy, whether or not coupled with robotic assistance, is often considered less invasive than open radical retropubic prostatectomy (RRP). Minimal postoperative pain has been reported following robot assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy (RALP) but there have been few comparative studies with RRP. We compared perioperative narcotic use and patient reported pain in a prospective patient series. Materials and Methods: Between June 2003 and May 2004, 314 patients underwent radical prostatectomy at our institution, including RALP in 159, RRP in 154 and conversion in 1. All patients were treated on a postoperative clinical pathway that included 30 mg ketorolac intravenously immediately postoperatively, followed by 15 mg intravenously every 6 hours. No regional anesthesia (epidural/spinal) narcotics or patient controlled analgesic pumps were used. All narcotic use was converted to morphine 11
12 sulfate equivalents for purpose of analysis. A Likert scale of 0 to 10 was used to assess pain on the day of surgery, and on postoperative days 1 and 14. Results: The total mean morphine sulfate equivalent ± SD in patients in the RALP and RRP groups was low and, when corrected for length of stay, it was not statistically different (22.41 ± 1.13 vs ± 1.16 mg, p = 0.72). Mean Likert pain perception scores were low at all time points in the RALP and RRP groups but statistically lower on the day of surgery in the RALP cohort (2.05 ± 1.99 vs 2.60 ± 2.25, p = 0.027). Patient reported mean pain scores were almost identical for RALP vs RRP on postoperative days 1 (1.76 ± 1.87 vs 1.73 ± 1.77, p = 0.880) and 14 (2.51 ± 1.91 vs 2.42 ± 1.84, p = 0.722). Conclusions: Perioperative narcotic use and patient reported pain are low regardless of the surgical approach used for radical prostatectomy. RALP did not provide a clinically meaningful decrease in pain compared with RRP, primarily because of the low pain scores reported in each group. Outcomes other than pain will ultimately determine the role of laparoscopic radical prostatectomy and RALP. Return to Activities I have collected over 500 pictures from patients engaged in various activities within 3 weeks of their open radical prostatectomy. These photographs show men flying to California to attend a baseball game, playing golf and tennis, and boating within a week of their surgery. I recently published an article in the peer-reviewed literature where we evaluated the actual time to return to work and activities. Over 50% of the men had returned to work within 14 days following open radical prostatectomy. There is no comparable study in the literature regarding robotic prostatectomy. There is absolutely no reason to assume that robotics would exceed our published outcomes. Time to Return to Work and Physical Activity Following Open Radical Retropubic Prostatectomy Raymond Sultan, Denisa Slova, Bob Thiel, Herbert Lepor Received 28 October 2005 Purpose: We identified factors that predict return to part-time and full-time work and resumption of unlimited physical activity following open radical retropubic prostatectomy. 12
13 Materials and Methods: Between July 1, 2002 and February 28, 2005, 537 men with clinically localized prostate cancer underwent open radical retropubic prostatectomy, as performed by a single surgeon. Intraoperative, perioperative and postoperative parameters were recorded in real time and entered into a database. An assessment was made 1 and 3 months postoperatively regarding time to return to work and unrestricted physical activity. Results: Of the men 50% returned to part-time and full-time work, and unrestricted activity within 14, 21 and 30 days after discharge home, respectively. Patient age and hematocrit at hospital discharge significantly predicted return to part-time and full-time work, and unlimited physical activity. The number of days that the urinary catheter was indwelling was also associated with return to part-time work. Occupation (blue vs white collar) and marital status were also associated with return to full-time work. In the multivariate model a unit increase in hematocrit decreased the time to return to part-time and full-time work, and unrestricted physical activity by 0.50, 0.60 and 0.59 days, respectively. Men with discharge hematocrit greater than 32% were 1.57 (p = 0.059), 1.65 (p = 0.041) and 2.03 (p = 0.002) times more likely to return to part-time and full-time work, and unlimited activity before 14, 21 and 30 days, respectively. Overall models were developed that accounted for 9.4%, 14.0% and 4.0% of the time to return to part-time work, full-time work and unrestricted physical activity, respectively. Conclusions: Efforts to increase discharge hematocrit by minimizing intraoperative blood loss or using preoperative blood management strategies and earlier removal of the urinary catheter have a favorable impact on the return to work and physical activity. Work (days) Activity Statistic Part Time Full Time (days) Mean SD Minimum th Percentile Median th Percentile Max
14 IS THERE LESS BLOOD LOSS FOLLOWING ROBOTIC PROSTATECTOMY? I must concede that the average amount of blood loss following robotic prostatectomy is about 300cc less than the open approach. However, this modest advantage does not translate into a lower transfusion rate. I do believe that less blood loss is associated with an earlier return to activities. Over 90% of my patients follow my recommendation to use preoperative erythropoietin to increase red blood cell mass preoperatively. I have demonstrated that the increase in the red cell volume following erythropoietin increases the red blood cell mass equivalent to 400cc of blood volume. In essence, the use of erythropoietin preoperatively totally neutralizes the advantage of robotic prostatectomy. The blood count of my patients at the time of hospital discharge following open radical prostatectomy is identical to that of men undergoing robotic prostatectomy by expert surgeons. I have also published that the use of erythropoietin is extraordinary safe. WHAT HAPPENS WHEN THE ROBOT BREAKS DOWN? A group of expert robotic surgeons from Virginia Mason Medical Center in Seattle recently reported that the robot dysfunctioned in 3% of cases. Mechanical Failure Rate Of Da Vinci Robotic System. Borden LS Jr, Kozlowski PM, Porter CR, Corman JM. Section of Urology and Renal Transplantation, Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, Washington, USA. Introduction: Robotic-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy (RLRP) is playing an increasing role in the surgical management of prostate cancer. The benefits of minimally invasive surgery, enhanced surgeon familiarity with the instrumentation, and increased patient demand has led to the popularity of this surgical technique. There are, however, shortcomings specifically associated with this technology. Notably, instrumentation failure associated with robotic procedures represents a new and unique problem in urological surgery. We examine the rate of mechanical failure of the da Vinci robotic system and its impact on our prostate cancer program. Materials and methods: We reviewed our prospective, institutional review board-approved database of the first 350 RLRP procedures that were scheduled for surgery at our institution. We identified all cases in which mechanical failure of the da Vinci robotic system resulted in surgery being cancelled, postponed, or converted to a conventional laparoscopic or an open radical prostatectomy. 14
15 Results: Nine of the 350 (2.6%) scheduled RLRPs were unable to be completed robotically secondary to device malfunction. Six of the malfunctions were detected prior to anesthesia induction and surgery was rescheduled. Three other malfunctions occurred intraoperatively and were converted either to a conventional laparoscopic (1 case) or an open surgical approach (2 cases). The etiology of the malfunctions included the following: set-up joint malfunction (2), arm malfunction (2), power error (1), monocular monitor loss (1), camera malfunction (1), metal fatigue/ break of surgeon's console hand piece (1) and software incompatibility (1). Conclusions: Although uncommon, malfunction of the da Vinci robotic system does occur and may lead to psychological, financial, and logistical burdens for patients, physicians, and hospitals. Patients should be carefully counseled preoperatively regarding the possibility of robotic mechanical failure. I have never broken down during any of the 3,400 cases performed. What happens when the robot dysfunctions and the robotic surgeon is not experienced performing an open radical prostatectomy? I obviously would never want to be the patient who finds themselves in this predicament. WHO SHOULD PERFORM YOUR RADICAL PROSTATECTOMY? A critical evidenced based assessment of the literature demonstrates that there are no major differences between open and robotic prostatectomy when it comes to: length of hospital stay, severity of pain, catheter time, transfusion rate, return to work, continence rates, and potency rates. The only advantage of robotic prostatectomy is lower blood loss which can be totally counterbalanced by the use of preoperative erythropoietin. The primary disadvantages of the robotic prostatectomy are a steep learning curve, increase cost, uncertainty of cancer control and dysfunction of the robot. Therefore, the decision who should perform your radical prostatectomy should not be determined by whether your surgeon is an open or robotic surgeon, rather it should be based on 1) experience 2) is the experienced surgeon performing my surgery? 3) does the surgeon provide credible information to validate their outcomes? 4) is there a commitment to provide a pathway for recovery of continence and potency? I have performed over 3,400 radical prostatectomies which ranks amongst the highest in the world. I will do your prostatectomy! All of the outcomes presented to you are based on a prospective study and these outcomes are published in the peer-reviewed scientific literature. The easiest one hour for the patient and myself is the one hour during the open radical prostatectomy. The greatest challenge is helping you achieve continence and potency, and guiding you through other issues during your recovery. You have my commitment I will be there all along the way. 15
Robotic Radical Prostatectomy: What s s the Advantage? Matthew T. Gettman, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Urology
 Robotic Radical Prostatectomy: What s s the Advantage? Matthew T. Gettman, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Urology Prostate Cancer Epidemiology: 2009 Estimated new cases: 230,000 Estimated deaths:
Robotic Radical Prostatectomy: What s s the Advantage? Matthew T. Gettman, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Urology Prostate Cancer Epidemiology: 2009 Estimated new cases: 230,000 Estimated deaths:
Thomas A. Kollmorgen, M.D. Oregon Urology Institute
 Thomas A. Kollmorgen, M.D. Oregon Urology Institute None 240,000 new diagnosis per year, and an estimated 28,100 deaths (2012) 2 nd leading cause of death from cancer in U.S.A. Approximately 1 in 6 men
Thomas A. Kollmorgen, M.D. Oregon Urology Institute None 240,000 new diagnosis per year, and an estimated 28,100 deaths (2012) 2 nd leading cause of death from cancer in U.S.A. Approximately 1 in 6 men
da Vinci Prostatectomy Information Guide (Robotically-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy)
 da Vinci Prostatectomy Information Guide (Robotically-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy) Prostate Cancer Overview Prostate cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the
da Vinci Prostatectomy Information Guide (Robotically-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy) Prostate Cancer Overview Prostate cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the
These rare variants often act aggressively and may respond differently to therapy than the more common prostate adenocarcinoma.
 Prostate Cancer OVERVIEW Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer diagnosed among American men, accounting for nearly 200,000 new cancer cases in the United States each year. Greater than 65% of
Prostate Cancer OVERVIEW Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer diagnosed among American men, accounting for nearly 200,000 new cancer cases in the United States each year. Greater than 65% of
Facing Prostate Cancer Surgery? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery
 Facing Prostate Cancer Surgery? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Prostate Cancer Your prostate is a walnut-sized gland that is part of the male reproductive system. The prostate
Facing Prostate Cancer Surgery? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Prostate Cancer Your prostate is a walnut-sized gland that is part of the male reproductive system. The prostate
The Business of Prostate Cancer Care: A Clinician-Researcher s Perspective
 The Business of Prostate Cancer Care: A Clinician-Researcher s Perspective David F. Penson, MD, MPH Departments of Urology and Preventive Medicine Keck School of Medicine University of Southern California
The Business of Prostate Cancer Care: A Clinician-Researcher s Perspective David F. Penson, MD, MPH Departments of Urology and Preventive Medicine Keck School of Medicine University of Southern California
Precise, Minimally Invasive Prostate Cancer Removal
 Precise, Minimally Invasive Prostate Cancer Removal Learn why da Vinci Surgery may be your best treatment option 1 Beyond Minimally Invasive For Prostate Cancer 1 Facing Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer
Precise, Minimally Invasive Prostate Cancer Removal Learn why da Vinci Surgery may be your best treatment option 1 Beyond Minimally Invasive For Prostate Cancer 1 Facing Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer
PROSTATE CANCER. Get the facts, know your options. Samay Jain, MD, Assistant Professor,The University of Toledo Chief, Division of Urologic Oncology
 PROSTATE CANCER Get the facts, know your options Samay Jain, MD, Assistant Professor,The University of Toledo Chief, Division of Urologic Oncology i What is the Prostate? Unfortunately, you have prostate
PROSTATE CANCER Get the facts, know your options Samay Jain, MD, Assistant Professor,The University of Toledo Chief, Division of Urologic Oncology i What is the Prostate? Unfortunately, you have prostate
Questions to Ask My Doctor About Prostate Cancer
 Questions to Ask My Doctor Being told you have prostate cancer can be scary and stressful. You probably have a lot of questions and concerns. Learning about the disease, how it s treated, and how this
Questions to Ask My Doctor Being told you have prostate cancer can be scary and stressful. You probably have a lot of questions and concerns. Learning about the disease, how it s treated, and how this
Facing a Hysterectomy? If you ve been diagnosed with early stage gynecologic cancer, learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery
 Facing a Hysterectomy? If you ve been diagnosed with early stage gynecologic cancer, learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Early Stage Gynecologic Cancer A variety of gynecologic
Facing a Hysterectomy? If you ve been diagnosed with early stage gynecologic cancer, learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Early Stage Gynecologic Cancer A variety of gynecologic
Questions to ask my doctor: About prostate cancer
 Questions to ask my doctor: About prostate cancer Being diagnosed with prostate cancer can be scary and stressful. You probably have a lot of questions and concerns. Learning about the disease, how it
Questions to ask my doctor: About prostate cancer Being diagnosed with prostate cancer can be scary and stressful. You probably have a lot of questions and concerns. Learning about the disease, how it
Recovery of Erectile Function After Radical Prostatectomy Vanderbilt University Department of Urologic Surgery
 Recovery of Erectile Function After Radical Prostatectomy Vanderbilt University Department of Urologic Surgery Postoperative erectile dysfunction is a potential risk of surgery for prostate cancer, whether
Recovery of Erectile Function After Radical Prostatectomy Vanderbilt University Department of Urologic Surgery Postoperative erectile dysfunction is a potential risk of surgery for prostate cancer, whether
New Technologies in Surgery
 New Technologies in Surgery Jim C. Hu MD, MPH Center for Advanced Surgical and Interventional Technology (CASIT) Director of Robotic and Minimally Invasive Surgery Associate Professor Department of Urology
New Technologies in Surgery Jim C. Hu MD, MPH Center for Advanced Surgical and Interventional Technology (CASIT) Director of Robotic and Minimally Invasive Surgery Associate Professor Department of Urology
Prostate Cancer Patients Report on Benefits of Proton Therapy
 Prostate Cancer Patients Report on Benefits of Proton Therapy Dobson DaVanzo & Associates, LLC Vienna, VA 703.260.1760 www.dobsondavanzo.com Prostate Cancer Patients Report on Benefits of Proton Therapy
Prostate Cancer Patients Report on Benefits of Proton Therapy Dobson DaVanzo & Associates, LLC Vienna, VA 703.260.1760 www.dobsondavanzo.com Prostate Cancer Patients Report on Benefits of Proton Therapy
Therapies for Prostate Cancer and Treatment Selection
 Prostatic Diseases Therapies for Prostate Cancer and Treatment Selection JMAJ 47(12): 555 560, 2004 Yoichi ARAI Professor and Chairman, Department of Urology, Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine
Prostatic Diseases Therapies for Prostate Cancer and Treatment Selection JMAJ 47(12): 555 560, 2004 Yoichi ARAI Professor and Chairman, Department of Urology, Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine
Treatment of Incidental Prostate Cancer Diagnosed during BPH Surgery with Radical Prostatectomy: Appropriate or over Treatment?
 Journal of Cancer Therapy, 2012, 3, 256-262 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jct.2012.34036 Published Online August 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jct) Treatment of Incidental Prostate Cancer Diagnosed during
Journal of Cancer Therapy, 2012, 3, 256-262 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jct.2012.34036 Published Online August 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jct) Treatment of Incidental Prostate Cancer Diagnosed during
855-DRSAMADI or 212-241-8779
 SMART SURGERY NEWS MARCH 2013 Dr. David Samadi 855-DRSAMADI or 212-241-8779 YOUR PROSTATE CANCER NEWS PREVENTION DIAGNOSIS TREATMENT LIFE AFTER PROSTATE CANCER PREVENTION Prostate Cancer Need-to-Knows
SMART SURGERY NEWS MARCH 2013 Dr. David Samadi 855-DRSAMADI or 212-241-8779 YOUR PROSTATE CANCER NEWS PREVENTION DIAGNOSIS TREATMENT LIFE AFTER PROSTATE CANCER PREVENTION Prostate Cancer Need-to-Knows
Beyond the PSA: Genomic Testing in Localized Prostate Cancer
 Beyond the PSA: Genomic Testing in Localized Prostate Cancer Kelvin A. Moses, MD, PhD Vanderbilt University Medical Center Wednesday, December 2, 2015 5:00 p.m. ET/2:00 p.m. PT About ZERO ZERO s mission
Beyond the PSA: Genomic Testing in Localized Prostate Cancer Kelvin A. Moses, MD, PhD Vanderbilt University Medical Center Wednesday, December 2, 2015 5:00 p.m. ET/2:00 p.m. PT About ZERO ZERO s mission
PSA Screening for Prostate Cancer Information for Care Providers
 All men should know they are having a PSA test and be informed of the implications prior to testing. This booklet was created to help primary care providers offer men information about the risks and benefits
All men should know they are having a PSA test and be informed of the implications prior to testing. This booklet was created to help primary care providers offer men information about the risks and benefits
Prostate Cancer Screening in Taiwan: a must
 Prostate Cancer Screening in Taiwan: a must 吳 俊 德 基 隆 長 庚 醫 院 台 灣 醫 學 會 105 th What is the PSA test? The blood level of PSA is often elevated in men with prostate cancer, and the PSA test was originally
Prostate Cancer Screening in Taiwan: a must 吳 俊 德 基 隆 長 庚 醫 院 台 灣 醫 學 會 105 th What is the PSA test? The blood level of PSA is often elevated in men with prostate cancer, and the PSA test was originally
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW
 Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Your Questions, Our Answers.
 Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Your Questions, Our Answers. When you re looking for the right treatment for your prostate cancer, nothing s more important than accurate information. Read on, and learn
Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Your Questions, Our Answers. When you re looking for the right treatment for your prostate cancer, nothing s more important than accurate information. Read on, and learn
Prostate Cancer Treatment Comparison
 Prostate Cancer Treatment Comparison Treatment Comparative Data Outcome Comparison: Surgery vs. Radiotherapy Outcome Radical Prostatectomy* Radiation** Survival duration compared to conservative disease
Prostate Cancer Treatment Comparison Treatment Comparative Data Outcome Comparison: Surgery vs. Radiotherapy Outcome Radical Prostatectomy* Radiation** Survival duration compared to conservative disease
Launching a Successful Robotic Program
 2 Launching a Successful Robotic Program Kenneth J. Palmer, Marcelo A. Orvieto, Bernardo M. Rocco, and Vipul R. Patel Keywords Robotic surgery Robotic surgical program Marketing Operating room setup Training
2 Launching a Successful Robotic Program Kenneth J. Palmer, Marcelo A. Orvieto, Bernardo M. Rocco, and Vipul R. Patel Keywords Robotic surgery Robotic surgical program Marketing Operating room setup Training
Prostate Cancer. Treatments as unique as you are
 Prostate Cancer Treatments as unique as you are UCLA Prostate Cancer Program Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer among men. The UCLA Prostate Cancer Program brings together the elements essential
Prostate Cancer Treatments as unique as you are UCLA Prostate Cancer Program Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer among men. The UCLA Prostate Cancer Program brings together the elements essential
restricted to certain centers and certain patients, preferably in some sort of experimental trial format.
 Managing Pancreatic Cancer, Part 4: Pancreatic Cancer Surgery, Complications, & the Importance of Surgical Volume Dr. Matthew Katz, Surgeon, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX I m going to talk a little
Managing Pancreatic Cancer, Part 4: Pancreatic Cancer Surgery, Complications, & the Importance of Surgical Volume Dr. Matthew Katz, Surgeon, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX I m going to talk a little
NEW HYBRID IMAGING TECHNOLOGY MAY HAVE BIG POTENTIAL FOR IMPROVING DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATE CANCER
 Media Release April 7, 2009 For Immediate Release NEW HYBRID IMAGING TECHNOLOGY MAY HAVE BIG POTENTIAL FOR IMPROVING DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATE CANCER London, Ontario Improved hybrid imaging techniques developed
Media Release April 7, 2009 For Immediate Release NEW HYBRID IMAGING TECHNOLOGY MAY HAVE BIG POTENTIAL FOR IMPROVING DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATE CANCER London, Ontario Improved hybrid imaging techniques developed
7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse
 7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse A patient with prostate cancer in PSA relapse is one who, having received a primary treatment with intent to cure, has a raised PSA (prostate-specific antigen) level defined
7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse A patient with prostate cancer in PSA relapse is one who, having received a primary treatment with intent to cure, has a raised PSA (prostate-specific antigen) level defined
Early Prostate Cancer: Questions and Answers. Key Points
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
The 4Kscore blood test for risk of aggressive prostate cancer
 The 4Kscore blood test for risk of aggressive prostate cancer Prostate cancer tests When to use the 4Kscore Test? Screening Prior to 1 st biopsy Prior to negative previous biopsy Prognosis in Gleason 6
The 4Kscore blood test for risk of aggressive prostate cancer Prostate cancer tests When to use the 4Kscore Test? Screening Prior to 1 st biopsy Prior to negative previous biopsy Prognosis in Gleason 6
Treating Prostate Cancer
 Treating Prostate Cancer A Guide for Men With Localized Prostate Cancer Most men have time to learn about all the options for treating their prostate cancer. You have time to talk with your family and
Treating Prostate Cancer A Guide for Men With Localized Prostate Cancer Most men have time to learn about all the options for treating their prostate cancer. You have time to talk with your family and
Prostate Cancer Treatment Comparison
 Prostate Cancer Treatment Comparison Treatment Comparative Data Outcome Comparison: Surgery vs. Radiotherapy Outcome Radical Prostatectomy* Radiation** Survival duration compared to conservative disease
Prostate Cancer Treatment Comparison Treatment Comparative Data Outcome Comparison: Surgery vs. Radiotherapy Outcome Radical Prostatectomy* Radiation** Survival duration compared to conservative disease
Secondary Cancer and Relapse Rates Following Radical Prostatectomy for Prostate-Confined Cancer
 Copyright E 2007 Journal of Insurance Medicine J Insur Med 2007;39:242 250 MORTALITY Secondary Cancer and Relapse Rates Following Radical Prostatectomy for Prostate-Confined Cancer David Wesley, MD; Hugh
Copyright E 2007 Journal of Insurance Medicine J Insur Med 2007;39:242 250 MORTALITY Secondary Cancer and Relapse Rates Following Radical Prostatectomy for Prostate-Confined Cancer David Wesley, MD; Hugh
visualized. The correct level is then identified again. With the use of a microscope and
 SURGERY FOR SPINAL STENOSIS Laminectomy A one inch (or longer for extensive stenosis) incision is made in the middle of the back over the effected region of the spine. The muscles over the bone are moved
SURGERY FOR SPINAL STENOSIS Laminectomy A one inch (or longer for extensive stenosis) incision is made in the middle of the back over the effected region of the spine. The muscles over the bone are moved
A Woman s Guide to Prostate Cancer Treatment
 A Woman s Guide to Prostate Cancer Treatment Supporting the man in your life Providing prostate cancer support and resources for women and families WOMEN AGAINST PROSTATE CANCER A Woman s Guide to Prostate
A Woman s Guide to Prostate Cancer Treatment Supporting the man in your life Providing prostate cancer support and resources for women and families WOMEN AGAINST PROSTATE CANCER A Woman s Guide to Prostate
An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER
 An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER Being diagnosed with prostate cancer can be a life-altering experience. It requires making some very difficult decisions about treatments that can affect not only the
An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER Being diagnosed with prostate cancer can be a life-altering experience. It requires making some very difficult decisions about treatments that can affect not only the
Ryan C. Hedgepeth,* Jessica Labo, LingLing Zhang and David P. Wood, Jr.
 Expanded Prostate Cancer Index Composite Versus Incontinence Symptom Index and Sexual Health Inventory for Men to Measure Functional Outcomes After Prostatectomy Ryan C. Hedgepeth,* Jessica Labo, LingLing
Expanded Prostate Cancer Index Composite Versus Incontinence Symptom Index and Sexual Health Inventory for Men to Measure Functional Outcomes After Prostatectomy Ryan C. Hedgepeth,* Jessica Labo, LingLing
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Treatment options and future directions
 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Treatment options and future directions David Weksberg, M.D., Ph.D. PinnacleHealth Cancer Institute September 12, 2015 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Treatment
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Treatment options and future directions David Weksberg, M.D., Ph.D. PinnacleHealth Cancer Institute September 12, 2015 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Treatment
Role of Robotic Surgery in Obese Women with Endometrial Cancer
 Role of Robotic Surgery in Obese Women with Endometrial Cancer Anil Tailor Consultant Gynaecological Oncologist Royal Surrey County Hospital Guildford, Surrey, UK St Peters Hospital Chertsey, Surrey, UK
Role of Robotic Surgery in Obese Women with Endometrial Cancer Anil Tailor Consultant Gynaecological Oncologist Royal Surrey County Hospital Guildford, Surrey, UK St Peters Hospital Chertsey, Surrey, UK
MINIMALLY INVASIVE SURGERY FOR WOMEN Back to Life. Faster.
 MINIMALLY INVASIVE SURGERY FOR WOMEN Back to Life. Faster. Pictured above: UF gynecologists Sharon Byun, MD, Shireen Madani Sims, MD, and Michael Lukowski, MD, with the robotic surgery equipment. Make
MINIMALLY INVASIVE SURGERY FOR WOMEN Back to Life. Faster. Pictured above: UF gynecologists Sharon Byun, MD, Shireen Madani Sims, MD, and Michael Lukowski, MD, with the robotic surgery equipment. Make
Does my patient need more therapy after prostate cancer surgery?
 Does my patient need more therapy after prostate cancer surgery? Contact the GenomeDx Patient Care Team at: 1.888.792.1601 (toll-free) or e-mail: client.service@genomedx.com Prostate Cancer Classifier
Does my patient need more therapy after prostate cancer surgery? Contact the GenomeDx Patient Care Team at: 1.888.792.1601 (toll-free) or e-mail: client.service@genomedx.com Prostate Cancer Classifier
Historical Basis for Concern
 Androgens After : Are We Ready? Mohit Khera, MD, MBA Assistant Professor of Urology Division of Male Reproductive Medicine and Surgery Scott Department of Urology Baylor College of Medicine Historical
Androgens After : Are We Ready? Mohit Khera, MD, MBA Assistant Professor of Urology Division of Male Reproductive Medicine and Surgery Scott Department of Urology Baylor College of Medicine Historical
NERVE GRAFT TO RESTORE ERECTILE FUNCTION DURING RADICAL PROSTATECTOMY
 CLINICAL POLICY NERVE GRAFT TO RESTORE ERECTILE FUNCTION DURING RADICAL PROSTATECTOMY Policy Number: SURGERY 043.13 T Effective Date: October 1, 015 Table of Contents BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS. APPLICABLE
CLINICAL POLICY NERVE GRAFT TO RESTORE ERECTILE FUNCTION DURING RADICAL PROSTATECTOMY Policy Number: SURGERY 043.13 T Effective Date: October 1, 015 Table of Contents BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS. APPLICABLE
Saturation Biopsy vs. 3D Spatial Biopsy vs. Free Hand Ultrasound biopsy for Targeted Prostate Cancer Therapies
 Saturation Biopsy vs. 3D Spatial Biopsy vs. Free Hand Ultrasound biopsy for Targeted Prostate Cancer Therapies John F. Ward, MD Assistant Professor University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center Ablation
Saturation Biopsy vs. 3D Spatial Biopsy vs. Free Hand Ultrasound biopsy for Targeted Prostate Cancer Therapies John F. Ward, MD Assistant Professor University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center Ablation
Considering Surgery for Fibroids? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery
 Considering Surgery for Fibroids? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Uterine Fibroid (Fibroid Tumor) A uterine fibroid is a benign (non-cancerous) tumor that grows in the uterine
Considering Surgery for Fibroids? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Uterine Fibroid (Fibroid Tumor) A uterine fibroid is a benign (non-cancerous) tumor that grows in the uterine
150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2. Patient Information. Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate
 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2 Patient Information Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 3 GreenLight Laser Therapy 1 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page
150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2 Patient Information Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 3 GreenLight Laser Therapy 1 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page
Prostate Cancer Action Plan: Choosing the treatment that s right for you
 Prostate Cancer Action Plan: Choosing the treatment that s right for you Segment 1: Introduction Trust me, there's a better way to choose a treatment for your prostate cancer. Watching this program is
Prostate Cancer Action Plan: Choosing the treatment that s right for you Segment 1: Introduction Trust me, there's a better way to choose a treatment for your prostate cancer. Watching this program is
Prostate cancer. Christopher Eden. The Royal Surrey County Hospital, Guildford & The Hampshire Clinic, Old Basing.
 Prostate cancer Christopher Eden The Royal Surrey County Hospital, Guildford & The Hampshire Clinic, Old Basing. Screening Screening men for PCa (prostate cancer) using PSA (Prostate Specific Antigen blood
Prostate cancer Christopher Eden The Royal Surrey County Hospital, Guildford & The Hampshire Clinic, Old Basing. Screening Screening men for PCa (prostate cancer) using PSA (Prostate Specific Antigen blood
Prostate Cancer 2014
 Prostate Cancer 2014 Eric A. Klein, M.D. Chairman Glickman Urological and Kidney Institute Professor of Surgery Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine Incidence rates, US Men Mortality Rates, US Men
Prostate Cancer 2014 Eric A. Klein, M.D. Chairman Glickman Urological and Kidney Institute Professor of Surgery Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine Incidence rates, US Men Mortality Rates, US Men
Analysis of Prostate Cancer at Easter Connecticut Health Network Using Cancer Registry Data
 The 2014 Cancer Program Annual Public Reporting of Outcomes/Annual Site Analysis Statistical Data from 2013 More than 70 percent of all newly diagnosed cancer patients are treated in the more than 1,500
The 2014 Cancer Program Annual Public Reporting of Outcomes/Annual Site Analysis Statistical Data from 2013 More than 70 percent of all newly diagnosed cancer patients are treated in the more than 1,500
Gleason Score. Oncotype DX GPS. identified for. about surveillance. time to get sophisticated
 patient: MARK SMITH PSA 6.2 Gleason Score 6 Oncotype DX GPS 8 identified for active surveillance time to get sophisticated about surveillance Accurate prediction of prostate cancer risk is needed at the
patient: MARK SMITH PSA 6.2 Gleason Score 6 Oncotype DX GPS 8 identified for active surveillance time to get sophisticated about surveillance Accurate prediction of prostate cancer risk is needed at the
PROSTATE CANCER. Diagnosis and Treatment
 Diagnosis and Treatment Table of Contents Introduction... 1 Patient and Coach Information... 1 About Your Prostate... 1 What You Should Know About Prostate Cancer... 2 Screening and Diagnosis... 2 Digital
Diagnosis and Treatment Table of Contents Introduction... 1 Patient and Coach Information... 1 About Your Prostate... 1 What You Should Know About Prostate Cancer... 2 Screening and Diagnosis... 2 Digital
Prostate cancer is the most common cause of death from cancer in men over age 75. Prostate cancer is rarely found in men younger than 40.
 A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. Prostate cancer Cancer - prostate; Biopsy - prostate; Prostate biopsy; Gleason score Last reviewed: October 2, 2013. Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate
A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. Prostate cancer Cancer - prostate; Biopsy - prostate; Prostate biopsy; Gleason score Last reviewed: October 2, 2013. Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate
Prostate Cancer Guide. A resource to help answer your questions about prostate cancer
 Prostate Cancer Guide A resource to help answer your questions about prostate cancer Thank you for downloading this guide to prostate cancer treatment. We know that all the information provided online
Prostate Cancer Guide A resource to help answer your questions about prostate cancer Thank you for downloading this guide to prostate cancer treatment. We know that all the information provided online
Surgeon perception is not a good predictor of peri-operative outcomes in robot-assisted radical prostatectomy
 DOI 10.1007/s11701-011-0293-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Surgeon perception is not a good predictor of peri-operative outcomes in robot-assisted radical prostatectomy Joshua Stern Saurabh Sharma Pierre Mendoza Mary
DOI 10.1007/s11701-011-0293-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Surgeon perception is not a good predictor of peri-operative outcomes in robot-assisted radical prostatectomy Joshua Stern Saurabh Sharma Pierre Mendoza Mary
The 4Kscore blood test for risk of aggressive prostate cancer
 The 4Kscore blood test for risk of aggressive prostate cancer Early detection of aggressive prostate cancer Challenges Serum PSA has a high false positive rate Over 1 million prostate biopsies performed
The 4Kscore blood test for risk of aggressive prostate cancer Early detection of aggressive prostate cancer Challenges Serum PSA has a high false positive rate Over 1 million prostate biopsies performed
Types of surgery for kidney cancer
 Useful information for cancer patients Contents This information is about the different operations that you may have for kidney cancer. Surgery can be used to treat almost any stage of kidney cancer. There
Useful information for cancer patients Contents This information is about the different operations that you may have for kidney cancer. Surgery can be used to treat almost any stage of kidney cancer. There
Facing a Hernia Repair? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery
 Facing a Hernia Repair? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Hernia A hernia happens when part of an internal organ or tissue bulges through a hole or weak area in the belly wall
Facing a Hernia Repair? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Hernia A hernia happens when part of an internal organ or tissue bulges through a hole or weak area in the belly wall
SRO Tutorial: Prostate Cancer Treatment Options
 SRO Tutorial: Prostate Cancer Treatment Options May 7th, 2010 Daniel M. Aebersold Klinik und Poliklinik für Radio-Onkologie Universität Bern, Inselspital Is cure necessary in those in whom it may be possible,
SRO Tutorial: Prostate Cancer Treatment Options May 7th, 2010 Daniel M. Aebersold Klinik und Poliklinik für Radio-Onkologie Universität Bern, Inselspital Is cure necessary in those in whom it may be possible,
Advances in Diagnostic and Molecular Testing in Prostate Cancer
 Advances in Diagnostic and Molecular Testing in Prostate Cancer Ashley E. Ross MD PhD Assistant Professor Urology, Oncology, Pathology Johns Hopkins School of Medicine September 24, 2015 1 Disclosures
Advances in Diagnostic and Molecular Testing in Prostate Cancer Ashley E. Ross MD PhD Assistant Professor Urology, Oncology, Pathology Johns Hopkins School of Medicine September 24, 2015 1 Disclosures
Prostate Cancer. What is prostate cancer?
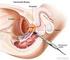 Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
Advances in Robotic Technology
 Advances in Robotic Technology Reza Ghavamian M.D. Professor of Urology Director of Urologic Oncology and Robotic Surgery Montefiore Medical Center Albert Einstein College of Medicine New York Disclosure
Advances in Robotic Technology Reza Ghavamian M.D. Professor of Urology Director of Urologic Oncology and Robotic Surgery Montefiore Medical Center Albert Einstein College of Medicine New York Disclosure
Strategic Acquisition
 Date: Fiscal Year 2013 To: From: Re: Hospital Executives Kathryn Barry, MPH, MSN, RN Health Policy Specialist for Intuitive Surgical Planning for Long Term Success with a Robotic Surgery Program As the
Date: Fiscal Year 2013 To: From: Re: Hospital Executives Kathryn Barry, MPH, MSN, RN Health Policy Specialist for Intuitive Surgical Planning for Long Term Success with a Robotic Surgery Program As the
FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System
 FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System P. 4 Prostate Cancer Background SpaceOAR Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) 1. What is prostate cancer? The vast majority of prostate cancers develop
FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System P. 4 Prostate Cancer Background SpaceOAR Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) 1. What is prostate cancer? The vast majority of prostate cancers develop
Prostate Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Treatment Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam,
Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Treatment Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam,
STATE OF MICHIGAN DEPARTMENT OF INSURANCE AND FINANCIAL SERVICES Before the Director of Insurance and Financial Services
 STATE OF MICHIGAN DEPARTMENT OF INSURANCE AND FINANCIAL SERVICES Before the Director of Insurance and Financial Services In the matter of: Petitioner, v Blue Care Network of Michigan, Respondent. File
STATE OF MICHIGAN DEPARTMENT OF INSURANCE AND FINANCIAL SERVICES Before the Director of Insurance and Financial Services In the matter of: Petitioner, v Blue Care Network of Michigan, Respondent. File
sexual after Being prostate cancer... Manitoba Prostate Centre Visit our website at www.cancercare.mb.ca
 Manitoba Prostate Centre Being sexual after prostate cancer... Visit our website at www.cancercare.mb.ca This publication is supported by an unrestricted educational grant from Pfizer Canada Inc. Treatment
Manitoba Prostate Centre Being sexual after prostate cancer... Visit our website at www.cancercare.mb.ca This publication is supported by an unrestricted educational grant from Pfizer Canada Inc. Treatment
2010 SITE REPORT St. Joseph Hospital PROSTATE CANCER
 2010 SITE REPORT St. Joseph Hospital PROSTATE CANCER Humboldt County is located on the Redwood Coast of Northern California. U.S census data for 2010 reports county population at 134,623, an increase of
2010 SITE REPORT St. Joseph Hospital PROSTATE CANCER Humboldt County is located on the Redwood Coast of Northern California. U.S census data for 2010 reports county population at 134,623, an increase of
Bridging Techniques. What s between EMR and Traditional Surgery? Elisabeth C. McLemore, MD, FACS, FASCRS
 Bridging Techniques What s between EMR and Traditional Surgery? Elisabeth C. McLemore, MD, FACS, FASCRS Associate Professor of Surgery Assistant Program Director, General Surgery Residency Disclosures
Bridging Techniques What s between EMR and Traditional Surgery? Elisabeth C. McLemore, MD, FACS, FASCRS Associate Professor of Surgery Assistant Program Director, General Surgery Residency Disclosures
DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATE CANCER
 DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATE CANCER Determining the presence of prostate cancer generally involves a series of tests and exams. Before starting the testing process, the physician will ask questions about the
DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATE CANCER Determining the presence of prostate cancer generally involves a series of tests and exams. Before starting the testing process, the physician will ask questions about the
The PLCO Trial Not a comparison of Screening vs no Screening
 PSA Screening: Science, Politics and Uncertainty David F. Penson, MD, MPH Hamilton and Howd Chair of Urologic Oncology Professor and Chair, Department of Urologic Surgery Director, Center for Surgical
PSA Screening: Science, Politics and Uncertainty David F. Penson, MD, MPH Hamilton and Howd Chair of Urologic Oncology Professor and Chair, Department of Urologic Surgery Director, Center for Surgical
2.0 Synopsis. Vicodin CR (ABT-712) M05-765 Clinical Study Report R&D/07/095. (For National Authority Use Only) to Part of Dossier: Volume:
 2.0 Synopsis Abbott Laboratories Name of Study Drug: Vicodin CR Name of Active Ingredient: Hydrocodone/Acetaminophen Extended Release (ABT-712) Individual Study Table Referring to Part of Dossier: Volume:
2.0 Synopsis Abbott Laboratories Name of Study Drug: Vicodin CR Name of Active Ingredient: Hydrocodone/Acetaminophen Extended Release (ABT-712) Individual Study Table Referring to Part of Dossier: Volume:
Considering a Hysterectomy?
 Considering a Hysterectomy? Learn more about virtually scarless surgery using da Vinci Single-Site technology { {Symptoms & Conditions: Chronic Pain, Heavy Bleeding, Fibroids, Endometriosis, Pelvic Prolapse
Considering a Hysterectomy? Learn more about virtually scarless surgery using da Vinci Single-Site technology { {Symptoms & Conditions: Chronic Pain, Heavy Bleeding, Fibroids, Endometriosis, Pelvic Prolapse
Update on Prostate Cancer: Screening, Diagnosis, and Treatment Making Sense of the Noise and Directions Forward
 Update on Prostate Cancer: Screening, Diagnosis, and Treatment Making Sense of the Noise and Directions Forward 33 rd Annual Internal Medicine Update December 5, 2015 Ryan C. Hedgepeth, MD, MS Chief of
Update on Prostate Cancer: Screening, Diagnosis, and Treatment Making Sense of the Noise and Directions Forward 33 rd Annual Internal Medicine Update December 5, 2015 Ryan C. Hedgepeth, MD, MS Chief of
Understanding Prostate Cancer. The Urology Group Guide for Newly Diagnosed Patients. Advanced Care. Improving Lives.
 Understanding Prostate Cancer The Urology Group Guide for Newly Diagnosed Patients Advanced Care. Improving Lives. UNDERSTANDING PROSTATE CANCER The Urology Group has created this publication to provide
Understanding Prostate Cancer The Urology Group Guide for Newly Diagnosed Patients Advanced Care. Improving Lives. UNDERSTANDING PROSTATE CANCER The Urology Group has created this publication to provide
Robotic Assisted Laparoscopic Salvage Prostatectomy for Radiation Resistant Prostate Cancer
 Robotic Assisted Laparoscopic Salvage Prostatectomy for Radiation Resistant Prostate Cancer Jonathan A. Eandi,* Brian A. Link, Rebecca A. Nelson, David Y. Josephson, Clayton Lau, Mark H. Kawachi and Timothy
Robotic Assisted Laparoscopic Salvage Prostatectomy for Radiation Resistant Prostate Cancer Jonathan A. Eandi,* Brian A. Link, Rebecca A. Nelson, David Y. Josephson, Clayton Lau, Mark H. Kawachi and Timothy
Advances In Spine Care. James D. Bruffey M.D. Scripps Clinic Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Section of Spinal Surgery
 Advances In Spine Care James D. Bruffey M.D. Scripps Clinic Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Section of Spinal Surgery Introduction The Spine - A common source of problems Back pain is the #2 presenting
Advances In Spine Care James D. Bruffey M.D. Scripps Clinic Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Section of Spinal Surgery Introduction The Spine - A common source of problems Back pain is the #2 presenting
Prostate Cancer What Are the Outcomes of Radical Prostatectomy for High-risk Prostate Cancer?
 Prostate Cancer What Are the Outcomes of Radical Prostatectomy for High-risk Prostate Cancer? Stacy Loeb, Edward M. Schaeffer, Bruce J. Trock, Jonathan I. Epstein, Elizabeth B. Humphreys, and Patrick C.
Prostate Cancer What Are the Outcomes of Radical Prostatectomy for High-risk Prostate Cancer? Stacy Loeb, Edward M. Schaeffer, Bruce J. Trock, Jonathan I. Epstein, Elizabeth B. Humphreys, and Patrick C.
Information sheet: Robotic-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy
 6 Pages, English Information sheet: Robotic-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy This information sheet is to provide you and your family with information regarding your treatment and recovery from
6 Pages, English Information sheet: Robotic-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy This information sheet is to provide you and your family with information regarding your treatment and recovery from
Screening for Prostate Cancer
 Screening for Prostate Cancer It is now clear that screening for Prostate Cancer discovers the disease at an earlier and more curable stage. It is not yet clear whether this translates into reduced mortality
Screening for Prostate Cancer It is now clear that screening for Prostate Cancer discovers the disease at an earlier and more curable stage. It is not yet clear whether this translates into reduced mortality
Oncological and functional outcomes of laparoscopic radical prostatectomy following fellowship training.
 Oncological and functional outcomes of laparoscopic radical prostatectomy following fellowship training. Journal: BJU International Manuscript ID: Draft Manuscript Type: Original Article Date Submitted
Oncological and functional outcomes of laparoscopic radical prostatectomy following fellowship training. Journal: BJU International Manuscript ID: Draft Manuscript Type: Original Article Date Submitted
4/8/13. Pre-test Audience Response. Prostate Cancer 2012. Screening and Treatment of Prostate Cancer: The 2013 Perspective
 Pre-test Audience Response Screening and Treatment of Prostate Cancer: The 2013 Perspective 1. I do not offer routine PSA screening, and the USPSTF D recommendation will not change my practice. 2. In light
Pre-test Audience Response Screening and Treatment of Prostate Cancer: The 2013 Perspective 1. I do not offer routine PSA screening, and the USPSTF D recommendation will not change my practice. 2. In light
Facing Lung Cancer? Learn why da Vinci Surgery may be your best treatment option for lung cancer.
 Facing Lung Cancer? Learn why da Vinci Surgery may be your best treatment option for lung cancer. The Condition: Lung Cancer The lung is the organ that moves oxygen through your body. You have two lungs
Facing Lung Cancer? Learn why da Vinci Surgery may be your best treatment option for lung cancer. The Condition: Lung Cancer The lung is the organ that moves oxygen through your body. You have two lungs
Combined Harvard Urologic Oncology Fellowship Program
 Combined Harvard Urologic Oncology Fellowship Program 1 Goal: Department of Urology To reduce the disease burden for patients with urologic issues by improving: Clinical Care Teaching Research 2 History
Combined Harvard Urologic Oncology Fellowship Program 1 Goal: Department of Urology To reduce the disease burden for patients with urologic issues by improving: Clinical Care Teaching Research 2 History
da Vinci Myomectomy Changing the Experience of Surgery Are you a candidate for the latest treatment option for uterine fibroids?
 da Vinci Myomectomy Changing the Experience of Surgery Are you a candidate for the latest treatment option for uterine fibroids? Your doctor may be able to offer you a new, minimally invasive surgical
da Vinci Myomectomy Changing the Experience of Surgery Are you a candidate for the latest treatment option for uterine fibroids? Your doctor may be able to offer you a new, minimally invasive surgical
Individual Prediction
 Individual Prediction Michael W. Kattan, Ph.D. Professor of Medicine, Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine of Case Western Reserve University Chairman, Department
Individual Prediction Michael W. Kattan, Ph.D. Professor of Medicine, Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine of Case Western Reserve University Chairman, Department
How To Perform Da Vinci Surgery
 Facing a Hysterectomy? If you ve been diagnosed with early stage gynecologic cancer, learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Early Stage Gynecologic Cancer A variety of gynecologic
Facing a Hysterectomy? If you ve been diagnosed with early stage gynecologic cancer, learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Early Stage Gynecologic Cancer A variety of gynecologic
Urinary Diversion: Ileovesicostomy/Ileal Loop/Colon Loop
 Urinary Diversion: Ileovesicostomy/Ileal Loop/Colon Loop Why do I need this surgery? A urinary diversion is a surgical procedure that is performed to allow urine to safely pass from the kidneys into a
Urinary Diversion: Ileovesicostomy/Ileal Loop/Colon Loop Why do I need this surgery? A urinary diversion is a surgical procedure that is performed to allow urine to safely pass from the kidneys into a
9/26/14. Joel E. Rand, MPAS, PA-C DMU Luncheon May 1, 2014
 Joel E. Rand, MPAS, PA-C DMU Luncheon May 1, 2014 No financial relationship or commercial interest in any of the technologies discussed Not supporting any non-fda off label uses of any product or service
Joel E. Rand, MPAS, PA-C DMU Luncheon May 1, 2014 No financial relationship or commercial interest in any of the technologies discussed Not supporting any non-fda off label uses of any product or service
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ABLATION THERAPY
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ABLATION THERAPY THE DIVISION OF VASCULAR/INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY THE ROBERT WOOD JOHNSON UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL Treatment options for patients with cancer continue to expand, providing
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ABLATION THERAPY THE DIVISION OF VASCULAR/INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY THE ROBERT WOOD JOHNSON UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL Treatment options for patients with cancer continue to expand, providing
Laparoscopic Repair of Hernias. A simple guide to help answer your questions
 Laparoscopic Repair of Hernias A simple guide to help answer your questions What is a hernia? A hernia is defined as a hole or defect in the abdominal (belly) wall. A hernia can either be congenital (a
Laparoscopic Repair of Hernias A simple guide to help answer your questions What is a hernia? A hernia is defined as a hole or defect in the abdominal (belly) wall. A hernia can either be congenital (a
Use Of Testosterone In Men With Prostate Cancer. Traditional view: T is dangerous for PCa
 Use Of Testosterone In Men With Prostate Cancer Abraham Morgentaler, MD, FACS Director, Men s s Health Boston Associate Clinical Professor of Urology Harvard Medical School Boston, USA Traditional view:
Use Of Testosterone In Men With Prostate Cancer Abraham Morgentaler, MD, FACS Director, Men s s Health Boston Associate Clinical Professor of Urology Harvard Medical School Boston, USA Traditional view:
PATIENT GUIDE. Localized Prostate Cancer
 PATIENT GUIDE Localized Prostate Cancer The prostate* is part of the male reproductive system. It is about the same size as a walnut and weighs about an ounce. As pictured in Figure 1, the prostate is
PATIENT GUIDE Localized Prostate Cancer The prostate* is part of the male reproductive system. It is about the same size as a walnut and weighs about an ounce. As pictured in Figure 1, the prostate is
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Considering Endometriosis Surgery? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery
 Considering Endometriosis Surgery? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Endometriosis Endometriosis is a condition in which the tissue that lines your uterus (the endometrium)
Considering Endometriosis Surgery? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Endometriosis Endometriosis is a condition in which the tissue that lines your uterus (the endometrium)
Laparoscopic Colectomy. What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery?
 Laparoscopic Colectomy What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery? Traditionally, colon & rectal surgery requires a large, abdominal and/or pelvic incision, which often requires a
Laparoscopic Colectomy What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery? Traditionally, colon & rectal surgery requires a large, abdominal and/or pelvic incision, which often requires a
Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing
 Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing for Prostate Cancer Patients Today s speaker is Manish Bhandari, MD Program moderator is Pam Barrett, Us TOO International Made possible by
Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing for Prostate Cancer Patients Today s speaker is Manish Bhandari, MD Program moderator is Pam Barrett, Us TOO International Made possible by
A918: Prostate: adenocarcinoma
 A918: Prostate: adenocarcinoma General facts of prostate cancer The prostate is about the size of a walnut. It is just below the bladder and in front of the rectum. The tube that carries urine (the urethra)
A918: Prostate: adenocarcinoma General facts of prostate cancer The prostate is about the size of a walnut. It is just below the bladder and in front of the rectum. The tube that carries urine (the urethra)
Prostate cancer screening. It s YOUR decision!
 Prostate cancer screening It s YOUR decision! For many years now, a test has been available to screen for. The test is called the prostate-specific antigen blood test (or PSA test). It is used in combination
Prostate cancer screening It s YOUR decision! For many years now, a test has been available to screen for. The test is called the prostate-specific antigen blood test (or PSA test). It is used in combination
male sexual dysfunction
 male sexual dysfunction lack of desire Both men and women often lose interest in sex during cancer treatment, at least for a time. At first, concern for survival is so overwhelming that sex is far down
male sexual dysfunction lack of desire Both men and women often lose interest in sex during cancer treatment, at least for a time. At first, concern for survival is so overwhelming that sex is far down
