MODULE FIVE. ORGANIZATIONAL DESIGN, CHANGE AND INNOVATION (four hours) CHAPTER TWENTY TWO-Organizational Structure and Design (three hours)
|
|
|
- Osborn Montgomery
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MODULE FIVE ORGANIZATIONAL DESIGN, CHANGE AND INNOVATION (four hours) CHAPTER TWENTY TWO-Organizational Structure and Design (three hours) (one hour) CHAPTER TWENTY THREE- Managing Change and Innovation Reference: Prepared By 1. Organizational Behaviour, Stephen P.Robbins, Timothi A.Judge and Seema Sanghi, 12 th ed, Prentice Hall India 2. Organizational behaviour-human behaviour at work by John W Newstrom, 12 th edition, McGrawHill 3. Organizational behavior and management by Ivancevich, Konopaske and Matteson - 7th edition, Tata McGrawHill 4. Organisational Behaviour by Steven L Mc Shane Mary Ann Von Glinow Radha R Sharma Tata McGrawHill 5. Organizational behavior by Don Hellriegel; John W. Slocum; Richard W. Woodman-8 th edition, Thomson South-Western 6. Understanding the theory and Design of Organizations, Richard L Daft, SouthWestern Cengage Learning 7. Organizational Theory, Design and Change, 5 th edition, Gareth R Jones, Pearson Education Dr Susmita Mukhopadhyay Assistant Professor, VGSOM, IIT Kharagpur [email protected]
2 Chapter Twenty Two Organizational Structure and Design Objectives To develop an understanding of: Organizational Structure and Design Key Elements for Organizational Structure (a)work specialization (b) Departmentalization (c) Chain of command (d)span of control (e) Centralization and decentralization (f)formalization Organization Structure: Its Determinants and Outcomes Organizational Designs and Employee Behavior Challenges in Designing an Organizational Structure Organizational Designs Indian organizations Empowerment Styles in Indian Perspective Restructuring Indian organizations: Challenges and responses Impact of culture on Indian Business Organizations
3 Introduction Organizational Structure and Design are important factors influencing behavior of individuals and groups that comprise the organization; they establish expectations for what individuals and groups will do to achieve the organization's purposes. Design: Managers make a conscious effort to predetermine the way employees do their work. Structure: Defined as "stable relationships and processes of the organization." It is also the "anatomy" or framework of an organization. It focuses on different positions, formulations of rules and procedures, and prescriptions of authority. It is used to regulate, or at least reduce uncertainty in the behavior of individual employees. Organizational Structure defines how job tasks are formally divided, grouped, and coordinated. Key Elements for Organizational Structure are (a)work specialization (b) Departmentalization (c) Chain of command (d)span of control (e) Centralization and decentralization (f)formalization Work Specialization The degree to which tasks in the organization are subdivided into separate jobs Division of Labor (a)makes efficient use of employee skills (b)increases employee skills through repetition (c)less between-job downtime increases productivity (d)specialized training is more efficient (e)allows use of specialized equipment Departmentalization-The basis by which jobs are grouped together. Activities are grouped by: (a)function (b)product (c)geography (d)process (e)customer (f)authority-the rights inherent in a managerial position to give orders and to expect the orders to be obeyed Complexity is the number of distinctly different job titles, or occupational groupings, and the number of distinctly different units, or departments. a. Horizontal differentiation the number of different units at the same level. b. Vertical differentiation the number of levels in the organization. Chain of Command-The unbroken line of authority that extends from the top of the organization to the lowest echelon and clarifies who reports to whom. Unity of Command-A subordinate should have only one superior to whom he or she is directly responsible
4 Span of Management /Span of Control- Span of Control refers to the act of establishing the number of jobs to be included in a specific group. It is the volume of interpersonal relationships that a single manager can handle.wider spans of management increase organizational efficiency. Three types of interpersonal relationships: 1. Direct single between manager and each subordinate. 2. Direct group between manager and each permutation of subordinate groups. 3. Cross subordinates interacting with each other. Designing Span of Management: A Contingency Viewpoint Some factors relating to an optimal plan of control are known, but the answer remains elusive as industry and communications change. Similarity of functions Geographic continuity Complexity of functions Coordination Planning Span of control is increased when subordinates have similar functions, are physically close, have simple tasks, needs little coordination and manager spends little time planning. Frequency and intensity of actual relationships is critical, not the total number. 1. Required contact the more ambiguity, the more contact needed. 2. Degree of specialization managers are able to oversee more people, if they are doing less complicated work. 3. Ability to communicate clear communicators can manage more people. Height of Organization Chart Tall chart: Greater height - Smaller span
5 Flat chart: Lower height - Greater span Narrow Versus Wide Spans A. V. Graicunas Ralph Davis Subordinate interactions Direct the manager s relationship with each subordinate. Cross among the subordinates themselves. Group between groups of subordinates. Formula for the number of interactions of all types:» I = N(2N/2 + N - 1), where I is the total number of interactions and N is number of subordinates. Operative span for lower-level managers up to 30 workers. Executive span for middle and top managers at 3 to 9. Determining the Appropriate Span: Factors Influencing the Span of Management (reference: Houghton Mifflin Company). 1.Competency of supervisor and subordinates 2. Physical dispersion of subordinates.3. Extent of non supervisory work in a manager s job 4 Degree of required interaction. 5. Extent of standardized procedure. 6. Similarity of tasks being supervised. 7.Frequency of new problem.8.preference of supervisor and subordinates
6 Drawbacks of Narrow Span (a)expense of additional layers of management(b) Increased complexity of vertical communication(c)encouragement of overly tight supervision and discouragement of employee autonomy Centralization and Decentralization Centralization is the location of the decision-making authority in the hierarchy of the organization.it is the degree to which decision making is concentrated at a single point in the organization Decentralization is the degree to which decision making is spread throughout the organization. Formalization The degree to which jobs within the organization are standardized. It is the extent to which expectations regarding the means and ends of work are specified and written down.it is effective only if are enforced. The relationships between dimensions of organizational structures and the four design decisions are summarized below Key Design Questions and Answers for Designing the Proper Organization Structure 1.To what degree are articles subdivided into separate jobs? Work specialization. 2.On what basis jobs will be grouped together? Departmentalization 3.To whom do the individual and group report to? Chain of command 4.How many individuals can a manager efficiently and effectively direct? Span of control 5.Where does decision making authority lie? Centralization and decentralization 6.To what degree there will be rules and regulations to direct the employees?formalization (Reference: Organizational Behaviour, Stephen P.Robbins, Timothi A.Judge and Seema Sanghi, 12 th ed, Pearson education, pp590) Organization Structure: Its Determinants and Outcomes Strategy, Size, technology, environment determines structural designs like mechanistic or organic which moderated by individual differences and cultural norms leads to performance and satisfaction.
7 Why Do Structures Differ? Strategy Innovation Strategy A strategy that emphasizes the introduction of major new products and services Cost-minimization Strategy A strategy that emphasizes tight cost controls, avoidance of unnecessary innovation or marketing expenses, and price cutting Imitation Strategy A strategy that seeks to move into new products or new markets only after their viability has already been proven The Strategy-Structure Relationship Innovation strategy leads to Organic structure which is loose in nature; low specialization, low formalization and decentralized. Cost minimization strategy leads to mechanistic structure which is tight control; extensive work specialization, high formalization and high decentralization. Imitation strategy leads to a mix of mechanistic and organic structure- mix of loose with tight properties, tight control over current activities and loose control over new undertakings. Why Do Structures Differ? Size The size of an organization affects its structure. As an organization grows larger, it becomes more mechanistic. Characteristics of large organizations: More specialization More vertical levels More rules and regulations Why Do Structures Differ? Technology Technology determines how an organization transfers its inputs into outputs. Characteristics of routineness (standardized or customized) in activities:
8 Routine technologies are associated with tall, departmentalized structures and formalization in organizations. Routine technologies lead to centralization when formalization is low. Nonroutine technologies are associated with delegated decision authority. Why Do Structures Differ? Environment Institutions or forces outside the organization that potentially affect the organization s performance Key Dimensions of Environment Capacity: The degree to which an environment can support growth Volatility: The degree of instability in the environment Complexity: The degree of heterogeneity and concentration among environmental elements Structure-Effectiveness Relationship Structures like organizations are: a. Purposive. b. Goal-oriented. Structure should be focused toward organizational effectiveness. However the exact relationship between structure and effectiveness is difficult to know as people hold perceptions regarding structural variables that are formed by observing things around them in an unscientific fashion. This is called Implicit Models of Organizational Structure Organizational Designs and Employee Behavior Research Findings Work specialization contributes to higher employee productivity, but it reduces job satisfaction. The benefits of specialization have decreased rapidly as employees seek more intrinsically rewarding jobs. The effect of span of control on employee performance is contingent upon individual differences and abilities, task structures, and other organizational factors. Participative decision making in decentralized organizations is positively related to job satisfaction. Lawrence & Lorsch: Differentiation, Integration, and the Environment Investigated how companies in different industries differentiate and integrate their structures to fit the environment
9 Three industries that experienced different levels of uncertainty: 1. The plastics industry 2. The food-processing industry 3. The container or can-manufacturing industry When environment is perceived as more unstable and uncertain:effective organizations are less formalized, more decentralized and rely more on mutual adjustment. When environment is perceived as stable and certain:effective organizations have a more centralized, standardized, and formalized structure. Burns and Stalker: Uncertainty, Differentiation and Integration When degree of uncertainty (complexity, dynamism, richness) is high it leads to high degree of departmental differentiation and cross functional integration. Environmental Uncertainty and Structure Organizations need different kinds of structure to control their activities based on the environment Unstable and changing environment: Organic structures are more effective.organic structure is a complex structure with high differentiation, high integration,decentralized decision making,mutual adjustment. Stable environment: Centralized, formalized and standardized characteristic of mechanistic structures are more effective. Mechanistic structures are simple structures with low differentiation, low integration,centralized decision making anmd standardization. Designing an Organizational Structure Organizational design the decisions and actions that result in an organizational structure. Decisions to be made when designing an organization. 1. How to divide the task into successively smaller jobs. a. Smaller sets of related activities. b. Specialized activities and responsibilities. 2. How to distribute authority. a. The right to make decisions without higher approval.
10 Design Challenge 1 Differentiation b. The right to extract obedience. 3. Which jobs should be grouped together? 4. What is the appropriate size of the group? People in this organization take on new tasks as the need arises and it s very unclear who is responsible for what, and who should report to whom. This makes it difficult to know on whom to call when the need arises and to coordinate people s activities so they work together as a team. Differentiation is the process by which an organization allocates people and resources to organizational tasks.it establishes the task and authority relationships that allow the organization to achieve its goals. Division of labor is the process of establishing and controlling the degree of specialization in the organization.in a simple organization, differentiation is low because the division of labor is low. Individuals typically perform all organizational tasks. In a complex organization, differentiation is high because the division of labor is high.total process is divided up so that individuals perform separate tasks Historic economic advantages of dividsion of labour are: 1. Mass production relies on specialized labor. 2. Specialized labor is obtained through organizations. Building Blocks of Differentiation The four building blocks of differentiation are Organization, Division, Function, Role. Organizational level Vertical differentiation: the way an organization designs its hierarchy of authority and creates reporting relationships to link organizational roles and subunits Horizontal differentiation: the way an organization groups organizational tasks into roles and roles into subunits (functions and divisions) Organizational Roles are set of task-related behaviors required of a person by his or her position in an organization.as the division of labor increases, managers specialize in some roles and hire people to specialize in others. Specialization allows people to develop their individual abilities and knowledge within their specific role.the identification of roles leads to authority and control issues.
11 Authority is the power to hold people accountable for their actions and to make decisions concerning the use of organizational resources. Control is the ability to coordinate and motivate people to work in the organization s interests Subunits: Functions and Divisions Function is a subunit composed of a group of people, working together, who possess similar skills or use the same kind of knowledge, tools, or techniques to perform their jobs Division is a subunit that consists of a collection of functions or departments that share responsibility for producing a particular good or services Five Function Types 1. Support functions: facilitate an organization s control of its relations with its environment and its stakeholders.eg-purchasing, sales and marketing, public relations and legal affairs 2. Production functions: manage and improve the efficiency of an organization s conversion processes so that more value is created.eg-production operations, production control, and quality control 3. Maintenance functions: enable an organization to keep its departments in operation.eg- Personnel, engineering and janitorial services 4. Adaptive functions: allow an organization to adjust to changes in the environment.eg-research and development, market research, and long-range planning 5. Managerial function: facilitate the control and coordination of activities within and among departments.eg-top management, middle management, and lower-level management Departmental Bases are the reasons for grouping certain tasks.it refers to grouping of tasks and is necessary for coordination. Departmentalization bases 1. Functional Departmentalization a. Divisions based on function. b. Advantage efficiency. c. Disadvantage organizational goals may be sacrificed in favor of departmental goals. 2. Territorial departmentalization
12 Design Challenge 2 a. Divisions based on geographical area. b. Helpful in large organizations where centralization is difficult. 3. Product departmentalization a. Division based on product line. b. Helpful in large, diversified companies. c. Advantage managers develop expertise in many areas. d. Disadvantage some redundancy exists because each product line has its own research, engineering, marketing, etc. 4. Customer departmentalization a. Divisions based on customer group or clients. b. Better able to satisfy customer-identified needs. 5. Mixed and changing departmentalization a. Organizations use a mixture of bases at different levels. b. Organizations will change departmental bases over time, as conditions change. Balancing Differentiation and Integration We can t get people to communicate and coordinate in this organization. Specifying tasks and roles is supposed to help coordinate the work process, but here it builds barriers between people and functions.horizontal differentiation is supposed to enable people to specialize and become more productive.however, specialization often limits communication between subunits as people develop subunit orientation.subunit orientation is a tendency to view one s role in the organization strictly from the perspective of the time frame, goals, and interpersonal orientations of one s subunit. Integration is the process of coordinating various tasks, functions, and divisions so that they work together and not at cross-purposes Seven Types of Integration Mechanisms 1. Hierarchy of authority: who reports to whom 2. Direct contact: managers meet face to face to coordinate activities 3. Liaison roles: a specific manager is given responsibility for coordinating with managers from other subunits on behalf of their subunits
13 4. Task force: managers meet in temporary committees to coordinate cross-functional activities 5. Teams: managers meet regularly in permanent committees to coordinate activities 6. Integrating role: a new role is established to coordinate the activities of two or more functions or divisions 7. Integrating department: a new department is created to coordinate the activities of functions or divisions Balancing Differentiation and Integration Managers facing the challenge of deciding how and how much to differentiate and integrate must do two things: 1. Carefully guide the process of differentiation so that it develops the core competences that give the organization a competitive advantage 2. Carefully integrate the organization by choosing appropriate integrating mechanisms that allow subunits to cooperate and that build up the organization s core competences Design Challenge 3 Balancing Centralization and Decentralization Centralization versus decentralization of authority Centralized: organizational setup whereby the authority to make important decisions is retained by top level managers.people in this organization don t take responsibility or risks. They are always looking to the boss for direction and supervision. As a result, decision making is slow and cumbersome, and we miss out on a lot of opportunities to create values. Decentralized: an organizational setup whereby the authority to make important decisions is delegated to managers at all levels in the hierarchy Decisions about how to distribute decision-making authority in an organization change as the organization grows and differentiates.balancing authority is an ongoing managerial task. Delegation of Authority Every job has a range of alternative configurations of authority delegation; each has gains and losses. Advantages of high delegation of authority: 1. Develops professional managers.
14 2. Leads to competitive climate. 3. Managers exercise more authority, satisfying their problem-solving desires. Costs of high delegation of authority: Design Challenge 4 1. Costly training in decision-making may be necessary. 2. Managers may not delegate to subordinates, for fear of losing control. 3. Monitoring systems to evaluate decision-making are expensive to develop and use. Balancing Standardization and Mutual Adjustment Standardization: conformity to specific models or examples that are considered proper in a given situation Mutual adjustment: the compromise that emerges when decision making and coordination are evolutionary processes and people use their judgment rather than standardized rules to address a problem Formalization: the use of written rules and procedures to standardize operations.people in this organization pay too much attention to the rules. Whenever I need somebody to satisfy an unusual customer request or need real quick service from another function, I can t get it because no one is willing to bend or break the rules. Rules: formal, written statement that specify the appropriate means for reaching desired goals Norms: standards or styles of behavior that are considered acceptable or typical for a group of people Socialization: the process by which organizational members learn the norms of an organization and internalize these unwritten rules of conduct Challenge facing managers is to find a way of using rules and norms to standardize behavior. However, at the same time, managers need to allow for mutual adjustment to give managers opportunity to discover new and better ways to achieve goals Organizational Designs Simple Structure
15 A structure characterized by a low degree of departmentalization, wide spans of control, authority centralized in a single person, and little formalization Bureaucracy A structure of highly operating routine tasks achieved through specialization, very formalized rules and regulations, tasks that are grouped into functional departments, centralized authority, narrow spans of control, and decision making that follows the chain of command. Strengths Weaknesses Functional economies of scale Minimum duplication of personnel and equipment Enhanced communication Weaknesses Subunit conflicts with organizational goals Obsessive concern with rules and regulations Lack of employee discretion to deal with problems Centralized decision making Subunit conflicts with organizational goals Obsessive concern with rules and regulations Lack of employee discretion to deal with problems Why Bureaucracy Survives Large size prevails Environmental turbulence can be largely managed Standardization achieved through hiring people who have undergone extensive educational training Technology maintains control Two design models have significantly influenced management theory/practice: the mechanistic model and the organic model.
16 Mechanistic model: A highly centralized, formalized and complex organizational structure developed by management theorists and practitioners in the early 1900s (e.g., Fayol, Weber, Follett) and characterized by: a. Emphasis on efficiency. b. Highly specialized jobs. c. Centralized problem solving and decision-making. d. Standardized policies, procedures and rules directing much of the decisionmaking. e. Rewards based on obeying supervisors. Organic model: Seeks to maximize organizational flexibility and adaptation via: Advantages: a. De-emphasizing job descriptions and specialization and status/rank differences. b. Assuming that higher-level employees are not necessarily better informed than those at lower levels. c. Emphasizing horizontal and lateral organizational relationships as much or more than vertical ones. d. Maintaining a less permanent and more flexible structure. a. Flexible and adaptable to changing environments. b. Encourages greater use of human potential. c. Multidirectional communications flow. d. Decentralized decision-making. e. Control and goal setting. Overall, the mechanistic structure is relatively simple, decentralized, and informal.
17 A design that gives individuals a sense of personal worth and motivation, and that facilitates flexibility and adaptability would have three characteristics: 1. Relatively simple. 2. Relatively decentralized. 3. Relatively informal. Neither the mechanistic or organic model is best in all situations; both have strengths and weaknesses. The Matrix Model Matrix Structure is a structure that creates dual lines of authority and combines functional and product departmentalization. It refers to a combination of the functional and product departmental bases; a balanced compromise between departmentalization by process and by purpose. Key Elements Gains the advantages of functional and product departmentalization while avoiding their weaknesses. It overlays a horizontal structure of authority, influence, and communication on the vertical structure. It has Dual authority system where people report to two managers, a functional supervisor and a product supervisor Facilitates coordination of complex and interdependent activities Breaks down unity-of-command concept Matrix designs are used by organizations that: Advantages of matrix organization: a. Must respond quickly to rapid change in two or more environments (e.g., technological and markets). b. Face uncertainties due to high information-processing requirements. c. Deal with financial and human resources constraints. 1. Efficient use of resources involves sharing rather than duplicating specialized resources. 2. Flexibility in conditions of change and uncertainty timely response to environmental demands because of effective communications channels inherent in the design. 3. Technical excellence because interaction of specialists encourages cross fertilization if ideas.
18 WEAKNESSES: 4. Freeing top management for long-range planning enables top management to delegate ongoing decision making. 5. Improving motivation and commitment offers more opportunities to participate in key decisions. 6. Providing opportunities for personal development exposes members to diverse parts of the organization and other viewpoints; lets them learn about other specialties and become more aware of the total organization. Causes participants to experience dual authority, which can be frustrating and confusing Means participants need good interpersonal skills and extensive training Is time consuming; involves frequent meetings and conflict resolution sessions Will not work unless participants understand it and adopt collegial rather than verticaltype relationships Requires great effort to maintain power balance Source: Adapted from Robert Duncan, What Is the Right Organization Structure? Decision Tree Analysis Provides the Answer, Organizational Dynamics (Winter 1979): 429. Different forms of matrix organization: 1. Forms can be seen as existing on a continuum from extremely mechanistic to extremely organic. 2. Development typically follows an evolutionary process: Multinational Structure & Design a. Task force new product results in a temporary task force of members from each functional department to expedite the process. b. Teams if new product development continues, permanent teams comprising members from the functional departments become permanent. The teams meet regularly to resolve interdepartmental issues and achieve coordination. c. Product managers if new product development becomes a way of life, product managers chair the teams and report to top management; however they are temporary and have no formal authority over the team members. d. Product management departments created with subproduct managers for each product line.
19 It is described as consisting of a group of geographically dispersed organizations with different national subsidiaries. It often exists in very divergent environments. Approaches to setting up subsidiaries: 1. Replication using the same organization structure and operating policies and procedures as in the domestic organization. May result in reliance upon organizational designs and management practices unsuitable for the local environment. 2. Designing in response to unique factors, such as: a. National boundaries. b. The varying importance of national boundaries on different elements of organizational structure. c. Desire of a subsidiary to act as a conduit to introduce change into the host country's environment. d. Desire to use subsidiary to introduce features of the host country's environment throughout the organization. Four Stages of International evolution are: Domestic International Multinational Global Strategic orientation Domestically oriented Export oriented multi domestic Multinational Global Stage of development Initial foreign involvement Competitive positioning Explosion Global Structure Domestic structure plus export department Domestic structure plus international division Worldwide geographic, product Matrix Transnational
20 Market potential Moderate, mostly domestic Large multidomestic Very large multinational Whole world Ref: Matching organizational structure to International advantage Forces for global integration are Forces for national responsiveness are Strategy Structure Low Low Export International division High Low Globalization Global product structure Low High Multidomestic Global geographic structure High High Globalization and Multidomestic Global matrix structure. Ref: Emergent Structural Forms Inter-organizational network Global international network structure Transnational Corporate structure Transnational corporations involves linking foreign operations to each other and to headquarters in a flexible way. It is a network of company units and a system of horizontal communication. The characteristics of TNCs are dispersed subunits, specialized operations and interdependent relationships. It requires the dispersal of responsibility and decision making to local subsidiaries. The effectiveness of TNCs is dependant on the ability and willingness to share current and new learning and technology across the network. Multinational Structures Output Control Bureaucratic Control Decision-making Control Organizational Control International division structure Most likely profit control Must follow company policies Some centralization Treated like other divisions
21 possible Global geographic structure Profit centre most common Some policies and procedures necessary Local units have autonomy Local subsidiary culture often most important Global product structure Unit output for supply; sales volume for sales Tight process controls for product quality and consistency Centralized at product division headquarters Possible for some companies but not always necessary Transnational network structure Used for supplier units and some independent profit centres Less important Few decisions centralized at head quarters; more decisions centralized at key network nodes Organizational culture transcends national culture; supports sharing and learning, the most important control mechanism New Design Options Team Structure The use of teams as the central device to coordinate work activities Characteristics Breaks down departmental barriers Decentralizes decision making to the team level Requires employees to be generalists as well as specialists Creates a flexible bureaucracy However for teams amount of horizontal coordination required is high and cost of coordination in time and human resources is also high.
22 Network organization A small core organization that out sources its major business function in order to concentrate on what it does best Modular organization A manufacturing organization that uses outside suppliers to provide product component for its final assembly operations. Virtual Organization A small, core organization that outsources its major business functions Highly centralized with little or no departmentalization Concepts Advantage: Provides maximum flexibility while concentrating on what the organization does best Disadvantage: Reduced control over key parts of the business A. Many complex factors and variables must be considered in designing an optimal organizational structure. B. The overall structure results from the key decisions in a specific design. C. Overall goal to develop a structure that channels individual and group behavior into patterns that contribute to organizational performance. D. Organizations of the future likely to be flatter, less hierarchical, and more decentralized and design are driven by technology and its capacity. E. Boundary-less organizations are another design approach it is an attempt to eliminate vertical and horizontal structure, tightly defined work roles, and top-down control. The minimized layers results in a flatter hierarchy. Boundary-less Organization An organization that seeks to eliminate the chain of command, have limitless spans of control, and replace departments with empowered teams T-form Concepts
23 Eliminate vertical (hierarchical) and horizontal (departmental) internal boundaries Breakdown external barriers to customers and suppliers The Learning Organization An organization that has developed the capacity to continuously learn, adapt, and change through the practice of knowledge management by employees. Characteristics of a learning organization: An open team-based organization design that empowers employees Extensive and open information sharing which is timely and accurate. Leadership that provides a shared vision of the organization s future, support and encouragement A strong culture of shared values, trust, openness, and a sense of community. (Important reading about learning organization: df) Sociotechnical systems model It is designed for the joint optimization of the social system (individual and team behaviour,organization and team culture, management practices,leadership style, degree of communication openness and individual needs and desires) and the technical system (type of production technology-small batch,mass production; level of interdependence- pooled,sequential, reciprocal;physical work setting;complexity of production process- variety and analyzability;nature of raw materials, time pressure) through work roles, task and work flow, setting of goals and values and matching the skills and abilities with the job. Indian organizations Empowerment Styles in Indian Perspective(Reference: Organizational Behaviour, Stephen P.Robbins, Timothi A.Judge and Seema Sanghi, 12 th ed, Pearson education, pp607) 1. Information sharing 2. Upward problem solving 3. Task autonomy 4. Attitudinal shaping 5. Self Management
24 Restructuring Indian organizations: Challenges and responses(reference: Organizational Behaviour, Stephen P.Robbins, Timothi A.Judge and Seema Sanghi, 12 th ed, Pearson education, pp615) Challenges The pressure of competition as a result of liberalization is squeezing margins and profits The globalization of business has compelled more and more companies to establish export departments New developments in IT have made it necessary to adopt new organizational arrangements. The shift in fiscal policy and reduction of government expenditure have forced companies to identify new customers and markets. Cost cutting and increased productivity is demanding downsizing of workforce at both worker and managerial level. Responses Regrouping business activities Strategic Business Units Impact of culture on Indian Business Organizations (Reference: Organizational Behaviour, Stephen P.Robbins, Timothi A.Judge and Seema Sanghi, 12 th ed, Pearson education, pp617) 1. Centralized decision making 2. Slow decision making 3. Short term focus 4. Individual Orientation 5. Avoidance of conflict 6. Low risk tolerance 7. Focus on results 8. Individual accountability
25 9. Little or no horizontal cooperation 10. Highly politicized environment 11. Bureaucratic structure 12. Resistance to change 13. Guarded communication 14. Slow communication 15. Adoption of indirect communication style Questions 1. Define Organizational Structure and Design. Describe the Key Elements for Organizational Structure 2. What are the determinants of Organization Structure? What are the Outcomes of Organization Structure? 3. Explain the effects of Organizational Designs on Employee Behavior. Justify with research findings. 4. Describe with suitable examples the challenges faced in designing an Organizational Structure 5. Describe with suitable examples the various Organizational Designs. Which according to you is the best design and why? 6. What are the empowerment styles in Indian perspective. What are the challenges and responses Restructuring Indian organizations. State the impact of culture on Indian Business Organizations 7. Discuss in details the organizational structure of MNCs. 8.Write short notes on (a) Learning organization (b) socio-technical system
Organization architecture and profitability. Organizational architecture. Organizational architecture. Organizational architecture
 13-1 Organization architecture and profitability Organizational architecture 13-2 Totality of a firm s organization, including structure, control systems, incentives, processes, culture and people. Superior
13-1 Organization architecture and profitability Organizational architecture 13-2 Totality of a firm s organization, including structure, control systems, incentives, processes, culture and people. Superior
Fundamentals of Organization Structure. Organizations and ICT 2014/2015 Fabiano Dalpiaz
 Fundamentals of Organization Structure Organizations and ICT 2014/2015 Fabiano Dalpiaz 1 Acknowledgements Most of these slides are taken from Daft s book Organization Theory and Design, chapter 3 Not part
Fundamentals of Organization Structure Organizations and ICT 2014/2015 Fabiano Dalpiaz 1 Acknowledgements Most of these slides are taken from Daft s book Organization Theory and Design, chapter 3 Not part
Chapter Thirteen. Informal and Formal Groups
 Chapter Thirteen Informal and Formal Groups Objectives To develop an understanding of: Nature of groups Types of groups Reasons of group formation Stages of Group Development Characteristics of groups
Chapter Thirteen Informal and Formal Groups Objectives To develop an understanding of: Nature of groups Types of groups Reasons of group formation Stages of Group Development Characteristics of groups
EMPLOYEE EMPOWERMENT
 EMPLOYEE EMPOWERMENT Empowerment Defined Webster dictionary defines empowerment as : giving the means, ability or authority To empower someone is to give the individual authority To make decisions To contribute
EMPLOYEE EMPOWERMENT Empowerment Defined Webster dictionary defines empowerment as : giving the means, ability or authority To empower someone is to give the individual authority To make decisions To contribute
CHAPTER 11 INTERNATIONAL STRATEGY AND ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 11 INTERNATIONAL STRATEGY AND ORGANIZATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain the stages of identification and analysis that precede strategy selection. 2. Identify the two international strategies
CHAPTER 11 INTERNATIONAL STRATEGY AND ORGANIZATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain the stages of identification and analysis that precede strategy selection. 2. Identify the two international strategies
Organizational Structure: Mintzberg s Framework
 VOLUME 14, NUMBER 1, 2012 Organizational Structure: Mintzberg s Framework Fred C. Lunenburg Sam Houston State University ABSTRACT Henry Mintzberg suggests that organizations can be differentiated along
VOLUME 14, NUMBER 1, 2012 Organizational Structure: Mintzberg s Framework Fred C. Lunenburg Sam Houston State University ABSTRACT Henry Mintzberg suggests that organizations can be differentiated along
Competitive Organisational Structures
 Competitive Organisational Structures Organisational structure basics Introduction The way in which a business is organised has a direct effect on its competitiveness. For a business to be able to achieve
Competitive Organisational Structures Organisational structure basics Introduction The way in which a business is organised has a direct effect on its competitiveness. For a business to be able to achieve
pm4dev, 2007 management for development series Project Management Organizational Structures PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS
 pm4dev, 2007 management for development series Project Management Organizational Structures PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS A methodology
pm4dev, 2007 management for development series Project Management Organizational Structures PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS A methodology
Chapter 11: ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURES: CONCEPTS AND F0RMATS
 Montana, P. and Charnov, B. Management: A Streamlined Course for Students and Business People. (Hauppauge, New York: Barron s Business Review Series, 1993), pp. 155-169. Chapter 11: ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURES:
Montana, P. and Charnov, B. Management: A Streamlined Course for Students and Business People. (Hauppauge, New York: Barron s Business Review Series, 1993), pp. 155-169. Chapter 11: ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURES:
Organizational Design Basics
 15.320 Strategic Organizational Design Organizational Design Basics Elements of organizational patterns What Who Why How Elements of organizational patterns (cont.) Galbraith 15.311 What is being done?
15.320 Strategic Organizational Design Organizational Design Basics Elements of organizational patterns What Who Why How Elements of organizational patterns (cont.) Galbraith 15.311 What is being done?
Organization structure changes at Body Shop
 Student Self-administered case study Organization structure changes at Body Shop Case duration (Min): 45-60 Organizational Behaviour (OB) Organization structure and design Worldwide Case summary: There
Student Self-administered case study Organization structure changes at Body Shop Case duration (Min): 45-60 Organizational Behaviour (OB) Organization structure and design Worldwide Case summary: There
Chapter 8: The Internal Environment
 Chapter 8: The Internal Environment Key Revision Points The Internal Functions of Commercial Organisations In competitive business environments, customers are at the centre of all of an organisation's
Chapter 8: The Internal Environment Key Revision Points The Internal Functions of Commercial Organisations In competitive business environments, customers are at the centre of all of an organisation's
Organisational Structure - Basics
 Name: Class: Date Taken: Total Possible Marks: Organisational Structure - Basics Complete the following questions in the time allowed by your teacher. Define the term "organisational structure". List three
Name: Class: Date Taken: Total Possible Marks: Organisational Structure - Basics Complete the following questions in the time allowed by your teacher. Define the term "organisational structure". List three
ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR
 Overview ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR Lesson 2 In last lecture we tried to understand the term of organizational behavior its need and its impact on the organization. The focus in this discussion is to have
Overview ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR Lesson 2 In last lecture we tried to understand the term of organizational behavior its need and its impact on the organization. The focus in this discussion is to have
Designing a Proper Organizational Chart for a Project-oriented Company through Studying its Conceptual and Structural Dimensions
 2011 3rd International Conference on Information and Financial Engineering IPEDR vol.12 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Designing a Proper Organizational Chart for a Project-oriented Company through
2011 3rd International Conference on Information and Financial Engineering IPEDR vol.12 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Designing a Proper Organizational Chart for a Project-oriented Company through
Strategy & the firm. Value creation. Value creation
 1 Strategy & the firm Strategy: actions that managers must take to attain the goals of the firm Main goal usually to maximize long- term profit (П)( Profitability defined by return on sales or return on
1 Strategy & the firm Strategy: actions that managers must take to attain the goals of the firm Main goal usually to maximize long- term profit (П)( Profitability defined by return on sales or return on
Seminar. The Organization of International Business Chapter 15. 11 Kasım 14 Salı 15-
 Seminar The Organization of International Business Chapter 15 Learning Objectives p Profile the evolving process of organizing a company for international business p Describe the features of classical
Seminar The Organization of International Business Chapter 15 Learning Objectives p Profile the evolving process of organizing a company for international business p Describe the features of classical
structures stack up Tom McMullen
 Making sure your organization structures stack up October 21, 2009 Tom McMullen Building effective organizations Trends in organization design Optimizing Focusing resources and reducing headcounts Removing
Making sure your organization structures stack up October 21, 2009 Tom McMullen Building effective organizations Trends in organization design Optimizing Focusing resources and reducing headcounts Removing
Rialto Report: Successfully Operating in Matrix Organisations
 Rialto Report: Successfully Operating in Matrix Organisations 1 Contents Introduction & Historical Context of Matrix Management... 3 Matrix Management... 4 Key Roles... 4 Conditions and Rationale for a
Rialto Report: Successfully Operating in Matrix Organisations 1 Contents Introduction & Historical Context of Matrix Management... 3 Matrix Management... 4 Key Roles... 4 Conditions and Rationale for a
Legal Aid Board Training. 2010 Legal Aid Education P, Session 1, Page 1 Session 1. Introduction
 to Legal Aid 2010 Legal Aid Education P, Session 1, Page 1 Session 1 Governance as Leadership What is governance? Governance is the exercise of authority, direction and control of an organization in order
to Legal Aid 2010 Legal Aid Education P, Session 1, Page 1 Session 1 Governance as Leadership What is governance? Governance is the exercise of authority, direction and control of an organization in order
Strategic Management: Concepts and Cases 9e
 Strategic Management: Concepts and Cases 9e Part II: Strategic Actions: Strategy Formulation Chapter 8: International Strategy 2011 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or
Strategic Management: Concepts and Cases 9e Part II: Strategic Actions: Strategy Formulation Chapter 8: International Strategy 2011 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or
Project Management connected to Creativity and Entrepreneurship
 Project Management connected to Creativity and Entrepreneurship [email protected] Department of Business Administration School of Management and Economics University of Lund, Sweden Interaction
Project Management connected to Creativity and Entrepreneurship [email protected] Department of Business Administration School of Management and Economics University of Lund, Sweden Interaction
Chapter 3: Team Building
 Chapter 3: When students finish studying this part, they should be able to: 1. Define the stages of team development. 2. Explain the selection process of team members. 3. Define the interaction process
Chapter 3: When students finish studying this part, they should be able to: 1. Define the stages of team development. 2. Explain the selection process of team members. 3. Define the interaction process
1.2 ORGNISATION BEHAVIOUR - CONCEPTS. 1.2.1 Organization. 1.2.2 Management. 1.3 Key Elements of Organisational Behavior
 UNIT I INTRODUCTION TO ORGANISATIONAL BEHAVIOUR LESSON 1 IMPORTANCE OF ORGANISATIONAL BEHAVIOUR Contents 1.0 Aims and Objectives 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Organization behaviour concepts 1.2.1 Organisation
UNIT I INTRODUCTION TO ORGANISATIONAL BEHAVIOUR LESSON 1 IMPORTANCE OF ORGANISATIONAL BEHAVIOUR Contents 1.0 Aims and Objectives 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Organization behaviour concepts 1.2.1 Organisation
International Business Environment THE MULTINATIONAL CORPORATIONS ARE ALSO KNOWN AS:
 Chapter No. 4 Page No. 210 MULTINATIONAL CORPORATIONS / ORGANIZATIONAL MODELS THE MULTINATIONAL CORPORATIONS ARE ALSO KNOWN AS: INTERNATIONAL CORPORATIONS. TRANSNATIONAL CORPORATIONS. GLOBAL CORPORATIONS.
Chapter No. 4 Page No. 210 MULTINATIONAL CORPORATIONS / ORGANIZATIONAL MODELS THE MULTINATIONAL CORPORATIONS ARE ALSO KNOWN AS: INTERNATIONAL CORPORATIONS. TRANSNATIONAL CORPORATIONS. GLOBAL CORPORATIONS.
Complexity Leadership Theory:
 Complexity Leadership Theory: Shifting leadership from the industrial age to the knowledge era Mary Uhl-Bien, Russ Marion, Bill McKelvey the clarion group REAL. CLEAR. INSIGHT. Abstract: The most widely
Complexity Leadership Theory: Shifting leadership from the industrial age to the knowledge era Mary Uhl-Bien, Russ Marion, Bill McKelvey the clarion group REAL. CLEAR. INSIGHT. Abstract: The most widely
TYPES OF ORGANIZATIONAL ADAPTATION. Stăncuţ Anca, Drd. University of Craiova Borcoşi Corina Ana, Drd. University of Craiova
 Constantin Brâncuşi University of Târgu Jiu ENGINEERING FACULTY SCIENTIFIC CONFERENCE 13 th edition with international participation November 07-08, 2008 Târgu Jiu TYPES OF ORGANIZATIONAL ADAPTATION Stăncuţ
Constantin Brâncuşi University of Târgu Jiu ENGINEERING FACULTY SCIENTIFIC CONFERENCE 13 th edition with international participation November 07-08, 2008 Târgu Jiu TYPES OF ORGANIZATIONAL ADAPTATION Stăncuţ
Roadmap for Service Excellence
 15.778 Summer 2004 Management of Supply Networks for Products and Services: Concepts, Design, and Delivery Roadmap for Service Excellence G. Bitran S. Gurumurthi 15.778 Management of Supply Networks for
15.778 Summer 2004 Management of Supply Networks for Products and Services: Concepts, Design, and Delivery Roadmap for Service Excellence G. Bitran S. Gurumurthi 15.778 Management of Supply Networks for
Faculty of Business Economics and Entrepreneurship International Review (2015 No.3-4) 33
 Faculty of Business Economics and Entrepreneurship International Review (2015 No.3-4) 33 SCIENTIFIC REVIEW Advantages and disadvantages of line and staff style of organizations Omolaja Muhammad 7 Abstract
Faculty of Business Economics and Entrepreneurship International Review (2015 No.3-4) 33 SCIENTIFIC REVIEW Advantages and disadvantages of line and staff style of organizations Omolaja Muhammad 7 Abstract
Strategic Choices and Key Success Factors for Law Firms June, 2010. Alan Hodgart
 Strategic Choices and Key Success Factors for Law Firms June, 2010 Alan Hodgart The Association of Danish Law Firms 1 Huron Consulting Group Inc. All rights reserved. Huron is a management consulting firm
Strategic Choices and Key Success Factors for Law Firms June, 2010 Alan Hodgart The Association of Danish Law Firms 1 Huron Consulting Group Inc. All rights reserved. Huron is a management consulting firm
Organizational Theory, Design, and Change
 Organizational Theory, Design, and Change SEVENTH EDITION Gareth R. Jones Texas A&M University PEARSON Boston Columbus Indianapolis New York San Francisco Upper Saddle River Amsterdam Cape Town Dubai London
Organizational Theory, Design, and Change SEVENTH EDITION Gareth R. Jones Texas A&M University PEARSON Boston Columbus Indianapolis New York San Francisco Upper Saddle River Amsterdam Cape Town Dubai London
LIST OF SUBJECTS MBA (EXECUTIVE) SEM.I 2015 1. Fundamental of Management 2. Organizational Behaviour 3. Accounting for Managers 4.
 LIST OF SUBJECTS MBA (EXECUTIVE) SEM.I 2015 1. Fundamental of Management 2. Organizational Behaviour 3. Accounting for Managers 4. Statistics for Management 5. Business Communication 6. Managerial Economics
LIST OF SUBJECTS MBA (EXECUTIVE) SEM.I 2015 1. Fundamental of Management 2. Organizational Behaviour 3. Accounting for Managers 4. Statistics for Management 5. Business Communication 6. Managerial Economics
E-Business: Use of Information Systems
 E-Business: Use of Information Systems Reading: Laudon & Laudon chapter 2 Additional Reading: Brien & Marakas chapter 1 COMP 5131 1 Outline Components of Business Business Process Managing Business and
E-Business: Use of Information Systems Reading: Laudon & Laudon chapter 2 Additional Reading: Brien & Marakas chapter 1 COMP 5131 1 Outline Components of Business Business Process Managing Business and
the Defence Leadership framework
 the Defence Leadership framework Growing Leaders at all Levels Professionalism Loyalty Integrity Courage Innovation Teamwork Foreword One of the founding elements of Building Force 2030, as outlined in
the Defence Leadership framework Growing Leaders at all Levels Professionalism Loyalty Integrity Courage Innovation Teamwork Foreword One of the founding elements of Building Force 2030, as outlined in
How To Understand The Relationship Between Organization And Performance
 Organizational Behavior and Development Michael Beer Harvard University Organizational studies is a fragmented field. Its foundations are the disciplines of Psychology, Sociology, and Economics and applied
Organizational Behavior and Development Michael Beer Harvard University Organizational studies is a fragmented field. Its foundations are the disciplines of Psychology, Sociology, and Economics and applied
Total Quality Management
 Total Quality Management 1 Chapter 12: Total Employee involvement 2 Human factor is very important in implementation of any process or principle. It is all the more important in Quality Management. Organization
Total Quality Management 1 Chapter 12: Total Employee involvement 2 Human factor is very important in implementation of any process or principle. It is all the more important in Quality Management. Organization
A Sample Organization Chart
 Chapter Three Fundamentals of Organization A Sample Organization Chart CEO Fianance Manufacturing Director Human Resources Chief Accountant Budget Analyst Plant Superintendent Maintenance Superintendent
Chapter Three Fundamentals of Organization A Sample Organization Chart CEO Fianance Manufacturing Director Human Resources Chief Accountant Budget Analyst Plant Superintendent Maintenance Superintendent
The Job of the Project Manager. Robert Youker World Bank (retired) 5825 Rockmere Drive Bethesda, Md. USA 20816 [email protected].
 The Job of the Project Manager Robert Youker World Bank (retired) 5825 Rockmere Drive Bethesda, Md. USA 20816 [email protected] For any organization and for any project manager it is vitally important
The Job of the Project Manager Robert Youker World Bank (retired) 5825 Rockmere Drive Bethesda, Md. USA 20816 [email protected] For any organization and for any project manager it is vitally important
Managerial Decision Making when values take over rational economical thought
 Student Self-administered case study Managerial Decision Making when values take over rational economical thought Case duration (Min): 45-60 Principles of Management (PoM) Organizational Behaviour (OB)
Student Self-administered case study Managerial Decision Making when values take over rational economical thought Case duration (Min): 45-60 Principles of Management (PoM) Organizational Behaviour (OB)
Chapter-3 Organization Structure &
 MGMT 4135 Project Management Chapter-3 Organization Structure & Culture 1 Three different project management structures to choose from: 1. Functional organization 2. Projectized or dedicated teams 3. Matrix
MGMT 4135 Project Management Chapter-3 Organization Structure & Culture 1 Three different project management structures to choose from: 1. Functional organization 2. Projectized or dedicated teams 3. Matrix
DoD CIVILIAN LEADER DEVELOPMENT FRAMEWORK COMPETENCY DEFINITIONS. Leading Change
 DoD CIVILIAN LEADER DEVELOPMENT FRAMEWORK COMPETENCY DEFINITIONS Leading Change Definition: This core competency involves the ability to bring about strategic change, both within and outside the organization,
DoD CIVILIAN LEADER DEVELOPMENT FRAMEWORK COMPETENCY DEFINITIONS Leading Change Definition: This core competency involves the ability to bring about strategic change, both within and outside the organization,
Alexander Nikov. 3. Information Systems and Organisational Issues. Learning Objectives. Verizon or AT&T: Which Company Has the Best Digital Strategy?
 INFO 1500 Introduction to IT Fundamentals Learning Objectives 3. Information Systems and Organisational Issues 1. Identify and describe important features of organizations that managers need to know about
INFO 1500 Introduction to IT Fundamentals Learning Objectives 3. Information Systems and Organisational Issues 1. Identify and describe important features of organizations that managers need to know about
Organizational Design Toolkit
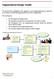 Organizational Design Toolkit We provide below highlights of the approach to developing/confirming the preferred service delivery model and organizational structure for an organization. The key steps are:
Organizational Design Toolkit We provide below highlights of the approach to developing/confirming the preferred service delivery model and organizational structure for an organization. The key steps are:
Motivation Questionnaire
 Motivation Questionnaire > Employee Motivation Report Name: Sample Report Date: 12 August 2009 Employee Motivation Report Introduction This report describes the factors that are likely to have an impact
Motivation Questionnaire > Employee Motivation Report Name: Sample Report Date: 12 August 2009 Employee Motivation Report Introduction This report describes the factors that are likely to have an impact
Organizational Renewal: The Challenge of Change. Chapter 2
 Organizational Renewal: The Challenge of Change Chapter 2 Objectives Recognize the factors contributing to the accelerating rate of change Identify the ways an organization uses renewing processes to adapt
Organizational Renewal: The Challenge of Change Chapter 2 Objectives Recognize the factors contributing to the accelerating rate of change Identify the ways an organization uses renewing processes to adapt
Supervision. Samuel C. Certo. Steinmetz Professor of Management Crummer Graduate School of Business Rollins College. I McGraw-Hill I Irwin
 Supervision Concepts and Skill-Building Seventh Edition Samuel C. Certo Steinmetz Professor of Management Crummer Graduate School of Business Rollins College I McGraw-Hill I Irwin Contents Preface iv About
Supervision Concepts and Skill-Building Seventh Edition Samuel C. Certo Steinmetz Professor of Management Crummer Graduate School of Business Rollins College I McGraw-Hill I Irwin Contents Preface iv About
SEMS/NIMS MANAGEMENT SYSTEM REVISED SEPTEMBER 2007
 SEMS/NIMS MANAGEMENT SYSTEM REVISED SEPTEMBER 2007 SEMS/NIMS - SYSTEM (ICS) is the model tool for command, control, and coordination of a response and provides a means to coordinate the efforts of individual
SEMS/NIMS MANAGEMENT SYSTEM REVISED SEPTEMBER 2007 SEMS/NIMS - SYSTEM (ICS) is the model tool for command, control, and coordination of a response and provides a means to coordinate the efforts of individual
INFO1400. Define an organization and compare the technical definition of organizations with the behavioral definition.
 Chapter 3 INFO1400 Review Questions 1. Which features of organizations do managers need to know about to build and use information systems successfully? What is the impact of information systems on organizations?
Chapter 3 INFO1400 Review Questions 1. Which features of organizations do managers need to know about to build and use information systems successfully? What is the impact of information systems on organizations?
Challenges of Intercultural Management: Change implementation in the context of national culture
 12-ICIT 9-11/4/07 in RoC Going for Gold ~ Best Practices in Ed. & Public Paper #: 07-08 Page- 1 /7 Challenges of Intercultural Management: Change implementation in the context of national culture Prof.
12-ICIT 9-11/4/07 in RoC Going for Gold ~ Best Practices in Ed. & Public Paper #: 07-08 Page- 1 /7 Challenges of Intercultural Management: Change implementation in the context of national culture Prof.
LEADERSHIP DEVELOPMENT FRAMEWORK
 LEADERSHIP DEVELOPMENT FRAMEWORK February 13, 2008 LEADERSHJP PERSPECTIVE I consider succession planning to be the most important duty I have as the Director of the NOAA Corps. As I look toward the future,
LEADERSHIP DEVELOPMENT FRAMEWORK February 13, 2008 LEADERSHJP PERSPECTIVE I consider succession planning to be the most important duty I have as the Director of the NOAA Corps. As I look toward the future,
Designing Productive and Satisfying Work. Lesson 4
 Designing Productive and Satisfying Work Lesson 4 Learning objectives After this lecture you should be able to: Describe how the design of work tasks and roles can align with overall HR strategy. Explain
Designing Productive and Satisfying Work Lesson 4 Learning objectives After this lecture you should be able to: Describe how the design of work tasks and roles can align with overall HR strategy. Explain
Sarajevo,2008.god.p.32 2 Ibid,p.34. 1 Zećir H.,Senad S.,Dženan K., Organisation, Faculty of Economics in
 INTERNAL FACTORS OF ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE Mr.Elida Cirikovic [email protected] Abstract In order to realize the mission of business organization, which is the reason of its existence, it requires
INTERNAL FACTORS OF ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE Mr.Elida Cirikovic [email protected] Abstract In order to realize the mission of business organization, which is the reason of its existence, it requires
Leading Self. Leading Others. Leading Performance and Change. Leading the Coast Guard
 Coast Guard Leadership Competencies Leadership competencies are the knowledge, skills, and expertise the Coast Guard expects of its leaders. The 28 leadership competencies are keys to career success. Developing
Coast Guard Leadership Competencies Leadership competencies are the knowledge, skills, and expertise the Coast Guard expects of its leaders. The 28 leadership competencies are keys to career success. Developing
ADAPTATION OF EMPLOYEES IN THE ORGANIZATION AND ITS IMPORTANCE IN TERMS OF HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
 114 Management and Economics ADAPTATION OF EMPLOYEES IN THE ORGANIZATION AND ITS IMPORTANCE IN TERMS OF HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT Jaroslav NEKORANEC [email protected] Lenka NAGYOVÁ [email protected]
114 Management and Economics ADAPTATION OF EMPLOYEES IN THE ORGANIZATION AND ITS IMPORTANCE IN TERMS OF HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT Jaroslav NEKORANEC [email protected] Lenka NAGYOVÁ [email protected]
Which is more effective and beneficial to the success of a business, a Democratic or
 Which is more effective and beneficial to the success of a business, a Democratic or Hierarchical organisation? Introduction What is the right and the best way to manage people to maximize their productivity
Which is more effective and beneficial to the success of a business, a Democratic or Hierarchical organisation? Introduction What is the right and the best way to manage people to maximize their productivity
Internal Marketing Orientation in Cultural Change Management for Organisation Development
 MEB 2008 6 th International Conference on Management, Enterprise and Benchmarking May 30-31, 2008 Budapest, Hungary Internal Marketing Orientation in Cultural Change Management for Organisation Development
MEB 2008 6 th International Conference on Management, Enterprise and Benchmarking May 30-31, 2008 Budapest, Hungary Internal Marketing Orientation in Cultural Change Management for Organisation Development
PERFORMANCE PLANNING WORKSHEET FOR PROFESSIONAL EMPLOYEES (PS-35LC)
 PERFORMANCE PLANNING WORKSHEET FOR PROFESSIONAL EMPLOYEES (PS-35LC) NAME: JOB TITLE: This worksheet should be given to the employee prior to the scheduled performance review. The employee should complete
PERFORMANCE PLANNING WORKSHEET FOR PROFESSIONAL EMPLOYEES (PS-35LC) NAME: JOB TITLE: This worksheet should be given to the employee prior to the scheduled performance review. The employee should complete
ORGANIZATIONAL ASSESSMENT TOOL FOR NGOs WORKING ON DRUG PREVENTION, DEMAND REDUCTION AND DRUG CONTROL
 Anti Drugs Association Belgrade Operations Branch www.stopdrogama.org (Drustvo za borbu protiv narkomanije Beograd) UNODC Global Youth Network member UNODC Vienna NGO Committee on Narcotic Drugs member
Anti Drugs Association Belgrade Operations Branch www.stopdrogama.org (Drustvo za borbu protiv narkomanije Beograd) UNODC Global Youth Network member UNODC Vienna NGO Committee on Narcotic Drugs member
Emerson Job Description Matrix
 S2 S3 S4 Job Family Support Support Support Job Level Grade Level Entry Grade 12 Intermediate Grade 13 Senior Grade 14 Aon Hewitt Job Characteristic Definitions and Descriptions Responsible for the delivery
S2 S3 S4 Job Family Support Support Support Job Level Grade Level Entry Grade 12 Intermediate Grade 13 Senior Grade 14 Aon Hewitt Job Characteristic Definitions and Descriptions Responsible for the delivery
ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR
 Fact Sheet ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR TEST INFORMATION This test was developed to enable schools to award credit to students for knowledge equivalent to that, which is learned, by students taking the course.
Fact Sheet ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR TEST INFORMATION This test was developed to enable schools to award credit to students for knowledge equivalent to that, which is learned, by students taking the course.
Business Process Change and the Role of the Management Accountant
 Butler University Digital Commons @ Butler University Scholarship and Professional Work - Business College of Business 1998 Business Process Change and the Role of the Management Accountant Sakthi Mahenthiran
Butler University Digital Commons @ Butler University Scholarship and Professional Work - Business College of Business 1998 Business Process Change and the Role of the Management Accountant Sakthi Mahenthiran
Chapter 5. The Structure and Design of Student Affairs Organizations
 Chapter 5. The Structure and Design of Student Affairs Organizations The telephone rang, and Dr. Pat Harris, the Vice President for Student Affairs answered. The University President began the conversation
Chapter 5. The Structure and Design of Student Affairs Organizations The telephone rang, and Dr. Pat Harris, the Vice President for Student Affairs answered. The University President began the conversation
SOLUTION: BUSINESS MANAGEMENT, MAY 2014. (b) Factors to consider when deciding on the appropriate structure for an organization include the following:
 SOLUTION 1 (a) The structure of an organization defines the patterns of communication, the system of control and the command structure. (b) Factors to consider when deciding on the appropriate structure
SOLUTION 1 (a) The structure of an organization defines the patterns of communication, the system of control and the command structure. (b) Factors to consider when deciding on the appropriate structure
MODERN INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY AND ORGANIZATIONAL THINKING OPEN A WINDOW OF OPPORTUNITY FOR ENTREPRENEURIAL SMES
 MODERN INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY AND ORGANIZATIONAL THINKING OPEN A WINDOW OF OPPORTUNITY FOR ENTREPRENEURIAL SMES by Tor Jarl Trondsen, Ph.D. Associate Professor Norwegian School of Management PO Box 580,
MODERN INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY AND ORGANIZATIONAL THINKING OPEN A WINDOW OF OPPORTUNITY FOR ENTREPRENEURIAL SMES by Tor Jarl Trondsen, Ph.D. Associate Professor Norwegian School of Management PO Box 580,
Executive Assistant Competency Profile
 Executive Assistant Competency Profile Description of Work: Positions in this banded class serve as staff/management assistants to highest-level administrators in a university or agency whose responsibilities
Executive Assistant Competency Profile Description of Work: Positions in this banded class serve as staff/management assistants to highest-level administrators in a university or agency whose responsibilities
How To Understand Organizational Structure
 VOLUME 27, NUMBER 4, 2010 The Management Function of Principals Fred C. Lunenburg Sam Houston State University ABSTRACT Some scholars believe that management is a prerequisite to leadership. You can t
VOLUME 27, NUMBER 4, 2010 The Management Function of Principals Fred C. Lunenburg Sam Houston State University ABSTRACT Some scholars believe that management is a prerequisite to leadership. You can t
Advanced Level: Module summaries
 Advanced Level: Module summaries Contents HRM in context 3 Leading managing and developing people 4 Developing skills for business leadership 5 Investigating a business issue from an HR perspective 6 Leadership
Advanced Level: Module summaries Contents HRM in context 3 Leading managing and developing people 4 Developing skills for business leadership 5 Investigating a business issue from an HR perspective 6 Leadership
Management levels. Middle-level managers
 MANAGEMENT LEVELS 2 Management levels Managers are organizational members who are responsible for the work performance of other organizational members. Managers have formal authority to use organizational
MANAGEMENT LEVELS 2 Management levels Managers are organizational members who are responsible for the work performance of other organizational members. Managers have formal authority to use organizational
STRENGTHS AND WEAKNESSES OF CURRENT SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT AND INITIATIVES FOR THE FUTURE. Diana-Maria DIACONU (NIDELEA) 1 Cristina ALPOPI 2
 STRENGTHS AND WEAKNESSES OF CURRENT SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT AND INITIATIVES FOR THE FUTURE Diana-Maria DIACONU (NIDELEA) 1 Cristina ALPOPI 2 ABSTRACT Supply Chain Management is the potential way of securing
STRENGTHS AND WEAKNESSES OF CURRENT SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT AND INITIATIVES FOR THE FUTURE Diana-Maria DIACONU (NIDELEA) 1 Cristina ALPOPI 2 ABSTRACT Supply Chain Management is the potential way of securing
A review of Structure in Fives; Designing Effective Organizations
 A review of Structure in Fives; Designing Effective Organizations Thomas Schmidt [email protected] July 7, 2006 Abstract This review of Henry Mintzbergs book is a part of my thesis literature study. Here
A review of Structure in Fives; Designing Effective Organizations Thomas Schmidt [email protected] July 7, 2006 Abstract This review of Henry Mintzbergs book is a part of my thesis literature study. Here
CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES OF ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR
 CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES OF ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR 1. The creation of Q global village 2. Workforce diversity 3. Improving quality and productivity 4. Improving People skills 5. Management control
CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES OF ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR 1. The creation of Q global village 2. Workforce diversity 3. Improving quality and productivity 4. Improving People skills 5. Management control
Strategic human resource management toolkit
 19 205 Strategic human resource management toolkit The purpose of the toolkit is to provide the basis for conducting a strategic review of human resource management practices in order to develop and implement
19 205 Strategic human resource management toolkit The purpose of the toolkit is to provide the basis for conducting a strategic review of human resource management practices in order to develop and implement
An organization consists of individuals with different tasks attempting
 2 Chapter Organizational Behavior An organization consists of individuals with different tasks attempting to accomplish a common purpose. (For a business, this purpose is the creation and delivery of goods
2 Chapter Organizational Behavior An organization consists of individuals with different tasks attempting to accomplish a common purpose. (For a business, this purpose is the creation and delivery of goods
HEALTH CARE MANAGEMENT
 1 HEALTH CARE MANAGEMENT For English speaking students Kateřina Ivanova WHAT IS MANAGEMENT 1? Basic of Management (definitions of term; basic function of managements; managerial school; evolution of management
1 HEALTH CARE MANAGEMENT For English speaking students Kateřina Ivanova WHAT IS MANAGEMENT 1? Basic of Management (definitions of term; basic function of managements; managerial school; evolution of management
THE OPEN UNIVERSITY OF TANZANIA FACULTY OF BUSINESS MANAGEMENT OME 212: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT AND STRATEGIES COURSE OUTLINE
 THE OPEN UNIVERSITY OF TANZANIA FACULTY OF BUSINESS MANAGEMENT OME 212: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT AND STRATEGIES COURSE OUTLINE 2010 1 INTRODUCTION This course focuses on the external and internal environment
THE OPEN UNIVERSITY OF TANZANIA FACULTY OF BUSINESS MANAGEMENT OME 212: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT AND STRATEGIES COURSE OUTLINE 2010 1 INTRODUCTION This course focuses on the external and internal environment
Creating the climate to get the most from your team
 Creating the climate to get the most from your team Helping leaders to create high-performing organisations NOVEMBER 2011 SHARON CRABTREE MICHAEL DODDS About Hay Group Our objectives today Look at what
Creating the climate to get the most from your team Helping leaders to create high-performing organisations NOVEMBER 2011 SHARON CRABTREE MICHAEL DODDS About Hay Group Our objectives today Look at what
pm4dev, 2016 management for development series Project Scope Management PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS
 pm4dev, 2016 management for development series Project Scope Management PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS A methodology to manage development
pm4dev, 2016 management for development series Project Scope Management PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS A methodology to manage development
Human Resource Management in Multinational Enterprises. [Writer Name] [Institute Name]
![Human Resource Management in Multinational Enterprises. [Writer Name] [Institute Name] Human Resource Management in Multinational Enterprises. [Writer Name] [Institute Name]](/thumbs/22/1512415.jpg) 1 Paper: Dissertation Proposal Style: Harvard Pages: 7 Sources: 8 Level: Masters Human Resource Management in Multinational Enterprises [Writer Name] [Institute Name] 2 Human Resource Management in Multinational
1 Paper: Dissertation Proposal Style: Harvard Pages: 7 Sources: 8 Level: Masters Human Resource Management in Multinational Enterprises [Writer Name] [Institute Name] 2 Human Resource Management in Multinational
SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT AT A GLOBAL LEVEL A CHALLENGE AND AN OPPORTUNITY FOR A LEADING OILFIELD SERVICE COMPANY. Amaar Saeed Khan
 SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT AT A GLOBAL LEVEL A CHALLENGE AND AN OPPORTUNITY FOR A LEADING OILFIELD SERVICE COMPANY Amaar Saeed Khan EXECUTIVE SUMMARY: Due to the complex nature of the oil and gas industry,
SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT AT A GLOBAL LEVEL A CHALLENGE AND AN OPPORTUNITY FOR A LEADING OILFIELD SERVICE COMPANY Amaar Saeed Khan EXECUTIVE SUMMARY: Due to the complex nature of the oil and gas industry,
PLS 308 Public Administration. Topic: Organizational Design and Culture
 Topic: Organizational Design and Culture Organizational Design and Structure! Organizational structure defines how job tasks are formally divided, grouped, and coordinated. This structure can be depicted
Topic: Organizational Design and Culture Organizational Design and Structure! Organizational structure defines how job tasks are formally divided, grouped, and coordinated. This structure can be depicted
SAMPLE TRAINING PLAN
 SAMPLE TRAINING PLAN The United States Department of State requires that all applicants to the J-1 Practical Training program submit a bona fide training plan. To make sure that every individual training
SAMPLE TRAINING PLAN The United States Department of State requires that all applicants to the J-1 Practical Training program submit a bona fide training plan. To make sure that every individual training
CHAPTER 3 - CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT (CRM)
 CHAPTER 3 - CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT (CRM) 3.1 INTRODUCTION The most important purpose of any service orientated organisation is to retain customers. It is critical for any organization to keep
CHAPTER 3 - CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT (CRM) 3.1 INTRODUCTION The most important purpose of any service orientated organisation is to retain customers. It is critical for any organization to keep
Strategic Management: Concepts and Cases 9e
 Strategic Management: Concepts and Cases 9e Part III: Strategic Actions: Strategy Implementation Chapter 12: Strategic Leadership 2011 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied
Strategic Management: Concepts and Cases 9e Part III: Strategic Actions: Strategy Implementation Chapter 12: Strategic Leadership 2011 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied
Developing International Human Resources Firms
 Developing International Human Resources Firms Yueh-shian Lee Assistant Professor National Taichung University of Education Department of International Business 140 Min-Shen Road, Taichung 40306, Taiwan
Developing International Human Resources Firms Yueh-shian Lee Assistant Professor National Taichung University of Education Department of International Business 140 Min-Shen Road, Taichung 40306, Taiwan
Information Systems, Organizations, and Strategy
 Information Systems, Organizations, and Strategy VIDEO CASES Chapter 3 Case 1: National Basketball Association: Competing on Global Delivery with Akamai OS Streaming Case 2: IT and Geo-Mapping Help a Small
Information Systems, Organizations, and Strategy VIDEO CASES Chapter 3 Case 1: National Basketball Association: Competing on Global Delivery with Akamai OS Streaming Case 2: IT and Geo-Mapping Help a Small
Choosing Human Resources Development Interventions
 Choosing Human Resources Development Interventions JP Singh Singh argues that top management should examine the managerial culture of the group and the organization before introducing change through human
Choosing Human Resources Development Interventions JP Singh Singh argues that top management should examine the managerial culture of the group and the organization before introducing change through human
Analytical Report On Case Study titled Human Resources at Hewlett-Packard By Richard Werssowelz & Michael Beer
 Analytical Report On Case Study titled Human Resources at Hewlett-Packard By Richard Werssowelz & Michael Beer Table of Contents Sl. Contents Page No Remarks 1 Cover Page 2 Table of Contents 3 Executive
Analytical Report On Case Study titled Human Resources at Hewlett-Packard By Richard Werssowelz & Michael Beer Table of Contents Sl. Contents Page No Remarks 1 Cover Page 2 Table of Contents 3 Executive
DevOps Engineer Position Description
 Engineer Position Description February 9, 2015 Engineer Position Description February 9, 2015 Page i Table of Contents General Characteristics... 1 Career Path... 2 Explanation of Proficiency Level Definitions...
Engineer Position Description February 9, 2015 Engineer Position Description February 9, 2015 Page i Table of Contents General Characteristics... 1 Career Path... 2 Explanation of Proficiency Level Definitions...
QUALITY TOOLBOX. Understanding Processes with Hierarchical Process Mapping. Robert B. Pojasek. Why Process Mapping?
 QUALITY TOOLBOX Understanding Processes with Hierarchical Process Mapping In my work, I spend a lot of time talking to people about hierarchical process mapping. It strikes me as funny that whenever I
QUALITY TOOLBOX Understanding Processes with Hierarchical Process Mapping In my work, I spend a lot of time talking to people about hierarchical process mapping. It strikes me as funny that whenever I
3 SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT METHODOLOGIES
 3 SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT METHODOLOGIES 3.1 INTRODUCTION Different types of system development methodologies are used in designing information system. Depending upon the actual requirement of the system, different
3 SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT METHODOLOGIES 3.1 INTRODUCTION Different types of system development methodologies are used in designing information system. Depending upon the actual requirement of the system, different
SigmaRADIUS Leadership Effectiveness Report
 SigmaRADIUS Leadership Effectiveness Report Sample Report NOTE This is a sample report, containing illustrative results for only two dimensions on which 360 performance ratings were obtained. The full
SigmaRADIUS Leadership Effectiveness Report Sample Report NOTE This is a sample report, containing illustrative results for only two dimensions on which 360 performance ratings were obtained. The full
THE ORGANISATION. Senior Management Major end users (divisions) Information Systems Department
 THE ORGANISATION Senior Management Major end users (divisions) Information Systems Department Technology Hardware Software Information Systems Specialists CIO Managers Systems analysts Systems designers
THE ORGANISATION Senior Management Major end users (divisions) Information Systems Department Technology Hardware Software Information Systems Specialists CIO Managers Systems analysts Systems designers
Robarge - 1 - Change, Leadership, and Vision. Trisa Robarge ORG 502. Don Gienty. January 28, 2004
 Robarge - 1 - Change, Leadership, and Vision Trisa Robarge ORG 502 Don Gienty January 28, 2004 It is change, continuing change, inevitable change, that is the dominant factor in society today. No sensible
Robarge - 1 - Change, Leadership, and Vision Trisa Robarge ORG 502 Don Gienty January 28, 2004 It is change, continuing change, inevitable change, that is the dominant factor in society today. No sensible
Overview of Position Classification Process
 Overview of Position Classification Process Mansfield University of Pennsylvania, one of the 14 state-owned universities comprising the Pennsylvania State System of Higher Education, uses prescribed and
Overview of Position Classification Process Mansfield University of Pennsylvania, one of the 14 state-owned universities comprising the Pennsylvania State System of Higher Education, uses prescribed and
Motivation Self Assessment. Autonomy, Mastery and Purpose
 Motivation Self Assessment Autonomy, Mastery and Purpose What is Motivation? Human beings are motivated by both extrinsic and intrinsic factors. In the workplace today in which creative, non-routine jobs
Motivation Self Assessment Autonomy, Mastery and Purpose What is Motivation? Human beings are motivated by both extrinsic and intrinsic factors. In the workplace today in which creative, non-routine jobs
Would I Follow Me? An Introduction to Management Leadership in the Workplace
 Would I Follow Me? An Introduction to Management Leadership in the Workplace This dynamic program clearly shows the right and wrong ways to deal with the very important human dimension of team performance.
Would I Follow Me? An Introduction to Management Leadership in the Workplace This dynamic program clearly shows the right and wrong ways to deal with the very important human dimension of team performance.
The European Financial Reporting Advisory Group (EFRAG) and the Autorité des Normes Comptables (ANC) jointly publish on their websites for
 The European Financial Reporting Advisory Group (EFRAG) and the Autorité des Normes Comptables (ANC) jointly publish on their websites for information purpose a Research Paper on the proposed new Definition
The European Financial Reporting Advisory Group (EFRAG) and the Autorité des Normes Comptables (ANC) jointly publish on their websites for information purpose a Research Paper on the proposed new Definition
