REBEL monorail. Platinum Chromium Coronary Stent System ONLY. over-the-wire < EN >
|
|
|
- Morgan Morris
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 REBEL monorail over-the-wire Platinum Chromium Coronary Stent System < EN > Table of Contents 1 WARNING: device description:... 1 Table 2.1 REBEL Stent System Product Description Device Component Description... 2 Contents for (1) REBEL Monorail Stent System... 2 Contents for (1) REBEL Over-the-Wire Stent System INTENDED USE/INDICATIONS FOR USE: CONTRAINDICATIONS: WARNINGS: PRECAUTIONS: General Precautions Pre- and Post-Procedure Anti-platelet Regimen Longitudinal Stent Deformation Use of Multiple Stents Brachytherapy Use in Conjunction with Other Procedures Use in Special Populations Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)... 2 Medical Registration Stent Handling (also see tion 13, Operational Instructions) Stent Placement... 2 Preparation... 2 Placement Stent Delivery System Removal Pre-deployment Stent Delivery System Removal Post-deployment... 3 Table 6.1 Delivery System Deflation Time Specifications Post-Procedure OVERVIEW OF CLINICAL STUDIES: ADVERSE EVENTS: Observed Adverse Events... 3 Table 8.1 OMEGA Major Clinical Events From Post-Procedure to 9-Month Follow-Up Potential Adverse Events CLINICAL STUDIES:... 4 OMEGA Clinical Trial Month Clinical Outcomes... 4 Table 9.1 OMEGA 9-Month Clinical Results, Intent-to-Treat Patients... 4 Table 9.2 OMEGA Primary Endpoint... 4 Table 9.3 OMEGA 9-Month TLF Results by Gender, Intent-to-Treat, All Patients (N=328)... 5 Table Month Clinical Endpoints by Gender, Intent-to-Treat, All Patients INDIVIDUALIZATION OF TREATMENT: PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION: HOW SUPPLIED:... 5 Handling and Storage OPERATIONAL INSTRUCTIONS: Inspection Prior to Use Materials Required (not included in Stent Delivery System package) Preparation Packaging Removal Guidewire Lumen Flush Delivery System Preparation Delivery Procedure Deployment Procedure Removal Procedure Post-Deployment Dilatation of Stented Segments In Vitro Information... 6 Table 13.1 Typical REBEL Stent System Compliance... 6 warranty... 7 ONLY Caution: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. This device is supplied in sterile condition. All materials inside the sterile barrier pouch (the delivery system and stent, as well as the carrier tube and pouch liner) are sterile. The external surface of the sterile barrier pouch, as well as the product carton, should not be considered sterile. 1 WARNING: Contents supplied STERILE using an ethylene oxide (EO) process. Do not use if sterile barrier is damaged. If damage is found, call your Boston Scientific representative. For single use only. DO NOT REUSE, REPROCESS OR RESTERILIZE. Reuse, reprocessing or resterilization may compromise the structural integrity of the device and/or lead to device failure which, in turn, may result in patient injury, illness or death. Reuse, reprocessing or resterilization may also create a risk of contamination of the device and/or cause patient infection or cross-infection, including, but not limited to, the transmission of infectious disease(s) from one patient to another. Contamination of the device may lead to injury, illness or death of the patient. After use, dispose of product and packaging in accordance with hospital, administrative and/or local government policy. 2 device description: REBEL Platinum Chromium Coronary Stent System: The REBEL Platinum Chromium Coronary Stent System is a device product consisting of a balloon expandable stent, pre-mounted on a Monorail (MR) or Over-The-Wire (OTW) delivery catheter. The stent is made from a platinum chromium alloy (PtCr). The characteristics of the REBEL Stent System are described in Table 2.1. Table 2.1 REBEL Stent System Product Description REBEL Monorail Stent Delivery System REBEL Over-the-Wire Stent Delivery System Stent Available Stent Lengths (mm) 8*, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32* Available Stent Diameters (mm) 2.25*, 2.50*, 2.75, 3.00, 3.50, 4.00, 4.50* Stent Material Platinum Chromium (PtCr) Alloy Stent Strut Thickness inches (0.081 mm) for diameters 2.25 mm to 3.50 mm inches (0.086 mm) for diameters 4.00 mm and 4.50 mm Delivery System Effective Length 144 cm Delivery System Ports Y-Connector (Side arm for access to Single access port to inflation lumen. Guidewire balloon inflation/deflation lumen. Straight exit port is located approximately 25 cm from tip. arm is continuous with shaft inner lumen). Designed for guidewire inches (0.36 mm) Designed for guidewire inches (0.36 mm) Stent Delivery Balloon Inflation Pressure Catheter Shaft Outer Diameter Guide Catheter Minimum Inner Diameter Requirement A balloon, with two radiopaque balloon markers, nominally placed 0.4 mm (0.016 inches) beyond the stent at each end. Nominal Inflation Pressure: 11 atm (1117 kpa) Rated Burst Inflation Pressure: 18 atm (1827 kpa) 2.1 F (0.70 mm) proximal and 2.7 F (0.95 mm) distal inches (1.42 mm) for mm sizes inches (1.68 mm) for 4.50 mm size * 32 mm length is not available in 2.25 mm and 2.50 mm diameter sizes. 8 mm length is not available in 4.50 mm diameter size. 3.4F ( 1.20 mm) proximal for 2.25 to 4.50 mm sizes 2.4F ( 0.85 mm) distal for 2.25 to 2.75 mm sizes 2.7F ( 0.95 mm) distal for 3.00 to 4.50 mm sizes inches (1.68 mm)
2 2.1 Device Component Description The REBEL Stent component is made from a platinum chromium alloy mounted onto a Monorail or Over-the-Wire Delivery System. The REBEL Stent System is available in four stent models, each engineered for specific diameters to provide consistent stentto-artery ratios across the range of reference vessel diameters indicated: Small Vessel (SV): 2.25 mm Small Workhorse (SWH): 2.50, 2.75 mm Workhorse (WH): 3.00, 3.50 mm Large Vessel (LV): 4.00, 4.50 mm Contents for (1) REBEL Monorail Stent System One (1) REBEL Monorail Stent System Two (2) CLIPIT Coil clips One (1) Flushing needle with luer fitting Contents for (1) REBEL Over-the-Wire Stent System One (1) REBEL Over-the-Wire Stent System 3 INTENDED USE/INDICATIONS FOR USE: The REBEL Coronary Stent System is indicated for improving coronary luminal diameter in patients with de novo lesions 28 mm in length in native coronary arteries with a reference vessel diameter (RVD) of 2.25 mm to 4.50 mm. 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS: Use of the REBEL Stent System is contraindicated in patients with the following: Known hypersensitivity to platinum, the platinum chromium alloy, or similar alloy types such as stainless steel. Known severe reaction to contrast agents that cannot be adequately premedicated prior to the REBEL Stent placement procedure. Coronary artery stenting is contraindicated for use in the following: Patients who cannot receive recommended anti-platelet and/or anticoagulant therapy. Patients judged to have a lesion that prevents complete inflation of an angioplasty balloon or proper placement of the stent or delivery device. 5 WARNINGS: This product should not be used in patients who are not likely to comply with recommended anti-platelet therapy. The use of this product carries the risks associated with coronary artery stenting, including: stent thrombosis, vascular complications, and/or bleeding events. 6 PRECAUTIONS: 6.1 General Precautions Only physicians who have received adequate training should perform implantation of the stent. Stent placement should only be performed at hospitals where emergency coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery is readily available. Subsequent stent blockage may require repeat dilatation of the arterial segment containing the stent. The long-term outcome following repeat dilatation of previously implanted stents is not well characterized. Do not expose the delivery system to organic solvents such as alcohol or detergents. Care should be taken to control the position of the guide catheter tip during stent delivery, deployment, and balloon withdrawal. Before withdrawing the stent delivery system, visually confirm complete balloon deflation by fluoroscopy (see Table 6.1 System Deflation Time Specifications). Failure to do so may cause increased stent delivery system withdrawal forces and result in guide catheter movement into the vessel and subsequent arterial damage. 6.2 Pre- and Post-Procedure Anti-platelet Regimen Administer appropriate anticoagulant/anti-platelet therapy according to current medical guidelines. The 2011 ACCF/AHA/SCAI Guideline for Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) are provided at the following website: Longitudinal Stent Deformation Longitudinal stent deformation is a recognized potential failure mode of thin strut coronary stents. 1 Crossing a newly deployed stent with a second device, such as a balloon catheter, stent system, or IVUS catheter can lead to the second device transmitting force to the implanted stent. In this situation, if the second device is advanced or retracted, longitudinal stent deformation (i.e., longitudinal compression or elongation) of the implanted stent may occur. Although a rare event, longitudinal stent deformation may result in adverse clinical events and/or the need for additional treatment including repeat dilation of the implanted stent, placement of a second stent and/or surgical intervention An analysis of complaint reports suggests that coronary artery calcification, vessel tortuosity, and stent malapposition in conjunction with crossing a newly deployed stent with an ancillary device may be associated with an increased risk of longitudinal stent deformation. Implantation techniques that may reduce the likelihood of procedure related complications, including stent deformation, are described in the appropriate sections of this DFU (see sections 13.4 Delivery Procedure, 13.5 Deployment Procedure, 13.6 Removal Procedure, and 13.7 Post-Deployment Dilatation of Stented Segment). Please see section 7 Overview of Clinical Studies for a description of the enhancements made to the REBEL Coronary Stent System. 1 Hanratty CG, Walsh SJ. Longitudinal Compression: A new Complication with Modern Coronary Stent Platforms Time to Think Beyond Deliverability? Eurointervention 2011;7: Use of Multiple Stents In the OMEGA Clinical trial, the protocol specified that lesions were to be treated with no more than one stent, except in situations involving bailout stenting. When more than one stent is required, resulting in stent-to-stent contact, stent materials should be of similar composition to avoid the possibility of corrosion due to the presence of dissimilar metals in a conducting medium. 6.5 Brachytherapy The safety and effectiveness of the REBEL stent in patients with prior brachytherapy of the target lesion have not been established. The safety and effectiveness of the use of brachytherapy to treat in-stent restenosis in a REBEL stent have not been established. Both vascular brachytherapy and the REBEL stent alter arterial remodeling. The interaction between these two treatments has not been determined. 6.6 Use in Conjunction with Other Procedures The safety and effectiveness of using mechanical atherectomy devices (directional atherectomy catheters or rotational atherectomy catheters) or laser angioplasty catheters in conjunction with REBEL stent implantation have not been established. 6.7 Use in Special Populations The safety and effectiveness of the REBEL stent have not been established in the following patient populations: Patients with vessel thrombus at the lesion site. Patients with coronary artery reference vessel diameters < 2.25 or > 4.50 mm. Patients with coronary artery lesions longer than 28 mm or requiring more than one REBEL stent. Patients with lesions located in the saphenous vein grafts, in the left main coronary artery, ostial lesions, or lesions located at a bifurcation. Patients with diffuse disease or poor flow distal to the identified lesions. Patients with tortuous vessels (> 60 degrees) in the region of the obstruction or proximal to the lesion. Patients with a recent acute myocardial infarction where there is evidence of thrombus or poor flow. Patients with in-stent restenosis. Patients with moderate or severe calcification in the lesion or a chronic total occlusion. Patients with 3 vessel disease. 6.8 Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Non-clinical testing has demonstrated that the REBEL stent is MR Conditional for single and overlapped conditions up to 74 mm. A patient with this device can be safely scanned in a Magnetic Resonance system meeting the following conditions: Static magnetic field of 3.0 and 1.5 Tesla only Maximum spatial gradient magnetic field of 2200 gauss/cm (22 T/m) Maximum Magnetic Resonance system reported, whole body averaged specific absorption rate (SAR) of < 2 W/kg (Normal Operating Mode) 2 Under the scan conditions defined above, the REBEL stent is expected to produce a maximum temperature rise of 2.6ºC after 15 minutes of continuous scanning. In non-clinical testing, the image artifact caused by the device extends approximately 8 mm from the REBEL stent when imaged with a spin echo pulse sequence and a 3.0 Tesla MRI system. The artifact does not obscure the device lumen. Medical Registration It is recommended that patients register the conditions under which the implant can be scanned safely with the MedicAlert Foundation ( or equivalent organization. 6.9 Stent Handling (also see tion 13, Operational Instructions) For single use only. Do not resterilize or reuse this product. Note product Use By date. (see tion 1, Warning) The premounted REBEL stent and its delivery system are designed for use as a unit. The stent is not to be removed from its delivery balloon. The stent is not designed to be crimped onto another balloon. Removing the stent from its delivery balloon may damage the stent and/or lead to stent embolization. Special care must be taken not to handle or in any way disrupt the stent position on the delivery balloon. This is most important during catheter removal from packaging, placement over guidewire, and advancement through hemostasis valve adapter and guide catheter hub. Excessive manipulation or handling may cause stent damage, contamination, or dislodgment of the stent from the delivery balloon. Use only the appropriate balloon inflation media (see tion , Delivery System Preparation). DO NOT USE air or any gas medium to inflate the balloon. In the event the REBEL stent is not deployed, do not use the product and contact your local Boston Scientific Representative for return information Stent Placement Preparation DO NOT PREPARE OR PRE-INFLATE BALLOON PRIOR TO STENT DEPLOYMENT OTHER THAN AS DIRECTED. Use the balloon purging technique described in tion , Delivery System Preparation. An unexpanded stent should be introduced into the coronary arteries one time only. An unexpanded stent should not be subsequently moved in and out through the distal end of the guide catheter as stent damage or stent dislodgment from the balloon may occur. Placement The vessel should be pre-dilated with an appropriate sized balloon. Failure to do so may increase the risk of placement difficulty and procedural complications. If unusual resistance is felt at any time during lesion access before stent implantation, the stent delivery system and the guide catheter should be removed as a single unit (see tion 6.11, Stent Delivery System Removal Pre-deployment). Do not expand the stent if it is not properly positioned in the vessel (see tion 6.11, Stent Delivery System Removal Pre-deployment). Balloon pressures should be monitored during inflation. Do not exceed rated burst pressure as indicated on product label (Table 13.1, Typical REBEL Stent System Compliance). Use of pressures higher than specified on product label may result in a ruptured balloon and intimal damage and dissection. The stent inner diameter should approximate 1.1 times the distal reference diameter of the vessel. Placement of the stent has the potential to compromise side branch patency if stenting near a side branch (see tion 13.7, Post-Deployment Dilatation of Stented Segments). Implanting a stent may lead to dissection of the vessel distal and/or proximal to the stented portion, and may cause acute closure of the vessel requiring additional intervention (e.g., CABG, further dilation, placement of additional stents, or other).
3 When treating multiple lesions, the distal lesion should generally be stented first, followed by stenting of the more proximal lesion(s). Stenting in this order alleviates the requirement to cross the proximal stent when placing the distal stent and reduces the chances of dislodging the proximal stent Stent Delivery System Removal Pre-deployment If unusual resistance is felt at any time during lesion access before stent implantation, the stent delivery system and the guide catheter should be removed as a single unit under direct visualization using fluoroscopy. Do not attempt to pull an unexpanded stent back into the guide catheter, as stent damage or stent dislodgment from the balloon may occur. Stent retrieval methods (use of additional wires, snares, and/or forceps) may result in additional trauma to the vascular site. Complications can include bleeding, hematoma, or pseudoaneurysm Stent Delivery System Removal Post-deployment Following stent placement, confirm complete balloon deflation (See Table 6.1, Delivery System Deflation Time Specifications). If greater than usual resistance is felt during delivery system withdrawal, pay particular attention to guide catheter position. In some cases it may be necessary to pull back slightly on the guide catheter in order to prevent deep seating (unplanned advancement) of the guide catheter and subsequent vessel damage. In cases where unplanned guide catheter movement has occurred, angiographic assessment of the coronary tree should be undertaken to ensure that there is no damage to the coronary vasculature. Maintain guidewire placement across the lesion during the entire removal process. Carefully pull back the stent delivery system until the proximal balloon marker of the stent delivery system is just distal to the guide catheter distal tip. The stent delivery system and the guide catheter should be pulled back until the tip of the guide catheter is just distal to the arterial sheath, allowing the guide catheter to straighten. Carefully retract the stent delivery system into the guide catheter and remove the stent delivery system and the guide catheter from the patient as a single unit while leaving the guidewire across the lesion. Note: Failure to follow these steps, and/or applying excessive force to the stent delivery system, can potentially result in stent damage, stent dislodgment from the balloon, and/or damage to the delivery system. Table 6.1 Delivery System Deflation Time Specifications Balloon Diameter (mm) Stent Length (mm) N/A N/A Post-Procedure Care must be exercised when crossing a newly deployed stent with any wire, catheter or ancillary device to avoid disrupting the stent placement, apposition, and/or geometry. If the patient requires imaging, see tion 6.8, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). 7 OVERVIEW OF CLINICAL STUDIES: The principal safety and effectiveness for the REBEL Stent System is derived from the global OMEGA Clinical Trial, a clinical trial conducted on the OMEGA Stent System. The OMEGA and REBEL stents utilize the same platinum chromium alloy. The REBEL Stent System has supplementary proximal stent connectors for increased axial strength, a short flexible stent delivery system tip, and a PTFE coated proximal hypotube for improved stent deliverability. Given the similarities between the OMEGA and REBEL Stent Systems and supportive bench and animal study information, the findings from the OMEGA Clinical Trial are applicable to the REBEL Stent System. 8 ADVERSE EVENTS: 8.1 Observed Adverse Events Observed adverse event experience comes from the OMEGA Clinical Trial. Major clinical events for this study are shown in Table 8.1. Table 8.1 OMEGA Major Clinical Events From Post-Procedure to 9-Month Follow-Up OMEGA (N=328) In-Hospital 30 Days 9 Months All Death, MI, TVR 3.0% (10/328) 3.4% (11/327) 12.9% (42/325) All Death or MI 3.0% (10/328) 3.4% (11/327) 5.5% (18/325) All Death 0.0% (0/328) 0.3% (1/327) 1.8% (6/325) Cardiac Death 0.0% (0/328) 0.3% (1/327) 1.2% (4/325) Non-Cardiac Death 0.0% (0/328) 0.0% (0/327) 0.6% (2/325) MI 3.0% (10/328) 3.1% (10/327) 3.7% (12/325) Q-wave MI 0.0% (0/328) 0.0% (0/327) 0.0% (0/325) Non-Q-wave MI 3.0% (10/328) 3.1% (10/327) 3.7% (12/325) TVR 0.0% (0/328) 0.3% (1/327) 8.6% (28/325) TLR 0.0% (0/328) 0.3% (1/327) 7.4% (24/325) Non-TLR 0.0% (0/328) 0.0% (0/327) 1.8% (6/325) Cardiac Death or MI 3.0% (10/328) 3.4% (11/327) 4.9% (16/325) TLF 3.0% (10/328) 3.4% (11/327) 11.5% (37/323) TVF 3.0% (10/328) 3.4% (11/327) 12.4% (40/323) ARC Stent Thrombosis 0.0% (0/328) 0.3% (1/326) 0.6% (2/318) Definite or Probable 0.0% (0/328) 0.3% (1/326) 0.6% (2/318) Definite 0.0% (0/328) 0.3% (1/326) 0.6% (2/318) Probable 0.0% (0/328) 0.0% (0/326) 0.0% (0/318) Numbers are % (count/sample size). Abbreviations: ARC=Academic Research Consortium; MI=myocardial infarction; PCI=percutaneous coronary intervention; TLR=target lesion revascularization; TVR=target vessel revascularization. 3
4 8.2 Potential Adverse Events Potential adverse events (in alphabetical order) which may be associated with the use of a coronary stent in native coronary arteries include but are not limited to: Abrupt closure Allergic reaction (including to medications, contrast, stent materials) Aneurysm (coronary) Angina Arrhythmias, including ventricular fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia Arteriovenous fistula Bleeding Cardiac tamponade Cardiogenic shock Cardiomyopathy Death Emboli (including air, tissue, thrombus, plaque, or device materials) Heart failure Hematoma Hemorrhage Hypotension/hypertension Infection, local and/or systemic Ischemia, myocardial Myocardial infarction Pain Pericardial effusion Pseudoaneurysm, femoral Pulmonary edema Renal insufficiency or failure Respiratory failure Restenosis of stented segment Shock Stent embolization Stent fracture Stent migration Stent thrombosis and/or vessel occlusion Stroke/cerebrovascular accident/transient ischemic attack Total occlusion of coronary artery Vessel spasm Vessel injury (including dissection, perforation, rupture or trauma) There may be other potential adverse events that are unforeseen at this time. 9 CLINICAL STUDIES: OMEGA Clinical Trial Primary Objective: To evaluate the safety and effectiveness of the OMEGA Coronary Stent System for the treatment of de novo atherosclerotic coronary artery lesions 28 mm in length (by visual estimate) in a native coronary arteries 2.25 mm to 4.50 mm in diameter (by visual estimate). Design: The OMEGA Clinical Trial is a prospective, single-arm, multicenter study. Eligible patients were to be 18 years of age and with left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) 30% and symptomatic coronary artery disease or documented silent ischemia. Lesions were to be coverable by a single study stent and to have visually estimated stenosis 50% and < 100% with Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) flow > 1. Patients could have 1 target lesion treated. Patients with a single target lesion could also have 1 de novo native coronary artery lesion within a different epicardial vessel (non-target lesion) treated with a commercially-available treatment (e.g., stent, balloon angioplasty, excluding brachytherapy) during the index procedure. The non-target lesion had to be treated before the target lesion and the treatment had to be a clinical angiographic success (defined as visually assessed stenosis < 50% [< 3 0% for stents] with TIMI 3 flow without prolonged chest pain or electrocardiogram [ECG] changes consistent with MI) before the patient could be enrolled. The protocol mandated antiplatelet therapy compliance in accordance with the 2007 ACC/AHA/SCAI Guidelines for PCI. 2 Baseline and post-procedure angiographic data were collected and assessed by quantitative analysis at a designated core laboratory. An independent Clinical Events Committee adjudicated major adverse clinical events and stent thrombosis. The primary endpoint was the rate of target lesion failure (TLF), defined as any ischemia-driven revascularization of the target lesion (TLR), myocardial infarction (MI; Q-wave and non Q-wave) related to the target vessel, or cardiac death, at 9 months post-index procedure. The rate of the primary endpoint was compared to a predefined performance goal (PG) of 21.2%, which was calculated based on historical bare metal stent (BMS) results. A total of 328 patients were enrolled at 37 sites in the United States and Europe. Of the 328 patients included in the intent-to-treat (ITT) analysis set, a total of 323 patients were evaluable for the 9-month primary endpoint. Follow-up included clinical assessments at 30 days, 9, and 12 months post-index procedure. The study is now considered complete with regard to the 9-month primary endpoint. Demographics: Baseline characteristics for the OMEGA Clinical Trial indicated 67.7% were male with an average age of 65.46±11.23, 17.4% had diabetes requiring medication, 70.8% had known hyperlipidemia requiring medication, 28.2% were known current smokers, and 75.0% had known hypertension requiring medication. 4 Baseline lesion characteristics: Baseline lesion characteristics included average reference vessel diameter (RVD) of 2.77±0.53 mm, average minimum lumen diameter (MLD) of 0.90±0.38 mm, average percent diameter stenosis (%DS) of 67.41±11.34, and average lesion length of 12.49±5.15 mm. 9-Month Clinical Outcomes Table 9.1 OMEGA 9-Month Clinical Results, Intent-to-Treat Patients OMEGA (N=328) EFFICACY TVR, Overall 8.6% (28/325) TLR, Overall 7.4% (24/325) TLR, PCI 7.4% (24/325) TLR, CABG 0.0% (0/325) Non-TLR TVR, Overall 1.8% (6/325) Non-TLR TVR, PCI 1.8% (6/325) Non-TLR TVR, CABG 0.0% (0/325) SAFETY All Death 1.8% (6/325) Cardiac Death or MI 4.9% (16/325) Cardiac Death 1.2% (4/325) MI 3.7% (12/325) Q-wave MI 0.0% (0/325) Non-Q-wave MI 3.7% (12/325) ARC Stent Thrombosis 0.6% (2/318) Definite or Probable 0.6% (2/318) Definite 0.6% (2/318) Probable 0.0% (0/318) Peri-Procedural Endpoints Procedural Success 95.4% (313/328) Technical Success a 98.5% (332/337) a denominator is number of study stents attempted Numbers are % (count/sample size). This trial was not sized to determine the rate of low frequency events with a pre-specified precision. Abbreviations: ARC=Academic Research Consortium; CABG=coronary artery bypass graft; MI=myocardial infarction; PCI=percutaneous coronary intervention; TLR=target lesion revascularization; TVR=target vessel revascularization. Primary Endpoint (9-Month TLF): The primary endpoint was met. The 9 month TLF rate was 11.5% and the upper 1-sided 95% confidence bound of 14.79% was less that the prespecified PG of 21.2% (p<0.0001). Similar results were found whether the per protocol or the ITT subject populations were analyzed. Table 9.2 OMEGA Primary Endpoint ITT c (N=328) Per protocol (N=325) OMEGA 11.5% (37/323) 11.6% (37/320) 95% Confidence Interval 95% UCB a Performance Goal b 1-sided P value [8.2%, 15.4%] 14.79% 21.2% < [8.3%, 15.6%] 14.93% 21.2% < P value is based on the exact binomial test. a: One-sided 95% Clopper-Pearson upper confidence bound b: Based on historical BMS results c: Primary analysis Results in Males and Females: OMEGA data were evaluated retrospectively for possible genderbased differences in clinical outcomes. OMEGA was not designed or powered to study safety or effectiveness of the OMEGA Stent in gender-specific subgroups, so these analyses were performed post hoc and are considered hypothesis-generating. In the OMEGA ITT population, of the 328 enrolled patients, 222 patients were male (67.7%) and 106 patients were female (32.3%). In the United States, an estimated 15.4 million adults of 20 years and older (7.9% of men and 5.1% of women) suffer from coronary artery disease (CAD). 3 However, it is estimated that only about 33% of the annual PCIs are performed in women. In PCI clinical trials, women represent only 25-35% of the enrolled populations, and there are relatively little gender specific data. The disproportionate enrollment distribution in this trial may be partly attributable to gender differences in pathophysiology, risk factors, and symptoms which may lead to underdiagnosis and under-referral of female patients with CAD. 4,5 Once diagnosed and treated, poorer revascularization outcomes have been reported in women due to smaller coronary arteries and increased prevalence of baseline comorbidities including advanced age, diabetes, hypertension, and peripheral vascular disease compared with men. In patients treated with the OMEGA stent, the 9-month rate of TLF was 12.3% in males and 9.6% in females. This post hoc analysis shows similar treatment effect between genders for the primary endpoint of 9-month TLF and its components. This suggests that the overall conclusions of the trial regarding both safety and effectiveness of the OMEGA stent can be generalized to males and females.
5 Table 9.3 OMEGA 9-Month TLF Results by Gender, Intent-to-Treat, All Patients (N=328) Event OMEGA Females (N=106) [95% CI] OMEGA Males (N=222) [95% CI] 9 Month TLF 9.6% (10/104) [4.7%, 17.0%] 12.3% (27/219) [8.3%, 17.4%] This trial was not sized to determine the rate of low frequency events with a pre-specified precision. Numbers are % (count/sample size). 9-Month TLF is the proportion of patients who experience a target lesion failure (defined as any ischemia-driven revascularization of the target lesion [TLR], MI [Q-wave and non -Q wave] related to the target vessel, or cardiac death) up to 270 days post-procedure out of the population that have been followed for at least 240 days or who have experienced a TLF up to 270 days post-procedure. Table 9.4 shows OMEGA 9-Month clinical results for male and female patients. Given the small number of patients enrolled, no conclusions can be drawn from these data. Table Month Clinical Endpoints by Gender, Intent-to-Treat, All Patients OMEGA Female Patients (N=106) OMEGA Male Patients (N=222) EFFICACY TVR, Overall 7.6% (8/105) 9.1% (20/220) TLR, Overall 6.7% (7/105) 7.7% (17/220) TLR, PCI 6.7% (7/105) 7.7% (17/220) TLR, CABG 0.0% (0/105) 0.0% (0/220) Non-TLR TVR, Overall 2.9% (3/105) 1.4% (3/220) Non-TLR TVR, PCI 2.9% (3/105) 1.4% (3/220) Non-TLR TVR, CABG 0.0% (0/105) 0.0% (0/220) SAFETY All Death 1.0% (1/105) 2.3% (5/220) Cardiac Death or MI 3.8% (4/105) 5.5% (12/220) Cardiac Death 0.0% (0/105) 1.8% (4/220) MI 3.8% (4/105) 3.6% (8/220) Q-wave MI 0.0% (0/105) 0.0% (0/220) Non-Q-wave MI 3.8% (4/105) 3.6% (8/220) ARC Stent Thrombosis 1.0% (1/104) 0.5% (1/214) Definite or Probable 1.0% (1/104) 0.5% (1/214) Definite 1.0% (1/104) 0.5% (1/214) Probable 0.0% (0/104) 0.0% (0/214) Peri-Procedural Endpoints Procedural Success 95.3% (101/106) 95.5% (212/222) Technical Success a 99.1% (106/107) 98.3% (226/230) a denominator is number of study stents attempted Numbers are % (count/sample size). This trial was not sized to determine the rate of low frequency events with a pre-specified precision. Abbreviations: ARC=Academic Research Consortium; CABG=coronary artery bypass graft; MI=myocardial infarction; PCI=percutaneous coronary intervention; TLR=target lesion revascularization; TVR=target vessel revascularization. 2 King SB, 3rd, Smith SC, Jr., Hirshfeld JW, Jr., et al Focused Update of the ACC/AHA/SCAI 2005 Guideline Update for Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines: 2007 Writing Group to Review New Evidence and Update the ACC/AHA/SCAI 2005 Guideline Update for Percutaneous Coronary Intervention, Writing on Behalf of the 2005 Writing Committee. Circulation 2008;117: Alan S. Go, Dariush Mozaffarian, Veronique L. Roger et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics Update: A Report From the American Heart Association Circulation 2014, 29:e28-d292 4 Shaw LJ, Bairey Merz CN, Pepine CJ, et al. Insights from the NHLBI-Sponsored Women s Ischemia Syndrome Evaluation (WISE) Study: Part 1: gender differences in traditional and novel risk factors, symptom evaluation, and gender-optimized diagnostic strategies. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006; 47(3):S4-S20. 5 Lori Mosca, Emilia J. Benjamin, Kathy Berra et al. Effectiveness Based Guidelines for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease in Women Update: A Guideline From the American Heart Association Circulation 2011, 123: INDIVIDUALIZATION OF TREATMENT: The risks and benefits should be carefully considered for each patient before use of the REBEL Stent System. Patient selection factors to be assessed should include a judgment regarding risk of prolonged antiplatelet therapy. Aspirin should be administered indefinitely. Stenting is generally avoided in those patients at heightened risk of bleeding (e.g., those patients with recently active gastritis or peptic ulcer disease) in whom antiplatelet therapy would be contraindicated. Premorbid conditions that increase the risk of poor initial results or the risks of emergency referral for bypass surgery (diabetes mellitus, renal failure, and severe obesity) should be reviewed. 11 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION: Physicians should consider the following in counseling patients about this product: Discuss the risks associated with stent placement. Discuss the risks/benefits issues for this particular patient. Discuss alteration to current lifestyle immediately following the procedure and over the long term. The following patient materials are available for this product: A Patient Information Guide (included in the package and available on-line) which includes both product information and a stent implant card. 5 An Angioplasty and Stent Education Guide (available on-line or by request) which includes information on coronary artery disease, the implant procedure, and frequently asked questions 12 HOW SUPPLIED: Do not use if package is opened or damaged. Do not use if labeling is incomplete or illegible. Handling and Storage Store in cool, dry, dark place. 13 OPERATIONAL INSTRUCTIONS: 13.1 Inspection Prior to Use Do not use the product after the Use By date. Carefully inspect the sterile package before opening. If the integrity of sterile package has been compromised prior to the product Use By date (e.g., damage of the package), contact your local Boston Scientific representative for return information. Do not use if any defects are noted Materials Required (not included in Stent Delivery System package) Quantity Material 1 Appropriate guide catheter (see Table 2.1, REBEL Stent System Product Description) ml (cc) syringe 1000 u /500 cc Normal heparinized sterile saline in (0.36 mm) guidewire 1 Rotating hemostatic valve 1 Diluted contrast medium 1:1 with normal heparinized sterile saline 1 Inflation Device 1 Torque Device 1 Pre-deployment dilation catheter 1 Three-way stopcock 1 Appropriate arterial sheath 13.3 Preparation Packaging Removal 1. Open the outer box to reveal the pouch and carefully inspect the pouch for damage. 2. Carefully peel open the sterile barrier using aseptic techniques and extract the stent delivery system. 3. Carefully remove the stent delivery system from its protective tubing for preparation of the delivery system. When using a Monorail system, do not bend or kink proximal shaft during removal. 4. Remove the product mandrel and stent protector by grasping the catheter just proximal to the stent (at the proximal balloon bond site), and, with the other hand, grasp the stent protector and gently remove distally. Note: If unusual resistance is felt during product mandrel and stent protector removal, do not use the product and replace with another. 5. Examine the device for any damage. If it is suspected that the sterility or performance of the device has been compromised, the device should not be used. 6. A Monorail Catheter may be coiled once and secured using the CLIPIT Coil Clips provided in the catheter package. Only the proximal shaft should be inserted into the CLIPIT device; the clip is not intended for the distal end of the catheter. Note: Care should be taken not to kink or bend the shaft upon application or removal of the CLIPIT Coil Clip Guidewire Lumen Flush 1. (Over-The-Wire only) Flush the stent delivery system guidewire lumen with normal heparinized saline through the straight arm of the Y-connector manifold. 2. (Monorail only) Flush the stent delivery system guidewire lumen with normal heparinized saline using the flushing needle supplied for the Monorail delivery system at the distal end. 3. Verify that the stent is positioned between the proximal and distal balloon markers. Check for bends, kinks, and other damage. Do not use if any defects are noted. Note: Avoid manipulation of the stent during flushing of the guidewire lumen, as this may disrupt the placement of the stent on the balloon Delivery System Preparation 1. Prepare inflation device/syringe with diluted contrast medium. 2. Attach inflation device/syringe to stopcock; attach to inflation port. Do not bend the proximal shaft/hypotube when connecting to inflation device/syringe. 3. With tip down, orient stent delivery system vertically.
6 4. Open stopcock to stent delivery system; pull negative for 15 seconds; release to neutral for contrast fill. 5. Close stopcock to stent delivery system; purge inflation device/ syringe of all air. 6. Repeat steps 4 through 6 until all air is expelled. If bubbles persist, do not use product. 7. If a syringe was used, attach a prepared inflation device to stopcock. 8. Open stopcock to stent delivery system. 9. Leave inflation device on neutral pressure Delivery Procedure 1. Prepare the vascular access site according to standard PTCA practice. 2. Predilate the lesion/vessel with appropriate diameter balloon. 3. Maintain neutral pressure on inflation device attached to stent delivery system. 4. Backload stent delivery system onto proximal end of guidewire while maintaining guidewire position across target lesion. 5. Fully open rotating hemostatic valve to allow for easy passage of the stent and prevent damage to the stent. 6. Carefully advance the stent delivery system into the hub of the guide catheter. When using a Monorail stent delivery system be sure to keep the proximal shaft/hypotube straight. Ensure guide catheter stability before advancing the stent delivery system into the coronary artery. 5. Repeat angiography to assess the stented area. If an adequate expansion has not been obtained, exchange back to the original stent delivery catheter or exchange to another balloon catheter of appropriate balloon diameter to achieve proper stent apposition to the vessel wall Post-Deployment Dilatation of Stented Segments Precaution: Do not dilate the stent beyond the limits tabulated below. Nominal Stent Diameter (ID) Dilatation Limits (ID)* 2.25 mm 2.75 mm 2.50 mm 2.75 mm 3.50 mm 3.00 mm 3.50 mm 4.25 mm 4.00 mm 4.50 mm 5.75 mm *Maximum Stent Inner Diameter All efforts should be taken to assure that the stent is not under-dilated. If the deployed stent size is still inadequate with respect to vessel diameter, or if full contact with the vessel wall is not achieved, a larger balloon may be used to expand the stent. The stent may be expanded using a low profile and high pressure balloon catheter. If this is required, the stented segment should be recrossed carefully with a prolapsed guidewire to avoid dislodging the stent. The balloon should be centered within the stent and should not extend outside of the stented region. Note: If unusual resistance is felt before the stent exits the guide catheter, do not force passage. Resistance may indicate a problem, and use of excessive force may result in stent damage or stent dislodgment from the balloon. Maintain guidewire placement across the lesion, and remove the stent delivery system and guide catheter as a single unit. 7. Advance the stent delivery system over the guidewire to target lesion under direct fluoroscopic visualization. Utilize the proximal and distal radiopaque balloon markers as a reference point. If the position of the stent is not optimal, it should be carefully repositioned or removed (See also Precautions tion 6.11, Stent Delivery System Removal Pre-deployment). The inside edges of the marker bands indicate both the stent edges and balloon shoulders. Expansion of the stent should not be undertaken if the stent is not properly positioned in the target lesion segment of the vessel. Note: If unusual resistance is felt at any time during lesion access before stent implantation, the stent delivery system and the guide catheter should be removed as a single unit. (See also Precautions tion 6.11, Stent Delivery System Removal Predeployment). Once the stent delivery system has been removed do not re-use. 8. Sufficiently tighten the rotating hemostatic valve. The stent is now ready to be deployed Deployment Procedure 1. Under fluoroscopic visualization, inflate the delivery system expanding the stent to a minimum pressure of 11 atm (1117 kpa). Higher pressure may be necessary to optimize stent apposition to the arterial wall. Accepted practice generally targets an initial deployment pressure that would achieve a stent inner diameter of about 1.1 times the reference vessel diameter (see Table 13.1). Balloon pressure must not exceed rated burst pressure of 18 atm (1827 kpa). 2. Maintain inflation pressure for seconds for full expansion of the stent. 3. Deflate balloon by pulling negative pressure on inflation device until balloon is fully deflated (see Table 6.1, Delivery System Deflation Time Specifications). 4. Confirm stent position and deployment using standard angiographic techniques. For optimal results, the entire stenosed arterial segment should be covered by the stent. Fluoroscopic visualization during stent expansion should be used in order to properly judge the optimum expanded stent diameter as compared to the proximal and distal coronary artery diameter(s). Optimal expansion requires that the stent be in full contact with the artery wall. Stent wall contact should be verified through routine angiography or intravascular ultrasound (IVUS). 5. If stent sizing/apposition requires optimization, readvance the stent delivery system balloon, or another high-pressure, balloon catheter of the appropriate size, to the stented area using standard angioplasty techniques. 6. Inflate the balloon to the desired pressure while observing under fluoroscopy (refer to product labeling and/or Table 13.1 for compliance chart). Deflate the balloon (see Table 6.1, Delivery System Deflation Time Specifications). 7. If more than one REBEL stent is needed to cover the lesion and balloon treated area, it is suggested that, to avoid the potential for gap restenosis, the stents be adequately overlapped. To ensure that there are no gaps between stents, the balloon marker bands of the second REBEL stent should be positioned inside of the deployed stent prior to expansion. 8. Reconfirm stent position(s) and angiographic result. Repeat inflations until optimal stent deployment is achieved Removal Procedure 1. Ensure balloon is fully deflated before delivery system withdrawal. 2. Fully open rotating hemostatic valve. 3. While maintaining guidewire position and negative pressure on inflation device, withdraw delivery system. 4. Monorail Catheters may be coiled once and secured using the CLIPIT Coil Clip (see tion , Packaging Removal). 6 Note: In line with tion 6.13, Post-Procedure: Care must be exercised when crossing a newly deployed stent with any wire, catheter or ancillary device to avoid disrupting the stent placement, apposition, and/or geometry In Vitro Information Table 13.1 Typical REBEL Stent System Compliance Pressure Stent I.D. (mm) atm - kpa N/A Nominal Rated* * Rated Burst Pressure. DO NOT EXCEED. Pressure Stent O.D. (mm) atm - kpa N/A Nominal Rated* * Rated Burst Pressure. DO NOT EXCEED.
7 warranty Boston Scientific Corporation (BSC) warrants that reasonable care has been used in the design and manufacture of this instrument. This warranty is in lieu of and excludes all other warranties not expressly set forth herein, whether express or implied by operation of law or otherwise, including, but not limited to, any implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose. Handling, storage, cleaning and sterilization of this instrument as well as other factors relating to the patient, diagnosis, treatment, surgical procedures and other matters beyond BSC s control directly affect the instrument and the results obtained from its use. BSC s obligation under this warranty is limited to the repair or replacement of this instrument and BSC shall not be liable for any incidental or consequential loss, damage or expense directly or indirectly arising from the use of this instrument. BSC neither assumes, nor authorizes any other person to assume for it, any other or additional liability or responsibility in connection with this instrument. BSC assumes no liability with respect to instruments reused, reprocessed or resterilized and makes no warranties, express or implied, including but not limited to merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose, with respect to such instruments. 7
8 Argentina ARG Local Contact Para obtener información de contacto de Boston Scientific Argentina SA, por favor, acceda al link Brazil BRA Local Contact Para informações de contato da Boston Scientific do Brasil Ltda, por favor, acesse o link EC REP Boston Scientific Limited Ballybrit Business Park Galway IRELAND EU Authorized Representative Australian AUS Sponsor Address Boston Scientific (Australia) Pty Ltd PO Box 332 BOTANY NSW 1455 Australia Free Phone Free Fax Legal Manufacturer Boston Scientific Corporation 300 Boston Scientific Way Marlborough, MA USA USA Customer Service Do not use if package is damaged. Recyclable Package 2014 Boston Scientific Corporation or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Table 1. Balloon and Stent Specifications. Nominal Pressure During Stent Deployment (atm/kpa) Stent Length (mm)
 90590772-01 ONLY Caution: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. warning 2010-05 < EN > VeriFLEX (Liberté ) m o n o r a i l o v e r - t h e - w i r e Bare-Metal
90590772-01 ONLY Caution: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. warning 2010-05 < EN > VeriFLEX (Liberté ) m o n o r a i l o v e r - t h e - w i r e Bare-Metal
GRAFTMASTER RX Coronary Stent Graft System PPL2082232 (2/1/13)
 GRAFTMASTER RX Coronary Stent Graft System PPL2082232 (2/1/13) Graphical Symbols for Medical Device Labeling Manufacturer Sterilized using ethylene oxide Catalogue number Batch code French size Outer diameter
GRAFTMASTER RX Coronary Stent Graft System PPL2082232 (2/1/13) Graphical Symbols for Medical Device Labeling Manufacturer Sterilized using ethylene oxide Catalogue number Batch code French size Outer diameter
Instructions for Use. Device Description The AMPLATZER Vascular Plug II is a self-expandable nitinol mesh occlusion device (see Figure 1).
 Vascular Plug II Instructions for Use Device Description The AMPLATZER Vascular Plug II is a self-expandable nitinol mesh occlusion device (see Figure 1). A B Figure 1. AMPLATZER Vascular Plug II A. Nitinol
Vascular Plug II Instructions for Use Device Description The AMPLATZER Vascular Plug II is a self-expandable nitinol mesh occlusion device (see Figure 1). A B Figure 1. AMPLATZER Vascular Plug II A. Nitinol
LifeStent XL Biliary Stent System
 B05688 Rev.2/07-13 LifeStent XL Biliary Stent System Recommended Guidewire Length Table Catheter Working Length Recommended Guidewire Length 130 cm 300 cm 80 cm 260 cm 130 cm & 80 cm 160 cm & 110 cm Figure
B05688 Rev.2/07-13 LifeStent XL Biliary Stent System Recommended Guidewire Length Table Catheter Working Length Recommended Guidewire Length 130 cm 300 cm 80 cm 260 cm 130 cm & 80 cm 160 cm & 110 cm Figure
Wingspan Stent System with Gateway PTA Balloon Catheter
 Wingspan System with Gateway PTA Balloon Catheter Directions for Use AUS Australian Sponsor Address Boston Scientific (Australia) Pty Ltd PO Box 332 BOTANY NSW 1455 Australia Free Phone 1800 676 133 Free
Wingspan System with Gateway PTA Balloon Catheter Directions for Use AUS Australian Sponsor Address Boston Scientific (Australia) Pty Ltd PO Box 332 BOTANY NSW 1455 Australia Free Phone 1800 676 133 Free
XIENCE V and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Examination
 XIENCE V and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Examination To Whom it May Concern: Thank you for your inquiry regarding magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) examinations of patients implanted with the Abbott Vascular
XIENCE V and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Examination To Whom it May Concern: Thank you for your inquiry regarding magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) examinations of patients implanted with the Abbott Vascular
Majestic Trial 12 Month Results
 Majestic Trial 12 Month Results S.Müller-Hülsbeck, MD, EBIR, FCIRSE, FICA ACADEMIC HOSPITALS Flensburg of Kiel University Ev.-Luth. Diakonissenanstalt zu Flensburg Knuthstraße 1, 24939 FLENSBURG Dept.
Majestic Trial 12 Month Results S.Müller-Hülsbeck, MD, EBIR, FCIRSE, FICA ACADEMIC HOSPITALS Flensburg of Kiel University Ev.-Luth. Diakonissenanstalt zu Flensburg Knuthstraße 1, 24939 FLENSBURG Dept.
Bard LifeStar Biliary Stent System
 Bard LifeStar Biliary Stent System Instructions For Use (IFU) Bard LifeStar Biliary Stent System Delivery System Diagram B05686 Vers.1/08-11 1 Information for use Read the Bard LifeStar Biliary Stent System
Bard LifeStar Biliary Stent System Instructions For Use (IFU) Bard LifeStar Biliary Stent System Delivery System Diagram B05686 Vers.1/08-11 1 Information for use Read the Bard LifeStar Biliary Stent System
Clinical Programs. Medtronic Coronary Stent Systems. driver BMS
 Clinical Programs Medtronic Coronary Stent Systems Endeavor DES driver BMS July 2010 Contents Overview of Clinical Programs... 2 Drug-Eluting Stents ENDEAVOR I*... 4 ENDEAVOR II*... 6 ENDEAVOR II Continued
Clinical Programs Medtronic Coronary Stent Systems Endeavor DES driver BMS July 2010 Contents Overview of Clinical Programs... 2 Drug-Eluting Stents ENDEAVOR I*... 4 ENDEAVOR II*... 6 ENDEAVOR II Continued
PRECOMBAT Trial. Seung-Whan Lee, MD, PhD On behalf of the PRECOMBAT Investigators
 Premier of Randomized Comparison of Bypass Surgery versus Angioplasty Using Sirolimus-Eluting Stent in Patients with Left Main Coronary Artery Disease PRECOMBAT Trial Seung-Whan Lee, MD, PhD On behalf
Premier of Randomized Comparison of Bypass Surgery versus Angioplasty Using Sirolimus-Eluting Stent in Patients with Left Main Coronary Artery Disease PRECOMBAT Trial Seung-Whan Lee, MD, PhD On behalf
PATIENT INFORMATION BOOKLET
 PATIENT INFORMATION BOOKLET Wingspan Stent System with Gateway PTA Balloon Catheter TABLE OF CONTENTS Definitions... 2 What is the Purpose of This Booklet?... 3 What is an Intracranial Lesion?... 3 Who
PATIENT INFORMATION BOOKLET Wingspan Stent System with Gateway PTA Balloon Catheter TABLE OF CONTENTS Definitions... 2 What is the Purpose of This Booklet?... 3 What is an Intracranial Lesion?... 3 Who
RX Herculink Elite Renal and Biliary Stent system Instructions for Use. RX Herculink Elite Renal Stent System. Table of Contents
 RX Herculink Elite Renal and Biliary Stent system Instructions for Use Table of Contents RX Herculink Elite Renal Stent System 1.0 DEVICE DESCRIPTION Table 1. In Vitro* Device Specifications 2.0 HOW SUPPLIED
RX Herculink Elite Renal and Biliary Stent system Instructions for Use Table of Contents RX Herculink Elite Renal Stent System 1.0 DEVICE DESCRIPTION Table 1. In Vitro* Device Specifications 2.0 HOW SUPPLIED
MEDICAL POLICY No. 91580-R1 DRUG-ELUTING STENTS FOR ISCHEMIC HEART DISEASE
 DRUG-ELUTING STENTS FOR ISCHEMIC HEART DISEASE Effective Date: October 1, 2015 Review Dates: 10/11, 10/12, 10/13, 8/14, 8/15 Date Of Origin: October 12, 2011 Status: Current Summary of Changes Clarifications:
DRUG-ELUTING STENTS FOR ISCHEMIC HEART DISEASE Effective Date: October 1, 2015 Review Dates: 10/11, 10/12, 10/13, 8/14, 8/15 Date Of Origin: October 12, 2011 Status: Current Summary of Changes Clarifications:
Ostial LAD: Single stent approach is the best. Antonio A. Pocoví, MD, FSCAI, MTSAC, Advisory Council Member, CACI
 Ostial LAD: Single stent approach is the best Antonio A. Pocoví, MD, FSCAI, MTSAC, Advisory Council Member, CACI Chair, Interventional Cardiology Sanatorio San Lucas Instituto Alexander Fleming Buenos
Ostial LAD: Single stent approach is the best Antonio A. Pocoví, MD, FSCAI, MTSAC, Advisory Council Member, CACI Chair, Interventional Cardiology Sanatorio San Lucas Instituto Alexander Fleming Buenos
Contraindications: Malign or benign strictures in the upper part of esophagus close to the cricopharyngeal muscle.
 Manufactured by: ELLA CS, s.r.o. Milady Horákové 504 500 06 Hradec Králové 6 Czech Republic Phone: +420 49 527 91 11 Fax: +420 49 526 56 55 E-mail: volenec@ellacs.cz Instructions for Use FerX-ELLA Esophageal
Manufactured by: ELLA CS, s.r.o. Milady Horákové 504 500 06 Hradec Králové 6 Czech Republic Phone: +420 49 527 91 11 Fax: +420 49 526 56 55 E-mail: volenec@ellacs.cz Instructions for Use FerX-ELLA Esophageal
Supera Peripheral Stent System Instructions for Use
 Supera Peripheral Stent System Instructions for Use Table of Contents 1.0 DEVICE DESCRIPTION 2.0 HOW SUPPLIED 3.0 INDICATIONS 4.0 CONTRAINDICATIONS 5.0 WARNINGS 6.0 PRECAUTIONS 6.1 Stent Delivery System
Supera Peripheral Stent System Instructions for Use Table of Contents 1.0 DEVICE DESCRIPTION 2.0 HOW SUPPLIED 3.0 INDICATIONS 4.0 CONTRAINDICATIONS 5.0 WARNINGS 6.0 PRECAUTIONS 6.1 Stent Delivery System
A Post-market Study to Assess the STENTYS Self-exPanding COronary Stent In AcuTe myocardial InfarctiON in Real Life APPOSITION III
 A Post-market Study to Assess the STENTYS Self-exPanding COronary Stent In AcuTe myocardial InfarctiON in Real Life APPOSITION III Gilles Montalescot, MD, PhD Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital, Paris, France
A Post-market Study to Assess the STENTYS Self-exPanding COronary Stent In AcuTe myocardial InfarctiON in Real Life APPOSITION III Gilles Montalescot, MD, PhD Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital, Paris, France
PROMUS Element Plus. Everolimus-Eluting Platinum Chromium Coronary Stent System. Patient Information Guide
 PROMUS Element Plus Patient Information Guide PROMUS Element Plus Patient Information Guide You have recently had a PROMUS Element drug-coated stent implanted in the coronary arteries of your heart. The
PROMUS Element Plus Patient Information Guide PROMUS Element Plus Patient Information Guide You have recently had a PROMUS Element drug-coated stent implanted in the coronary arteries of your heart. The
Innova Vascular OVER-THE-WIRE
 POTENTIAL ADVERSE EVENTS... HOW SUPPLIED...6 909580-0 Innova Vascular OVER-THE-WIRE Self-Expanding Stent System TABLE OF CONTENTS 05-07 < en > WARNING... DEVICE DESCRIPTION... Contents... INTENDED USE
POTENTIAL ADVERSE EVENTS... HOW SUPPLIED...6 909580-0 Innova Vascular OVER-THE-WIRE Self-Expanding Stent System TABLE OF CONTENTS 05-07 < en > WARNING... DEVICE DESCRIPTION... Contents... INTENDED USE
AERO. Tracheobronchial Stent Technology System
 AERO Tracheobronchial Stent Technology System Review Instructions For Use Before Using This System. Single Use Non-sterile MR Conditional CONTENTS Instructions For Use.............................. 3 IMPORTANT
AERO Tracheobronchial Stent Technology System Review Instructions For Use Before Using This System. Single Use Non-sterile MR Conditional CONTENTS Instructions For Use.............................. 3 IMPORTANT
GENERAL HEART DISEASE KNOW THE FACTS
 GENERAL HEART DISEASE KNOW THE FACTS WHAT IS Heart disease is a broad term meaning any disease affecting the heart. It is commonly used to refer to coronary heart disease (CHD), a more specific term to
GENERAL HEART DISEASE KNOW THE FACTS WHAT IS Heart disease is a broad term meaning any disease affecting the heart. It is commonly used to refer to coronary heart disease (CHD), a more specific term to
Angioplasty and Stent Education Guide
 Angioplasty and Stent Education Guide Table of Contents Treating coronary artery disease...2 What is coronary artery disease...3 Coronary artery disease treatment options...4 What are coronary artery
Angioplasty and Stent Education Guide Table of Contents Treating coronary artery disease...2 What is coronary artery disease...3 Coronary artery disease treatment options...4 What are coronary artery
Bard LifeStar Vascular Stent System
 Bard LifeStar Vascular Stent System Instructions For Use (IFU) Bard LifeStar Vascular Stent System Delivery System Diagram B05685 Vers.1/08-11 1 Instructions for use Read the Bard LifeStar Vascular Stent
Bard LifeStar Vascular Stent System Instructions For Use (IFU) Bard LifeStar Vascular Stent System Delivery System Diagram B05685 Vers.1/08-11 1 Instructions for use Read the Bard LifeStar Vascular Stent
Understanding Coronary Artery Disease, Cardiac Catheterization, and Treatment Options. A Guide for Patients
 Understanding Coronary Artery Disease, Cardiac Catheterization, and Treatment Options A Guide for Patients Coronary Artery Disease If you or a member of your family has been diagnosed with coronary artery
Understanding Coronary Artery Disease, Cardiac Catheterization, and Treatment Options A Guide for Patients Coronary Artery Disease If you or a member of your family has been diagnosed with coronary artery
100000002022.2. Instructions for Use. Cordis S.M.A.R.T. CONTROL Vascular Stent System
 100000002022.2 Instructions for Use Cordis S.M.A.R.T. CONTROL Vascular Stent System Symbols Catalog Number LOT NonPyrogenic Lot Number Store in cool, dark, dry place Use By Date Sterilized with ethylene
100000002022.2 Instructions for Use Cordis S.M.A.R.T. CONTROL Vascular Stent System Symbols Catalog Number LOT NonPyrogenic Lot Number Store in cool, dark, dry place Use By Date Sterilized with ethylene
RELAY Plus Thoracic Stent-Graft System with Transport Delivery System
 RELAY Plus Thoracic Stent-Graft System with Transport Delivery System TABLE OF CONTENTS Section Page DEVICE DESCRIPTION 8 RADIOPAQUE MARKER BANDS 8 RELAY PLUS TRANSPORT DELIVERY SYSTEM 8 INDICATIONS FOR
RELAY Plus Thoracic Stent-Graft System with Transport Delivery System TABLE OF CONTENTS Section Page DEVICE DESCRIPTION 8 RADIOPAQUE MARKER BANDS 8 RELAY PLUS TRANSPORT DELIVERY SYSTEM 8 INDICATIONS FOR
Instructions for Use Cordis PRECISE Nitinol Stent System (5.5F and 6F) 10368453-2
 Instructions for Use Cordis PRECISE Nitinol Stent System (5.5F and 6F) 10368453-2 Caution: Federal (USA) law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. Read all instructions carefully.
Instructions for Use Cordis PRECISE Nitinol Stent System (5.5F and 6F) 10368453-2 Caution: Federal (USA) law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. Read all instructions carefully.
The Bioresorbable Vascular Stent Dr Albert Ko
 The Bioresorbable Vascular Stent Dr Albert Ko Dr Albert Ko MB BS, FRACP, FCSANZ Interventional/General Cardiologist Ascot Cardiology Symposium 2013 Treatment Goals for Coronary Artery Disease Relieve of
The Bioresorbable Vascular Stent Dr Albert Ko Dr Albert Ko MB BS, FRACP, FCSANZ Interventional/General Cardiologist Ascot Cardiology Symposium 2013 Treatment Goals for Coronary Artery Disease Relieve of
The Cardiac Society of Australia and New Zealand
 The Cardiac Society of Australia and New Zealand Guidelines on Support Facilities for Coronary Angiography and Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) including Guidelines on the Performance of Procedures
The Cardiac Society of Australia and New Zealand Guidelines on Support Facilities for Coronary Angiography and Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) including Guidelines on the Performance of Procedures
California Health and Safety Code, Section 1256.01
 California Health and Safety Code, Section 1256.01 1256.01. (a) The Elective Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Pilot Program is hereby established in the department. The purpose of the pilot program
California Health and Safety Code, Section 1256.01 1256.01. (a) The Elective Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Pilot Program is hereby established in the department. The purpose of the pilot program
IN.PACT ADMIRAL DRUG-COATED BALLOON NEW TECHNOLOGY ADD-ON PAYMENT (NTAP)
 IN.PACT ADMIRAL DRUG-COATED BALLOON NEW TECHNOLOGY ADD-ON PAYMENT (NTAP) New Technology Add-on (NTAP) for DCB OVERVIEW Effective October 1, 2015, hospital inpatient cases using a drug-coated balloon (DCB)
IN.PACT ADMIRAL DRUG-COATED BALLOON NEW TECHNOLOGY ADD-ON PAYMENT (NTAP) New Technology Add-on (NTAP) for DCB OVERVIEW Effective October 1, 2015, hospital inpatient cases using a drug-coated balloon (DCB)
Cilostazol versus Clopidogrel after Coronary Stenting
 Cilostazol versus Clopidogrel after Coronary Stenting Seong-Wook Park, MD, PhD, FACC Division of Cardiology, Asan Medical Center University of Ulsan College of Medicine Seoul, Korea AMC, 2004 Background
Cilostazol versus Clopidogrel after Coronary Stenting Seong-Wook Park, MD, PhD, FACC Division of Cardiology, Asan Medical Center University of Ulsan College of Medicine Seoul, Korea AMC, 2004 Background
Drug-Eluting Balloons. Klaus Bonaventura Department of Cardiology and Angiology Heart Thorax Vascular Center, Klinikum Ernst von Bergmann, Potsdam
 Drug-Eluting Balloons Klaus Bonaventura Department of Cardiology and Angiology Heart Thorax Vascular Center, Klinikum Ernst von Bergmann, Potsdam Potential conflicts of interest Speaker s name: Klaus Bonaventura
Drug-Eluting Balloons Klaus Bonaventura Department of Cardiology and Angiology Heart Thorax Vascular Center, Klinikum Ernst von Bergmann, Potsdam Potential conflicts of interest Speaker s name: Klaus Bonaventura
TAXUS Express 2. Paclitaxel-Eluting Coronary Stent System. Patient Information Guide
 TAXUS Express 2 Paclitaxel-Eluting Coronary Stent System Patient Information Guide 1 Table of Contents Coronary Artery Disease...2 Who Is at Risk?...3 Diagnosis of Coronary Artery Disease...3 Treatment
TAXUS Express 2 Paclitaxel-Eluting Coronary Stent System Patient Information Guide 1 Table of Contents Coronary Artery Disease...2 Who Is at Risk?...3 Diagnosis of Coronary Artery Disease...3 Treatment
GUIDELINES ON MEDICAL DEVICES EVALUATION OF CLINICAL DATA - A GUIDE FOR MANUFACTURERS AND NOTIFIED BODIES -
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION ENTERPRISE AND INDUSTRY DIRECTORATE-GENERAL Consumer goods Cosmetics and Medical Devices MEDDEV 2.7.1 Appendix 1 December 2008 GUIDELINES ON MEDICAL DEVICES EVALUATION OF CLINICAL DATA
EUROPEAN COMMISSION ENTERPRISE AND INDUSTRY DIRECTORATE-GENERAL Consumer goods Cosmetics and Medical Devices MEDDEV 2.7.1 Appendix 1 December 2008 GUIDELINES ON MEDICAL DEVICES EVALUATION OF CLINICAL DATA
Instructions For Use
 Instructions For Use B05667 Rev.4/05-14 INFORMATION FOR USE Caution: Federal law (U.S.) restricts the use of this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. Device Description The Fluency Plus
Instructions For Use B05667 Rev.4/05-14 INFORMATION FOR USE Caution: Federal law (U.S.) restricts the use of this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. Device Description The Fluency Plus
OCT ASSESSMENT OF CUTTING BALLOON ANGIOPLASTY FOR IN-STENT RESTENOSIS
 OCT ASSESSMENT OF CUTTING BALLOON ANGIOPLASTY FOR IN-STENT RESTENOSIS Division of Cardiology, Mount Sinai Hospital, New York, NY, USA Yuliya Vengrenyuk, PhD; and Annapoorna Kini, MD OCT ASSESSMENT OF CUTTING
OCT ASSESSMENT OF CUTTING BALLOON ANGIOPLASTY FOR IN-STENT RESTENOSIS Division of Cardiology, Mount Sinai Hospital, New York, NY, USA Yuliya Vengrenyuk, PhD; and Annapoorna Kini, MD OCT ASSESSMENT OF CUTTING
TAXUS Express2 Paclitaxel-Eluting Coronary Stent System TAXUS Liberté Paclitaxel-Eluting Coronary Stent System. A Patient s Guide
 TAXUS Express2 Paclitaxel-Eluting Coronary Stent System TAXUS Liberté Paclitaxel-Eluting Coronary Stent System A Patient s Guide Table of Contents Coronary Artery Disease... 2 Who Is at Risk?... 3 Diagnosis
TAXUS Express2 Paclitaxel-Eluting Coronary Stent System TAXUS Liberté Paclitaxel-Eluting Coronary Stent System A Patient s Guide Table of Contents Coronary Artery Disease... 2 Who Is at Risk?... 3 Diagnosis
Allium Ureteral Stent (URS)
 Allium Ureteral Stent (URS) Instructions For Use Manufactured by Allium Ltd. DEVICE NAME: ALLIUM Ureteral Stent (URS) is intended to be inserted into the lower ureter to allow free flow of urine from the
Allium Ureteral Stent (URS) Instructions For Use Manufactured by Allium Ltd. DEVICE NAME: ALLIUM Ureteral Stent (URS) is intended to be inserted into the lower ureter to allow free flow of urine from the
Imaging of Thoracic Endovascular Stent-Grafts
 Imaging of Thoracic Endovascular Stent-Grafts Tariq Hameed, M.D. Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, Indiana Disclosures: No relevant financial
Imaging of Thoracic Endovascular Stent-Grafts Tariq Hameed, M.D. Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, Indiana Disclosures: No relevant financial
Understanding your Renal Stent Procedure. A patient Guide (COVER PAGE) TABLE OF CONTENTS (inside front page)
 Understanding your Renal Stent Procedure. A patient Guide (COVER PAGE) TABLE OF CONTENTS (inside front page) The Kidney and the Renal Arteries... 1 Renal Artery Disease... 2 Diagnosis of Renal.Artery Disease...
Understanding your Renal Stent Procedure. A patient Guide (COVER PAGE) TABLE OF CONTENTS (inside front page) The Kidney and the Renal Arteries... 1 Renal Artery Disease... 2 Diagnosis of Renal.Artery Disease...
A Patient Information Guide for the CYPHER Sirolimus-eluting Coronary Stent
 bringing evidence to life Understanding Coronary Artery Disease, Cardiac Catheterization, and Treatment Options A Patient Information Guide for the CYPHER Sirolimus-eluting Coronary Stent Patient s Name
bringing evidence to life Understanding Coronary Artery Disease, Cardiac Catheterization, and Treatment Options A Patient Information Guide for the CYPHER Sirolimus-eluting Coronary Stent Patient s Name
Duration of Dual Antiplatelet Therapy After Coronary Stenting
 Duration of Dual Antiplatelet Therapy After Coronary Stenting C. DEAN KATSAMAKIS, DO, FACC, FSCAI INTERVENTIONAL CARDIOLOGIST ADVOCATE LUTHERAN GENERAL HOSPITAL INTRODUCTION Coronary artery stents are
Duration of Dual Antiplatelet Therapy After Coronary Stenting C. DEAN KATSAMAKIS, DO, FACC, FSCAI INTERVENTIONAL CARDIOLOGIST ADVOCATE LUTHERAN GENERAL HOSPITAL INTRODUCTION Coronary artery stents are
Copenhagen University Hospital Rigshospitalet Aarhus University Hospital Skejby Denmark
 Long-term outcome after drug-eluting versus bare-metal stent implantation in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction 3 year follow-up of the randomised trial Peter Clemmensen, Henning Kelbæk,
Long-term outcome after drug-eluting versus bare-metal stent implantation in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction 3 year follow-up of the randomised trial Peter Clemmensen, Henning Kelbæk,
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures Diagnostic and therapeutic cardiovascular s are central to the evaluation and management of patients with cardiovascular disease. Consistent with the other sections,
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures Diagnostic and therapeutic cardiovascular s are central to the evaluation and management of patients with cardiovascular disease. Consistent with the other sections,
Overview of Newer Stent Devices for Aneurysm Treatment
 Overview of Newer Stent Devices for Aneurysm Treatment Randall C. Edgell, M.D. Associate Professor Vascular and Interventional Neurology Saint Louis University Disclosure Outcome adjudication for THERAPY,
Overview of Newer Stent Devices for Aneurysm Treatment Randall C. Edgell, M.D. Associate Professor Vascular and Interventional Neurology Saint Louis University Disclosure Outcome adjudication for THERAPY,
PROTEGE. Carotid Stent System INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE. CAUTION: Federal (U.S.A.) law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician.
 THE ENDOVASCULAR COMPANY PROTEGE RX Carotid Stent System INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE CAUTION: Federal (U.S.A.) law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. . DEVICE DESCRIPTION The PROTÉGÉ
THE ENDOVASCULAR COMPANY PROTEGE RX Carotid Stent System INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE CAUTION: Federal (U.S.A.) law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. . DEVICE DESCRIPTION The PROTÉGÉ
SCORM. For more patient education, please visit www.cypherusa.com
 Attach Label Understanding Coronary Artery Disease, Cardiac Catheterization, and Treatment Options Stent Implant Card CYPHER Sirolimus-eluting Coronary Stent SCORM P.O. Box 025700 Miami, FL 33102-5700,
Attach Label Understanding Coronary Artery Disease, Cardiac Catheterization, and Treatment Options Stent Implant Card CYPHER Sirolimus-eluting Coronary Stent SCORM P.O. Box 025700 Miami, FL 33102-5700,
Clinical Study Synopsis
 Clinical Study Synopsis This Clinical Study Synopsis is provided for patients and healthcare professionals to increase the transparency of Bayer's clinical research. This document is not intended to replace
Clinical Study Synopsis This Clinical Study Synopsis is provided for patients and healthcare professionals to increase the transparency of Bayer's clinical research. This document is not intended to replace
Automatic External Defibrillators
 Last Review Date: May 27, 2016 Number: MG.MM.DM.10dC2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
Last Review Date: May 27, 2016 Number: MG.MM.DM.10dC2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
JUL 2 2008. Ms. Kendra Basler Regulatory Affairs Associate Abbott Vascular Cardiac Therapies 3200 Lakeside Drive Santa Clara, CA 95054-2807
 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service JUL 2 2008 Food and Drug Administration 9200 Corporate Boulevard Rockville MD 20850 Ms. Kendra Basler Regulatory Affairs Associate Abbott Vascular
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service JUL 2 2008 Food and Drug Administration 9200 Corporate Boulevard Rockville MD 20850 Ms. Kendra Basler Regulatory Affairs Associate Abbott Vascular
Vascular Stent System (6F, 20 100mm stents)
 100000000922.2 Instructions for Use Cordis S.M.A.R.T. CONTROL Vascular Stent System (6F, 20 100mm stents) Cordis S.M.A.R.T. Vascular Stent System (6F, 120 150mm stents) Symbols Catalog Number LOT NonPyrogenic
100000000922.2 Instructions for Use Cordis S.M.A.R.T. CONTROL Vascular Stent System (6F, 20 100mm stents) Cordis S.M.A.R.T. Vascular Stent System (6F, 120 150mm stents) Symbols Catalog Number LOT NonPyrogenic
When Procedural Support really matters. Navien TM A+ Intracranial Support Catheter
 When Procedural Support really matters Navien TM A+ Intracranial Support Catheter Coils / Liquid Embolics DURABLE ovalization resistance, Maintains patent lumen in tortuosity for smooth micro catheter
When Procedural Support really matters Navien TM A+ Intracranial Support Catheter Coils / Liquid Embolics DURABLE ovalization resistance, Maintains patent lumen in tortuosity for smooth micro catheter
Is Stenting or Coronary Artery By-pass Grafting the Better Treatment for This Patient?
 Is Stenting or Coronary Artery By-pass Grafting the Better Treatment for This Patient? --- NIRS-IVUS TVC Imaging Adds Additional Information for the Heart Team Dr. Luis Tami Memorial Regional Hospital
Is Stenting or Coronary Artery By-pass Grafting the Better Treatment for This Patient? --- NIRS-IVUS TVC Imaging Adds Additional Information for the Heart Team Dr. Luis Tami Memorial Regional Hospital
The largest clinical study of Bayer's Xarelto (rivaroxaban) Wednesday, 14 November 2012 07:38
 Bayer HealthCare has announced the initiation of the COMPASS study, the largest clinical study of its oral anticoagulant Xarelto (rivaroxaban) to date, investigating the prevention of major adverse cardiac
Bayer HealthCare has announced the initiation of the COMPASS study, the largest clinical study of its oral anticoagulant Xarelto (rivaroxaban) to date, investigating the prevention of major adverse cardiac
A Patient s Guide to Minimally Invasive Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair
 A Patient s Guide to Minimally Invasive Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair Table of Contents The AFX Endovascular AAA System............................................ 1 What is an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
A Patient s Guide to Minimally Invasive Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair Table of Contents The AFX Endovascular AAA System............................................ 1 What is an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
Coronary Bifurcation Treatment: Update from the European Bifurcation Club. Remo Albiero, MD Ist. Clinico S. Rocco Brescia (Italy)
 Coronary Bifurcation Treatment: Update from the European Bifurcation Club Remo Albiero, MD Ist. Clinico S. Rocco Brescia (Italy) Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest Within the past 12 months, I
Coronary Bifurcation Treatment: Update from the European Bifurcation Club Remo Albiero, MD Ist. Clinico S. Rocco Brescia (Italy) Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest Within the past 12 months, I
Listen to Your Heart. What Everyone Needs To Know About Atrial Fibrillation & Stroke. The S-ICD System. The protection you need
 Listen to Your Heart The S-ICD System What Everyone Needs To Know About Atrial Fibrillation & Stroke The protection you need without Stroke. touching Are you your at heart risk? Increase your knowledge.
Listen to Your Heart The S-ICD System What Everyone Needs To Know About Atrial Fibrillation & Stroke The protection you need without Stroke. touching Are you your at heart risk? Increase your knowledge.
Coronary Stents. What is a Coronary Artery stent?
 What is a Coronary Artery stent? Coronary Stents A coronary stent is stainless tube with slots. It is mounted on a balloon catheter in a "crimped" or collapsed state. When the balloon of is inflated, the
What is a Coronary Artery stent? Coronary Stents A coronary stent is stainless tube with slots. It is mounted on a balloon catheter in a "crimped" or collapsed state. When the balloon of is inflated, the
Talent Thoracic Stent Graft with THE Xcelerant Delivery System. Expanding the Indications for TEVAR
 Talent Thoracic with THE Xcelerant Delivery System Expanding the Indications for TEVAR Talent Thoracic Precise placement 1 Broad patient applicability 1 Excellent clinical outcomes 1, a + Xcelerant Delivery
Talent Thoracic with THE Xcelerant Delivery System Expanding the Indications for TEVAR Talent Thoracic Precise placement 1 Broad patient applicability 1 Excellent clinical outcomes 1, a + Xcelerant Delivery
INTRODUCTION TO EECP THERAPY
 INTRODUCTION TO EECP THERAPY is an FDA cleared, Medicare approved, non-invasive medical therapy for the treatment of stable and unstable angina, congestive heart failure, acute myocardial infarction, and
INTRODUCTION TO EECP THERAPY is an FDA cleared, Medicare approved, non-invasive medical therapy for the treatment of stable and unstable angina, congestive heart failure, acute myocardial infarction, and
12276408.3. Instructions for Use Cordis EXOSEAL TM VASCULAR CLOSURE DEVICE
 12276408.3 Instructions for Use Cordis EXOSEAL TM VASCULAR CLOSURE DEVICE Figure 1: Components of the EXOSEAL TM Vascular Closure Device 1. Handle Assembly 2. Plug Deployment Button 3. Indicator Window
12276408.3 Instructions for Use Cordis EXOSEAL TM VASCULAR CLOSURE DEVICE Figure 1: Components of the EXOSEAL TM Vascular Closure Device 1. Handle Assembly 2. Plug Deployment Button 3. Indicator Window
LEADERS: 5-Year Follow-up
 LEADERS: -Year Follow-up from a Prospective, Randomized Trial of Biolimus A9-eluting Stents with a Biodegradable Polymer vs. Sirolimus-eluting Stents with a Durable Polymer : Final Report of the LEADERS
LEADERS: -Year Follow-up from a Prospective, Randomized Trial of Biolimus A9-eluting Stents with a Biodegradable Polymer vs. Sirolimus-eluting Stents with a Durable Polymer : Final Report of the LEADERS
Renovascular Disease. Renal Artery and Arteriosclerosis
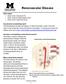 Other names: Renal Artery Stenosis (RAS) Renal Vascular Hypertension (RVH) Renal Artery Aneurysm (RAA) How does the normal kidney work? The blood passes through the kidneys to remove the body s waste.
Other names: Renal Artery Stenosis (RAS) Renal Vascular Hypertension (RVH) Renal Artery Aneurysm (RAA) How does the normal kidney work? The blood passes through the kidneys to remove the body s waste.
Aspira* Pleural Drainage Catheter
 Aspira* Pleural Drainage Catheter Instructions For Use Access Systems Product Description: The Aspira* Pleural Drainage Catheter is a tunneled, long-term catheter used to drain accumulated fluid from the
Aspira* Pleural Drainage Catheter Instructions For Use Access Systems Product Description: The Aspira* Pleural Drainage Catheter is a tunneled, long-term catheter used to drain accumulated fluid from the
TURQUOISE PTCA BALLOON DILATATION CATHETER
 TURQUOISE PTCA BALLOON DILATATION CATHETER TURQUOISE PTCA BallOOn Dilatation CATheter The right BAlance TO meet the clinical need TURQUOISE PTCA s advanced catheter technology offers the right balance
TURQUOISE PTCA BALLOON DILATATION CATHETER TURQUOISE PTCA BallOOn Dilatation CATheter The right BAlance TO meet the clinical need TURQUOISE PTCA s advanced catheter technology offers the right balance
Antonio Colombo MD on behalf of the SECURITY Investigators
 Second Generation Drug-Eluting Stents Implantation Followed by Six Versus Twelve-Month - Dual Antiplatelet Therapy - The SECURITY Randomized Clinical Trial Antonio Colombo MD on behalf of the SECURITY
Second Generation Drug-Eluting Stents Implantation Followed by Six Versus Twelve-Month - Dual Antiplatelet Therapy - The SECURITY Randomized Clinical Trial Antonio Colombo MD on behalf of the SECURITY
Biliary and Endovascular Product Catalog
 Biliary and Endovascular Product Catalog To navigate within this catalog: - Single click on a chapter or section letter - Type the product name or catalog number in the Find box on the Adobe tool bar Table
Biliary and Endovascular Product Catalog To navigate within this catalog: - Single click on a chapter or section letter - Type the product name or catalog number in the Find box on the Adobe tool bar Table
Aspira* Peritoneal Drainage Catheter
 Aspira* Peritoneal Drainage Catheter Instructions For Use Access Systems Product Description: The Aspira* Peritoneal Drainage Catheter is a tunneled, long-term catheter used to drain accumulated fluid
Aspira* Peritoneal Drainage Catheter Instructions For Use Access Systems Product Description: The Aspira* Peritoneal Drainage Catheter is a tunneled, long-term catheter used to drain accumulated fluid
Yukon Choice DES + Translumina - The polymer-free DES solution. www.translumina.de. Coronary Stent System for Drug Application
 Coronary Stent System for Drug Application Yukon Choice DES + new catheter polymer-free DES Translumina - The polymer-free DES solution www.translumina.de A First Class Stent The YUKON Choice DES+ is the
Coronary Stent System for Drug Application Yukon Choice DES + new catheter polymer-free DES Translumina - The polymer-free DES solution www.translumina.de A First Class Stent The YUKON Choice DES+ is the
Cook Celect and Günther Tulip Vena Cava Filter Patient Guide
 Cook Celect and Günther Tulip Vena Cava Filter Patient Guide www.cookmedical.com Filter patient guide Contents Pulmonary embolism 4 5 What is pulmonary embolism? What causes it? What are the symptoms of
Cook Celect and Günther Tulip Vena Cava Filter Patient Guide www.cookmedical.com Filter patient guide Contents Pulmonary embolism 4 5 What is pulmonary embolism? What causes it? What are the symptoms of
Coronary Artery Disease leading cause of morbidity & mortality in industrialised nations.
 INTRODUCTION Coronary Artery Disease leading cause of morbidity & mortality in industrialised nations. Although decrease in cardiovascular mortality still major cause of morbidity & burden of disease.
INTRODUCTION Coronary Artery Disease leading cause of morbidity & mortality in industrialised nations. Although decrease in cardiovascular mortality still major cause of morbidity & burden of disease.
PERCUTANEOUS PD CATHETER IMPLANTATION SYSTEM
 Place on Patient s Cranial Border of the Pubic Symphysis IMPLANTATION STENCIL Classic Exit Cuff Site PERCUTANEOUS PD CATHETER IMPLANTATION SYSTEM INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE VP 511 and VP-511M Implantation System
Place on Patient s Cranial Border of the Pubic Symphysis IMPLANTATION STENCIL Classic Exit Cuff Site PERCUTANEOUS PD CATHETER IMPLANTATION SYSTEM INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE VP 511 and VP-511M Implantation System
A Patient s Guide to Primary and Secondary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Using Blood-Thinning (Anticoagulant) Drugs
 A Patient s Guide to Primary and Secondary Prevention of PATIENT EDUCATION GUIDE What Is Cardiovascular Disease? Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a broad term that covers any disease of the heart and circulatory
A Patient s Guide to Primary and Secondary Prevention of PATIENT EDUCATION GUIDE What Is Cardiovascular Disease? Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a broad term that covers any disease of the heart and circulatory
Policies and Procedures. Related to. IABP Therapy
 Policies and Procedures Related to IABP Therapy Courtesy of Datascope Corp. Clinical Support Services The following policies and procedures are intended to serve as guidelines for developing hospital policy.
Policies and Procedures Related to IABP Therapy Courtesy of Datascope Corp. Clinical Support Services The following policies and procedures are intended to serve as guidelines for developing hospital policy.
Patient Information Guide Morpheus CT Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter
 Patient Information Guide Morpheus CT Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter IC 192 Rev C A measure of flexibility and strength. Table of Contents 1. Introduction 2. What is the Morpheus CT PICC? 3. What
Patient Information Guide Morpheus CT Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter IC 192 Rev C A measure of flexibility and strength. Table of Contents 1. Introduction 2. What is the Morpheus CT PICC? 3. What
Vaxcel PICCs Valved and Non-Valved. A Patient s Guide
 Vaxcel PICCs Valved and Non-Valved A Patient s Guide Information about your Vaxcel PICC is available by calling the Navilyst Medical Vascular Access Information Line 800.513.6876 Vaxcel Peripherally Inserted
Vaxcel PICCs Valved and Non-Valved A Patient s Guide Information about your Vaxcel PICC is available by calling the Navilyst Medical Vascular Access Information Line 800.513.6876 Vaxcel Peripherally Inserted
Christopher M. Wright, MD, MBA Pioneer Cardiovascular Consultants Tempe, Arizona
 Christopher M. Wright, MD, MBA Pioneer Cardiovascular Consultants Tempe, Arizona Areas to be covered Historical, current, and future treatments for various cardiovascular disease: Atherosclerosis (Coronary
Christopher M. Wright, MD, MBA Pioneer Cardiovascular Consultants Tempe, Arizona Areas to be covered Historical, current, and future treatments for various cardiovascular disease: Atherosclerosis (Coronary
PERIPHERALLY INSERTED CENTRAL CATHETERS (PICC) Fong So Kwan APN, Haematology unit Medical Department, QMH
 PERIPHERALLY INSERTED CENTRAL CATHETERS (PICC) Fong So Kwan APN, Haematology unit Medical Department, QMH 1 What is a PICC catheter? Primary vascular access device since their introduction in the mid-1970s,
PERIPHERALLY INSERTED CENTRAL CATHETERS (PICC) Fong So Kwan APN, Haematology unit Medical Department, QMH 1 What is a PICC catheter? Primary vascular access device since their introduction in the mid-1970s,
Endovascular Repair of an Axillary Artery Aneurysm: A Novel Approach
 Endovascular Repair of an Axillary Artery Aneurysm: A Novel Approach Bao- Thuy D. Hoang, MD 1, Jonathan- Hien Vu, MD 2, Jerry Matteo, MD 3 1 Department of Surgery, University of Florida College of Medicine,
Endovascular Repair of an Axillary Artery Aneurysm: A Novel Approach Bao- Thuy D. Hoang, MD 1, Jonathan- Hien Vu, MD 2, Jerry Matteo, MD 3 1 Department of Surgery, University of Florida College of Medicine,
Orsiro Hybrid Drug Eluting Stent Industry's first hybrid DES
 Vascular Intervention Drug Eluting Stents Orsiro Orsiro Hybrid Drug Eluting Stent Industry's first hybrid DES Orsiro An ideal combination of passive and active components The Orsiro Hybrid Drug Eluting
Vascular Intervention Drug Eluting Stents Orsiro Orsiro Hybrid Drug Eluting Stent Industry's first hybrid DES Orsiro An ideal combination of passive and active components The Orsiro Hybrid Drug Eluting
Hemostasis Solutions Boston Scientific is committed to improving patient care in the management of gastrointestinal bleeding.
 Hemostasis Solutions Boston Scientific is committed to improving patient care in the management of gastrointestinal bleeding. Through innovation and continuous educational support, we offer a wide range
Hemostasis Solutions Boston Scientific is committed to improving patient care in the management of gastrointestinal bleeding. Through innovation and continuous educational support, we offer a wide range
Therapeutic Approach in Patients with Diabetes and Coronary Artery Disease
 Home SVCC Area: English - Español - Português Therapeutic Approach in Patients with Diabetes and Coronary Artery Disease Martial G. Bourassa, MD Research Center, Montreal Heart Institute, Montreal, Quebec,
Home SVCC Area: English - Español - Português Therapeutic Approach in Patients with Diabetes and Coronary Artery Disease Martial G. Bourassa, MD Research Center, Montreal Heart Institute, Montreal, Quebec,
2009/JUL/20 at 9:18 a.m. Doc number: M710950B001 [Uni+] VALIANT THORACIC STENT GRAFT WITH THE CAPTIVIA DELIVERY SYSTEM Instructions for Use
![2009/JUL/20 at 9:18 a.m. Doc number: M710950B001 [Uni+] VALIANT THORACIC STENT GRAFT WITH THE CAPTIVIA DELIVERY SYSTEM Instructions for Use 2009/JUL/20 at 9:18 a.m. Doc number: M710950B001 [Uni+] VALIANT THORACIC STENT GRAFT WITH THE CAPTIVIA DELIVERY SYSTEM Instructions for Use](/thumbs/40/21239668.jpg) VALIANT THORACIC STENT GRAFT WITH THE CAPTIVIA DELIVERY SYSTEM Instructions for Use 0086 EXPLANATION OF SYMBOLS Explanation of symbols that may appear on product labeling. Consult instructions for use
VALIANT THORACIC STENT GRAFT WITH THE CAPTIVIA DELIVERY SYSTEM Instructions for Use 0086 EXPLANATION OF SYMBOLS Explanation of symbols that may appear on product labeling. Consult instructions for use
Polymer-Based, Paclitaxel-Eluting TAXUS Liberté Stent in De Novo Lesions: The Pivotal TAXUS ATLAS Trial
 Polymer-Based, Paclitaxel-Eluting Stent in De Novo Lesions: The Pivotal TAXUS ATLAS Trial Mark A. Turco, John A. Ormiston, Jeffrey J. Popma, Lazar Mandinov, Charles D. O'Shaughnessy, Tift Mann, Thomas
Polymer-Based, Paclitaxel-Eluting Stent in De Novo Lesions: The Pivotal TAXUS ATLAS Trial Mark A. Turco, John A. Ormiston, Jeffrey J. Popma, Lazar Mandinov, Charles D. O'Shaughnessy, Tift Mann, Thomas
Patient Information Booklet. Endovascular Stent Grafts: A Treatment for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms
 Patient Information Booklet Endovascular Stent Grafts: A Treatment for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 1 Glossary 2 Abdominal Aorta 4 Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm 5 Causes 6 Symptoms
Patient Information Booklet Endovascular Stent Grafts: A Treatment for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 1 Glossary 2 Abdominal Aorta 4 Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm 5 Causes 6 Symptoms
WATCHMAN Left Atrial Appendage Closure Device
 WATCHMAN Left Atrial Appendage Closure Device Patient Information Guide WATCHMAN Left Atrial Appendage Closure Device PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE Your doctor has recommended that you consider undergoing
WATCHMAN Left Atrial Appendage Closure Device Patient Information Guide WATCHMAN Left Atrial Appendage Closure Device PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE Your doctor has recommended that you consider undergoing
Lifecheque Basic Critical Illness Insurance
 Lifecheque Basic Critical Illness Insurance Strong. Reliable. Trustworthy. Forward-thinking. Extra help on the road to recovery Surviving a critical illness can be very challenging financially Few of us
Lifecheque Basic Critical Illness Insurance Strong. Reliable. Trustworthy. Forward-thinking. Extra help on the road to recovery Surviving a critical illness can be very challenging financially Few of us
6/5/2014. Objectives. Acute Coronary Syndromes. Epidemiology. Epidemiology. Epidemiology and Health Care Impact Pathophysiology
 Objectives Acute Coronary Syndromes Epidemiology and Health Care Impact Pathophysiology Unstable Angina NSTEMI STEMI Clinical Clues Pre-hospital Spokane County EMS Epidemiology About 600,000 people die
Objectives Acute Coronary Syndromes Epidemiology and Health Care Impact Pathophysiology Unstable Angina NSTEMI STEMI Clinical Clues Pre-hospital Spokane County EMS Epidemiology About 600,000 people die
2015 European Coronary Stent New Product Innovation Award
 2015 European Coronary Stent New Product Innovation Award 2015 Contents Background and Company Performance... 3 Industry Challenges... 3 New Product Attributes and Customer Impact... 3 Conclusion... 4
2015 European Coronary Stent New Product Innovation Award 2015 Contents Background and Company Performance... 3 Industry Challenges... 3 New Product Attributes and Customer Impact... 3 Conclusion... 4
ANGIO-SEAL EVOLUTION VASCULAR CLOSURE DEVICE INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
 ANGIO-SEAL EVOLUTION VASCULAR CLOSURE DEVICE INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE TO ENSURE PROPER DEPLOYMENT AND USE OF THIS DEVICE AND TO PREVENT INJURY TO PATIENTS, READ ALL INFORMATION CONTAINED IN THESE INSTRUCTIONS
ANGIO-SEAL EVOLUTION VASCULAR CLOSURE DEVICE INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE TO ENSURE PROPER DEPLOYMENT AND USE OF THIS DEVICE AND TO PREVENT INJURY TO PATIENTS, READ ALL INFORMATION CONTAINED IN THESE INSTRUCTIONS
Ch. 138 CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION SERVICES 28 138.1 CHAPTER 138. CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION SERVICES GENERAL PROVISIONS
 Ch. 138 CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION SERVICES 28 138.1 CHAPTER 138. CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION SERVICES Sec. 138.1 Principle. 138.2. Definitions. GENERAL PROVISIONS PROGRAM, SERVICE, PERSONNEL AND AGREEMENT REQUIREMENTS
Ch. 138 CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION SERVICES 28 138.1 CHAPTER 138. CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION SERVICES Sec. 138.1 Principle. 138.2. Definitions. GENERAL PROVISIONS PROGRAM, SERVICE, PERSONNEL AND AGREEMENT REQUIREMENTS
NAME OF THE HOSPITAL: 1. Coronary Balloon Angioplasty: M7F1.1/ Angioplasty with Stent(PTCA with Stent): M7F1.3
 1. Coronary Balloon Angioplasty: M7F1.1/ Angioplasty with Stent(PTCA with Stent): M7F1.3 1. Name of the Procedure: Coronary Balloon Angioplasty 2. Select the Indication from the drop down of various indications
1. Coronary Balloon Angioplasty: M7F1.1/ Angioplasty with Stent(PTCA with Stent): M7F1.3 1. Name of the Procedure: Coronary Balloon Angioplasty 2. Select the Indication from the drop down of various indications
Cardiovascular diseases. pathology
 Cardiovascular diseases pathology Atherosclerosis Vascular diseases A disease that results in arterial wall thickens as a result of build- up of fatty materials such cholesterol, resulting in acute and
Cardiovascular diseases pathology Atherosclerosis Vascular diseases A disease that results in arterial wall thickens as a result of build- up of fatty materials such cholesterol, resulting in acute and
Perspectives on the Selection and Duration of Dual Antiplatelet Therapy
 Perspectives on the Selection and Duration of Dual Antiplatelet Therapy Dominick J. Angiolillo, MD, PhD, FACC, FESC, FSCAI Director of Cardiovascular Research Associate Professor of Medicine University
Perspectives on the Selection and Duration of Dual Antiplatelet Therapy Dominick J. Angiolillo, MD, PhD, FACC, FESC, FSCAI Director of Cardiovascular Research Associate Professor of Medicine University
ON-Q * Catheters and Introducers
 Instructions For Use ON-Q * Catheters and Introducers MANUFACTURED BY: Kimberly-Clark 1400 Holcomb Bridge Road Roswell, GA 30076 USA Kimberly-Clark N.V. Da Vincilaan 1 1935 Zaventem, Belgium Figure 1 4
Instructions For Use ON-Q * Catheters and Introducers MANUFACTURED BY: Kimberly-Clark 1400 Holcomb Bridge Road Roswell, GA 30076 USA Kimberly-Clark N.V. Da Vincilaan 1 1935 Zaventem, Belgium Figure 1 4
NOVOSTE BETA-CATH SYSTEM
 HOSPITAL INPATIENT AND OUTPATIENT BILLING GUIDE FOR THE NOVOSTE BETA-CATH SYSTEM INTRAVASCULAR BRACHYTHERAPY DEVICE This guide is intended solely for use as a tool to help hospital billing staff resolve
HOSPITAL INPATIENT AND OUTPATIENT BILLING GUIDE FOR THE NOVOSTE BETA-CATH SYSTEM INTRAVASCULAR BRACHYTHERAPY DEVICE This guide is intended solely for use as a tool to help hospital billing staff resolve
Acute Coronary Syndrome. What Every Healthcare Professional Needs To Know
 Acute Coronary Syndrome What Every Healthcare Professional Needs To Know Background of ACS Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) is an umbrella term used to cover a spectrum of clinical conditions that are caused
Acute Coronary Syndrome What Every Healthcare Professional Needs To Know Background of ACS Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) is an umbrella term used to cover a spectrum of clinical conditions that are caused
HA Territory-wide PCI Audit 2003-05
 HA Territory-wide PCI Audit 23-5 5 PCI Audit Working Group Central Committee (Cardiac Services) HA Convention 26 Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Background HA AP target 2/3, coordinated by PCI Working
HA Territory-wide PCI Audit 23-5 5 PCI Audit Working Group Central Committee (Cardiac Services) HA Convention 26 Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Background HA AP target 2/3, coordinated by PCI Working
European Heart Journal (1999) 20, 1014 1019 Article No. euhj.1998.1395, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on
 European Heart Journal (1999) 20, 1014 1019 Article No. euhj.1998.1395, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Working Group Report Indications for intracoronary stent placement: the European
European Heart Journal (1999) 20, 1014 1019 Article No. euhj.1998.1395, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Working Group Report Indications for intracoronary stent placement: the European
