Prevalence and Risk Factors of Diabetic Nephropathy in an Urban South Indian Population. The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study (CURES 45)
|
|
|
- Lionel Flynn
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Epidemiology/Health Services Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Prevalence and Risk Factors of Diabetic Nephropathy in an Urban South Indian Population The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study (CURES 45) RANJIT UNNIKRISHNAN, I,MD MOHAN REMA, MBBS, DO, PHD RAJENDRA PRADEEPA, MSC MOHAN DEEPA, MSC COIMBATORE SUBRAMANIAM SHANTHIRANI, PHD RAJ DEEPA, MPHIL, PHD VISWANATHAN MOHAN, MD, FRCP, PHD, DSC OBJECTIVE The aim of this study was to determine the prevalence of diabetic nephropathy among urban Asian-Indian type 2 diabetic subjects. RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODS Type 2 diabetic subjects (n 1,716), inclusive of known diabetic subjects (KD subjects) (1,363 of 1,529; response rate 89.1%) and randomly selected newly diagnosed diabetic subjects (NDD subjects) (n 353) were selected from the Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study (CURES). Microalbuminuria was estimated by immunoturbidometric assay and diagnosed if albumin excretion was between 30 and 299 g/mg of creatinine, and overt nephropathy was diagnosed if albumin excretion was 300 g/mg of creatinine in the presence of diabetic retinopathy, which was assessed by stereoscopic retinal color photography. RESULTS The prevalence of overt nephropathy was 2.2% (95% CI ). Microalbuminuria was present in 26.9% ( ). Compared with the NDD subjects, KD subjects had greater prevalence rates of both microalbuminuria with retinopathy and overt nephropathy (8.4 vs. 1.4%, P 0.001; and 2.6 vs. 0.8%, P 0.043, respectively). Logistic regression analysis showed that A1C (odds ratio [95% CI ], P 0.001), smoking (odds ratio 1.464, P 0.011), duration of diabetes (1.023, P 0.046), systolic blood pressure (1.020, P 0.001), and diastolic blood pressure (1.016, P 0.022) were associated with microalbuminuria. A1C (1.483, P ), duration of diabetes (1.073, P 0.003), and systolic blood pressure (1.031, P 0.004) were associated with overt nephropathy. CONCLUSIONS The results of the study suggest that in urban Asian Indians, the prevalence of overt nephropathy and microalbuminuria was 2.2 and 26.9%, respectively. Duration of diabetes, A1C, and systolic blood pressure were the common risk factors for overt nephropathy and microalbuminuria. Diabetic nephropathy is the leading cause of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) worldwide, and it is estimated that 20% of type 2 diabetic patients reach ESRD during their lifetime (1). Kidney disease in diabetic patients Diabetes Care 30: , 2007 is clinically characterized by increasing rates of urinary albumin excretion, starting from normoalbuminuria, which progresses to microalbuminuria, macroalbuminuria, and eventually to ESRD. Microalbuminuria is the earliest From the Madras Diabetes Research Foundation and Dr. Mohan s Diabetes Specialties Centre, Gopalapuram, Chennai, India. Address correspondence and reprint requests to Dr. V. Mohan, MD, FRCP, FRCP, PhD, DSc, Chairman and Chief of Diabetes Research, Madras Diabetes Research Foundation and Dr. Mohan s Diabetes Specialities Centre, 4 Conran Smith Rd., Gopalapuram, Chennai, , India. drmohans@vsnl.net. Received for publication 18 December 2006 and accepted in revised form 2 May Published ahead of print at on 8 May DOI: /dc Abbreviations: ACEI, ACE inhibitor; ARB, angiotensin receptor blocker; CURES, Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study; ESRD, end-stage renal disease. A table elsewhere in this issue shows conventional and Système International (SI) units and conversion factors for many substances by the American Diabetes Association. The costs of publication of this article were defrayed in part by the payment of page charges. This article must therefore be hereby marked advertisement in accordance with 18 U.S.C. Section 1734 solely to indicate this fact. clinically detectable stage of diabetic kidney disease at which appropriate interventions can retard, or reverse, the progress of the disease. According to the most recent estimates published in the Diabetes Atlas 2006 (2), India has the largest number of diabetic patients in the world, estimated to be 40.9 million in the year 2007 and expected to increase to 69.9 million by the year Type 2 diabetes in Asian Indians differs from that in Europeans in several aspects: the onset is at a younger age, obesity is less common, and genetic factors appear to be more common (3). Some studies (4 6) conducted in migrant Asian Indians in the U.K. and Europe have reported increased prevalence of diabetic nephropathy compared with white Caucasians. The few studies published on the prevalence of diabetic nephropathy in India have all been clinic based (7,8). Indeed, the Diabetes Atlas 2006 (2) does not list a single population-based study on diabetic nephropathy from South Asia. This article reports on the first populationbased data on the prevalence of diabetic nephropathy in India. RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODS Study subjects were recruited from the Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study (CURES), conducted on a representative population of Chennai (formerly Madras) in southern India, the fourth largest city in India with a population of 5 million. The city of Chennai is divided into 155 corporation wards representing a socioeconomically diverse group. The methodology of the study has been published elsewhere (9). Briefly, in phase 1 of CURES (urban component), 26,001 individuals aged 20 years were screened for diabetes using a systematic sampling technique from 46 corporation wards representative of the various social tiers in Chennai. The selection criterion was taken as 20 years of age due to younger age at onset of type 2 diabetes in Indians (9). Self-reported diabetic subjects identified in phase 1 (n DIABETES CARE, VOLUME 30, NUMBER 8, AUGUST
2 Diabetic nephropathy in Asian Indians Table 1 Prevalence of microalbuminuria and macroalbuminuria in the study population Groups 1,529) were classified as known diabetic subjects (KD subjects). Fasting capillary blood glucose was determined using a One Touch Basic glucose meter (LifeScan, Johnson & Johnson, Milpitas, CA) in all subjects. Diabetes was diagnosed using American Diabetes Association criteria (10). In phase 2 of CURES, all the KD subjects (n 1,529) were invited to our center for detailed studies on vascular complications, and 1,363 consented for both retinal examination and estimation of microalbuminuria (response rate: 89.1%). In addition, 15% percent of subjects with impaired fasting glucose and 10% of subjects with normal fasting glucose in phase 1 were requested to take an oral glucose tolerance test. Thirty-seven of the former group and 14 of the latter group who were detected to have diabetes according to World Health Organization Consulting Group criteria (2-h plasma glucose 11.1 mmol/l) (11) were added to the 320 randomly chosen newly detected diabetic subjects (NDD subjects) from phase 1 of the study. Of the total 371 NDD subjects, 353 consented for this study (response rate: 95.1%). Thus, the final study numbers were 1,716 diabetic subjects (KD: 1,363 NDD: 353). The institutional ethics committee approval was obtained, and informed consent was obtained from all study subjects. Clinical and biochemical studies Measurements of weight, height, and waist circumference were obtained using standardized techniques. The BMI was calculated using the following formula: weight (kg)/height (m 2 ). Blood pressure was recorded in the sitting position in the right arm with a mercury sphygmomanometer (Diamond Deluxe Industrial Electronics and Products, Pune, India) Overall diabetes NDD KD P value for KD vs. NDD n 1, ,363 Microalbuminuria Overall 462 (26.9) 84 (23.8) 378 (27.7) NS With retinopathy 119 (6.9) 5 (1.4) 114 (8.4) Without retinopathy 343 (20.0) 79 (22.4) 264 (19.4) NS Overt nephropathy (macroalbuminuria 38 (2.2) 3 (0.8) 35 (2.6) with retinopathy) Macroalbuminuria without retinopathy 53 (3.1) 10 (2.8) 43 (3.2) NS Data are n (%). NS, not significant. and rounded off to the nearest 2 mmhg. Two readings were taken 5 min apart, and the mean of the two was taken as the final blood pressure reading. A fasting blood sample was taken for estimation of plasma glucose and serum lipids using a Hitachi 912 autoanalyser (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany). A1C was measured by the highperformance liquid chromatography method using the Variant machine (Bio- Rad, Hercules, California). Estimation of microalbuminuria Microalbumin concentration was measured in a fasting urine sample using a immunoturbidometric assay (Hitachi 902 autoanalyser; Roche Diagnostics). The mean inter- and intra-assay coefficients of variation were 3.5 and 4.2%, respectively. Retinopathy The ocular fundi were photographed using four-field stereo color retinal photography (Zeiss FF 450 plus camera). Photographs were graded by an ophthalmologist (R.M.). The minimum criterion for diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy was the presence of at least one definite microaneurysm in any field photographed. Photographs were assessed and assigned a retinopathy level, and the final diagnosis for each patient was determined from the grading of the worse eye according to the Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study criteria for severity of an individual eye (12). Definitions Hypertension. Subjects with selfreported hypertension and those who had a systolic blood pressure of 140 mmhg and/or diastolic blood pressure of 90 mmhg (13) were considered to have hypertension. Smoking. Individuals were classified as nonsmokers and current smokers. Microalbuminuria. Microalbuminuria was diagnosed if the albumin excretion was between 30 and 299 g/mg of creatinine (8). Overt nephropathy was diagnosed if albumin excretion was 300 g/mg of creatinine in the presence of diabetic retinopathy. Statistical analysis Data were expressed as means SD. Students t test or one-way ANOVA (Tukey s honestly significant difference comparison) was used to compare continuous variables, and the 2 test was used to compare proportions among groups. Logistic regression analysis was done using either microalbuminuria or overt nephropathy as the dependent variable to identify the risk factors. Subjects were also categorized based on the presence of retinopathy to study the risk factors for albuminuria with and without retinopathy. P 0.05 was considered significant. All analysis was done using Windows-based SPSS statistical package (version 10.0; SPSS, Chicago, IL). RESULTS There were no significant differences in the baseline values between the 1,363 responders and the 166 nonresponders among the KD subjects (responders versus nonresponders: aged vs years, P 0.27; 46.3 vs. 51.7% male, P 0.20; fasting plasma glucose vs mmol/l, P 0.43; systolic blood pressure vs mmhg, P 0.581; diastolic blood pressure vs mmhg, P 0.31). The mean age of the total study population (n 1,716) was years, and 44.7% (n 744) were male subjects. Of the total 1,716 diabetic subjects studied, 462 (26.9% [95% CI ]) had microalbuminuria, 38 (2.2% [ ]) had overt nephropathy (i.e., macroalbuminuria with retinopathy), and 53 (3.1% [ ]) had macroalbuminuria without retinopathy (Table 1). Compared with the NDD subjects, KD subjects had greater prevalence rates of both microalbuminuria with retinopathy and overt nephropathy (8.4 vs. 1.4%, P 0.001; and 2.6 vs. 0.8%, P 0.043, respectively). Table 2 presents the clinical and biochemical characteristics of the study subjects. Subjects with overt nephropathy 2020 DIABETES CARE, VOLUME 30, NUMBER 8, AUGUST 2007
3 Unnikrishnan and Associates Table 2 Clinical and biochemical characteristics of the study population Parameters Normoalbuminuria Microalbuminuria Overt nephropathy (macroalbuminuria with retinopathy) P value for trend n 1, Age (years) * Sex (male) 503 (43.3) 225 (48.7) 16 (42.1) Duration of diabetes (years) Smoking 183 (15.7) 100 (21.6) 7 (18.4) BMI (kg/m 2 ) * Waist circumference (cm) Systolic blood pressure (mmhg) Diastolic blood pressure (mmhg) Fasting plasma glucose (mmol/l) A1C (%) Hypertension (%) Data are means SD or n (%), unless otherwise indicated. *P 0.05 vs. normal; P 0.01 vs. normal; P 0.05 vs. microalbuminuria; P vs. normal; P vs. microalbuminuria. were older and had a longer duration of diabetes (P for trend ). Systolic and diastolic blood pressure, fasting plasma glucose, and A1C values were highest among the overt nephropathy group, followed by microalbuminuric and normoalbuminuric subjects (P for trend ). Prevalence of hypertension was higher among subjects with microalbuminuria and overt nephropathy compared with the normoalbuminuric group (P 0.001). Subjects with microalbuminuria who had retinopathy had lower BMI ( vs kg/m 2 ) and waist circumference (88 9 vs cm) but higher fasting plasma glucose ( vs mmol/l) and A1C values ( vs %) and longer duration of diabetes (8 6 vs. 5 5 years) compared with those without retinopathy. Other parameters like age and blood pressure did not vary significantly between the study groups. Prevalence of microalbuminuria and overt nephropathy was computed in relation to duration of diabetes and A1C. There was an increase in the prevalence of microalbuminuria with the increase in duration of diabetes (duration of diabetes 1.0 year: 22.3%, 1 5 years: 25.7%, 6 10 years: 33.5%, and 10 years: 30.2%; P for trend 0.001). There was a significant increase in the prevalence of overt nephropathy with the increase in duration of diabetes (duration of diabetes 1.0 year: 0.7%, 1 5 years: 1.1%, 6 10 years: 3.5%, and 10 years: 7.7%; P for trend 0.001). Prevalence of both microalbuminuria (A1C 7.0%: 14.5%, %: 22.6%, %: 35.1%, and 10.9%: 43.4%, and overt nephropathy (A1C 7.0%: 0.2%, %: 1.1%, %: 3.5%, and 10.9%: 5.5%) increased with the increase in A1C levels (P for trend 0.001). Prevalence of microalbuminuria and overt nephropathy was computed in relation to use of antihypertensive drugs. Of 1,716 subjects, 425 were on antihypertensive medications. Prevalence of microalbuminuria and overt nephropathy (antihypertensive drug users versus others: microlbuminuria: 33.9 vs. 24.6%, P 0.001; overt nephropathy: 6.6 vs. 0.8%, P 0.001) were higher in antihypertensive medication users. Subjects on antihypertensive medications were further categorized as ACE inhibitors (ACEIs)/angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) users (n 121) and others. There was no significant difference between these two groups with respect to microalbuminuria, whereas overt nephropathy was higher in those on ACEIs/ARBs (ACEI/ARB users vs. others: microalbuminuria: 35.5 vs. 33.2%, P 0.26; overt nephropathy: 11.6 vs. 4.6%, P 0.004). There were 23 subjects, 21 with KD and 2 NDD, who had renal insufficiency defined as serum creatinine levels 1.5 mg/dl. Retinopathy was present in 7 of 21 (33.3%) of KD subjects, which included nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy in 4 and proliferative diabetic retinopathy in 3 subjects. Neither of the NDD subjects with renal insufficiency had retinopathy. Regression analysis revealed that A1C (P 0.001), smoking (P 0.011), duration of diabetes (P 0.046), systolic blood pressure (P ), and diastolic blood pressure (P 0.022) were associated with microalbuminuria. Regression analysis was carried out after categorizing microalbuminuric patients with and without retinopathy. A1C and systolic blood pressure were common risk factors for microalbuminuria with retinopathy (A1C odds ratio [95% CI ], P 0.001; systolic blood pressure [ ], P 0.007) as well as without retinopathy (A1C [ ], P 0.001; systolic blood pressure [ ], P 0.001). Smoking (1.613 [ ], P 0.005) and diastolic blood pressure (1.018 [ ], P 0.028) showed association only with microalbuminuria without retinopathy, while duration of diabetes (1.085 [ ], P 0.001) showed an association only with microalbuminuria with retinopathy. Overt nephropathy showed significant association with A1C (P ), duration of diabetes (P 0.003), and systolic blood pressure (P 0.004) (Table 3). None of the risk factors except diastolic blood pressure showed an association with macroalbuminuria without retinopathy (odds ratio [95% CI ], P 0.048). Table 4 compares the prevalence of microalbuminuria and nephropathy in different populations (14 19). The prevalence of overt nephropathy in Indians appears to be lower, while that of microalbuminuria is comparable to that reported earlier studies in other populations. DIABETES CARE, VOLUME 30, NUMBER 8, AUGUST
4 Diabetic nephropathy in Asian Indians Table 3 Multiple logistic regression analysis Dependent variable and parameters Odds ratio (95% CI) P value Overt nephropathy Age ( ) Smoking (yes 1, no 0) ( ) A1C ( ) Duration of diabetes ( ) Systolic blood pressure ( ) Diastolic blood pressure ( ) Microalbuminuria Age ( ) Smoking (yes 1, no 0) ( ) A1C ( ) Duration of diabetes ( ) Systolic blood pressure ( ) Diastolic blood pressure ( ) CONCLUSIONS This, to our knowledge, is the first population-based study from India on the prevalence of, and risk factors for, diabetic nephropathy. The main findings of this study are that in urban Asian Indians 1) prevalence of overt diabetic nephropathy was 2.2% and that of microalbuminuria 26.9% and 2) risk factors for diabetic nephropathy include A1C, duration of diabetes, and systolic blood pressure, while for microalbuminuria smoking and diastolic blood pressure were also risk factors. We compared our prevalence rates with other population-based studies on diabetic nephropathy. Prevalence of nephropathy was extremely high among Nauruans (75% in self-reported KD subjects and 63% in NDD subjects) (20) and Pima Indians (47%) (21). A population-based study in Egypt recorded a prevalence of albuminuria of 21% among KD subjects (22). It had been earlier reported that migrant Indians have a higher prevalence of diabetic nephropathy compared with the host populations (4 6,23). Compared with these studies and others presented in Table 4, our study shows a lower prevalence of diabetic nephropathy. The large differences observed in the prevalence of nephropathy among different studies could be attributed to the differences in study design and methodologies adopted for defining the disease. Many of the studies were clinic based, and this could have introduced a referral bias. In addition, most of these studies have not included retinopathy in the definition for diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy. The strength of our study is that it is population based and has included diabetic retinopathy in the definition with the latter diagnosed using retinal color photography. These differences in methodologies used could probably explain the lower prevalence of overt nephropathy observed in our study. However, one cannot rule out the possibility of true ethnic differences in the prevalence of nephropathy due to decreased susceptibility to microvascular disease in native Asian Indians. In support of this, in an earlier study (24) we had reported that the prevalence of diabetic retinopathy is lower in Indians compared with other ethnic groups. These findings, if confirmed by future studies, would be of great interest, as Asian Indians are known to have much higher rates of premature coronary artery disease compared with other ethnic groups (25). There could be several explanations for the lower prevalence of microvascular complications noted in our studies. It is possible that due to wide publicity of the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial and the U.K. Prospective Diabetes Study results control of diabetes is improving globally, including in India, which could have resulted in lower rates of microvascular complications. Second, the prevalence of hypertension is known to be lower in native south Asians, and this may afford a relative protection against diabetic kidney disease (26). Finally, consequent to the greater awareness of the nephroprotective action of ACEIs and ARBs, usage of these drugs for preventing nephropathy has increased. This could also affect the prevalence rates of nephropathy compared with older studies. These are, however, purely speculative and need to be addressed by future, preferably longitudinal, studies. The criteria used for the diagnosis of Table 4 Prevalence of nephropathy and microalbuminuria in type 2 diabetes in different population-based studies Author (reference) Place, year Sample size, type of study Prevalence of microalbuminuria (criteria) Prevalence of macroalbuminuria (criteria) Bruno et al. (14) Italy, ,574, population based 32.1% ( g/min) 17.6% ( 200 g/min) Gatling et al. (15) Poole, U.K., , population based 7.0% ( 300 mg/g creatinine) Neil et al. (16) Oxford, U.K., , population based 15% ( 40 mg/l) 4% ( 200 mg/l) Wirta et al. (17) Finland, , population based NDD subjects: 29%; KD subjects: NDD subjects: 4%; KD subjects: Collins et al. (18) Western Samoa, % ( mg/24 h) 162, population based NDD subjects: 22.0%; KD subjects: 17.2% ( g/ ml) 7% ( 300 mg/24 h) NDD subjects 3.9%; KD subjects: 6.3% ( 300 g/ml) Klein et al. (19) Wisconsin, , population based 25.9% ( mg/l) 16.0% ( 300 mg/l) Unnikrishnan et al. Chennai, India, ,716, population based 26.9% (albumin excretion: 30 (present study) 299 g/mg of creatinine) 2.2% (albumin excretion 300 g/mg of creatinine in the presence of diabetic retinopathy) 2022 DIABETES CARE, VOLUME 30, NUMBER 8, AUGUST 2007
5 overt nephropathy in this study included retinopathy, as it makes the diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy more specific. However, we compared the risk factors for albuminuria with and without retinopathy to highlight the possible differences in risk factors. Poor glycemic control, long duration of diabetes, and systolic blood pressure were the risk factors for overt nephropathy. This is similar to results reported in several other studies (1,27). In the subset of individuals who had macroalbuminuria without retinopathy (possibly suggestive of nondiabetic renal disease), diastolic blood pressure was the only associated risk factor. Moreover, the fact that the prevalence of this entity was higher among the newly detected diabetic subjects suggests that a significant proportion of these individuals could have nonspecific proteinuria/macroalbuminuria associated with uncontrolled hyperglycemia. However, some may indeed have diabetic nephropathy, as studies have shown that some patients in this category have histological changes of diabetic nephropathy (28,29). The prevalence of microalbuminuria in this study was not remarkably different from that reported in other studies. For microalbuminuria, the risk factors were similar to those for overt nephropathy, but smoking and diastolic blood pressures were additional risk factors. The major limitation of the study is that being an epidemiological study, due to logistic reasons, only one measure of albuminuria was done in spot urine. However, this may not alter the inferences drawn, as most epidemiological studies have only used a single measure. The prevalence of microalbuminuria could, however, have been lower if repeated measurements of albumin were done, as has been shown in clinic-based studies (30). Another limitation is that renal biopsies were not performed, as it is difficult to carry out these procedures in population-based studies due to logistic and ethical reasons. This study is of importance given the growing epidemic of diabetes in India. It is estimated that as of the year 2007, there are 40.9 million diabetic individuals in India (2). The prevalence of overt nephropathy in this study (i.e., 2.2%), when translated into numbers, would imply that 850,000 individuals in India have overt nephropathy. Most patients with macroproteinuria eventually reach ESRD (1,31). The cost of a renal transplant in India is $4,760 U.S. (Rs. 2,00,000), which is unaffordable to the majority of people in India (32). The absolute number of subjects with diabetic nephropathy thus presents an economic burden to both the individual and the society. The large pool of microalbuminuria also suggests that there could be large increases in overt nephropathy with time, unless aggressive control of diabetes and hypertension is initiated. In conclusion, the results of this study suggest that the prevalence of overt diabetic nephropathy in Asian Indians is lower, while that of microalbuminuria is comparable to that reported in other ethnic groups. Risk factors for overt nephropathy are found to be poor glycemic control, long duration of diabetes, and systolic blood pressure, while for microalbuminuria smoking and diastolic blood pressure were additional risk factors. There is an urgent need to launch a national diabetes control program to tackle the potential economic burden due to diabetic nephropathy in India. Acknowledgments The authors thank the Chennai Willingdon Corporate Foundation for their support for the CURES field studies. This is the 45th report from CURES. References 1. Ayodele OE, Alebiosu CO, Salako BL: Diabetic nephropathy: a review of the natural history, burden, risk factors and treatment. J Natl Med Assoc 96: , Sicree R, Shaw J, Zimmet P: Diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance. In Diabetes Atlas. 3rd ed. Gan D, Ed. Kortrijik (Heule), Belgium, International Diabetes Federation, 2006, p Mohan V, Alberti KGMM: Diabetes in the tropics. In International Text Book of Diabetes Mellitus. 2nd ed. Alberti KGMM, Zimmet P, Defronzo RA, Keen H, Eds. Chichester, U.K., John Wiley and Sons, 1997, p Samanta A, Burden AC, Feehally J, Walls J: Diabetic renal disease: differences between Asian and white patients. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 293: , Mather HM, Chaturvedi N, Fuller JH: Mortality and morbidity from diabetes in South Asians and Europeans: 11-year follow-up of the Southall Diabetes Survey, London, UK. Diabet Med 15:53 59, Chandie Shaw PK, Baboe F, van Es LA, van der Vijver JC, van de Ree MA, de Jonge N, Rabelink TJ: South-Asian type 2 diabetic patients have higher incidence and faster progression of renal disease Unnikrishnan and Associates compared with Dutch-European diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 29: , Vijay V, Snehalatha C, Ramachandran A, Viswanathan M: Prevalence of proteinuria in non-insulin dependent diabetes. J Assoc Physicians India 42: , Mohan V, Meera R, Premalatha G, Deepa R, Miranda P, Rema M: Frequency of proteinuria in type 2 diabetes mellitus seen at a diabetes centre in southern India. Postgrad Med J 76: , Deepa M, Pradeepa R, Rema M, Mohan A, Deepa R, Shanthirani S, Mohan V: The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study (CURES): study design and methodology (urban component) (CURES-I). J Assoc Physicians India 51: , The Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus: Report of the Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care 20: , Alberti KG, Zimmet PZ: Definition diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus, provisional report of a WHO Consultation. Diabet Med 15: , Early Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy Study Research Group: Grading diabetic retinopathy from stereoscopic colour fundus photographs: an extension of the modified Airlie House classification. ETDRS report number 10. Ophthalmology 98: , National High Blood Pressure Education Program: The seventh report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. JNC 7 Express. Bethesda, MD, National Heart Lung and Blood Institute Health Information Center, 2003, p Bruno G, Cavallo-Perin P, Bargero G, Borra M, Calvi V, D Errico N, Deambrogio P, Pagano G: Prevalence and risk factors for micro- and macroalbuminuria in an Italian population-based cohort of NIDDM subjects. Diabetes Care 19:43 47, Gatling W, Knight C, Mullee MA, Hill RD: Microalbuminuria in diabetes: a population study of the prevalence and an assessment of three screening tests. Diabet Med 5: , Neil A, Hawkins M, Potok M, Thorogood M, Cohen D, Mann J: A prospective population-based study of microalbuminuria as a predictor of mortality in NIDDM. Diabetes Care 16: , Wirta OR, Pasternack AI, Oksa HH, Mustonen JT, Koivula TA, Helin HJ, Lahde YE: Occurrence of late specific complications in type II (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Complications 9: , 1995 DIABETES CARE, VOLUME 30, NUMBER 8, AUGUST
6 Diabetic nephropathy in Asian Indians 18. Collins VR, Dowse GK, Plehwe WE, Imo TT, Toelupe PM, Taylor HR, Zimmet PZ: High prevalence of diabetic retinopathy and nephropathy in Polynesians of Western Samoa. Diabetes Care 18: , Klein R, Klein BE, Moss SE: Prevalence of microalbuminuria in older-onset diabetes. Diabetes Care 16: , Collins VR, Dowse GK, Finch CF, Zimmet PZ, Linnane AW: Prevalence and risk factors for micro- and macroalbuminuria in diabetic subjects and entire population of Nauru. Diabetes 38: , Nelson RG, Kunzelman CL, Pettitt DJ, Saad MF, Bennett PH, Knowler WC: Albuminuria in type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose tolerance in Pima Indians. Diabetologia 32: , Herman WH, Aubert RE, Engelgau MM, Thompson TJ, Ali MA, Sous ES, Hegazy M, Badran A, Kenny SJ, Gunter EW, Malarcher AM, Brechner RJ, Wetterhall SF, DeStefano F, Smith PJ, Habib M, abd el Shakour S, Ibrahim AS, el Behairy EM: Diabetes mellitus in Egypt: glycaemic control and microvascular and neuropathiccomplications.diabetmed15: , Unnikrishnan RI: Diabetic nephropathy in south Asians. In Type 2 Diabetes in South Asians:Epidemiology, Risk Factors and Prevention. 1st ed. Mohan V, Rao GHR, Eds. New Delhi, India, Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers, 2006, p Rema M, Premkumar S, Anitha B, Deepa R, Pradeepa R, Mohan V: Prevalence of diabetic retinopathy in urban India: the Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study (CURES) Eye Study I. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46: , Reddy KS, Yusuf S: Emerging epidemic of cardiovascular disease in developing countries. Circulation 97: , Bhopal R, Unwin N, White M, Yallop J, Walker L, Alberti KG, Harland J, Patel S, Ahmad N, Turner C, Watson B, Kaur D, Kulkarni A, Laker M, Tavridou A: Heterogeneity of coronary heart disease risk factors in Indian, Pakistani, Bangladeshi, and European origin populations: cross sectional study. Br Med J 319: , Schmitz A, Vaeth M: Microalbuminuria: a major risk factor in non-insulin-dependent diabetes: a 1 year follow-up study of 503 patients. Diabet Med 5: , Olsen S, Mogensen CE: How often is NIDDM complicated with non-diabetic renal disease? An analysis of renal biopsies and the literature. Diabetologia 39: , Premalatha G, Vidhya K, Deepa R, Ravikumar R, Rema M, Mohan V: Prevalence of non-diabetic renal disease in type 2 diabetic patients in a diabetes centre in southern India. J Assoc Physicians India 50: , Vijay V, Seena R, Lalitha S, Snehalata C, Jayaraman M, Ramachandran A: Significance of microalbuminuria at diagnosis of type 2 diabetes. Int J Diab Dev Countries 18:5 6, Marshall SM: Recent advances in diabetic nephropathy. Postgrad Med J 80: , Mani MK: Clinical and epidemiological programme on renal disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 14: , DIABETES CARE, VOLUME 30, NUMBER 8, AUGUST 2007
How To Know If You Have Microalbuminuria
 3 PREVALENCE AND PREDICTORS OF MICROALBUMINURIA IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: A CROSS-SECTIONAL OBSERVATIONAL STUDY Dr Ashok S Goswami *, Dr Janardan V Bhatt**; Dr Hitesh Patel *** *Associate
3 PREVALENCE AND PREDICTORS OF MICROALBUMINURIA IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: A CROSS-SECTIONAL OBSERVATIONAL STUDY Dr Ashok S Goswami *, Dr Janardan V Bhatt**; Dr Hitesh Patel *** *Associate
How To Determine The Prevalence Of Microalbuminuria
 Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences Prevalence of Microalbuminuria in relation to HbA1c among known Type2 Diabetic Patients in Puducherry population Muraliswaran P 1 *,
Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences Prevalence of Microalbuminuria in relation to HbA1c among known Type2 Diabetic Patients in Puducherry population Muraliswaran P 1 *,
Prevalence of Micro and Macrovascular Complications and their Risk Factors in Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus
 44 Journal of the association of physicians of india vol 62 published on 1st of every month 1st june, 2014 review article Prevalence of Micro and Macrovascular Complications and their Risk Factors in Type-2
44 Journal of the association of physicians of india vol 62 published on 1st of every month 1st june, 2014 review article Prevalence of Micro and Macrovascular Complications and their Risk Factors in Type-2
ADVANCE: a factorial randomised trial of blood pressure lowering and intensive glucose control in 11,140 patients with type 2 diabetes
 ADVANCE: a factorial randomised trial of blood pressure lowering and intensive glucose control in 11,140 patients with type 2 diabetes Effects of a fixed combination of the ACE inhibitor, perindopril,
ADVANCE: a factorial randomised trial of blood pressure lowering and intensive glucose control in 11,140 patients with type 2 diabetes Effects of a fixed combination of the ACE inhibitor, perindopril,
How To Know If You Have Microalbuminuria
 HIPPOKRATIA 2013, 17, 4: 337-341 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prevalence of microalbuminuria and risk factor analysis in type 2 diabetes patients in Albania: the need for accurate and early diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy
HIPPOKRATIA 2013, 17, 4: 337-341 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prevalence of microalbuminuria and risk factor analysis in type 2 diabetes patients in Albania: the need for accurate and early diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy
Diabetic nephropathy is detected clinically by the presence of persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria.
 Kidney Complications Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is detected clinically by the presence of persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria. The peak incidence of nephropathy is usually 15-25 years
Kidney Complications Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is detected clinically by the presence of persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria. The peak incidence of nephropathy is usually 15-25 years
Understanding diabetes Do the recent trials help?
 Understanding diabetes Do the recent trials help? Dr Geoffrey Robb Consultant Physician and Diabetologist CMO RGA UK Services and Partnership Assurance AMUS 25 th March 2010 The security of experience.
Understanding diabetes Do the recent trials help? Dr Geoffrey Robb Consultant Physician and Diabetologist CMO RGA UK Services and Partnership Assurance AMUS 25 th March 2010 The security of experience.
Guidelines for the management of hypertension in patients with diabetes mellitus
 Guidelines for the management of hypertension in patients with diabetes mellitus Quick reference guide In the Eastern Mediterranean Region, there has been a rapid increase in the incidence of diabetes
Guidelines for the management of hypertension in patients with diabetes mellitus Quick reference guide In the Eastern Mediterranean Region, there has been a rapid increase in the incidence of diabetes
Prescription Pattern of Anti Hypertensive Drugs used in Hypertensive Patients with Associated Type2 Diabetes Mellitus in A Tertiary Care Hospital
 Research Article Prescription Pattern of Anti Hypertensive Drugs used in Hypertensive Patients with Associated Type2 Diabetes Mellitus in A Tertiary Care Hospital *T. JANAGAN 1, R. KAVITHA 1, S. A. SRIDEVI
Research Article Prescription Pattern of Anti Hypertensive Drugs used in Hypertensive Patients with Associated Type2 Diabetes Mellitus in A Tertiary Care Hospital *T. JANAGAN 1, R. KAVITHA 1, S. A. SRIDEVI
In many diabetes units, people with type
 Renal Microalbuminuria: Screening and management in type 2 diabetes Julia Arundale Introduction In many diabetes units, patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes are screened for proteinuria. Screening for
Renal Microalbuminuria: Screening and management in type 2 diabetes Julia Arundale Introduction In many diabetes units, patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes are screened for proteinuria. Screening for
Diabetes and the Kidneys
 Diabetes and the Kidneys Aim(s) and objective(s) This guideline focuses on the detection, prevention, and management of kidney disease in people with diabetes. The management of end-stage renal disease
Diabetes and the Kidneys Aim(s) and objective(s) This guideline focuses on the detection, prevention, and management of kidney disease in people with diabetes. The management of end-stage renal disease
Diabetic Nephropathy
 Diabetic Nephropathy Kidney disease is common in people affected by diabetes mellitus Definition Urinary albumin excretion of more than 300mg in a 24 hour collection or macroalbuminuria Abnormal renal
Diabetic Nephropathy Kidney disease is common in people affected by diabetes mellitus Definition Urinary albumin excretion of more than 300mg in a 24 hour collection or macroalbuminuria Abnormal renal
Prevalence of Diabetic Retinopathy: A Pilot Study from the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study
 Prevalence of Diabetic Retinopathy: A Pilot Study from the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study Elizabeth J Mayer-Davis, PhD University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill For the SEARCH Study Group, May 2014
Prevalence of Diabetic Retinopathy: A Pilot Study from the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study Elizabeth J Mayer-Davis, PhD University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill For the SEARCH Study Group, May 2014
Risk factors associated with the development of overt nephropathy in type 2 diabetes patients: A 12 years observational study
 Indian J Med Res 136, July 2012, pp 46-53 Risk factors associated with the development of overt nephropathy in type 2 diabetes patients: A 12 years observational study Vijay Viswanathan, Priyanka Tilak
Indian J Med Res 136, July 2012, pp 46-53 Risk factors associated with the development of overt nephropathy in type 2 diabetes patients: A 12 years observational study Vijay Viswanathan, Priyanka Tilak
GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT OF DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY*
 71 GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT OF DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY* Ryuichi KIKKAWA** Asian Med. J. 44(2): 71 75, 2001 Abstract: Diabetic nephropathy is the most devastating complication of diabetes and is now the
71 GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT OF DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY* Ryuichi KIKKAWA** Asian Med. J. 44(2): 71 75, 2001 Abstract: Diabetic nephropathy is the most devastating complication of diabetes and is now the
World Kidney Day 11 March 2010: we must act on diabetic kidney disease
 November 11, 2009 Diabetic kidney disease: Act now or pay later Robert C Atkins and Paul Zimmet For the 2010 International Society of Nephrology/International Federation of Kidney Foundations World Kidney
November 11, 2009 Diabetic kidney disease: Act now or pay later Robert C Atkins and Paul Zimmet For the 2010 International Society of Nephrology/International Federation of Kidney Foundations World Kidney
Frequency of Microalbuminuria in Type 1 Diabetic Children
 Original Article Iran J Pediatr Dec 2009; Vol 19 (No 4), Pp:404-408 Frequency of Microalbuminuria in Type 1 Diabetic Children Zahra Razavi*, MD; Hossein Emad Momtaz, MD; Somayeh Sahari 1. Department of
Original Article Iran J Pediatr Dec 2009; Vol 19 (No 4), Pp:404-408 Frequency of Microalbuminuria in Type 1 Diabetic Children Zahra Razavi*, MD; Hossein Emad Momtaz, MD; Somayeh Sahari 1. Department of
嘉 義 長 庚 醫 院 藥 劑 科 Speaker : 翁 玟 雯
 The Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Sodium Glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus 嘉 義 長 庚 醫 院 藥 劑 科 Speaker : 翁 玟 雯 Diabetes Mellitus : A group of diseases characterized
The Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Sodium Glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus 嘉 義 長 庚 醫 院 藥 劑 科 Speaker : 翁 玟 雯 Diabetes Mellitus : A group of diseases characterized
Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT) Principal Results
 Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT) Principal Results Paul K. Whelton, MB, MD, MSc Chair, SPRINT Steering Committee Tulane University School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine, and
Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT) Principal Results Paul K. Whelton, MB, MD, MSc Chair, SPRINT Steering Committee Tulane University School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine, and
Scottish Diabetes Survey 2014. Scottish Diabetes Survey Monitoring Group
 Scottish Diabetes Survey 2014 Scottish Diabetes Survey Monitoring Group Contents Table of Contents Contents... 2 Foreword... 4 Executive Summary... 6 Prevalence... 8 Undiagnosed diabetes... 21 Duration
Scottish Diabetes Survey 2014 Scottish Diabetes Survey Monitoring Group Contents Table of Contents Contents... 2 Foreword... 4 Executive Summary... 6 Prevalence... 8 Undiagnosed diabetes... 21 Duration
Prevalence of microalbuminuria among sudanese type 2 diabetic patients at elmusbah center at ombadda - omdurman
 IOSR Journal of Pharmacy ISSN: 2250-3013, www.iosrphr.org Volume 2 Issue 5 Sep-Oct. 2012 PP.51-55 Prevalence of microalbuminuria among sudanese type 2 diabetic patients at elmusbah center at ombadda -
IOSR Journal of Pharmacy ISSN: 2250-3013, www.iosrphr.org Volume 2 Issue 5 Sep-Oct. 2012 PP.51-55 Prevalence of microalbuminuria among sudanese type 2 diabetic patients at elmusbah center at ombadda -
Epidemiology of Diabetic Kidney Disease
 Epidemiology of Diabetic Kidney Disease Anne T. Reutens, MBBS, PhD, FRACP a,b, * KEYWORDS Diabetes Prevalence Incidence Microalbuminuria Macroalbuminuria End-stage renal disease KEY POINTS Diabetic kidney
Epidemiology of Diabetic Kidney Disease Anne T. Reutens, MBBS, PhD, FRACP a,b, * KEYWORDS Diabetes Prevalence Incidence Microalbuminuria Macroalbuminuria End-stage renal disease KEY POINTS Diabetic kidney
TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: NEW HOPE FOR PREVENTION. Robert Dobbins, M.D. Ph.D.
 TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: NEW HOPE FOR PREVENTION Robert Dobbins, M.D. Ph.D. Learning Objectives Recognize current trends in the prevalence of type 2 diabetes. Learn differences between type 1 and type
TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: NEW HOPE FOR PREVENTION Robert Dobbins, M.D. Ph.D. Learning Objectives Recognize current trends in the prevalence of type 2 diabetes. Learn differences between type 1 and type
Diabetes Prevention in Latinos
 Diabetes Prevention in Latinos Matthew O Brien, MD, MSc Assistant Professor of Medicine and Public Health Northwestern Feinberg School of Medicine Institute for Public Health and Medicine October 17, 2013
Diabetes Prevention in Latinos Matthew O Brien, MD, MSc Assistant Professor of Medicine and Public Health Northwestern Feinberg School of Medicine Institute for Public Health and Medicine October 17, 2013
PROCEEDINGS DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY: DETECTION AND TREATMENT OF RENAL DISEASE IN PATIENTS WITH DIABETES* Jiten Vora, MA, MD, FRCP ABSTRACT
 DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY: DETECTION AND TREATMENT OF RENAL DISEASE IN PATIENTS WITH DIABETES* Jiten Vora, MA, MD, FRCP ABSTRACT Diabetic nephropathy affects people with either type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus.
DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY: DETECTION AND TREATMENT OF RENAL DISEASE IN PATIENTS WITH DIABETES* Jiten Vora, MA, MD, FRCP ABSTRACT Diabetic nephropathy affects people with either type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus.
The Long-term Effects of Laser Photocoagulation Treatment in Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy
 The Long-term Effects of Laser Photocoagulation Treatment in Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy The Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Follow-up Study Emily Y. Chew, MD, 1 Frederick L. Ferris III, MD,
The Long-term Effects of Laser Photocoagulation Treatment in Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy The Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Follow-up Study Emily Y. Chew, MD, 1 Frederick L. Ferris III, MD,
Microalbuminuria: We are in the midst of an epidemic: the epidemic. So What s a Little Protein? Malcolm s diabetes. How much is too much?
 Focus on CME at the University of Saskatchewan Microalbuminuria: So What s a Little Protein? By Judith T. Klassen, BSc, MD, FRCPC University of Saskatchewan Practical Management of Common Medical Problems
Focus on CME at the University of Saskatchewan Microalbuminuria: So What s a Little Protein? By Judith T. Klassen, BSc, MD, FRCPC University of Saskatchewan Practical Management of Common Medical Problems
Mortality Associated with Diabetes
 Mortality Associated with Diabetes A review paper prepared for the 7th Global Conference of Actuaries, New Delhi, 15-16 February, 2005 Dr. David Muiry, MB;BS, FIA, FASI David_Muiry@swissre.com Introduction
Mortality Associated with Diabetes A review paper prepared for the 7th Global Conference of Actuaries, New Delhi, 15-16 February, 2005 Dr. David Muiry, MB;BS, FIA, FASI David_Muiry@swissre.com Introduction
Awareness and Knowledge of Diabetes in Chennai - The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study [CURES - 9]
![Awareness and Knowledge of Diabetes in Chennai - The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study [CURES - 9] Awareness and Knowledge of Diabetes in Chennai - The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study [CURES - 9]](/thumbs/28/12601472.jpg) Original Article Awareness and Knowledge of Diabetes in Chennai - The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study [CURES - 9] Deepa Mohan*, Deepa Raj*, CS Shanthirani*, Manjula Datta**, NC Unwin***, A Kapur
Original Article Awareness and Knowledge of Diabetes in Chennai - The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study [CURES - 9] Deepa Mohan*, Deepa Raj*, CS Shanthirani*, Manjula Datta**, NC Unwin***, A Kapur
Mortality Assessment Technology: A New Tool for Life Insurance Underwriting
 Mortality Assessment Technology: A New Tool for Life Insurance Underwriting Guizhou Hu, MD, PhD BioSignia, Inc, Durham, North Carolina Abstract The ability to more accurately predict chronic disease morbidity
Mortality Assessment Technology: A New Tool for Life Insurance Underwriting Guizhou Hu, MD, PhD BioSignia, Inc, Durham, North Carolina Abstract The ability to more accurately predict chronic disease morbidity
Absolute cardiovascular disease risk assessment
 Quick reference guide for health professionals Absolute cardiovascular disease risk assessment This quick reference guide is a summary of the key steps involved in assessing absolute cardiovascular risk
Quick reference guide for health professionals Absolute cardiovascular disease risk assessment This quick reference guide is a summary of the key steps involved in assessing absolute cardiovascular risk
Scottish Diabetes Survey
 Scottish Diabetes Survey 2011 Scottish Diabetes Survey Monitoring Group Foreword The Scottish Diabetes Survey 2011 data reflects many aspects of the quality of diabetes care across the whole of Scotland.
Scottish Diabetes Survey 2011 Scottish Diabetes Survey Monitoring Group Foreword The Scottish Diabetes Survey 2011 data reflects many aspects of the quality of diabetes care across the whole of Scotland.
1. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF METABOLIC SYNDROME
 1. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF METABOLIC SYNDROME Izet Aganović, Tina Dušek Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Endocrinology, University Hospital Center Zagreb, Croatia 1 Introduction The metabolic syndrome
1. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF METABOLIC SYNDROME Izet Aganović, Tina Dušek Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Endocrinology, University Hospital Center Zagreb, Croatia 1 Introduction The metabolic syndrome
Prevalence and Risk Factors of Microalbuminuria in Type 2 Diabetic Patients in a Diabetic Clinic of Ardabil-Iran
 Int J Endocrinol Metab 2006; 4: 8-12 Prevalence and Risk Factors of Microalbuminuria in Type 2 Diabetic Patients in a Diabetic Clinic of Ardabil-Iran ORIGINAL ARTICLE Iranparvar Alamdari M, Aminisani N,
Int J Endocrinol Metab 2006; 4: 8-12 Prevalence and Risk Factors of Microalbuminuria in Type 2 Diabetic Patients in a Diabetic Clinic of Ardabil-Iran ORIGINAL ARTICLE Iranparvar Alamdari M, Aminisani N,
Use of Glycated Hemoglobin and Microalbuminuria in the Monitoring of Diabetes Mellitus
 Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Evidence Report/Technology Assessment Number 84 Use of Glycated Hemoglobin and Microalbuminuria in the Monitoring of Diabetes Mellitus Summary Overview Clinical
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Evidence Report/Technology Assessment Number 84 Use of Glycated Hemoglobin and Microalbuminuria in the Monitoring of Diabetes Mellitus Summary Overview Clinical
THE STUDY OF NEWLY DISCOVERED CASES OF DIABETES MELLITUS IN BIHOR COUNTY
 Analele UniversităŃii din Oradea Fascicula:Ecotoxicologie, Zootehnie şi Tehnologii de Industrie Alimentară, 2012 THE STUDY OF NEWLY DISCOVERED CASES OF DIABETES MELLITUS IN BIHOR COUNTY *University of
Analele UniversităŃii din Oradea Fascicula:Ecotoxicologie, Zootehnie şi Tehnologii de Industrie Alimentară, 2012 THE STUDY OF NEWLY DISCOVERED CASES OF DIABETES MELLITUS IN BIHOR COUNTY *University of
Original Article. Risk factors for diabetic retinopathy in selfreported rural population with diabetes
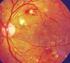 Original Article www.jpgmonline.com Risk factors for diabetic retinopathy in selfreported rural population with diabetes Rani PK, Raman R, Chandrakantan A, Pal SS, Perumal GM, Sharma T Vision Research
Original Article www.jpgmonline.com Risk factors for diabetic retinopathy in selfreported rural population with diabetes Rani PK, Raman R, Chandrakantan A, Pal SS, Perumal GM, Sharma T Vision Research
Albuminuria as a Marker of the Risk of Developing Type 2 Diabetes in Non- Diabetic Aboriginal Australians
 Albuminuria as a Marker of the Risk of Developing Type 2 Diabetes in Non- Diabetic Aboriginal Australians Zhiqiang Wang 1 and Wendy E Hoy 1 Centre for Chronic Disease, Department of Medicine, Central Clinical
Albuminuria as a Marker of the Risk of Developing Type 2 Diabetes in Non- Diabetic Aboriginal Australians Zhiqiang Wang 1 and Wendy E Hoy 1 Centre for Chronic Disease, Department of Medicine, Central Clinical
Aggressive Lowering of Blood Pressure in type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: The Diastolic Cost
 Aggressive Lowering of Blood Pressure in type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: The Diastolic Cost Naftali Stern Institute of Endocrinology, Metabolism and Hypertension Tel Aviv -Sourasky Medical Center and Sackler
Aggressive Lowering of Blood Pressure in type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: The Diastolic Cost Naftali Stern Institute of Endocrinology, Metabolism and Hypertension Tel Aviv -Sourasky Medical Center and Sackler
St Lucia Diabetes and Hypertension Screening and Disease Management Programs
 St Lucia Diabetes and Hypertension Screening and Disease Management Programs Michael Graven, MD, MSc,, MPH, FAAP Health Informatics and Neonatal Pediatrics Dalhousie University Halifax, Nova Scotia CANADA
St Lucia Diabetes and Hypertension Screening and Disease Management Programs Michael Graven, MD, MSc,, MPH, FAAP Health Informatics and Neonatal Pediatrics Dalhousie University Halifax, Nova Scotia CANADA
InDependent Diabetes Trust
 InDependent Diabetes Trust Kidneys and Diabetes Updated July 2015 Registered Company Number 3148360 Registered Charity No 1058284 Contents Introduction Healthy Kidneys Kidney disease and diabetes The use
InDependent Diabetes Trust Kidneys and Diabetes Updated July 2015 Registered Company Number 3148360 Registered Charity No 1058284 Contents Introduction Healthy Kidneys Kidney disease and diabetes The use
The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes The Rapid Evolution and Positive Results of Bariatric Surgery
 The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes The Rapid Evolution and Positive Results of Bariatric Surgery Michael E. Farkouh, MD, MSc Peter Munk Chair in Multinational Clinical Trials Director, Heart and Stroke
The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes The Rapid Evolution and Positive Results of Bariatric Surgery Michael E. Farkouh, MD, MSc Peter Munk Chair in Multinational Clinical Trials Director, Heart and Stroke
Drug Treatment in Type 2 Diabetes with Hypertension
 Hypertension is 1.5 2 times more prevalent in Type 2 diabetes (prevalence up to 80 % in diabetic subjects). This exacerbates the risk of cardiovascular disease by ~ two-fold. Drug therapy reduces the risk
Hypertension is 1.5 2 times more prevalent in Type 2 diabetes (prevalence up to 80 % in diabetic subjects). This exacerbates the risk of cardiovascular disease by ~ two-fold. Drug therapy reduces the risk
Renal Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
 Renal Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus 6th Collaborative DiGP/HSE/UCC Conference 25 th September 2013 Dr. Eoin O Sullivan Consultant Endocrinologist Bon Secours Hospital Cork Case 69 year old woman
Renal Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus 6th Collaborative DiGP/HSE/UCC Conference 25 th September 2013 Dr. Eoin O Sullivan Consultant Endocrinologist Bon Secours Hospital Cork Case 69 year old woman
Improving cardiometabolic health in Major Mental Illness
 Improving cardiometabolic health in Major Mental Illness Dr. Adrian Heald Consultant in Endocrinology and Diabetes Leighton Hospital, Crewe and Macclesfield Research Fellow, Manchester University Metabolic
Improving cardiometabolic health in Major Mental Illness Dr. Adrian Heald Consultant in Endocrinology and Diabetes Leighton Hospital, Crewe and Macclesfield Research Fellow, Manchester University Metabolic
Clinical Research on Lifestyle Interventions to Treat Obesity and Asthma in Primary Care Jun Ma, M.D., Ph.D.
 Clinical Research on Lifestyle Interventions to Treat Obesity and Asthma in Primary Care Jun Ma, M.D., Ph.D. Associate Investigator Palo Alto Medical Foundation Research Institute Consulting Assistant
Clinical Research on Lifestyle Interventions to Treat Obesity and Asthma in Primary Care Jun Ma, M.D., Ph.D. Associate Investigator Palo Alto Medical Foundation Research Institute Consulting Assistant
Using multiple biomarkers to predict renal and cardiovascular drug efficacy: Implications for drug development and registration
 Using multiple biomarkers to predict renal and cardiovascular drug efficacy: Implications for drug development and registration Hiddo Lambers Heerspink Department of Clinical Pharmacology University Medical
Using multiple biomarkers to predict renal and cardiovascular drug efficacy: Implications for drug development and registration Hiddo Lambers Heerspink Department of Clinical Pharmacology University Medical
Prediction of Kidney Disease Progression in Patients with Diabetes
 Prediction of Kidney Disease Progression in Patients with Diabetes John Arthur, MD, PhD Medical University of South Carolina SEKDC Meeting September 8, 2012 Objectives Understand the importance of predicting
Prediction of Kidney Disease Progression in Patients with Diabetes John Arthur, MD, PhD Medical University of South Carolina SEKDC Meeting September 8, 2012 Objectives Understand the importance of predicting
Definition, Prevalence, Pathophysiology and Complications of CKD. JM Krzesinski CHU Liège-ULg Core curriculum Nephrology September 28 th 2013
 Definition, Prevalence, Pathophysiology and Complications of CKD JM Krzesinski CHU Liège-ULg Core curriculum Nephrology September 28 th 2013 KI supplements January 2013 Objectives of the course on CKD:
Definition, Prevalence, Pathophysiology and Complications of CKD JM Krzesinski CHU Liège-ULg Core curriculum Nephrology September 28 th 2013 KI supplements January 2013 Objectives of the course on CKD:
Scottish Diabetes Survey 2013. Scottish Diabetes Survey Monitoring Group
 Scottish Diabetes Survey 2013 Scottish Diabetes Survey Monitoring Group Contents Contents... 2 Foreword... 4 Executive Summary... 6 Prevalence... 8 Undiagnosed diabetes... 18 Duration of Diabetes... 18
Scottish Diabetes Survey 2013 Scottish Diabetes Survey Monitoring Group Contents Contents... 2 Foreword... 4 Executive Summary... 6 Prevalence... 8 Undiagnosed diabetes... 18 Duration of Diabetes... 18
NHS Diabetes Prevention Programme (NHS DPP) Non-diabetic hyperglycaemia. Produced by: National Cardiovascular Intelligence Network (NCVIN)
 NHS Diabetes Prevention Programme (NHS DPP) Non-diabetic hyperglycaemia Produced by: National Cardiovascular Intelligence Network (NCVIN) Date: August 2015 About Public Health England Public Health England
NHS Diabetes Prevention Programme (NHS DPP) Non-diabetic hyperglycaemia Produced by: National Cardiovascular Intelligence Network (NCVIN) Date: August 2015 About Public Health England Public Health England
Appropriate blood pressure control in hypertensive and normotensive type 2 diabetes mellitus: a summary of the ABCD trial
 Appropriate in hypertensive and normotensive type 2 diabetes mellitus: a summary of the ABCD trial Robert W Schrier*, Raymond O Estacio, Philip S Mehler and William R Hiatt SUMMARY The hypertensive and
Appropriate in hypertensive and normotensive type 2 diabetes mellitus: a summary of the ABCD trial Robert W Schrier*, Raymond O Estacio, Philip S Mehler and William R Hiatt SUMMARY The hypertensive and
DRUG UTILIZATION EVALUATION OF ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUGS IN DIABETIC PATIENTS WITH CKD
 WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES Elhami et al. SJIF Impact Factor 5.210 Volume 4, Issue 11, 1159-1166 Research Article ISSN 2278 4357 DRUG UTILIZATION EVALUATION OF ANTIHYPERTENSIVE
WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES Elhami et al. SJIF Impact Factor 5.210 Volume 4, Issue 11, 1159-1166 Research Article ISSN 2278 4357 DRUG UTILIZATION EVALUATION OF ANTIHYPERTENSIVE
Risk factors and complications of type 2 diabetes in Asians
 Risk factors and complications of type 2 diabetes in Asians Rajbharan Yadav, Pramil Tiwari* and Ethiraj Dhanaraj Department of Pharmacy Practice National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research
Risk factors and complications of type 2 diabetes in Asians Rajbharan Yadav, Pramil Tiwari* and Ethiraj Dhanaraj Department of Pharmacy Practice National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research
Prevalence and risk factor of chronic kidney disease in elderly diabetic patients in Korea 성애병원 내과 김정한
 Prevalence and risk factor of chronic kidney disease in elderly diabetic patients in Korea 성애병원 내과 김정한 Introduction CKD의 정의와 egfr의 측정 CKD의 risk factor와 mechanism 한국의 CKD prevalence 와 prognosis CKD의 치료와
Prevalence and risk factor of chronic kidney disease in elderly diabetic patients in Korea 성애병원 내과 김정한 Introduction CKD의 정의와 egfr의 측정 CKD의 risk factor와 mechanism 한국의 CKD prevalence 와 prognosis CKD의 치료와
Proliferative diabetic retinopathy is associated with microalbuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2006) 39: 1033-1039 Diabetic retinopathy and microalbuminuria ISSN 0100-879X 1033 Proliferative diabetic retinopathy is associated with microalbuminuria
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2006) 39: 1033-1039 Diabetic retinopathy and microalbuminuria ISSN 0100-879X 1033 Proliferative diabetic retinopathy is associated with microalbuminuria
Control of hypertension in Nigerians with Diabetes Mellitus: A report of the Ibadan Diabetic / Kidney Disease Study Group.
 Int J Diabetes & Metabolism (2007) 15: 82-86 Control of hypertension in Nigerians with Diabetes Mellitus: A report of the Ibadan Diabetic / Kidney Disease Study Group. Ayodeji Arije, 1 Modupe Kuti, 2 Adesoji
Int J Diabetes & Metabolism (2007) 15: 82-86 Control of hypertension in Nigerians with Diabetes Mellitus: A report of the Ibadan Diabetic / Kidney Disease Study Group. Ayodeji Arije, 1 Modupe Kuti, 2 Adesoji
Higher pulse pressure, systolic arterial hypertension, duration of diabetes and family history of diabetes in Central Africans
 Int J Diabetes & Metabolism (2008) 16: 17-23 Higher pulse pressure, systolic arterial hypertension, duration of diabetes and family history of diabetes in Central Africans Longo- Mbenza B 1, Nkondi Mbadi
Int J Diabetes & Metabolism (2008) 16: 17-23 Higher pulse pressure, systolic arterial hypertension, duration of diabetes and family history of diabetes in Central Africans Longo- Mbenza B 1, Nkondi Mbadi
Treatment of diabetes In order to survive, people with type 1 diabetes must have insulin delivered by a pump or injections.
 National Diabetes Statistics What is diabetes? Diabetes mellitus is a group of diseases characterized by high levels of blood glucose resulting from defects in insulin production, insulin action, or both.
National Diabetes Statistics What is diabetes? Diabetes mellitus is a group of diseases characterized by high levels of blood glucose resulting from defects in insulin production, insulin action, or both.
Diabetes now accounts for ~35% of all new
 hapter 16 Kidney Diseases in Diabetes Robert G. Nelson, MD, MPH; William. Knowler, MD, DrPH; David J. Pettitt, MD; and Peter H. Bennett, MB, FRP, FFM SUMMARY Diabetes now accounts for ~35% of all new cases
hapter 16 Kidney Diseases in Diabetes Robert G. Nelson, MD, MPH; William. Knowler, MD, DrPH; David J. Pettitt, MD; and Peter H. Bennett, MB, FRP, FFM SUMMARY Diabetes now accounts for ~35% of all new cases
Metabolic Syndrome Overview: Easy Living, Bitter Harvest. Sabrina Gill MD MPH FRCPC Caroline Stigant MD FRCPC BC Nephrology Days, October 2007
 Metabolic Syndrome Overview: Easy Living, Bitter Harvest Sabrina Gill MD MPH FRCPC Caroline Stigant MD FRCPC BC Nephrology Days, October 2007 Evolution of Metabolic Syndrome 1923: Kylin describes clustering
Metabolic Syndrome Overview: Easy Living, Bitter Harvest Sabrina Gill MD MPH FRCPC Caroline Stigant MD FRCPC BC Nephrology Days, October 2007 Evolution of Metabolic Syndrome 1923: Kylin describes clustering
PEER REVIEW HISTORY ARTICLE DETAILS TITLE (PROVISIONAL)
 PEER REVIEW HISTORY BMJ Open publishes all reviews undertaken for accepted manuscripts. Reviewers are asked to complete a checklist review form (http://bmjopen.bmj.com/site/about/resources/checklist.pdf)
PEER REVIEW HISTORY BMJ Open publishes all reviews undertaken for accepted manuscripts. Reviewers are asked to complete a checklist review form (http://bmjopen.bmj.com/site/about/resources/checklist.pdf)
HYPERTENSION ASSOCIATED WITH RENAL DISEASES
 RENAL DISEASE v Patients with renal insufficiency should be encouraged to reduce dietary salt and protein intake. v Target blood pressure is less than 135-130/85 mmhg. If patients have urinary protein
RENAL DISEASE v Patients with renal insufficiency should be encouraged to reduce dietary salt and protein intake. v Target blood pressure is less than 135-130/85 mmhg. If patients have urinary protein
C-Reactive Protein and Diabetes: proving a negative, for a change?
 C-Reactive Protein and Diabetes: proving a negative, for a change? Eric Brunner PhD FFPH Reader in Epidemiology and Public Health MRC Centre for Causal Analyses in Translational Epidemiology 2 March 2009
C-Reactive Protein and Diabetes: proving a negative, for a change? Eric Brunner PhD FFPH Reader in Epidemiology and Public Health MRC Centre for Causal Analyses in Translational Epidemiology 2 March 2009
Use of antihypertensive medications in patients with diabetes in Ajman, UAE
 Use of antihypertensive medications in patients with diabetes in Ajman, UAE Mohammed Arifulla 1*, Lisha J John 1, Jayadevan Sreedharan 2, Jayakumary Muttappallymyalil 2, Jenny Cheriathu 3, Sheikh Altaf
Use of antihypertensive medications in patients with diabetes in Ajman, UAE Mohammed Arifulla 1*, Lisha J John 1, Jayadevan Sreedharan 2, Jayakumary Muttappallymyalil 2, Jenny Cheriathu 3, Sheikh Altaf
The Burden of the Complicated Type 2 Diabetes Patient in China. White Paper
 White Paper Catalysts driving successful decisions in life sciences. The Burden of the Complicated Type 2 Diabetes Patient in China by Marco DiBonaventura, Ph.D. Director, Health Economics and Outcomes
White Paper Catalysts driving successful decisions in life sciences. The Burden of the Complicated Type 2 Diabetes Patient in China by Marco DiBonaventura, Ph.D. Director, Health Economics and Outcomes
National Diabetes Fact Sheet, 2011
 National Diabetes Fact Sheet, 2011 FAST FACTS ON DIABETES Diabetes affects 25.8 million people 8.3% of the U.S. population DIAGNOSED 18.8 million people UNDIAGNOSED 7.0 million people All ages, 2010 Citation
National Diabetes Fact Sheet, 2011 FAST FACTS ON DIABETES Diabetes affects 25.8 million people 8.3% of the U.S. population DIAGNOSED 18.8 million people UNDIAGNOSED 7.0 million people All ages, 2010 Citation
Insulin degludec (Tresiba) for the Management of Diabetes: Effectiveness, Value, and Value-Based Price Benchmarks
 Background: Insulin degludec (Tresiba) for the Management of Diabetes: Effectiveness, Value, and Value-Based Price Benchmarks Final Background and Scope November 19, 2015 The Centers for Disease Control
Background: Insulin degludec (Tresiba) for the Management of Diabetes: Effectiveness, Value, and Value-Based Price Benchmarks Final Background and Scope November 19, 2015 The Centers for Disease Control
Albuminuria versus GFR as markers of diabetic CKD progression
 Albuminuria versus GFR as markers of diabetic CKD progression KDIGO Controversies Conference: Diabetic Kidney Disease New Delhi, March 2012 Richard J MacIsaac PhD FRACP Director of Endocrinology & Diabetes,
Albuminuria versus GFR as markers of diabetic CKD progression KDIGO Controversies Conference: Diabetic Kidney Disease New Delhi, March 2012 Richard J MacIsaac PhD FRACP Director of Endocrinology & Diabetes,
Obesity in the United States Workforce. Findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) III and 1999-2000
 P F I Z E R F A C T S Obesity in the United States Workforce Findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) III and 1999-2000 p p Obesity in The United States Workforce One
P F I Z E R F A C T S Obesity in the United States Workforce Findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) III and 1999-2000 p p Obesity in The United States Workforce One
Correspondence to: Rima B Shah (rima_1223@yahoo.co.in) DOI: 10.5455/ijmsph.2013.2.167-172 Received Date: 29.11.2012 Accepted Date: 03.12.
 RESEARCH ARTICLE STUDY OF UTILIZATION PATTERN OF ANTI-HYPERTENSIVE DRUGS IN HYPERTENSIVE DIABETIC PATIENTS WITH OR WITHOUT REDUCED RENAL FUNCTION AT TERTIARY CARE TEACHING HOSPITAL Jay Shah 1, Tejas Khakhkhar
RESEARCH ARTICLE STUDY OF UTILIZATION PATTERN OF ANTI-HYPERTENSIVE DRUGS IN HYPERTENSIVE DIABETIC PATIENTS WITH OR WITHOUT REDUCED RENAL FUNCTION AT TERTIARY CARE TEACHING HOSPITAL Jay Shah 1, Tejas Khakhkhar
Measure #236 (NQF 0018): Controlling High Blood Pressure National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care
 Measure #236 (NQF 0018): Controlling High Blood Pressure National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS, REGISTRY DESCRIPTION: Percentage of patients
Measure #236 (NQF 0018): Controlling High Blood Pressure National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS, REGISTRY DESCRIPTION: Percentage of patients
Deakin Research Online
 Deakin Research Online This is the published version: Cameron, Adrian J., Shaw, J.E. and Zimmet, P.Z. 2003, Diabetes, in Diabetes and kidney disease : time to act, nternational Diabetes Federation, Brussels,
Deakin Research Online This is the published version: Cameron, Adrian J., Shaw, J.E. and Zimmet, P.Z. 2003, Diabetes, in Diabetes and kidney disease : time to act, nternational Diabetes Federation, Brussels,
Managing diabetes in the post-guideline world. Dr Helen Snell Nurse Practitioner PhD, FCNA(NZ)
 Managing diabetes in the post-guideline world Dr Helen Snell Nurse Practitioner PhD, FCNA(NZ) Overview Pathogenesis of T2DM Aims of treatment The place of glycaemic control Strategies to improve glycaemic
Managing diabetes in the post-guideline world Dr Helen Snell Nurse Practitioner PhD, FCNA(NZ) Overview Pathogenesis of T2DM Aims of treatment The place of glycaemic control Strategies to improve glycaemic
Diabetes Mellitus. Melissa Meredith M.D. Diabetes Mellitus
 Melissa Meredith M.D. Diabetes mellitus is a group of metabolic diseases characterized by high blood glucose resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both Diabetes is a chronic,
Melissa Meredith M.D. Diabetes mellitus is a group of metabolic diseases characterized by high blood glucose resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both Diabetes is a chronic,
DCCT and EDIC: The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial and Follow-up Study
 DCCT and EDIC: The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial and Follow-up Study National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What
DCCT and EDIC: The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial and Follow-up Study National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What
The Prevalence and Determinants of Undiagnosed and Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes in Middle-Aged Irish Adults
 The Prevalence and Determinants of Undiagnosed and Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes in Middle-Aged Irish Adults Seán R. Millar, Jennifer M. O Connor, Claire M. Buckley, Patricia M. Kearney, Ivan J. Perry Email:
The Prevalence and Determinants of Undiagnosed and Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes in Middle-Aged Irish Adults Seán R. Millar, Jennifer M. O Connor, Claire M. Buckley, Patricia M. Kearney, Ivan J. Perry Email:
1990 Life Insurance and Diabetes
 ADS Position Statements 1990 Life Insurance and Diabetes John Carter, John Greenway, Royal Prince Alfred Hospital, Concord Hospital and Hornsby Hospital, NSW Page 1 LIFE INSURANCE AND DIABETES MELLITUS
ADS Position Statements 1990 Life Insurance and Diabetes John Carter, John Greenway, Royal Prince Alfred Hospital, Concord Hospital and Hornsby Hospital, NSW Page 1 LIFE INSURANCE AND DIABETES MELLITUS
Incidence of Complications in Insulin-dependent Diabetes Mellitus: A Survival Analysis
 American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright O 1996 by The Johns HopWns University School of Hygiene and Public Health All rights reserved Vol. 143, No. 5 Printed In U.S.A Incidence of Complications in Insulin-dependent
American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright O 1996 by The Johns HopWns University School of Hygiene and Public Health All rights reserved Vol. 143, No. 5 Printed In U.S.A Incidence of Complications in Insulin-dependent
Adherence to insulin therapy at a tertiary care diabetes center in South India
 Original Article: Adherence to insulin therapy at a tertiary care diabetes center in South India M.S. Raut, J. Balasubramanian, R.M. Anjana, R Unnikrishnan, *V. Mohan Abstract To assess patient adherence
Original Article: Adherence to insulin therapy at a tertiary care diabetes center in South India M.S. Raut, J. Balasubramanian, R.M. Anjana, R Unnikrishnan, *V. Mohan Abstract To assess patient adherence
Diabetes mellitus. Lecture Outline
 Diabetes mellitus Lecture Outline I. Diagnosis II. Epidemiology III. Causes of diabetes IV. Health Problems and Diabetes V. Treating Diabetes VI. Physical activity and diabetes 1 Diabetes Disorder characterized
Diabetes mellitus Lecture Outline I. Diagnosis II. Epidemiology III. Causes of diabetes IV. Health Problems and Diabetes V. Treating Diabetes VI. Physical activity and diabetes 1 Diabetes Disorder characterized
Hypertension and Diabetes
 Hypertension and Diabetes C.W. Spellman, D.O., Ph.D., FACOI Professor & Associate Dean Research Dir. Center Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders Texas Tech University Health Science Center Midland-Odessa, Texas
Hypertension and Diabetes C.W. Spellman, D.O., Ph.D., FACOI Professor & Associate Dean Research Dir. Center Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders Texas Tech University Health Science Center Midland-Odessa, Texas
Guidance for Industry Diabetes Mellitus Evaluating Cardiovascular Risk in New Antidiabetic Therapies to Treat Type 2 Diabetes
 Guidance for Industry Diabetes Mellitus Evaluating Cardiovascular Risk in New Antidiabetic Therapies to Treat Type 2 Diabetes U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center
Guidance for Industry Diabetes Mellitus Evaluating Cardiovascular Risk in New Antidiabetic Therapies to Treat Type 2 Diabetes U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center
AusDiab 2005. The Australian Diabetes, Obesity and Lifestyle Study. Tracking the Accelerating Epidemic: Its Causes and Outcomes
 AusDiab 2005 The Australian Diabetes, Obesity and Lifestyle Study Tracking the Accelerating Epidemic: Its Causes and Outcomes AusDiab 2005 The Australian Diabetes, Obesity and Lifestyle Study Tracking
AusDiab 2005 The Australian Diabetes, Obesity and Lifestyle Study Tracking the Accelerating Epidemic: Its Causes and Outcomes AusDiab 2005 The Australian Diabetes, Obesity and Lifestyle Study Tracking
Diabetes mellitus care in Malta
 Diabetes mellitus care in Malta The role of the family doctor Jean K Soler Diabetes mellitus care in Malta The role of the family doctor Aims and objectives of care Aims of diabetes care Avoiding complications
Diabetes mellitus care in Malta The role of the family doctor Jean K Soler Diabetes mellitus care in Malta The role of the family doctor Aims and objectives of care Aims of diabetes care Avoiding complications
Chronic diseases in low and middle income countries: more research or more action? Shah Ebrahim London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine
 Chronic diseases in low and middle income countries: more research or more action? Shah Ebrahim London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine More action needed Overview Growing burden of chronic diseases
Chronic diseases in low and middle income countries: more research or more action? Shah Ebrahim London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine More action needed Overview Growing burden of chronic diseases
Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes
 Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Lipids Hypercholesterolaemia is an important reversible risk factor for cardiovascular disease and should be tackled aggressively in all diabetic patients. In Type 1 patients,
Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Lipids Hypercholesterolaemia is an important reversible risk factor for cardiovascular disease and should be tackled aggressively in all diabetic patients. In Type 1 patients,
Primary prevention of chronic kidney disease: managing diabetes mellitus to reduce the risk of progression to CKD
 Primary prevention of chronic kidney disease: managing diabetes mellitus to reduce the risk of progression to CKD Date written: July 2012 Author: Kate Wiggins, Graeme Turner, David Johnson GUIDELINES We
Primary prevention of chronic kidney disease: managing diabetes mellitus to reduce the risk of progression to CKD Date written: July 2012 Author: Kate Wiggins, Graeme Turner, David Johnson GUIDELINES We
Prognostic impact of uric acid in patients with stable coronary artery disease
 Prognostic impact of uric acid in patients with stable coronary artery disease Gjin Ndrepepa, Siegmund Braun, Martin Hadamitzky, Massimiliano Fusaro, Hans-Ullrich Haase, Kathrin A. Birkmeier, Albert Schomig,
Prognostic impact of uric acid in patients with stable coronary artery disease Gjin Ndrepepa, Siegmund Braun, Martin Hadamitzky, Massimiliano Fusaro, Hans-Ullrich Haase, Kathrin A. Birkmeier, Albert Schomig,
Does Microalbuminuria Predict Diabetic Nephropathy?
 Epidemiology/Health Services/Psychosocial Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Does Microalbuminuria Predict Diabetic Nephropathy? BAHMAN P. TABAEI, MPH ABDUL S. AL-KASSAB, MD, PHD LIZA L. ILAG, MD CATHERINE
Epidemiology/Health Services/Psychosocial Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Does Microalbuminuria Predict Diabetic Nephropathy? BAHMAN P. TABAEI, MPH ABDUL S. AL-KASSAB, MD, PHD LIZA L. ILAG, MD CATHERINE
How To Test For Microalbuminuria
 Original Article Iran J Ped Sep 2007; Vol 17 ( No 3), Pp: 252-256 Evaluation of Microalbuminuria 4 to 6 Years Following Type 1 Diabetes in Children Ali Derakhshan* 1, MD; Mohsen Akhavan 1, MD; Hamdollah
Original Article Iran J Ped Sep 2007; Vol 17 ( No 3), Pp: 252-256 Evaluation of Microalbuminuria 4 to 6 Years Following Type 1 Diabetes in Children Ali Derakhshan* 1, MD; Mohsen Akhavan 1, MD; Hamdollah
The contribution of chronic kidney disease to the global burden of major noncommunicable diseases
 http://www.kidney-international.org & 2011 International Society of Nephrology The contribution of chronic kidney disease to the global burden of major noncommunicable diseases William G. Couser 1, Giuseppe
http://www.kidney-international.org & 2011 International Society of Nephrology The contribution of chronic kidney disease to the global burden of major noncommunicable diseases William G. Couser 1, Giuseppe
Renal Hyperfiltration and the Development of Microalbuminuria in Type 1 Diabetes
 Renal Hyperfiltration and the Development of Microalbuminuria in Type 1 Diabetes The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
Renal Hyperfiltration and the Development of Microalbuminuria in Type 1 Diabetes The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
Clinician Guide: Bridges to Excellence Diabetes Care Recognition Program
 Clinician Guide: Bridges to Excellence Diabetes Care Recognition Program Health Care Incentives Improvement Institute 13 Sugar Street Newtown, CT 06470 bteinformation@bridgestoexcellence.org http://www.hci3.org
Clinician Guide: Bridges to Excellence Diabetes Care Recognition Program Health Care Incentives Improvement Institute 13 Sugar Street Newtown, CT 06470 bteinformation@bridgestoexcellence.org http://www.hci3.org
Adult Diabetes Clinician Guide
 Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Adult Diabetes Clinician Guide Introduction JANUARY 2016 This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2016 National Diabetes Guideline.
Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Adult Diabetes Clinician Guide Introduction JANUARY 2016 This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2016 National Diabetes Guideline.
LATE TRANSITIONAL MORBIDITY: DIABETES COMPLICATIONS
 Diabetes morbidity CHAPTER 7 LATE TRANSITIONAL MORBIDITY: DIABETES COMPLICATIONS 7.1. SUMMARY Introduction This chapter reports multi-state modelling in a guidelines development setting. In the Netherlands
Diabetes morbidity CHAPTER 7 LATE TRANSITIONAL MORBIDITY: DIABETES COMPLICATIONS 7.1. SUMMARY Introduction This chapter reports multi-state modelling in a guidelines development setting. In the Netherlands
definition and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and intermediate hyperglycemia Report of a WHO/IDF Consultation
 definition and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and intermediate hyperglycemia Report of a WHO/IDF Consultation WHO Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data Definition and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and
definition and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and intermediate hyperglycemia Report of a WHO/IDF Consultation WHO Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data Definition and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and
Medical Regimen Adherence in the Management of Diabetes: What Psychologists Need to Know
 Medical Regimen Adherence in the Management of Diabetes: What Psychologists Need to Know Suzanne Bennett Johnson Distinguished Research Professor Florida State University College of Medicine 2012 President,
Medical Regimen Adherence in the Management of Diabetes: What Psychologists Need to Know Suzanne Bennett Johnson Distinguished Research Professor Florida State University College of Medicine 2012 President,
Position Statement Diabetic Nephropathy American Diabetes Association
 Information obtained from the American Diabetes Association 2002 by the American Diabetes Association, Inc. Publication Date January 2002 in Diabetes Care 25:S85-S89, 2002 Edited by the Nephrology Department,
Information obtained from the American Diabetes Association 2002 by the American Diabetes Association, Inc. Publication Date January 2002 in Diabetes Care 25:S85-S89, 2002 Edited by the Nephrology Department,
Diabetes, hypertension and a lot more `in the elderly` JORIS SCHAKEL INTERNIST- CLINICAL GERIATRICIAN JGSCHAKEL@SEHOS.CW
 Diabetes, hypertension and a lot more `in the elderly` JORIS SCHAKEL INTERNIST- CLINICAL GERIATRICIAN JGSCHAKEL@SEHOS.CW IT`S HARD TO GIVE GENERAL ADVICE! ``The Elderly`` Heterogeneous group ;widely varying
Diabetes, hypertension and a lot more `in the elderly` JORIS SCHAKEL INTERNIST- CLINICAL GERIATRICIAN JGSCHAKEL@SEHOS.CW IT`S HARD TO GIVE GENERAL ADVICE! ``The Elderly`` Heterogeneous group ;widely varying
