Clinical Pathways for Assessment and Habilitation of babies following Newborn Hearing Screening in Wales
|
|
|
- Bertina Moore
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Clinical Pathways for Assessment and Habilitation of babies following Newborn Hearing Screening in Wales Page 1
2 Process Map Screening Assessment Confirmation of Significant Hearing Loss Child & Family Support Paediatric & Developmental Assessment Early Years Support Team Early Language & Listening Programme Hearing Assessment Hearing Aid Fitting Multi-Agency Review and Evaluation and Planning Links to other Services Depending on Child and Family Needs Page 2
3 Introduction The aim of the newborn hearing screening programme in Wales is to identify babies with significant hearing impairment of sufficient severity to cause or potentially cause a disability without the introduction of habilitation in infancy. Significant hearing impairment is defined as a bilateral hearing loss of a level greater than 40dBHL in the better ear taken as an average over frequencies of 500, 1000, 2000 and 4000 Hz (1). The screening programme ends at the completion of the assessment process for each baby or at three months of age whichever is the sooner although audiological confirmation or certainty may not be complete at this stage. The screening programme has a role in ensuring that habilitation services are available for hearing impaired babies and their families up to two years of age. Minimum Standards for Habilitation of babies in Wales were produced at the time of introduction of the screening programme taking into account best practice guidelines, available resources, feasibility of improvements and realistic resource requirements (2). Clinical audit has been completed using standards in the (3, 4). Evaluation of implementation of key stages in the care pathway at Health Board sites has been a core component of Quality Assurance of Newborn Hearing Screening Wales (5). Quality Assurance of habilitation has identified the need for robust mechanisms of recording key events in the to facilitate clinical care and ongoing evaluation of services (5). The has therefore been reviewed and documentation developed for professionals to record key stages ( Appendix 1). Page 3
4 Clinical Pathways A clinical pathway allows a multi disciplinary team to co-ordinate care by setting out all the activities involved in the care of the patient with a defined condition. A pathway leads each patient towards a set of desired outcomes and ensures that specific interventions are delivered at the appropriate time, in the right way and by the right professional (6). The newborn hearing screening clinical pathway therefore provides a multi disciplinary template for a plan of care but takes into account the need for clinical and professional judgement in caring for individual babies. It must also be flexible to allow for variations reflecting individual baby s and family s needs. provides the opportunity to provide consistent management with the baby and family at the centre of the care cycle. Information on the clinical care pathway for each family and baby can encourage involvement. offers increased opportunities for collaboration between professionals and agencies and can promote a greater awareness of the role of each professional within a team. can be used to support clinical effectiveness, clinical audit and risk management. The implementation and use of a clinical care pathway for babies referred for assessment following newborn hearing screening should help to ensure delivery of Family Friendly Hearing Services (7). Page 4
5 Pathways of care for assessment and habilitation following newborn hearing screening. Pathways are provided for: babies referred for assessment; babies with significant permanent bilateral hearing loss > 40 dbehl; babies with permanent unilateral hearing loss; babies with permanent conductive hearing loss; babies with temporary conductive hearing loss. Each pathway lists: steps; actions to be taken; who should take the action; time allowed for the action; accommodation requirements; outcome measures; Guidelines and Standards. Professionals involved in the care pathway: audiologist/clinical scientist( Audiology) paediatrician/professional lead; teacher of the deaf; speech and language therapist; social worker; clerical support and administration. These professionals are members of the Early Years Support Team. Not all early years support teams have the benefit of specialist speech and language therapy or social worker. Other individuals and organisations who support children and families need to be aware of the pathway. Page 5
6 Use of the clinical care pathways These pathways provide a framework for use by local teams. Each local team can use the pathways to support clinical audit, clinical effectiveness and risk management. References: 1. Newborn Hearing Screening Wales Quality Manual ( Version 3,) Objectives and Standards Newborn Hearing Screening Wales Minimum Standards for Habilitation.( Internal Report 2002) 3. Newborn Hearing Screening Wales. Audit of audiology, medical and multidisciplinary clinical pathways for babies identified with permanent hearing loss following newborn screening (Internal Report 2010) 4. Newborn Hearing Screening Wales. An audit of aetiological investigation performed for babies identified with bilateral permanent hearing loss following newborn screening and assessment (Internal Report 2008) 5. Newborn Hearing Screening Wales Quality Assurance Report %20NBHSW%20QA%20report%20finalc%20version.pdf 6. Assembly Government Clinical Pathways (September 2002) 7. Baguley D, Davies A, Bamford J Principles of family friendly hearing services for children, BSA News Page 6
7 Guidelines and Standards Assessment and Management of Auditory Neuropathy /Auditory Dys-synchrony: A Recommended Protocol Version 1.1 May Baguely D, Davis A, Bamford J. Principles of family friendly hearing services for children, BSA News British Association of Audiovestibular Physicians. British Association of Community Doctors in Audiology. Guidelines for Good Practice. Investigation of new cases of severe and profound hearing loss in children %20Children%20Aetiological%20Investigation%20BAAP%20BAPA%20Guideline% pdf British Association of Audiovestibular Physicians. Medical Evaluation of children with permanent unilateral hearing loss Medical%20Investigation%20BAAP%20BAPA%20Guideline% pdf Competencies for investigating the cause of hearing impairment in babies identified through the Newborn Hearing Screening Programme. BACDA Newsletter April 2005 Counselling for Audiologists. The Ear Foundation 2008 Department for Education and Skills. Department of Health. Together from the Start- practical guidance on working with disabled children (birth to 2) and their families Distraction Diagnostic Test Protocol. Down s Syndrome Medical Interest Group. Surveillance Guidelines Hearing Impairment Facilities: Welsh Health Estates Health Building Note 12, Outpatient Department, Supplement 3,ENT and audiology clinics, hearing aid centres( 1994) Guidelines for aetiological Investigation of infants with congenital hearing loss identified through newborn hearing screening. NHSP Clinical Group. January Guidelines for the Identification and Management of Infants and Young Children with Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum disorder. Guidelines Development Conference at NHS 2008, Como, Italy. Page 7
8 Guidelines for the fitting of Hearing Aids to Young Infants. December Modernising Children s Hearing Aid Service (MCHAS) Guideline No 1. Ear Impressions and Earmoulds for Children Guideline No 2. (A) Notes on Testing DSP Aids in the Field (B) Guidelines for Testing DSP Hearing Aids in the Field Guideline No 3. Hearing Aids for Children: Fitting, Verification and Evaluation Guidelines Guideline No 6. Audiology Service Links between Health and Education Services for Childrens Hearing Management National Deaf Children s Society. Quality Standards s in Bone Anchored Hearing Aids for Children and Young People: Guidelines for Professionals Working with Deaf Children and Young People. May earchreferer_id=2&submit.x=9&submit.y=7 National Deaf Children s Society. Quality Standards in Paediatric Audiology. Guidelines for the Early Identification and Audiological Management of Children with Hearing Loss. Volume IV. October 2000 National Deaf Children's Society. Quality Standards in the Early Years. Guidance on working with deaf children under 2 years old and their families.2002 National Deaf Children's Society/SENSE. Vision care for deaf children and young people Guidelines for professionals Newborn Hearing Screening and Assessment. Guidance for Auditory Brainstem Response testing in Babies. Version 1.1 April Stevens, Lightfoot : Co editors Newborn Hearing Screening Wales. Quality Manual Operational Procedures Page 8
9 NBHSW Process for Peer Review. Version 9. August 2011 Quality Standards in Paediatric Audiology.( Wales.) Welsh Assembly Government Royal College of Surgeons. Steering Group on Cleft Lip and Palate 1996 The Royal National Institute for Deaf People. Effective early intervention for deaf children and their families Scope. Right from the Start. Looking at diagnosis and disclosure-parents describe how they found out about their child's disability.1999 Surgical management of otitis media with effusion in children. Clinical Guidelines. National Institute of Clinical Excellence. February Visual Reinforcement Audiometry Testing of Infants. Welsh Cleft lip and Palate Service. Managed Clinical Network 2000 Other references and resources: Early Support Programme Positive practices in Social Services for Deaf Children 2001 British Association of Audiovestibular Physicians and British Association of Paediatricians in Audiology. Aetiological Investigation into bilateral mild and moderate permanent hearing loss in children children%20Aetiological%20Investigation%20BAAP%20BAPA%20Guideline% pdf Investigation of the child with permanent hearing impairment Breege Mac Ardle,Maria Bitner- Glindzicz Arch Dis Child Educ Pract Ed 2010;95:14-23 National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Cochlear Implants for children and adults with severe to profound deafness. February Page 9
10 Quality Standards for Paediatric Audiology: Cochlear Implants for children and young people. Guidelines for professionals working with deaf children and young people. British Cochlear Implant Group and National Deaf Childrens Society. March Voluntary Organisations British Deaf Association National Children s Bureau National Deaf Children s Society Royal National Institute for Deaf People Leaflets Contact a Family Fact Sheet: Fathers. Contact Family Fact Sheet: A Genetic Condition in the Family. Newborn Hearing Screening Wales. Your Baby s Visit to the Audiology Clinic Newborn Hearing Screening Wales. Your Baby has a Hearing Loss Newborn Hearing Screening Wales. Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder Newborn Hearing Screening Wales. Your baby has glue ear Newborn Hearing Screening Wales. Your baby has a hearing loss in one ear National Deaf Children's Society. Unilateral hearing loss National Deaf Children's Society. Glue ear National Deaf Children's Society. Family information pack National Deaf Children Society. Genetic counselling National Deaf Childrens Society. Microtia National Deaf Childrens Society. Why does my child have a hearing loss? National Deaf Childrens Society. Downs Syndrome and Hearing loss. Hearing Aids: A Guide NDCS 2000 Tips on how to get your Child to wear their hearing aids NDCS 2002 Page 10
11 Pathway for assessment of referrals from the screening programme STEPS ACTIONS BY WHOM WHERE TIME OUTCOMES GUIDELINES/STANDARDS Assessment Ensure translator/health advocate availability Contact with parents Check parents/carer received information and understand assessment Explanation of assessment Consent verbal History taking Complete peer reviewed hearing assessment Audiology administration Audiologist/Clinical Scientist + Professional Lead for Advanced Assessment Assessment Clinic Appropriate sound treated or sound proofed room in child/baby friendly environment Prior to clinic Initial assessment within 4 weeks of screen result for well babies and within 8 weeks of screen result for NICU babies Advanced assessment within timescale agreed with parents and ensuring timely (<3months) completion of assessment Parental participation in assessment process informed understanding and consent to assessment Minimum number of babies lost to follow up Parental participation in assessment process Informed understanding and consent to assessment Ear specific thresholds established determining outcome of assessment 1. consideration for hearing aids 2. audiological follow up 3. targeted behavioural hearing test 4. no further follow up TBT for babies who DNA assessment Family friendly Hearing Services (Baguley et al, 2000) NDCS Quality Standards Volume IV. Oct Counselling for Audiologists. The Ear Foundation 2008 Guidelines for the early audiological assessment and management of babies referred from the newborn hearing screening programme Version 5 (Welsh) March 2011 Guidelines for the assessment and management of ANSD in young infants. Version 2.1 October 2012 NBHSW Process for Peer Review Version 9 August 2011 NBHSW Quality Manual 2008 Provide information on outcome of assessment to parents. ( see pathway for confirmation Inform Professional Lead and NBHSW programme(dc)+/- PHCT and other involved professionals At time of assessment Within 1 working day Written report within 10 days Parents informed of hearing assessment result and follow up ( see pathway for confirmation) NBHSW programme and PHCT informed of assessment result and follow up. Page 11
12 Pathway: Confirmation of permanent bilateral hearing loss >40dBeHL or Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder STEPS ACTIONS BY WHOM WHERE TIME OUTCOMES GUIDELINES/STANDARDS Confirmation of sensorineural hearing loss or auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder Ensure translator/ health advocate availability Verbal explanation of results Written information on hearing loss Information on voluntary organisations and contact numbers Information on Early years support team and contact numbers Arrange appointment for hearing aid moulds or take impressions in consultation with parents (sensorineural hearing loss) Arrange appointment for hearing aid fitting if required Arrange audiological follow up for ANSD. Arrange for medical review/assessment Early years support teacher informed Professional lead informed ( if not present) Audiology administration Audiologist/Clinical Scientist Appropriate quiet room Prior to appointment Immediately following assessment and repeated as required by family As soon as possible Within 4 weeks of decision to offer hearing aids Within 9 months or at developmentally appropriate time. Within 5 days if Professional Lead not present at assessment. Within 24 hours Within 24 hours Parental participation in assessment process informed understanding and consent to assessment Parental access to clear information on hearing loss or ANSD. Support network established Timescales for moulds and hearing aid fitting or follow up behavioural test agreed with parents Medical follow up arranged Family friendly Hearing Services (Baguley et al, 2000) NDCS Quality Standards. Volume IV. October 2000 Disclosure of deafness. Peter Watkin. Counselling for Audiologists. The Ear Foundation 2008 Guidelines for the early audiological assessment and management of babies referred from the newborn hearing screening programme Version 5 (Welsh) March 2011 Guidelines for the assessment and management of ANSD in young infants. Version 2.1 October 2012 Quality Standards in Paediatric Audiology (Wales) Written report for Professional Lead and Divisional Coordinator NBHSW Quality Manual 2008 Letter to GP/other professionals Page 12
13 Guidance notes for clinical pathways for babies with confirmed hearing loss. The pathway for babies with confirmed hearing loss will depend on: Audiological evaluation and certainty Family needs e.g. parental choice, social factors Baby needs e.g. other significant medical conditions Page 13
14 Pathway for Audiological Care of babies with permanent bilateral >40 dbehl : Decision to aid (1) STEPS ACTIONS BY WHOM WHERE TIME OUTCOMES GUIDELINES/STANDARDS Hearing aid fitting Ensure translator/ health advocate availability Ensure parental understanding of procedure and consent to fit. Fit appropriate hearing aids binaurally Undertake real ear measurements if appropriate Provide verbal and written information on hearing aid management Provide hearing aid care and maintenance pack (inc battery supply) Ensure parental understanding of access to Audiology Department and arrangements for provision of ear moulds. Appointment made if required Individual Management plan developed and distributed to Early support team and parents Inform early years support team/ professional/medical lead and Divisional Coordinator NBHSW. Arrange hearing aid review Ensure follow up in Multi-agency Planning meeting Audiology administration Audiologist/Clinical Scientist and audiology support staff Professional Lead Appropriate quiet room Prior to clinic appointment Within 4 weeks of confirmation of hearing loss At time of fitting Within 3 weeks Within 10 working days Within 10 working days Within 1 month Within 9 months Provision of appropriate amplification Optimal amplification Early habilitation and support Family Friendly Hearing Services (Baguley et al, 2000) NDCS Quality Standards. Volume IV. Oct Facilities: Welsh Health Estates Health Building Note 12, MCHAS (Wales) Guideline No 1- Guideline No Guidelines for the fitting of Hearing Aids to Young Infants. December 2009 Quality Standards in Paediatric Audiology ( Wales) 2010 Page 14
15 Pathway for Audiological Care of babies with permanent bilateral >40dBeHL : Decision to aid (2) STEPS ACTIONS BY WHOM WHERE TIME OUTCOMES GUIDELINES/STANDARDS Review of fitting and ongoing care Ensure translator/health advocate availability Liaison with family key worker Seek parental view of amplification New moulds Check aids in test box as appropriate Undertake real ear measurements and sound field verification, as indicated Provide verbal information to parents on fitting Audiology administration Audiologist/Clinical Scientist Appropriate quiet room Prior to every appointment At appointment or by telephone prior to appointment At appointment Parental participation in review Co-ordinated care/team working Parental involvement Maintenance of optimal amplification Family Friendly Hearing Services (Baguley et al, 2000) NDCS Quality Standards. Volume IV. Oct Facilities: Welsh Health Estates Health Building Note 12, MCHAS(Wales) 2005 Guideline No 1. Guideline No 2. Guidelines No 3. Guidelines No 6. Quality Standards in Paediatric Audiology ( Wales) 2010 Develop Individual Management Plan to be shared with parents and Early Years team Replace hearing aids if not functioning/lost/ destroyed Provide batteries As necessary Page 15
16 Pathway for Audiological Care of babies with permanent bilateral >40 dbehl : Decision to aid and ANSD.(3) STEPS ACTIONS BY WHOM WHERE TIME OUTCOMES GUIDELINES/ STANDARDS Ongoing audiological assessment Ensure translator/health advocate availability Audiology administration Prior to every appointment Parental participation in review Liaison with family key worker Seek parental view of hearing responses Unaided behavioural test of hearing Middle ear impedance measures Provide verbal information to parents on hearing levels Develop Individual Management Plan to be shared with parents and Early Years Team Arrange review Audiologist/Clinical Scientist Sound proofed room with VRA facilities At appointment or by telephone prior to appointment At appointment Begin at 6 months developmental age At appointment As required to determine ear and frequency specific hearing levels as soon as possible Coordinated care/team working Parental involvement Verification of objective measures of hearing Establish minimum response levels Obtain ear specific and frequency specific response levels Determine amplification requirements include suitability for cochlear implant. Inform care plan and ongoing habilitation including medical/surgical management of OME if required Family Friendly Hearing Services (Baguley et al, 2000) NDCS Quality Standards. Volume IV. Oct Distraction Diagnostic Test Protocol. Visual Reinforcement Audiometry Testing of Infants. A Recommended Test Protocol. MCHAS (Wales) Guidelines No 6. Audiology Service Links between Health and Education Services for Children s Hearing Aid Management Quality standards in Paediatric Audiology : (Wales ) Guidelines for the assessment and management of ANSD in young infants. Version 2.1 October 2012 Page 16
17 Pathway for Medical Care (1) STEPS ACTIONS BY WHOM WHERE TIME OUTCOMES GUIDELINES/ STANDARDS Medical support and assessment Ensure translator/health advocate availability for Audiology/Child Health Administration Prior to appointment NDCS Quality Standards Volume IV. Oct Liaison with neonatologist /paediatrician (baby already identified as having significant medical condition) Ensure early support is in place with parents understanding the role of the key worker Ensure initial MASP developed and circulated to all professionals including parents Provide opportunity to discuss assessment results, proposed management plan and aetiology investigations as dictated by needs of parents Provision of verbal and written information on aetiological investigations Professional Lead Suitable consulting room or home visit Following confirmation of hearing loss/ansd Referral within 24 hours Within 3 months Within 5 days of confirmation of hearing loss Within 4-6 weeks of Confirmation of hearing loss OR as dictated by other medical conditions or parental/social factors Urine for CMV as soon as Parents informed and understand purpose of examination and investigations. Identifications of medical conditions to: Inform ongoing medical and audiological management including suitability for cochlear implant Quality standards in Paediatric Audiology : (Wales ) BACDA/BAPP Guidelines for Good Practice. Investigation of new cases of severe and profound hearing loss in children Guidelines for aetiological investigation of infants with congenital hearing loss identified through newborn hearing screening. January 2009 Competencies for investigating the cause of hearing impairment in babies identified through the NBHSP. BACDA Newsletter April 2005 NBHSW Proforma Medical Assessment (2004) Identification and Management of Infants and Young Children with Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder Page 17
18 possible. Other investigations as agreed with parents. Inform family Inform habilitation Guidelines for the assessment and management of ANSD in young infants. Version 2.1 October 2012 Arrange appointment for baby examination as determined by clinical need Improved epidemiological data Complete recommended medical examination and investigations agreed with parents Results of investigations discussed with parents and written summary provided Contribute to team planning relevant medical factors as agreed with parents Information to PHCT and Paediatric team(s) as appropriate Ensure Multi- Agency planning meeting scheduled Within 9 months Page 18
19 Pathway for Multi-Agency Involvement STEPS ACTIONS BY WHOM WHERE TIME OUTCOMES GUIDELINES/ STANDARDS Multi agency planning meeting Ensure interpreter/ health advocate present Meet with family members Audiology Administration Prior to appointment Parental participation in support Seek parental views and needs Summarise/review Audiology support Summarise/review Education early support Summarise/review other support provided Audiologist/Clinical Scientist Professional Lead Early Years Support Teacher and other team members. (Health Visitor, Speech and Language Therapist, Social Worker & other agencies) Family friendly environment At time agreed with parents and within 9 months of confirmation of hearing loss/ansd Shared information and understanding of roles of team member Written shared management plan between parents and early years support team. NDCS Quality Standards in the Early Years.2002 RNID Effective early intervention for deaf children and their families.2001 Department of Health. Together from the Start.2002 Quality Standards in Paediatric Audiology (Wales) 2010 Review role of key worker Develop agreed Family Support Plan /Multi Agency Support Plan Agreed follow up arrangements for Multi agency meeting. Arrange review Distribute Care Plan Designated Coordinator (Professional Lead) Audiology/Paediatric Administration Page 19
20 Pathway for babies with better ear <30dBeHL and worse ear > 40dBeHL-unilateral permanent hearing loss and ANSD STEPS ACTIONS BY WHOM WHERE TIME OUTCOMES GUIDELINES/ STANDARDS Confirmation of unilateral hearing loss Ensure translator/health advocate available Audiology administration Prior to appointment Parental participation in consultation Follow up Audiological assessment Verbal explanation of results Written information regarding unilateral loss Contact numbers provided Arrange audiological follow up Letter to GP, HV and Professional Lead and parents Consider medical review Ensure translator/health advocate available Audiologist/Clinical Scientist Professional Lead Audiology administration Clinical Assessment clinic Appropriate sound treated / Sound proofed room At time of assessment Prior to appointment Parental access to clear, unbiased information Parental understanding and implications of diagnosis Identify specific conditions Parental participation in consultation Guidance for Auditory Brainstem Response testing in Babies. Version1. 1 April 2010 Guidelines for the assessment and management of ANSD in young infants. Version 2.1 October 2012 Visual Reinforcement Audiometry Testing of Infants. A Recommended Test Protocol Seek parental view of hearing responses Behavioural test of hearing Middle ear impedance measures Provide parents with information on hearing responses and Individual Management Plan Arrange review Consider medical review/multi agency planning Information to PHCT and Professional Lead/other professionals as required. (Individual Management Plan) Scientist/Audiologist/Paediatric Audiology Service Clinical Scientist/Professional Lead Sound proofed room with VRA Within 9 months of initial assessment 6 monthly unless otherwise indicated. As appropriate Continued monitoring of better ear Ear specific hearing responses obtained OME management Coordinated care NDCS Quality Standards Volume IV. Oct 2000 Quality Standards in Paediatric Audiology (Wales) 2010 BAAP. Medical Evaluation of children with permanent unilateral hearing loss Page 20
21 Guidance notes on pathway for babies with confirmed bilateral conductive hearing loss not associated with ear abnormalities and/or other conditions This pathway is for babies who, following assessment are found to have a bilateral conductive hearing loss the likely cause of which is middle ear effusions. These babies require monitoring of hearing response levels and middle ear function. Page 21
22 Pathway for babies with confirmed bilateral conductive hearing loss not associated with ear abnormalities or other conditions STEPS ACTIONS BY WHOM WHERE TIME OUTCOMES GUIDELINES/ STANDARDS Confirmation of bilateral conductive hearing loss Ensure translator/ health advocate available Audiology administration Assessment clinic Sound proofed room Prior to appointment Parental participation in consultation Guidance for Auditory Brainstem Response testing in Babies. Version1.1April 2010 Verbal explanation of results Provide written information Contact numbers provided Arrange follow up behavioural hearing test Letter to GP, HV/other professionals/parents Clinical Scientist/Audiologist Assessment clinic Appropriate Sound treated or sound proofed room At time of assessment Within 9 months or at developmentally appropriate time Parental access to clear, unbiased information Parental understanding of assessment results Follow up plan Distraction Diagnostic Test Protocol Visual Reinforcement Audiometry Testing of Infants. A Recommended Test Protocol Follow up audiological assessment Ensure translator/ health advocate available Seek parental view of hearing responses Behavioural test of hearing- Middle ear impedance measures Information for parents on hearing level (Individual Management Plan) IMP circulated to Primary Care team and other professionals as required Arrange hearing review Consider amplification or surgical opinion as indicated. Audiology administration Clinical Scientist/ Audiologist/Paediatric Audiology Service Appropriate sound proofed room Prior to appointment Within 9 months of initial assessment or at developmentally appropriate time 3 6 months unless otherwise indicated Parental participation in consultation Minimum response levels ( ear specific) and middle ear status established Management of glue ear. NDCS Quality Standards Volume IV. Oct Quality Standards in Paediatric Audiology (Wales) 2010 NICE Guidelines on Glue Ear Page 22
23 Guidance notes on pathway for babies with confirmed bilateral conductive hearing loss associated with ear abnormalities or other conditions This pathway is for babies who, following assessment are found to have a bilateral or unilateral conductive hearing loss in association with ear abnormalities. These babies may have other medical conditions or syndromes. The audiological care and ongoing care of these babies will require liaison with a wide range of professionals e.g. Cleft Palate Team members, Consultant Otolaryngologist, Paediatrician. Babies with the conditions and syndromes listed below may follow this pathway: Down s Syndrome; Cleft Lip and Palate; Microtia; Goldenhar Syndrome; Moebius Syndrome Robin Syndrome; Treacher Collins Syndrome; Symphalangism; Osteogenesis Imperfecta; Klippel Feil Syndrome. Page 23
24 Pathway for babies with confirmed unilateral or bilateral conductive hearing loss associated with ear abnormalities or other conditions STEPS ACTIONS BY WHOM WHERE TIME OUTCOMES GUIDELINES/ STANDARDS Confirmation of unilateral or bilateral conductive hearing loss Follow up audiological assessment Ensure translator/ health advocate available Verbal explanation of results Provide written information Liaise with and provide written information for other professionals involved in care Consider amplification ( see Pathways for fitting and multiagency planning) Arrange follow up Audiological assessment Letter to GP, HV/other professionals and parents Consider medical review Ensure translator/ health advocate available Seek parental view of hearing responses Behavioural test of hearing Middle ear impedance measures Information for parents on hearing levels Arrange follow up behavioural tests Information to Professional Lead/ PHCT/parents Individual Management Plan Audiology administration Prior to appointment Parental access to clear, unbiased information Clinical Scientist/Audiologist and Professional Lead Assessment clinic Appropriate sound treated or Sound proofed room in baby friendly environment At time of assessment Within 9 months or developmentally appropriate time Parental understanding and implications of assessment results Coordinated care Early amplification Audiology administration Prior to appointment Parental participation in consultation Audiological Scientist / Audiology clinic minimum response Audiologist/ VRA facilities in sound levels( ear specific) and Paediatric proofed room middle ear status Audiology Service established Within 9 months of initial assessment or sooner if offered amplification 3-6 months Provision of amplification if appropriate Management OME Guidance for Auditory Brainstem Response testing in Babies. Version 1. 1 April 2010 Welsh Cleft Lip and Palate Service Guidelines 2000 DSMIG Surveillance for Guidelines Hearing Impairment. Version Distraction Diagnostic Test Protocol Visual Reinforcement Audiometry Testing of Infants Quality Standards in Paediatric Audiology (Wales) 2010 NDCS Quality Standards: Bone anchored hearing aids for children and young people: Guidelines for professionals working with children and young people. May 2010 NICE Guidelines on Glue Ear Page 24
The Role of the Educational Audiologist 2014. Introduction:
 The Role of the Educational Audiologist 2014. Introduction: As the current CHAIR of the BAEA I felt that it was time for the Role of the Educational Audiologist to be updated. There has been a period of
The Role of the Educational Audiologist 2014. Introduction: As the current CHAIR of the BAEA I felt that it was time for the Role of the Educational Audiologist to be updated. There has been a period of
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY OF JOINT COMMITTEE ON INFANT HEARING YEAR 2007 POSITION STATEMENT. Intervention Programs
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY OF JOINT COMMITTEE ON INFANT HEARING YEAR 2007 POSITION STATEMENT Principles and Guidelines for Early Hearing Detection and Intervention Programs The Joint Committee on Infant Hearing
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY OF JOINT COMMITTEE ON INFANT HEARING YEAR 2007 POSITION STATEMENT Principles and Guidelines for Early Hearing Detection and Intervention Programs The Joint Committee on Infant Hearing
Fundamental Components of Hearing Aid Fitting for Infants. Josephine Marriage PhD
 Fundamental Components of Hearing Aid Fitting for Infants Josephine Marriage PhD Neonatal Hearing Screening Screening efforts have far out stripped our habilitation efforts, leaving parents with diagnosis
Fundamental Components of Hearing Aid Fitting for Infants Josephine Marriage PhD Neonatal Hearing Screening Screening efforts have far out stripped our habilitation efforts, leaving parents with diagnosis
Unilateral (Hearing Loss in One Ear) Hearing Loss Guidance
 Unilateral (Hearing Loss in One Ear) Hearing Loss Guidance Indiana s Early Hearing Detection and Intervention Program Before universal newborn hearing screening, most children with unilateral hearing loss
Unilateral (Hearing Loss in One Ear) Hearing Loss Guidance Indiana s Early Hearing Detection and Intervention Program Before universal newborn hearing screening, most children with unilateral hearing loss
Statewide Infant Screening - Hearing (SWISH) Program
 Guideline Department of Health, NSW 73 Miller Street North Sydney NSW 2060 Locked Mail Bag 961 North Sydney NSW 2059 Telephone (02) 9391 9000 Fax (02) 9391 9101 http://www.health.nsw.gov.au/policies/ Statewide
Guideline Department of Health, NSW 73 Miller Street North Sydney NSW 2060 Locked Mail Bag 961 North Sydney NSW 2059 Telephone (02) 9391 9000 Fax (02) 9391 9101 http://www.health.nsw.gov.au/policies/ Statewide
Audiology Services. Carolyn Dando Audiology Services Manager South Warwickshire NHS
 Audiology Services Carolyn Dando Audiology Services Manager South Warwickshire NHS What are we going to cover today? General overview of the ear Hearing loss Hearing assessments, results Hearing aids Paediatric
Audiology Services Carolyn Dando Audiology Services Manager South Warwickshire NHS What are we going to cover today? General overview of the ear Hearing loss Hearing assessments, results Hearing aids Paediatric
Transforming Services for Children with Hearing Difficulty and their Families. A Good Practice Guide
 Transforming Services for Children with Hearing Difficulty and their Families A Good Practice Guide Transforming Services for Children with Hearing Difficulty and their Families: A Good Practice Guide
Transforming Services for Children with Hearing Difficulty and their Families A Good Practice Guide Transforming Services for Children with Hearing Difficulty and their Families: A Good Practice Guide
Parents views: A survey about speech and language therapy
 Parents views: A survey about speech and language therapy 1 Executive summary NDCS carried out a survey to find out what parents think about the speech and language therapy services that their children
Parents views: A survey about speech and language therapy 1 Executive summary NDCS carried out a survey to find out what parents think about the speech and language therapy services that their children
Questions and Answers for Parents
 Questions and Answers for Parents There are simple, inexpensive tests available to detect hearing impairment in infants during the first days of life. In the past, most hearing deficits in children were
Questions and Answers for Parents There are simple, inexpensive tests available to detect hearing impairment in infants during the first days of life. In the past, most hearing deficits in children were
Paediatric Hearing Assessment
 Information for parents Paediatric Hearing Assessment Hearing assessment of infants is limited by their ability to respond to sounds. This is determined by both the development of the hearing system and
Information for parents Paediatric Hearing Assessment Hearing assessment of infants is limited by their ability to respond to sounds. This is determined by both the development of the hearing system and
Case Study THE IMPORTANCE OF ACCURATE BEHAVIOURAL TESTING IN INFANT HEARING AID FITTINGS
 Case Study THE IMPORTANCE OF ACCURATE BEHAVIOURAL TESTING IN INFANT HEARING AID FITTINGS Andrea Kelly, PhD, MNZAS Auckland District Health Board Suzanne Purdy, PhD, MNZAS University of Auckland Asymmetrical
Case Study THE IMPORTANCE OF ACCURATE BEHAVIOURAL TESTING IN INFANT HEARING AID FITTINGS Andrea Kelly, PhD, MNZAS Auckland District Health Board Suzanne Purdy, PhD, MNZAS University of Auckland Asymmetrical
Behavioural Audiometry for Infants and Young Children Whose hearing loss has been detected in infancy
 Behavioural Audiometry for Infants and Young Children Whose hearing loss has been detected in infancy Alison King, Principal Audiologist, Paediatric Services, Australian Hearing International Paediatric
Behavioural Audiometry for Infants and Young Children Whose hearing loss has been detected in infancy Alison King, Principal Audiologist, Paediatric Services, Australian Hearing International Paediatric
DIAGNOSTIC TESTING GUIDELINES for Audiology
 DIAGNOSTIC TESTING GUIDELINES for Audiology In 1999, the Illinois legislature passed the Hearing Screening for Newborns Act. By December 31, 2002, hospitals delivering babies were required to provide hearing
DIAGNOSTIC TESTING GUIDELINES for Audiology In 1999, the Illinois legislature passed the Hearing Screening for Newborns Act. By December 31, 2002, hospitals delivering babies were required to provide hearing
The NSW Statewide Infant Screening Hearing (SWISH) Program
 The NSW Statewide Infant Screening Hearing (SWISH) Program The NSW Statewide Infant Screening Hearing (SWISH) Program is aimed at identifying all babies born in NSW with significant permanent bilateral
The NSW Statewide Infant Screening Hearing (SWISH) Program The NSW Statewide Infant Screening Hearing (SWISH) Program is aimed at identifying all babies born in NSW with significant permanent bilateral
Infant hearing screening will not hurt your baby, and will only take between 5 and 20 minutes. Ideally it is done whilst baby is asleep or settled.
 Early diagnosis of hearing loss will make a difference to your baby s life. Significant hearing loss is the most common condition present at birth. In the private sector, 3 in every 1000 babies are born
Early diagnosis of hearing loss will make a difference to your baby s life. Significant hearing loss is the most common condition present at birth. In the private sector, 3 in every 1000 babies are born
Confirmation of Diagnosis of Disability (To determine eligibility under section 18(2)(b) of the Income Tax Act, 1962 (as amended))
 Confirmation of Diagnosis of Disability (To determine eligibility under section 18(2)(b) of the Income Tax Act, 1962 (as amended)) ITR-DD This certificate must not be submitted with your tax return but
Confirmation of Diagnosis of Disability (To determine eligibility under section 18(2)(b) of the Income Tax Act, 1962 (as amended)) ITR-DD This certificate must not be submitted with your tax return but
NHS public health functions agreement 2015-16. Service specification no.20 NHS Newborn Hearing Screening Programme
 NHS public health functions agreement 2015-16 Service specification no.20 NHS Newborn Hearing Screening Programme February 2015 Title: Public health functions to be exercised by NHS England Service specification
NHS public health functions agreement 2015-16 Service specification no.20 NHS Newborn Hearing Screening Programme February 2015 Title: Public health functions to be exercised by NHS England Service specification
Getting Started Kei Te Timata
 Getting Started Kei Te Timata AN INTRODUCTION FOR THE FAMILIES AND WHANAU OF CHILDREN DIAGNOSED WITH A HEARING LOSS. THIS IS A JOINT PROJECT BY DEAF EDUCATION AOTEAROA NEW ZEALAND AND THE NATIONAL AUDIOLOGY
Getting Started Kei Te Timata AN INTRODUCTION FOR THE FAMILIES AND WHANAU OF CHILDREN DIAGNOSED WITH A HEARING LOSS. THIS IS A JOINT PROJECT BY DEAF EDUCATION AOTEAROA NEW ZEALAND AND THE NATIONAL AUDIOLOGY
CRIDE report on 2012 survey on educational provision for deaf children in England
 INTRODUCTION CRIDE report on 2012 survey on educational provision for deaf children in England In 2012, the Consortium for Research into Deaf Education (CRIDE) carried out its second annual survey on educational
INTRODUCTION CRIDE report on 2012 survey on educational provision for deaf children in England In 2012, the Consortium for Research into Deaf Education (CRIDE) carried out its second annual survey on educational
Understanding Hearing Loss 404.591.1884. www.childrensent.com
 Understanding Hearing Loss 404.591.1884 www.childrensent.com You just found out your child has a hearing loss. You know what the Audiologist explained to you, but it is hard to keep track of all the new
Understanding Hearing Loss 404.591.1884 www.childrensent.com You just found out your child has a hearing loss. You know what the Audiologist explained to you, but it is hard to keep track of all the new
CHAPTER 30. MEDICAL PROVIDERS-FEE FOR SERVICE SUBCHAPTER 5. INDIVIDUAL PROVIDERS AND SPECIALTIES PART 103
 CHAPTER 30. MEDICAL PROVIDERS-FEE FOR SERVICE SUBCHAPTER 5. INDIVIDUAL PROVIDERS AND SPECIALTIES PART 103. QUALIFIED SCHOOLS AS PROVIDERS OF HEALTH RELATED SERVICES 317:30-5-1023. Coverage by category
CHAPTER 30. MEDICAL PROVIDERS-FEE FOR SERVICE SUBCHAPTER 5. INDIVIDUAL PROVIDERS AND SPECIALTIES PART 103. QUALIFIED SCHOOLS AS PROVIDERS OF HEALTH RELATED SERVICES 317:30-5-1023. Coverage by category
Section 4. Hearing loss and hearing tests
 Section 4 Hearing loss and hearing tests How we hear Outer Ear Middle Ear Inner Ear 4. 7. 8. 1. 3. 6. 2. 5. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Ear canal Ear drum Middle ear cavity Middle ear bones the malleus, incus,
Section 4 Hearing loss and hearing tests How we hear Outer Ear Middle Ear Inner Ear 4. 7. 8. 1. 3. 6. 2. 5. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Ear canal Ear drum Middle ear cavity Middle ear bones the malleus, incus,
Bone Anchored Hearing Aid Programme
 Information Leaflet for parents Bone Anchored Hearing Aid Programme (BAHA) & Facial Prosthetics (FAITEC) This Information Leaflet is available in Large Print and on Computer Disk (it is also available
Information Leaflet for parents Bone Anchored Hearing Aid Programme (BAHA) & Facial Prosthetics (FAITEC) This Information Leaflet is available in Large Print and on Computer Disk (it is also available
Early Intervention Service Procedure Codes, Limits and Rates
 BABIES INFORMATION AND BILLING SYSTEM Early Intervention Service Procedure Codes, Limits and Rates Georgia Department of Public Health Office of Maternal and Child Health Children and Youth with Special
BABIES INFORMATION AND BILLING SYSTEM Early Intervention Service Procedure Codes, Limits and Rates Georgia Department of Public Health Office of Maternal and Child Health Children and Youth with Special
G/12.a HAMILTON LODGE SCHOOL & COLLEGE. Audiology Policy. June 2015 To be reviewed: June 2017 (Gov)
 G/12.a HAMILTON LODGE SCHOOL & COLLEGE Audiology Policy June 2015 To be reviewed: June 2017 (Gov) 1 Introduction Hamilton Lodge School and College (HLSC) provides audiology services to all pupils and students.
G/12.a HAMILTON LODGE SCHOOL & COLLEGE Audiology Policy June 2015 To be reviewed: June 2017 (Gov) 1 Introduction Hamilton Lodge School and College (HLSC) provides audiology services to all pupils and students.
Hearing Screening Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Pediatricians
 Hearing Screening Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Pediatricians While coding for hearing screening is relatively straightforward, ensuring that appropriate payment is received for such services is a
Hearing Screening Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Pediatricians While coding for hearing screening is relatively straightforward, ensuring that appropriate payment is received for such services is a
Guide for families of infants and children with hearing loss
 With early detection, Early Intervention can begin! Guide for families of infants and children with hearing loss Birth to 3 2008 Cover photograph Geneva Marie Durgin was born January 20, 2007. She lives
With early detection, Early Intervention can begin! Guide for families of infants and children with hearing loss Birth to 3 2008 Cover photograph Geneva Marie Durgin was born January 20, 2007. She lives
Public health functions to be exercised by NHS England. Service specification No.20 NHS Newborn Hearing Screening Programme
 Public health functions to be exercised by NHS England Service specification No.20 NHS Newborn Hearing Screening Programme November 2013 You may re-use the text of this document (not including logos) free
Public health functions to be exercised by NHS England Service specification No.20 NHS Newborn Hearing Screening Programme November 2013 You may re-use the text of this document (not including logos) free
Audiology as a School Based Service. Purpose. Audiology (IDEA 2004) Arkansas SPED Regulations. IDEA 2004 Part B
 Audiology as a School Based Service 2008 Medicaid in the Schools (MITS) Summit January 24, 2008 Donna Fisher Smiley, Ph.D., CCC-A Audiologist Arkansas Children s Hospital and Conway Public Schools Purpose
Audiology as a School Based Service 2008 Medicaid in the Schools (MITS) Summit January 24, 2008 Donna Fisher Smiley, Ph.D., CCC-A Audiologist Arkansas Children s Hospital and Conway Public Schools Purpose
2013 report for England
 Introduction 2013 report for England CRIDE report on 2013 survey on educational provision for deaf children in England In 2013, the Consortium for Research into Deaf Education (CRIDE) carried out its third
Introduction 2013 report for England CRIDE report on 2013 survey on educational provision for deaf children in England In 2013, the Consortium for Research into Deaf Education (CRIDE) carried out its third
Hearing Aids - Adult HEARING AIDS - ADULT HS-159. Policy Number: HS-159. Original Effective Date: 3/18/2010. Revised Date(s): 3/18/2011; 3/1/2012
 Harmony Behavioral Health, Inc. Harmony Behavioral Health of Florida, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. HealthEase of Florida, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance
Harmony Behavioral Health, Inc. Harmony Behavioral Health of Florida, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. HealthEase of Florida, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance
Curriculum Policy for Audiology Primary and Secondary
 ELMFIELD SCHOOL FOR DEAF CHILDREN Curriculum Policy for Audiology Primary and Secondary - 2 - Throughout this document the terms deaf and deafness are used to denote all type and degrees of hearing loss.
ELMFIELD SCHOOL FOR DEAF CHILDREN Curriculum Policy for Audiology Primary and Secondary - 2 - Throughout this document the terms deaf and deafness are used to denote all type and degrees of hearing loss.
CALIFORNIA CHILDREN S SERVICES MANUAL OF PROCEDURES 3.42 STANDARDS FOR INFANT HEARING SCREENING SERVICES
 3.42 STANDARDS FOR 3.42.1 INPATIENT INFANT HEARING SCREENING PROVIDER A. Definition An Inpatient Infant Hearing Screening Provider shall be a general acute care hospital with licensed perinatal services
3.42 STANDARDS FOR 3.42.1 INPATIENT INFANT HEARING SCREENING PROVIDER A. Definition An Inpatient Infant Hearing Screening Provider shall be a general acute care hospital with licensed perinatal services
What happens when you refer a patient to Audiology? Modernising patient pathways and services
 What happens when you refer a patient to Audiology? Modernising patient pathways and services Paediatrics Adult Rehab RBFT AUDIOLOGY Balance Hearing Therapy To provide high quality services for people
What happens when you refer a patient to Audiology? Modernising patient pathways and services Paediatrics Adult Rehab RBFT AUDIOLOGY Balance Hearing Therapy To provide high quality services for people
Local Offer: Community Paediatrics (West Lancashire)
 Local Offer: Community Paediatrics (West Lancashire) Service Provider Nominated Individual Ormskirk & District General Hospital Southport and Ormskirk NHS Trust Dr Anthony Asakpa Speciality Doctor Community
Local Offer: Community Paediatrics (West Lancashire) Service Provider Nominated Individual Ormskirk & District General Hospital Southport and Ormskirk NHS Trust Dr Anthony Asakpa Speciality Doctor Community
Education Adjustment Program (EAP) Handbook
 Education Adjustment Program (EAP) Handbook Current as at September 2015 The State of Queensland (2015) This document is licensed under CC-BY 4.0, with the exception of the government coat of arms, logos
Education Adjustment Program (EAP) Handbook Current as at September 2015 The State of Queensland (2015) This document is licensed under CC-BY 4.0, with the exception of the government coat of arms, logos
The Disability Tax Credit Certificate Tip sheet for Audiologists
 The Disability Tax Credit Certificate Tip sheet for Audiologists Developed by: The Canadian Academy of Audiology (CAA) & Speech- Language and Audiology Canada (SAC) Purpose of This Document The Canada
The Disability Tax Credit Certificate Tip sheet for Audiologists Developed by: The Canadian Academy of Audiology (CAA) & Speech- Language and Audiology Canada (SAC) Purpose of This Document The Canada
Mater Misericordiae University Hospital Dublin. Job Description & Person Specification
 Mater Misericordiae University Hospital Dublin Job Description & Person Specification Audiologist Job Title / Grade: Audiologist Department / Division: Audiology / Ear, Nose, Throat (ENT) Departments Location:
Mater Misericordiae University Hospital Dublin Job Description & Person Specification Audiologist Job Title / Grade: Audiologist Department / Division: Audiology / Ear, Nose, Throat (ENT) Departments Location:
CHILDREN, YOUTH AND WOMEN S HEALTH SERVICE JOB AND PERSON SPECIFICATION
 CHILDREN, YOUTH AND WOMEN S HEALTH SERVICE JOB AND PERSON SPECIFICATION POSITION DETAILS Position Title: Paediatric Audiologist Classification: PO2 Position No: Cost centre: Reports to: Manager Newborn
CHILDREN, YOUTH AND WOMEN S HEALTH SERVICE JOB AND PERSON SPECIFICATION POSITION DETAILS Position Title: Paediatric Audiologist Classification: PO2 Position No: Cost centre: Reports to: Manager Newborn
OCR Levels 2 and 3 in Supporting Teaching and Learning in Schools. Unit 39 Support pupils with communication and interaction needs
 OCR Levels 2 and 3 in Supporting Teaching and Learning in Schools Unit 39 Support pupils with communication and interaction needs UNIT SUMMARY Who is this unit for? This unit is for those who provide support
OCR Levels 2 and 3 in Supporting Teaching and Learning in Schools Unit 39 Support pupils with communication and interaction needs UNIT SUMMARY Who is this unit for? This unit is for those who provide support
Why does my child have a hearing loss?
 Introduction This factsheet will tell you about the range of tests that can be carried out to try to find the cause of your child s hearing loss. The process to find out why a child is deaf is sometimes
Introduction This factsheet will tell you about the range of tests that can be carried out to try to find the cause of your child s hearing loss. The process to find out why a child is deaf is sometimes
Audiologist and Hearing Aid Dispenser. Provider Manual
 Audiologist and Hearing Aid Provider Manual Provider 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Chapter I. General Program Policies Chapter II. Member Eligibility Chapter IV. Billing Iowa Medicaid Appendix III. Provider-Specific
Audiologist and Hearing Aid Provider Manual Provider 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Chapter I. General Program Policies Chapter II. Member Eligibility Chapter IV. Billing Iowa Medicaid Appendix III. Provider-Specific
COCHLEAR NERVE APLASIA : THE AUDIOLOGIC PERSPECTIVE A CASE REPORT. Eva Orzan, MD Pediatric Audiology University Hospital of Padova, Italy
 COCHLEAR NERVE APLASIA : THE AUDIOLOGIC PERSPECTIVE A CASE REPORT Eva Orzan, MD Pediatric Audiology University Hospital of Padova, Italy Congenital absence or underdevelopment of the cochlear nerve has
COCHLEAR NERVE APLASIA : THE AUDIOLOGIC PERSPECTIVE A CASE REPORT Eva Orzan, MD Pediatric Audiology University Hospital of Padova, Italy Congenital absence or underdevelopment of the cochlear nerve has
Department of Developmental Services Terrence W. Macy, Ph.D., Commissioner Linda Goodman, System Director
 Acknowledgments This guideline was revised and updated in July 2012 to add more current information and resources. The Connecticut Birth to Three System would like to thank the following people who worked
Acknowledgments This guideline was revised and updated in July 2012 to add more current information and resources. The Connecticut Birth to Three System would like to thank the following people who worked
PUBLIC HEALTH IMPROVEMENT PARTNERSHIP
 PUBLIC HEALTH IMPROVEMENT PARTNERSHIP PUBLIC HEALTH ACTIVITIES & SERVICES INVENTORY TECHNICAL NOTES HEALTHY FAMILY DEVELOPMENT Nurse-Family Partnership Nurse-Family Partnership is a voluntary program of
PUBLIC HEALTH IMPROVEMENT PARTNERSHIP PUBLIC HEALTH ACTIVITIES & SERVICES INVENTORY TECHNICAL NOTES HEALTHY FAMILY DEVELOPMENT Nurse-Family Partnership Nurse-Family Partnership is a voluntary program of
Care Pathway for Rehabilitation Team (Following allocation of Cochlear Implant surgery date)
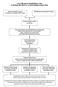 Care Pathway for Rehabilitation Team (Following allocation of Cochlear Implant surgery date) Home information session (Carried out by a member of the CI team) Rehabilitationist allocated to family Cochlear
Care Pathway for Rehabilitation Team (Following allocation of Cochlear Implant surgery date) Home information session (Carried out by a member of the CI team) Rehabilitationist allocated to family Cochlear
Supporting Families in Transition between Early Intervention and School Age Programs
 Supporting Families in Transition between Early Intervention and School Age Programs by Cheryl Johnson, Special Education Unit, Colorado Department of Education The transitions between early intervention
Supporting Families in Transition between Early Intervention and School Age Programs by Cheryl Johnson, Special Education Unit, Colorado Department of Education The transitions between early intervention
Register of Students with Severe Disabilities
 Department of Education Learners first, connected and inspired Register of Students with Severe Disabilities Department of Education Register of Students with Severe Disabilities 1. Eligibility Criteria
Department of Education Learners first, connected and inspired Register of Students with Severe Disabilities Department of Education Register of Students with Severe Disabilities 1. Eligibility Criteria
Guidance on professional practice for Hearing Aid Audiologists
 Guidance on professional practice for Hearing Aid Audiologists Assuring High Quality Professional Hearing Care Introduction This booklet is intended to be guidance on good professional practices for Registered
Guidance on professional practice for Hearing Aid Audiologists Assuring High Quality Professional Hearing Care Introduction This booklet is intended to be guidance on good professional practices for Registered
My child has a hearing loss
 My child has a hearing loss A guide for parents Content You are not alone 3 Hearing impairment 5 Methods of testing hearing 6 Audiogram 7 Types and causes of hearing loss 8 Degree of hearing loss 10 Where
My child has a hearing loss A guide for parents Content You are not alone 3 Hearing impairment 5 Methods of testing hearing 6 Audiogram 7 Types and causes of hearing loss 8 Degree of hearing loss 10 Where
Causeway Child Development Centre
 Causeway Child Development Centre What is the Causeway Child Development Centre? This is a centre where children, especially those with special needs, can be seen, assessed or treated by health, social
Causeway Child Development Centre What is the Causeway Child Development Centre? This is a centre where children, especially those with special needs, can be seen, assessed or treated by health, social
4 Quality Standards - Human Resources. Contents. 4.0 Introduction. 4.1 Management Structure and Staffing Levels
 4 Quality Standards - Human Resources Contents 4.0 Introduction 4.1 Management Structure and Staffing Levels 4.2 Contracts, Job Descriptions & Person Specifications 4.3 Recruitment, Selection and Leaving
4 Quality Standards - Human Resources Contents 4.0 Introduction 4.1 Management Structure and Staffing Levels 4.2 Contracts, Job Descriptions & Person Specifications 4.3 Recruitment, Selection and Leaving
Guidelines for Fitting Hearing Aids to Young Infants. Version 2.0. February 2014
 Guidelines for Fitting Hearing Aids to Young Infants Version 2.0 February 2014 Rachel Feirn 1 (Editor) 1 Formerly of Children s Hearing Centre, University Hospitals Bristol, UK These guidelines were originally
Guidelines for Fitting Hearing Aids to Young Infants Version 2.0 February 2014 Rachel Feirn 1 (Editor) 1 Formerly of Children s Hearing Centre, University Hospitals Bristol, UK These guidelines were originally
Harold C. Pillsbury III, MD, FACS
 Harold C. Pillsbury III, MD, FACS University of North Carolina Ear & Hearing Center Department of Otolaryngology / Head & Neck Surgery, University of North Carolina Chapel Hill, USA Audiologists: Erika
Harold C. Pillsbury III, MD, FACS University of North Carolina Ear & Hearing Center Department of Otolaryngology / Head & Neck Surgery, University of North Carolina Chapel Hill, USA Audiologists: Erika
The Victorian Infant Hearing Screening Program: Update
 The Victorian Infant Hearing Screening Program: Update Dr Melinda Barker Co-director, Victorian Infant Hearing Screening Program Royal Children s Hospital October 2014 VIHSP a brief history 1992 Victorian
The Victorian Infant Hearing Screening Program: Update Dr Melinda Barker Co-director, Victorian Infant Hearing Screening Program Royal Children s Hospital October 2014 VIHSP a brief history 1992 Victorian
School-based Support Personnel
 L. SUPPORT SERVICES School-based Support Personnel Yukon Education provides both professional and paraprofessional support to schools to address the diverse learning of students. Learning Assistance Program
L. SUPPORT SERVICES School-based Support Personnel Yukon Education provides both professional and paraprofessional support to schools to address the diverse learning of students. Learning Assistance Program
Learners Who are Deaf or Hard of Hearing Kalie Carlisle, Lauren Nash, and Allison Gallahan
 Learners Who are Deaf or Hard of Hearing Kalie Carlisle, Lauren Nash, and Allison Gallahan Definition Deaf A deaf person is one whose hearing disability precludes successful processing of linguistic information
Learners Who are Deaf or Hard of Hearing Kalie Carlisle, Lauren Nash, and Allison Gallahan Definition Deaf A deaf person is one whose hearing disability precludes successful processing of linguistic information
Early Intervention For children ages 0-3 years
 Early Intervention For children ages 0-3 years IDEA 2004 AND CHILDREN WHO ARE DEAF OR HARD OF HEARING Early intervention, serving children from birth to age 3, is required by law. Public law 94-142 was
Early Intervention For children ages 0-3 years IDEA 2004 AND CHILDREN WHO ARE DEAF OR HARD OF HEARING Early intervention, serving children from birth to age 3, is required by law. Public law 94-142 was
Edited by Victor de Andrade Page 1
 Guidelines for Hearing Aid Selection and Fitting for Adults This document serves to function as a guideline for hearing care professionals who select and dispense hearing aids to adult patients. Its purpose
Guidelines for Hearing Aid Selection and Fitting for Adults This document serves to function as a guideline for hearing care professionals who select and dispense hearing aids to adult patients. Its purpose
Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Pediatricians
 1/1/2015 Hearing Testing Coding Fact Sheet Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Pediatricians While coding for hearing screening is relatively straightforward, ensuring that appropriate payment is received
1/1/2015 Hearing Testing Coding Fact Sheet Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Pediatricians While coding for hearing screening is relatively straightforward, ensuring that appropriate payment is received
Infant & Toddler Connections of Virginia DRAFT Provider Qualifications 1 Table
 Infant & Toddler Connections of Virginia DRAFT Provider Qualifications 1 Table Audiologist Master s degree plus state licensure Specialist Associate Assistant Screening Audiology, Certified Therapeutic
Infant & Toddler Connections of Virginia DRAFT Provider Qualifications 1 Table Audiologist Master s degree plus state licensure Specialist Associate Assistant Screening Audiology, Certified Therapeutic
A British Columbia Initiative for Early Hearing Detection and Intervention
 HEARING SCREENING FOR EVERY BABY A Sound Start: A British Columbia Initiative for Early Hearing Detection and Intervention Prepared by The Early Hearing Detection and Intervention BC (EHDI-BC) Steering
HEARING SCREENING FOR EVERY BABY A Sound Start: A British Columbia Initiative for Early Hearing Detection and Intervention Prepared by The Early Hearing Detection and Intervention BC (EHDI-BC) Steering
NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM HEARING AID/AUDIOLOGY MANUAL
 NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM HEARING AID/AUDIOLOGY MANUAL POLICY GUIDELINES Table of Contents SECTION I - REQUIREMENTS FOR PARTICIPATION IN MEDICAID...2 SERVICES PROVIDED TO PATIENTS UNDER 21 YEARS
NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM HEARING AID/AUDIOLOGY MANUAL POLICY GUIDELINES Table of Contents SECTION I - REQUIREMENTS FOR PARTICIPATION IN MEDICAID...2 SERVICES PROVIDED TO PATIENTS UNDER 21 YEARS
APPENDIX A SCHOOL-BASED RESOURCES
 APPENDIX A SCHOOL-BASED RESOURCES Classroom Teacher - The classroom teacher is responsible for providing a quality education to all students. Duties include: classroom organization and management, assessment,
APPENDIX A SCHOOL-BASED RESOURCES Classroom Teacher - The classroom teacher is responsible for providing a quality education to all students. Duties include: classroom organization and management, assessment,
NHS STANDARD CONTRACT FOR IMPLANTABLE HEARING AIDS FOR MICROTIA, BONE ANCHORED HEARING AIDS AND MIDDLE EAR IMPLANTS (ALL AGES)
 D09/S/b NHS STANDARD CONTRACT FOR IMPLANTABLE HEARING AIDS FOR MICROTIA, BONE ANCHORED HEARING AIDS AND MIDDLE EAR IMPLANTS (ALL AGES) SCHEDULE 2, THE SERVICES A. SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS Service Specification
D09/S/b NHS STANDARD CONTRACT FOR IMPLANTABLE HEARING AIDS FOR MICROTIA, BONE ANCHORED HEARING AIDS AND MIDDLE EAR IMPLANTS (ALL AGES) SCHEDULE 2, THE SERVICES A. SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS Service Specification
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Bone Anchored Hearing Aids. April 2013. Reference: NHSCB/ D09/P/a
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Bone Anchored Hearing Aids April 2013 Reference: NHSCB/ D09/P/a NHS Commissioning Board Clinical Commissioning Policy: Bone Anchored Hearing Aids First published: April 2013
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Bone Anchored Hearing Aids April 2013 Reference: NHSCB/ D09/P/a NHS Commissioning Board Clinical Commissioning Policy: Bone Anchored Hearing Aids First published: April 2013
We are the regulator: Our job is to check whether hospitals, care homes and care services are meeting essential standards.
 Inspection Report We are the regulator: Our job is to check whether hospitals, care homes and care services are meeting essential standards. University of Southampton Auditory Implant Service Building
Inspection Report We are the regulator: Our job is to check whether hospitals, care homes and care services are meeting essential standards. University of Southampton Auditory Implant Service Building
EARLY INTERVENTION: COMMUNICATION AND LANGUAGE SERVICES FOR FAMILIES OF DEAF AND HARD-OF-HEARING CHILDREN
 EARLY INTERVENTION: COMMUNICATION AND LANGUAGE SERVICES FOR FAMILIES OF DEAF AND HARD-OF-HEARING CHILDREN Our child has a hearing loss. What happens next? What is early intervention? What can we do to
EARLY INTERVENTION: COMMUNICATION AND LANGUAGE SERVICES FOR FAMILIES OF DEAF AND HARD-OF-HEARING CHILDREN Our child has a hearing loss. What happens next? What is early intervention? What can we do to
NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM HEARING AID/ AUDIOLOGY SERVICES PROCEDURE CODES
 NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM HEARING AID/ AUDIOLOGY SERVICES PROCEDURE CODES Table of Contents GENERAL INFORMATION AND INSTRUCTIONS----------------------------------------------- 2 A. DIAGNOSTIC SERVICES
NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM HEARING AID/ AUDIOLOGY SERVICES PROCEDURE CODES Table of Contents GENERAL INFORMATION AND INSTRUCTIONS----------------------------------------------- 2 A. DIAGNOSTIC SERVICES
NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM HEARING AID/ AUDIOLOGY SERVICES FEE SCHEDULE
 NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM HEARING AID/ AUDIOLOGY SERVICES FEE SCHEDULE Table of Contents GENERAL INFORMATION AND INSTRUCTIONS----------------------------------------------- 2 CODES -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM HEARING AID/ AUDIOLOGY SERVICES FEE SCHEDULE Table of Contents GENERAL INFORMATION AND INSTRUCTIONS----------------------------------------------- 2 CODES -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Education and Culture committee. Attainment of school pupils with sensory impairment. Call for evidence April 2015
 Education and Culture committee Attainment of school pupils with sensory impairment Call for evidence April 2015 North Ayrshire Council, Education and Youth Employment have a number of strategies in place
Education and Culture committee Attainment of school pupils with sensory impairment Call for evidence April 2015 North Ayrshire Council, Education and Youth Employment have a number of strategies in place
Cochlear implants for children and adults with severe to profound deafness
 Issue date: January 2009 Review date: February 2011 Cochlear implants for children and adults with severe to profound deafness National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Page 1 of 41 Final appraisal
Issue date: January 2009 Review date: February 2011 Cochlear implants for children and adults with severe to profound deafness National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Page 1 of 41 Final appraisal
Children s Cochlear Implant Program (W.A.)
 It is with much pleasure that Australian Hearing is able to provide your copy of the Western Australian supplement to Choices. This booklet provides simple explanations about the various education and
It is with much pleasure that Australian Hearing is able to provide your copy of the Western Australian supplement to Choices. This booklet provides simple explanations about the various education and
BEST PRACTICES Pediatric Bilateral Sensorineural Hearing Loss
 BEST PRACTICES Pediatric Bilateral Sensorineural Hearing Loss Christina L. Runge, PhD, CCC-A Associate Professor Chief, Division of Communication Sciences Director, Koss Cochlear Implant Program Resources
BEST PRACTICES Pediatric Bilateral Sensorineural Hearing Loss Christina L. Runge, PhD, CCC-A Associate Professor Chief, Division of Communication Sciences Director, Koss Cochlear Implant Program Resources
Hearing Devices Policy and Administration Manual
 Hearing Devices Policy and Administration Manual Assistive Devices Program, Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care Table of Amendments This page will list all substantive changes to policies and procedures
Hearing Devices Policy and Administration Manual Assistive Devices Program, Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care Table of Amendments This page will list all substantive changes to policies and procedures
STATE OF NEBRASKA STATUTES RELATING TO AUDIOLOGY AND SPEECH-LANGUAGE PATHOLOGY PRACTICE ACT
 2009 STATE OF NEBRASKA STATUTES RELATING TO AUDIOLOGY AND SPEECH-LANGUAGE PATHOLOGY PRACTICE ACT Department of Health and Human Services Division of Public Health Licensure Unit 301 Centennial Mall South,
2009 STATE OF NEBRASKA STATUTES RELATING TO AUDIOLOGY AND SPEECH-LANGUAGE PATHOLOGY PRACTICE ACT Department of Health and Human Services Division of Public Health Licensure Unit 301 Centennial Mall South,
A Practitioner s Guide
 A Practitioner s Guide Social care for deaf children and young people: A guide to assessment and child protection investigations for social care practitioners Our vision is of a world without barriers
A Practitioner s Guide Social care for deaf children and young people: A guide to assessment and child protection investigations for social care practitioners Our vision is of a world without barriers
JOB DESCRIPTION. Clinical Nurse Specialist in Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Specialist Hospitals, Women & Child Health Directorate
 JOB DESCRIPTION Title of Post: Grade/ Band: Directorate: Reports to: Accountable to: Location: Hours: Clinical Nurse Specialist in Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Band 8A Specialist Hospitals,
JOB DESCRIPTION Title of Post: Grade/ Band: Directorate: Reports to: Accountable to: Location: Hours: Clinical Nurse Specialist in Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Band 8A Specialist Hospitals,
Complaints Policy. Complaints Policy. Page 1
 Complaints Policy Page 1 Complaints Policy Policy ref no: CCG 006/14 Author (inc job Kat Tucker Complaints & FOI Manager title) Date Approved 25 November 2014 Approved by CCG Governing Body Date of next
Complaints Policy Page 1 Complaints Policy Policy ref no: CCG 006/14 Author (inc job Kat Tucker Complaints & FOI Manager title) Date Approved 25 November 2014 Approved by CCG Governing Body Date of next
SPECIAL EDUCATION AND RELATED SERVICES
 i SPECIAL EDUCATION AND RELATED SERVICES Updated May 2008 i It is the policy of the South Dakota Department of Education, Office of Educational Services and Supports to provide services to all persons
i SPECIAL EDUCATION AND RELATED SERVICES Updated May 2008 i It is the policy of the South Dakota Department of Education, Office of Educational Services and Supports to provide services to all persons
School Nurse Presentation to New Parents. why me. Continence in children and young people. Registered charity number: 1002424
 School Nurse Presentation to New Parents why me? Continence in children and young people Aims of this session To introduce parents / carers to the school nursing service To inform parents carers about
School Nurse Presentation to New Parents why me? Continence in children and young people Aims of this session To introduce parents / carers to the school nursing service To inform parents carers about
Information for parents. Deafness
 About this publication This is a guide for parents with young children who have recently been told that their child is deaf, or who are in the process of getting a diagnosis. It was developed by the Early
About this publication This is a guide for parents with young children who have recently been told that their child is deaf, or who are in the process of getting a diagnosis. It was developed by the Early
NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM HEARING AID/ AUDIOLOGY SERVICES PROCEDURE CODES
 NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM HEARING AID/ AUDIOLOGY SERVICES PROCEDURE CODES Table of Contents WHAT S NEW FOR THE 2016 MANUAL? --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM HEARING AID/ AUDIOLOGY SERVICES PROCEDURE CODES Table of Contents WHAT S NEW FOR THE 2016 MANUAL? --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
CONVENTIONAL AND DIGITAL HEARING AIDS
 CONVENTIONAL AND DIGITAL HEARING AIDS Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical
CONVENTIONAL AND DIGITAL HEARING AIDS Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical
Nevada Division of Public and Behavioral Health
 Nevada Division of Public and Behavioral Health Early Hearing Detection and Intervention (EHDI) Program GUIDELINES FOR INFANT AUDIOLOGIC ASSESSMENT STATE OF NEVADA BRIAN SANDOVAL Governor CODY L. PHINNEY,
Nevada Division of Public and Behavioral Health Early Hearing Detection and Intervention (EHDI) Program GUIDELINES FOR INFANT AUDIOLOGIC ASSESSMENT STATE OF NEVADA BRIAN SANDOVAL Governor CODY L. PHINNEY,
Developing Early Intervention/Support Services for Deaf Children and their Families
 Consultation Developing Early Intervention/Support Services for Deaf Children and their Families Executive summary Overview This is a consultation document containing draft guidance for LEAs. It considers
Consultation Developing Early Intervention/Support Services for Deaf Children and their Families Executive summary Overview This is a consultation document containing draft guidance for LEAs. It considers
Specialist Children s Service
 Specialist Children s Service Information and Guidelines for Referrers March 2009, Version 3.0 Contents CONTENTS... 2 INTRODUCTION... 3 TEAMS BASED AT THE WOOD STREET HEALTH CENTRE:... 3 TEAMS BASED ELSEWHERE
Specialist Children s Service Information and Guidelines for Referrers March 2009, Version 3.0 Contents CONTENTS... 2 INTRODUCTION... 3 TEAMS BASED AT THE WOOD STREET HEALTH CENTRE:... 3 TEAMS BASED ELSEWHERE
Speech Pathology Funding Information for Clients
 Speech Pathology Funding Information for Clients www.communicatespeech.com.au Private Health Cover - All Ages Children and Adults Speech Pathology Assessment and Therapy sessions can be claimed through
Speech Pathology Funding Information for Clients www.communicatespeech.com.au Private Health Cover - All Ages Children and Adults Speech Pathology Assessment and Therapy sessions can be claimed through
Chapter 41 Speech-Language Pathology and Audiology Licensing Act
 Chapter 41 Speech-Language Pathology and Audiology Licensing Act 58-41-1 Title of chapter. This chapter is known as the "Speech-language Pathology and Audiology Licensing Act." 58-41-2 Definitions. In
Chapter 41 Speech-Language Pathology and Audiology Licensing Act 58-41-1 Title of chapter. This chapter is known as the "Speech-language Pathology and Audiology Licensing Act." 58-41-2 Definitions. In
Florida Medicaid. Hearing Services Coverage Policy
 Florida Medicaid Agency for Health Care Administration June 2016 Table of Contents 1.0 Introduction... 1 1.1 Description... 1 1.2 Legal Authority... 1 1.3 Definitions... 1 2.0 Eligible Recipient... 2 2.1
Florida Medicaid Agency for Health Care Administration June 2016 Table of Contents 1.0 Introduction... 1 1.1 Description... 1 1.2 Legal Authority... 1 1.3 Definitions... 1 2.0 Eligible Recipient... 2 2.1
Children's Therapy Services - Occupational Therapy
 Children's Therapy Services - Occupational Therapy Our Occupational Therapists support babies, children and young people who have conditions which affect their physical and functional development. What
Children's Therapy Services - Occupational Therapy Our Occupational Therapists support babies, children and young people who have conditions which affect their physical and functional development. What
KANSAS MEDICAL ASSISTANCE PROGRAM PROVIDER MANUAL. Audiology
 KANSAS MEDICAL ASSISTANCE PROGRAM PROVIDER MANUAL Audiology PART II Introduction Section BILLING INSTRUCTIONS Page 7000 Audiology Billing Instructions............... 7-1 Submission of Claim................
KANSAS MEDICAL ASSISTANCE PROGRAM PROVIDER MANUAL Audiology PART II Introduction Section BILLING INSTRUCTIONS Page 7000 Audiology Billing Instructions............... 7-1 Submission of Claim................
COMPLEX LEARNING DIFFICULTIES AND DISABILITIES RESEARCH PROJECT (CLDD)
 Page 1 This is a general overview of the implications of vision impairment, hearing impairment and multi-sensory impairment. The impact of impairments for individual students with complex learning difficulties
Page 1 This is a general overview of the implications of vision impairment, hearing impairment and multi-sensory impairment. The impact of impairments for individual students with complex learning difficulties
Allied, Therapeutic and Psychology Extender Benefit
 Allied, Therapeutic and Psychology Extender Benefit 2015 Allied, Therapeutic and Psychology Extender Benefit The Allied, Therapeutic and Psychology Extender Benefit is available on the Executive and Comprehensive
Allied, Therapeutic and Psychology Extender Benefit 2015 Allied, Therapeutic and Psychology Extender Benefit The Allied, Therapeutic and Psychology Extender Benefit is available on the Executive and Comprehensive
Once your baby has good head control and can turn towards something interesting, a more advanced behavioural procedure can be used.
 How do we test the hearing of babies and children? An audiologist will select from a range of different tests to evaluate your child s hearing. The choice of test depends on the information that is needed
How do we test the hearing of babies and children? An audiologist will select from a range of different tests to evaluate your child s hearing. The choice of test depends on the information that is needed
Hearing Tests for Children with Multiple or Developmental Disabilities by Susan Agrawal
 www.complexchild.com Hearing Tests for Children with Multiple or Developmental Disabilities by Susan Agrawal Hearing impairment is a common problem in children with developmental disabilities or who have
www.complexchild.com Hearing Tests for Children with Multiple or Developmental Disabilities by Susan Agrawal Hearing impairment is a common problem in children with developmental disabilities or who have
Facts and figures on hearing loss, deafness and tinnitus
 FACTSHEET Facts and figures on hearing loss, deafness and tinnitus This factsheet gives you information about the latest available figures on hearing loss, deafness and tinnitus among adults in the UK.
FACTSHEET Facts and figures on hearing loss, deafness and tinnitus This factsheet gives you information about the latest available figures on hearing loss, deafness and tinnitus among adults in the UK.
Australian Hearing Aided Cortical Evoked Potentials Protocols
 Australian Hearing Aided Cortical Evoked Potentials Protocols Alison King, Principal Audiologist, Paediatric Services. Lyndal Carter (NAL), Bram Van Dun (NAL), Vicky Zhang (NAL) Wendy Pearce (Principal
Australian Hearing Aided Cortical Evoked Potentials Protocols Alison King, Principal Audiologist, Paediatric Services. Lyndal Carter (NAL), Bram Van Dun (NAL), Vicky Zhang (NAL) Wendy Pearce (Principal
EARLY INTERVENTION SERVICE DESCRIPTIONS, BILLING CODES AND RATES
 EARLY INTERVENTION SERVICE DESCRIPTIONS, BILLING CODES AND RATES EARLY INTERVENTION PROVIDER HANDBOOK Illinois Department of Human Services Community Health and Prevention Bureau of Early Intervention
EARLY INTERVENTION SERVICE DESCRIPTIONS, BILLING CODES AND RATES EARLY INTERVENTION PROVIDER HANDBOOK Illinois Department of Human Services Community Health and Prevention Bureau of Early Intervention
Allied, Therapeutic and Psychology Extender Benefit
 Allied, Therapeutic and Psychology Extender Benefit 2013 The Allied, Therapeutic and Psychology Extender Benefit is available on the Enhanced Option only. Overview This document tells you about the Allied,
Allied, Therapeutic and Psychology Extender Benefit 2013 The Allied, Therapeutic and Psychology Extender Benefit is available on the Enhanced Option only. Overview This document tells you about the Allied,
