21. Because the biceps brachii muscle flexes the forearm when it contracts, most of the muscle lies
|
|
|
- Amy Montgomery
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MUSCLE REVIEW Because the biceps brachii muscle flexes the forearm when it contracts, most of the muscle lies a. anterior to the humerus b. posterior to the humerus c. anterior to the ulna and radius d. posterior to the ulna and radius 22. The trapezius muscle is named on the basis of a. shape b. size c. location d. action 23. The muscle that turns the palm upward or anterior is the a. tibialis anterior b.plantaris c. adductor longus d. supinator 24. The facial muscle that is used to wrinkle the forehead is the a. orbicularis oculi b. frontalis c. temporalis d. masseter 25. A major muscle used to abduct the arm is the a. teres minor b. teres major c. pectoralis major d. deltoid 26. All of the following are flexors of the leg except the a. biceps femoris b. rectus femoris c. semitendinosus d. semimembranosus 27. All of the following flex the forearm except the a. brachialis b. brachioradialis c. biceps brachii d. triceps brachii 28. The latissimus dorsi, triceps brachii, and sacrospinalis all a. are located on the posterior surface of the body b. serve as extensors of some part of the body c. serve as extensors of one part but flexors of another d. none of the above e. both a and b 29. Which movements are possible at both the shoulder and elbow joint? a. abduction and flexion b. circumduction and flexion c. abduction, circumduction and flexion d. extension and flexion
2 30. Which is not a diarthrotic type of joint? a. between vertebral articular processes b. intercarpal c. distal tibio-fibular joint d. elbow e. all are diarthrotic Answers: 21-a, 22-a, 23-d, 24-b, 25-d, 26-b, 27-d, 28-e, 29-d, 30-c 31. A muscle that originates on both the spine of the scapula and the clavicle is the a. pectoralis major b. trapezius c. deltoid d. sternocleidomastoid 32. The functional relationship between the tibialis anterior and the soleus is comparable to that between the: a. deltoid and biceps brachii b. pectoralis major and serratus anterior c. pectoralis major and trapezius d. sternocleidomastoid and semispinalis 33. Which of the following is a functional joint classification? a. fibrous b. synarthrosis c. synovial d. cartilaginous 34. A joint cavity is present in a. fibrous joints b. amphiarthrotic joints c. cartilaginous joints d. synovial joints 35. Motion that increases the joint angle anteriorly is a. abduction b. extension c. eversion d. flexion 36. Structurally, diarthroses are a. fibrous joints b. synovial joints c. cartilaginous joints d. slightly movable 37. The circular, conelike movement of a body segment is a. rotation b. pronation c. circumduction d. eversion 38. Which of the following is not characteristic of all diarthroses? a. articular surfaces of hyaline cartilage b. joint capsule c. synovial membrane d. meniscus 39. In the cervical region all of the following movements are possible except a. flexion b. hyperextension c. dorsiflexion d. lateral rotation 40. Which of the following joints can be readily and comfortably hyperextended?
3 a. tibiofemoral b. interphalangeal c. atlantooccipital d. elbow Answers: 31-c, 32-d, 33-b, 34-d, 35-b, 36-b, 37-c, 38-d, 39-c, 40-c 41. Which of the following word pairs is incorrect? a. syndesmosis - synarthrosis b. pivot - diarthrosis c. symphysis - amphiarthrosis d. suture - synarthrosis 42. Which of the following is an agonist along with the supinator of the forearm? a. brachioradialis b. flexor carpi radialis c. brachialis d. biceps brachii 43. Contraction of which of the following muscles would never result in an extension movement? a. sacrospinalis b. biceps femoris c. rectus abdominis d. latissimus dorsi 44. The muscle tissue that can be consciously controlled is a. smooth b. skeletal c. intercalated d. cardiac 45. Cardiac muscle is found in the wall of the a. stomach b. intestine c. urinary bladder d. none of the above 46. The innermost layer of connective tissue in a skeletal muscle is called the a. epimysium b. perimysium c. endomysium d. sarcomysium 47. Intercalated discs are found in a. cardiac muscle b. smooth muscle c. skeletal muscle d. a and c 48. Which of the following is under voluntary control? a. skeletal muscle b. smooth muscle c. cardiac muscle d. a and c 49. Which of the following connective tissues is in direct contact with individual skeletal muscle fibers? a. periosteum b. epimysium c. perimysium d. endomysium 50. The extensor carpi ulnaris contracts to a. supinate the forearm b. flex the thumb c. extend the arm d. adduct the hand Answers: 41-a, 42-d, 43-c, 44-b, 45-d, 46-c, 47-a, 48-a, 49-d, 50-d 51. The latissimus dorsi originates primarily on the
4 a. humerus b. linea alba c. vertebral column d. clavicle 52. Which pair of muscles would not function as antagonists to one another? a. biceps brachii and triceps brachii b. anterior deltoid and latissimus dorsi c. rectus abdominis and sacrospinalis d. biceps femoris and gastrocnemius 53. Which of the following is not a rotator cuff muscle? a. supraspinatis b. subscapularis c. teres minor d. deltoid 54. Which one of the following is located entirely or mostly on the posterior surface of some part of the body? a. biceps brachii b. external oblique c. tricps brachii d. quadriceps femoris 55. Paralysis of which of the following would make an individual unable to flex his thigh? a. iliopsoas b. biceps femoris c. semitendinosus d. vastus medialis 56. Paralysis of which of the following muscles would make an individual unable to flex his leg? a. gastrocnemius b. soleus c. rectus femoris d. gluteus medius 57. An injection in the rump would be given in which muscle? a. gluteus medius b. tensor fascia latae c. gluteus minimus d. gluteus maximus 58. A pulled hamstring would include which muscle? a. semitendinosus b. rectus femoris c. iliopsoas d. vastus medialis 59. Which muscle elevates the ribs? a. serratus anterior b. pectoralis minor c. scalene d. transversus thoracis 60. Which muscle is a synergist in adduction of the arm? a. pectoralis major b. deltoid c. supraspinatus d. rhomboid Answers: 51-c, 52-d, 53-d, 54-c, 55-a, 56-a, 57-d, 58-a, 59-c, 60-d 61. The joints between the articular processes of vertebrae and between most carpal and tarsal bones are termed a. hinge b. gliding c. condyloid d. symphyses
5 62. The first metacarpal/carpal joint is a a. condyloid b. saddle c. gliding d. hinge 63. Both the shoulder joint and the hip joint contain a. an articular capsule b. menisci c. an iliofemoral ligament d. an scapulohumeral ligament 64. What is the action of the muscles located in the anterior compartment of the leg? a. flex the leg b. dorsiflex the foot and/or extend the toes c. plantar flex the foot and flex the toes d. extend the leg 65. The joint found between the flat bones of the skull is classified as a. syndesmosis b. suture c. amphiarthrosis d. synchondrosis 66. Most joints of the body are a. synchondroses b. symphyses c. synarthroses d. synovial 67. Which one of the following exemplifies a symphysis? a. junction of two pubic bones b. junctions between vertebral articular facets c. epiphyses of a long bone to the diaphysis d. junction between parietal bones 68. The inability to produce the fluid that keeps most joints moist would likely be due to a disorder in the a. bursae b. articular discs c. articular cartilages d. synovial membrane 69. The elbow is an example of a joint. a. uniaxial b. biaxial c. triaxial d. nonaxial 70. This movement is characteristic of the hip and shoulder joints. a. pronation b. supination c. eversion d. lateral rotation Answers: 61-b, 62-b, 63-a, 64-b, 65-b, 66-d, 67-a, 68-d, 69-a, 70-d 71. The shoulder joint is a. triaxial b. ball and socket c. synovial d. all of the above 72. Which joint would not allow circumduction? a. metacarpal/phalangeal II b. radioulnar/carpals c. carpometacarpal of the thumb d. interphalangeal
6 73. Which muscle could elevate the ribs as well as flex the neck? a. sternocleidomastoid b. scalene c. splenius d. semispinalis 74. Which muscle is an antagonist to the action(s) provided by the pectoralis major? a. pectoralis minor b. subscapularis c. serratus anterior d. supraspinatus 75. Which muscle is not a rotator of the arm? a. subscapularis b. infraspinatus c. supraspinatus d. latissimus dorsi 76. Which muscle is not superficial in the body, seen just below the skin? a. latissimus dorsi b. gastrocnemius c. internal oblique d. pectoralis major 77. A sphincter muscle includes the a. temporalis b. platysma c. occipitofrontalis d. orbicularis oculi 78. Which action(s) does the soleus and gastrocnemius have in common? a. plantar flexion of the foot b. dorsiflexion of the foot c. flexion of the leg d. a and c 79. Which muscle is involved in chewing? a. temporalis b. orbicularis oculi c. occipitofrontalis d. sternocleidomastoid 80. Which of the following characterizes all cartilaginous joints? a. contain plates of hyaline cartilage b. lack joint cavities c. are immovable d. all of the above do Answers: 71-d, 72-d, 73-b, 74-d, 75-c, 76-c, 77-d, 78-a, 79-a, 80-b 81. When the movement at a joint is limited to rotation around only one axis, the joint is said to be a. uniaxial b. biaxial c. nonaxial d. amphiarthrotic 82. Which of the following tends to form septa within the skeletal muscle, to reinforce the muscle? a. fasciculus b. epimysium c. perimysium d. endomysium 83. Which action(s) would the brachialis and biceps brachii have in common? a. supination of the forearm b. flexion of the arm c. flexion of the forearm d. a and c 84. Which action occurs for the rectus femoris but not the vastus muscles? a. extension of the thigh b. extension of the leg c. flexion of the thigh d. flexion of the leg
7 85. If a pin enters a skeletal muscle, which of the following layers would be encountered secondly? a. deep fascia b. endomysium c. perimysium d. epimysium 86. Which muscle name indicates the relative size of the muscle in its name? a. transversus abdominis b. pectoralis major c. trapezius d. sartorius 87. Which muscle might act as a synergist in plantar flexion of the foot? a. tibialis anterior b. quadriceps femoris c. flexor digitorum longus d. extensor digitorum longus 88. Which muscle name indicates the shape of the muscle? a. gluteus maximus b. rectus abdominis c. rhomboid d. biceps brachii 89. All synovial joints possess all of the following features except: a. articular cartilage b. a joint capsule c. a synovial membrane d. an articular disc 90. Flexion and extension movements at the wrist take place at a. the joint between radius and ulna and the proximal row of carpals b. the joint between the proximal and distal rows of carpals c. the joints between carpals and metacarpals d. the joint between the distal radius and distal ulna Answers: 81-a, 82-b, 83-c, 84-c, 85-d, 86-b, 87-b, 88-c, 89-d, 90-a 91. Which of the following would not be under the control of the autonomic nervous system? a. iris of the eye b. muscular layer of the uterus c. muscular layer of the pharynx d. muscular layer of a small artery 92. Which muscle is an agonist for adduction of the arm? a. pectoralis major b. pectoralis minor c. teres minor d. supraspinatus 93. Which muscle does not form part of the abdominal wall musculature? a. external oblique b. rectus abdominis c. transversus abdominis d. transversus thoracis 94. Which muscle is not a hamstring? a. semitendinosus b. gastrocnemius c. biceps femoris d. semimembranosus
8 95. The agonist for jaw closure is the a. platysma b. sternocleidomastoid c. masseter d. orbicularis oris 96. Which muscle moves the ribs? a. diaphragm b. serratus anterior c. serratus posterior inferior d. splenius 97. Which of the following is not a fibrous joint? a. suture b. syndesmosis c. synchondrosis d. interosseus membrane 98. Which muscle is not involved in a medial or lateral rotational movement within the forearm? a. supinator b. biceps brachii c. pronator teres d. palmaris longus 99. Which of the following is not a synovial joint? a. odontoid process and atlas b. between vertebral articular facets c. joint between bodies of two vertebrae d. joint between two tarsals 100.A synergist in abduction of the arm would be a. rhomboideus b. anterior deltoid c. biceps brachii d. pectoralis major Answers:91-c, 92-a, 93-d, 94-b, 95-c, 96-c, 97-c, 98-d, 99-c, 100-a MATCHING. Match muscle on left with action on the right. 1. sternocleidomastoid 2. temporalis 3. orbicularis oris 4. rhomboideus 5. deltoid 6. brachialis 7. supinator 8. serratus anterior 9. palmaris longus 10. adductor femoris 11. quadriceps femoris 12. gastrocnemius 13. gluteus maximus a. extension of thigh b. flexion of head c. abduction of arm d. close eyelids e. flexion of leg f. puckers lipsg. G.flexion of thigh h. flexion of forearm i. lateral rotation of forearm j. elevation of mandible
9 k. retraction of scapula l. protraction of scapula m. flexion of hand n. extension of leg Answers: 1-b, 2-j, 3-f, 4-k, 5-c, 6-h, 7-i, 8-l, 9-m, 10-g, 11-n, 12-e, 13-a MATCHING. Match movement term with appropriate description. 20. flexion a. arching the back 21. hyperextension b. moving a limb away from the midline 22. abduction of the body 23. adduction c. moving a bone in an anterior- 24. plantar flexion posterior plane;decreasing the 25. dorsiflexion angle between the two bones d. lowering the toe region of the foot toward the floor e. raising the toe region of the foot toward the shin f. moving the fingers toward the midline of the hand Answers: 20-c, 21-a, 22-b, 23-f, 24-d, 25-e MATCHING. Match statement on left with muscle tissue on the right. 26. greatest blood supply a. cardiac muscle
10 27. striated b. skeletal muscle 28. intercalated discs c. smooth muscle 29. tongue muscles d. more than one of these 30. diaphragm 31. unstriated 32. involuntary 33. many peripheral nuclei 34. voluntary Answers: 26-a, 27-d, 28-a, 29-b, 30-b, 31-c, 32-d, 33-b, 34-b TRUE/FALSE 1. In order to move a bone, a muscle must have its origin on that bone. 2. The rectus femoris muscle may function as a flexor of the thigh, trunk, or leg. 3. The sartorius is one of the hamstrings. 4. The hamstring muscles function as leg flexors, as does the gastrocnemius. 5. Muscles of the back (posterior trunk) function as extensors of the trunk. 6. Extensor muscles play a more important part in the maintenance of upright posture than do flexors. 7. The gastrocnemius and the tibialis anterior are examples of antagonists. 8. All diarthroses permit free movement, but not necessarily the same kinds of movements, between articulating bones. 9. The term synarthroses is another name for synovial joints. 10. A large majority of joints in the body are synovial in type. Answers: 1-F, 2-F, 3-F, 4-T, 5-T, 6-T, 7-T, 8-T, 9-F, 10-T
Anatomy & Physiology 120. Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles
 Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
Muscular System. Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body
 Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body
 Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Anatomy of Human Muscles
 Anatomy of Human Muscles PURPOSE: To develop skill in identifying muscle names and locations relative to other regional structures. To determine origin, insertion and principle action of muscles through
Anatomy of Human Muscles PURPOSE: To develop skill in identifying muscle names and locations relative to other regional structures. To determine origin, insertion and principle action of muscles through
Chapter 10: The Muscular System
 Chapter 10: The Muscular System Objectives: 1. Describe the function of prime movers, antagonists, synergists, and fixators. 2. List the criteria used in naming muscles. Provide an example to illustrate
Chapter 10: The Muscular System Objectives: 1. Describe the function of prime movers, antagonists, synergists, and fixators. 2. List the criteria used in naming muscles. Provide an example to illustrate
Chapter 8. Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body
 Chapter 8 Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body INTRODUCTION This chapter continues our study of the muscular system by examining the distribution of muscles throughout the body. We learned in
Chapter 8 Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body INTRODUCTION This chapter continues our study of the muscular system by examining the distribution of muscles throughout the body. We learned in
The Muscular System General & Anatomy
 The Muscular System General & Anatomy General Functions: 1. movement voluntary skeletal muscles 2. internal movement of substances through various tubes and passageways eg blood, food, urine heart pumps
The Muscular System General & Anatomy General Functions: 1. movement voluntary skeletal muscles 2. internal movement of substances through various tubes and passageways eg blood, food, urine heart pumps
Chapter 6: The Muscular System
 Chapter 6: The Muscular System I. Overview of Muscle Tissues Objectives: Describe the similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three types of muscle tissue, and indicate where
Chapter 6: The Muscular System I. Overview of Muscle Tissues Objectives: Describe the similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three types of muscle tissue, and indicate where
CHAPTER 8: JOINTS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM. 4. Name the three types of fibrous joints and give an example of each.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Define the term articulation. 2. Distinguish between the functional and structural classification of joints, and relate the terms that are essentially synonymous. 3. Compare and contrast
OBJECTIVES: 1. Define the term articulation. 2. Distinguish between the functional and structural classification of joints, and relate the terms that are essentially synonymous. 3. Compare and contrast
Deltoid Trapezius. Identify the muscle pair(s) that work together to produce the movements listed above.
 Shoulder- the major muscles in this group are the infraspinatus, subscapularis, terems major, teres minor deltoid, and trapezius. These muscles work together to move the shoulder area, allowing you, for
Shoulder- the major muscles in this group are the infraspinatus, subscapularis, terems major, teres minor deltoid, and trapezius. These muscles work together to move the shoulder area, allowing you, for
Buccinator Presses cheek against molar teeth Facial (CNVII) wrinkles forehead
 Muscles to Identify on the Cadaver and/or Models You are required to identify each of the following muscles or associated structures on the cadavers and/or models in lab. If the box is shaded in a particular
Muscles to Identify on the Cadaver and/or Models You are required to identify each of the following muscles or associated structures on the cadavers and/or models in lab. If the box is shaded in a particular
Skin of eyebrows galea aponeurotica. Muscle and skin of mouth
 : SEE ALSO THE AP SITE FOR OTHER TABLES GROSS ANATOMY OF THE MUSCULAR SYSTEMM Muscles of the Head and Neck: Occipitofrontalis Frontalis Occipitalis Orbicularis oculi Orbicularis oris Buccinator Masseter
: SEE ALSO THE AP SITE FOR OTHER TABLES GROSS ANATOMY OF THE MUSCULAR SYSTEMM Muscles of the Head and Neck: Occipitofrontalis Frontalis Occipitalis Orbicularis oculi Orbicularis oris Buccinator Masseter
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names
 Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together.
 Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
Chapter 9 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 Chapter 9 1 JOINTS Chapter 9 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 9 2 JOINTS (Bones are too rigid to bend without causing damage.) (Bones are held together at joints by flexible connective tissue.) (Imagine
Chapter 9 1 JOINTS Chapter 9 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 9 2 JOINTS (Bones are too rigid to bend without causing damage.) (Bones are held together at joints by flexible connective tissue.) (Imagine
Chapter 8 - Muscular System 8.1 Introduction (p. 178 ) A. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. B.
 Chapter 8 - Muscular System 8.1 Introduction (p. 178 ) A. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. B. This chapter focuses on skeletal muscle. 8.2 Structure of a
Chapter 8 - Muscular System 8.1 Introduction (p. 178 ) A. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. B. This chapter focuses on skeletal muscle. 8.2 Structure of a
SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY
 2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity K/507/4452 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016
2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity K/507/4452 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016
Muscles of the Neck and Vertebral Column Sternocleidomastoid (anterior neck) Origin Insertion Action
 Muscular movements of the head (at the cervical spine/neck) and of the torso (thoracic and lumbar spine/upper, middle, and lower back): flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation. Muscles of the Neck
Muscular movements of the head (at the cervical spine/neck) and of the torso (thoracic and lumbar spine/upper, middle, and lower back): flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation. Muscles of the Neck
MUSCLES. b. labor in female's uterus at birth I. GENERAL FUNCTIONS OF MUSCLES. 5. Heart and Blood vessels
 MUSCLES I. GENERAL FUNCTIONS OF MUSCLES The major function of muscle tissue is contraction(the ability to shorten and thus cause movement in the body), and relaxation(the ability to lengthen again and
MUSCLES I. GENERAL FUNCTIONS OF MUSCLES The major function of muscle tissue is contraction(the ability to shorten and thus cause movement in the body), and relaxation(the ability to lengthen again and
Muscular System. Principles of Health Science Dr. Wood
 Muscular System Principles of Health Science Dr. Wood Characteristics of muscles Excitability: : irritability or ability to respond to stimulus Contractibility: : ability to contract (become short and
Muscular System Principles of Health Science Dr. Wood Characteristics of muscles Excitability: : irritability or ability to respond to stimulus Contractibility: : ability to contract (become short and
The Muscular System. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres. Lone Star College North Harris. 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 11 The Muscular System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Muscular System Learning Outcomes 11-1 Describe the arrangement of
11 The Muscular System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Muscular System Learning Outcomes 11-1 Describe the arrangement of
MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW. 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system
 MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system 2. Define the four characteristics of muscular tissue a. irritability (excitability) - b. extensibility- c. contractibility
MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system 2. Define the four characteristics of muscular tissue a. irritability (excitability) - b. extensibility- c. contractibility
TOTAL BODY: POWER/EXPLOSIVE EXERCISES
 Referring to Chapters 12-14 TOTAL BODY: POWER/EXPLOSIVE EXERCISES Power Snatch hip extension Muscle group/ gluteals gluteus maximis hamstrings semimembranosus semitendinosus biceps femoris knee extension
Referring to Chapters 12-14 TOTAL BODY: POWER/EXPLOSIVE EXERCISES Power Snatch hip extension Muscle group/ gluteals gluteus maximis hamstrings semimembranosus semitendinosus biceps femoris knee extension
Chapter 11 The Muscular System. Muscle Attachment Sites: Origin and Insertion
 Chapter 11 The Muscular System Skeletal muscle major groupings How movements occur at specific joints Learn the origin, insertion, function and innervation of all major muscles Important to allied health
Chapter 11 The Muscular System Skeletal muscle major groupings How movements occur at specific joints Learn the origin, insertion, function and innervation of all major muscles Important to allied health
PRIMARY HUMAN ANATOMY: BIOL20600 SPRING 2014
 PRIMARY HUMAN ANATOMY: BIOL20600 SPRING 2014 Instructors: Kit Muma, Rm. 158 CNS, (607) 274-3610, muma@ithaca.edu Michelle Bamberger, Rm. 118A Williams Hall, mbamberger@ithaca.edu Mark Baustian, Rm. 118A
PRIMARY HUMAN ANATOMY: BIOL20600 SPRING 2014 Instructors: Kit Muma, Rm. 158 CNS, (607) 274-3610, muma@ithaca.edu Michelle Bamberger, Rm. 118A Williams Hall, mbamberger@ithaca.edu Mark Baustian, Rm. 118A
Ken Ross BSc ST, Nat Dip ST
 Ken Ross BSc ST, Nat Dip ST Trunk Most people will suffer from back pain at some point in their lives. Good spinal posture places minimal strain on the muscles which maintain the natural curve of the spine
Ken Ross BSc ST, Nat Dip ST Trunk Most people will suffer from back pain at some point in their lives. Good spinal posture places minimal strain on the muscles which maintain the natural curve of the spine
Muscles of Mastication
 Muscles of Mastication Masseter Zygomatic Arch Mandibular angle Elevates mandible Mandibular ramus Temporalis Temporal fossa of the temporal bone Coronoid process of the mandible Elevates mandible Retracts
Muscles of Mastication Masseter Zygomatic Arch Mandibular angle Elevates mandible Mandibular ramus Temporalis Temporal fossa of the temporal bone Coronoid process of the mandible Elevates mandible Retracts
Practice Chapter 6. Figure 6.3. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Practice Chapter 6 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Voluntary muscle tissue is; a. smooth muscle b. skeletal muscle c. dense regular d.
Practice Chapter 6 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Voluntary muscle tissue is; a. smooth muscle b. skeletal muscle c. dense regular d.
Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper Extremity Pectoralis Major Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal
 Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper Extremity Pectoralis Major Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal Crest of greater tubercle (Lateral lip of bicipital groove)
Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper Extremity Pectoralis Major Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal Crest of greater tubercle (Lateral lip of bicipital groove)
Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements
 Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements Note: MSK Ultrasound-Guided Interventional Procedures (USGIP) is considered a separate specialty. Corresponds with 4/21/16 Accred Newsletter* From the main site:
Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements Note: MSK Ultrasound-Guided Interventional Procedures (USGIP) is considered a separate specialty. Corresponds with 4/21/16 Accred Newsletter* From the main site:
EXERCISE MANUAL PERSONALITY GYM
 EXERCISE MANUAL PERSONALITY GYM EXERCISE MANUAL PERSONALITY GYM legs. 1 calves raise Stand with the wide part of one foot on the seated row foot support. Start in a position with your calves stretched.
EXERCISE MANUAL PERSONALITY GYM EXERCISE MANUAL PERSONALITY GYM legs. 1 calves raise Stand with the wide part of one foot on the seated row foot support. Start in a position with your calves stretched.
The Pilates Studio of Los Angeles / PilatesCertificationOnline.com
 Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
Objectives continued- Answer each of the objectives on a separate sheet of paper to demonstrate content mastery. Attach answers to back of packet.
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6: The Muscular System Name: Objectives- By the end of this chapter I will be able to: 1. Describe similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6: The Muscular System Name: Objectives- By the end of this chapter I will be able to: 1. Describe similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three
Flexibility Assessment and Improvement Compiled and Adapted by Josh Thompson
 Flexibility Assessment and Improvement Compiled and Adapted by Josh Thompson Muscles must have a full and normal range of motion in order for joints and skeletal structure to function properly. Flexibility
Flexibility Assessment and Improvement Compiled and Adapted by Josh Thompson Muscles must have a full and normal range of motion in order for joints and skeletal structure to function properly. Flexibility
International Standards for the Classification of Spinal Cord Injury Motor Exam Guide
 C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
Figure 6.1. 2) The A band within a skeletal muscle fiber is indicated by letter. Answer: A Diff: 2 Page Ref: 188
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 6 The Muscular System Short Answer Figure 6.1 Using Figure 6.1, match the following: 1) The I band within a skeletal muscle fiber is indicated
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 6 The Muscular System Short Answer Figure 6.1 Using Figure 6.1, match the following: 1) The I band within a skeletal muscle fiber is indicated
CHAPTER 9: THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM. 2. Describe three similarities among the three muscle tissues.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Compare and contrast the types of muscle tissues in terms of structure, control, location, and type of contraction, and function. 2. Describe three similarities among the three muscle tissues.
OBJECTIVES: 1. Compare and contrast the types of muscle tissues in terms of structure, control, location, and type of contraction, and function. 2. Describe three similarities among the three muscle tissues.
Stretching the Major Muscle Groups of the Lower Limb
 2 Stretching the Major Muscle Groups of the Lower Limb In this chapter, we present appropriate stretching exercises for the major muscle groups of the lower limb. All four methods (3S, yoga, slow/static,
2 Stretching the Major Muscle Groups of the Lower Limb In this chapter, we present appropriate stretching exercises for the major muscle groups of the lower limb. All four methods (3S, yoga, slow/static,
THE SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS
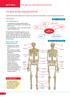 SECTION A A general overview of the skeletal system is required, but will not be directly examined, so we include a general overview here. Introduction The skeletal system The appendicular skeletal system
SECTION A A general overview of the skeletal system is required, but will not be directly examined, so we include a general overview here. Introduction The skeletal system The appendicular skeletal system
DSM Spine+Sport - Mobility
 To set yourself up for success, practice keeping a neutral spine throughout all of these movements. This will ensure the tissue mobilization is being applied to the correct area, and make the techniques
To set yourself up for success, practice keeping a neutral spine throughout all of these movements. This will ensure the tissue mobilization is being applied to the correct area, and make the techniques
Name the muscle, A: (Action), O: (Origin), and I: (Insertion)
 FRONTALIS - A: (Action) Elevates eyebrows in glancing upward and expressions of surprise or fright; draws scalp forward and wrinkles skin of forehead; O: (Origin) Galea aponeurotica; I: Subcutaneous tissue
FRONTALIS - A: (Action) Elevates eyebrows in glancing upward and expressions of surprise or fright; draws scalp forward and wrinkles skin of forehead; O: (Origin) Galea aponeurotica; I: Subcutaneous tissue
The skeletal and muscular systems
 anatomy and physiology The skeletal and muscular systems CHAPTER 1: Anatomy and physiology LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe an overview of the skeletal system
anatomy and physiology The skeletal and muscular systems CHAPTER 1: Anatomy and physiology LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe an overview of the skeletal system
THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T
 THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T CLARIFICATION OF TERMS Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus Lippert, p115
THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T CLARIFICATION OF TERMS Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus Lippert, p115
UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 9: MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 LEARNING OUTCOMES: 9.1 Introduction UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 9: MUSCULAR SYSTEM 1. List various outcomes of muscle actions. 9.2 Structure of a Skeletal Muscle 2. Describe the structure of a skeletal muscle. 3.
LEARNING OUTCOMES: 9.1 Introduction UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 9: MUSCULAR SYSTEM 1. List various outcomes of muscle actions. 9.2 Structure of a Skeletal Muscle 2. Describe the structure of a skeletal muscle. 3.
Skeletal system. 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
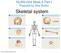 NURS1004 Week 6 Part I Prepared by Didy Button Skeletal system An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues 6-1
NURS1004 Week 6 Part I Prepared by Didy Button Skeletal system An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues 6-1
Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Hip joint
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Hip joint
Upper Limb QUESTIONS UPPER LIMB: QUESTIONS
 1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS
 ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY 1. Define "anatomy" and "physiology." 2. Describe homeostasis. 3. Identify examples of homeostasis 4. Describe the organization of the body according
ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY 1. Define "anatomy" and "physiology." 2. Describe homeostasis. 3. Identify examples of homeostasis 4. Describe the organization of the body according
Muscle Organization and Function. Chapter 10: The Muscular System. Parallel (Fusiform) Muscles. Organization of Skeletal Muscle Fibers
 Muscle Organization and Function Chapter 10: The Muscular System Muscle organization affects power, range, and speed of muscle movement Muscle cells (fibers) are organized in bundles (fascicles) Fibers
Muscle Organization and Function Chapter 10: The Muscular System Muscle organization affects power, range, and speed of muscle movement Muscle cells (fibers) are organized in bundles (fascicles) Fibers
The Muscular System. Appendicular Musculature
 11 The Muscular System Appendicular Musculature CHAPTER OBJECTIVES 1. Describe the functions of the appendicular musculature. 2. Identify and locate the principal appendicular muscles of the body, together
11 The Muscular System Appendicular Musculature CHAPTER OBJECTIVES 1. Describe the functions of the appendicular musculature. 2. Identify and locate the principal appendicular muscles of the body, together
EHFA Assessment Strategy (EAD 03) Name of Training Organisation:
 EHFA Assessment Strategy (EAD 03) Name of Training Organisation: Introduction European Health and Fitness Association (EHFA) Standards The following EHFA standards are currently available: Fitness Instructor
EHFA Assessment Strategy (EAD 03) Name of Training Organisation: Introduction European Health and Fitness Association (EHFA) Standards The following EHFA standards are currently available: Fitness Instructor
Vertebrate Skeletal Muscle Structure
 VertebrateSkeletalMuscleStructure HumanAnatomy&PhysiologyLab#1 Todaywewillexaminethemuscularsystemoftherat,withparticularemphasison themusclesofthehindlimb.thegoalofthislabistoconsidertherelationship betweenfineandgrossmusclestructureandfunction.byfocusingonrathindlimb
VertebrateSkeletalMuscleStructure HumanAnatomy&PhysiologyLab#1 Todaywewillexaminethemuscularsystemoftherat,withparticularemphasison themusclesofthehindlimb.thegoalofthislabistoconsidertherelationship betweenfineandgrossmusclestructureandfunction.byfocusingonrathindlimb
Joints. The graceful movements of ballet dancers and the rough-and-tumble. Classification of Joints
 Classification of Joints (pp. 24 249) Fibrous Joints (pp. 249 250) Sutures (p. 249) Syndesmoses (pp. 249 250) Gomphoses (p. 250) Cartilaginous Joints (pp. 250 251) Synchondroses (pp. 250 251) Symphyses
Classification of Joints (pp. 24 249) Fibrous Joints (pp. 249 250) Sutures (p. 249) Syndesmoses (pp. 249 250) Gomphoses (p. 250) Cartilaginous Joints (pp. 250 251) Synchondroses (pp. 250 251) Symphyses
UNIT 5 - MUSCULAR SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 5 - MUSCULAR SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 5.0I MUSCLE TISSUE FUNCTIONS A. Motion by moving the skeletal levers of the body B. Posture - stabilizing body positions C. Regulation of organ volume D. Thermogenesis
UNIT 5 - MUSCULAR SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 5.0I MUSCLE TISSUE FUNCTIONS A. Motion by moving the skeletal levers of the body B. Posture - stabilizing body positions C. Regulation of organ volume D. Thermogenesis
LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT
 UNIT - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 18 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT Movement is an important feature of living organism. Both the microbes and macrobes show wide range of movements. The movements results in change
UNIT - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 18 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT Movement is an important feature of living organism. Both the microbes and macrobes show wide range of movements. The movements results in change
9/3/2013 JOINTS. Joints. Axial Skeleton STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION:
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM freedom Functional potential of the joint Axial
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM freedom Functional potential of the joint Axial
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone
THE SKELETAL & ARTICULAR SYSTEMS. The Bones & Joints
 THE SKELETAL & ARTICULAR SYSTEMS The Bones & Joints CLOSE YOUR POWERPOINT HANDOUTS!! Think-Pair-Share: Why do we need bones? Try to think of 3 reasons. THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Is made up of numerous bones
THE SKELETAL & ARTICULAR SYSTEMS The Bones & Joints CLOSE YOUR POWERPOINT HANDOUTS!! Think-Pair-Share: Why do we need bones? Try to think of 3 reasons. THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Is made up of numerous bones
Muscular System Teacher s lecture notes, curriculum and guides 2012
 MUSCULAR SYSTEM INTRODUCTION A. Muscular tissue enables the body and its parts to move a. Movement caused by ability of muscle cells (called fibers) to shorten or contract b. Muscle cells shorten by converting
MUSCULAR SYSTEM INTRODUCTION A. Muscular tissue enables the body and its parts to move a. Movement caused by ability of muscle cells (called fibers) to shorten or contract b. Muscle cells shorten by converting
Clarification of Terms
 Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Surgical Art. Formulaic Drawing Method. DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes
 DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes Surgical Art Formulaic Drawing Method Formulaic figure drawing systems involve using abstract rhythms and interlocking shapes to construct the human
DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes Surgical Art Formulaic Drawing Method Formulaic figure drawing systems involve using abstract rhythms and interlocking shapes to construct the human
How Muscles are Named
 How Muscles are Named There are over 600 muscles in the human body. Identifying these six hundred muscles is a daunting task. Furthermore, the names of these muscles seem foreign to most of us. Most of
How Muscles are Named There are over 600 muscles in the human body. Identifying these six hundred muscles is a daunting task. Furthermore, the names of these muscles seem foreign to most of us. Most of
Chapter 5. The Shoulder Joint. The Shoulder Joint. Bones. Bones. Bones
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. Chapter 5 The Shoulder Joint Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Structural Kinesiology The Shoulder Joint 5-1 The Shoulder
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. Chapter 5 The Shoulder Joint Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Structural Kinesiology The Shoulder Joint 5-1 The Shoulder
Detailed Knowledge of Anatomy, Physiology, and Kinesiology
 Detailed Knowledge of Anatomy, Physiology, and Kinesiology 2 chapter CHAPTER OUTLINE Areas of Competence Anatomical Position Planes of Motion Cavities of the Body Body Movements Types of Contractions Muscle
Detailed Knowledge of Anatomy, Physiology, and Kinesiology 2 chapter CHAPTER OUTLINE Areas of Competence Anatomical Position Planes of Motion Cavities of the Body Body Movements Types of Contractions Muscle
8/25/2014 JOINTS. The Skeletal System. Axial Skeleton STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION:
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS The Skeletal System Made up of the numerous bones of the human body Gives support and framework to the body Protects vital organs Manufactures blood cells Storage of calcium
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS The Skeletal System Made up of the numerous bones of the human body Gives support and framework to the body Protects vital organs Manufactures blood cells Storage of calcium
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM Degrees of freedom Functional potential of the
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM Degrees of freedom Functional potential of the
GROSS ANATOMY. Unit #4: Upper and Lower Limbs. Lecture Syllabus 2008
 GROSS ANATOMY Lecture Syllabus 2008 Unit #4: Upper and Lower Limbs ANAT 6010 - Gross Anatomy Department of Neurobiology and Anatomy University of Utah School of Medicine G24- Upper Limb Overview, Shoulder,
GROSS ANATOMY Lecture Syllabus 2008 Unit #4: Upper and Lower Limbs ANAT 6010 - Gross Anatomy Department of Neurobiology and Anatomy University of Utah School of Medicine G24- Upper Limb Overview, Shoulder,
www.ghadialisurgery.com
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Biology 105 Human Biology PRACTICE MIDTERM EXAM 1. Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 7 The Muscular System
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 7 The Muscular System Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following is (are) a function of skeletal muscle? A) produce movement B)
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 7 The Muscular System Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following is (are) a function of skeletal muscle? A) produce movement B)
Massage and Movement
 Massage and Movement Incorporating Movement into Massage Part One: Theory and Technique in Prone With Lee Stang, LMT NCBTMB #450217-06 1850 West Street Southington, CT 06489 860.747.6388 www.bridgestohealthseminars.com
Massage and Movement Incorporating Movement into Massage Part One: Theory and Technique in Prone With Lee Stang, LMT NCBTMB #450217-06 1850 West Street Southington, CT 06489 860.747.6388 www.bridgestohealthseminars.com
Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review
 Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
NDT Treatment Planning Worksheet
 Child s Name: Kalab DOB: 01/01/02 Diagnosis: CP-Right-sided Heimplegia DOE: May 29, 2009 Therapist s Name: Mary Rose Franjoine Discipline: PT Current Participation: Attends his neighborhood school with
Child s Name: Kalab DOB: 01/01/02 Diagnosis: CP-Right-sided Heimplegia DOE: May 29, 2009 Therapist s Name: Mary Rose Franjoine Discipline: PT Current Participation: Attends his neighborhood school with
THE SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS
 i A Wealth of Information. A World of Ideas. Instructor s Guide The Human Body: How It Works Introduction This program is part of the nine-part series The Human Body: How It Works. The series uses physiologic
i A Wealth of Information. A World of Ideas. Instructor s Guide The Human Body: How It Works Introduction This program is part of the nine-part series The Human Body: How It Works. The series uses physiologic
LABS 8 & 9: CAT MUSCULATURE
 ZOO 4377L - VERTEBRATE MORPHOLOGY LAB LABS 8 & 9: CAT MUSCULATURE Name: Name: SSN: SSN: ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ZOO 4377L - VERTEBRATE MORPHOLOGY LAB LABS 8 & 9: CAT MUSCULATURE Name: Name: SSN: SSN: ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Anatomy for Sport and Exercise
 Unit 1: Anatomy for Sport and Exercise Unit code: M/600/0038 QCF Level 3: BTEC National Credit value: 10 Guided learning hours: 60 Aim and purpose This unit explores the structure and function of the skeletal,
Unit 1: Anatomy for Sport and Exercise Unit code: M/600/0038 QCF Level 3: BTEC National Credit value: 10 Guided learning hours: 60 Aim and purpose This unit explores the structure and function of the skeletal,
Chapter 4 The Shoulder Girdle
 Chapter 4 The Shoulder Girdle Key Manubrium Clavicle Coracoidprocess Acromionprocess bony landmarks Glenoid fossa Bones Lateral Inferior Medial border angle McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved.
Chapter 4 The Shoulder Girdle Key Manubrium Clavicle Coracoidprocess Acromionprocess bony landmarks Glenoid fossa Bones Lateral Inferior Medial border angle McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved.
Women s Home Workout Bible
 Women s Home Workout Bible CORRESPONDENCE EDUCATION PROGRAM #125. Check your receipt for course expiration date.. After that date no credit will be awarded for this program. How to Complete this Program
Women s Home Workout Bible CORRESPONDENCE EDUCATION PROGRAM #125. Check your receipt for course expiration date.. After that date no credit will be awarded for this program. How to Complete this Program
Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis. Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University
 Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University Simplify Everything There are actually only three bones: Two innominates, one sacrum.
Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University Simplify Everything There are actually only three bones: Two innominates, one sacrum.
Elbow & Forearm. Notes. Notes. Lecture Slides - A.D.A.M. Lab Pics. Bones & Joints: Elbow & Forearm
 Elbow & Forearm Elbow & Forearm Notes Lecture Slides - A.D.A.M. Lab Pics Notes Bones & Joints: The elbow joint is a combination of joints but common reference is usually to the articulation of the distal
Elbow & Forearm Elbow & Forearm Notes Lecture Slides - A.D.A.M. Lab Pics Notes Bones & Joints: The elbow joint is a combination of joints but common reference is usually to the articulation of the distal
Unit 8 SPECIFIC SPORTS INJURIES Lecture Notes
 Unit 8 SPECIFIC SPORTS INJURIES Lecture Notes STANDARD 8 Students will explore specific sports injuries. Objective 1: Recognize common injuries to the head and neck to include: concussion, cervical spine
Unit 8 SPECIFIC SPORTS INJURIES Lecture Notes STANDARD 8 Students will explore specific sports injuries. Objective 1: Recognize common injuries to the head and neck to include: concussion, cervical spine
UNIT 5: FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE BASIC ANATOMY MAJOR MUSCLE GROUPS & BONES PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE
 UNIT 5: FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE TOPIC 1: TOPIC 2: BASIC ANATOMY MAJOR MUSCLE GROUPS & BONES PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE GRADES 6-7 UNIT 5 FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & GRADES PROPER
UNIT 5: FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE TOPIC 1: TOPIC 2: BASIC ANATOMY MAJOR MUSCLE GROUPS & BONES PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE GRADES 6-7 UNIT 5 FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & GRADES PROPER
A Woman s Guide to Muscle & Strength
 A Woman s Guide to Muscle & Strength CORRESPONDENCE EDUCATION PROGRAM # 140. Check your receipt for course expiration date. After that date no credit will be awarded for this program. 2012 by Exercise
A Woman s Guide to Muscle & Strength CORRESPONDENCE EDUCATION PROGRAM # 140. Check your receipt for course expiration date. After that date no credit will be awarded for this program. 2012 by Exercise
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology
 Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
MOCK PAPER Level 3 Anatomy and Physiology For Exercise and Health. Unit Accreditation Number A/600/9051
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APEH 3.01 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 60 minutes MOCK PAPER Level 3 Anatomy
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APEH 3.01 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 60 minutes MOCK PAPER Level 3 Anatomy
Elbow & Forearm H O W V I T A L I S T H E E L B O W T O O U R D A I L Y L I V E S?
 Elbow & Forearm H O W V I T A L I S T H E E L B O W T O O U R D A I L Y L I V E S? Clarification of Terms The elbow includes: 3 bones (humerus, radius, and ulna) 2 joints (humeroulnar and humeroradial)
Elbow & Forearm H O W V I T A L I S T H E E L B O W T O O U R D A I L Y L I V E S? Clarification of Terms The elbow includes: 3 bones (humerus, radius, and ulna) 2 joints (humeroulnar and humeroradial)
Chapter 11. What are the functions of the skeletal system? More detail on bone
 Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
MUSCLES G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION. Unit 1. Factors Affecting Participation and Performance. G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:.
 G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance MUSCLES Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should: Be able to describe and explain how muscles
G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance MUSCLES Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should: Be able to describe and explain how muscles
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines. IV. Hip
 European Society of MusculoSkeletal Radiology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines IV. Ian Beggs, UK Stefano Bianchi, Switzerland Angel Bueno, Spain Michel Cohen, France Michel Court-Payen,
European Society of MusculoSkeletal Radiology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines IV. Ian Beggs, UK Stefano Bianchi, Switzerland Angel Bueno, Spain Michel Cohen, France Michel Court-Payen,
Dr. Larry VanSuch s BASEBALL SWING MECHANICS. Identifying the movements and muscles of the baseball swing for exceptional hitting!
 Dr. Larry VanSuch s BASEBALL SWING MECHANICS Identifying the movements and muscles of the baseball swing for exceptional hitting! Copyright 2013 by Dr. Larry VanSuch. First Edition. All rights reserved.
Dr. Larry VanSuch s BASEBALL SWING MECHANICS Identifying the movements and muscles of the baseball swing for exceptional hitting! Copyright 2013 by Dr. Larry VanSuch. First Edition. All rights reserved.
Hemiplegic shoulder pain/shoulder subluxation
 UPPER LIMB NEUROMUSCULAR ELECTRICAL STIMULATION: Electrode positions Please note that the polarity (red and black leads) can be altered according to your clinical reasoning. The area in which you want
UPPER LIMB NEUROMUSCULAR ELECTRICAL STIMULATION: Electrode positions Please note that the polarity (red and black leads) can be altered according to your clinical reasoning. The area in which you want
EXTENSOR POLLICIS TENDONITIS SYNDROME
 EXTENSOR POLLICIS TENDONITIS SYNDROME The extensor pollicis longus muscle has its origin on the lateral part of the middle third of the ulnar shaft on the dorsal border below the abductor pollicis longus
EXTENSOR POLLICIS TENDONITIS SYNDROME The extensor pollicis longus muscle has its origin on the lateral part of the middle third of the ulnar shaft on the dorsal border below the abductor pollicis longus
SKELETON AND JOINTS G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION. Unit 1. Factors Affecting Participation and Performance. G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:.
 G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance SKELETON AND JOINTS Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should be able to: Understand what the
G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance SKELETON AND JOINTS Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should be able to: Understand what the
10. The Muscular System Text The McGraw Hill Companies, 2003 CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 10 Muscles of the thigh to upper calf (MRI) The Muscular System CHAPTER OUTLINE The Structural and Functional Organization of Muscles 326 The Functions of Muscles 326 Connective Tissues of a Muscle
CHAPTER 10 Muscles of the thigh to upper calf (MRI) The Muscular System CHAPTER OUTLINE The Structural and Functional Organization of Muscles 326 The Functions of Muscles 326 Connective Tissues of a Muscle
Muscle is the only human tissue capable of shortening, or
 Chapter The Muscular System 5 Muscle is the only human tissue capable of shortening, or contracting. This unique ability is what makes body movements possible. Without muscle the powerful movements required
Chapter The Muscular System 5 Muscle is the only human tissue capable of shortening, or contracting. This unique ability is what makes body movements possible. Without muscle the powerful movements required
Rehabilitation with Pilates
 Rehabilitation with Pilates Flat Feet Pes Planus Naiké Durel January 2016 Montreal, Canada Table of contents Title Table of contents Abstract Anatomy of the foot p.1 p.2 p.3 p.4-5- 6-7 Case of study BASI
Rehabilitation with Pilates Flat Feet Pes Planus Naiké Durel January 2016 Montreal, Canada Table of contents Title Table of contents Abstract Anatomy of the foot p.1 p.2 p.3 p.4-5- 6-7 Case of study BASI
Pilates to correct overactive upper trapezius muscles and prevent scapular elevation.
 Pilates to correct overactive upper trapezius muscles and prevent scapular elevation. Stephanie Blum July 13 th, 2014 Flow Studios, Chicago, IL Page 1 of 19 Abstract It s important to recognize where your
Pilates to correct overactive upper trapezius muscles and prevent scapular elevation. Stephanie Blum July 13 th, 2014 Flow Studios, Chicago, IL Page 1 of 19 Abstract It s important to recognize where your
Flat foot and lower back pain
 Flat foot and lower back pain Dr James Tang, MBA, BDS, LDS RCS General Dental Practitioner, NASM Corrective Exercise Specialist with special interest in postural dysfunction & lower back problems, Level
Flat foot and lower back pain Dr James Tang, MBA, BDS, LDS RCS General Dental Practitioner, NASM Corrective Exercise Specialist with special interest in postural dysfunction & lower back problems, Level
The Shoulder Complex & Shoulder Girdle
 The Shoulder Complex & Shoulder Girdle The shoulder complex 4 articulations involving The sternum The clavicle The ribs The scapula and The humerus Bony Landmarks provide attachment points for muscles
The Shoulder Complex & Shoulder Girdle The shoulder complex 4 articulations involving The sternum The clavicle The ribs The scapula and The humerus Bony Landmarks provide attachment points for muscles
Part 1: Introduction Tell the name of your organ system and describe the major functions.
 Team Members: System: Your team s job is prepare a presentation to educate your classmates about one of the body systems that makes up the human body. Your presentation must include the following requirements:
Team Members: System: Your team s job is prepare a presentation to educate your classmates about one of the body systems that makes up the human body. Your presentation must include the following requirements:
