CT Scans 101: Be an Informed Consumer
|
|
|
- Warren Hudson
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CT Scans 101: Be an Informed Consumer Introduction CT (computerized tomography) scans, also sometimes called CAT scans, combine X-rays and computers to produce remarkably clear images of many parts of the body. Sometimes compared to slicing a loaf of bread (but with no knife, of course!), the CT scanner can peek inside your head, neck, chest, abdomen, arms or legs in search of injury or disease. CT scans provide much finer detail than regular X-rays, evaluating organs that can t even be seen with X-rays. And because the scanning process is so quick, CT is especially useful for patients who have been injured, such as in traffic accidents or falls. When there are complex bone injuries, such as hip fractures for example, the CT images can be combined into a lifelike three-dimensional view to provide the surgeon with a virtual roadmap for making repairs. But CT s contributions aren t limited to patients who ve been injured. It also is a primary tool for finding tumors nearly everywhere in the body. After it reveals the tumor, repeat CT scans are used for evaluating whether the tumor is responding to therapy. Exciting new uses are being found for CT scanning, such as checking arteries (including the ones in the heart) for blockage. What CT scans can show CT isn t perfect. It doesn t find every disease in every patient. But it can detect many different types of illness and injury including: Tumors Infections Internal bleeding in the brain or body Bone fractures and dislocations Kidney stones Blocked arteries and veins Congenital heart diseases MRI vs. PET/CT MRI Instead of using X-rays to create images of the body, MRI uses magnets and radio waves. CT vs. MRI Sometimes, either CT or MRI would be an option for a patient s particular situation. In other cases, one examination would be preferred over the other. Searching for brain tumors, for example, is better handled with MRI, while checking for blood clots in the lung is a job for CT. Your doctor and the imaging specialist reading your scan can tailor the examination to find the best answer for you. MRI scans take longer to do, sometimes require long periods without moving, and can be a problem for very sick or young patients or those with a fear of small, tight places. CT can provide a rapid alternative if MRI scanning isn t possible.
2 PET/CT PET stands for positron emission tomography. This test can show how tissues and organs in the body are working, rather than just how they look. A tiny dose of radioactive material called a tracer is injected into an arm vein and is taken up by organs throughout the body. The tracer gives off a low dose of radiation that can be detected by a scanner surrounding the patient. Body tissues that are using a lot of energy, such as tumors, take up more of the tracer, and the scanner detects that abnormal activity. Sometimes this can be referred to as a hot spot. Images from a CT scan performed at the same time then are combined with the PET scan to form a 3-D view that shows exactly where in the body the abnormality is. How is a PET/CT different from a CT or MRI scan? CT and MRI scans are great for showing normal and abnormal anatomy but can t always tell whether something is benign or malignant just an old scar or a living tumor, for example. Often, PET/CT can help to answer that question. In patients being treated for a known cancer, PET/CT can be a great way to see if the therapy is working and to search for any spread of the tumor. Radiation exposure: Risky or not? Radiation exposure should be a concern for everyone, and it certainly is for us at UK HealthCare. We want our patients to receive the lowest possible radiation dose in all of our testing. But some questions remain: Can this radiation be harmful? Might it cause cancer years from now? How much radiation is too much? Any radiation is too much if you really don t need the test. When your doctor prescribes an examination involving radiation, it s perfectly acceptable to express your concern about radiation, to ask what they hope to learn from the test, and to ask whether other non-radiation tests could be used instead. While the radiation risk from a single scan is quite small, the radiation dose from multiple X-ray tests over a lifetime can be significant. Patients with chronic illnesses such as cancer or Crohn s disease are the ones most likely to have multiple scans. But every patient should take common-sense steps to protect themselves from excess radiation: Keep a record of any test that involves radiation. If you re unsure whether the test uses radiation, ask the person who is performing it. Carry the record with you. Keep and update a wallet-size card listing the imaging tests that you ve had and where and when each was done. Many patients now keep the record electronically. If and when your doctor advises you to have a test that uses radiation, express your concern and ask a lot of questions. In particular, ask whether a test that doesn t use radiation could provide the same information. Be aware of dosages. After your CT scan, ask the person who performed it what dose of radiation you received. Include that information in your radiation record. Safety first! UK HealthCare employs a radiation safety officer (RSO) who ensures that all activities involving radioactive materials and all tests using equipment that produce radiation are performed in accordance with approved policies and regulatory requirements. Frequent testing is done to ensure that the equipment and procedures are up to standards. The radiation safety officer is authorized to prohibit use of any equipment that does not meet safety and quality guidelines as defined by UK HealthCare policies and federal and state regulations. You are more likely to die being struck by a car, drowning, or by radon in your home than from cancer caused by the radiation of a CT scan. Scott D. Stevens, MD, Chief, Abdominal Imaging, UK Radiology
3 Radiation exposure comparison Humans have always lived in a radioactive world we are exposed to natural sources of radiation constantly. Soil, rocks, building materials, air, water and cosmic radiation emit small amounts of background radiation all the time. If you think of the very low dose of radiation from a standard chest X-ray as equaling 1, then background radiation would equal about 30. Just living in the United States gives you as much radiation in a year as 30 chest X-rays. So how does CT imaging compare to background radiation? The table on the right presents the average relative radiation dose-per-person for a variety of sources both medical and non-medical. * Will you get the lowest possible dose? Companies that manufacture CT equipment know that you and your doctor want the best-quality scan with the lowest radiation dose. To achieve that goal here at UK HealthCare, we use a dose-reduction system. During your CT scan, a computer in the CT scanner will analyze each body section to make sure that it gets only enough radiation to get a clear view. For example, it takes a lot less radiation to see through your lungs than to look inside your liver, and so our system adjusts the radiation dose during your scan to make sure that s what happens. We re especially proud of how our system can reduce radiation exposure for our pediatric patients. Source Average background 30 Chest X-ray 1 Head CT 20 Chest CT 70 Abdomen/Pelvis CT 150 Radon gas in the home Coast-to-coast flight 3 to 5 Watching TV Living in a stone or brick building Smoke detector Relative Radiation Dose (chest X-ray dose=1)) 20 per year 0.15 per year 0.07 per year per year * The doses are typical values for an average-size adult. The actual dose can vary significantly, depending on the patient s size and other variables. Is iodinated contrast (X-ray dye) safe? Iodinated contrasts are particularly safe medications that have been used for many years with few serious side effects. Because iodinated contrast can increase the diagnostic usefulness of a CT scan, its benefits are considered to outweigh the low risk. The most common effect of iodinated contrast is a warm or flushed feeling during the actual injection, sometimes with a metallic taste, that typically lasts for less than a minute. This sensation is expected and needs no treatment. Another mild reaction is itching or hives over various parts of the body that can last from minutes to hours. Medications are available to help relieve the itch. Very rarely, more significant side effects such as low blood pressure or difficulty breathing can occur shortly after contrast injection. Radiology department personnel will observe you during and for a short time after your scan to be certain that you ve had no problem. Even more rarely, delayed side effects, particularly rashes, can appear several hours after your scan. If you experience anything unusual, call your doctor or visit a hospital emergency department and mention that you ve recently received intravenous contrast for a CT scan. It is important for patients to notify their physician and CT technologist if they have had prior contrast reactions. On the rare occasions, when patients experience delayed side effects, they should phone their physician or visit an emergency care provider.
4 CT is particularly useful... When a very detailed image of bone or blood vessels is needed. In emergency situations, when scanning has to be quick. When a patient would have difficulty lying still. In patients with pacemakers or certain metallic implants. During some image-guided procedures, such as needle biopsies. Preparation Typically, your doctor will order a CT scan to evaluate a particular problem, and the imaging physician will then tailor the scan to answer the specific question. If the problem could be better evaluated with a different test, the imaging specialist might call your doctor to discuss other options. Before your scan begins, you ll be asked to provide information about your medical history and any previous experience with X-ray contrast ( dye ). Preparation for a CT scan depends upon which part of the body is being scanned. You might be asked to remove clothing and wear a hospital gown. Metal objects, such as jewelry, should be removed so as to not interfere with the image results. Additionally, certain dietary restrictions might be necessary, such as no food or drink for a certain period of time before the examination. Be certain your doctor is aware of all current medications you are taking before you undergo a scan. Certain medications may need to be stopped and others may be given prior to scanning. Contrast material Patients having a CT scan often are asked to drink a flavored liquid, or to receive an intravenous injection into their arm. These contrast materials ( X-ray dye ) highlight abnormalities on the CT scan so that they are more apparent. In some cases, a CT scan can still provide valuable information without the administration of a contrast agent. Contrast material can be introduced into the body in different ways: By mouth Fruit-flavored liquid contrast is very safe, and passes through the intestinal tract like regular food or drink. Side effects are uncommon. Temporary diarrhea occurs occasionally, and very rarely patients can be allergic to the iodine or flavoring in the drink. Intravenous injection Some patients describe a warm flushed sensation or a metallic taste as the contrast is being injected. These sensations typically last only a few moments and are not dangerous. Rectal Contrast material occasionally is administered into the rectum to evaluate colon and rectal abnormalities. Patients often experience a full sensation and more rarely cramping. A restroom is available nearby so the contrast can be eliminated promptly at the end of the examination. Skill of the CT technologists CT technologists have had specific training in performing these scans, and their education includes anatomy and physiology, radiation physics and safety training. In order to become certified, they must pass an examination that tests their knowledge and skill. At UK HealthCare, our CT technologists are accredited by the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists, ensuring expertise and professionalism in their area of care. During the scan: What to expect A CT scan is painless, but does require lying still and sometimes short periods of breath-holding. Patients with claustrophobia or difficulty remaining still may benefit from a mild sedative given before the scan. Women should always inform their physician and CT technologist if there is any possibility that they could be or are pregnant. CT scanning is, in general, not recommended for pregnant women, unless specifically necessary, because of potential risk to the fetus. Nursing mothers should follow their doctor s advice on how long to wait after contrast material injection before resuming breast-feeding.
5 The scanner is shaped like a large doughnut with a table running through it. After you lie down, the table will move to the correct position for scanning the specific body part. Expect occasional clicking and buzzing sounds as the machine revolves during the actual scanning process. Although patients typically are alone in the examination room during the scan, the radiology technologist will be able to see, hear and speak with you at all times, so that any discomfort or problem can be attended to promptly. At the conclusion of the scan, the technologist will check the images to be certain that they are adequate. Afterward, you can go on about your day as usual. If the scan included contrast material by mouth or intravenously, drinking plenty of fluids is recommended. You can return to your usual schedule of medications as soon as your scan is completed. After the scan Your CT scan will be interpreted by a doctor specially trained in reading advanced X-ray studies. At UK HealthCare, these imaging specialists typically have undergone additional training to become experts at reading specific types of scans, such as brain, chest, heart, abdomen and extremities.this makes them particularly well qualified to handle complex cases. CT Scans and Children Image Gently Image Gently is an educational and awareness campaign created by the Alliance for Radiation Safety in Pediatric Imaging. Its goal is to provide safe, high-quality pediatric imaging nationwide. The coalition represents more than 500,000 health care professionals in radiology, pediatrics, medical physics and radiation safety. The Image Gently campaign promotes optimal scanning strategies for children: Image only when there is a clear medical benefit. Use the lowest amount of radiation possible. Image only the indicated area. Avoid multiple scans. Use nonradiation studies (such as ultrasound or MRI) when possible. UK HealthCare is proud to apply the Image Gently principles to better serve our youngest patients, but UK HealthCare CT UK HealthCare houses eight CT scanners, performing well over 5,000 examinations each month. These versatile machines accommodate patients from newborns to 650 pound adults. Our CT resources include scanners that acquire 64 or 40 slices at once, CT fluoroscopy for guidance during biopsies, and a dual energy scanner with exciting prospects for kidney stones and heart disease. CT scan appointments are scheduled in 15-minute time slots. importantly, also applies this model to our adult patients as well. A special concern for pediatric CT scanning: How to keep the little ones still Just as in adult CT scans, having a patient who doesn t move is critical to obtaining the best quality scan for a child. Technologists use a variety of age-appropriate methods that help children hold still during a CT scan. Below is a list of the most common ways children are kept still: Sandbags: Long sandbags can keep a child s arms or legs still and correctly positioned and act as a reminder not to move. Velcro straps: Velcro bands not only immobilize the child s body, but also prevent them from falling off the table. The straps are attached to the table and are drawn snugly over the body. Swaddling: Infants and very young children might be wrapped tightly in a blanket. While some children are annoyed by the confinement, others are comforted by the security and even fall asleep. Holding techniques: At times, a child may be gently held by radiologic staff to keep a limb or body part in the correct position. If parents are asked to help hold their child, the staff will give you specific instructions so that safe radiation practices are observed.
6 What you can do to help Children may be upset or sense parental anxiety. Be sure to speak calmly and firmly to reassure your child. Praise him or her for being cooperative and helping the CT technologist. Feel free to ask if you can remain in the room during the test. If so, radiation safety equipment will be provided. Resources UK HealthCare Radiology UK HealthCare Radiology offers a full range of state-of-the-art diagnostic imaging services for patients. We conduct imaging of patients at multiple sites. Please visit ukhealthcare.uky.edu/services/radiology. htm for more information. Patient Appointments: Fax: American College of Radiology 1891 Preston White Drive Reston VA Phone: This health care professional membership group is dedicated to making imaging safe, effective and accessible to those who need it. American Society of Radiologic Technologists Central Ave. SE Albuquerque NM The mission of the American Society of Radiologic Technologists is to advance the medical imaging and radiation therapy profession and to enhance the quality of patient care. MedlinePlus (CT Scans) HealthFinder (CT Scan) healthfinder.gov/scripts/searchcontext. asp?topic=2686 National Cancer Institute (Computed Tomography: Questions and Answers) Detection/CT Related information: Advances & Insights: Can noninvasive CT scans replace conventional coronary angiography? ukhealthcare.uky.edu/ct-angiographs Advances & Insights: Studies examine radiation exposure, long-term cancer risks of CT scans ukhealthcare.uky.edu/ct-risks Call UK Health Connection at or toll free to make an appointment or request a referral. Visit us online at ukhealthcare.uky.edu.
X-Rays Benefits and Risks. Techniques that use x-rays
 X-Rays Benefits and Risks X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation, just like light waves and radiowaves. Because X-rays have higher energy than light waves, they can pass through the body. X-rays
X-Rays Benefits and Risks X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation, just like light waves and radiowaves. Because X-rays have higher energy than light waves, they can pass through the body. X-rays
Procedures/risks: Radiology (CT, DXA, MRI, ultrasound, X-ray)
 Procedures/risks: Radiology (CT, DXA, MRI, ultrasound, X-ray) Computerized Axial Tomography (CT): Procedure: A Computerized Axial Tomography (CT) scan [of your heart] involves holding your breath for a
Procedures/risks: Radiology (CT, DXA, MRI, ultrasound, X-ray) Computerized Axial Tomography (CT): Procedure: A Computerized Axial Tomography (CT) scan [of your heart] involves holding your breath for a
Children's (Pediatric) CT (Computed Tomography)
 Scan for mobile link. Children's (Pediatric) CT (Computed Tomography) Pediatric computed tomography (CT) is a fast, painless exam that uses special x-ray equipment to create detailed images of your child
Scan for mobile link. Children's (Pediatric) CT (Computed Tomography) Pediatric computed tomography (CT) is a fast, painless exam that uses special x-ray equipment to create detailed images of your child
Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients
 Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients A physician s written order is required for any PET-CT tests. How should I prepare for my PET-CT? PET-CT is more complicated than most other tests you may be
Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients A physician s written order is required for any PET-CT tests. How should I prepare for my PET-CT? PET-CT is more complicated than most other tests you may be
How To Prepare For A Ct Scan
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Radiology Department Information for patients having a CT scan page 2 The radiology department has received a request for you to have a CT scan. This leaflet tells
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Radiology Department Information for patients having a CT scan page 2 The radiology department has received a request for you to have a CT scan. This leaflet tells
Computed Tomography (CT) - Sinuses
 Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Sinuses Computed tomography (CT) of the sinuses uses special x-ray equipment to evaluate the paranasal sinus cavities hollow, air-filled spaces within the
Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Sinuses Computed tomography (CT) of the sinuses uses special x-ray equipment to evaluate the paranasal sinus cavities hollow, air-filled spaces within the
Computed Tomography (CT) - Chest
 Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Chest Computed tomography (CT) of the chest uses special x-ray equipment to examine abnormalities found in other imaging tests and to help diagnose the
Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Chest Computed tomography (CT) of the chest uses special x-ray equipment to examine abnormalities found in other imaging tests and to help diagnose the
CT Scan UHN. Information for patients and families
 CT Scan UHN Information for patients and families Read this information to learn: what a CT scan is how to prepare for the scan what to expect who to contact if you have any questions Joint Department
CT Scan UHN Information for patients and families Read this information to learn: what a CT scan is how to prepare for the scan what to expect who to contact if you have any questions Joint Department
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Hysterosalpingography
 Scan for mobile link. Hysterosalpingography Hysterosalpingography uses a real-time form of x-ray called fluoroscopy to examine the uterus and fallopian tubes of a woman who is having difficulty becoming
Scan for mobile link. Hysterosalpingography Hysterosalpingography uses a real-time form of x-ray called fluoroscopy to examine the uterus and fallopian tubes of a woman who is having difficulty becoming
Computed Tomography (CT) - Spine
 Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Spine Computed tomography (CT) of the spine is a diagnostic imaging test used to help diagnose or rule out spinal column damage in injured patients. CT
Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Spine Computed tomography (CT) of the spine is a diagnostic imaging test used to help diagnose or rule out spinal column damage in injured patients. CT
An abdominal ultrasound produces a picture of the organs and other structures in the upper abdomen.
 Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Abdomen Ultrasound imaging of the abdomen uses sound waves to produce pictures of the structures within the upper abdomen. It is used to help diagnose pain or distention
Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Abdomen Ultrasound imaging of the abdomen uses sound waves to produce pictures of the structures within the upper abdomen. It is used to help diagnose pain or distention
Society of Nuclear Medicine 1850 Samuel Morse Drive Reston, VA 20190-5316 www.snm.org
 What is nuclear medicine? Nuclear medicine is a medical specialty that is used to diagnose and treat diseases in a safe and painless way. Nuclear medicine procedures permit the determination of medical
What is nuclear medicine? Nuclear medicine is a medical specialty that is used to diagnose and treat diseases in a safe and painless way. Nuclear medicine procedures permit the determination of medical
X-ray (Radiography) - Abdomen
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Abdomen Abdominal x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the abdominal cavity. It is used to evaluate the stomach,
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Abdomen Abdominal x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the abdominal cavity. It is used to evaluate the stomach,
X-ray (Radiography), Lower GI Tract
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography), Lower GI Tract What is Lower GI Tract X-ray Radiography (Barium Enema)? Lower gastrointestinal (GI) tract radiography, also called a lower GI or barium enema,
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography), Lower GI Tract What is Lower GI Tract X-ray Radiography (Barium Enema)? Lower gastrointestinal (GI) tract radiography, also called a lower GI or barium enema,
Nerve Blocks. What is a Nerve Block? What are some common uses of the procedure?
 Scan for mobile link. Nerve Blocks A nerve block is an injection to decrease inflammation or "turn off" a pain signal along a specific distribution of nerve. Imaging guidance may be used to place the needle
Scan for mobile link. Nerve Blocks A nerve block is an injection to decrease inflammation or "turn off" a pain signal along a specific distribution of nerve. Imaging guidance may be used to place the needle
THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR:
 central east regional cancer program in partnership with cancer care ontario THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR: Thoracic dap booklet March2012.indd 1 SCHEDULED TESTS YOUR
central east regional cancer program in partnership with cancer care ontario THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR: Thoracic dap booklet March2012.indd 1 SCHEDULED TESTS YOUR
CT Angiography (CTA) What is CT Angiography?
 Scan for mobile link. CT Angiography (CTA) Computed tomography angiography (CTA) uses an injection of iodine-rich contrast material and CT scanning to help diagnose and evaluate blood vessel disease or
Scan for mobile link. CT Angiography (CTA) Computed tomography angiography (CTA) uses an injection of iodine-rich contrast material and CT scanning to help diagnose and evaluate blood vessel disease or
Lymphoscintigraphy is a special type of nuclear medicine imaging that provides pictures called scintigrams of the lymphatic system.
 Scan for mobile link. Lymphoscintigraphy Lymphoscintigraphy helps evaluate your body s lymphatic system for disease using small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers that are typically injected
Scan for mobile link. Lymphoscintigraphy Lymphoscintigraphy helps evaluate your body s lymphatic system for disease using small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers that are typically injected
Computed Tomography (CT) - Body
 Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Body Computed tomography (CT) of the body uses special x-ray equipment to help detect a variety of diseases and conditions. CT scanning is fast, painless,
Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Body Computed tomography (CT) of the body uses special x-ray equipment to help detect a variety of diseases and conditions. CT scanning is fast, painless,
X-ray (Radiography) - Bone
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Bone Bone x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of any bone in the body. It is commonly used to diagnose fractured bones or
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Bone Bone x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of any bone in the body. It is commonly used to diagnose fractured bones or
First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year
 First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year General Radiology (X-ray) Fluoroscopy Ultrasound (Sonography) Nuclear Medicine P.E.T. imaging Computed Tomography (CT scan) Magnetic
First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year General Radiology (X-ray) Fluoroscopy Ultrasound (Sonography) Nuclear Medicine P.E.T. imaging Computed Tomography (CT scan) Magnetic
Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy
 Scan for mobile link. Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy Ureteral stenting and nephrostomy help restore urine flow through blocked ureters and return the kidney to normal function. Ureters are long, narrow
Scan for mobile link. Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy Ureteral stenting and nephrostomy help restore urine flow through blocked ureters and return the kidney to normal function. Ureters are long, narrow
Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT)
 Scan for mobile link. Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) uses linear accelerators to safely and painlessly deliver precise radiation doses to a tumor while
Scan for mobile link. Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) uses linear accelerators to safely and painlessly deliver precise radiation doses to a tumor while
Cardiac CT for Calcium Scoring
 Scan for mobile link. Cardiac CT for Calcium Scoring Cardiac computed tomography (CT) for Calcium Scoring uses special x-ray equipment to produce pictures of the coronary arteries to determine if they
Scan for mobile link. Cardiac CT for Calcium Scoring Cardiac computed tomography (CT) for Calcium Scoring uses special x-ray equipment to produce pictures of the coronary arteries to determine if they
What are contrast materials and how do they work? Contrast materials enter the body in one of three ways. They can be:
 Scan for mobile link. Contrast Materials What are contrast materials and how do they work? Contrast materials, also called contrast agents or contrast media, are used to improve pictures of the inside
Scan for mobile link. Contrast Materials What are contrast materials and how do they work? Contrast materials, also called contrast agents or contrast media, are used to improve pictures of the inside
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal
 Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
CT Colonography. What is CT Colonography?
 Scan for mobile link. CT Colonography Computed tomography (CT) colonography or virtual colonoscopy uses special x-ray equipment to examine the large intestine for cancer and growths called polyps. During
Scan for mobile link. CT Colonography Computed tomography (CT) colonography or virtual colonoscopy uses special x-ray equipment to examine the large intestine for cancer and growths called polyps. During
CT Scan Thorax and Upper Abdomen. Respiratory Unit Patient Information Leaflet
 CT Scan Thorax and Upper Abdomen Respiratory Unit Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet gives you general information about your CT (computerised tomography) scan. It does not replace the
CT Scan Thorax and Upper Abdomen Respiratory Unit Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet gives you general information about your CT (computerised tomography) scan. It does not replace the
Mesothelioma. 1995-2013, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com ocft0101 Last reviewed: 03/21/2013 1
 Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
X-ray (Radiography) - Chest
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray produces images of
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray produces images of
X-ray (Radiography), Chest
 X-ray (Radiography), Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray makes images of the heart, lungs, airways,
X-ray (Radiography), Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray makes images of the heart, lungs, airways,
CT scan. Useful information. Contents. This information is about CT scans. There are sections on
 CT scan Useful information Contents This information is about CT scans. There are sections on How a CT scanner works What happens Preparation for the scan Abdominal CT scans CT scans of the head CT scans
CT scan Useful information Contents This information is about CT scans. There are sections on How a CT scanner works What happens Preparation for the scan Abdominal CT scans CT scans of the head CT scans
Magnetic Resonance, Functional (fmri) - Brain
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance, Functional (fmri) - Brain Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fmri) measures the metabolic changes that occur within the brain. It may be used to examine the
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance, Functional (fmri) - Brain Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fmri) measures the metabolic changes that occur within the brain. It may be used to examine the
MRI of the Breast. What is MRI of the Breast?
 MRI of the Breast What is MRI of the Breast? Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a noninvasive, usually painless medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. MRI uses a powerful
MRI of the Breast What is MRI of the Breast? Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a noninvasive, usually painless medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. MRI uses a powerful
Radiation Exposure in X-ray and CT Examinations
 Patient Safety-Xray: Radiation Exposure in X-ray and CT Examinations What are x-rays and what do they do? X-rays are forms of radiant energy, like light or radio waves. Unlike light, x-rays can penetrate
Patient Safety-Xray: Radiation Exposure in X-ray and CT Examinations What are x-rays and what do they do? X-rays are forms of radiant energy, like light or radio waves. Unlike light, x-rays can penetrate
Percutaneous Abscess Drainage
 Scan for mobile link. Percutaneous Abscess Drainage An abscess is an infected fluid collection within the body. Percutaneous abscess drainage uses imaging guidance to place a thin needle through the skin
Scan for mobile link. Percutaneous Abscess Drainage An abscess is an infected fluid collection within the body. Percutaneous abscess drainage uses imaging guidance to place a thin needle through the skin
Proton Therapy. What is proton therapy and how is it used?
 Scan for mobile link. Proton Therapy Proton therapy delivers radiation to tumor tissue in a much more confined way than conventional photon therapy thus allowing the radiation oncologist to use a greater
Scan for mobile link. Proton Therapy Proton therapy delivers radiation to tumor tissue in a much more confined way than conventional photon therapy thus allowing the radiation oncologist to use a greater
University College Hospital. Contrast agent for radiotherapy CT (computed tomography) scans. Radiotherapy Department Patient information series
 University College Hospital Contrast agent for radiotherapy CT (computed tomography) scans Radiotherapy Department Patient information series 11 2 If you need a large print, audio or translated copy of
University College Hospital Contrast agent for radiotherapy CT (computed tomography) scans Radiotherapy Department Patient information series 11 2 If you need a large print, audio or translated copy of
Suspected pulmonary embolism (PE) in pregnant women
 Suspected pulmonary embolism (PE) in pregnant women What is a pulmonary embolus? A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in one of the deep veins of the leg. If the clot moves to the lung,
Suspected pulmonary embolism (PE) in pregnant women What is a pulmonary embolus? A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in one of the deep veins of the leg. If the clot moves to the lung,
What are some common uses of the procedure?
 Scan for mobile link. Cardiac Nuclear Medicine Cardiac nuclear medicine imaging evaluates the heart for coronary artery disease and cardiomyopathy. It also may be used to help determine whether the heart
Scan for mobile link. Cardiac Nuclear Medicine Cardiac nuclear medicine imaging evaluates the heart for coronary artery disease and cardiomyopathy. It also may be used to help determine whether the heart
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
This handout is for informational purposes only. Talk with your doctor or health care team if you have any questions about your care.
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu PET stands for Positron Emission Tomography. The scan looks at metabolic activity (cell activity) inside the body. Your doctor uses this information to help
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu PET stands for Positron Emission Tomography. The scan looks at metabolic activity (cell activity) inside the body. Your doctor uses this information to help
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Cardiac (Heart)
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Cardiac (Heart) Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Cardiac (Heart) Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures
Nuclear medicine. Answering your questions
 Nuclear medicine Answering your questions ANSTO s OPAL research reactor in Sydney What is nuclear medicine? This is a branch of medicine that uses radiation from radioactive tracers to provide information
Nuclear medicine Answering your questions ANSTO s OPAL research reactor in Sydney What is nuclear medicine? This is a branch of medicine that uses radiation from radioactive tracers to provide information
Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal
 Scan for mobile link. Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? In an inferior vena cava filter placement procedure, interventional radiologists
Scan for mobile link. Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? In an inferior vena cava filter placement procedure, interventional radiologists
Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine Bronchial-Artery Embolisation Information for patients
 Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine Bronchial-Artery Embolisation Information for patients This leaflet tells you about the bronchial-artery embolisation procedure. It explains what is involved and
Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine Bronchial-Artery Embolisation Information for patients This leaflet tells you about the bronchial-artery embolisation procedure. It explains what is involved and
Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography or MRCP uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to evaluate the liver,
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography or MRCP uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to evaluate the liver,
Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too.
 Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
INTENSITY MODULATED RADIATION THERAPY (IMRT) FOR PROSTATE CANCER PATIENTS
 INTENSITY MODULATED RADIATION THERAPY (IMRT) FOR PROSTATE CANCER PATIENTS HOW DOES RADIATION THERAPY WORK? Cancer is the unrestrained growth of abnormal cells within the body. Radiation therapy kills both
INTENSITY MODULATED RADIATION THERAPY (IMRT) FOR PROSTATE CANCER PATIENTS HOW DOES RADIATION THERAPY WORK? Cancer is the unrestrained growth of abnormal cells within the body. Radiation therapy kills both
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Shoulder
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Shoulder Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the shoulder uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Shoulder Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the shoulder uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures
Ultrasound - Vascular
 Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Vascular Vascular ultrasound uses sound waves to evaluate the body s circulatory system and help identify blockages and detect blood clots. A Doppler ultrasound study
Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Vascular Vascular ultrasound uses sound waves to evaluate the body s circulatory system and help identify blockages and detect blood clots. A Doppler ultrasound study
Mammography. What is Mammography?
 Scan for mobile link. Mammography Mammography is a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early before women experience symptoms when it is most treatable. Tell your
Scan for mobile link. Mammography Mammography is a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early before women experience symptoms when it is most treatable. Tell your
Having denervation of the renal arteries for treatment of high blood pressure
 Having denervation of the renal arteries for treatment of high blood pressure The aim of this information sheet is to help answer some of the questions you may have about having denervation of the renal
Having denervation of the renal arteries for treatment of high blood pressure The aim of this information sheet is to help answer some of the questions you may have about having denervation of the renal
RADIATION THERAPY FOR LYMPHOMA. Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY
 RADIATION THERAPY FOR Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY FACTS ABOUT The lymphatic system is a network of tiny vessels extending
RADIATION THERAPY FOR Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY FACTS ABOUT The lymphatic system is a network of tiny vessels extending
Colorectal Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Knee
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Knee Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the knee uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures of the
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Knee Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the knee uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures of the
Do I Have Epilepsy? Diagnosing Epilepsy and Seizures. Epilepsy & Seizures: Diagnosis
 Epilepsy & Seizures: Diagnosis Do I Have Epilepsy? Diagnosing Epilepsy and Seizures Artwork by Studio E participant Ashley N. (details on inside cover) About the Cover: Cover artwork was created by Ashley
Epilepsy & Seizures: Diagnosis Do I Have Epilepsy? Diagnosing Epilepsy and Seizures Artwork by Studio E participant Ashley N. (details on inside cover) About the Cover: Cover artwork was created by Ashley
Small cell lung cancer
 Small cell lung cancer Small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found within
Small cell lung cancer Small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found within
X-ray (Radiography), Upper GI Tract
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography), Upper GI Tract What is Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract Radiography? Upper gastrointestinal tract radiography, also called an upper GI, is an x-ray examination
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography), Upper GI Tract What is Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract Radiography? Upper gastrointestinal tract radiography, also called an upper GI, is an x-ray examination
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Spine
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Spine Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the spine uses radio waves, a magnetic field and a computer to produce detailed pictures of the spine
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Spine Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the spine uses radio waves, a magnetic field and a computer to produce detailed pictures of the spine
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Prostate
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Prostate Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the prostate uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Prostate Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the prostate uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures
University of Pennsylvania RESEARCH Subject Informed Consent Form AND RESEARCH SUBJECT HIPAA AUTHORIZATION
 University of Pennsylvania RESEARCH Subject Informed Consent Form AND RESEARCH SUBJECT HIPAA AUTHORIZATION Protocol Title: Evaluating the impact of cocaine use and HIV infection in arterial wall inflammation
University of Pennsylvania RESEARCH Subject Informed Consent Form AND RESEARCH SUBJECT HIPAA AUTHORIZATION Protocol Title: Evaluating the impact of cocaine use and HIV infection in arterial wall inflammation
Mesenteric Angiography
 Information for patients Mesenteric Angiography Sheffield Vascular Institute Northern General Hospital You have been given this leaflet because you need a procedure known as a Mesenteric Angiogram. This
Information for patients Mesenteric Angiography Sheffield Vascular Institute Northern General Hospital You have been given this leaflet because you need a procedure known as a Mesenteric Angiogram. This
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Musculoskeletal
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Musculoskeletal Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures of joints,
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Musculoskeletal Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures of joints,
How To Use An Ultrasound For Medical Research
 Scan for mobile link. General Ultrasound What is General Ultrasound Imaging? Ultrasound is safe and painless, and produces pictures of the inside of the body using sound waves. Ultrasound imaging, also
Scan for mobile link. General Ultrasound What is General Ultrasound Imaging? Ultrasound is safe and painless, and produces pictures of the inside of the body using sound waves. Ultrasound imaging, also
YOUR MRI EXAM: QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
 YOUR MRI EXAM: QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS What is MRI? MRI is short for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. MRI is an advanced technology that lets your doctor see internal organs, blood vessels, muscles, joints, tumors,
YOUR MRI EXAM: QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS What is MRI? MRI is short for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. MRI is an advanced technology that lets your doctor see internal organs, blood vessels, muscles, joints, tumors,
The degree of liver inflammation or damage (grade) Presence and extent of fatty liver or other metabolic liver diseases
 ilearning about your health Liver Biopsy www.cpmc.org/learning What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a specially trained doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist, or gastroenterologist)
ilearning about your health Liver Biopsy www.cpmc.org/learning What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a specially trained doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist, or gastroenterologist)
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Aortic Stenosis. What is heart valve disease? What is aortic stenosis?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
RADIOLOGY SERVICES. By Dr Lim Eng Kok 1
 INTRODUCTION RADIOLOGY SERVICES By Dr Lim Eng Kok 1 Radiology is the branch of medicine that deals with the use of ionising (e.g. x- rays and radio-isotopes) and non-ionising radiation (e.g. ultrasound
INTRODUCTION RADIOLOGY SERVICES By Dr Lim Eng Kok 1 Radiology is the branch of medicine that deals with the use of ionising (e.g. x- rays and radio-isotopes) and non-ionising radiation (e.g. ultrasound
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to cardiac catheterization. In the following pages, we will
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to cardiac catheterization. In the following pages, we will
CT Virtual Colonoscopy
 CT Virtual Colonoscopy Ladywell Building Radiology 2 0161 206 1233 All Rights Reserved 2015. Document for issue as handout. This information booklet tells you about virtual colonoscopy, which is a test
CT Virtual Colonoscopy Ladywell Building Radiology 2 0161 206 1233 All Rights Reserved 2015. Document for issue as handout. This information booklet tells you about virtual colonoscopy, which is a test
Stereotactic Breast Biopsy
 Scan for mobile link. Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Stereotactic breast biopsy uses mammography a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to help locate a breast lump or abnormality and
Scan for mobile link. Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Stereotactic breast biopsy uses mammography a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to help locate a breast lump or abnormality and
University College Hospital. Having a CT scan. Imaging Department
 University College Hospital Having a CT scan Imaging Department If you need a large print, audio, or a translated copy of this document, please contact us on: 020 345 67002 We will do our best to meet
University College Hospital Having a CT scan Imaging Department If you need a large print, audio, or a translated copy of this document, please contact us on: 020 345 67002 We will do our best to meet
General Nuclear Medicine
 Scan for mobile link. General Nuclear Medicine Nuclear medicine imaging uses small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers that are typically injected into the bloodstream, inhaled or swallowed.
Scan for mobile link. General Nuclear Medicine Nuclear medicine imaging uses small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers that are typically injected into the bloodstream, inhaled or swallowed.
Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment Cancer begins in our cells. Cells are the building blocks of our tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body.
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment Cancer begins in our cells. Cells are the building blocks of our tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body.
RADIATION THERAPY & CANCER
 CANCERCARE MANITOBA Mission Statement CancerCare Manitoba, by an act of the legislature, is responsible for cancer prevention, detection, care, research and education throughout Manitoba. RADIATION THERAPY
CANCERCARE MANITOBA Mission Statement CancerCare Manitoba, by an act of the legislature, is responsible for cancer prevention, detection, care, research and education throughout Manitoba. RADIATION THERAPY
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Radiology Tech
 From the: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics Radiology Tech What They Do Radiologic technologists (RTs) perform diagnostic imaging examinations, such as x rays, on patients. Duties RTs typically do the following:
From the: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics Radiology Tech What They Do Radiologic technologists (RTs) perform diagnostic imaging examinations, such as x rays, on patients. Duties RTs typically do the following:
Smoking and misuse of certain pain medicines can affect the risk of developing renal cell cancer.
 Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) of Liver Tumors
 Scan for mobile link. Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) of Liver Tumors Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a treatment that uses imaging guidance to place a needle electrode through the skin into a liver tumor.
Scan for mobile link. Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) of Liver Tumors Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a treatment that uses imaging guidance to place a needle electrode through the skin into a liver tumor.
Prostate Cancer Guide. A resource to help answer your questions about prostate cancer
 Prostate Cancer Guide A resource to help answer your questions about prostate cancer Thank you for downloading this guide to prostate cancer treatment. We know that all the information provided online
Prostate Cancer Guide A resource to help answer your questions about prostate cancer Thank you for downloading this guide to prostate cancer treatment. We know that all the information provided online
PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION
 PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION This booklet was designed to help you and the important people in your life understand the treatment of high dose chemotherapy with stem cell support: a procedure
PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION This booklet was designed to help you and the important people in your life understand the treatment of high dose chemotherapy with stem cell support: a procedure
Disease/Illness GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER. What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? www.simpsonmillar.co.uk Telephone 0844 858 3200
 GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
Video Fluoroscopic Swallowing Exam (VFSE)
 Scan for mobile link. Video Fluoroscopic Swallowing Exam (VFSE) A video fluoroscopic swallowing exam (VFSE) uses a form of real-time x-ray called fluoroscopy to evaluate a patient s ability to swallow
Scan for mobile link. Video Fluoroscopic Swallowing Exam (VFSE) A video fluoroscopic swallowing exam (VFSE) uses a form of real-time x-ray called fluoroscopy to evaluate a patient s ability to swallow
Understanding. Pancreatic Cancer
 Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Yttrium-90 Radiotherapy Treatment for liver tumors
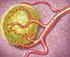 Patient Education Yttrium-90 Radiotherapy Treatment for liver tumors This handout explains what Yttrium-90 radiotherapy is and what to expect when you have it done. Why do I need this treatment? Your doctors
Patient Education Yttrium-90 Radiotherapy Treatment for liver tumors This handout explains what Yttrium-90 radiotherapy is and what to expect when you have it done. Why do I need this treatment? Your doctors
Imaging Technology. Diagnostic Medical Sonographer, Dosimetrist, Nuclear Medicine Technologist, Radiation Therapist, Radiologic Technologist
 Imaging Technology Diagnostic Medical Sonographer, Dosimetrist, Nuclear Medicine Technologist, Radiation Therapist, Radiologic Technologist Diagnostic Medical Sonographer, Dosimetrist Diagnostic Medical
Imaging Technology Diagnostic Medical Sonographer, Dosimetrist, Nuclear Medicine Technologist, Radiation Therapist, Radiologic Technologist Diagnostic Medical Sonographer, Dosimetrist Diagnostic Medical
ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND (EUS)
 ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND (EUS) What you need to know before your procedure Your Doctor has decided that an EUS is necessary for further evaluation and treatment of your condition. This information sheet has
ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND (EUS) What you need to know before your procedure Your Doctor has decided that an EUS is necessary for further evaluation and treatment of your condition. This information sheet has
How To Prepare For An Imaging Test
 Imaging (Radiology) Tests What are imaging tests? An imaging test is a way to let doctors see what s going on inside your body. These tests send forms of energy (x-rays, sound waves, radioactive particles,
Imaging (Radiology) Tests What are imaging tests? An imaging test is a way to let doctors see what s going on inside your body. These tests send forms of energy (x-rays, sound waves, radioactive particles,
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)? Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a valuable diagnostic study that has been used
Magnetic Resonance Imaging North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)? Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a valuable diagnostic study that has been used
National Emphysema Treatment Trial (NETT) Consent for Screening and Patient Registry
 National Emphysema Treatment Trial (NETT) Consent for Screening and Patient Registry Instructions: This consent statement is to be signed and dated by the patient in the presence of a certified study staff
National Emphysema Treatment Trial (NETT) Consent for Screening and Patient Registry Instructions: This consent statement is to be signed and dated by the patient in the presence of a certified study staff
Who can have an MRI scan?
 i MRI Scan Contents What is an MRI scan? 1 Why am I having an MRI scan? 1 Who can have an MRI scan? 1 What preparation will I need? 2 What happens when I come for the scan? 2 Who will I see when I have
i MRI Scan Contents What is an MRI scan? 1 Why am I having an MRI scan? 1 Who can have an MRI scan? 1 What preparation will I need? 2 What happens when I come for the scan? 2 Who will I see when I have
Elective Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
 General Surgery Elective Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy This information aims to explain what will happen before, during and after your surgery to remove your gallbladder. It includes information about the
General Surgery Elective Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy This information aims to explain what will happen before, during and after your surgery to remove your gallbladder. It includes information about the
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Breast Cancer. Sometimes cells keep dividing and growing without normal controls, causing an abnormal growth called a tumor.
 Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
RADIATION THERAPY AUCKLAND CITY HOSPITAL
 RADIATION THERAPY AUCKLAND CITY HOSPITAL What is Radiation Therapy? Radiation Therapy is the use of radiation to treat cancer and some non-malignant growths. A machine, called a linear accelerator, is
RADIATION THERAPY AUCKLAND CITY HOSPITAL What is Radiation Therapy? Radiation Therapy is the use of radiation to treat cancer and some non-malignant growths. A machine, called a linear accelerator, is
Thymus Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand what thymus cancer is and what treatment options are available.
 Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Catheter Embolization and YOU
 Catheter Embolization and YOU What is catheter embolization? Embolization therapy is a minimally invasive (non-surgical) treatment that occludes or blocks one or more blood vessels or vascular channels
Catheter Embolization and YOU What is catheter embolization? Embolization therapy is a minimally invasive (non-surgical) treatment that occludes or blocks one or more blood vessels or vascular channels
Patients who fail to bring a driver/someone to stay with them for the night will have their procedure cancelled immediately.
 Preparing for your Colonoscopy You must have someone and/or a driver accompany you and stay with you for 24 hours after your procedure. Patients who fail to bring a driver/someone to stay with them for
Preparing for your Colonoscopy You must have someone and/or a driver accompany you and stay with you for 24 hours after your procedure. Patients who fail to bring a driver/someone to stay with them for
Patient Prep Information
 Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
