MONOPOLY PROJECT PATRICIA CARLSON ACCOUNTING 104 INSTRUCTOR: CATHERINE CONDRON
|
|
|
- Joanna McDaniel
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MONOPOLY PROJECT PATRICIA CARLSON ACCOUNTING 104 INSTRUCTOR: CATHERINE CONDRON JANUARY 06, 2011
2 Comments on ing Monopoly Project This was a very creative way to play monopoly by making a journal entry for the different moves by each player. It was quite a task entering each move that created a journal entry but it was still fun.
3 ing 104 Monopoly Project Patricia Carlson Chart of s Assets 100 Cash 110 s Receivable 120 Steven Melissa Victoria John Game Piece 130 Accum Depr. - Game Piece 140 Property Purchased 150 St. James Place New York Avenue Baltic Avenue Vermont Pennsylvania Avenue Railroads 160 Reading Railroad Pennsylvania Railroad Liabilities 200 s Payable 210 Hollada Hayes Murguia Branch Taxes 220 Owners Equity 300 Owner, Capital 310 Owner, Drawing 320 Income Summary 350 Revenue 400 Go Revenue 410 Rent Revenue 420 Railroad Revenue 430 Other Revenue: e.g. Chance, C.Chest 440 Expenses 500 Rent Expense 510 Railroad Expense 520 Tax Expense 530 Other Expenses e.g. Chance, C.Chest 540 Depr. Expense - Game Piece 560
4 JOURNAL Page 1 Patricia Carlson ing 104 Date Description Post Ref Debit Credit 1 Nov 1 Cash 110 $ 1, Owner, Capital 310 $ 1, Owner's initial investment Game Piece 130 $ A/P Condron 210 $ Purchased game piece on account Property: St. James Place $ Cash 110 $ Property: New York Avenue $ Cash 110 $ Owner's Drawing 320 $ Cash: Non-business expense 110 $ Jail bond Property: Baltic Avenue $ Cash 110 $ Property: Vermont Avenue $ Cash 110 $ A/R Victoria $ Rent Revenue 420 $ Earned rent on Vermont Avenue Cash 110 $ A/R Victoria $ Received payment on account for Vermont Ave A/R Victoria $ Rent Revenue 420 $ Earned Rent on St. James Place Cash 110 $ Go Revenue 410 $ Property: Reading Railroad $ Cash 110 $ Page 2 of 21
5 JOURNAL Page 2 Patricia Carlson ing 104 Date Description Post Ref Debit Credit 1 Nov 6 Cash 110 $ A/R Victoria $ St. James Place rent Rent Expense 510 $ A/P Branch $ Electric Company Utilites A/P Branch $ Cash 110 $ Electric Company Utilities A/R John $ Rent Revenue 420 $ Earned rent on Baltic Cash 110 $ A/R John $ Received payment on account for Baltic Cash 110 $ Other Revenue 440 $ Cash 110 $ Go Revenue 410 $ A/R Steven $ Railroad Revenue 430 $ Earned rent on Reading Railroad A/R John $ Rent Revenue 420 $ Earned rent on Vermont Cash 110 $ A/R Steven $ Received payment on account for Reading RR Cash 110 $ A/R John $ Received payment on account for Vermont Ave 41 Page 3 of 21
6 JOURNAL Page 3 Patricia Carlson ing 104 Date Description Post Ref Debit Credit 1 Nov 13 Property: Pennsylvania Railroad $ Cash 110 $ A/R Victoria $ RR Revenue 430 $ Earned rent on Pennsylvania Railroad Rent Expense 510 $ A/P Murguia $ Indiana Avenue rent Cash 110 $ A/R Victoria $ Received payment on account for Pennsylvania RR A/P Muguia $ Cash 110 $ Made payment on account for Indiana Avenue rent Tax Expense 530 $ A/P Taxes: Chance Card 220 $ Paid Income Tax A/R Victoria $ Rent Revenue 420 $ Earned rent on St. James Place Cash 110 $ Other Revenue 440 $ Chance Card A/P Taxes 220 $ Cash 110 $ Made payment on Income Tax Cash 110 $ A/R Victoria $ Received payment on account for St. James Place Page 4 of 21
7 JOURNAL Page 4 Patricia Carlson ing 104 Date Description Post Ref Debit Credit 1 Nov 18 Rent Expense 510 $ A/P Murguia $ Marvin Gardens rent A/P Murguia $ Cash 110 $ Made payment on account for Marvin Gardens rent RR Rent Expense 520 $ $ A/P Branch Shortline Railroad Cash 110 $ Go Revenue 410 $ Other Expense 540 $ Cash 110 $ School Fees A/R Steven $ Rent Revenue 420 $ Earned rent on Vermont Avenue A/R Steven $ RR Revenue 430 $ Earned rent on Pennsylvania Railroad A/R Victoria $ Rent Revenue 420 $ Earned rent on St. James Place A/P Branch $ Cash 110 $ Shortline Railroad Rent Expense 510 $ A/P Branch $ Electric Company Utility Page 5 of 21
8 JOURNAL Page 5 Patricia Carlson ing 104 Date Description Post Ref Debit Credit 1 Nov 21 Cash 110 $ A/R Steven $ Received payment on account for Vermont Ave Cash 110 $ A/R Steven $ Received payment on account for Pennsylvania RR Cash 110 $ s Receivable: Victoria $ Received payment on account for St. James Place s Receivable: Melissa $ Railroad Revenue 430 $ Earned rent on Pennsylvania Railroad s Payable: Branch $ Cash 110 $ Made payment on accont for Electric Company Cash 110 $ A/R Melissa $ Received payment on account for Pennsylvania RR A/R Melissa $ Rent Revenue 420 $ Earned rent on Vermont Avenue Rent Expense 510 $ A/P Branch $ Electric Company Utility Tax Expense 530 $ A/P Taxes 220 $ Paid Luxary Tax Cash 110 $ A/R Melissa $ Received payment on account for Vermont Avenue A/P Branch $ Cash 110 $ Made payment on accont for Electric Company A/R Melissa $ RR Rent Revenue 430 $ Earned rent on Pennsylvania Railroad 47 Page 6 of 21
9 Patricia Carlson ing Page 7 of 21
10 JOURNAL Page 6 Patricia Carlson ing 104 Date Description Post Ref Debit Credit 1 Nov 25 Cash 110 $ Go Revenue 410 $ Tax Expense 530 $ Taxes Payable 220 $ Paid Income Tax Taxes Payable 220 $ Cash 110 $ Paid Luxary Tax Cash 110 $ A/R Melissa $ Received payment on account for Pennsylvania RR Property: Pennlysvania Avenue $ Cash 110 $ Rent Expense 510 $ A/P Murguia $ Tennessee A/R Steven $ Rent Revenue 420 $ Earned rent on Pennsylvanie Avenue Other Expense 540 $ Cash 110 $ Community Chest: Steven's Birthday A/P Murguia $ Cash 110 $ Made payment on account for Tennessee Ave rent Cash 110 $ A/R Steven $ Received payment on account for Pennsylvania Ave rent A/P Taxes 220 $ Cash 110 $ Made payment on taxes A/R Victoria $ Rent Revenue 420 $ Earned rent on Vermont Avenue A/P Condron 210 $ Page 8 of 21
11 Patricia Carlson ing Cash 110 $ Made payment for Game Piece 49 Page 9 of 21
12 JOURNAL Page 7 Patricia Carlson ing 104 Date Closing Entries Post Ref Debit Credit 1 Nov 30 Revenue $ 1, Go Revenue Rent Revenue Railroad Revenue Other Revenue Income Summary $ Rent Expense Railroad Expense Tax Other Expense Depreciation Expense Income Summary $ 1, Patricia Carlson, capital Patricia Carlson, capital $ Patricia Carlson, drawing Page 10 of 21
13 GENERAL LEDGER : CASH No. 110 Nov 1 Owners capital J St James Place J New York Avenue J Non-business expense J Baltic Avenue J Vermont Avenue J Vermont Rent J Go Revenue J Reading Railroad J St James Place J Utilities Expense J Baltic Rent J Other Revenue J Go Revenue J RR Rent J Vermont Rent J Pennsylvania RR J Pennsylvania RR Rent J Indiana Avenue Rent J Other Revenue J Income Tax J St James Place Rent J Marvin Gardens rent J Go Revenue J School Fees J Shortline RR rent J Vermont Avenue rent J Pennsylvania RR Rent J St James Place Rent J Electric Co J Pennsylvania RR rent J Vermont Avenue rent J Electric Co J Go Revenue J Taxes J Pennsylvania RR Rent J Pennsylvania Avenue J Other Espense J Pennsylvania Avenue rent J Tennessee Rent J Taxes J Game Piece J Page 11 of 21
14 GENERAL LEDGER A/R Steven No Nov 11 Reading RR rent J Reading RR rent J Vermont rent J Pennsylvania rent J Vermont rent J Pennsylvania rent J Pennsylvania rent J Pennsylvania rent J A/R Melissa No Nov 22 Pennsylvanie RR rent J Pennsylvania RR rent J Vermont rent J Vermont rent J Pennsylvania RR rent J Pennsylvania RR rent J A/R Victoria No Nov 4 Vermont rent J Vermont rent J St James Place rent J St James Place rent J Pennsylvania RR rent J Pennsylvania RR rent J St James Place rent J St James Place rent J St James Place rent J St James Place rent J Vermont rent J A/R John No Nov 8 Baltic rent J Baltic rent J Vermont rent J Vermont rent J Game Piece No. 130 Page 12 of 21
15 Nov 1 Purchased game piece J GENERAL LEDGER Accum Depr - Game Piece No. 140 Nov 30 Purchased game piece J Property: St James Place No Nov 1 Purchased property J Property: New York Avenue No Nov 2 Purchased property J Property: Baltic Avenue No Nov 3 Purchased property J Property: Vermont Avenue No Nov 4 Purchasaed property J Pennsylvania Avenue No Nov 26 Purchased property J Reading Railroad No Nov 6 Purchased Property J Pennsylvania Railroad No Nov 13 Purchased property J3 Page 13 of
16 A/P: Condron No. 210 Nov 1 Purchase game piece J Paid for game piece J GENERAL LEDGER A/P: Muguia No Nov 14 Indiana Ave rent J Indiana Ave rent J Marvin Gardens rent J Marvin Gardens rent J Tenessee rent J Tenessee rent J A/P: Branch No Nov 7 Electric Co. J Electric Co. J Shortline RR rent J Shortline RR rent J Electric Co. J Electric Co. J Electric Co J Electric Co J A/P: Taxes No. 220 Nov 16 Income Tax J Income Tax J Luxury Tax J Income Tax J Luxury Tax J Income Tax J Owners Equity No. 310 Nov 1 Patricia Carlson Capital J Owners Drawing No. 320 DATE ITEM Post Ref Page 14 DEBIT of 21 CREDIT
17 DEBIT Nov 2 Non-business expense J CREDIT Go Revenue No. 410 Nov 6 J J J J Closing J GENERAL LEDGER Rent Revenue No. 420 Nov 4 Vermont Ave J St James Place J Baltic Avenue J Vermont Ave J St James Place J Vermont Ave J St James Place J Vermont Ave J Pennsylvania Ave J Vermont Ave J Closing J Railroad Revenue No. 430 Nov 11 Reading J Pennsylvania J Pennsylvania J Pennsylvania J Pennsylvania J Closing J Other Revenue No. 440 Nov 10 J J Closing J Rent Expense No. 510 Page 15 of 21
18 Nov 7 Electric Company J Indiana Avenue J Marvin Gardens J Electric Company J Electric Company J Tennessee Avenue J Closing J Railroad Expense No. 520 Nov 19 Shortline J Closing J GENERAL LEDGER Tax Expense No. 530 Nov 16 Income tax J Luxury tax J Income tax J Closing J Other Expense No. 540 Nov 20 J J Closing J Depr. Expense - Game Piece No. 560 Nov 30 J Closing J Page 16 of 21
19 Patricia Carlson Monopoly Worksheet For Month End November 30, 2010 ACCOUNT TITLE TRIAL ADJUSTMENTS 1 Cash s Receivable Game Piece Accum Depr. - Game Piece Property Railroads s Payable 8 Patricia Carlson, Capital Patricia Carlson, Drawing Revenue Rent Expense Railroad Expense Tax Expense Other Expense Depr. Expense - Game Piece
20 Patricia Carlson Monopoly Worksheet For Month End November 30, 2010 ADJUSTED TRIAL INCOME STATEMENT SHEET
21 Patricia Carlson Monopoly Project Income Statement For the Month Ended November 30, 2010 Revenue $ - Rent & Other Revenue $ 1, Expenses Rent Expense Railroad Expense Tax Expense Other Expense Depr. Exp. - Game Piece Total Expense Net Income $
22 Patricia Carlson Monopoly Project Statement of Owners Equity For the Month Ended November 30, 2010 Patricia Carlson, capital, November 1, 2010 $ 1, Investments during November $ - Total Investment $ 1, Net Income for November $ Less withdrawals for November $ Increase in Capital $ Patricia Carlson, capital, November 30, $ 1,922.00
23 Patricia Carlson Monopoly Project Balance Sheet Assets November 30, 2010 Cash s receivable 6.00 Game Piece Property Railroads Total Current Assets Less Accum. Dep. - Game Piece Total Assets Liabilities Current Liabilities s Payable 0.00 Owner's Equity Patricia Carlson, capital, November 30, Total Liabilities & Owner's equity
Closing Entries and the Postclosing Trial Balance
 6-1 McGraw-Hill 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter Closing Entries and the Postclosing Trial Balance 6 Section 1: Closing Entries Section Objectives 1. Journalize and post
6-1 McGraw-Hill 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter Closing Entries and the Postclosing Trial Balance 6 Section 1: Closing Entries Section Objectives 1. Journalize and post
Assignment 6: Adjusting Journal Entries and
 Name: Due Date: December 12, 2011 Score: out of a possible 47 Course value: 7.5% Assignment 6: Adjusting Journal Entries and Worksheets A series of transactions are presented and their journal entries
Name: Due Date: December 12, 2011 Score: out of a possible 47 Course value: 7.5% Assignment 6: Adjusting Journal Entries and Worksheets A series of transactions are presented and their journal entries
SOLUTIONS. Learning Goal 16
 Learning Goal 16: Prepare Closing Entries S1 Learning Goal 16 Multiple Choice 1. d 2. a 3. b 4. d Because drawing is closed directly into the capital account, not into income summary. 5. c 6. b This a
Learning Goal 16: Prepare Closing Entries S1 Learning Goal 16 Multiple Choice 1. d 2. a 3. b 4. d Because drawing is closed directly into the capital account, not into income summary. 5. c 6. b This a
CHAPTER 12 ACCRUALS, DEFERRALS, AND THE WORKSHEET
 CHAPTER 12 ACCRUALS, DEFERRALS, AND THE WORKSHEET Chapter Opener: Thinking Critically Students may assess that an unexpected decline in sales would mean surplus inventory which would have to be reduced
CHAPTER 12 ACCRUALS, DEFERRALS, AND THE WORKSHEET Chapter Opener: Thinking Critically Students may assess that an unexpected decline in sales would mean surplus inventory which would have to be reduced
Chapter 5: Adjustments and the Worksheet
 Chapter 5: Adjustments and the Worksheet Chapter Opener: Thinking Critically Students should suggest that accountants estimate the amount of wear and tear on the equipment. This expense should be charged
Chapter 5: Adjustments and the Worksheet Chapter Opener: Thinking Critically Students should suggest that accountants estimate the amount of wear and tear on the equipment. This expense should be charged
CHAPTER 4. Adjusting the accounts and preparing financial statements CONTENTS
 CHAPTER 4 Adjusting the accounts and preparing financial statements CONTENTS Demonstration problem 4.1 Adjusting entries and corrections 4.2 Adjusting centries and effect on financial statements 4.3 Adjusting
CHAPTER 4 Adjusting the accounts and preparing financial statements CONTENTS Demonstration problem 4.1 Adjusting entries and corrections 4.2 Adjusting centries and effect on financial statements 4.3 Adjusting
SOLUTIONS. Learning Goal 15
 Learning Goal 15: Prepare a Classified S1 Learning Goal 15 Multiple Choice 1. b 2. c 3. a 4. b 5. d 6. a 7. c Their importance in paying current liabilities is the main reason current assets are shown
Learning Goal 15: Prepare a Classified S1 Learning Goal 15 Multiple Choice 1. b 2. c 3. a 4. b 5. d 6. a 7. c Their importance in paying current liabilities is the main reason current assets are shown
Vol. 1, Chapter 3 - Accounting Adjustments
 Vol. 1, Chapter 3 - Accounting Adjustments Problem 1 1. ($20,000 2,000) 48 = $375 per month 2. Jan. 31 Depreciation Expense $375 Accumulated Depreciation Van $375 To record depreciation expense for January
Vol. 1, Chapter 3 - Accounting Adjustments Problem 1 1. ($20,000 2,000) 48 = $375 per month 2. Jan. 31 Depreciation Expense $375 Accumulated Depreciation Van $375 To record depreciation expense for January
Adjusting Entries and the Work Sheet
 Heintz & Parry th Edition Chapter 5 th Edition College Accounting Adjusting Entries and the Work Sheet 1 Prepare end-of-period adjustments. END-OF-PERIOD ADJUSTMENTS Changes occur that affect the business
Heintz & Parry th Edition Chapter 5 th Edition College Accounting Adjusting Entries and the Work Sheet 1 Prepare end-of-period adjustments. END-OF-PERIOD ADJUSTMENTS Changes occur that affect the business
Closing the Books Section 7 Accounting 11
 Closing the Books At the end of a fiscal year once all the transactions for the entity have been recorded, the revenue and expense accounts must be closed out to a zero balance. These accounts have been
Closing the Books At the end of a fiscal year once all the transactions for the entity have been recorded, the revenue and expense accounts must be closed out to a zero balance. These accounts have been
Accounting Notes. Cash - includes money and any medium of exchange that a bank accepts at face value
 Asset Accounts: Cash - includes money and any medium of exchange that a bank accepts at face value Accounts Receivable - a record of an oral or implied promise of future cash receipts in exchange for goods
Asset Accounts: Cash - includes money and any medium of exchange that a bank accepts at face value Accounts Receivable - a record of an oral or implied promise of future cash receipts in exchange for goods
Chapter 6 Statement of Cash Flows
 Chapter 6 Statement of Cash Flows The Statement of Cash Flows describes the cash inflows and outflows for the firm based upon three categories of activities. Operating Activities: Generally include transactions
Chapter 6 Statement of Cash Flows The Statement of Cash Flows describes the cash inflows and outflows for the firm based upon three categories of activities. Operating Activities: Generally include transactions
CHAPTER 3 THE ADJUSTING PROCESS
 1. a. Under cash-basis accounting, revenues are reported in the period in which cash is received and expenses are reported in the period in which cash is paid. b. Under accrual-basis accounting, revenues
1. a. Under cash-basis accounting, revenues are reported in the period in which cash is received and expenses are reported in the period in which cash is paid. b. Under accrual-basis accounting, revenues
Time Period Assumption
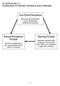 ILLUSTRATION 3-1 GUIDELINES TO REPORT REVENUE AND EXPENSES Time Period Assumption Economic life of business can be divided into artificial time periods Revenue Recognition Principle Revenue recognized
ILLUSTRATION 3-1 GUIDELINES TO REPORT REVENUE AND EXPENSES Time Period Assumption Economic life of business can be divided into artificial time periods Revenue Recognition Principle Revenue recognized
Chapter 3: Double-Entry Bookkeeping
 Chapter 3: Double-Entry Bookkeeping Double-entry bookkeeping underpins accounting A way of systematically recording the financial transactions of a company so that each transaction is recorded twice. Basic
Chapter 3: Double-Entry Bookkeeping Double-entry bookkeeping underpins accounting A way of systematically recording the financial transactions of a company so that each transaction is recorded twice. Basic
Chapter 2. Analyzing transactions
 1 Chapter 2 Analyzing transactions 2 Learning objectives 1. Explain the steps in the accounting cycle and each step s supporting documentation 2. Explain the purpose of source documents 3. Describe an
1 Chapter 2 Analyzing transactions 2 Learning objectives 1. Explain the steps in the accounting cycle and each step s supporting documentation 2. Explain the purpose of source documents 3. Describe an
The General Journal and the General Ledger
 4-1 McGraw-Hill 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 4 The General Journal and the General Ledger Section 1: The General Journal Section Objectives 1. Record transactions in
4-1 McGraw-Hill 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 4 The General Journal and the General Ledger Section 1: The General Journal Section Objectives 1. Record transactions in
COMPLETION OF THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE - Closing Entries -
 COMPLETION OF THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE - Closing Entries - Worksheet Overview Trial Balance Adjustments Adjusted Trial Balance Income Statement Balance Sheet Account Titles Debit Credit Debit Credit Debit
COMPLETION OF THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE - Closing Entries - Worksheet Overview Trial Balance Adjustments Adjusted Trial Balance Income Statement Balance Sheet Account Titles Debit Credit Debit Credit Debit
Welcome to the financial reports topic. 5-1-1
 Welcome to the financial reports topic. 5-1-1 We will explore the effect of standard processes in SAP Business One on Financial Reports: such as the Balance Sheet, the Trial Balance, and the Profit and
Welcome to the financial reports topic. 5-1-1 We will explore the effect of standard processes in SAP Business One on Financial Reports: such as the Balance Sheet, the Trial Balance, and the Profit and
Marist College ACCT 203 Financial Accounting Quiz Prep Chapter 3
 Marist College ACCT 203 Financial Accounting Quiz Prep Chapter 3 The Accounting Cycle: Capturing Economic Events Peter Rivera August 2011 Disclaimer This Quiz Prep is provided as an outline of the key
Marist College ACCT 203 Financial Accounting Quiz Prep Chapter 3 The Accounting Cycle: Capturing Economic Events Peter Rivera August 2011 Disclaimer This Quiz Prep is provided as an outline of the key
Accounting Cycle. Matching Principle
 CHAPTER 3 Accounting Cycle Analyze and record the transactions Post the transactions and prepare trial balance Adjust the accounts and prepare trial balance Prepare the financial statements Close the accounts
CHAPTER 3 Accounting Cycle Analyze and record the transactions Post the transactions and prepare trial balance Adjust the accounts and prepare trial balance Prepare the financial statements Close the accounts
Baseline Assessment. Date Accounting 1
 Name Baseline Assessment Date Accounting 1 Part 1: Instructions: Place a check mark under the column for each account to determine which Financial the accounts belongs on. Financial Information 1. Cash
Name Baseline Assessment Date Accounting 1 Part 1: Instructions: Place a check mark under the column for each account to determine which Financial the accounts belongs on. Financial Information 1. Cash
CHAPTER 2 ACCOUNTING FOR TRANSACTIONS
 CHAPTER 2 ACCOUNTING FOR TRANSACTIONS Key Terms and Concepts to Know Double entry accounting: Debits and Credits Total debits must always equal total credits Accounting Books: Accounts General Journal
CHAPTER 2 ACCOUNTING FOR TRANSACTIONS Key Terms and Concepts to Know Double entry accounting: Debits and Credits Total debits must always equal total credits Accounting Books: Accounts General Journal
Student s name: SSN s: (Last, First Name) (Last 4#) Comprehensive Problem Fall 03
 Student s name: SSN s: (Last, First Name) (Last 4#) Comprehensive Problem Fall 03 Ken Harper, Master Chef A.k.a., Ken Harper Cooking School Company Profile and Background: For the past several months,
Student s name: SSN s: (Last, First Name) (Last 4#) Comprehensive Problem Fall 03 Ken Harper, Master Chef A.k.a., Ken Harper Cooking School Company Profile and Background: For the past several months,
EXERCISES. Does not normally require adjustment. Normally requires adjustment (AE).
 EXERCISES Ex. 3 1 1. Prepaid expense 2. Accrued revenue 3. Unearned revenue 4. Accrued expense 5. Unearned revenue 6. Prepaid expense 7. Accrued expense 8. Accrued expense Ex. 3 2 Account Accounts Receivable...
EXERCISES Ex. 3 1 1. Prepaid expense 2. Accrued revenue 3. Unearned revenue 4. Accrued expense 5. Unearned revenue 6. Prepaid expense 7. Accrued expense 8. Accrued expense Ex. 3 2 Account Accounts Receivable...
Accounting Self Study Guide for Staff of Micro Finance Institutions
 Accounting Self Study Guide for Staff of Micro Finance Institutions LESSON 5 Summarizing Changes in Financial Position OBJECTIVES The purpose of this lesson is to show how to summarize the transactions
Accounting Self Study Guide for Staff of Micro Finance Institutions LESSON 5 Summarizing Changes in Financial Position OBJECTIVES The purpose of this lesson is to show how to summarize the transactions
Last update: August 20, 2008 Word count: 21,073
 Last update: August 20, 2008 Word count: 21,073 Copyright Information Real Money 2003, by W. David Albrecht, is a financial accounting and investment simulation game for use in accounting classes. The
Last update: August 20, 2008 Word count: 21,073 Copyright Information Real Money 2003, by W. David Albrecht, is a financial accounting and investment simulation game for use in accounting classes. The
PART A: TRUE/FALSE (1 point each):
 CHABOT COLLEGE General Accounting (BUS-7) Dmitriy Kalyagin PART A: TRUE/FALSE (1 point each): EXAM #4 (Chapters 10, 12, 13) 1. Employees who are exempt from the FLSA are entitled for overtime pay for hours
CHABOT COLLEGE General Accounting (BUS-7) Dmitriy Kalyagin PART A: TRUE/FALSE (1 point each): EXAM #4 (Chapters 10, 12, 13) 1. Employees who are exempt from the FLSA are entitled for overtime pay for hours
CHAPTER 6. Accounting for retailing CONTENTS
 CHAPTER 6 Accounting for retailing CONTENTS 6.1 Journal entries periodic inventory system 6.2 Journal entries involving discounts, closing entries and statements of financial performance both perpetual
CHAPTER 6 Accounting for retailing CONTENTS 6.1 Journal entries periodic inventory system 6.2 Journal entries involving discounts, closing entries and statements of financial performance both perpetual
Accumulated Depreciation Equipment
 Chapter 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle > DO IT! Worksheet Balance sheet: Extend assets to debit column. Extend liabilities to credit column. Extend contra assets to credit column. Extend drawings account
Chapter 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle > DO IT! Worksheet Balance sheet: Extend assets to debit column. Extend liabilities to credit column. Extend contra assets to credit column. Extend drawings account
TRANSACTIONS ANALYSIS EXAMPLE. Maxwell Partners Medical Diagnostic Services report the following information for 2011, their first year of operations:
 TRANSACTIONS ANALYSIS EXAMPLE Maxwell Partners Medical Diagnostic Services report the following information for 2011, their first year of operations: 1. Billings to clients for services provided: $350,000
TRANSACTIONS ANALYSIS EXAMPLE Maxwell Partners Medical Diagnostic Services report the following information for 2011, their first year of operations: 1. Billings to clients for services provided: $350,000
Chapter 4: Accounting Records
 Chapter 4: Accounting Records Structure and terminology of Double Entry Bookkeeping The T account records the effect of transactions under one accounting aspect two opposite effects possible, e.g. inflows
Chapter 4: Accounting Records Structure and terminology of Double Entry Bookkeeping The T account records the effect of transactions under one accounting aspect two opposite effects possible, e.g. inflows
Basic Accounting Principles
 Basic Accounting Principles Basic Accounting Model The basic accounting model represents the relationship between assets (what the company owns), liabilities (what the company owes), and owner s equity
Basic Accounting Principles Basic Accounting Model The basic accounting model represents the relationship between assets (what the company owns), liabilities (what the company owes), and owner s equity
Financial Accounting. (Exam)
 Financial Accounting (Exam) Your AccountingCoach PRO membership includes lifetime access to all of our materials Take a quick tour by visiting wwwaccountingcoachcom/quicktour Table of Contents (click to
Financial Accounting (Exam) Your AccountingCoach PRO membership includes lifetime access to all of our materials Take a quick tour by visiting wwwaccountingcoachcom/quicktour Table of Contents (click to
Statement of Cash Flows
 PREPARING THE STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS: THE INDIRECT METHOD OF REPORTING CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES The work sheet method described in the text book is not the recommended approach. We will provide
PREPARING THE STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS: THE INDIRECT METHOD OF REPORTING CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES The work sheet method described in the text book is not the recommended approach. We will provide
> DO IT! Chapter 3 Adjusting the Accounts. Timing Concepts. Adjusting Entries for Deferrals D-12. Solution
 Chapter 3 Adjusting the Accounts Timing Concepts Review the glossary terms. Study carefully the revenue recognition principle, the expense recognition principle, and the time period assumption. Several
Chapter 3 Adjusting the Accounts Timing Concepts Review the glossary terms. Study carefully the revenue recognition principle, the expense recognition principle, and the time period assumption. Several
CHAPTER 3 ADJUSTING THE ACCOUNTS
 CHAPTER 3 ADJUSTING THE ACCOUNTS TIME PERIOD ASSUMPTION The time period (or periodicity) assumption assumes that the economic life of a business can be divided into artificial time periods generally a
CHAPTER 3 ADJUSTING THE ACCOUNTS TIME PERIOD ASSUMPTION The time period (or periodicity) assumption assumes that the economic life of a business can be divided into artificial time periods generally a
The Adjusting Process
 Chapter 03.qxd 5/21/08 7:07 PM Page 99 C H A P T E R 3 AP Photo/Jeff Kravitz Fo r Sa le The Adjusting Process M A R V E L D E N T E R T A I N M E N T, N ot o you subscribe to any magazines? Most of us
Chapter 03.qxd 5/21/08 7:07 PM Page 99 C H A P T E R 3 AP Photo/Jeff Kravitz Fo r Sa le The Adjusting Process M A R V E L D E N T E R T A I N M E N T, N ot o you subscribe to any magazines? Most of us
b. Do not recognize revenue until steel is shipped. c. Do not recognize revenue until next year after the games are played.
 CHAPTER FOUR SE4-2 Revenue recognition a. Recognize revenue from car sales for 12,000. Notes receivable $12,000 Sales revenue $12,000 b. Do not recognize revenue until steel is shipped. c. Do not recognize
CHAPTER FOUR SE4-2 Revenue recognition a. Recognize revenue from car sales for 12,000. Notes receivable $12,000 Sales revenue $12,000 b. Do not recognize revenue until steel is shipped. c. Do not recognize
2-8. Identify whether each of the following items increases or decreases cash flow:
 Problems 2-8. Identify whether each of the following items increases or decreases cash flow: Increase in accounts receivable Increase in notes payable Depreciation expense Increase in investments Decrease
Problems 2-8. Identify whether each of the following items increases or decreases cash flow: Increase in accounts receivable Increase in notes payable Depreciation expense Increase in investments Decrease
COMPLETING THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE
 4 COMPLETING THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE objectives After studying this chapter, you should be able to: Review the seven basic steps of the accounting cycle. Prepare a work sheet. Prepare financial statements
4 COMPLETING THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE objectives After studying this chapter, you should be able to: Review the seven basic steps of the accounting cycle. Prepare a work sheet. Prepare financial statements
CHART OF ACCOUNTS. OWNER S EQUITY 301 Jack Hines, Capital 305 Jack Hines, Withdrawals. REVENUE 401 Web Service Fees
 MINI PRACTICE SET 1 CHART OF S ASSETS 101 Cash in Bank 105 Accounts Receivable Andrew Hospital 110 Accounts Receivable Indiana Trucking 115 Accounts Receivable Sunshine Products 130 Office Supplies 135
MINI PRACTICE SET 1 CHART OF S ASSETS 101 Cash in Bank 105 Accounts Receivable Andrew Hospital 110 Accounts Receivable Indiana Trucking 115 Accounts Receivable Sunshine Products 130 Office Supplies 135
Learn Accounting Understand Business: Course Review Answers
 Learn Accounting Understand Business: Course Review Answers 1. What type of accounting measures the activity of the company by looking at economic events regardless of when cash transactions occur? A.
Learn Accounting Understand Business: Course Review Answers 1. What type of accounting measures the activity of the company by looking at economic events regardless of when cash transactions occur? A.
Accounting I/DMACC ACC 111
 Accounting I/DMACC ACC 111 Accounting is the study of the accounting cycle for both a sole proprietorship and a partnership. The learner is expected to complete an accounting packet covering the whole
Accounting I/DMACC ACC 111 Accounting is the study of the accounting cycle for both a sole proprietorship and a partnership. The learner is expected to complete an accounting packet covering the whole
Objective Evidence. Unit of Measurement. Accounting Period Cycle. Business Entity. Going Concern. Adequate Disclosure. Matching Expenses with Revenue
 Accounting Concept: A source document is prepared for each transaction Objective Evidence Accounting Concept: Business transactions are stated in numbers that have common values; that is, using a common
Accounting Concept: A source document is prepared for each transaction Objective Evidence Accounting Concept: Business transactions are stated in numbers that have common values; that is, using a common
Chapter 6: Closing Entries and the Postclosing Trial Balance
 Chapter 6: Closing Entries and the Postclosing Trial Chapter Opener: Thinking Critically Students should recognize that financial statements can be used to evaluate net profit or loss, return on investments,
Chapter 6: Closing Entries and the Postclosing Trial Chapter Opener: Thinking Critically Students should recognize that financial statements can be used to evaluate net profit or loss, return on investments,
Unit 2 The Basic Accounting Cycle
 Unit 2 The Basic Accounting Cycle Chapter 3 Chapter 4 Chapter 5 Chapter 6 Chapter 7 Chapter 8 Chapter 9 Business Transactions and the Accounting Equation Transactions That Affect Assets, Liabilities, and
Unit 2 The Basic Accounting Cycle Chapter 3 Chapter 4 Chapter 5 Chapter 6 Chapter 7 Chapter 8 Chapter 9 Business Transactions and the Accounting Equation Transactions That Affect Assets, Liabilities, and
E2-2: Identifying Financing, Investing and Operating Transactions?
 E2-2: Identifying Financing, Investing and Operating Transactions? Listed below are eight transactions. In each case, identify whether the transaction is an example of financing, investing or operating
E2-2: Identifying Financing, Investing and Operating Transactions? Listed below are eight transactions. In each case, identify whether the transaction is an example of financing, investing or operating
The Accounting Cycle Completed
 5 The Accounting Cycle Completed Adjusting, Closing, and Post-Closing Trial Balance THE BIG PICTURE You are planning your school schedule for next term. Your goal is to take a full course load and find
5 The Accounting Cycle Completed Adjusting, Closing, and Post-Closing Trial Balance THE BIG PICTURE You are planning your school schedule for next term. Your goal is to take a full course load and find
Review of Accounting Principles
 Appendix A Review of Accounting Principles Appendix A is a review of basic accounting principles and procedures. Standard accounting procedures are based on the double-entry system. This means that each
Appendix A Review of Accounting Principles Appendix A is a review of basic accounting principles and procedures. Standard accounting procedures are based on the double-entry system. This means that each
A Simple Model. The Accounting Equation
 An introduction to the accounting equation in the context of building a financial model. This series introduces the financial statements in the context of a financial model. NOTES TO ACCOMPANY VIDEOS These
An introduction to the accounting equation in the context of building a financial model. This series introduces the financial statements in the context of a financial model. NOTES TO ACCOMPANY VIDEOS These
Accounting for a Merchandising Business
 CHAPTER 10 Accounting for a Merchandising Business SECTION 10.1 REVIEW QUESTIONS (page 401) 1. A service business sells a service to the general public but does not deal in merchandise. For example, a
CHAPTER 10 Accounting for a Merchandising Business SECTION 10.1 REVIEW QUESTIONS (page 401) 1. A service business sells a service to the general public but does not deal in merchandise. For example, a
Billing Matters Accounting Sunset
 WHITE PAPER Billing Matters Accounting Sunset May 2013 Introduction... 2 Key Differences in Process... 2 How to Transition... 3 QuickBooks Setup... 4 What Do I Need... 4 QuickBooks Installation and Creation
WHITE PAPER Billing Matters Accounting Sunset May 2013 Introduction... 2 Key Differences in Process... 2 How to Transition... 3 QuickBooks Setup... 4 What Do I Need... 4 QuickBooks Installation and Creation
Chapter 8. Describe an effective accounting information system. Learning Objectives. Objective 1. Accounting Information Systems
 PowerPoint to accompany Chapter 8 Accounting Information Systems Learning Objectives 1. Describe an effective accounting information system 2. Understand both computerised and manual accounting systems
PowerPoint to accompany Chapter 8 Accounting Information Systems Learning Objectives 1. Describe an effective accounting information system 2. Understand both computerised and manual accounting systems
Prerequisite: None or as established by individual college. 3.0 semester credit hours/4.5 quarter credit hours/45 contact hours
 I. CATALOG DESCRIPTION ACCT-1200 Principles of Accounting I Prerequisite: None or as established by individual college This course is designed to provide introductory knowledge of accounting principles,
I. CATALOG DESCRIPTION ACCT-1200 Principles of Accounting I Prerequisite: None or as established by individual college This course is designed to provide introductory knowledge of accounting principles,
THEME: CLOSING THE BOOKS
 THEME: CLOSING THE BOOKS By John W. Day, MBA ACCOUNTING TERM: Support Document A support document is one that verifies that the ending balance of a general ledger (GL) account is accurate. For example,
THEME: CLOSING THE BOOKS By John W. Day, MBA ACCOUNTING TERM: Support Document A support document is one that verifies that the ending balance of a general ledger (GL) account is accurate. For example,
Bookkeeping Tips & T Accounts Prepared by Accomp Services (www.accompservices.ca)
 Bookkeeping Tips & T Accounts Prepared by Accomp Services (www.accompservices.ca) Further valuable accounting and bookkeeping website resources are listed at the end of this document. A business is one
Bookkeeping Tips & T Accounts Prepared by Accomp Services (www.accompservices.ca) Further valuable accounting and bookkeeping website resources are listed at the end of this document. A business is one
CHAPTER 3 The Accounting Information System
 CHAPTER 3 The Accounting Information System 3-1 LECTURE OUTLINE Chapter 3 provides a review of accounting procedures throughout the accounting cycle. Depending on time constraints and students accounting
CHAPTER 3 The Accounting Information System 3-1 LECTURE OUTLINE Chapter 3 provides a review of accounting procedures throughout the accounting cycle. Depending on time constraints and students accounting
The worksheet for Hancock Company shows the following in the financial statement
 Chapter 4 Do it! Susan Elbe is preparing a worksheet. Explain to Susan how she should extend the following adjusted trial balance accounts to the financial statement columns of the worksheet. Cash Accumulated
Chapter 4 Do it! Susan Elbe is preparing a worksheet. Explain to Susan how she should extend the following adjusted trial balance accounts to the financial statement columns of the worksheet. Cash Accumulated
ACCT 652 Accounting. Review of last week. Review of last time (2) 1/25/16. Week 3 Merchandisers and special journals
 ACCT 652 Accounting Week 3 Merchandisers and special journals Some slides Times Mirror Higher Education Division, Inc. Used by permission Michael D. Kinsman, Ph.D. Review of last week Some highlights of
ACCT 652 Accounting Week 3 Merchandisers and special journals Some slides Times Mirror Higher Education Division, Inc. Used by permission Michael D. Kinsman, Ph.D. Review of last week Some highlights of
Haddon Township High School Course Overview
 Haddon Township High School Course Overview Subject Area: Business Education Course Name: Accounting I Summary: This course is designed to enable students to learn how to set up and maintain financial
Haddon Township High School Course Overview Subject Area: Business Education Course Name: Accounting I Summary: This course is designed to enable students to learn how to set up and maintain financial
CHAPTER 16. Non-current assets: Revaluation, disposal and other aspects CONTENTS
 CHAPTER 16 Non-current assets: Revaluation, disposal and other aspects CONTENTS 16.1 Non-current asset disposals 16.2 Revaluation and disposal 16.3 Intangibles and natural resources 16.4 Goodwill and discount
CHAPTER 16 Non-current assets: Revaluation, disposal and other aspects CONTENTS 16.1 Non-current asset disposals 16.2 Revaluation and disposal 16.3 Intangibles and natural resources 16.4 Goodwill and discount
Unit 2 The Basic Accounting Cycle
 Unit 2 The Basic Accounting Cycle Chapter 3 Chapter 4 Chapter 5 Chapter 6 Chapter 7 Chapter 8 Chapter 9 Business Transactions and the Accounting Equation Transactions That Affect Assets, Liabilities, and
Unit 2 The Basic Accounting Cycle Chapter 3 Chapter 4 Chapter 5 Chapter 6 Chapter 7 Chapter 8 Chapter 9 Business Transactions and the Accounting Equation Transactions That Affect Assets, Liabilities, and
WHY ADJUSTING JOURNAL ENTRIES? CHAPTER FIVE. ADJUSTING ENTRIES Page 145 MATCHING PRINCIPLE WHY ENDING BALANCE NOT CORRECT?
 CHAPTER FIVE ADJUSTING ENTRIES Page 1 WHY ADJUSTING JOURNAL ENTRIES?! All amounts must be correct before financial statements printed! Test ending balance in each account! Auditing! Test accounting system,
CHAPTER FIVE ADJUSTING ENTRIES Page 1 WHY ADJUSTING JOURNAL ENTRIES?! All amounts must be correct before financial statements printed! Test ending balance in each account! Auditing! Test accounting system,
The Double-Entry System EFFECTS OF TRANSACTIONS ON THE BALANCE SHEET. Initial Paid-in Capital. An Example Entity. Transaction 2.
 The Double-Entry System EFFECTS OF TRANSACTIONS ON THE BALANCE SHEET 2001 Richard S. Barr Transaction: Any event that affects the entity's financial position and requires recording Every accounting transaction
The Double-Entry System EFFECTS OF TRANSACTIONS ON THE BALANCE SHEET 2001 Richard S. Barr Transaction: Any event that affects the entity's financial position and requires recording Every accounting transaction
Financial Basics for Non-Financial Managers
 Financial Basics for Non-Financial Managers Presented By: Amy Gil of the Jessup Group AmyG@Jessup-group.com May 13, 2015 Discussion Items Role of finance in organization Basic Accounting Concepts Accounting
Financial Basics for Non-Financial Managers Presented By: Amy Gil of the Jessup Group AmyG@Jessup-group.com May 13, 2015 Discussion Items Role of finance in organization Basic Accounting Concepts Accounting
CENTURY 21 ACCOUNTING, 8e General Journal Chapter Objectives
 CENTURY 21 ACCOUNTING, 8e General Journal Chapter Objectives Chapter 1 Starting A Proprietorship: Changes that Affect the Accounting Equation After studying Chapter 1, you will be able to: 1. Define accounting
CENTURY 21 ACCOUNTING, 8e General Journal Chapter Objectives Chapter 1 Starting A Proprietorship: Changes that Affect the Accounting Equation After studying Chapter 1, you will be able to: 1. Define accounting
PART 5. External Reporting and Performance Evaluation. Statements of financial performance and position. Statement of cash flows 19
 PART 5 External Reporting and Performance Evaluation Statements of financial performance and position 18 Statement of cash flows 19 Analysis and interpretation of financial statements 20 CHAPTER 18 Statements
PART 5 External Reporting and Performance Evaluation Statements of financial performance and position 18 Statement of cash flows 19 Analysis and interpretation of financial statements 20 CHAPTER 18 Statements
Chapter 5 Accounting for Merchandising Operations
 Chapter 5 Accounting for Merchandising Operations Purchase Transactions Purchaser records goods at cost. When goods are returned, purchaser reduces Inventory. On September 5, De La Hoya Company buys merchandise
Chapter 5 Accounting for Merchandising Operations Purchase Transactions Purchaser records goods at cost. When goods are returned, purchaser reduces Inventory. On September 5, De La Hoya Company buys merchandise
The General Journal and the General Ledger
 3 The General Journal and the General Ledger DEMONSTRATION PROBLEM G. Bell, a fitness enthusiast, buys an existing exercise center, Body Firm. The following chart of accounts now applies: Assets Revenue
3 The General Journal and the General Ledger DEMONSTRATION PROBLEM G. Bell, a fitness enthusiast, buys an existing exercise center, Body Firm. The following chart of accounts now applies: Assets Revenue
ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems. Functional Area Systems. Lecture 4
 ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems Instructor: David Tenjo Functional Area Systems Lecture 4 1 Overview Overview of Functional Areas in the organization Functional Area: Accounting Accounting
ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems Instructor: David Tenjo Functional Area Systems Lecture 4 1 Overview Overview of Functional Areas in the organization Functional Area: Accounting Accounting
Course- Financial Management.
 Course- Financial Management. PHAR 4233 Semester/Year: Spring 2013 Course dates2/2/2013-2/27/2013 Lecture Objective Template Lecture #1/2 Date/time: 10:00 AM 1/3/2013 Lecture/Name Topic: Introduction to
Course- Financial Management. PHAR 4233 Semester/Year: Spring 2013 Course dates2/2/2013-2/27/2013 Lecture Objective Template Lecture #1/2 Date/time: 10:00 AM 1/3/2013 Lecture/Name Topic: Introduction to
Course- Financial Management.
 Course- Financial Management. PHAR 4233 Semester/Year: Spring 2015 Lecture Objective Template Lecture #1/2 Date/time: 10:00 AM 1/6-7/2015 Lecture/Name Topic: Introduction to Financial Management and Accounting
Course- Financial Management. PHAR 4233 Semester/Year: Spring 2015 Lecture Objective Template Lecture #1/2 Date/time: 10:00 AM 1/6-7/2015 Lecture/Name Topic: Introduction to Financial Management and Accounting
ACCT 652 Accounting. Review of last week. Should you always take discounts? 5/17/15. ACCT652 Week 4 1
 ACCT 652 Accounting Week 4 Special Journals, Cash, and Internal Controls Some slides Times Mirror Higher Education Division, Inc. Used by permission Michael D. Kinsman, Ph.D. Review of last week Some highlights
ACCT 652 Accounting Week 4 Special Journals, Cash, and Internal Controls Some slides Times Mirror Higher Education Division, Inc. Used by permission Michael D. Kinsman, Ph.D. Review of last week Some highlights
CHAPTER 4 COMPLETING THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY. True-False Statements
 CHAPTER 4 COMPLETING THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT True-False Statements 1. 1 K 9. 2 K 17. 4
CHAPTER 4 COMPLETING THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT True-False Statements 1. 1 K 9. 2 K 17. 4
Farm families have traditionally used the single entry (often referred to as cash) method of accounting
 File C6-33 July 2009 www.extension.iastate.edu/agdm Understanding Double Entry Accounting Farm families have traditionally used the single entry (often referred to as cash) method of accounting for their
File C6-33 July 2009 www.extension.iastate.edu/agdm Understanding Double Entry Accounting Farm families have traditionally used the single entry (often referred to as cash) method of accounting for their
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF THE ACCOUNTING PROCESS. Lecture Outline
 CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF THE ACCOUNTING PROCESS Overview Chapter 1 explained that the primary means of conveying financial information to investors, creditors, and other external users is through financial
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF THE ACCOUNTING PROCESS Overview Chapter 1 explained that the primary means of conveying financial information to investors, creditors, and other external users is through financial
Financial Statement Consolidation
 Financial Statement Consolidation We will consolidate the previously completed worksheets in this financial plan. In order to complete this section of the plan, you must have already completed all of the
Financial Statement Consolidation We will consolidate the previously completed worksheets in this financial plan. In order to complete this section of the plan, you must have already completed all of the
RAPID REVIEW Chapter Content
 RAPID REVIEW BASIC ACCOUNTING EQUATION (Chapter 2) INVENTORY (Chapters 5 and 6) Basic Equation Assets Owner s Equity Expanded Owner s Owner s Assets Equation = Liabilities Capital Drawing Revenues Debit
RAPID REVIEW BASIC ACCOUNTING EQUATION (Chapter 2) INVENTORY (Chapters 5 and 6) Basic Equation Assets Owner s Equity Expanded Owner s Owner s Assets Equation = Liabilities Capital Drawing Revenues Debit
Chapter 4. Completing the accounting cycle. Appendix 4A: Reversing entries
 1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle Appendix 4A: Reversing entries 2 Learning objective 1. Prepare reversing entries and describe their purpose 3 Reversing entries Reversing entries are optional
1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle Appendix 4A: Reversing entries 2 Learning objective 1. Prepare reversing entries and describe their purpose 3 Reversing entries Reversing entries are optional
Valencia Community College
 Valencia Community College Program Learning Outcomes Assessment Plan The following plan was developed by Accounting faculty during Destination 2009 for implementation during the 2009 2010 academic year.
Valencia Community College Program Learning Outcomes Assessment Plan The following plan was developed by Accounting faculty during Destination 2009 for implementation during the 2009 2010 academic year.
The Accounting Cycle Completed
 5 The Accounting Cycle Completed T HE B IG P ICTURE Accountants have come a long way from the old stereotype of bean counter a pale figure with a green eyeshade who tends cloth-bound ledgers and journals
5 The Accounting Cycle Completed T HE B IG P ICTURE Accountants have come a long way from the old stereotype of bean counter a pale figure with a green eyeshade who tends cloth-bound ledgers and journals
T Accounts, Debits and Credits, Trial Balance, and Financial Statements
 2 T Accounts, Debits and Credits, Trial Balance, and Financial Statements DEMONSTRATION PROBLEM maintains an office for the practice of veterinary medicine. The account balances as of September 1 are given
2 T Accounts, Debits and Credits, Trial Balance, and Financial Statements DEMONSTRATION PROBLEM maintains an office for the practice of veterinary medicine. The account balances as of September 1 are given
Student Solutions Manual to Accompany. Introduction to Financial Accounting. David Annand. Based on International Financial Reporting Standards
 Student Solutions Manual to Accompany Introduction to Financial Accounting Based on International Financial Reporting Standards David Annand Copyright 2014 David Annand Published by David Annand 4910C
Student Solutions Manual to Accompany Introduction to Financial Accounting Based on International Financial Reporting Standards David Annand Copyright 2014 David Annand Published by David Annand 4910C
How To Account For Revenue Under Accrual Accounting
 BAT 4M: Chapter 3 ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 01. (a) Under the time period assumption, an accountant is required to determine the relevance of each business transaction to specific accounting periods, and its
BAT 4M: Chapter 3 ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 01. (a) Under the time period assumption, an accountant is required to determine the relevance of each business transaction to specific accounting periods, and its
ACCT1115. Review Package - Midterm SOLUTION Fall 2013
 ACCT1115 Review Package - Midterm SOLUTION Fall 2013 Part I Multiple Choice 1) How should you record the purchase of an expensive automobile? a) Decrease cash, increase assets b) Decrease cash, increase
ACCT1115 Review Package - Midterm SOLUTION Fall 2013 Part I Multiple Choice 1) How should you record the purchase of an expensive automobile? a) Decrease cash, increase assets b) Decrease cash, increase
FBLA: ACCOUNTING I. Competency: Journalizing
 Competency: Journalizing 1. Prepare a multi-column journal for recording data. 2. Record transactions such as accounts receivables and accounts payables in appropriate journals. 3. Journalize or record
Competency: Journalizing 1. Prepare a multi-column journal for recording data. 2. Record transactions such as accounts receivables and accounts payables in appropriate journals. 3. Journalize or record
Definition of Accounting
 SOLUTIONS TO EXERCISES Lesson 1: Definition of Accounting 1. What is accounting? What are its main functions? Accounting is the process of financially measuring, recording, summarizing and communicating
SOLUTIONS TO EXERCISES Lesson 1: Definition of Accounting 1. What is accounting? What are its main functions? Accounting is the process of financially measuring, recording, summarizing and communicating
Changing from Cash to Accrual Accounting
 Changing from Cash to Accrual Accounting Contents About Changing the Accounting Method Creating a Client Disb Recov (1210) Account Contacting LexisNexis PCLaw Technical Support Adjusting Disbursements
Changing from Cash to Accrual Accounting Contents About Changing the Accounting Method Creating a Client Disb Recov (1210) Account Contacting LexisNexis PCLaw Technical Support Adjusting Disbursements
In the event of a tie, the score on the last ten questions will be used as a tie-breaker.
 NEW YORK STATE ASSOCIATION FUTURE BUSINESS LEADERS OF AMERICA SPRING DISTRICT MEETING ACCOUNTING I 2010 TEST DIRECTIONS 1. Complete the information requested on the answer sheet. PRINT your name on the
NEW YORK STATE ASSOCIATION FUTURE BUSINESS LEADERS OF AMERICA SPRING DISTRICT MEETING ACCOUNTING I 2010 TEST DIRECTIONS 1. Complete the information requested on the answer sheet. PRINT your name on the
CHAPTER 3. BE3-2 Advertising. Dec. 31 Advertising Supplies Expense 7200 Advertising Supplies 7200 to adjust. BE3-3 Bere Co.
 CHAPTER 3 BE3-2 Advertising Advertising Supplies Supplies Expense 8700 7200 7200 1500 7200 Dec. Advertising Supplies Expense 7200 Advertising Supplies 7200 BE3-3 Bere Co. Prepaid Insurance Insurance Expense
CHAPTER 3 BE3-2 Advertising Advertising Supplies Supplies Expense 8700 7200 7200 1500 7200 Dec. Advertising Supplies Expense 7200 Advertising Supplies 7200 BE3-3 Bere Co. Prepaid Insurance Insurance Expense
Section 2: The Bookkeeping Process (Module 3)
 Section 2: The Bookkeeping Process Dermott Crofton dcrofton@sd62.bc.ca 1 This Section of the Course Bookkeeping Process Double Entry Bookkeeping Rules of Debits and Credits The T-Account Representing transactions
Section 2: The Bookkeeping Process Dermott Crofton dcrofton@sd62.bc.ca 1 This Section of the Course Bookkeeping Process Double Entry Bookkeeping Rules of Debits and Credits The T-Account Representing transactions
Mastering the Cash Flow Statement & Free Cash Flow
 Mastering the Cash & Free Cash Flow CFA Levels I & II Jonathan.bone@kaplan.co.uk Financial Reporting and Analysis LOS 27.a Compare/Classify: CFAI pg 253 Schweser pg 109 Importance of Cash Net income from
Mastering the Cash & Free Cash Flow CFA Levels I & II Jonathan.bone@kaplan.co.uk Financial Reporting and Analysis LOS 27.a Compare/Classify: CFAI pg 253 Schweser pg 109 Importance of Cash Net income from
Fundamentals of Financial Accounting
 Fundamentals of Financial Accounting CHAPTER I Accounting in action. What is accounting? Accounting is the recording of financial transactions plus storing, sorting, retrieving, summarizing, and presenting
Fundamentals of Financial Accounting CHAPTER I Accounting in action. What is accounting? Accounting is the recording of financial transactions plus storing, sorting, retrieving, summarizing, and presenting
COURSE GUIDELINE--Accounting
 COURSE GUIDELINE--Accounting Grade: 9- (Elective Course, offered one semester at a time) SUBJECT: Accounting TEACHER: Reimer STANDARD QTR. RESOURCES STRATEGIES ASSESSMENTS. Define accounting and explain
COURSE GUIDELINE--Accounting Grade: 9- (Elective Course, offered one semester at a time) SUBJECT: Accounting TEACHER: Reimer STANDARD QTR. RESOURCES STRATEGIES ASSESSMENTS. Define accounting and explain
Accounting II Second Semester Final
 Name: Class: Date: Accounting II Second Semester Final Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Profit is the difference between:
Name: Class: Date: Accounting II Second Semester Final Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Profit is the difference between:
Chapter 4. Completing the accounting cycle
 1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle 2 Learning objectives 1. Prepare an accounting worksheet and describe its purpose 2. Prepare a classified balance sheet and explain the major headings 3. Explain
1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle 2 Learning objectives 1. Prepare an accounting worksheet and describe its purpose 2. Prepare a classified balance sheet and explain the major headings 3. Explain
Supplement to CHAPTER 3 CLOSING ENTRIES AND THE WORK SHEET
 Supplement to CHAPTER 3 CLOSING ENTRIES AND THE WORK SHEET Answers to Review Questions 1. No, the work sheet cannot be used as a substitute for the financial statements. It is a tool used in preparing
Supplement to CHAPTER 3 CLOSING ENTRIES AND THE WORK SHEET Answers to Review Questions 1. No, the work sheet cannot be used as a substitute for the financial statements. It is a tool used in preparing
