Muscular Force and Biomechanical Implications
|
|
|
- Shawn Flowers
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Page 1 of 6 Biomechanics Muscular Force and Biomechanical Implications William L. Cornelius, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Education University of North Texas Understanding basic concepts of biomechanics continues to be an important consideration for the gymnastics practitioner. Command of these anatomical and mechanical ideas may be the essence of constructively dealing with gymnastics movements. Using what has been scientifically established as truth provides the coach and athlete with an invaluable tool in striving for artistic performance. Actually, there are not that many different biomechanical concepts and principles needed by the practitioner to make an impact on the analysis of a specific motor skill (Kreighbaum and Barthels, 1996). One example of an important area of consideration deals with the internal muscle force produced during a performance. Internal Muscular Force Muscular strength is considered to be the ability to do work against resistance or the capacity to exert force Arnheim and Prentice, 1993) and is derived through muscle tension produced during muscle contraction. The outcome is a force internal to the human system. This internal force produces tension on the skeletal system, resulting in angular motion about a joint. Examples of this phenomenon are shown in Figures 2-4 by furnishing illustrations of gymnastics movements and associated muscle forces. Resolution of force Resolution of force or vector resolution is an example of a biomechanical technique that provides a means of establishing the two component forces directly associated with a net force. This net force can be responsible for a movement and is known as the resultant force (Figure 1). An explanation is now possible for why a particular force results in a specific movement when the resultant vector is known. This leads to resolving the component forces. Component forces provide a clearer picture of what the resultant force contributes to the performance. Component forces Angular and stabilizing vectors represent the two components derived from a resultant force. Figure 1 illustrates the relationship between the resultant vector and component forces. When dealing with internal forces created from muscle contractions, the resultant force (F) is applied at the muscle insertion located on the attachment (apophysis) of the bone to be mobilized and is directed toward the muscle origin. This resultant force is directed through the belly of the particular muscle. The angular vector is directed perpendicular to the bone that is being moved and the stabilizing vector is directed along the same bone, into the joint (Kreighbaum and
2 Page 2 of 6 Barthels, 1996). Consequently, the angular force component is responsible for moving the skeletal part, while the stabilizing force component serves as a means of adding to joint integrity (stability). The angular vector (F1) and stabilizing vector (F2) begin from the point of force application and are directed at right angles, one to the other. Figures 2-4 provide examples of resultant vectors and their component vectors, originating from concentric muscle contractions during the performance of gymnastics skills. The cast Initiating a cast on such apparatus as the horizontal bar or uneven bars can require elbow flexion (Figure 2, frames A to B). The biceps brachii muscle acts as one of the primary movers, with elbow flexion occurring around the mediolateral axis in the sagittal plane. Figure 2 (frames a-b) illustrates a relationship between the resultant force (F) of the biceps brachii and the component forces (F1 and F2) during this maneuver. The F1 and F2 vectors demonstrate the direction and magnitude of the angular and stabilizing force components, respectively. Elbow joint stabilization is maximized in frame A because the long hang is the position associated with the initial stage of biceps brachii concentric contraction. Although F does begin moving the lower arm into elbow flexion at frame A, F1 is smaller than F2 because F is slightly less than 20 degrees at the biceps brachii muscle insertion. Consequently, the larger portion of F acts to stabilize the elbow joint at frame A. This relationship begins changing from frame A to B as the angle of insertion progressively increases for the biceps brachii muscle. At frame B the resultant force is approximately 70 degrees to the radius at the biceps brachii insertion and suggests F1 is considerably larger than F2. Consequently, the majority of the resultant force produced by the biceps brachii in frame B is now directed toward moving the lower arm segment at the elbow joint; a smaller portion is focused on stabilizing the joint. It is by this means that the angle of muscle insertion becomes a critical mechanism in producing F1 and F2 magnitudes. The closer the resultant angle of muscle insertion is to 90 degrees, the larger the angular vector for moving a bony segment, and conversely the smaller the stabilizing force vector for improving joint integrity (Kreighbaum and Barthels, 1996). Stabilizing the shoulder joint can be particularly important when the gymnast is at the
3 Page 3 of 6 bottom of the swing (frame A) immediately prior to elbow flexion. In this case, the joint experiences distraction with the external force of gravity. Muscle tension produced by such shoulder joint muscles as the rotator cuff are essential in acting to maintain joint integrity. Assistance from these muscles is beneficial because the shoulder joint is inherently lacking in stability when considering the shallow depth of the glenoid fossa and the few ligaments strapping the joint. In fact. the articulating relationship between the humerus and glenoid fossa provide for less than one-third of the humeral head at the shoulder joint. The combined tension force of the rotator cuff muscles, therefore, is particularly suited to limiting the dislocation effect of the gravity force on the shoulder joint in frame A. Biceps brachii muscle tension, across the shoulder joint to its attachment on the upper rim of the glenoid fossa, provides added stability needed for maintaining joint integrity. The extension action at the shoulder joint in frames A to B, from such muscles as the latissimus dorsi and teres major, adds further to the developing tension created across the shoulder joint. The triceps brachii (long head) adds another dimension to stabilizing the shoulder joint as it lengthens during the initial stage of the cast in the two joint action of elbow flexion and shoulder extension (frames A to B). Stability is improved because there are a number of musculotendinous units acting to supplement ligaments as the strap across the shoulder joint. Gravity can be used as a motive force through part of the cast (Figure 2). An example of this phenomenon occurs in a counter clockwise direction around the bar axis from frame B to C. Internal action forces from muscle contraction result in bar external reaction forces on the gymnast that couple with the gravity force. The force diagram in frame C depicts the anterior deltoid in acting to move the humerous into shoulder joint flexion. The resultant angle of insertion shown in frame C is relatively small; therefore, F1 is relatively small, providing a large stabilizing effect (F2) at the shoulder joint. More muscle fibers must now be recruited subsequent to frame C, when the body begins to move upward against the resistive force of gravity. As the humerous moves further into shoulder joint flexion, however, F1 increases in magnitude while F2 decreases in magnitude. The mechanism for the larger F1 and resulting torque enhancement is the increasing angle of muscle insertion. The resulting increase in F1 provides enhanced torque, but decreasing F2 tends to place more stress on ligaments and other connective tissues providing for joint stability. The dislocate
4 Page 4 of 6 The dislocate is a dynamic skill with explosive movement through a large angular displacement. As the gymnast moves toward a pike position below the rings in Figure 3, frame A and b, it is essential to have the cooperation of shoulder complex stabilizing muscles. Shoulder girdle adductors (rhomboids, trapezius 3) and shoulder joint rotator cuff muscles must resist the external force of gravity. The shoulder girdle adductors act to provide a firm scapula base upon which the humerous can function at the glenoid fossa through a large range of motion. This firm base is necessary because the shoulder joint muscles attach on the scapula at their origin; force application is then improved at the humeral insertion points for angular and stabilizing purposes. The center of gravity translates upward from frame B to C (Figure 3) as the humerous begins moving away from the midline of the body as will as displacing forward (anterior). Humeral head accommodation is again essential in order for the humerus to be moved toward frame C and beyond. This requires that the serratus anterior and trapezius 2 and 4 upwardly rotate the scapula, while the serratus anterior and pectoralis minor abduct the scapula. These shoulder girdle muscles act as scapula stabilizers in frames C and D as the humerous moves in a diagonal pattern (abduction and transverse abduction). This part of the dislocate provides an example of overcoming the resistive force of gravity when moving from below the rings to a point above the rings in frames B-D. The supraspinatus muscle acts as a prime mover during abduction of the humerus when initiating the dislocate from frame B to C. Frame C illustrates a force diagram that helps depict the angular and stabilizing force components elicited by the supraspinatus muscle. Frame C illustrates the resultant internal tension force is approximately 45 degrees to the head of the humerus at the greater tuberosity insertion point (frame D). This angle of the resultant force suggests the angular (F1) and stabilizing (F2) vector components are equal. As the humerous moves progressively into abduction and transverse adduction, from frame B to D, the supraspinatus angular force component increases while the stabilizing force component decreases. Reliance on the supraspinatus muscle in frame C is apparent because the medial deltoid is less effective as an abductor when the humerus is below 60 degrees to the trunk (Kreighbaum and Barthels, 1996). The medial deltoid primarily acts to stabilize the glenohumeral joint in frames B to C. Both the medial deltoid and the supraspinatus contribute in frames B through E to moving the humerus into abduction in preparing body
5 Page 5 of 6 alignment for the downward swing in frames E to F. Both muscles are essential in neutralizing the effects of gravity by reducing the separation between the humerus and the glenoid fossa. When reaching the bottom of the swing in frame F, muscles of the rotator cuff, and other muscles crossing the shoulder joint, act as strapping mechanisms for improving joint integrity. The effects of gravity are particularly stressful to the shoulder joint at the bottom point for individuals experiencing shoulder joint instability. Such conditions as the rotator cuff impingement syndrome and biceps brachii tendonitis (near the origin) are examples of trauma that create shoulder joint instability. The takeoff Extension is the main knee joint action at the point of takeoff in vaulting (Figure 4). The quadriceps muscle group serves as the primary mover in this maneuver, around the mediolateral axis and along the sagittal plane. A force diagram in frame A acts as a means of describing the relationship between the resultant quadriceps force (F), angular force component (F1), and the stabilizing force component (F2). The takeoff is a point in the total vaulting skill where the gymnast has a opportunity to increase or decrease angular momentum (Cornelius, 1994). Angular momentum is produced in Figure 4, frame A, for vaulting preflight (frames B-D). The production of angular momentum is dependent upon the magnitude of the overall internal action force established in frame A by muscles crossing the shoulder, hip, knee, and ankle joints. This in turn creates the external reaction force issued from the board. Frame D is the second point in a vault where angular momentum can be influenced by an external force for subsequent postflight. Shoulder girdle elevation is the mechanism for repulsion and is linked with shoulder girdle elevator muscles, such as trapezious 1 and 2, levator scapula, and rhomboids. Consequently, the total vault is highly dependent upon increasing the magnitude of the angular force component (F1) at board takeoff ant at vaulting horse repulsion. The net force produced by the quadriceps during knee joint extension can be improved by a moveable patella. The patella functions as a mechanical pulley at the knee joint (Figure 4, frame A) and possesses the capacity to change the angle of muscle insertion at the tibial
6 Page 6 of 6 tuberosity (point of quadriceps insertion). Without this accommodating effect from the patella, there would be reduced joint range of motion in knee flexion and extension and certainly torque about the knee would be reduced. Changing patellar positions can move the angle of muscle insertion to a more favorable resultant (F). This in turn can increase F1 and decrease F2, providing a greater amount of the total force produced by the quadriceps for increasing the angular vector (F1). For example, the quick stretch of the quadriceps musculotendinous unit during knee flexion (frame A) in initial board contact, moves the patella downward in the intercondylar gemoral grove to a position that increases the angle of muscle insertion at the tibial tuberosity. This results in an increase in F1 and improved torque for the explosive takeoff maneuver. Summary Understanding the contribution made by the component vectors of a muscle contraction will greatly assist the practitioner. There is an improved understanding of why an individual moves in a particular manner when the line of action of the internal muscle force is known. Exact or precise points of muscle attachments and the technical names for these locations are not essential; in fact, only the line of action is needed. Consequently, a mental image of the muscle location and line of action is quite useful. This provides relationships between the resultant force and associated force components acting on a skeletal segment. The practitioner is now provided with greater insight into ways in which the internal muscle force can assist in changing gymnastics performance. References Arnheim, D.D., and Prentice, W.E. (1993). Principles of Athletic Training (8th ed.). St. Louis: Mosby Year Book. Cornelius, W.L. (1994). Vaulting vertical displacement. Technique. USA Gymnastics 14 (2):8-10. Kreighbaum, E. and Barthels, K.M. (1996). Biomechanics: A Qualitative Approach for Studying Human Movement (4th ed.). Boston: Allyn and Bacon. Figures 2-4 are based on drawings by James Stephenson in the USA Gymnastics Junior Olympic Age Group Compulsories. This article appears in the January 1997 issue of Technique, Vol. 17, No. 1.
Chapter 5. The Shoulder Joint. The Shoulder Joint. Bones. Bones. Bones
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. Chapter 5 The Shoulder Joint Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Structural Kinesiology The Shoulder Joint 5-1 The Shoulder
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. Chapter 5 The Shoulder Joint Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Structural Kinesiology The Shoulder Joint 5-1 The Shoulder
Chapter 4 The Shoulder Girdle
 Chapter 4 The Shoulder Girdle Key Manubrium Clavicle Coracoidprocess Acromionprocess bony landmarks Glenoid fossa Bones Lateral Inferior Medial border angle McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved.
Chapter 4 The Shoulder Girdle Key Manubrium Clavicle Coracoidprocess Acromionprocess bony landmarks Glenoid fossa Bones Lateral Inferior Medial border angle McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved.
THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T
 THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T CLARIFICATION OF TERMS Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus Lippert, p115
THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T CLARIFICATION OF TERMS Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus Lippert, p115
Clarification of Terms
 Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Muscular System. Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body
 Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
TOTAL BODY: POWER/EXPLOSIVE EXERCISES
 Referring to Chapters 12-14 TOTAL BODY: POWER/EXPLOSIVE EXERCISES Power Snatch hip extension Muscle group/ gluteals gluteus maximis hamstrings semimembranosus semitendinosus biceps femoris knee extension
Referring to Chapters 12-14 TOTAL BODY: POWER/EXPLOSIVE EXERCISES Power Snatch hip extension Muscle group/ gluteals gluteus maximis hamstrings semimembranosus semitendinosus biceps femoris knee extension
The Shoulder Complex & Shoulder Girdle
 The Shoulder Complex & Shoulder Girdle The shoulder complex 4 articulations involving The sternum The clavicle The ribs The scapula and The humerus Bony Landmarks provide attachment points for muscles
The Shoulder Complex & Shoulder Girdle The shoulder complex 4 articulations involving The sternum The clavicle The ribs The scapula and The humerus Bony Landmarks provide attachment points for muscles
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names
 Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
Anatomy & Physiology 120. Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles
 Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
Ken Ross BSc ST, Nat Dip ST
 Ken Ross BSc ST, Nat Dip ST Trunk Most people will suffer from back pain at some point in their lives. Good spinal posture places minimal strain on the muscles which maintain the natural curve of the spine
Ken Ross BSc ST, Nat Dip ST Trunk Most people will suffer from back pain at some point in their lives. Good spinal posture places minimal strain on the muscles which maintain the natural curve of the spine
Hemiplegic shoulder pain/shoulder subluxation
 UPPER LIMB NEUROMUSCULAR ELECTRICAL STIMULATION: Electrode positions Please note that the polarity (red and black leads) can be altered according to your clinical reasoning. The area in which you want
UPPER LIMB NEUROMUSCULAR ELECTRICAL STIMULATION: Electrode positions Please note that the polarity (red and black leads) can be altered according to your clinical reasoning. The area in which you want
Muscle Energy Technique. Applied to the Shoulder
 Muscle Energy Technique Applied to the Shoulder MUSCLE ENERGY Theory Muscle energy technique is a manual therapy procedure which involves the voluntary contraction of a muscle in a precisely controlled
Muscle Energy Technique Applied to the Shoulder MUSCLE ENERGY Theory Muscle energy technique is a manual therapy procedure which involves the voluntary contraction of a muscle in a precisely controlled
International Standards for the Classification of Spinal Cord Injury Motor Exam Guide
 C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
Chapter 6. Components of Elasticity. Musculotendinous Unit. Behavioral Properties of the Musculotendinous Unit. Biomechanics of Skeletal Muscle
 Chapter 6 Behavioral Properties of the Musculotendinous Unit 1) extensibility: ability to be stretched or to increase in length 2) elasticity: ability to return to normal resting length following a stretch
Chapter 6 Behavioral Properties of the Musculotendinous Unit 1) extensibility: ability to be stretched or to increase in length 2) elasticity: ability to return to normal resting length following a stretch
Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body
 Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
The Pilates Studio of Los Angeles / PilatesCertificationOnline.com
 Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology. treatment program that will effectively treat it. The tricky part about the shoulder is that it is a ball and
 Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology Shoulder injuries occur to most people at least once in their life. This highly mobile and versatile joint is one of the most common reasons people visit their health care
Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology Shoulder injuries occur to most people at least once in their life. This highly mobile and versatile joint is one of the most common reasons people visit their health care
Elbow & Forearm H O W V I T A L I S T H E E L B O W T O O U R D A I L Y L I V E S?
 Elbow & Forearm H O W V I T A L I S T H E E L B O W T O O U R D A I L Y L I V E S? Clarification of Terms The elbow includes: 3 bones (humerus, radius, and ulna) 2 joints (humeroulnar and humeroradial)
Elbow & Forearm H O W V I T A L I S T H E E L B O W T O O U R D A I L Y L I V E S? Clarification of Terms The elbow includes: 3 bones (humerus, radius, and ulna) 2 joints (humeroulnar and humeroradial)
Orthopaedic and Spine Institute 21 Spurs Lane, Suite 245, San Antonio, TX 78240 www.saspine.com Tel# 210-487-7463
 Phase I Passive Range of Motion Phase (postop week 1-2) Minimize shoulder pain and inflammatory response Achieve gradual restoration of gentle active range of motion Enhance/ensure adequate scapular function
Phase I Passive Range of Motion Phase (postop week 1-2) Minimize shoulder pain and inflammatory response Achieve gradual restoration of gentle active range of motion Enhance/ensure adequate scapular function
EXERCISE MANUAL PERSONALITY GYM
 EXERCISE MANUAL PERSONALITY GYM EXERCISE MANUAL PERSONALITY GYM legs. 1 calves raise Stand with the wide part of one foot on the seated row foot support. Start in a position with your calves stretched.
EXERCISE MANUAL PERSONALITY GYM EXERCISE MANUAL PERSONALITY GYM legs. 1 calves raise Stand with the wide part of one foot on the seated row foot support. Start in a position with your calves stretched.
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines. I. Shoulder
 European Society of MusculoSkeletal Radiology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines I. Shoulder Ian Beggs, UK Stefano Bianchi, Switzerland Angel Bueno, Spain Michel Cohen, France Michel Court-Payen,
European Society of MusculoSkeletal Radiology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines I. Shoulder Ian Beggs, UK Stefano Bianchi, Switzerland Angel Bueno, Spain Michel Cohen, France Michel Court-Payen,
CAPPAGH NATIONAL ORTHOPAEDIC HOSPITAL, FINGLAS, DUBLIN 11. The Sisters of Mercy. Rotator Cuff Repair
 1.0 Policy Statement... 2 2.0 Purpose... 2 3.0 Scope... 2 4.0 Health & Safety... 2 5.0 Responsibilities... 2 6.0 Definitions and Abbreviations... 3 7.0 Guideline... 3 7.1 Pre-Operative... 3 7.2 Post-Operative...
1.0 Policy Statement... 2 2.0 Purpose... 2 3.0 Scope... 2 4.0 Health & Safety... 2 5.0 Responsibilities... 2 6.0 Definitions and Abbreviations... 3 7.0 Guideline... 3 7.1 Pre-Operative... 3 7.2 Post-Operative...
Muscular System. Principles of Health Science Dr. Wood
 Muscular System Principles of Health Science Dr. Wood Characteristics of muscles Excitability: : irritability or ability to respond to stimulus Contractibility: : ability to contract (become short and
Muscular System Principles of Health Science Dr. Wood Characteristics of muscles Excitability: : irritability or ability to respond to stimulus Contractibility: : ability to contract (become short and
Knee Kinematics and Kinetics
 Knee Kinematics and Kinetics Definitions: Kinematics is the study of movement without reference to forces http://www.cogsci.princeton.edu/cgi-bin/webwn2.0?stage=1&word=kinematics Kinetics is the study
Knee Kinematics and Kinetics Definitions: Kinematics is the study of movement without reference to forces http://www.cogsci.princeton.edu/cgi-bin/webwn2.0?stage=1&word=kinematics Kinetics is the study
Flexibility Assessment and Improvement Compiled and Adapted by Josh Thompson
 Flexibility Assessment and Improvement Compiled and Adapted by Josh Thompson Muscles must have a full and normal range of motion in order for joints and skeletal structure to function properly. Flexibility
Flexibility Assessment and Improvement Compiled and Adapted by Josh Thompson Muscles must have a full and normal range of motion in order for joints and skeletal structure to function properly. Flexibility
BRIDGET LAWLOR, PH.TH RESISTANCE TRAINING INJURIES THE ROTATOR CUFF INJURY WATCH. the glenoid cavity to the neck of the humerus.
 Common resistance training injuries shouldn't have to be common. In this article we re looking at causes and prevention of resistance training injuries and taking a closer look at the shoulder joint, and
Common resistance training injuries shouldn't have to be common. In this article we re looking at causes and prevention of resistance training injuries and taking a closer look at the shoulder joint, and
Biomechanics. State of equilibrium is when the sum (or net effect) of forces acting on a body equals zero
 Biomechanics Kinesiology is the science of, or study of, human motion. It brings together the fields of anatomy, physiology, biomechanics, physics and geometry relating them to human movement. Bio refers
Biomechanics Kinesiology is the science of, or study of, human motion. It brings together the fields of anatomy, physiology, biomechanics, physics and geometry relating them to human movement. Bio refers
Rehabilitation Guidelines For SLAP Lesion Repair
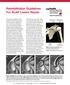 Rehabilitation Guidelines For SLAP Lesion Repair The anatomic configuration of the shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) is often compared to a golf ball on a tee. This is because the articular surface of
Rehabilitation Guidelines For SLAP Lesion Repair The anatomic configuration of the shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) is often compared to a golf ball on a tee. This is because the articular surface of
Understanding Planes and Axes of Movement
 Understanding Planes and Axes of Movement Terminology When describing the relative positions of the body parts or relationship between those parts it is advisable to use the same standard terminology.
Understanding Planes and Axes of Movement Terminology When describing the relative positions of the body parts or relationship between those parts it is advisable to use the same standard terminology.
REHAB 442: Advanced Kinesiology and Biomechanics INTRODUCTION - TERMS & CONCEPTS
 Rehab 442: Introduction - Page 1 REHAB 442: Advanced Kinesiology and Biomechanics INTRODUCTION - TERMS & CONCEPTS Readings: Norkin & Levangie, Chapters 1 & 2 or Oatis, Ch. 1 & 2 (don't get too bogged down
Rehab 442: Introduction - Page 1 REHAB 442: Advanced Kinesiology and Biomechanics INTRODUCTION - TERMS & CONCEPTS Readings: Norkin & Levangie, Chapters 1 & 2 or Oatis, Ch. 1 & 2 (don't get too bogged down
MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW. 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system
 MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system 2. Define the four characteristics of muscular tissue a. irritability (excitability) - b. extensibility- c. contractibility
MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system 2. Define the four characteristics of muscular tissue a. irritability (excitability) - b. extensibility- c. contractibility
Shoulder Instability. Fig 1: Intact labrum and biceps tendon
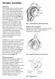 Shoulder Instability What is it? The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint, with the humeral head (upper arm bone) as the ball and the glenoid as the socket. The glenoid (socket) is a shallow bone
Shoulder Instability What is it? The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint, with the humeral head (upper arm bone) as the ball and the glenoid as the socket. The glenoid (socket) is a shallow bone
Anatomy of Human Muscles
 Anatomy of Human Muscles PURPOSE: To develop skill in identifying muscle names and locations relative to other regional structures. To determine origin, insertion and principle action of muscles through
Anatomy of Human Muscles PURPOSE: To develop skill in identifying muscle names and locations relative to other regional structures. To determine origin, insertion and principle action of muscles through
Terminology of Human Walking From North American Society for Gait and Human Movement 1993 and AAOP Gait Society 1994
 Gait Cycle: The period of time from one event (usually initial contact) of one foot to the following occurrence of the same event with the same foot. Abbreviated GC. Gait Stride: The distance from initial
Gait Cycle: The period of time from one event (usually initial contact) of one foot to the following occurrence of the same event with the same foot. Abbreviated GC. Gait Stride: The distance from initial
Biomechanics of Overarm Throwing. Deborah L. King, PhD
 Biomechanics of Overarm Throwing Deborah L. King, PhD Ithaca College, Department of Exercise and Sport Science Outline Review Fundamental Concepts Breakdown Throwing Motion o Identify Key Movements o Examine
Biomechanics of Overarm Throwing Deborah L. King, PhD Ithaca College, Department of Exercise and Sport Science Outline Review Fundamental Concepts Breakdown Throwing Motion o Identify Key Movements o Examine
Biceps Tenodesis Protocol
 Department of Rehabilitation Services Physical Therapy The intent of this protocol is to provide the clinician with a guideline of the postoperative rehabilitation course of a patient that has undergone
Department of Rehabilitation Services Physical Therapy The intent of this protocol is to provide the clinician with a guideline of the postoperative rehabilitation course of a patient that has undergone
DSM Spine+Sport - Mobility
 To set yourself up for success, practice keeping a neutral spine throughout all of these movements. This will ensure the tissue mobilization is being applied to the correct area, and make the techniques
To set yourself up for success, practice keeping a neutral spine throughout all of these movements. This will ensure the tissue mobilization is being applied to the correct area, and make the techniques
Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Hip joint
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Hip joint
SAMPLE WORKOUT Full Body
 SAMPLE WORKOUT Full Body Perform each exercise: 30 secs each x 2 rounds or 2-3 sets of 8-12 reps Monday & Wednesday or Tuesday & Thursday Standing Squat Muscles: glutes (butt), quadriceps (thigh) Stand
SAMPLE WORKOUT Full Body Perform each exercise: 30 secs each x 2 rounds or 2-3 sets of 8-12 reps Monday & Wednesday or Tuesday & Thursday Standing Squat Muscles: glutes (butt), quadriceps (thigh) Stand
Shoulder Injuries. Why Bother? QAS Injury Prevalence. Screening Injury 29.2% 12 month cumulative injury prevalence. Dr Simon Locke
 Shoulder Injuries Dr Simon Locke Why Bother? Are shoulder and upper limb injuries common? Some anatomy What, where, what sports? How do they happen? Treatment, advances? QAS Injury Prevalence Screening
Shoulder Injuries Dr Simon Locke Why Bother? Are shoulder and upper limb injuries common? Some anatomy What, where, what sports? How do they happen? Treatment, advances? QAS Injury Prevalence Screening
Shoulder MRI for Rotator Cuff Tears. Conor Kleweno,, Harvard Medical School Year III Gillian Lieberman, MD
 Shoulder MRI for Rotator Cuff Tears Conor Kleweno,, Harvard Medical School Year III Goals of Presentation Shoulder anatomy Function of rotator cuff MRI approach to diagnose cuff tear Anatomy on MRI images
Shoulder MRI for Rotator Cuff Tears Conor Kleweno,, Harvard Medical School Year III Goals of Presentation Shoulder anatomy Function of rotator cuff MRI approach to diagnose cuff tear Anatomy on MRI images
MUSCLES G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION. Unit 1. Factors Affecting Participation and Performance. G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:.
 G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance MUSCLES Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should: Be able to describe and explain how muscles
G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance MUSCLES Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should: Be able to describe and explain how muscles
HYPERLORDOSIS & PILATES TREATMENT
 HYPERLORDOSIS & PILATES TREATMENT Grace Tiangco 3/18/15 2012-2013 Abstract Sacramento/Mountain View Lordosis or Hyperlordosis is defined as a postural type in which the natural curves of the spine are
HYPERLORDOSIS & PILATES TREATMENT Grace Tiangco 3/18/15 2012-2013 Abstract Sacramento/Mountain View Lordosis or Hyperlordosis is defined as a postural type in which the natural curves of the spine are
A BIOMECHANICAL COMPARISON OF THE FRONT AND REAR LAT PULL- DOWN EXERCISE
 A BIOMECHANICAL COMPARISON OF THE FRONT AND REAR LAT PULL- DOWN EXERCISE By GARY MICHAEL (GM) PUGH A THESIS PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS
A BIOMECHANICAL COMPARISON OF THE FRONT AND REAR LAT PULL- DOWN EXERCISE By GARY MICHAEL (GM) PUGH A THESIS PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS
Ms. Ruth Delaney ROTATOR CUFF DISEASE Orthopaedic Surgeon, Shoulder Specialist
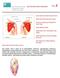 WHAT DOES THE ROTATOR CUFF DO? WHAT DOES THE ROTATOR CUFF DO? WHO GETS ROTATOR CUFF TEARS? HOW DO I CLINICALLY DIAGNOSE A CUFF TEAR? WHO NEEDS AN MRI? DOES EVERY CUFF TEAR NEED TO BE FIXED? WHAT DOES ROTATOR
WHAT DOES THE ROTATOR CUFF DO? WHAT DOES THE ROTATOR CUFF DO? WHO GETS ROTATOR CUFF TEARS? HOW DO I CLINICALLY DIAGNOSE A CUFF TEAR? WHO NEEDS AN MRI? DOES EVERY CUFF TEAR NEED TO BE FIXED? WHAT DOES ROTATOR
Integrated Manual Therapy & Orthopedic Massage For Complicated Knee Conditions
 Integrated Manual Therapy & Orthopedic Massage For Complicated Knee Conditions Assessment Protocols Treatment Protocols Treatment Protocols Corrective Exercises Artwork and slides taken from the book Clinical
Integrated Manual Therapy & Orthopedic Massage For Complicated Knee Conditions Assessment Protocols Treatment Protocols Treatment Protocols Corrective Exercises Artwork and slides taken from the book Clinical
Chapter 8. Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body
 Chapter 8 Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body INTRODUCTION This chapter continues our study of the muscular system by examining the distribution of muscles throughout the body. We learned in
Chapter 8 Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body INTRODUCTION This chapter continues our study of the muscular system by examining the distribution of muscles throughout the body. We learned in
Addressing Pelvic Rotation
 1 of 5 4/20/2008 10:31 AM http://www.strengthcoach.com Addressing Pelvic Rotation Aaron Brooks of Perfect Postures When trying to address your athlete's or client's limitations due to pain or joint restriction,
1 of 5 4/20/2008 10:31 AM http://www.strengthcoach.com Addressing Pelvic Rotation Aaron Brooks of Perfect Postures When trying to address your athlete's or client's limitations due to pain or joint restriction,
Massage and Movement
 Massage and Movement Incorporating Movement into Massage Part One: Theory and Technique in Prone With Lee Stang, LMT NCBTMB #450217-06 1850 West Street Southington, CT 06489 860.747.6388 www.bridgestohealthseminars.com
Massage and Movement Incorporating Movement into Massage Part One: Theory and Technique in Prone With Lee Stang, LMT NCBTMB #450217-06 1850 West Street Southington, CT 06489 860.747.6388 www.bridgestohealthseminars.com
Shoulder Examination
 Shoulder Examination Summary Inspection Palpation Movement Special Tests Neurological examination Introduction Shoulder disorders are can be broadly classified into the following types: Pain Stiffness
Shoulder Examination Summary Inspection Palpation Movement Special Tests Neurological examination Introduction Shoulder disorders are can be broadly classified into the following types: Pain Stiffness
THE BIG SIX. Six Best Volleyball Strength Training Exercises. By Dennis Jackson, CSCS www.strength-and
 THE BIG SIX Six Best Volleyball Strength Training Exercises By Dennis Jackson, CSCS www.strength-and and-power power-for for-volleyball.com THE SQUAT What it is The two most common squatting exercises
THE BIG SIX Six Best Volleyball Strength Training Exercises By Dennis Jackson, CSCS www.strength-and and-power power-for for-volleyball.com THE SQUAT What it is The two most common squatting exercises
The Muscular System. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres. Lone Star College North Harris. 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 11 The Muscular System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Muscular System Learning Outcomes 11-1 Describe the arrangement of
11 The Muscular System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Muscular System Learning Outcomes 11-1 Describe the arrangement of
Strength Training for the Runner
 Strength Training for the Runner Strength Training for the Runner What? The goal of resistance training for runners is not necessarily adding muscle mass but 1. improving muscular strength, 2. improving
Strength Training for the Runner Strength Training for the Runner What? The goal of resistance training for runners is not necessarily adding muscle mass but 1. improving muscular strength, 2. improving
Rotator Cuff Tears in Football
 Disclosures Rotator Cuff Tears in Football Roger Ostrander, MD Consultant: Mitek Consultant: On-Q Research Support: Arthrex Research Support: Breg Research Support: Arthrosurface 2 Anatomy 4 major muscles:
Disclosures Rotator Cuff Tears in Football Roger Ostrander, MD Consultant: Mitek Consultant: On-Q Research Support: Arthrex Research Support: Breg Research Support: Arthrosurface 2 Anatomy 4 major muscles:
Chapter 6: The Muscular System
 Chapter 6: The Muscular System I. Overview of Muscle Tissues Objectives: Describe the similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three types of muscle tissue, and indicate where
Chapter 6: The Muscular System I. Overview of Muscle Tissues Objectives: Describe the similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three types of muscle tissue, and indicate where
Aerobics: Knowledge and Practice
 Aerobics: Knowledge and Practice Brought to you by the Wellness Center and Vanderbilt Recreation Group Fitness Program Overview The goal of this self-study course is to provide aspiring aerobics instructors
Aerobics: Knowledge and Practice Brought to you by the Wellness Center and Vanderbilt Recreation Group Fitness Program Overview The goal of this self-study course is to provide aspiring aerobics instructors
Overhead Throwing: A Strength & Conditioning Approach to Preventative Injury
 By: Michael E. Bewley, MA, CSCS, C-SPN, USAW-I, President, Optimal Nutrition Systems Strength & Conditioning Coach for Basketball Sports Nutritionist for Basketball University of Dayton Overhead Throwing:
By: Michael E. Bewley, MA, CSCS, C-SPN, USAW-I, President, Optimal Nutrition Systems Strength & Conditioning Coach for Basketball Sports Nutritionist for Basketball University of Dayton Overhead Throwing:
Anterior Capsular Repair Rehabilitation Program Methodist Sports Medicine Center, Indianapolis, IN Department of Physical Therapy
 Anterior Capsular Repair Rehabilitation Program Methodist Sports Medicine Center, Indianapolis, IN Department of Physical Therapy Anterior Capsule reconstruction is a surgical procedure utilized for anterior
Anterior Capsular Repair Rehabilitation Program Methodist Sports Medicine Center, Indianapolis, IN Department of Physical Therapy Anterior Capsule reconstruction is a surgical procedure utilized for anterior
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Posterior Shoulder Reconstruction with or without Labral Repair
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Posterior Shoulder Reconstruction with or without Labral Repair The anatomic configuration of the shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) is often compared to a golf ball on a
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Posterior Shoulder Reconstruction with or without Labral Repair The anatomic configuration of the shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) is often compared to a golf ball on a
Name. Most of the bones of the limbs (arms & legs) act as levers. These levers are powered by muscles.
 Bones as Levers 1 Name Bones as Levers You may not think of your limbs as being machines, but they are. The action of a muscle pulling on a bone often works like a type of simple machine called a lever.
Bones as Levers 1 Name Bones as Levers You may not think of your limbs as being machines, but they are. The action of a muscle pulling on a bone often works like a type of simple machine called a lever.
Chapter 10: The Muscular System
 Chapter 10: The Muscular System Objectives: 1. Describe the function of prime movers, antagonists, synergists, and fixators. 2. List the criteria used in naming muscles. Provide an example to illustrate
Chapter 10: The Muscular System Objectives: 1. Describe the function of prime movers, antagonists, synergists, and fixators. 2. List the criteria used in naming muscles. Provide an example to illustrate
The skeletal and muscular systems
 anatomy and physiology The skeletal and muscular systems CHAPTER 1: Anatomy and physiology LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe an overview of the skeletal system
anatomy and physiology The skeletal and muscular systems CHAPTER 1: Anatomy and physiology LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe an overview of the skeletal system
Injury Prevention Strategies and Mechanics for Softball Players. Jason Yoder, DPT. Clinic Coordinator Sports Rehab Center for Sports Medicine
 Injury Prevention Strategies and Mechanics for Softball Players Jason Yoder, DPT Clinic Coordinator Sports Rehab Center for Sports Medicine Objectives Identify similarities and differences among the sports
Injury Prevention Strategies and Mechanics for Softball Players Jason Yoder, DPT Clinic Coordinator Sports Rehab Center for Sports Medicine Objectives Identify similarities and differences among the sports
Indian Club Sw. Complement your kettlebell training with Indian clubs. Use them for warm-ups or as a great workout on their own.
 Complement your kettlebell training with Indian clubs. Use them for warm-ups or as a great workout on their own. Indian Club Sw Russell Ogata, Mike Simpson, Tracey Freitas and Anil Sahal 26 The Kettlebell
Complement your kettlebell training with Indian clubs. Use them for warm-ups or as a great workout on their own. Indian Club Sw Russell Ogata, Mike Simpson, Tracey Freitas and Anil Sahal 26 The Kettlebell
Softball Pitching Technique Softball Pitching Technique FIG. 1:
 1 Softball Pitching Technique Marion J.L. Alexander, PhD. Carolyn Taylor, MSc Sport Biomechanics Laboratory Faculty of Kinesiology and Recreation Management University of Manitoba Softball Pitching Technique
1 Softball Pitching Technique Marion J.L. Alexander, PhD. Carolyn Taylor, MSc Sport Biomechanics Laboratory Faculty of Kinesiology and Recreation Management University of Manitoba Softball Pitching Technique
REHAB 544 FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY OF THE UPPER EXTREMITY & LOWER EXTREMITY
 REHAB 544 FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY OF THE UPPER EXTREMITY & LOWER EXTREMITY Mark Guthrie, PhD Rehabilitation Medicine University of Washington REHAB 544: Musculoskeletal Anatomy of the Upper & Lower Extremities,
REHAB 544 FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY OF THE UPPER EXTREMITY & LOWER EXTREMITY Mark Guthrie, PhD Rehabilitation Medicine University of Washington REHAB 544: Musculoskeletal Anatomy of the Upper & Lower Extremities,
Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis. Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University
 Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University Simplify Everything There are actually only three bones: Two innominates, one sacrum.
Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University Simplify Everything There are actually only three bones: Two innominates, one sacrum.
PN 001-6979 Rev. A (08/21/06) The Bowflex Xtreme SE Home Gym Owner s Manual and Fitness Guide
 PN 001-6979 Rev. A (08/21/06) The Bowflex Xtreme SE Home Gym Owner s Manual and Fitness Guide CONGRATULATIONS on your commitment to improving your health and fitness! With the Bowflex Xtreme SE home gym,
PN 001-6979 Rev. A (08/21/06) The Bowflex Xtreme SE Home Gym Owner s Manual and Fitness Guide CONGRATULATIONS on your commitment to improving your health and fitness! With the Bowflex Xtreme SE home gym,
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Arthroscopic Capsular Shift
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Arthroscopic Capsular Shift The anatomic configuration of the shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) is often compared to a golf ball on a tee. This is because the articular
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Arthroscopic Capsular Shift The anatomic configuration of the shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) is often compared to a golf ball on a tee. This is because the articular
Functional Anatomy of the Shoulder Complex
 Functional Anatomy of the Shoulder Complex MALCOLM PEAT The shoulder complex, together with other joint and muscle mechanisms of the upper limb, primarily is concerned with the ability to place and control
Functional Anatomy of the Shoulder Complex MALCOLM PEAT The shoulder complex, together with other joint and muscle mechanisms of the upper limb, primarily is concerned with the ability to place and control
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Anterior Shoulder Reconstruction with Arthroscopic Bankart Repair
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Anterior Shoulder Reconstruction with Arthroscopic Bankart Repair The anatomic configuration of the shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) is often compared to a golf ball on
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Anterior Shoulder Reconstruction with Arthroscopic Bankart Repair The anatomic configuration of the shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) is often compared to a golf ball on
A Patient s Guide to Shoulder Pain
 A Patient s Guide to Shoulder Pain Part 2 Evaluating the Patient James T. Mazzara, M.D. Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Sports Medicine Occupational Orthopedics Patient Education Disclaimer This presentation
A Patient s Guide to Shoulder Pain Part 2 Evaluating the Patient James T. Mazzara, M.D. Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Sports Medicine Occupational Orthopedics Patient Education Disclaimer This presentation
Rehabilitation after shoulder dislocation
 Physiotherapy Department Rehabilitation after shoulder dislocation Information for patients This information leaflet gives you advice on rehabilitation after your shoulder dislocation. It is not a substitute
Physiotherapy Department Rehabilitation after shoulder dislocation Information for patients This information leaflet gives you advice on rehabilitation after your shoulder dislocation. It is not a substitute
Read a chapter on Angular Kinematics
 Read a chapter on Angular Kinematics Angular Kinematics Hamill & Knutzen (Ch 9) Hay (Ch. 4), Hay & Ried (Ch. 10), Kreighbaum & Barthels (Module Ι) or Hall (Ch. 11) Reporting Angles Measurement of Angles
Read a chapter on Angular Kinematics Angular Kinematics Hamill & Knutzen (Ch 9) Hay (Ch. 4), Hay & Ried (Ch. 10), Kreighbaum & Barthels (Module Ι) or Hall (Ch. 11) Reporting Angles Measurement of Angles
Important rehabilitation management concepts to consider for a postoperative physical therapy rtsa program are:
 : General Information: Reverse or Inverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty (rtsa) is designed specifically for the treatment of glenohumeral (GH) arthritis when it is associated with irreparable rotator cuff
: General Information: Reverse or Inverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty (rtsa) is designed specifically for the treatment of glenohumeral (GH) arthritis when it is associated with irreparable rotator cuff
Upper Limb QUESTIONS UPPER LIMB: QUESTIONS
 1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
ACL plastik, erfarenheter av. tidig kirurgisk behandling. tidig kirurgisk behandling 6/12/2013
 in sports Per Renström, MD, PhD Professor emeritus,,, Sweden Member ATP and ITF Sports Science and Medical Committees Physician Swedish Football Association Presentation at the IOC Advanced team physician
in sports Per Renström, MD, PhD Professor emeritus,,, Sweden Member ATP and ITF Sports Science and Medical Committees Physician Swedish Football Association Presentation at the IOC Advanced team physician
or to swimming may make the muscle flexibility, re- shoulder less stable, increasor duce the risk of musculoskeletal
 TABILITY Swimmers often Incorrect stretching to increase joint flexibility just pri- stretch with the idea that they will increase or to swimming may make the muscle flexibility, re- shoulder less stable,
TABILITY Swimmers often Incorrect stretching to increase joint flexibility just pri- stretch with the idea that they will increase or to swimming may make the muscle flexibility, re- shoulder less stable,
Injuries to Upper Limb
 Injuries to Upper Limb 1 The following is a list of common sporting conditions and injuries. The severity of each condition may lead to different treatment protocols and certainly varying levels of intervention.
Injuries to Upper Limb 1 The following is a list of common sporting conditions and injuries. The severity of each condition may lead to different treatment protocols and certainly varying levels of intervention.
Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities. John A. Schneider, M.D.
 Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities John A. Schneider, M.D. Biographical Sketch Dr. Schneider is an orthopedic surgeon that specializes in the treatment of hand and upper extremity
Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities John A. Schneider, M.D. Biographical Sketch Dr. Schneider is an orthopedic surgeon that specializes in the treatment of hand and upper extremity
SHOULDER INSTABILITY IN PATIENTS WITH EDS
 EDNF 2012 CONFERENCE LIVING WITH EDS SHOULDER INSTABILITY IN PATIENTS WITH EDS Keith Kenter, MD Associate Professor Sports Medicine & Shoulder Reconstruction Director, Orthopaedic Residency Program Department
EDNF 2012 CONFERENCE LIVING WITH EDS SHOULDER INSTABILITY IN PATIENTS WITH EDS Keith Kenter, MD Associate Professor Sports Medicine & Shoulder Reconstruction Director, Orthopaedic Residency Program Department
Biomechanical Analysis of the Deadlift (aka Spinal Mechanics for Lifters) Tony Leyland
 Biomechanical Analysis of the Deadlift (aka Spinal Mechanics for Lifters) Tony Leyland Mechanical terminology The three directions in which forces are applied to human tissues are compression, tension,
Biomechanical Analysis of the Deadlift (aka Spinal Mechanics for Lifters) Tony Leyland Mechanical terminology The three directions in which forces are applied to human tissues are compression, tension,
Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle
 Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Hip relatively joint (acetabularfemoral) functions bony strong large stable due to The enhanced architecture
Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Hip relatively joint (acetabularfemoral) functions bony strong large stable due to The enhanced architecture
Shoulder. Clinical Assessment of the. The approach to a physical examination of the
 Focus on CME at the University of British Columbia Clinical Assessment of the Shoulder When assessing shoulder pain, a structured physical examination, as directed by the patient s history, allows the
Focus on CME at the University of British Columbia Clinical Assessment of the Shoulder When assessing shoulder pain, a structured physical examination, as directed by the patient s history, allows the
Muscles of Mastication
 Muscles of Mastication Masseter Zygomatic Arch Mandibular angle Elevates mandible Mandibular ramus Temporalis Temporal fossa of the temporal bone Coronoid process of the mandible Elevates mandible Retracts
Muscles of Mastication Masseter Zygomatic Arch Mandibular angle Elevates mandible Mandibular ramus Temporalis Temporal fossa of the temporal bone Coronoid process of the mandible Elevates mandible Retracts
Overhead Strength Training for the Shoulder: Guidelines for Injury Prevention and Performance Training Success
 Overhead Strength Training for the Shoulder: Guidelines for Injury Prevention and Performance Training Success Robert Panariello MS, PT, ATC, CSCS Strength training is an important component in the overall
Overhead Strength Training for the Shoulder: Guidelines for Injury Prevention and Performance Training Success Robert Panariello MS, PT, ATC, CSCS Strength training is an important component in the overall
Shoulder Injury Prevention and Rehabilitation for Health & Fitness Professionals
 s EDUCATION WORKSHOPS Shoulder Injury Prevention and Rehabilitation for Health & Fitness Professionals with B.App.Sc (Physio), Dip.Ed (P.E.) CONTENTS Topic Page 1. Functional Anatomy 3 2. Scapulohumeral
s EDUCATION WORKSHOPS Shoulder Injury Prevention and Rehabilitation for Health & Fitness Professionals with B.App.Sc (Physio), Dip.Ed (P.E.) CONTENTS Topic Page 1. Functional Anatomy 3 2. Scapulohumeral
Surgical Art. Formulaic Drawing Method. DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes
 DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes Surgical Art Formulaic Drawing Method Formulaic figure drawing systems involve using abstract rhythms and interlocking shapes to construct the human
DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes Surgical Art Formulaic Drawing Method Formulaic figure drawing systems involve using abstract rhythms and interlocking shapes to construct the human
Pilates to correct overactive upper trapezius muscles and prevent scapular elevation.
 Pilates to correct overactive upper trapezius muscles and prevent scapular elevation. Stephanie Blum July 13 th, 2014 Flow Studios, Chicago, IL Page 1 of 19 Abstract It s important to recognize where your
Pilates to correct overactive upper trapezius muscles and prevent scapular elevation. Stephanie Blum July 13 th, 2014 Flow Studios, Chicago, IL Page 1 of 19 Abstract It s important to recognize where your
Completing the Loop: Management of the Adolescent Sports Injury. Adam Thomas, PT, DPT, ATC
 : Management of the Adolescent Sports Injury Adam Thomas, PT, DPT, ATC https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vbufpo 8s3As On field assessment can be the most efficient when the health care provider has observed
: Management of the Adolescent Sports Injury Adam Thomas, PT, DPT, ATC https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vbufpo 8s3As On field assessment can be the most efficient when the health care provider has observed
NDT Treatment Planning Worksheet
 Child s Name: Kalab DOB: 01/01/02 Diagnosis: CP-Right-sided Heimplegia DOE: May 29, 2009 Therapist s Name: Mary Rose Franjoine Discipline: PT Current Participation: Attends his neighborhood school with
Child s Name: Kalab DOB: 01/01/02 Diagnosis: CP-Right-sided Heimplegia DOE: May 29, 2009 Therapist s Name: Mary Rose Franjoine Discipline: PT Current Participation: Attends his neighborhood school with
No Equipment Agility/Core/Strength Program for Full Body No Equip Trainer: Rick Coe
 No Equipment Agility/Core/Strength Program for Full Body No Equip Trainer: Rick Coe Introduction Program designed to be performed in a circuit. Perform exercises in sequence without rest 2-3 times. Increase
No Equipment Agility/Core/Strength Program for Full Body No Equip Trainer: Rick Coe Introduction Program designed to be performed in a circuit. Perform exercises in sequence without rest 2-3 times. Increase
VertiMax V8 Vertical Jump & Speed Training Program
 ANY ATHLETE, ANY SPORT, VERTIMAX WILL TAKE YOU TO THE NEXT LEVEL VertiMax V8 Vertical Jump & Speed Training Program Advanced Off Platform Speed Training Simultaneous leg & arm loading for maximum vertical
ANY ATHLETE, ANY SPORT, VERTIMAX WILL TAKE YOU TO THE NEXT LEVEL VertiMax V8 Vertical Jump & Speed Training Program Advanced Off Platform Speed Training Simultaneous leg & arm loading for maximum vertical
I tro r duct c io i n t o Exercise Technique
 Introduction to Exercise Technique Is Exercise Technique Important? It is the actual technique used for a resistance training exercise that determines; The precise movement pattern the body will be attempting
Introduction to Exercise Technique Is Exercise Technique Important? It is the actual technique used for a resistance training exercise that determines; The precise movement pattern the body will be attempting
Chapter 3 Basic Biomechanical Factors & Concepts
 Chapter 3 Basic Biomechanical Factors & Concepts Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Structural Kinesiology Basic Biomechanical Factors & Concepts 3-1 Biomechanics-study as anatomical systems
Chapter 3 Basic Biomechanical Factors & Concepts Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Structural Kinesiology Basic Biomechanical Factors & Concepts 3-1 Biomechanics-study as anatomical systems
SCAPULAR FRACTURES. Jai Relwani, Shoulder Fellow, Reading Shoulder Unit, Reading.
 SCAPULAR FRACTURES Jai Relwani, Shoulder Fellow, Reading Shoulder Unit, Reading. Aims Anatomy Incidence/Importance Mechanism Classification Principles of treatment Specific variations Conclusion Anatomy
SCAPULAR FRACTURES Jai Relwani, Shoulder Fellow, Reading Shoulder Unit, Reading. Aims Anatomy Incidence/Importance Mechanism Classification Principles of treatment Specific variations Conclusion Anatomy
Muscle Fibres. Anatomy and Physiology Advanced Diploma Course Sample Pages Page 1
 Muscle Fibres Muscles are composed of thousands of individual muscle fibres, which are held together by connective tissue. However, muscle fibres may differ in physiological makeup. Anatomy and Physiology
Muscle Fibres Muscles are composed of thousands of individual muscle fibres, which are held together by connective tissue. However, muscle fibres may differ in physiological makeup. Anatomy and Physiology
Fundamental Movement Skills: Balancing Mobility and Stability
 Fundamental Movement Skills: Balancing Mobility and Stability Of the three components of RAW functional fitness, movement skills tend to get the least emphasis. However, the other two components (strength
Fundamental Movement Skills: Balancing Mobility and Stability Of the three components of RAW functional fitness, movement skills tend to get the least emphasis. However, the other two components (strength
REVERSE SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY
 William J. Robertson, MD UT Southwestern Orthopedics 1801 Inwood Rd. Dallas, TX 75390-8882 Office: (214) 645-3300 Fax: (214) 3301 billrobertsonmd.com REVERSE SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY The shoulder is a ball
William J. Robertson, MD UT Southwestern Orthopedics 1801 Inwood Rd. Dallas, TX 75390-8882 Office: (214) 645-3300 Fax: (214) 3301 billrobertsonmd.com REVERSE SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY The shoulder is a ball
