Gravity and the Earth Newtonian Gravity and Earth Rotation Effects
|
|
|
- Steven Maxwell
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Gavity and th Eath Nwtonian Gavity and Eath Rotation Effcts Jams R. Clynch, 003 I. Nwtonian Gavity A. Nwtonian Gavitational Foc B. Nwtonian Gavitational Fild C. Nwtonian Gavitational Potntial D. Gavity Vcto and th Gadint Opato E. Sphical Eath Exampl F. Potntial Diffncs Na th Eath's Sufac II. Th Ral Gavity Fild of th Eath - Ovviw III. Rotational Effcts A. Ellipsoid Modl of Eath B. Gavity of Pfct Ellipsoid / Godtic Latitud IV. Potntial sufacs, Goid, and Hights V. Goid and Topogaphy 1
2 I. Nwtonian Gavity A. Nwtonian Gavitational Foc Nwton publishd his law of gavitational attaction in This says that all things that hav mass attach ach oth. Th attaction is popotional to th poduct of th masss and invsly popotional to th distanc btwn thm. Th valu G is a constant that was fist masud by Cavndish in 1798 using lad balls. Th two masss a assumd to b points. Howv it can b shown that if th masss a sphical symmtic th sam quation holds using th cnt of symmty as th location fo th total mass of th objct. Th quation holds fo xtndd masss in this spcial, but usful cas.
3 This can b povd by looking at th mass as bing mad up of an infinit numb of small points of volum dv and mass dm ρdv wh th dnsity is ρ. Th ffcts of all ths points is addd up. This is th intgal of calculus. (S th basic physics not fo a fw dtails.) This pocdu is quid fo th gnal cas. In th sphically symmtic cas you gt th sult abov, but only fo points outsid th mass. Fo points insid th mass, only th mass that is at a adius lss than that of th tst mass counts. So th foc dcass as you go insid a sphical mass. (Ths sults a just dpndnt on th invs squa law natu of th foc. So thy also hold fo th lctical foc.) Th cas of non-sphical Nwtonian gavity will b takn up shotly. B. Nwtonian Gavitational Fild Nwton s scond law stats that th foc and acclation a latd though th mass. Th mass occus in both th quation fo th gavitational foc and th quation fo th acclation that foc causs. Assuming that som small tst mass, m is usd, thn th foc on that mass is: 3
4 F F a g GMm ê ma GM ê a wh w hav intoducd th Nwtonian gavitational acclation g. (This is not what w call th gavitational acclation of th ath, that is slightly diffnt.) Notic that w can find th valu of th acclation of gavity fom ths fomulas, at last in th sphical appoximation: GM g. This is th valu on th sufac of a sphical ath. It can b masud, fo xampl with a falling pbbl o a pndulum. Evn if you hav an ida of th siz of th ath, and hnc, you still do not know th mass of th ath M, but only th poduct GM. This is why Cavndish said h had "wightd th ath" whn h masud G. Th is an acclation at ach point in spac du to th mass M, whth th is a tst mass th o not. W say th is a gavitational fild. This concpt is vy common in physics. Things poduc ffcts vn if th is nothing th to fl it. C. Nwtonian Gavitational Potntial Th will b a foc quid to mov a tst mass away fom ou fild souc mass, M. This mans that w hav addd potntial ngy to th tst mass. Call this potntial ngy V. It will b a function of th position lativ to th mass M. This potntial ngy must b latd to th foc though its spatial gadint. Th at of chang of this potntial ngy with spct to distanc is th sam foc as th Nwtonian gavitational foc. In mathmatical tms w say that: F V V GMm ê GMm This fom fo th potntial ngy, V has th ngy zo at an infinit distanc fom th objct M, (wh is infinit). Th ngy gts mo ngativ as th tst mass m appoachs th mass M. It bcoms infinitly lag at th oigin, but this is insid th mass and th quation dos not hold th. 4
5 Th valu of th potntial ngy p unit mass is latd to th nominal gavity on th sufac of th ath V() m GM g GM Th standad scintific units of th acclation of gavity a m/s/s. Th units of th potntial ngy p unit mass a thfo m /s, o vlocity squad. (Rmmb kintic ngy is half th mass tims th vlocity squad, so th units a consistnt with th dfinition of ngy.) D. Gavity vcto and th Gadint Opato Th diffntial opato opating on a function of position is just a vcto that xpsss th at of chang of th function in diffnt dictions: V V ê x x V + ê y V V V,, x y z y V + ê z z H th two notations fo Catsian vctos a usd. Th diction of this vcto will b along th gatst chang in V, and th magnitud is th at of chang in that diction. To obtain th at of chang in any paticula diction, just tak th dot poduct with a unit vcto in that diction. (Th is an xtnsiv tchnical not on vctos availabl. In addition th gadint opato is covd mo xtnsivly in a tchnical not on basic physics.) Th a two impotant facts about th gadint. If you tak th gadint of a potntial function V, you gt th foc. Th following is tu of this gadint and th foc: 1. Th diction of th gadint vcto is ppndicula to sufacs of constant V,. Th magnitud of th gadint is invsly popotional to th spacing of sufacs of constant potntial. If th sufacs a clos togth, th gadint is lag, if fa apat it is small. This is shown blow wh a diagam of a vtical cut of th qual potntial sufacs is shown. Th lins a spacd at qually diffncs of potntial. Th sufacs, of cous, com out of th pag and a th dimnsional. 5
6 Th distotion a gatly magnifid fo puposs of illustation. Th masud diction of gavity, and hnc th "nomal" way w dfin down, a ppndicula to ths qual potntial sufacs. If thy hav bumps (as thy do in th al wold) thn th up-down lin has vaiations. 6
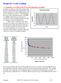
7 E. Sphical Eath Exampl Th ath is vy lag compad to vyday distancs w xpinc. This is why w can assum that th ath is flat and only mak small os in most things w do. Blow is a sis of diagams of a sgmnt of th ath, with ach stp having high magnification ( small scal in th mapping tminology.) It is cla that nomal hights, such as a 100 m ( 300 ft ) 30 stoy building, a ssntially invisibl on tu scal plots of any significant sgmnt of th ath. A plot of som na ath hights and th gavitational valus fo a sphical ath a shown blow. Th valus a fo points vy na th ath. 7
8 Th valus of th potntial ngy p unit mass ( that is V/m ) a shown fo a nominal ath siz that is sphical. Notic that th potntials gt small in absolut valu vy slowly as you incas in hight. Th diffnc of ths valus, dividd by th hight diffnc is a good appoximation fo th divativ in th vtical diction, which is th gadint h. Notic that th gadint, which is th local valu of g, also dcass in magnitud as you go up, but also vy slowly. W can oftn tat th acclation of gavity na th ath sufac as a constant. (This is not tu fo satllit wok howv.) F. Potntial Diffncs Na Eath's Sufac In lmntay physics txts, w lan that th gavitational potntial ngy is givn by V V m g h m g h Th scond fom is mo coct, as w a almost always daling in diffncs of potntial ngis. This fomula can b divd fom th gnal Nwtonian Law of Gavity assuming that th hight diffnc is small compad to th adius of th ath. 8
9 Many appoximations usd fo computation a divd using som small, dimnsionlss paamt. Both bing dimnsionlss and small a impotant. H th paamt will b h/, th hight abov th ath dividd by th nominal adius of th ath. Th Nwtonian potntial is givn by: V GM m Consid this quation fo two locations, on on th sufac of th ath and th scond at a hight h abov th ath. It is th diffnc in potntials that w nd. Fo th scond w hav V(h) GMm + h Th only diffnc btwn ths two is th dnominato. W wish to comput th diffnc of ths two potntials V V(h) V(0) 1 1 [ GM m] + h Th ky to finding th most significant tm is to lt: 1 + h (1 + h / 1 (1 + α) ) wh th small paamt h/ has bn calld α. Substituting this fom into th quation fo obtains V on V GM m 1 mg α mgh α + α This is th sult dsid. In this th valu of th acclation of gavity, g, found abov has bn usd. Th appoximation 1+ α 1 was also usd. H th hight is masud fom th sufac of th ath. 9
10 II. Th Ral Gavity Fild of th Eath - Ovviw Th a sval diffncs btwn th al gavity fild of th ath and th abov simplification. Th two majo physical diffncs a: 1. Th ath is otating. This causs an additional ffctiv foc to b flt fo all objcts otating with th ath. This includs appls, pndulums, and popl. It dos not includ ath satllits. This lads to ffcts on th od of 1/300 of th Nwtonian gavitation valus.. Th ath is not homognous. Ths ffcts a 1/10,000 o lss than th main ffcts. But thy can b masud and hav som pactical consquncs. Th otational ffcts a not insignificant. Not only do thy modify th valu of th acclation of gavity, thy sult in a chang in th shap of th ath. Th ath is appoximatly an llips volvd about th pola axis. This shap chang lads to significant changs is th valus of latitud. It also indictly lads to many of th map us poblms as diffnt popl and oganizations us diffnt appoximations fo th tu figu of th ath. This lads to most of th diffnc in datums. (Th is an xtnsiv tchnical not on datums.) In addition th a som tminology diffncs btwn what Godsy uss and physics. In th fild of Godsy, th a som tms and concpts that look and fl lik things studid in lmntay physics, but a slightly diffnt. This can caus som confusion, spcially if on taks quations fom both physics books and godsy books. Physics Godsy Gavity Nwtonian Gavitation Nwtonian Gavitation Plus Rotational Effcts Foc Foc, Fma Body Foc f F/m Foc p unit mass, Acclation, g, As sn on Rotating Eath Potntial Foc - Gadint (Potntial) Acclation + Gadint (Potntial) F V g + V Coodinats Pola Angl Masud fom Pol (0 to 180 dgs) Masud fom Equato ( φ ' ) (-90 to 90 dgs) Th main souc of diffnc is th inclusion of th otational ffcts in th tms usd in godsy. This is don to flct th masumnts sn by an obsv otating on th ath s sufac, that is masumnts mad on th al wold. Th dfinitions of sval itms w mad bfo many of th concpts usd in today s lmntay physics w discovd. Nwton o his contmpoais mad many dfinitions. Th concpts of potntial ngy, kintic ngy, and th consvation of ngy followd this wok by 100 yas. Th scond diffnc is th lation btwn th foc o acclation and a potntial function. Fist godsy dals in acclations, not focs. This is bcaus th ffcts of th mass of an objct in Nwton s scond law (F ma) and his law of gavity ( F GMm/ ) cancl out. 10
11 In godsy th acclation is takn as th gadint 1 of th potntial. In physics th foc is th ngativ gadint of th potntial ngy. In godsy th ngativ sign is omittd. In physics tms, th potntial ngy of somthing sitting on th ath is ngativ. You hav to add ngy to mov it off th ath. In godsy th gavity potntial is a positiv numb. It is th absolut valu of th physics valu of potntial ngy p unit mass. Th two potntials a latd by a minus sign. W will hav th diffnt sts of quantitis usd in godsy, 1. Quantitis basd on a sphical, non-otating ath,. Quantitis basd on a otating, llipsoidal ath without dnsity vaiations, 3. Quantitis basd on th al ath. Th fist st is usd in lmntay physics books. Thy a not usd in godsy. Th scond st is usd as a baslin o fnc st in godsy. Diffncs fom th smooth llipsoidal modl a potd. Eath Gavity Fild Quantitis Potntial Gavity Acclation Sphical Eath V Ellipsoidal Eath UV+Φ γ Ral Eath WU+T g H, V is th Nwtonian Potntial fo th modl ath ( sphical o llipsoidal) U is th gavity potntial fo th modl ath - with otational ffcts includd, Φ is th potntial fo otational ffcts. Φ ω p /, wh p and ω a discussd blow, W is th gavity potntial fo th al ath, T is th ffct of th inhomognitis in th ath, γ is th acclation du to th modl potntial, U, and g is th al gavity acclation of a body co-otating with th ath. 1 Th gadint is a masu of how fast a function changs. In this cas th changs a with spct to position, a at of chang with distanc. Th gadint is a divativ. It is also a vcto. It points in th diction of maximum positiv chang. Fo a sphical ath, th gadint of th gavity potntial points to th cnt of th ath. Fo th al ath it points in th local down diction. (Invs of th local vtical). 11
12 III. Rotational Effcts A. Ellipsoid Modl of Eath What w call "gavity" in godsy is th sum of th Nwtonian gavitational attaction and otational ffcts. Th otation ffct is calld cntifugal acclation. All things co-otating with th ath fl it. This causs th ath to hav a bulg at th quato. Fo a unifom ath, th shap is an llipsoid of volution. (This is also calld a sphoid). This is th godtic modl w will discuss in this sction. Th complxity of th bumps in th al wold will b discussd in th lat sctions. On of th ways to dfin th amount th llips diffs fom a cicl is calld th flattning, f. Th flattning, f, is givn by th quation f a b b 1, a a wh a is th long quatoial adius and b is th shot pola adius. Th flattning of th ath is about 1/300. If th ath w a fluid it would b about 1/30. Th ath acts almost as a fluid ov long tim fams. Nwton was th fist to pdict th flattning of th ath. Anoth common way to dscib th shap of th llips is with th ccnticity,. This is dfind as: a 1 b, o a 1. b Th obsvd acclation of gavity is th sum of th Nwtonian gavitational attaction and th otational foc. Th shap of th ath minimizs th potntial ngy du to th two focs. This maks 1
13 th diction of th obsvd acclation of gavity ppndicula to th llipsoid. This lin dos not go to th cnt of th ath xcpt fo th pols and points on th quato. Th Nwtonian acclations is givn by g n GM ê wh G is th univsal gavitational constant, M is th mass of th ath, is th adius of th ath (o distanc fom ath cnt of mass to obsv), and ê is a unit vcto that points outwad fom th cnt of th ath to th obsvation point. This quation is only valid outsid th ath. Insid th ath only th blow th obsv contibuts to th Nwtonian acclation. Th cntifugal acclation is givn by wh a c ω pê p ω π / T is th otation at of th ath (T is 1 sidal day ), p is th distanc fom th axis of otation to th obsv shown in th figu, and ê is a unit vcto along th outwad diction of p. p This applis only to objcts that otat with th ath. Satllits in spac do not fl this acclation. 13
14 B. Gavity of Pfct Ellipsoid / Godtic Latitud Th figu blow is a summay of th acclation vctos and th up-down lins fo a point on th otating ath. Th up lin is dfind by th obsvd gavity acclation, g, fo an objct co-otating with th ath. This is th sum of th otational and Nwtonian gavitation ffcts. Ths togth caus th shap of th ath to budg at quato and fom an llipsoid in th pfct ath cas. Th Nwtonian gavitational attaction, which w will dnot g n, dos point at th cnt of mass of th ath. But th sum of focs w fl dos not. Th otational acclation, which w will call a c, acts outwad fom th axis of otation. Ths acclations a shown in th diagam. Not that th vctos a not dawn to scal. Th lin fom th obsvd up-down lin gnats th usual latitud w us. This is calld Godtic (φ ). It is th kind found on maps. A latitud fom th lin to th cnt of th ath also can b dfind. This is gocntic (φ ) latitud. It would b th obsvd latitud on a sphical ath. In th al wold, it is usd mostly in satllit wok. Th obsvd acclation, g, is dfind by th vcto sum of th g n and a c. Th total is th ath's acclation of "gavity" as dfind in godsy. Th otational acclation tm is maximum at th quato and zo at th pols bcaus th momnt am p vais with latitud. In th al wold, th maximum a c is small than g n by a facto of 300. Thfo th ffcts on g, and angls, a small. But th ath is lag and vn small ffcts on angls can caus changs of 10 s of km. 14
15 Th nominal Nwtonian acclation is about 980 cm/s and th maximum otational tm about 3 cm/s. In godsy acclations of gavity a calld gal's, shot fo Galilo. On gal is on cm/s. This is a lag unit fo masuing vaiations, so th milligal, mgal o 1/1000th gal, commonly occus. Th gavity valu at ach godtic latitud fo an llipsoid is givn by: g g cos φ + g p 1 1 sin φ sin φ wh g is th acclation at th quato, g p, is th acclation at th pols, and is th ccnticity. This is not as complicatd as it looks. It is asy to show that b a 1. This quation is oftn wittn using th symbol gamma, γ, instad of g. Oftn gamma is usd fo thotical gavity fom a pfct llipsoid and g fo th al gavity fom th lumpy, non-unifom al ath. Anoth fom of this quation is with th auxiliay valu k givn by 1+ k sin φ γ g, 1+ sin φ k b g p 1. a g This valu is gaphd in th nxt figu along with th two componnts. 15
16 Th two componnts and th total acclation of gavity on th llipsoid a a function of latitud as show in th abov figu. Th total acclation is obtaind by adding th Nwtonian tm and th cntifugal tm as vctos. Th Nwtonian acclation is opposd by th otation tms vywh xcpt at th pols. It is thfo lag than th total valu. Th Nwtonian tm incass at th pols bcaus th sufac is clos to th cnt of mass. Th gavity at th pols is about 5 gal ( 5 cm/s/s ) lag than at th quato. About half of this ffct is bing clos to th cnt and th st is th diffnc in th otation tm, th cntifugal acclation. Th diction Up is also dfind fom th sum of th focs. It is ppndicula to th llipsoid sufac. It s invs, Down, dos not point to th cnt of th ath. W histoically dfind latitud fom obsvations of stas, with spct to th local up calld th local vtical. Th histoical dfinition of latitud cosponds to th angl mad th lin ppndicula to th llipsoid, not th on to th cnt of th ath. Th local vtical is ppndicula to th llipsoid in th absnc of inhomognats. 16
17 Th latitud w s on maps, calld godtic latitud, coms fom this ppndicula to th llipsoid. This latitud is commonly calld gogaphic latitud, but this tm is not wll dfind in th scintific litatu. Officially it is godtic latitud. Usually whn you s a tm calld godtic somthing, it fs to dfinitions basd on th llipsoid. Th coodinats using th vtical snsd by a bubbl lvl, which sponds to th al vaiation in th gavity fild, a discussd in sction VII. Th angl mad by th lin to th cnt of th ath is calld gocntic latitud. This is th only latitud in th sphical ath modl. Today gocntic latitud is usd mainly in th fild of atificial ath satllits. 17
18 IV. Potntial Sufacs, Goid, and Hights Th sufacs of constant W a sufacs of constant potntial in th godsy nomnclatu. Ths a also sufacs of constant potntial ngy. Th minus sign dosn't chang th fom of a constant sufac. Wat would assum on of ths sufacs in a bowl, lak o ocan. Ths sufacs a calld Lvl Sufacs. Man sa lvl is on paticula sufac of constant W. This paticula sufac can b xtndd ov land. This paticula lvl sufac is calld th goid. To this point, th ath has bn idalizd. But th al ath has ocans, mountains and oth dnsity vaiations. Ths vaiations a small, but caus th al gavity valus to diff fom th simpl llipsoid modl. In th llipsoid modl, th goid is an llipsoid. In th al wold th goid has bumps. Now w will tun to th ffcts of th inhomognats of th al wold. Th lagst ffcts will b on hights. Th fom of th sufacs of W must b masud; thy cannot b computd fom a fw constants and a modl. Thy dpnd on th al wold mass vaiations, which vais on many distanc scals. Computing th distanc fom th goid to th cnt of th ath is not possibl without lag numbs of al wold masumnts. Th llipsoid is dfind mathmatically with spct to th cnt of th ath and its adius is asily computd. Knowing th distanc btwn th llipsoid and goid thfo would dfin th goid. Th fom of th goid ov lag distancs was not wll known until satllits w launchd. Stating with a "stak in th sand" that dfins man sa lvl at th sho, th hights of th land can b masud. With classical suvy tchniqus, this is don with a sis of masumnts mad fom point to point. Ths hights masud by classical mthods a masud fom th goid. This happns bcaus of th way hights a masud. Tansits (tlscops on a tipod) a usd, with angls masud with spct to th local vtical. Th local up vcto masud with a plumb bob o spiit lvl is th ppndicula to th al goid. Lvl Sufacs a th th-dimnsional analogu of contous in two dimnsions. In on dimnsion if you find th locations wh th function has a paticula valu, you gt a st of points. If you hav a function of two dimnsions, such as hight as a function of latitud and longitud, th st of points of a paticula valu is a lin. This is on of th contous. If you hav a function of latitud, longitud and hight th st of points of a paticula valu is a sufac. Picking on potntial dfins a sufac. On paticula valu dfins th goid. 18
19 As th tansit is movd fom plac to plac, th local vtical will follow th hills and vallys of W. Thfo th goid is th fnc sufac fo classical hight masumnts. As on chif of th US National Godtic Suvy onc said, w a in th position of knowing hights vy accuatly with spct to a sufac w know pooly. Hights dtmind in this mano a calld othomtic hights o man sa lvl (msl) hights. (Othomtic and msl hight a slightly diffnt, but th two tms a commonly usd to man th sam thing.) 19
20 Hights dtmind in this mano a calld othomtic hights o man sa lvl (msl) hights. Excpt in godtic scinc litatu, wh you s msl hight, it usually mans othomtic hight. Tchnically othomtic and msl hight a slightly diffnt. Ocan cunts and oth ffcts slightly modify th al sufac hight of th sa. All th diffnc btwn al msl and othomtic hights can b classifid as ocanogaphy. Hights masud fom th llipsoid a calld llipsoidal hights o godtic hights. Satllit systms masu llipsoidal hights. This is not what w s on maps o in databass. Ths contain othomtic hight. Bcaus satllit basd positioning is now vy impotant, th is a nd fo a good masumnt of th goid location. This is don by masuing th vtical distanc btwn th llipsoid and th al wold goid as a function of location. This diffnc is calld undulation of th vtical o spaation of th goid. Th symbol N is usd fo th undulation. Whil th symbols h and H a commonly usd fo th two hights, th is no standad fo which mans othomtic o llipsoidal. H w will us th DoD standad, h H fo llipsoidal, and fo othomtic hight. Not that in all cass th undulation, N is th othomtic minus th llipsoidal hights. It is th distanc fom th llipsoid to th goid. 0
21 h N Thus H H + N h, wh th valus a takn at th sam point. N is a function of location. Finding N as a function of latitud and longitud is how w dtmin th goid. Th abov figu givs a woldwid viw of th goid sufac. Th valus ang fom about -100 m to m. Wold wid llipsoids a chosn so that th avag undulation is zo ov th wold. This mans that th a as many placs with th goid abov th llipsoid as th a with th goid blow th llipsoid. Th a many small aa vaiations in th goid that do not show up in this figu. Bcaus othomtic hights (msl) w th only ons histoically masuabl, thy a th hights shown on maps and in databass. All hights on maps a othomtic. Howv position masumnts mad using satllit systms, such as GPS, a inhntly don in an ath cntd, ath fixd Catsian X-Y-Z systm. Ths can asily b convtd to latitud, longitud, and llipsoidal hight. (Also calld godtic hight). Th goid undulation, N, is ndd to convt ths to map typ (othomtic o msl) hights. This valu is only know at th mt lvl in most placs. 1
22 V. Goid and Topogaphy Th goid has vaiations, o componnts, at many spatial scals. At long lngths it fls th influncs of most of th ath and its vaiations in dnsity. Howv on a shot scal, small vaiations a dominatd by local ffcts such as na by mountains tc. This is illustatd in th abov figu. Th goid sms to follow th mountain ang up and down. This can b sn fom th condition that th goid is ppndicula to th local gavity vcto. Th absolut valu of th goid lvl can vay a lot bcaus it is influncd by mass vaiations ov a vy long ang, but th small bumps look lik local topogaphy - at last on th km ang.
Problem Solving Session 1: Electric Dipoles and Torque
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Dpatmnt of Physics 8.02 Poblm Solving Sssion 1: Elctic Dipols and Toqu Sction Tabl (if applicabl) Goup Mmbs Intoduction: In th fist poblm you will lan to apply Coulomb
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Dpatmnt of Physics 8.02 Poblm Solving Sssion 1: Elctic Dipols and Toqu Sction Tabl (if applicabl) Goup Mmbs Intoduction: In th fist poblm you will lan to apply Coulomb
Chapter 3. Electric Potential
 Chapt 3 Elctic Potntial 3.1 Potntial and Potntial Engy...3-3. Elctic Potntial in a Unifom Fild...3-5 3.3 Elctic Potntial du to Point Chags...3-6 3.3.1 Potntial Engy in a Systm of Chags...3-8 3.4 Continuous
Chapt 3 Elctic Potntial 3.1 Potntial and Potntial Engy...3-3. Elctic Potntial in a Unifom Fild...3-5 3.3 Elctic Potntial du to Point Chags...3-6 3.3.1 Potntial Engy in a Systm of Chags...3-8 3.4 Continuous
Physics. Lesson Plan #9 Energy, Work and Simple Machines David V. Fansler Beddingfield High School
 Physics Lsson Plan #9 Engy, Wok an Simpl Machins Davi V. Fansl Bingfil High School Engy an Wok Objctivs: Dscib th lationship btwn wok an ngy; Display an ability to calculat wok on by a foc; Intify th foc
Physics Lsson Plan #9 Engy, Wok an Simpl Machins Davi V. Fansl Bingfil High School Engy an Wok Objctivs: Dscib th lationship btwn wok an ngy; Display an ability to calculat wok on by a foc; Intify th foc
HEAT TRANSFER ANALYSIS OF LNG TRANSFER LINE
 Scintific Jounal of Impact Facto(SJIF): 3.34 Intnational Jounal of Advanc Engining and sach Dvlopmnt Volum,Issu, Fbuay -05 HEAT TANSFE ANALYSIS OF LNG TANSFE LINE J.D. Jani -ISSN(O): 348-4470 p-issn(p):
Scintific Jounal of Impact Facto(SJIF): 3.34 Intnational Jounal of Advanc Engining and sach Dvlopmnt Volum,Issu, Fbuay -05 HEAT TANSFE ANALYSIS OF LNG TANSFE LINE J.D. Jani -ISSN(O): 348-4470 p-issn(p):
Handout 3. Free Electron Gas in 2D and 1D
 Handout 3 F lcton Gas in D and D In this lctu ou will lan: F lcton gas in two dinsions and in on dinsion Dnsit o Stats in -spac and in ng in low dinsions C 47 Sping 9 Fahan Rana Conll Univsit lcton Gass
Handout 3 F lcton Gas in D and D In this lctu ou will lan: F lcton gas in two dinsions and in on dinsion Dnsit o Stats in -spac and in ng in low dinsions C 47 Sping 9 Fahan Rana Conll Univsit lcton Gass
Newton s Law of Gravitation
 Physics 106 Lctu 9 Nwton s Law of Gavitation SJ 7 th Ed.: Chap 1.1 to, 1.4 to 5 Histoical ovviw Nwton s invs-squa law of avitation i oc Gavitational acclation Supposition Gavitation na th Eath s sufac
Physics 106 Lctu 9 Nwton s Law of Gavitation SJ 7 th Ed.: Chap 1.1 to, 1.4 to 5 Histoical ovviw Nwton s invs-squa law of avitation i oc Gavitational acclation Supposition Gavitation na th Eath s sufac
Incorporating Statistical Process Control and Statistical Quality Control Techniques into a Quality Assurance Program
 Incooating Statistical Pocss Contol and Statistical Quality Contol Tchniqus into a Quality Assuanc Pogam Robyn Sikis U.S. Cnsus Buau Puos Incooat SPC and SQC mthods into quality assuanc ogam Monito and
Incooating Statistical Pocss Contol and Statistical Quality Contol Tchniqus into a Quality Assuanc Pogam Robyn Sikis U.S. Cnsus Buau Puos Incooat SPC and SQC mthods into quality assuanc ogam Monito and
PHYSICS 206a HOMEWORK #11 SOLUTIONS
 PHYSICS 0a HOEWORK # SOLUTIONS. Using Nwton s law of gavitation, div th acclation du to gavity xpincd by an objct of ass at th sufac of th Eath. Show that this acclation is indpndnt of th ass of th objct.
PHYSICS 0a HOEWORK # SOLUTIONS. Using Nwton s law of gavitation, div th acclation du to gavity xpincd by an objct of ass at th sufac of th Eath. Show that this acclation is indpndnt of th ass of th objct.
Factors that Influence Memory
 Ovlaning Factos that Influnc Mmoy Continu to study somthing aft you can call it pfctly. Psychology 390 Psychology of Laning Stvn E. Mi, Ph.D. Listn to th audio lctu whil viwing ths slids 1 2 Oganization
Ovlaning Factos that Influnc Mmoy Continu to study somthing aft you can call it pfctly. Psychology 390 Psychology of Laning Stvn E. Mi, Ph.D. Listn to th audio lctu whil viwing ths slids 1 2 Oganization
Reach Versus Competition in Channels with Internet and Traditional Retailers
 Rach Vsus Comptition in Channls with Intnt and Taditional Rtails Bai R Nault Haskayn School of Businss, Univsity of Calgay, Calgay, Albta, Canada, nault@ucalgayca Mohammad S Rahman Haskayn School of Businss,
Rach Vsus Comptition in Channls with Intnt and Taditional Rtails Bai R Nault Haskayn School of Businss, Univsity of Calgay, Calgay, Albta, Canada, nault@ucalgayca Mohammad S Rahman Haskayn School of Businss,
Episode 401: Newton s law of universal gravitation
 Episode 401: Newton s law of univesal gavitation This episode intoduces Newton s law of univesal gavitation fo point masses, and fo spheical masses, and gets students pactising calculations of the foce
Episode 401: Newton s law of univesal gavitation This episode intoduces Newton s law of univesal gavitation fo point masses, and fo spheical masses, and gets students pactising calculations of the foce
fiziks Institute for NET/JRF, GATE, IIT JAM, JEST, TIFR and GRE in PHYSICAL SCIENCES NUCLEAR AND PARTICLE PHYSICS NET/JRF (JUNE-2011)
 Institut fo NET/JRF, GTE, IIT JM, JEST, TIFR and GRE in PHYSICL SCIENCES Had offic fiziks, H.No., G.F, Jia Saai, Na IIT, Hauz Khas, Nw Dlhi 6 Phon: 6865455/9 98745498 NUCLER ND PRTICLE PHYSICS NET/JRF
Institut fo NET/JRF, GTE, IIT JM, JEST, TIFR and GRE in PHYSICL SCIENCES Had offic fiziks, H.No., G.F, Jia Saai, Na IIT, Hauz Khas, Nw Dlhi 6 Phon: 6865455/9 98745498 NUCLER ND PRTICLE PHYSICS NET/JRF
New Basis Functions. Section 8. Complex Fourier Series
 Nw Basis Functions Sction 8 Complx Fourir Sris Th complx Fourir sris is prsntd first with priod 2, thn with gnral priod. Th connction with th ral-valud Fourir sris is xplaind and formula ar givn for convrting
Nw Basis Functions Sction 8 Complx Fourir Sris Th complx Fourir sris is prsntd first with priod 2, thn with gnral priod. Th connction with th ral-valud Fourir sris is xplaind and formula ar givn for convrting
Design of Extended Warranties in Supply Chains. Abstract
 Dsign of Extndd Waantis in Supply Chains Kunpng Li Univsity of Illinois at Ubana Champaign, Collg of Businss Dilip Chhajd Univsity of Illinois at Ubana Champaign, Collg of Businss Suman Mallik Univsity
Dsign of Extndd Waantis in Supply Chains Kunpng Li Univsity of Illinois at Ubana Champaign, Collg of Businss Dilip Chhajd Univsity of Illinois at Ubana Champaign, Collg of Businss Suman Mallik Univsity
Tank Level GPRS/GSM Wireless Monitoring System Solutions
 Tank Lvl GPRS/GSM Wilss Monitoing Systm Solutions HOLYKELL TECHNOLOGY CO.LTD May,2014 Ⅰ. Solution Rquimnts 1. Intoduction Th solution is mainly including: wilss data tansciv tminal, lvl snso and PC sv
Tank Lvl GPRS/GSM Wilss Monitoing Systm Solutions HOLYKELL TECHNOLOGY CO.LTD May,2014 Ⅰ. Solution Rquimnts 1. Intoduction Th solution is mainly including: wilss data tansciv tminal, lvl snso and PC sv
A Model for Antenna-Plasma Wave Coupling towards Control of Uniformity in Slot-Excited Microwave Discharges
 J. Plasa Fusion Rs. SERIES, Vol. 9 () A Modl fo Antnna-Plasa Wav Couling towads Contol of Unifoity in Slot-Excitd Micowav Dischags Daichi SAWADA, Akihio TSUJI, Takanoi KITSUDO, Yasuyoshi YASAKA, and Hioasa
J. Plasa Fusion Rs. SERIES, Vol. 9 () A Modl fo Antnna-Plasa Wav Couling towads Contol of Unifoity in Slot-Excitd Micowav Dischags Daichi SAWADA, Akihio TSUJI, Takanoi KITSUDO, Yasuyoshi YASAKA, and Hioasa
Superconducting gravimeter calibration by co-located gravity observations results from GWR C025
 Supconducting gavimt calibation by co-locatd gavity obsvations sults fom GWR C25 B. us Dpatmnt of toology and Gophysics, Univsity of Vinna, Althanstass 19, A- 19 Win, Austia. Cospondnc should b addssd
Supconducting gavimt calibation by co-locatd gavity obsvations sults fom GWR C25 B. us Dpatmnt of toology and Gophysics, Univsity of Vinna, Althanstass 19, A- 19 Win, Austia. Cospondnc should b addssd
Question 3: How do you find the relative extrema of a function?
 ustion 3: How do you find th rlativ trma of a function? Th stratgy for tracking th sign of th drivativ is usful for mor than dtrmining whr a function is incrasing or dcrasing. It is also usful for locating
ustion 3: How do you find th rlativ trma of a function? Th stratgy for tracking th sign of th drivativ is usful for mor than dtrmining whr a function is incrasing or dcrasing. It is also usful for locating
CPS 220 Theory of Computation REGULAR LANGUAGES. Regular expressions
 CPS 22 Thory of Computation REGULAR LANGUAGES Rgular xprssions Lik mathmatical xprssion (5+3) * 4. Rgular xprssion ar built using rgular oprations. (By th way, rgular xprssions show up in various languags:
CPS 22 Thory of Computation REGULAR LANGUAGES Rgular xprssions Lik mathmatical xprssion (5+3) * 4. Rgular xprssion ar built using rgular oprations. (By th way, rgular xprssions show up in various languags:
FXA 2008. Candidates should be able to : Describe how a mass creates a gravitational field in the space around it.
 Candidates should be able to : Descibe how a mass ceates a gavitational field in the space aound it. Define gavitational field stength as foce pe unit mass. Define and use the peiod of an object descibing
Candidates should be able to : Descibe how a mass ceates a gavitational field in the space aound it. Define gavitational field stength as foce pe unit mass. Define and use the peiod of an object descibing
ME 612 Metal Forming and Theory of Plasticity. 6. Strain
 Mtal Forming and Thory of Plasticity -mail: azsnalp@gyt.du.tr Makin Mühndisliği Bölümü Gbz Yüksk Tknoloji Enstitüsü 6.1. Uniaxial Strain Figur 6.1 Dfinition of th uniaxial strain (a) Tnsil and (b) Comprssiv.
Mtal Forming and Thory of Plasticity -mail: azsnalp@gyt.du.tr Makin Mühndisliği Bölümü Gbz Yüksk Tknoloji Enstitüsü 6.1. Uniaxial Strain Figur 6.1 Dfinition of th uniaxial strain (a) Tnsil and (b) Comprssiv.
Lecture 3: Diffusion: Fick s first law
 Lctur 3: Diffusion: Fick s first law Today s topics What is diffusion? What drivs diffusion to occur? Undrstand why diffusion can surprisingly occur against th concntration gradint? Larn how to dduc th
Lctur 3: Diffusion: Fick s first law Today s topics What is diffusion? What drivs diffusion to occur? Undrstand why diffusion can surprisingly occur against th concntration gradint? Larn how to dduc th
12. Rolling, Torque, and Angular Momentum
 12. olling, Toque, and Angula Momentum 1 olling Motion: A motion that is a combination of otational and tanslational motion, e.g. a wheel olling down the oad. Will only conside olling with out slipping.
12. olling, Toque, and Angula Momentum 1 olling Motion: A motion that is a combination of otational and tanslational motion, e.g. a wheel olling down the oad. Will only conside olling with out slipping.
High Voltage Cables. Figure 5.1 - Layout of three, single-core cables
 High oltag Cabls 5.0 High oltag Cabls High oltag Cabls a usd whn undgound tansmission is quid. Ths cabls a laid in ducts o may b buid in th gound. Unlik in ovhad lins, ai dos not fom pat of th insulation,
High oltag Cabls 5.0 High oltag Cabls High oltag Cabls a usd whn undgound tansmission is quid. Ths cabls a laid in ducts o may b buid in th gound. Unlik in ovhad lins, ai dos not fom pat of th insulation,
by John Donald, Lecturer, School of Accounting, Economics and Finance, Deakin University, Australia
 Studnt Nots Cost Volum Profit Analysis by John Donald, Lcturr, School of Accounting, Economics and Financ, Dakin Univrsity, Australia As mntiond in th last st of Studnt Nots, th ability to catgoris costs
Studnt Nots Cost Volum Profit Analysis by John Donald, Lcturr, School of Accounting, Economics and Financ, Dakin Univrsity, Australia As mntiond in th last st of Studnt Nots, th ability to catgoris costs
(a) The centripetal acceleration of a point on the equator of the Earth is given by v2. The velocity of the earth can be found by taking the ratio of
 Homewok VI Ch. 7 - Poblems 15, 19, 22, 25, 35, 43, 51. Poblem 15 (a) The centipetal acceleation of a point on the equato of the Eath is given by v2. The velocity of the eath can be found by taking the
Homewok VI Ch. 7 - Poblems 15, 19, 22, 25, 35, 43, 51. Poblem 15 (a) The centipetal acceleation of a point on the equato of the Eath is given by v2. The velocity of the eath can be found by taking the
QUANTITATIVE METHODS CLASSES WEEK SEVEN
 QUANTITATIVE METHODS CLASSES WEEK SEVEN Th rgrssion modls studid in prvious classs assum that th rspons variabl is quantitativ. Oftn, howvr, w wish to study social procsss that lad to two diffrnt outcoms.
QUANTITATIVE METHODS CLASSES WEEK SEVEN Th rgrssion modls studid in prvious classs assum that th rspons variabl is quantitativ. Oftn, howvr, w wish to study social procsss that lad to two diffrnt outcoms.
Mathematics. Mathematics 3. hsn.uk.net. Higher HSN23000
 hsn uknt Highr Mathmatics UNIT Mathmatics HSN000 This documnt was producd spcially for th HSNuknt wbsit, and w rquir that any copis or drivativ works attribut th work to Highr Still Nots For mor dtails
hsn uknt Highr Mathmatics UNIT Mathmatics HSN000 This documnt was producd spcially for th HSNuknt wbsit, and w rquir that any copis or drivativ works attribut th work to Highr Still Nots For mor dtails
Gravitation. AP Physics C
 Gavitation AP Physics C Newton s Law of Gavitation What causes YOU to be pulled down? THE EARTH.o moe specifically the EARTH S MASS. Anything that has MASS has a gavitational pull towads it. F α Mm g What
Gavitation AP Physics C Newton s Law of Gavitation What causes YOU to be pulled down? THE EARTH.o moe specifically the EARTH S MASS. Anything that has MASS has a gavitational pull towads it. F α Mm g What
DEGRADATION MODEL OF BREAST IMAGING BY DISPERSED RADIATION
 THE PUBLISHING HOUSE PROCEEDINGS OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY, Sis A, OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY Volum 1, Numb 4/011, pp. 347 35 DEGRADATION MODEL OF BREAST IMAGING BY DISPERSED RADIATION Migul BUSTAMANTE 1, Gastón
THE PUBLISHING HOUSE PROCEEDINGS OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY, Sis A, OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY Volum 1, Numb 4/011, pp. 347 35 DEGRADATION MODEL OF BREAST IMAGING BY DISPERSED RADIATION Migul BUSTAMANTE 1, Gastón
Agilent Basics of Measuring the Dielectric Properties of Materials. Application Note
 Agilnt Basics of Masuing th Dilctic Poptis of Matials Application Not Contnts Intoduction...3 Dilctic thoy...4 Dilctic Constant...4 Pmability...7 Elctomagntic popagation...8 Dilctic mchanisms...10 Ointation
Agilnt Basics of Masuing th Dilctic Poptis of Matials Application Not Contnts Intoduction...3 Dilctic thoy...4 Dilctic Constant...4 Pmability...7 Elctomagntic popagation...8 Dilctic mchanisms...10 Ointation
PHYSICS 111 HOMEWORK SOLUTION #13. May 1, 2013
 PHYSICS 111 HOMEWORK SOLUTION #13 May 1, 2013 0.1 In intoductoy physics laboatoies, a typical Cavendish balance fo measuing the gavitational constant G uses lead sphees with masses of 2.10 kg and 21.0
PHYSICS 111 HOMEWORK SOLUTION #13 May 1, 2013 0.1 In intoductoy physics laboatoies, a typical Cavendish balance fo measuing the gavitational constant G uses lead sphees with masses of 2.10 kg and 21.0
Exam 3: Equation Summary
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Depatment of Physics Physics 8.1 TEAL Fall Tem 4 Momentum: p = mv, F t = p, Fext ave t= t f t= Exam 3: Equation Summay total = Impulse: I F( t ) = p Toque: τ = S S,P
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Depatment of Physics Physics 8.1 TEAL Fall Tem 4 Momentum: p = mv, F t = p, Fext ave t= t f t= Exam 3: Equation Summay total = Impulse: I F( t ) = p Toque: τ = S S,P
Traffic Flow Analysis (2)
 Traffic Flow Analysis () Statistical Proprtis. Flow rat distributions. Hadway distributions. Spd distributions by Dr. Gang-Ln Chang, Profssor Dirctor of Traffic safty and Oprations Lab. Univrsity of Maryland,
Traffic Flow Analysis () Statistical Proprtis. Flow rat distributions. Hadway distributions. Spd distributions by Dr. Gang-Ln Chang, Profssor Dirctor of Traffic safty and Oprations Lab. Univrsity of Maryland,
I N S T I T U T D E S T A T I S T I Q U E B I O S T A T I S T I Q U E E T S C I E N C E S A C T U A R I E L L E S (I S B A)
 I S T I T U T D E S T A T I S T I Q U E B I O S T A T I S T I Q U E E T S C I E C E S A C T U A R I E L L E S (I S B A UIVERSITÉ CATHOLIQUE DE LOUVAI D I S C U S S I O P A P E R 0/5 SOLVECY REQUIREMET
I S T I T U T D E S T A T I S T I Q U E B I O S T A T I S T I Q U E E T S C I E C E S A C T U A R I E L L E S (I S B A UIVERSITÉ CATHOLIQUE DE LOUVAI D I S C U S S I O P A P E R 0/5 SOLVECY REQUIREMET
Implied volatility formula of European Power Option Pricing
 Impli volatility fomula of Euopan Pow Option Picing Jingwi Liu * ing hn chool of Mathmatics an ystm cincs, Bihang Univsity, LMIB of th Ministy of Eucation,, Bijing, 009, P.R hina Abstact:W iv th impli
Impli volatility fomula of Euopan Pow Option Picing Jingwi Liu * ing hn chool of Mathmatics an ystm cincs, Bihang Univsity, LMIB of th Ministy of Eucation,, Bijing, 009, P.R hina Abstact:W iv th impli
A Note on Approximating. the Normal Distribution Function
 Applid Mathmatical Scincs, Vol, 00, no 9, 45-49 A Not on Approimating th Normal Distribution Function K M Aludaat and M T Alodat Dpartmnt of Statistics Yarmouk Univrsity, Jordan Aludaatkm@hotmailcom and
Applid Mathmatical Scincs, Vol, 00, no 9, 45-49 A Not on Approimating th Normal Distribution Function K M Aludaat and M T Alodat Dpartmnt of Statistics Yarmouk Univrsity, Jordan Aludaatkm@hotmailcom and
Load Balancing Algorithm Based on QoS Awareness Applied in Wireless Networks
 , pp.191-195 http://x.oi.og/10.14257/astl.2015.111.37 Loa Balancing Algoithm Bas on QoS Awanss Appli in Wilss Ntwoks CHEN Xiangqian, MA Shaohui Dpatmnt of Comput Scinc an Tchnology, Hnan Mchanic an Elctical
, pp.191-195 http://x.oi.og/10.14257/astl.2015.111.37 Loa Balancing Algoithm Bas on QoS Awanss Appli in Wilss Ntwoks CHEN Xiangqian, MA Shaohui Dpatmnt of Comput Scinc an Tchnology, Hnan Mchanic an Elctical
Basis risk. When speaking about forward or futures contracts, basis risk is the market
 Basis risk Whn spaking about forward or futurs contracts, basis risk is th markt risk mismatch btwn a position in th spot asst and th corrsponding futurs contract. Mor broadly spaking, basis risk (also
Basis risk Whn spaking about forward or futurs contracts, basis risk is th markt risk mismatch btwn a position in th spot asst and th corrsponding futurs contract. Mor broadly spaking, basis risk (also
Before attempting to connect or operate this product, please read these instructions carefully and save this manual for future use.
 Modl No. RAID Boad Instuctions WJ-NDB301 Bfo attmpting to connct o opat this poduct, plas ad ths instuctions cafully and sav this manual fo futu us. Waning: All ok latd to th installation of this poduct
Modl No. RAID Boad Instuctions WJ-NDB301 Bfo attmpting to connct o opat this poduct, plas ad ths instuctions cafully and sav this manual fo futu us. Waning: All ok latd to th installation of this poduct
2 r2 θ = r2 t. (3.59) The equal area law is the statement that the term in parentheses,
 3.4. KEPLER S LAWS 145 3.4 Keple s laws You ae familia with the idea that one can solve some mechanics poblems using only consevation of enegy and (linea) momentum. Thus, some of what we see as objects
3.4. KEPLER S LAWS 145 3.4 Keple s laws You ae familia with the idea that one can solve some mechanics poblems using only consevation of enegy and (linea) momentum. Thus, some of what we see as objects
Section 7.4: Exponential Growth and Decay
 1 Sction 7.4: Exponntial Growth and Dcay Practic HW from Stwart Txtbook (not to hand in) p. 532 # 1-17 odd In th nxt two ction, w xamin how population growth can b modld uing diffrntial quation. W tart
1 Sction 7.4: Exponntial Growth and Dcay Practic HW from Stwart Txtbook (not to hand in) p. 532 # 1-17 odd In th nxt two ction, w xamin how population growth can b modld uing diffrntial quation. W tart
Instruction: Solving Exponential Equations without Logarithms. This lecture uses a four-step process to solve exponential equations:
 49 Instuction: Solving Eponntil Equtions without Logithms This lctu uss fou-stp pocss to solv ponntil qutions: Isolt th bs. Wit both sids of th qution s ponntil pssions with lik bss. St th ponnts qul to
49 Instuction: Solving Eponntil Equtions without Logithms This lctu uss fou-stp pocss to solv ponntil qutions: Isolt th bs. Wit both sids of th qution s ponntil pssions with lik bss. St th ponnts qul to
Physics 235 Chapter 5. Chapter 5 Gravitation
 Chapte 5 Gavitation In this Chapte we will eview the popeties of the gavitational foce. The gavitational foce has been discussed in geat detail in you intoductoy physics couses, and we will pimaily focus
Chapte 5 Gavitation In this Chapte we will eview the popeties of the gavitational foce. The gavitational foce has been discussed in geat detail in you intoductoy physics couses, and we will pimaily focus
Phys 2101 Gabriela González. cos. sin. sin
 1 Phys 101 Gabiela González a m t t ma ma m m T α φ ω φ sin cos α τ α φ τ sin m m α τ I We know all of that aleady!! 3 The figue shows the massive shield doo at a neuton test facility at Lawence Livemoe
1 Phys 101 Gabiela González a m t t ma ma m m T α φ ω φ sin cos α τ α φ τ sin m m α τ I We know all of that aleady!! 3 The figue shows the massive shield doo at a neuton test facility at Lawence Livemoe
Events and Constraints: A Graphical Editor for Capturing Logic Requirements of Programs
 Evnts and Constaints: A Gaphical Edito fo Captuing Logic Rquimnts of Pogams Magat H. Smith Bll Laboatois Rm. 2C-407 600 Mountain Avnu Muay Hill, NJ 07974 mhs@sach.bll-labs.com Gad J. Holzmann Bll Laboatois
Evnts and Constaints: A Gaphical Edito fo Captuing Logic Rquimnts of Pogams Magat H. Smith Bll Laboatois Rm. 2C-407 600 Mountain Avnu Muay Hill, NJ 07974 mhs@sach.bll-labs.com Gad J. Holzmann Bll Laboatois
A Systematic Approach to the Comparison of Roles in the Software Development Processes
 A Systmatic Appoach to th Compaison of Rols in th Softwa Dvlopmnt Pocsss uat Yilmaz 1, Roy V. O Conno 2 and Paul Clak 1 1 Lo Gaduat School in Softwa Engining, Dublin City Univsity, Iland 2 Lo, th Iish
A Systmatic Appoach to th Compaison of Rols in th Softwa Dvlopmnt Pocsss uat Yilmaz 1, Roy V. O Conno 2 and Paul Clak 1 1 Lo Gaduat School in Softwa Engining, Dublin City Univsity, Iland 2 Lo, th Iish
Coordinate Systems L. M. Kalnins, March 2009
 Coodinate Sstems L. M. Kalnins, Mach 2009 Pupose of a Coodinate Sstem The pupose of a coodinate sstem is to uniquel detemine the position of an object o data point in space. B space we ma liteall mean
Coodinate Sstems L. M. Kalnins, Mach 2009 Pupose of a Coodinate Sstem The pupose of a coodinate sstem is to uniquel detemine the position of an object o data point in space. B space we ma liteall mean
An AnyLogic Simulation Model for Power and Performance Analysis of Data Centres
 An AnyLogic Simulation Modl fo Pow and Pfomanc Analysis of Data Cnts Bjön F. Postma and Boudwijn R. Havkot Cnt fo Tlmatics and Infomation Tchnology, Univsity of Twnt, th Nthlands {b.f.postma, b..h.m.havkot}@utwnt.nl
An AnyLogic Simulation Modl fo Pow and Pfomanc Analysis of Data Cnts Bjön F. Postma and Boudwijn R. Havkot Cnt fo Tlmatics and Infomation Tchnology, Univsity of Twnt, th Nthlands {b.f.postma, b..h.m.havkot}@utwnt.nl
Voltage ( = Electric Potential )
 V-1 Voltage ( = Electic Potential ) An electic chage altes the space aound it. Thoughout the space aound evey chage is a vecto thing called the electic field. Also filling the space aound evey chage is
V-1 Voltage ( = Electic Potential ) An electic chage altes the space aound it. Thoughout the space aound evey chage is a vecto thing called the electic field. Also filling the space aound evey chage is
The example is taken from Sect. 1.2 of Vol. 1 of the CPN book.
 Rsourc Allocation Abstract This is a small toy xampl which is wll-suitd as a first introduction to Cnts. Th CN modl is dscribd in grat dtail, xplaining th basic concpts of C-nts. Hnc, it can b rad by popl
Rsourc Allocation Abstract This is a small toy xampl which is wll-suitd as a first introduction to Cnts. Th CN modl is dscribd in grat dtail, xplaining th basic concpts of C-nts. Hnc, it can b rad by popl
Fluids Lecture 15 Notes
 Fluids Lectue 15 Notes 1. Unifom flow, Souces, Sinks, Doublets Reading: Andeson 3.9 3.12 Unifom Flow Definition A unifom flow consists of a velocit field whee V = uî + vĵ is a constant. In 2-D, this velocit
Fluids Lectue 15 Notes 1. Unifom flow, Souces, Sinks, Doublets Reading: Andeson 3.9 3.12 Unifom Flow Definition A unifom flow consists of a velocit field whee V = uî + vĵ is a constant. In 2-D, this velocit
THE NAVAJO NATION Department of Personnel Management JOB VACANCY ANNOUNCEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEMS TECHNICIAN
 THE NAVAJO NATION Dpatmnt of Psonnl Managmnt JOB VACANCY ANNOUNCEMENT REQUISITION NO: EPA0158783 DATE POSTED: 06/30/14 POSITION NO: 241518 CLOSING DATE: 07/14/14 POSITION TITLE: INFORMATION SYSTEMS TECHNICIAN
THE NAVAJO NATION Dpatmnt of Psonnl Managmnt JOB VACANCY ANNOUNCEMENT REQUISITION NO: EPA0158783 DATE POSTED: 06/30/14 POSITION NO: 241518 CLOSING DATE: 07/14/14 POSITION TITLE: INFORMATION SYSTEMS TECHNICIAN
Chapter 22. Outside a uniformly charged sphere, the field looks like that of a point charge at the center of the sphere.
 Chapte.3 What is the magnitude of a point chage whose electic field 5 cm away has the magnitude of.n/c. E E 5.56 1 11 C.5 An atom of plutonium-39 has a nuclea adius of 6.64 fm and atomic numbe Z94. Assuming
Chapte.3 What is the magnitude of a point chage whose electic field 5 cm away has the magnitude of.n/c. E E 5.56 1 11 C.5 An atom of plutonium-39 has a nuclea adius of 6.64 fm and atomic numbe Z94. Assuming
5.4 Exponential Functions: Differentiation and Integration TOOTLIFTST:
 .4 Eponntial Functions: Diffrntiation an Intgration TOOTLIFTST: Eponntial functions ar of th form f ( ) Ab. W will, in this sction, look at a spcific typ of ponntial function whr th bas, b, is.78.... This
.4 Eponntial Functions: Diffrntiation an Intgration TOOTLIFTST: Eponntial functions ar of th form f ( ) Ab. W will, in this sction, look at a spcific typ of ponntial function whr th bas, b, is.78.... This
Cloud and Big Data Summer School, Stockholm, Aug., 2015 Jeffrey D. Ullman
 Cloud and Big Data Summr Scool, Stockolm, Aug., 2015 Jffry D. Ullman Givn a st of points, wit a notion of distanc btwn points, group t points into som numbr of clustrs, so tat mmbrs of a clustr ar clos
Cloud and Big Data Summr Scool, Stockolm, Aug., 2015 Jffry D. Ullman Givn a st of points, wit a notion of distanc btwn points, group t points into som numbr of clustrs, so tat mmbrs of a clustr ar clos
Design for Cyclic Loading
 Dsign o Cyclic Loading 1. Compltly vsing cyclic stss and ndanc stngth A ply vsing o cyclic stss mans whn th stss altnats btwn qal positiv and ngativ pak stsss sinsoidally ding ach 300 cycl o opation, as
Dsign o Cyclic Loading 1. Compltly vsing cyclic stss and ndanc stngth A ply vsing o cyclic stss mans whn th stss altnats btwn qal positiv and ngativ pak stsss sinsoidally ding ach 300 cycl o opation, as
Projections - 3D Viewing. Overview Lecture 4. Projection - 3D viewing. Projections. Projections Parallel Perspective
 Ovrviw Lctur 4 Projctions - 3D Viwing Projctions Paralll Prspctiv 3D Viw Volum 3D Viwing Transformation Camra Modl - Assignmnt 2 OFF fils 3D mor compl than 2D On mor dimnsion Displa dvic still 2D Analog
Ovrviw Lctur 4 Projctions - 3D Viwing Projctions Paralll Prspctiv 3D Viw Volum 3D Viwing Transformation Camra Modl - Assignmnt 2 OFF fils 3D mor compl than 2D On mor dimnsion Displa dvic still 2D Analog
Should I Stay or Should I Go? Migration under Uncertainty: A New Approach
 Should Stay o Should Go? Migation und Unctainty: A Nw Appoach by Yasmn Khwaja * ctob 000 * patmnt of Economics, School of intal and Afican Studis, Unisity of ondon, Thonhaugh Stt, Russll Squa, ondon WC
Should Stay o Should Go? Migation und Unctainty: A Nw Appoach by Yasmn Khwaja * ctob 000 * patmnt of Economics, School of intal and Afican Studis, Unisity of ondon, Thonhaugh Stt, Russll Squa, ondon WC
SPECIAL VOWEL SOUNDS
 SPECIAL VOWEL SOUNDS Plas consult th appropriat supplmnt for th corrsponding computr softwar lsson. Rfr to th 42 Sounds Postr for ach of th Spcial Vowl Sounds. TEACHER INFORMATION: Spcial Vowl Sounds (SVS)
SPECIAL VOWEL SOUNDS Plas consult th appropriat supplmnt for th corrsponding computr softwar lsson. Rfr to th 42 Sounds Postr for ach of th Spcial Vowl Sounds. TEACHER INFORMATION: Spcial Vowl Sounds (SVS)
Constraint-Based Analysis of Gene Deletion in a Metabolic Network
 Constraint-Basd Analysis of Gn Dltion in a Mtabolic Ntwork Abdlhalim Larhlimi and Alxandr Bockmayr DFG-Rsarch Cntr Mathon, FB Mathmatik und Informatik, Fri Univrsität Brlin, Arnimall, 3, 14195 Brlin, Grmany
Constraint-Basd Analysis of Gn Dltion in a Mtabolic Ntwork Abdlhalim Larhlimi and Alxandr Bockmayr DFG-Rsarch Cntr Mathon, FB Mathmatik und Informatik, Fri Univrsität Brlin, Arnimall, 3, 14195 Brlin, Grmany
Sale Mode Choice of Product Extended Warranty based on the Service Level
 Intnational Jonal of - and - Svic, Scinc and Tchnology Vol8, No 8 (015, pp1-1 http://dxdoiog/101457/ijnsst0158801 Sal od Choic of Podct Extndd Waanty basd on th Svic Lvl Li Ji School of Infoation Tchnology,
Intnational Jonal of - and - Svic, Scinc and Tchnology Vol8, No 8 (015, pp1-1 http://dxdoiog/101457/ijnsst0158801 Sal od Choic of Podct Extndd Waanty basd on th Svic Lvl Li Ji School of Infoation Tchnology,
The (Bad?) Timing of Mutual Fund Investors. Oded Braverman,* Shmuel Kandel,** and Avi Wohl*** First version: February 2005 This version: August 2005
 Th (Bad? Timing of Mutual Fund Invstos by Odd Bavman,* Shmul Kandl,** and Avi Wohl*** Fist vsion: Fbuay 2005 This vsion: August 2005 W thank Invstmnt Comany Institut (ICI fo oviding us th mutual fund data
Th (Bad? Timing of Mutual Fund Invstos by Odd Bavman,* Shmul Kandl,** and Avi Wohl*** Fist vsion: Fbuay 2005 This vsion: August 2005 W thank Invstmnt Comany Institut (ICI fo oviding us th mutual fund data
F G r. Don't confuse G with g: "Big G" and "little g" are totally different things.
 G-1 Gavity Newton's Univesal Law of Gavitation (fist stated by Newton): any two masses m 1 and m exet an attactive gavitational foce on each othe accoding to m m G 1 This applies to all masses, not just
G-1 Gavity Newton's Univesal Law of Gavitation (fist stated by Newton): any two masses m 1 and m exet an attactive gavitational foce on each othe accoding to m m G 1 This applies to all masses, not just
Voltage ( = Electric Potential )
 V-1 of 9 Voltage ( = lectic Potential ) An electic chage altes the space aound it. Thoughout the space aound evey chage is a vecto thing called the electic field. Also filling the space aound evey chage
V-1 of 9 Voltage ( = lectic Potential ) An electic chage altes the space aound it. Thoughout the space aound evey chage is a vecto thing called the electic field. Also filling the space aound evey chage
Contents Stochastic Ray Tracing
 Contnts Stochastc Ray Tacng Kad Bouatouch IRISA Emal: kad@sa.f Mont Calo Intgaton Applcaton to dct lghtng by aa lght soucs Solvng th adanc quaton wth th Mont Calo Mthod Dstbutd Ray Tacng Path Taycng 2
Contnts Stochastc Ray Tacng Kad Bouatouch IRISA Emal: kad@sa.f Mont Calo Intgaton Applcaton to dct lghtng by aa lght soucs Solvng th adanc quaton wth th Mont Calo Mthod Dstbutd Ray Tacng Path Taycng 2
PY1052 Problem Set 8 Autumn 2004 Solutions
 PY052 Poblem Set 8 Autumn 2004 Solutions H h () A solid ball stats fom est at the uppe end of the tack shown and olls without slipping until it olls off the ight-hand end. If H 6.0 m and h 2.0 m, what
PY052 Poblem Set 8 Autumn 2004 Solutions H h () A solid ball stats fom est at the uppe end of the tack shown and olls without slipping until it olls off the ight-hand end. If H 6.0 m and h 2.0 m, what
81-1-ISD Economic Considerations of Heat Transfer on Sheet Metal Duct
 Air Handling Systms Enginring & chnical Bulltin 81-1-ISD Economic Considrations of Hat ransfr on Sht Mtal Duct Othr bulltins hav dmonstratd th nd to add insulation to cooling/hating ducts in ordr to achiv
Air Handling Systms Enginring & chnical Bulltin 81-1-ISD Economic Considrations of Hat ransfr on Sht Mtal Duct Othr bulltins hav dmonstratd th nd to add insulation to cooling/hating ducts in ordr to achiv
[ ] These are the motor parameters that are needed: Motor voltage constant. J total (lb-in-sec^2)
![[ ] These are the motor parameters that are needed: Motor voltage constant. J total (lb-in-sec^2) [ ] These are the motor parameters that are needed: Motor voltage constant. J total (lb-in-sec^2)](/thumbs/40/20779684.jpg) MEASURING MOOR PARAMEERS Fil: Motor paramtrs hs ar th motor paramtrs that ar ndd: Motor voltag constant (volts-sc/rad Motor torqu constant (lb-in/amp Motor rsistanc R a (ohms Motor inductanc L a (Hnris
MEASURING MOOR PARAMEERS Fil: Motor paramtrs hs ar th motor paramtrs that ar ndd: Motor voltag constant (volts-sc/rad Motor torqu constant (lb-in/amp Motor rsistanc R a (ohms Motor inductanc L a (Hnris
Gravity. A. Law of Gravity. Gravity. Physics: Mechanics. A. The Law of Gravity. Dr. Bill Pezzaglia. B. Gravitational Field. C.
 Physics: Mechanics 1 Gavity D. Bill Pezzaglia A. The Law of Gavity Gavity B. Gavitational Field C. Tides Updated: 01Jul09 A. Law of Gavity 3 1a. Invese Squae Law 4 1. Invese Squae Law. Newton s 4 th law
Physics: Mechanics 1 Gavity D. Bill Pezzaglia A. The Law of Gavity Gavity B. Gavitational Field C. Tides Updated: 01Jul09 A. Law of Gavity 3 1a. Invese Squae Law 4 1. Invese Squae Law. Newton s 4 th law
http://www.wwnorton.com/chemistry/tutorials/ch14.htm Repulsive Force
 ctivation nrgis http://www.wwnorton.com/chmistry/tutorials/ch14.htm (back to collision thory...) Potntial and Kintic nrgy during a collision + + ngativly chargd lctron cloud Rpulsiv Forc ngativly chargd
ctivation nrgis http://www.wwnorton.com/chmistry/tutorials/ch14.htm (back to collision thory...) Potntial and Kintic nrgy during a collision + + ngativly chargd lctron cloud Rpulsiv Forc ngativly chargd
Intermediate Macroeconomic Theory / Macroeconomic Analysis (ECON 3560/5040) Final Exam (Answers)
 Intrmdiat Macroconomic Thory / Macroconomic Analysis (ECON 3560/5040) Final Exam (Answrs) Part A (5 points) Stat whthr you think ach of th following qustions is tru (T), fals (F), or uncrtain (U) and brifly
Intrmdiat Macroconomic Thory / Macroconomic Analysis (ECON 3560/5040) Final Exam (Answrs) Part A (5 points) Stat whthr you think ach of th following qustions is tru (T), fals (F), or uncrtain (U) and brifly
Gauss Law. Physics 231 Lecture 2-1
 Gauss Law Physics 31 Lectue -1 lectic Field Lines The numbe of field lines, also known as lines of foce, ae elated to stength of the electic field Moe appopiately it is the numbe of field lines cossing
Gauss Law Physics 31 Lectue -1 lectic Field Lines The numbe of field lines, also known as lines of foce, ae elated to stength of the electic field Moe appopiately it is the numbe of field lines cossing
Multiple choice questions [60 points]
![Multiple choice questions [60 points] Multiple choice questions [60 points]](/thumbs/40/20623569.jpg) 1 Multiple choice questions [60 points] Answe all o the ollowing questions. Read each question caeully. Fill the coect bubble on you scanton sheet. Each question has exactly one coect answe. All questions
1 Multiple choice questions [60 points] Answe all o the ollowing questions. Read each question caeully. Fill the coect bubble on you scanton sheet. Each question has exactly one coect answe. All questions
Figure 2. So it is very likely that the Babylonians attributed 60 units to each side of the hexagon. Its resulting perimeter would then be 360!
 1. What ae angles? Last time, we looked at how the Geeks intepeted measument of lengths. Howeve, as fascinated as they wee with geomety, thee was a shape that was much moe enticing than any othe : the
1. What ae angles? Last time, we looked at how the Geeks intepeted measument of lengths. Howeve, as fascinated as they wee with geomety, thee was a shape that was much moe enticing than any othe : the
Introduction to Finite Element Modeling
 Introduction to Finit Elmnt Modling Enginring analysis of mchanical systms hav bn addrssd by driving diffrntial quations rlating th variabls of through basic physical principls such as quilibrium, consrvation
Introduction to Finit Elmnt Modling Enginring analysis of mchanical systms hav bn addrssd by driving diffrntial quations rlating th variabls of through basic physical principls such as quilibrium, consrvation
Department of Health & Human Services (DHHS) Pub. 100-04 Medicare Claims Processing Centers for Medicare &
 anual ystm patmnt of alth & uman vics () Pub. 100-04 dica laims Pocssing nts fo dica & dicaid vics () Tansmittal 931 at: APL 28, 2006 ANGE EQUET 5013 UBJET: Billing quimnts fo Baiatic ugy fo Tatmnt of
anual ystm patmnt of alth & uman vics () Pub. 100-04 dica laims Pocssing nts fo dica & dicaid vics () Tansmittal 931 at: APL 28, 2006 ANGE EQUET 5013 UBJET: Billing quimnts fo Baiatic ugy fo Tatmnt of
CPU. Rasterization. Per Vertex Operations & Primitive Assembly. Polynomial Evaluator. Frame Buffer. Per Fragment. Display List.
 Elmntary Rndring Elmntary rastr algorithms for fast rndring Gomtric Primitivs Lin procssing Polygon procssing Managing OpnGL Stat OpnGL uffrs OpnGL Gomtric Primitivs ll gomtric primitivs ar spcifid by
Elmntary Rndring Elmntary rastr algorithms for fast rndring Gomtric Primitivs Lin procssing Polygon procssing Managing OpnGL Stat OpnGL uffrs OpnGL Gomtric Primitivs ll gomtric primitivs ar spcifid by
7 Circular Motion. 7-1 Centripetal Acceleration and Force. Period, Frequency, and Speed. Vocabulary
 7 Cicula Motion 7-1 Centipetal Acceleation and Foce Peiod, Fequency, and Speed Vocabulay Vocabulay Peiod: he time it takes fo one full otation o evolution of an object. Fequency: he numbe of otations o
7 Cicula Motion 7-1 Centipetal Acceleation and Foce Peiod, Fequency, and Speed Vocabulay Vocabulay Peiod: he time it takes fo one full otation o evolution of an object. Fequency: he numbe of otations o
UNIT CIRCLE TRIGONOMETRY
 UNIT CIRCLE TRIGONOMETRY The Unit Cicle is the cicle centeed at the oigin with adius unit (hence, the unit cicle. The equation of this cicle is + =. A diagam of the unit cicle is shown below: + = - - -
UNIT CIRCLE TRIGONOMETRY The Unit Cicle is the cicle centeed at the oigin with adius unit (hence, the unit cicle. The equation of this cicle is + =. A diagam of the unit cicle is shown below: + = - - -
Lecture 20: Emitter Follower and Differential Amplifiers
 Whits, EE 3 Lctur 0 Pag of 8 Lctur 0: Emittr Followr and Diffrntial Amplifirs Th nxt two amplifir circuits w will discuss ar ry important to lctrical nginring in gnral, and to th NorCal 40A spcifically.
Whits, EE 3 Lctur 0 Pag of 8 Lctur 0: Emittr Followr and Diffrntial Amplifirs Th nxt two amplifir circuits w will discuss ar ry important to lctrical nginring in gnral, and to th NorCal 40A spcifically.
Econ 371: Answer Key for Problem Set 1 (Chapter 12-13)
 con 37: Answr Ky for Problm St (Chaptr 2-3) Instructor: Kanda Naknoi Sptmbr 4, 2005. (2 points) Is it possibl for a country to hav a currnt account dficit at th sam tim and has a surplus in its balanc
con 37: Answr Ky for Problm St (Chaptr 2-3) Instructor: Kanda Naknoi Sptmbr 4, 2005. (2 points) Is it possibl for a country to hav a currnt account dficit at th sam tim and has a surplus in its balanc
Semipartial (Part) and Partial Correlation
 Semipatial (Pat) and Patial Coelation his discussion boows heavily fom Applied Multiple egession/coelation Analysis fo the Behavioal Sciences, by Jacob and Paticia Cohen (975 edition; thee is also an updated
Semipatial (Pat) and Patial Coelation his discussion boows heavily fom Applied Multiple egession/coelation Analysis fo the Behavioal Sciences, by Jacob and Paticia Cohen (975 edition; thee is also an updated
The Role of Gravity in Orbital Motion
 ! The Role of Gavity in Obital Motion Pat of: Inquiy Science with Datmouth Developed by: Chistophe Caoll, Depatment of Physics & Astonomy, Datmouth College Adapted fom: How Gavity Affects Obits (Ohio State
! The Role of Gavity in Obital Motion Pat of: Inquiy Science with Datmouth Developed by: Chistophe Caoll, Depatment of Physics & Astonomy, Datmouth College Adapted fom: How Gavity Affects Obits (Ohio State
Hydrogen-like Atoms. We can separate the center of mass motion from the internal motion by the transformation
 Hydogn-ik Atos A hydogn ik ato consists of on nucus of chag Z and a sing cton of chag -. Th cassica ngy of this syst is th su of th kintic ngis of both patics and thi Couobic attaction' Z E = N & N+ &
Hydogn-ik Atos A hydogn ik ato consists of on nucus of chag Z and a sing cton of chag -. Th cassica ngy of this syst is th su of th kintic ngis of both patics and thi Couobic attaction' Z E = N & N+ &
Gravitation and Kepler s Laws Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation in vectorial. Gm 1 m 2. r 2
 F Gm Gavitation and Keple s Laws Newton s Law of Univesal Gavitation in vectoial fom: F 12 21 Gm 1 m 2 12 2 ˆ 12 whee the hat (ˆ) denotes a unit vecto as usual. Gavity obeys the supeposition pinciple,
F Gm Gavitation and Keple s Laws Newton s Law of Univesal Gavitation in vectoial fom: F 12 21 Gm 1 m 2 12 2 ˆ 12 whee the hat (ˆ) denotes a unit vecto as usual. Gavity obeys the supeposition pinciple,
Overview. COSC 6397 Big Data Analytics. Fundamentals. Edgar Gabriel Spring 2015. Data Characteristics. Performance Characteristics
 COSC 6397 Big Data Analtics Fundantals Edga Gabil Sping 2015 Ovviw Data Chaactistics Pfanc Chaactistics Platf Cnsidatins 1 What aks lag scal Data Analsis had? Oftn suaizd as VVVV Vlu: 5 Exabts f data catd
COSC 6397 Big Data Analtics Fundantals Edga Gabil Sping 2015 Ovviw Data Chaactistics Pfanc Chaactistics Platf Cnsidatins 1 What aks lag scal Data Analsis had? Oftn suaizd as VVVV Vlu: 5 Exabts f data catd
Multiple choice questions [70 points]
![Multiple choice questions [70 points] Multiple choice questions [70 points]](/thumbs/27/9758213.jpg) Multiple choice questions [70 points] Answe all of the following questions. Read each question caefull. Fill the coect bubble on ou scanton sheet. Each question has exactl one coect answe. All questions
Multiple choice questions [70 points] Answe all of the following questions. Read each question caefull. Fill the coect bubble on ou scanton sheet. Each question has exactl one coect answe. All questions
1240 ev nm 2.5 ev. (4) r 2 or mv 2 = ke2
 Chapte 5 Example The helium atom has 2 electonic enegy levels: E 3p = 23.1 ev and E 2s = 20.6 ev whee the gound state is E = 0. If an electon makes a tansition fom 3p to 2s, what is the wavelength of the
Chapte 5 Example The helium atom has 2 electonic enegy levels: E 3p = 23.1 ev and E 2s = 20.6 ev whee the gound state is E = 0. If an electon makes a tansition fom 3p to 2s, what is the wavelength of the
Carter-Penrose diagrams and black holes
 Cate-Penose diagams and black holes Ewa Felinska The basic intoduction to the method of building Penose diagams has been pesented, stating with obtaining a Penose diagam fom Minkowski space. An example
Cate-Penose diagams and black holes Ewa Felinska The basic intoduction to the method of building Penose diagams has been pesented, stating with obtaining a Penose diagam fom Minkowski space. An example
(Analytic Formula for the European Normal Black Scholes Formula)
 (Analytic Formula for th Europan Normal Black Schols Formula) by Kazuhiro Iwasawa Dcmbr 2, 2001 In this short summary papr, a brif summary of Black Schols typ formula for Normal modl will b givn. Usually
(Analytic Formula for th Europan Normal Black Schols Formula) by Kazuhiro Iwasawa Dcmbr 2, 2001 In this short summary papr, a brif summary of Black Schols typ formula for Normal modl will b givn. Usually
HOMEWORK FOR UNIT 5-1: FORCE AND MOTION
 Nam Dat Partnrs HOMEWORK FOR UNIT 51: FORCE AND MOTION 1. You ar givn tn idntial springs. Dsrib how you would dvlop a sal of for (i., a mans of produing rpatabl fors of a varity of sizs) using ths springs.
Nam Dat Partnrs HOMEWORK FOR UNIT 51: FORCE AND MOTION 1. You ar givn tn idntial springs. Dsrib how you would dvlop a sal of for (i., a mans of produing rpatabl fors of a varity of sizs) using ths springs.
Adverse Selection and Moral Hazard in a Model With 2 States of the World
 Advrs Slction and Moral Hazard in a Modl With 2 Stats of th World A modl of a risky situation with two discrt stats of th world has th advantag that it can b natly rprsntd using indiffrnc curv diagrams,
Advrs Slction and Moral Hazard in a Modl With 2 Stats of th World A modl of a risky situation with two discrt stats of th world has th advantag that it can b natly rprsntd using indiffrnc curv diagrams,
The force between electric charges. Comparing gravity and the interaction between charges. Coulomb s Law. Forces between two charges
 The foce between electic chages Coulomb s Law Two chaged objects, of chage q and Q, sepaated by a distance, exet a foce on one anothe. The magnitude of this foce is given by: kqq Coulomb s Law: F whee
The foce between electic chages Coulomb s Law Two chaged objects, of chage q and Q, sepaated by a distance, exet a foce on one anothe. The magnitude of this foce is given by: kqq Coulomb s Law: F whee
Slow Power Control in a CDMA Network
 Slow Pow Cotol i a CDM Ntwok Stph V. Haly ad Chu C. Cha Dpatmt of Elctical ad Elctoic Egiig Uivsity of Mlbou Pakvill Victoia 3052 ustalia fax: +61 3 9344 9188, mail: s.haly@.mu.oz.au bstact W suggst a
Slow Pow Cotol i a CDM Ntwok Stph V. Haly ad Chu C. Cha Dpatmt of Elctical ad Elctoic Egiig Uivsity of Mlbou Pakvill Victoia 3052 ustalia fax: +61 3 9344 9188, mail: s.haly@.mu.oz.au bstact W suggst a
Experiment 6: Centripetal Force
 Name Section Date Intoduction Expeiment 6: Centipetal oce This expeiment is concened with the foce necessay to keep an object moving in a constant cicula path. Accoding to Newton s fist law of motion thee
Name Section Date Intoduction Expeiment 6: Centipetal oce This expeiment is concened with the foce necessay to keep an object moving in a constant cicula path. Accoding to Newton s fist law of motion thee
Vector Calculus: Are you ready? Vectors in 2D and 3D Space: Review
 Vecto Calculus: Ae you eady? Vectos in D and 3D Space: Review Pupose: Make cetain that you can define, and use in context, vecto tems, concepts and fomulas listed below: Section 7.-7. find the vecto defined
Vecto Calculus: Ae you eady? Vectos in D and 3D Space: Review Pupose: Make cetain that you can define, and use in context, vecto tems, concepts and fomulas listed below: Section 7.-7. find the vecto defined
Displacement, Velocity And Acceleration
 Displacement, Velocity And Acceleation Vectos and Scalas Position Vectos Displacement Speed and Velocity Acceleation Complete Motion Diagams Outline Scala vs. Vecto Scalas vs. vectos Scala : a eal numbe,
Displacement, Velocity And Acceleation Vectos and Scalas Position Vectos Displacement Speed and Velocity Acceleation Complete Motion Diagams Outline Scala vs. Vecto Scalas vs. vectos Scala : a eal numbe,
Fundamentals: NATURE OF HEAT, TEMPERATURE, AND ENERGY
 Fundamntals: NATURE OF HEAT, TEMPERATURE, AND ENERGY DEFINITIONS: Quantum Mchanics study of individual intractions within atoms and molculs of particl associatd with occupid quantum stat of a singl particl
Fundamntals: NATURE OF HEAT, TEMPERATURE, AND ENERGY DEFINITIONS: Quantum Mchanics study of individual intractions within atoms and molculs of particl associatd with occupid quantum stat of a singl particl
