Section of DBMS Selection & Evaluation Questionnaire
|
|
|
- Rose Copeland
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Section of DBMS Selection & Evaluation Questionnaire Whitemarsh Information Systems Corporation 2008 Althea Lane Bowie, Maryland Tele: Web:
2 2 LOGICAL DATABASE 2.1 Database schema 1. Can a database schema be named 2. Can a database schema contain a version 3. Can a database schema contain an author 4. Can a database schema contain a restricted user access 5. Can a database schema contain a description 6. Can a database schema utilize copy from clauses 2.2 Tables Table description naming 1. Can a table be named 2. Can a table contain a version 3. Can a table contain an author 4. Can a table contain a restricted user access 5. Can a table contain a description 6. Can a table utilize copy from clauses 7. Does the table definition clause contain options for declaring the various DBMS strategies for row storage and selection, for example, hash/calc, direct, sorted, and so forth 2
3 Logical database 8. Does the DBMS support derived columns, whose values are affected algorithmically through value changes to other columns, row insertions, and the like 9. Are there any restriction on the number of columns that can be defined in a table Table integrity 1. Can table based procedures be defined that are automatically invoked whenever rows are inserted, deleted, or modified by any and all interrogation languages 2. Can table integrity procedures be defined that are automatically invoked whenever certain conditions resulting from the insertion, deletion, or modification of the row is not met. 3. Can table integrity procedures be defined that are automatically invoked whenever certain conditions resulting from the insertion, deletion, or modification of the row are met. 4. Can compiler languages, such as COBOL, be used to define these procedures 5. Can natural languages be used to define these procedures 6. Are procedure definition clauses specified in the logical database's schema definition languages 7. Are procedure definition clauses specified in the physical database 8. Can table integrity clauses be defined that evaluate column values individually, or in collections of column values through unary, binary, ternary, and boolean operators prior to the storage of a row in a database 2.3 Columns Column descriptions 1. Version 2. Author 3. Restricted user access 4. Description 3
4 5. Copy from clauses 6. Can column names be at least 15 characters 7. Can a column name contain any ASCII character 8. Can a column be defined to only represent only a single value, known as a single-valued column 9. Can a column reference a domain relieving the DBA from having to define the characteristics of the column's data Column data types 1. Fixed length character 2. Variable length character 3. Fixed 4. Integer 5. Packed decimal 6. Float, single precision 7. Float, double precision 8. Complex Numeric 9. Date 10. Money 11. Boolean 12. Binary Large Object 13. Character Large Object 14. Is there a maximum size or value for each column's data type 4
5 Logical database 15. Are there corresponding data types from third generation languages such as COBOL, Fortran, C, etc. to which each data type does not translate. 16. Is the translation to the corresponding programming language data type automatically performed by the DBMS rather than requiring the programmer create the routines in the application program Column Data Structures 1. Can a column within a row represent multiple values configured as an array. 2. Can the sequence of the values in the array be defined. 3. Is the sequence of the values in the array persistent 4. Can a column contain subordinate columns each of which is defined as a column and that the collection of values represented by the contained column set is equivalent to a row in a table. 5. Can a column within a subordinate set of columns contain subordinate columns 6. Is there any limit to the quantity of levels of subordinate collections of columns Column Editing & Validation 1. Does the proposed DBMS contain the ability to define automatic data editing and validation clauses such that these editing and validation clauses are automatically invoked whenever data is entered from any and all interrogation languages 2. Can this facility prohibit duplicate values 3. Can this facility specify valid values 4. Can this facility specify invalid values 5. Can this facility specify ranges of valid or invalid values 6. Can this facility specify combinations of valid and invalid values 5
6 7. Is there any situation under which data, represented by a column, that is to be stored in a table, can trespass its column defined characteristic boundaries and overwrite an adjacently stored column 8. Does the DBMS recognize the difference between the character column value of blank or a numeric column value of zero and a column that has not been valued, i.e., Null 9. Does the DBMS support three-way logic in support of nulls 10. Does the DBA have the ability to establish default values--other than blank, zero, or null--for columns that are not valued during an update or insert 11. Can column names be the same when they appear in different table within the same schema 12. Can certain columns be defined to automatically contain the O/S time and date stamps whenever the row is inserted or modified Column use types Primary keys 1. Are multiple columns able to participate in this use designation 2. If multiple columns participate in this use designation, does the DBMS redundantly store the column's data, once for each participating column, and once for the compound column use designation 3. Can columns from different data types participate in compound use designations 4. Can the columns participating in a primary key be defined in the table in any order 5. Can duplicate values be allowed 6. Can duplicate values be disallowed Candidate keys 1. Are multiple columns able to participate in this use designation 6
7 Logical database 2. If multiple columns participate in this use designation, does the DBMS redundantly store the column's data, once for each participating column, and once for the compound column use designation 3. Can columns from different data types participate in compound use designations 4. Can the columns participating in a candidate key be defined in the table in any order 5. Can duplicate values be allowed 6. Can duplicate values be disallowed Secondary keys 1. Are multiple columns able to participate in this use designation 2. If multiple columns participate in this use designation, does the DBMS redundantly store the column's data, once for each participating column, and once for the compound column use designation 3. Can columns from different data types participate in compound use designations 4. Can the columns participating in a secondary key be defined in the table in any order Foreign keys 1. Are multiple columns able to participate in this use designation 2. If multiple columns participate in this use designation, does the DBMS redundantly store the column's data, once for each participating column, and once for the compound column use designation 3. Can columns from different data types participate in compound use designations 4. Can the columns participating in a foreign key be defined in the table in any order 5. Can duplicate values be disallowed 7
8 Multiple Use Designators 1. Can a single column be both a primary key and foreign key 2. Can a single column be both a candidate key and foreign key 2.4 Relationships Relationship Definition 1. Can a relationship be named 2. Can a relationship contain a version 3. Can a relationship contain an author 4. Can a relationship contain a restricted user access 5. Can a relationship contain a description 6. Can a relationship utilize copy from clauses Relationship Types 1. Can a one-to one relationship be defined between two tables 2. Can a single table relationship be defined that has no owner 3. Can a multiple table relationship be defined that has no owner 4. Can a single owner table with single member table relationship be defined 5. Can a single owner table with multiple member table relationship be defined 6. Can a many to many relationship between two tables be defined 7. Can an inferential relationship be defined 8. Can a recursive relationship be defined Relationship Persistence 8
9 Logical database 1. Can the sequence of the rows within a defined relationship be defined on an arbitrary basis 2. Can the sequence of the rows within a defined relationship be defined on the basis of a defined column within the member table. 3. Can the sequence of the rows within a defined relationship be defined on the basis of a multiply identified columns within the member table. 2.5 Relationship Integrity Ambiguity Detection 1. Does the DBMS examine all the then-defined referential integrity definitions, rejecting those that could result in ambiguous insert, delete or modify situations Value-Based Referential Integrity Definition 1. Can the DBMS DDL explicitly declare that an owner row and one or more member rows are related by the value of the primary key of the owner being equal in value to a column value contained in the member rows 2. Can the DBMS DDL explicitly declare that a member row will not be allowed to be stored if the corresponding owner row (member's foreign key value = owner's primary key value) is not already stored 3. Can the DBMS DDL explicitly declare that a member row is allowed to be stored with its foreign key being set to null, notwithstanding the owner's row failure to exist 4. Can the DBMS DDL explicitly declare that an owner row will not be allowed to be deleted if the corresponding member row (primary key value = foreign key value) is still stored 5. Can the DBMS DDL explicitly declare that an owner row will be allowed to be deleted only after the corresponding member row's foreign key value is set to null 6. Can the DBMS DDL explicitly declare that when a member table instance's foreign key is updated that it will only allow the update if the foreign key's value already matches an existing primary key 9
10 7. Can the DBMS DDL explicitly declare that when a member table instance's foreign key is updated to a value not represented by any existing primary key that the update will be accepted and the foreign key value will be set to null NonValue-Based Referential Integrity Definition 1. Can the DBMS DDL explicitly declare that an owner row and one or more member rows are related 2. Can the DBMS DDL explicitly declare that a member row will not be allowed to be stored if the related owner row is not already stored 3. Can the DBMS DDL explicitly declare that a member row is allowed to be stored with its foreign key being set to null, notwithstanding the owner's row failure to exist 4. Can the DBMS DDL explicitly declare that an owner row will not be allowed to be deleted if the corresponding member row is still stored 5. Can the DBMS DDL explicitly declare that an owner row will be allowed to be deleted only after the corresponding member row relationship indicator is set to null 6. Can the DBMS DDL explicitly declare that when a member table row's relationship membership is updated that it will only allow the update if the member is then related to an already existing owner record 7. Can the DBMS DDL explicitly declare that when a member table row's relationship membership is updated that it will allow the update even if the member is not then related to an already existing owner record 2.6 Data Definition Language 1. Can the DBMS's central version know of multiple databases, and have these multiple schemas operate independently and concurrently 2. Can the table names for different databases within the same central version be named the same 3. Upon submittal, are schema DDL error messages returned, and is the flawed clauses then able to be modified to correct any syntax errors 10
11 Logical database 2.7 Schema maintenance Table maintenance 1. Can new tables be interactively added/deleted/modified to a schema 2. Can a column within a table be declared to be its primary key 3. Can one or more columns within a table be declared to be secondary keys 4. Can one or more table check clauses or procedures be added, deleted, or modified 11
CSC 443 Data Base Management Systems. Basic SQL
 CSC 443 Data Base Management Systems Lecture 6 SQL As A Data Definition Language Basic SQL SQL language Considered one of the major reasons for the commercial success of relational databases SQL Structured
CSC 443 Data Base Management Systems Lecture 6 SQL As A Data Definition Language Basic SQL SQL language Considered one of the major reasons for the commercial success of relational databases SQL Structured
Introduction to Databases
 Page 1 of 5 Introduction to Databases An introductory example What is a database? Why do we need Database Management Systems? The three levels of data abstraction What is a Database Management System?
Page 1 of 5 Introduction to Databases An introductory example What is a database? Why do we need Database Management Systems? The three levels of data abstraction What is a Database Management System?
How To Create A Table In Sql 2.5.2.2 (Ahem)
 Database Systems Unit 5 Database Implementation: SQL Data Definition Language Learning Goals In this unit you will learn how to transfer a logical data model into a physical database, how to extend or
Database Systems Unit 5 Database Implementation: SQL Data Definition Language Learning Goals In this unit you will learn how to transfer a logical data model into a physical database, how to extend or
Database Programming with PL/SQL: Learning Objectives
 Database Programming with PL/SQL: Learning Objectives This course covers PL/SQL, a procedural language extension to SQL. Through an innovative project-based approach, students learn procedural logic constructs
Database Programming with PL/SQL: Learning Objectives This course covers PL/SQL, a procedural language extension to SQL. Through an innovative project-based approach, students learn procedural logic constructs
CHAPTER 2 DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM AND SECURITY
 CHAPTER 2 DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM AND SECURITY 2.1 Introduction In this chapter, I am going to introduce Database Management Systems (DBMS) and the Structured Query Language (SQL), its syntax and usage.
CHAPTER 2 DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM AND SECURITY 2.1 Introduction In this chapter, I am going to introduce Database Management Systems (DBMS) and the Structured Query Language (SQL), its syntax and usage.
Introduction to Microsoft Jet SQL
 Introduction to Microsoft Jet SQL Microsoft Jet SQL is a relational database language based on the SQL 1989 standard of the American Standards Institute (ANSI). Microsoft Jet SQL contains two kinds of
Introduction to Microsoft Jet SQL Microsoft Jet SQL is a relational database language based on the SQL 1989 standard of the American Standards Institute (ANSI). Microsoft Jet SQL contains two kinds of
CS2Bh: Current Technologies. Introduction to XML and Relational Databases. The Relational Model. The relational model
 CS2Bh: Current Technologies Introduction to XML and Relational Databases Spring 2005 The Relational Model CS2 Spring 2005 (LN6) 1 The relational model Proposed by Codd in 1970. It is the dominant data
CS2Bh: Current Technologies Introduction to XML and Relational Databases Spring 2005 The Relational Model CS2 Spring 2005 (LN6) 1 The relational model Proposed by Codd in 1970. It is the dominant data
The Relational Model. Why Study the Relational Model? Relational Database: Definitions
 The Relational Model Database Management Systems, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Why Study the Relational Model? Most widely used model. Vendors: IBM, Microsoft, Oracle, Sybase, etc. Legacy systems in
The Relational Model Database Management Systems, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Why Study the Relational Model? Most widely used model. Vendors: IBM, Microsoft, Oracle, Sybase, etc. Legacy systems in
A. TRUE-FALSE: GROUP 2 PRACTICE EXAMPLES FOR THE REVIEW QUIZ:
 GROUP 2 PRACTICE EXAMPLES FOR THE REVIEW QUIZ: Review Quiz will contain very similar question as below. Some questions may even be repeated. The order of the questions are random and are not in order of
GROUP 2 PRACTICE EXAMPLES FOR THE REVIEW QUIZ: Review Quiz will contain very similar question as below. Some questions may even be repeated. The order of the questions are random and are not in order of
www.gr8ambitionz.com
 Data Base Management Systems (DBMS) Study Material (Objective Type questions with Answers) Shared by Akhil Arora Powered by www. your A to Z competitive exam guide Database Objective type questions Q.1
Data Base Management Systems (DBMS) Study Material (Objective Type questions with Answers) Shared by Akhil Arora Powered by www. your A to Z competitive exam guide Database Objective type questions Q.1
SQL Server An Overview
 SQL Server An Overview SQL Server Microsoft SQL Server is designed to work effectively in a number of environments: As a two-tier or multi-tier client/server database system As a desktop database system
SQL Server An Overview SQL Server Microsoft SQL Server is designed to work effectively in a number of environments: As a two-tier or multi-tier client/server database system As a desktop database system
Relational model. Relational model - practice. Relational Database Definitions 9/27/11. Relational model. Relational Database: Terminology
 COS 597A: Principles of Database and Information Systems elational model elational model A formal (mathematical) model to represent objects (data/information), relationships between objects Constraints
COS 597A: Principles of Database and Information Systems elational model elational model A formal (mathematical) model to represent objects (data/information), relationships between objects Constraints
Chapter 6: Physical Database Design and Performance. Database Development Process. Physical Design Process. Physical Database Design
 Chapter 6: Physical Database Design and Performance Modern Database Management 6 th Edition Jeffrey A. Hoffer, Mary B. Prescott, Fred R. McFadden Robert C. Nickerson ISYS 464 Spring 2003 Topic 23 Database
Chapter 6: Physical Database Design and Performance Modern Database Management 6 th Edition Jeffrey A. Hoffer, Mary B. Prescott, Fred R. McFadden Robert C. Nickerson ISYS 464 Spring 2003 Topic 23 Database
ICAB4136B Use structured query language to create database structures and manipulate data
 ICAB4136B Use structured query language to create database structures and manipulate data Release: 1 ICAB4136B Use structured query language to create database structures and manipulate data Modification
ICAB4136B Use structured query language to create database structures and manipulate data Release: 1 ICAB4136B Use structured query language to create database structures and manipulate data Modification
Fundamentals of Database Design
 Fundamentals of Database Design Zornitsa Zaharieva CERN Data Management Section - Controls Group Accelerators and Beams Department /AB-CO-DM/ 23-FEB-2005 Contents : Introduction to Databases : Main Database
Fundamentals of Database Design Zornitsa Zaharieva CERN Data Management Section - Controls Group Accelerators and Beams Department /AB-CO-DM/ 23-FEB-2005 Contents : Introduction to Databases : Main Database
Data Modeling. Database Systems: The Complete Book Ch. 4.1-4.5, 7.1-7.4
 Data Modeling Database Systems: The Complete Book Ch. 4.1-4.5, 7.1-7.4 Data Modeling Schema: The structure of the data Structured Data: Relational, XML-DTD, etc Unstructured Data: CSV, JSON But where does
Data Modeling Database Systems: The Complete Book Ch. 4.1-4.5, 7.1-7.4 Data Modeling Schema: The structure of the data Structured Data: Relational, XML-DTD, etc Unstructured Data: CSV, JSON But where does
Micro Focus Database Connectors
 data sheet Database Connectors Executive Overview Database Connectors are designed to bridge the worlds of COBOL and Structured Query Language (SQL). There are three Database Connector interfaces: Database
data sheet Database Connectors Executive Overview Database Connectors are designed to bridge the worlds of COBOL and Structured Query Language (SQL). There are three Database Connector interfaces: Database
SQL Server. 2012 for developers. murach's TRAINING & REFERENCE. Bryan Syverson. Mike Murach & Associates, Inc. Joel Murach
 TRAINING & REFERENCE murach's SQL Server 2012 for developers Bryan Syverson Joel Murach Mike Murach & Associates, Inc. 4340 N. Knoll Ave. Fresno, CA 93722 www.murach.com [email protected] Expanded
TRAINING & REFERENCE murach's SQL Server 2012 for developers Bryan Syverson Joel Murach Mike Murach & Associates, Inc. 4340 N. Knoll Ave. Fresno, CA 93722 www.murach.com [email protected] Expanded
4 Simple Database Features
 4 Simple Database Features Now we come to the largest use of iseries Navigator for programmers the Databases function. IBM is no longer developing DDS (Data Description Specifications) for database definition,
4 Simple Database Features Now we come to the largest use of iseries Navigator for programmers the Databases function. IBM is no longer developing DDS (Data Description Specifications) for database definition,
Database Query 1: SQL Basics
 Database Query 1: SQL Basics CIS 3730 Designing and Managing Data J.G. Zheng Fall 2010 1 Overview Using Structured Query Language (SQL) to get the data you want from relational databases Learning basic
Database Query 1: SQL Basics CIS 3730 Designing and Managing Data J.G. Zheng Fall 2010 1 Overview Using Structured Query Language (SQL) to get the data you want from relational databases Learning basic
The Relational Model. Why Study the Relational Model? Relational Database: Definitions. Chapter 3
 The Relational Model Chapter 3 Database Management Systems 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Why Study the Relational Model? Most widely used model. Vendors: IBM, Informix, Microsoft, Oracle, Sybase,
The Relational Model Chapter 3 Database Management Systems 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Why Study the Relational Model? Most widely used model. Vendors: IBM, Informix, Microsoft, Oracle, Sybase,
IT2305 Database Systems I (Compulsory)
 Database Systems I (Compulsory) INTRODUCTION This is one of the 4 modules designed for Semester 2 of Bachelor of Information Technology Degree program. CREDITS: 04 LEARNING OUTCOMES On completion of this
Database Systems I (Compulsory) INTRODUCTION This is one of the 4 modules designed for Semester 2 of Bachelor of Information Technology Degree program. CREDITS: 04 LEARNING OUTCOMES On completion of this
Instant SQL Programming
 Instant SQL Programming Joe Celko Wrox Press Ltd. INSTANT Table of Contents Introduction 1 What Can SQL Do for Me? 2 Who Should Use This Book? 2 How To Use This Book 3 What You Should Know 3 Conventions
Instant SQL Programming Joe Celko Wrox Press Ltd. INSTANT Table of Contents Introduction 1 What Can SQL Do for Me? 2 Who Should Use This Book? 2 How To Use This Book 3 What You Should Know 3 Conventions
SQL NULL s, Constraints, Triggers
 CS145 Lecture Notes #9 SQL NULL s, Constraints, Triggers Example schema: CREATE TABLE Student (SID INTEGER PRIMARY KEY, name CHAR(30), age INTEGER, GPA FLOAT); CREATE TABLE Take (SID INTEGER, CID CHAR(10),
CS145 Lecture Notes #9 SQL NULL s, Constraints, Triggers Example schema: CREATE TABLE Student (SID INTEGER PRIMARY KEY, name CHAR(30), age INTEGER, GPA FLOAT); CREATE TABLE Take (SID INTEGER, CID CHAR(10),
Lecture 6. SQL, Logical DB Design
 Lecture 6 SQL, Logical DB Design Relational Query Languages A major strength of the relational model: supports simple, powerful querying of data. Queries can be written intuitively, and the DBMS is responsible
Lecture 6 SQL, Logical DB Design Relational Query Languages A major strength of the relational model: supports simple, powerful querying of data. Queries can be written intuitively, and the DBMS is responsible
IT2304: Database Systems 1 (DBS 1)
 : Database Systems 1 (DBS 1) (Compulsory) 1. OUTLINE OF SYLLABUS Topic Minimum number of hours Introduction to DBMS 07 Relational Data Model 03 Data manipulation using Relational Algebra 06 Data manipulation
: Database Systems 1 (DBS 1) (Compulsory) 1. OUTLINE OF SYLLABUS Topic Minimum number of hours Introduction to DBMS 07 Relational Data Model 03 Data manipulation using Relational Algebra 06 Data manipulation
DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS. Question Bank:
 DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS Question Bank: UNIT 1 1. Define Database? 2. What is a DBMS? 3. What is the need for database systems? 4. Define tupule? 5. What are the responsibilities of DBA? 6. Define schema?
DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS Question Bank: UNIT 1 1. Define Database? 2. What is a DBMS? 3. What is the need for database systems? 4. Define tupule? 5. What are the responsibilities of DBA? 6. Define schema?
SQL Server. 1. What is RDBMS?
 SQL Server 1. What is RDBMS? Relational Data Base Management Systems (RDBMS) are database management systems that maintain data records and indices in tables. Relationships may be created and maintained
SQL Server 1. What is RDBMS? Relational Data Base Management Systems (RDBMS) are database management systems that maintain data records and indices in tables. Relationships may be created and maintained
Advance DBMS. Structured Query Language (SQL)
 Structured Query Language (SQL) Introduction Commercial database systems use more user friendly language to specify the queries. SQL is the most influential commercially marketed product language. Other
Structured Query Language (SQL) Introduction Commercial database systems use more user friendly language to specify the queries. SQL is the most influential commercially marketed product language. Other
Physical Design. Meeting the needs of the users is the gold standard against which we measure our success in creating a database.
 Physical Design Physical Database Design (Defined): Process of producing a description of the implementation of the database on secondary storage; it describes the base relations, file organizations, and
Physical Design Physical Database Design (Defined): Process of producing a description of the implementation of the database on secondary storage; it describes the base relations, file organizations, and
Introduction This document s purpose is to define Microsoft SQL server database design standards.
 Introduction This document s purpose is to define Microsoft SQL server database design standards. The database being developed or changed should be depicted in an ERD (Entity Relationship Diagram). The
Introduction This document s purpose is to define Microsoft SQL server database design standards. The database being developed or changed should be depicted in an ERD (Entity Relationship Diagram). The
Relational Databases
 Relational Databases Jan Chomicki University at Buffalo Jan Chomicki () Relational databases 1 / 18 Relational data model Domain domain: predefined set of atomic values: integers, strings,... every attribute
Relational Databases Jan Chomicki University at Buffalo Jan Chomicki () Relational databases 1 / 18 Relational data model Domain domain: predefined set of atomic values: integers, strings,... every attribute
BCA. Database Management System
 BCA IV Sem Database Management System Multiple choice questions 1. A Database Management System (DBMS) is A. Collection of interrelated data B. Collection of programs to access data C. Collection of data
BCA IV Sem Database Management System Multiple choice questions 1. A Database Management System (DBMS) is A. Collection of interrelated data B. Collection of programs to access data C. Collection of data
There are five fields or columns, with names and types as shown above.
 3 THE RELATIONAL MODEL Exercise 3.1 Define the following terms: relation schema, relational database schema, domain, attribute, attribute domain, relation instance, relation cardinality, andrelation degree.
3 THE RELATIONAL MODEL Exercise 3.1 Define the following terms: relation schema, relational database schema, domain, attribute, attribute domain, relation instance, relation cardinality, andrelation degree.
Triggers & Packages. {INSERT [OR] UPDATE [OR] DELETE}: This specifies the DML operation.
![Triggers & Packages. {INSERT [OR] UPDATE [OR] DELETE}: This specifies the DML operation. Triggers & Packages. {INSERT [OR] UPDATE [OR] DELETE}: This specifies the DML operation.](/thumbs/26/7800807.jpg) Triggers & Packages An SQL trigger is a mechanism that automatically executes a specified PL/SQL block (referred to as the triggered action) when a triggering event occurs on the table. The triggering
Triggers & Packages An SQL trigger is a mechanism that automatically executes a specified PL/SQL block (referred to as the triggered action) when a triggering event occurs on the table. The triggering
Databases What the Specification Says
 Databases What the Specification Says Describe flat files and relational databases, explaining the differences between them; Design a simple relational database to the third normal form (3NF), using entityrelationship
Databases What the Specification Says Describe flat files and relational databases, explaining the differences between them; Design a simple relational database to the third normal form (3NF), using entityrelationship
1 File Processing Systems
 COMP 378 Database Systems Notes for Chapter 1 of Database System Concepts Introduction A database management system (DBMS) is a collection of data and an integrated set of programs that access that data.
COMP 378 Database Systems Notes for Chapter 1 of Database System Concepts Introduction A database management system (DBMS) is a collection of data and an integrated set of programs that access that data.
The Relational Model. Ramakrishnan&Gehrke, Chapter 3 CS4320 1
 The Relational Model Ramakrishnan&Gehrke, Chapter 3 CS4320 1 Why Study the Relational Model? Most widely used model. Vendors: IBM, Informix, Microsoft, Oracle, Sybase, etc. Legacy systems in older models
The Relational Model Ramakrishnan&Gehrke, Chapter 3 CS4320 1 Why Study the Relational Model? Most widely used model. Vendors: IBM, Informix, Microsoft, Oracle, Sybase, etc. Legacy systems in older models
Embedded Systems. Review of ANSI C Topics. A Review of ANSI C and Considerations for Embedded C Programming. Basic features of C
 Embedded Systems A Review of ANSI C and Considerations for Embedded C Programming Dr. Jeff Jackson Lecture 2-1 Review of ANSI C Topics Basic features of C C fundamentals Basic data types Expressions Selection
Embedded Systems A Review of ANSI C and Considerations for Embedded C Programming Dr. Jeff Jackson Lecture 2-1 Review of ANSI C Topics Basic features of C C fundamentals Basic data types Expressions Selection
Databases and BigData
 Eduardo Cunha de Almeida [email protected] Outline of the course Introduction Database Systems (E. Almeida) Distributed Hash Tables and P2P (C. Cassagnes) NewSQL (D. Kim and J. Meira) NoSQL (D. Kim)
Eduardo Cunha de Almeida [email protected] Outline of the course Introduction Database Systems (E. Almeida) Distributed Hash Tables and P2P (C. Cassagnes) NewSQL (D. Kim and J. Meira) NoSQL (D. Kim)
COWLEY COLLEGE & Area Vocational Technical School
 COWLEY COLLEGE & Area Vocational Technical School COURSE PROCEDURE FOR COBOL PROGRAMMING CIS1866 3 Credit Hours Student Level: This course is open to students on the college level in either Freshman or
COWLEY COLLEGE & Area Vocational Technical School COURSE PROCEDURE FOR COBOL PROGRAMMING CIS1866 3 Credit Hours Student Level: This course is open to students on the college level in either Freshman or
A Brief Introduction to MySQL
 A Brief Introduction to MySQL by Derek Schuurman Introduction to Databases A database is a structured collection of logically related data. One common type of database is the relational database, a term
A Brief Introduction to MySQL by Derek Schuurman Introduction to Databases A database is a structured collection of logically related data. One common type of database is the relational database, a term
Data Modeling Basics
 Information Technology Standard Commonwealth of Pennsylvania Governor's Office of Administration/Office for Information Technology STD Number: STD-INF003B STD Title: Data Modeling Basics Issued by: Deputy
Information Technology Standard Commonwealth of Pennsylvania Governor's Office of Administration/Office for Information Technology STD Number: STD-INF003B STD Title: Data Modeling Basics Issued by: Deputy
INFORMATION BROCHURE Certificate Course in Web Design Using PHP/MySQL
 INFORMATION BROCHURE OF Certificate Course in Web Design Using PHP/MySQL National Institute of Electronics & Information Technology (An Autonomous Scientific Society of Department of Information Technology,
INFORMATION BROCHURE OF Certificate Course in Web Design Using PHP/MySQL National Institute of Electronics & Information Technology (An Autonomous Scientific Society of Department of Information Technology,
Enterprise Architectures
 Michael M. Gorman Whitemarsh Information Systems Corporation 2008 Althea Lane Bowie, Maryland 20716 Tele: 301-249-1142 Email: [email protected] Web: www.wiscorp.com 4 Enterprise s Architecture Chapter
Michael M. Gorman Whitemarsh Information Systems Corporation 2008 Althea Lane Bowie, Maryland 20716 Tele: 301-249-1142 Email: [email protected] Web: www.wiscorp.com 4 Enterprise s Architecture Chapter
3. Relational Model and Relational Algebra
 ECS-165A WQ 11 36 3. Relational Model and Relational Algebra Contents Fundamental Concepts of the Relational Model Integrity Constraints Translation ER schema Relational Database Schema Relational Algebra
ECS-165A WQ 11 36 3. Relational Model and Relational Algebra Contents Fundamental Concepts of the Relational Model Integrity Constraints Translation ER schema Relational Database Schema Relational Algebra
CA IDMS SQL. Programming Guide. Release 18.5.00
 CA IDMS SQL Programming Guide Release 18500 This Documentation, which includes embedded help systems and electronically distributed materials, (hereinafter referred to as the Documentation ) is for your
CA IDMS SQL Programming Guide Release 18500 This Documentation, which includes embedded help systems and electronically distributed materials, (hereinafter referred to as the Documentation ) is for your
Chapter 4. SQL Concepts & Facilities. Is SQL an End User Tool? AS/400 ANSI SQL Advanced Facilities
 Chapter 4 SQL Concepts & Facilities Is SQL an End User Tool? When you first look at SQL, each statement makes a lot of sense, and it would be reasonable to conclude that a sharp knowledge worker (end user)
Chapter 4 SQL Concepts & Facilities Is SQL an End User Tool? When you first look at SQL, each statement makes a lot of sense, and it would be reasonable to conclude that a sharp knowledge worker (end user)
Basic Concepts of Database Systems
 CS2501 Topic 1: Basic Concepts 1.1 Basic Concepts of Database Systems Example Uses of Database Systems - account maintenance & access in banking - lending library systems - airline reservation systems
CS2501 Topic 1: Basic Concepts 1.1 Basic Concepts of Database Systems Example Uses of Database Systems - account maintenance & access in banking - lending library systems - airline reservation systems
SQL Simple Queries. Chapter 3.1 V3.0. Copyright @ Napier University Dr Gordon Russell
 SQL Simple Queries Chapter 3.1 V3.0 Copyright @ Napier University Dr Gordon Russell Introduction SQL is the Structured Query Language It is used to interact with the DBMS SQL can Create Schemas in the
SQL Simple Queries Chapter 3.1 V3.0 Copyright @ Napier University Dr Gordon Russell Introduction SQL is the Structured Query Language It is used to interact with the DBMS SQL can Create Schemas in the
Database Migration from MySQL to RDM Server
 MIGRATION GUIDE Database Migration from MySQL to RDM Server A Birdstep Technology, Inc. Raima Embedded Database Division Migration Guide Published: May, 2009 Author: Daigoro F. Toyama Senior Software Engineer
MIGRATION GUIDE Database Migration from MySQL to RDM Server A Birdstep Technology, Inc. Raima Embedded Database Division Migration Guide Published: May, 2009 Author: Daigoro F. Toyama Senior Software Engineer
Oracle Database 10g: Introduction to SQL
 Oracle University Contact Us: 1.800.529.0165 Oracle Database 10g: Introduction to SQL Duration: 5 Days What you will learn This course offers students an introduction to Oracle Database 10g database technology.
Oracle University Contact Us: 1.800.529.0165 Oracle Database 10g: Introduction to SQL Duration: 5 Days What you will learn This course offers students an introduction to Oracle Database 10g database technology.
5. CHANGING STRUCTURE AND DATA
 Oracle For Beginners Page : 1 5. CHANGING STRUCTURE AND DATA Altering the structure of a table Dropping a table Manipulating data Transaction Locking Read Consistency Summary Exercises Altering the structure
Oracle For Beginners Page : 1 5. CHANGING STRUCTURE AND DATA Altering the structure of a table Dropping a table Manipulating data Transaction Locking Read Consistency Summary Exercises Altering the structure
Teradata Utilities Class Outline
 Teradata Utilities Class Outline CoffingDW education has been customized for every customer for the past 20 years. Our classes can be taught either on site or remotely via the internet. Education Contact:
Teradata Utilities Class Outline CoffingDW education has been customized for every customer for the past 20 years. Our classes can be taught either on site or remotely via the internet. Education Contact:
ATTACHMENT 6 SQL Server 2012 Programming Standards
 ATTACHMENT 6 SQL Server 2012 Programming Standards SQL Server Object Design and Programming Object Design and Programming Idaho Department of Lands Document Change/Revision Log Date Version Author Description
ATTACHMENT 6 SQL Server 2012 Programming Standards SQL Server Object Design and Programming Object Design and Programming Idaho Department of Lands Document Change/Revision Log Date Version Author Description
D61830GC30. MySQL for Developers. Summary. Introduction. Prerequisites. At Course completion After completing this course, students will be able to:
 D61830GC30 for Developers Summary Duration Vendor Audience 5 Days Oracle Database Administrators, Developers, Web Administrators Level Technology Professional Oracle 5.6 Delivery Method Instructor-led
D61830GC30 for Developers Summary Duration Vendor Audience 5 Days Oracle Database Administrators, Developers, Web Administrators Level Technology Professional Oracle 5.6 Delivery Method Instructor-led
Duration Vendor Audience 5 Days Oracle End Users, Developers, Technical Consultants and Support Staff
 D80198GC10 Oracle Database 12c SQL and Fundamentals Summary Duration Vendor Audience 5 Days Oracle End Users, Developers, Technical Consultants and Support Staff Level Professional Delivery Method Instructor-led
D80198GC10 Oracle Database 12c SQL and Fundamentals Summary Duration Vendor Audience 5 Days Oracle End Users, Developers, Technical Consultants and Support Staff Level Professional Delivery Method Instructor-led
Pseudo code Tutorial and Exercises Teacher s Version
 Pseudo code Tutorial and Exercises Teacher s Version Pseudo-code is an informal way to express the design of a computer program or an algorithm in 1.45. The aim is to get the idea quickly and also easy
Pseudo code Tutorial and Exercises Teacher s Version Pseudo-code is an informal way to express the design of a computer program or an algorithm in 1.45. The aim is to get the idea quickly and also easy
Study Notes for DB Design and Management Exam 1 (Chapters 1-2-3) record A collection of related (logically connected) fields.
 Study Notes for DB Design and Management Exam 1 (Chapters 1-2-3) Chapter 1 Glossary Table data Raw facts; that is, facts that have not yet been processed to reveal their meaning to the end user. field
Study Notes for DB Design and Management Exam 1 (Chapters 1-2-3) Chapter 1 Glossary Table data Raw facts; that is, facts that have not yet been processed to reveal their meaning to the end user. field
PART-A Questions. 2. How does an enumerated statement differ from a typedef statement?
 1. Distinguish & and && operators. PART-A Questions 2. How does an enumerated statement differ from a typedef statement? 3. What are the various members of a class? 4. Who can access the protected members
1. Distinguish & and && operators. PART-A Questions 2. How does an enumerated statement differ from a typedef statement? 3. What are the various members of a class? 4. Who can access the protected members
Oracle Database: Develop PL/SQL Program Units
 Oracle University Contact Us: 1.800.529.0165 Oracle Database: Develop PL/SQL Program Units Duration: 3 Days What you will learn This Oracle Database: Develop PL/SQL Program Units course is designed for
Oracle University Contact Us: 1.800.529.0165 Oracle Database: Develop PL/SQL Program Units Duration: 3 Days What you will learn This Oracle Database: Develop PL/SQL Program Units course is designed for
Conventional Files versus the Database. Files versus Database. Pros and Cons of Conventional Files. Pros and Cons of Databases. Fields (continued)
 Conventional Files versus the Database Files versus Database File a collection of similar records. Files are unrelated to each other except in the code of an application program. Data storage is built
Conventional Files versus the Database Files versus Database File a collection of similar records. Files are unrelated to each other except in the code of an application program. Data storage is built
KB_SQL SQL Reference Guide Version 4
 KB_SQL SQL Reference Guide Version 4 1995, 1999 by KB Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. KB Systems, Inc., Herndon, Virginia, USA. Printed in the United States of America. No part of this manual may be
KB_SQL SQL Reference Guide Version 4 1995, 1999 by KB Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. KB Systems, Inc., Herndon, Virginia, USA. Printed in the United States of America. No part of this manual may be
The Relational Model. Why Study the Relational Model?
 The Relational Model Chapter 3 Instructor: Vladimir Zadorozhny [email protected] Information Science Program School of Information Sciences, University of Pittsburgh 1 Why Study the Relational Model?
The Relational Model Chapter 3 Instructor: Vladimir Zadorozhny [email protected] Information Science Program School of Information Sciences, University of Pittsburgh 1 Why Study the Relational Model?
What is a database? COSC 304 Introduction to Database Systems. Database Introduction. Example Problem. Databases in the Real-World
 COSC 304 Introduction to Systems Introduction Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan [email protected] What is a database? A database is a collection of logically related data for
COSC 304 Introduction to Systems Introduction Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan [email protected] What is a database? A database is a collection of logically related data for
Demystified CONTENTS Acknowledgments xvii Introduction xix CHAPTER 1 Database Fundamentals CHAPTER 2 Exploring Relational Database Components
 Acknowledgments xvii Introduction xix CHAPTER 1 Database Fundamentals 1 Properties of a Database 1 The Database Management System (DBMS) 2 Layers of Data Abstraction 3 Physical Data Independence 5 Logical
Acknowledgments xvii Introduction xix CHAPTER 1 Database Fundamentals 1 Properties of a Database 1 The Database Management System (DBMS) 2 Layers of Data Abstraction 3 Physical Data Independence 5 Logical
Physical Database Design Process. Physical Database Design Process. Major Inputs to Physical Database. Components of Physical Database Design
 Physical Database Design Process Physical Database Design Process The last stage of the database design process. A process of mapping the logical database structure developed in previous stages into internal
Physical Database Design Process Physical Database Design Process The last stage of the database design process. A process of mapping the logical database structure developed in previous stages into internal
Oracle Database 10g: Program with PL/SQL
 Oracle University Contact Us: Local: 1800 425 8877 Intl: +91 80 4108 4700 Oracle Database 10g: Program with PL/SQL Duration: 5 Days What you will learn This course introduces students to PL/SQL and helps
Oracle University Contact Us: Local: 1800 425 8877 Intl: +91 80 4108 4700 Oracle Database 10g: Program with PL/SQL Duration: 5 Days What you will learn This course introduces students to PL/SQL and helps
Programming Database lectures for mathema
 Programming Database lectures for mathematics students April 25, 2015 Functions Functions are defined in Postgres with CREATE FUNCTION name(parameter type,...) RETURNS result-type AS $$ function-body $$
Programming Database lectures for mathematics students April 25, 2015 Functions Functions are defined in Postgres with CREATE FUNCTION name(parameter type,...) RETURNS result-type AS $$ function-body $$
2. Basic Relational Data Model
 2. Basic Relational Data Model 2.1 Introduction Basic concepts of information models, their realisation in databases comprising data objects and object relationships, and their management by DBMS s that
2. Basic Relational Data Model 2.1 Introduction Basic concepts of information models, their realisation in databases comprising data objects and object relationships, and their management by DBMS s that
More SQL: Assertions, Views, and Programming Techniques
 9 More SQL: Assertions, Views, and Programming Techniques In the previous chapter, we described several aspects of the SQL language, the standard for relational databases. We described the SQL statements
9 More SQL: Assertions, Views, and Programming Techniques In the previous chapter, we described several aspects of the SQL language, the standard for relational databases. We described the SQL statements
Files. Files. Files. Files. Files. File Organisation. What s it all about? What s in a file?
 Files What s it all about? Information being stored about anything important to the business/individual keeping the files. The simple concepts used in the operation of manual files are often a good guide
Files What s it all about? Information being stored about anything important to the business/individual keeping the files. The simple concepts used in the operation of manual files are often a good guide
VB.NET Programming Fundamentals
 Chapter 3 Objectives Programming Fundamentals In this chapter, you will: Learn about the programming language Write a module definition Use variables and data types Compute with Write decision-making statements
Chapter 3 Objectives Programming Fundamentals In this chapter, you will: Learn about the programming language Write a module definition Use variables and data types Compute with Write decision-making statements
B.1 Database Design and Definition
 Appendix B Database Design B.1 Database Design and Definition Throughout the SQL chapter we connected to and queried the IMDB database. This database was set up by IMDB and available for us to use. But
Appendix B Database Design B.1 Database Design and Definition Throughout the SQL chapter we connected to and queried the IMDB database. This database was set up by IMDB and available for us to use. But
Oracle Database 10g Express
 Oracle Database 10g Express This tutorial prepares the Oracle Database 10g Express Edition Developer to perform common development and administrative tasks of Oracle Database 10g Express Edition. Objectives
Oracle Database 10g Express This tutorial prepares the Oracle Database 10g Express Edition Developer to perform common development and administrative tasks of Oracle Database 10g Express Edition. Objectives
Information Technology NVEQ Level 2 Class X IT207-NQ2012-Database Development (Basic) Student s Handbook
 Students Handbook ... Accenture India s Corporate Citizenship Progra as well as access to their implementing partners (Dr. Reddy s Foundation supplement CBSE/ PSSCIVE s content. ren s life at Database
Students Handbook ... Accenture India s Corporate Citizenship Progra as well as access to their implementing partners (Dr. Reddy s Foundation supplement CBSE/ PSSCIVE s content. ren s life at Database
SQL DATA DEFINITION: KEY CONSTRAINTS. CS121: Introduction to Relational Database Systems Fall 2015 Lecture 7
 SQL DATA DEFINITION: KEY CONSTRAINTS CS121: Introduction to Relational Database Systems Fall 2015 Lecture 7 Data Definition 2 Covered most of SQL data manipulation operations Continue exploration of SQL
SQL DATA DEFINITION: KEY CONSTRAINTS CS121: Introduction to Relational Database Systems Fall 2015 Lecture 7 Data Definition 2 Covered most of SQL data manipulation operations Continue exploration of SQL
Table and field properties Tables and fields also have properties that you can set to control their characteristics or behavior.
 Create a table When you create a database, you store your data in tables subject-based lists that contain rows and columns. For instance, you can create a Contacts table to store a list of names, addresses,
Create a table When you create a database, you store your data in tables subject-based lists that contain rows and columns. For instance, you can create a Contacts table to store a list of names, addresses,
Creating Database Tables in Microsoft SQL Server
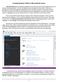 Creating Database Tables in Microsoft SQL Server Microsoft SQL Server is a relational database server that stores and retrieves data for multi-user network-based applications. SQL Server databases are
Creating Database Tables in Microsoft SQL Server Microsoft SQL Server is a relational database server that stores and retrieves data for multi-user network-based applications. SQL Server databases are
Utility Software II lab 1 Jacek Wiślicki, [email protected] original material by Hubert Kołodziejski
 MS ACCESS - INTRODUCTION MS Access is an example of a relational database. It allows to build and maintain small and medium-sized databases and to supply them with a graphical user interface. The aim of
MS ACCESS - INTRODUCTION MS Access is an example of a relational database. It allows to build and maintain small and medium-sized databases and to supply them with a graphical user interface. The aim of
Export of audit trail events from Salto software. Version 2.0
 Export of audit trail events from Salto software Version 2.0 Historic of changes Version Status Date Author Change description 1.0 Stable 20/12/2011 Mikel Larreategi First version of the specs. 2.0 Stable
Export of audit trail events from Salto software Version 2.0 Historic of changes Version Status Date Author Change description 1.0 Stable 20/12/2011 Mikel Larreategi First version of the specs. 2.0 Stable
A Basic introduction to Microsoft Access
 A Basic introduction to Microsoft Access By Ojango J.M.K Department of Animal Sciences, Egerton University, Njoro, Kenya and International Livestock Research Institute, Nairobi, Kenya Ms Access is a database
A Basic introduction to Microsoft Access By Ojango J.M.K Department of Animal Sciences, Egerton University, Njoro, Kenya and International Livestock Research Institute, Nairobi, Kenya Ms Access is a database
Guide to SQL Programming: SQL:1999 and Oracle Rdb V7.1
 Guide to SQL Programming: SQL:1999 and Oracle Rdb V7.1 A feature of Oracle Rdb By Ian Smith Oracle Rdb Relational Technology Group Oracle Corporation 1 Oracle Rdb Journal SQL:1999 and Oracle Rdb V7.1 The
Guide to SQL Programming: SQL:1999 and Oracle Rdb V7.1 A feature of Oracle Rdb By Ian Smith Oracle Rdb Relational Technology Group Oracle Corporation 1 Oracle Rdb Journal SQL:1999 and Oracle Rdb V7.1 The
WESTMORELAND COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS 2011 2012 Integrated Instructional Pacing Guide and Checklist Computer Math
 Textbook Correlation WESTMORELAND COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS 2011 2012 Integrated Instructional Pacing Guide and Checklist Computer Math Following Directions Unit FIRST QUARTER AND SECOND QUARTER Logic Unit
Textbook Correlation WESTMORELAND COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS 2011 2012 Integrated Instructional Pacing Guide and Checklist Computer Math Following Directions Unit FIRST QUARTER AND SECOND QUARTER Logic Unit
Oracle Database: SQL and PL/SQL Fundamentals
 Oracle University Contact Us: +966 12 739 894 Oracle Database: SQL and PL/SQL Fundamentals Duration: 5 Days What you will learn This Oracle Database: SQL and PL/SQL Fundamentals training is designed to
Oracle University Contact Us: +966 12 739 894 Oracle Database: SQL and PL/SQL Fundamentals Duration: 5 Days What you will learn This Oracle Database: SQL and PL/SQL Fundamentals training is designed to
DBF Chapter. Note to UNIX and OS/390 Users. Import/Export Facility CHAPTER 7
 97 CHAPTER 7 DBF Chapter Note to UNIX and OS/390 Users 97 Import/Export Facility 97 Understanding DBF Essentials 98 DBF Files 98 DBF File Naming Conventions 99 DBF File Data Types 99 ACCESS Procedure Data
97 CHAPTER 7 DBF Chapter Note to UNIX and OS/390 Users 97 Import/Export Facility 97 Understanding DBF Essentials 98 DBF Files 98 DBF File Naming Conventions 99 DBF File Data Types 99 ACCESS Procedure Data
5.1 Database Schema. 5.1.1 Schema Generation in SQL
 5.1 Database Schema The database schema is the complete model of the structure of the application domain (here: relational schema): relations names of attributes domains of attributes keys additional constraints
5.1 Database Schema The database schema is the complete model of the structure of the application domain (here: relational schema): relations names of attributes domains of attributes keys additional constraints
Chapter 6: Programming Languages
 Chapter 6: Programming Languages Computer Science: An Overview Eleventh Edition by J. Glenn Brookshear Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 6: Programming Languages 6.1 Historical Perspective
Chapter 6: Programming Languages Computer Science: An Overview Eleventh Edition by J. Glenn Brookshear Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 6: Programming Languages 6.1 Historical Perspective
When an exception occur a message which explains its cause is received. PL/SQL Exception message consists of three parts.
 ERROR HANDLING IN PLSQL When an SQL statement fails, the Oracle engine recognizes this as an Exception Condition. What is Exception Handling? PLSQL provides a feature to handle the Exceptions which occur
ERROR HANDLING IN PLSQL When an SQL statement fails, the Oracle engine recognizes this as an Exception Condition. What is Exception Handling? PLSQL provides a feature to handle the Exceptions which occur
1.204 Lecture 3. SQL: Basics, Joins SQL
 1.204 Lecture 3 SQL: Basics, Joins SQL Structured query language (SQL) used for Data definition (DDL): tables and views (virtual tables). These are the basic operations to convert a data model to a database
1.204 Lecture 3 SQL: Basics, Joins SQL Structured query language (SQL) used for Data definition (DDL): tables and views (virtual tables). These are the basic operations to convert a data model to a database
www.dotnetsparkles.wordpress.com
 Database Design Considerations Designing a database requires an understanding of both the business functions you want to model and the database concepts and features used to represent those business functions.
Database Design Considerations Designing a database requires an understanding of both the business functions you want to model and the database concepts and features used to represent those business functions.
MS Access Lab 2. Topic: Tables
 MS Access Lab 2 Topic: Tables Summary Introduction: Tables, Start to build a new database Creating Tables: Datasheet View, Design View Working with Data: Sorting, Filtering Help on Tables Introduction
MS Access Lab 2 Topic: Tables Summary Introduction: Tables, Start to build a new database Creating Tables: Datasheet View, Design View Working with Data: Sorting, Filtering Help on Tables Introduction
Managing Objects with Data Dictionary Views. Copyright 2006, Oracle. All rights reserved.
 Managing Objects with Data Dictionary Views Objectives After completing this lesson, you should be able to do the following: Use the data dictionary views to research data on your objects Query various
Managing Objects with Data Dictionary Views Objectives After completing this lesson, you should be able to do the following: Use the data dictionary views to research data on your objects Query various
Informatica e Sistemi in Tempo Reale
 Informatica e Sistemi in Tempo Reale Introduction to C programming Giuseppe Lipari http://retis.sssup.it/~lipari Scuola Superiore Sant Anna Pisa October 25, 2010 G. Lipari (Scuola Superiore Sant Anna)
Informatica e Sistemi in Tempo Reale Introduction to C programming Giuseppe Lipari http://retis.sssup.it/~lipari Scuola Superiore Sant Anna Pisa October 25, 2010 G. Lipari (Scuola Superiore Sant Anna)
Data Tool Platform SQL Development Tools
 Data Tool Platform SQL Development Tools ekapner Contents Setting SQL Development Preferences...5 Execution Plan View Options Preferences...5 General Preferences...5 Label Decorations Preferences...6
Data Tool Platform SQL Development Tools ekapner Contents Setting SQL Development Preferences...5 Execution Plan View Options Preferences...5 General Preferences...5 Label Decorations Preferences...6
Name: Class: Date: 9. The compiler ignores all comments they are there strictly for the convenience of anyone reading the program.
 Name: Class: Date: Exam #1 - Prep True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Programming is the process of writing a computer program in a language that the computer can respond to
Name: Class: Date: Exam #1 - Prep True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Programming is the process of writing a computer program in a language that the computer can respond to
Optimum Database Design: Using Normal Forms and Ensuring Data Integrity. by Patrick Crever, Relational Database Programmer, Synergex
 Optimum Database Design: Using Normal Forms and Ensuring Data Integrity by Patrick Crever, Relational Database Programmer, Synergex Printed: April 2007 The information contained in this document is subject
Optimum Database Design: Using Normal Forms and Ensuring Data Integrity by Patrick Crever, Relational Database Programmer, Synergex Printed: April 2007 The information contained in this document is subject
1. Relational database accesses data in a sequential form. (Figures 7.1, 7.2)
 Chapter 7 Data Structures for Computer Graphics (This chapter was written for programmers - option in lecture course) Any computer model of an Object must comprise three different types of entities: 1.
Chapter 7 Data Structures for Computer Graphics (This chapter was written for programmers - option in lecture course) Any computer model of an Object must comprise three different types of entities: 1.
Oracle Database: SQL and PL/SQL Fundamentals
 Oracle University Contact Us: 1.800.529.0165 Oracle Database: SQL and PL/SQL Fundamentals Duration: 5 Days What you will learn This course is designed to deliver the fundamentals of SQL and PL/SQL along
Oracle University Contact Us: 1.800.529.0165 Oracle Database: SQL and PL/SQL Fundamentals Duration: 5 Days What you will learn This course is designed to deliver the fundamentals of SQL and PL/SQL along
Guide to Performance and Tuning: Query Performance and Sampled Selectivity
 Guide to Performance and Tuning: Query Performance and Sampled Selectivity A feature of Oracle Rdb By Claude Proteau Oracle Rdb Relational Technology Group Oracle Corporation 1 Oracle Rdb Journal Sampled
Guide to Performance and Tuning: Query Performance and Sampled Selectivity A feature of Oracle Rdb By Claude Proteau Oracle Rdb Relational Technology Group Oracle Corporation 1 Oracle Rdb Journal Sampled
