The Child with Sickle Cell Disease A Teaching Manual
|
|
|
- Anastasia Miller
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 The Child with Sickle Cell Disease A Teaching Manual Written and Developed by Debra A. Vedro, MSN, RN, CPNP And Rebecca A. Morrison, MSN, RN, CPNP Children's Medical Center of Dallas, Dallas, Texas Illustrated by Mary Ann Zaplac, MA In Coordination with The Texas Department of Health Supported in part by project # MCJ from The Women and Children Program (Title V, Social Security Act), Heath Resources and Services Administration, US Department of Health and Human Services Reprinted by Permission from the Texas Department of Health 06/26/03
2 2 Contents Origin and Distribution of Sickle Cell Disease Page 3 Genetics Page 4 Sickle Red Blood Cells Page 9 Infections Page 10 Splenic Sequestration Page 12 Pain Page 14 Chest Syndrome Page 17 Aplastic Crisis Page 18 Strokes Page 19 Gall Stones and Jaundice Page 20 Growth and Development Page 21 Retinopathy Page 23 Priapism Page 24
3 3 Origin and Distribution of Sickle Cell Disease Sickle cell trait occurred as a natural mutation of the hemoglobin gene. Sickle trait serves as a protective mechanism against malaria. Malaria is a deadly disease found in countries along the equator. People with sickle cell trait are protected from malaria while those with sickle cell anemia and normal hemoglobin are susceptible to it. Over (he years people with sickle trait migrated to other continents. Sickle cell disease is seen predominantly in the black population but is also seen in people of other ethnic groups. These ethnic groups include individuals from parts of the Middle East, Central India, and countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea, especially Italy and Greece.
4 4 Genetics Sickle Cell Anemia Sickle Cell Anemia (SS) is an inherited blood disorder (autosomal recessive). Approximately one in 400 black babies are born with Sickle Cell Anemia, and about one in Ii have Sickle Cell Trait (AS). The two hemoglobin types inherited will determine the shape of the red blood cell (RBC). When both parents have Sickle Cell Trait, there is a l-in-4 chance (25 percent) the baby will have normal hemoglobin (AA), a 50 percent chance the baby will have Sickle Cell Trait (AS), and a l-in-4 chance (25 percent) the baby will have Sickle Cell Anemia (SS). These chances remain the same with each pregnancy.
5 5 Sickle Hemoglobin C Disease Sickle Hemoglobin C (SC Disease) is a milder form of Sickle Cell Disease. The baby has inherited two (2) abnormal hemoglobins, hemoglobin S and hemoglobin C. Approximately one in l,000 black babies are born with SC Disease. Hemoglobin C Trail (AC) occurs in about one 1n 40 black babies. If one parent has AS and the other AC, there is a 1-in-4 chance (25 percent) the baby will inherit AA, AS, AC, or SC Disease. AS and AC are carrier states, not disease conditions.
6 6 Sickle Beta Zero Thalassemia Sickle Beta Zero Thalassemia (ST0) is clinically similar to Sickle Cell Anemia. STO occurs in approximately one in 10,000 black babies. STO is treated the same as Sickle Cell Anemia. When one parent has Sickle Trait (AS) and the other parent has Beta Thalassemia Zero Trait (AT) there is a l-in-4 chance the baby will have normal hemoglobin (AA), Beta Thalasseinia Zero Trait (AT, Sickle Beta Zero Thalassemia (STO), or Sickle Trait (AS). These chances remain the same for each pregnancy. Sickle Beta Plus Thalassemia Sickle Beta Plus Thalassemia (ST+) is the mildest form of Sickle Cell Disease. ST- I- occurs in approximately one in 4,000 black babies, When one parent has Sickle Trait (AS) and the other parent has Beta Thalassemia Plus Trait (AT+), them is a l-in-4 chance (25 percent) the baby will have normal hemoglobin (AA), Sickle Trait (AS), Beta Thalassemia Plus Trait (AT+), or Sickle Beta Plus Thalassemia (ST +). These chances remain the same for each pregnancy.
7 7 Hemoglobin C Disease Hemoglobin C Disease, a condition found mostly in the black population (approximately one in 6,000), consists of a minor abnormality of the hemoglobin. When both parents have C Trait (AC), there is a 1-in-4 chance (25 percent) that the baby will have normal hemoglobin (AA) or Hemoglobin C Disease (CC), and a 50 percent chance the baby will have Hemoglobin C Trait (AC). These chances remain the same for each pregnancy.
8 8 RED BLOOD CELLS Sickle Red Blood Cells
9 9 Sickle Red Blood Cells It is the inheritance of the sickle genes that causes red blood cell (RBC) abnormality. All complications of Sickle Cell Disease can he traced to changes in the make-up of the RBC. Normal RBC s are smooth surfaced, enabling them to change their shape to flow through small blood vessels. Under certain conditions (i.e., acidosis, dehydration, infection, and low oxygen. etc.) RBC s containing Sickle Hemoglobin become rigid, elongated, and sickle shaped. Some RBCs sickle immediately, while others remain normal for hours before sickling. Most RBCs containing Sickle Hemoglobin can sickle and then unsick-le. After repeated cycles of sickling and unsickling, the RBC s become irreversibly sickled. In Sickle C Disease, some RBCs are sickle cells. The C Hemoglobin forms slightly misshapened RBCs but they are of normal size and color. The C Hemoglobin tends to reduce the complications caused by the sickled calls. In Sickle Beta Plus or Zero ThaIassemia, a portion of the RBCs are sickle cells. The Thalassemia cells are paler than usual and too small. There is no Hemoglobin A present in Sickle Beta Zero Thalassemia. There is a small amount of Hemoglobin A present in Sickle Beta Plus Thalassemia which tends to minimize the complications caused by the sickled cells. Blood Flow Sickled RBC's can become trapped within the blood vessels and thus interfere with normal blood flow. This obstruction can lead to sudden pain anywhere in the body as well as cause damage to body tissues and organs over time.
10 10 INFECTIONS Infection is the major cause of death in children with Sickle Cell Anemia under the age of five years. The spleen functions as part of the body s defense against infection by serving as a filter to remove bacteria from the blood stream. The sickle RBC s damage the spleen by about four months of age so that the spleen does not function normally. This can allow bacteria to grow in the blood stream and cause septicemia, which can be fatal. Children under the age of five years are at highest risk for septicemia. Streptococcus Pneumoniae, (also called the pneumococcus) and Hemophilus influenzae are the two bacteria most likely to cause septicemia in the child with Sickle Cell Anemia, Ninety percent (90 percent) of the infections occur before the age of three years. Thirty-five percent (35 percent) of children with Sickle Cell Anemia who get pneumococcal sepsis die from the infection. Signs & Symptoms Fever* F degrees or higher Coughing Vomiting and or Diarrhea Crankiness Rapid breathing Pale Color Unusual sleepiness Trouble Breathing A fever may be the ONLY initial sign of septicemia Other potentially serious infectious which are more likely to occur in the child with Sickle Cell Anemia are meningitis, pneumonia and osteomyelitis. Any infection in the child with Sickle Cell Disease is an emergency. Infection is treatable and complete recovery is possible only if it is recognized and treated early enough. However, even with treatment, permanent disabilities and even death can result. Penicillin is often prescribed prophylactically twice daily to help fight infection. Septicemia can still occur even if penicillin is taken regularly.
11 11 The child with SC Disease or Sickle Beta Pills Thalassemia is not at as high a risk for septicemia as the child with Sickle Cell Anemia or Sickle beta Zero Thalassemia. Penicillin is not always recommended for these children. Pneumococcal and Hemophilus influenza vaccine should be given to children with Sickle Cell Disease to help boost their immunity.
12 12 ACUTE SPLENIC SEQUESTRATION CRISIS The spleen is normally a small organ located on the upper left side of the abdomen under the rib cage. When sickle cells are trapped in blood vessels inside and leading out of the spleen, the normal flow of the blood is blocked. Blood stays inside of the spleen instead of flowing through it. This is called sequestration, As a result, the blood count falls and the spleen gels very large and is easy to feel, If the spleen suddenly enlarges with a significant drop in the blood count, this is a serious and potentially life-threatening problem. When the spleen gradually gets larger over several weeks, the blood count does not change much, so it is not as serious. Any enlargement of the spleen is of concern and must be watched for
13 13 changes. Parents should know how their child s spleen normally feels, so that whenever the child seems sick they can check the spleen to see if it is bigger. If the spleen suddenly becomes larger, the child should he checked by a physician immediately. If the blood count is dangerously low from sequestration, blood transfusion may he necessary. Recurrent episodes are common, and a splenectomy (removal of the spleen) is sometimes required. Babies and young children with Sickle Cell Anemia are at greatest risk of splenic sequestration. After age five years, the spleen becomes smaller and in most cases it cannot enlarge any more. Children with Sickle C Disease usually experience this complication after the age of five years.
14 14 PAIN Painful episodes are common complications in children with Sickle Cell Disease. When the sickled cells are unable to flow through small blood vessels they obstruct blood flow causing vascular occlusion (vaso-occlusion). Vaso-occluision reduces blood flow to an area of the body resulting in pain. This can occur anywhere in The body, including fingers, arms, legs, ribs, abdomen, and organs such as the spleen, brain, and eyes. During infancy, vaso-occlusive crises (VOC s) are generally manifested as dactylitis or hand-foot syndrome. This is characterized by soft tissue swelling warmth and/or pain in the hands and/or feet due to ischemia (decreased oxygen) in
15 15 these small bones. Dactylitis call be recurrent hut usually does not occur after two or three years of age. The most common sites of pain in children over two years of age are the long bones, joints, back, and abdomen. VOC s can vary in duration, intensity. location, and time between episodes. They can be mild! moderate, or severe in terms of pain. Sometimes swelling is seen in the area of pain. VOC s may be preceded by a fever! dehydration, trauma, swimming, exposure to cold and/or emotional stress and unknown factors. Infection may occur at the same time. MANAGEMENT OF PAIN Painful episodes can often be treated and managed at home with regular acetaminophen (Tylenol), ibuprofen, or acetaminophen with codeine and hydration (an extra two to four ounces of water or juice every hour). Rubbing or application of heat with a heating pad or hot water bottle to the painful area may also alleviate discomfort.
16 16 Sometimes pain is unresponsive to home therapy. During those dines, the child should go to the emergency room for intravenous (IV) hydration and pain medication. IV morphine is usually used. Most of the time this is adequate treatment so that home therapy will then he effective. In very severe painful crises, the child may need to he admitted to the hospital for IV therapy. Sometimes the child can he taught to give his or her own pain medication by vein. This is called patient controlled analgesia, or PCA.
17 17 CHEST SYNDROME Chest syndrome is a common cause of hospitalization in children with sickle cell disease. It is clinically similar to pneumonia. Chest syndrome can be fatal in the child with sickle cell disease. Chest syndrome is the result of sickling in the lungs. It is believed that sickled cells clump up in the small blood vessels in the lungs or move there from some place else in the body. This may be triggered by a lung infection like pneumonia. Chest syndrome may develop right before, during, or after an episode of pain in the abdomen or bones Chest pain Fast breathing and/or retractions Congested pneumonia-like cough Abdominal pain Fever Trouble breathing Signs & Symptoms Treatment Analgesia, hydration, antibiotics and oxygen are used. Sometimes a blood transfusion is necessary if the blood count or if the chest syndrome is severe.
18 18 APLASTIC CRISIS An aplastic crisis results from an infection caused by Parvovirus B19. It causes production of RBC s to be shut down for about 10 days. This means that RBC s are not being made during this period. Because the RBC's in children with Sickle Cell Anemia live only 10 to 15 days (compared to 120 days in children who do not have Sickle Cell Anemia), the blood count (hemoglobin and hematocrit) drop very rapidly to a dangerously low level during the infection. Aplastic crisis usually occurs in children under the age of 16 years. It occurs in the general population but can only be noticed in those people with chronic hemolytic anemia (e.g. Sickle Cell Anemia). Recurrences of aplastic crisis are rare.
19 19 Treatment Most often a blood transfusion is given to raise the blood count until the body can start making its own RBC s again. Brothers and sisters with Sickle Cell Anemia should have their blood count checked since Parvovirus B19 is very contagious and they may be at risk of an aplastic crisis too. STROKE A stroke is a sudden and severe complication of sickle cell anemia. The most common cause of a stroke in children with sickle cell anemia is cerebral infarction (b1ockage of the oxygen supply to the brain by sickled cells). Strokes occur in six to 12 percent of individuals with sickle cell anemia, more commonly between three and 10 years of age. A stroke may occur with a painful episode or an infection, but in most cases there are no related illnesses. Although recovery from a stroke may be complete in some cases, frequently the stroke can cause brain damage, paralysis, convulsions, coma and even death. Repeat strokes occur in at least 60 percent of the children who have already suffered one stroke. A repeat stroke causes greater brain damage and increases the risk of death. To prevent recurrent strokes, blood transfusions are often given at four or five week intervals.. It is not known how long these transfusions must be given to prevent another stroke from occurring.
20 20 GALLSTONES AND JAUNDICE Gallstones in children whit sickle cell disease are the result of elevated bilirubin excretion due to the increased hemolysis. Gallstones are found in about 30 to 50 percent of children with sickle cell anemia. They may be symptomatic or asymptomatic. Most physicians monitor the child with asyniptomatic gallstones and do not recommend a cholecystectomy (removal of the gallbladder) until symptoms occur, Elective cholecystectomy may be indicated when gallstones are symptomatic (chronic right upper quadrant pain, nausea, vomiting, and fullness after meals). The complications of gallstones can include passage of stones causing colic, common bile duct obstruction, cholecystitis, and rarely, pancreatitis. Often the eyes of children with sickle cell anemia may appear yellow or jaundiced. This is due to the accumulation of a waste product (called bilirubin) from the increased RBC hemolysis associated with sickle cell disease. It is a benign complication.
21 21 GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT- FEMALES Females with sickle cell anemia maintain a lower average height and weight than those females with normal hemoglobin. This lower than average height and weight continues until late adolescence. Puberty is usually delayed by several years. Menarche (beginning of the menstrual period) is also delayed. It is important to reassure the adolescent that she will eventually catch up with her peers.
22 22 GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT- MALES Males with sickle cell anemia maintain a lower average height and weight than those males with normal hemoglobin. This lower than average height and weight continues until late adolescence. Puberty is usually delayed by several years. It is important to reassure the adolescent that he will eventually catch up with his peers.
23 23. RETINOPATHY Retinopathy can occur in children with sickle cell disease. Sickle cells can damage blood vessels in the retina and vision can be affected. Retinopathy is more common in adolescents with Sickle Hemoglobin C Disease. It is recommended that after the age of 10 years, children with sickle cell disease have periodic ophthalmology examinations
24 24 PRIAPISM Priapism is a persistent, unwanted erection of the penis that is often extremely painful. Priapism may present in the following ways: Stuttering There may be repeated, reversible. painful erections occurring over several hours (the penis becomes erect, the erection goes away, then becomes erect again, etc.). There are no problems with sexual functioning. Prolonged There may be a prolonged, painful erection that does not go away for more than several hours. This can last up to several days or weeks. This type of priapism needs attention by a doctor. Severe priapism can lead to partial or complete impotence. Sometimes a blood transfusion and liberal analgesics are given during the episode. Persistent There maybe a persistent penile erection that may last for weeks to years, This type of priapism is usually painless. It usually develops after a long episode of prolonged or stuttering priapism (as described above), Sexual functioning is often impaired. Specific causes are unknown. Acute episodes often begin during sleep or following sexual activity, hut frequently there is no identifiable event or cause. There is no current therapy to prevent episodes of priapism. There is no way to predict who will develop priapism and impotence. Those individuals experiencing repeated episodes are encouraged to avoid long periods of bladder distention, dehydration, and extended sexual activities.
25 25
Sickle Cell Anemia: A Parent s Guide for the Infant and Young Child
 Sickle Cell Anemia: A Parent s Guide for the Infant and Young Child Important Facts About Sickle Cell Anemia (Hb SS) Sickle cell anemia is the most common serious genetic disease in Black Americans. About
Sickle Cell Anemia: A Parent s Guide for the Infant and Young Child Important Facts About Sickle Cell Anemia (Hb SS) Sickle cell anemia is the most common serious genetic disease in Black Americans. About
Sickle Cell Disease: A Resource for the School Nurse and Educator
 Sickle Cell Disease: A Resource for the School Nurse and Educator INTRODUCTION This resource is designed to provide teachers, school nurses, and other school personnel, with information about sickle cell
Sickle Cell Disease: A Resource for the School Nurse and Educator INTRODUCTION This resource is designed to provide teachers, school nurses, and other school personnel, with information about sickle cell
Parent s Guide to Sickle Cell and School
 Parent s Guide to Sickle Cell and School Parent s Guide to Sickle Cell and School Parent s Guide to Sickle Cell and School Table of Contents Introduction Understanding Sickle Cell What is Sickle Cell Disease?
Parent s Guide to Sickle Cell and School Parent s Guide to Sickle Cell and School Parent s Guide to Sickle Cell and School Table of Contents Introduction Understanding Sickle Cell What is Sickle Cell Disease?
Educator s Guide to Sickle Cell Disease
 Educator s Guide to Sickle Cell Disease Educator s Guide to Sickle Cell Disease Sickle cell disease is an inherited blood disorder affecting about one out of every 350 African Americans. Most children
Educator s Guide to Sickle Cell Disease Educator s Guide to Sickle Cell Disease Sickle cell disease is an inherited blood disorder affecting about one out of every 350 African Americans. Most children
Sickle Cell Disease At a Glance
 Sickle Cell Disease At a Glance Sickle cell disease (SCD) is an inherited blood condition that is characterized by pain crises and anemia. In the US, newborn screening in most states can diagnose sickle
Sickle Cell Disease At a Glance Sickle cell disease (SCD) is an inherited blood condition that is characterized by pain crises and anemia. In the US, newborn screening in most states can diagnose sickle
Taking Control: Teens with Sickle Cell Disease
 Taking Control: Teens with Sickle Cell Disease Taking Control: Teens with Sickle Cell Disease Produced by St. Jude Children s Research Hospital Departments of Hematology, Patient Education, and Biomedical
Taking Control: Teens with Sickle Cell Disease Taking Control: Teens with Sickle Cell Disease Produced by St. Jude Children s Research Hospital Departments of Hematology, Patient Education, and Biomedical
Hydroxyurea Treatment for Sickle Cell Disease
 Hydroxyurea Treatment for Sickle Cell Disease Before hydroxyurea After hydroxyurea Hydroxyurea Treatment for Sickle Cell Disease 1 This document is not intended to take the place of the care and attention
Hydroxyurea Treatment for Sickle Cell Disease Before hydroxyurea After hydroxyurea Hydroxyurea Treatment for Sickle Cell Disease 1 This document is not intended to take the place of the care and attention
Cystic Fibrosis. Cystic fibrosis affects various systems in children and young adults, including the following:
 Cystic Fibrosis What is cystic fibrosis? Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an inherited disease characterized by an abnormality in the glands that produce sweat and mucus. It is chronic, progressive, and is usually
Cystic Fibrosis What is cystic fibrosis? Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an inherited disease characterized by an abnormality in the glands that produce sweat and mucus. It is chronic, progressive, and is usually
Red Blood Cell Transfusions for Sickle Cell Disease
 Red Blood Cell Transfusions for Sickle Cell Disease Red Blood Cell Transfusions for Sickle Cell Disease 1 Produced by St. Jude Children s Research Hospital, Departments of Hematology, Patient Education,
Red Blood Cell Transfusions for Sickle Cell Disease Red Blood Cell Transfusions for Sickle Cell Disease 1 Produced by St. Jude Children s Research Hospital, Departments of Hematology, Patient Education,
Childhood Diseases and potential risks during pregnancy: (All information available on the March of Dimes Web Site.) http://www.modimes.
 Childhood Diseases and potential risks during pregnancy: (All information available on the March of Dimes Web Site.) http://www.modimes.org/ Fifth disease (erythema infectiosum) is a common, mild, childhood
Childhood Diseases and potential risks during pregnancy: (All information available on the March of Dimes Web Site.) http://www.modimes.org/ Fifth disease (erythema infectiosum) is a common, mild, childhood
School-age child 5-1 THE BLOOD
 C A S E S T U D Y 5 : School-age child Adapted from Thomson Delmar Learning s Case Study Series: Pediatrics, by Bonita E. Broyles, RN, BSN, MA, PhD. Copyright 2006 Thomson Delmar Learning, Clifton Park,
C A S E S T U D Y 5 : School-age child Adapted from Thomson Delmar Learning s Case Study Series: Pediatrics, by Bonita E. Broyles, RN, BSN, MA, PhD. Copyright 2006 Thomson Delmar Learning, Clifton Park,
SICKLE CELL DISEASE: A FAMILY GUIDE
 SICKLE CELL DISEASE: A FAMILY GUIDE (Third Edition) Division of Family Health Services Newborn Screening and Genetic Services Special Child Health and Early Intervention Services TABLE OF CONTENTS Acknowledgments...ii
SICKLE CELL DISEASE: A FAMILY GUIDE (Third Edition) Division of Family Health Services Newborn Screening and Genetic Services Special Child Health and Early Intervention Services TABLE OF CONTENTS Acknowledgments...ii
What is sickle cell disease? Who gets sickle cell disease? Common symptoms of sickle cell disease. What you can do to help
 What is sickle cell disease? Who gets sickle cell disease? Common symptoms of sickle cell disease What you can do to help Treatment for sickle cell disease Pain management Helpful sickle cell disease resources
What is sickle cell disease? Who gets sickle cell disease? Common symptoms of sickle cell disease What you can do to help Treatment for sickle cell disease Pain management Helpful sickle cell disease resources
Information for couples where both partners carry Haemoglobin S (sickle cell)
 Information for couples where both partners carry Haemoglobin S (sickle cell) Including information on prenatal diagnosis Contacts for prenatal diagnosis centre Couple at risk for Sickle Cell Anaemia Ms
Information for couples where both partners carry Haemoglobin S (sickle cell) Including information on prenatal diagnosis Contacts for prenatal diagnosis centre Couple at risk for Sickle Cell Anaemia Ms
Blood Transfusion. There are three types of blood cells: Red blood cells. White blood cells. Platelets.
 Blood Transfusion Introduction Blood transfusions can save lives. Every second, someone in the world needs a blood transfusion. Blood transfusions can replace the blood lost from a serious injury or surgery.
Blood Transfusion Introduction Blood transfusions can save lives. Every second, someone in the world needs a blood transfusion. Blood transfusions can replace the blood lost from a serious injury or surgery.
MEDICATION GUIDE ACTOPLUS MET (ak-tō-plus-met) (pioglitazone hydrochloride and metformin hydrochloride) tablets
 MEDICATION GUIDE (ak-tō-plus-met) (pioglitazone hydrochloride and metformin hydrochloride) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking and each time you get a refill. There may
MEDICATION GUIDE (ak-tō-plus-met) (pioglitazone hydrochloride and metformin hydrochloride) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking and each time you get a refill. There may
Blood Transfusion. Red Blood Cells White Blood Cells Platelets
 Blood Transfusion Introduction Blood transfusions are very common. Each year, almost 5 million Americans need a blood transfusion. Blood transfusions are given to replace blood lost during surgery or serious
Blood Transfusion Introduction Blood transfusions are very common. Each year, almost 5 million Americans need a blood transfusion. Blood transfusions are given to replace blood lost during surgery or serious
WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION. Sickle-cell anaemia
 WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION FIFTY-NINTH WORLD HEALTH ASSEMBLY A59/9 Provisional agenda item 11.4 24 April 2006 Sickle-cell anaemia Report by the Secretariat PREVALENCE OF SICKLE-CELL ANAEMIA 1. Sickle-cell
WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION FIFTY-NINTH WORLD HEALTH ASSEMBLY A59/9 Provisional agenda item 11.4 24 April 2006 Sickle-cell anaemia Report by the Secretariat PREVALENCE OF SICKLE-CELL ANAEMIA 1. Sickle-cell
Patient Guide. Important information for patients starting therapy with LEMTRADA (alemtuzumab)
 Patient Guide Important information for patients starting therapy with LEMTRADA (alemtuzumab) This medicinal product is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety
Patient Guide Important information for patients starting therapy with LEMTRADA (alemtuzumab) This medicinal product is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety
Sickle Cell Disease. A Handbook for School Personnel UNDERSTANDING THE CHILD WITH
 UNDERSTANDING THE CHILD WITH Sickle Cell Disease A Handbook for School Personnel Distributed by The Virginia Sickle Cell Awareness Program Virginia Department of Health 109 Governor Street Richmond, Virginia
UNDERSTANDING THE CHILD WITH Sickle Cell Disease A Handbook for School Personnel Distributed by The Virginia Sickle Cell Awareness Program Virginia Department of Health 109 Governor Street Richmond, Virginia
2 P age. Babies from Birth to Age 2
 Contents Babies from Birth to Age 2... 2 Vaccines give parents the power... 2 Vaccines are recommended throughout our lives... 3 Talk to your doctor... 3 Vaccines are very safe... 3 Whooping Cough (Pertussis)...
Contents Babies from Birth to Age 2... 2 Vaccines give parents the power... 2 Vaccines are recommended throughout our lives... 3 Talk to your doctor... 3 Vaccines are very safe... 3 Whooping Cough (Pertussis)...
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT PERTUSSIS (WHOOPING COUGH)
 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT PERTUSSIS (WHOOPING COUGH) What is pertussis? General Questions About Pertussis Pertussis, or whooping cough, is a contagious illness that is spread when an infected person
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT PERTUSSIS (WHOOPING COUGH) What is pertussis? General Questions About Pertussis Pertussis, or whooping cough, is a contagious illness that is spread when an infected person
X-Plain Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - Adriamycin, Cytoxan, and Tamoxifen Reference Summary
 X-Plain Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - Adriamycin, Cytoxan, and Tamoxifen Reference Summary Introduction Breast cancer is a common condition that affects one out of every 11 women. Your doctor has recommended
X-Plain Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - Adriamycin, Cytoxan, and Tamoxifen Reference Summary Introduction Breast cancer is a common condition that affects one out of every 11 women. Your doctor has recommended
35-40% of GBS disease occurs in the elderly or in adults with chronic medical conditions.
 What is Group B Strep (GBS)? Group B Streptococcus (GBS) is a type of bacteria that is found in the lower intestine of 10-35% of all healthy adults and in the vagina and/or lower intestine of 10-35% of
What is Group B Strep (GBS)? Group B Streptococcus (GBS) is a type of bacteria that is found in the lower intestine of 10-35% of all healthy adults and in the vagina and/or lower intestine of 10-35% of
Multiple Myeloma. This reference summary will help you understand multiple myeloma and its treatment options.
 Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
AC: Doxorubicin and Cyclophosphamide
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is AC? It is the short name for the drugs used for this chemotherapy treatment. The two drugs you will receive during this treatment are Doxorubicin (Adriamycin
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is AC? It is the short name for the drugs used for this chemotherapy treatment. The two drugs you will receive during this treatment are Doxorubicin (Adriamycin
SICKLE CELL DISEASE. Low Incidence Specialist 2010 Page 1
 SICKLE CELL DISEASE Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a genetic condition that causes red blood cells to change shape, harden and not function as well as regular red blood cells. The sickled cells do not carry
SICKLE CELL DISEASE Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a genetic condition that causes red blood cells to change shape, harden and not function as well as regular red blood cells. The sickled cells do not carry
Gallbladder Diseases and Problems
 Gallbladder Diseases and Problems Introduction Your gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ under your liver. It stores bile, a fluid made by your liver to digest fat. There are many diseases and problems that
Gallbladder Diseases and Problems Introduction Your gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ under your liver. It stores bile, a fluid made by your liver to digest fat. There are many diseases and problems that
Chickenpox in pregnancy: what you need to know
 Chickenpox in pregnancy: what you need to know First published December 2003 Revised edition published November 2008 What is chickenpox? Chickenpox is a very infectious illness caused by a virus called
Chickenpox in pregnancy: what you need to know First published December 2003 Revised edition published November 2008 What is chickenpox? Chickenpox is a very infectious illness caused by a virus called
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
 Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Removal of Gall Bladder Page 12 Patient Information Further Information We endeavour to provide an excellent service at all times, but should you have any concerns please,
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Removal of Gall Bladder Page 12 Patient Information Further Information We endeavour to provide an excellent service at all times, but should you have any concerns please,
MANAGING ANEMIA. When You Have Kidney Disease or Kidney Failure. www.kidney.org
 MANAGING ANEMIA When You Have Kidney Disease or Kidney Failure www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) offers guidelines and commentaries
MANAGING ANEMIA When You Have Kidney Disease or Kidney Failure www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) offers guidelines and commentaries
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems
 Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
Frequently asked questions about whooping cough (pertussis)
 Frequently asked questions about whooping cough (pertussis) About whooping cough What is whooping cough? Whooping cough is a highly contagious illness caused by bacteria. It mainly affects the respiratory
Frequently asked questions about whooping cough (pertussis) About whooping cough What is whooping cough? Whooping cough is a highly contagious illness caused by bacteria. It mainly affects the respiratory
What You Need to Know About LEMTRADA (alemtuzumab) Treatment: A Patient Guide
 For Patients What You Need to Know About LEMTRADA (alemtuzumab) Treatment: A Patient Guide Patients: Your doctor or nurse will go over this patient guide with you. It is important to ask any questions
For Patients What You Need to Know About LEMTRADA (alemtuzumab) Treatment: A Patient Guide Patients: Your doctor or nurse will go over this patient guide with you. It is important to ask any questions
Pain, Coping and Sleep in Children and Adolescents With Sickle Cell Disease J. Kelly Graves, PhD, RN Eufemia Jacob, PhD, RN
 Pain, Coping and Sleep in Children and Adolescents With Sickle Cell Disease J. Kelly Graves, PhD, RN Eufemia Jacob, PhD, RN Sigma Theta Tau International 24 th International Nursing Research Congress July
Pain, Coping and Sleep in Children and Adolescents With Sickle Cell Disease J. Kelly Graves, PhD, RN Eufemia Jacob, PhD, RN Sigma Theta Tau International 24 th International Nursing Research Congress July
Pneumonia. Pneumonia is an infection that makes the tiny air sacs in your lungs inflamed (swollen and sore). They then fill with liquid.
 Pneumonia Pneumonia is an infection that makes the tiny air sacs in your lungs inflamed (swollen and sore). They then fill with liquid. People with mild (not so bad) pneumonia can usually be treated at
Pneumonia Pneumonia is an infection that makes the tiny air sacs in your lungs inflamed (swollen and sore). They then fill with liquid. People with mild (not so bad) pneumonia can usually be treated at
Information for you Treatment of venous thrombosis in pregnancy and after birth. What are the symptoms of a DVT during pregnancy?
 Information for you Treatment of venous thrombosis in pregnancy and after birth Published in September 2011 What is venous thrombosis? Thrombosis is a blood clot in a blood vessel (a vein or an artery).
Information for you Treatment of venous thrombosis in pregnancy and after birth Published in September 2011 What is venous thrombosis? Thrombosis is a blood clot in a blood vessel (a vein or an artery).
SICKLE CELL DISEASE IN GEORGIA
 SICKLE CELL DISEASE IN GEORGIA Peter A Lane, MD Professor of Pediatrics Emory University School of Medicine Director, Sickle Cell Disease Program Children s Healthcare of Atlanta SICKLE CELL DISEASE IN
SICKLE CELL DISEASE IN GEORGIA Peter A Lane, MD Professor of Pediatrics Emory University School of Medicine Director, Sickle Cell Disease Program Children s Healthcare of Atlanta SICKLE CELL DISEASE IN
HOW TO CARE FOR A PATIENT WITH DIABETES
 HOW TO CARE FOR A PATIENT WITH DIABETES INTRODUCTION Diabetes is one of the most common diseases in the United States, and diabetes is a disease that affects the way the body handles blood sugar. Approximately
HOW TO CARE FOR A PATIENT WITH DIABETES INTRODUCTION Diabetes is one of the most common diseases in the United States, and diabetes is a disease that affects the way the body handles blood sugar. Approximately
H1N1 Flu Vaccine Available to All Virginia Beach City Public Schools Students
 V i r g i n i a B e a c h C i t y P u b l i c S c h o o l s apple-a-day F o r O u r F a m i l y o f I n t e r e s t e d C i t i z e n s Special Edition H1N1 Flu Vaccine Available to All Virginia Beach
V i r g i n i a B e a c h C i t y P u b l i c S c h o o l s apple-a-day F o r O u r F a m i l y o f I n t e r e s t e d C i t i z e n s Special Edition H1N1 Flu Vaccine Available to All Virginia Beach
What is Thalassemia Trait?
 What is Thalassemia Trait? Introduction Being tested for the thalassemia trait is easy This book contains basic information about the thalassemia trait. Whether you have been diagnosed with the thalassemia
What is Thalassemia Trait? Introduction Being tested for the thalassemia trait is easy This book contains basic information about the thalassemia trait. Whether you have been diagnosed with the thalassemia
Nursing Care of the Child with Sickle Cell Disease: Acute Complications Louise D. Jakubik, PhD, RN-BC Nursing of Children Network Conference 2010
 Learning Objectives At the completion of this program, the participants will be able to: 1. Review the incidence and genetics of sickle cell disease. 2. Review the basic pathophysiolgy of sickle cell disease.
Learning Objectives At the completion of this program, the participants will be able to: 1. Review the incidence and genetics of sickle cell disease. 2. Review the basic pathophysiolgy of sickle cell disease.
Darlene Langhoff St. Thomas More High Ron Gerrits MSOE
 Darlene Langhoff St. Thomas More High Ron Gerrits MSOE Investigating the Scene DNA analysis The Findings Crime scene is set up (optional power point ) Tip: Set up crime scene and have students take photos
Darlene Langhoff St. Thomas More High Ron Gerrits MSOE Investigating the Scene DNA analysis The Findings Crime scene is set up (optional power point ) Tip: Set up crime scene and have students take photos
GASTRIC BYPASS SURGERY CONSENT FORM
 Page 1 of 6 I, have been asked to read carefully all of the (name of patient or substitute decision-maker) information contained in this consent form and to consent to the procedure described below on
Page 1 of 6 I, have been asked to read carefully all of the (name of patient or substitute decision-maker) information contained in this consent form and to consent to the procedure described below on
X-Plain Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Vascular Surgery Reference Summary
 X-Plain Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Vascular Surgery Reference Summary Ballooning of the aorta, also known as an "abdominal aortic aneurysm," can lead to life threatening bleeding. Doctors may recommend
X-Plain Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Vascular Surgery Reference Summary Ballooning of the aorta, also known as an "abdominal aortic aneurysm," can lead to life threatening bleeding. Doctors may recommend
A newsletter of the Newborn Screening Program and the Newborn Screening Laboratory
 NEWBORN SCREENING August 2001 Be Kind To Tiny Feet A newsletter of the Newborn Screening Program and the Newborn Screening Laboratory HEMOGLOBINOPATHIES Second Edition Follow-up procedures for hemoglobinopathy
NEWBORN SCREENING August 2001 Be Kind To Tiny Feet A newsletter of the Newborn Screening Program and the Newborn Screening Laboratory HEMOGLOBINOPATHIES Second Edition Follow-up procedures for hemoglobinopathy
MEDICATION GUIDE POMALYST (POM-uh-list) (pomalidomide) capsules. What is the most important information I should know about POMALYST?
 MEDICATION GUIDE POMALYST (POM-uh-list) (pomalidomide) capsules What is the most important information I should know about POMALYST? Before you begin taking POMALYST, you must read and agree to all of
MEDICATION GUIDE POMALYST (POM-uh-list) (pomalidomide) capsules What is the most important information I should know about POMALYST? Before you begin taking POMALYST, you must read and agree to all of
Influenza Education Presentation Prepared by Peel Public Health 2014
 Influenza Education Presentation Prepared by Peel Public Health 2014 Disclaimer We are pleased to be able to offer you the use of our Influenza PowerPoint presentation for your use. Peel Public Health
Influenza Education Presentation Prepared by Peel Public Health 2014 Disclaimer We are pleased to be able to offer you the use of our Influenza PowerPoint presentation for your use. Peel Public Health
Premature Infant Care
 Premature Infant Care Introduction A premature baby is born before the 37th week of pregnancy. Premature babies are also called preemies. Premature babies may have health problems because their organs
Premature Infant Care Introduction A premature baby is born before the 37th week of pregnancy. Premature babies are also called preemies. Premature babies may have health problems because their organs
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy (Removal of the Gallbladder)
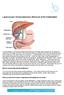 Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy (Removal of the Gallbladder) The gall bladder is a small pear-shaped organ that lies in the right upper quadrant of your abdomen under your liver (under your ribs). The liver
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy (Removal of the Gallbladder) The gall bladder is a small pear-shaped organ that lies in the right upper quadrant of your abdomen under your liver (under your ribs). The liver
Genetic Mutations. Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes.
 Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
The Family Library. Understanding Diabetes
 The Family Library Understanding Diabetes What is Diabetes? Diabetes is caused when the body has a problem in making or using insulin. Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas and is needed for the
The Family Library Understanding Diabetes What is Diabetes? Diabetes is caused when the body has a problem in making or using insulin. Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas and is needed for the
Trait Counseling Manual: Sickle Cell Trait and Hemoglobin C Trait
 Trait ounseling Manual: ickle ell Trait and Hemoglobin Trait Trait ounseling Manual: ickle ell Trait and Hemoglobin Trait Produced by t. Jude hildren s Research Hospital, Departments of Hematology, Patient
Trait ounseling Manual: ickle ell Trait and Hemoglobin Trait Trait ounseling Manual: ickle ell Trait and Hemoglobin Trait Produced by t. Jude hildren s Research Hospital, Departments of Hematology, Patient
MEDICATION GUIDE. PROCRIT (PRO KRIT) (epoetin alfa)
 MEDICATION GUIDE PROCRIT (PROKRIT) (epoetin alfa) Read this Medication Guide: before you start PROCRIT. if you are told by your healthcare provider that there is new information about PROCRIT. if you are
MEDICATION GUIDE PROCRIT (PROKRIT) (epoetin alfa) Read this Medication Guide: before you start PROCRIT. if you are told by your healthcare provider that there is new information about PROCRIT. if you are
X-Plain Trigeminal Neuralgia Reference Summary
 X-Plain Trigeminal Neuralgia Reference Summary Introduction Trigeminal neuralgia is a condition that affects about 40,000 patients in the US every year. Its treatment mostly involves the usage of oral
X-Plain Trigeminal Neuralgia Reference Summary Introduction Trigeminal neuralgia is a condition that affects about 40,000 patients in the US every year. Its treatment mostly involves the usage of oral
MINISTRY OF HEALTH PANDEMIC INFLUENZA A / H1N1 2009 VACCINE FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
 Government of the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago MINISTRY OF HEALTH PANDEMIC INFLUENZA A / H1N1 2009 VACCINE FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS Influenza vaccines are one of the most effective ways to protect
Government of the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago MINISTRY OF HEALTH PANDEMIC INFLUENZA A / H1N1 2009 VACCINE FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS Influenza vaccines are one of the most effective ways to protect
What is whooping cough. (pertussis)? Information and Prevention. Ocument dn
 What is whooping cough Ocument dn (pertussis)? Information and Prevention IMPORTANT Pertussis (or whooping cough) is a highly contagious infection that can cause uncontrollable, violent coughing. If you
What is whooping cough Ocument dn (pertussis)? Information and Prevention IMPORTANT Pertussis (or whooping cough) is a highly contagious infection that can cause uncontrollable, violent coughing. If you
CorCap Cardiac Support Device Patient Information Booklet
 What is Heart Failure? CorCap Cardiac Support Device Patient Information Booklet Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the needs of the body. To compensate
What is Heart Failure? CorCap Cardiac Support Device Patient Information Booklet Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the needs of the body. To compensate
Like cocaine, heroin is a drug that is illegal in some areas of the world. Heroin is highly addictive.
 Heroin Introduction Heroin is a powerful drug that affects the brain. People who use it can form a strong addiction. Addiction is when a drug user can t stop taking a drug, even when he or she wants to.
Heroin Introduction Heroin is a powerful drug that affects the brain. People who use it can form a strong addiction. Addiction is when a drug user can t stop taking a drug, even when he or she wants to.
Key Facts about Influenza (Flu) & Flu Vaccine
 Key Facts about Influenza (Flu) & Flu Vaccine mouths or noses of people who are nearby. Less often, a person might also get flu by touching a surface or object that has flu virus on it and then touching
Key Facts about Influenza (Flu) & Flu Vaccine mouths or noses of people who are nearby. Less often, a person might also get flu by touching a surface or object that has flu virus on it and then touching
Remove this cover sheet before redistributing and replace it with your own. Please ensure that DPHHS is included on your HAN distribution list.
 State of Montana Health Alert Network DPHHS HAN ADVISORY Cover Sheet DATE: May 15, 2012 SUBJECT: Pertussis INSTRUCTIONS: DISTRIBUTE to your local HAN contacts. This HAN is intended for general sharing
State of Montana Health Alert Network DPHHS HAN ADVISORY Cover Sheet DATE: May 15, 2012 SUBJECT: Pertussis INSTRUCTIONS: DISTRIBUTE to your local HAN contacts. This HAN is intended for general sharing
Urinary Tract Infections
 1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
95% of childhood kidney cancer cases are Wilms tumours. Childhood kidney cancer is extremely rare, with only 90 cases a year in
 James Whale Fund for Kidney Cancer Childhood kidney cancer factsheet Kidney cancer rarely afflicts children and about 90 paediatric cases are diagnosed in the UK each year. About 75% of childhood kidney
James Whale Fund for Kidney Cancer Childhood kidney cancer factsheet Kidney cancer rarely afflicts children and about 90 paediatric cases are diagnosed in the UK each year. About 75% of childhood kidney
THE KIDNEY. Bulb of penis Abdominal aorta Scrotum Adrenal gland Inferior vena cava Urethra Corona glandis. Kidney. Glans penis Testicular vein
 29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
PATIENT CONSENT TO PROCEDURE - ROUX-EN-Y GASTRIC BYPASS
 As a patient you must be adequately informed about your condition and the recommended surgical procedure. Please read this document carefully and ask about anything you do not understand. Please initial
As a patient you must be adequately informed about your condition and the recommended surgical procedure. Please read this document carefully and ask about anything you do not understand. Please initial
Medicines To Treat Alcohol Use Disorder A Review of the Research for Adults
 Medicines To Treat Alcohol Use Disorder A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor* said you have alcohol use disorder
Medicines To Treat Alcohol Use Disorder A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor* said you have alcohol use disorder
Ear Infections Chickenpox chickenpox
 Ear Chickenpox Infections chickenpox Chickenpox Chickenpox is a common, very contagious viral infection that over 90% of people get during childhood unless they have been immunised. After an infection,
Ear Chickenpox Infections chickenpox Chickenpox Chickenpox is a common, very contagious viral infection that over 90% of people get during childhood unless they have been immunised. After an infection,
CERVICAL MEDIASTINOSCOPY WITH BIOPSY
 INFORMED CONSENT INFORMATION ADDRESSOGRAPH DATA CERVICAL MEDIASTINOSCOPY WITH BIOPSY You have decided to have an important procedure and we appreciate your selection of UCLA Healthcare to meet your needs.
INFORMED CONSENT INFORMATION ADDRESSOGRAPH DATA CERVICAL MEDIASTINOSCOPY WITH BIOPSY You have decided to have an important procedure and we appreciate your selection of UCLA Healthcare to meet your needs.
Elective Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
 General Surgery Elective Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy This information aims to explain what will happen before, during and after your surgery to remove your gallbladder. It includes information about the
General Surgery Elective Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy This information aims to explain what will happen before, during and after your surgery to remove your gallbladder. It includes information about the
VAD Chemotherapy Regimen for Multiple Myeloma Information for Patients
 VAD Chemotherapy Regimen for Multiple Myeloma Information for Patients The Regimen contains: V = vincristine (Oncovin ) A = Adriamycin (doxorubicin) D = Decadron (dexamethasone) How Is This Regimen Given?
VAD Chemotherapy Regimen for Multiple Myeloma Information for Patients The Regimen contains: V = vincristine (Oncovin ) A = Adriamycin (doxorubicin) D = Decadron (dexamethasone) How Is This Regimen Given?
SARCOIDOSIS. Signs and symptoms associated with specific organ involvement can include the following:
 SARCOIDOSIS Sarcoidosis is a disease that occurs when areas of inflammation develop in different organs of the body. Very small clusters of inflammation, called granulomas, are seen with sarcoidosis. They
SARCOIDOSIS Sarcoidosis is a disease that occurs when areas of inflammation develop in different organs of the body. Very small clusters of inflammation, called granulomas, are seen with sarcoidosis. They
Marrying a relative. Is there an increased chance that a child will have genetic problems if its parents are related to each other?
 Marrying a relative Is there an increased chance that a child will have genetic problems if its parents are related to each other? The simple answer to this question is Yes, there is an increased chance.
Marrying a relative Is there an increased chance that a child will have genetic problems if its parents are related to each other? The simple answer to this question is Yes, there is an increased chance.
Tuberculosis: FAQs. What is the difference between latent TB infection and TB disease?
 Tuberculosis: FAQs What is TB disease? Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease caused by bacteria (germs) that are spread from person to person through the air. TB usually affects the lungs, but it can also affect
Tuberculosis: FAQs What is TB disease? Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease caused by bacteria (germs) that are spread from person to person through the air. TB usually affects the lungs, but it can also affect
Amylase and Lipase Tests
 Amylase and Lipase Tests Also known as: Amy Formal name: Amylase Related tests: Lipase The Test The blood amylase test is ordered, often along with a lipase test, to help diagnose and monitor acute or
Amylase and Lipase Tests Also known as: Amy Formal name: Amylase Related tests: Lipase The Test The blood amylase test is ordered, often along with a lipase test, to help diagnose and monitor acute or
MEDICATION GUIDE mitoxantrone (mito-xan-trone) for injection concentrate
 MEDICATION GUIDE mitoxantrone (mito-xan-trone) for injection concentrate Read this Medication Guide before you start receiving mitoxantrone and each time you receive mitoxantrone. There may be new information.
MEDICATION GUIDE mitoxantrone (mito-xan-trone) for injection concentrate Read this Medication Guide before you start receiving mitoxantrone and each time you receive mitoxantrone. There may be new information.
The flu vaccination WINTER 2016/17. Who should have it and why. Flu mmunisation 2016/17
 The flu vaccination WINTER 2016/17 Who should have it and why Flu mmunisation 2016/17 The flu vaccination 1 Winter 2016/17 Helping to protect everyone, every winter This leaflet explains how you can help
The flu vaccination WINTER 2016/17 Who should have it and why Flu mmunisation 2016/17 The flu vaccination 1 Winter 2016/17 Helping to protect everyone, every winter This leaflet explains how you can help
American Psychological Association (APA) Style Guide for. Allied Health Sciences
 Running Head: SICKLE CELL ANEMIA 1 American Psychological Association (APA) Style Guide for Allied Health Sciences By Richard Boan, Ph.D., Candace Doyle, M.S.Ed., Patricia Shahbahrami, B.S. This guide
Running Head: SICKLE CELL ANEMIA 1 American Psychological Association (APA) Style Guide for Allied Health Sciences By Richard Boan, Ph.D., Candace Doyle, M.S.Ed., Patricia Shahbahrami, B.S. This guide
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Xofigo Therapy. For metastatic prostate cancer. What is Xofigo? How does it work?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Xofigo Therapy For metastatic prostate cancer This handout explains how the drug Xofigo is used to treat metastatic prostate cancer. What is Xofigo? Xofigo is a radioactive
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Xofigo Therapy For metastatic prostate cancer This handout explains how the drug Xofigo is used to treat metastatic prostate cancer. What is Xofigo? Xofigo is a radioactive
Understanding Diabetes
 Patient Education Understanding Diabetes This handout describes diabetes, the complications related to the disease, and how you can prevent these complications. Blood Sugar Control Diabetes is a disease
Patient Education Understanding Diabetes This handout describes diabetes, the complications related to the disease, and how you can prevent these complications. Blood Sugar Control Diabetes is a disease
CMF: Cyclophosphamide, Methotrexate and Fluorouracil
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu CMF: Cyclophosphamide, Methotrexate and Fluorouracil What is CMF? This is the short name for the drugs used for this chemotherapy treatment. The three drugs
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu CMF: Cyclophosphamide, Methotrexate and Fluorouracil What is CMF? This is the short name for the drugs used for this chemotherapy treatment. The three drugs
Ear Disorders and Problems
 Ear Disorders and Problems Introduction Your ear has three main parts: outer, middle and inner. You use all of them to hear. There are many disorders and problems that can affect the ear. The symptoms
Ear Disorders and Problems Introduction Your ear has three main parts: outer, middle and inner. You use all of them to hear. There are many disorders and problems that can affect the ear. The symptoms
Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR): A Decision Aid For. KGH Patients And Their Families
 Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR): A Decision Aid For KGH Patients And Their Families The goal of this pamphlet is to provide information about cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) so you can be adequately
Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR): A Decision Aid For KGH Patients And Their Families The goal of this pamphlet is to provide information about cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) so you can be adequately
Laparoscopic Gallbladder Removal (Cholecystectomy) Patient Information from SAGES
 Laparoscopic Gallbladder Removal (Cholecystectomy) Patient Information from SAGES Gallbladder removal is one of the most commonly performed surgical procedures. Gallbladder removal surgery is usually performed
Laparoscopic Gallbladder Removal (Cholecystectomy) Patient Information from SAGES Gallbladder removal is one of the most commonly performed surgical procedures. Gallbladder removal surgery is usually performed
A Study of Malaria and Sickle Cell Anemia: A Hands-on Mathematical Investigation Student Materials: Reading Assignment
 4/15/99 1 A Study of Malaria and Sickle Cell Anemia: A Hands-on Mathematical Investigation Student Materials: Reading Assignment Malaria is a parasitic disease which is spread by the female Anopheles mosquitoes.
4/15/99 1 A Study of Malaria and Sickle Cell Anemia: A Hands-on Mathematical Investigation Student Materials: Reading Assignment Malaria is a parasitic disease which is spread by the female Anopheles mosquitoes.
Consent for Treatment/Procedure Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy
 Patient's Name: Today's Date: / / The purpose of this document is to confirm, in the presence of witnesses, your informed request to have Surgery for obesity. You are asked to read the following document
Patient's Name: Today's Date: / / The purpose of this document is to confirm, in the presence of witnesses, your informed request to have Surgery for obesity. You are asked to read the following document
What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms
 What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Interventions Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Radiology Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D.,
What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Interventions Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Radiology Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D.,
Saint Francis Kidney Transplant Program Issue Date: 6/9/15
 Kidney Transplant Candidate Informed Consent Education Here are educational materials about Kidney Transplant. Please review and read these before your evaluation visit. The RN Transplant Coordinator will
Kidney Transplant Candidate Informed Consent Education Here are educational materials about Kidney Transplant. Please review and read these before your evaluation visit. The RN Transplant Coordinator will
READ THIS LEAFLET VERY CAREFULLY, AND KEEP IT IN A SAFE PLACE. FLU IS SPREADING IN IRELAND, AND THIS INFORMATION IS IMPORTANT FOR YOU AND YOUR FAMILY.
 READ THIS LEAFLET VERY CAREFULLY, AND KEEP IT IN A SAFE PLACE. FLU IS SPREADING IN IRELAND, AND THIS INFORMATION IS IMPORTANT FOR YOU AND YOUR FAMILY. Information and medical advice for the public on Pandemic
READ THIS LEAFLET VERY CAREFULLY, AND KEEP IT IN A SAFE PLACE. FLU IS SPREADING IN IRELAND, AND THIS INFORMATION IS IMPORTANT FOR YOU AND YOUR FAMILY. Information and medical advice for the public on Pandemic
QUESTIONS TO ASK MY DOCTOR
 Be a part of the treatment decision by asking questions QUESTIONS TO ASK MY DOCTOR FOR PATIENTS WITH ADVANCED STOMACH OR GASTROESOPHAGEAL JUNCTION (GEJ) CANCER CYRAMZA (ramucirumab) is used alone or in
Be a part of the treatment decision by asking questions QUESTIONS TO ASK MY DOCTOR FOR PATIENTS WITH ADVANCED STOMACH OR GASTROESOPHAGEAL JUNCTION (GEJ) CANCER CYRAMZA (ramucirumab) is used alone or in
INTRAPERITONEAL HYPERTHERMIC CHEMOTHERAPY (IPHC) FOR PERITONEAL CARCINOMATOSIS AND MALIGNANT ASCITES. INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILY MEMBERS
 INTRAPERITONEAL HYPERTHERMIC CHEMOTHERAPY (IPHC) FOR PERITONEAL CARCINOMATOSIS AND MALIGNANT ASCITES. INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILY MEMBERS Description of Treatment A major difficulty in treating
INTRAPERITONEAL HYPERTHERMIC CHEMOTHERAPY (IPHC) FOR PERITONEAL CARCINOMATOSIS AND MALIGNANT ASCITES. INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILY MEMBERS Description of Treatment A major difficulty in treating
THE AYURVEDIC CENTER OF VERMONT, LLC Health Information and History
 THE AYURVEDIC CENTER OF VERMONT, LLC Health Information and History Name DOB Date Age Occupation Email Address Home address City State Zip Home phone Cell Phone Referred By Physician Physician Phone Please
THE AYURVEDIC CENTER OF VERMONT, LLC Health Information and History Name DOB Date Age Occupation Email Address Home address City State Zip Home phone Cell Phone Referred By Physician Physician Phone Please
INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia deep vein thrombosis DVT pulmonary embolism PE inherited thrombophilia
 INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia (Hypercoagulability) is a condition in which a person forms blood clots more than normal. Blood clots may occur in the arms or legs (e.g., deep vein thrombosis DVT), the lungs
INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia (Hypercoagulability) is a condition in which a person forms blood clots more than normal. Blood clots may occur in the arms or legs (e.g., deep vein thrombosis DVT), the lungs
ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA (AML),
 1 ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA (AML), ALSO KNOWN AS ACUTE MYELOGENOUS LEUKEMIA WHAT IS CANCER? The body is made up of hundreds of millions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide, and die in an orderly
1 ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA (AML), ALSO KNOWN AS ACUTE MYELOGENOUS LEUKEMIA WHAT IS CANCER? The body is made up of hundreds of millions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide, and die in an orderly
Human Normal Immunoglobulin Solution for Intravenous Infusion.
 CONSUMER MEDICINE INFORMATION (CMI) OCTAGAM Human Normal Immunoglobulin Solution for Intravenous Infusion. OCTAGAM is available in single use bottles of 20 ml, 50 ml, 100 ml and 200 ml. OCTAGAM contains
CONSUMER MEDICINE INFORMATION (CMI) OCTAGAM Human Normal Immunoglobulin Solution for Intravenous Infusion. OCTAGAM is available in single use bottles of 20 ml, 50 ml, 100 ml and 200 ml. OCTAGAM contains
2. What Should Advocates Know About Diabetes? O
 2. What Should Advocates Know About Diabetes? O ften a school district s failure to properly address the needs of a student with diabetes is due not to bad faith, but to ignorance or a lack of accurate
2. What Should Advocates Know About Diabetes? O ften a school district s failure to properly address the needs of a student with diabetes is due not to bad faith, but to ignorance or a lack of accurate
For the Patient: Dasatinib Other names: SPRYCEL
 For the Patient: Dasatinib Other names: SPRYCEL Dasatinib (da sa' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have ever
For the Patient: Dasatinib Other names: SPRYCEL Dasatinib (da sa' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have ever
Recognizing and Treating Fevers in Children with Complex Medical Issues by Susan Agrawal
 www.complexchild.com Recognizing and Treating Fevers in Children with Complex Medical Issues by Susan Agrawal Fevers can be some of the scariest symptoms we see in our children, but they are also some
www.complexchild.com Recognizing and Treating Fevers in Children with Complex Medical Issues by Susan Agrawal Fevers can be some of the scariest symptoms we see in our children, but they are also some
Leader's Resource. Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms.
 Leader's Resource Information on Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Signs and Symptoms of STDs Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms. Any of the following can indicate to
Leader's Resource Information on Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Signs and Symptoms of STDs Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms. Any of the following can indicate to
- 301-17. SICKLE CELL SCREENING AND SELECT TOPICS IN PREVENTION OF COMPLICATIONS Mark Schuster, M.D., Ph.D.
 - 301-17. SICKLE CELL SCREENING AND SELECT TOPICS IN PREVENTION OF COMPLICATIONS Mark Schuster, M.D., Ph.D. We used the following sources to construct indicators for sickle cell disease screening for newborns
- 301-17. SICKLE CELL SCREENING AND SELECT TOPICS IN PREVENTION OF COMPLICATIONS Mark Schuster, M.D., Ph.D. We used the following sources to construct indicators for sickle cell disease screening for newborns
Dizziness and Vertigo
 Dizziness and Vertigo Introduction When you are dizzy, you may feel lightheaded or lose your balance. If you also feel that the room is spinning, you may have vertigo. Vertigo is a type of severe dizziness.
Dizziness and Vertigo Introduction When you are dizzy, you may feel lightheaded or lose your balance. If you also feel that the room is spinning, you may have vertigo. Vertigo is a type of severe dizziness.
