How To Understand The Cycle Of A Human Egg
|
|
|
- Hillary Cross
- 3 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 28 Oogensis and the Female Sexual Cycle
2 Oogensis and Sexual Cycle reproductive cycle sequence of events from fertilization to giving birth sexual cycle - events that recur every month when pregnancy does not intervene consists of two interrelated cycles controlled by shifting patterns of hormone secretion ovarian cycle - events in ovaries menstrual cycle - parallel changes in uterus 28-2
3 Oogenesis oogenesis egg production produces haploid gametes by means of meiosis distinctly cyclic event that normally releases one egg each month accompanied by cyclic changes in hormone secretion cyclic changes in histological structure of the ovaries and uterus uterine changes result in monthly menstrual flow embryonic development of ovary female germ cells arise from yolk sac colonize gonadal ridges the first 5 to 6 weeks of development differentiate into oogonia and multiply until the fifth month 5 to 6 million in number transform into primary oocytes - early meiosis I most degenerate (atresia) by the time the girl is born egg, or ovum any stage from the primary oocyte to the time of fertilization by puberty 400,000 oocytes remain a lifetime supply probably will ovulate around 480 times 28-3
4 Oogenesis egg development resumes in adolescence FSH stimulates monthly cohorts of oocytes to complete meiosis I each oocyte divides into two haploid daughter cells of unequal size and different destinies important to produce an egg with as much cytoplasm as possible if fertilized, it must divide repeatedly and produce numerous daughter cells secondary oocyte large daughter cell that is the product of meiosis I first polar body smaller one that sometimes undergoes meiosis II, but ultimately disintegrates merely a means of discarding the extra set of haploid chromosomes secondary oocyte proceeds as far as metaphase II arrests until after ovulation if not fertilized, it dies and never finishes meiosis if fertilized, it completes meiosis II and casts off a second polar body chromosomes of the large remaining egg unite with those of the sperm 28-4
5 Oogenesis and Follicle Development Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Development of egg (oogenesis) Before birth Development of follicle (folliculogenesis) Mitosis 2n 2n Multiplication of oogonia Primary oocyte Oocyte Nucleus Follicular cells Primordial follicle No change Adolescence to menopause Meiosis I n Secondary oocyte Granulosa cells Primary follicle n First polar body (dies) Granulosa cells Zona pellucida Theca folliculi Secondary follicle Figure If not fertilized n n Dies n Second polar body (dies) Antrum Cumulus oophorus Theca Secondary oocyte interna (ovulated) Theca externa If fertilized Zygote n 2n n Embryo Meiosis II Bleeding into antrum Ovulated oocyte Follicular fluid Tertiary follicle Ovulation of mature (graafian) follicle Corpus luteum (Primordial & Primary follicle): Ed Reschke;(Secondary follicle): The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc./Photo by Dr. Alvin Telser; (Tertiary follicle): Manfred Kage/Peter Arnold, Inc.; (Graafian): Landrum Dr. Shettles; (Corpus luteum): The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc./Photo by Dr. Alvin Telser 28-5
6 Ovarian Follicles Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Tunica albuginea of ovary Primordial follicles Follicular cells Primary follicles Oocytes Granulosa cells Oocyte (egg) Oocyte nucleus Zona pellucida Cumulus oophorus Antrum Theca folliculi (a) 50 µm (b) 100 µm a: Ed Reschke; b: Manfred Kage/Peter Arnold, Inc Figure a-b 28-6
7 Folliculogenesis folliculogenesis the development of the follicles around the egg than undergoes oogenesis primordial follicles consists of a primary oocyte in early meiosis surrounded by a single layer of squamous follicular cells follicular cells connected to the oocyte by fine cytoplasmic processes for passage of nutrients and chemical signals concentrated in the cortex of the ovary most wait 13 to 50 years before they develop further adult ovary has 90% to 95% primordial follicles primary follicles have larger oocytes and follicular cells that still form a single layer secondary follicles still larger oocytes and follicular cells now stratified (granulosa cells) zona pellucida layer of glycoprotein gel secreted by granulosa cells around the oocyte theca folliculi connective tissue around the granulosa cells condenses to form a fibrous husk 28-7
8 Folliculogenesis tertiary follicles granulosa cells begin secreting follicular fluid accumulate in little pools in the follicular wall - this defines the tertiary follicles as they enlarge, the pools merge forming a single fluid-filled cavity, the antrum antral follicles tertiary and mature follicles preantral follicles earlier stages of the follicles cumulus oophorus a mound of granulosa cells on one side of the antrum that covers the oocyte and secures it to the follicular wall corona radiata innermost layer of cells in the cumulus surrounding the zona pellucida and the oocyte protective barrier around the egg with a similar function as the bloodtestis barrier theca folliculi continues to differentiate forming two layers theca externa outer fibrous capsule rich in blood vessels theca interna inner cellular, hormone secreting layer producing androgens (androstenedione and testosterone), and granulosa cells converts them to estradiol mature (graafian) follicles normally only one follicle from each month s cohort becomes a mature follicle destined to ovulate remainder degenerate 28-8
9 Histology of Ovarian Follicles Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Granulosa cells Oocyte (egg) Oocyte nucleus Zona pellucida Cumulus oophorus Antrum Theca folliculi (b) Figure 28.12b Manfred Kage/Peter Arnold, Inc 100 µm 28-9
10 The Sexual Cycle sexual cycle averages 28 days, varies from 20 to 45 days hormones of the hypothalamus regulate the pituitary gland pituitary hormones regulate the ovaries ovaries secrete hormones that regulate the uterus basic hierarchy of hormonal control hypothalamus pituitary ovaries uterus ovaries exert feedback control over hypothalamus and pituitary cycle begins with 2 week follicular phase menstruation occurs during first 3 to 5 days of cycle uterus replaces lost tissue by mitosis and cohort of follicles grow ovulation around day 14 remainder the of follicle becomes corpus luteum next 2 weeks the luteal phase corpus luteum stimulates endometrial secretion and thickening if pregnancy does not occur, endometrium breaks down in the last 2 days menstruation begins and the cycle starts over 28-10
11 The Ovarian Cycle ovarian cycle in three principal steps follicular phase, ovulation, and luteal phase this cycle reflects what happens in the ovaries and their relationship to the hypothalamus and pituitary much remains unknown about the timing of folliculogenesis 28-11
12 Follicular Phase follicular phase extends from the beginning of menstruation until ovulation day 1 to day 14 of an average cycle preovulatory phase from the end of menstruation until ovulation most variable part of the cycle and it is seldom possible to reliably predict the date of ovulation preparation for the follicular phase begins almost two month earlier shortly after ovulation a new cohort of preantral follicles descend form the cortex deeper into the ovary begins to grow and each develops an antrum selection window of 5 days in which one of them is selected as the dominant follicle to mature and ultimately ovulate in the next cycle FSH stimulates continued growth of the cohort, but the dominant follicle above all FSH stimulates the granulosa cells of the antral follicles to secrete estradiol dominant follicle becomes more sensitive to FSH and LH grows and becomes mature (graafian) follicle while others degenerate 28-12
13 Ovarian Cycle - Follicular Phase Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Ovarian events Gonadotropin secretion (a) Ovarian cycle FSH Developing follicles Secondary Primary Tertiary LH Ovulation Corpus luteum Involution Corpus albicans New primordial follicles Days Follicular phase Luteal phase Figure 28.14a 28-13
14 Ovulation ovulation the rupture of the mature follicle and the release of its egg and attendant cells typically around day 14 estradiol stimulates a surge of LH and a lesser spike of FSH by anterior pituitary LH induces several events primary oocyte completes meiosis I produces secondary oocyte and first polar body follicular fluid builds rapidly and follicle swells looks like a blister on the ovary surface follicular wall weakened by inflammation and proteolytic enzymes mature follicle approaches rupture ovulation takes only 2 or 3 minutes nipple-like stigma appears on ovary surface over follicle seeps follicular fluid for 1 or 2 minutes follicle bursts and remaining fluid oozes out carrying the secondary oocyte and cumulus oophorus normally swept up by ciliary current and taken into the uterine tube 28-14
15 Ovulation and Uterine Tube uterine tube prepares to catch the oocyte when it emerges it swells with edema its fimbriae envelop and caress the ovary in synchrony with the woman s heartbeat cilia create gentle current in the nearby peritoneal fluid many oocytes fall into the pelvic cavity and die 28-15
16 Signs of Ovulation couples attempting to conceive a child or avoid pregnancy need to be able to tell when ovulation occurs cervical mucus becomes thinner and more stretchy resting body temperature rises 0.4 to 0.6 F best measured first thing in the morning before arising from bed record for several days to see the difference LH surge occurs about 24 hours prior to ovulation detected with home testing kit twinges of ovarian pain (mittelschmerz) lasts from a few hours to a day or so at the time of ovulation best time for conception within 24 hours after the cervical mucus changes and the basal temperature rises 28-16
17 Ovarian Cycle - Ovulation Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Ovarian events Gonadotropin secretion (a) Ovarian cycle FSH Developing follicles Secondary Primary Tertiary LH Ovulation Corpus luteum Involution Corpus albicans New primordial follicles Days Follicular phase Luteal phase Figure 28.14a 28-17
18 Endoscopic View of Ovulation Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Infundibulum of uterine tube Fimbriae Cumulus oophorus Oocyte Stigma Ovary Figure Landrum B. Shettles, MD 0.1 mm 28-18
19 Pituitary-Ovarian Axis Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 2 Estradiol stimulates hypothalamus and anterior pituitary GnRH Hypothalamus Anterior pituitary 3 Hypothalamus secretes GnRH LH FSH 1 Maturing follicle secretes estradiol 4 GnRH and estradiol stimulate pituitary to secrete LH and FSH Figure Oocyte completes meiosis I; follicle rapidly enlarges and then ovulates Ovulated secondary oocyte 28-19
20 Luteal (Postovulatory) Phase luteal (postovulatory) phase - days 15 to day 28, from just after ovulation to the onset of menstruation if pregnancy does not occur, events happen as follows: when follicle ruptures it collapses and bleeds into antrum clotted blood is slowly absorbed granulosa and theca interna cells multiply and fill antrum dense bed of capillaries grows amid them ovulated follicle has now become the corpus luteum named for a yellow lipid that accumulates in the theca interna cells cells now called lutein cells 28-20
21 Luteal (Postovulatory) Phase transformation from ruptured follicle to corpus luteum is regulated by LH LH stimulates the corpus luteum to continue to grow and secrete rising levels of estradiol and progesterone 10 fold increase in progesterone is the most important aspect of the luteal phase progesterone has a crucial role in preparing the uterus for the possibility of pregnancy LH and FSH secretion declines over the rest of the cycle high levels of estradiol and progesterone, along with inhibin from the corpus luteum has a negative feedback effect on the pituitary if pregnancy does not occur, the corpus luteum begins the process of involution (shrinkage) beginning about day 22 (8 days after ovulation) by day 26 involution is complete and becomes inactive bit of scar tissue, the corpus albicans with diminishing ovarian steroid secretion, FSH levels rise ripening a new cohort of follicles ovaries usually alternate from month to month 28-21
22 Ovarian Cycle - Luteal Phase Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Ovarian events Gonadotropin secretion (a) Ovarian cycle FSH Developing follicles Secondary Primary Tertiary LH Ovulation Corpus luteum Involution Corpus albicans New primordial follicles Days Follicular phase Luteal phase Figure 28.14a 28-22
23 Menstrual Cycle menstrual cycle - consists of a buildup of the endometrium during most of the sexual cycle, followed by its breakdown and vaginal discharge divided into four phases: proliferative phase, secretory phase, premenstrual phase, and menstrual phase first day of noticeable vaginal discharge is defined as day 1 of the sexual cycle averages 5 days long proliferative phase layer of endometrial tissue (stratum functionalis) lost in the last menstruation is rebuilt at day 5 of menstruation, the endometrium is about 0.5 mm thick consists only of stratum basalis as new cohort of follicles develop, they secrete more and more estrogen estrogen stimulates mitosis in the stratum basalis and the prolific regrowth of blood vessels regenerating the functionalis by day 14 is 2 to 3 mm thick estrogen also stimulates endometrial cells to produce progesterone receptors 28-23
24 Menstrual Cycle - Proliferative Phase Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Thickness of endometrium Ovarian hormone secretion (b) Menstrual cycle Menstrual fluid Estradiol Progesterone Days Menstrual phase Proliferative phase Secretory phase Figure 28.14b day 6-14 rebuild endometrial tissue result of estrogen from developing follicles Premenstrual phase 28-24
25 Menstrual Cycle secretory phase endometrium thickens still more in response to progesterone from corpus luteum day 15 to day 26 secretion and fluid accumulation rather than mitosis progesterone stimulates endometrial glands to secrete glycogen glands grow wider, longer and more coiled endometrium 5 to 6 mm thick a soft, wet, nutritious bed available for embryonic development premenstrual phase period of endometrial degeneration last 2 days of the cycle corpus luteum atrophies and progesterone levels fall sharply triggers spasmodic contractions of spiral arteries causes endometrial ischemia (interrupted blood flow) brings about tissue necrosis and menstrual cramps pools of blood accumulate in stratum functionalis necrotic endometrium mixes with blood and serous fluid menstrual fluid 28-25
26 Menstrual Cycle - Secretory Phase Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Thickness of endometrium Ovarian hormone secretion (b) Menstrual cycle Menstrual fluid Estradiol Days Menstrual phase Proliferative phase Secretory phase Figure 28.14b Progesterone further thickening of endometrium due to secretion and fluid accumulation - not mitosis due to progesterone stimulation of glands Premenstrual phase 28-26
27 Menstrual Cycle Premenstrual Phase Thickness of endometrium Ovarian hormone secretion (b) Menstrual cycle Menstrual fluid Estradiol Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Days Menstrual phase Proliferative phase Secretory phase Figure 28.14b Progesterone involution of corpus luteum, progesterone falls spiral arteries constrict causes endometrial ischemia stratum functionalis sloughs Premenstrual phase 28-27
28 Menstrual Cycle menstrual phase discharge of menstrual fluid from the vagina (menses) first day of discharge is day 1 of the new cycle average woman expels about 40 ml of blood and 35 ml of serous fluid over a 5 day period contains fibrinolysin so it does not clot 28-28
29 Menstrual Cycle - Menstrual Phase Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Thickness of endometrium Ovarian hormone secretion (b) Menstrual cycle Menstrual fluid Estradiol Progesterone Days Menstrual phase Proliferative phase Secretory phase Figure 28.14b blood, serous fluid and endometrial tissue are discharged Premenstrual phase 28-29
30 Endometrial Changes Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Secretion Endometrial gland Stratum functionalis Spiral artery Stratum basalis Myometrium (a) Proliferative phase (b) Secretory phase (c) Menstrual phase Figure
The Menstrual Cycle. Model 1: Ovarian Cycle follicular cells
 The Menstrual Cycle REVIEW questions to complete before starting this POGIL activity 1. Gonads produce both gametes and sex steroid hormones. For the female, name the: A. gonads ovaries B. gametes oocyte/ovum/egg
The Menstrual Cycle REVIEW questions to complete before starting this POGIL activity 1. Gonads produce both gametes and sex steroid hormones. For the female, name the: A. gonads ovaries B. gametes oocyte/ovum/egg
Reproduction and its Hormonal Control
 Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Page 1 Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Different mammals have different patterns of reproduction Eg mammals, rats and mice can breed all year round, whereas
Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Page 1 Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Different mammals have different patterns of reproduction Eg mammals, rats and mice can breed all year round, whereas
Outline Fertilization Gametes Germ Cells Meiosis Male Reproductive Tract Spermatogenesis Female Reproductive Tract Oogenesis Menstrual Cycle Hormones
 Outline Fertilization Gametes Germ Cells Meiosis Male Reproductive Tract Spermatogenesis Female Reproductive Tract Oogenesis Menstrual Cycle Hormones Fertilization Gametes Oocyte, Sperm Acrosomal reaction
Outline Fertilization Gametes Germ Cells Meiosis Male Reproductive Tract Spermatogenesis Female Reproductive Tract Oogenesis Menstrual Cycle Hormones Fertilization Gametes Oocyte, Sperm Acrosomal reaction
Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE
 Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, the learner should be able to: Explain the importance of understanding the male and female reproductive
Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, the learner should be able to: Explain the importance of understanding the male and female reproductive
The Menstrual Cycle, Hormones and Fertility Treatment
 The Menstrual Cycle, Hormones and Fertility Treatment How many of us understand how our monthly cycle works? Every 28 days (or thereabouts), between the ages of around 13 and 51, a woman will release a
The Menstrual Cycle, Hormones and Fertility Treatment How many of us understand how our monthly cycle works? Every 28 days (or thereabouts), between the ages of around 13 and 51, a woman will release a
2. What muscle pulls the testis down into the scrotum during development?
 Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System
 Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface) sperm producing organs testes ducts that
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface) sperm producing organs testes ducts that
Reproduction Multiple Choice questions
 Reproduction Multiple Choice questions 1. In mammals that are seasonal breeders, females are receptive only once a year. This is called A) a follicular cycle B) an estrous cycle C) a menstrual cycle D)
Reproduction Multiple Choice questions 1. In mammals that are seasonal breeders, females are receptive only once a year. This is called A) a follicular cycle B) an estrous cycle C) a menstrual cycle D)
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System
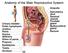 Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface)
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface)
1. AMOUNT OF FSH PRESENT
 The Menstrual Cycle Name Date Period PRE-LAB 1. Write down three facts you know about the menstrual cycle. A. B. C. FOLLICULAR PHASE Within the ovaries are located many egg cells. Each egg is enclosed
The Menstrual Cycle Name Date Period PRE-LAB 1. Write down three facts you know about the menstrual cycle. A. B. C. FOLLICULAR PHASE Within the ovaries are located many egg cells. Each egg is enclosed
Page 1. 1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems
 1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on the diagram below of the female reproductive
1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on the diagram below of the female reproductive
Anatomy and Physiology of Human Reproduction. Module 10a
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Chapter 28: The Reproductive System
 Chapter 28: The Reproductive System Chapter Objectives MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 1. List the major components of the male reproductive system and their general functions. 2. Explain the structure of the
Chapter 28: The Reproductive System Chapter Objectives MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 1. List the major components of the male reproductive system and their general functions. 2. Explain the structure of the
Revised Spring 2006 1
 It is important that you know the anatomy and the histology BEFORE the physiology can be covered in lecture. Study the anatomy of the reproductive system using this handout in conjunction with Text Chapter
It is important that you know the anatomy and the histology BEFORE the physiology can be covered in lecture. Study the anatomy of the reproductive system using this handout in conjunction with Text Chapter
Reproductive System. Anatomy of Male Reproductive System
 Function: producing offspring Reproductive System propagation of the species in terms of evolution the only reason all the other systems exist only major system that doesn t work continuously only activated
Function: producing offspring Reproductive System propagation of the species in terms of evolution the only reason all the other systems exist only major system that doesn t work continuously only activated
Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system.
 Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
PART 3: FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 PART 3: FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM CONTENTS 1. Normal female reproductive tract histology 2. Endocrine control of the oestrous cycle 3. Morphological changes during the oestrous cycle 4. Normal background
PART 3: FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM CONTENTS 1. Normal female reproductive tract histology 2. Endocrine control of the oestrous cycle 3. Morphological changes during the oestrous cycle 4. Normal background
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES
 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES: 1. List the organs and functions of the reproductive system. Female Organs Male Organs Functions 1 OVARIES 1 TESTES 1 Produce gametes 2 fallopian tubes 2 scrotum
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES: 1. List the organs and functions of the reproductive system. Female Organs Male Organs Functions 1 OVARIES 1 TESTES 1 Produce gametes 2 fallopian tubes 2 scrotum
From Menses to Menopause: How Hormones Can Affect Blood Glucose Levels. Christine Day, RN, MS, CNS-BC Lake Superior College
 From Menses to Menopause: How Hormones Can Affect Blood Glucose Levels Christine Day, RN, MS, CNS-BC Lake Superior College Overview Will review hormonal changes over the female lifespan Discuss the effects
From Menses to Menopause: How Hormones Can Affect Blood Glucose Levels Christine Day, RN, MS, CNS-BC Lake Superior College Overview Will review hormonal changes over the female lifespan Discuss the effects
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1
 Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Age and Fertility. A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES
 Age and Fertility A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
Age and Fertility A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
Chapter 28: Reproductive System
 I. Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System A. Scrotum 1. What does the scrotum contain? 2. An incomplete connective tissue septum divides the scrotum into 3. Externally the scrotum has an irregular ridge
I. Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System A. Scrotum 1. What does the scrotum contain? 2. An incomplete connective tissue septum divides the scrotum into 3. Externally the scrotum has an irregular ridge
FERTILITY AND AGE. Introduction. Fertility in the later 30's and 40's. Am I fertile?
 FERTILITY AND AGE Introduction Delaying pregnancy is a common choice for women in today's society. The number of women in their late 30s and 40s attempting pregnancy and having babies has increased in
FERTILITY AND AGE Introduction Delaying pregnancy is a common choice for women in today's society. The number of women in their late 30s and 40s attempting pregnancy and having babies has increased in
Timing is everything. Ovulation Tracking. Patient Information Booklet
 Timing is everything Ovulation Tracking Patient Information Booklet Contents Getting pregnant naturally 3 Getting pregnant the basics 3 What is ovulation? 3 Menstrual cycle 4 When does ovulation take place?
Timing is everything Ovulation Tracking Patient Information Booklet Contents Getting pregnant naturally 3 Getting pregnant the basics 3 What is ovulation? 3 Menstrual cycle 4 When does ovulation take place?
Endocrinology of the Female Reproductive Axis
 Endocrinology of the Female Reproductive Axis girlontheriver.com Geralyn Lambert-Messerlian, PhD, FACB Professor Women and Infants Hospital Alpert Medical School at Brown University Women & Infants BROWN
Endocrinology of the Female Reproductive Axis girlontheriver.com Geralyn Lambert-Messerlian, PhD, FACB Professor Women and Infants Hospital Alpert Medical School at Brown University Women & Infants BROWN
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM. Dr. Paul W. L. Kwan Tufts University School of Medicine
 FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Dr. Paul W. L. Kwan Tufts University School of Medicine Learning Objectives 1. Understand the organization of the ovary. 2. Understand the arrangement of cells that make up an
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Dr. Paul W. L. Kwan Tufts University School of Medicine Learning Objectives 1. Understand the organization of the ovary. 2. Understand the arrangement of cells that make up an
Female Reproductive System. Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued
 Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 10; Lecture 1; Monday Stuart Sumida. Human Reproductive Physiology and Reproductive Cycles
 Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 10; Lecture 1; Monday Stuart Sumida Human Reproductive Physiology and Reproductive Cycles OVARY Location : near kidneys, anchored by fallopian tubes to
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 10; Lecture 1; Monday Stuart Sumida Human Reproductive Physiology and Reproductive Cycles OVARY Location : near kidneys, anchored by fallopian tubes to
Germ cell formation / gametogenesis And Fertilisation
 Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lecture 3 The first steps to forming a new organism Descriptive embryology I Germ cell formation / gametogenesis And Fertilisation Why bother with sex? In terms of
Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lecture 3 The first steps to forming a new organism Descriptive embryology I Germ cell formation / gametogenesis And Fertilisation Why bother with sex? In terms of
OVARIAN CYSTS. Types of Ovarian Cysts There are many types of ovarian cysts and these can be categorized into functional and nonfunctional
 OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
Ovarian Cyst. Homoeopathy Clinic. Introduction. Types of Ovarian Cysts. Contents. Case Reports. 21 August 2002
 Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
Female Reproduction: Control of Ovarian Function
 2 Female Reproduction: Control of Ovarian Function F E Robinson and R A Renema Alberta Poultry Research Centre, University of Alberta Edmonton, AB, Canada T6G 2P5 Introduction The control of the release
2 Female Reproduction: Control of Ovarian Function F E Robinson and R A Renema Alberta Poultry Research Centre, University of Alberta Edmonton, AB, Canada T6G 2P5 Introduction The control of the release
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
LECTURE 10: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS
 LECTURE 10: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS INTRODUCTION The only system not essential for life, but ensures continued human existence. However all living organisms must reproduce in order to continue their species.
LECTURE 10: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS INTRODUCTION The only system not essential for life, but ensures continued human existence. However all living organisms must reproduce in order to continue their species.
Reproduction in Mammals
 Reproduction in Mammals A. Introduction 1. The organs of the male and female reproductive systems ensure the continuation of the species. 2. They do this by producing gametes and by providing a method
Reproduction in Mammals A. Introduction 1. The organs of the male and female reproductive systems ensure the continuation of the species. 2. They do this by producing gametes and by providing a method
Glossary. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty.
 Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
The Endocrine System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 9 The Endocrine System Slides 9.1 9.48 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Endocrine System Second messenger
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 9 The Endocrine System Slides 9.1 9.48 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Endocrine System Second messenger
How do fertility drugs work?
 How do fertility drugs work? Under normal circumstances, ovulation occurs once a month when a ripened egg which is ready to be fertilised is released from the ovaries. For couples who are trying to conceive,
How do fertility drugs work? Under normal circumstances, ovulation occurs once a month when a ripened egg which is ready to be fertilised is released from the ovaries. For couples who are trying to conceive,
Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum
 Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum Lesson title: In Vitro Fertilization Grade level: 9-12, with adaptation for younger students Subject area: Life Science Duration: Two class periods Objectives: Students
Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum Lesson title: In Vitro Fertilization Grade level: 9-12, with adaptation for younger students Subject area: Life Science Duration: Two class periods Objectives: Students
Welcome to chapter 8. The following chapter is called "Monitoring IVF Cycle & Oocyte Retrieval". The author is Professor Jie Qiao.
 Welcome to chapter 8. The following chapter is called "Monitoring IVF Cycle & Oocyte Retrieval". The author is Professor Jie Qiao. The learning objectives of this chapter are 2 fold. The first section
Welcome to chapter 8. The following chapter is called "Monitoring IVF Cycle & Oocyte Retrieval". The author is Professor Jie Qiao. The learning objectives of this chapter are 2 fold. The first section
Artificial insemination with donor sperm
 Artificial insemination with donor sperm Ref. 123 / 2009 Reproductive Medicine Unit Servicio de Medicina de la Reproducción Gran Vía Carlos III 71-75 08028 Barcelona Tel. (+34) 93 227 47 00 Fax. (+34)
Artificial insemination with donor sperm Ref. 123 / 2009 Reproductive Medicine Unit Servicio de Medicina de la Reproducción Gran Vía Carlos III 71-75 08028 Barcelona Tel. (+34) 93 227 47 00 Fax. (+34)
In - Vitro Fertilization Handbook
 In - Vitro Fertilization Handbook William F. Ziegler, D.O. Medical Director Scott Kratka, ELD, TS Embryology Laboratory Director Lauren F. Lucas, P.A.-C, M.S. Physician Assistant Frances Cerniak, R.N.
In - Vitro Fertilization Handbook William F. Ziegler, D.O. Medical Director Scott Kratka, ELD, TS Embryology Laboratory Director Lauren F. Lucas, P.A.-C, M.S. Physician Assistant Frances Cerniak, R.N.
Understanding Fertility
 Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley
 Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Final Exam Name: Instructions This exam consists of 40 questions. You may write on the exam itself, but be sure to answer all your questions on a Scantron
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Final Exam Name: Instructions This exam consists of 40 questions. You may write on the exam itself, but be sure to answer all your questions on a Scantron
Infertility: An Overview
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Infertility: An Overview A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Infertility: An Overview A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
Systematic review by: Dr. Ashraf Ahmed ElDaly, M.Sc., M.D.
 Role of luteinizing hormone supplementation in the follicular phase and pregnancy, during controlled ovarian hyperstimulation in in vitro fertilization Systematic review by: Dr. Ashraf Ahmed ElDaly, M.Sc.,
Role of luteinizing hormone supplementation in the follicular phase and pregnancy, during controlled ovarian hyperstimulation in in vitro fertilization Systematic review by: Dr. Ashraf Ahmed ElDaly, M.Sc.,
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Ovarian Cysts
 Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
CHAPTER 23: HUMAN GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT. 1. Define the term fertilization and name the site where fertilization typically occurs.
 1. Define the term fertilization and name the site where fertilization typically occurs. 2. Explain what is meant by capacitation of a sperm. 3. Describe the structure of a secondary oocyte when it is
1. Define the term fertilization and name the site where fertilization typically occurs. 2. Explain what is meant by capacitation of a sperm. 3. Describe the structure of a secondary oocyte when it is
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Endometriosis
 Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma)
 Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Basics of infertility Student Lecture Dr. A. Vilos, MD, FRCSC, Ass. Professor Department of OB/Gyn, REI Division Western University
 Definitions Basics of infertility Student Lecture Dr. A. Vilos, MD, FRCSC, Ass. Professor Department of OB/Gyn, REI Division Western University Infertility One year of frequent unprotected intercourse
Definitions Basics of infertility Student Lecture Dr. A. Vilos, MD, FRCSC, Ass. Professor Department of OB/Gyn, REI Division Western University Infertility One year of frequent unprotected intercourse
Hormonal Oral Contraceptives: An Overview By Kelsie Court. A variety of methods of contraception are currently available, giving men and
 Hormonal Oral Contraceptives: An Overview By Kelsie Court A variety of methods of contraception are currently available, giving men and women plenty of options in choosing a method suitable to his or her
Hormonal Oral Contraceptives: An Overview By Kelsie Court A variety of methods of contraception are currently available, giving men and women plenty of options in choosing a method suitable to his or her
Reproductive System. from the Human Body System Series. catalog # 3322. Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING
 Reproductive System from the Human Body System Series catalog # 3322 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Reproductive System from the Human Body System Series catalog # 3322 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Welcome. Thank you for purchasing the OvaCue Fertility Monitor!
 Owners Manual Welcome Thank you for purchasing the OvaCue Fertility Monitor! Recommended by fertility specialists, this convenient, easy to use fertility monitor provides up to seven days advance notice
Owners Manual Welcome Thank you for purchasing the OvaCue Fertility Monitor! Recommended by fertility specialists, this convenient, easy to use fertility monitor provides up to seven days advance notice
Medications for Inducing Ovulation
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Medications for Inducing Ovulation A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Medications for Inducing Ovulation A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction
How Your Fertility Works
 How Your Fertility Works These pages give a simple explanation of how male and female fertility work and complement each other, enabling couples to plan, space and limit family size, without using any
How Your Fertility Works These pages give a simple explanation of how male and female fertility work and complement each other, enabling couples to plan, space and limit family size, without using any
Assisted Reproductive Technologies at IGO
 9339 Genesee Avenue, Suite 220 San Diego, CA 92121 858 455 7520 Assisted Reproductive Technologies at IGO Although IGO no longer operates an IVF laboratory or program as such, we work closely with area
9339 Genesee Avenue, Suite 220 San Diego, CA 92121 858 455 7520 Assisted Reproductive Technologies at IGO Although IGO no longer operates an IVF laboratory or program as such, we work closely with area
Getting Pregnant: The Natural Approach Revealing the Secrets to Increase Your Fertility
 Getting Pregnant: The Natural Approach Revealing the Secrets to Increase Your Fertility Page 1 Contents Introduction 3 Part I Understanding Fertility and Infertility Chapter 1: What is Fertility? 4 - Signs
Getting Pregnant: The Natural Approach Revealing the Secrets to Increase Your Fertility Page 1 Contents Introduction 3 Part I Understanding Fertility and Infertility Chapter 1: What is Fertility? 4 - Signs
AGE & FERTILITY: Effective Evaluation & Treatment I. LANE WONG, MD, FACOG. www.hopefertilitycenter.com www.hopeivf.com
 Page 1 of 6 AGE & FERTILITY: Effective Evaluation & Treatment I. LANE WONG, MD, FACOG. www.hopefertilitycenter.com www.hopeivf.com Age has a profound effect on female fertility. This is common knowledge,
Page 1 of 6 AGE & FERTILITY: Effective Evaluation & Treatment I. LANE WONG, MD, FACOG. www.hopefertilitycenter.com www.hopeivf.com Age has a profound effect on female fertility. This is common knowledge,
CHAPTER 22: THE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS. 3. Define the terms meiosis, DNA, somatic cells, gametes, diploid, haploid and zygote.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Briefly explain why human reproduction is significant, and how sexual reproduction always results in a unique zygote. 2. List the functions of the reproductive systems. 3. Define the terms
OBJECTIVES: 1. Briefly explain why human reproduction is significant, and how sexual reproduction always results in a unique zygote. 2. List the functions of the reproductive systems. 3. Define the terms
Reproductive System. Anatomy of Male Reproductive System. Major Organs. Function: producing offspring. External Reproductive Organs
 Reproductive System Function: producing offspring propagation of the species!in terms of evolution the only reason all the other systems exist only major system that doesn t work continuously! only activated
Reproductive System Function: producing offspring propagation of the species!in terms of evolution the only reason all the other systems exist only major system that doesn t work continuously! only activated
Anatomy of Male Reproductive System
 Anatomy of Male Reproductive System A. Reproductive Systems 1. Gonads: primary sex organs a. Produce gametes b. Produce hormones c. Male Gonads: testes d. Female Gonads: ovaries 2. Gametes: sex cells a.
Anatomy of Male Reproductive System A. Reproductive Systems 1. Gonads: primary sex organs a. Produce gametes b. Produce hormones c. Male Gonads: testes d. Female Gonads: ovaries 2. Gametes: sex cells a.
Sex for the purposes of this class refers to 4 components
 Sex for the purposes of this class refers to 4 components Gonadal sex Gonads or where gametes are produced by meiosis Somatic sex Somatic cells are cells that undergo mitosis. They can be divided into
Sex for the purposes of this class refers to 4 components Gonadal sex Gonads or where gametes are produced by meiosis Somatic sex Somatic cells are cells that undergo mitosis. They can be divided into
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Menstruation
 Menstruation WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Menstruation is a normal and healthy part of growing up. The discharge of blood and tissue from the lining of your uterus each
Menstruation WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Menstruation is a normal and healthy part of growing up. The discharge of blood and tissue from the lining of your uterus each
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle
 Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
Hormonal regulation of gonad function overview
 Hormonal regulation of gonad function overview Role of hormones in reproductive functions production and maintenance of mature gametes optimization of the circumstances of impregnation support of pregnancy,
Hormonal regulation of gonad function overview Role of hormones in reproductive functions production and maintenance of mature gametes optimization of the circumstances of impregnation support of pregnancy,
POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME
 POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is polycystic ovary syndrome? (PCOS) Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the most common hormonal disorder in women
POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is polycystic ovary syndrome? (PCOS) Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the most common hormonal disorder in women
EVERY LIVING THING has a number of
 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems EVERY LIVING THING has a number of organ systems operating to perform specific functions. If you were to examine one of these systems, you would observe
Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems EVERY LIVING THING has a number of organ systems operating to perform specific functions. If you were to examine one of these systems, you would observe
Artificial insemination
 Artificial insemination What is involved? Artificial insemination is an assisted reproduction technique that consists of inserting laboratory-treated spermatozoa into the woman s uterus or cervical canal.
Artificial insemination What is involved? Artificial insemination is an assisted reproduction technique that consists of inserting laboratory-treated spermatozoa into the woman s uterus or cervical canal.
COVENTRY HEALTH CARE OF ILLINOIS, INC. COVENTRY HEALTH CARE OF MISSOURI, INC. Medical Management Policy and Procedure PROPRIETARY
 COVENTRY HEALTH CARE OF ILLINOIS, INC. COVENTRY HEALTH CARE OF MISSOURI, INC. Medical Management Policy and Procedure PROPRIETARY Policy: Infertility Evaluation and Treatment Number: MM 1306 Date Effective:
COVENTRY HEALTH CARE OF ILLINOIS, INC. COVENTRY HEALTH CARE OF MISSOURI, INC. Medical Management Policy and Procedure PROPRIETARY Policy: Infertility Evaluation and Treatment Number: MM 1306 Date Effective:
Ovarian Cysts in Dairy Cattle
 AS-451-W Reviewed 2001 Purdue University Cooperative Extension Service West Lafayette, IN 47907 Ovarian Cysts in Dairy Cattle R. D. Allrich, Department of Animal Sciences Purdue University, West Lafayette,
AS-451-W Reviewed 2001 Purdue University Cooperative Extension Service West Lafayette, IN 47907 Ovarian Cysts in Dairy Cattle R. D. Allrich, Department of Animal Sciences Purdue University, West Lafayette,
HEALTH UPDATE. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
 HEALTH UPDATE PO Box 800760 Charlottesville, VA 22908 Gynecology: (434) 924-2773 Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) What is it? An endocrine (hormonal) disorder. Because there is such variability in how
HEALTH UPDATE PO Box 800760 Charlottesville, VA 22908 Gynecology: (434) 924-2773 Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) What is it? An endocrine (hormonal) disorder. Because there is such variability in how
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Birth Control Pills
 Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
Endocrine System Review Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.
 Endocrine System Review Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Endocrine System Review Consists of discrete individual
Endocrine System Review Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Endocrine System Review Consists of discrete individual
Fertility Preservation in Women with Cancer. Objectives. Patient #1 10/24/2011. The audience will understand: How cancer therapy affects fertility.
 Fertility Preservation in Women with Cancer Leslie R. DeMars Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center Objectives The audience will understand: How cancer therapy affects fertility. Who should be considered for
Fertility Preservation in Women with Cancer Leslie R. DeMars Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center Objectives The audience will understand: How cancer therapy affects fertility. Who should be considered for
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) Page 1 of 11
 In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) Page 1 of 11 This document is a part of your informed consent process. Both partners should read the entire document carefully. In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a treatment
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) Page 1 of 11 This document is a part of your informed consent process. Both partners should read the entire document carefully. In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a treatment
GLOSSARY. A Abstinence: having no vaginal, anal, or oral sex. It is the only method that is 100% effective in preventing pregnancy and STI s.
 WOMEN S HEALTH GLOSSARY We encourage you to learn the meanings behind these words for your personal health and to fully understand the words being used during your appointments at the Falcon Health Center.
WOMEN S HEALTH GLOSSARY We encourage you to learn the meanings behind these words for your personal health and to fully understand the words being used during your appointments at the Falcon Health Center.
regulation of ECF composition and volume regulation of metabolism thyroid hormones, epinephrine, growth hormone, insulin and glucagon
 Hormonal Effects regulation of ECF composition and volume ADH, aldosterone, ANF regulation of metabolism thyroid hormones, epinephrine, growth hormone, insulin and glucagon regulation of muscle contraction
Hormonal Effects regulation of ECF composition and volume ADH, aldosterone, ANF regulation of metabolism thyroid hormones, epinephrine, growth hormone, insulin and glucagon regulation of muscle contraction
Uterine Fibroids. More than half of all women have fibroids. They are a common, benign, uterine growth.
 Uterine Fibroids More than half of all women have fibroids. They are a common, benign, uterine growth. Fibroids are not a disease. Much like the genetic blueprint that determines the color of your eyes
Uterine Fibroids More than half of all women have fibroids. They are a common, benign, uterine growth. Fibroids are not a disease. Much like the genetic blueprint that determines the color of your eyes
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle
 Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation (men-stray-shuhn) is a woman's monthly bleeding. When you menstruate, your body sheds the lining of the uterus (womb). Menstrual
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation (men-stray-shuhn) is a woman's monthly bleeding. When you menstruate, your body sheds the lining of the uterus (womb). Menstrual
SYNCHRONIZATION OF CATTLE
 UNDER ESTRUS SYNCHRONIZATION OF CATTLE FS921C Robin Salverson, Extension Livestock Educator, Harding County, and George Perry, Extension Beef Reproduction and Management Specialist Reproductive failure
UNDER ESTRUS SYNCHRONIZATION OF CATTLE FS921C Robin Salverson, Extension Livestock Educator, Harding County, and George Perry, Extension Beef Reproduction and Management Specialist Reproductive failure
Understanding Blood Tests - Pregnancy/Fertility Monitoring by Beth Anne Ary M.D
 Understanding Blood Tests - Pregnancy/Fertility Monitoring by Beth Anne Ary M.D Blood tests are the most common and most important method of monitoring pregnancy-- both assisted pregnancies, and unassisted.
Understanding Blood Tests - Pregnancy/Fertility Monitoring by Beth Anne Ary M.D Blood tests are the most common and most important method of monitoring pregnancy-- both assisted pregnancies, and unassisted.
Explore and Discover... Human growth. You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Teacher information
 You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Explore and Discover... Teacher information Gallery visited Human Biology Suitable for Key Stage 3 (ages 11 to
You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Explore and Discover... Teacher information Gallery visited Human Biology Suitable for Key Stage 3 (ages 11 to
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
 Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome What is Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome? Polycystic ovary syndrome (or PCOS) is a common condition affecting 3 to 5% of women of reproductive age. It is linked with hormonal imbalances,
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome What is Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome? Polycystic ovary syndrome (or PCOS) is a common condition affecting 3 to 5% of women of reproductive age. It is linked with hormonal imbalances,
HOW IS OVARIAN RESERVE ASSESSED?
 HOW IS OVARIAN RESERVE ASSESSED? The majority of indicators we have to assess OR assess egg quantity rather than egg quality and these two do not always go hand in hand. No individual test is a perfect
HOW IS OVARIAN RESERVE ASSESSED? The majority of indicators we have to assess OR assess egg quantity rather than egg quality and these two do not always go hand in hand. No individual test is a perfect
The IUI procedure Who should consider an IUI IUI success rates IUI cost What to consider if IUI is unsuccessful. The IUI procedure:
 A Complete Guide to understanding IUI (intrauterine insemination) and artificial insemination (Eric Daiter, MD Board Certified in Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility) The IUI procedure Who should
A Complete Guide to understanding IUI (intrauterine insemination) and artificial insemination (Eric Daiter, MD Board Certified in Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility) The IUI procedure Who should
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE UTERINE FIBROIDS A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE UTERINE FIBROIDS A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient
Egg Donation Process, Risks, Consent and Agreement
 THE CENTER FOR HUMAN REPRODUCTION (CHR) 21 East 69 th Street, New York, NY 10021 T: 212-994-4400; F: 212-994-4499 Egg Donation Process, Risks, Consent and Agreement Updated on: 10/8/2014 Date: Egg Donor
THE CENTER FOR HUMAN REPRODUCTION (CHR) 21 East 69 th Street, New York, NY 10021 T: 212-994-4400; F: 212-994-4499 Egg Donation Process, Risks, Consent and Agreement Updated on: 10/8/2014 Date: Egg Donor
Connecting the Dots: Basal Body Temperature Charting BBT charting: A useful tool to identify your body composition and monitor your progress
 Connecting the Dots: Basal Body Temperature Charting BBT charting: A useful tool to identify your body composition and monitor your progress By Michelle Buchanan, Certified Acupuncturist The History of
Connecting the Dots: Basal Body Temperature Charting BBT charting: A useful tool to identify your body composition and monitor your progress By Michelle Buchanan, Certified Acupuncturist The History of
Cell Division CELL DIVISION. Mitosis. Designation of Number of Chromosomes. Homologous Chromosomes. Meiosis
 Cell Division CELL DIVISION Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial purpose.
Cell Division CELL DIVISION Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial purpose.
Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I
 Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I TOPIC: Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I SUBJECT: Life Skills TARGET AGE RANGE: 9 15 TIME: 45 minutes IDEAL NUMBER OF LEARNERS:
Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I TOPIC: Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I SUBJECT: Life Skills TARGET AGE RANGE: 9 15 TIME: 45 minutes IDEAL NUMBER OF LEARNERS:
Ovaries Ovarian Cysts Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD) Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
 Ovaries Ovarian Cysts Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD) Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) Your Ovaries are very active glands. Many women can feel it when they ovulate; they say it feels like a pinching
Ovaries Ovarian Cysts Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD) Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) Your Ovaries are very active glands. Many women can feel it when they ovulate; they say it feels like a pinching
THE WHY, HOW-TO, AND COST OF PROGRAMED AI BREEDING OF DAIRY COWS. J. S. Stevenson
 Dairy Day 1998 THE WHY, HOW-TO, AND COST OF PROGRAMED AI BREEDING OF DAIRY COWS J. S. Stevenson Summary Management of the estrous cycle is now more practical than it was a decade ago because of our understanding
Dairy Day 1998 THE WHY, HOW-TO, AND COST OF PROGRAMED AI BREEDING OF DAIRY COWS J. S. Stevenson Summary Management of the estrous cycle is now more practical than it was a decade ago because of our understanding
Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: Cervix. Cervix. Nabothian cysts. cervical polyps. leiomyomas. Cervical stenosis
 Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Cervix Nabothian cysts result from chronic cervicitis most
Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Cervix Nabothian cysts result from chronic cervicitis most
AB N O R M A LUT E R I N E BL E E D I N G
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE AB N O R M A LUT E R I N E BL E E D I N G A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE AB N O R M A LUT E R I N E BL E E D I N G A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the
STUDENT S WORKSHEETS. Eva M. Zamudio Zamudio
 STUDENT S WORKSHEETS January April 2009 HUMAN LIFE CYCLE HANDOUT 1 1. Write the name of each stage in the right order: retirement adolescence babyhood adulthood - childhood 2. What stage does it belong
STUDENT S WORKSHEETS January April 2009 HUMAN LIFE CYCLE HANDOUT 1 1. Write the name of each stage in the right order: retirement adolescence babyhood adulthood - childhood 2. What stage does it belong
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Hormone Therapy
 Hormone Therapy WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 At menopause, a woman's body makes less estrogen and she stops having menstrual periods. This is a natural stage in a woman's
Hormone Therapy WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 At menopause, a woman's body makes less estrogen and she stops having menstrual periods. This is a natural stage in a woman's
The following chapter is called "Follow-ups with a Positive or a Negative Pregnancy Test".
 Slide 1 Welcome to chapter 7. The following chapter is called "Follow-ups with a Positive or a Negative Pregnancy Test". The author is Professor Pasquale Patrizio. Slide 2 This chapter has the following
Slide 1 Welcome to chapter 7. The following chapter is called "Follow-ups with a Positive or a Negative Pregnancy Test". The author is Professor Pasquale Patrizio. Slide 2 This chapter has the following
From this site: http://www.energeticnutrition.com /vitalzym/fibroid_tumors.html Uterine Fibroid Tumors
 From this site: http://www.energeticnutrition.com /vitalzym/fibroid_tumors.html Uterine Fibroid Tumors Uterine Fibroid Tumors A woman s fibroisis condition usually associated with estrogen dominance. Uterine
From this site: http://www.energeticnutrition.com /vitalzym/fibroid_tumors.html Uterine Fibroid Tumors Uterine Fibroid Tumors A woman s fibroisis condition usually associated with estrogen dominance. Uterine
