imaging of craniopharyngioma
|
|
|
- Winifred Palmer
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
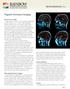
1 Childs Nerv Syst (2005) 21: DOI /s y SPECIAL ANNUAL ISSUE John G. Curran Erin O Connor Imaging of craniopharyngioma Received: 30 May 2005 Published online: 3 August 2005 # Springer-Verlag 2005 J. G. Curran (*). E. O Connor Department of Medical Imaging, Children s Memorial Hospital, 2300 Children s Plaza, Chicago, IL, 60614, USA jcurran@childrensmemorial.org Tel.: Fax: Abstract Background: Craniopharyngiomas are present with a wide range of appearances, but the existence of cysts, calcification, and enhancement in a suprasellar tumor strongly favors the diagnosis. Discussion: There is a significant differential diagnosis that must be considered. The pre- and postoperative imaging of craniopharyngioma is reviewed. Keywords Cerebral angiography. Child. Craniopharyngioma/ diagnosis. Craniopharyngioma/ surgery. Image processing, computerassisted. Magnetic resonance imaging. Pituitary neoplasms/ diagnosis. Tomography, X-ray computed General imaging features of craniopharyngioma The characteristic imaging finding of craniopharyngioma in a child is an enhancing suprasellar mass that is calcified and cystic on CT. When two out of these three features are present, craniopharyngioma is still the most likely diagnosis [1]. The tumor usually demonstrates T1 high intensity on MR, reflecting the protein or cholesterol content of the motor oil-like fluid found in the tumor cysts [2]. Rarely on plain skull film, craniopharyngioma may be suspected by the presence of sellar or suprasellar calcifications. Usually from the initial imaging, a craniopharyngioma can be located in the sella, and/or if partially or entirely suprasellar, can be described as pre- or retrochiasmatic. Determination of size is important at presentation, as tumors greater than 5 cm in diameter have a recurrence rate of more than 80%, whereas in tumors less than 5 cm, the recurrence rate is 20% [2]. Rate of growth is slow, so a rapid interval change in size in the absence of tissue diagnosis may require a reassessment of the etiology of the tumor. By CT examination, approximately 90% of childhood craniopharyngiomas calcify. The percentage drops to approximately 70% in adults. The typical appearance of an adamantinomatous type craniopharyngioma is a mixed cystic and solid mass on CT, usually with a solid focus in the sella, and cystic components arising above it. The papillary type of tumor is more often solid with less common incidence of calcification [2]. By MRI examination, the tumor is of variable T1 signal, often hyperintense. The T1 hyperintensity is usually secondary to high protein content in the cyst fluid. However, other causes of T1 hyperintensity in craniopharyngiomas have been described fat, cholesterol, hemorrhage, or even mild calcification [4]. The mixed solid and cystic nature of the tumor is clearer on MR than on CT. Occasionally with small cysts, even on postcontrast study, the heterogeneous nature of the tumor may not be apparent on CT. This problem does not occur with MR [3]. Even small cysts are identifiable and the smaller solid portion of the tumor is usually heterogeneous or even isointense with brain (Fig. 1). On MR T2-weighted sequences, including Fluid Attenuated Inversion Recovery (FLAIR), the solid portion is again usually heterogeneous, whereas the cysts are invariably hyperintense (Fig. 2). The calcifications, in the solid portion of the tumor or in the peripheral rim, are
2 636 Fig. 1 Eleven-year-old boy with several week history of vomiting, weight loss, ataxia, and abnormal behavior. a Axial CT noncontrast image demonstrating a sellar mass with an irregular calcified component. b Sagittal noncontrast T1 image demonstrating a large sellar and suprasellar mass with cysts of varying intensity, mainly hyperintense. c Coronal noncontrast T1 image demonstrating multiple cysts of varying intensity. Hydrocephalus is also apparent. d Axial T2 image showing cysts mainly hyperintense, but of varying intensity. e Axial FLAIR image showing cysts more uniformly hyperintense. f Sagittal postcontrast T1 image showing peripheral rim enhancement of the cysts, and heterogeneous enhancement of the solid lower portion of the tumor. g Coronal postcontrast T1 image showing mainly the peripheral rim enhancement of the cysts hypointense on T2. They stand out particularly on a susceptibility sequence such as Gradient Recalled Echo (GRE) [3]. Following contrast, there is almost invariable enhancement of the solid portion and the peripheral rim of the cystic portion on both CT and MR (Fig. 3). Contrast is essential for the diagnosis on CT. In one study, three of nine tumors were not identified on the noncontrast CT [3]. The enhancement of the solid portion may be either uniform or patchy and heterogeneous. Enhancement patterns in a given tumor are similar on both CT and MR [3]. One CT and MR study of 26 patients sought to divide the appearance of craniopharyngioma into patterns, i.e., solid, calcified, proteic-like, CSF-like, hematic-like, and fatty [5] (Table 1). There were no correlations between patterns except that in no case did the CSF-like and the proteic-like pattern coexist. Calcified and proteic-like tumors tended to be large. Hematic-like and CSF-like tumors tended to be small [5]. The most useful radiological findings to describe craniopharyngiomas are lesion size, cyst characteristics, and vessel encasement [5]. On angiography, the tumor is usually avascular with displacement of the major vessels of the circle of Willis. Recommended imaging technique MR is the imaging modality of choice [3]. An MR examination should include thin T1 sagittal and coronal sections both pre- and postcontrast through the sella and suprasellar region. It is useful to include a precontrast fat saturation T1 sequence as it will help to identify the posterior pituitary bright spot. Additional sequences may be helpful in answering specific questions: FLAIR is useful in delineating cystic portions of tumor (which will be hyperintense) vs loculated portions of the third ventricle or other CSF spaces (which will tend to be isointense). GRE is useful as a susceptibility sequence in demonstrating calcification more clearly, or possibly demonstrating blood products if there is a question of hemorrhage. Diffusion Weighted Imaging (DWI) (diffusion imaging) is useful in the differential diagnosis if an epidermoid is suspected. MR spectroscopy demonstrating a significant lipid content may be useful.
3 637 Imaging in the differential diagnosis of craniopharyngioma The most commonly listed differential diagnoses are: 1. Pituitary adenoma 2. Hypothalamic or optic pathway glioma 3. Rathke s pouch cyst 4. Epidermoid tumor Other considerations would include: 5. Thrombosed aneurysm 6. Simple arachnoid cyst 7. Masses of infectious or inflammatory origin 8. Pituicytoma 9. Colloid cyst of the third ventricle Pituitary adenoma is uncommon in children, whereas the peak age group for craniopharyngioma is 5 15 years, but nonetheless, this tumor is occasionally seen. It is often noncalcified, so a noncontrast CT is a helpful component of the diagnostic workup. Pituitary adenoma often is greater Fig. 2 Nine-year-old girl with acute visual loss in the left eye. Provisional diagnosis of optic neuritis. a Axial noncontrast CT image showing a sellar mass with faint peripheral calcification. b Axial noncontrast CT image showing partially solid, partially cystic tumor. c Sagittal noncontrast T1 image showing mainly hypointense, partly solid, partly cystic tumor with both sellar and suprasellar components. d Coronal T2 image showing a heterogeneous hyperintense sellar and suprasellar mass. e Sagittal postcontrast T1 image demonstrating fairly uniform enhancement of the majority solid portion of the tumor in bulk within the sella and has a tendency to expand the sella. Craniopharyngioma will on the other hand tend to show greater superior expansion, often with a small sellar component without expansion of the bony sella. A pituitary tumor with a cystic component and/or a degree of hemorrhage can be difficult to distinguish from a craniopharyngioma. Factors supporting the diagnosis of pituitary adenoma in a giant intra- and suprasellar mass include infrasellar extension, absence of calcification, and presence of low-signal cysts on T1-weighted images [6]. Hypothalamic or optic pathway gliomas lack two common features of craniopharyngiomas. They rarely have a sellar component (although when large may erode the sphenoid bone) and are rarely calcified. The tumors are usually isointense on T1 and usually lack a cystic component. If a cystic component or necrosis is present, it is usually dominated by the solid component of the tumor, whereas the cystic component is usually dominant in craniopharyngioma.
4 638 Fig. 3 Two and a half-year-old boy with several month history of polyuria and polydipsia. Now with strange eye movements. a Sagittal noncontrast T1 image demonstrating cysts of mixed hyper- and hypointensity. b Axial noncontrast T1 image demonstrating mixed hyper- and hypointense cysts. c Coronal T2 image demonstrating cysts of varying intensity, mainly hyperintense. d Sagittal postcontrast T1 image demonstrating heterogeneous enhancement of the lower solid portion of the tumor, with peripheral rim enhancement in the cystic portion Table 1 Semiological patterns of craniopharyngioma on MRI and CT Solid pole 100% Cystic component 92.3% Calcification 65.3% Proteic like 53.8% CSF like 23% Hematic like 19.2% Fatty component 15.3% Rathke s cleft cysts may at times be difficult to differentiate from small craniopharyngiomas. However, larger Rathke s cleft cysts are easier to differentiate as they typically do not contain a solid component, do not enhance, and are not calcified [7]. Epidermoid tumors may rarely occur in the suprasellar region. The substance of an epidermoid tumor may be identified by restricted diffusion; hence, the use of diffusion weighted imaging is recommended if that possibility is under consideration. Peripheral rim enhancement is less common in epidermoids [8]. Thrombosed aneurysms are a consideration in an older age group. They typically have an eccentric pattern of concentric circles within the mass. Identification of a residual lumen assists in confirming the diagnosis. Simple suprasellar arachnoid cysts contain neither calcification nor solid portion. They are typically bounded posterior by the membrane of Lilliquist. Inflammatory masses may occur in the suprasellar region. Usually, these are infective in nature such as granulomatous infections, but occasionally, other inflammations such as sarcoid or histiocytosis may manifest as suprasellar disease. Typically, these lesions are infiltrative, layering along the pituitary stalk and the adjacent undersurface of the brain, but occasionally, frank granulomas may occur in the suprasellar region giving rise to diagnostic difficulty. Granulomas are not usually calcified, are somewhat heterogeneous in signal, and often show diffuse enhancement. Lymphocytic hypophysitis, an adult condition, is an inflammation of the anterior pituitary gland and usually presents with an infiltrative appearance including thickened pituitary stalk rather than a mass. Pituicytoma, or granular cell tumor, a rare adult tumor of the neurohypophysis and infundibulum, gives rise to a suprasellar mass without significant compression of adjacent structures. The mass is noncystic and noncalcified and is closely associated with the pituitary stalk. Colloid cyst of the third ventricle may cause confusion with a high third ventricular craniopharyngioma. The tumor is of high signal on all sequences. However, the presence of a heterogenous suprasellar solid component and the noncollapse of the posterior third ventricle, despite a lesion
5 639 in the anterior, make the diagnosis of craniopharyngioma much more likely [8]. Postsurgical evaluation of craniopharyngioma The main focus of postsurgical evaluation is the determination of the presence and extent of residual tumor. However, in addition, the potential complications of surgery must be borne in mind. These include hypothalamic injury with associated endocrine abnormalities, injury to the pituitary gland, and vascular injury including pseudoaneurysm formation of adjacent structures. MR is essential in the immediate aftermath of craniopharyngioma surgery. Exact timing is not established, but imaging within the first postoperative week is the usual standard. The normal appearance is of interval reduction in tumor size. It is also common to identify residual tumor (best delineated on the postcontrast T1 images), even when there has been no residual tumor identified at the end of surgery [9]. There is usually no change in signal intensity of the cystic or of the solid portion of the tumor between the preoperative and postoperative scans. A fluid collection, isointense to CSF, and usually resolved by the second postoperative scan, is typically seen on all immediate postoperative scans [9]. With intraaxial lesions, luxury perfusion and disruption of the blood brain barrier may give rise to new or more extensive contrast enhancement postoperatively. However, in the case of craniopharyngioma as an extraaxial lesion, no new areas of enhancement are to be expected postsurgery. The emergence of such findings would therefore be a matter of concern [9]. Finally, the postoperative scan should usually demonstrate a resolution of hydrocephalus if present preoperatively and better visualization of the normal structures, such as the chiasm or pituitary stalk, in the suprasellar region, if these are intact. The second postoperative scan may show reduction of residual tumor volume when compared to the first postoperative scan. Although this may be attributed to interval radiation therapy [10], such a volume reduction may be seen in patients who have received no interval therapy [9]. As residual tumor volume reduction over months has also been seen in pituitary adenoma, presumably related to edema resolution, it has been suggested that an accurate estimation of residual tumor volume in craniopharyngioma may be obtained only at 2 3 months postsurgery [9]. The period of tumor shrinkage after radiation therapy is often long and varied (mean 29 months) [10]. Increase in size of residual tumor between the first and second postoperative scan has been identified in certain patients as attributable to interval radiation therapy, with further follow-up scans demonstrating a regression of the tumor [9]. Conclusion The imaging modality of choice for craniopharyngioma is MR. However, CT is very useful in determining the presence of calcification. The tumors present a wide variety of appearances, but the presence of cysts, calcification, and enhancement in a suprasellar tumor strongly favors the diagnosis. There is a significant differential diagnosis that must be considered. Postoperative follow-up with MR is essential, but potential pitfalls such as the relatively frequent presence of residual tumor even in a gross total resection, interval short-term increase in treated tumor, and the potentially long period of tumor shrinkage must be borne in mind. References 1. Fitz CR, Wortzman G, Harwood-Nash DC, Holgate RC, Barry JF, Boldt DW (1978) Computer tomography in craniopharyngiomas. Radiology 127: Osborn AG (2004) Diagnostic imaging brain. Amirsys Inc., Salt Lake City 3. Hald JK, Eldevik OP, Skalpe IO (1995) Craniopharyngioma identification by CT and MR imaging at 1.5 T. Acta Radiol 36(2): Ahmadi J, Destian S, Apuzzo MLJ, Segall HD, Zee CS (1992) Cystic fluid in craniopharyngiomas. MR imaging and quantitative analysis. Radiology 182: Molla E, Marti-Bonmati L, Revert A, Arana E, Menor F, Dosda R, Poyatos C (2002) Craniopharyngiomas: identification of different semiological patterns with MRI. Eur Radiol 12: Majos C, Coli S, Aguilera C, Acebes JJ, Pons LC (1998) Imaging of giant pituitary adenomas. Neuroradiology 40: Igarashi T, Saeki N, Yamaura A (1999) Long term magnetic resonance imaging follow-up of asymptomatic sellar tumors their natural history and surgical indications. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 39: Wang YXJ, Jiang H, He GX (2001) Atypical magnetic resonance imaging findings of craniopharyngioma. Australas Radiol 45: Hald JK, Eldevik OP, Quint DJ, Chandler WF, Kollevold T (1996) Pre- and postoperative MR imaging of craniopharyngiomas. Acta Radiol 37: Hamamoto Y, Niino K, Adachi M, Hosoya T (2002) MR and CT findings of craniopharyngioma during and after radiation therapy. Neuroradiology 44:
Case Report. Central Neurocytoma. Fotis Souslian, MD; Dino Terzic, MD; Ramachandra Tummala, MD. Department of Neurosurgery, University of Minnesota
 1 Case Report Central Neurocytoma Fotis, MD; Dino Terzic, MD; Ramachandra Tummala, MD Department of Neurosurgery, University of Minnesota Case This is a previously healthy 20 year old female, with 3 months
1 Case Report Central Neurocytoma Fotis, MD; Dino Terzic, MD; Ramachandra Tummala, MD Department of Neurosurgery, University of Minnesota Case This is a previously healthy 20 year old female, with 3 months
Anatomy: The sella is a depression in the sphenoid bone that makes up part of the skull base located behind the eye sockets.
 Pituitary Tumor Your doctor thinks you may have a pituitary tumor. Pituitary tumors are benign (non-cancerous) overgrowth of cells that make up the pituitary gland (the master gland that regulates other
Pituitary Tumor Your doctor thinks you may have a pituitary tumor. Pituitary tumors are benign (non-cancerous) overgrowth of cells that make up the pituitary gland (the master gland that regulates other
Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD
 Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD With the widespread use of cross-sectional imaging, many renal masses are incidentally found. These need to be accurately
Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD With the widespread use of cross-sectional imaging, many renal masses are incidentally found. These need to be accurately
MRI for Paediatric Surgeons
 MRI for Paediatric Surgeons Starship David Perry Paediatric Radiologist Starship Children s Hospital CHILDREN S HEALTH What determines the brightness of a pixel in MRI? i.e. What determines the strength
MRI for Paediatric Surgeons Starship David Perry Paediatric Radiologist Starship Children s Hospital CHILDREN S HEALTH What determines the brightness of a pixel in MRI? i.e. What determines the strength
CYSTS. Arachnoid Cyst also called Leptomeningeal Cyst
 CYSTS This article was provided to us by David Schiff, MD, Associate Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Medicine at University of Virginia, Charlottesville. We appreciate his generous donation of
CYSTS This article was provided to us by David Schiff, MD, Associate Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Medicine at University of Virginia, Charlottesville. We appreciate his generous donation of
NEURO MRI PROTOCOLS TABLE OF CONTENTS
 TABLE OF CONTENTS NEURO MRI PROTOCOLS BRAIN...2 Brain 1 Screen... 2 Brain 2 Brain Tumor... 2 Brain 3 Brain Infection / Meningitis... 2 Brain 4 Trauma... 3 Brain 5 Hemorrhage... 3 Brain 6 Demyelinating
TABLE OF CONTENTS NEURO MRI PROTOCOLS BRAIN...2 Brain 1 Screen... 2 Brain 2 Brain Tumor... 2 Brain 3 Brain Infection / Meningitis... 2 Brain 4 Trauma... 3 Brain 5 Hemorrhage... 3 Brain 6 Demyelinating
Differential Diagnosis of Sellar Lesions
 Differential Diagnosis of Sellar Lesions Manish K. Aghi, M.D., Ph.D. Assistant Professor California Center for Pituitary Disorders Department of Neurosurgery University of California, San Francisco (UCSF)
Differential Diagnosis of Sellar Lesions Manish K. Aghi, M.D., Ph.D. Assistant Professor California Center for Pituitary Disorders Department of Neurosurgery University of California, San Francisco (UCSF)
What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms
 What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Interventions Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Radiology Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D.,
What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Interventions Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Radiology Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D.,
Table 11: Pros and Cons of 1.5 T MRI vs. 3.0 T MRI; Safety and Technical Issues, and Clinical Applications
 Safety Issue 3.0 T MRI Pro 3.0 T MRI Con Immediate fringe field surrounding magnet A ferromagnetic object inadvertently brought into the scan room will experience a sharp increase in attraction toward
Safety Issue 3.0 T MRI Pro 3.0 T MRI Con Immediate fringe field surrounding magnet A ferromagnetic object inadvertently brought into the scan room will experience a sharp increase in attraction toward
WHAT S WRONG WITH MY GALL BLADDER? GALL BLADDER POLYPS
 WHAT S WRONG WITH MY GALL BLADDER? GALL BLADDER POLYPS This is a patient information booklet providing specific practical information about gall bladder polyps in brief. Its aim is to provide the patient
WHAT S WRONG WITH MY GALL BLADDER? GALL BLADDER POLYPS This is a patient information booklet providing specific practical information about gall bladder polyps in brief. Its aim is to provide the patient
Pediatric Brain Tumors. Asim Mian M.D.
 Pediatric Brain Tumors Asim Mian M.D. Overview Pediatric brain tumors(pbt) are 15-20% of all brain tumors. Second most common pediatric tumor. Only leukemia more common. Overall, supratentorial and infratentorial
Pediatric Brain Tumors Asim Mian M.D. Overview Pediatric brain tumors(pbt) are 15-20% of all brain tumors. Second most common pediatric tumor. Only leukemia more common. Overall, supratentorial and infratentorial
.org. Osteochondroma. Solitary Osteochondroma
 Osteochondroma Page ( 1 ) An osteochondroma is a benign (noncancerous) tumor that develops during childhood or adolescence. It is an abnormal growth that forms on the surface of a bone near the growth
Osteochondroma Page ( 1 ) An osteochondroma is a benign (noncancerous) tumor that develops during childhood or adolescence. It is an abnormal growth that forms on the surface of a bone near the growth
MRI of Bone Marrow Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 MRI of Bone Marrow Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel, M.D. Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University School of Medicine St. Louis, MO and Visiting Scientist, AFIP, Washington,
MRI of Bone Marrow Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel, M.D. Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University School of Medicine St. Louis, MO and Visiting Scientist, AFIP, Washington,
Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases.
 Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases. Abstract This paper describes the staging, imaging, treatment, and prognosis of renal cell carcinoma. Three case studies
Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases. Abstract This paper describes the staging, imaging, treatment, and prognosis of renal cell carcinoma. Three case studies
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones. Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke
 Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
POST-OPERATIVE SPINE IMAGING M.Muto Chief Neuroradiology Dept Cardarelli Hospital Naples ITALY
 POST-OPERATIVE SPINE IMAGING M.Muto Chief Neuroradiology Dept Cardarelli Hospital Naples ITALY Postoperative spine imaging, either by surgery or by mini-invasive procedures, is a complex tool and depends
POST-OPERATIVE SPINE IMAGING M.Muto Chief Neuroradiology Dept Cardarelli Hospital Naples ITALY Postoperative spine imaging, either by surgery or by mini-invasive procedures, is a complex tool and depends
Update on Surgical Treatment of Pituitary Tumors. Kristen Riley, MD, FACS Associate Professor, Division of Neurosurgery, Department of Surgery
 Update on Surgical Treatment of Pituitary Tumors Kristen Riley, MD, FACS Associate Professor, Division of Neurosurgery, Department of Surgery Pituitary Tumors Pituitary adenoma: common intracranial neoplasm
Update on Surgical Treatment of Pituitary Tumors Kristen Riley, MD, FACS Associate Professor, Division of Neurosurgery, Department of Surgery Pituitary Tumors Pituitary adenoma: common intracranial neoplasm
NEUROIMAGING in Parkinsonian Syndromes
 NEUROIMAGING in Parkinsonian Syndromes (Focus on Structural Techniques: CT and MRI) Dr. Roberto Cilia Parkinson Institute, ICP, Milan, Italy OUTLINE Primary Parkinsonism Idiopathic Parkinson s Disease
NEUROIMAGING in Parkinsonian Syndromes (Focus on Structural Techniques: CT and MRI) Dr. Roberto Cilia Parkinson Institute, ICP, Milan, Italy OUTLINE Primary Parkinsonism Idiopathic Parkinson s Disease
CHARACTERSTIC RADIOGRAPHIC APPEARANCE
 OSTEOLYTIC LESIONS APPROACH AGE Metastatic Neuroblastoma in infant and young child. Metastases and multiple myeloma in middle aged and elderly. Ewing s sarcoma and simple bone cyst in children and teens.
OSTEOLYTIC LESIONS APPROACH AGE Metastatic Neuroblastoma in infant and young child. Metastases and multiple myeloma in middle aged and elderly. Ewing s sarcoma and simple bone cyst in children and teens.
Brain Cancer. This reference summary will help you understand how brain tumors are diagnosed and what options are available to treat them.
 Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Renal Cysts What should I do now?
 Renal Cysts What should I do now? Dr Edmund Chiong Asst. Professor & Consultant Department of Urology National University Hospital What are renal cysts? Fluid-filled structures in the kidney that are not
Renal Cysts What should I do now? Dr Edmund Chiong Asst. Professor & Consultant Department of Urology National University Hospital What are renal cysts? Fluid-filled structures in the kidney that are not
CMS Manual System Pub. 100-03 Medicare National Coverage Determinations
 CMS Manual System Pub. 100-03 Medicare National Coverage Determinations Department of Health & Human Services (DHHS) Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) Transmittal 21 Date: September 10, 2004
CMS Manual System Pub. 100-03 Medicare National Coverage Determinations Department of Health & Human Services (DHHS) Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) Transmittal 21 Date: September 10, 2004
Spine University s Guide to Vertebral Osteonecrosis (Kummel's Disease)
 Spine University s Guide to Vertebral Osteonecrosis (Kummel's Disease) 2 Introduction Kummel's disease is a collapse of the vertebrae (the bones that make up the spine). It is also called vertebral osteonecrosis.
Spine University s Guide to Vertebral Osteonecrosis (Kummel's Disease) 2 Introduction Kummel's disease is a collapse of the vertebrae (the bones that make up the spine). It is also called vertebral osteonecrosis.
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW
 Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)?
 What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
Continuing Medical Education Article Imaging of Multiple Myeloma and Related Plasma Cell Dyscrasias JNM, July 2012, Volume 53, Number 7
 Continuing Medical Education Article Imaging of Multiple Myeloma and Related Plasma Cell Dyscrasias JNM, July 2012, Volume 53, Number 7 Authors Ronald C. Walker 1,2, Tracy L. Brown 3, Laurie B. Jones-Jackson
Continuing Medical Education Article Imaging of Multiple Myeloma and Related Plasma Cell Dyscrasias JNM, July 2012, Volume 53, Number 7 Authors Ronald C. Walker 1,2, Tracy L. Brown 3, Laurie B. Jones-Jackson
Headache: Differential diagnosis and Evaluation. Raymond Rios PGY-1 Pediatrics
 Headache: Differential diagnosis and Evaluation Raymond Rios PGY-1 Pediatrics You are evaluating a 9 year old male patient at the ED brought by his mother, who says that her son has had a fever, cough,
Headache: Differential diagnosis and Evaluation Raymond Rios PGY-1 Pediatrics You are evaluating a 9 year old male patient at the ED brought by his mother, who says that her son has had a fever, cough,
Nuno Morais 1 José António Moreira da Costa 2
 Nuno Morais 1 José António Moreira da Costa 2 1 Neurosurgery Department, Hospital de Braga, Braga, Portugal 2 Private Practice, Clínica Neurológica e da Coluna Vertebral, Braga, Portugal Disclosure Funding
Nuno Morais 1 José António Moreira da Costa 2 1 Neurosurgery Department, Hospital de Braga, Braga, Portugal 2 Private Practice, Clínica Neurológica e da Coluna Vertebral, Braga, Portugal Disclosure Funding
Ulnar sided Wrist Pain
 Ulnar sided Wrist Pain 1 Susan Cross, 1 Anshul Rastogi, 2 Brian Cohen, 1 Rosy Jalan 1 Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK 2 London Orthopaedic Centre Contact: susan.cross@bartshealth.nhs.uk
Ulnar sided Wrist Pain 1 Susan Cross, 1 Anshul Rastogi, 2 Brian Cohen, 1 Rosy Jalan 1 Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK 2 London Orthopaedic Centre Contact: susan.cross@bartshealth.nhs.uk
AI CPT Codes. x x. 70336 MRI Magnetic resonance (eg, proton) imaging, temporomandibular joint(s)
 Code Category Description Auth Required Medicaid Medicare 0126T IMT Testing Common carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) study for evaluation of atherosclerotic burden or coronary heart disease risk factor
Code Category Description Auth Required Medicaid Medicare 0126T IMT Testing Common carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) study for evaluation of atherosclerotic burden or coronary heart disease risk factor
Brain Tumor Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumor Treatment Brain Tumors Overview A brain tumor is a group of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. Tumors can directly destroy healthy brain cells. They can
Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumor Treatment Brain Tumors Overview A brain tumor is a group of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. Tumors can directly destroy healthy brain cells. They can
Chapter 10. All chapters, full text, free download, available at http://www.divingmedicine.info SINUS BAROTRAUMA ANATOMY OF THE SINUSES
 Chapter 10 All chapters, full text, free download, available at http://www.divingmedicine.info SINUS BAROTRAUMA ANATOMY OF THE SINUSES The sinuses are air filled cavities contained within the bones of
Chapter 10 All chapters, full text, free download, available at http://www.divingmedicine.info SINUS BAROTRAUMA ANATOMY OF THE SINUSES The sinuses are air filled cavities contained within the bones of
SARCOIDOSIS AND THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 SARCOIDOSIS AND THE NERVOUS SYSTEM www.stopsarcoidosis.org SARCOIDOSIS AND THE NERVOUS SYSTEM What Is Neurosarcoidosis? Sarcoidosis is an inflammatory disease that can affect almost any organ in the body.
SARCOIDOSIS AND THE NERVOUS SYSTEM www.stopsarcoidosis.org SARCOIDOSIS AND THE NERVOUS SYSTEM What Is Neurosarcoidosis? Sarcoidosis is an inflammatory disease that can affect almost any organ in the body.
Cardiac Masses and Tumors
 Cardiac Masses and Tumors Question: What is the diagnosis? A. Aortic valve myxoma B. Papillary fibroelastoma C. Vegetation from Infective endocarditis D. Thrombus in transit E. None of the above Answer:
Cardiac Masses and Tumors Question: What is the diagnosis? A. Aortic valve myxoma B. Papillary fibroelastoma C. Vegetation from Infective endocarditis D. Thrombus in transit E. None of the above Answer:
Optic Disc Drusen. Normal Enlarged view of Optic Disc. Lumpy Appearance of Optic Disc. Optic Disc Drusen With Drusen
 Optic Disc Drusen Your doctor has diagnosed you with optic disc drusen. Optic disc drusen are abnormal deposits of protein-like material in the optic disc the front part of the optic nerve. We do not know
Optic Disc Drusen Your doctor has diagnosed you with optic disc drusen. Optic disc drusen are abnormal deposits of protein-like material in the optic disc the front part of the optic nerve. We do not know
SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS?
 SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS? The spinal canal is best imagined as a bony tube through which nerve fibres pass. The tube is interrupted between each pair of adjacent
SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS? The spinal canal is best imagined as a bony tube through which nerve fibres pass. The tube is interrupted between each pair of adjacent
Diaphragma sellae meningioma mimicking pituitary macroadenoma: a case report
 Diaphragma sellae meningioma mimicking pituitary macroadenoma: a case report Saleh Rasras, Mohammad Javad Alemzadeh Ansari, Mohammad Hasan Alemzadeh Ansari, Farhad Rahbarian, Iran Rashidi Corresponding
Diaphragma sellae meningioma mimicking pituitary macroadenoma: a case report Saleh Rasras, Mohammad Javad Alemzadeh Ansari, Mohammad Hasan Alemzadeh Ansari, Farhad Rahbarian, Iran Rashidi Corresponding
In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer
 In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide, accounting for 15% of all new cancer cases. 1 Great strides have
In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide, accounting for 15% of all new cancer cases. 1 Great strides have
Clinical guidance for MRI referral
 MRI for cervical radiculopathy Referral by a medical practitioner (excluding a specialist or consultant physician) for a scan of spine for a patient 16 years or older for suspected: cervical radiculopathy
MRI for cervical radiculopathy Referral by a medical practitioner (excluding a specialist or consultant physician) for a scan of spine for a patient 16 years or older for suspected: cervical radiculopathy
Hemorrhagic venous infarction Heather Borders, MD
 Hemorrhagic venous infarction Heather Borders, MD 12/13/2010 History 16 year old female with four day history of headache and acute change in mental status. History of two days of oral contraceptive use
Hemorrhagic venous infarction Heather Borders, MD 12/13/2010 History 16 year old female with four day history of headache and acute change in mental status. History of two days of oral contraceptive use
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS. Diagnosis/Initial evaluation. Treatment and Prognosis
 LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation
 J Clin Ultrasound 17:327-332, June 1989 Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation Mark A. Helvie, MD,* and Terry M. Silver, MDI Abstract: The sonographic and clinical findings of 13 patients with surgically
J Clin Ultrasound 17:327-332, June 1989 Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation Mark A. Helvie, MD,* and Terry M. Silver, MDI Abstract: The sonographic and clinical findings of 13 patients with surgically
Intracranial Tuberculoma: Comparison of MR with Pathologic Findings
 Intracranial Tuberculoma: Comparison of MR with Pathologic Findings Tae Kyoung Kim, Kee Hyun Chang, Chong Jai Kim, Jin Mo Goo, Myeong Cherl Kook, and Moon Hee Han PURPOSE: To compare the MR signal intensity
Intracranial Tuberculoma: Comparison of MR with Pathologic Findings Tae Kyoung Kim, Kee Hyun Chang, Chong Jai Kim, Jin Mo Goo, Myeong Cherl Kook, and Moon Hee Han PURPOSE: To compare the MR signal intensity
CT and MRI features of the Pathologic Subtypes of Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma. Melissa Price, MD Aoife Kilcoyne, MD Mukesh G.
 CT and MRI features of the Pathologic Subtypes of Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma Melissa Price, MD Aoife Kilcoyne, MD Mukesh G. Harisinghani, MD Disclosures Neither I nor my immediate family members have
CT and MRI features of the Pathologic Subtypes of Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma Melissa Price, MD Aoife Kilcoyne, MD Mukesh G. Harisinghani, MD Disclosures Neither I nor my immediate family members have
Parts of the Brain. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Types of Brain Injury
 Types of Brain Injury The bones of your skull are hard and they protect your brain. Your brain is soft, like firm Jell-O. When your head moves, your brain moves inside your skull. When your head is hit
Types of Brain Injury The bones of your skull are hard and they protect your brain. Your brain is soft, like firm Jell-O. When your head moves, your brain moves inside your skull. When your head is hit
Benign Liver Tumors. Cameron Schlegel PGY-1 3/6/2013
 Benign Liver Tumors Cameron Schlegel PGY-1 3/6/2013 Outline Benign Liver Tumors are, in general. Asymptomatic Diagnosed: imaging Treatment: Do no harm Unless Malignant potential Causing symptoms Differential
Benign Liver Tumors Cameron Schlegel PGY-1 3/6/2013 Outline Benign Liver Tumors are, in general. Asymptomatic Diagnosed: imaging Treatment: Do no harm Unless Malignant potential Causing symptoms Differential
Neural Tube Defects - NTDs
 Neural Tube Defects - NTDs Introduction Neural tube defects are also known as NTDs. They happen when the spine and brain do not fully develop while the fetus is forming in the uterus. Worldwide, there
Neural Tube Defects - NTDs Introduction Neural tube defects are also known as NTDs. They happen when the spine and brain do not fully develop while the fetus is forming in the uterus. Worldwide, there
Radiologic Diagnosis of Spinal Metastases
 September 2002 Radiologic Diagnosis of Spinal Metastases Natalie J. M. Dailey, Harvard Medical Student Year III Our Patient s Presenting Story 70 year old male Presents to the hospital for laparascopic
September 2002 Radiologic Diagnosis of Spinal Metastases Natalie J. M. Dailey, Harvard Medical Student Year III Our Patient s Presenting Story 70 year old male Presents to the hospital for laparascopic
Standardized MRI Protocol for Brain Tumor Clinical Trials. Benjamin M. Ellingson, Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Radiology at UCLA
 Standardized MRI Protocol for Brain Tumor Clinical Trials Benjamin M. Ellingson, Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Radiology at UCLA Standardized MRI Protocol for Therapeutic Studies FDA Meeting in January
Standardized MRI Protocol for Brain Tumor Clinical Trials Benjamin M. Ellingson, Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Radiology at UCLA Standardized MRI Protocol for Therapeutic Studies FDA Meeting in January
Reversibility of Acute Demyelinating Lesions in relapsingremitting
 Reversibility of Acute Demyelinating Lesions in relapsingremitting Multiple Sclerosis Omar A. Khan ( Division of Neuroimmunology, Department of Neurology, Neurology and Research Services. Veterans Affairs
Reversibility of Acute Demyelinating Lesions in relapsingremitting Multiple Sclerosis Omar A. Khan ( Division of Neuroimmunology, Department of Neurology, Neurology and Research Services. Veterans Affairs
AORTOENTERIC FISTULA. Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005
 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA diagnosis and management Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA Aortoenteric
AORTOENTERIC FISTULA Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA diagnosis and management Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA Aortoenteric
Cavernous Angioma. Cerebral Cavernous Malformation ...
 Cavernous Angioma... Cerebral Cavernous Malformation Information For Patients And Loved Ones 107 Quaker Meeting House Road Williamsburg, Virginia 23188 USA 1-866-HEAL-CCM 1-757-258-3355 www.angiomaalliance.org
Cavernous Angioma... Cerebral Cavernous Malformation Information For Patients And Loved Ones 107 Quaker Meeting House Road Williamsburg, Virginia 23188 USA 1-866-HEAL-CCM 1-757-258-3355 www.angiomaalliance.org
Brain Spots on Imaging Tests
 Brain Spots on Imaging Tests To Be or Not to Be Concerned Metropolitan Underwriting Discussion Group 1/29/13 Charles Levy, MD Aviva USA CT and MRI 2 most common forms of brain imaging today As with any
Brain Spots on Imaging Tests To Be or Not to Be Concerned Metropolitan Underwriting Discussion Group 1/29/13 Charles Levy, MD Aviva USA CT and MRI 2 most common forms of brain imaging today As with any
Approach to Lower Extremity Osteomyelitis. A radiologic tour of a patient encounter
 Approach to Lower Extremity Osteomyelitis A radiologic tour of a patient encounter David Guo,, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC, October 2009 Our learning goals Review lower extremity anatomy Discuss
Approach to Lower Extremity Osteomyelitis A radiologic tour of a patient encounter David Guo,, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC, October 2009 Our learning goals Review lower extremity anatomy Discuss
Contents. Introduction 1. Anatomy of the Spine 1. 2. Spinal Imaging 7. 3. Spinal Biomechanics 23. 4. History and Physical Examination of the Spine 33
 Contents Introduction 1. Anatomy of the Spine 1 Vertebrae 1 Ligaments 3 Intervertebral Disk 4 Intervertebral Foramen 5 2. Spinal Imaging 7 Imaging Modalities 7 Conventional Radiographs 7 Myelography 9
Contents Introduction 1. Anatomy of the Spine 1 Vertebrae 1 Ligaments 3 Intervertebral Disk 4 Intervertebral Foramen 5 2. Spinal Imaging 7 Imaging Modalities 7 Conventional Radiographs 7 Myelography 9
Apparent Diffusion Coefficients in the Evaluation of High-grade Cerebral Gliomas
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:60 64, January 2001 Apparent Diffusion Coefficients in the Evaluation of High-grade Cerebral Gliomas Mauricio Castillo, J. Keith Smith, Lester Kwock, and Kathy Wilber BACKGROUND
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:60 64, January 2001 Apparent Diffusion Coefficients in the Evaluation of High-grade Cerebral Gliomas Mauricio Castillo, J. Keith Smith, Lester Kwock, and Kathy Wilber BACKGROUND
MR Imaging of the Postoperative Lumbar Spine: Assessment with Gadopentetate Dimeglumine
 771 MR Imaging of the Postoperative Lumbar Spine: Assessment with Gadopentetate Dimeglumine Jeffrey S. Ross 1.2 Thomas J. Masaryk 1 2 Mauricio Schrader 1 Amilcare Gentili 1 Henry Bohlman 3 Michael T. Modic
771 MR Imaging of the Postoperative Lumbar Spine: Assessment with Gadopentetate Dimeglumine Jeffrey S. Ross 1.2 Thomas J. Masaryk 1 2 Mauricio Schrader 1 Amilcare Gentili 1 Henry Bohlman 3 Michael T. Modic
Guidance for evaluation of new neurological symptoms in patients receiving TYSABRI
 Guidance for evaluation of new neurological symptoms in patients receiving TYSABRI Background information Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) PML is a demyelinating disease that attacks the
Guidance for evaluation of new neurological symptoms in patients receiving TYSABRI Background information Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) PML is a demyelinating disease that attacks the
Image. 3.11.3 SW Review the anatomy of the EAC and how this plays a role in the spread of tumors.
 Neoplasms of the Ear and Lateral Skull Base Image 3.11.1 SW What are the three most common neoplasms of the auricle? 3.11.2 SW What are the four most common neoplasms of the external auditory canal (EAC)
Neoplasms of the Ear and Lateral Skull Base Image 3.11.1 SW What are the three most common neoplasms of the auricle? 3.11.2 SW What are the four most common neoplasms of the external auditory canal (EAC)
Case Report: Whole-body Oncologic Imaging with syngo TimCT
 Case Report: Whole-body Oncologic Imaging with syngo TimCT Eric Hatfield, M.D. 1 ; Agus Priatna, Ph.D. 2 ; John Kotyk, Ph.D. 1 ; Benjamin Tan, M.D. 1 ; Alto Stemmer 3 ; Stephan Kannengiesser, Ph.D. 3 ;
Case Report: Whole-body Oncologic Imaging with syngo TimCT Eric Hatfield, M.D. 1 ; Agus Priatna, Ph.D. 2 ; John Kotyk, Ph.D. 1 ; Benjamin Tan, M.D. 1 ; Alto Stemmer 3 ; Stephan Kannengiesser, Ph.D. 3 ;
Management of spinal cord compression
 Management of spinal cord compression (SUMMARY) Main points a) On diagnosis, all patients should receive dexamethasone 10mg IV one dose, then 4mg every 6h. then switched to oral dose and tapered as tolerated
Management of spinal cord compression (SUMMARY) Main points a) On diagnosis, all patients should receive dexamethasone 10mg IV one dose, then 4mg every 6h. then switched to oral dose and tapered as tolerated
Pancreatic masses: What is there besides cancer
 Pancreatic masses: What is there besides cancer Poster No.: C-0201 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Abdominal Viscera (Solid Organs) Authors: M. A. Portilha, C. Ruivo, I. Santiago, M.
Pancreatic masses: What is there besides cancer Poster No.: C-0201 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Abdominal Viscera (Solid Organs) Authors: M. A. Portilha, C. Ruivo, I. Santiago, M.
Diagnostic performance of MRI in differentiating metastatic from acute osteoporotic compression fractures of the spine
 Diagnostic performance of MRI in differentiating metastatic from acute osteoporotic compression fractures of the spine Poster No.: C-1399 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Martel,
Diagnostic performance of MRI in differentiating metastatic from acute osteoporotic compression fractures of the spine Poster No.: C-1399 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Martel,
Ovarian Teratomas Appearing as Solid Masses on Ultrasonography
 Ovarian Teratomas Appearing as Solid Masses on Ultrasonography Dong Kyung Lee, MD, Seung Hyup Kim, MD, Jeong Yeon Cho, MD, Sang Joon Shin, MD, Kyung Mo Yeon, MD The purposes of this study were to evaluate
Ovarian Teratomas Appearing as Solid Masses on Ultrasonography Dong Kyung Lee, MD, Seung Hyup Kim, MD, Jeong Yeon Cho, MD, Sang Joon Shin, MD, Kyung Mo Yeon, MD The purposes of this study were to evaluate
Cystic Neoplasms of the Pancreas: A multidisciplinary approach to the prevention and early detection of invasive pancreatic cancer.
 This lecture is drawn from the continuing medical education program Finding Hope: Prevention, Early Detection and Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer, Nov, 2011. Robert P. Jury, MD Cystic Neoplasms of the Pancreas:
This lecture is drawn from the continuing medical education program Finding Hope: Prevention, Early Detection and Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer, Nov, 2011. Robert P. Jury, MD Cystic Neoplasms of the Pancreas:
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Rehabilitation Best Practice Documentation
 Rehabilitation Best Practice Documentation Click on the desired Diagnoses link or press Enter to view all information. Diagnoses: Reason for Admission to Inpatient Rehab CVA Deficits Fractures Secondary
Rehabilitation Best Practice Documentation Click on the desired Diagnoses link or press Enter to view all information. Diagnoses: Reason for Admission to Inpatient Rehab CVA Deficits Fractures Secondary
2.1 Who first described NMO?
 History & Discovery 54 2 History & Discovery 2.1 Who first described NMO? 2.2 What is the difference between NMO and Multiple Sclerosis? 2.3 How common is NMO? 2.4 Who is affected by NMO? 2.1 Who first
History & Discovery 54 2 History & Discovery 2.1 Who first described NMO? 2.2 What is the difference between NMO and Multiple Sclerosis? 2.3 How common is NMO? 2.4 Who is affected by NMO? 2.1 Who first
PE finding: Left side extremities mild weakness No traumatic wound No bloody otorrhea, nor rhinorrhea
 Case report A 82-year-old man was suffered from sudden onset spasm of extremities then he fell down to the ground with loss of consciousness. He recovered his consciousness 7-8 mins later but his conscious
Case report A 82-year-old man was suffered from sudden onset spasm of extremities then he fell down to the ground with loss of consciousness. He recovered his consciousness 7-8 mins later but his conscious
Normal CT scan of the chest
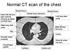 Normal CT scan of the chest Heart with left and right ventricle showing up lighter (contrast dye) Breast tissue Breast bone (sternum) Breast tissue Left lung (dark area) Right lung (dark area) Rib Main
Normal CT scan of the chest Heart with left and right ventricle showing up lighter (contrast dye) Breast tissue Breast bone (sternum) Breast tissue Left lung (dark area) Right lung (dark area) Rib Main
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging What are the uses of MRI? To begin, not only are there a variety of scanning methodologies available, but there are also a variety of MRI methodologies available which provide
Magnetic Resonance Imaging What are the uses of MRI? To begin, not only are there a variety of scanning methodologies available, but there are also a variety of MRI methodologies available which provide
Thyroid Eye Disease. Anatomy: There are 6 muscles that move your eye.
 Thyroid Eye Disease Your doctor thinks you have thyroid orbitopathy. This is an autoimmune condition where your body's immune system is producing factors that stimulate enlargement of the muscles that
Thyroid Eye Disease Your doctor thinks you have thyroid orbitopathy. This is an autoimmune condition where your body's immune system is producing factors that stimulate enlargement of the muscles that
DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES. Anthony Hewitt
 DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES Anthony Hewitt Introduction Anatomy of the scaphoid Resembles a deformed peanut Articular cartilage covers 80% of the surface It rests in a plane 45 degrees to the longitudinal
DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES Anthony Hewitt Introduction Anatomy of the scaphoid Resembles a deformed peanut Articular cartilage covers 80% of the surface It rests in a plane 45 degrees to the longitudinal
Thyroid Eye Disease. A Patient s Guide
 Sashank Prasad, MD www.brighamandwomens.org/neuro-ophthalmology A Patient s Guide Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Prognosis What are the symptoms of Thyroid Eye Disease? Patients with Thyroid Eye Disease
Sashank Prasad, MD www.brighamandwomens.org/neuro-ophthalmology A Patient s Guide Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Prognosis What are the symptoms of Thyroid Eye Disease? Patients with Thyroid Eye Disease
Benign Ovarian Masses
 Benign Ovarian Masses Anthony Hanbidge Learning Objectives Describe technique for assessment of ovarian masses Explain importance of transvaginal scan List the common benign masses Specify distinguishing
Benign Ovarian Masses Anthony Hanbidge Learning Objectives Describe technique for assessment of ovarian masses Explain importance of transvaginal scan List the common benign masses Specify distinguishing
Accounts for approximately 46% of cervical spine injuries.
 Flexion Fracture of the Cervical Spine 2 Definition " Epidemiology Accounts for approximately 46% of cervical spine injuries. " Etiology, pathophysiology, pathogenesis Results from maximum flexion of the
Flexion Fracture of the Cervical Spine 2 Definition " Epidemiology Accounts for approximately 46% of cervical spine injuries. " Etiology, pathophysiology, pathogenesis Results from maximum flexion of the
MRI in Differential Diagnosis
 MRI in Differential Diagnosis Jill Conway, MD, MA, MSCE Director, Carolinas MS Center Clerkship Director, UNCSOM-Charlotte Campus Charlotte, NC DISCLOSURES Speaking, consulting, and/or advisory boards
MRI in Differential Diagnosis Jill Conway, MD, MA, MSCE Director, Carolinas MS Center Clerkship Director, UNCSOM-Charlotte Campus Charlotte, NC DISCLOSURES Speaking, consulting, and/or advisory boards
False positive PET in lymphoma
 False positive PET in lymphoma Thomas Krause Introduction and conclusion 2 3 Introduction 4 FDG-PET in staging of lymphoma 34 studies with 2227 Patients CT FDG-PET Sensitivity 63 % 89 % (58%-100%) (63%-100%)
False positive PET in lymphoma Thomas Krause Introduction and conclusion 2 3 Introduction 4 FDG-PET in staging of lymphoma 34 studies with 2227 Patients CT FDG-PET Sensitivity 63 % 89 % (58%-100%) (63%-100%)
sound or ringing in the ears.
 (Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension) Sashank Prasad, MD www.brighamandwomens.org/neuro-ophthalmology A Patient s Guide Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Prognosis Symptoms The symptoms of include: Headaches
(Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension) Sashank Prasad, MD www.brighamandwomens.org/neuro-ophthalmology A Patient s Guide Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Prognosis Symptoms The symptoms of include: Headaches
.org. Metastatic Bone Disease. Description
 Metastatic Bone Disease Page ( 1 ) Cancer that begins in an organ, such as the lungs, breast, or prostate, and then spreads to bone is called metastatic bone disease (MBD). More than 1.2 million new cancer
Metastatic Bone Disease Page ( 1 ) Cancer that begins in an organ, such as the lungs, breast, or prostate, and then spreads to bone is called metastatic bone disease (MBD). More than 1.2 million new cancer
Juvenile Dermatomyositis Joseph Junewick, MD FACR
 Juvenile Dermatomyositis Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 10/11/2015 History Child with several month history of weakness, arthralgias and palpable abnormalities at the knee Diagnosis Juvenile Dermatomyositis
Juvenile Dermatomyositis Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 10/11/2015 History Child with several month history of weakness, arthralgias and palpable abnormalities at the knee Diagnosis Juvenile Dermatomyositis
A case of labyrinthitis diagnosed with MRI
 A case of labyrinthitis diagnosed with MRI Saiz-Mendiguren R, García-Lallana A, Simon I, Slon P, Etxano J, Dominguez PD, Zubieta JL, García-Eulate R. Radiology Service. Clínica Universidad de Navarra,
A case of labyrinthitis diagnosed with MRI Saiz-Mendiguren R, García-Lallana A, Simon I, Slon P, Etxano J, Dominguez PD, Zubieta JL, García-Eulate R. Radiology Service. Clínica Universidad de Navarra,
Thymus Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand what thymus cancer is and what treatment options are available.
 Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Neurosarcoidosis. Jeffrey M. Gelfand, MD
 Neurosarcoidosis WASOG Meeting Cleveland October 2012 Patient Education Session Relevant Financial Disclosures: None Jeffrey M. Gelfand, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Neurology UCSF MS Center, Dept
Neurosarcoidosis WASOG Meeting Cleveland October 2012 Patient Education Session Relevant Financial Disclosures: None Jeffrey M. Gelfand, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Neurology UCSF MS Center, Dept
Cardiovascular diseases. pathology
 Cardiovascular diseases pathology Atherosclerosis Vascular diseases A disease that results in arterial wall thickens as a result of build- up of fatty materials such cholesterol, resulting in acute and
Cardiovascular diseases pathology Atherosclerosis Vascular diseases A disease that results in arterial wall thickens as a result of build- up of fatty materials such cholesterol, resulting in acute and
Computed Tomography, Head Or Brain; Without Contrast Material, Followed By Contrast Material(S) And Further Sections
 1199SEIU BENEFIT AND PENSION FUNDS High Tech Diagnostic Radiology and s # 1 70336 Magnetic Resonance (Eg, Proton) Imaging, Temporomandibular Joint(S) 2 70450 Computed Tomography, Head Or Brain; Without
1199SEIU BENEFIT AND PENSION FUNDS High Tech Diagnostic Radiology and s # 1 70336 Magnetic Resonance (Eg, Proton) Imaging, Temporomandibular Joint(S) 2 70450 Computed Tomography, Head Or Brain; Without
Multimodality imaging of brain tumours: High Grade Brain Tumours
 20th Advance Course Multimodality imaging of brain tumours: High Grade Brain Tumours Àlex Rovira Unitat de Ressonància Magnètica Servei de Radiologia Hospital Vall d Hebron. Barcelona. alex.rovira@idi
20th Advance Course Multimodality imaging of brain tumours: High Grade Brain Tumours Àlex Rovira Unitat de Ressonància Magnètica Servei de Radiologia Hospital Vall d Hebron. Barcelona. alex.rovira@idi
CPT Radiology Codes Requiring Review by AIM Effective 01/01/2016
 CPT Radiology Codes Requiring Review by AIM Effective 01/01/2016 When a service is authorized only one test per group is payable. *Secondary codes or add-on codes do not require preauthorization or separate
CPT Radiology Codes Requiring Review by AIM Effective 01/01/2016 When a service is authorized only one test per group is payable. *Secondary codes or add-on codes do not require preauthorization or separate
Head Position and Impact Direction in Whiplash Injuries: Associations with MRI-Verified Lesions of Ligaments and Membranes in the Upper Cervical Spine
 Head Position and Impact Direction in Whiplash Injuries: Associations with MRI-Verified Lesions of Ligaments and Membranes in the Upper Cervical Spine 1 Journal of Neurotrauma Volume 22, Number 11, November
Head Position and Impact Direction in Whiplash Injuries: Associations with MRI-Verified Lesions of Ligaments and Membranes in the Upper Cervical Spine 1 Journal of Neurotrauma Volume 22, Number 11, November
Smoking and misuse of certain pain medicines can affect the risk of developing renal cell cancer.
 Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Technological Innovation: High Field Open Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
 Technological Innovation: High Field Open Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Student Investigator: Thomas R. Pace UVM COM Class of 2012 Faculty Mentor: Christopher Filippi Department of Radiology Fletcher
Technological Innovation: High Field Open Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Student Investigator: Thomas R. Pace UVM COM Class of 2012 Faculty Mentor: Christopher Filippi Department of Radiology Fletcher
Multiple Sclerosis: An imaging review and update on new treatments.
 Multiple Sclerosis: An imaging review and update on new treatments. Dr Marcus Likeman Consultant Neuroradiologist North Bristol NHS Trust Bristol Royal Hospital for Children MRI appearances - White Matter
Multiple Sclerosis: An imaging review and update on new treatments. Dr Marcus Likeman Consultant Neuroradiologist North Bristol NHS Trust Bristol Royal Hospital for Children MRI appearances - White Matter
Incidence of Incidental Thyroid Nodules on Computed Tomography (CT) Scan of the Chest Performed for Reasons Other than Thyroid Disease
 International Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2011, 2, 264-268 doi:10.4236/ijcm.2011.23042 Published Online July 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijcm) Incidence of Incidental Thyroid Nodules on Computed
International Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2011, 2, 264-268 doi:10.4236/ijcm.2011.23042 Published Online July 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijcm) Incidence of Incidental Thyroid Nodules on Computed
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER
 GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER BY Ali Shamseddine, MD (Coordinator); as04@aub.edu.lb Fady Geara, MD Bassem Shabb, MD Ghassan Jamaleddine, MD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER BY Ali Shamseddine, MD (Coordinator); as04@aub.edu.lb Fady Geara, MD Bassem Shabb, MD Ghassan Jamaleddine, MD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT
.org. Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine. Cause. Description
 Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Page ( 1 ) Spinal fractures can vary widely in severity. While some fractures are very serious injuries that require emergency treatment, other fractures can
Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Page ( 1 ) Spinal fractures can vary widely in severity. While some fractures are very serious injuries that require emergency treatment, other fractures can
THYROID CANCER. I. Introduction
 THYROID CANCER I. Introduction There are over 11,000 new cases of thyroid cancer each year in the US. Females are more likely to have thyroid cancer than men by a ratio of 3:1, and it is more common in
THYROID CANCER I. Introduction There are over 11,000 new cases of thyroid cancer each year in the US. Females are more likely to have thyroid cancer than men by a ratio of 3:1, and it is more common in
Measure #405: Appropriate Follow-up Imaging for Incidental Abdominal Lesions National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care
 Measure #405: Appropriate Follow-up Imaging for Incidental Abdominal Lesions National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS, REGISTRY DESCRIPTION:
Measure #405: Appropriate Follow-up Imaging for Incidental Abdominal Lesions National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS, REGISTRY DESCRIPTION:
Residency Competency and Proficiency Statements
 Residency Competency and Proficiency Statements 1. REQUEST AND RESPOND TO REQUESTS FOR CONSULTATIONS Identify needs and make referrals to appropriate health care providers for the treatment of physiologic,
Residency Competency and Proficiency Statements 1. REQUEST AND RESPOND TO REQUESTS FOR CONSULTATIONS Identify needs and make referrals to appropriate health care providers for the treatment of physiologic,
Nervous System: PNS and CNS
 Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
