Would a significant increase in the top income tax rate substantially alter income inequality?
|
|
|
- Douglas Holmes
- 3 years ago
- Views:
From this document you will learn the answers to the following questions:
What would happen if the tax rate was increased to 50 percent?
How many points are there in the simulation?
What is the implication of explicit redistribution of new revenue to households in the bottom 20 percent of the income distribution?
Transcription
1 September 2015 Would a significant increase in the top income tax rate substantially alter income inequality? William G. Gale, Melissa S. Kearney, and Peter R. Orszag Executive Summary The high level of income inequality in the United States is at the forefront of policy attention. This paper focuses on one potential policy response: an increase in the top personal income tax rate. We conduct a simulation analysis using the Tax Policy Center (TPC) microsimulation model to determine how much of a reduction in income inequality would be achieved from increasing the top individual tax rate to as much as 50 percent. We calculate the resulting change in income inequality assuming an explicit redistribution of all new revenue to households in the bottom 20 percent of the income distribution. The resulting effects on overall income inequality are exceedingly modest. That such a sizable increase in top income tax rates leads to such a limited reduction in income inequality speaks to the limitations of this particular approach to addressing the broader challenge. To be sure, our results do not speak to the general desirability of a more progressive tax-and-transfer schedule, just to the fact that even a significant tax increase on high-income households and corresponding transfer to low-income households has a small effect on overall inequality.
2 The high level of income inequality in the United States continues to receive substantial policy attention, for good reason. While there is general agreement that it is a challenge our nation should address, how to address it is much less clear. In this analysis, we examine the potential effects of one policy option: an increase in the top income marginal tax rate. We conduct a simulation analysis using the Tax Policy Center (TPC) microsimulation model to determine how much of a reduction in income inequality would be achieved simply by taxing high levels of personal income at a higher marginal rate, and redistributing the associated revenue to the lowest-income households. The results of this analysis lead to the conclusion that fairly substantial increases in the top income tax rate would have a relatively small effect on the distribution of after-tax income, even with explicit redistribution. A March 2015 analysis for The Hamilton Project written by one of us (Kearney), along with Brad Hershbein and Larry Summers, showed that a sizable increase in the share of men with a college degree would reduce inequality in the bottom half of the earnings distribution, largely by pulling up the earnings of those near the 25 th percentile. But that analysis also revealed that such an improvement in college attainment would not significantly reduce overall earnings inequality. The reason is that a large share of earnings inequality is at the top of the earnings distribution, and changing college shares will hardly affect those differences. That analysis prompts a follow-up question: if a reasonable expansion in educational attainment would not substantially reduce overall inequality, what would? An obvious candidate policy to consider is raising top income tax rates. We thus investigate whether a large increase in marginal tax rates at the top end of the income distribution would have a more notable effect on inequality than the increase in educational attainment previously analyzed. 1 1 To be sure, the policy conversation about income inequality should not be framed as a set of mutually exclusive solutions e.g., through changes in education versus changes in taxes and transfers. But clarifying how much any one policy lever could be expected to accomplish will help determine which combination of policy responses is likely to be most effective. It is with that goal in mind that we pursue this analysis. A Simulation Exercise We conduct a simulation exercise using the Tax Policy Center microsimulation model to examine how the distribution of post-tax income would change under three tax schedule scenarios 2 : 1. Raise the top individual income tax rate from 39.6 percent to 45 percent; 2. Raise the top individual income tax rate from 39.6 percent to 50 percent; or 3. Raise the top individual income tax rate to 50 percent for income greater than $1 million for joint filers and $750,000 for single filers. We restrict our attention to changes in the top marginal tax rate and do not consider other options, such as scaling back exemptions to expand the tax base or applying the highest income tax rate to households at lower levels of income. Our initial analysis does not adjust for any behavioral responses to the change in taxes (i.e., we assume households will earn the same pre-tax income regardless of the change in the top marginal income tax rate). In these results the only effect on household incomes and on the corresponding income distribution is the reduction of post-tax income by households subject to the higher tax rate. We subsequently model explicit redistribution of the new tax revenue and behavioral responses among highincome households. 3 2 TPC s microsimulation model uses the 2006 public-use file from the Internal Revenue Service s Statistics of Income (SOI) Division, which contains information from 145,858 income tax returns filed in The 2006 data are then transformed to represent the tax filing population in Pre-tax income is defined as expanded cash income, which is adjusted gross income (AGI) plus above-the-line adjustments, employer-paid health insurance and other nontaxable fringe benefits, employee and employer contributions to tax-deferred retirement savings plans, taxexempt interest, nontaxable Social Security benefits, nontaxable pension and retirement income, accruals within defined benefit pension plans, inside buildup within defined contribution retirement accounts, cash and cash-like transfer income, employer s share of payroll taxes, and imputed corporate income tax liability. Post-tax income is expanded cash income less federal individual income taxes net of refundable credits, corporate income taxes, payroll taxes, estate taxes, and excise taxes. State and local taxes are not considered. 3 In this essay our reference to households is technically a reference to tax filing units. 1
3 Increasing the top income tax rate from 39.6 to 45 percent would increase the income tax burden of households in the th percentiles of income (as defined before taxes are paid) by an average of $3,508. Households in the top 1 percent would see their income tax liability go up by $58,233 on average. And households in the top 0.1 percent would experience an average income tax increase of $297,582. A larger hike in the top income tax rate to 50 percent would result, not surprisingly, in larger tax increases for the highest income households: an additional $6,464, on average, for households in the th percentiles of income and an additional $110,968, on average, for households in the top 1 percent. Households in the top 0.1 percent would experience an average income tax increase of $568,617. How would these reductions in after-tax income affect overall income inequality? To answer that question, we calculate the Gini coefficient on the full distribution of post-tax income under the three different tax policy scenarios. (The Gini coefficient is an index that ranges from 0, if everyone had the same earnings, to 1, if a single person had all the earnings and everyone else had none.) Perhaps surprisingly, increasing the top marginal tax rate to 45 percent or 50 percent has a trivial effect on overall income inequality. This can be seen in Table 1 below. Under current tax provisions, the after-tax Gini coefficient is.574. This compares to a Gini of.610 calculated over pre-tax income. Raising the top income tax rate to 45 percent reduces the Gini coefficient only from.575 to.573. Raising it to 50 percent brings the Gini to.571. If the 50 percent top tax rate is applied to income only above $1 million for married filers and $750,000 for single filers, the resulting Gini is.572. By way of comparison, the Hershbein, Kearney, Summers education simulation analysis referred to above resulted in a.021 drop in the Gini coefficient for earnings inequality, from.568 to.547. That is only a small nudge toward the lower level of earnings inequality in 1979: a Gini of.435. In other words, increasing the top marginal income tax rate to 50 percent has the same, almost imperceptible, impact on overall inequality as does substantially increasing the share of the population receiving a college degree. 4 Table 1: simulated impacts of top tax rate increases on Gini coefficient Before tax income After tax income Current law After tax income Top rate to 45% After tax income Top rate to 50% After tax income Top rate to 50%, at $1M/$750K In the next set of calculations, we tabulate what would happen to income inequality under all three tax scenarios if all of the additional revenue collected were redistributed evenly to all households in the bottom 20 percent. Increasing the top rate to 45 percent would bring in an additional $49.4 billion in revenue. Dividing that evenly among the 36.1 million households in the bottom income quintile (defined over households) would give each of those households an additional $1,370 in post-tax income. Increasing the top rate to 50 percent with the same redistribution scheme would bring in an additional $95.6 billion in revenue, leading to an additional $2,650 in post-tax income for the bottom fifth of households. Applying a new top rate of 50 percent to income above $1 million for married filers and above $750,000 for single filers would bring in an additional $63.5 billion in revenue, which would result in $1,760 in additional post-tax income for households in the lowest quintile. The reduction in income inequality resulting from each of these tax and redistributive plans is quite modest. The Gini coefficient falls from.574 under the current income tax schedule to.567,.560, and.565 respectively. These are very small reductions in the calculated statistic:.007, 4 Note that the current analysis considers total tax-filing-unit income; the Hershbein, Kearney, and Summers simulation focused on individual earnings. 2
4 .015, and.010, under the three tax increase scenarios. Incorporating potential behavioral responses does not alter this general finding. 5 Essentially, adjusting for a reduction in taxable income among the highest-income households in response to a higher marginal tax rate leads to the same overall reduction in inequality. (The highest income households reduce their pre-tax income, which would amplify the reduction in income inequality, but that leaves less revenue to redistribute.) Under the three plans of a higher top rate with explicit redistribution and a behavioral response at the top end, the Gini coefficient falls from.575 to.569,.565, and.568, respectively. Table 2: simulated impacts of top tax rate increases with explicit redistribution on Gini coefficient Gini Before tax income After tax income - Current law After tax income - Top rate to 45% After tax income - Top rate to 50% After tax income - Top rate to 50%, at $1M/$750K We have also examined how income ratios change in response to these three tax proposals. The use of percentile ratios to measure income inequality has the advantage of being simple to calculate and understand. 6 Under the current income tax schedule, the ratio of household after-tax income at the 99 th percentile to the median is Increasing the top income tax rate to 45 percent reduces this to A raise in the top rate to 50 percent does not do much more, bringing the ratio to The 90/50 ratio is 3.51 under current tax policy. (The large difference in the 99/50 and 90/50 reflects the skewness in the income distribution.) Increasing the top income tax rate has no effect on the 90 th or 50 th percentile of the distribution, so this ratio is unchanged. As can be seen in Table 3, the simulated tax policy changes have a larger impact on the 99/10 and 90/10 ratios of income, since the assumed redistribution appreciably increases the after-tax income of those in the bottom 20 percent. Under the three scenarios, with the explicit redistribution, the 99/10 ratio falls from to 42.23, 37.06, and 40.53, respectively. The 90/10 ratio falls from to 14.23, 12.49, and 13.65, respectively. 7 It is important to note that these improved ratios reflect increases in income at the bottom of the income distribution, driven by an explicit targeted redistribution to low-income households. Without redistribution, there is no change at all in the 90/10 ratio. Conclusion In this analysis we have simulated the effects of increasing the top income tax rate under three possible reforms: (a) raise the top individual income tax rate from 39.6 to 45 percent; (2) raise the top individual income tax rate from 39.6 to 50 percent; and (3) raise the top individual income tax rate to 50 percent for income greater than $1 million for joint filers, $750,000 for single filers. We calculate the resulting change in income inequality under these scenarios assuming an explicit redistribution of all new revenue to households in the bottom 20 percent of the income distribution. The resulting effects on overall income inequality are exceedingly modest, with changes in the Gini coefficient of less than That such a sizable increase in the top personal income tax rate leads to a strikingly limited reduction in overall income inequality speaks to the limitations of this particular approach to addressing the broader challenge. It also reflects 5 We redo the simulation assuming that households with more than $100,000 in pre-tax income reduce their pre-tax income in response to an increase in the income tax rate, with an income elasticity of.4. 6 Under the current tax schedule, household after-tax income is $7,795 at the 10 th percentile, $37,147 at the 50 th, $130,440 at the 90 th, and $387,284 at the 99 th. The top 0.1 percent of households have after-tax income above $1.66 million. 7 By way of comparison, the Hershbein, Kearney, Summers simulation that considered a 10 percent increase in college attainment among high-school educated males had the effect of reducing the 90/25 earnings ratio from to
5 the fact that the high level of U.S. income inequality is characterized by a wide divergence in income between higher-income households and those at the middle and below. The top income tax rate only applies to households above the 95 th percentile of income. To be sure, there might be good reasons to increase top income tax rates for other purposes beyond reducing income inequality for example to raise much needed revenue for the federal government. In addition, the tax-andtransfer policies analyzed would provide substantial benefits to low-income households if the revenue were explicitly redistributed. Thus, Table 3: simulated impacts of top tax rate increases with explicit redistribution on income percentile ratios r99/50 r90/50 r99/10 r90/10 Before tax income After tax income - Current law After tax income - Top rate to 45% After tax income - Top rate to 50% After tax income - Top rate to 50%, at $1M/$750K our results do not speak to the desirability of the tax-and-transfer policy, just to the fact that even a significant tax increase on the highest-income households and transfer to low-income households has a small effect on overall inequality. This analysis, coupled with the previous one, in turn leaves us with the open and important question: if neither a substantial expansion in education nor a big increase in the top marginal tax rate would significantly affect measured income inequality, what would? *The authors are grateful to Jeff Rohaly and Aaron Krupkin at the Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center and Lucas Goodman at the University of Maryland for research assistance. 4
MEASURING INCOME FOR DISTRIBUTIONAL ANALYSIS. Joseph Rosenberg Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center July 25, 2013 ABSTRACT
 MEASURING INCOME FOR DISTRIBUTIONAL ANALYSIS Joseph Rosenberg Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center July 25, 2013 ABSTRACT This document describes the income measure the Tax Policy Center (TPC) uses to analyze
MEASURING INCOME FOR DISTRIBUTIONAL ANALYSIS Joseph Rosenberg Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center July 25, 2013 ABSTRACT This document describes the income measure the Tax Policy Center (TPC) uses to analyze
Why Some Tax Units Pay No Income Tax
 Why Some Tax Units Pay No Income Tax Rachel Johnson, James Nunns, Jeffrey Rohaly, Eric Toder, Roberton Williams Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center July 2011 ABSTRACT About 46 percent of American households
Why Some Tax Units Pay No Income Tax Rachel Johnson, James Nunns, Jeffrey Rohaly, Eric Toder, Roberton Williams Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center July 2011 ABSTRACT About 46 percent of American households
SPECIAL REPORT. tax notes. Automatic Enrollment in IRAs: Costs and Benefits. By Benjamin H. Harris and Rachel M. Johnson. I.
 Automatic Enrollment in IRAs: Costs and Benefits By Benjamin H. Harris and Rachel M. Johnson Benjamin H. Harris is a senior research associate at the Brookings Institution and is affiliated with the Urban-Brookings
Automatic Enrollment in IRAs: Costs and Benefits By Benjamin H. Harris and Rachel M. Johnson Benjamin H. Harris is a senior research associate at the Brookings Institution and is affiliated with the Urban-Brookings
budget brief On Tuesday, August 3, legislative leaders proposed a new budget plan, including a tax swap that would increase some
 UNDERSTANDING THE TAX SWAP budget brief AUGUST JUNE 2010 2005 On Tuesday, August 3, legislative leaders proposed a new budget plan, including a tax swap that would increase some of the state s personal
UNDERSTANDING THE TAX SWAP budget brief AUGUST JUNE 2010 2005 On Tuesday, August 3, legislative leaders proposed a new budget plan, including a tax swap that would increase some of the state s personal
Reducing the Deficit by Increasing Individual Income Tax Rates
 Reducing the Deficit by Increasing Individual Income Tax Rates Eric Toder, Jim Nunns, and Joseph Rosenberg March 2012 The authors are all affiliated with the Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center. Toder is
Reducing the Deficit by Increasing Individual Income Tax Rates Eric Toder, Jim Nunns, and Joseph Rosenberg March 2012 The authors are all affiliated with the Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center. Toder is
Research Report. Economic Effects of Automatic Enrollment in Individual Retirement Accounts. AARP Public Policy Institute. years
 AARP Public Policy Institute C E L E B R A T I N G years Economic Effects of Automatic Enrollment in Individual Retirement Accounts Benjamin H. Harris The Brookings Institution 1 Rachel M. Johnson The
AARP Public Policy Institute C E L E B R A T I N G years Economic Effects of Automatic Enrollment in Individual Retirement Accounts Benjamin H. Harris The Brookings Institution 1 Rachel M. Johnson The
OPTIONS TO REFORM THE DEDUCTION FOR HOME MORTGAGE INTEREST
 OPTIONS TO REFORM THE DEDUCTION FOR HOME MORTGAGE INTEREST Chenxi Lu, Joseph Rosenberg, and Eric Toder December 8, 2015 ABSTRACT Taxpayers can currently deduct interest on up to $1 million in acquisition
OPTIONS TO REFORM THE DEDUCTION FOR HOME MORTGAGE INTEREST Chenxi Lu, Joseph Rosenberg, and Eric Toder December 8, 2015 ABSTRACT Taxpayers can currently deduct interest on up to $1 million in acquisition
How Much Do Americans Pay in Federal Taxes? April 15, 2014
 How Much Do Americans Pay in Federal Taxes? April 15, 2014 One of the most hotly debated issues of our time is the fairness of our federal tax system. But too often, discussions are clouded and confused
How Much Do Americans Pay in Federal Taxes? April 15, 2014 One of the most hotly debated issues of our time is the fairness of our federal tax system. But too often, discussions are clouded and confused
Individual Retirement Accounts
 Distributional Effects of Defined Contribution Plans and Individual Retirement Accounts Leonard E. Burman William G. Gale Matthew Hall Peter R. Orszag Discussion Paper No. 16 August 2004 (revised) Leonard
Distributional Effects of Defined Contribution Plans and Individual Retirement Accounts Leonard E. Burman William G. Gale Matthew Hall Peter R. Orszag Discussion Paper No. 16 August 2004 (revised) Leonard
CONGRESS OF THE UNITED STATES CONGRESSIONAL BUDGET OFFICE CBO. The Distribution of Household Income and Federal Taxes, 2008 and 2009
 CONGRESS OF THE UNITED STATES CONGRESSIONAL BUDGET OFFICE Percent 70 The Distribution of Household Income and Federal Taxes, 2008 and 2009 60 50 Before-Tax Income Federal Taxes Top 1 Percent 40 30 20 81st
CONGRESS OF THE UNITED STATES CONGRESSIONAL BUDGET OFFICE Percent 70 The Distribution of Household Income and Federal Taxes, 2008 and 2009 60 50 Before-Tax Income Federal Taxes Top 1 Percent 40 30 20 81st
How Would Expanding Oregon s Deduction for Federal Income Taxes Paid Affect Elderly Oregonians? A Distributional Analysis of Ballot Measures 88 and 91
 Executive Summary 204 N. First St., Suite C PO Box 7 Silverton, OR 97381 www.ocpp.org 503-873-1201 fax 503-873-1947 October 16, 2000 How Would Expanding Oregon s Deduction for Federal Income Taxes Paid
Executive Summary 204 N. First St., Suite C PO Box 7 Silverton, OR 97381 www.ocpp.org 503-873-1201 fax 503-873-1947 October 16, 2000 How Would Expanding Oregon s Deduction for Federal Income Taxes Paid
Flattening Tax Incentives for Retirement Saving
 Flattening Tax Incentives for Retirement Saving BARBARA A. BUTRICA BENJAMIN H. HARRIS PAMELA PERUN C. EUGENE STEUERLE AN OPPORTUNITY AND OWNERSHIP INITIATIVE REPORT MAY 2014 Tax Policy Center Urban Institute
Flattening Tax Incentives for Retirement Saving BARBARA A. BUTRICA BENJAMIN H. HARRIS PAMELA PERUN C. EUGENE STEUERLE AN OPPORTUNITY AND OWNERSHIP INITIATIVE REPORT MAY 2014 Tax Policy Center Urban Institute
Options to Reform the Home Mortgage Interest Deduction
 Options to Reform the Home Mortgage Interest Deduction Eric J. Toder Institute Fellow, Urban Institute, and co-director, Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center www.taxpolicycenter.org Testimony Before the Committee
Options to Reform the Home Mortgage Interest Deduction Eric J. Toder Institute Fellow, Urban Institute, and co-director, Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center www.taxpolicycenter.org Testimony Before the Committee
Tax Subsidies for Private Health Insurance
 Tax Subsidies for Private Health Insurance Matthew Rae, Gary Claxton, Nirmita Panchal, Larry Levitt The federal and state tax systems provide significant financial benefits for people with private health
Tax Subsidies for Private Health Insurance Matthew Rae, Gary Claxton, Nirmita Panchal, Larry Levitt The federal and state tax systems provide significant financial benefits for people with private health
Tax Expenditures and Social Policy: A Primer
 Percent Tax Expenditures and Social Policy: A Primer Daniel Mandel What Are Tax Expenditures? Congress uses the tax code to promote a broad range of policy objectives. Rather than directly spend government
Percent Tax Expenditures and Social Policy: A Primer Daniel Mandel What Are Tax Expenditures? Congress uses the tax code to promote a broad range of policy objectives. Rather than directly spend government
After a severe slowdown in the early 1990s, General Fund
 Forecasting Revenue Receipts in the States Forecasting Revenue Receipts in the States: Current Challenges in California Abstract - General Fund revenue growth in California has been quite strong in recent
Forecasting Revenue Receipts in the States Forecasting Revenue Receipts in the States: Current Challenges in California Abstract - General Fund revenue growth in California has been quite strong in recent
INTERACTION OF AUTOMATIC IRAS AND THE RETIREMENT SAVINGS CONTRIBUTIONS CREDIT (SAVER S CREDIT)
 INTERACTION OF AUTOMATIC IRAS AND THE RETIREMENT SAVINGS CONTRIBUTIONS CREDIT (SAVER S CREDIT) A Report Prepared for AARP By: Optimal Benefit Strategies, LLC Judy Xanthopoulos, PhD Mary M. Schmitt, Esq.
INTERACTION OF AUTOMATIC IRAS AND THE RETIREMENT SAVINGS CONTRIBUTIONS CREDIT (SAVER S CREDIT) A Report Prepared for AARP By: Optimal Benefit Strategies, LLC Judy Xanthopoulos, PhD Mary M. Schmitt, Esq.
AN ANALYSIS OF DONALD TRUMP S TAX PLAN
 AN ANALYSIS OF DONALD TRUMP S TAX PLAN Jim Nunns, Len Burman, Jeff Rohaly, and Joe Rosenberg December 22, 2015 ABSTRACT This paper analyzes presidential candidate Donald Trump s tax proposal. His plan
AN ANALYSIS OF DONALD TRUMP S TAX PLAN Jim Nunns, Len Burman, Jeff Rohaly, and Joe Rosenberg December 22, 2015 ABSTRACT This paper analyzes presidential candidate Donald Trump s tax proposal. His plan
Executive Summary. 204 N. First St., Suite C PO Box 7 Silverton, OR 97381 www.ocpp.org 503-873-1201 fax 503-873-1947
 Executive Summary 204 N. First St., Suite C PO Box 7 Silverton, OR 97381 www.ocpp.org 503-873-1201 fax 503-873-1947 On Whose Backs? Tax Distribution, Income Inequality, and Plans for Raising Revenue By
Executive Summary 204 N. First St., Suite C PO Box 7 Silverton, OR 97381 www.ocpp.org 503-873-1201 fax 503-873-1947 On Whose Backs? Tax Distribution, Income Inequality, and Plans for Raising Revenue By
ADDING EMPLOYER CONTRIBUTIONS TO HEALTH INSURANCE TO SOCIAL SECURITY S EARNINGS AND TAX BASE. Karen E. Smith and Eric Toder
 ADDING EMPLOYER CONTRIBUTIONS TO HEALTH INSURANCE TO SOCIAL SECURITY S EARNINGS AND TAX BASE Karen E. Smith and Eric Toder CRR WP 2014-3 Submitted: January 2014 Released: April 2014 Center for Retirement
ADDING EMPLOYER CONTRIBUTIONS TO HEALTH INSURANCE TO SOCIAL SECURITY S EARNINGS AND TAX BASE Karen E. Smith and Eric Toder CRR WP 2014-3 Submitted: January 2014 Released: April 2014 Center for Retirement
INSIGHT on the Issues
 INSIGHT on the Issues The Saver s Credit: What Does It Do For Saving? AARP Public Policy Institute The saver s credit is one of very few tax incentives to promote savings that targets lowand middle-income
INSIGHT on the Issues The Saver s Credit: What Does It Do For Saving? AARP Public Policy Institute The saver s credit is one of very few tax incentives to promote savings that targets lowand middle-income
Reforming the Mortgage Interest Deduction. Eric Toder Margery Austin Turner Katherine Lim Liza Getsinger April 2010
 Reforming the Mortgage Interest Deduction Eric Toder Margery Austin Turner Katherine Lim Liza Getsinger April 2010 Reforming the Mortgage Interest Deduction TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION...1 Issues and
Reforming the Mortgage Interest Deduction Eric Toder Margery Austin Turner Katherine Lim Liza Getsinger April 2010 Reforming the Mortgage Interest Deduction TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION...1 Issues and
Under current tax law, health insurance premiums are largely taxexempt
 The Cost Of Tax-Exempt Health Benefits In 2004 Tax policies for health insurance will cost the federal government $188.5 billion in lost revenue in 2004, and most of the benefit goes to those with the
The Cost Of Tax-Exempt Health Benefits In 2004 Tax policies for health insurance will cost the federal government $188.5 billion in lost revenue in 2004, and most of the benefit goes to those with the
Making the Tax System Work for Low-Income Savers The Saver s Credit
 Tax Policy Issues and Options URBAN BROOKINGS TAX POLICY CENTER No. No. 13, 13, July July 2005 2005 Making the Tax System Work for Low-Income Savers The Saver s Credit William G. Gale, J. Mark Iwry, and
Tax Policy Issues and Options URBAN BROOKINGS TAX POLICY CENTER No. No. 13, 13, July July 2005 2005 Making the Tax System Work for Low-Income Savers The Saver s Credit William G. Gale, J. Mark Iwry, and
CBO STAFF DISTRIBUTIONAL EFFECTS OF SUBSTITUTING A FLAT-RATE INCOME TAX AND AVALUE-ADDEDTAXFORCURRENT FEDERAL INCOME, PAYROLL, AND EXCISE TAXES
 CBO STAFF MEMORANDUM DISTRIBUTIONAL EFFECTS OF SUBSTITUTING A FLAT-RATE INCOME TAX AND AVALUE-ADDEDTAXFORCURRENT FEDERAL INCOME, PAYROLL, AND EXCISE TAXES April 1992 CONGRESSIONAL BUDGET OFFICE SECOND
CBO STAFF MEMORANDUM DISTRIBUTIONAL EFFECTS OF SUBSTITUTING A FLAT-RATE INCOME TAX AND AVALUE-ADDEDTAXFORCURRENT FEDERAL INCOME, PAYROLL, AND EXCISE TAXES April 1992 CONGRESSIONAL BUDGET OFFICE SECOND
The 2001 and 2003 Tax Relief: The Benefit of Lower Tax Rates
 FISCAL Au 2008 No. 141 FACT The 2001 and 2003 Tax Relief: The Benefit of Lower Tax Rates By Robert Carroll Summary Recent research on President Bush's tax relief in 2001 and 2003 has found that the lower
FISCAL Au 2008 No. 141 FACT The 2001 and 2003 Tax Relief: The Benefit of Lower Tax Rates By Robert Carroll Summary Recent research on President Bush's tax relief in 2001 and 2003 has found that the lower
Governor Walker's Tax Reform Initiative. Wisconsin Department of Revenue February 2013
 Governor Walker's Tax Reform Initiative Wisconsin Department of Revenue February 2013 1 Tax Reform Goals Reduce Wisconsin's high tax burden Put more money in people's pockets Make Wisconsin more competitive
Governor Walker's Tax Reform Initiative Wisconsin Department of Revenue February 2013 1 Tax Reform Goals Reduce Wisconsin's high tax burden Put more money in people's pockets Make Wisconsin more competitive
The Tax (and Wage) Implications of Bernie Sanders s Medicare for All Health Plan
 The Tax (and Wage) Implications of Bernie Sanders s Medicare for All Health Plan Citizens for Tax Justice February 2016 The Tax (and Wage) Implications of Bernie Sanders s Medicare for All Health Plan
The Tax (and Wage) Implications of Bernie Sanders s Medicare for All Health Plan Citizens for Tax Justice February 2016 The Tax (and Wage) Implications of Bernie Sanders s Medicare for All Health Plan
AN UNWISE DEAL: WHY ELIMINATING THE INCOME LIMIT ON ROTH IRA S IS TOO STEEP A PRICE TO PAY FOR A REFUNDABLE SAVER S CREDIT
 820 First Street, NE, Suite 510, Washington, DC 20002 Tel: 202-408-1080 Fax: 202-408-1056 center@cbpp.org www.cbpp.org June 4, 2004 AN UNWISE DEAL: WHY ELIMINATING THE INCOME LIMIT ON ROTH IRA S IS TOO
820 First Street, NE, Suite 510, Washington, DC 20002 Tel: 202-408-1080 Fax: 202-408-1056 center@cbpp.org www.cbpp.org June 4, 2004 AN UNWISE DEAL: WHY ELIMINATING THE INCOME LIMIT ON ROTH IRA S IS TOO
Finance and Economics Discussion Series Divisions of Research & Statistics and Monetary Affairs Federal Reserve Board, Washington, D.C.
 Finance and Economics Discussion Series Divisions of Research & Statistics and Monetary Affairs Federal Reserve Board, Washington, D.C. Changes in the Distribution of After-Tax Wealth: Has Income Tax Policy
Finance and Economics Discussion Series Divisions of Research & Statistics and Monetary Affairs Federal Reserve Board, Washington, D.C. Changes in the Distribution of After-Tax Wealth: Has Income Tax Policy
President Bush s Health Care Tax Deduction Proposal: Coverage, Cost and Distributional Impacts. John Sheils and Randy Haught
 www.lewin.com President Bush s Health Care Tax Deduction Proposal: Coverage, Cost and Distributional Impacts John Sheils and Randy Haught President Bush proposes to replace the existing tax exemption for
www.lewin.com President Bush s Health Care Tax Deduction Proposal: Coverage, Cost and Distributional Impacts John Sheils and Randy Haught President Bush proposes to replace the existing tax exemption for
INCOME TAX REFORM. What Does It Mean for Taxpayers?
 BRIEFING PAPER INCOME TAX REFORM What Does It Mean for Taxpayers? Office of Legislative Research and General Counsel DECEMBER 2006 UTAH LEGISLATURE HIGHLIGHTS SB 4001, passed in the 2006 4th Special Session,
BRIEFING PAPER INCOME TAX REFORM What Does It Mean for Taxpayers? Office of Legislative Research and General Counsel DECEMBER 2006 UTAH LEGISLATURE HIGHLIGHTS SB 4001, passed in the 2006 4th Special Session,
United States General Accounting Office. Testimony Before the Committee on Finance, United States Senate
 GAO United States General Accounting Office Testimony Before the Committee on Finance, United States Senate For Release on Delivery Expected at 10:00 a.m. EST on Thursday March 8, 2001 ALTERNATIVE MINIMUM
GAO United States General Accounting Office Testimony Before the Committee on Finance, United States Senate For Release on Delivery Expected at 10:00 a.m. EST on Thursday March 8, 2001 ALTERNATIVE MINIMUM
The Minnesota and Federal Dependent Care Tax Credits
 INFORMATION BRIEF Research Department Minnesota House of Representatives 600 State Office Building St. Paul, MN 55155 Nina Manzi, Legislative Analyst 651-296-5204 Updated: February 2014 The Minnesota and
INFORMATION BRIEF Research Department Minnesota House of Representatives 600 State Office Building St. Paul, MN 55155 Nina Manzi, Legislative Analyst 651-296-5204 Updated: February 2014 The Minnesota and
New Estimates Of Personal Taxes In Consumer Expenditure Survey
 APRIL 2015 New Estimates Of Personal Taxes In Consumer Expenditure Survey Aaron E. Cobet The Consumer Expenditure Survey provides information on the buying habits of American consumers, their income, and
APRIL 2015 New Estimates Of Personal Taxes In Consumer Expenditure Survey Aaron E. Cobet The Consumer Expenditure Survey provides information on the buying habits of American consumers, their income, and
MICHIGAN EARNED INCOME TAX CREDIT Tax Year 2013
 MICHIGAN EARNED INCOME TAX CREDIT Office of Revenue and Tax Analysis Michigan Department of Treasury February 2015 MICHIGAN EARNED INCOME TAX CREDIT Office of Revenue and Tax Analysis Michigan Department
MICHIGAN EARNED INCOME TAX CREDIT Office of Revenue and Tax Analysis Michigan Department of Treasury February 2015 MICHIGAN EARNED INCOME TAX CREDIT Office of Revenue and Tax Analysis Michigan Department
The Saver s Credit: Issues and Options
 The Saver s Credit: Issues and Options William G. Gale, J. Mark Iwry, and Peter R. Orszag Retirement Security Project The Brookings Institution April 2004 William G. Gale is Arjay and Frances Fearing Miller
The Saver s Credit: Issues and Options William G. Gale, J. Mark Iwry, and Peter R. Orszag Retirement Security Project The Brookings Institution April 2004 William G. Gale is Arjay and Frances Fearing Miller
APPENDIX A The PSID Sample and Family Income
 1 APPENDIX A The PSID Sample and Family Income The sample for this analysis is 2,367 individuals who were between the ages of 0 and 18 in 1968 and have been tracked into adulthood through the Panel Study
1 APPENDIX A The PSID Sample and Family Income The sample for this analysis is 2,367 individuals who were between the ages of 0 and 18 in 1968 and have been tracked into adulthood through the Panel Study
Real Mean and Median Income, Families and Individuals, 1947-2012, and Households, 1967-2012 (Reported in $2012).
 Income Real Mean and Median Income, Families and Individuals, 1947-2012, and Households, 1967-2012 (Reported in $2012). $80,000 $60,000 Median Family Income Mean Family Income Median Household Income Mean
Income Real Mean and Median Income, Families and Individuals, 1947-2012, and Households, 1967-2012 (Reported in $2012). $80,000 $60,000 Median Family Income Mean Family Income Median Household Income Mean
Roth IRA Conversion... Does Taking Action Get You to Point A or Point B
 Roth IRA Conversion... Does Taking Action Get You to Point A or Point B If only it were that simple. There is no black and white here. Everything has its risks and is based on assumptions. Upfront, this
Roth IRA Conversion... Does Taking Action Get You to Point A or Point B If only it were that simple. There is no black and white here. Everything has its risks and is based on assumptions. Upfront, this
Tax Expenditures for Owner-Occupied Housing: Deductions for Property Taxes and Mortgage Interest and the Exclusion of Imputed Rental Income AUTHORS
 Tax Expenditures for Owner-Occupied Housing: Deductions for Property Taxes and Mortgage Interest and the Exclusion of Imputed Rental Income AUTHORS James Poterba (corresponding) Todd Sinai Department of
Tax Expenditures for Owner-Occupied Housing: Deductions for Property Taxes and Mortgage Interest and the Exclusion of Imputed Rental Income AUTHORS James Poterba (corresponding) Todd Sinai Department of
Five Flaws of the Current Pension System
 The Administration s Savings Accounts Proposals: A Critique Peter Orszag and Gene Sperling November 13, 2003 Five Flaws of the Current Pension System 1. Few People Participate in the Current System Limited
The Administration s Savings Accounts Proposals: A Critique Peter Orszag and Gene Sperling November 13, 2003 Five Flaws of the Current Pension System 1. Few People Participate in the Current System Limited
Tax Subsidies for Health Insurance An Issue Brief
 Tax Subsidies for Health Insurance An Issue Brief Prepared by the Kaiser Family Foundation July 2008 Tax Subsidies for Health Insurance Most workers pay both federal and state taxes for wages paid to them
Tax Subsidies for Health Insurance An Issue Brief Prepared by the Kaiser Family Foundation July 2008 Tax Subsidies for Health Insurance Most workers pay both federal and state taxes for wages paid to them
Average Federal Income Tax Rates for Median-Income Four-Person Families
 820 First Street, NE, Suite 510, Washington, DC 20002 Tel: 202-408-1080 Fax: 202-408-1056 center@cbpp.org http://www.cbpp.org April 10, 2002 OVERALL FEDERAL TAX BURDEN ON MOST FAMILIES INCLUDING MIDDLE-
820 First Street, NE, Suite 510, Washington, DC 20002 Tel: 202-408-1080 Fax: 202-408-1056 center@cbpp.org http://www.cbpp.org April 10, 2002 OVERALL FEDERAL TAX BURDEN ON MOST FAMILIES INCLUDING MIDDLE-
REVISITING THE STATE AND LOCAL TAX DEDUCTION
 REVISITING THE STATE AND LOCAL TAX DEDUCTION Frank Sammartino and Kim Rueben March 31, 2016 ABSTRACT Many federal tax reform proposals would eliminate the state and local tax (SALT) deduction. Although
REVISITING THE STATE AND LOCAL TAX DEDUCTION Frank Sammartino and Kim Rueben March 31, 2016 ABSTRACT Many federal tax reform proposals would eliminate the state and local tax (SALT) deduction. Although
Traditional and Roth Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs): A Primer
 Order Code RL34397 Traditional and Roth Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs): A Primer March 3, 2008 John J. Topoleski Analyst in Income Security Domestic Social Policy Division Traditional and Roth Individual
Order Code RL34397 Traditional and Roth Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs): A Primer March 3, 2008 John J. Topoleski Analyst in Income Security Domestic Social Policy Division Traditional and Roth Individual
Retirement Income Effects of Changing theincometaxtreatmentofdc Pension Plans
 Retirement Income Effects of Changing theincometaxtreatmentofdc Pension Plans Martin Holmer, Policy Simulation Group May 14, 2012 Abstract This paper presents estimates of the after-tax retirement income
Retirement Income Effects of Changing theincometaxtreatmentofdc Pension Plans Martin Holmer, Policy Simulation Group May 14, 2012 Abstract This paper presents estimates of the after-tax retirement income
Create a Simple, Pro-Growth Tax System 5
 Create a Simple, Pro-Growth Tax System 5 Introduction Reducing the federal debt to sustainable levels will require the tax system to raise more money as a share of the economy than it historically has
Create a Simple, Pro-Growth Tax System 5 Introduction Reducing the federal debt to sustainable levels will require the tax system to raise more money as a share of the economy than it historically has
Article: Main results from the Wealth and Assets Survey: July 2012 to June 2014
 Article: Main results from the Wealth and Assets Survey: July 2012 to June 2014 Coverage: GB Date: 18 December 2015 Geographical Area: Region Theme: Economy Main points In July 2012 to June 2014: aggregate
Article: Main results from the Wealth and Assets Survey: July 2012 to June 2014 Coverage: GB Date: 18 December 2015 Geographical Area: Region Theme: Economy Main points In July 2012 to June 2014: aggregate
income inequality The takeoff in income inequality over the By Jeffrey Thompson and Timothy Smeeding January 2014
 national report card 30 income inequality income inequality January 2014 The Stanford Center on Poverty and Inequality By Jeffrey Thompson and Timothy Smeeding Key findings The Great Recession had a mixed
national report card 30 income inequality income inequality January 2014 The Stanford Center on Poverty and Inequality By Jeffrey Thompson and Timothy Smeeding Key findings The Great Recession had a mixed
Proposal 11: Building on the Success of the Earned Income Tax Credit
 Proposal 11: Building on the Success of the Earned Income Tax Credit Hilary Hoynes University of California, Berkeley Introduction The Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) provides a refundable tax credit to
Proposal 11: Building on the Success of the Earned Income Tax Credit Hilary Hoynes University of California, Berkeley Introduction The Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) provides a refundable tax credit to
Is A Roth 401(k) Right For You?
 Is A Roth 401(k) Right For You? A Decision Guide For Plan Participants Standard Retirement Services, Inc. The Roth 401(k) And Your Retirement Plan Should I Or Shouldn t I? We probably ask ourselves some
Is A Roth 401(k) Right For You? A Decision Guide For Plan Participants Standard Retirement Services, Inc. The Roth 401(k) And Your Retirement Plan Should I Or Shouldn t I? We probably ask ourselves some
The U.S. Tax Reform Experience 1
 The U.S. Tax Reform Experience 1 Alan J. Auerbach University of California, Berkeley The Tax Reform Act of 1986 (TRA86) represented the most sweeping change in the U.S. federal income tax since World War
The U.S. Tax Reform Experience 1 Alan J. Auerbach University of California, Berkeley The Tax Reform Act of 1986 (TRA86) represented the most sweeping change in the U.S. federal income tax since World War
Retirement. A Guide to Roth IRAs
 Retirement A Guide to Roth IRAs A Roth IRA is an individual retirement account named for the late Senate Finance Committee Chairman, William Roth, Jr. who championed the creation of this new type of IRA.
Retirement A Guide to Roth IRAs A Roth IRA is an individual retirement account named for the late Senate Finance Committee Chairman, William Roth, Jr. who championed the creation of this new type of IRA.
INDIVIDUALS -- 2000 DEPARTMENT OF TAXATION -- STATE OF HAWAII
 hawaii income patterns INDIVIDUALS -- 2000 DEPARTMENT OF TAXATION -- STATE OF HAWAII STATE OF HAWAII Benjamin J. Cayetano, Governor DEPARTMENT OF TAXATION Marie Y. Okamura, Director Grant B. Tanimoto,
hawaii income patterns INDIVIDUALS -- 2000 DEPARTMENT OF TAXATION -- STATE OF HAWAII STATE OF HAWAII Benjamin J. Cayetano, Governor DEPARTMENT OF TAXATION Marie Y. Okamura, Director Grant B. Tanimoto,
How To Know If A Health Insurance Tax Is Progressive
 Citizens for Tax Justice December 11, 2009 Would the Senate Democrats proposed excise tax on highcost employer-paid health insurance benefits be progressive? Summary Senate Democrats have proposed a new,
Citizens for Tax Justice December 11, 2009 Would the Senate Democrats proposed excise tax on highcost employer-paid health insurance benefits be progressive? Summary Senate Democrats have proposed a new,
Hawaii Individual Income Tax Statistics
 Hawaii Individual Income Tax Statistics Tax Year 2012 Department of Taxation State of Hawaii Hawaii Individual Income Tax Statistics Tax Year 2012 Department of Taxation State of Hawaii November 2014 Prepared
Hawaii Individual Income Tax Statistics Tax Year 2012 Department of Taxation State of Hawaii Hawaii Individual Income Tax Statistics Tax Year 2012 Department of Taxation State of Hawaii November 2014 Prepared
MEMO. Comparing Traditional and Roth IRAs. Connecticut Retirement Security Board. Mercer Traditional vs. Roth IRA. contributions.
 1166 Avenue of the Americas New York, NY 10036 www.mercer.com MEMO TO: DATE: FROM: SUBJECT: Mercer Traditional vs. Roth IRA Introduction The legislation anticipates that the Retirement Security Program
1166 Avenue of the Americas New York, NY 10036 www.mercer.com MEMO TO: DATE: FROM: SUBJECT: Mercer Traditional vs. Roth IRA Introduction The legislation anticipates that the Retirement Security Program
An updated method for calculating income and payroll taxes from PSID data using the NBERʼs TAXSIM, for PSID survey years 1999 through 2011
 An updated method for calculating income and payroll taxes from PSID data using the NBERʼs TAXSIM, for PSID survey years 1999 through 2011 Sara Kimberlin, Jiyoun Kim, & Luke Shaefer December 2014 Overview
An updated method for calculating income and payroll taxes from PSID data using the NBERʼs TAXSIM, for PSID survey years 1999 through 2011 Sara Kimberlin, Jiyoun Kim, & Luke Shaefer December 2014 Overview
How do the 2016 Presidential Tax Plans Compare So Far?
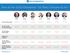 How do the 2016 Presidential Tax Plans Compare So Far? 10-Year GDP Growth 10.0% 16.0% -1.0% 13.9% 15.0% -9.5% 11.5% 10-Year Capital Investment Growth 28.8% 46.6% -2.8% 43.9% 48.9% -18.6% 29% 10-Year Wage
How do the 2016 Presidential Tax Plans Compare So Far? 10-Year GDP Growth 10.0% 16.0% -1.0% 13.9% 15.0% -9.5% 11.5% 10-Year Capital Investment Growth 28.8% 46.6% -2.8% 43.9% 48.9% -18.6% 29% 10-Year Wage
DO INCOME TAXES AFFECT THE PROGRESSIVITY OF SOCIAL SECURITY?
 January 2012, Number 12-3 RETIREMENT RESEARCH DO INCOME TAXES AFFECT THE PROGRESSIVITY OF SOCIAL SECURITY? By Norma B. Coe, Zhenya Karamcheva, Richard Kopcke, and Alicia H. Munnell* Introduction Policymakers
January 2012, Number 12-3 RETIREMENT RESEARCH DO INCOME TAXES AFFECT THE PROGRESSIVITY OF SOCIAL SECURITY? By Norma B. Coe, Zhenya Karamcheva, Richard Kopcke, and Alicia H. Munnell* Introduction Policymakers
Taxes and Income: Where Does Kentucky Stand?
 Taxes and Income: Where Does Stand? William H. Hoyt Much recent debate has focused on the substantial tax burden on lower-income households in relative to other states and relative to higher-income households
Taxes and Income: Where Does Stand? William H. Hoyt Much recent debate has focused on the substantial tax burden on lower-income households in relative to other states and relative to higher-income households
INDIVIDUAL TAX STRATEGIES
 BY SCOTT HENSLEY SHENSLEY@STANCILCPA.COM DECEMBER 4, 2014 STANCIL & COMPANY CERTIFIED PUBLIC ACCOUNTANTS 4909 WINDY HILL DRIVE RALEIGH, NC 27609 919-872-1260 TOPICS TO BE COVERED TODAY WHAT IS TAX PLANNING
BY SCOTT HENSLEY SHENSLEY@STANCILCPA.COM DECEMBER 4, 2014 STANCIL & COMPANY CERTIFIED PUBLIC ACCOUNTANTS 4909 WINDY HILL DRIVE RALEIGH, NC 27609 919-872-1260 TOPICS TO BE COVERED TODAY WHAT IS TAX PLANNING
The primary purpose of a tax system is to support public goods and services. State and local taxes
 Issue Brief UPDATED APRIL 2015 BY WILLIAM CHEN Who Pays Taxes in California? The primary purpose of a tax system is to support public goods and services. State and local taxes are the way that Californians
Issue Brief UPDATED APRIL 2015 BY WILLIAM CHEN Who Pays Taxes in California? The primary purpose of a tax system is to support public goods and services. State and local taxes are the way that Californians
Tax Facts Quick Reference 2012
 Wealth Management Services Tax Facts Quick Reference 2012 Income Investment Estate Retirement Social Security FOR USE BY FINANCIAL ADVISORS AND CLIENTS IN CONSULTATION WITH THEIR FINANCIAL ADVISOR FOR
Wealth Management Services Tax Facts Quick Reference 2012 Income Investment Estate Retirement Social Security FOR USE BY FINANCIAL ADVISORS AND CLIENTS IN CONSULTATION WITH THEIR FINANCIAL ADVISOR FOR
2015 Individual Tax Planning Letter
 2015 Individual Tax Planning Letter Just as the daylight hours are getting shorter, so is the time for fine tuning any last-minute strategies to lower your 2015 tax bill. While year-end legislation extending
2015 Individual Tax Planning Letter Just as the daylight hours are getting shorter, so is the time for fine tuning any last-minute strategies to lower your 2015 tax bill. While year-end legislation extending
Children s Savings Accounts: Why Design Matters
 11194-01_Cover.qxd:11194-01_Cover.qxd 5/21/08 5:08 PM Page C1 THE URBAN INSTITUTE Children s Savings Accounts: Why Design Matters Barbara A. Butrica Adam Carasso C. Eugene Steuerle Desmond J. Toohey Opportunity
11194-01_Cover.qxd:11194-01_Cover.qxd 5/21/08 5:08 PM Page C1 THE URBAN INSTITUTE Children s Savings Accounts: Why Design Matters Barbara A. Butrica Adam Carasso C. Eugene Steuerle Desmond J. Toohey Opportunity
EXECUTIVE CHANGE IN CONTROL REPORT 2013 / 2014
 EXECUTIVE CHANGE IN CONTROL REPORT 2013 / 2014 ANALYSIS OF EXECUTIVE CHANGE IN CONTROL ARRANGEMENTS OF THE TOP 200 COMPANIES Prepared By The Compensation and Benefits Practice of Alvarez & Marsal Taxand,
EXECUTIVE CHANGE IN CONTROL REPORT 2013 / 2014 ANALYSIS OF EXECUTIVE CHANGE IN CONTROL ARRANGEMENTS OF THE TOP 200 COMPANIES Prepared By The Compensation and Benefits Practice of Alvarez & Marsal Taxand,
Personal Income Tax Bulletin 2008-1. IRAs
 PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF REVENUE ISSUED: JANUARY 16, 2008 Section 1. Introduction. 1. FEDERAL TAX PERSPECTIVE. Personal Income Tax Bulletin 2008-1 IRAs When Congress enacted ERISA in 1974 to regulate
PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF REVENUE ISSUED: JANUARY 16, 2008 Section 1. Introduction. 1. FEDERAL TAX PERSPECTIVE. Personal Income Tax Bulletin 2008-1 IRAs When Congress enacted ERISA in 1974 to regulate
LIQUIDATING RETIREMENT ASSETS
 LIQUIDATING RETIREMENT ASSETS IN A TAX-EFFICIENT MANNER By William A. Raabe and Richard B. Toolson When you enter retirement, you retire from work, not from decision-making. Among the more important decisions
LIQUIDATING RETIREMENT ASSETS IN A TAX-EFFICIENT MANNER By William A. Raabe and Richard B. Toolson When you enter retirement, you retire from work, not from decision-making. Among the more important decisions
The Wealth of Households: An Analysis of the 2013 Survey of Consumer Finances
 November 214 The Wealth of Households: An Analysis of the 213 Survey of Consumer Finances By David Rosnick and Dean Baker* Center for Economic and Policy Research 1611 Connecticut Ave. NW Suite 4 Washington,
November 214 The Wealth of Households: An Analysis of the 213 Survey of Consumer Finances By David Rosnick and Dean Baker* Center for Economic and Policy Research 1611 Connecticut Ave. NW Suite 4 Washington,
ENTITY CHOICE AND EFFECTIVE TAX RATES
 ENTITY CHOICE AND EFFECTIVE TAX RATES Prepared by Quantria Strategies, LLC for the National Federation of Independent Business and the S Corporation Association ENTITY CHOICE AND EFFECTIVE TAX RATES CONTENTS
ENTITY CHOICE AND EFFECTIVE TAX RATES Prepared by Quantria Strategies, LLC for the National Federation of Independent Business and the S Corporation Association ENTITY CHOICE AND EFFECTIVE TAX RATES CONTENTS
CRS Report for Congress
 Order Code RL32554 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web An Overview of Tax Benefits for Higher Education Expenses Updated January 17, 2006 Pamela J. Jackson Analyst in Public Sector Economics
Order Code RL32554 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web An Overview of Tax Benefits for Higher Education Expenses Updated January 17, 2006 Pamela J. Jackson Analyst in Public Sector Economics
Providing Federal Assistance for Low-Income Families through the Tax System: A Primer
 Providing Federal Assistance for Low-Income Families through the Tax System: A Primer Frank Sammartino Eric Toder Elaine Maag Discussion Paper No. 4 July 2002 Frank Sammartino is a principal economist
Providing Federal Assistance for Low-Income Families through the Tax System: A Primer Frank Sammartino Eric Toder Elaine Maag Discussion Paper No. 4 July 2002 Frank Sammartino is a principal economist
Details and Analysis of Senator Bernie Sanders s Tax Plan
 FISCAL FACT Jan. 2016 No. 498 Details and Analysis of Senator Bernie Sanders s Tax Plan By Alan Cole and Scott Greenberg Economist Analyst Key Findings: Senator Sanders (I-VT) would enact a number of policies
FISCAL FACT Jan. 2016 No. 498 Details and Analysis of Senator Bernie Sanders s Tax Plan By Alan Cole and Scott Greenberg Economist Analyst Key Findings: Senator Sanders (I-VT) would enact a number of policies
Volume Title: Tax Policy and the Economy, Volume 15. Volume Author/Editor: James M. Poterba, editor. Volume URL: http://www.nber.
 This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from the National Bureau of Economic Research Volume Title: Tax Policy and the Economy, Volume 15 Volume Author/Editor: James M. Poterba, editor Volume
This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from the National Bureau of Economic Research Volume Title: Tax Policy and the Economy, Volume 15 Volume Author/Editor: James M. Poterba, editor Volume
*Brackets adjusted for inflation in future years. 2015 Long Term Capital Gains & Dividends Taxable income up to $413,200/$457,600 0% - 15%*
 Income Tax Planning Overview The American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012 extended prior law for certain income tax rates; however, it also increased income tax rates on upper income earners. Specifically,
Income Tax Planning Overview The American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012 extended prior law for certain income tax rates; however, it also increased income tax rates on upper income earners. Specifically,
IRAs Traditional Individual Retirement Accounts. 2008 and 2009. Questions & Answers
 IRAs Traditional Individual Retirement Accounts 2008 and 2009 Questions & Answers What is the purpose of this brochure? It summarizes the primary laws which govern traditional IRAs for 2008 and 2009. What
IRAs Traditional Individual Retirement Accounts 2008 and 2009 Questions & Answers What is the purpose of this brochure? It summarizes the primary laws which govern traditional IRAs for 2008 and 2009. What
Impact on households: distributional analysis to accompany Spending Review and Autumn Statement 2015
 Impact on households: distributional analysis to accompany Spending Review and Autumn Statement 2015 November 2015 Impact on households: distributional analysis to accompany Spending Review and Autumn
Impact on households: distributional analysis to accompany Spending Review and Autumn Statement 2015 November 2015 Impact on households: distributional analysis to accompany Spending Review and Autumn
Over the last 40 years, the U.S. federal tax system has undergone three
 Journal of Economic Perspectives Volume 21, Number 1 Winter 2007 Pages 3 24 How Progressive is the U.S. Federal Tax System? A Historical and International Perspective Thomas Piketty and Emmanuel Saez Over
Journal of Economic Perspectives Volume 21, Number 1 Winter 2007 Pages 3 24 How Progressive is the U.S. Federal Tax System? A Historical and International Perspective Thomas Piketty and Emmanuel Saez Over
THE Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) annually
 35 Comparison of BEA Estimates of Income and IRS Estimates of Adjusted Gross Income New Estimates for 2005 Revised Estimates for 2004 By Mark Ledbetter THE Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) annually publishes
35 Comparison of BEA Estimates of Income and IRS Estimates of Adjusted Gross Income New Estimates for 2005 Revised Estimates for 2004 By Mark Ledbetter THE Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) annually publishes
The Consequences of Increasing Oregon s Income Tax Deduction for Federal Income Taxes Paid
 Oregon Center for Public Policy 204 North First Street, Suite C P.O. Box 7, Silverton, OR 97381-0007 Telephone: 503.873.1201 Facsimile: 503.873.1947 e-mail: info@ocpp.org www.ocpp.org The Consequences
Oregon Center for Public Policy 204 North First Street, Suite C P.O. Box 7, Silverton, OR 97381-0007 Telephone: 503.873.1201 Facsimile: 503.873.1947 e-mail: info@ocpp.org www.ocpp.org The Consequences
Simplify and Focus the Education Tax Incentives. June, 2006
 Simplify and Focus the Education Tax Incentives June, 2006 Susan Dynarski, Harvard University & National Bureau of Economic Research Judith Scott Clayton, Harvard University A college education is a good
Simplify and Focus the Education Tax Incentives June, 2006 Susan Dynarski, Harvard University & National Bureau of Economic Research Judith Scott Clayton, Harvard University A college education is a good
THE MAGNITUDE AND CAUSES OF ARIZONA S LOW PER CAPITA INCOME
 THE MAGNITUDE AND CAUSES OF ARIZONA S LOW PER CAPITA INCOME February 2010 Dennis Hoffman, Ph.D. Professor, Department of Economics; Director, L. William Seidman Research Institute; and Director, Office
THE MAGNITUDE AND CAUSES OF ARIZONA S LOW PER CAPITA INCOME February 2010 Dennis Hoffman, Ph.D. Professor, Department of Economics; Director, L. William Seidman Research Institute; and Director, Office
Income Tax Liabilities Statistics 2012-13 to 2014-15
 Coverage: United Kingdom Theme: The Economy Released: 13 February 2015 Next Release: May 2015 Frequency of release: Twice yearly (Jan/Feb and Apr/May) Income Tax Liabilities Statistics 2012-13 to 2014-15
Coverage: United Kingdom Theme: The Economy Released: 13 February 2015 Next Release: May 2015 Frequency of release: Twice yearly (Jan/Feb and Apr/May) Income Tax Liabilities Statistics 2012-13 to 2014-15
HOW TO MAKE CHARITABLE GIFTS FROM YOUR IRA DONOR S GUIDE
 HOW TO MAKE CHARITABLE GIFTS FROM YOUR IRA DONOR S GUIDE H OW TO M AKE C HARITABLE G IFTS F ROM Y OUR IRA Thanks to the success of tax-deferred investments within qualified retirement plans, many people
HOW TO MAKE CHARITABLE GIFTS FROM YOUR IRA DONOR S GUIDE H OW TO M AKE C HARITABLE G IFTS F ROM Y OUR IRA Thanks to the success of tax-deferred investments within qualified retirement plans, many people
ACTIONABLE STRATEGIES FOR REDUCING MEDICARE TAXES
 ACTIONABLE STRATEGIES FOR REDUCING MEDICARE TAXES Medicare taxes increased in 2013 for high-income earners. Timely action can help reduce the impact of higher taxes. KEY TAKEAWAYS High-income taxpayers
ACTIONABLE STRATEGIES FOR REDUCING MEDICARE TAXES Medicare taxes increased in 2013 for high-income earners. Timely action can help reduce the impact of higher taxes. KEY TAKEAWAYS High-income taxpayers
Crunch or Crucible? Upcoming Changes in the Federal Tax Law A Special Edition Tax Guide for Friends and Alumni of Pomona College
 Upcoming Changes in the Federal Tax Law A Special Edition Tax Guide for Friends and Alumni of Pomona College Pomona College, Office of Trusts & Estates, 550 N. College Ave., Claremont, CA 91711 www.pomona.planyourlegacy.org
Upcoming Changes in the Federal Tax Law A Special Edition Tax Guide for Friends and Alumni of Pomona College Pomona College, Office of Trusts & Estates, 550 N. College Ave., Claremont, CA 91711 www.pomona.planyourlegacy.org
Tax Alpha. Robert S. Keebler, CPA, M.S.T., AEP. Keebler & Associates, LLP 420 South Washington Street Green Bay, WI 54301.
 Tax Alpha Presented by Robert S. Keebler, CPA, M.S.T., AEP Keebler & Associates, LLP 420 South Washington Street Green Bay, WI 54301 Agenda 1. Five Dimensional Tax System Ordinary Income Rates Capital
Tax Alpha Presented by Robert S. Keebler, CPA, M.S.T., AEP Keebler & Associates, LLP 420 South Washington Street Green Bay, WI 54301 Agenda 1. Five Dimensional Tax System Ordinary Income Rates Capital
FEDERAL INCOME TAX CUTS AND LOW-INCOME FAMILIES. Frank J. Sammartino. January 2001. Urban Institute 2100 M Street, NW Washington, DC 20037
 FEDERAL INCOME TAX CUTS AND LOW-INCOME FAMILIES Frank J. Sammartino January 2001 Urban Institute 2100 M Street, NW Washington, DC 20037 For copies of this report, please contact the Office of Public Affairs,
FEDERAL INCOME TAX CUTS AND LOW-INCOME FAMILIES Frank J. Sammartino January 2001 Urban Institute 2100 M Street, NW Washington, DC 20037 For copies of this report, please contact the Office of Public Affairs,
The Consequences of Increasing Oregon s Income Tax Deduction for Federal Income Taxes Paid
 The Consequences of Increasing Oregon s Income Tax Deduction for Federal Income Taxes Paid Prepared By: The Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy Washington, DC 20005 www.ctj.org/itep For: Oregon Center
The Consequences of Increasing Oregon s Income Tax Deduction for Federal Income Taxes Paid Prepared By: The Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy Washington, DC 20005 www.ctj.org/itep For: Oregon Center
Testimony embargoed until 4.17.2012 at 10am.
 Statement of William F. Sweetnam Principal, Groom Law Group, Chartered Before the Committee on Ways and Means United States House of Representatives April 17, 2012 Chairman Camp and Ranking Member Levin
Statement of William F. Sweetnam Principal, Groom Law Group, Chartered Before the Committee on Ways and Means United States House of Representatives April 17, 2012 Chairman Camp and Ranking Member Levin
Giving Secondary Earners a Tax Break: A Proposal to Help Low- and Middle-Income Families
 Discussion Paper 2013-07 DECEMber 2013 Giving Secondary Earners a Tax Break: A Proposal to Help Low- and Middle-Income Families Melissa S. Kearney and Lesley J. Turner The Hamilton Project Brookings 1
Discussion Paper 2013-07 DECEMber 2013 Giving Secondary Earners a Tax Break: A Proposal to Help Low- and Middle-Income Families Melissa S. Kearney and Lesley J. Turner The Hamilton Project Brookings 1
16. Individual Retirement Accounts
 16. Individual Retirement Accounts Introduction Through enactment of the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974 (ERISA), Congress established individual retirement accounts (IRAs) to provide workers
16. Individual Retirement Accounts Introduction Through enactment of the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974 (ERISA), Congress established individual retirement accounts (IRAs) to provide workers
RECENT EVIDENCE ON TAXPAYERS RESPONSE TO THE RATE INCREASES IN THE 1990 S FRANK SAMMARTINO DAVID WEINER *
 TAXPAYERS RESPONSE TO THE RATE INCREASES IN THE 1990S RECENT EVIDENCE ON TAXPAYERS RESPONSE TO THE RATE INCREASES IN THE 1990 S FRANK SAMMARTINO DAVID WEINER * * & * Tax Analysis Division, Congressional
TAXPAYERS RESPONSE TO THE RATE INCREASES IN THE 1990S RECENT EVIDENCE ON TAXPAYERS RESPONSE TO THE RATE INCREASES IN THE 1990 S FRANK SAMMARTINO DAVID WEINER * * & * Tax Analysis Division, Congressional
How To Pass The 2001/2003 Tax Cuts
 A PRELIMINARY ANALYSIS OF THE 2008 PRESIDENTIAL CANDIDATES TAX PLANS The Tax Policy Center * An Updated Analysis is available http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/taxtopics/presidential_candidates.cfm Urban-Brookings
A PRELIMINARY ANALYSIS OF THE 2008 PRESIDENTIAL CANDIDATES TAX PLANS The Tax Policy Center * An Updated Analysis is available http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/taxtopics/presidential_candidates.cfm Urban-Brookings
Roth IRA. Introduction
 roth ira Roth IRA Introduction Since its beginnings more than 100 years ago, Pension Fund has supported others in their time of need. Pension Fund provides retirement, disability and death benefits, as
roth ira Roth IRA Introduction Since its beginnings more than 100 years ago, Pension Fund has supported others in their time of need. Pension Fund provides retirement, disability and death benefits, as
Living Standard Trends in Australia: Report for Anglicare Australia. BEN PHILLIPS NATSEM UNIVERSITY OF CANBERRA, September 2015
 Living Standard Trends in Australia: Report for Anglicare Australia BEN PHILLIPS NATSEM UNIVERSITY OF CANBERRA, September 2015 2 Contents 1 Executive Sumary 3 2 Introduction 5 3 Methodology 6 4 Results
Living Standard Trends in Australia: Report for Anglicare Australia BEN PHILLIPS NATSEM UNIVERSITY OF CANBERRA, September 2015 2 Contents 1 Executive Sumary 3 2 Introduction 5 3 Methodology 6 4 Results
Benjamin Franklin observed that nothing in life is certain except
 Middle-Income Tax Rates: Trends and Prospects By Troy A. Davig and C. Alan Garner Benjamin Franklin observed that nothing in life is certain except death and taxes. But he was referring to the existence
Middle-Income Tax Rates: Trends and Prospects By Troy A. Davig and C. Alan Garner Benjamin Franklin observed that nothing in life is certain except death and taxes. But he was referring to the existence
Beginning in 2010, the Tax Increase Prevention and ROTH IRA CONVERSION
 ROTH IRA CONVERSION Assessing Suitability of the Strategy for Individuals and their Heirs Executive Summary A Roth IRA conversion may benefit individuals during their retirement years by potentially reducing
ROTH IRA CONVERSION Assessing Suitability of the Strategy for Individuals and their Heirs Executive Summary A Roth IRA conversion may benefit individuals during their retirement years by potentially reducing
