Viruses, Viroids & Prions. Viruses. ! millions could fit on the head of a pin. nonliving infectious agents capable of causing diseases
|
|
|
- Dorthy Hollie Long
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Viruses, Viroids & Prions nonliving infectious agents capable of causing diseases too small to see with regular microscope even though they are not alive; we still use the terminology of biology to describe them and how they work Viruses viruses are not alive (remember characteristics of life)! they do not consist of cells! they do not contain both DNA and RNA many completely lack DNA! they do not grow! they do not take in nutrients or release waste products! they don t have the machinery to reproduce themselves viruses are strict parasites!infect virtually every form of life, every kingdom viruses are by far the most abundant and diverse of all genetic entities viruses are millions of times more common than previously thought they are also the smallest Microbiology & Diseases: Viruses, Prions & Viroids; Ziser Lecture Notes ! millions could fit on the head of a pin yet if you stacked all the world s viruses end to end they would reach a distance of over 200 million light years (almost to the Andromeda galaxy) History of Study of Viruses: remained part of the invisible world until late 1800 s 1880 s: Pasteur knew that rabies was caused by something smaller than bacteria 1890 s: viruses were first isolated 1930 s: viruses crystallized; life doesn t crystallize, cannot be living organisms 1940 s: viruses first seen in with newly invented electron microscope most of our knowledge of viruses has come in the last 50 years Viral Structure size: millions could fit on head of pin nm (0.2 14!m) bacteria are 1000 s - 10 s of 1000 s of times larger (1-10!m) there may be about 100 Million different kinds of viruses all viruses are made of at least 2 parts; Microbiology & Diseases: Viruses, Prions & Viroids; Ziser Lecture Notes an inner core of nucleic acid 2. enclosed in protein capsid 3. some also contain lipoprotein envelope 1. Nucleic Acid viruses contain a single kind of nucleic acid can be circular, linear or in several separate segments can be DNA or RNA, never both only a few genes: viruses don t need lots of genes like living cells they use the genes, synthesis machinery and enzymes of host cells to reproduce no one gene is found in all viruses but a small group of genes are found in most viruses most viruses have 6-10 genes smallest have 4, largest have 100 s of genes eg. smallpox has genes (but bacteria, eg. E. coli 16 time more) Microbiology & Diseases: Viruses, Prions & Viroids; Ziser Lecture Notes includes few 1000 to 250,000 pairs of nucleotides (E. coli! 4M pairs of nucleotides) 2. capsid or protein shell surrounds the nucleic acid makes up most of the mass of the virus particles many different shapes of capsids 3. some covered with viral envelope derived from membrane of host cell Origin of Viruses 80% of the genes found in individual virus particles are completely unknown and not found anywhere else, not even in other kinds of viruses we used to think that viruses were degenerate fragments of their hosts DNA most virologists now think that they arose as independent genetic entities probably prior to the first living cells we cannot construct an evolutionary tree of viruses each virus seems to be a random grab-bag of genetic material assembled from a worldwide pool of nucleic acids Microbiology & Diseases: Viruses, Prions & Viroids; Ziser Lecture Notes
2 this and their rapid rate of mutation make viruses the most fertile sources of novel nucleic acid sequences 10-20% of the DNA in all life forms seems to be derived from viral DNA these viral genes apparently play important roles in the function and evolution of many life forms some now believe that life arose, probably many different times, from a primoridal stew of virus particles trading genes and continuously generating new and more efficient metabolic pathways Typical Virus Life Cycle : 1. attachment onto specific host cell! its what makes them host specific 2. penetration either by 1. injection of nucleic acid!injection can by hypodermic like Microbiology & Diseases: Viruses, Prions & Viroids; Ziser Lecture Notes enzymes may dissolve a hole in cell membrane of host 3. entire virus particle gets taken in by phagocytosis triggered by virus 3. Synthesis of new virus particles once inside, host protein synthesis is stopped then virus has host make proteins to: seal cell puncture wound copy viral genome make capsid proteins produce enzmes for lysis of host enzymes needed for protein synthesis, ribosomes, energy production are supplied by host cell 4. Lysis release of virus and death of host cell a single virus can give rise to up to 1000 new virus particles from one host cell (average = ) duration of viral life cycle in host cell averages minutes polio: 6-8hrs herpes: 12-30min Microbiology & Diseases: Viruses, Prions & Viroids; Ziser Lecture Notes some viruses remain dormant for a time in host cell and become part of the hosts genome temporarily Role of Viruses in Biosphere viruses outnumber bacteria 10 to 1 in most ecosystems est 10 quintillion (1 followed by 31 0 s) viruses infect every form of life Beneficial Effects: eg. bacterial viruses play an important role in protecting our bodies our membranes are filled with bacteriophages (viruses that kill bacteria) by destroying invading bacteria eg. we are learning that viruses play a major role in transferring genes from one organism to another often a major part of adaptation and evolution of life when viruses are replicated by host cell the new virus particles are often released containing genes from their host when they infect a new host cell those genes can be introduced into it Microbiology & Diseases: Viruses, Prions & Viroids; Ziser Lecture Notes Microbiology & Diseases: Viruses, Prions & Viroids; Ziser Lecture Notes
3 in many cases the virus lies dormant for extended periods allowing the host to incorporate the new genes into its genome in this way viruses have been a main force in the evolution of life on earth eg. a sea slug is able to use the chloroplasts from algae that it eats only because it has incorporated a couple of essential genes given to it by a virus eg. viruses also play a huge role in controlling nutrient and energy cycles in the biosphere viruses are the most numerous entities in the ocean! a thimble of seawater contains millions! placed end to end, all the virus particles in the ocean would stretch into space further than the nearest 60 galaxies eg. viruses infect and kill ~20% of algae and cyanobacteria in the ocean every day such large scale death of these microorganisms profoundly affects:! the makeup of the oceans microbial communities! the cycling of nutrients in biogeochemical cycles Microbiology & Diseases: Viruses, Prions & Viroids; Ziser Lecture Notes ! sedimentation and accumulation of biogenic deposits eg. white cliffs of dover! affect global climate by removing 3 gigatonnes of carbon from the sea each year a completely new kind of virus has been recently discovered = pandora viruses they are the largest viruses known, they have almost as many genes as some bacteria ( ), and 90% of their genes are new to science Pathogenicity of Viruses pathogenicity = how easily disease is spread most viruses are easily spread most common means of transfer is by contact with secretions from infected person eg. Colds & Flu when you cough you can deposit up to 1M viruses in your hand one person can leave 1000 s of viral particles behind by touching things takes as few as 10 particles to infect average person cold viruses can survive up to 72 hrs on glass, steel and formica surfaces susceptibility to any microbial disease depends in part Microbiology & Diseases: Viruses, Prions & Viroids; Ziser Lecture Notes on its infectious dose (ID) = the number of particles required to be likely to cause an infection if only a few they may be overcome by a persons defense system humans tend to be susceptible to a lower ID for viruses than for most other kinds of pathogens eg. infectious hepatitis (hep A) ~ eg. rabies ~10 virus particles Examples of Viruses 1. viral diseases eg rabies, cold, flu, HIV 2. viruses have also been implicated in some chronic diseases but connections are still unclear: diabetes obesity breast cancer prostate cancer eg. polio ~2 eg. measles ~1 Virulence virulence = how bad the disease actually is; how much damage it causes symptoms of viral diseases range from very mild (asymptomatic) to lethal acute to chronic infections many are childhood diseases, some self limiting others remain a lifetime Microbiology & Diseases: Viruses, Prions & Viroids; Ziser Lecture Notes Microbiology & Diseases: Viruses, Prions & Viroids; Ziser Lecture Notes
4 eg. Rabies Examples of viral Diseases: animal disease = zoonosis worldwide most commonly passed to humans by dog bites; in US mainly by wild animals in nature rabies is a viral disease of carnivores skunks, foxes, raccoons, bats, coyotes also infects other domesticated animals: cats, cattle, sheep transmission to humans is rare and almost always fatal if not treated 100 s/yr in US infected usually transmitted by bite or lick from infected animal! virus particles are in saliva ~80% from bites of wild animals ~20% from bites of domestic animals might also be transmitted by aerosols and enter the lungs eg. in bat caves long incubation time (1-1.5 months) before symptoms appear Microbiology & Diseases: Viruses, Prions & Viroids; Ziser Lecture Notes !can be vaccinated after exposure if in the first week or so vaccines are typically given BEFORE exposure initially the virus multiplies in skeletal muscle and connective tissues! remains localized for days or months then it enters peripheral nerves and travels along nerves to CNS (can take up to 3 months) once it enters the CNS it is no longer accessible to the immune system there causes encephalitis and painful death if the original bite is in an area rich in nerve fibers (eg. hands or face) the incubation period is shorter Symptoms: Initial: mild then muscle spasms!esp in face and neck Once it gets in CNS: agitation vs calm periods spasms of mouth and throat muscles esp when swallowing! painful throat spasms & convulsive choking Microbiology & Diseases: Viruses, Prions & Viroids; Ziser Lecture Notes causes fear of swallowing=hydrophobia End Stage: extensive brain & spinal cord damage, delerium, renal failure, coma death usually occurs within 6 days of onset of final symptoms eg. Herpes simplex large group of viruses relative of chicken pox and Epstein Barr viruses herpes simplex: fever blisters & genital infections herpes zoster: chickenpox & shingles cytomegalovirus; infects internal organs Epstein-Barr virus: lymphatic tissue tendency to produce creeping rash some have tendency for oncogenesis humans are only host requires direct contact to spread very high infection rate!90% infected in US initial infection often goes unnoticed! ~15% develop lesions once infected 20-50% of cases virus enters nerves latent virus persists in nerves!lifetime infection = chronic recurrence triggered by stress: Microbiology & Diseases: Viruses, Prions & Viroids; Ziser Lecture Notes fever, menstruation, injury, colds, etc Microbiology & Diseases: Viruses, Prions & Viroids; Ziser Lecture Notes
5 recurrent infection usually less severe than initial outbreaks become less frequent with age two major forms cold sores (type I) and genital herpes (type II) both can occur in either area often lethal!newborns can be infected during birth esp if active lesions are present! caesarian may be required severe or fatal in patients with immunologic deficiencies no good treatment; no vaccine yet HSV-1 (type I) - cold sores usually in skin, eyes, mucous membranes, nervous system alternate with latency when virus hides in nerves symptoms often exhibit during stress, less frequent with age Herpes gladiatorum esp head and neck 3% incidence in HS wrestlers HSV-2 (type I) - genital herpes sexually transmitted; esp yr olds more severe form of virus: can cause painful urination one of top 5 STD s!5 M cases total! 300,000/yr condoms not particularly effective especially dangerous for pregnant women!fetus can be infected before birth! virus can cross placenta Microbiology & Diseases: Viruses, Prions & Viroids; Ziser Lecture Notes Microbiology & Diseases: Viruses, Prions & Viroids; Ziser Lecture Notes eg. HIV/AIDS second most lethal infectious disease in the world: ~10 s of millions are infected,3 Million die each year worldwide (2008) first recognized in US in 1981! today (2005) 1 M in US have the disease many are people who do not know they are infected originated in central Africa similar virus infects green monkeys in central Africa! harmless infection for monkeys! probably mutated from common primate virus Infection requires direct contact with body fluids; sexually transmitted, needles, mothers milk, organ transplants only slight risk today from blood transfusions; was once a major source of infections most dangerous sexual contact is anal intercourse vaginal intercourse! woman more at risk than male rare! oral genital contact Microbiology & Diseases: Viruses, Prions & Viroids; Ziser Lecture Notes % of children born to HIV+ mothers are infected one possible case of spread by saliva Can t get it from kissing, touching, sharing utensils, etc HIV particles in body fluids of infected person: Blood inf particles/ml Semen IP/ml Saliva <1 IP/ml highest risk group in US: male homosexuals and bisexuals those with multisexual partners IV drug users today incidence is declining in these groups but increasing in heterosexual contact in SubSaharan Africa and parts of Asia males are as likely to contract the disease as females a crucial factor in heterosexual spread in eg. Africa poor obstetric care multiple births high incidence of VD malnutrition a few individuals of high risk groups seem to be completely resistant to HIV once inside body it hides in body s own immune cells to avoid detection and immune response Microbiology & Diseases: Viruses, Prions & Viroids; Ziser Lecture Notes
6 can spread directly from cell to cell without entering the blood where it would be more easily detected Symptoms begins with sudden flu-like symptoms few weeks may produce fever, fatigue, swollen glands, some get rash but most show no symptoms at all for several years the only indication of its presence may be swollen glands! virus hides in lymph nodes progression of the disease depends on: how much virus a person is exposed to condition of patient Incubation period lasts years before AIDS symptoms appear typical incubation period is ~10 yrs eventually HIV infections are so widespread that they begin to produce recognizable symptoms: AIDS night sweats malaise nausea headaches Microbiology & Diseases: Viruses, Prions & Viroids; Ziser Lecture Notes symptoms may persist for years Its virulence is due to the fact that it infects the T-cells of the immune system!these are the cells that control the entire system if they are knocked out the immune system fails eventually, immune system is inactivated! opportunistic infections and cancers ravage the body HIV reproduces and mutates so fast that body cannot produce antibodies to fight it few actually die of HIV! they die of pneumonia, cancer, TB, hepatitis, etc in past couple of years incidence and death rate has decreased dramatically in US with intensive treatment regimes but still a very deadly disease in the rest of the world Microbiology & Diseases: Viruses, Prions & Viroids; Ziser Lecture Notes Viral Applications 2. Some viruses cause cancer ~100 s different kinds of cancer numerous causes: genetic, chemicals, viruses viral causes not contageous eg. Epstein Barr virus: mononucleosus! lymphatic cancer 90% of US carry latent stage of this virus in WBC s with no signs of disease eg. Hepatitis B virus! implicated in liver cancers eg. HTLV 1&2! leukemia 1. Genetic Engineering viruses are sometimes used as vectors in genetic engineering research to transmit a specific gene to engineered cells eg. cystic fibrosis eg. plants tobacco mosaic virus 2. Bacteriophages (bacteria viruses) are being looked at as a way to treat some bacterial infections without the use of antibiotics, to which many bacterial are becoming resistant. 3. using viruses to protect food products (2006) FDA approved a 6 virus coctail to be sprayed onto ready to eat meats protects against Listeria which causes 2500 cases of severe food poisoning and 500 deaths annually in US 4. using viruses to treat cancer when healthy cells are infected by a virus they commit suicide Microbiology & Diseases: Viruses, Prions & Viroids; Ziser Lecture Notes Microbiology & Diseases: Viruses, Prions & Viroids; Ziser Lecture Notes
7 ideal tool to kill cancer cells mutated herpes virus that can only multiply in tumor cells still only experimental 5. as biological controls of insect pests over 300 viruses have been discovered with biological control potential against insect pests 6. New generation of antiviral drugs viruses are completely dependent on genetics of their hosts trying to find some host protein that is essential for viral replication but not necessary for survival of its host then attack that protein with vaccine single vaccine would work for many similar viruses since most viruses conscript the same host genes Viroids even viruses are not the smallest infectious particles around. viroids! naked RNA molecules no capsid no coatings = disease causing prions! pieces of proteins molecules no nucleic acids involved Viroids viroids have 0.1 th the genetic material of the smallest virus (350 bases) if bases were 1mm wide: human sperm! 1800 miles T2 virus! 2 football fields viroids! 1 foot long too small to encode for even a single enzyme don t know how they cause disease about a dozen known viroids so far only infect plants: tomatoes, potatoes, cucumbers, citrus trees, chrysanthemums Microbiology & Diseases: Viruses, Prions & Viroids; Ziser Lecture Notes Microbiology & Diseases: Viruses, Prions & Viroids; Ziser Lecture Notes eg. killed 12 million coconut trees in Phillipines eg. in 50 s killed most of the chrysanthemums in US no one has been able to isolate an animal viroid but they may be involved in animal diseases like: arthritis encephalopathies cancerous lymphomas Prions an infectious agent that can replicate without genetic material also called slow viruses not really virus! protein fragments seem to be mutated proteins from hosts own brain cells that are able to be passed from host to host the normal proteins play vital roles in brain function and memory! stimulates glial cells to make myelin insulation around neurons at least one genetic disease seems to be due to a similar kind of mutation eg. a genetic disease in a few families! when they reach middle age they can no longer sleep! die in a few weeks from exhaustion prions are similar kinds of mutated proteins that can be transmitted from one host to another prions cause 8 known animal diseases long term infections; but typically fatal Microbiology & Diseases: Viruses, Prions & Viroids; Ziser Lecture Notes Microbiology & Diseases: Viruses, Prions & Viroids; Ziser Lecture Notes
8 all 8 are neurological diseases:!cause mental derangement!loss of muscle control!progressive and fatal eg. kuru New Guinea eat brain to spread disease eg. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (= Mad Cow Disease) first identified in England and found to be spreading to humans from eating contaminated beef (eg hamburger) spread cow to cow in animal feed that contains ground brains from infected animals strong measures were taken to identify and destroy infected cows and prevent the contamination of cow feed by people had died and 4 people are known to have the disease eg. scrapie in sheep a newly discovered prion disease attacks the PNS rather than the brain causing chronic diarrhea some evidence prions may be involved in: Microbiology & Diseases: Viruses, Prions & Viroids; Ziser Lecture Notes Parkinsons disease progressive loss of motor function begins in 50 s or 60 s can be hereditary due to degeneration of dopamine releasing neurons in substantia nigra (inhibitory neurons) leads to hyperactivity of basal nuclei and involuntary muscle contractions results in shaking hands, facial muscles become rigid, range of motion decreases develops smaller steps, slow shuffling gait with forward bent posture and a tendency to fall forward speech becomes slurred, handwriting illegible Alzheimers Disease affect 11% in us over 65; 47% by 85 ~half of all nursing home admissions leading cause of death among elderly AD may begin before 50 with very mild, undiagnosed symptoms one of 1 st symptoms is memory loss, esp of recent events progresses with reduced attention span, disorientation, moody, confused, paranoid, combative or hallucinatory may lose ability to read, write, talk, walk, and eat death usually from pneumonia or other complications of confinement and immobility possibly also: Huntington s Disease a neurodegenerative genetic disorder that affects muscle coordination and leads to cognitive decline and psychiatric problems. It typically becomes noticeable in mid-adult life. HD is the most common genetic cause of abnormal involuntary writhing movements called chorea, which is why the disease used to be called Huntington's chorea. Microbiology & Diseases: Viruses, Prions & Viroids; Ziser Lecture Notes Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (Lou Gehrig's disease) is a debilitating disease with varied etiology characterized by rapidly progressive weakness, muscle atrophy, muscle spasticity, difficulty speaking (dysarthria), difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), and difficulty breathing (dyspnea). Microbiology & Diseases: Viruses, Prions & Viroids; Ziser Lecture Notes
Recognition of a host cell Attachment is a specific process
 Viruses: The Ultimate Parasites Reading How many childhood diseases can you recall having: mumps, measles, German measles? A generation ago or so ago, these diseases attacked mainly children and were extremely
Viruses: The Ultimate Parasites Reading How many childhood diseases can you recall having: mumps, measles, German measles? A generation ago or so ago, these diseases attacked mainly children and were extremely
10. T and B cells are types of a. endocrine cells. c. lymphocytes. b. platelets. d. complement cells.
 Virus and Immune System Review Directions: Write your answers on a separate piece of paper. 1. Why does a cut in the skin threaten the body s nonspecific defenses against disease? a. If a cut bleeds, disease-fighting
Virus and Immune System Review Directions: Write your answers on a separate piece of paper. 1. Why does a cut in the skin threaten the body s nonspecific defenses against disease? a. If a cut bleeds, disease-fighting
Multiple Choice Questions
 C hapter 13 WHY DO WE FALL ILL Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which one of the following is not a viral disease? (a) Dengue (b) AIDS (c) Typhoid (d) Influenza 2. Which one of the following is not a bacterial
C hapter 13 WHY DO WE FALL ILL Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which one of the following is not a viral disease? (a) Dengue (b) AIDS (c) Typhoid (d) Influenza 2. Which one of the following is not a bacterial
Accent on Health Obgyn, PC HERPES Frequently Asked Questions
 1. What is herpes? 2. How common is herpes? 3. Is there a cure for herpes? 4. What is oral herpes (cold sores)? 5. How is oral herpes spread? 6. What is genital herpes? 7. How is genital herpes spread?
1. What is herpes? 2. How common is herpes? 3. Is there a cure for herpes? 4. What is oral herpes (cold sores)? 5. How is oral herpes spread? 6. What is genital herpes? 7. How is genital herpes spread?
HIV/AIDS. HIV- Human Immunodeficiency Virus. AIDS immume system severely damaged
 HIV/AIDS HIV- Human Immunodeficiency Virus Person is infected with virus. May have no s/s (but may transmit virus) More common to have brief flu-like illness 2-6 wks after becoming infected (swollen lymph
HIV/AIDS HIV- Human Immunodeficiency Virus Person is infected with virus. May have no s/s (but may transmit virus) More common to have brief flu-like illness 2-6 wks after becoming infected (swollen lymph
CHAPTER 35 HUMAN IMMUNE SYSTEM STANDARDS:SC.912.L.14.52 & SC.912.L.14.6
 CHAPTER 35 HUMAN IMMUNE SYSTEM STANDARDS:SC.912.L.14.52 & SC.912.L.14.6 SECTION 1 - Infectious Disease 1.Identify the causes of infectious disease. 2.Explain how infectious diseases are spread. Causes
CHAPTER 35 HUMAN IMMUNE SYSTEM STANDARDS:SC.912.L.14.52 & SC.912.L.14.6 SECTION 1 - Infectious Disease 1.Identify the causes of infectious disease. 2.Explain how infectious diseases are spread. Causes
One of the more complex systems we re looking at. An immune response (a response to a pathogen) can be of two types:
 Immune system. One of the more complex systems we re looking at. An immune response (a response to a pathogen) can be of two types: (pathogen - disease causing organism) 1) Non specific. Anything foreign
Immune system. One of the more complex systems we re looking at. An immune response (a response to a pathogen) can be of two types: (pathogen - disease causing organism) 1) Non specific. Anything foreign
The Immune System and Disease
 Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1029 1033) This section describes the causes of disease and explains how infectious diseases are transmitted Introduction
Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1029 1033) This section describes the causes of disease and explains how infectious diseases are transmitted Introduction
Name Date Class. This section explains what kinds of organisms cause infectious disease and how infectious diseases are spread.
 Fighting Disease Name Date Class Infectious Disease This section explains what kinds of organisms cause infectious disease and how infectious diseases are spread. Use Target Reading Skills Before you read,
Fighting Disease Name Date Class Infectious Disease This section explains what kinds of organisms cause infectious disease and how infectious diseases are spread. Use Target Reading Skills Before you read,
Basic Presentation HIV/AIDS. For Use by Students, Teachers and the Public Seeking Basic Information About HIV/AIDS
 Basic Presentation HIV/AIDS For Use by Students, Teachers and the Public Seeking Basic Information About HIV/AIDS Objectives- Define and understand the difference between HIV Infection and AIDS Describe
Basic Presentation HIV/AIDS For Use by Students, Teachers and the Public Seeking Basic Information About HIV/AIDS Objectives- Define and understand the difference between HIV Infection and AIDS Describe
KEY CONCEPT Organisms can be classified based on physical similarities. binomial nomenclature
 Section 17.1: The Linnaean System of Classification Unit 9 Study Guide KEY CONCEPT Organisms can be classified based on physical similarities. VOCABULARY taxonomy taxon binomial nomenclature genus MAIN
Section 17.1: The Linnaean System of Classification Unit 9 Study Guide KEY CONCEPT Organisms can be classified based on physical similarities. VOCABULARY taxonomy taxon binomial nomenclature genus MAIN
The Polio Virus. Getting to Know Your Old Enemy. Marcia Falconer, Ph.D.
 The Polio Virus Getting to Know Your Old Enemy Marcia Falconer, Ph.D. The Polio Virus Virus is smallest living thing that can reproduce itself Outer shell (capsid) Inner genetic material (RNA) and one
The Polio Virus Getting to Know Your Old Enemy Marcia Falconer, Ph.D. The Polio Virus Virus is smallest living thing that can reproduce itself Outer shell (capsid) Inner genetic material (RNA) and one
Bacteria vs. Virus: What s the Difference? Grade 11-12
 Bacteria vs. Virus: What s the Difference? Grade 11-12 Subject: Biology Topic: Bacteria, viruses, and the differences between them. The role that water plays in spreading bacteria and viruses, and the
Bacteria vs. Virus: What s the Difference? Grade 11-12 Subject: Biology Topic: Bacteria, viruses, and the differences between them. The role that water plays in spreading bacteria and viruses, and the
FAQs HIV & AIDS. What is HIV? A virus that reduces the effectiveness of your immune system, meaning you are less protected against disease.
 HIV & AIDS What is HIV? A virus that reduces the effectiveness of your immune system, meaning you are less protected against disease. What does HIV stand for? Human Immunodeficiency Virus Where did HIV
HIV & AIDS What is HIV? A virus that reduces the effectiveness of your immune system, meaning you are less protected against disease. What does HIV stand for? Human Immunodeficiency Virus Where did HIV
Management in the pre-hospital setting
 Management in the pre-hospital setting Inflammation of the joints Two main types: Osteoarthritis - cartilage loss from wear and tear Rheumatoid arthritis - autoimmune disorder Affects all age groups,
Management in the pre-hospital setting Inflammation of the joints Two main types: Osteoarthritis - cartilage loss from wear and tear Rheumatoid arthritis - autoimmune disorder Affects all age groups,
20.3 Diseases Caused by Bacteria and Viruses
 20.3 Diseases Caused by Bacteria and Viruses Lesson Objectives Explain how bacteria cause disease. Explain how viruses cause disease. Define emerging disease and explain why emerging diseases are a threat
20.3 Diseases Caused by Bacteria and Viruses Lesson Objectives Explain how bacteria cause disease. Explain how viruses cause disease. Define emerging disease and explain why emerging diseases are a threat
Childhood Diseases and potential risks during pregnancy: (All information available on the March of Dimes Web Site.) http://www.modimes.
 Childhood Diseases and potential risks during pregnancy: (All information available on the March of Dimes Web Site.) http://www.modimes.org/ Fifth disease (erythema infectiosum) is a common, mild, childhood
Childhood Diseases and potential risks during pregnancy: (All information available on the March of Dimes Web Site.) http://www.modimes.org/ Fifth disease (erythema infectiosum) is a common, mild, childhood
How can herpes simplex spread to an infant?
 CHAPTER 3 HERPES AND PREGNANCY As an expectant parent eagerly awaiting the birth of your new baby, you are probably taking a number of steps to ensure your baby s health. One step many experts recommend
CHAPTER 3 HERPES AND PREGNANCY As an expectant parent eagerly awaiting the birth of your new baby, you are probably taking a number of steps to ensure your baby s health. One step many experts recommend
BASIC INFORMATION ABOUT HIV, HEPATITIS B and C, and TUBERCULOSIS Adapted from the CDC
 BASIC INFORMATION ABOUT HIV, HEPATITIS B and C, and TUBERCULOSIS Adapted from the CDC HIV What are HIV and AIDS? HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. This is the virus that causes AIDS. HIV is
BASIC INFORMATION ABOUT HIV, HEPATITIS B and C, and TUBERCULOSIS Adapted from the CDC HIV What are HIV and AIDS? HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. This is the virus that causes AIDS. HIV is
2 P age. Babies from Birth to Age 2
 Contents Babies from Birth to Age 2... 2 Vaccines give parents the power... 2 Vaccines are recommended throughout our lives... 3 Talk to your doctor... 3 Vaccines are very safe... 3 Whooping Cough (Pertussis)...
Contents Babies from Birth to Age 2... 2 Vaccines give parents the power... 2 Vaccines are recommended throughout our lives... 3 Talk to your doctor... 3 Vaccines are very safe... 3 Whooping Cough (Pertussis)...
Developing Human Fetus
 Period Date LAB. DEVELOPMENT OF A HUMAN FETUS After a human egg is fertilized with human sperm, the most amazing changes happen that allow a baby to develop. This amazing process, called development, normally
Period Date LAB. DEVELOPMENT OF A HUMAN FETUS After a human egg is fertilized with human sperm, the most amazing changes happen that allow a baby to develop. This amazing process, called development, normally
Mutations: 2 general ways to alter DNA. Mutations. What is a mutation? Mutations are rare. Changes in a single DNA base. Change a single DNA base
 Mutations Mutations: 2 general ways to alter DNA Change a single DNA base Or entire sections of DNA can move from one place to another What is a mutation? Any change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA Here
Mutations Mutations: 2 general ways to alter DNA Change a single DNA base Or entire sections of DNA can move from one place to another What is a mutation? Any change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA Here
The State Hospital HIV / AIDS
 The State Hospital HIV / AIDS The red ribbon is the international symbol of HIV & AIDS awareness. What is HIV? HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus: H is for Human - This virus infects human beings.
The State Hospital HIV / AIDS The red ribbon is the international symbol of HIV & AIDS awareness. What is HIV? HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus: H is for Human - This virus infects human beings.
Ear Infections Chickenpox chickenpox
 Ear Chickenpox Infections chickenpox Chickenpox Chickenpox is a common, very contagious viral infection that over 90% of people get during childhood unless they have been immunised. After an infection,
Ear Chickenpox Infections chickenpox Chickenpox Chickenpox is a common, very contagious viral infection that over 90% of people get during childhood unless they have been immunised. After an infection,
The challenge of herpes
 The challenge of herpes Herpes is a common and personally challenging disease Herpes is very common. One out of four adults has genital herpes. When people first hear that they are infected, many become
The challenge of herpes Herpes is a common and personally challenging disease Herpes is very common. One out of four adults has genital herpes. When people first hear that they are infected, many become
Key Facts about Influenza (Flu) & Flu Vaccine
 Key Facts about Influenza (Flu) & Flu Vaccine mouths or noses of people who are nearby. Less often, a person might also get flu by touching a surface or object that has flu virus on it and then touching
Key Facts about Influenza (Flu) & Flu Vaccine mouths or noses of people who are nearby. Less often, a person might also get flu by touching a surface or object that has flu virus on it and then touching
Leader's Resource. Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms.
 Leader's Resource Information on Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Signs and Symptoms of STDs Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms. Any of the following can indicate to
Leader's Resource Information on Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Signs and Symptoms of STDs Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms. Any of the following can indicate to
COMMUNICABLE DISEASE
 Public Health Activities & Services Inventory Technical Notes COMMUNICABLE DISEASE CLINICAL SERVICES, SURVEILLANCE AND CONTROL In 2014, decision was made to adopt number of national public health activities
Public Health Activities & Services Inventory Technical Notes COMMUNICABLE DISEASE CLINICAL SERVICES, SURVEILLANCE AND CONTROL In 2014, decision was made to adopt number of national public health activities
Chapter 21. What Are HIV and AIDS?
 Section 1 HIV and AIDS Today What Are HIV and AIDS? Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the virus that primarily affects cells of the immune system and that causes AIDS. Acquired immune deficiency syndrome
Section 1 HIV and AIDS Today What Are HIV and AIDS? Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the virus that primarily affects cells of the immune system and that causes AIDS. Acquired immune deficiency syndrome
Plan early - get your vaccinations in time for full protection. To prepare for your trip, schedule an appointment: (910) 347-2154, option #2.
 The Onslow County Health Department Travel Clinic offers a complete line of immunizations and prescriptions to protect you while traveling abroad. The most appropriate immunizations and travel medications
The Onslow County Health Department Travel Clinic offers a complete line of immunizations and prescriptions to protect you while traveling abroad. The most appropriate immunizations and travel medications
Bloodborne Pathogens. Scott Anderson CCEMTP. Materials used with permission from the Oklahoma State University
 Bloodborne Pathogens Scott Anderson CCEMTP Materials used with permission from the Oklahoma State University What is a Bloodborne Pathogen? Microorganisms that are carried in the blood that can cause disease
Bloodborne Pathogens Scott Anderson CCEMTP Materials used with permission from the Oklahoma State University What is a Bloodborne Pathogen? Microorganisms that are carried in the blood that can cause disease
You are planning to travel on vacation or business does your destination require a vaccination?
 Disease, travel and vaccinations You are planning to travel on vacation or business does your destination require a vaccination? If you are planning to stay in a resort or a city and you are in good health,
Disease, travel and vaccinations You are planning to travel on vacation or business does your destination require a vaccination? If you are planning to stay in a resort or a city and you are in good health,
Figure 14.2 Overview of Innate and Adaptive Immunity
 I M M U N I T Y Innate (inborn) Immunity does not distinguish one pathogen from another Figure 14.2 Overview of Innate and Adaptive Immunity Our first line of defense includes physical and chemical barriers
I M M U N I T Y Innate (inborn) Immunity does not distinguish one pathogen from another Figure 14.2 Overview of Innate and Adaptive Immunity Our first line of defense includes physical and chemical barriers
WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT?
 CHAPTER 8 EMERGING AND RE-EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASES National Museum of Health and Medicine, Washington, D.C., United States WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? The world is facing challenges from both new diseases
CHAPTER 8 EMERGING AND RE-EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASES National Museum of Health and Medicine, Washington, D.C., United States WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? The world is facing challenges from both new diseases
1) Siderophores are bacterial proteins that compete with animal A) Antibodies. B) Red blood cells. C) Transferrin. D) White blood cells. E) Receptors.
 Prof. Lester s BIOL 210 Practice Exam 4 (There is no answer key. Please do not email or ask me for answers.) Chapters 15, 16, 17, 19, HIV/AIDS, TB, Quorum Sensing 1) Siderophores are bacterial proteins
Prof. Lester s BIOL 210 Practice Exam 4 (There is no answer key. Please do not email or ask me for answers.) Chapters 15, 16, 17, 19, HIV/AIDS, TB, Quorum Sensing 1) Siderophores are bacterial proteins
What is HIV? What is AIDS? The HIV pandemic HIV transmission Window period Stages of HIV infection
 Module 1 Overview of HIV Infection Purpose Pre-requisite Modules Learning Objectives To provide you with the basic terms and concepts related to HIV infection. None At the end of this module, you will
Module 1 Overview of HIV Infection Purpose Pre-requisite Modules Learning Objectives To provide you with the basic terms and concepts related to HIV infection. None At the end of this module, you will
Genetic Mutations. Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes.
 Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
HIV/AIDS: General Information & Testing in the Emergency Department
 What Is HIV? HIV/AIDS: General Information & Testing in the Emergency Department HIV is the common name for the Human Immunodeficiency Virus. HIV is a retrovirus. This means it can enter the body s own
What Is HIV? HIV/AIDS: General Information & Testing in the Emergency Department HIV is the common name for the Human Immunodeficiency Virus. HIV is a retrovirus. This means it can enter the body s own
The Immune System. 2 Types of Defense Mechanisms. Lines of Defense. Line of Defense. Lines of Defense
 The Immune System 2 Types of Defense Mechanisms Immune System the system that fights infection by producing cells to inactivate foreign substances to avoid infection and disease. Immunity the body s ability
The Immune System 2 Types of Defense Mechanisms Immune System the system that fights infection by producing cells to inactivate foreign substances to avoid infection and disease. Immunity the body s ability
The Body s Defenses CHAPTER 24
 CHAPTER 24 The Body s Defenses PowerPoint Lectures for Essential Biology, Third Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece, and Eric Simon Essential Biology with Physiology, Second Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece,
CHAPTER 24 The Body s Defenses PowerPoint Lectures for Essential Biology, Third Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece, and Eric Simon Essential Biology with Physiology, Second Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece,
Structure and Function of DNA
 Structure and Function of DNA DNA and RNA Structure DNA and RNA are nucleic acids. They consist of chemical units called nucleotides. The nucleotides are joined by a sugar-phosphate backbone. The four
Structure and Function of DNA DNA and RNA Structure DNA and RNA are nucleic acids. They consist of chemical units called nucleotides. The nucleotides are joined by a sugar-phosphate backbone. The four
A guide for people with genital herpes
 A guide for people with genital herpes Contents Getting the facts 4 The key facts 6 What is genital herpes? 8 Genital herpes symptoms 10 Getting tested 12 The first outbreak 14 Recurrent outbreaks 16 Common
A guide for people with genital herpes Contents Getting the facts 4 The key facts 6 What is genital herpes? 8 Genital herpes symptoms 10 Getting tested 12 The first outbreak 14 Recurrent outbreaks 16 Common
1.How did I get Hepatitis C?
 1.How did I get Hepatitis C? Sharing needles and syringes ( iv drug use ) or using contaminated straws to snort cocaine Reused needles or medications in a health care setting- (LV endoscopy outbreak, glucometers
1.How did I get Hepatitis C? Sharing needles and syringes ( iv drug use ) or using contaminated straws to snort cocaine Reused needles or medications in a health care setting- (LV endoscopy outbreak, glucometers
Yes, I know I have genital herpes:
 Counseling Messages for Herpes Simplex Type II (HSV-II) Genital herpes Always take the time to attend to the participant s feelings and emotional state; for some people, this is the most devastating news
Counseling Messages for Herpes Simplex Type II (HSV-II) Genital herpes Always take the time to attend to the participant s feelings and emotional state; for some people, this is the most devastating news
HEPATITIS C. The Facts. Get Tested. Get Cured! Health
 HEPATITIS C The Facts Get Tested. Get Cured! Health EVEN IF YOU FEEL HEALTHY, HEPATITIS C MAY BE DAMAGING YOUR LIVER. Your liver keeps you healthy in many ways, such as by removing toxins from your blood
HEPATITIS C The Facts Get Tested. Get Cured! Health EVEN IF YOU FEEL HEALTHY, HEPATITIS C MAY BE DAMAGING YOUR LIVER. Your liver keeps you healthy in many ways, such as by removing toxins from your blood
Zika Virus. Fred A. Lopez, MD, MACP Richard Vial Professor Department of Medicine Section of Infectious Diseases
 Zika Virus Fred A. Lopez, MD, MACP Richard Vial Professor Department of Medicine Section of Infectious Diseases What is the incubation period for Zika virus infection? Unknown but likely to be several
Zika Virus Fred A. Lopez, MD, MACP Richard Vial Professor Department of Medicine Section of Infectious Diseases What is the incubation period for Zika virus infection? Unknown but likely to be several
Overview of the Cattle Immune System 1
 Oregon State University BEEF043 Beef Cattle Library Beef Cattle Sciences Overview of the Cattle Immune System 1 Reinaldo F. Cooke 2 Introduction On average, the U.S. cattle industry loses more than $1
Oregon State University BEEF043 Beef Cattle Library Beef Cattle Sciences Overview of the Cattle Immune System 1 Reinaldo F. Cooke 2 Introduction On average, the U.S. cattle industry loses more than $1
READ THIS LEAFLET VERY CAREFULLY, AND KEEP IT IN A SAFE PLACE. FLU IS SPREADING IN IRELAND, AND THIS INFORMATION IS IMPORTANT FOR YOU AND YOUR FAMILY.
 READ THIS LEAFLET VERY CAREFULLY, AND KEEP IT IN A SAFE PLACE. FLU IS SPREADING IN IRELAND, AND THIS INFORMATION IS IMPORTANT FOR YOU AND YOUR FAMILY. Information and medical advice for the public on Pandemic
READ THIS LEAFLET VERY CAREFULLY, AND KEEP IT IN A SAFE PLACE. FLU IS SPREADING IN IRELAND, AND THIS INFORMATION IS IMPORTANT FOR YOU AND YOUR FAMILY. Information and medical advice for the public on Pandemic
Brain Cancer. This reference summary will help you understand how brain tumors are diagnosed and what options are available to treat them.
 Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
The symptoms of HIV infection
 2 The symptoms of HIV infection Saleema s story HIV infection and HIV disease The first weeks of HIV infection The quiet stage of HIV infection The beginning of HIV disease Answering Saleema s questions
2 The symptoms of HIV infection Saleema s story HIV infection and HIV disease The first weeks of HIV infection The quiet stage of HIV infection The beginning of HIV disease Answering Saleema s questions
Bites, Bats, and being safe a a quiz about RABIES. Dr. Emily Beeler, DVM Los Angeles County Public Health Veterinary Public Health and Rabies Control
 Bites, Bats, and being safe a a quiz about RABIES Dr. Emily Beeler, DVM Los Angeles County Public Health Veterinary Public Health and Rabies Control Overview What is rabies? What animals transmit rabies?
Bites, Bats, and being safe a a quiz about RABIES Dr. Emily Beeler, DVM Los Angeles County Public Health Veterinary Public Health and Rabies Control Overview What is rabies? What animals transmit rabies?
Stem Cell Quick Guide: Stem Cell Basics
 Stem Cell Quick Guide: Stem Cell Basics What is a Stem Cell? Stem cells are the starting point from which the rest of the body grows. The adult human body is made up of hundreds of millions of different
Stem Cell Quick Guide: Stem Cell Basics What is a Stem Cell? Stem cells are the starting point from which the rest of the body grows. The adult human body is made up of hundreds of millions of different
Methamphetamine. Like heroin, meth is a drug that is illegal in some areas of the world. Meth is a highly addictive drug.
 Methamphetamine Introduction Methamphetamine is a very addictive stimulant drug. People who use it can form a strong addiction. Addiction is when a drug user can t stop taking a drug, even when he or she
Methamphetamine Introduction Methamphetamine is a very addictive stimulant drug. People who use it can form a strong addiction. Addiction is when a drug user can t stop taking a drug, even when he or she
SHINGLES (Herpes zoster infection)
 SHINGLES (Herpes zoster infection) What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about shingles. It will tell you what it is, what causes it, what can be
SHINGLES (Herpes zoster infection) What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about shingles. It will tell you what it is, what causes it, what can be
WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT?
 CHAPTER 1 WHAT IS MICROBIOLOGY AND WHY IS IT IMPORTANT? WHO / TDR / Crump WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? Microbiology is more relevant than ever in today s world. Infectious diseases are a leading health-related
CHAPTER 1 WHAT IS MICROBIOLOGY AND WHY IS IT IMPORTANT? WHO / TDR / Crump WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? Microbiology is more relevant than ever in today s world. Infectious diseases are a leading health-related
Viruses. Viral components: Capsid. Chapter 10: Viruses. Viral components: Nucleic Acid. Viral components: Envelope
 Viruses Chapter 10: Viruses Lecture Exam #3 Wednesday, November 22 nd (This lecture WILL be on Exam #3) Dr. Amy Rogers Office Hours: MW 9-10 AM Too small to see with a light microscope Visible with electron
Viruses Chapter 10: Viruses Lecture Exam #3 Wednesday, November 22 nd (This lecture WILL be on Exam #3) Dr. Amy Rogers Office Hours: MW 9-10 AM Too small to see with a light microscope Visible with electron
Swine Flu and Common Infections to Prepare For. Rochester Recreation Club for the Deaf October 15, 2009
 Swine Flu and Common Infections to Prepare For Rochester Recreation Club for the Deaf October 15, 2009 Supporters Deaf Health Community Committee Members Julia Aggas Cathie Armstrong Michael McKee Mistie
Swine Flu and Common Infections to Prepare For Rochester Recreation Club for the Deaf October 15, 2009 Supporters Deaf Health Community Committee Members Julia Aggas Cathie Armstrong Michael McKee Mistie
Cocaine. Like heroin, cocaine is a drug that is illegal in some areas of the world. Cocaine is a commonly abused drug.
 Cocaine Introduction Cocaine is a powerful drug that stimulates the brain. People who use it can form a strong addiction. Addiction is when a drug user can t stop taking a drug, even when he or she wants
Cocaine Introduction Cocaine is a powerful drug that stimulates the brain. People who use it can form a strong addiction. Addiction is when a drug user can t stop taking a drug, even when he or she wants
41 Viral rashes and skin infections
 41 Viral rashes and skin infections Clinical There are several kinds of skin infections caused by viruses, and these are best considered in the four categories that group together similar symptoms for
41 Viral rashes and skin infections Clinical There are several kinds of skin infections caused by viruses, and these are best considered in the four categories that group together similar symptoms for
The * Immune System and Disease
 The * Immune System and Disease pre 1600s - cause of disease not known Punishment from God, bad luck, bad air, witchcraft, curses, maternal impressions etc. After 1600s, microscopy and germ theory of disease
The * Immune System and Disease pre 1600s - cause of disease not known Punishment from God, bad luck, bad air, witchcraft, curses, maternal impressions etc. After 1600s, microscopy and germ theory of disease
Immunity. Humans have three types of immunity innate, adaptive, and passive: Innate Immunity
 Immunity Humans have three types of immunity innate, adaptive, and passive: Innate Immunity Everyone is born with innate (or natural) immunity, a type of general protection. Many of the germs that affect
Immunity Humans have three types of immunity innate, adaptive, and passive: Innate Immunity Everyone is born with innate (or natural) immunity, a type of general protection. Many of the germs that affect
Tuberculosis: FAQs. What is the difference between latent TB infection and TB disease?
 Tuberculosis: FAQs What is TB disease? Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease caused by bacteria (germs) that are spread from person to person through the air. TB usually affects the lungs, but it can also affect
Tuberculosis: FAQs What is TB disease? Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease caused by bacteria (germs) that are spread from person to person through the air. TB usually affects the lungs, but it can also affect
Connie Austin June 2012
 Rabies Exposures: When is Prophylaxis Recommended and Update on Communicable Disease Rule Changes Connie Austin June 2012 Rabies Transmission Bite from infected mammal (not birds, amphibians, reptiles)
Rabies Exposures: When is Prophylaxis Recommended and Update on Communicable Disease Rule Changes Connie Austin June 2012 Rabies Transmission Bite from infected mammal (not birds, amphibians, reptiles)
Disease Surveillance in New Jersey Spring 2006
 Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease Surveillance in New Jersey Spring 2006 Shereen Brynildsen, MS Epidemiologist, Infectious & Zoonotic Disease Program New Jersey Department of Health & Senior Services Phone: 609-588
Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease Surveillance in New Jersey Spring 2006 Shereen Brynildsen, MS Epidemiologist, Infectious & Zoonotic Disease Program New Jersey Department of Health & Senior Services Phone: 609-588
Adult Vaccination Frequently Asked Questions: The Basics
 The Basics Why should I get vaccinated? Vaccination is the best way to protect against infections that can make you sick and be passed on to those around you. 1 What kinds of side effects will I get from
The Basics Why should I get vaccinated? Vaccination is the best way to protect against infections that can make you sick and be passed on to those around you. 1 What kinds of side effects will I get from
 CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY CENTRE FOR BRAIN REPAIR A layman's account of our scientific objectives What is Brain Damage? Many forms of trauma and disease affect the nervous system to produce permanent neurological
CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY CENTRE FOR BRAIN REPAIR A layman's account of our scientific objectives What is Brain Damage? Many forms of trauma and disease affect the nervous system to produce permanent neurological
Alzheimer s and Herpes Zoster
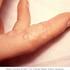 The relationship between Alzheimer's and herpes zoster should be studied. A solid link between herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV1) and Alzheimer's has been found. See: "Cold Sore Virus Linked To Alzheimer's
The relationship between Alzheimer's and herpes zoster should be studied. A solid link between herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV1) and Alzheimer's has been found. See: "Cold Sore Virus Linked To Alzheimer's
Multiple Myeloma. This reference summary will help you understand multiple myeloma and its treatment options.
 Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
Blood: The Body s Vital Defense Force
 Blood: The body s vital defense force Ouch you ve cut your finger! A familiar red substance oozes out. As you reach for a bandage, take a moment to ponder the vital role this remarkable fluid performs.
Blood: The body s vital defense force Ouch you ve cut your finger! A familiar red substance oozes out. As you reach for a bandage, take a moment to ponder the vital role this remarkable fluid performs.
disease causing micro-organisms
 disease causing micro-organisms What are disease causing micro-organisms? How many times have we been told to wash our hands before sitting down at the supper table or after touching money and other dirty
disease causing micro-organisms What are disease causing micro-organisms? How many times have we been told to wash our hands before sitting down at the supper table or after touching money and other dirty
Lesson 7: Respiratory and Skeletal Systems and Tuberculosis
 Glossary 1. asthma: when the airways of the lungs narrow, making breathing difficult 2. bacteria: tiny living creatures that can only be seen with a microscope; some bacteria help the human body, and other
Glossary 1. asthma: when the airways of the lungs narrow, making breathing difficult 2. bacteria: tiny living creatures that can only be seen with a microscope; some bacteria help the human body, and other
LOEWENBERG SCHOOL OF NURSING LOEWENBERG SCHOOL OF NURSING HEALTH EXAMINATION FORM (FORM 003)
 SECTION I: To be completed by STUDENT: Name: DOB: Address: Phone (H): Phone (C): Health History: Please complete the following information: Recent weight loss or gain Fatigue, fever, sweats Difficulty
SECTION I: To be completed by STUDENT: Name: DOB: Address: Phone (H): Phone (C): Health History: Please complete the following information: Recent weight loss or gain Fatigue, fever, sweats Difficulty
Chickenpox in pregnancy: what you need to know
 Chickenpox in pregnancy: what you need to know First published December 2003 Revised edition published November 2008 What is chickenpox? Chickenpox is a very infectious illness caused by a virus called
Chickenpox in pregnancy: what you need to know First published December 2003 Revised edition published November 2008 What is chickenpox? Chickenpox is a very infectious illness caused by a virus called
Understanding How Existing and Emerging MS Therapies Work
 Understanding How Existing and Emerging MS Therapies Work This is a promising and hopeful time in the field of multiple sclerosis (MS). Many new and different therapies are nearing the final stages of
Understanding How Existing and Emerging MS Therapies Work This is a promising and hopeful time in the field of multiple sclerosis (MS). Many new and different therapies are nearing the final stages of
Patient Guide. Important information for patients starting therapy with LEMTRADA (alemtuzumab)
 Patient Guide Important information for patients starting therapy with LEMTRADA (alemtuzumab) This medicinal product is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety
Patient Guide Important information for patients starting therapy with LEMTRADA (alemtuzumab) This medicinal product is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety
Borderless Diseases By Sunny Thai
 Borderless Diseases By Sunny Thai Millennium Development Goal #6 6. Combat HIV/AIDS, malaria and other borderless diseases. A. Halt and begin reversing spread of HIV by 2015. B. Achieve universal access
Borderless Diseases By Sunny Thai Millennium Development Goal #6 6. Combat HIV/AIDS, malaria and other borderless diseases. A. Halt and begin reversing spread of HIV by 2015. B. Achieve universal access
Genetic material of all living organisms. Biology - 100
 Genetic material of all living organisms. Biology - 100 This antibiotic is made from a fungus that was first discovered growing on an orange and it became the first antibiotic to treat infection. Biology
Genetic material of all living organisms. Biology - 100 This antibiotic is made from a fungus that was first discovered growing on an orange and it became the first antibiotic to treat infection. Biology
Blood & Marrow Transplant Glossary. Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant Program Patient Guide
 Blood & Marrow Transplant Glossary Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant Program Patient Guide Glossary Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) -- Also called "absolute granulocyte count" amount of white blood
Blood & Marrow Transplant Glossary Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant Program Patient Guide Glossary Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) -- Also called "absolute granulocyte count" amount of white blood
FIGHTING AIDS AT THE GATE
 FIGHTING AIDS AT THE GATE T h e r a m p a n t s p r e a d o f H I V i n f e c t i o n a c r o s s t h e g l o b e i s n o l o n g e r t h e m e d i a c r i s i s o f t h e m o m e n t. B u t A I D S h
FIGHTING AIDS AT THE GATE T h e r a m p a n t s p r e a d o f H I V i n f e c t i o n a c r o s s t h e g l o b e i s n o l o n g e r t h e m e d i a c r i s i s o f t h e m o m e n t. B u t A I D S h
Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV) and Feline Leukaemia Virus (FeLV)
 Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV) and Feline Leukaemia Virus (FeLV) VETERINARY GUIDE 9 FIV and FeLV are both viruses within the same family of retroviruses, but are in different groups within that family.
Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV) and Feline Leukaemia Virus (FeLV) VETERINARY GUIDE 9 FIV and FeLV are both viruses within the same family of retroviruses, but are in different groups within that family.
X-Plain Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - Adriamycin, Cytoxan, and Tamoxifen Reference Summary
 X-Plain Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - Adriamycin, Cytoxan, and Tamoxifen Reference Summary Introduction Breast cancer is a common condition that affects one out of every 11 women. Your doctor has recommended
X-Plain Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - Adriamycin, Cytoxan, and Tamoxifen Reference Summary Introduction Breast cancer is a common condition that affects one out of every 11 women. Your doctor has recommended
Exposure. What Healthcare Personnel Need to Know
 Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Infectious Diseases Divison of Healthcare Quality Promotion and Division of Viral Hepatitis For additional brochures
Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Infectious Diseases Divison of Healthcare Quality Promotion and Division of Viral Hepatitis For additional brochures
C. difficile Infections
 C. difficile Infections Introduction C. difficile is a type of bacteria that can cause diarrhea and infection of the colon. This bacterium is more likely to infect patients at hospitals and other healthcare
C. difficile Infections Introduction C. difficile is a type of bacteria that can cause diarrhea and infection of the colon. This bacterium is more likely to infect patients at hospitals and other healthcare
1: Motor neurone disease (MND)
 1: Motor neurone disease (MND) This section provides basic facts about motor neurone disease (MND) and its diagnosis. The following information is an extracted section from our full guide Living with motor
1: Motor neurone disease (MND) This section provides basic facts about motor neurone disease (MND) and its diagnosis. The following information is an extracted section from our full guide Living with motor
BE SURE. BE SAFE. VACCINATE.
 DON T GET OR GIVE THE FLU THIS YEAR THANK YOU Vaccination is the only protection. www.immunisation.ie BE SURE. BE SAFE. VACCINATE. FLU VACCINE 2013-2014 Healthcare workers prevent the spread of flu and
DON T GET OR GIVE THE FLU THIS YEAR THANK YOU Vaccination is the only protection. www.immunisation.ie BE SURE. BE SAFE. VACCINATE. FLU VACCINE 2013-2014 Healthcare workers prevent the spread of flu and
X-Plain Pediatric Tuberculosis Reference Summary
 X-Plain Pediatric Tuberculosis Reference Summary Introduction Tuberculosis, or TB, is a bacterial infection that causes more deaths in the world than any other infectious disease. When a child gets TB,
X-Plain Pediatric Tuberculosis Reference Summary Introduction Tuberculosis, or TB, is a bacterial infection that causes more deaths in the world than any other infectious disease. When a child gets TB,
Frequently asked questions about whooping cough (pertussis)
 Frequently asked questions about whooping cough (pertussis) About whooping cough What is whooping cough? Whooping cough is a highly contagious illness caused by bacteria. It mainly affects the respiratory
Frequently asked questions about whooping cough (pertussis) About whooping cough What is whooping cough? Whooping cough is a highly contagious illness caused by bacteria. It mainly affects the respiratory
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT PERTUSSIS (WHOOPING COUGH)
 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT PERTUSSIS (WHOOPING COUGH) What is pertussis? General Questions About Pertussis Pertussis, or whooping cough, is a contagious illness that is spread when an infected person
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT PERTUSSIS (WHOOPING COUGH) What is pertussis? General Questions About Pertussis Pertussis, or whooping cough, is a contagious illness that is spread when an infected person
THE A, B, C S OF HEPATITIS. Matt Eidem, M.D. Digestive Health Associates of Texas 1600 Coit Road Suite #301 Plano, Texas 75075 (972) 867-0019
 THE A, B, C S OF HEPATITIS Matt Eidem, M.D. Digestive Health Associates of Texas 1600 Coit Road Suite #301 Plano, Texas 75075 (972) 867-0019 WHAT IS HEPATITIS? Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver
THE A, B, C S OF HEPATITIS Matt Eidem, M.D. Digestive Health Associates of Texas 1600 Coit Road Suite #301 Plano, Texas 75075 (972) 867-0019 WHAT IS HEPATITIS? Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver
What You Need to Know About Lung Cancer Immunotherapy
 What You Need to Know About Lung Cancer Immunotherapy Lung.org/immunotherapy What is immunotherapy? Immunotherapy for cancer, sometimes called immune-oncology, is a type of medicine that treats cancer
What You Need to Know About Lung Cancer Immunotherapy Lung.org/immunotherapy What is immunotherapy? Immunotherapy for cancer, sometimes called immune-oncology, is a type of medicine that treats cancer
Facts About Chickenpox and Shingles for Adults
 Facts About Chickenpox and Shingles for Adults What is chickenpox? Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a very contagious disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus. It is spread easily through the
Facts About Chickenpox and Shingles for Adults What is chickenpox? Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a very contagious disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus. It is spread easily through the
Blood borne Pathogens
 Blood borne Pathogens What Are Blood borne Pathogens? Blood borne pathogens are microorganisms such as viruses or bacteria that are carried in blood and can cause disease in people. Types of Blood borne
Blood borne Pathogens What Are Blood borne Pathogens? Blood borne pathogens are microorganisms such as viruses or bacteria that are carried in blood and can cause disease in people. Types of Blood borne
Like cocaine, heroin is a drug that is illegal in some areas of the world. Heroin is highly addictive.
 Heroin Introduction Heroin is a powerful drug that affects the brain. People who use it can form a strong addiction. Addiction is when a drug user can t stop taking a drug, even when he or she wants to.
Heroin Introduction Heroin is a powerful drug that affects the brain. People who use it can form a strong addiction. Addiction is when a drug user can t stop taking a drug, even when he or she wants to.
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Compartmentalization of the Cell. Objectives. Recommended Reading. Professor Alfred Cuschieri. Department of Anatomy University of Malta
 Compartmentalization of the Cell Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Objectives By the end of this session the student should be able to: 1. Identify the different organelles
Compartmentalization of the Cell Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Objectives By the end of this session the student should be able to: 1. Identify the different organelles
School of Health & Rehabilitation Sciences INFORMATION FOR HEALTH CARE STUDENTS RE: VACCINATIONS AND INFECTIOUS DISEASES
 School of Health & Rehabilitation Sciences INFORMATION FOR HEALTH CARE STUDENTS RE: VACCINATIONS AND INFECTIOUS DISEASES Adults as well as children need protection against infectious diseases. As Health
School of Health & Rehabilitation Sciences INFORMATION FOR HEALTH CARE STUDENTS RE: VACCINATIONS AND INFECTIOUS DISEASES Adults as well as children need protection against infectious diseases. As Health
Chickenpox and Shingles Vaccines
 Chickenpox and Shingles Vaccines The chicken pox/shingles connection DISCLAIMER: The following is not intended as advice on whether or not to receive a chicken pox, shingles, or any other vaccine. The
Chickenpox and Shingles Vaccines The chicken pox/shingles connection DISCLAIMER: The following is not intended as advice on whether or not to receive a chicken pox, shingles, or any other vaccine. The
The most serious symptoms of this stage are:
 The Natural Progression of Hepatitis C The natural history of hepatitis C looks at the likely outcomes for people infected with the virus if there is no medical intervention. However, the process of trying
The Natural Progression of Hepatitis C The natural history of hepatitis C looks at the likely outcomes for people infected with the virus if there is no medical intervention. However, the process of trying
Quick Hit Activity Using UIL Science Contests For Formative and Summative Assessments of Pre-AP and AP Biology Students
 Quick Hit Activity Using UIL Science Contests For Formative and Summative Assessments of Pre-AP and AP Biology Students Activity Title: Quick Hit Goal of Activity: To perform formative and summative assessments
Quick Hit Activity Using UIL Science Contests For Formative and Summative Assessments of Pre-AP and AP Biology Students Activity Title: Quick Hit Goal of Activity: To perform formative and summative assessments
El Paso ISD Health Grade Level: H.S. Unit 8: Diseases and Disorders Two Week Unit. Chapter 24: Communicable Diseases
 El Paso ISD Health Grade Level: H.S. Unit 8: Diseases and Disorders Two Week Unit : Communicable Diseases : Sexually Transmitted Infections and HIV/AIDS Chapter 26: Noncommunicable Diseases and Disabilities
El Paso ISD Health Grade Level: H.S. Unit 8: Diseases and Disorders Two Week Unit : Communicable Diseases : Sexually Transmitted Infections and HIV/AIDS Chapter 26: Noncommunicable Diseases and Disabilities
