Ureteral Stent Insertion in the Management of Renal Colic during Pregnancy
|
|
|
- Oswald Young
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article Ureteral Stent Insertion in the Management of Renal Colic during Pregnancy Chang Il Choi, Young Dong Yu, and Dong Soo Park* Department of Urology, CHA University Medical School, Seongnam, Korea To determine an optimal invasive intervention for renal colic patients during pregnancy after conservative treatments have been found to be unhelpful. Among the available invasive interventions, we investigated the reliability of a ureteral stent insertion, which is considered the least invasive intervention during pregnancy. Between June 2006 and February 2015, a total of 826 pregnant patients came to the emergency room or urology outpatient department, and 39 of these patients had renal colic. The mean patient age was years. In this retrospective cohort study, the charts of the patients were reviewed to collect data that included age, symptoms, the lateralities and locations of urolithiasis, trimester, pain following treatment and pregnancy complications. Based on ultrasonography diagnoses, 13 patients had urolithiasis, and 13 patients had hydronephrosis without definite echogenicity of the ureteral calculi. Conservative treatments were successful in 25 patients. Among these treatments, antibiotics were used in 15 patients, and the remaining patients received only hydration and analgesics without antibiotics. Several urological interventions were required in 14 patients. The most common intervention was ureteral stent insertion, which was performed in 13 patients to treat hydronephrosis or urolithiasis. The patients pain was relieved following these interventions. Only one patient received percutaneous nephrostomy due to pyonephrosis. No pregnancy complications were noted. is regarded as a reliable and stable first-line urological intervention for pregnant patients with renal colic following conservative treatments. has been found to be equally effective and safe as percutaneous nephrostomy, which is associated with complications that include bleeding and dislocation, and the inconvenience of using external drainage system. Key Words: Urinary catheters; Renal colic; Hydronephrosis; Urolithiasis; Pregnancy This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Article History: Received January 11, 2016 Revised January 29, 2016 Accepted February 15, 2016 Corresponding Author: Dong Soo Park Department of Urology, CHA University Medical School, 59 Yatap-ro, Bundang-gu, Seongnam 13496, Korea Tel: Fax: dsparkmd@cha.ac.kr INTRODUCTION Unlike the abdominal discomfort that is frequently observed during pregnancy, renal colic while often infrequent during pregnancy is potentially dangerous because it can lead to hospitalization and adverse effects for both the mother and the fetus. 1 One of the main causes of renal colic is urolithiasis. 2,3 The incidence of symptomatic urolithiasis during pregnancy varies widely from 1/200 to 1/2,000 women, and this incidence is not different from the incidence that has been reported in the non-pregnant female population of reproductive age. 4 The occurrence of a urolithiasis during pregnancy is a risk to both the mother and fetus and may be a contributing factor in premature birth. 5,6 Furthermore, normal anatomic changes within the urinary tract of the pregnant patient may not only predispose the patient to urolithiasis formation but may also pose a diagnostic challenge. Physiologic hydronephrosis can occur in 90% of right kidneys and up to 67% of left kidneys during pregnancy. 7 The predominance of right upper tract dilation compared to that of the left may be caused by a combination of various factors that include the preferential compression of the right ureter due to uterine dextro- C Chonnam Medical Journal, Chonnam Med J 2016;52:
2 Ureteral Stenting to Renal Colic in Pregnancy rotation and the protection of the left ureter by the gas-filled sigmoid colon. 8 Regarding the treatment of renal colic during pregnancy, conservative management results in spontaneous calculi passage in approximately 70-80% of pregnant women. 9,10 In cases in which invasive interventions are required, ureteral stent insertion and percutaneous nephrostomy (PCN) are preferred and less invasive interventions. Ureteroscopic stone removal is also occasionally performed. In this study, the reliability and stability of ureteral stent insertions in pregnant patients with renal colic following unsuccessful conservative treatments were analyzed. MATERIALS AND METHODS Between June 2006 and February 2015, a total of 826 pregnant patients came to emergency room and urology outpatient department. Of these patients, 39 patients had renal colic. In this retrospective cohort study, the charts of the patients were reviewed to collect data that included age, symptoms, the laterality of renal colic, sizes and locations of urolithiasis, trimester of diagnosis, pain after treatment and pregnancy complications. The pregnancy complications included preterm labor, preterm premature membrane rupture, and pre-eclampsia. The diagnoses of urolithiasis in the pregnant women were based on the clinical presentation, the presence of microscopic hematuria on urinalysis and transabdominal ultrasonography. Cases with demonstrable hydronephrosis and no evidence of calculi were classified as having renal colic attributable to physiological hydronephrosis consistent with pregnancy. Microscopic hematuria was defined as >5 red blood cells/high power field (RBCs/HPF), and pyuria was diagnosed when >5 white blood cells/high power field (WBCs/HPF) were observed. included observation with hydration or analgesics and antibiotics when bacterial infections were present. The urological interventions included ureteral stent insertion, PCN, and ureteroscopic stone removal and were considered when renal colic resistant to pharmacological treatment, sepsis, or obstruction of a solitary kidney were present. The follow-up information included the outcome for the infant and the additional procedures that were required after the initial procedures. Research involving human subjects that is reported in the manuscript must have been performed with the approval of an appropriate ethics committee in compliance with the Helsinki Declaration. Moreover, written informed consent for participation in the study was obtained from all participants. RESULTS Of the total thirty-nine patients with renal colic, twenty-seven patients (74.4%) were in the second trimester, four (10.2%) were in the first trimester, and eight patients (20.4%) were in the third trimester. The mean patient age at presentation was 30.49±3.24 years. Twenty-five renal colic patients (64.1%) had right-sided colic, and fourteen patients (35.9%) had left-sided colic. The clinical features included gross hematuria in six patients (15.4%), fever in five patients (12.8%), and increased urinary frequency in one patient (2.56%). The laboratory tests revealed microscopic hematuria in ten patients (25.6%) and pyuria in twelve patients (30.8%). Asymptomatic urinary tract infections were found in eight patients (20.5%), and pyelonephritis was observed in seven patients (17.9%). One patient (2.56%) had only one kidney (Table 1). Based on ultrasonography results, thirteen patients (33.3%) were diagnosed with urolithiasis, and thirteen patients (33.3%) were diagnosed with hydronephrosis without definite echogenicity of ureteral calculi using ultrasonography. Among the patients with urolithiasis, the sizes of the calculi varied from 2 mm to 10 mm (mean: 5.2 mm). Regarding their locations, distal ureteral calculi were observed in seven patients, proximal ureteral calculi were found in six patients, and nephrolithiases were observed in three patients. One patient had proximal ureteral and renal calculi, and another single patient had proximal ureteral, distal ureteral and renal calculi (Fig. 1). Management was initially conservative for all patients. Twenty-five patients (64.1%) were successfully treated TABLE 1. Clinical presentation in renal colic during pregnancy Trimester First 4 (10.2%) Second 27 (74.4%) Third 8 (20.4%) Laterality Right 25 (64.1%) Left 14 (35.9%) Accompanied symptoms and signs Gross hematuria 6 (15.4%) Fever 5 (12.8%) Urinary frequency 1 (2.56%) Microscopic hematuria 10 (25.6%) Pyuria 12 (30.8%) Asymptomatic urinary tract infection 8 (20.5%) Pyelonephritis 7 (17.9%) Patient with solitary kidney 1 (2.56%) 124
3 Chang Il Choi, et al FIG. 1. Diagnosis by transabdominal ultrasonography during pregnancy. (A) Two kidney stones, (B) A proximal ureteral calculus at the ureteropelvic junction, (C) A distal ureteral calculus at the ureterovesical junction, (D) Hydronephrosis without definite echogenicity of ureteral calculi in ultrasonography. TABLE 2. Diagnosis and Treatment of renal colic during pregnancy Diagnosis Urolithiasis Hydronephrosis Without diagnosed by ultrasonography Treatment only With antibiotics Without antibiotics Invasive intervention Percutaneous nephrostomy 15 (38.5%) 10 (25.6%) 1 (2.56%) with conservative management. included hydration, and analgesics and antibiotics to treat bacterial infections. Among these management strategies, antibiotics were used in fifteen patients (38.5%), and the remaining patients received only hydration and analgesics. Another fourteen patients (35.9%) required urological interventions due to persistent pain, prolonged infection, hydronephrosis, and urolithiasis. The most common intervention was ureteral stent insertion, which was performed TABLE 3. Treatment of renal colic in gestational trimesters Trimester First (n=4) Second (n=27) PCN Third (n=8) 4 (100%) 18 (66.7%) 8 (29.6%) 1 (3.7%) 3 (37.5%) 5 (62.5%) PCN: percutaneous nephrostomy. in thirteen patients (33.3%) to treat hydronephrosis or urolithiasis. All of the patients pain was relieved following the interventions. Only one patient (2.56%) underwent PCN due to pyonephrosis (Table 2). We divided renal colic patients by gestational trimesters at presentation. The diagnosis was four patients (10.3%) in the first trimester, twenty-seven patients (69.2%) in the second trimester, and eight patients (20.5%) in the third trimester. All the renal colic patients in the first trimester were successfully managed with conservative management. Among the twenty-seven patients in the second trimester, 125
4 Ureteral Stenting to Renal Colic in Pregnancy eighteen patients were successfully treated with conservative management. was perfomed in eight patients and the remaining patient was managed by PCN. Of the eight patients in the third trimester, three patients were completely relieved with conservative management and five patients were treated by ureteral stent insertion (Table 3). None of the patients underwent ureteroscopic stone removal or open surgery. No pregnancy complication was noted in any of the patients, and all of the fetuses were delivered without complications. DISCUSSION The diagnosis of renal colic in pregnancy is based on clinical symptoms and findings from radiographic imaging modalities. The use of imaging to investigate conditions such as urolithiasis or hydronephrosis in pregnant women remains controversial due to the potential teratogenic, carcinogenic, and mutagenic risks to the fetuses. Computed tomography exposes the fetus a momentous radiation dose. Single-shot intravenous pyelography involves the acquisition of a single radiograph 30 minutes after the introduction of contrast medium and is considered to be confirmatory in up to 96% of patients. 11 A series of intravenous urography procedures delivers the fetus to a mean radiation dose of 1.7 mgy and a maximal dose of 10 mgy. In contrary, a single X-ray exposes the fetus to a mean radiation dose of 1.4 mgy and a maximal dose of 4.2 mgy. 2 Therefore, before deciding to choose a suitable imaging modality, pregnant women should be provided with detailed cautions about the teratogenic, carcinogenic, and mutagenic risks to the fetuses which are associated with each imaging technique. Transabdominal ultrasonography is considered to be the imaging method of choice for routine evaluations of renal colic in pregnant women because it has no risk of radiation exposure. Moreover, in the diagnosis of urolithiasis, transabdominal ultrasonography has an appropriate sensitivity and specificity of 34% and 86% The management of renal colic during pregnancy is principally conservative. Approximately 70-80% of women with symptomatic hydronephrosis or urolithiasis during pregnancy are sufficiently treated with hydration, analgesics and antibiotics. Additional further medical treatments are needed in 20-30% of women. Those therapeutic procedures are epidural block for pain relief and the use of beta-adrenoreceptor blockers. 5 Beta-adrenoreceptor blockers are thought to stimulate the contractility of the renal pelvis and ureter and thus increase the urine flow rate and assist in the spontaneous expulsion of urolithiasis. 6 The indications for invasive treatment are the severe pain which is resistant to pharmacological treatment, sepsis, and obstruction in a solitary kidney. In pregnant women, ureteral stent insertion and PCN have been used to treat renal colic because these techniques are minimally invasive and are used as the gold standard for the surgical treatment of renal colic in pregnancy. These techniques also have the advantage that they can be performed under local anesthesia. The goal of treatment is to relieve the obstruction and prevent further regression in renal function. PCN is very effective, but is associated with complications that include bleeding and the inconvenience of draining externally. In pregnancy, ureteral stent insertion can be performed through ureteroscopy and the location of the ureteral stent could be confirmed by ultrasonography. is as effective as PCN and considered to be a safe and effective first-line intervention for later stage pregnant patients with hydronephrosis or urolithiasis. 15 Both ureteral stent and PCN therapies should be exchanged periodically to avoid incrustation. Additionally, ureteroscopic stone removal during pregnancy is a safe procedure that can be performed with a rigid, semi-rigid, or flexible instrument. 16 Ureteroscopic stone removal, on the other hand, typically requires general anesthesia and has the possibility of ureteral perforation and sepsis. Ureteroscopic stone removal should be avoided during the third trimester due to the anatomical changes in the bladder that are secondary to compression by the gravid uterus. 17 Johnson et al. 18 and Lifshitz and Lingeman 19 found no statistically significant risk factors for the development of an obstetric complication following ureteroscopic stone removal during pregnancy. During pregnancy, percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) is not advised, nonetheless there have been two case reports which informed successful PCNLs in early pregnancy. 20,21 Extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy is contraindicated in pregnant patients due to the effects of the shockwave on the fetus, which can cause a miscarriage. 22 In this study, we mainly considered which surgical intervention could avoid the most side effects when pain is not resolved by conservative management. Although both ureteral stent insertion and PCN were known as safe interventions, we performed ureteral stent insertion mainly to avoid bleeding and the inconvenience of using external drainage. Thirteen patients were treated by ureteral stent insertion and their treatments were successful. There were no pregnancy complications and all of the fetuses were delivered without any complications. Consequently, this study could suggest ureteral stent insertion as the most effective and safe treatment in renal colic during pregnancy without leading to complications. Further prospective studies with a follow-up are needed to compare the distinctions between ureteral stent insertion and PCN. is considered to be a reliable and stable first-line urological intervention for pregnant patients with renal colic following the failure of conservative treatment. is equally effective and safe with PCN which is associated with complications that include bleeding and the inconvenience of using an external drainage system. Therefore, ureteral stent insertion 126
5 Chang Il Choi, et al is considered to be a first-line intervention for pregnant renal colic patients when pain is not resolved by conservative management. CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT None declared. REFERENCES 1. Andreoiu M, MacMahon R. Renal colic in pregnancy: lithiasis or physiological hydronephrosis? Urology 2009;74: Srirangam SJ, Hickerton B, Van Cleynenbreugel B. Management of urinary calculi in pregnancy: a review. J Endourol 2008;22: Wayment RO, Schwartz BF. Pregnancy and Urolithiasis [Internet]. USA: Emedicine; c2009 [Updated 2015 Apr 17; Cited 2014 Nov 19]. Available from: 4. Gorton E, Whitfield HN. Renal calculi in pregnancy. Br J Urol 1997;80 Suppl 1: Biyani CS, Joyce AD. Urolithiasis in pregnancy. II: management. BJU Int 2002;89: Charalambous S, Fotas A, Rizk DE. Urolithiasis in pregnancy. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct 2009;20: Peake SL, Roxburgh HB, Langlois SL. Ultrasonic assessment of hydronephrosis of pregnancy. Radiology 1983;146: Roberts JA. Hydronephrosis of pregnancy. Urology 1976;8: Hendricks SK, Ross SO, Krieger JN. An algorithm for diagnosis and therapy of management and complications of urolithiasis during pregnancy. Surg Gynecol Obstet 1991;172: Juan YS, Wu WJ, Chuang SM, Wang CJ, Shen JT, Long CY, et al. Management of symptomatic urolithiasis during pregnancy. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 2007;23: Butler EL, Cox SM, Eberts EG, Cunningham FG. Symptomatic nephrolithiasis complicating pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol 2000; 96: Patel SJ, Reede DL, Katz DS, Subramaniam R, Amorosa JK. Imaging the pregnant patient for nonobstetric conditions: algorithms and radiation dose considerations. Radiographics 2007; 27: Swanson SK, Heilman RL, Eversman WG. Urinary tract stones in pregnancy. Surg Clin North Am 1995;75: Dhar M, Denstedt JD. Imaging in diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of stone patients. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 2009;16: Evans HJ, Wollin TA. The management of urinary calculi in pregnancy. Curr Opin Urol 2001;11: Scarpa RM, De Lisa A, Usai E. Diagnosis and treatment of ureteral calculi during pregnancy with rigid ureteroscopes. J Urol 1996;155: Travassos M, Amselem I, Filho NS, Miguel M, Sakai A, Consolmagno H, et al. Ureteroscopy in pregnant women for ureteral stone. J Endourol 2009;23: Johnson EB, Krambeck AE, White WM, Hyams E, Beddies J, Marien T, et al. Obstetric complications of ureteroscopy during pregnancy. J Urol 2012;188: Lifshitz DA, Lingeman JE. Ureteroscopy as a first-line intervention for ureteral calculi in pregnancy. J Endourol 2002;16: Shah A, Chandak P, Tiptaft R, Glass J, Dasgupta P. Percutaneous nephrolithotomy in early pregnancy. Int J Clin Pract 2004;58: Tóth C, Tóth G, Varga A, Flaskó T, Salah MA. Percutaneous nephrolithotomy in early pregnancy. Int Urol Nephrol 2005; 37: Streem SB. Contemporary clinical practice of shock wave lithotripsy: a reevaluation of contraindications. J Urol 1997;157:
URETEROSCOPY (AND TREATMENT OF KIDNEY STONES)
 URETEROSCOPY (AND TREATMENT OF KIDNEY STONES) AN INFORMATION LEAFLET Written by: Department of Urology May 2011 Stockport: 0161 419 5698 Website: w w w. s t o c k p o r t. n h s. u k Tameside: 0161 922
URETEROSCOPY (AND TREATMENT OF KIDNEY STONES) AN INFORMATION LEAFLET Written by: Department of Urology May 2011 Stockport: 0161 419 5698 Website: w w w. s t o c k p o r t. n h s. u k Tameside: 0161 922
Ureteroscopy with Laser Lithotripsy
 Ureteroscopy with Laser Lithotripsy Introduction Kidney stones are fairly common. Although kidney stones can be very painful, they are treatable, and in many cases preventable. Your doctor may recommend
Ureteroscopy with Laser Lithotripsy Introduction Kidney stones are fairly common. Although kidney stones can be very painful, they are treatable, and in many cases preventable. Your doctor may recommend
NEPHROLITHIASIS Diagnosis & Treatment
 Learning Objectives NEPHROLITHIASIS Diagnosis & Treatment Jai Radhakrishnan, MD, MS Professor of Clinical Medicine Columbia University Management of the first episode of renal colic: Optimal Imaging Treatment
Learning Objectives NEPHROLITHIASIS Diagnosis & Treatment Jai Radhakrishnan, MD, MS Professor of Clinical Medicine Columbia University Management of the first episode of renal colic: Optimal Imaging Treatment
Evaluation and Follow-up of Fetal Hydronephrosis
 Evaluation and Follow-up of Fetal Hydronephrosis Deborah M. Feldman, MD, Marvalyn DeCambre, MD, Erin Kong, Adam Borgida, MD, Mujgan Jamil, MBBS, Patrick McKenna, MD, James F. X. Egan, MD Objective. To
Evaluation and Follow-up of Fetal Hydronephrosis Deborah M. Feldman, MD, Marvalyn DeCambre, MD, Erin Kong, Adam Borgida, MD, Mujgan Jamil, MBBS, Patrick McKenna, MD, James F. X. Egan, MD Objective. To
Urolithiasis/Endourology
 Urolithiasis/Endourology Use of Ureteral Stent in Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy for Upper Urinary Calculi: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Shen Pengfei, Jiang Min, Yang Jie, Li Xiong, Li
Urolithiasis/Endourology Use of Ureteral Stent in Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy for Upper Urinary Calculi: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Shen Pengfei, Jiang Min, Yang Jie, Li Xiong, Li
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones. Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke
 Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
surg urin Surgery: Urinary System 1
 Surgery: Urinary System 1 This section contains information to assist providers in billing for surgical procedures related to the urinary system. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy Medi-Cal covers Extracorporeal
Surgery: Urinary System 1 This section contains information to assist providers in billing for surgical procedures related to the urinary system. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy Medi-Cal covers Extracorporeal
Medical Malpractice in Endourology: Analysis of Closed Cases From the State of New York
 Medical Malpractice in Endourology: Analysis of Closed Cases From the State of New York Brian Duty,* Zhamshid Okhunov, Zeph Okeke and Arthur Smith From the Department of Urology, North Shore-Long Island
Medical Malpractice in Endourology: Analysis of Closed Cases From the State of New York Brian Duty,* Zhamshid Okhunov, Zeph Okeke and Arthur Smith From the Department of Urology, North Shore-Long Island
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
Kidney Stones. This reference summary will help you understand kidney stones and how to treat and prevent them. Kidney
 Introduction A kidney stone is a solid piece of material that forms in the kidney from substances in the urine. Kidney stones are fairly common. Although kidney stones can be painful, they are treatable.
Introduction A kidney stone is a solid piece of material that forms in the kidney from substances in the urine. Kidney stones are fairly common. Although kidney stones can be painful, they are treatable.
Bladder Injury during Cesarean Section: A Case Control Study for 10 Years
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol., No., September Bladder Injury during Cesarean Section: A Case Control Study for Years Mesfer Al-Shahrani, MD, FRCSC* Objective: To determine the incidence, risk factors
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol., No., September Bladder Injury during Cesarean Section: A Case Control Study for Years Mesfer Al-Shahrani, MD, FRCSC* Objective: To determine the incidence, risk factors
Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy
 Scan for mobile link. Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy Ureteral stenting and nephrostomy help restore urine flow through blocked ureters and return the kidney to normal function. Ureters are long, narrow
Scan for mobile link. Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy Ureteral stenting and nephrostomy help restore urine flow through blocked ureters and return the kidney to normal function. Ureters are long, narrow
Patient. Frequently Asked Questions. Transvaginal Surgical Mesh for Pelvic Organ Prolapse
 Patient Frequently Asked Questions Transvaginal Surgical Mesh for Pelvic Organ Prolapse Frequently Asked Questions WHAT IS PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE AND HOW IS IT TREATED? Q: What is pelvic organ prolapse
Patient Frequently Asked Questions Transvaginal Surgical Mesh for Pelvic Organ Prolapse Frequently Asked Questions WHAT IS PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE AND HOW IS IT TREATED? Q: What is pelvic organ prolapse
Recurrent Kidney Stones
 Recurrent Kidney Stones Sean A. Pierre, MD; and Darren T. Beiko, MD, FRCSC As presented at the College of Canadian Family Physicians Annual Family Medicine Forum, Toronto, Ontario. Family physicians are
Recurrent Kidney Stones Sean A. Pierre, MD; and Darren T. Beiko, MD, FRCSC As presented at the College of Canadian Family Physicians Annual Family Medicine Forum, Toronto, Ontario. Family physicians are
Diclofenac versus Tramadol in the Treatment of Renal Colic: A Prospective, Randomized Trial
 The Open Emergency Medicine Journal, 2011, 4, 9-13 9 Open Access Diclofenac versus Tramadol in the Treatment of Renal Colic: A Prospective, Randomized Trial Shaden Salameh*,1, Nurit Hiller 2, Meir Antopolsky
The Open Emergency Medicine Journal, 2011, 4, 9-13 9 Open Access Diclofenac versus Tramadol in the Treatment of Renal Colic: A Prospective, Randomized Trial Shaden Salameh*,1, Nurit Hiller 2, Meir Antopolsky
Renal Cysts What should I do now?
 Renal Cysts What should I do now? Dr Edmund Chiong Asst. Professor & Consultant Department of Urology National University Hospital What are renal cysts? Fluid-filled structures in the kidney that are not
Renal Cysts What should I do now? Dr Edmund Chiong Asst. Professor & Consultant Department of Urology National University Hospital What are renal cysts? Fluid-filled structures in the kidney that are not
Blood in the urine (hematuria)
 Blood in the urine (hematuria) Hematuria refers to the presence of blood in the urine. It is important to investigate the cause of hematuria because rarely, it is caused by a serious condition, such as
Blood in the urine (hematuria) Hematuria refers to the presence of blood in the urine. It is important to investigate the cause of hematuria because rarely, it is caused by a serious condition, such as
Squamous cell carcinoma located in the renal caliceal system: A case report and review of the literature
 Turkish Journal of Cancer Vol.32/ No. 1/2002 Squamous cell carcinoma located in the renal caliceal system: A case report and review of the literature AYHAN KARABULUT 1, LEVENT EMİR 1, MEHMET GÖNÜLTAŞ 2,
Turkish Journal of Cancer Vol.32/ No. 1/2002 Squamous cell carcinoma located in the renal caliceal system: A case report and review of the literature AYHAN KARABULUT 1, LEVENT EMİR 1, MEHMET GÖNÜLTAŞ 2,
Sonographic Diagnosis of Ureteral Tumors
 Sonographic Diagnosis of Ureteral Tumors Irith Hadas-Halpern, MD, micur Farkas, MD, Michael Patlas, MD, Ibrahim Zaghal, MD, Shoshana Sabag-Gottschalk, MD, Drora Fisher, MD We present our experience with
Sonographic Diagnosis of Ureteral Tumors Irith Hadas-Halpern, MD, micur Farkas, MD, Michael Patlas, MD, Ibrahim Zaghal, MD, Shoshana Sabag-Gottschalk, MD, Drora Fisher, MD We present our experience with
Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package. Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula
 Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula Early detection and treatment If a woman has recently survived a
Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula Early detection and treatment If a woman has recently survived a
MODULE 6: KIDNEY STONES
 MODULE 6: KIDNEY STONES KEYWORDS: Nephrolithiasis, urinary stones, kidney, calciuria, oxaluria LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this clerkship, the medical student will be able to: 1. List risk factors
MODULE 6: KIDNEY STONES KEYWORDS: Nephrolithiasis, urinary stones, kidney, calciuria, oxaluria LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this clerkship, the medical student will be able to: 1. List risk factors
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma)
 Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Effects of Pregnancy & Delivery on Pelvic Floor
 Effects of Pregnancy & Delivery on Pelvic Floor 吳 銘 斌 M.D., Ph.D. 財 團 法 人 奇 美 醫 院 婦 產 部 婦 女 泌 尿 暨 骨 盆 醫 學 科 ; 台 北 醫 學 大 學 醫 學 院 婦 產 學 科 ; 古 都 府 城 台 南 Introduction Pelvic floor disorders (PFDs) include
Effects of Pregnancy & Delivery on Pelvic Floor 吳 銘 斌 M.D., Ph.D. 財 團 法 人 奇 美 醫 院 婦 產 部 婦 女 泌 尿 暨 骨 盆 醫 學 科 ; 台 北 醫 學 大 學 醫 學 院 婦 產 學 科 ; 古 都 府 城 台 南 Introduction Pelvic floor disorders (PFDs) include
Percutaneous Abscess Drainage
 Scan for mobile link. Percutaneous Abscess Drainage An abscess is an infected fluid collection within the body. Percutaneous abscess drainage uses imaging guidance to place a thin needle through the skin
Scan for mobile link. Percutaneous Abscess Drainage An abscess is an infected fluid collection within the body. Percutaneous abscess drainage uses imaging guidance to place a thin needle through the skin
Migration of an intrauterine contraceptive device to the sigmoid colon: a case report
 The European Journal of Contraception and Reproductive Health Care 2003;8:229 232 Case Report Migration of an intrauterine contraceptive device to the sigmoid colon: a case report Ü. S. nceboz, H. T. Özçakir,
The European Journal of Contraception and Reproductive Health Care 2003;8:229 232 Case Report Migration of an intrauterine contraceptive device to the sigmoid colon: a case report Ü. S. nceboz, H. T. Özçakir,
X-ray (Radiography) - Abdomen
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Abdomen Abdominal x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the abdominal cavity. It is used to evaluate the stomach,
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Abdomen Abdominal x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the abdominal cavity. It is used to evaluate the stomach,
US for Detecting Renal Calculi with Nonenhanced CT as a Reference Standard 1
 Genitourinary Imaging Keir A. B. Fowler, MD Julie A. Locken, MD Joshua H. Duchesne Michael R. Williamson, MD Index terms: Kidney, calculi, 811.811, 813.811 Kidney, CT, 81.12111, 81.12115 Kidney, US, 81.1298
Genitourinary Imaging Keir A. B. Fowler, MD Julie A. Locken, MD Joshua H. Duchesne Michael R. Williamson, MD Index terms: Kidney, calculi, 811.811, 813.811 Kidney, CT, 81.12111, 81.12115 Kidney, US, 81.1298
GENTLY DOES IT. Stonemanagement
 GENTLY DOES IT Kidney and ureteral stone retrieval by Sur-catch NT Basket from Olympus Stonemanagement content Content... 2 Introduction... 3 The Disease... 4-5 Causes... 5 Prevention... 6 Symptoms...
GENTLY DOES IT Kidney and ureteral stone retrieval by Sur-catch NT Basket from Olympus Stonemanagement content Content... 2 Introduction... 3 The Disease... 4-5 Causes... 5 Prevention... 6 Symptoms...
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Preparing for your laparoscopic pyeloplasty
 Preparing for your laparoscopic pyeloplasty Welcome We look forward to welcoming you to The Royal London Hospital. You have been referred to us for a laparoscopic pyeloplasty, which is an operation using
Preparing for your laparoscopic pyeloplasty Welcome We look forward to welcoming you to The Royal London Hospital. You have been referred to us for a laparoscopic pyeloplasty, which is an operation using
Prognosis of Very Large First-Trimester Hematomas
 Case Series Prognosis of Very Large First-Trimester Hematomas Juliana Leite, MD, Pamela Ross, RDMS, RDCS, A. Cristina Rossi, MD, Philippe Jeanty, MD, PhD Objective. The aim of this study was to evaluate
Case Series Prognosis of Very Large First-Trimester Hematomas Juliana Leite, MD, Pamela Ross, RDMS, RDCS, A. Cristina Rossi, MD, Philippe Jeanty, MD, PhD Objective. The aim of this study was to evaluate
THE KIDNEY. Bulb of penis Abdominal aorta Scrotum Adrenal gland Inferior vena cava Urethra Corona glandis. Kidney. Glans penis Testicular vein
 29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
Kidney Stones removal Without surgery
 Patient Education Service Lithotripsy - The world s latest treatment for Kidney Stones removal Without surgery With COMPUTERISED high tech DIREX LITHOTRIPTER Experience counts PIONEERS in North INDIA -
Patient Education Service Lithotripsy - The world s latest treatment for Kidney Stones removal Without surgery With COMPUTERISED high tech DIREX LITHOTRIPTER Experience counts PIONEERS in North INDIA -
X-Plain Kidney Stones Reference Summary
 X-Plain Kidney Stones Reference Summary Introduction Kidney stones are fairly common. Although they can be very painful, they are treatable, and in many cases preventable. This reference summary will help
X-Plain Kidney Stones Reference Summary Introduction Kidney stones are fairly common. Although they can be very painful, they are treatable, and in many cases preventable. This reference summary will help
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN Reviewed by Finnish Centre for Health Promotion Publisher: Ylioppilaiden terveydenhoitosäätiö Töölönkatu 37 A 00260 Helsinki Orders: julkaisutilaukset@yths.fi Author:
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN Reviewed by Finnish Centre for Health Promotion Publisher: Ylioppilaiden terveydenhoitosäätiö Töölönkatu 37 A 00260 Helsinki Orders: julkaisutilaukset@yths.fi Author:
NICE Pathways bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic.
 Initial assessment and investigation of urinary incontinence bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used
Initial assessment and investigation of urinary incontinence bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used
University College Hospital at Westmoreland Street. Lithotripsy. Urology Directorate
 University College Hospital at Westmoreland Street Lithotripsy Urology Directorate 2 3 If you require a large print, audio or translated version of this leaflet, please contact us on 020 3447 9179. We
University College Hospital at Westmoreland Street Lithotripsy Urology Directorate 2 3 If you require a large print, audio or translated version of this leaflet, please contact us on 020 3447 9179. We
thirteen, it was more marked and here one could see a certain degree of beading along the lines which radiated out from the calyx.
 CONGENITAL CYSTIC DILATATION OF THE RENAL COLLECTING TUBULES A NEW DISEASE ENTITY* VINCENT VERMOOTEN** In 1943, while I was in the U. S. Army, a young soldier was referred to me because of gross, painless,
CONGENITAL CYSTIC DILATATION OF THE RENAL COLLECTING TUBULES A NEW DISEASE ENTITY* VINCENT VERMOOTEN** In 1943, while I was in the U. S. Army, a young soldier was referred to me because of gross, painless,
TRANSVAGINAL MESH IN PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE REPAIR.
 TRANSVAGINAL MESH IN PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE REPAIR. Spanish full text SUMMARY Introduction: Pelvic organ prolapse (POP) is characterised by the descent or herniation of the uterus, vaginal vault, bladder
TRANSVAGINAL MESH IN PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE REPAIR. Spanish full text SUMMARY Introduction: Pelvic organ prolapse (POP) is characterised by the descent or herniation of the uterus, vaginal vault, bladder
Effectiveness of Day-case Surgery in Urology: Single Surgeon Experience
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin 29, No. 3, September 2007 Effectiveness of Day-case Surgery in Urology: Single Surgeon Experience Mohamed H. Durazi, FRCS ED, FRCSI* Reem Al-Bareeq, MRCSI, CAB(Urol)** Mohamed
Bahrain Medical Bulletin 29, No. 3, September 2007 Effectiveness of Day-case Surgery in Urology: Single Surgeon Experience Mohamed H. Durazi, FRCS ED, FRCSI* Reem Al-Bareeq, MRCSI, CAB(Urol)** Mohamed
CHLAMYDIA SCREENING IN WOMEN
 CHLAMYDIA SCREENING IN WOMEN APPLICATIONS OBJECTIVE Purpose of Measure: ELIGIBLE POPULATION Which members are included? STANDARD OF CARE What screening should be done? NCQA ACCEPTED CODES DOCUMENTATION
CHLAMYDIA SCREENING IN WOMEN APPLICATIONS OBJECTIVE Purpose of Measure: ELIGIBLE POPULATION Which members are included? STANDARD OF CARE What screening should be done? NCQA ACCEPTED CODES DOCUMENTATION
Urinary Diversion: Ileovesicostomy/Ileal Loop/Colon Loop
 Urinary Diversion: Ileovesicostomy/Ileal Loop/Colon Loop Why do I need this surgery? A urinary diversion is a surgical procedure that is performed to allow urine to safely pass from the kidneys into a
Urinary Diversion: Ileovesicostomy/Ileal Loop/Colon Loop Why do I need this surgery? A urinary diversion is a surgical procedure that is performed to allow urine to safely pass from the kidneys into a
CHAPTER 5 PELVIC FRACTURES AND CRUSH INJURIES OF THE BLADDER 113
 PELVIC FRACTURES AND CRUSH INJURIES OF THE BLADDER 113 CHAPTER 5 PELVIC FRACTURES AND CRUSH INJURIES OF THE BLADDER GU Tract Ch 2 Ch 3 Ch 4,5 Ch 6,7,8,11 Ch 8,9 Ch 8,9 Ch 8,10 Structure Kidney Ureter Bladder
PELVIC FRACTURES AND CRUSH INJURIES OF THE BLADDER 113 CHAPTER 5 PELVIC FRACTURES AND CRUSH INJURIES OF THE BLADDER GU Tract Ch 2 Ch 3 Ch 4,5 Ch 6,7,8,11 Ch 8,9 Ch 8,9 Ch 8,10 Structure Kidney Ureter Bladder
Get the Facts, Be Informed, Make YOUR Best Decision. Pelvic Organ Prolapse
 Pelvic Organ Prolapse ETHICON Women s Health & Urology, a division of ETHICON, INC., a Johnson & Johnson company, is dedicated to providing innovative solutions for common women s health problems and to
Pelvic Organ Prolapse ETHICON Women s Health & Urology, a division of ETHICON, INC., a Johnson & Johnson company, is dedicated to providing innovative solutions for common women s health problems and to
35-40% of GBS disease occurs in the elderly or in adults with chronic medical conditions.
 What is Group B Strep (GBS)? Group B Streptococcus (GBS) is a type of bacteria that is found in the lower intestine of 10-35% of all healthy adults and in the vagina and/or lower intestine of 10-35% of
What is Group B Strep (GBS)? Group B Streptococcus (GBS) is a type of bacteria that is found in the lower intestine of 10-35% of all healthy adults and in the vagina and/or lower intestine of 10-35% of
A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections
 A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections By Gary R. Skankey, MD, FACP, Infectious Disease, Las Vegas, NV Sponsored
A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections By Gary R. Skankey, MD, FACP, Infectious Disease, Las Vegas, NV Sponsored
A Very Rare Indication in Urology: Ablation of all the Urinary Organs: About A Case
 Article ID: WMC002102 ISSN 2046-1690 A Very Rare Indication in Urology: Ablation of all the Urinary Organs: About A Case Author(s):Dr. Hatim El Karni, Dr. Bezzaz Aicha, Dr. El Ghanmi Jihad, Dr. Koutani
Article ID: WMC002102 ISSN 2046-1690 A Very Rare Indication in Urology: Ablation of all the Urinary Organs: About A Case Author(s):Dr. Hatim El Karni, Dr. Bezzaz Aicha, Dr. El Ghanmi Jihad, Dr. Koutani
Hysterosalpingography
 Scan for mobile link. Hysterosalpingography Hysterosalpingography uses a real-time form of x-ray called fluoroscopy to examine the uterus and fallopian tubes of a woman who is having difficulty becoming
Scan for mobile link. Hysterosalpingography Hysterosalpingography uses a real-time form of x-ray called fluoroscopy to examine the uterus and fallopian tubes of a woman who is having difficulty becoming
CHAPTER 10 Uterine Synechiae
 CHAPTER 10 Uterine Synechiae Uterine synechiae are intrauterine adhesions. They may involve small focal areas of the endometrium (Figures 10.1a e), or they can be so extensive that they obliterate the
CHAPTER 10 Uterine Synechiae Uterine synechiae are intrauterine adhesions. They may involve small focal areas of the endometrium (Figures 10.1a e), or they can be so extensive that they obliterate the
About the Uterus. Hysterectomy may be done to treat conditions that affect the uterus. Some reasons a hysterectomy may be needed include:
 Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Fetal Therapy Center. Phone: 305-585-6636 Fax: 305-325-1282 www.uhealthobgyn.com www.jhsmiami.org AMNIOPATCH INFORMATION PACKET
 Fetal Therapy Center Phone: 305-585-6636 Fax: 305-325-1282 www.uhealthobgyn.com www.jhsmiami.org AMNIOPATCH INFORMATION PACKET 2 AMNIOPATCH FOR TREATMENT OF PREVIABLE PREMATURE RUPTURE OF MEMBRANES Premature
Fetal Therapy Center Phone: 305-585-6636 Fax: 305-325-1282 www.uhealthobgyn.com www.jhsmiami.org AMNIOPATCH INFORMATION PACKET 2 AMNIOPATCH FOR TREATMENT OF PREVIABLE PREMATURE RUPTURE OF MEMBRANES Premature
Parvovirus B19 Infection in Pregnancy
 Parvovirus B19 Infection in Pregnancy Information Pack Parvovirus B19 Infection in Pregnancy Information Booklet CONTENTS: THE VIRUS page 3 CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS page 6 DIAGNOSIS page 8 PATIENT MANAGEMENT
Parvovirus B19 Infection in Pregnancy Information Pack Parvovirus B19 Infection in Pregnancy Information Booklet CONTENTS: THE VIRUS page 3 CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS page 6 DIAGNOSIS page 8 PATIENT MANAGEMENT
Red Flags that should not be ignored
 Pregnancy that should not be ignored If a pregnant woman tells you she is experiencing any of the following symptoms during pregnancy, assist her to contact her emergency care professional right away.
Pregnancy that should not be ignored If a pregnant woman tells you she is experiencing any of the following symptoms during pregnancy, assist her to contact her emergency care professional right away.
Considering a Hysterectomy?
 Considering a Hysterectomy? Learn more about virtually scarless surgery using da Vinci Single-Site technology { {Symptoms & Conditions: Chronic Pain, Heavy Bleeding, Fibroids, Endometriosis, Adenomyosis,
Considering a Hysterectomy? Learn more about virtually scarless surgery using da Vinci Single-Site technology { {Symptoms & Conditions: Chronic Pain, Heavy Bleeding, Fibroids, Endometriosis, Adenomyosis,
Uterine Fibroid Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
 Fibroids and IR Uterine Fibroid Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment Interventional radiologists use MRIs to determine if fibroids can be embolised, detect alternate causes for the symptoms and rule out misdiagnosis,
Fibroids and IR Uterine Fibroid Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment Interventional radiologists use MRIs to determine if fibroids can be embolised, detect alternate causes for the symptoms and rule out misdiagnosis,
Uterus myomatosus. 10-May-15. Clinical presentation. Incidence. Causes? 3 out of 4 women. Growth rate vary. Most common solid pelvic tumor in women
 Uterus myomatosus A.J. Henriquez March 14, 2015 Uterus myomatosus Definition, incidence, clinical presentation and diagnosis. New FIGO classification for uterine leiomyomas Brief description on treatment
Uterus myomatosus A.J. Henriquez March 14, 2015 Uterus myomatosus Definition, incidence, clinical presentation and diagnosis. New FIGO classification for uterine leiomyomas Brief description on treatment
POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE
 POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE Acute Pylonephritis DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Male Known or suspected renal impairment (egfr < 60) Abnormality of renal tract Known or suspected renal
POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE Acute Pylonephritis DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Male Known or suspected renal impairment (egfr < 60) Abnormality of renal tract Known or suspected renal
150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2. Patient Information. Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate
 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2 Patient Information Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 3 GreenLight Laser Therapy 1 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page
150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2 Patient Information Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 3 GreenLight Laser Therapy 1 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page
CHAPTER 13 Pediatric Urologic Diseases
 CHAPTER 13 Pediatric Urologic Diseases Urinary Incontinence Hypospadias Ureterocele Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction Posterior Urethral Valves Vesicoureteral Reflux Disease Upper Urinary Tract Stones
CHAPTER 13 Pediatric Urologic Diseases Urinary Incontinence Hypospadias Ureterocele Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction Posterior Urethral Valves Vesicoureteral Reflux Disease Upper Urinary Tract Stones
Are Urinary Catheters necessary during Endovascular Procedures? A prospective randomized pilot study. Medical Student Research Project.
 Are Urinary Catheters necessary during Endovascular Procedures? A prospective randomized pilot study Medical Student Research Project Jordan Knepper Faculty advisor: Mark Langsfeld, MD Introduction Background
Are Urinary Catheters necessary during Endovascular Procedures? A prospective randomized pilot study Medical Student Research Project Jordan Knepper Faculty advisor: Mark Langsfeld, MD Introduction Background
Refer to Coaptite Injectable Implant Instructions for Use provided with product for complete instructions for use.
 Questions for my Doctor Refer to Coaptite Injectable Implant Instructions for Use provided with product for complete instructions for use. INDICATIONS: Coaptite Injectable Implant is indicated for soft
Questions for my Doctor Refer to Coaptite Injectable Implant Instructions for Use provided with product for complete instructions for use. INDICATIONS: Coaptite Injectable Implant is indicated for soft
Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection
 Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is pyelonephritis? Pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is pyelonephritis? Pyelonephritis
Venous Thromboembolic Treatment Guidelines
 Venous Thromboembolic Treatment Guidelines About the NYU Venous Thromboembolic Center (VTEC) The center s mission is to deliver advanced screening, detection, care, and management services for patients
Venous Thromboembolic Treatment Guidelines About the NYU Venous Thromboembolic Center (VTEC) The center s mission is to deliver advanced screening, detection, care, and management services for patients
Colocutaneous Fistula. Disclosures
 Colocutaneous Fistula Madhulika G. Varma MD Associate Professor Chief, Colorectal Surgery University of California, San Francisco Honoraria Applied Medical Covidien Disclosures 1 Colocutaneous Fistula
Colocutaneous Fistula Madhulika G. Varma MD Associate Professor Chief, Colorectal Surgery University of California, San Francisco Honoraria Applied Medical Covidien Disclosures 1 Colocutaneous Fistula
Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place.
 What is an abdominal myomectomy? Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place. When is this surgery used? Treatment
What is an abdominal myomectomy? Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place. When is this surgery used? Treatment
General and Objectives Clinical Skills for. Nursing Students in Maternity and Gynecology. Nursing Department
 General and Objectives Clinical Skills for Nursing Students in Maternity and Gynecology Nursing Department Objectives and clinical skills of Antenatal unit Provide antenatal care to woman during normal
General and Objectives Clinical Skills for Nursing Students in Maternity and Gynecology Nursing Department Objectives and clinical skills of Antenatal unit Provide antenatal care to woman during normal
Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Short-term Catheter Bladder Drainage in adults. A Systematic Review (Cochrane database August 2013)
 Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Short-term Catheter Bladder Drainage in adults A Systematic Review (Cochrane database August 2013) Gail Lusardi, Senior Lecturer Dr Allyson Lipp, Principal Lecturer, Dr Chris
Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Short-term Catheter Bladder Drainage in adults A Systematic Review (Cochrane database August 2013) Gail Lusardi, Senior Lecturer Dr Allyson Lipp, Principal Lecturer, Dr Chris
Urinary Tract Infection in Stone Patients and in Patients with Indwelling Urethral Catheters
 Urinary Tract Infection in Stone Patients and in Patients with Indwelling Urethral Catheters Pages with reference to book, From 254 To 258 Farakh A. Khan, Salman H. Siddiqui, Nasreen Akhtar ( Department
Urinary Tract Infection in Stone Patients and in Patients with Indwelling Urethral Catheters Pages with reference to book, From 254 To 258 Farakh A. Khan, Salman H. Siddiqui, Nasreen Akhtar ( Department
Considering Surgery for Fibroids? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery
 Considering Surgery for Fibroids? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Uterine Fibroid (Fibroid Tumor) A uterine fibroid is a benign (non-cancerous) tumor that grows in the uterine
Considering Surgery for Fibroids? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Uterine Fibroid (Fibroid Tumor) A uterine fibroid is a benign (non-cancerous) tumor that grows in the uterine
190.12 - Urine Culture, Bacterial Summary Information Highlighted items indicate most frequently used codes.
 Medicare National Coverage Determination (NCD) (Jan 2011) Source: CMS: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services To view full document: www.cms.gov/coveragegeninfo. Select Lab NCDs, then select NCD Coding
Medicare National Coverage Determination (NCD) (Jan 2011) Source: CMS: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services To view full document: www.cms.gov/coveragegeninfo. Select Lab NCDs, then select NCD Coding
Considering Endometriosis Surgery? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery
 Considering Endometriosis Surgery? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Endometriosis Endometriosis is a condition in which the tissue that lines your uterus (the endometrium)
Considering Endometriosis Surgery? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Endometriosis Endometriosis is a condition in which the tissue that lines your uterus (the endometrium)
Crohn's disease and pregnancy.
 Gut, 1984, 25, 52-56 Crohn's disease and pregnancy. R KHOSLA, C P WILLOUGHBY, AND D P JEWELL From the Gastroenterology Unit, Radcliffe Infirmary, Oxford SUMMARY Infertility and the outcome of pregnancy
Gut, 1984, 25, 52-56 Crohn's disease and pregnancy. R KHOSLA, C P WILLOUGHBY, AND D P JEWELL From the Gastroenterology Unit, Radcliffe Infirmary, Oxford SUMMARY Infertility and the outcome of pregnancy
Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization
 Client HMSA: PQSR 2009 Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization Strength of Recommendation Organizations
Client HMSA: PQSR 2009 Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization Strength of Recommendation Organizations
Article ID: WMC001893 2046-1690
 Article ID: WMC001893 2046-1690 Hyperkalaemia, Renal Failure, and Right-Sided Hydro-Uretero-Nephrosis a Sequel of Intravesical Debris in the Presence of an Indwelling Long-Term Urethral Catheter: Case
Article ID: WMC001893 2046-1690 Hyperkalaemia, Renal Failure, and Right-Sided Hydro-Uretero-Nephrosis a Sequel of Intravesical Debris in the Presence of an Indwelling Long-Term Urethral Catheter: Case
Blood in the Urine (Haematuria)
 Kidney Health Information Blood in the Urine (Haematuria) What is blood in the urine? Sometimes blood in the urine can be seen, but at other times it is present in such small quantities that it is not
Kidney Health Information Blood in the Urine (Haematuria) What is blood in the urine? Sometimes blood in the urine can be seen, but at other times it is present in such small quantities that it is not
A potential treatment for your abnormal uterine bleeding
 TRUCLEAR System A potential treatment for your abnormal uterine bleeding Do You Suffer from Abnormal Uterine Bleeding? What is a Hysteroscopy? What is the TRUCLEAR Procedure? What Happens Before Your
TRUCLEAR System A potential treatment for your abnormal uterine bleeding Do You Suffer from Abnormal Uterine Bleeding? What is a Hysteroscopy? What is the TRUCLEAR Procedure? What Happens Before Your
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Endometriosis
 Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
A Guide to Hysteroscopy. Patient Education
 A Guide to Hysteroscopy Patient Education QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ABOUT HYSTEROSCOPY Your doctor has recommended that you have a procedure called a hysteroscopy. Naturally, you may have questions about
A Guide to Hysteroscopy Patient Education QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ABOUT HYSTEROSCOPY Your doctor has recommended that you have a procedure called a hysteroscopy. Naturally, you may have questions about
CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE
 URINARY INCONTINENCE CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE ASSESSMENT/PROBLEM RECOGNITION 1. Did the staff and physician seek and document risk factors for urinary incontinence and any history of urinary
URINARY INCONTINENCE CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE ASSESSMENT/PROBLEM RECOGNITION 1. Did the staff and physician seek and document risk factors for urinary incontinence and any history of urinary
Bile Leaks After Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy. Kings County Hospital Center Eliana A. Soto, MD
 Bile Leaks After Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Kings County Hospital Center Eliana A. Soto, MD Biliary Injuries during Cholecystectomy In the 1990s, high rate of biliary injury was due in part to learning
Bile Leaks After Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Kings County Hospital Center Eliana A. Soto, MD Biliary Injuries during Cholecystectomy In the 1990s, high rate of biliary injury was due in part to learning
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment
 Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
The American Academy of Pediatrics
 Revised AAP Guideline on UTI in Febrile Infants and Young Children KENNETH B. ROBERTS, MD, University of rth Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, rth Carolina In 2011, the American Academy of Pediatrics
Revised AAP Guideline on UTI in Febrile Infants and Young Children KENNETH B. ROBERTS, MD, University of rth Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, rth Carolina In 2011, the American Academy of Pediatrics
A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page
 A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page IX0200: Prevention & Control of Catheter Associated
A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page IX0200: Prevention & Control of Catheter Associated
Acute abdominal conditions Key Points
 7 Acute abdominal conditions Key Points 7.1 ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS Referred abdominal pain Fore gut pain (stomach, duodenum, gall bladder) is referred to the upper abdomen Mid gut pain (small intestine,
7 Acute abdominal conditions Key Points 7.1 ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS Referred abdominal pain Fore gut pain (stomach, duodenum, gall bladder) is referred to the upper abdomen Mid gut pain (small intestine,
This Protocol is adapted from the University of Colorado Protocol dated August 26, 2009.
 Protocol for Post-Placental IUD insertion July 14, 2010 This Protocol is adapted from the University of Colorado Protocol dated August 26, 2009. Background Post-placental intrauterine device (IUD) insertion
Protocol for Post-Placental IUD insertion July 14, 2010 This Protocol is adapted from the University of Colorado Protocol dated August 26, 2009. Background Post-placental intrauterine device (IUD) insertion
Study Design Of Medical Research
 Study Design Of Medical Research By Ahmed A.Shokeir, MD,PHD, FEBU Prof. Urology, Urology & Nephrology Center, Mansoura, Egypt Study Designs In Medical Research Topics Classification Case series studies
Study Design Of Medical Research By Ahmed A.Shokeir, MD,PHD, FEBU Prof. Urology, Urology & Nephrology Center, Mansoura, Egypt Study Designs In Medical Research Topics Classification Case series studies
Ultrasound Billing CPT Codes Summary and Notes
 Ultrasound Billing CPT Codes Summary and Notes CPT codes for ultrasound examinations are considered to be complete studies unless specified as limited studies in their code definitions. A limited study
Ultrasound Billing CPT Codes Summary and Notes CPT codes for ultrasound examinations are considered to be complete studies unless specified as limited studies in their code definitions. A limited study
PREVENTION OF CATHETER ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS. (CAUTIs)
 PREVENTION OF CATHETER ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS (CAUTIs) CAUTIs A UTI where an indwelling urinary catheter was in place for >2 calendar days on the date of event. OR If an indwelling urinary
PREVENTION OF CATHETER ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS (CAUTIs) CAUTIs A UTI where an indwelling urinary catheter was in place for >2 calendar days on the date of event. OR If an indwelling urinary
Cancer of the Cervix
 Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
High quality follow up support and care
 High quality follow up support and care How do you think the benefits of high quality follow up care? Client satisfaction Safe and effective continuation of the method What are the tasks involved in routine
High quality follow up support and care How do you think the benefits of high quality follow up care? Client satisfaction Safe and effective continuation of the method What are the tasks involved in routine
Jessica Konvicka, MPAS, PA-C University Of Texas Southwestern Medical Center Dallas, TX
 Kidney Stones Jessica Konvicka, MPAS, PA-C University Of Texas Southwestern Medical Center Dallas, TX Objectives Recognize signs and symptoms of a kidney stone. Evaluate a patient suspected to have a kidney
Kidney Stones Jessica Konvicka, MPAS, PA-C University Of Texas Southwestern Medical Center Dallas, TX Objectives Recognize signs and symptoms of a kidney stone. Evaluate a patient suspected to have a kidney
Complications related to a Percutaneous Nephrostomy Catheter
 Research Protocol Complications related to a Percutaneous Nephrostomy Catheter Project Group: Rikke Knudsen Erica Grainger Lone Aarvig Susanne Kristensen Bente Thoft Jensen Introduction Obstruction in
Research Protocol Complications related to a Percutaneous Nephrostomy Catheter Project Group: Rikke Knudsen Erica Grainger Lone Aarvig Susanne Kristensen Bente Thoft Jensen Introduction Obstruction in
Guidance for Preconception Care of Women with Thyroid Disease
 Before, Between & Beyond Pregnancy The National Preconception Curriculum and Resources Guide for Clinicians Guidance for Preconception Care of Women with Thyroid Disease Avi Alkalay, MD Department of Obstetrics
Before, Between & Beyond Pregnancy The National Preconception Curriculum and Resources Guide for Clinicians Guidance for Preconception Care of Women with Thyroid Disease Avi Alkalay, MD Department of Obstetrics
Kaiser Oakland Urology
 Kaiser Oakland Urology The Main Purpose of Bladder Catheterization Complete Bladder Emptying! Help maintain a healthy bladder Help maintain healthy kidneys Reduce the chances of significant urinary tract
Kaiser Oakland Urology The Main Purpose of Bladder Catheterization Complete Bladder Emptying! Help maintain a healthy bladder Help maintain healthy kidneys Reduce the chances of significant urinary tract
Appendicitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Appendicitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH The appendix is a small, tube-like structure
Appendicitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH The appendix is a small, tube-like structure
1in 3. women experience bladder leakage.1. Do You? Reclaim your life. Your Resource Guide to Stress Urinary Incontinence
 1in 3 women experience bladder leakage.1 Do You? Reclaim your life Your Resource Guide to Stress Urinary Incontinence Urinary Incontinence Bladder leakage, also known as urinary incontinence is the loss
1in 3 women experience bladder leakage.1 Do You? Reclaim your life Your Resource Guide to Stress Urinary Incontinence Urinary Incontinence Bladder leakage, also known as urinary incontinence is the loss
Coding Companion for Urology/Nephrology. A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement
 Coding Companion for Urology/Nephrology A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement Contents Getting Started with Coding Companion... i Integumentary...1 Arteries and Veins...15 Lymph
Coding Companion for Urology/Nephrology A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement Contents Getting Started with Coding Companion... i Integumentary...1 Arteries and Veins...15 Lymph
LOSS OF BLADDER CONTROL IS TREATABLE TAKE CONTROL AND RESTORE YOUR LIFESTYLE
 LOSS OF BLADDER CONTROL IS TREATABLE TAKE CONTROL AND RESTORE YOUR LIFESTYLE TALKING ABOUT STRESS INCONTINENCE (SUI) Millions of women suffer from stress incontinence (SUI). This condition results in accidental
LOSS OF BLADDER CONTROL IS TREATABLE TAKE CONTROL AND RESTORE YOUR LIFESTYLE TALKING ABOUT STRESS INCONTINENCE (SUI) Millions of women suffer from stress incontinence (SUI). This condition results in accidental
Patient with: 3 or more UTI in 6 months 4 or more UTI in 12 months
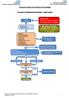 Recurrent UTI Management Pathway adult females Initial assessment Assessment questionnaire questionnaire bladder scan dipstick dipstick of of urine urine pregnancy neurological disease long - term catheters
Recurrent UTI Management Pathway adult females Initial assessment Assessment questionnaire questionnaire bladder scan dipstick dipstick of of urine urine pregnancy neurological disease long - term catheters
