3D Triculture Model for Evaluating Breast Cancer Progression
|
|
|
- Ralph Thompson
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 3D Triculture Model for Evaluating reast Cancer Progression reast cancer cell lines (MCF7 / MDA-M-231) Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (s) Human adipose-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (s) Application Note Overview Current models for evaluating breast cancer progression lack a comprehensive, physiological approach to modeling the complex tumor microenvironment. There has been much evidence supporting the use of tumor spheroids to mimic tumor physiology. In the outer layers, they exhibit cell-cell bond formation, comparable morphology, elevated cell survival and proliferation; whereas in the inner layers, they have reduced proliferation rates and a hypoxic core. While Multi- Cellular Tumor Spheroids (MCTS) provide a physiological tumor model, other cell types within the surrounding tumor microenvironment are essential for tumor behavior and subsequent cancer progression. The tissue vasculature provides a critical component for tumor progression given the metabolic requirements of a growing tumor and known tumorvascular interactions, and by incorporating endothelial tubules with the MCTS, we are able to model interactions between vascular networks and growing tumors. At the same time, there is also an important stromal component involved in cancer progression where stromal cells have been shown to promote cell proliferation, dissemination, and drug resistance during cancer development. y using extracellular matrix proteins, we are able to promote the proper physiology for each of these cell types and assess their activities. To evaluate interactions, each cell type is fluorescently labeled with fluorophores with different excitation and emission spectra; MCF7 and MDA-M-231, human breast cancer cell lines, express a red fluorescence protein, while human umbilical vein endothelial cells (s) and human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (s) are labeled with stable lipophilic membrane dyes. MCTS are formed using low adhesion microwells and deposited into fully formed tubular networks, and the s are then added within a hydrogel overlay matrix. Cellular interactions and dissemination are monitored via fluorescence microscopy, and breast cancer cell proliferation is monitored using a fluorescence plate reader. The breast cancer MCTS exhibit cell-cell interactions with endothelial tubules and stromal cells, and there is an increase in both cell proliferation and invasion over standard spheroid monoculture model.
2 ackground Many anticancer drugs fail in human trials despite showing efficacy in in vitro studies and in animal models. It has become clear that the in vitro assays involving 2D monoculture do not reflect the complex cellular and matrix microenvironment of the tumor tissue, and this may explain the failure of 2D models to predict clinical efficacy (1). The 3D environment of the tumor has a different architecture; cells are adherent on all surfaces; there is stiffness to the matrix; and the matrix is tumorspecific and unique (2,3). Furthermore, it is well known that by changing the in vitro culture conditions to accommodate some of these aspects of the tumor microenvironment, the biological response of the cells is altered (4-6). Development of an in vitro screen that exhibits the physiology of the tumor will provide a more accurate assessment of candidate drugs for cancer therapy, saving time and money for drug development and delivering more effective therapies for patients. The ideal model would incorporate extracellular matrix, cellular, and biochemical components that are present in tumor tissues. Extracellular matrix proteins provide specific structural and cell binding motifs that direct gene expression determining protein production, attachment, morphology, motility, and survival (7). The basement membrane underlies epithelial and endothelial tissues while collagen is the primary component of the mesenchyme. asement membrane extract (ME) promotes a tumor phenotype while collagen I promotes a motile phenotype (8). asement membrane proteins can be used to promote assembly of multicellular tumor spheroids (MCTS), Figures 1A-1D, that exhibit the appropriate size and structure to create the physiological gradients present in tumors providing a more predictive response, and mixtures of ME and collagen I may be used to model a metastasizing tumor (9,10). Similarly, these proteins direct the assembly of endothelial cells into vascular, tubule networks, Figure 1C, giving rise to in vivo structure and function (11-13). The addition of endothelial cells and other cell types provide factors that influence tumor cell behavior. For example, studies with cocultures on ME have already shown that breast cancer cells are more invasive when either resident adipose-derived stem cells, Figure 1D, or macrophages are present (14,15) and that stromal cells increase proliferation (16). Tumor microenvironments also exhibit acidity (low ph), hypoxia (low O2), and low glucose concentrations (17,18). y incorporating all of these elements into one model, we can more accurately recapitulate the tumor microtissue to provide a more predictive model for evaluating drug response.
3 2D Culture 3D Culture Cell Line Fig 1. The morphology for different cell types are more physiological in 3D than 2D culture. In 2D culture, breast cancer cells, MDA-M-231 (A) and (C), grow in clusters and exhibit a cobblestone morphology, similar to s (E) and (G). In 3D culture, breast cancer MCTS, MDA-M-231 () and (D), most accurately depict tumors based on size and the establishment of physiological gradients. s form tubules representative of vascular networks (F), and s form branching structures (H).
4 A Cell Lines Cancer Cells s s RFP Neuro-DiO Di Merge I 14,000 12,000 C RFU 10,000 8,000 6,000 4,000 2,000 D J -,,,, E 8,000 7,000 6,000 F G H RFU 5,000 4,000 3,000 2,000 1,000 0,,,, Fig 2. Coculture of breast cancer cells, s, and s during MCTS formation increases breast cancer cell proliferation. MCTS were formed in 96 well low adhesion plates using breast cancer cells (2,000 cells/well); s (500 cells/well); and/ or s (500 cells/well) over a 72 hour period. (A-D) and MDA-M-231 (E-H) expressed red fluorescent protein; s (,D,F,H) were labeled with Neuro-DiO (green); and s (C,D,G,H) were labeled with Di (blue). Plates were read in a 96 well plate reader at excitation 540 nm/ 587 nm emission to compare proliferation of (I) and MDA- M-231 (J). P < 0.05, P < 0.01.
5 A Cell Lines C D E F G H Fig 3. Coculture of reast Cancer Cells,, and for MCTS formation and subsequent invasion into ECM hydrogels demonstrate that MCTS containing promote a more physiological phenotype. MCTS were formed in 96 well low adhesion plates using breast cancer cells (2,000 cells/well); s (500 cells/well); and/or s (500 cells/well) over a 72 hour period. MCTS were then embedded within an ECM hydrogel to facilitate cell invasion over 96 hours. (A-D) and MDA-M-231 (E-H) expressed red fluorescent protein; s (,D,F,H) were labeled with Neuro-DiO (green); and (C,D,G,H) were labeled with Di (blue).
6 Cell Lines right Cancer Cells s s Field RFP Neuro-DiO Di Merge A C D E F G H I FU J 500, , , , , ,000 (µm 2 )
7 F G H I RFU K ,,,, Area (µm 2 ) J L 500, , , , , , , , ,000 50,000 -,,,, RFU ,,,, Area (µm 2 ) 1,600,000 1,400,000 1,200,000 1,000, , , , ,000 0,,,, Fig 4. Tricultures of MCTS,, and endothelial tubules increase proliferation and invasion for breast cancer spheroids. MCTS were generated by culturing breast cancer cells (2,000 cells/well) at 37 C under hypoxia in 96 well, ultra-low adhesion plates for 72 hours. Then 96 well, flat bottom plates were coated with 50 µl of tubule formation matrix and incubated for one hour at 37 C, 5% CO2 to polymerize hydrogel. For s, 12,500 cells were added to each well (,D,F,H), and for remaining samples, EGM-2 was added. s were allowed to assemble into tubules for two hours. One MCTS, (A-D) or MDA-M-231 (E-F), was transferred to each of the wells in the plate containing tubules. MCTS were allowed to settle for one hour. At this time, 100 µl of medium was aspirated from each well. s were suspended in invasion matrix (10,000 cells/ml), and 50 µl was added to each well (C,D,G,H). For the remaining samples, 50 µl of tumor aligned Invasion Matrix was added to each well. The plates were then incubated at 37 C, 5% CO2 for one hour to polymerize hydrogel, and 100 µl of tumor aligned RPMI, 10% FS as added to each well. Cultures were conducted under hypoxia for 96 hours and photographed using bright field, TRITC, FITC, and DAPI filters (A-H), and photographs were analyzed using ImageJ to determine MCTS area (J and L). Plates were then read in a 96 well plate reader at excitation 540 nm/ 587 nm emission to compare proliferation of breast cancer cells (I and K). P < 0.05, P < 0.01.
8 right s s Field Neuro-DiO Di Merge A C + D + Fig 5. s and s colocalize in 3D culture suggesting a role for s to support and stabilize tubules. 96 well plates were coated with 50 µl of ME hydrogel and polymerized for one hour at 37 C. s were seeded at 15,000 cells/well (A, C, D), and s were seeded at 3,000 cells/well (, C, D). When were added first (A, C) tubules would form, and colocalized with s (C). When s were added first, there was no tubule formation (, D); however, s colocalized with (D).
9 A Day 0 right Cancer Cells s s Field RFP Neuro-DiO Di Merge Fig 6. Tricultures of MCTS,, and endothelial tubules produce physiological breast cancer niche with tumor growth, tumor invasion, and endothelial recruitment. MCTS were generated by culturing breast cancer cells (2,000 cells/well) and s (500 cells/well) at 37 C under hypoxia in 96 well, ultra-low adhesion plates for 72 hours. Then 96 well, flat bottom plates were coated with 50 µl of tubule formation matrix and incubated for one hour at 37 C, 5% CO2 to polymerize hydrogel. s (at 12,500 cells/ml) were added to each well and were allowed to assemble into tubules for two hours. s (1,000 cells/well) were added to networks, and incubate for one hour. Then one MCTS was transferred to each well in the 96 well, flat bottom plate. MCTS were allowed to settle for one hour. At this time, 100 µl of medium was aspirated from each well, and 50 µl of Tumor Aligned Invasion Matrix was added to each well. The plates were then incubated at 37 C, 5% CO2 for one hour to polymerize hydrogel, and 100 µl of Tumor Aligned RPMI, 10% FS as added to each well. Tricultures were conducted under hypoxia and photographed using bright field, TRITC, FITC, and DAPI filters (A and ) at days 0, 4, and 10.
10 Summary y properly mimicking the tumor extracellular environment and cellular architecture, breast cancer Multi-Cellular Tumor Spheroids (MCTS), endothelial tubules, and stromal cells coordinate a physiological response and provide a more predictable model for evaluating clinical efficacy for known effective cancer agents. In developing a functional model, we made the following determinations: s and s provide factors that promote breast cancer proliferation and invasion: s and/or s promote proliferation for (Figure 2A), and s with or without promote proliferation of MDA-M-231 (Figure 2). When MCTS were embedded in an invasion matrix, MCTS containing s promote lobule formation for and an invasive morphology for MDA-M-231 while there was little discernable difference for MCTS containing s (Figure 3). For both and MDA-M-231 cells, the incorporation of both tubules and dispersed increased both proliferation and invasion (Figure 4). Direct cell-cell interactions are necessary to elicit the physiological phenotypes: Dispersed s (Figure 4) did not induce the same phenotypic properties as experiments where the s were incorporated into the MCTS (Figure 3). tubules without appeared quiescent (Figure 4). s and s demonstrated an affinity for colocalization, and adding s directly to preformed networks yielded the desired tubule phenotype (Figure 5). Incorporation of s into the MCTS and endothelial tubules, separately, provided a more dynamic model, allowing for invasion and proliferation of MCTS with a more physiological tumor phenotype, as well as recruitment of endothelial tubules (Figure 6).
11 A A A C D E F G C D E F G Spheroid Formation Medium Tubule Formation Medium Tumor Aligned Medium Tubule Formation Matrix Spheroid Invasion Matrix Formation Medium Tubule Mesenchymal Formation Stem Medium Cells Cancer Tumor Aligned Cells Medium Endothelial Tubule Formation Cells Matrix Spheroid Invasion Matrix Formation Medium Tubule Mesenchymal Formation Stem Medium Cells Tumor Cancer Aligned Cells Medium Tubule Endothelial Formation Cells Matrix Invasion Matrix Mesenchymal Stem Cells Cancer Cells Endothelial Cells C D E F G J I H J I H J I H Figure 7. The stepwise process for the 3D triculture assay for evaluating breast cancer progression: (1) reast cancer cells and s in Spheroid Formation Medium are seeded in a low adhesion plate.(2) Over the course of 72 hours MCTS spontaneously assemble.(3) s form networks on tubule formation matrix over a two hour period. s are added to networks to form tubules.(4) MCTS are transferred on top of the tubules. (5) The MCTS and tubules are embedded in a tumor aligned invasion matrix. (6) Tumor aligned medium with or without treatment is added to culture. (7) Triculture is conducted under hypoxia. reast cancer cells proliferate and invade; tubules are recruited. (8) Tricultures may be evaluated for spheroid invasion and/or high content screening using microscopy. (9) Tricultures may be evaluated for breast cancer MCTS proliferation by evaluating fluorescence intensity in a plate reader.
12 References Joyce, JA, Pollard JW. Microenvironmental regulations of metastasis Nature Rev. Cancer 9: , utcher DT, Alliston T, Weaver, VM. A tense situation: forcing tumour progression. Nature Rev. Cancer 9: , Paszek MJ, Zahir N, Johnson KR et al Tensional homeostasis and the malignant phenotype. Cancer Cell 8: , Nguyen-Ngoc KV, Cheung KJ, renot A, Shamir, Er et al. ECM microenvironment regulates collective migration and local dissemination in normal and malignant mammary epithelium. PNAS 109:E , 2012 Price DJ, Miralem T, Jiang S, Steinberg R, Avraham H. role of vascular endothelial growth factor in the stimulation of cellular invasion and signaling of breast cancer cells. Cell Growth Diff 12: , Miralem, T, Steinberg R, Price D, Avraham H. VEGF 165 requires extracellular matrix componenets to induce mitogenic effects and migratory response in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 20: , enton, G., George, J., Kleinman, H.K., Arnaoutova, I. Advancing science and technology via 3D culture on basement membrane matrix. J. Cellul. Physiol., 221:18-25, enton, G., Crooke E, George, J. Laminin-1 induces E-cadherin expression in 3-dimensional cultured breast cancer cells by inhibiting DNA methyltransferase 1 and reversing promoter methylation status. FASE J 23: , Vinci, M.M., Advances in establishment and analysis of 3D tumour spheroid-based functional assays for target validation and drug evaluation. MC iology, (1): p. 29. Sutherland, R.M., et al., Oxygenation and Differentiation in Multicellular Spheroids of Human Colon Carcinoma. Cancer Research, (10): p Arnaoutova, I., George, J., Kleinman, H.K., and enton, G. The endothelial cell tube formation assay on basement membrane turns 20. Angiogenesis, 12: , Arnaoutova, I. and Kleinman H.K. In vitro angiogenesis: endothelial cell tube formation on a gelled basement membrane extract. Nature Protocols 5: , Arnaoutova, I., Kleinman, H.K., George, J., and enton, G. The in vitro endothelial cell tube formation assay in 3D culture on gelled basement membrane extract. In Textbook of Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis: Methods and Applications, edited by E. Zudaire Ubani and F. Cuttitta, in press, Pinilla S, Alt E, Khalek FJA, Jotzu C, et al Tissue resident stem cells produce CCL5 under the influence of cancer cells and thereby promote breast cancer invasion. Cancer Lett. 284:80-85, Hagemann T, Robinson SC, Schultz, M, Trumper L et al. Enhanced invasion of breast cancer cell lines upon co-cultivation with macrophages is due to TNF-alpha dependent up-regulation of matrix metalloproteinases. Carcinogenesis 25: , Sasser KA, Mundy L, Smith KM, Studebaker AW, et al. Human bone marrow stromal cells enhance breast cancer cell growth rates in a cell linedependent manner with evaluated in 3D tumor environments. Cancer Lett 254: , Dai Y, Kyungmi, Seimann DW. Impact of hypoxia on the metastatic potential of human prostate cancer cells. Int. J Radiation Oncolongy1-8, Ryu MH, Park HM, Chung J, Lee, CH, Park HR. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha mediates oral squamous cell carcinoma invasion via upregulations of alpha 5 integrin and fibronectin. iochem iophys Res Commun. 393:11-15,
CytoSelect 48-Well Cell Adhesion Assay (ECM Array, Fluorometric Format)
 Product Manual CytoSelect 48-Well Cell Adhesion Assay (ECM Array, Fluorometric Format) Catalog Number CBA-071 CBA-071-5 48 assays 5 x 48 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures
Product Manual CytoSelect 48-Well Cell Adhesion Assay (ECM Array, Fluorometric Format) Catalog Number CBA-071 CBA-071-5 48 assays 5 x 48 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures
CytoSelect 48-Well Cell Adhesion Assay (ECM Array, Colorimetric Format)
 Product Manual CytoSelect 48-Well Cell Adhesion Assay (ECM Array, Colorimetric Format) Catalog Number CBA-070 CBA-070-5 48 assays 5 x 48 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures
Product Manual CytoSelect 48-Well Cell Adhesion Assay (ECM Array, Colorimetric Format) Catalog Number CBA-070 CBA-070-5 48 assays 5 x 48 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures
Cell Migration, Chemotaxis and Invasion Assay Protocol
 Cell Migration, Chemotaxis and Invasion Assay Protocol Hilary Sherman, Pilar Pardo and Todd Upton Corning Life Sciences 900 Chelmsford Street Lowell, MA 01851 Introduction Cell migration, the movement
Cell Migration, Chemotaxis and Invasion Assay Protocol Hilary Sherman, Pilar Pardo and Todd Upton Corning Life Sciences 900 Chelmsford Street Lowell, MA 01851 Introduction Cell migration, the movement
Cancer SBL101. James Gomes School of Biological Sciences Indian Institute of Technology Delhi
 Cancer SBL101 James Gomes School of Biological Sciences Indian Institute of Technology Delhi All Figures in this Lecture are taken from 1. Molecular biology of the cell / Bruce Alberts et al., 5th ed.
Cancer SBL101 James Gomes School of Biological Sciences Indian Institute of Technology Delhi All Figures in this Lecture are taken from 1. Molecular biology of the cell / Bruce Alberts et al., 5th ed.
Radius 24-Well Cell Migration Assay (Laminin Coated)
 Product Manual Radius 24-Well Cell Migration Assay (Laminin Coated) Catalog Number CBA-125-LN 24 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cell migration is a highly
Product Manual Radius 24-Well Cell Migration Assay (Laminin Coated) Catalog Number CBA-125-LN 24 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cell migration is a highly
Department of BioScience Technology Chung Yuan Christian University 2015/08/13
 Department of BioScience Technology Chung Yuan Christian University 2015/08/13 Cancer Cells Cancer, the 1st leading cause of death, is an example of a disease that arises from abnormalities in cell function
Department of BioScience Technology Chung Yuan Christian University 2015/08/13 Cancer Cells Cancer, the 1st leading cause of death, is an example of a disease that arises from abnormalities in cell function
Empower 3D cell culture with simplicity and versatility. VitroGel TM 3D. a ready-to-use hydrogel system for 3D cell culture and beyond
 Empower 3D cell culture with simplicity and versatility VitroGel TM 3D a ready-to-use hydrogel system for 3D cell culture and beyond VitroGel TM 3D is an animal origin-free polysaccharide hydrogel system
Empower 3D cell culture with simplicity and versatility VitroGel TM 3D a ready-to-use hydrogel system for 3D cell culture and beyond VitroGel TM 3D is an animal origin-free polysaccharide hydrogel system
HyStem. Hydrogels CELLULAR MATRICES FOR TRANSLATIONAL RESEARCH. esibio.com
 HyStem Hydrogels CELLULAR MATRICES FOR TRANSLATIONAL RESEARCH HyStem Hydrogel Extracellular Matrices Chemically-defined For use in 2D and 3D formats in vitro and in vivo applications Customizable for many
HyStem Hydrogels CELLULAR MATRICES FOR TRANSLATIONAL RESEARCH HyStem Hydrogel Extracellular Matrices Chemically-defined For use in 2D and 3D formats in vitro and in vivo applications Customizable for many
Modulating Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Myotubes:
 icell Skeletal Myoblasts Application Protocol Introduction Modulating Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Myotubes: Insulin Induction with Bioluminescent Glucose Uptake Analysis The skeletal muscle is one of the
icell Skeletal Myoblasts Application Protocol Introduction Modulating Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Myotubes: Insulin Induction with Bioluminescent Glucose Uptake Analysis The skeletal muscle is one of the
Fighting the Battles: Conducting a Clinical Assay
 Fighting the Battles: Conducting a Clinical Assay 6 Vocabulary: In Vitro: studies in biology that are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings
Fighting the Battles: Conducting a Clinical Assay 6 Vocabulary: In Vitro: studies in biology that are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings
BD PuraMatrix Peptide Hydrogel
 BD PuraMatrix Peptide Hydrogel Catalog No. 354250 Guidelines for Use FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY NOT FOR CLINICAL, DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE SPC-354250-G rev 2.0 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Intended Use... 2 Materials
BD PuraMatrix Peptide Hydrogel Catalog No. 354250 Guidelines for Use FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY NOT FOR CLINICAL, DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE SPC-354250-G rev 2.0 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Intended Use... 2 Materials
Cell Viability Assays: Microtitration (MTT) Viability Test Live/Dead Fluorescence Assay. Proliferation Assay: Anti-PCNA Staining
 Cell Viability Assays: Microtitration (MTT) Viability Test Live/Dead Fluorescence Assay Proliferation Assay: Anti-PCNA Staining Spring 2008 1 Objectives To determine the viability of cells under different
Cell Viability Assays: Microtitration (MTT) Viability Test Live/Dead Fluorescence Assay Proliferation Assay: Anti-PCNA Staining Spring 2008 1 Objectives To determine the viability of cells under different
Biotechnology. Srivatsan Kidambi, Ph.D.
 Stem Stem Cell Cell Engineering-What, Biology and it Application Why, How?? to Biotechnology Srivatsan Kidambi, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering University of
Stem Stem Cell Cell Engineering-What, Biology and it Application Why, How?? to Biotechnology Srivatsan Kidambi, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering University of
3D Cell Culture mimsys G
 3D Cell Culture mimsys G xeno-free & nutrient permeable hydrogel for 3D cell culture mimsys G is a xeno-free and non-immunogenic, easy to handle hydrogel for cell encapsulation in 3D experiments in vitro
3D Cell Culture mimsys G xeno-free & nutrient permeable hydrogel for 3D cell culture mimsys G is a xeno-free and non-immunogenic, easy to handle hydrogel for cell encapsulation in 3D experiments in vitro
LESSON 3.5 WORKBOOK. How do cancer cells evolve? Workbook Lesson 3.5
 LESSON 3.5 WORKBOOK How do cancer cells evolve? In this unit we have learned how normal cells can be transformed so that they stop behaving as part of a tissue community and become unresponsive to regulation.
LESSON 3.5 WORKBOOK How do cancer cells evolve? In this unit we have learned how normal cells can be transformed so that they stop behaving as part of a tissue community and become unresponsive to regulation.
Types of Cancers [-oma growth ]!
![Types of Cancers [-oma growth ]! Types of Cancers [-oma growth ]!](/thumbs/27/10363750.jpg) Cancer: disease of transcription factors and replication 1 Uncontrolled cell growth and division -> immortalized cells -> tumor growth -> metastasis (cells float away from tumor and spread throughout the
Cancer: disease of transcription factors and replication 1 Uncontrolled cell growth and division -> immortalized cells -> tumor growth -> metastasis (cells float away from tumor and spread throughout the
Cryoinjury of Breast Cancer Cells in Tissue Equivalent Constructs
 Cryoinjury of Breast Cancer Cells in Tissue Equivalent Constructs Bumsoo Han Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of Texas at Arlington Cryosurgery Minimally invasive surgical
Cryoinjury of Breast Cancer Cells in Tissue Equivalent Constructs Bumsoo Han Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of Texas at Arlington Cryosurgery Minimally invasive surgical
Z-Stacking and Z-Projection using a Scaffold-based 3D Cell Culture Model
 A p p l i c a t i o n N o t e Z-Stacking and Z-Projection using a Scaffold-based 3D Cell Culture Model Brad Larson and Peter Banks, BioTek Instruments, Inc., Winooski, VT Grant Cameron, TAP Biosystems
A p p l i c a t i o n N o t e Z-Stacking and Z-Projection using a Scaffold-based 3D Cell Culture Model Brad Larson and Peter Banks, BioTek Instruments, Inc., Winooski, VT Grant Cameron, TAP Biosystems
Measuring Cell Viability/Cytotoxicity: Cell Counting Kit-F
 Introduction The Cell Counting Kit-F is a fluorometic assay for the determination of viable cell numbers. Calcein-AM in this kit passes through the cell membrane and is hydrolized by the esterase in the
Introduction The Cell Counting Kit-F is a fluorometic assay for the determination of viable cell numbers. Calcein-AM in this kit passes through the cell membrane and is hydrolized by the esterase in the
Osteoblast Differentiation and Mineralization
 Osteoblast Differentiation and Mineralization Application Note Background Osteoblasts are specialized fibroblasts that secrete and mineralize the bone matrix. They develop from mesenchymal precursors.
Osteoblast Differentiation and Mineralization Application Note Background Osteoblasts are specialized fibroblasts that secrete and mineralize the bone matrix. They develop from mesenchymal precursors.
5 Reasons Cancer Researchers Adopt 3D Cell Culture: A Review of Recent Literature
 5 Reasons Cancer Researchers Adopt 3D Cell Culture: A Review of Recent Literature Summary Numerous cancer model systems are available to investigate disease mechanisms and to screen therapies. While all
5 Reasons Cancer Researchers Adopt 3D Cell Culture: A Review of Recent Literature Summary Numerous cancer model systems are available to investigate disease mechanisms and to screen therapies. While all
Mitochondria Organelle Transplantation: The Mitochondrion, An Intracellular Organelle for Cell-Based Therapy Opinion Commentary
 Mitochondria Organelle Transplantation: The Mitochondrion, An Intracellular Organelle for Cell-Based Therapy Opinion Commentary R. L. Elliott, X.P. Jiang, J. F. Head Elliott-Baucom-Head Breast Cancer Research
Mitochondria Organelle Transplantation: The Mitochondrion, An Intracellular Organelle for Cell-Based Therapy Opinion Commentary R. L. Elliott, X.P. Jiang, J. F. Head Elliott-Baucom-Head Breast Cancer Research
3D Cell Culture Systems
 3D Cell Culture Systems Marshall J. Kosovsky, Ph.D. BD Biosciences February 16, 2011 Topics for Discussion Overview of Cell Culture Systems: 2D vs. 3D Extracellular Matrix (ECM) Proteins Epithelial cell
3D Cell Culture Systems Marshall J. Kosovsky, Ph.D. BD Biosciences February 16, 2011 Topics for Discussion Overview of Cell Culture Systems: 2D vs. 3D Extracellular Matrix (ECM) Proteins Epithelial cell
Basic Science in Medicine
 Medical Journal of th e Islamic Republic of Iran Volume 18 Number 3 Fall 1383 November 2004 Basic Science in Medicine ] EXPANSION OF HUMAN CORD BLOOD PRIMITIVE PROGENITORS IN SERUM-FREE MEDIA USING HUMAN
Medical Journal of th e Islamic Republic of Iran Volume 18 Number 3 Fall 1383 November 2004 Basic Science in Medicine ] EXPANSION OF HUMAN CORD BLOOD PRIMITIVE PROGENITORS IN SERUM-FREE MEDIA USING HUMAN
What is Cancer? Cancer is a genetic disease: Cancer typically involves a change in gene expression/function:
 Cancer is a genetic disease: Inherited cancer Sporadic cancer What is Cancer? Cancer typically involves a change in gene expression/function: Qualitative change Quantitative change Any cancer causing genetic
Cancer is a genetic disease: Inherited cancer Sporadic cancer What is Cancer? Cancer typically involves a change in gene expression/function: Qualitative change Quantitative change Any cancer causing genetic
Our body is a community of
 Fundamental Understandings Tumor cells roam the body by evading the controls that keep normal cells in place. That fact offers clues to fighting cancer by Erkki Ruoslahti Our body is a community of cells,
Fundamental Understandings Tumor cells roam the body by evading the controls that keep normal cells in place. That fact offers clues to fighting cancer by Erkki Ruoslahti Our body is a community of cells,
GASTRIC ORGANOID CULTURE PROTOCOL
 GASTRIC ORGANOID CULTURE PROTOCOL THIS PROTOCOL PROVIDES THE PROCEDURE FOR SUBCULTURING NORMAL HUMAN GASTRIC ORGANOIDS WHICH WAS DERIVED FROM THE SUBMERGED METHOD AS DESCRIBED IN BARKER N, ET AL. LGR5+VE
GASTRIC ORGANOID CULTURE PROTOCOL THIS PROTOCOL PROVIDES THE PROCEDURE FOR SUBCULTURING NORMAL HUMAN GASTRIC ORGANOIDS WHICH WAS DERIVED FROM THE SUBMERGED METHOD AS DESCRIBED IN BARKER N, ET AL. LGR5+VE
CFSE Cell Division Assay Kit
 CFSE Cell Division Assay Kit Item No. 10009853 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 4 Precautions
CFSE Cell Division Assay Kit Item No. 10009853 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 4 Precautions
Cell, Tissue and Tumor Kinetics
 Cell, issue and umor Kinetics Proliferation Kinetics: rate of growth of a population, change in total cell number. Adult tissues are in homeostasis. Children (and tumors) grow. I. Quantitative Assessment
Cell, issue and umor Kinetics Proliferation Kinetics: rate of growth of a population, change in total cell number. Adult tissues are in homeostasis. Children (and tumors) grow. I. Quantitative Assessment
Chondrogenical Differentiation of Umbilical Cord Lining. Stem Cells
 Chondrogenical Differentiation of Umbilical Cord Lining Stem Cells He Xi, Masilamani Jeyakumar, Phan Toan Thang Bioengineering, National University of Bioengineering Abstract Cartilage defects, such as
Chondrogenical Differentiation of Umbilical Cord Lining Stem Cells He Xi, Masilamani Jeyakumar, Phan Toan Thang Bioengineering, National University of Bioengineering Abstract Cartilage defects, such as
Related topics: Application Note 27 Data Analysis of Tube Formation Assays.
 Tube Formation Assays in µ-slide Angiogenesis Related topics: Application Note 27 Data Analysis of Tube Formation Assays. Contents 1. General Information... 1 2. Material... 2 3. Work Flow Overview...
Tube Formation Assays in µ-slide Angiogenesis Related topics: Application Note 27 Data Analysis of Tube Formation Assays. Contents 1. General Information... 1 2. Material... 2 3. Work Flow Overview...
Migratory behaviour of tumor cells: a scanning electron microscopy study
 Ann Ist Super Sanità 2015 Vol. 51, No. 2 www.iss.it/anna for Migratory behaviour of tumor cells: a scanning electron microscopy study Giuseppina Bozzuto*, Maria Condello and Agnese Molinari *Corresponding
Ann Ist Super Sanità 2015 Vol. 51, No. 2 www.iss.it/anna for Migratory behaviour of tumor cells: a scanning electron microscopy study Giuseppina Bozzuto*, Maria Condello and Agnese Molinari *Corresponding
WntResearch. Foxy-5 A unique Phase 1 opportunity to combat the spreading of cancer
 WntResearch Foxy-5 A unique Phase 1 opportunity to combat the spreading of cancer Why WntResearch is developing novel anti-cancer drugs Approximately 55 000 Swedish citizens are diagnosed with cancer every
WntResearch Foxy-5 A unique Phase 1 opportunity to combat the spreading of cancer Why WntResearch is developing novel anti-cancer drugs Approximately 55 000 Swedish citizens are diagnosed with cancer every
TITLE: Treatment of Prostate Cancer with a DBP-MAF-Vitamin D Complex to Target Angiogenesis and Tumorigenesis
 AD AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-04-1-0010 TITLE: Treatment of Prostate Cancer with a DBP-MAF-Vitamin D Complex to Target Angiogenesis and Tumorigenesis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Michael W. Fannon, Ph.D. CONTRACTING
AD AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-04-1-0010 TITLE: Treatment of Prostate Cancer with a DBP-MAF-Vitamin D Complex to Target Angiogenesis and Tumorigenesis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Michael W. Fannon, Ph.D. CONTRACTING
Routine Assessment of Cancer Cell Cytotoxicity in a Novel Three Dimensional Culture Assay. Introduction
 Routine Assessment of Cancer Cell Cytotoxicity in a Novel Three Dimensional Culture Assay Application Note 2 Introduction Cancer is a leading cause of death worldwide, accounting for around 7.6 million
Routine Assessment of Cancer Cell Cytotoxicity in a Novel Three Dimensional Culture Assay Application Note 2 Introduction Cancer is a leading cause of death worldwide, accounting for around 7.6 million
Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress Test Kit
 Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress Test Kit Part # 103015-100 User Guide For use with Seahorse XF e and XF Extracellular Flux Analyzers For Research Use Only 1 Table of Contents Product Description... 2 Introduction...
Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress Test Kit Part # 103015-100 User Guide For use with Seahorse XF e and XF Extracellular Flux Analyzers For Research Use Only 1 Table of Contents Product Description... 2 Introduction...
Pathophysiology of bone metastasis : how does it apply to pain treatment in palliative care? JP Vuillez, Grenoble, France
 Pathophysiology of bone metastasis : how does it apply to pain treatment in palliative care? JP Vuillez, Grenoble, France Bone metastases 70 % of prostate and breast cancers 30 % of lung, bladder and thyroid
Pathophysiology of bone metastasis : how does it apply to pain treatment in palliative care? JP Vuillez, Grenoble, France Bone metastases 70 % of prostate and breast cancers 30 % of lung, bladder and thyroid
Routine Assessment of Cancer Cell Cytotoxicity in a Novel Three Dimensional Culture Assay. Introduction
 Routine Assessment of Cancer Cell Cytotoxicity in a Novel Three Dimensional Culture Assay Application Note Introduction Cancer is a leading cause of death worldwide, accounting for around 7.6 million deaths
Routine Assessment of Cancer Cell Cytotoxicity in a Novel Three Dimensional Culture Assay Application Note Introduction Cancer is a leading cause of death worldwide, accounting for around 7.6 million deaths
Cancer: DNA Synthesis, Mitosis, and Meiosis
 Chapter 5 Cancer: DNA Synthesis, Mitosis, and Meiosis Copyright 2007 Pearson Copyright Prentice Hall, 2007 Inc. Pearson Prentice Hall, Inc. 1 What Is Cancer? Benign tumors do not invade surrounding tissue
Chapter 5 Cancer: DNA Synthesis, Mitosis, and Meiosis Copyright 2007 Pearson Copyright Prentice Hall, 2007 Inc. Pearson Prentice Hall, Inc. 1 What Is Cancer? Benign tumors do not invade surrounding tissue
How Cancer Begins???????? Chithra Manikandan Nov 2009
 Cancer Cancer is one of the most common diseases in the developed world: 1 in 4 deaths are due to cancer 1 in 17 deaths are due to lung cancer Lung cancer is the most common cancer in men Breast cancer
Cancer Cancer is one of the most common diseases in the developed world: 1 in 4 deaths are due to cancer 1 in 17 deaths are due to lung cancer Lung cancer is the most common cancer in men Breast cancer
New Advances in Cancer Treatments. March 2015
 New Advances in Cancer Treatments March 2015 Safe Harbour Statement This presentation document contains certain forward-looking statements and information (collectively, forward-looking statements ) within
New Advances in Cancer Treatments March 2015 Safe Harbour Statement This presentation document contains certain forward-looking statements and information (collectively, forward-looking statements ) within
Intracellular Calcium and Phosphatidylserine Exposure in the red Blood Cells
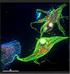 Intracellular Calcium and Phosphatidylserine Exposure in the red Blood Cells Biotechnology Seminar 2 Yaser Alkhaled 30.10.13 Table of Content 1. Introduction.... 3 2. Membrane of red blood cell.... 4 3.
Intracellular Calcium and Phosphatidylserine Exposure in the red Blood Cells Biotechnology Seminar 2 Yaser Alkhaled 30.10.13 Table of Content 1. Introduction.... 3 2. Membrane of red blood cell.... 4 3.
How To Make A Vascular Graft
 LCL-GRAFT TM - Innovative Large and Small Caliber Vascular Grafts for Coronary Bypass and Peripheral Vascular Surgery. A. Perets 1, M. Li 1, P. Uttayarat 1, P. Pimton 1, A. Wu 2, R. J. Levy 3, R. J. Composto
LCL-GRAFT TM - Innovative Large and Small Caliber Vascular Grafts for Coronary Bypass and Peripheral Vascular Surgery. A. Perets 1, M. Li 1, P. Uttayarat 1, P. Pimton 1, A. Wu 2, R. J. Levy 3, R. J. Composto
Development of Bone Metastases in Men With Prostate Cancer
 Development of Bone Metastases in Men With Prostate Cancer Explore the Causes Understand the Consequences Natural History of Prostate Cancer Progression Many prostate tumors may become castrate-resistant
Development of Bone Metastases in Men With Prostate Cancer Explore the Causes Understand the Consequences Natural History of Prostate Cancer Progression Many prostate tumors may become castrate-resistant
CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Alabama at Birmingham Birmingham, AL 35294
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-08-1-0030 TITLE: Regulation of Prostate Cancer Bone Metastasis by DKK1 PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Gregory A. Clines, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Alabama at
AD Award Number: W81XWH-08-1-0030 TITLE: Regulation of Prostate Cancer Bone Metastasis by DKK1 PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Gregory A. Clines, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Alabama at
Uses of Flow Cytometry
 Uses of Flow Cytometry 1. Multicolour analysis... 2 2. Cell Cycle and Proliferation... 3 a. Analysis of Cellular DNA Content... 4 b. Cell Proliferation Assays... 5 3. Immunology... 6 4. Apoptosis... 7
Uses of Flow Cytometry 1. Multicolour analysis... 2 2. Cell Cycle and Proliferation... 3 a. Analysis of Cellular DNA Content... 4 b. Cell Proliferation Assays... 5 3. Immunology... 6 4. Apoptosis... 7
Animal Cell Culture. Third Edition. A Practical Approach OXJORD VNIVVRSITY 1'RVSS
 Animal Cell Culture Third Edition A Practical Approach Edited by John R. W. Masters 3rd Floor Research Laboratories, University College London OXJORD VNIVVRSITY 1'RVSS Contents List of protocols page xiii
Animal Cell Culture Third Edition A Practical Approach Edited by John R. W. Masters 3rd Floor Research Laboratories, University College London OXJORD VNIVVRSITY 1'RVSS Contents List of protocols page xiii
micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved
 microrna 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions of target mrnas Act as negative
microrna 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions of target mrnas Act as negative
Paclitaxel-Loaded Expansile Nanoparticles Enhance Chemotheraputic Drug-delivery in Mesothelioma 3D Multicellular Spheroids
 Paclitaxel-Loaded Expansile Nanoparticles Enhance Chemotheraputic Drug-delivery in Mesothelioma 3D Multicellular Spheroids Hongyi Lei 1, Rong Liu 1, Aaron Colby 2, Mark W. Grinstaff 2, Yolonda L. Colson
Paclitaxel-Loaded Expansile Nanoparticles Enhance Chemotheraputic Drug-delivery in Mesothelioma 3D Multicellular Spheroids Hongyi Lei 1, Rong Liu 1, Aaron Colby 2, Mark W. Grinstaff 2, Yolonda L. Colson
New strategies in anticancer therapy
 癌 症 診 療 指 引 簡 介 及 臨 床 應 用 New strategies in anticancer therapy 中 山 醫 學 大 學 附 設 醫 院 腫 瘤 內 科 蔡 明 宏 醫 師 2014/3/29 Anti-Cancer Therapy Surgical Treatment Radiotherapy Chemotherapy Target Therapy Supportive
癌 症 診 療 指 引 簡 介 及 臨 床 應 用 New strategies in anticancer therapy 中 山 醫 學 大 學 附 設 醫 院 腫 瘤 內 科 蔡 明 宏 醫 師 2014/3/29 Anti-Cancer Therapy Surgical Treatment Radiotherapy Chemotherapy Target Therapy Supportive
H. Richard Alexander, Jr., M.D. Department of Surgery and The Greenebaum Cancer Center University of Maryland School of Medicine Baltimore, Md
 Major Advances in Cancer Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment~ Why Mesothelioma Leads the Way H. Richard Alexander, Jr., M.D. Department of Surgery and The Greenebaum Cancer Center University of Maryland
Major Advances in Cancer Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment~ Why Mesothelioma Leads the Way H. Richard Alexander, Jr., M.D. Department of Surgery and The Greenebaum Cancer Center University of Maryland
BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING NEURO-ONCOLOGY
 BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING NEURO-ONCOLOGY SCAFFOLDING 10 MICRONS THIN NEUROSURGERY DEPLOYMENT THROUGH CATHETERS BRAIN EXVADERS A NOVEL BIOENGINEERING SOLUTION AIMED AT PEDIATRIC BRAIN TUMORS COULD SOMEDAY
BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING NEURO-ONCOLOGY SCAFFOLDING 10 MICRONS THIN NEUROSURGERY DEPLOYMENT THROUGH CATHETERS BRAIN EXVADERS A NOVEL BIOENGINEERING SOLUTION AIMED AT PEDIATRIC BRAIN TUMORS COULD SOMEDAY
PRODUCT INFORMATION...
 VIROMER RED In vitro plasmid DNA and mrna Standard Transfection PRODUCT INFORMATION... 2 GENERAL... 2 RED OR YELLOW?... 3 PROTOCOL GUIDELINES... 4 GENERAL REMARKS... 4 CELL CULTURE AND PLATING... 4 FORWARD/REVERSE
VIROMER RED In vitro plasmid DNA and mrna Standard Transfection PRODUCT INFORMATION... 2 GENERAL... 2 RED OR YELLOW?... 3 PROTOCOL GUIDELINES... 4 GENERAL REMARKS... 4 CELL CULTURE AND PLATING... 4 FORWARD/REVERSE
Incorporation of a Novel 3D Cell Culture System to Perform in vitro Cytotoxicity Analyses using Human Primary Hepatocytes
 A p p l i c a t i o n N o t e Incorporation of a Novel 3D Cell Culture System to Perform in vitro Cytotoxicity Analyses using Human Primary Hepatocytes Brad Larson, Senior Scientist, Applications Department,
A p p l i c a t i o n N o t e Incorporation of a Novel 3D Cell Culture System to Perform in vitro Cytotoxicity Analyses using Human Primary Hepatocytes Brad Larson, Senior Scientist, Applications Department,
Modelling cell motion: From microscopic to macroscopic scale. Luigi Preziosi Luigi.preziosi@polito.it calvino.polito.it/~preziosi
 Modelling cell motion: From microscopic to macroscopic scale Luigi Preziosi Luigi.preziosi@polito.it calvino.polito.it/~preziosi Modelling cell-ecm interaction: An opportunity to present different modelling
Modelling cell motion: From microscopic to macroscopic scale Luigi Preziosi Luigi.preziosi@polito.it calvino.polito.it/~preziosi Modelling cell-ecm interaction: An opportunity to present different modelling
Figure 5. Energy of activation with and without an enzyme.
 Biology 20 Laboratory ENZYMES & CELLULAR RESPIRATION OBJECTIVE To be able to list the general characteristics of enzymes. To study the effects of enzymes on the rate of chemical reactions. To demonstrate
Biology 20 Laboratory ENZYMES & CELLULAR RESPIRATION OBJECTIVE To be able to list the general characteristics of enzymes. To study the effects of enzymes on the rate of chemical reactions. To demonstrate
M. Ugolini 1,2, G. Babini 1,2, G. Baiocco 1,2, D. Cappelletti 1,2, L. Mariotti 1,2, J. Morini 1,2,3 and A. Ottolenghi 1,2
 M. Ugolini 1,2, G. Babini 1,2, G. Baiocco 1,2, D. Cappelletti 1,2, L. Mariotti 1,2, J. Morini 1,2,3 and A. Ottolenghi 1,2 1 Department of Physics, University of Pavia, Pavia, Italy 2 Istituto Nazionale
M. Ugolini 1,2, G. Babini 1,2, G. Baiocco 1,2, D. Cappelletti 1,2, L. Mariotti 1,2, J. Morini 1,2,3 and A. Ottolenghi 1,2 1 Department of Physics, University of Pavia, Pavia, Italy 2 Istituto Nazionale
No-wash, no-lyse detection of leukocytes in human whole blood on the Attune NxT Flow Cytometer
 APPLICATION NOTE Attune NxT Flow Cytometer No-wash, no-lyse detection of leukocytes in human whole blood on the Attune NxT Flow Cytometer Introduction Standard methods for isolating and detecting leukocytes
APPLICATION NOTE Attune NxT Flow Cytometer No-wash, no-lyse detection of leukocytes in human whole blood on the Attune NxT Flow Cytometer Introduction Standard methods for isolating and detecting leukocytes
Preliminary Results from a Phase 2 Study of ARQ 197 in Patients with Microphthalmia Transcription Factor Family (MiT) Associated Tumors
 Preliminary Results from a Phase 2 Study of ARQ 197 in Patients with Microphthalmia Transcription Factor Family (MiT) Associated Tumors John Goldberg 1 *, George Demetri 2, Edwin Choy 3, Lee Rosen 4, Alberto
Preliminary Results from a Phase 2 Study of ARQ 197 in Patients with Microphthalmia Transcription Factor Family (MiT) Associated Tumors John Goldberg 1 *, George Demetri 2, Edwin Choy 3, Lee Rosen 4, Alberto
How To Expand Hematopoietic Stem Cells
 Purification and Expansion of Hematopoietic Stem Cells Based on Proteins Expressed by a Novel Stromal Cell Population Our bodies are constantly killing old, nonfunctional, and unneeded cells and making
Purification and Expansion of Hematopoietic Stem Cells Based on Proteins Expressed by a Novel Stromal Cell Population Our bodies are constantly killing old, nonfunctional, and unneeded cells and making
TransIT -2020 Transfection Reagent
 Quick Reference Protocol, MSDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/5400 INTRODUCTION TransIT -2020 Transfection Reagent is a high-performance, animal-origin free, broad spectrum reagent
Quick Reference Protocol, MSDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/5400 INTRODUCTION TransIT -2020 Transfection Reagent is a high-performance, animal-origin free, broad spectrum reagent
In vitro co-culture model of the inflamed intestinal mucosa
 In vitro co-culture model of the inflamed intestinal mucosa Berlin, December 13, 2011 Eva-Maria Collnot, e.collnot@mx.uni-saarland.de Helmholtz Institute for Pharmaceutical Research Saarland Departement
In vitro co-culture model of the inflamed intestinal mucosa Berlin, December 13, 2011 Eva-Maria Collnot, e.collnot@mx.uni-saarland.de Helmholtz Institute for Pharmaceutical Research Saarland Departement
Supplemental Information. McBrayer et al. Supplemental Data
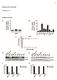 1 Supplemental Information McBrayer et al. Supplemental Data 2 Figure S1. Glucose consumption rates of MM cell lines exceed that of normal PBMC. (A) Normal PBMC isolated from three healthy donors were
1 Supplemental Information McBrayer et al. Supplemental Data 2 Figure S1. Glucose consumption rates of MM cell lines exceed that of normal PBMC. (A) Normal PBMC isolated from three healthy donors were
Softwell. Petrisoft. Collagen. Ultrasoft. 25 kpa. 8 kpa. Easy Coat. 1 kpa. Softview. Hydrogel-coated wells for cell culture. Non-activated 0.
 Softwell Hydrogel-coated wells for cell culture Non-activated 0.2 kpa 25 kpa Collagen 8 kpa Easy Coat Petrisoft Ultrasoft Softview 1 kpa Introducing Softwell It s like a Petri dish. Only to a cell, it
Softwell Hydrogel-coated wells for cell culture Non-activated 0.2 kpa 25 kpa Collagen 8 kpa Easy Coat Petrisoft Ultrasoft Softview 1 kpa Introducing Softwell It s like a Petri dish. Only to a cell, it
EVALUATION OF THE EFFECT OF THE COMPOUND RIBOXYL ON THE ATP LEVEL AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION FROM HUMAN DERMAL FIBROBLASTS
 EVALUATION OF THE EFFECT OF THE COMPOUND RIBOXYL ON THE ATP LEVEL AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION FROM HUMAN DERMAL FIBROBLASTS FINAL REPORT OF THE STUDY GT050923 Study promoter: LUCAS MEYER COSMETICS ZA Les
EVALUATION OF THE EFFECT OF THE COMPOUND RIBOXYL ON THE ATP LEVEL AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION FROM HUMAN DERMAL FIBROBLASTS FINAL REPORT OF THE STUDY GT050923 Study promoter: LUCAS MEYER COSMETICS ZA Les
How To Treat Mesothelioma With A Tumor Stem Cell Inhibitor
 FAK INHIBITOR DEFACTINIB (VS-6063) TARGETS MESOTHELIOMA CANCER STEM CELLS Rationale for maintenance therapy after conventional therapy Jonathan Pachter, Ph.D. Vice President of Research, Verastem, Inc.
FAK INHIBITOR DEFACTINIB (VS-6063) TARGETS MESOTHELIOMA CANCER STEM CELLS Rationale for maintenance therapy after conventional therapy Jonathan Pachter, Ph.D. Vice President of Research, Verastem, Inc.
Chapter 8. Summary and Perspectives
 Chapter 8 Summary and Perspectives 131 Chapter 8 Summary Overexpression of the multidrug resistance protein MRP1 confer multidrug resistance (MDR) to cancer cells. The contents of this thesis describe
Chapter 8 Summary and Perspectives 131 Chapter 8 Summary Overexpression of the multidrug resistance protein MRP1 confer multidrug resistance (MDR) to cancer cells. The contents of this thesis describe
Avastin: Glossary of key terms
 Avastin: Glossary of key terms Adenocarcinoma Adenoma Adjuvant therapy Angiogenesis Anti-angiogenics Antibody Antigen Avastin (bevacizumab) Benign A form of carcinoma that originates in glandular tissue.
Avastin: Glossary of key terms Adenocarcinoma Adenoma Adjuvant therapy Angiogenesis Anti-angiogenics Antibody Antigen Avastin (bevacizumab) Benign A form of carcinoma that originates in glandular tissue.
Human Adult Mesothelial Cell Manual
 Human Adult Mesothelial Cell Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0025.01 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human Adult Mesothelial Cells Orders are delivered via Federal Express courier. All US and Canada orders are shipped
Human Adult Mesothelial Cell Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0025.01 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human Adult Mesothelial Cells Orders are delivered via Federal Express courier. All US and Canada orders are shipped
Mechanism of short-term ERK activation by electromagnetic fields at mobile phone frequencies. Biochemistry Journal. August 1, 2007 405, pp.
 Mechanism of short-term ERK activation by electromagnetic fields at mobile phone frequencies 1 Biochemistry Journal August 1, 2007 405, pp. 559 568 Joseph Friedman, Sarah Kraus, Yirmi Hauptman, Yoni Schiff
Mechanism of short-term ERK activation by electromagnetic fields at mobile phone frequencies 1 Biochemistry Journal August 1, 2007 405, pp. 559 568 Joseph Friedman, Sarah Kraus, Yirmi Hauptman, Yoni Schiff
Culture and Assay Systems Used for 3D Cell Culture
 Culture and Assay Systems Used for 3D Cell Culture Review Article Suparna Sanyal, Ph.D. Introduction Mammalian cell culture has served as an invaluable tool in cell biology for several decades. Monolayers
Culture and Assay Systems Used for 3D Cell Culture Review Article Suparna Sanyal, Ph.D. Introduction Mammalian cell culture has served as an invaluable tool in cell biology for several decades. Monolayers
Supplementary Information. Engineering an in vitro air-blood barrier by 3D bioprinting
 Supplementary Information Engineering an in vitro air-blood barrier by 3D bioprinting Lenke Horváth 1, Yuki Umehara 1, Corinne Jud 1,3, Fabian Blank 2, Alke Petri- Fink 1, Barbara Rothen-Rutishauser 1
Supplementary Information Engineering an in vitro air-blood barrier by 3D bioprinting Lenke Horváth 1, Yuki Umehara 1, Corinne Jud 1,3, Fabian Blank 2, Alke Petri- Fink 1, Barbara Rothen-Rutishauser 1
Chemotherapy resistance in acute myeloid leukemia: the role of adhesion
 Chemotherapy resistance in acute myeloid leukemia: the role of adhesion Joe C. Huang, M.D. Research Elective 8/09-10/09 Mentor: Pamela S. Becker, M.D., Ph.D. Associate Professor of Medicine/Hematology
Chemotherapy resistance in acute myeloid leukemia: the role of adhesion Joe C. Huang, M.D. Research Elective 8/09-10/09 Mentor: Pamela S. Becker, M.D., Ph.D. Associate Professor of Medicine/Hematology
OPG-Fc inhibits ovariectomy-induced growth of disseminated breast cancer cells in bone.
 Title of the poster Authors Sheffield Cancer Research Centre University of Sheffield OPG-Fc inhibits ovariectomy-induced growth of disseminated breast cancer cells in bone. Dr Penelope Ottewell Background
Title of the poster Authors Sheffield Cancer Research Centre University of Sheffield OPG-Fc inhibits ovariectomy-induced growth of disseminated breast cancer cells in bone. Dr Penelope Ottewell Background
Western Blot Analysis with Cell Samples Grown in Channel-µ-Slides
 Western Blot Analysis with Cell Samples Grown in Channel-µ-Slides Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) and subsequent analyses are common tools in biochemistry and molecular biology. This Application
Western Blot Analysis with Cell Samples Grown in Channel-µ-Slides Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) and subsequent analyses are common tools in biochemistry and molecular biology. This Application
What is New in Oncology. Michael J Messino, MD Cancer Care of WNC An affiliate of Mission hospitals
 What is New in Oncology Michael J Messino, MD Cancer Care of WNC An affiliate of Mission hospitals Personalized Medicine Personalized Genomics Genomic Medicine Precision Medicine Definition Application
What is New in Oncology Michael J Messino, MD Cancer Care of WNC An affiliate of Mission hospitals Personalized Medicine Personalized Genomics Genomic Medicine Precision Medicine Definition Application
Cell Cycle Phase Determination Kit
 Cell Cycle Phase Determination Kit Item No. 10009349 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 3 Safety
Cell Cycle Phase Determination Kit Item No. 10009349 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 3 Safety
SeedEZ TM PROTOCOLS. SeedEZ TM COATINGS FOR SPHEROID CULTURES AND 3D CELL CULTURES OF SUBSTRATE-ADHERED CELLS. support@lenabio.com
 SeedEZ TM PROTOCOLS Lena Biosciences SeedEZ TM COATINGS FOR SPHEROID CULTURES AND 3D CELL CULTURES OF SUBSTRATE-ADHERED CELLS support@lenabio.com MARCH 2013 V1.7 SeedEZ IS A TRADEMARK OF LENA BIOSCIENCES,
SeedEZ TM PROTOCOLS Lena Biosciences SeedEZ TM COATINGS FOR SPHEROID CULTURES AND 3D CELL CULTURES OF SUBSTRATE-ADHERED CELLS support@lenabio.com MARCH 2013 V1.7 SeedEZ IS A TRADEMARK OF LENA BIOSCIENCES,
In vivo dose response assays
 In vivo dose response assays Tumor assays 1. Tumor growth measurements; tumor growth delay. After irradiation, the tumor is measured daily to determine the mean diameter, or volume. Plot tumor size versus
In vivo dose response assays Tumor assays 1. Tumor growth measurements; tumor growth delay. After irradiation, the tumor is measured daily to determine the mean diameter, or volume. Plot tumor size versus
STEM CELL FELLOWSHIP
 Module I: The Basic Principles of Stem Cells 1. Basics of Stem Cells a. Understanding the development of embryonic stem cells i. Embryonic stem cells ii. Embryonic germ cells iii. Differentiated stem cell
Module I: The Basic Principles of Stem Cells 1. Basics of Stem Cells a. Understanding the development of embryonic stem cells i. Embryonic stem cells ii. Embryonic germ cells iii. Differentiated stem cell
Humoral response to therapeutic low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) treatment of rat maxillary socket after the removal of a molar tooth
 Humoral response to therapeutic low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) treatment of rat maxillary socket after the removal of a molar tooth Kouki Hidaka *1, Chihiro Miyamoto *2, Satoko Wada-Takahashi
Humoral response to therapeutic low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) treatment of rat maxillary socket after the removal of a molar tooth Kouki Hidaka *1, Chihiro Miyamoto *2, Satoko Wada-Takahashi
Mesenchymal Stem Cells
 Mesenchymal Stem Cells Instruction Manual Product Size Catalog Number from Bone Marrow (hmsc-bm) from Umbilical Cord Matrix (hmsc-uc) from Adipose Tissue (hmsc-at) 500,000 cryopreserved cells 500,000 proliferating
Mesenchymal Stem Cells Instruction Manual Product Size Catalog Number from Bone Marrow (hmsc-bm) from Umbilical Cord Matrix (hmsc-uc) from Adipose Tissue (hmsc-at) 500,000 cryopreserved cells 500,000 proliferating
Radius 24-Well Cell Migration Assay
 Product Manual Radius 24-Well Cell Migration Assay Catalog Number CBA-125 CBA-125-5 24 assays 5 x 24 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cell migration is a highly
Product Manual Radius 24-Well Cell Migration Assay Catalog Number CBA-125 CBA-125-5 24 assays 5 x 24 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cell migration is a highly
Unit 1 Higher Human Biology Summary Notes
 Unit 1 Higher Human Biology Summary Notes a. Cells tissues organs body systems Division of labour occurs in multicellular organisms (rather than each cell carrying out every function) Most cells become
Unit 1 Higher Human Biology Summary Notes a. Cells tissues organs body systems Division of labour occurs in multicellular organisms (rather than each cell carrying out every function) Most cells become
Exelixis Showcases R&D Pipeline at JPMorgan Healthcare Conference
 Exelixis Showcases R&D Pipeline at JPMorgan Healthcare Conference Two New Clinical Programs and Significant Expansion of Cancer Pipeline Planned for 2004 SOUTH SAN FRANCISCO, Calif., Jan. 13 /PRNewswire-FirstCall/
Exelixis Showcases R&D Pipeline at JPMorgan Healthcare Conference Two New Clinical Programs and Significant Expansion of Cancer Pipeline Planned for 2004 SOUTH SAN FRANCISCO, Calif., Jan. 13 /PRNewswire-FirstCall/
March 19, 2014. Dear Dr. Duvall, Dr. Hambrick, and Ms. Smith,
 Dr. Daniel Duvall, Medical Officer Center for Medicare, Hospital and Ambulatory Policy Group Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services 7500 Security Boulevard Baltimore, Maryland 21244 Dr. Edith Hambrick,
Dr. Daniel Duvall, Medical Officer Center for Medicare, Hospital and Ambulatory Policy Group Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services 7500 Security Boulevard Baltimore, Maryland 21244 Dr. Edith Hambrick,
Hydrogen Peroxide Cell-Based Assay Kit
 Hydrogen Peroxide Cell-Based Assay Kit Item No. 600050 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Hydrogen Peroxide Cell-Based Assay Kit Item No. 600050 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
MULTIPLE MYELOMA. Dr Malkit S Riyat. MBChB, FRCPath(UK) Consultant Haematologist
 MULTIPLE MYELOMA Dr Malkit S Riyat MBChB, FRCPath(UK) Consultant Haematologist Multiple myeloma is an incurable malignancy that arises from postgerminal centre, somatically hypermutated B cells.
MULTIPLE MYELOMA Dr Malkit S Riyat MBChB, FRCPath(UK) Consultant Haematologist Multiple myeloma is an incurable malignancy that arises from postgerminal centre, somatically hypermutated B cells.
Annexin V-EGFP Apoptosis Detection Kit
 ab14153 Annexin V-EGFP Apoptosis Detection Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in various samples This product is for research use only and is not intended
ab14153 Annexin V-EGFP Apoptosis Detection Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in various samples This product is for research use only and is not intended
Title: Mapping T cell epitopes in PCV2 capsid protein - NPB #08-159. Date Submitted: 12-11-09
 Title: Mapping T cell epitopes in PCV2 capsid protein - NPB #08-159 Investigator: Institution: Carol Wyatt Kansas State University Date Submitted: 12-11-09 Industry summary: Effective circovirus vaccines
Title: Mapping T cell epitopes in PCV2 capsid protein - NPB #08-159 Investigator: Institution: Carol Wyatt Kansas State University Date Submitted: 12-11-09 Industry summary: Effective circovirus vaccines
FITC Annexin V/Dead Cell Apoptosis Kit with FITC annexin V and PI, for Flow Cytometry
 FITC Annexin V/Dead Cell Apoptosis Kit with FITC annexin V and PI, for Flow Cytometry Catalog no. V13242 Table 1. Contents and storage information. Material Amount Composition Storage* Stability FITC annexin
FITC Annexin V/Dead Cell Apoptosis Kit with FITC annexin V and PI, for Flow Cytometry Catalog no. V13242 Table 1. Contents and storage information. Material Amount Composition Storage* Stability FITC annexin
Overview of 3D Cell Culture Model Systems & Validating Cell-based Assays for Use with 3D Cultures Terry Riss, PhD March 2014
 Overview of 3D Cell Culture Model Systems & Validating Cell-based Assays for Use with 3D Cultures Terry Riss, PhD March 2014 Promega Corporation Outline Justification for using 3D culture models Overview
Overview of 3D Cell Culture Model Systems & Validating Cell-based Assays for Use with 3D Cultures Terry Riss, PhD March 2014 Promega Corporation Outline Justification for using 3D culture models Overview
Early detection of breast cancer
 Early detection of breast cancer Professor Denise Kendrick Division of Primary Care 1 5/26/2016 Average Number of New Cases Per Year and Age-Specific Incidence Rates per 100,000 Population Females, UK
Early detection of breast cancer Professor Denise Kendrick Division of Primary Care 1 5/26/2016 Average Number of New Cases Per Year and Age-Specific Incidence Rates per 100,000 Population Females, UK
A disease of populations of cells that live, divide, invade and spread without regard to normal limits
 1 Targeted Cancer Therapies Mark McKeage Medical Oncology Specialist Professor in Clinical Pharmacology 2 Cancer Definition- A disease of populations of cells that live, divide, invade and spread without
1 Targeted Cancer Therapies Mark McKeage Medical Oncology Specialist Professor in Clinical Pharmacology 2 Cancer Definition- A disease of populations of cells that live, divide, invade and spread without
Metastasis. brain metastasis from bronchial carcinoma
 metastasis Metastasis brain metastasis from bronchial carcinoma How many genetic changes are needed for neoplastic transformation?... if you have some of these changes, but not all, you will never become
metastasis Metastasis brain metastasis from bronchial carcinoma How many genetic changes are needed for neoplastic transformation?... if you have some of these changes, but not all, you will never become
Head of College Scholars List Scheme. Summer Studentship. Report Form
 Head of College Scholars List Scheme Summer Studentship Report Form This report should be completed by the student with his/her project supervisor. It should summarise the work undertaken during the project
Head of College Scholars List Scheme Summer Studentship Report Form This report should be completed by the student with his/her project supervisor. It should summarise the work undertaken during the project
Role Of Mitochondria In Mesenchymal Stem Cells
 Role Of Mitochondria In Mesenchymal Stem Cells Roman Eliseev, MD, PhD, Tamara Raymond, Regis O'Keefe, MD, PhD. University of Rochester, Rochester, NY, USA. Disclosures: R. Eliseev: None. T. Raymond: None.
Role Of Mitochondria In Mesenchymal Stem Cells Roman Eliseev, MD, PhD, Tamara Raymond, Regis O'Keefe, MD, PhD. University of Rochester, Rochester, NY, USA. Disclosures: R. Eliseev: None. T. Raymond: None.
Smoking and misuse of certain pain medicines can affect the risk of developing renal cell cancer.
 Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Development and validation of neutralising anti-drug antibody (Nabs) assays
 Development and validation of neutralising anti-drug antibody (Nabs) assays Clare Kingsley Sector Manager, Bioanalytical Sciences, Quotient Bioresearch EBF 2012 Overview Anti-drug antibody and neutralising
Development and validation of neutralising anti-drug antibody (Nabs) assays Clare Kingsley Sector Manager, Bioanalytical Sciences, Quotient Bioresearch EBF 2012 Overview Anti-drug antibody and neutralising
Cell Biology Questions and Learning Objectives
 Cell Biology Questions and Learning Objectives (with hypothetical learning materials that might populate the objective) The topics and central questions listed here are typical for an introductory undergraduate
Cell Biology Questions and Learning Objectives (with hypothetical learning materials that might populate the objective) The topics and central questions listed here are typical for an introductory undergraduate
