Care of a normal newborn baby
|
|
|
- Claud Gallagher
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Care of a normal newborn baby Slide NC-l,2 The events during first few minutes and hours of life have an immense bearing on the immediate and long term outcome of the infant. The basic principles of care at birth are the same whether the baby is managed by a doctor or any other health professional and whether the baby is delivered at home or in the hospital. The aims of neonatal care at birth include the following: (i) Establishment of respiration (ii) Prevention of hypothermia (iii) Establishment of breastfeeding (iv) Prevention of infection (v) Identification of at risk neonates Slide NC-3 Care of the normal newborn can be divided in four sections. (i) Preparations before delivery (ii) Immediate care at birth. (iii) Care after birth (iv) Essential postnatal care Slide NC-4, 5, 6,7 In our country nearly eighty percent of births take place at home. It is necessary that at least the following minimum preparations are done before birth of a baby: Preparation for home delivery 1. Select a clean part of the home for delivery. It must be a well lighted and ventilated area. 2. Keep enough linen which has been washed and sun-dried for use at 1
2 the time of delivery of the baby. Ensure that clean and boiled water is readily available before/during delivery. 3. Ensure that a DDK (disposable delivery kit) is available (with the family) for use at the time of delivery. If not, ensure that a new boiled blade is available for cutting the cord at birth. 4. Ensure that a clean sheet is spread on the floor, the room is kept warm and free of draught. 5. Ensure that a trained health personnel is contacted before delivery so that the birth is attended by a trained personnel. 6. Provide the mother with information as to when she must seek medical help during her pregnancy. 7. Follow the 'five cleans' which must be followed to prevent infection in the newborn - Clean hands, clean cord tie, clean cord, clean surface and clean blade. Preparation for institutional delivery Each delivery room must have a well-lighted, well-ventilated and warm microenvironment without droughts to receive the newly born baby. This baby care area meant for the baby in the delivery room should have (a) Warming device which may be either an overhead radiant warmer or electric heater or bakery heating lamp or simple 100 or 200 watt electric bulb kept about 18 to 20 inches (50 cm) above the baby. Preferably a room thermometer and wall clock with seconds hand may be fitted in the same corner. (b) Clean sterile linen (preferably autoclaved) in the form of towels, bed sheets, baby caps, blankets etc should be available. At least two towels should be provided for each baby, one for drying and one for wrapping. (c) Cord clamps, cord cutting instruments, cord tying material, cotton swabs, gauze pieces. (d) Oxygen supply, suction device, resuscitation equipments including extra bulbs and cells for the laryngoscope, tape, scissors etc. must be checked well in advance and arranged in such a fashion that they are easily available, ready to use during emergency situations. (e) Weighing scales, measuring tapes, identification tags, clinical 2
3 (f) thermometers (if available, rectal and low reading one). A tray of medication may include spirit for cord dressing, distilled water / normal saline for cleaning eyes, silver nitrate, tetracycline or erythromycin ointment, Vit. K ampoules and medication needed during resuscitation i.e. epinephrine, 7.5% sodium bicarbonate, injection syringes 2cc, 5cc and insulin syringes for small dosages. Slide NC - 8, 9, 10 Immediate care at birth The umbilical cord should be clamped as soon as the infant is completely delivered. There should be no undue delay or unnecessary anxiety or hurry to clamp the cord. Early and immediate clamping of the cord is indicated in babies with severe birth asphyxia, cord around the neck and rhesus isoimmunization. To determine whether the baby requires resuscitation or not, five questions regarding the state of the baby need to be asked. These questions are 1. Is the baby clear of meconium? 2. Is the baby breathing or crying? 3. Is there good muscle tone? 4. Is the baby pink? 5. Is the baby born at term? If the answers to all these questions are in the affirmative then the baby requires only routine care. Over 90 per cent of the newborn babies are vigorous term babies with no risk factors and clear amniotic fluid. They do not require any active resuscitation and hence they do not need to be separated from their mothers. These babies are provided initial steps in a modified manner by putting the baby over the mother s chest and wiping the baby dry. Now the baby and the mother are in close skin to skin contact and the duo should be covered by dry warm linen. The airway can be cleared by wiping the baby s nose and mouth if needed. Ongoing assessment of the breathing, colour and activity must be continued even as the baby is with the mother to determine need for additional interventions. 3
4 Supportive care is provided to those babies who have prenatal or intrapartum risk factors, meconium staining of the skin, cord or amniotic fluid, depressed breathing or activity, and/or cyanosis. These babies should be evaluated and managed under a warmer and should receive the initial steps as appropriate. The baby should be placed flat with 1/2 inch to 3/4 of an inch towel roll under the shoulders to maintain slight extension of the neck for ensuring open airways. The mouth should be suctioned first followed by suctioning of the nose using a 10 Fr catheter. The suction force should be gentle and intermittent with a maximum suction pressure of 100 mm of Hg (130 cm of water). Suctioning should not be for more than 2-3 seconds at a time. The baby should be dried from top to bottom and the wet linen should be discarded. Reposition the baby supine using the shoulder roll and assess for breathing/crying. If the baby is not breathing stimulate the baby by two firm flicks on the sole or two firm rubs on the back. These steps usually take around 20 to 30 seconds and by this time most babies are vigorously crying, moving actively and are pink. Centrally cyanosed baby should be provided free flow oxygen for 30 seconds. Prolonged stimulation or use of violent maneuvers like pouring cold water on the baby's face and slapping the back are not only dangerous, but useless resulting in delay in the resuscitation of the baby. All those babies who do not start breathing after the initial steps need further resuscitation using positive pressure ventilation and/or chest compression along with/without medications and these need to be transferred into the neonatal unit for Ongoing care; For neonatal resuscitation refer to module on Neonatal Advanced Life Support, AAP / AHA recommendations. Slide NC -11, 12, 13 Care after birth After having ensured that the baby has established effective breathing, it is essential that all efforts are made to prevent the occurrence of hypothermia. The baby should be resuscitated under a radiant warmer or any heat source and should be adequately covered thereafter. A sterile disposable delivery kit should be used for each baby to prevent cross infection. The eyes should be cleaned with sterile normal saline using one 4
5 swab for each eye. When prophlyaxis against gonococcal ophthalmia is required, it can be ensured either by instillation of 1.0 per cent silver nitrate drops or 0.5 per cent tetracycline or erythromycin ophthalmic ointment. The umbilical cord should be tied using two sterile ligatures or rubber band or a disposable clamp. The clamp or ligature should be applied at least 2 to 3 cm beyond the base of the cord to avoid inadvertent incision of gut contained in minor exomphalos. Do not apply anything on the cord. Vitamin K 1.0 mg is administered intramuscularly to all babies weighing more than 1000 gms, and 0.5 mg to babies weighing less than 1,000 gms at birth. Quick but thorough clinical screening is essential to identify any life threatening congenital anomalies and birth injuries. The cut end of the umbilical cord should be inspected for the number of vessels. Normally there are two umbilical arteries and one umbilical vein. The presence of a single umbilical artery is associated with internal congenital malformations in 15 to 20 per cent of cases. The commonly associated malformations include oesophageal atresia, imperforate anus and genito-urinary anomalies. Single palmar crease (Simian crease) has increased association with additional anomalies including Down Syndrome. The face and head should be closely observed for any asymmetry and dysmorphic features. While crying, if the angle of the mouth and the mandible are pulled down and the infant has asymmetric crying, it is indicative of hypoplasia of the depressor angularis oris muscle. This is a useful marker of associated cardiovascular anomalies and congenital dislocation of hips. The infant should be examined for location and patency of all the orifices because anomalies are frequently encountered around the orifices. The oral cavity must be examined to exclude cleft palate. The patency of the oesophagus should be checked by passing a stiff rubber catheter into the stomach in the following situations: (i) Small-for-dates baby (ii) Single umbilical artery (iii) Polyhydramnios (iv) Excessive drooling of saliva If there is no oesophageal atresia and the catheter has reached the 5
6 stomach, gastric contents should be aspirated. If gastric aspirate exceeds 20 ml in volume, it is strongly suggestive of high intestinal obstruction due to pyloric or duodenal atresia. The anomalies are concentrated over the mid-line areas in the front and back e.g. spina bifida, meningomyelocele, pilonidal sinus, ambiguous genitalia, hypospadias, exomphalos, cleft lip and cleft palate etc. The abdomen should palpated for any masses and heart examined for its position and any murmurs. Displacement of the heart towards the right side in association with respiratory difficulty and resuscitation problems is suggestive of either diaphragmatic hernia or pneumothorax on the left side. Slide NC-14 Essential postnatal care (1) Nurse the baby in thermo-neutral environment. The baby should be warm to touch and soles should be pink. (2) Check the umbilical stump It should be clean and dry The tie should be tight There should be no bleeding (3) Check the skin specially at the creases i.e. neck, groin and axilla for any pyoderma. (4) Check that the baby has good sucking. If sucking is poor, ensure correct positioning and attachment to breast. (5) Check that the baby is crying well and, has no breathing difficulty. If baby has breathing difficulty or any other danger signals refer to appropriate healthcare facility. (6) Advise the mother regarding the immunization schedule. Maintenance of body temperature Newborn babies are homeothermic but their thermoregulatory mechanisms are physiologically unsatisfactory. They are prone to develop hypothermia unless adequate precautions are taken to protect them. For details of temperature regulation refer to topic on hypothermia in newborn. 6
7 Slide NC -15 Care of the umbilical stump The umbilical cord is an important portal of entry for Clostridium tetani in domicilliary midwifery. Health personnel must be told the importance of using a sterile disposable dai-kit to prevent the occurrence of tetanus neonatorum. Cord should be cut with a sterilized blade or a new boiled stainless steel blade. Umbilical stump must be inspected after 2 to 4 hours of ligation. Bleeding may occur at this time due to shrinkage of cord and loosening of the ligature. The use of a rubber band or disposable clamp safeguard against this hazard. Nothing should be applied on the cord. The cord must be left open without any dressing. It usually falls after 5 to 10 days but may take longer if it has been kept moist or if it gets infected and in immunocompromised babies. The stump should be inspected for any discharge or infection and kept clean and dry till complete healing takes place. Slide NC -16 Skin care Clean the baby off blood, mucus and meconium before presenting to the mother. Bathing of babies soon after birth is not recommended. Postpone bathing preferably for 24 hours and ensure that baby's temperature is normal before giving bath. For details of baby bath, refer to topic on hypothermia in newborn. It is preferable to perform the ritual of bathing and nursing toilet of each baby by the cot-side. This would provide a unique opportunity for imparting health education and seeking active participation of the mother. Special attention should be paid to cleaning of the scalp, skin creases (neck, axillae, groins) and the diaper area. Vigorous attempts should not be made to scrub off the vernix caseosa which provides a protective covering to the delicate skin of the baby. During the procedure of bathing or sponging, the nurse should specifically look for any superficial infections like pyoderma, umbilical sepsis, conjunctivitis or oral thrush, etc. and bring them to the notice of the physician. Hand washing, barrier nursing, as also 7
8 storing separately the various articles for baby use in individual lockers, is desirable to prevent nosocomial infections. Slide NC -17 Care of the eyes The eyes should be cleaned at birth and once every day using sterile cotton swabs soaked in sterile water or normal saline. Each eye should be cleaned using a separate swab. The cultural practice of instillation of human colostrum in the eyes has been found to be useful in reducing the incidence of sticky eyes. The practice of applying kajal in the eyes is not recommended because it may cause trauma, transmit infections like trachoma or may even cause lead poisoning. Tetracycline 1% or erythromycin 0.5% ointment is recommended for prophylaxis of gonococcal opthalmia. If the eyes are sticky they can either be managed by frequent cleaning using sterile cotton swabs soaked in normal saline or by instillation of 10% sulphacetamide eye drops every two to four hours. Some neonates may develop persistent epiphora due to blockage of nasolacrimal duct by epithelial debris. The mother should be advised to massage the nasolacrimal duct area (by massaging the outer side of the nose adjacent to the medial canthus) 5 to 8 times a day, each time before she feeds the baby. Slide NC -18 Summary: Home care 1. Keep the umbilical stump clean and dry Do not apply anything on the cord stump 2. Protect the baby from cold\heat by wrapping\clothing according to the climate. If baby is cold to touch, rewarm by skin-to-skin contact and thereafter dress in appropriate clothing including cap and stockings If baby is too warm, undress the baby 3. Exclusively breastfeed the baby till 6 months frequently day and night. (Do not give the baby any other food, including water, give only breast milk). Feed the baby on demand day and night 4. Do not apply anything in the eyes 8
9 Slide NC -19 Weight change pattern in term baby Most healthy term babies lose weight during the first 2 to 3 days of life. The weight loss is usually upto 5 to 7 per cent of birth weight. The weight remains stationary during next one to two days and birth weight is regained by the end of first week. There is no need to monitor early weight changes in a healthy newborn baby because it can cause unnecessary anxiety to the mother and may lead to lactation failure. Babies who are adequately fed, are contented, playful, have good sleep and are satisfied for atleast two to three hours after a feed. An adequately fed baby passes urine at least 5 to 6 times in a day while babies pass urine (even stools) after each feed during the first 3 months of life. The average daily weight gain in term babies is around 30 g, 20g and 10g during the first, second and third, 4-month periods respectively during the first year of life. Normally a baby gains about 800 gms per month during the first 3 months. Slide NC -20 Early identification of disease (Danger signs) Most mothers observe their babies carefully and are often concerned about minor physical peculiarities and problems which are of no serious consequence. She must be adequately informed and appropriately advised regarding the innocuous nature of these minor problems to allay her anxiety. The infant should be closely watched for following danger signs which should be brought to the attention of the physician for prompt management. Lethargy, bleeding from any site, appearance of jaundice within 24 hours of age or yellow staining of palms or soles, failure to pass meconium within 24 hours or urine within 48 hours, persistent vomiting or diarrhea, poor feeding, excessive weight loss (>10% in term and 15% in preterm), undue lethargy or excessive crying, drooling of saliva or choking during feeding, respiratory difficulty, apneic attacks or cyanosis, sudden rise or fall in body 9
10 temperature, seizures and evidences of superficial infections such as conjunctivitis, pustules, umbilical sepsis or oral thrush. Refer topic on Danger signs. Slide NC -21 Follow up Each baby should be followed up in the well baby clinic for assessment of growth and development, early diagnosis and management of illnesses and health education of parents. Follow up visits should be made to coincide with immunization schedule as far as possible. Slide NC -22 Immunizations It is recommended to give BCG, Hepatitis B and a dose of oral polio vaccine as early as possible, preferably within the first week of life. The mother should be explained that the child must receive all the vaccinations at the proper time as recommended in the National Immunization Schedule (Table I). TABLE 1: Schedule of immunization Age Vaccine Optional 0-7 days BCG, OPV, Hepatitis B - 6 weeks OPV, DPT, Hepatitis B Hib 10 weeks OPV, DPT, Hepatitis B* Hib 14 weeks OPV, DPT, Hepatitis B Hib 9 months Measles - 15 months MMR 18 months OPV, DPT Hib School entry (4-5 years) OPV, DT - 10 years Tetanus toxoid (every 5 years) * If first dose is not given at birth then this dose of Hepatitis B vaccine needs to be given 10
Routine care of a newborn baby
 Routine care of a newborn baby Slide NC-l,2 Introduction All mothers need help, support, and advice in the first few days after delivery to ensure proper care of their newly born babies. The care and help
Routine care of a newborn baby Slide NC-l,2 Introduction All mothers need help, support, and advice in the first few days after delivery to ensure proper care of their newly born babies. The care and help
Obstetrical Emergencies
 Date: July 18, 2014 Page 1 of 5 Obstetrical Emergencies Purpose: To provide the process for the assessment and management of the patient with an obstetrical related emergency. Pre-Medical Control 1. Follow
Date: July 18, 2014 Page 1 of 5 Obstetrical Emergencies Purpose: To provide the process for the assessment and management of the patient with an obstetrical related emergency. Pre-Medical Control 1. Follow
NRP 2012 Putting New Resuscitation Guidelines into Practice
 Outreach Education Online Video Library for Healthcare Professionals NRP 2012 Putting New Resuscitation Guidelines into Practice. Jeanette Zaichkin, RN, MN, NNP-BC December 2, 2010 Program Handouts This
Outreach Education Online Video Library for Healthcare Professionals NRP 2012 Putting New Resuscitation Guidelines into Practice. Jeanette Zaichkin, RN, MN, NNP-BC December 2, 2010 Program Handouts This
Neonatal Emergencies. Care of the Neonate. Care of the Neonate. Care of the Neonate. Student Objectives. Student Objectives continued.
 Student Objectives Neonatal Emergencies After completing this section the student will be able to: 1. Identify three physiologic and/or anatomic features unique to the newborn 2. List three perinatal factors
Student Objectives Neonatal Emergencies After completing this section the student will be able to: 1. Identify three physiologic and/or anatomic features unique to the newborn 2. List three perinatal factors
Why is prematurity a concern?
 Prematurity What is prematurity? A baby born before 37 weeks of pregnancy is considered premature. Approximately 12% of all babies are born prematurely. Terms that refer to premature babies are preterm
Prematurity What is prematurity? A baby born before 37 weeks of pregnancy is considered premature. Approximately 12% of all babies are born prematurely. Terms that refer to premature babies are preterm
COUNSELING CARDS FOR MATERNAL & NEONATAL HEALTH: NEWBORN AND POSTPARTUM CARE For Community Health Workers
 info@calcuttakids.org COUNSELING CARDS FOR MATERNAL & NEONATAL HEALTH: NEWBORN AND POSTPARTUM CARE For Community Health Workers Source credit: Images taken from and counseling points adapted from NIPI
info@calcuttakids.org COUNSELING CARDS FOR MATERNAL & NEONATAL HEALTH: NEWBORN AND POSTPARTUM CARE For Community Health Workers Source credit: Images taken from and counseling points adapted from NIPI
Understand nurse aide skills needed to promote skin integrity.
 Unit B Resident Care Skills Essential Standard NA5.00 Understand nurse aide s role in providing residents hygiene, grooming, and skin care. Indicator Understand nurse aide skills needed to promote skin
Unit B Resident Care Skills Essential Standard NA5.00 Understand nurse aide s role in providing residents hygiene, grooming, and skin care. Indicator Understand nurse aide skills needed to promote skin
Thermal protection in neonates
 Thermal protection in neonates Slide NT-1,2,3 Importance of temperature regulation Warmth is one of the basic needs of a newborn baby; it is critical to the baby s survival and well being. Unlike adults,
Thermal protection in neonates Slide NT-1,2,3 Importance of temperature regulation Warmth is one of the basic needs of a newborn baby; it is critical to the baby s survival and well being. Unlike adults,
NEWBORN ASSESSMENT AND CARE
 Unit Seven NEWBORN ASSESSMENT AND CARE Purpose This unit has three primary purposes -- to review: 1. how to assess the health of a newborn during a home visit; 2. warning signs of serious newborn health
Unit Seven NEWBORN ASSESSMENT AND CARE Purpose This unit has three primary purposes -- to review: 1. how to assess the health of a newborn during a home visit; 2. warning signs of serious newborn health
The Newborn With a Congenital Disorder. Chapter 14. Copyright 2008 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
 The Newborn With a Congenital Disorder Chapter 14 Congenital Anomalies or Malformations May be caused by genetic or environmental factors Approximately 2% to 3% of all infants born have a major malformation
The Newborn With a Congenital Disorder Chapter 14 Congenital Anomalies or Malformations May be caused by genetic or environmental factors Approximately 2% to 3% of all infants born have a major malformation
Southern Stone County Fire Protection District Emergency Medical Protocols
 TITLE Pediatric Medical Assessment PM 2.4 Confirm scene safety Appropriate body substance isolation procedures Number of patients Nature of illness Evaluate the need for assistance B.L.S ABC s & LOC Focused
TITLE Pediatric Medical Assessment PM 2.4 Confirm scene safety Appropriate body substance isolation procedures Number of patients Nature of illness Evaluate the need for assistance B.L.S ABC s & LOC Focused
Gastroschisis and My Baby
 Patient and Family Education Gastroschisis and My Baby Gastroschisis is a condition where a baby is born with the intestine outside the body. Learning about the diagnosis What is gastroschisis? (pronounced
Patient and Family Education Gastroschisis and My Baby Gastroschisis is a condition where a baby is born with the intestine outside the body. Learning about the diagnosis What is gastroschisis? (pronounced
NEONATAL RESUSCITATION PROVIDER (NRP) RECERTIFICATION TABLE OF CONTENTS
 NEONATAL RESUSCITATION PROVIDER (NRP) RECERTIFICATION TABLE OF CONTENTS NEONATAL FLOW ALGORITHM.2 INTRODUCTION 3 ANTICIPATION OF RESUSCITATION 4 TEMPERATURE CONTROL.4 CLEARING THE AIRWAY OF MECONIUM 5
NEONATAL RESUSCITATION PROVIDER (NRP) RECERTIFICATION TABLE OF CONTENTS NEONATAL FLOW ALGORITHM.2 INTRODUCTION 3 ANTICIPATION OF RESUSCITATION 4 TEMPERATURE CONTROL.4 CLEARING THE AIRWAY OF MECONIUM 5
Caring for a Tenckhoff Catheter
 Caring for a Tenckhoff Catheter UHN A Patient s Guide What is a Pleural Effusion? There is a small space between the outside of your lung and the chest wall (ribs). This space is called the pleural space.
Caring for a Tenckhoff Catheter UHN A Patient s Guide What is a Pleural Effusion? There is a small space between the outside of your lung and the chest wall (ribs). This space is called the pleural space.
call 811 to get advice from a nurse, or have someone drive the patient to a hospital Emergency Department. Patients should NOT drive themselves.
 Taking Care at Home After Surgery This checklist is to help you and your support person know what to do after you go home following your surgery. If you are given instructions verbally or in writing by
Taking Care at Home After Surgery This checklist is to help you and your support person know what to do after you go home following your surgery. If you are given instructions verbally or in writing by
 GUIDELINES FOR HOSPITALS WITH NEONATAL INTENSIVE CARE SERVICE : REGULATION 4 OF THE PRIVATE HOSPITALS AND MEDICAL CLINICS REGULATIONS [CAP 248, Rg 1] I Introduction 1. These Guidelines serve as a guide
GUIDELINES FOR HOSPITALS WITH NEONATAL INTENSIVE CARE SERVICE : REGULATION 4 OF THE PRIVATE HOSPITALS AND MEDICAL CLINICS REGULATIONS [CAP 248, Rg 1] I Introduction 1. These Guidelines serve as a guide
Water Birth Online Course. Women s Services
 Water Birth Online Course Women s Services 1 Water Birth Instructions for Online Class 1. Read through all the slides. 2. Print out the certificate at the end of the slides. 3. Sign and date the certificate.
Water Birth Online Course Women s Services 1 Water Birth Instructions for Online Class 1. Read through all the slides. 2. Print out the certificate at the end of the slides. 3. Sign and date the certificate.
PICC & Midline Catheters Patient Information Guide
 PICC & Midline Catheters Patient Information Guide medcompnet.com 1 table of contents Introduction 4 What is a PICC or Midline Catheter? 4 How is the PICC or Midline Catheter Inserted? 6 Catheter Care
PICC & Midline Catheters Patient Information Guide medcompnet.com 1 table of contents Introduction 4 What is a PICC or Midline Catheter? 4 How is the PICC or Midline Catheter Inserted? 6 Catheter Care
Biliary Drain. What is a biliary drain?
 Biliary Drain What is a biliary drain? A biliary drain is a tube to drain bile from your liver. It is put in by a doctor called an Interventional Radiologist. The tube or catheter is placed through your
Biliary Drain What is a biliary drain? A biliary drain is a tube to drain bile from your liver. It is put in by a doctor called an Interventional Radiologist. The tube or catheter is placed through your
PATIENT GUIDE. Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Clinician s Signature: Every drainage Weekly
 PATIENT GUIDE Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Every drainage Weekly Clinician s Signature: ACCESS SYSTEMS Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter
PATIENT GUIDE Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Every drainage Weekly Clinician s Signature: ACCESS SYSTEMS Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter
Central Venous Catheter (CVC) Sterile Dressing Change - The James
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Central Venous Catheter (CVC) Sterile Dressing Change - The James A dressing protects your catheter site and helps reduce the risk of infection. You will need
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Central Venous Catheter (CVC) Sterile Dressing Change - The James A dressing protects your catheter site and helps reduce the risk of infection. You will need
All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC)
 All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) General Information Intravenous (IV) therapy is the delivery of fluid directly into a vein. An intravenous catheter is a hollow tube that is
All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) General Information Intravenous (IV) therapy is the delivery of fluid directly into a vein. An intravenous catheter is a hollow tube that is
Common Concerns About Breastfeeding
 Patient Education Page 51 Caring for Yourself and Your New Baby Common Concerns About Breastfeeding Breastfeeding is healthy and natural. So are the questions and concerns that come with it. Whether you
Patient Education Page 51 Caring for Yourself and Your New Baby Common Concerns About Breastfeeding Breastfeeding is healthy and natural. So are the questions and concerns that come with it. Whether you
PICCs and Midline Catheters
 Patient Education PICCs and Midline Catheters Patient s guide to PICC (peripherally inserted central catheter) and midline catheters What are PICCs and midline catheters used for? Any medicine given over
Patient Education PICCs and Midline Catheters Patient s guide to PICC (peripherally inserted central catheter) and midline catheters What are PICCs and midline catheters used for? Any medicine given over
Section 6: Your Hemodialysis Catheter
 Section 6: Your Hemodialysis Catheter What you should know about your dialysis catheter How to change your catheter TEGO connectors Starting dialysis using a catheter End of dialysis using a catheter Changing
Section 6: Your Hemodialysis Catheter What you should know about your dialysis catheter How to change your catheter TEGO connectors Starting dialysis using a catheter End of dialysis using a catheter Changing
Sterile Dressing Change with Tegaderm CHG for Central Venous Catheter (CVC)
 Sterile Dressing Change with Tegaderm CHG for Central Venous Catheter (CVC) The dressing protects your catheter site. It also helps prevent infection at the site. Keep your dressing clean and dry at all
Sterile Dressing Change with Tegaderm CHG for Central Venous Catheter (CVC) The dressing protects your catheter site. It also helps prevent infection at the site. Keep your dressing clean and dry at all
Guidelines for Hand Foot and Mouth Disease HFMD
 Guidelines for Hand Foot and Mouth Disease HFMD Hand, foot, and mouth disease, or HFMD, is a contagious illness caused by different viruses. Infants and children younger than 5 years are more likely to
Guidelines for Hand Foot and Mouth Disease HFMD Hand, foot, and mouth disease, or HFMD, is a contagious illness caused by different viruses. Infants and children younger than 5 years are more likely to
Addendum to the NRP Provider Textbook 6 th Edition Recommendations for specific modifications in the Canadian context
 Addendum to the NRP Provider Textbook 6 th Edition Recommendations for specific modifications in the Canadian context A subcommittee of the Canadian Neonatal Resuscitation Program (NRP) Steering Committee
Addendum to the NRP Provider Textbook 6 th Edition Recommendations for specific modifications in the Canadian context A subcommittee of the Canadian Neonatal Resuscitation Program (NRP) Steering Committee
NRP Study Guide. This packet is intended for review only. Requirements to successfully complete NRP:
 This packet is intended for review only Requirements to successfully complete NRP: Completed NRP Pretest is required for admission to the course. Score 84% on the multiplechoice posttest. You may be allowed
This packet is intended for review only Requirements to successfully complete NRP: Completed NRP Pretest is required for admission to the course. Score 84% on the multiplechoice posttest. You may be allowed
35-40% of GBS disease occurs in the elderly or in adults with chronic medical conditions.
 What is Group B Strep (GBS)? Group B Streptococcus (GBS) is a type of bacteria that is found in the lower intestine of 10-35% of all healthy adults and in the vagina and/or lower intestine of 10-35% of
What is Group B Strep (GBS)? Group B Streptococcus (GBS) is a type of bacteria that is found in the lower intestine of 10-35% of all healthy adults and in the vagina and/or lower intestine of 10-35% of
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
 SOMAVERT pegvisomant for injection PATIENT INFORMATION SOMAVERT (SOM-ah-vert) (pegvisomant for injection) Read the patient information that comes with SOMAVERT before you start using it and each time you
SOMAVERT pegvisomant for injection PATIENT INFORMATION SOMAVERT (SOM-ah-vert) (pegvisomant for injection) Read the patient information that comes with SOMAVERT before you start using it and each time you
Your Guide to Peritoneal Dialysis Module 3: Doing Peritoneal Dialysis at Home
 Your Guide to Peritoneal Dialysis Module 3: 6.0959 in Preparing to do PD One of the most important things about PD is to keep the dialysis area and anything that comes in contact with the PD equipment
Your Guide to Peritoneal Dialysis Module 3: 6.0959 in Preparing to do PD One of the most important things about PD is to keep the dialysis area and anything that comes in contact with the PD equipment
How To Recover From A Surgical Wound From A Cast
 Care of Your Wounds After Amputation Surgery by Paddy Rossbach, RN Depending on the reason for your amputation and the state of your limb at the time of surgery, definitive closure of the wound may take
Care of Your Wounds After Amputation Surgery by Paddy Rossbach, RN Depending on the reason for your amputation and the state of your limb at the time of surgery, definitive closure of the wound may take
Atrium Pneumostat Chest Drain Valve. Discharge Instructions
 Atrium Pneumostat Chest Drain Valve Discharge Instructions Your Physician Name: Contact Number for Emergencies: Introduction Your physician has decided to change your chest drainage system to a smaller
Atrium Pneumostat Chest Drain Valve Discharge Instructions Your Physician Name: Contact Number for Emergencies: Introduction Your physician has decided to change your chest drainage system to a smaller
AHA/AAP Neonatal Resuscitation Guidelines 2010: Summary of Major Changes and Comment on its Utility in Resource-Limited Settings
 AHA/AAP Neonatal Resuscitation Guidelines 2010: Summary of Major Changes and Comment on its Utility in Resource-Limited Settings Resuscitation step Recommendations (2005) Recommendations (2010) Comments/LOE
AHA/AAP Neonatal Resuscitation Guidelines 2010: Summary of Major Changes and Comment on its Utility in Resource-Limited Settings Resuscitation step Recommendations (2005) Recommendations (2010) Comments/LOE
Guy s, King s and St Thomas Cancer Centre The Cancer Outpatient Clinic Central venous catheter: Peripherally inserted central catheter
 Guy s, King s and St Thomas Cancer Centre The Cancer Outpatient Clinic Central venous catheter: Peripherally inserted central catheter This information leaflet aims to help answer some of the questions
Guy s, King s and St Thomas Cancer Centre The Cancer Outpatient Clinic Central venous catheter: Peripherally inserted central catheter This information leaflet aims to help answer some of the questions
Having a companion you can lean on and who can support you during your labour can be helpful. It has been shown to reduce the need for pain relief.
 The pregnancy care planner Your NHS guide to having a baby www.nhs.uk/pregnancy My birth plan Name: Due date: Where to give birth You will have a choice about where to have your baby. Your midwife or doctor
The pregnancy care planner Your NHS guide to having a baby www.nhs.uk/pregnancy My birth plan Name: Due date: Where to give birth You will have a choice about where to have your baby. Your midwife or doctor
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary
 X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
How to Care for Your Premature Baby s Skin
 The Emily Center How to Care for Your Premature Baby s Skin Child Care/Health Promotion Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. Name of Child: Date: How
The Emily Center How to Care for Your Premature Baby s Skin Child Care/Health Promotion Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. Name of Child: Date: How
Patient Information Guide Morpheus CT Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter
 Patient Information Guide Morpheus CT Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter IC 192 Rev C A measure of flexibility and strength. Table of Contents 1. Introduction 2. What is the Morpheus CT PICC? 3. What
Patient Information Guide Morpheus CT Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter IC 192 Rev C A measure of flexibility and strength. Table of Contents 1. Introduction 2. What is the Morpheus CT PICC? 3. What
RSV infection. Information about RSV and how you can reduce the risk of your infant developing a severe infection.
 RSV infection Information about RSV and how you can reduce the risk of your infant developing a severe infection. What is RSV? RSV is one of the most common respiratory viruses and is spread easily. By
RSV infection Information about RSV and how you can reduce the risk of your infant developing a severe infection. What is RSV? RSV is one of the most common respiratory viruses and is spread easily. By
JAC-CEN-DEL COMMUNITY SCHOOLS BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS A BACK TO SCHOOL TRADITION
 JAC-CEN-DEL COMMUNITY SCHOOLS BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS A BACK TO SCHOOL TRADITION UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS AGAINST BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Employees working in a school system are potentially
JAC-CEN-DEL COMMUNITY SCHOOLS BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS A BACK TO SCHOOL TRADITION UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS AGAINST BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Employees working in a school system are potentially
PATIENT GUIDE. Understand and care for your peripherally inserted central venous catheter (PICC). MEDICAL
 PATIENT GUIDE Understand and care for your peripherally inserted central venous catheter (PICC). MEDICAL Introduction The following information is presented as a guideline for your reference. The best
PATIENT GUIDE Understand and care for your peripherally inserted central venous catheter (PICC). MEDICAL Introduction The following information is presented as a guideline for your reference. The best
PATIENT GUIDE. Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Clinician s Signature: Every drainage Weekly
 PATIENT GUIDE Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Every drainage Weekly Clinician s Signature: ACCESS SYSTEMS Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter
PATIENT GUIDE Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Every drainage Weekly Clinician s Signature: ACCESS SYSTEMS Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter
TAKING CARE OF WOUNDS KEY FIGURE:
 Chapter 9 TAKING CARE OF WOUNDS KEY FIGURE: Gauze Wound care represents a major area of concern for the rural health provider. This chapter discusses the treatment of open wounds, with emphasis on dressing
Chapter 9 TAKING CARE OF WOUNDS KEY FIGURE: Gauze Wound care represents a major area of concern for the rural health provider. This chapter discusses the treatment of open wounds, with emphasis on dressing
EVERY NEWBORN S HEALTH
 SAVING NEWBORN LIVES EVERY NEWBORN S HEALTH Recommendations for Care for All Newborns IMMEDIATE CARE AFTER BIRTH AND CONTINUING POSTNATAL CARE IMMEDIATE CARE AFTER BIRTH Be sure that attendants wash hands
SAVING NEWBORN LIVES EVERY NEWBORN S HEALTH Recommendations for Care for All Newborns IMMEDIATE CARE AFTER BIRTH AND CONTINUING POSTNATAL CARE IMMEDIATE CARE AFTER BIRTH Be sure that attendants wash hands
Care for your child s Central Venous Catheter (CVC)
 Care for your child s Central Venous Catheter (CVC) This booklet is intended for general informational purposes only. You should consult your doctor for medical advice. Please call the clinic or your home
Care for your child s Central Venous Catheter (CVC) This booklet is intended for general informational purposes only. You should consult your doctor for medical advice. Please call the clinic or your home
Chapter 31 Obstetrics and Neonatal Care 1137. Scene Size-up. Primary Assessment
 Chapter 31 Obstetrics and Neonatal Care 1137 Scene Size-up Scene Safety Mechanism of Injury (MOI)/ Nature of Illness (NOI) Ensure scene safety and safe access to the patient. Standard precautions should
Chapter 31 Obstetrics and Neonatal Care 1137 Scene Size-up Scene Safety Mechanism of Injury (MOI)/ Nature of Illness (NOI) Ensure scene safety and safe access to the patient. Standard precautions should
Infant CPR. What You Need to Know. How to Do Infant CPR
 Infant CPR Infant CPR also called Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is emergency care given to a baby who has stopped breathing. This sheet has the steps for CPR for newborns or babies less than 1 year old.
Infant CPR Infant CPR also called Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is emergency care given to a baby who has stopped breathing. This sheet has the steps for CPR for newborns or babies less than 1 year old.
Are any artificial parts used in the ACE Malone surgery?
 ACE Malone (Antegrade Continence Enema) What is the ACE Malone? The Antegrade Continence Enema (ACE) is a type of surgery designed for the child who has chronic bowel problems with bouts of constipation,
ACE Malone (Antegrade Continence Enema) What is the ACE Malone? The Antegrade Continence Enema (ACE) is a type of surgery designed for the child who has chronic bowel problems with bouts of constipation,
MINI - COURSE On TEMPERATURE CONTROL IN THE NEWBORN
 MINI - COURSE On TEMPERATURE CONTROL IN THE NEWBORN Instructions: Read each sheet and answer any questions as honestly as possible The first sheets have four questions to allow you to give your thoughts
MINI - COURSE On TEMPERATURE CONTROL IN THE NEWBORN Instructions: Read each sheet and answer any questions as honestly as possible The first sheets have four questions to allow you to give your thoughts
Premature Infant Care
 Premature Infant Care Introduction A premature baby is born before the 37th week of pregnancy. Premature babies are also called preemies. Premature babies may have health problems because their organs
Premature Infant Care Introduction A premature baby is born before the 37th week of pregnancy. Premature babies are also called preemies. Premature babies may have health problems because their organs
5420-R STUDENT HEALTH SERVICES REGULATION NORTH COLONIE CENTRAL SCHOOLS NEWTONVILLE, NEW YORK Emergency Procedures and Approved First Aid Methods
 STUDENT HEALTH SERVICES REGULATION NORTH COLONIE CENTRAL SCHOOLS NEWTONVILLE, NEW YORK Emergency Procedures and Approved First Aid Methods EMERGENCY PROCEDURES Contact parents and cooperate with them in
STUDENT HEALTH SERVICES REGULATION NORTH COLONIE CENTRAL SCHOOLS NEWTONVILLE, NEW YORK Emergency Procedures and Approved First Aid Methods EMERGENCY PROCEDURES Contact parents and cooperate with them in
IMPORTANT: PLEASE READ
 PART III: CONSUMER INFORMATION combined hepatitis A (inactivated) and hepatitis B (recombinant) vaccine This leaflet is part III of a three-part "Product Monograph" published when was approved for sale
PART III: CONSUMER INFORMATION combined hepatitis A (inactivated) and hepatitis B (recombinant) vaccine This leaflet is part III of a three-part "Product Monograph" published when was approved for sale
PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION
 READ THIS FOR SAFE AND EFFECTIVE USE OF YOUR MEDICINE PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION Pr CYRAMZA ramucirumab Read this carefully before you receive CYRAMZA (pronounced "si ram - ze"). This leaflet is a
READ THIS FOR SAFE AND EFFECTIVE USE OF YOUR MEDICINE PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION Pr CYRAMZA ramucirumab Read this carefully before you receive CYRAMZA (pronounced "si ram - ze"). This leaflet is a
Taking Out a Tooth. Before You Begin: Ask Questions! CHAPTER11
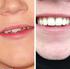 159 CHAPTER11 Taking Out a Tooth Not every painful tooth needs to come out. You must decide how serious the problem is, and then decide if you can treat and save the tooth. Some problems such as root canal
159 CHAPTER11 Taking Out a Tooth Not every painful tooth needs to come out. You must decide how serious the problem is, and then decide if you can treat and save the tooth. Some problems such as root canal
How to care for a Midline Catheter
 How to care for a Midline Catheter Developed by the health care professionals of the IV Program with assistance from the Department of Learning and Development. All rights reserved. No part of this book
How to care for a Midline Catheter Developed by the health care professionals of the IV Program with assistance from the Department of Learning and Development. All rights reserved. No part of this book
CPR/AED for Professional Rescuers and Health Care Providers HANDBOOK
 CPR/AED for Professional Rescuers and Health Care Providers HANDBOOK TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 1: THE PROFESSIONAL RESCUER The Duty to Respond 2 Preventing the Spread of Bloodborne Pathogens 3 Taking Action
CPR/AED for Professional Rescuers and Health Care Providers HANDBOOK TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 1: THE PROFESSIONAL RESCUER The Duty to Respond 2 Preventing the Spread of Bloodborne Pathogens 3 Taking Action
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA 40 MG/0.8 ML, 20 MG/0.4 ML AND 10 MG/0.2 ML SINGLE-USE PREFILLED SYRINGE
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA (Hu-MARE-ah) (adalimumab) 40 MG/0.8 ML, 20 MG/0.4 ML AND 10 MG/0.2 ML SINGLE-USE PREFILLED SYRINGE Do not try to inject HUMIRA yourself until you have been shown the right way
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA (Hu-MARE-ah) (adalimumab) 40 MG/0.8 ML, 20 MG/0.4 ML AND 10 MG/0.2 ML SINGLE-USE PREFILLED SYRINGE Do not try to inject HUMIRA yourself until you have been shown the right way
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Basic Program Outlines Outline Topic: OB/GYN Revised: 11/2013
 Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Basic Program Outlines Outline Topic: OB/GYN Revised: 11/2013 A&P Vagina - known as birth canal. Cervix - head of vagina. Fallopian tubes
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Basic Program Outlines Outline Topic: OB/GYN Revised: 11/2013 A&P Vagina - known as birth canal. Cervix - head of vagina. Fallopian tubes
Safety FIRST: Infection Prevention Tips
 Reading Hospital Safety FIRST: Infection Prevention Tips Reading Hospital is committed to providing high quality care to our patients. Your healthcare team does many things to help prevent infections.
Reading Hospital Safety FIRST: Infection Prevention Tips Reading Hospital is committed to providing high quality care to our patients. Your healthcare team does many things to help prevent infections.
Delivering nutrition, fluids & medication via a PEG. By Julia Pointer & Caroline Ross, Staff Nurses, Hospice Day Service
 Delivering nutrition, fluids & medication via a PEG By Julia Pointer & Caroline Ross, Staff Nurses, Hospice Day Service Aims of this session? To give an explanation of the theory and practice of a Percutaneous
Delivering nutrition, fluids & medication via a PEG By Julia Pointer & Caroline Ross, Staff Nurses, Hospice Day Service Aims of this session? To give an explanation of the theory and practice of a Percutaneous
How To Treat A Pregnant Woman With A Miscarriage
 Special Patient Populations Obstetrics EMR Education Standard Recognizes and manages life threats based on simple assessment findings for a patient with special needs while awaiting additional emergency
Special Patient Populations Obstetrics EMR Education Standard Recognizes and manages life threats based on simple assessment findings for a patient with special needs while awaiting additional emergency
Important Things to Know
 EXERGEN TemporalScanner Important Things to Know TA temperature is real time temperature Just like pulmonary artery temperature, TA temperature identifies changes in your patient s temperature sooner than
EXERGEN TemporalScanner Important Things to Know TA temperature is real time temperature Just like pulmonary artery temperature, TA temperature identifies changes in your patient s temperature sooner than
Challenges of Foster Parents who Care for Infants with Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome
 Challenges of Foster Parents who Care for Infants with Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome All Health Care Providers are required by law to make a referral to the Department of Children s Services (DCS) Child
Challenges of Foster Parents who Care for Infants with Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome All Health Care Providers are required by law to make a referral to the Department of Children s Services (DCS) Child
Pentavalent Vaccine. Guide for Health Workers. with Answers to Frequently Asked Questions
 Pentavalent Vaccine Guide for Health Workers with Answers to Frequently Asked Questions Ministry of Health and Family Welfare Government of India 2012 Immunization is one of the most well-known and effective
Pentavalent Vaccine Guide for Health Workers with Answers to Frequently Asked Questions Ministry of Health and Family Welfare Government of India 2012 Immunization is one of the most well-known and effective
Certified Nursing Assistant Essential curriculum- Maryland Board of Nursing
 Certified Nursing Assistant Essential curriculum- Maryland Board of Nursing Module I Orientation/Introduction A. Identify general information pertaining to the nursing assistant course B. List requirements
Certified Nursing Assistant Essential curriculum- Maryland Board of Nursing Module I Orientation/Introduction A. Identify general information pertaining to the nursing assistant course B. List requirements
SUPPORT OF BREASTFEEDING FAMILIES IN NICU THE WOMEN S HOSPITAL AT JACKSON MEMORIAL
 SUPPORT OF BREASTFEEDING FAMILIES IN NICU THE WOMEN S HOSPITAL AT JACKSON MEMORIAL OBJECTIVES To verbalize the benefits of breast milk for preterm and critical ill infants To recognize how to assist mother
SUPPORT OF BREASTFEEDING FAMILIES IN NICU THE WOMEN S HOSPITAL AT JACKSON MEMORIAL OBJECTIVES To verbalize the benefits of breast milk for preterm and critical ill infants To recognize how to assist mother
GJ TUBE (GASTROJEJUNOSTOMY TUBE) Daily Care
 GJ TUBE (GASTROJEJUNOSTOMY TUBE) Daily Care Your child has a Picture 1 The GJ Tube inside the body. gastrojejunostomy (GJ) tube Disc (Picture 1). This set of tubes lets food or medicine go into either
GJ TUBE (GASTROJEJUNOSTOMY TUBE) Daily Care Your child has a Picture 1 The GJ Tube inside the body. gastrojejunostomy (GJ) tube Disc (Picture 1). This set of tubes lets food or medicine go into either
To maintain a port of entry to venous flow when all available peripheral ports have failed.
 I. Purpose: To maintain a port of entry to venous flow when all available peripheral ports have failed. II. General Comments: Since its development, these catheters have been used with increasing frequency
I. Purpose: To maintain a port of entry to venous flow when all available peripheral ports have failed. II. General Comments: Since its development, these catheters have been used with increasing frequency
Care of Your Hickman Catheter
 Care of Your Hickman Catheter Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center, Revised 7/11 Contents What is a Hickman Catheter? Page 3 Does the Catheter Limit My Activities? Page 4 How Do I Care for My Catheter? Page
Care of Your Hickman Catheter Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center, Revised 7/11 Contents What is a Hickman Catheter? Page 3 Does the Catheter Limit My Activities? Page 4 How Do I Care for My Catheter? Page
Objectives At the completion of this module, unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) should be able to:
 Objectives At the completion of this module, unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) should be able to: 1. administer medications by subcutaneous injections. 2. document medication administration in the client
Objectives At the completion of this module, unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) should be able to: 1. administer medications by subcutaneous injections. 2. document medication administration in the client
American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Breastfeeding. Ten Steps to Support Parents Choice to Breastfeed Their Baby
 American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Breastfeeding 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Ten Steps to Support Parents Choice to Breastfeed Their Baby This practice enthusiastically supports parents plans to breastfeed
American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Breastfeeding 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Ten Steps to Support Parents Choice to Breastfeed Their Baby This practice enthusiastically supports parents plans to breastfeed
Medication Guide Rebif (Re-bif) Interferon beta-1a (in-ter-feer-on beta-one-â)
 Medication Guide Rebif (Re-bif) Interferon beta-1a (in-ter-feer-on beta-one-â) Please read this leaflet carefully before you start to use Rebif and each time your prescription is refilled since there may
Medication Guide Rebif (Re-bif) Interferon beta-1a (in-ter-feer-on beta-one-â) Please read this leaflet carefully before you start to use Rebif and each time your prescription is refilled since there may
Bottle Feeding Puppies and Kittens
 Bottle Feeding Puppies and Kittens Formula Goats milk works as a temporary substitute, but it can get expensive. Goats milk is sold at Wal-Mart and most grocery stores. Cow s milk is not an alternative;
Bottle Feeding Puppies and Kittens Formula Goats milk works as a temporary substitute, but it can get expensive. Goats milk is sold at Wal-Mart and most grocery stores. Cow s milk is not an alternative;
BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS
 BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS AIDS and other blood-borne pathogens such as Hepatitis B and C are deadly diseases that are present in today s society. All blood-borne pathogens are transmitted in blood and other
BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS AIDS and other blood-borne pathogens such as Hepatitis B and C are deadly diseases that are present in today s society. All blood-borne pathogens are transmitted in blood and other
Medications or therapeutic solutions may be injected directly into the bloodstream
 Intravenous Therapy Medications or therapeutic solutions may be injected directly into the bloodstream for immediate circulation and use by the body. State practice acts designate which health care professionals
Intravenous Therapy Medications or therapeutic solutions may be injected directly into the bloodstream for immediate circulation and use by the body. State practice acts designate which health care professionals
Health Technician skills checklist Health Services Department Lincoln Public Schools TEMPERATURE
 Rev. 2/07 Health Technician skills checklist TEMPERATURE 1. Explain to student what you are going to do. 2. Wait for Welch-Allyn thermometer to beep, then apply probe cover. Make sure probe cover is secure.
Rev. 2/07 Health Technician skills checklist TEMPERATURE 1. Explain to student what you are going to do. 2. Wait for Welch-Allyn thermometer to beep, then apply probe cover. Make sure probe cover is secure.
Flushing and Dressing a Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC Line): a Guide for Nurses
 Flushing and Dressing a Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC Line): a Guide for Nurses Information for Nurses Introduction This information is for community nursing staffs who have been asked to
Flushing and Dressing a Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC Line): a Guide for Nurses Information for Nurses Introduction This information is for community nursing staffs who have been asked to
Tracheostomy Care at Home
 Tracheostomy Care at Home Patient Education CARE AND TREATMENT This information will help you understand how to care for a person with a tracheostomy at home. It is a supplement to the teaching offered
Tracheostomy Care at Home Patient Education CARE AND TREATMENT This information will help you understand how to care for a person with a tracheostomy at home. It is a supplement to the teaching offered
American Red Cross First Aid EXAMPLE ANSWER SHEET
 American Red Cross First Aid Exam A IMPORTANT: Read all instructions before beginning the exam. INSTRUCTIONS: Do not write on this exam. Mark all answers in pencil on the separate answer sheet as directed
American Red Cross First Aid Exam A IMPORTANT: Read all instructions before beginning the exam. INSTRUCTIONS: Do not write on this exam. Mark all answers in pencil on the separate answer sheet as directed
BLS TREATMENT GUIDELINES - CARDIAC
 BLS TREATMENT GUIDELINES - CARDIAC CARDIOPULMONARY ARREST - NON-TRAUMATIC (SJ-B101) effective 07/01/99 Defibrillation CPR Apply S-AED and assess rhythm as trained. Defib as indicated Simultaneous OXYGEN:
BLS TREATMENT GUIDELINES - CARDIAC CARDIOPULMONARY ARREST - NON-TRAUMATIC (SJ-B101) effective 07/01/99 Defibrillation CPR Apply S-AED and assess rhythm as trained. Defib as indicated Simultaneous OXYGEN:
Your Recovery After a Cesarean Delivery
 Your Recovery After a Cesarean Delivery It is normal to have many questions about your care after delivery. Cesarean delivery is surgery and your body needs time to heal and recover for the next 6 weeks,
Your Recovery After a Cesarean Delivery It is normal to have many questions about your care after delivery. Cesarean delivery is surgery and your body needs time to heal and recover for the next 6 weeks,
TREATMENT 1. Control bleeding by applying pressure over wound with Gauze Pads (Surgical Supply-4). 2. Contact Surgeon for laceration repair options.
 Page 1 of 8 pages NOTE Contact Surgeon before giving any medication marked with an asterisk. In an emergency or during Loss of Signal, begin appropriate treatment; then call Surgeon as soon as possible.
Page 1 of 8 pages NOTE Contact Surgeon before giving any medication marked with an asterisk. In an emergency or during Loss of Signal, begin appropriate treatment; then call Surgeon as soon as possible.
Understanding your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Information
 Understanding your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Information The Purpose of this Information Sheet This information sheet has been written by patients, members of the public and
Understanding your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Information The Purpose of this Information Sheet This information sheet has been written by patients, members of the public and
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA 40 MG/0.8 ML SINGLE-USE PEN
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA (Hu-MARE-ah) (adalimumab) 40 MG/0.8 ML SINGLE-USE PEN Do not try to inject HUMIRA yourself until you have been shown the right way to give the injections and have read and understand
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA (Hu-MARE-ah) (adalimumab) 40 MG/0.8 ML SINGLE-USE PEN Do not try to inject HUMIRA yourself until you have been shown the right way to give the injections and have read and understand
What to do about Diaper Rash
 What to do about Diaper Rash Diaper rash is a skin eruption in the area covered by your baby s diaper. It is extremely common and often clears away within a few days, if you keep the baby clean and dry.
What to do about Diaper Rash Diaper rash is a skin eruption in the area covered by your baby s diaper. It is extremely common and often clears away within a few days, if you keep the baby clean and dry.
Breastfeeding Your Baby
 Getting the Help You Need If you have questions or problems, don t wait. Another nursing mother or mothers support group can often help. Your hospital, WIC office, baby s doctor, midwife, or obstetrician/gynecologist
Getting the Help You Need If you have questions or problems, don t wait. Another nursing mother or mothers support group can often help. Your hospital, WIC office, baby s doctor, midwife, or obstetrician/gynecologist
CASAID THE AIMS OF FIRST AID, INCIDENT ACTION PLAN, INITIAL ASSESSMENT AND THE RECOVERY POSITION. Airway must be open so oxygen can enter the body.
 CASAID THE AIMS OF FIRST AID, INCIDENT ACTION PLAN, INITIAL ASSESSMENT AND THE RECOVERY POSITION The Aims of First Aid The aims of first aid (the three Ps) are to: Preserve the casualty s life. Prevent
CASAID THE AIMS OF FIRST AID, INCIDENT ACTION PLAN, INITIAL ASSESSMENT AND THE RECOVERY POSITION The Aims of First Aid The aims of first aid (the three Ps) are to: Preserve the casualty s life. Prevent
Ebola Virus Precaution guidelines
 Ebola Virus Precaution guidelines 1 Introduction Who is this guidance for? The guidance is designed for crew to protect themselves, their colleagues, guests and others around them. The guidance focuses
Ebola Virus Precaution guidelines 1 Introduction Who is this guidance for? The guidance is designed for crew to protect themselves, their colleagues, guests and others around them. The guidance focuses
How to prepare your baby s bottle
 How to prepare your baby s bottle Cleaning and Sterilising Using or storing sterilised bottles Preparing a bottle feed Storing and warming feeds Feeding your baby Crèches, childminders and other childcare
How to prepare your baby s bottle Cleaning and Sterilising Using or storing sterilised bottles Preparing a bottle feed Storing and warming feeds Feeding your baby Crèches, childminders and other childcare
Sanitary Food Preparation & Safe Food Handling
 70 Feeding Infants 10 Sanitary Food Preparation & Safe Food Handling Babies are more susceptible to bacteria than older children, and unsanitary food conditions can cause serious infections. General cleanliness,
70 Feeding Infants 10 Sanitary Food Preparation & Safe Food Handling Babies are more susceptible to bacteria than older children, and unsanitary food conditions can cause serious infections. General cleanliness,
PATIENT INFORMATION. Medicine To Treat: D iabetes. What You Need to Know About. Insulin
 PATIENT INFORMATION Medicine To Treat: D iabetes What You Need to Know About Insulin INTRODUCTION The insulin preparations currently available in Singapore are mostly from human origin; pork or bovine
PATIENT INFORMATION Medicine To Treat: D iabetes What You Need to Know About Insulin INTRODUCTION The insulin preparations currently available in Singapore are mostly from human origin; pork or bovine
Breast-feeding. You have one of the volumes of The Growth Guide series in your hands. The Growth Guide consists of seven practical booklets:
 Breast-feeding Dear (prospective) parents, You have one of the volumes of The Growth Guide series in your hands. The Growth Guide consists of seven practical booklets: Planning for Parenthood Pregnancy
Breast-feeding Dear (prospective) parents, You have one of the volumes of The Growth Guide series in your hands. The Growth Guide consists of seven practical booklets: Planning for Parenthood Pregnancy
NIH Clinical Center Patient Education Materials Giving a subcutaneous injection
 NIH Clinical Center Patient Education Materials What is a subcutaenous injection? A subcutaneous injection is given in the fatty layer of tissue just under the skin. A subcutaneous injection into the fatty
NIH Clinical Center Patient Education Materials What is a subcutaenous injection? A subcutaneous injection is given in the fatty layer of tissue just under the skin. A subcutaneous injection into the fatty
First Responder (FR) and Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) Progress Log
 First Responder (FR) and Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) Progress Log Note: Those competencies that are for EMR only are denoted by boldface type. For further details on the National Occupational Competencies
First Responder (FR) and Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) Progress Log Note: Those competencies that are for EMR only are denoted by boldface type. For further details on the National Occupational Competencies
INJECTION TECHNIQUE. IVF NURSING OFFICE: (301) 400-2151 Darshana (301) 400-2146 Nicole
 IVF NURSING OFFICE: (301) 400-2151 Darshana (301) 400-2146 Nicole PLEASE NOTE: If you do not have medications for the next day s dose, you MUST go to the clinic that morning at 6:30 AM for more medications.
IVF NURSING OFFICE: (301) 400-2151 Darshana (301) 400-2146 Nicole PLEASE NOTE: If you do not have medications for the next day s dose, you MUST go to the clinic that morning at 6:30 AM for more medications.
Module 7 Expanded Programme of Immunization (EPI)
 Module 7 Expanded Programme of Immunization (EPI) (including Vitamin A, Tetanus Toxoid and Growth Monitoring) CONTENTS 7.1 What are the tools used for data collection?....................................2
Module 7 Expanded Programme of Immunization (EPI) (including Vitamin A, Tetanus Toxoid and Growth Monitoring) CONTENTS 7.1 What are the tools used for data collection?....................................2
X-Plain Foley Catheter Male Reference Summary
 X-Plain Foley Catheter Male Reference Summary Introduction A Foley catheter is a tube that is put through the urinary opening and into your bladder to drain urine. Your doctor may have placed or may ask
X-Plain Foley Catheter Male Reference Summary Introduction A Foley catheter is a tube that is put through the urinary opening and into your bladder to drain urine. Your doctor may have placed or may ask
Giving Yourself Dalteparin (Fragmin) or Heparin
 Contents www.bcwomens.ca What is Dalteparin (Fragmin)...1 Where do I get this medication from?...1 How often do I give myself this medication?...1 Side effects...1 Steps to Giving Yourself Dalteparin (Fragmin)..1
Contents www.bcwomens.ca What is Dalteparin (Fragmin)...1 Where do I get this medication from?...1 How often do I give myself this medication?...1 Side effects...1 Steps to Giving Yourself Dalteparin (Fragmin)..1
