How To Treat Diabetes With A Diabetes
|
|
|
- Geraldine Ellen Rose
- 3 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 WORKING TOGETHER TO MANAGE DIABETES DIABETES MEDICATIONS SUPPLEMENT
2 SECTION A DIABETES MEDICATIONS Agent Class Primary Action Typical Dosage Side Effects Tolbutamide (Ornase TM ) Tolazamide (Tolinase TM ) Chlorpropamide (Diabenese TM ) Sulfonylureas (1st generation) Increases insulin production in pancreas Tolbutamide: g/day in divided doses; maximum, 3 g/day Tolazamide: 100 1,000 mg/day in divided doses; maximum, 1 g/day Chlorpropamide: mg/day twice a day; maximum, 750 mg/day Hypoglycemia, weight gain, hyperinsulinemia Disulfiram reaction with alcohol Glyburide (Micronase TM, Diabeta TM, Glynase TM ) glipizide (Glucotrol, Glucotrol XL TM ), glimepiride (Amaryl TM ) Repaglinide (Prandin TM ) Sulfonylureas (2nd generation) Meglitinide Increases insulin production in pancreas Increases insulin release from pancreas Glyburide: mg/day twice a day; Hypoglycemia, weight maximum 29 mg/day gain, hyperinsulinemia Glynase: mg/day; maximum 20 mg/day Glipizide: mg/day twice a day; Maximum, 40 mg/day; or XL* mg/day twice a day; maximum, 20 mg/day Glimepiride: 1 8 mg/day; maximum, 8 mg/day Hypoglycemia, weight New diagnosis or HbAlc <8% 0.5 mg gain, hyperinsulinemia before meals 2 4 times a day HbA1c >8: 1 2 mg, min after each meal; increase weekly until results are obtained; maximum, 16 mg/day Nateglinide (Starlix TM ) Phenylalanine derivative Increases insulin release from pancreas 120, or 60 mg 3 times a day before meals Hypoglycemia, weight gain, hyperinsulinemia Metformin (Glucophage TM ) Biguanide Increases insulin sensitivity 500 mg/day twice a day with meals increase by 500 mg every 1 3 wk, twice or three times a day; usually most effective at 2,000 mg/day; maximum, 2,550 mg/day Nausea, diarrhea, metallic taste, very rare lactic acidosis Rosiglitazone (Avandia TM ) Thiazolidinedione Increases insulin sensitivity 4 mg/day in single or divided doses Increase to 8 mg/day in 12 wk, if needed; maximum, 8 mg/day with or without food Weight gain, fluid retention, edema Pioglitazone (Actos TM ) Thiazolidinedione Increases insulin sensitivity 15 or 30 mg/day; Maximum with or without food 45 mg for monotherapy 30 mg for combination therapy Weight gain, fluid retention, edema Acarbose (Precose Miglitol (Glyset ) TM TM ) Alpha-glucosidase inhibitor Blocks gut absorption of complex sugars 25 mg/day; increase by 25 mg/day every 4 6 wk; maximum, split dose before meals with first bite of food 300 mg/day (150 mg/day for weight <60 kg) Gas and bloating, sometimes diarrhea for both drugs Combinations Glucovance TM glyburide and metformin Decreases hepatic glucose production and increases insulin secretion. Initial, 1.25 mg/250 mg once or twice a day with meals; increase every 2 wk by 1.25 mg/250 mg per day; 2nd line, 2.5mg/500 mg or 5 mg glyburide/ 500 mg twice a day with meals; maximum, 20 mg/2000 mg per day Possible hypoglycemia, nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain for this combination drug Metaglip TM glipizide and metformin Decreases hepatic glucose production and increases insulin secretion Initial, 2.5 mg/250 mg once or twice a day with meals. Increase every 2 wk to maximum of 10 mg/1000 mg or 10 mg/2000 mg per day. 2nd line, 2.5 mg/500 mg or 5 mg/500 mg twice a day with meals. Maximum, 20 mg/2000 mg per day Diarrhea, nausea/ vomiting, headache for this combination drug Avandamet TM rosiglitazone and metformin Decreases hepatic glucose production, increases glucose uptake, and decreases insulin resistance 1 mg/500 mg, 2 mg/500 mg or 4 mg/500 mg twice a day; dosage individualized based on current therapy. Maximum, 8 mg/2000mg per day Diarrhea, edema, anemia for this combination drug Adapted from 2002 The Diabetes Center, Old Saybrook, CT, used by permission. ALT = alanine aminotransferase CHF = congestive heart failure GI = gastrointestinal HbA1c = glycated hemoglobin XL = extended release 1 WORKING TOGETHER TO MANAGE DIABETES
3 TABLE 1. ORAL AGENTS TO TREAT TYPE 2 DIABETES* Precautions Chlorpropamide remains active for up to 60 hours. Use extreme caution with elderly patients or patients with hepatic or renal impairment. Critical Tests Metabolized in liver. Periodic evaluation of liver function tests. Comments Use of these agents is not recommended unless the patient has a well-established history of taking them. Second-generation sulfonylureas provide more predictable results with fewer side effects and more convenient dosing. Clearance may be diminished in patients with hepatic or renal impairment. Metabolized in liver. Periodic evaluation of liver function tests. Glipizide is preferred with renal impairment. Doses >15 mg should be split. Should not be used in patients with diabetic ketoacidosis and known hypersensitivity to drug or its inactive ingredients. Metabolized in liver. Periodic evaluation of liver function tests. Patients should be instructed to take medication δ30 min before a meal. If meals are skipped or added, medication should be skipped or added as well. Should not be used in patients with diabetic ketoacidosis and known hypersensitivity to drug or its inactive ingredients. Metabolized in liver. Periodic evaluation of liver function tests. Patients should be instructed to take medication δ30 min before a meal. If meals are skipped or added, medication should be skipped or added as well. Nateglinide is approved only as monotherapy or in combination with Metformin. Should not be used in patients who use alcohol frequently, liver, kidney disease or CHF because of risk of lactic acidosis. Contraindicated if serum creatinine is: >1.5 mg/dl in men or >1.4 mg/dl women, or use if creatinine clearance is abnormal. Monitor hematological and renal function annually. Metformin is especially beneficial in obese patients due to potential for weight loss, improved lipid profile, and lack of potential for hypoglycemia requiring supplemental carbohydrate intake. Discontinue for 48 hr after procedure using contrast dye. Should not be used in patients with CHF or hepatic disease. Can cause mild-to-moderate edema. Clearance may be diminished in patients with hepatic or renal impairment. Should not be used if GI disorders are concurrent. Avoid initiation with patients with increased baseline liver enzyme levels (ALT >2.5 times upper limit of normal). Liver enzymes monitored every 2 months for 12 months, then periodically. If ALT levels increase to >3 times the upper limit of normal, discontinue use and recheck liver enzyme levels. Avoid initiation with patients who have liver disease or ALT levels >2.5 times the upper limit of normal. Patients with mildly elevated liver enzymes (ALT levels times the upper limit of normal) should be evaluated. Discontinue if >3 times the upper limit of normal. Rosiglitazone is approved for use as monotherapy and in combination with metformin or sulfonylureas. Pioglitazone is approved for use as monotherapy or with metformin, sulfonylureas, or insulin. Should not be used if frequent alcohol use, liver or kidney disease, or CHF is suspected. Avoid if serum creatinine is >2.0 mg/dl. Monitor serum transaminase every 3 months for 1st year of therapy. Contraindicated if serum creatinine is >1.5 mg/dl in men or 1.4 mg/dl in women, or if creatinine clearance is abnormal. Monitor hematological and renal function annually. May use 1.25mg/250mg and 2.5mg/500mg doses at different times of day for best glucose control. Incidence of hypoglycemia is higher for combination than for single agent use. Should not be used if frequent alcohol use, liver or kidney disease, or CHF is suspected. Contraindicated if serum creatinine is >1.5 mg/dl in men, or >1.4 mg/dl in women, or if creatinine clearance <60 75 ml/min. Monitor hematologic and renal function annually. May use 1.25mg/250mg and 2.5mg/500mg doses at different times of day for best glucose control. Incidence of hypoglycemia is higher for combination than for single agent use. Should be avoided in patients with hepatic disease, CHF, renal disease. Contraindicated if serum creatinine is >1.5 mg/dl in men or >1.4 mg/dl in women, or if creatinin clearance is abnormal. Agent is less expensive than its components separately. Decrease in GI upset is reported with metformin compared with rosiglitazone alone. *Agents in a class of medicines share mechanisms of action, require similar precautions, and generally have similar side effects. For proper usage, please read label. Agents should not be used in patients with type 1 diabetes. DIABETES MEDICATIONS SUPPLEMENT 2
4 TABLE 2. IMPORTANT INSULIN INFORMATION* Insulin Onset Peak Effective Maximal Duration Duration Human Lispro (humalog) Aspart (novalog) Regular NPH Lente Ultralente 70/30 <15 min <15 min hr 2 4 hr 3 4 hr 6 10 hr hr 1 2 hr 1 3 hr 2 4 hr 4 10 hr 4 12 hr Minimal 2 10 hr 2 4 hr 3 5 hr 3 5 hr hr hr hr hr 3 5 hr 4 6 hr 4 8 hr hr hr hr hr Comments Must be taken just before or immediately after eating. Best if administered 30 min before meal. Frequently used instead of NPH in children. Humalog mix 75/25 <15 min 1 2 hr hr hr Must be taken before or immediately after eating. Insulin glargine (Lantus ) TM 4 6 hr None 24 hr 24 hr Administered at bedtime once a day. Cannot be mixed in same syringe and should not be given with use of same needle in same place as previous injection. Animal Source Regular NPH Lente hr 4 6 hr 4 6 hr 3 4 hr 8 14 hr 8 14 hr 4 6 hr hr hr 6 8 hr hr hr Adapted from 2002, The Diabetes Center, Old Saybrook, CT, used by permission. *Site rotation for injections is necessary for all types of insulin. Change over to human insulin recommended. Dose changes required; consult physician. TABLE 3. RECOMMENDED INSULIN STORAGE Recommended Insulin Storage Refrigerated (36 F 46 F) Room Temperature (59 F 86 F) VIAL Humalog, novolog, humulin, novolin Novalog (release pending) Lantus TM (10 ml) Lantus TM (5 ml) PENS/CARTRIDGES Humalog Humulin R (cartridge) Humulin N Humulin 70/30 Humalog Mix 75/25 Novolog Novolin R (prefilled and 1.5-mL cartridge) Novolin R (3-mL cartridge) Novolin N (prefilled and 1.5-mL cartridge) Novolin N (3-mL cartridge) Novolin 70/30 (prefilled and 1.5-mL cartridge) Novolin 70/30 (3-mL cartridge) Lantus TM Self-filled syringes Opened Unopened until expiration date until expiration date until expiration date until expiration date Not in use 14 days* Adapted from 2002, The Diabetes Center, Old Saybrook, CT, used by permission. *Suggested, not clinically established Opened 14 days In use 14 days 10 days 10 days 30 days 7 days 14 days 7 days 10 days 7 days* Unopened 14 days 3 WORKING TOGETHER TO MANAGE DIABETES
5 TABLE 4. GLUCOSE LOWERING ACTIVITY ORAL DIABETES AGENT Medication Blood Glucose Most Affected SMBG* Testing to Recommend Greatest Risk for Hypoglycemia Sulfonylureas Fasting and postprandial 2 3 times per day, 4 6 hr after meal and fasting especially fasting Meglitinide phenylalanine derivative Postprandial 2 hr after meal 2 3 hr after meal Biguanide Alpha-glucosidase inhibitor Thiazolidinedione Glucovance Fasting Postprandial Fasting and postprandial Fasting and postprandial Fasting 2 hr after meal 2 3 times per day, especially fasting 2 3 times per day, especially fasting Adapted from 2002, The Diabetes Center, Old Saybrook, CT, used by permission. SMBG = self-monitoring of blood glucose None if used as single agent None if used as single agent After exercise when used with sulfonylureas or insulin 4 6 hr after meal and fasting TABLE 5. MEASURES TO CONTROL GLYCEMIA Biochemical Index Normal Goal Action Suggested Before meals (mg/dl) plasma whole blood Bedtime (mg/dl) plasma whole blood HbA1c* <110 <100 <120 <110 < Adapted from 2002, The Diabetes Center, Old Saybrook, CT, used by permission. HbA1c = glycated hemoglobin <7 <90, >150 <80, >140 <110, >180 <100, >160 >8 Diagnosis: Diabetes On what was supposed to be one of the happiest days of our lives, my husband, Tim Hanf, collapsed to the floor during our wedding reception. He had diabetes which was left undiagnosed until that night. Too much champagne and wedding cake caused his glucose levels to spike landing him in the emergency room. I don t have to tell any of you how painfully scary this can be. What can be equally as intimidating is the plethora of information received from the doctors and nurses. Unfortunately, over-information and misinformation were a big part of the problem. One doctor recommended a certain type of drug while other doctors recommended a different type while still others spoke out against drugs all together. This prompted me to do some research myself. After talking with doctors, nurses, dieticians, and numerous patients who had beaten the disease, I discovered how my husband could be naturally cured of this disease without the use of medications. DIABETES MEDICATIONS SUPPLEMENT 4
6 Side Effects As you can see from the charts detailing today s current treatments, there are numerous medications for assisting diabetics in keeping their glucose levels in check. You can also see the myriad of side-effects and precautions involved with each of them. Hypoglycemia - Hypoglycemia, also called low blood sugar, occurs when your blood glucose (blood sugar) level drops too low to provide enough energy for your body's activities. In adults or children older than 10 years, hypoglycemia is uncommon except as a side effect of diabetes treatment. Hyperinsulinemia - Hyperinsulinemia is a disorder characterized by a failure of our Blood Sugar Control System to work properly. This occurs when insulin progressively loses its effectiveness in removing the blood glucose from the blood stream into the cells that constitute our bodies. Edema - Edema is the swelling caused by fluid in your body's tissues. It commonly occurs in the feet, ankles and legs, but it can involve your entire body. Anemia - Anemia is a condition where there is a lower than normal number of red blood cells in the blood, measured by a decrease in the amount of hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is the oxygen-carrying part of red blood cells. Nausea, diarrhea, fluid retention, gas, bloating, headaches, vomiting and weight can are also common side-effects to many diabetic medications. Precautions & Procedures Along with side-effects, each medication offers precautions and procedures for its use. Having other health issues may limit your ability to take certain prescriptions. You and your doctor must also consider other medications you are taking and how they interact. You have to consider the time of day at which you take each medication, whether you ve eaten, and the proper storage of each one. The Cure Diabetes and the management of the disease could easily take over your life. This was not the life my husband and I wanted for us. We didn t want to spend every waking moment thinking about or treating this disease. Through research, trial and tribulation, we were able to eliminate his diabetes through natural methods. Today Tim is diabetes free and takes no medications to regulate his glucose levels. Through proper nutrition, exercise and dietary supplements, diabetes is no longer a part of our daily lives. He is active, healthy and has more energy than ever before. Talk to your doctor and discover if a natural treatment is right for you. Instead of living your life dealing with diabetes, you can live a naturally healthy life. 5 WORKING TOGETHER TO MANAGE DIABETES
7
8 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Working Together to Manage Diabetes: Diabetes Medications Supplement. Atlanta, GA: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, NDEP-54-S
9 ii WORKING TOGETHER TO MANAGE DIABETES
Diabetes: Medications
 Diabetes: Medications Presented by: APS Healthcare Southwestern PA Health Care Quality Unit (APS HCQU) May 2008 sh Disclaimer Information or education provided by the HCQU is not intended to replace medical
Diabetes: Medications Presented by: APS Healthcare Southwestern PA Health Care Quality Unit (APS HCQU) May 2008 sh Disclaimer Information or education provided by the HCQU is not intended to replace medical
10/30/2012. Anita King, DNP, RN, FNP, CDE, FAADE Clinical Associate Professor University of South Alabama Mobile, Alabama
 Faculty Medications for Diabetes Satellite Conference and Live Webcast Wednesday, November 7, 2012 2:00 4:00 p.m. Central Time Anita King, DNP, RN, FNP, CDE, FAADE Clinical Associate Professor University
Faculty Medications for Diabetes Satellite Conference and Live Webcast Wednesday, November 7, 2012 2:00 4:00 p.m. Central Time Anita King, DNP, RN, FNP, CDE, FAADE Clinical Associate Professor University
Pills for Type 2 Diabetes. A Guide for Adults
 Pills for Type 2 Diabetes A Guide for Adults December 2007 Fast Facts on Diabetes Pills n Different kinds of diabetes pills work in different ways to control blood sugar (blood glucose). n All the diabetes
Pills for Type 2 Diabetes A Guide for Adults December 2007 Fast Facts on Diabetes Pills n Different kinds of diabetes pills work in different ways to control blood sugar (blood glucose). n All the diabetes
Medications for Diabetes
 AGS Diab Med Brochure 4/18/03 3:43 PM Page 1 Medications for Diabetes An Older Adult s Guide to Safe Use of Diabetes Medications THE AGS FOUNDATION FOR HEALTH IN AGING AGS Diab Med Brochure 4/18/03 3:43
AGS Diab Med Brochure 4/18/03 3:43 PM Page 1 Medications for Diabetes An Older Adult s Guide to Safe Use of Diabetes Medications THE AGS FOUNDATION FOR HEALTH IN AGING AGS Diab Med Brochure 4/18/03 3:43
DIABETES MEDICATION-ORAL AGENTS AND OTHER HYPOGLYCEMIC AGENTS
 Section Two DIABETES MEDICATION-ORAL AGENTS AND OTHER HYPOGLYCEMIC AGENTS This section will: Describe oral agents (pills) are specific for treating type 2 diabetes. Describe other hypoglycemic agents used
Section Two DIABETES MEDICATION-ORAL AGENTS AND OTHER HYPOGLYCEMIC AGENTS This section will: Describe oral agents (pills) are specific for treating type 2 diabetes. Describe other hypoglycemic agents used
Medicines Used to Treat Type 2 Diabetes
 Goodman Diabetes Service Medicines Used to Treat Type 2 Diabetes People who have type 2 diabetes may need to take medicine to help lower their blood glucose, in addition to being active & choosing healthy
Goodman Diabetes Service Medicines Used to Treat Type 2 Diabetes People who have type 2 diabetes may need to take medicine to help lower their blood glucose, in addition to being active & choosing healthy
FYI: (Acceptable range for blood glucose usually 70-110 mg/dl. know your institutions policy.)
 How Insulin Works: Each type of insulin has an onset, a peak, and a duration time. Onset is the length of time before insulin reaches the bloodstream and begins lowering blood Peak is the time during which
How Insulin Works: Each type of insulin has an onset, a peak, and a duration time. Onset is the length of time before insulin reaches the bloodstream and begins lowering blood Peak is the time during which
Diabetes Treatments: Options for Insulin Delivery. Bonnie Pepon, RN, BSN, CDE Certified Diabetes Educator Conemaugh Diabetes Institute
 Diabetes Treatments: Options for Insulin Delivery Bonnie Pepon, RN, BSN, CDE Certified Diabetes Educator Conemaugh Diabetes Institute Diabetes 21 million people in the U.S. have diabetes $132 billion each
Diabetes Treatments: Options for Insulin Delivery Bonnie Pepon, RN, BSN, CDE Certified Diabetes Educator Conemaugh Diabetes Institute Diabetes 21 million people in the U.S. have diabetes $132 billion each
Add: 2 nd generation sulfonylurea or glinide or Add DPP-4 inhibitor Start or intensify insulin therapy if HbA1c goals not achieved with the above
 Guidelines for Type Diabetes - Diagnosis Fasting Plasma Glucose (confirm results if borderline) HbAIC Normal FPG < 00 < 5.5 Impaired Fasting Glucose (IFG) 00 to < 5.7%-.5% Diabetes Mellitus (or random
Guidelines for Type Diabetes - Diagnosis Fasting Plasma Glucose (confirm results if borderline) HbAIC Normal FPG < 00 < 5.5 Impaired Fasting Glucose (IFG) 00 to < 5.7%-.5% Diabetes Mellitus (or random
Diabetes Fundamentals
 Diabetes Fundamentals Prevalence of Diabetes in the U.S. Undiagnosed 10.7% of all people 20+ 23.1% of all people 60+ (12.2 million) Slide provided by Roche Diagnostics Sources: ADA, WHO statistics Prevalence
Diabetes Fundamentals Prevalence of Diabetes in the U.S. Undiagnosed 10.7% of all people 20+ 23.1% of all people 60+ (12.2 million) Slide provided by Roche Diagnostics Sources: ADA, WHO statistics Prevalence
Pharmaceutical Management of Diabetes Mellitus
 1 Pharmaceutical Management of Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes Mellitus (cont d) Signs and symptoms 2 Elevated fasting blood glucose (higher than 126 mg/dl) or a hemoglobin A1C (A1C) level greater than or equal
1 Pharmaceutical Management of Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes Mellitus (cont d) Signs and symptoms 2 Elevated fasting blood glucose (higher than 126 mg/dl) or a hemoglobin A1C (A1C) level greater than or equal
Comparing Medications for Adults With Type 2 Diabetes Focus of Research for Clinicians
 Clinician Research Summary Diabetes Type 2 Diabetes Comparing Medications for Adults With Type 2 Diabetes Focus of Research for Clinicians A systematic review of 166 clinical studies published between
Clinician Research Summary Diabetes Type 2 Diabetes Comparing Medications for Adults With Type 2 Diabetes Focus of Research for Clinicians A systematic review of 166 clinical studies published between
Management of Clients with Diabetes Mellitus
 Management of Clients with Diabetes Mellitus Black, J.M. & Hawks, J.H. (2005) Chapters 47, (pp 1243-1288) 1288) Baptist Health School of Nursing NSG 4037: Adult Nursing III Carole Mackey, MNSc,, RN, PNP
Management of Clients with Diabetes Mellitus Black, J.M. & Hawks, J.H. (2005) Chapters 47, (pp 1243-1288) 1288) Baptist Health School of Nursing NSG 4037: Adult Nursing III Carole Mackey, MNSc,, RN, PNP
What I need to know about. Diabetes Medicines. National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse
 What I need to know about Diabetes Medicines National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse What I need to know about Diabetes Medicines Contents What do diabetes medicines do?... 1 What targets are recommended
What I need to know about Diabetes Medicines National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse What I need to know about Diabetes Medicines Contents What do diabetes medicines do?... 1 What targets are recommended
Medicines for Type 2 Diabetes A Review of the Research for Adults
 Medicines for Type 2 Diabetes A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: Your doctor or health care provider has told you that you have type 2 diabetes and have high
Medicines for Type 2 Diabetes A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: Your doctor or health care provider has told you that you have type 2 diabetes and have high
Noninsulin Diabetes Medications Summary Chart Medications marked with an asterisk (*) can cause hypoglycemia MED GROUP DESCRIPTOR
 Noninsulin Diabetes Medications Summary Chart Medications marked with an asterisk (*) can cause MED GROUP DESCRIPTOR INSULIN SECRETAGOGUES Sulfonylureas* GLYBURIDE* (Diabeta) (Micronase) MICRONIZED GLYBURIDE*
Noninsulin Diabetes Medications Summary Chart Medications marked with an asterisk (*) can cause MED GROUP DESCRIPTOR INSULIN SECRETAGOGUES Sulfonylureas* GLYBURIDE* (Diabeta) (Micronase) MICRONIZED GLYBURIDE*
Diabetes, Type 2. RelayClinical Patient Education Sample Topic Diabetes, Type 2. What is type 2 diabetes? How does it occur?
 What is type 2 diabetes? Type 2 diabetes is a disorder that happens when your body does not make enough insulin or is unable to use its own insulin properly. The inability to use insulin is called insulin
What is type 2 diabetes? Type 2 diabetes is a disorder that happens when your body does not make enough insulin or is unable to use its own insulin properly. The inability to use insulin is called insulin
Anti-Diabetic Agents. Chapter. Charles Ruchalski, PharmD, BCPS. Drug Class: Biguanides. Introduction. Metformin
 Chapter Anti-Diabetic Agents 2 Charles Ruchalski, PharmD, BCPS Drug Class: Biguanides The biguanide metformin is the drug of choice as initial therapy for a newly diagnosed patient with type 2 diabetes
Chapter Anti-Diabetic Agents 2 Charles Ruchalski, PharmD, BCPS Drug Class: Biguanides The biguanide metformin is the drug of choice as initial therapy for a newly diagnosed patient with type 2 diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes Medicines: What You Need to Know
 Type 2 Diabetes Medicines: What You Need to Know Managing diabetes is complex because many hormones and body processes are at work controlling blood sugar (glucose). Medicines for diabetes include oral
Type 2 Diabetes Medicines: What You Need to Know Managing diabetes is complex because many hormones and body processes are at work controlling blood sugar (glucose). Medicines for diabetes include oral
Britni Hebert, MD PGY-1
 Britni Hebert, MD PGY-1 Importance of Diabetes treatment Types of treatment Comparison of treatment/article Review Summary Example cases 1 out of 13 Americans have diabetes Complications include blindness,
Britni Hebert, MD PGY-1 Importance of Diabetes treatment Types of treatment Comparison of treatment/article Review Summary Example cases 1 out of 13 Americans have diabetes Complications include blindness,
CME Test for AMDA Clinical Practice Guideline. Diabetes Mellitus
 CME Test for AMDA Clinical Practice Guideline Diabetes Mellitus Part I: 1. Which one of the following statements about type 2 diabetes is not accurate? a. Diabetics are at increased risk of experiencing
CME Test for AMDA Clinical Practice Guideline Diabetes Mellitus Part I: 1. Which one of the following statements about type 2 diabetes is not accurate? a. Diabetics are at increased risk of experiencing
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
 Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 What is it? Diabetes is a common health problem in the U.S. and the world. In diabetes, the body does not use the food it digests well. It is hard for the body to use carbohydrates
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 What is it? Diabetes is a common health problem in the U.S. and the world. In diabetes, the body does not use the food it digests well. It is hard for the body to use carbohydrates
How To Treat Diabetes
 Overview of Diabetes Medications Marie Frazzitta DNP, FNP c, CDE, MBA Senior Director of Disease Management North Shore LIJ Health Systems Normal Glucose Metabolism Insulin is produced by beta cells in
Overview of Diabetes Medications Marie Frazzitta DNP, FNP c, CDE, MBA Senior Director of Disease Management North Shore LIJ Health Systems Normal Glucose Metabolism Insulin is produced by beta cells in
Oral Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes
 Oral Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes Diabetes pills can help to manage your blood sugar. These pills are not insulin. They work to manage your blood sugar in several ways. You may be given a combination of
Oral Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes Diabetes pills can help to manage your blood sugar. These pills are not insulin. They work to manage your blood sugar in several ways. You may be given a combination of
Antidiabetic Drugs. Mosby items and derived items 2011, 2007, 2004 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Antidiabetic Drugs Mosby items and derived items 2011, 2007, 2004 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Diabetes Mellitus Two types Type 1 Type 2 Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Lack of insulin production
Antidiabetic Drugs Mosby items and derived items 2011, 2007, 2004 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Diabetes Mellitus Two types Type 1 Type 2 Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Lack of insulin production
Fundamentals of Diabetes Care Module 5, Lesson 1
 Module 5, Lesson 1 Fundamentals of Diabetes Care Module 5: Taking Medications Healthy Eating Being Active Monitoring Taking Medication Problem Solving Healthy Coping Reducing Risks Foundations For Control
Module 5, Lesson 1 Fundamentals of Diabetes Care Module 5: Taking Medications Healthy Eating Being Active Monitoring Taking Medication Problem Solving Healthy Coping Reducing Risks Foundations For Control
Mary Bruskewitz APN, MS, RN, BC-ADM Clinical Nurse Specialist Diabetes
 Mary Bruskewitz APN, MS, RN, BC-ADM Clinical Nurse Specialist Diabetes Objectives Pathophysiology of Diabetes Acute & Chronic Complications Managing acute emergencies Case examples 11/24/2014 UWHealth
Mary Bruskewitz APN, MS, RN, BC-ADM Clinical Nurse Specialist Diabetes Objectives Pathophysiology of Diabetes Acute & Chronic Complications Managing acute emergencies Case examples 11/24/2014 UWHealth
Chapter 4 Type 2 Diabetes
 Chapter 4 Type 2 Diabetes (previously referred to as adult onset diabetes or non-insulin dependent diabetes) H. Peter Chase, MD Cindy Cain, RN, CDE Philip Zeitler, MD This is the most common type of diabetes
Chapter 4 Type 2 Diabetes (previously referred to as adult onset diabetes or non-insulin dependent diabetes) H. Peter Chase, MD Cindy Cain, RN, CDE Philip Zeitler, MD This is the most common type of diabetes
Antidiabetic Agents. Chapter. Biguanides
 ajt/shutterstock, Inc. Chapter 2 Antidiabetic Agents Charles Ruchalski, PharmD, BCPS Biguanides Introduction For newly diagnosed patients with type 2 diabetes, the biguanide metformin is the drug of choice
ajt/shutterstock, Inc. Chapter 2 Antidiabetic Agents Charles Ruchalski, PharmD, BCPS Biguanides Introduction For newly diagnosed patients with type 2 diabetes, the biguanide metformin is the drug of choice
Medications for Type 2 Diabetes
 Main Page Risk Factors Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Screening Complications Reducing Your Risk Talking to Your Doctor Living With Type 2 Diabetes Resource Guide Medications for Type 2 Diabetes by Karen
Main Page Risk Factors Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Screening Complications Reducing Your Risk Talking to Your Doctor Living With Type 2 Diabetes Resource Guide Medications for Type 2 Diabetes by Karen
Treating Type 2 Diabetes: The Oral Diabetes Drugs. Comparing Effectiveness, Safety, and Price
 Treating Type 2 Diabetes: The Oral Diabetes Drugs Comparing Effectiveness, Safety, and Price Our Recommendations Six types of oral medicines (and 11 individual drugs) are now available to help the 21 million
Treating Type 2 Diabetes: The Oral Diabetes Drugs Comparing Effectiveness, Safety, and Price Our Recommendations Six types of oral medicines (and 11 individual drugs) are now available to help the 21 million
Type 2 diabetes Definition
 Type 2 diabetes Definition Type 2 diabetes is a lifelong (chronic) disease in which there are high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes. Causes Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes Definition Type 2 diabetes is a lifelong (chronic) disease in which there are high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes. Causes Diabetes
A Simplified Approach to Initiating Insulin. 4. Not meeting glycemic goals with oral hypoglycemic agents or
 A Simplified Approach to Initiating Insulin When to Start Insulin: 1. Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) levels >250 mg/dl or 2. Glycated hemoglobin (A1C) >10% or 3. Random plasma glucose consistently >300 mg/dl
A Simplified Approach to Initiating Insulin When to Start Insulin: 1. Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) levels >250 mg/dl or 2. Glycated hemoglobin (A1C) >10% or 3. Random plasma glucose consistently >300 mg/dl
10 to 30 minutes ½ to 3 hours 3 to 5 hours. 30 60 minutes 1 to 5 hours 8 hours. 1 to 4 hours
 Insulin Action There are several types of insulin. They are classified by how long they act: very fast, fast, slow and very slow acting. Each type of insulin has a certain time period in which it works.
Insulin Action There are several types of insulin. They are classified by how long they act: very fast, fast, slow and very slow acting. Each type of insulin has a certain time period in which it works.
DIABETES EDUCATION. *Read package insert each time you refill your medications in case there is new information SULFONYLUREAS
 DIABETES EDUCATION *Read package insert each time you refill your medications in case there is new information SULFONYLUREAS ACTION: Sulfonylureas stimulate the pancreas to make more insulin (pancreas
DIABETES EDUCATION *Read package insert each time you refill your medications in case there is new information SULFONYLUREAS ACTION: Sulfonylureas stimulate the pancreas to make more insulin (pancreas
Diabetes Update Lanita S. Shaverd, Pharm.D. Director, UAMS 12 th Street Health and Wellness Center Assistant Professor, UAMS College of Pharmacy
 Objectives Review oral medications used for the treatment of diabetes Explain how to effectively combine oral diabetes medications for optimal results Discuss insulins and non-insulin injectable diabetes
Objectives Review oral medications used for the treatment of diabetes Explain how to effectively combine oral diabetes medications for optimal results Discuss insulins and non-insulin injectable diabetes
SUBJECT: DIABETES MEDICATION MANAGEMENT PROTOCOLS
 SUBJECT: DIABETES MEDICATION MANAGEMENT PROTOCOLS PURPOSE To establish a process that will enable Certified Diabetes Educators (CDE) and/or staff with Board Certification in Advanced Diabetes Management
SUBJECT: DIABETES MEDICATION MANAGEMENT PROTOCOLS PURPOSE To establish a process that will enable Certified Diabetes Educators (CDE) and/or staff with Board Certification in Advanced Diabetes Management
Diabetes Medications. Minal Patel, PharmD, BCPS
 Diabetes Medications Minal Patel, PharmD, BCPS Objectives Examine advantages and disadvantages of oral anti-hyperglycemic medications Describe the differences between different classes of insulin Explore
Diabetes Medications Minal Patel, PharmD, BCPS Objectives Examine advantages and disadvantages of oral anti-hyperglycemic medications Describe the differences between different classes of insulin Explore
Type II diabetes: How to use the new oral medications
 Type II diabetes: How to use the new oral medications A TWO-PART INTERVIEW WITH NANCY J.V. BOHANNON, MD, BY DAVID B. JACK, MD Several new oral drugs have been approved for the management of type II diabetes.
Type II diabetes: How to use the new oral medications A TWO-PART INTERVIEW WITH NANCY J.V. BOHANNON, MD, BY DAVID B. JACK, MD Several new oral drugs have been approved for the management of type II diabetes.
Approximate Cost Reference List i for Antihyperglycemic Agents
 Alpha Glucosidase Inhibitor Acarbose (Glucobay ) Biguanides Metformin (Glucophage, generic) Metformin ER (Glumetza ) Approximate Cost Reference List i for Antihyperglycemic Agents Incretin Agents - DPP-4
Alpha Glucosidase Inhibitor Acarbose (Glucobay ) Biguanides Metformin (Glucophage, generic) Metformin ER (Glumetza ) Approximate Cost Reference List i for Antihyperglycemic Agents Incretin Agents - DPP-4
Endocrine Disorders. Diabetes Meds Objectives. Diabetes Type 1 and Type 2. Insulin Dynamics. Insulin is all about timing! Rapid acting insulin O P D
 Endocrine Disorders Diabetes Meds Objectives Explain the action of the various types of insulin currently available Identify the relationship between insulin peak and risk for hypoglycemia Discuss rationale
Endocrine Disorders Diabetes Meds Objectives Explain the action of the various types of insulin currently available Identify the relationship between insulin peak and risk for hypoglycemia Discuss rationale
MEDICATION GUIDE ACTOPLUS MET (ak-tō-plus-met) (pioglitazone hydrochloride and metformin hydrochloride) tablets
 MEDICATION GUIDE (ak-tō-plus-met) (pioglitazone hydrochloride and metformin hydrochloride) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking and each time you get a refill. There may
MEDICATION GUIDE (ak-tō-plus-met) (pioglitazone hydrochloride and metformin hydrochloride) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking and each time you get a refill. There may
Treating Type 2 Diabetes
 The Oral Diabetes Drugs Treating Type 2 Diabetes Comparing Effectiveness, Safety, and Price Contents Our Recommendations........................................... 3 Welcome....................................................
The Oral Diabetes Drugs Treating Type 2 Diabetes Comparing Effectiveness, Safety, and Price Contents Our Recommendations........................................... 3 Welcome....................................................
EFFIMET 1000 XR Metformin Hydrochloride extended release tablet
 BRAND NAME: Effimet XR. THERAPEUTIC CATEGORY: Anti-Diabetic PHARMACOLOGIC CLASS: Biguanides EFFIMET 1000 XR Metformin Hydrochloride extended release tablet COMPOSITION AND PRESENTATION Composition Each
BRAND NAME: Effimet XR. THERAPEUTIC CATEGORY: Anti-Diabetic PHARMACOLOGIC CLASS: Biguanides EFFIMET 1000 XR Metformin Hydrochloride extended release tablet COMPOSITION AND PRESENTATION Composition Each
Diabetes: When To Treat With Insulin and Treatment Goals
 Diabetes: When To Treat With Insulin and Treatment Goals Lanita. S. White, Pharm.D. Director, UAMS 12 th Street Health and Wellness Center Assistant Professor of Pharmacy Practice, UAMS College of Pharmacy
Diabetes: When To Treat With Insulin and Treatment Goals Lanita. S. White, Pharm.D. Director, UAMS 12 th Street Health and Wellness Center Assistant Professor of Pharmacy Practice, UAMS College of Pharmacy
My Diabetes Care Plan
 My Diabetes Care Plan You may use the charts below to help you better understand your diabetes. Ask your healthcare provider to review your goals and targets with you. Discuss the results and set up an
My Diabetes Care Plan You may use the charts below to help you better understand your diabetes. Ask your healthcare provider to review your goals and targets with you. Discuss the results and set up an
Treating Type 2 Diabetes
 The Oral Diabetes Drugs Treating Type 2 Diabetes Comparing Effectiveness, Safety, and Price Our Recommendations Six classes of oral medicines (and 12 individual drugs) are now available to help the 25.8
The Oral Diabetes Drugs Treating Type 2 Diabetes Comparing Effectiveness, Safety, and Price Our Recommendations Six classes of oral medicines (and 12 individual drugs) are now available to help the 25.8
medications for type 2 diabetes
 Talking diabetes No.25 Revised August 2010 medications for type 2 diabetes People with type 2 diabetes are often given medications including insulin to help control their blood glucose levels. Most of
Talking diabetes No.25 Revised August 2010 medications for type 2 diabetes People with type 2 diabetes are often given medications including insulin to help control their blood glucose levels. Most of
Section 5: Type 2 Diabetes
 SECTION OVERVIEW Definition and Symptoms Blood Glucose Monitoring Healthy Eating Physical Activity Oral Medication Insulin Sharps Disposal Definition and Symptoms Type 2 diabetes is occurring more frequently
SECTION OVERVIEW Definition and Symptoms Blood Glucose Monitoring Healthy Eating Physical Activity Oral Medication Insulin Sharps Disposal Definition and Symptoms Type 2 diabetes is occurring more frequently
Diabetes Mellitus 1. Chapter 43. Diabetes Mellitus, Self-Assessment Questions
 Diabetes Mellitus 1 Chapter 43. Diabetes Mellitus, Self-Assessment Questions 1. A 46-year-old man presents for his annual physical. He states that he has been going to the bathroom more frequently than
Diabetes Mellitus 1 Chapter 43. Diabetes Mellitus, Self-Assessment Questions 1. A 46-year-old man presents for his annual physical. He states that he has been going to the bathroom more frequently than
DRUGS FOR GLUCOSE MANAGEMENT AND DIABETES
 Page 1 DRUGS FOR GLUCOSE MANAGEMENT AND DIABETES Drugs to know are: Actrapid HM Humulin R, L, U Penmix SUNALI MEHTA The three principal hormones produced by the pancreas are: Insulin: nutrient metabolism:
Page 1 DRUGS FOR GLUCOSE MANAGEMENT AND DIABETES Drugs to know are: Actrapid HM Humulin R, L, U Penmix SUNALI MEHTA The three principal hormones produced by the pancreas are: Insulin: nutrient metabolism:
Making Clinical Sense of Diabetes Medications. Types of Diabetes. Pathophysiology. Beta Cell Function & Glucagon
 Making Clinical Sense of Diabetes Medications Kathy Reily, RD, CDE Prince William Hospital Diabetes Program Coordinator Virginia Dietetic Association April 4, 2011 Types of Diabetes Type 1 DM = Beta Cell
Making Clinical Sense of Diabetes Medications Kathy Reily, RD, CDE Prince William Hospital Diabetes Program Coordinator Virginia Dietetic Association April 4, 2011 Types of Diabetes Type 1 DM = Beta Cell
Antihyperglycemic Agents Comparison Chart
 Parameter Metformin Sulfonylureas Meglitinides Glitazones (TZD s) Mechanism of Action Efficacy (A1c Reduction) Hepatic glucose output Peripheral glucose uptake by enhancing insulin action insulin secretion
Parameter Metformin Sulfonylureas Meglitinides Glitazones (TZD s) Mechanism of Action Efficacy (A1c Reduction) Hepatic glucose output Peripheral glucose uptake by enhancing insulin action insulin secretion
25 mg QD-TID @ meals w/1st bite of. food, titrate Q 4 8 weeks; adjust based on 1 postprandial glucose; 100 mg TID max
 Table Selected Non-Insulin Antihyperglycemic Agents Class Drug (Brand) Dosing Comments -Glucosidase inhibitors Acarbose a (Precose) 25 mg QD-TID @ meals w/1st bite of MOA: Enzyme inhibitor, delays hydrolysis
Table Selected Non-Insulin Antihyperglycemic Agents Class Drug (Brand) Dosing Comments -Glucosidase inhibitors Acarbose a (Precose) 25 mg QD-TID @ meals w/1st bite of MOA: Enzyme inhibitor, delays hydrolysis
Onset Peak Duration Comments
 Rapid- Acting 5-15 minutes 0.5-3 hours 3-5 hours Meal should be available before administering, ideally taking within 10 minutes of eating). Good in refrigerator (36-46 F) until expiration date. Protect
Rapid- Acting 5-15 minutes 0.5-3 hours 3-5 hours Meal should be available before administering, ideally taking within 10 minutes of eating). Good in refrigerator (36-46 F) until expiration date. Protect
Diabetes: Beyond the D50. Leslie Huntington, BS, Paramedic Mobile Training Unit Oregon OHA-EMS and Trauma Systems
 Diabetes: Beyond the D50 Leslie Huntington, BS, Paramedic Mobile Training Unit Oregon OHA-EMS and Trauma Systems The EMS View of Diabetes Management BG low? Give some form of sugar. Hero! BG somewhere
Diabetes: Beyond the D50 Leslie Huntington, BS, Paramedic Mobile Training Unit Oregon OHA-EMS and Trauma Systems The EMS View of Diabetes Management BG low? Give some form of sugar. Hero! BG somewhere
INSULINThere are. T y p e 1 T y p e 2. many different insulins for
 T y p e 1 T y p e 2 INSULINThere are many different insulins for Characteristics The three characteristics of insulin are: Onset. The length of time before insulin reaches the bloodstream and begins lowering
T y p e 1 T y p e 2 INSULINThere are many different insulins for Characteristics The three characteristics of insulin are: Onset. The length of time before insulin reaches the bloodstream and begins lowering
E-mail: david.bruyette@vcahospitals.com www.veterinarydiagnosticinvestigation.com
 David Bruyette, DVM, DACVIM VCA West Los Angeles Animal Hospital 1818 South Sepulveda Blvd Los Angeles, CA 90025 310-473-2951 (ext 226) E-mail: david.bruyette@vcahospitals.com www.veterinarydiagnosticinvestigation.com
David Bruyette, DVM, DACVIM VCA West Los Angeles Animal Hospital 1818 South Sepulveda Blvd Los Angeles, CA 90025 310-473-2951 (ext 226) E-mail: david.bruyette@vcahospitals.com www.veterinarydiagnosticinvestigation.com
DIABETES MEDICATION INSULIN
 Section Three DIABETES MEDICATION INSULIN This section will tell you: About insulin. How to care and store your insulin. When to take your insulin. Different ways of taking insulin. WHAT IS INSULIN? Insulin
Section Three DIABETES MEDICATION INSULIN This section will tell you: About insulin. How to care and store your insulin. When to take your insulin. Different ways of taking insulin. WHAT IS INSULIN? Insulin
Types of insulin and How to Use Them
 Diabetes and Insulin Pumps Amy S. Pullen Pharm.D ISHP Spring Meeting April 2012 Objectives Describe the different types of insulin used in diabetes Identify the types of insulin that are compatible with
Diabetes and Insulin Pumps Amy S. Pullen Pharm.D ISHP Spring Meeting April 2012 Objectives Describe the different types of insulin used in diabetes Identify the types of insulin that are compatible with
INJEX Self Study Program Part 1
 INJEX Self Study Program Part 1 What is Diabetes? Diabetes is a disease in which the body does not produce or properly use insulin. Diabetes is a disorder of metabolism -- the way our bodies use digested
INJEX Self Study Program Part 1 What is Diabetes? Diabetes is a disease in which the body does not produce or properly use insulin. Diabetes is a disorder of metabolism -- the way our bodies use digested
Guidelines for Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosis
 Guidelines for Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosis Fasting Plasma Glucose (in asymptomatic individuals, repeat measurement to confirm the test) Normal FPG < 100 2-hr OGTT < 140 HbA1C < 5.5% Impaired Fasting Glucose
Guidelines for Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosis Fasting Plasma Glucose (in asymptomatic individuals, repeat measurement to confirm the test) Normal FPG < 100 2-hr OGTT < 140 HbA1C < 5.5% Impaired Fasting Glucose
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 What You Should Know
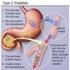 Please refer to the glossary for a definition of terms. What is Diabetes? Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 What You Should Know Erin K.P. Meyerhoff RN Instructor of Medicine Family Nurse Practitioner Certified
Please refer to the glossary for a definition of terms. What is Diabetes? Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 What You Should Know Erin K.P. Meyerhoff RN Instructor of Medicine Family Nurse Practitioner Certified
Let s Talk About Meters and Meds. Adapted for Upstate Medical University by: Kristi Shaver, BS, RN, CDE, MS-CNS Student (2014) January 2014
 Let s Talk About Meters and Meds Adapted for Upstate Medical University by: Kristi Shaver, BS, RN, CDE, MS-CNS Student (2014) January 2014 How to monitor diabetes control: Hemoglobin A 1 C, or just A 1
Let s Talk About Meters and Meds Adapted for Upstate Medical University by: Kristi Shaver, BS, RN, CDE, MS-CNS Student (2014) January 2014 How to monitor diabetes control: Hemoglobin A 1 C, or just A 1
Harmony Clinical Trial Medical Media Factsheet
 Overview Harmony is the global Phase III clinical trial program for Tanzeum (albiglutide), a product developed by GSK for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. The comprehensive program comprised eight individual
Overview Harmony is the global Phase III clinical trial program for Tanzeum (albiglutide), a product developed by GSK for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. The comprehensive program comprised eight individual
Effective pharmacological treatment regimens for diabetes usually require
 Medications Used in Diabetes in Patients Presenting for Anesthesia By Gabrielle O Connor, M.D., M.Sc., CCD, MRCP, FACP Dr. Gabrielle O Connor, a board certified endocrinologist who graduated from University
Medications Used in Diabetes in Patients Presenting for Anesthesia By Gabrielle O Connor, M.D., M.Sc., CCD, MRCP, FACP Dr. Gabrielle O Connor, a board certified endocrinologist who graduated from University
Exenatide (Byetta) for type 2 diabetes
 Exenatide (Byetta) for type 2 diabetes This Medicine Update is for people who are using, or thinking about using, exenatide. Summary Exenatide is a new injectable medicine that reduces blood glucose levels.
Exenatide (Byetta) for type 2 diabetes This Medicine Update is for people who are using, or thinking about using, exenatide. Summary Exenatide is a new injectable medicine that reduces blood glucose levels.
Causes, incidence, and risk factors
 Causes, incidence, and risk factors Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused by too little insulin, resistance to insulin, or both. To understand diabetes,
Causes, incidence, and risk factors Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused by too little insulin, resistance to insulin, or both. To understand diabetes,
Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes
 Improving Patient Care through Evidence Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes This information is based on a comprehensive review of the evidence for best practices in the treatment of type 2 diabetes and is sponsored
Improving Patient Care through Evidence Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes This information is based on a comprehensive review of the evidence for best practices in the treatment of type 2 diabetes and is sponsored
Insulin Pens & Improving Patient Adherence
 Insulin Pens & Improving Patient Adherence Bonnie Pepon, RN, BSN, CDE Certified Diabetes Educator Conemaugh Diabetes Institute Kip Benko, MD FACEP Asst Clinical Professor University of Pittsburgh School
Insulin Pens & Improving Patient Adherence Bonnie Pepon, RN, BSN, CDE Certified Diabetes Educator Conemaugh Diabetes Institute Kip Benko, MD FACEP Asst Clinical Professor University of Pittsburgh School
My Diabetes Care Plan
 My Diabetes Care Plan You may use the charts below to help you better understand your diabetes. Ask your healthcare provider to review your goals and targets with you. Discuss the results and set up an
My Diabetes Care Plan You may use the charts below to help you better understand your diabetes. Ask your healthcare provider to review your goals and targets with you. Discuss the results and set up an
The prevalence of diabetes in the United States in
 Medical Management of Type 2 Diabetes Celia Levesque, CNS-BC ABSTRACT More than 20 million Americans have type 2 diabetes. Managing blood glucose is an important component in delaying, slowing, or preventing
Medical Management of Type 2 Diabetes Celia Levesque, CNS-BC ABSTRACT More than 20 million Americans have type 2 diabetes. Managing blood glucose is an important component in delaying, slowing, or preventing
Volume 01, No. 08 November 2013
 State of New Jersey Department of Human Services Division of Medical Assistance & Health Services New Jersey Drug Utilization Review Board Volume 01, No. 08 November 2013 TO: SUBJECT: PURPOSE: Physicians,
State of New Jersey Department of Human Services Division of Medical Assistance & Health Services New Jersey Drug Utilization Review Board Volume 01, No. 08 November 2013 TO: SUBJECT: PURPOSE: Physicians,
Diabetes Mellitus. Background Information. Sri Prakash L. Mokshagundam and Vasti L. Broadstone
 15 Diabetes Mellitus Sri Prakash L. Mokshagundam and Vasti L. Broadstone I. Background Information II. Diagnosis III. Classification IV. Initial Evaluation of the Patient with Diabetes Mellitus V. Management
15 Diabetes Mellitus Sri Prakash L. Mokshagundam and Vasti L. Broadstone I. Background Information II. Diagnosis III. Classification IV. Initial Evaluation of the Patient with Diabetes Mellitus V. Management
Insulin T Y P E 1 T Y P E 2
 T Y P E 1 T Y P E 2 INSULIN There are many different insulins for many different situations and lifestyles. This section should help you and your doctor decide which insulin or insulins are best for you.
T Y P E 1 T Y P E 2 INSULIN There are many different insulins for many different situations and lifestyles. This section should help you and your doctor decide which insulin or insulins are best for you.
Management of Diabetes in the Elderly. Sylvia Shamanna Internal Medicine (R1)
 Management of Diabetes in the Elderly Sylvia Shamanna Internal Medicine (R1) Case 74 year old female with frontal temporal lobe dementia admitted for prolonged delirium and frequent falls (usually in the
Management of Diabetes in the Elderly Sylvia Shamanna Internal Medicine (R1) Case 74 year old female with frontal temporal lobe dementia admitted for prolonged delirium and frequent falls (usually in the
Abdulaziz Al-Subaie. Anfal Al-Shalwi
 Abdulaziz Al-Subaie Anfal Al-Shalwi Introduction what is diabetes mellitus? A chronic metabolic disorder characterized by high blood glucose level caused by insulin deficiency and sometimes accompanied
Abdulaziz Al-Subaie Anfal Al-Shalwi Introduction what is diabetes mellitus? A chronic metabolic disorder characterized by high blood glucose level caused by insulin deficiency and sometimes accompanied
Acarbose INITIAL: 25 mg PO TID ($45) Miglitol INITIAL: 25 mg PO TID ($145)
 PL Detail-Document #310601 This PL Detail-Document gives subscribers additional insight related to the Recommendations published in PHARMACIST S LETTER / PRESCRIBER S LETTER June 2015 Drugs for Type 2
PL Detail-Document #310601 This PL Detail-Document gives subscribers additional insight related to the Recommendations published in PHARMACIST S LETTER / PRESCRIBER S LETTER June 2015 Drugs for Type 2
ETIOLOGIC CLASSIFICATION. Type I diabetes Type II diabetes
 DIABETES MELLITUS DEFINITION It is a common, chronic, metabolic syndrome characterized by hyperglycemia as a cardinal biochemical feature. Resulting from absolute lack of insulin. Abnormal metabolism of
DIABETES MELLITUS DEFINITION It is a common, chronic, metabolic syndrome characterized by hyperglycemia as a cardinal biochemical feature. Resulting from absolute lack of insulin. Abnormal metabolism of
PANCREATIC HORMONES, ANTIDIABETIC AGENTS: INSULIN AND ORAL ANTIDIABETICS- handout Iwona Zaporowska-Stachowiak
 PANCREATIC HORMONES, ANTIDIABETIC AGENTS: INSULIN AND ORAL ANTIDIABETICS- handout Iwona Zaporowska-Stachowiak The endocrine pancreas (the islets of Langerhans) consists of four types of endocrine cells:
PANCREATIC HORMONES, ANTIDIABETIC AGENTS: INSULIN AND ORAL ANTIDIABETICS- handout Iwona Zaporowska-Stachowiak The endocrine pancreas (the islets of Langerhans) consists of four types of endocrine cells:
Nutrition. Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting NAME OF STUDENT
 1 Nutrition Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting NAME OF STUDENT 2 Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting Introduction and background of type 2 diabetes:
1 Nutrition Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting NAME OF STUDENT 2 Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting Introduction and background of type 2 diabetes:
Injectable Insulin During Pregnancy
 Injectable Insulin During Pregnancy What is insulin? Insulin is a hormone made by the pancreas. The pancreas is a small organ that lies behind and below the stomach. Insulin allows the food you eat to
Injectable Insulin During Pregnancy What is insulin? Insulin is a hormone made by the pancreas. The pancreas is a small organ that lies behind and below the stomach. Insulin allows the food you eat to
There seem to be inconsistencies regarding diabetic management in
 Society of Ambulatory Anesthesia (SAMBA) Consensus Statement on Perioperative Blood Glucose Management in Diabetic Patients Undergoing Ambulatory Surgery Review of the consensus statement and additional
Society of Ambulatory Anesthesia (SAMBA) Consensus Statement on Perioperative Blood Glucose Management in Diabetic Patients Undergoing Ambulatory Surgery Review of the consensus statement and additional
Hypoglycemia. National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse
 Hypoglycemia National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is hypoglycemia? Hypoglycemia, also called low blood glucose or
Hypoglycemia National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is hypoglycemia? Hypoglycemia, also called low blood glucose or
CLASS OBJECTIVES. Describe the history of insulin discovery List types of insulin Define indications and dosages Review case studies
 Insulins CLASS OBJECTIVES Describe the history of insulin discovery List types of insulin Define indications and dosages Review case studies INVENTION OF INSULIN 1921 The first stills used to make insulin
Insulins CLASS OBJECTIVES Describe the history of insulin discovery List types of insulin Define indications and dosages Review case studies INVENTION OF INSULIN 1921 The first stills used to make insulin
TREATMENT STRATEGIES FOR MANAGING TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS. Friday, August 16, 13
 TREATMENT STRATEGIES FOR MANAGING TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS 1 Heather Healy, FNP-BC Martha Shelver, CS, ACNP-BC Saint Alphonsus Regional Medical Center 2 OBJECTIVES 3 Review the current management algorithms
TREATMENT STRATEGIES FOR MANAGING TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS 1 Heather Healy, FNP-BC Martha Shelver, CS, ACNP-BC Saint Alphonsus Regional Medical Center 2 OBJECTIVES 3 Review the current management algorithms
2010 Partners & Peers for Diabetes Care, Inc. www.partnersandpeers.org
 Without a working knowledge of the way insulin works in your body it is very difficult to effectively manage diabetes... Kind of like driving a car without knowing how to use the gas pedal and brakes...
Without a working knowledge of the way insulin works in your body it is very difficult to effectively manage diabetes... Kind of like driving a car without knowing how to use the gas pedal and brakes...
Treatment Approaches to Diabetes
 Treatment Approaches to Diabetes Dr. Sarah Swofford, MD, MSPH & Marilee Bomar, GCNS, CDE Quick Overview Lifestyle Oral meds Injectables not insulin Insulin Summary 1 Lifestyle & DM Getting to the point
Treatment Approaches to Diabetes Dr. Sarah Swofford, MD, MSPH & Marilee Bomar, GCNS, CDE Quick Overview Lifestyle Oral meds Injectables not insulin Insulin Summary 1 Lifestyle & DM Getting to the point
BASAL BOLUS INSULIN FOR MEDICAL- SURGICAL INPATIENTS
 BASAL BOLUS INSULIN FOR MEDICAL- SURGICAL INPATIENTS C O N T A C T D I A B E T E S S E R V I C E S F O R M O R E I N F O R M A T I O N 8 4 7-9 1 7-6 9 0 7 THIS SLIDE PRESENTATION WAS PREPARED BY SUE DROGOS,
BASAL BOLUS INSULIN FOR MEDICAL- SURGICAL INPATIENTS C O N T A C T D I A B E T E S S E R V I C E S F O R M O R E I N F O R M A T I O N 8 4 7-9 1 7-6 9 0 7 THIS SLIDE PRESENTATION WAS PREPARED BY SUE DROGOS,
medications for type 2 diabetes
 Talking diabetes No.25 Revised 2012 medications for type 2 diabetes People with type 2 diabetes are often given medications including insulin to help manage their blood glucose levels. Most of these medications
Talking diabetes No.25 Revised 2012 medications for type 2 diabetes People with type 2 diabetes are often given medications including insulin to help manage their blood glucose levels. Most of these medications
Insulin Initiation and Intensification
 Insulin Initiation and Intensification ANDREW S. RHINEHART, MD, FACP, CDE MEDICAL DIRECTOR AND DIABETOLOGIST JOHNSTON MEMORIAL DIABETES CARE CENTER Objectives Understand the pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Insulin Initiation and Intensification ANDREW S. RHINEHART, MD, FACP, CDE MEDICAL DIRECTOR AND DIABETOLOGIST JOHNSTON MEMORIAL DIABETES CARE CENTER Objectives Understand the pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
A list of all medications you are taking also include any vitamins, supplements, over-the-counter medicines, or herbal products
 This is your customized insulin discussion guide to bring to your next doctor s visit. WHAT TO BRING TO YOUR NEXT CHECK UP A record of your recent blood sugar readings A list of all medications you are
This is your customized insulin discussion guide to bring to your next doctor s visit. WHAT TO BRING TO YOUR NEXT CHECK UP A record of your recent blood sugar readings A list of all medications you are
polyuria. polydipsia. polyphagia
 Diabetes Hormones of the Pancreas o Alpha Cells glucagon Secreted in response to blood glucose, protein intake, exercise, low CHO diet o Delta Cells somatostatin Inhibits glucagons and insulin o Beta Cells
Diabetes Hormones of the Pancreas o Alpha Cells glucagon Secreted in response to blood glucose, protein intake, exercise, low CHO diet o Delta Cells somatostatin Inhibits glucagons and insulin o Beta Cells
TYPE2DIABETES INSULIN TREATMENT 2009 UPDATE ON A HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONAL S GUIDE TO TREATMENT BY J. ROBIN CONWAY, MD. www.diabetesclinic.
 TYPE2DIABETES INSULIN TREATMENT 2009 UPDATE ON A HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONAL S GUIDE TO TREATMENT BY J. ROBIN CONWAY, MD www.diabetesclinic.ca Author: Dr. Robin Conway Note to readers The contents herein represent
TYPE2DIABETES INSULIN TREATMENT 2009 UPDATE ON A HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONAL S GUIDE TO TREATMENT BY J. ROBIN CONWAY, MD www.diabetesclinic.ca Author: Dr. Robin Conway Note to readers The contents herein represent
New and Standard Treatment Options for Patients With
 New and Standard Treatment Options for Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Jointly sponsored by The Dulaney Foundation and DIABETIC MICROVASCULAR COMPLICATIONS TODAY. Release Date: October 2006. Expiration Date:
New and Standard Treatment Options for Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Jointly sponsored by The Dulaney Foundation and DIABETIC MICROVASCULAR COMPLICATIONS TODAY. Release Date: October 2006. Expiration Date:
2T his section provides information about Medicare
 9 SECTION Medicare Part B-covered Diabetes Supplies 2T his section provides information about Medicare Part B (Medical Insurance) and its coverage of diabetes supplies. Medicare covers certain supplies
9 SECTION Medicare Part B-covered Diabetes Supplies 2T his section provides information about Medicare Part B (Medical Insurance) and its coverage of diabetes supplies. Medicare covers certain supplies
Vildagliptin (Galvus) for type 2 diabetes
 Vildagliptin (Galvus) for type 2 diabetes This Medicine Update is for people who are taking, or thinking about taking, vildagliptin. Summary Vildagliptin (brand name Galvus) is a new medicine. It is a
Vildagliptin (Galvus) for type 2 diabetes This Medicine Update is for people who are taking, or thinking about taking, vildagliptin. Summary Vildagliptin (brand name Galvus) is a new medicine. It is a
Type 2 Diabetes. Management and Medication. HELPLINE: 01604 622837 www.iddtinternational.org
 I N D E P E N D E N T D I A B E T E S T R U S T Type 2 Diabetes Management and Medication A charity supporting and listening to people who live with diabetes HELPLINE: 01604 622837 www.iddtinternational.org
I N D E P E N D E N T D I A B E T E S T R U S T Type 2 Diabetes Management and Medication A charity supporting and listening to people who live with diabetes HELPLINE: 01604 622837 www.iddtinternational.org
Diabetes may be classified as. i) Type - I Diabetes mellitus. Type - II Diabetes mellitus. Type - 1.5 Diabetes mellitus. Gestational Diabetes INSULIN
 HYPOGLYCEMIC AGENT Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder of multiple aetiology characterized by chronic hyperglycaemia with disturbances of carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism resulting
HYPOGLYCEMIC AGENT Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder of multiple aetiology characterized by chronic hyperglycaemia with disturbances of carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism resulting
Diabetes and the Elimination of Sliding Scale Insulin. Date: April 30 th 2013. Presenter: Derek Sanders, D.Ph.
 Diabetes and the Elimination of Sliding Scale Insulin Date: April 30 th 2013 Presenter: Derek Sanders, D.Ph. Background Information Epidemiology and Risk Factors Diabetes Its Definition and Its Impact
Diabetes and the Elimination of Sliding Scale Insulin Date: April 30 th 2013 Presenter: Derek Sanders, D.Ph. Background Information Epidemiology and Risk Factors Diabetes Its Definition and Its Impact
