Original Article. Diagnostic Utility of F Waves in Clinically Diagnosed Patients of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Abstract. Introduction
|
|
|
- Sibyl Cobb
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 372 Indian Joshi/Gargate J Physiol Pharmacol 2013; 57(4) : Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 2013; 57(4) Original Article Diagnostic Utility of F Waves in Clinically Diagnosed Patients of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Anand G. Joshi* and Ashwini R. Gargate Department of Physiology, Krishna Institute of Medical Sciences Deemed University, Karad, Maharashtra (India) Abstract Sensory nerve conduction velocity (SNCV) of median nerve measured across the carpal tunnel, difference between distal sensory latencies (DSLs) of median and ulnar nerves and difference between distal motor latencies (DMLs) of median and ulnar nerves are commonly used nerve conduction parameters for diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). These are having high degree of sensitivity and specificity. Study of median nerve F-wave minimal latency (FWML) and difference between F-wave minimal latencies (FWMLs) of median and ulnar nerves have also been reported to be useful parameters for diagnosis of CTS. However, there is controversy regarding superiority of F-wave study for diagnosis of CTS. So the aim of present study was to compare sensitivity and specificity of median FWML and difference between FWMLs of median and ulnar nerves with that of above mentioned electrophysiological parameters and to find out which parameters are having more sensitivity and specificity, for early diagnosis of CTS. Methods : Median and ulnar nerves sensory and motor conduction, median and ulnar nerves F-wave studies were carried out bilaterally in 125 clinically diagnosed patients of carpal tunnel syndrome. These parameters were also studied in 45 age matched controls. Results : Difference between DSLs of median and ulnar nerves, median SNCV and difference between DMLs of median and ulnar nerves were having highest sensitivity and specificity while median FWML and difference between FWMLs of median and ulnar nerves was having lowest sensitivity and specificity for diagnosis of CTS. So in conclusion F-wave study is not superior parameter for diagnosis of CTS. Introduction Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is most common entrapment neuropathy in upper extremity. The carpal tunnel is bounded by carpal bones and transverse ligaments which are attached to scaphoid, trapezoid *Corresponding author : anandjoshikarad@yahoo.com Dr. Anand G. Joshi, Department of Physiology, Krishna Institute of Medical Sciences, Deemed University, Karad, Maharashtra (India) (received on April 4, 2013) and hamate bones. The diameter of carpal tunnel is 2 to 2.5 cm and median nerve passes through it along with nine digital flexor tendons. Some degree of compression of median nerve and focal nerve conduction slowing is common at this level which is more pronounced 2-3 cm distal to the origin of the ligament. Autopsy study has also confirmed focal abnormality in median nerve in 5 out of 12 asymptomatic subjects (1, 2). CTS is also been reported to be the commonest entrapment neuropathy in western countries. In Rochester, Minnesota, the prevalence of CTS was
2 Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 2013; 57(4) Diagnostic Utility of F Waves in Clinically Diagnosed Patients 373 estimated at 125 per 100,000 in Earlier hospital based studies from India reported CTS rarely. In recent study from South India CTS accounted for 7% of patients with peripheral nerve disorders and 84% of entrapment neuropathies referred for electro diagnostic evaluation (3, 4). Good history taking and proper clinical examination helps for clinical diagnosis of CTS. Clinical examination includes Tinel s test (tapping of the nerve at wrist induces tingling), Phalan s test (maximum flexion at wrist for 1 min induces symptoms). However, these tests are rather non-specific and unreliable (5). Along with clinical examination following electrophysiological parameters which have greater sensitivity and specificity are commonly used to diagnose CTS. These parameters are median nerve sensory conduction velocity (SNCV) measured across carpal tunnel, difference in distal sensory latencies (DSL) of median and ulnar nerves and difference between distal motor latencies (DML) of median and ulnar nerves (7). Study of median nerve FWML and difference between FWMLs of median and ulnar nerves have also been reported to be useful parameters for diagnosis of CTS (8, 9, 10). However, there is controversy regarding superiority of F-wave study compared to above mentioned parameters for diagnosis of CTS. So the aim of present study was to compare sensitivity and specificity of median FWML and difference between FWMLs of median and ulnar nerves with that of above mentioned electrophysiological parameters and to find out which parameters are having more sensitivity and specificity, for early diagnosis of CTS. Methods Inclusion criteria for patients Patients having symptoms suggestive of CTS i.e. aching pain in hand and arm (especially at night), parasthesia in thumb, index finger and middle finger for more than 4 weeks (5), Phalan s test positive, Tinel s sign positive. Exclusion criteria Patients having clinical or laboratory diagnosis of cervical spondylitis radiculopathy, neuropathy, diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, trauma, hypothyroidism pregnancy, chronic alcohol intake or any major illness were excluded from the study (5). Nerve conduction study was also performed on 45 age matched controls those were selected from medical students, teaching and non teaching staff and peons form medical college and hospital. Inclusion criteria for controls Apparently healthy age matched controls were selected who were not having any signs and symptoms of neurological disorder or any major illness Institutional ethical committee approval was taken for the study (Institutional ethical committee approval letter number: KIMSU/240/2008). Patients and subjects were informed the detailed procedure of nerve conduction study and written consent was taken. Electro diagnostic study included motor and sensory nerve conduction and F wave study of Median and Ulnar nerves on both sides by conventional method (1). Following parameters were measured. (Onset latencies were measured) Motor conduction : Nerve conduction study was conducted on 125 patients, referred to electrophysiology laboratory of Department of Physiology in Krishna Institute of Medical Sciences Karad, Maharashtra (India). Duration of study was June 2009 to June Distal motor latency of Median nerve and ulnar nerve Difference between distal motor latencies of median and ulnar nerves F-wave minimal latencies of median and ulnar nerves
3 374 Joshi/Gargate Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 2013; 57(4) Difference between F-wave minimal latencies of median and ulnar nerves Sensory conduction : Distal sensory latency of Median nerve and ulnar nerve Sensory conduction velocity Difference between distal sensory latencies of median and ulnar nerves: For recording sensory and motor nerve conduction, surface metal electrodes were used. For recording motor conduction of Median nerve, recording electrode was placed close to the motor point of Abductor Pollicis Brevis and reference electrode 3 cm distal to it at first metacarpophalangeal joint. A supramaximal stimulus was given at wrist and at elbow near volar crease of brachial pulse. For recording motor conduction of Ulnar nerve, recording electrode was placed close to the motor point of abductor digiti minimi and reference electrode 3 cm distal to it at fifth metacarpophalangeal joint. A supramaximal stimulus was given at wrist and at elbow in cubital tunnel behind medial epicondyle. For ulnar nerve stimulation at elbow arm position was maintained at 135 C (1). Care was taken to keep same distance between stimulating and recording electrodes for both median and ulnar nerves at wrist so that distal latencies of Median and Ulnar nerves could be compared (1). For orthodromic sensory conduction of median nerve, surface recording electrode was placed 3cm proximal to distal wrist crease and reference electrode at 3 cm proximal to recording electrode. For stimulation ring electrodes were fixed on second digit. For orthodromic sensory conduction of ulnar nerve, recording electrode was placed 3 cm proximal to distal palmer crease and reference electrode at 3cm proximal to recording electrode. For sensory stimulation ring electrodes were fixed on fifth digit. Cathode is placed at first interphalangeal joint and anode at 3 cm distal to cathode. For both median and ulnar sensory conduction, 20 supramaximal stimuli were delivered and average was recorded. During both median and ulnar sensory conduction recording, ground electrode was placed between recording and stimulating electrodes. Care was taken to keep same distance between stimulating and recording electrode for both median and ulnar nerves at wrist. For recording of F-wave response the surface recording electrode was placed in a belly tendon montage similar to motor nerve conduction study. For median nerve recording electrode was kept on APB muscle and for ulnar nerve it was kept on ADM muscle. The distance between the stimulating electrode at the wrist and recording electrode at the muscles was kept constant (8 cm) for median and ulnar nerves (11, 12). The F-wave recording was done from relaxed muscle. Conventional supramaximal stimulation was used. Cathode was placed proximal to anode to avoid anodal block. 10 such stimuli were given. From 10 tracings of F-waves, minimal F-wave latency (FWML) was measured. During nerve conduction study, laboratory temperature was maintained between 21 C to 23 C. When skin temperature of limb was below 34 C, the limb was immersed in a warm water to correct the temperature (1). For nerve conduction studies, Recorder and Medicare System machine (RMS EMG EP MK 2) from Chandigarh (India) was used. Statistical analysis The standard statistical unpaired t test was used to compare in both control and patients and p value was calculated. Mean and SD for different electrophysiological parameters were measured in controls and patients. Normality range for each electrophysiological parameter was determined from mean and SD of controls (normal healthy subjects). 95% normality range determined as mean±1.96 SD.
4 Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 2013; 57(4) Diagnostic Utility of F Waves in Clinically Diagnosed Patients 375 Results TABLE II : Comparison of F wave min latencies of median and ulnar nerves. DML - Distal motor latency; FWML-F-wave minimal latency Table I depicts the mean±standard deviation of conduction studies of all the parameters in control and in patients groups on Rt. & Lt. sides. In patients group the difference between DSLs of median and ulnar nerves was significantly increased (P<0.001) when compared to that of control group. Median nerve sensory velocity (SNCV) was significantly decreased in patients than in control group (P<0.001). Compared to control group difference between DMLs of median and ulnar nerves was significantly increased in patients (P<0.001). Median nerve F-wave minimal latency was significantly prolonged in patients (P<0.001). Table II depicts comparison of F wave min latencies of median and ulnar nerves. In patients, FWML of median nerve was significantly prolonged than that of ulnar nerve on both sides (P<0.001). In controls there was no significant difference in FWMLs of median and ulnar nerves (P>0.05). TABLE I : Nerve conduction parameters. Mean±SD Mean±SD T P Parameter Control Patients value value n=45 n=125 Difference In DSL Rt. 0.12± ± <0.001* Lt. 0.18± ± <0.001* Difference in DML Rt. 0.83± ± <0.001* Lt. 0.76± ± <0.001* Median SNCV (m/s) Rt ± ± <0.001* Lt ± ± <0.001* Median FWML (ms.) Rt ± ± <0.001* Lt ± ± <0.001* *Highly significant. SNCV - Sensory nerve conduction velocity; DSL - Distal sensory latency. F-min Rt. Rt. T P (ms) Median Ulnar value value In patients ± ± <0.001* In control ± ± F-min Lt. Lt. T P (ms) Median Ulnar value value In patients 26.78± ± <0.001* In control ± ± *Highly significant. Table no. III depicts that difference between F-min latency of median and ulnar nerves is highly significant on both sides (P<0001). Table IV depicts sensitivity and specificity of different parameters of nerve conduction studies. Median SNCV and difference in DSL of median and ulnar nerves was having higher sensitivity and specificity. However, the F-min latency test was having lower sensitivity and specificity. Difference in F-min latencies of median and ulnar nerves was having lowest sensitivity and specificity. TABLE III : Difference between mean F-minimal latencies of median and ulnar nerves. Parameter In patients In controls T P Mean±SD Mean±SD value value Difference between F-min. latencies of median & ulnar Rt. 2.98± ± <0.001* Lt. 2.79± ± <0.001* *Highly Significant. TABLE IV : Sensitivity and specificity of different nerve conduction parameters. Screening test Sensitivity Specificity SNCV 69.26% 93.33% Difference in DSL 63.55% 100% Difference in DML 46.8% 100% F-min. Median 36.17% 91.11% Difference in F-min of 23% 85.55% Med. And Uln. nerves
5 376 Joshi/Gargate Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 2013; 57(4) Discussion Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common clinical problem due to median nerve entrapment. It occurs most often in patients between yrs of age and is 5 times more common in women than men (9). In our study average age of controls was 45 years and in patient it was 46yrs and male to female ratio was 1:3. Even with good history and clinical examination at times it is difficult to diagnose CTS. The electrophysiological studies are now regarded as the gold standard diagnostic tests. It has a high degree of sensitivity and specificity (11). The electrophysiological diagnosis of CTS is based on conduction abnormalities across carpal tunnel as median nerve gets compressed in carpal tunnel (1, 3). Characteristic findings in the electrophysiological diagnosis of CTS were slowing sensory conduction of median nerve, decrease in SNAP amplitude, and increase in DSL and DML in median nerve (13, 14, 15). As ulnar nerve does not pass through carpal tunnel and passes lateral to tunnel its DML and DSL are expected to be normal. So difference between DML and DSL of median and ulnar nerve may be considered as very sensitive indicator of CTS (2, 14, 16). The findings in our study also show that the difference between DML and DSL of median and ulnar nerves was having highest sensitivity and specificity. The American Association of Electro diagnostic Medicine (AAEM) has concluded that median nerve sensory transmission is also more sensitive indicator for diagnosis of CTS (17). In this study median nerve sensory velocity was reduced as it was measured across the carpal tunnel. In severely affected patients sensory response was absent (24%). There was significant decrease in SNCV of the patients, on both sides. In our study difference between DSLs of median and ulnar nerve, difference between DMLs of median and ulnar nerves and median SNCV measured across the carpal tunnel were having highest sensitivity and specificity. Our findings are comparable with the results of other workers (2, 3, 4). Sensitivity and specificity of median nerve FWML and difference between FWMLs of median and ulnar nerves was very low. Our findings are not consistent with findings of other workers (8, 11). F-wave is a late response resulting from antidromic activation of motor neurons involving conduction to and from spinal cord and occurs at the interface between the peripheral and central nervous system (1, 7). The possible explanation for low sensitivity and specificity for F-wave parameters could be F- wave may not appear after each stimulus and is variable in configuration. Individual motor neurons are activated infrequently with antidromic stimulation and there are no more than few motor units in F- wave. F-wave latency varies with each stimulus depending upon type of neurons activated and their conduction velocity (7). Because of this variability the number of F-waves used for analysis in clinical studies are varied, at times this number being as high as 50 or even greater whereas others have argued that study of 3-5 F-waves are sufficient for accurate determination of F-wave latency. Consensus has developed in the literature that analysis of 10 to 20 F-waves is reasonable balance between feasibility and adequate data (7). Studies of APB muscle however have indicated that evaluation of F- wave stimuli are needed for accurate measurement of true latencies (7). In present study we have evaluated only 10 stimuli to obtain median FWML, this could be primary explanation for low sensitivity and specificity. F-wave latencies seem to be directly related to patient s height, limb-length and to lesser degree to the age. We have not used corrected values of F-minimal latencies for these parameters. This could be another reason that F-wave parameters were having less sensitivity and specificity for diagnosis of CTS. The present study has limitations that sample size was relatively smaller. Larger studies are needed to strengthen the interpretation. Further research is required to evaluate F-wave parameters with more number of stimuli and use of corrected F-wave latencies for height and age to observe whether sensitivity and specificity improves.
6 Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 2013; 57(4) Diagnostic Utility of F Waves in Clinically Diagnosed Patients 377 Conclusion Difference between DSLs of median and ulnar nerves, difference between distal motor latencies of median and ulnar nerves and median nerve sensory conduction velocity are the electrophysiological parameters with high sensitivity and specificity for diagnosis CTS. Minimal F-wave latency of median nerve and difference between minimal F-wave latencies of median and ulnar nerves are the parameters with lowest sensitivity and specificity for diagnosis CTS. So in conclusion compared to above mentioned parameters F-wave study is not superior parameter for diagnosis of CTS. Acknowledgments The authors are thankful to vice chancellor, KIMSDU and Principal, KIMSDU, Karad for kindly providing laboratory and hospital facilities to carry out this work. References 1. Mishra UK, Kalita J. Clinical neurophysiology, 2 nd Ed. Reed Elsevier India Private Limited, 2008; Gilliatt R.W. Sensory conduction studies in early recognition of nerve disorders. Muscle Nerve 1978; 1: Murthy JM, Meena AK. Carpal tunnel syndrome- Electrodiagnostic aspects of fifty seven symptomatic hands. Neurology India, 1999; 47: Atroshi I, Gummesson C, Johnson R, Ornsteir E. Diagnostic properties of nerve conduction tests in population-based Carpal tunnel syndrome: BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, 2003; 4: Murray Longmore, Ian B. Wilkinson. Carpal tunnel syndrome: the commonest mononeuropathy. Oxford handbook of clinical medicine, Indian edition, 8 th edition p. 507, Joshi AG, Gargate AR, Patil SN. Electrophysiological assessment of clinically diagnosed patients of carpal tunnel syndrome in western Maharashtra (India), July- Sept. 2013; 7: Michael J Aminoff. Electrodiagnosis in clinical neurology, 5 th Ed. Ed by Susan Pioli Elsevier, Churchil Livingstone, 2005; 308: Frank Weber. The diagnostic sensitivity of different F- wave parameters. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1998; 65: Geetanjali Sharma, Sushama Sood, Vivek Sharma. Early diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome in Indian patients by nerve conduction studies: Internet Journal of Medical Update 2010 July; 5(2): Mohammad Yazdchi, Reza Khandaghi, MA Arami. Evaluation of F-wave in carpal tunnel syndrome and its prognostic value: Journal of neurological sciences (Turkish), 2005; Vol. 22: Ashraf Husain, Syed Omar, Abdul-Majeed Al-Drees. F- ratio, a surrogate marker of carpal tunnel syndrome. Neurosciences 2009; Vol. 14(1): Daniel L. Menkes, Daniel C. Hood, Anneke C. Inversion of the F-waves in median neuropathy at wrist (carpal tunnel syndrome). Neurology and Clinical Investigations 1997; Thomus JM, Xuan Kong, Shai N Gozani. Utility of nerve conduction studies for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome by Family Medicine, Primary care and Internal Medicine Physicians: The Journal of the American Board of Family Medicine 2007; 20: Aydyn G, Keles I, Ozbudak Demir S, Baysal AY. Sensitivity of median sensory conduction tests in digital branches for diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. Phys Med Rehabil 2004; 83: Padua L, Lo Monaco M, Valente EM, Tonali PA. A useful electrophysiological parameter for diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve 1996; Jackson DA, Cliford JC. Electrodiagnosis of mild carpal tunnel syndrome. Phys Med Rehabil 1989; 70: AAEM: Practice parameter for electrodiagnostic studies in carpal tunnel syndrome: summery statement. Muscle Nerve, 2002; 25:
LATE RESPONSES IN MEDIAN NERVE ENTRAPMENT NEUROPATHY IN THE CARPAL TUNNEL
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series VI: Medical Sciences Vol. 7 (56) No.2-2014 LATE RESPONSES IN MEDIAN NERVE ENTRAPMENT NEUROPATHY IN THE CARPAL TUNNEL A. M. GALAMB 1 I. D. MINEA
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series VI: Medical Sciences Vol. 7 (56) No.2-2014 LATE RESPONSES IN MEDIAN NERVE ENTRAPMENT NEUROPATHY IN THE CARPAL TUNNEL A. M. GALAMB 1 I. D. MINEA
Internet Journal of Medical Update
 Internet Journal of Medical Update 2010 July;5(2):15-20 Internet Journal of Medical Update Journal home page: http://www.akspublication.com/ijmu Original Work Early diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Internet Journal of Medical Update 2010 July;5(2):15-20 Internet Journal of Medical Update Journal home page: http://www.akspublication.com/ijmu Original Work Early diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Utility of Nerve Conduction Study in Early Diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Utility of Nerve Conduction Study in Early Diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) Suchitra Parkhad 1, Sachin Palve 2 1 Department of Physiology, Chennai Medical College Hospital and
RESEARCH ARTICLE Utility of Nerve Conduction Study in Early Diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) Suchitra Parkhad 1, Sachin Palve 2 1 Department of Physiology, Chennai Medical College Hospital and
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, an overview
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, an overview Jim Lewis, R.NCS.T. Learning Objectives: Median nerve compression at the wrist is the most common entrapment seen in the electrodiagnostic laboratory. Although it is
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, an overview Jim Lewis, R.NCS.T. Learning Objectives: Median nerve compression at the wrist is the most common entrapment seen in the electrodiagnostic laboratory. Although it is
Aetna Nerve Conduction Study Policy
 Aetna Nerve Conduction Study Policy Policy Aetna considers nerve conduction velocity (NCV) studies medically necessary when both of the following criteria are met: 1. Member has any of the following indications:
Aetna Nerve Conduction Study Policy Policy Aetna considers nerve conduction velocity (NCV) studies medically necessary when both of the following criteria are met: 1. Member has any of the following indications:
Differentiating Cervical Radiculopathy and Peripheral Neuropathy. Adam P. Smith, MD
 Differentiating Cervical Radiculopathy and Peripheral Neuropathy Adam P. Smith, MD I have no financial, personal, or professional conflicts of interest to report Radiculopathy versus Neuropathy Radiculopathy
Differentiating Cervical Radiculopathy and Peripheral Neuropathy Adam P. Smith, MD I have no financial, personal, or professional conflicts of interest to report Radiculopathy versus Neuropathy Radiculopathy
EMG and the Electrodiagnostic Consultation for the Family Physician
 EMG and the Electrodiagnostic Consultation for the Family Physician Stephanie Kopey, D.O., P.T. 9/27/15 The American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM) Marketing Committee
EMG and the Electrodiagnostic Consultation for the Family Physician Stephanie Kopey, D.O., P.T. 9/27/15 The American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM) Marketing Committee
The Carpal Tunnel CTS. Stålberg 1. Dysfunction of median nerve in the carpal tunnel resulting in
 The Carpal Tunnel CTS Dysfunction of median nerve in the carpal tunnel resulting in 1 Symptoms in CTS pain and numbness in the abd worse on finger activity aggravated by forceful gripping g symptoms more
The Carpal Tunnel CTS Dysfunction of median nerve in the carpal tunnel resulting in 1 Symptoms in CTS pain and numbness in the abd worse on finger activity aggravated by forceful gripping g symptoms more
a) Nerve conduction studies (NCS) test the peripheral nervous system for:
 Health Plan Coverage Policy ARBenefits Approval: 11/02/2011 Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Revision Date: 09/18/2013 Comments: Code additions only. Title: Electrodiagnostic Testing Document: ARB0256 Public
Health Plan Coverage Policy ARBenefits Approval: 11/02/2011 Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Revision Date: 09/18/2013 Comments: Code additions only. Title: Electrodiagnostic Testing Document: ARB0256 Public
3nd Biennial Contemporary Clinical Neurophysiological Symposium October 12, 2013 Fundamentals of NCS and NMJ Testing
 3nd Biennial Contemporary Clinical Neurophysiological Symposium October 12, 2013 Fundamentals of NCS and NMJ Testing Peter D. Donofrio, M.D. Professor of Neurology Vanderbilt University Medical Center
3nd Biennial Contemporary Clinical Neurophysiological Symposium October 12, 2013 Fundamentals of NCS and NMJ Testing Peter D. Donofrio, M.D. Professor of Neurology Vanderbilt University Medical Center
Ulnar Neuropathy Differential Diagnosis and Prognosis. Disclosures: None
 Ulnar Neuropathy Differential Diagnosis and Prognosis Disclosures: None Goals of Lecture Describe anatomy: sites of entrapment Ulnar nerve Discuss differential diagnosis of ulnar nerve pathology Identify
Ulnar Neuropathy Differential Diagnosis and Prognosis Disclosures: None Goals of Lecture Describe anatomy: sites of entrapment Ulnar nerve Discuss differential diagnosis of ulnar nerve pathology Identify
CTS the Best EDX. Ernest W Johnson MD Emeritus Professor Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation The Ohio State University
 CTS the Best EDX Ernest W Johnson MD Emeritus Professor Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation The Ohio State University 1 Definition of CTS A syndrome 2d to dysfunction of median nerve in carpal tunnel resulting
CTS the Best EDX Ernest W Johnson MD Emeritus Professor Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation The Ohio State University 1 Definition of CTS A syndrome 2d to dysfunction of median nerve in carpal tunnel resulting
Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI)
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Other Musculoskeletal Problems in the Workplace: What s the Solution? by Richard N. Hinrichs, Ph.D. Dept. of Kinesiology Arizona State University Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI)
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Other Musculoskeletal Problems in the Workplace: What s the Solution? by Richard N. Hinrichs, Ph.D. Dept. of Kinesiology Arizona State University Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI)
Proximal border = palmar wrist crease Distal border = Kaplan + ring finger axis
 FPL FCR Proximal border = palmar wrist crease Distal border = Kaplan + ring finger axis Thenar motor branch Kaplan s cardinal line: distal TCL thenar branch Superficial palmar arch superficial arch Originates
FPL FCR Proximal border = palmar wrist crease Distal border = Kaplan + ring finger axis Thenar motor branch Kaplan s cardinal line: distal TCL thenar branch Superficial palmar arch superficial arch Originates
Chapter 2 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, Electroneurography, Electromyography, and Statistics
 Chapter 2 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, Electroneurography, Electromyography, and Statistics After reading this chapter you should: Know what basic techniques are employed in electroneurography Know what basic
Chapter 2 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, Electroneurography, Electromyography, and Statistics After reading this chapter you should: Know what basic techniques are employed in electroneurography Know what basic
Medical Report Checklist: Upper Extremities Peripheral Nerve Disorders Impairments (PND)
 http://www.pdratings.com/ Craig Andrew Lange craig@pdratings.com California Workers Compensation Certified AMA Guides Impairment & Disability Rating Specialists Voice: (415) 861-4040 / Fax: (415) 276-3741
http://www.pdratings.com/ Craig Andrew Lange craig@pdratings.com California Workers Compensation Certified AMA Guides Impairment & Disability Rating Specialists Voice: (415) 861-4040 / Fax: (415) 276-3741
Automated Analysis of Electromyography Data
 Automated Analysis of Electromyography Data Jeffrey L. Sponsler, MD, MS Alaska Brain Center, LLC 4551 E Bogard Rd Wasilla, AK 99654 ABSTRACT Background: Interpretation of nerve conduction studies (NCS)
Automated Analysis of Electromyography Data Jeffrey L. Sponsler, MD, MS Alaska Brain Center, LLC 4551 E Bogard Rd Wasilla, AK 99654 ABSTRACT Background: Interpretation of nerve conduction studies (NCS)
Usefulness of Electrodiagnostic Techniques in the Evaluation of Suspected Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome: An Evidence-based Review
 Usefulness of Electrodiagnostic Techniques in the Evaluation of Suspected Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome: An Evidence-based Review Reviewed 07/08 CME Available 7/08-7/11 No one involved in the planning of this
Usefulness of Electrodiagnostic Techniques in the Evaluation of Suspected Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome: An Evidence-based Review Reviewed 07/08 CME Available 7/08-7/11 No one involved in the planning of this
Billing and Coding Guidelines: NEURO-005 Nerve Conduction Studies and Electromyography. Contractor Name Wisconsin Physicians Service (WPS)
 Billing and Coding Guidelines: NEURO-005 Nerve Conduction Studies and Electromyography Contractor Name Wisconsin Physicians Service (WPS) Contractor Number 00951, 00952, 00953, 00954 05101, 05201, 05301,
Billing and Coding Guidelines: NEURO-005 Nerve Conduction Studies and Electromyography Contractor Name Wisconsin Physicians Service (WPS) Contractor Number 00951, 00952, 00953, 00954 05101, 05201, 05301,
Most active and intricate part of the upper extremity Especially vulnerable to injury Do not respond well to serious trauma. Magee, 2008. pg.
 PTA 216 Most active and intricate part of the upper extremity Especially vulnerable to injury Do not respond well to serious trauma Magee, 2008. pg. 396 28 bones Numerous articulations 19 intrinsic muscles
PTA 216 Most active and intricate part of the upper extremity Especially vulnerable to injury Do not respond well to serious trauma Magee, 2008. pg. 396 28 bones Numerous articulations 19 intrinsic muscles
Efficacy of Short-term Low Dose Oral Steroid in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 Efficacy of Short-term Low Dose Oral Steroid in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome *Alam MM, 1 Bari MS, 2 Ullah AK, 3 Haque A, 4 Sardar AH, 5 Mohammad KD 6 To determine the efficacy of four weeks course of oral steroid
Efficacy of Short-term Low Dose Oral Steroid in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome *Alam MM, 1 Bari MS, 2 Ullah AK, 3 Haque A, 4 Sardar AH, 5 Mohammad KD 6 To determine the efficacy of four weeks course of oral steroid
EFFECT OF BODY MASS INDEX ON PARAMETERS OF NERVE CONDUCTION STUDY IN INDIAN POPULATION
 Indian 88 Pawar J Physiol et al Pharmacol 2012; 56(1) : 88 93 Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 2012; 56(1) EFFECT OF BODY MASS INDEX ON PARAMETERS OF NERVE CONDUCTION STUDY IN INDIAN POPULATION SACHIN M. PAWAR,
Indian 88 Pawar J Physiol et al Pharmacol 2012; 56(1) : 88 93 Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 2012; 56(1) EFFECT OF BODY MASS INDEX ON PARAMETERS OF NERVE CONDUCTION STUDY IN INDIAN POPULATION SACHIN M. PAWAR,
by joe muscolino body mechanics
 by joe muscolino body mechanics carpal tunnel syndrome The word carpal means wrist. Therefore, the carpal tunnel is a tunnel that is formed by the structural configuration of the wrist (carpal) bones.
by joe muscolino body mechanics carpal tunnel syndrome The word carpal means wrist. Therefore, the carpal tunnel is a tunnel that is formed by the structural configuration of the wrist (carpal) bones.
Nerve conduction studies
 clinical William Huynh Matthew C Kiernan Nerve conduction studies This article forms part of our Tests and results series for 2011 which aims to provide information about common tests that general practitioners
clinical William Huynh Matthew C Kiernan Nerve conduction studies This article forms part of our Tests and results series for 2011 which aims to provide information about common tests that general practitioners
Sensitivity and specificity of terminal latency index and residual latency in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Sensitivity and specificity of terminal latency index and residual latency in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome E. UZAR, Y. TAMAM, A. ACAR,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Sensitivity and specificity of terminal latency index and residual latency in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome E. UZAR, Y. TAMAM, A. ACAR,
WHEN TO ORDER; HOW TO INTERPRET
 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY AND 1 NERVE CONDUCTION TESTING: WHEN TO ORDER; HOW TO INTERPRET Ronald N. Kent, M.D., Ph.D. 2 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY AND NERVE CONDUCTION TESTING EMG/NCS Testing is a component of a complete
ELECTROMYOGRAPHY AND 1 NERVE CONDUCTION TESTING: WHEN TO ORDER; HOW TO INTERPRET Ronald N. Kent, M.D., Ph.D. 2 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY AND NERVE CONDUCTION TESTING EMG/NCS Testing is a component of a complete
Chapter 7 The Wrist and Hand Joints
 Chapter 7 The Wrist and Hand Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Many Archery, Relate wrist require sports require precise functioning of flexion, & hand & hand functional combined
Chapter 7 The Wrist and Hand Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Many Archery, Relate wrist require sports require precise functioning of flexion, & hand & hand functional combined
December 29, 2012. Dear Acting Administrator Tavenner:
 December 29, 2012 Marilyn B. Tavenner Acting Administrator Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Attention: CMS-1590-FC P.O. Box 8013 Baltimore, MD 21244
December 29, 2012 Marilyn B. Tavenner Acting Administrator Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Attention: CMS-1590-FC P.O. Box 8013 Baltimore, MD 21244
Not applicable. Medical Coverage Policy Automated Point of- Care Nerve Conduction Tests EFFECTIVE DATE: 09 01 2016 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 07 19 2016
 Medical Coverage Policy Automated Point of- Care Nerve Conduction Tests EFFECTIVE DATE: 09 01 2016 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 07 19 2016 OVERVIEW Portable devices have been developed to provide point-of-care
Medical Coverage Policy Automated Point of- Care Nerve Conduction Tests EFFECTIVE DATE: 09 01 2016 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 07 19 2016 OVERVIEW Portable devices have been developed to provide point-of-care
MedStar Health, Inc. POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL
 MedStar Health, Inc. POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SUBJECT: Nerve Conduction Velocity Studies/Electrodiagnostic INDEX TITLE: Studies/Neuromuscular Medical Management Junction Testing ORIGINAL DATE: March
MedStar Health, Inc. POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SUBJECT: Nerve Conduction Velocity Studies/Electrodiagnostic INDEX TITLE: Studies/Neuromuscular Medical Management Junction Testing ORIGINAL DATE: March
Electrodiagnostic Testing
 Electrodiagnostic Testing Electromyogram and Nerve Conduction Study North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Electrodiagnostic Testing? The term electrodiagnostic testing covers a
Electrodiagnostic Testing Electromyogram and Nerve Conduction Study North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Electrodiagnostic Testing? The term electrodiagnostic testing covers a
ELECTRODIAGNOSTIC MEDICINE
 ELECTRODIAGNOSTIC MEDICINE OBJECTIVES BEGINNER Patient Care Perform a comprehensive electrodiagnostic evaluation of each patient and to provide a concise diagnosis and plan for further treatment Describe
ELECTRODIAGNOSTIC MEDICINE OBJECTIVES BEGINNER Patient Care Perform a comprehensive electrodiagnostic evaluation of each patient and to provide a concise diagnosis and plan for further treatment Describe
Informed Patient Tutorial Copyright 2012 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
 Informed Patient Tutorial Copyright 2012 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Informed Patient - Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery Introduction Welcome to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons'
Informed Patient Tutorial Copyright 2012 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Informed Patient - Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery Introduction Welcome to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons'
Radiculopathy vs. Peripheral Neuropathy. What to do with arm pain? Defining Arm Pain. Arm Pain
 Radiculopathy vs. Peripheral Neuropathy What to do with arm pain? Miriana G. Popadich RN, MSN Clinical Care Coordinator Brachial Plexus Program Department of Neurosurgery University of Michigan Timing
Radiculopathy vs. Peripheral Neuropathy What to do with arm pain? Miriana G. Popadich RN, MSN Clinical Care Coordinator Brachial Plexus Program Department of Neurosurgery University of Michigan Timing
Basic Concepts. Focal and Entrapment Neuropathies and EMG. Pathophysiology. Median Nerve. A Clinical Approach
 Basic Concepts Focal and Entrapment Neuropathies and EMG A Clinical Approach Nerves predisposed by a narrow anatomic pathway or superficial course are most susceptible May occur acutely, intermittantly,
Basic Concepts Focal and Entrapment Neuropathies and EMG A Clinical Approach Nerves predisposed by a narrow anatomic pathway or superficial course are most susceptible May occur acutely, intermittantly,
ELECTROMYOGRAPHY (EMG), NEEDLE, NERVE CONDUCTION STUDIES (NCS) AND QUANTITATIVE SENSORY TESTING (QST)
 AND QUANTITATIVE SENSORY TESTING (QST) Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical
AND QUANTITATIVE SENSORY TESTING (QST) Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical
NOT DESIGNATED FOR PUBLICATION
 NOT DESIGNATED FOR PUBLICATION BEFORE THE ARKANSAS WORKERS' COMPENSATION COMMISSION CLAIM NO. F503749 EVLYNENE KIRKENDOLPH, EMPLOYEE C L A I M ANT DF&A REVENUE SERVICES DIVISION/ OFFICE OF CHILD SUPPORT
NOT DESIGNATED FOR PUBLICATION BEFORE THE ARKANSAS WORKERS' COMPENSATION COMMISSION CLAIM NO. F503749 EVLYNENE KIRKENDOLPH, EMPLOYEE C L A I M ANT DF&A REVENUE SERVICES DIVISION/ OFFICE OF CHILD SUPPORT
CENTER FOR HEALTH AND SAFETY IN THE WORKPLACE
 CENTER FOR HEALTH AND SAFETY IN THE WORKPLACE A study by the RAND Institute for Civil Justice and RAND Health CHILDREN AND FAMILIES EDUCATION AND THE ARTS ENERGY AND ENVIRONMENT HEALTH AND HEALTH CARE
CENTER FOR HEALTH AND SAFETY IN THE WORKPLACE A study by the RAND Institute for Civil Justice and RAND Health CHILDREN AND FAMILIES EDUCATION AND THE ARTS ENERGY AND ENVIRONMENT HEALTH AND HEALTH CARE
Nerve Conduction Velocity (NCV) & Electromyography (EMG) Studies
 Nerve Conduction Velocity (NCV) & Electromyography (EMG) Studies [Preauthorization Required] Medical Policy: MP-ME-09-09 Original Effective Date: November 5, 2010 Reviewed: November 5, 2010 Reviewed: November
Nerve Conduction Velocity (NCV) & Electromyography (EMG) Studies [Preauthorization Required] Medical Policy: MP-ME-09-09 Original Effective Date: November 5, 2010 Reviewed: November 5, 2010 Reviewed: November
Electroneuromyographic studies
 Electroneuromyographic studies in the diagnosis of Pudendal Entrapment Syndrome BY NAGLAA ALI GADALLAH PROFESSOR OF PHYSICAL MEDICINE, RHEUMATOLOGY& REHABILITATION AIN SHAMS UNIVERSITY Pudendal neuralgia
Electroneuromyographic studies in the diagnosis of Pudendal Entrapment Syndrome BY NAGLAA ALI GADALLAH PROFESSOR OF PHYSICAL MEDICINE, RHEUMATOLOGY& REHABILITATION AIN SHAMS UNIVERSITY Pudendal neuralgia
NERVE COMPRESSION DISORDERS
 Common Disorders of the Hand and Wrist Ryan Klinefelter, MD Associate Professor of Orthopaedics Department of Orthopaedics The Ohio State University Medical Center NERVE COMPRESSION DISORDERS 1 Carpal
Common Disorders of the Hand and Wrist Ryan Klinefelter, MD Associate Professor of Orthopaedics Department of Orthopaedics The Ohio State University Medical Center NERVE COMPRESSION DISORDERS 1 Carpal
APPENDIX F INTERJURISDICTIONAL RESEARCH
 Ontario Scheduled Presumption: Bursitis, listed in Schedule 3, of the Ontario Workers Compensation Act, entry number 18 Description of Disease Bursitis Process Any process involving constant or prolonged
Ontario Scheduled Presumption: Bursitis, listed in Schedule 3, of the Ontario Workers Compensation Act, entry number 18 Description of Disease Bursitis Process Any process involving constant or prolonged
Name of Policy: Neuromuscular and Electrodiagnostic Testing (EDX): Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS) and Electromyography (EMG) Studies
 Name of Policy: Neuromuscular and Electrodiagnostic Testing (EDX): Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS) and Electromyography (EMG) Studies Policy #: 228 Latest Review Date: August 2015 Category: Medicine Policy
Name of Policy: Neuromuscular and Electrodiagnostic Testing (EDX): Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS) and Electromyography (EMG) Studies Policy #: 228 Latest Review Date: August 2015 Category: Medicine Policy
How To Know If You Can Get A Carpal Tunnel Injury Compensation
 U. S. DEPARTMENT OF LABOR Employees Compensation Appeals Board In the Matter of BARBARA SNYDER and DEPARTMENT OF THE TREASURY, INTERNAL REVENUE SERVICE, Germansville, PA Docket No. 03-1467; Submitted on
U. S. DEPARTMENT OF LABOR Employees Compensation Appeals Board In the Matter of BARBARA SNYDER and DEPARTMENT OF THE TREASURY, INTERNAL REVENUE SERVICE, Germansville, PA Docket No. 03-1467; Submitted on
CERVICAL DISC HERNIATION
 CERVICAL DISC HERNIATION Most frequent at C 5/6 level but also occur at C 6 7 & to a lesser extent at C4 5 & other levels In relatively younger persons soft disk protrusion is more common than hard disk
CERVICAL DISC HERNIATION Most frequent at C 5/6 level but also occur at C 6 7 & to a lesser extent at C4 5 & other levels In relatively younger persons soft disk protrusion is more common than hard disk
A handheld nerve conduction measuring device in carpal tunnel syndrome
 Acta Neurol Scand DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.2007.00799.x Copyright Ó 2007 The Authors Journal compilation Ó 2007 Blackwell Munksgaard ACTA NEUROLOGICA SCANDINAVICA A handheld nerve conduction measuring
Acta Neurol Scand DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.2007.00799.x Copyright Ó 2007 The Authors Journal compilation Ó 2007 Blackwell Munksgaard ACTA NEUROLOGICA SCANDINAVICA A handheld nerve conduction measuring
Ergonomics Monitor Training Manual
 Table of contents I. Introduction Ergonomics Monitor Training Manual II. Definition of Common Injuries Common Hand & Wrist Injuries Common Neck & Back Injuries Common Shoulder & Elbow Injuries III. Ergonomics
Table of contents I. Introduction Ergonomics Monitor Training Manual II. Definition of Common Injuries Common Hand & Wrist Injuries Common Neck & Back Injuries Common Shoulder & Elbow Injuries III. Ergonomics
How To Diagnose And Diagnose Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 Electrodiagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Leilei Wang, MD, PhD* KEYWORDS Carpal tunnel syndrome Electrodiagnosis Combined Sensory Index Nerve conduction study KEY POINTS Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) will
Electrodiagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Leilei Wang, MD, PhD* KEYWORDS Carpal tunnel syndrome Electrodiagnosis Combined Sensory Index Nerve conduction study KEY POINTS Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) will
Ms. Jackson is the Manager of Health Finance and Reimbursement, Division of Health Policy and Practice Services, Washington, DC.
 Electrodiagnostic Testing with Same Day Evaluation Management By: Shane J. Burr, MD; Scott I. Horn, DO; Jenny J. Jackson, MPH, CPC; Joseph P. Purcell, DO Dr. Burr practices general inpatient and outpatient
Electrodiagnostic Testing with Same Day Evaluation Management By: Shane J. Burr, MD; Scott I. Horn, DO; Jenny J. Jackson, MPH, CPC; Joseph P. Purcell, DO Dr. Burr practices general inpatient and outpatient
Diagnosis and Treatment of Cervical Root and Peripheral Nerve Lesions of the Upper Extremity: Carpal and Cubital Tunnel Syndromes
 A Quarterly Publication for Continuing Medical Education Diagnosis and Treatment of Cervical Root and Peripheral Nerve Lesions of the Upper Extremity: Carpal and Cubital Tunnel Syndromes Ann R. Stroink,
A Quarterly Publication for Continuing Medical Education Diagnosis and Treatment of Cervical Root and Peripheral Nerve Lesions of the Upper Extremity: Carpal and Cubital Tunnel Syndromes Ann R. Stroink,
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences EFFECTS OF EXERCISES ON REPETITIVE STRAIN INJURIES OF HAND IN MILKMEN ABSTRACT
 Research Article Physiotherapy International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 EFFECTS OF EXERCISES ON REPETITIVE STRAIN INJURIES OF HAND IN MILKMEN PROF.TUSHAR J PALEKAR *1, ANIRUDHA VAIDYA
Research Article Physiotherapy International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 EFFECTS OF EXERCISES ON REPETITIVE STRAIN INJURIES OF HAND IN MILKMEN PROF.TUSHAR J PALEKAR *1, ANIRUDHA VAIDYA
How To Diagnose And Treat Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 AANEM MONOGRAPH ELECTRODIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION OF CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME ROBERT A. WERNER, MD, MS 1 and MICHAEL ANDARY, MD, MS 2 1 University of Michigan Health System, Ann Arbor Veterans Health System,
AANEM MONOGRAPH ELECTRODIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION OF CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME ROBERT A. WERNER, MD, MS 1 and MICHAEL ANDARY, MD, MS 2 1 University of Michigan Health System, Ann Arbor Veterans Health System,
2.01.77. Description. Section: Medicine Effective Date: October 15, 2014 Subsection: Medicine Original Policy Date: December 7, 2011 Subject:
 Last Review Status/Date: September 2014 Page: 1 of 11 Description Portable devices have been developed to provide point-of-care nerve conductions studies. These devices have computational algorithms that
Last Review Status/Date: September 2014 Page: 1 of 11 Description Portable devices have been developed to provide point-of-care nerve conductions studies. These devices have computational algorithms that
Sensory-Motor Index is Useful Parameter in Electroneurographical Diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 & Sensory-Motor Index is Useful Parameter in Electroneurographical Diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Zoran Perić¹, Osman Sinanović²* 1. Department of Neurology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Niš,
& Sensory-Motor Index is Useful Parameter in Electroneurographical Diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Zoran Perić¹, Osman Sinanović²* 1. Department of Neurology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Niš,
Electrodiagnostic Testing
 Electrodiagnostic Testing Table of Contents Related Policies Policy Number 359 Policy Statement Purpose.. 1 2 Competency in Electrophysiologic Testing Original Effective Date: Current Approval Date: 1/1997
Electrodiagnostic Testing Table of Contents Related Policies Policy Number 359 Policy Statement Purpose.. 1 2 Competency in Electrophysiologic Testing Original Effective Date: Current Approval Date: 1/1997
Not applicable. Medical Coverage Policy Automated Point-of-Care Nerve Conduction EFFECTIVE DATE: 03 03 2015 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 03 03 2015
 Medical Coverage Policy Automated Point-of-Care Nerve Conduction EFFECTIVE DATE: 03 03 2015 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 03 03 2015 OVERVIEW Portable devices have been developed to provide point-of-care nerve
Medical Coverage Policy Automated Point-of-Care Nerve Conduction EFFECTIVE DATE: 03 03 2015 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 03 03 2015 OVERVIEW Portable devices have been developed to provide point-of-care nerve
THE WRIST. At a glance. 1. Introduction
 THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
AN EDUCATION BASED ERGONOMIC INTERVENTION PROGRAMME FOR GAUTENG CALL CENTRE WORKERS WITH UPPER EXTREMITY REPETITIVE STRAIN INJURIES.
 AN EDUCATION BASED ERGONOMIC INTERVENTION PROGRAMME FOR GAUTENG CALL CENTRE WORKERS WITH UPPER EXTREMITY REPETITIVE STRAIN INJURIES. Sancha Eliot Johannesburg 2010 DECLARATION I SANCHA ELIOT declare that
AN EDUCATION BASED ERGONOMIC INTERVENTION PROGRAMME FOR GAUTENG CALL CENTRE WORKERS WITH UPPER EXTREMITY REPETITIVE STRAIN INJURIES. Sancha Eliot Johannesburg 2010 DECLARATION I SANCHA ELIOT declare that
Laboratory Guide. Anatomy and Physiology
 Laboratory Guide Anatomy and Physiology TBME04, Fall 2010 Name: Passed: Last updated 2010-08-13 Department of Biomedical Engineering Linköpings Universitet Introduction This laboratory session is intended
Laboratory Guide Anatomy and Physiology TBME04, Fall 2010 Name: Passed: Last updated 2010-08-13 Department of Biomedical Engineering Linköpings Universitet Introduction This laboratory session is intended
Electrodiagnostic Assessment: An Introduction to NCS and EMG
 Electrodiagnostic Assessment: An Introduction to NCS and EMG Barry Bernacki BSc MD FRCPC CSCN (EMG) Clinical Asst. Professor EMG Lab Director Saskatoon City Hospital Objectives Understand technique and
Electrodiagnostic Assessment: An Introduction to NCS and EMG Barry Bernacki BSc MD FRCPC CSCN (EMG) Clinical Asst. Professor EMG Lab Director Saskatoon City Hospital Objectives Understand technique and
Manual of Nerve Conduction Studies. Second Edition
 Manual of Nerve Conduction Studies Second Edition This page intentionally left blank Manual of Nerve Conduction Studies Second Edition Ralph M. Buschbacher, MD Nathan D. Prahlow, MD Indiana University
Manual of Nerve Conduction Studies Second Edition This page intentionally left blank Manual of Nerve Conduction Studies Second Edition Ralph M. Buschbacher, MD Nathan D. Prahlow, MD Indiana University
The wrist and hand are constructed of a series of complex, delicately balanced joints whose function is essential to almost every act of daily living.
 TOPIC OUTLINE 9- THE WRIST AND HAND. Introduction. The wrist and hand are constructed of a series of complex, delicately balanced joints whose function is essential to almost every act of daily living.
TOPIC OUTLINE 9- THE WRIST AND HAND. Introduction. The wrist and hand are constructed of a series of complex, delicately balanced joints whose function is essential to almost every act of daily living.
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME
 CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME Background 1. Definition: Entrapment neuropathy of median nerve as it courses through carpal tunnel o Stage I: Predominantly nocturnal symptoms of numbness and /or tingling in fingers
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME Background 1. Definition: Entrapment neuropathy of median nerve as it courses through carpal tunnel o Stage I: Predominantly nocturnal symptoms of numbness and /or tingling in fingers
Mini Medical School: Focus on Orthopaedics
 from The Cleveland Clinic Mini Medical School: Focus on Orthopaedics Common Disorders of the Hand and Wrist Jeffrey Lawton, MD Associate Staff, Department of Orthopaedic The Cleveland Clinic Appointments:
from The Cleveland Clinic Mini Medical School: Focus on Orthopaedics Common Disorders of the Hand and Wrist Jeffrey Lawton, MD Associate Staff, Department of Orthopaedic The Cleveland Clinic Appointments:
Symptoms and Signs of Irritation of the Brachial Plexus in Whiplash Injuries
 1 Symptoms and Signs of Irritation of the Brachial Plexus in Whiplash Injuries J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 2001 Mar;83(2):226-9 Ide M, Ide J, Yamaga M, Takagi K Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kumamoto University
1 Symptoms and Signs of Irritation of the Brachial Plexus in Whiplash Injuries J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 2001 Mar;83(2):226-9 Ide M, Ide J, Yamaga M, Takagi K Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kumamoto University
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Medical Treatment Guidelines Proposed by the State of New York Department of Insurance to the Workers Compensation Board
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Medical Treatment Guidelines Proposed by the State of New York Department of Insurance to the Workers Compensation Board July 2011 Draft TABLE OF CONTENTS I. INTRODUCTION 1 II. HISTORY
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Medical Treatment Guidelines Proposed by the State of New York Department of Insurance to the Workers Compensation Board July 2011 Draft TABLE OF CONTENTS I. INTRODUCTION 1 II. HISTORY
Medical Treatment Guidelines Washington State Department of Labor and Industries
 Medical Treatment Guidelines Washington State Department of Labor and Industries Work-Related Ulnar Neuropathy at the Elbow (UNE) Diagnosis and Treatment* I. Introduction Table of Contents II. III. Establishing
Medical Treatment Guidelines Washington State Department of Labor and Industries Work-Related Ulnar Neuropathy at the Elbow (UNE) Diagnosis and Treatment* I. Introduction Table of Contents II. III. Establishing
Original Policy Date
 MP 2.01.50 Automated Point-of-Care Nerve Conduction Tests Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature review/12:2013 Return
MP 2.01.50 Automated Point-of-Care Nerve Conduction Tests Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature review/12:2013 Return
Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities. John A. Schneider, M.D.
 Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities John A. Schneider, M.D. Biographical Sketch Dr. Schneider is an orthopedic surgeon that specializes in the treatment of hand and upper extremity
Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities John A. Schneider, M.D. Biographical Sketch Dr. Schneider is an orthopedic surgeon that specializes in the treatment of hand and upper extremity
Motor Unit Number Estimates and Quantitative Motor Unit Potentials Analysis Associated with Motor Deficits in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome.
 Motor Unit Number Estimates and Quantitative Motor Unit Potentials Analysis Associated with Motor Deficits in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome by Joseph Nashed A thesis submitted to the Department of Rehabilitation
Motor Unit Number Estimates and Quantitative Motor Unit Potentials Analysis Associated with Motor Deficits in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome by Joseph Nashed A thesis submitted to the Department of Rehabilitation
Original Article. Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine INTRODUCTION
 Original Article Ann Rehabil Med 2012; 36: 72-79 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2012.36.1.72 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Ultrasonography of Median Nerve and Electrophysiologic
Original Article Ann Rehabil Med 2012; 36: 72-79 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2012.36.1.72 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Ultrasonography of Median Nerve and Electrophysiologic
International Encyclopedia of Rehabilitation
 International Encyclopedia of Rehabilitation Copyright 2010 by the Center for International Rehabilitation Research Information and Exchange (CIRRIE). All rights reserved. No part of this publication may
International Encyclopedia of Rehabilitation Copyright 2010 by the Center for International Rehabilitation Research Information and Exchange (CIRRIE). All rights reserved. No part of this publication may
Pain Management. Practical Applications in Electrotherapy
 Pain Management Practical Applications in Electrotherapy The TENS Advantage Deliver Immediate Pain Relief using a unique waveform designed to help prevent nerve accommodation. Manage Dynamic Pain by adjusting
Pain Management Practical Applications in Electrotherapy The TENS Advantage Deliver Immediate Pain Relief using a unique waveform designed to help prevent nerve accommodation. Manage Dynamic Pain by adjusting
Role of Electrodiagnostic Tests in Neuromuscular Disease
 Role of Electrodiagnostic Tests in Neuromuscular Disease Electrodiagnostic tests Electroencephalogram (EEG) Electromyography (NCV, EMG) Cerebral evoked potentials (CEP) Motor evoked potentials (MEP) Electronystagmogram
Role of Electrodiagnostic Tests in Neuromuscular Disease Electrodiagnostic tests Electroencephalogram (EEG) Electromyography (NCV, EMG) Cerebral evoked potentials (CEP) Motor evoked potentials (MEP) Electronystagmogram
CONSTRUCTION WORK and CUMULATIVE TRAUMA DISORDERS
 Connecticut Department of Public Health Environmental and Occupational Health Assessment Program 410 Capitol Avenue MS # 11OSP, PO Box 340308 Hartford, CT 06134-0308 (860) 509-7740 http://www.ct.gov/dph
Connecticut Department of Public Health Environmental and Occupational Health Assessment Program 410 Capitol Avenue MS # 11OSP, PO Box 340308 Hartford, CT 06134-0308 (860) 509-7740 http://www.ct.gov/dph
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME
 THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME The Problem The term thoracic outlet syndrome is used to describe a condition of compression of the nerves and/or blood vessels in the region around the neck and collarbone, called
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME The Problem The term thoracic outlet syndrome is used to describe a condition of compression of the nerves and/or blood vessels in the region around the neck and collarbone, called
ISSN 2347-954X (Print) Research Article. *Corresponding author Dr. Abhijeet A. Adgaonkar Email:
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2014; 2(6A):1973-1977 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2014; 2(6A):1973-1977 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Podiatric Surgeon s Primer on Thyroid Pathology and Entrapment Neuropathies
 Podiatric Surgeon s Primer on Thyroid Pathology and Entrapment Neuropathies Damien M. Dauphinee, DPM, FACFAS, CWS-P Past President Association of Extremity Nerve Surgeons Goals and Objectives Is there
Podiatric Surgeon s Primer on Thyroid Pathology and Entrapment Neuropathies Damien M. Dauphinee, DPM, FACFAS, CWS-P Past President Association of Extremity Nerve Surgeons Goals and Objectives Is there
Entrapment and Compressive Neuropathies
 Entrapment and Compressive Neuropathies Barbara E. Shapiro, MD, PhD*, David C. Preston, MD KEYWORDS Entrapment neuropathy Compressive neuropathy Entrapment and compressive neuropathies of the upper and
Entrapment and Compressive Neuropathies Barbara E. Shapiro, MD, PhD*, David C. Preston, MD KEYWORDS Entrapment neuropathy Compressive neuropathy Entrapment and compressive neuropathies of the upper and
EXTENSOR POLLICIS TENDONITIS SYNDROME
 EXTENSOR POLLICIS TENDONITIS SYNDROME The extensor pollicis longus muscle has its origin on the lateral part of the middle third of the ulnar shaft on the dorsal border below the abductor pollicis longus
EXTENSOR POLLICIS TENDONITIS SYNDROME The extensor pollicis longus muscle has its origin on the lateral part of the middle third of the ulnar shaft on the dorsal border below the abductor pollicis longus
Background Š Compression neuropathy: Nerve compression resulting in nerve dysfunction. Upper Extremity Nerve Entrapments
 Upper Extremity Nerve Entrapments Compression Neuropathies: Pathophysiology Scott P. Olvey, MD 1 2 Goals Understand peripheral nerve histology Understand the pathophysiology of peripheral nerve compression
Upper Extremity Nerve Entrapments Compression Neuropathies: Pathophysiology Scott P. Olvey, MD 1 2 Goals Understand peripheral nerve histology Understand the pathophysiology of peripheral nerve compression
Lean-Ergonomic methods to reduce workers compensation costs (Part 2 of 2) Cumulative trauma disorders can be classified as: What is CTD?
 #425 Lean-ergonomic methods to reduce workers compensation costs, Part 2 of 2 Lean-Ergonomic methods to reduce workers compensation costs (Part 2 of 2) Govid Bharwani, Ph.D, Biomedical Engineering Thursday,
#425 Lean-ergonomic methods to reduce workers compensation costs, Part 2 of 2 Lean-Ergonomic methods to reduce workers compensation costs (Part 2 of 2) Govid Bharwani, Ph.D, Biomedical Engineering Thursday,
Muscles of the Forearm and Hand
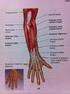 8 Muscles of the Forearm and Hand 132 PRONATOR TERES Strengthening exercises Pronation with strength bar Self stretches Weight of stick increases supination via gravity PRONATOR TERES 133 Latin, pronate,
8 Muscles of the Forearm and Hand 132 PRONATOR TERES Strengthening exercises Pronation with strength bar Self stretches Weight of stick increases supination via gravity PRONATOR TERES 133 Latin, pronate,
A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a
A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a
BEFORE THE APPEALS BOARD FOR THE KANSAS DIVISION OF WORKERS COMPENSATION
 BEFORE THE APPEALS BOARD FOR THE KANSAS DIVISION OF WORKERS COMPENSATION BARBARA SHEREE HUTSON ) Claimant ) ) VS. ) Docket No. 1,035,700 ) CUSTOM CAMPERS, INC. ) Self-Insured Respondent ) ORDER Claimant
BEFORE THE APPEALS BOARD FOR THE KANSAS DIVISION OF WORKERS COMPENSATION BARBARA SHEREE HUTSON ) Claimant ) ) VS. ) Docket No. 1,035,700 ) CUSTOM CAMPERS, INC. ) Self-Insured Respondent ) ORDER Claimant
CUMMULATIVE DISORDERS OF UPPER EXTIMITY DR HABIBOLLAHI
 CUMMULATIVE DISORDERS OF UPPER EXTIMITY DR HABIBOLLAHI Definition Musculoskeletal disorder (MSD) is an injury or disorder of the muscles, nerves, tendons, joints, cartilage,ligament and spinal discs. It
CUMMULATIVE DISORDERS OF UPPER EXTIMITY DR HABIBOLLAHI Definition Musculoskeletal disorder (MSD) is an injury or disorder of the muscles, nerves, tendons, joints, cartilage,ligament and spinal discs. It
A Hidden Challenge in WORKERS COMPENSATION
 Published by the Public Risk Management Association www.primacentral.org A Hidden Challenge in WORKERS COMPENSATION APRIL 2015 A Hidden Challenge in WORKERS COMPENSATION By Dr. John Robinton 2 PUBLIC RISK
Published by the Public Risk Management Association www.primacentral.org A Hidden Challenge in WORKERS COMPENSATION APRIL 2015 A Hidden Challenge in WORKERS COMPENSATION By Dr. John Robinton 2 PUBLIC RISK
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME A PATIENT GUIDE TO THE NURSE-LED CARPAL TUNNEL SERVICE
 CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME A PATIENT GUIDE TO THE NURSE-LED CARPAL TUNNEL SERVICE Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is carpal tunnel syndrome? It is entrapment of a nerve at the
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME A PATIENT GUIDE TO THE NURSE-LED CARPAL TUNNEL SERVICE Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is carpal tunnel syndrome? It is entrapment of a nerve at the
Work-related upper extremity disorders associated
 Nerve entrapments of the wrist Early treatment preserves function Nerve entrapment syndromes may affect as many as one in four office workers. Prompt diagnosis is critical to the selection of an appropriate
Nerve entrapments of the wrist Early treatment preserves function Nerve entrapment syndromes may affect as many as one in four office workers. Prompt diagnosis is critical to the selection of an appropriate
Elbow Examination. Haroon Majeed
 Elbow Examination Haroon Majeed Key Points Inspection Palpation Movements Neurological Examination Special tests Joints above and below Before Starting Introduce yourself Explain to the patient what the
Elbow Examination Haroon Majeed Key Points Inspection Palpation Movements Neurological Examination Special tests Joints above and below Before Starting Introduce yourself Explain to the patient what the
10/15/2012. The Hand. Clarification of Terms. Osteology of the Hand (Bones) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=idxuwerttj A&feature=related
 The Hand http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=idxuwerttj A&feature=related Clarification of Terms The hand is made up of the thumb, metacarpals, and phalanges The digits are numbered (with the thumb being #1
The Hand http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=idxuwerttj A&feature=related Clarification of Terms The hand is made up of the thumb, metacarpals, and phalanges The digits are numbered (with the thumb being #1
Topic: Automated Point-of-Care Nerve Conduction Studies Date of Origin: April 3, 2007. Section: Medicine Last Reviewed Date: December 2014
 Medical Policy Manual Topic: Automated Point-of-Care Nerve Conduction Studies Date of Origin: April 3, 2007 Section: Medicine Last Reviewed Date: December 2014 Policy No: 128 Effective Date: March 1, 2015
Medical Policy Manual Topic: Automated Point-of-Care Nerve Conduction Studies Date of Origin: April 3, 2007 Section: Medicine Last Reviewed Date: December 2014 Policy No: 128 Effective Date: March 1, 2015
OVERVIEW. NEUROSURGICAL ASSESSMENT CERVICAL PROBLEMS Dirk G. Franzen, M.D. WHAT IS THE MOST IMPORTANT PART OF THE PHYSICAL EXAM?
 NEUROSURGICAL ASSESSMENT CERVICAL PROBLEMS Dirk G. Franzen, M.D. Neurological Surgery Bluegrass Orthopaedics and Hand Care OVERVIEW SCOPE OF THE PROBLEM PREVALENCE PATHOLOGY ANATOMIC CONSIDERATIONS ASSESSMENT
NEUROSURGICAL ASSESSMENT CERVICAL PROBLEMS Dirk G. Franzen, M.D. Neurological Surgery Bluegrass Orthopaedics and Hand Care OVERVIEW SCOPE OF THE PROBLEM PREVALENCE PATHOLOGY ANATOMIC CONSIDERATIONS ASSESSMENT
Anatomy of the Carpal Tunnel. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Ultrasound: Normal Nerve. Ultrasound: Median Nerve/Carpal Tunnel
 Courses In Diagnostic Ultrasound Wake Forest School of Medicine US for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Lecture Outline Steven Shook, MD Staff, Neuromuscular Center Cleveland Clinic Neurological Institute April
Courses In Diagnostic Ultrasound Wake Forest School of Medicine US for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Lecture Outline Steven Shook, MD Staff, Neuromuscular Center Cleveland Clinic Neurological Institute April
CLINICAL NEUROPHYSIOLOGY
 CLINICAL NEUROPHYSIOLOGY Barry S. Oken, MD, Carter D. Wray MD Objectives: 1. Know the role of EMG/NCS in evaluating nerve and muscle function 2. Recognize common EEG findings and their significance 3.
CLINICAL NEUROPHYSIOLOGY Barry S. Oken, MD, Carter D. Wray MD Objectives: 1. Know the role of EMG/NCS in evaluating nerve and muscle function 2. Recognize common EEG findings and their significance 3.
Fractures around wrist
 Fractures around wrist Colles Fracture Smiths fracture Barton s fracture Chauffer s fracture Scaphoid fracture Lunate dislocation Vivek Pandey Colles fracture Definition: Fracture of the distal end radius
Fractures around wrist Colles Fracture Smiths fracture Barton s fracture Chauffer s fracture Scaphoid fracture Lunate dislocation Vivek Pandey Colles fracture Definition: Fracture of the distal end radius
Recommended Policy for Electrodiagnostic Medicine American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine
 Recommended Policy for Electrodiagnostic Medicine American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine Executive Summary The electrodiagnostic medicine (EDX) evaluation is an important and
Recommended Policy for Electrodiagnostic Medicine American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine Executive Summary The electrodiagnostic medicine (EDX) evaluation is an important and
Consensus & Practice Policy Guidelines July 7, 2015 - Volume 31
 American Association of Sensory Electrodiagnostic Medicine Consensus & Practice Policy Guidelines July 7, 2015 - Volume 31 GOLD STANDARD - PAIN DIAGNOSIS PAIN FIBER NERVE CONDUCTION STUDY (PF- NCS) NATIONAL
American Association of Sensory Electrodiagnostic Medicine Consensus & Practice Policy Guidelines July 7, 2015 - Volume 31 GOLD STANDARD - PAIN DIAGNOSIS PAIN FIBER NERVE CONDUCTION STUDY (PF- NCS) NATIONAL

 Full version is >>> HERE
Full version is >>> HERE