NORTH OF TYNE AND GATESHEAD GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF COMMON UROLOGICAL CONDITIONS IN ADULTS 18 YEARS. July 2013
|
|
|
- Theodora Tate
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NORTH OF TYNE AND GATESHEAD GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF COMMON UROLOGICAL CONDITIONS IN ADULTS 18 YEARS July
2 CONTENTS Page Introduction 3 Scrotal lumps 4 Haematuria 5 Urinary tract infection 6 Haematospermia 7 Renal cyst on ultrasound 8 Suspected urolithiasis 9 Management of PSA 10 Follow up of patients Raised PSA without cancer 11 Prostate cancer not currently on treatment, in whom radical treatment would be offered 11 Prostate cancer managed with hormonal therapy 12 Curative treatment for prostate cancer 13 Lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) assessment and management 14 International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) 15 Drug flow in patients with LUTS 16 Appendix 17 Membership of the group Declared conflicts of interest Date of guideline / review date 2
3 INTRODUCTION This guidance is intended to inform management of common urological conditions in primary care and has been developed as a consensus between representatives from primary and secondary care with reference to national guidelines, including from NICE as appropriate. The guidelines are intended to guide clinical management, but every patient should be assessed and managed individually. These guidelines are intended for all clinicians in primary care in the Newcastle, rth Tyneside, rthumberland and Gateshead areas involved in managing patients with urological conditions. This is the first iteration of these guidelines and any gaps should be identified for inclusion when the guideline is reviewed. How to use the guidelines The guidelines are a set of flow charts covering a variety of urological conditions. Each of these can be printed and laminated for easy reference if preferred. The BNF and the rth of Tyne / Gateshead Formulary should be referred to as appropriate. Referrals When referral to secondary care urology clinic is recommended in the guideline, referral for patients to be seen at a local outreach clinic may be preferred. It is anticipated that clinicians in localities where such clinics are available will be aware of them, but further information can be obtained from Newcastle Urology at the Freeman Hospital. 3
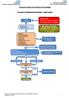
4 Scrotal lumps Presentation with scrotal lump History and examination Testis normal and separate to scrotal lump? tes If a varicocoele is diagnosed clinically, please follow recommendations as if diagnosed from an ultrasound scan. Patients with a varicocoele and concerns about infertility: this is beyond the scope of this guideline, refer to other guidelines for management of infertility. Aspiration of a hydrocoele is no longer recommended. Confident of diagnosis of epididymal cyst? Ultrasound scan Testis normal Testis abnormal Confirm diagnosis from ultrasound report Urgent referral to urology 2 week rule Epididymal cyst Hydrocoele Varicocoele Assess symptoms and patient preferences Symptomatic? (pain, discomfort, dragging sensation) Treatment required / clinical concern? Lump completely disappears when laid flat? Reassure (routine urology referral if patient wishes treatment, particularly when symptomatic) Routine referral to urology Urgent renal ultrasound scan to exclude renal carcinoma Reassure 4
5 Haematuria Visible haematuria Refer to haematuria clinic (2 week rule) tes visible haematuria Patients with visible haematuria should be referred to the haematuria clinic, irrespective of the presence of a UTI if cancer is suspected. Haematuria should not be attributed to oral anticoagulants in the therapeutic range and/or anti-platelet agents as a cause. Confirmed non-visible haematuria Exclude UTI Measure blood pressure Check serum U&E, creatinine, egfr and urine for PCR (or ACR) Symptomatic? (eg loin pain, voiding lower urinary tract symptoms: hesitancy, frequency, urgency, dysuria) tes non-visible haematuria n-visible haematuria is confirmed with 1+ blood or more on urine dipstick, on 2 or more occasions (urine microscopy should not be used to diagnose haematuria). In patients with a UTI, the UTI should be treated and the urine re-tested to confirm the haematuria has resolved. Haematuria should not be attributed to oral anticoagulants in the therapeutic range and/or anti-platelet agents as a cause. Recurrent presentation with asymptomatic non-visible haematuria which has previously been investigated does not require rereferral, unless symptoms develop or haematuria becomes visible Recurrent ie 2 out of 3 dipsticks positive of nonvisible haematuria) Aged 40 years? Refer to nephrology Refer to haematuria clinic (2 week rule) te: The guideline group recognised that the rthern Cancer Network is developing guidelines for haematuria, and the outcome is pending. This pathway will be updated if there is a significant difference in the recommendations e.g. with respect to age cut offs for referral to urology or nephrology. 5
6 Urinary tract infection Suspected UTI in a male* Obtain MSU prior to antibiotic treatment unless exceptional circumstances Course of antibiotics (refer to local antibiotic policy) Recurrent proven UTI (2 or more)? tes * Symptoms of a UTI in a man: review sexual history, consider need for referral to sexual health. Visible haematuria associated with a UTI in a woman should also prompt referral to the heamaturia clinic if cancer is possible (2 week rule). Use clinical judgement when deciding whether referral is indicated., 1 st UTI Symptoms settle quickly, no residual symptoms, no signs of pyelonephritis? Visible haematuria (single or recurrent) and cancer possible Refer to urology Reassure Refer haematuria clinic (2 week rule) 6
7 Haematospermia Haemospermia tes There is a low correlation between haemospermia and prostate cancer. Visible or confirmed nonvisible haematuria? It is important to exclude haematuria (visible or non-visible). n-visible haematuria is confirmed with 1+ blood or more on urine dipstick, on 2 or more occasions (urine microscopy should not be used to diagnose haematuria). * refer to PSA guideline Refer to haematuria guideline Digitial rectal examination and PSA* following appropriate counselling rmal and no clinical concern Reassure Refer to urology 7
8 Renal cyst on ultrasound Renal cyst on ultrasound Simple renal cyst reported? Clarify nature of cyst (review ultrasound report, if uncertain phone sonographer) Simple renal cyst (no calcification, no septae, no solid components) t a simple cyst Reassure (if a simple renal cyst is large, eg 5 cm diameter or more, and the patient has pain, consider referral to urology) Refer to urology 8
9 Suspected renal stones Suspected renal stones Symptomatic (eg flank pain - consider emergency / urgent referral if severe pain), ie coincidental finding on imaging Renal ultrasound and plain plain radiograph (no CT scan) Refer to urology for assessment and further management including recommendations about follow up (do not arrange CT scan before referral) Renal stones confirmed? Reassess, manage appropriately 9
10 Management of PSA PSA measured and digital rectal examination (DRE) after appropriate counselling PSA and DRE both normal? tes Do not measure PSA if suspicion of UTI. Treat UTI if MSU confirms infection, and measure PSA after 12 weeks if required. Men aged > 80 years, consider the presence of other co-morbidities including long term catheter, and only check PSA if: Clinically malignant prostate cancer on DRE Clinical suspicion of bony metastases te: nearly all men aged > 80 years have at least a focus of cancer, this only needs diagnosing if palliative treatment is required. Reassure DRE abnormal or uncertain? DRE normal and no immediate clinical concern, and PSA < 10 Repeat PSA after 8 weeks PSA > 10 Raised PSA using age related cut offs? Reassure Age specific cut off PSA levels (from rthern Cancer Network guideline) Aged years: 3.0 ng/ml Aged years: 4.0 ng/ml Aged 70 years and older: 5.0 ng/ml (There are no age-specific reference ranges for men aged over 80 years) Refer to urology (2 week rule) 10
11 Follow up of patients Raised PSA without cancer Patient with raised PSA been assessed and investigated in specialist urology care evidence of malignancy Discharge to primary care with clear instructions for follow up, to include: Frequency and content of follow up Indications to refer back Prostate cancer not currently on treatment, in whom radical treatment would be offered Patient with prostate cancer in whom radical treatment would be offered Active monitoring in urology clinic 3 month follow up with PSA and DRE Prostate biopsy at 1 and 5 years 11
12 Prostate cancer managed with hormonal therapy Prostate cancer managed with hormonal therapy Gleason score < 8 Follow up for 6 months in urology clinic Stable for 6 months, asymptomatic, no clinical concerns Follow up in primary care, in line with Local Enhanced Service arrangements, if in place Individual management plan from secondary care, including any recommendations for bone protection Patient management booklet 6 monthly review by GP in line with Local Enhanced Service arrangements, if in place (robust system for recall and action if non attendance) Measure PSA (interpret using recommendations in individual management plan) Review recommendations for bone protection Assess for new symptoms (ie deterioration in lower urinary tract symptoms, bone pain) DRE if change in symptoms Complete patient management booklet Red flags If patients develop the following symptoms: Lower limb neurology Suspicion of spinal cord compression Contact the urology team as an emergency with a view to same day admission Patients should only be discharged for follow up in primary care when an appropriate LES, or similar arrangements, are in place. 12
13 Curative treatment for prostate cancer Curative treatment for prostate cancer Follow up in urology clinic for at least 2 years Monitor highly sensitive PSA Assess for new symptoms Consider discharge to primary care after 2 years with individual management plan, unless on-going follow up in secondary care clinically indicated Annual review in primary care (robust system for recall and action if non attendance) Measure PSA (interpret using recommendations in individual management plan) Assess for new symptoms Use guidance in individual management plan for indications for re-referral to secondary care 13
14 Lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) in men: assessment and management Suspected LUTS in a man Initial assessment Assess symptoms: voiding, storage, nocturia, post micturition dribble Ask about lifestyle including caffeine, alcohol, prescribed and OTC drugs, fluid intake Assess how troublesome symptoms are and complete IPSS score (see next page) Examine abdomen and external genitalia Perform DRE Perform urine dipstick for blood, glucose, leucocytes, and nitrites Check egfr if renal impairment suspected Offer PSA testing after appropriate counselling if: Suspected BPH, or Prostate abnormal, or Prostate cancer suspected Refer to urology (2 week rule) if urological cancer suspected: Haematuria (refer to haematuria guideline Raised PSA (refer to PSA guideline) Abnormal prostate on DRE Other symptoms for urgent referral (use clinical judgement to determine urgency) Palpable bladder Neurological symptoms Consider if there is an underlying cause for obstructive symptoms (eg drugs, urethral stricture, urological cancer, neurological problems) PSA raised Refer to flow chart for raised PSA for further management If troublesome LUTS symptoms Assess severity with urinary frequency volume chart Refer for further assessment if clinically indicated. Use clinical judgement to determine urgency Symptoms not very troublesome and low risk of progression Lifestyle advice Review after 3 months Symptoms troublesome and or high risk of progression Lifestyle advice Consider conservative measures, which may include: Pelvic floor muscle training Bladder training Post void milking Prudent fluid intake Healthy lifestyle Containment products (pads, waterproof pants, external sheath). Catheter only if no other option Regular review If symptoms become more troublesome, consider drug treatment (see flow chart for drug treatment) Consider drug treatment (see flow chart for drug treatment) Risk of progression of benign prostatic enlargement is higher in men: Who are older With a poorer urine flow Have a higher symptom score Have evidence of bladder decompensation (eg chronic urinary retention) Larger prostate Higher PSA level 14
15 Delighted Pleased Mostly satisfied Mixed about equally satisfied and dissatisfied Mostly dissatisfied Unhappy Terrible ne 1 time 2 times 3 times 4 times 5 times or more Your score t at all Less than 1 time in 5 Less than half the time About half the time More than half the time Almost Always Your score International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) Name: Date: Incomplete Emptying Over the past month, how often have you had a sensation of not emptying your bladder completely after you finish urinating? Frequency Over the past month, how often have you had to urinate again less than 2 hours after you finished urinating? Intermittency Over the past month, how often have you found you stopped and started again several times when you urinated? Urgency Over the last month, how difficult have you found it to postpone urination? Weak stream Over the past month, how often have you had a weak urinary stream? Straining Over the past month, how often have you had to push or strain to begin urination? cturia Over the past month, how many times did you most typically get up to urinate from the time you went to bed until the time you got up in the morning? Total IPSS Score Bothersomeness Quality of life due to urinary symptoms If you were to spend the rest of you life with your urinary condition the way it is now, how would you feel about that?
16 Drug flow in patients with LUTS being considered for drug treatment Drug treatment for LUTS being considered (see LUTS management guideline above) Risk of progression of benign prostatic enlargement is higher in men: Who are older With a poorer urine flow Have a higher symptom score Have evidence of bladder decompensation (eg chronic urinary retention) Larger prostate Higher PSA level Symptoms troublesome and moderate to severe (IPSS score 8) and prostate is small and / or PSA < 1.4 nanogram/ml Symptoms troublesome and moderate to severe (IPSS score 8) and prostate appears large (PSA > 1.4 nanogram/ml) High risk of progression and prostate seems large (PSA > 1.4 nanogram/ ml), but symptoms NOT troublesome) Offer alpha blocker, Uroselective agent better tolerated, more effective, eg tamsulosin or other local formulary drug (if doxazosin is used minimum effective dose is 10 mg) Offer alpha blocker, uroselective agent better tolerated, more effective, eg tamsulosin or other local formulary drug (if doxazosin is used minimum effective dose is 10 mg) plus 5- alpha-reductase inhibitor, eg finasteride (remember to counsel to use a condom if sexual partner is pregnant or likely to become pregnant, women of child bearing age should not handle crushed or broken tablets) or other local formulary drug Offer 5- alpha-reductase inhibitor only, eg finasteride (remember to counsel to use a condom if sexual partner is pregnant or likely to become pregnant, women of child bearing age should not handle crushed or broken tablets) or other local formulary drug If storage symptoms persist once voiding symptoms managed: Refer to urologist, or If confident that prostate is small, consider cautious use of an antimuscarinic agent (consider side effects, tolerability: refer to local formulary) If treatment fails Refer to urology tes Refer to local formulary for additional information and for details of drugs on the local formulary Follow up Alpha-blocker: after 4-6 weeks, and then every 6-12 months 5-alpha-reductase inhibitor: after 3-6 months, then every 6-12 months Antimuscarinic agent: every 4-6 weeks until stable, then every 6-12 months Interpretation of PSA results After 6 months of 5-alpha reductase inhibitor use, PSA levels reduce by about 50%. When interpreting a PSA level measured after at least 6 months of 5-alpha reductase inhibitor treatment, double the PSA result 16
17 APPENDIX Membership of the guideline development group Dr Jane Skinner (guideline coordinator), Consultant Community Cardiologist, The Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Anne-Marie Bailey, Medicines Management, Newcastle and Gateshead CCG Alliance Dr David Brown, GP, rthumberland CCG Dr M Chaudhary, GP, Newcastle West CCG Dr Relton Cummings, GP, Newcastle rth and East CCG Dr Heather Galloway, GP, Gateshead CCG Dr Chris Jewitt, GP, Gateshead CCG Matthew Lowery, Formulary Pharmacist, The Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Miss Anna O Riordan, Consultant Urologist, Newcastle Urology, The Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Mr Toby Page, Consultant Urologist, Newcastle Urology, The Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Dr Helen Seymour, Medicines Management, rth of Tyne Mr Matthew Shaw, Consultant Urologist, Newcastle Urology, The Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Mr Naeem Soomro, Consultant Urologist, Newcastle Urology, The Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Dr Vivienne Tut, GP, rth Tyneside CCG Date of guideline and review date July 2013, review July
Primary Care Management of Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms. Matthew B.K. Shaw Consultant Urological Surgeon
 Primary Care Management of Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Matthew B.K. Shaw Consultant Urological Surgeon NICE LUTS Guidelines Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in men. NICE Clinical Guideline 97
Primary Care Management of Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Matthew B.K. Shaw Consultant Urological Surgeon NICE LUTS Guidelines Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in men. NICE Clinical Guideline 97
NICE Pathways bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic.
 Initial assessment and investigation of urinary incontinence bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used
Initial assessment and investigation of urinary incontinence bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used
POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE
 POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE Acute Pylonephritis DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Male Known or suspected renal impairment (egfr < 60) Abnormality of renal tract Known or suspected renal
POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE Acute Pylonephritis DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Male Known or suspected renal impairment (egfr < 60) Abnormality of renal tract Known or suspected renal
150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2. Patient Information. Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate
 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2 Patient Information Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 3 GreenLight Laser Therapy 1 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page
150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2 Patient Information Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 3 GreenLight Laser Therapy 1 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page
Identifying and treating long-term kidney problems (chronic kidney disease)
 Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services Identifying and treating long-term kidney problems (chronic kidney disease) NICE clinical guidelines advise the NHS on caring for
Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services Identifying and treating long-term kidney problems (chronic kidney disease) NICE clinical guidelines advise the NHS on caring for
HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE
 HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE Prostate comes from the Greek meaning to stand in front of ; this is very different than prostrate which means to lie down flat. The prostate is a walnut-sized
HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE Prostate comes from the Greek meaning to stand in front of ; this is very different than prostrate which means to lie down flat. The prostate is a walnut-sized
MANAGEMENT OF PROSTATE ENLARGEMENT/BPH
 MANAGEMENT OF PROSTATE ENLARGEMENT/BPH J E S S I C A E. P A O N E S S A, M. D. A S S I S T A N T P R O F E S S O R D E P A R T M E N T O F U R O L O G Y S U N Y U P S T A T E M E D I C A L U N I V E R
MANAGEMENT OF PROSTATE ENLARGEMENT/BPH J E S S I C A E. P A O N E S S A, M. D. A S S I S T A N T P R O F E S S O R D E P A R T M E N T O F U R O L O G Y S U N Y U P S T A T E M E D I C A L U N I V E R
Bladder Health Promotion
 Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation Content contributions provided by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence (NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence
Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation Content contributions provided by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence (NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence
Primary Care management of Overactive Bladder (OAB)
 DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) Primary Care management of Overactive Bladder (OAB) Prescribing Tips All medicines for OAB have similar dose-related efficacy. More than one agent (up
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) Primary Care management of Overactive Bladder (OAB) Prescribing Tips All medicines for OAB have similar dose-related efficacy. More than one agent (up
LCD for Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA)
 LCD for Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Applicable CPT Code(s): 84152 Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA); Complexed (Direct Measurement) 84153 Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA); Total 84154 Prostate Specific
LCD for Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Applicable CPT Code(s): 84152 Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA); Complexed (Direct Measurement) 84153 Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA); Total 84154 Prostate Specific
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options
 AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
1 ST JAMAICAN PAEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY CONFERENCE
 in association with 1 ST JAMAICAN PAEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY CONFERENCE Jamaica Conference Centre Kingston, Jamaica October 4 th 2014 VOIDING DISORDERS IN CHILDREN Dr. Colin Abel Paediatric Urologist Bustamante
in association with 1 ST JAMAICAN PAEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY CONFERENCE Jamaica Conference Centre Kingston, Jamaica October 4 th 2014 VOIDING DISORDERS IN CHILDREN Dr. Colin Abel Paediatric Urologist Bustamante
Guidelines for Management of Renal Cancer
 Guidelines for Management of Renal Cancer Date Approved by Network Governance July 2012 Date for Review July 2015 Changes Between Versions 2 and 3 Section 5 updated bullets 5.3 and 5.4 Section 6 updated
Guidelines for Management of Renal Cancer Date Approved by Network Governance July 2012 Date for Review July 2015 Changes Between Versions 2 and 3 Section 5 updated bullets 5.3 and 5.4 Section 6 updated
A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page
 A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page IX0200: Prevention & Control of Catheter Associated
A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page IX0200: Prevention & Control of Catheter Associated
Topic review: Clinical presentation and diagnosis of urinary incontinence in the elderly. Prapa Pattrapornpisut 7 June 2012
 1 Topic review: Clinical presentation and diagnosis of urinary incontinence in the elderly Prapa Pattrapornpisut 7 June 2012 2 Urinary incontinence Definition the complaint of any involuntary leakage of
1 Topic review: Clinical presentation and diagnosis of urinary incontinence in the elderly Prapa Pattrapornpisut 7 June 2012 2 Urinary incontinence Definition the complaint of any involuntary leakage of
symptoms of Incontinence
 Types, causes and symptoms of Urinary Incontinence Aims and Objectives Aim: To have an understanding of the types and causes of urinary incontinence. Objectives: To be aware of the incidence and prevalence
Types, causes and symptoms of Urinary Incontinence Aims and Objectives Aim: To have an understanding of the types and causes of urinary incontinence. Objectives: To be aware of the incidence and prevalence
Patient with: 3 or more UTI in 6 months 4 or more UTI in 12 months
 Recurrent UTI Management Pathway adult females Initial assessment Assessment questionnaire questionnaire bladder scan dipstick dipstick of of urine urine pregnancy neurological disease long - term catheters
Recurrent UTI Management Pathway adult females Initial assessment Assessment questionnaire questionnaire bladder scan dipstick dipstick of of urine urine pregnancy neurological disease long - term catheters
Overactive Bladder and/or Nocturia (Female)
 Overactive Bladder and/or Nocturia (Female) Definition: Increased urinary frequency > 8 voids / day More than 1 void/night in women 80 years old Diagnosis
Overactive Bladder and/or Nocturia (Female) Definition: Increased urinary frequency > 8 voids / day More than 1 void/night in women 80 years old Diagnosis
UTI in children. Quick reference guide. Issue date: August 2007. Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management
 Issue date: August 2007 UTI in children Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Women s and Children s Health
Issue date: August 2007 UTI in children Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Women s and Children s Health
PSA Screening for Prostate Cancer Information for Care Providers
 All men should know they are having a PSA test and be informed of the implications prior to testing. This booklet was created to help primary care providers offer men information about the risks and benefits
All men should know they are having a PSA test and be informed of the implications prior to testing. This booklet was created to help primary care providers offer men information about the risks and benefits
Guideline for Microalbuminuria Screening
 East Lancashire Diabetes Network Guideline for Microalbuminuria Screening Produced by: Task and Finish Group, Clinical Standards Group Produced: August 2006 Approved by: East Lancashire Diabetes Network
East Lancashire Diabetes Network Guideline for Microalbuminuria Screening Produced by: Task and Finish Group, Clinical Standards Group Produced: August 2006 Approved by: East Lancashire Diabetes Network
Bladder Health Promotion
 Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation endorsed by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence( NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence This presentation
Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation endorsed by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence( NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence This presentation
Bladder and Bowel Control
 Bladder and Bowel Control Dr Sue Woodward Lecturer, Florence Nightingale School of Nursing and Midwifery 2 Why do we need to understand anatomy? Normal physiology Normal adult bladder capacity = 450-500mls
Bladder and Bowel Control Dr Sue Woodward Lecturer, Florence Nightingale School of Nursing and Midwifery 2 Why do we need to understand anatomy? Normal physiology Normal adult bladder capacity = 450-500mls
Early Prostate Cancer: Questions and Answers. Key Points
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
Gwen Griffith Clinical Nurse Specialist Bolton NHS foundation Trust
 Gwen Griffith Clinical Nurse Specialist Bolton NHS foundation Trust Overview Setting the Scene Beginning of the journey & specialist nurse role Why people with MS experience bladder problems MS and the
Gwen Griffith Clinical Nurse Specialist Bolton NHS foundation Trust Overview Setting the Scene Beginning of the journey & specialist nurse role Why people with MS experience bladder problems MS and the
Enlarged prostate. A guide for men concerned about benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
 Enlarged prostate A guide for men concerned about benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) Introduction This booklet is for men who want to know more about a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland,
Enlarged prostate A guide for men concerned about benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) Introduction This booklet is for men who want to know more about a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland,
PLEASE COMPLETE THE ENCLOSED PAGES AND RETURN TO THE RECEPTIONIST AT YOUR APPOINTMENT
 NEW PATIENT PACK Dr Jehan Titus Dr Jimmy Lam (Please circle which Dr you will be seeing) PLEASE COMPLETE THE ENCLOSED PAGES AND RETURN TO THE RECEPTIONIST AT YOUR APPOINTMENT Please contact our rooms if
NEW PATIENT PACK Dr Jehan Titus Dr Jimmy Lam (Please circle which Dr you will be seeing) PLEASE COMPLETE THE ENCLOSED PAGES AND RETURN TO THE RECEPTIONIST AT YOUR APPOINTMENT Please contact our rooms if
CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE
 URINARY INCONTINENCE CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE ASSESSMENT/PROBLEM RECOGNITION 1. Did the staff and physician seek and document risk factors for urinary incontinence and any history of urinary
URINARY INCONTINENCE CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE ASSESSMENT/PROBLEM RECOGNITION 1. Did the staff and physician seek and document risk factors for urinary incontinence and any history of urinary
Bladder and Bowel Assessment Ann Yates Director of Continence Services. 18/07/2008 Cardiff and Vale NHS Trust
 Bladder and Bowel Assessment Ann Yates Director of Continence Services Types of continence problems Bladder Stress incontinence Urgency and urge Incontinence Mixed incontinence Obstructive incontinence
Bladder and Bowel Assessment Ann Yates Director of Continence Services Types of continence problems Bladder Stress incontinence Urgency and urge Incontinence Mixed incontinence Obstructive incontinence
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones. Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke
 Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women
 Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women Recurrent bladder or urinary tract infections (UTI s) are a very common diagnosis. In fact,
Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women Recurrent bladder or urinary tract infections (UTI s) are a very common diagnosis. In fact,
PROCEDURE FOR THE ASSESSMENT OF ADULTS AND CHILDREN WITH BLADDER OR BOWEL DYSFUNCTION
 PROCEDURE FOR THE ASSESSMENT OF ADULTS AND CHILDREN WITH BLADDER OR BOWEL DYSFUNCTION First Issued Issue Version One Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date Procedure for the effective
PROCEDURE FOR THE ASSESSMENT OF ADULTS AND CHILDREN WITH BLADDER OR BOWEL DYSFUNCTION First Issued Issue Version One Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date Procedure for the effective
Overactive bladder and urgency incontinence
 Overactive bladder and urgency incontinence As a health care provider you can make a significant difference to the quality of life of patients like these by addressing urinary incontinence, introducing
Overactive bladder and urgency incontinence As a health care provider you can make a significant difference to the quality of life of patients like these by addressing urinary incontinence, introducing
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Algorithm. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Algorithm Page 1
 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Algorithm Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Algorithm Page 1 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Algorithm (See NICE Clinical Guideline CG73 1 and Quality Standards 2 ) Who should have
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Algorithm Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Algorithm Page 1 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Algorithm (See NICE Clinical Guideline CG73 1 and Quality Standards 2 ) Who should have
Enlarged prostate A guide to diagnosis and treatment
 Enlarged prostate A guide to diagnosis and treatment 2 Enlarged prostate A guide to diagnosis and treatment About this booklet This booklet is for men who want to know more about a noncancerous enlargement
Enlarged prostate A guide to diagnosis and treatment 2 Enlarged prostate A guide to diagnosis and treatment About this booklet This booklet is for men who want to know more about a noncancerous enlargement
Urinary Tract Infections
 1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline
 Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline RECOMMENDATIONS 1 Conditional: Clinicians who are making
Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline RECOMMENDATIONS 1 Conditional: Clinicians who are making
RBH GUIDELINES FOR ULTRASOUND REFERRAL
 RBH GUIDELINES FOR ULTRASOUND REFERRAL Introduction Ultrasound can be very useful as a first line investigation; it is typically non-invasive and does not involve ionising radiation. However, a significant
RBH GUIDELINES FOR ULTRASOUND REFERRAL Introduction Ultrasound can be very useful as a first line investigation; it is typically non-invasive and does not involve ionising radiation. However, a significant
Medical Tests for Prostate Problems
 Medical Tests for Prostate Problems National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is the prostate? The
Medical Tests for Prostate Problems National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is the prostate? The
Chapter 31: Lower Urinary Tract Conditions in Elderly Patients
 Chapter 31: Lower Urinary Tract Conditions in Elderly Patients Damon Dyche and Jay Hollander William Beaumont Hospital, Royal Oak, Michigan As our population ages, the number of patients presenting to
Chapter 31: Lower Urinary Tract Conditions in Elderly Patients Damon Dyche and Jay Hollander William Beaumont Hospital, Royal Oak, Michigan As our population ages, the number of patients presenting to
Have a shower, rather than a bath to avoid exposing your genitals to the chemicals in your cleaning products for too long. Always empty your bladder
 Cystitis, Avenue Medical Practice Neat Guideline Introduction Cystitis means 'inflammation of the bladder'. It causes: an urgent and frequent need to urinate, and Pain, or stinging, when passing urine.
Cystitis, Avenue Medical Practice Neat Guideline Introduction Cystitis means 'inflammation of the bladder'. It causes: an urgent and frequent need to urinate, and Pain, or stinging, when passing urine.
1. What is the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test?
 1. What is the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test? Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is a protein produced by the cells of the prostate gland. The PSA test measures the level of PSA in the blood. The doctor
1. What is the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test? Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is a protein produced by the cells of the prostate gland. The PSA test measures the level of PSA in the blood. The doctor
PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER DO YOU KNOW YOUR RISK OF HAVING CANCER?
 PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER DO YOU KNOW YOUR RISK OF HAVING CANCER? PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER There is a range of methods available to your healthcare professional to verify the
PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER DO YOU KNOW YOUR RISK OF HAVING CANCER? PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER There is a range of methods available to your healthcare professional to verify the
Diabetic nephropathy is detected clinically by the presence of persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria.
 Kidney Complications Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is detected clinically by the presence of persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria. The peak incidence of nephropathy is usually 15-25 years
Kidney Complications Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is detected clinically by the presence of persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria. The peak incidence of nephropathy is usually 15-25 years
PROSTATE ENLARGEMENT A GUIDE TO URINARY SYMPTOMS IN MEN A BOOKLET IN THE SERIES OF CONSUMER GUIDES ON MALE REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH FROM
 PROSTATE ENLARGEMENT A GUIDE TO URINARY SYMPTOMS IN MEN A BOOKLET IN THE SERIES OF CONSUMER GUIDES ON MALE REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH FROM AT A GLANCE First published in March 2004 by Andrology Australia 4th
PROSTATE ENLARGEMENT A GUIDE TO URINARY SYMPTOMS IN MEN A BOOKLET IN THE SERIES OF CONSUMER GUIDES ON MALE REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH FROM AT A GLANCE First published in March 2004 by Andrology Australia 4th
Prostate Cancer Screening. Dr. J. McCracken, Urologist
 Prostate Cancer Screening Dr. J. McCracken, Urologist USPSTF Lifetime risk for diagnosis currently estimated at 15.9% Llifetime risk of dying of prostate cancer is 2.8% Seventy percent of deaths due to
Prostate Cancer Screening Dr. J. McCracken, Urologist USPSTF Lifetime risk for diagnosis currently estimated at 15.9% Llifetime risk of dying of prostate cancer is 2.8% Seventy percent of deaths due to
Prostate cancer is the most common cause of death from cancer in men over age 75. Prostate cancer is rarely found in men younger than 40.
 A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. Prostate cancer Cancer - prostate; Biopsy - prostate; Prostate biopsy; Gleason score Last reviewed: October 2, 2013. Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate
A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. Prostate cancer Cancer - prostate; Biopsy - prostate; Prostate biopsy; Gleason score Last reviewed: October 2, 2013. Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate
The Scottish Public Services Ombudsman Act 2002
 Scottish Public Services Ombudsman The Scottish Public Services Ombudsman Act 2002 Investigation Report UNDER SECTION 15(1)(a) SPSO 4 Melville Street Edinburgh EH3 7NS Tel 0800 377 7330 SPSO Information
Scottish Public Services Ombudsman The Scottish Public Services Ombudsman Act 2002 Investigation Report UNDER SECTION 15(1)(a) SPSO 4 Melville Street Edinburgh EH3 7NS Tel 0800 377 7330 SPSO Information
Urinary Incontinence. Causes of Incontinence. What s Happening?
 National Institute on Aging AgePage Urinary Incontinence Sarah loves to spend time with her friends talking about her grandchildren and going to exercise classes with neighbors. But she s started to have
National Institute on Aging AgePage Urinary Incontinence Sarah loves to spend time with her friends talking about her grandchildren and going to exercise classes with neighbors. But she s started to have
There are many different types of cancer and sometimes cancer is diagnosed when in fact you are not suffering from the disease at all.
 About Cancer Cancer is a disease where there is a disturbance in the normal pattern of cell replacement. The cells mutate and become abnormal or grow uncontrollably. Not all tumours are cancerous (i.e.
About Cancer Cancer is a disease where there is a disturbance in the normal pattern of cell replacement. The cells mutate and become abnormal or grow uncontrollably. Not all tumours are cancerous (i.e.
Incontinence. What is incontinence?
 Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
Learning Resource Guide. Understanding Incontinence. 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved
 Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved ElderCare Online s Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence Table of Contents Introduction
Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved ElderCare Online s Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence Table of Contents Introduction
Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC. OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract
 Detection, Early Management & Prevention, of Urinary Tract Infections in Older Adults Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract infections (UTIs)
Detection, Early Management & Prevention, of Urinary Tract Infections in Older Adults Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract infections (UTIs)
How prostate cancer is diagnosed
 How prostate cancer is diagnosed This information is an extract from the booklet Having tests for prostate cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. Contents
How prostate cancer is diagnosed This information is an extract from the booklet Having tests for prostate cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. Contents
Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test
 TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test An information guide Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA)
TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test An information guide Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA)
Guy s, King s and St Thomas Cancer Centre The Cancer Outpatient Clinic Maintenance BCG for nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer
 Guy s, King s and St Thomas Cancer Centre The Cancer Outpatient Clinic Maintenance BCG for nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer This information sheet has been given to you to explain the use of maintenance
Guy s, King s and St Thomas Cancer Centre The Cancer Outpatient Clinic Maintenance BCG for nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer This information sheet has been given to you to explain the use of maintenance
7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse
 7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse A patient with prostate cancer in PSA relapse is one who, having received a primary treatment with intent to cure, has a raised PSA (prostate-specific antigen) level defined
7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse A patient with prostate cancer in PSA relapse is one who, having received a primary treatment with intent to cure, has a raised PSA (prostate-specific antigen) level defined
Urinary Incontinence. Patient Information Sheet
 Urinary Incontinence Patient Information Sheet What is urinary incontinence (UI)? UI happens when you are not able to control when you urinate and you wet yourself. How common is urinary incontinence?
Urinary Incontinence Patient Information Sheet What is urinary incontinence (UI)? UI happens when you are not able to control when you urinate and you wet yourself. How common is urinary incontinence?
THE KIDNEY. Bulb of penis Abdominal aorta Scrotum Adrenal gland Inferior vena cava Urethra Corona glandis. Kidney. Glans penis Testicular vein
 29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER PROPECIA 1 mg film-coated Tablets (finasteride)
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER PROPECIA 1 mg film-coated Tablets (finasteride) This medicine is for use in men only Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start to take this medicine.
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER PROPECIA 1 mg film-coated Tablets (finasteride) This medicine is for use in men only Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start to take this medicine.
Urinary Continence. Second edition FAST FACTS. by Julian Shah and Gary Leach. Anatomy and physiology 7. Investigations and diagnosis 11
 FAST FACTS Urinary Continence Second edition Indispensable Guides to by Julian Shah and Gary Leach Clinical Practice Anatomy and physiology 7 Investigations and diagnosis 11 Detrusor instability 28 Primary
FAST FACTS Urinary Continence Second edition Indispensable Guides to by Julian Shah and Gary Leach Clinical Practice Anatomy and physiology 7 Investigations and diagnosis 11 Detrusor instability 28 Primary
Overview of Urinary Incontinence in the Long Term Care Setting
 Overview of Urinary Incontinence in the Long Term Care Setting Management Strategies for the Nursing Assistant Ann M. Spenard RN, C, MSN Courtney Lyder ND, GNP Learning Objectives Describe common types
Overview of Urinary Incontinence in the Long Term Care Setting Management Strategies for the Nursing Assistant Ann M. Spenard RN, C, MSN Courtney Lyder ND, GNP Learning Objectives Describe common types
Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing
 Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing for Prostate Cancer Patients Today s speaker is Manish Bhandari, MD Program moderator is Pam Barrett, Us TOO International Made possible by
Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing for Prostate Cancer Patients Today s speaker is Manish Bhandari, MD Program moderator is Pam Barrett, Us TOO International Made possible by
Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB)
 Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is OAB? An overactive bladder or OAB is where a person regularly gets a sudden and compelling need or desire to pass
Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is OAB? An overactive bladder or OAB is where a person regularly gets a sudden and compelling need or desire to pass
Nocturnal Enuresis Clinical Management Tool (CMT)
 Nocturnal Enuresis Clinical Management Tool (CMT) This tool and additional educational resources can be found at www.stopbedwetting.org Zinc Code: DN/360/2010/UKe(1)a Date of Preparation of website: August
Nocturnal Enuresis Clinical Management Tool (CMT) This tool and additional educational resources can be found at www.stopbedwetting.org Zinc Code: DN/360/2010/UKe(1)a Date of Preparation of website: August
Improving access and reducing costs of care for overactive bladder through a multidisciplinary delivery model
 Improving access and reducing costs of care for overactive bladder through a multidisciplinary delivery model Trafford Crump, Ph.D. Department of Surgery, University of Calgary Presentation to: Canadian
Improving access and reducing costs of care for overactive bladder through a multidisciplinary delivery model Trafford Crump, Ph.D. Department of Surgery, University of Calgary Presentation to: Canadian
Package Leaflet: Information for the user Propecia 1 mg film-coated Tablets Finasteride
 Package Leaflet: Information for the user Propecia 1 mg film-coated Tablets Finasteride This medicine is for use in men only Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because
Package Leaflet: Information for the user Propecia 1 mg film-coated Tablets Finasteride This medicine is for use in men only Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because
CONTENTS: WHAT S IN THIS BOOKLET
 Q Questions & A & Answers About Your Prostate Having a biopsy test to find out if you may have prostate cancer can bring up a lot of questions. This booklet will help answer those questions. CONTENTS:
Q Questions & A & Answers About Your Prostate Having a biopsy test to find out if you may have prostate cancer can bring up a lot of questions. This booklet will help answer those questions. CONTENTS:
Normal bladder function requires a coordinated effort between the brain, spinal cord, and the bladder.
 .. Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is not an inevitable part of aging, and it is not a disease. The loss of bladder control - called urinary incontinence - affects between 13 and 17 million adult
.. Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is not an inevitable part of aging, and it is not a disease. The loss of bladder control - called urinary incontinence - affects between 13 and 17 million adult
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections www.kidney.org Did you know that... n Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are responsible for nearly 10 million doctor visits each year. n One in five women will have at least one
Urinary Tract Infections www.kidney.org Did you know that... n Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are responsible for nearly 10 million doctor visits each year. n One in five women will have at least one
An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER
 An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER Being diagnosed with prostate cancer can be a life-altering experience. It requires making some very difficult decisions about treatments that can affect not only the
An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER Being diagnosed with prostate cancer can be a life-altering experience. It requires making some very difficult decisions about treatments that can affect not only the
How to Improve Bladder After Bowler Cancer
 Bladder changes after bowel cancer treatment This information is from the booklet Managing the late effects of bowel cancer treatment. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy
Bladder changes after bowel cancer treatment This information is from the booklet Managing the late effects of bowel cancer treatment. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy
LEFLUNOMIDE (Adults)
 Shared Care Guideline DRUG: Introduction: LEFLUNOMIDE (Adults) Indication: Disease modifying drug for rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis Licensing Information: Disease modifying drug for active
Shared Care Guideline DRUG: Introduction: LEFLUNOMIDE (Adults) Indication: Disease modifying drug for rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis Licensing Information: Disease modifying drug for active
Prostate Cancer Screening. A Decision Guide
 Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Is screening right for you?
Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Is screening right for you?
Rivaroxaban: Prescribing Guidance for the treatment of provoked venous thromboembolism (VTE)
 Rivaroxaban: Prescribing Guidance for the treatment of provoked venous thromboembolism (VTE) Amber Drug Level 2 Leeds We have started your patient on rivaroxaban for the treatment of provoked VTE (deep
Rivaroxaban: Prescribing Guidance for the treatment of provoked venous thromboembolism (VTE) Amber Drug Level 2 Leeds We have started your patient on rivaroxaban for the treatment of provoked VTE (deep
Overactive Bladder (OAB)
 Overactive Bladder (OAB) Overactive bladder is a problem with bladder storage function that causes a sudden urge to urinate. The urge may be difficult to suppress, and overactive bladder can lead to the
Overactive Bladder (OAB) Overactive bladder is a problem with bladder storage function that causes a sudden urge to urinate. The urge may be difficult to suppress, and overactive bladder can lead to the
Urology Nurse Practitioner Urology Research Nurse Australian Prostate Cancer Research Centre Epworth November 18, 2011
 Urology Nurse Practitioner Helen Crowe Urology Nurse Practitioner Urology Research Nurse Australian Prostate Cancer Research Centre Epworth November 18, 2011 Nurse Practitioner Registered nurse who has
Urology Nurse Practitioner Helen Crowe Urology Nurse Practitioner Urology Research Nurse Australian Prostate Cancer Research Centre Epworth November 18, 2011 Nurse Practitioner Registered nurse who has
Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package. Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula
 Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula Early detection and treatment If a woman has recently survived a
Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula Early detection and treatment If a woman has recently survived a
Talking about Prostate Cancer
 Talking about Prostate Cancer Talking about Prostate Cancer If I can avoid going to a doctor, I will but not when we re talking about prostate cancer. Why take chances with a condition that might be serious?
Talking about Prostate Cancer Talking about Prostate Cancer If I can avoid going to a doctor, I will but not when we re talking about prostate cancer. Why take chances with a condition that might be serious?
Blood in the Urine (Haematuria)
 Kidney Health Information Blood in the Urine (Haematuria) What is blood in the urine? Sometimes blood in the urine can be seen, but at other times it is present in such small quantities that it is not
Kidney Health Information Blood in the Urine (Haematuria) What is blood in the urine? Sometimes blood in the urine can be seen, but at other times it is present in such small quantities that it is not
GFR (Glomerular Filtration Rate) A Key to Understanding How Well Your Kidneys Are Working
 GFR (Glomerular Filtration Rate) A Key to Understanding How Well Your Kidneys Are Working www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National
GFR (Glomerular Filtration Rate) A Key to Understanding How Well Your Kidneys Are Working www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National
Transrectal Ultrasound (Trus) Guided Prostate Biopsies Urology Patient Information Leaflet
 Transrectal Ultrasound (Trus) Guided Prostate Biopsies Urology Patient Information Leaflet Page 1 What is the purpose of my appointment? Your doctor has informed us that you have an elevated Prostate Specific
Transrectal Ultrasound (Trus) Guided Prostate Biopsies Urology Patient Information Leaflet Page 1 What is the purpose of my appointment? Your doctor has informed us that you have an elevated Prostate Specific
Urinary tract and perineum
 9 Urinary tract and perineum Key Points 9.1 9.1 THE URINARY BLADDER URINARY RETENTION Acute retention of urine is an indication for emergency drainage of the bladder The common causes of acute retention
9 Urinary tract and perineum Key Points 9.1 9.1 THE URINARY BLADDER URINARY RETENTION Acute retention of urine is an indication for emergency drainage of the bladder The common causes of acute retention
Renal Cysts What should I do now?
 Renal Cysts What should I do now? Dr Edmund Chiong Asst. Professor & Consultant Department of Urology National University Hospital What are renal cysts? Fluid-filled structures in the kidney that are not
Renal Cysts What should I do now? Dr Edmund Chiong Asst. Professor & Consultant Department of Urology National University Hospital What are renal cysts? Fluid-filled structures in the kidney that are not
Case Based Urology Learning Program
 Case Based Urology Learning Program Resident s Corner: UROLOGY Case Number 21 CBULP 2011 068 Case Based Urology Learning Program Editor: Associate Editors: Manager: Case Contributors: Steven C. Campbell,
Case Based Urology Learning Program Resident s Corner: UROLOGY Case Number 21 CBULP 2011 068 Case Based Urology Learning Program Editor: Associate Editors: Manager: Case Contributors: Steven C. Campbell,
Information for Men Receiving Radiation and Hormone Treatments for Prostate Cancer
 Information for Men Receiving Radiation and Hormone Treatments for Prostate Cancer Treatment Plan Stage of prostate cancer: RADIATION THERAPY Radiation Treatments: Date for planning CT: Date to start radiation
Information for Men Receiving Radiation and Hormone Treatments for Prostate Cancer Treatment Plan Stage of prostate cancer: RADIATION THERAPY Radiation Treatments: Date for planning CT: Date to start radiation
Classification of Mixed Incontinence
 european urology supplements 5 (2006) 837 841 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Classification of Mixed Incontinence Christopher Chapple * Sheffield Hallam University,
european urology supplements 5 (2006) 837 841 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Classification of Mixed Incontinence Christopher Chapple * Sheffield Hallam University,
Nocturnal Enuresis Clinical Management Tool (CMT)
 Nocturnal Enuresis Clinical Management Tool (CMT) Nocturnal Enuresis Clinical Management Tool Why this management tool? 1. The aim of this tool is to use a simple questionnaire and non-invasive screening,
Nocturnal Enuresis Clinical Management Tool (CMT) Nocturnal Enuresis Clinical Management Tool Why this management tool? 1. The aim of this tool is to use a simple questionnaire and non-invasive screening,
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA
 Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Urinary Tract Infection About one of every
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Urinary Tract Infection About one of every
These rare variants often act aggressively and may respond differently to therapy than the more common prostate adenocarcinoma.
 Prostate Cancer OVERVIEW Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer diagnosed among American men, accounting for nearly 200,000 new cancer cases in the United States each year. Greater than 65% of
Prostate Cancer OVERVIEW Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer diagnosed among American men, accounting for nearly 200,000 new cancer cases in the United States each year. Greater than 65% of
Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter
 Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter The 5 parts of the urinary system work together to get rid of waste and make urine. Urine is made in your kidneys and travels down 2 thin
Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter The 5 parts of the urinary system work together to get rid of waste and make urine. Urine is made in your kidneys and travels down 2 thin
Female Urinary Disorders and Pelvic Organ Prolapse
 Female Urinary Disorders and Pelvic Organ Prolapse Richard S. Bercik, M.D. Director, Division of Urogynecology & Reconstruction Pelvic Surgery Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive Sciences
Female Urinary Disorders and Pelvic Organ Prolapse Richard S. Bercik, M.D. Director, Division of Urogynecology & Reconstruction Pelvic Surgery Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive Sciences
Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction in MS. Tracy Walker, WOCN, MSCN, FNP C Nurse Practitioner MS Institute at Shepherd Center. Bladder Dysfunction
 Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction in MS Tracy Walker, WOCN, MSCN, FNP C Nurse Practitioner MS Institute at Shepherd Center Bladder Dysfunction Approximately 75% of people with MS experience bladder problems
Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction in MS Tracy Walker, WOCN, MSCN, FNP C Nurse Practitioner MS Institute at Shepherd Center Bladder Dysfunction Approximately 75% of people with MS experience bladder problems
Prostate Cancer Screening. A Decision Guide for African Americans
 Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide for African Americans This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Published
Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide for African Americans This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Published
MATERNITY SERVICES GUIDELINE POSTPARTUM BLADDER CARE. Sandra Reading, Women s CAG Deputy Director
 MATERNITY SERVICES GUIDELINE POSTPARTUM BLADDER CARE Sandra Reading, APPROVING COMMITTEE(S) Women s CAG Date approved: Deputy Director EFFECTIVE FROM 9 th September 2013 DISTRIBUTION All staff in the maternity
MATERNITY SERVICES GUIDELINE POSTPARTUM BLADDER CARE Sandra Reading, APPROVING COMMITTEE(S) Women s CAG Date approved: Deputy Director EFFECTIVE FROM 9 th September 2013 DISTRIBUTION All staff in the maternity
Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection
 Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is pyelonephritis? Pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is pyelonephritis? Pyelonephritis
VAGINAL MESH FAQ. How do you decide who should get mesh as part of their repair?
 VAGINAL MESH FAQ How do you decide who should get mesh as part of their repair? Each patient with pelvic organ prolapse (POP) is considered individually. In younger women, women with an uncomplicated prolapse
VAGINAL MESH FAQ How do you decide who should get mesh as part of their repair? Each patient with pelvic organ prolapse (POP) is considered individually. In younger women, women with an uncomplicated prolapse
Registered Charity No. 5365
 THE MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS SOCIETY OF IRELAND Dartmouth House, Grand Parade, Dublin 6. Telephone: (01) 269 4599. Fax: (01) 269 3746 MS Helpline: 1850 233 233 E-mail: mscontact@ms-society.ie www.ms-society.ie
THE MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS SOCIETY OF IRELAND Dartmouth House, Grand Parade, Dublin 6. Telephone: (01) 269 4599. Fax: (01) 269 3746 MS Helpline: 1850 233 233 E-mail: mscontact@ms-society.ie www.ms-society.ie
Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet
 Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet Are you reluctant to talk to your doctor about your bladder control problem? Don t be. There is help. Loss of bladder control is called urinary incontinence. It can happen
Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet Are you reluctant to talk to your doctor about your bladder control problem? Don t be. There is help. Loss of bladder control is called urinary incontinence. It can happen
A Summary of the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of. Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care
 A Summary of the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care Exclusions Community acquired UTIs UTIs in acute care Prevention Limit use of catheters Ensure
A Summary of the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care Exclusions Community acquired UTIs UTIs in acute care Prevention Limit use of catheters Ensure
