Patient-centered CT imaging: New methods for patient-specific optimization 1 of image quality and radiation dose
|
|
|
- Gwendolyn Quinn
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Patient-centered CT imaging: New methods for patient-specific optimization 1 of image quality and radiation dose ipatient is an advanced platform that delivers focused innovations to facilitate patient-centered imaging, now and in the future. Based on the award-winning EBW, ipatient puts you in control of innovative solutions that drive confidence and consistency through personalized patient-centric workflow. It helps you deliver more from your investment by allowing you the ability to do complex and advanced procedures, and helps to prepare for future CT technologies that will help improve the care you deliver to your patients. The patient-centered approach to imaging is an increasing focus in Radiology departments. For patients undergoing CT, this includes a personalized examination, one that provides diagnostic image quality while managing radiation dose (As Low As Reasonably Achievable, or ALARA). The Philips ipatient approach to patientcentered imaging includes new, patientspecific methods to facilitate optimal management of both image quality and radiation dose. In the ipatient approach, considerations for optimizing 1 CT image quality and dose include clinical indication, body habitus (from infants to morbidly obese adults), scan region, age, and physiological and anatomical factors (Figure 1). Patient-specific imaging factors and solutions are reviewed for obese, pediatric, and cancer patients as well as trauma, chest, and cardiac examinations. These methods were designed to simplify the adaptation of scan protocols and advanced techniques such as dose modulation and iterative reconstruction techniques to the individual patient and diagnostic task. They are used in combination for a synergistic effect that is amplified by dose-efficient imaging components of the ict and Ingenuity CT platforms. 1 Optimization refers to the use of strategies and techniques that facilitate the management and control of both image quality and dose. Figure 1
2 Obese patients and DoseRight index and 3D Globally, it is estimated that more than 1 billion adults are overweight and at least 300 million are obese.[1] In some CT departments, scan protocol settings used for obese patients balance a trade-off between: Increased radiation exposure that can be required due to relatively higher body attenuation 2 The quantum image noise that can result from insufficient dose. Patient-specific parameters and settings Image quality DoseRight index (DRI) setting Iterative reconstruction technique (IRT) setting Estimated image noise Patient size Water equivalent diameter (D w ) relative to the reference diameter selection (D ref ) DoseRight CS mas or avg. mas with Z- or 3D modulation Table 1 To help manage this, the ipatient approach includes new settings and methods for dose modulation and iterative reconstruction techniques that are not only designed to be intuitive but also complementary. These include: The image quality reference setting ( DoseRight Index, DRI) An iterative reconstruction technique (IRT) setting The scan protocol reference size, D ref (Table 1). These are conveniently displayed with other patientspecific parameters prior to data acquisition. For dose (tube current) modulation, the patient s CT radiograph (Surview) is used to create an average and z-axis profile attenuation (represented in terms of water equivalent diameter, D w ). The water equivalent diameter represents the size of a circular water phantom that would provide the crosssectional attenuation characteristic of the patient. The DoseRight CS algorithm suggests adjustments to average tube current and image noise based on The DRI The difference between the average diameter, D w, in the scan region (assessed from the Surview) and the reference diameter, D ref. Figure 2 DoseRight CS suggests appropriate tube current settings (vertical axis) over a wide range of patient sizes (horizontal). The DRI, IRT and other settings in Table 1 are easily combined to optimize according to patient factors and needs. The z-axis D w profile can be highly variable and individualized. For example, the chest region can have a much lower average attenuation than the abdominal region due to air in the lungs. DoseRight Z-modulation adjusts the tube current profile along the z-axis to maintain approximate constant noise and displays the profile in correlation with the Surview. 2 For obese patients, absorbed dose tends to be overestimated by the 32 cm CTDI body phantom.[4,5] 2
3 The DoseRight Index (DRI) used to specify the image quality required for the diagnostic task at hand and the DoseRight Current Selection (CS) algorithm were developed in extensive clinical collaboration. For an obese patient, when the patient s diameter (D w ) is greater than the reference diameter (D ref ), e.g., D w = 37 cm and D ref = 33 cm, DoseRight CS suggests an increase in the average tube current 3 (green curve in Figure 2) 4 relative to the reference diameter and according to the specified DRI. The suggested increase does not occur at the exponential rate that would be required to maintain constant noise level (red line) with increasing patient size (D w ). For this, the tube current would need to double about every 4 cm increase of D w (double arrow). Sagittal CT images of an obese patient with D w = 42 cm are shown in Figure 3. To plan the same level of quantum image noise as a patient with reference diameter of 30 cm, the tube current would need to increase by a factor of 8 (((2)x2)x2 = 8) to 784 mas. Instead, a controlled increase in suggested noise levels for larger patients (and a decrease in noise for smaller adults when D w < D ref ) was found to be most appropriate for managing dose and image quality. To further optimize image quality and manage dose, the ipatient approach provides additional options (Table 1): The iterative reconstruction technique, idose 4, has seven noise reduction settings and preserves the natural image appearance. 5 Philips engineers designed the DRI to simplify adjustments: decreasing (increasing) it by -1 (+1) will decrease (increase) the average tube current by 12 % and increase (decrease) the image noise by 6% 6 (further discussed below), with other parameters unchanged. Additional size-specific scan protocols can be used if these are preferred. For example, separate protocols can easily be created with reference diameters for obese (37 cm), average (33 cm), and slim adults (29 cm) (as shown in Figure 2) each with a DRI and idose 4 setting. Size-specific scan protocols are particularly helpful with CT pediatric imaging (next section). Tools such as iterative reconstruction techniques are changing perspectives on the management of CT image quality and dose. Figure 3 Sagittal reformatted images of an obese patient (D w = 42) acquired with DoseRight settings of DRI 7 (98 mas), 120 kvp, and CTDI vol32 = 6.1 mgy. Standard reconstruction was used without idose 4 (left) and with idose 4 level 2 (right). Pediatric patients and reference size selections The need for highly patient-specific pediatric CT examinations has resulted in the Image Gently campaign.[5] Consistent use of the ALARA principle is paramount in this population due to relatively higher radiosensitivity and higher dose absorption of the relatively smaller body volume.[7] Accordingly, pediatric scan protocols need to be appropriately adjusted for patient size which can vary from infants to adults-sized adolescence. 7 Planning the set of scan protocols is usually based on weight intervals (e.g., 0-10 kg, kg, etc.), scan region, and the diagnostic task. 3 Tube current includes reference to tube current time product (mas) in this paper. 4 Tube current suggested by DoseRight CS is used as an average mas when Z- or 3D modulation is selected and is used as a fixed (constant) mas otherwise. 5 idose 4 can provide up to 57% improvement in spatial resolution for the Ingenuity CT and up to 50% improvement in spatial resolution for the ict, for a given dose. 6 As predicted by the Inverse Square Law. 7 Lower noise levels may be preferred due to less fat planes, smaller structures, and a need for higher diagnostic confidence. 3
4 In the ipatient approach, size-specific scan protocols (i.e., Exam Cards) can be easily generated (as mentioned above). Exam Cards can be based on one of eight (1 infant, 7 pediatric) midpoint reference diameters, D ref that are directly related to weight based intervals (as shown in Figure 4). The DoseRight CS algorithm can then adjust the average tube current and image noise relative to a more protocol-specific D ref (Figure 4) and DRI setting. Conversely, using a 6-year-old as reference size for a kg weight-based protocol, for example, could be counterintuitive, despite an understanding that the dose modulation algorithm would significantly decrease the tube current according to the size of the individual in the kg interval. Basing scan protocols on the appropriate size or weight groups can improve confidence when comparing patient-specific parameters (such as the patient diameter, suggested tube current, and others in Table 1) with reference parameters. The radiologist can then focus on image quality settings (DRI) to meet the diagnostic objective. Figure 4 Size-specific selections (horizontal axis) for pediatric and infant protocols allow patient-specific and intuitive control of the DoseRight Index and the average tube current (vertical axis), as needed in this population. The X-ray attenuation of the patient can also vary with tube rotation angle. For example, the shoulder region can have a higher attenuation laterally than anteroposteriorly. Average adults tend to have oval abdominal cross-section. Tube current is angularly modulated during helical scans according to the patients cross-sectional shape (eccentricity). Prior to the helical exam, the A-P Surview is processed at each z-location to determine angular adjustments in the tube current profile. The mas is increased and decreased for the maximum and minimum cross-sectional diameter respectively. DoseRight 3D modulation combines angular modulation with z-axis tube current modulation (ZDOM). The 3-D modulation can be implemented based on the acquisition of one Surview, the DRI setting, and the reference diameter. Oncology imaging: organ-based dose modulation and iterative reconstruction techniques CT is the examination of choice for detecting or evaluating liver lesions. This diagnostic task can pose challenges due to low contrast of the lesions.[2] Another feature of the ipatient approach to help optimize image quality and manage radiation exposure are organ-based adjustments with the DRI during dose modulation. This new method for the liver (and also the brain), goes beyond use of body eccentricity and attenuation characteristics. A new algorithm is used to detect the liver in the Surview and assist with the placement of organ delineation lines. The Z-axis tube current profile is then adjusted with a protocolspecific DRI setting. Figure 5 illustrates changes in beam intensity as the tube rotates from lateral to A-P (Angular Modulation) and to the liver region. This advanced technique enables an increase in image quality where needed without increasing radiation exposure to other regions or organs. 4
5 Figure 5 3D dose modulation adjusts angular and longitudinal exposure according to body habitus and the DRI. The DRI can be adjusted for the liver region in conjunction with settings for Iterative Model Reconstruction (Table 1). The strategy of increasing exposure to facilitate diagnostic confidence for liver lesions is consistent with the ALARA principle. To further optimize image quality and manage dose for this challenging task and many others, Philips provides an advanced method Iterative Model Reconstruction (IMR) for exceptional image quality improvements. IMR provides virtually noise-free* images with significant improvements in low contrast imaging (Figure 6). Consistent with the ipatient strategy, IMR can be adapted for the diagnostic task at hand: it has settings to emphasize low or high contrast resolution or both. Managing low dose (ALARA) scan protocols with the DRI A number of high contrast studies, for example, CT colonoscopy, calcium scoring, and some chest examinations, can occur earlier in the care cycle and have potential for low dose. This must be achieved without risking a non-diagnostic exam. A common practice is to gradually reduce the volume CTDI, review the results in terms of image quality and dose, and then consider the potential need for further optimization (Figure 7). Figure 6 Abdominal CT images acquired with 3D modulation and an increased DRI for the liver. These techniques were used in conjunction with Iterative Model Reconstruction (IMR) (right) shown in comparison with standard reconstruction (left). Clinical indication, previous scans Summary review of scan protocols CT image quality and radiation dose management cycle CT image quality and radiation dose management cycle Scan parameters based on patientspecific factors (DRI adjustment) Table 1 Intrascan Resulting images Interscan Retrospective feedback Adjustment DRI and IRT parameters in the Exam Card manager to optimize image quality and dose Review of image quality and radiation dose utilization Figure 7 Flow chart exemplifying CT image quality and dose management based on the ALARA principle. Reviews and adjustments of scan protocols are facilitated by the ipatient approach. * In clinical practice, IRT may reduce image noise depending on the clinical task, patient size, anatomical location, and clinical practice. A consultation with a radiologist and a physicist should be made to determine the appropriate dose to obtain diagnostic image quality for the particular task. As with any imaging reconstruction, the quality of the resulting IRT images is dependent on the scanning parameters required for your particular patient, clinical indication, and clinical practice. 5
6 As mentioned earlier, Philips engineers designed the DRI so that a step of one will change the volume CTDI by 12% and noise by 6% if other settings are unchanged. 8 This structured way to adjust and review CTDI and estimated noise levels can be easily combined with iterative reconstruction technique settings to further optimize image quality. After the appropriate number of cycles and consideration of the results, adjustments to the DRI and iterative reconstruction technique settings can then be incorporated into the Exam Card to manage individual patient examinations. Additional patient-specific approaches with ipatient CTA exams: DRI and tube potential For examinations with iodinated contrast media, a decrease in tube potential 9 leads to an increase in iodine attenuation and signal. The decrease in tube potential (with tube current held constant) decreases CTDI vol and, therefore, increases noise in a highly non-linear fashion. ipatient provides a more intuitive approach: if the planned tube potential (kvp) is modified for a particular DRI setting, the average tube current (mas) suggested by DoseRight CS automatically updates to maintain the same CTDI vol. Then, the DRI can be used for more intuitive steps of 6% and 12 % in planned image noise and dose, respectively. A 16 cm cylindrical phantom with five iodine samples (four peripheral, one central) was used to demonstrate this innovative approach (Figure 8). ict data was acquired using DRI 28, 120 kvp, and 83 mas (CTDI vol32 = 10.3 mgy) and standard reconstruction (left). The tube potential was decreased to 100 kvp and the tube current automatically adjusted to 250 mas to maintain the CTDI. The DRI was then incrementally decreased from 28 to 18 (88 mas and CTDI vol32 = 3.5 mgy) and idose 4 was used with a setting of 6. This resulted in a CNR increase of 45% and increased conspicuity of the center iodine sample (blue arrow). Figure 8 A 16 cm phantom with five iodine samples was used to show how the DRI can simplify adjustments in the tube potential, mas, and idose 4. These adjustments lead to an increase in the CNR at low dose. Radiation dose metrics are also changing from onesize-fits all approaches to more individualized metrics. The size-specific dose estimate,[6] for instance, provides a correction for CTDI based on a measure of effective diameter. This is a step toward patient-specific dose estimates such as organ dose estimation. Cardiac examinations and DoseRight CS Low doses have been achieved while maintaining image quality with the use of prospective Step & Shoot and ECG triggered dose modulation for retrospective gated helical scans.[8][9] The ipatient enhancements are fully integrated with these high temporal resolution scan modes of the ict and Ingenuity CT. As with non-gated scanning modes, DoseRight CS can be used to suggest the average tube current according to patient size and the DRI setting. This applies to Calcium scoring, prospectively-gated Step & Shoot examinations, and retrospective-gated cardiac exams. 8 Decreasing DRI by 3 from 15 to 12, for example, would decrease the average mas by a factor of ( ) 3 = (0.88) 3 = 0.68 or (1-0.68)*100% = 32% and would increase noise by a factor of (1.06) 3 = (1. 06) 3 = 1.19 or 19%. 9 Many patient-specific factors are considered when adjusting tube potential. 6
7 A low-dose feature for trauma examinations CT is clinically indicated for head trauma and acute abdominal conditions. The speed and diagnostic quality of the MDCT can provide immediate benefit. Brain and cervical spine imaging can be planned in a single acquisition. This is accomplished by semi-automatically detecting the base of the neck in the Surview. The technologist can then adjust the border between the base of the brain and C1 cervical spine if necessary. The scan parameters are set for each region as with those traditionally planned in the dual acquisition mode but without the overlap that would increase the total DLP of the examination.[4] Imaging orthopedic implants with O-MAR Metal implants can make diagnosis challenging due to beam hardening artifacts and other effects on image quality. To address this, the set of enhancements provided by the ipatient approach includes Metal Artifact Reduction for Orthopedic Implants (O-MAR) to help improve image quality. O-MAR is capable of reducing the effect of large metal artifacts from orthopedic implants such as hip prosthesis.[3] This can enhance the diagnostic quality of the images. Summary Patient-specific CT imaging and personalization of scan protocols will be a key aspect of patient-centered care in Radiology departments. Dose management is also becoming more patient-specific relative to use of the CT Dose Index.[6] ipatient follows the longstanding DoseWise philosophy to provide enhancements that are used in combination for a synergistic effect that is amplified by highly dose-efficient imaging components of the ict and Ingenuity CT platforms. ipatient includes patient-specific methods to simplify and easily control when needed the improved management of image quality and radiation dose. Innovations provided by ipatient will transform patient care by keeping the interest of the patient in the forefront of advanced diagnostic CT imaging. 7
8 References 1. Romero-Corral A, et al. Association of bodyweight with total mortality and with cardiovascular events in coronary artery disease: a systematic review of cohort studies. Lancet 2006;368: Liver imaging 3. Reduction-for-Orthopedic-Implants-(O-MAR) 4. Ardley N, Lau KK, Buchan K, Clayton, V, AU, Melbourne, Victoria/AU, ECR. Radiation dose reduction using a neck detection algorithm for single spiral brain and cervical spine CT acquisition in the trauma setting. 5. Image gently website: 6. Size-specific Dose of Pediatric and Adult Body Examination, AAPM Report Number 204, Morgan, HT. Dose reduction in pediatric imaging. Pediatric Radiology 2002: Klass O, Jeltsch M, Feuerlein S, Brunner H, Nagel HD, Walker MJ, Brambs HJ, Hoffmann MH. Prospectively Gated Axial CT Coronary Angiography: Preliminary Experiences With A Novel Low-Dose Technique. Eur Radiol Nov Hesse B, MD, et al. Use of Tissue Doppler Imaging to Guide Tube Current Modulation in Cardiac Multidetector Computed Tomographic Angiography. AJC Please visit Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. All rights are reserved. Philips Healthcare reserves the right to make changes in specifications and/or to discontinue any product at any time without notice or obligation and will not be liable for any consequences resulting from the use of this publication. Philips Healthcare is part of Royal Philips Electronics healthcare@philips.com Printed in The Netherlands * Nov 2012
The disclaimer on page 1 is an integral part of this document. Copyright February 23, 2016 by AAPM. All rights reserved.
 DISCLAIMER: TO THE EXTENT ALLOWED BY LOCAL LAW, THIS INFORMATION IS PROVIDED TO YOU BY THE AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF PHYSICISTS IN MEDICINE, A NON-PROFIT ORGANIZATION ORGANIZED TO PROMOTE THE APPLICATION
DISCLAIMER: TO THE EXTENT ALLOWED BY LOCAL LAW, THIS INFORMATION IS PROVIDED TO YOU BY THE AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF PHYSICISTS IN MEDICINE, A NON-PROFIT ORGANIZATION ORGANIZED TO PROMOTE THE APPLICATION
MDCT Technology. Kalpana M. Kanal, Ph.D., DABR Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Washington Seattle, Washington
 MDCT Technology Kalpana M. Kanal, Ph.D., DABR Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Washington Seattle, Washington ACMP Annual Meeting 2008 - Seattle, WA Educational Objectives Historical
MDCT Technology Kalpana M. Kanal, Ph.D., DABR Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Washington Seattle, Washington ACMP Annual Meeting 2008 - Seattle, WA Educational Objectives Historical
CT: Size Specific Dose Estimate (SSDE): Why We Need Another CT Dose Index. Acknowledgements
 CT: Size Specific Dose Estimate (SSDE): Why We Need Another CT Dose Index Keith J. Strauss, MSc, FAAPM, FACR Clinical Imaging Physicist Cincinnati Children s Hospital University of Cincinnati College of
CT: Size Specific Dose Estimate (SSDE): Why We Need Another CT Dose Index Keith J. Strauss, MSc, FAAPM, FACR Clinical Imaging Physicist Cincinnati Children s Hospital University of Cincinnati College of
Purchasing a cardiac CT scanner: What the radiologist needs to know
 Purchasing a cardiac CT scanner: What the radiologist needs to know Maria Lewis ImPACT St George s Hospital, London maria.lewis@stgeorges.nhs.uk CT scanner development Slice wars 1998 Increased z-coverage
Purchasing a cardiac CT scanner: What the radiologist needs to know Maria Lewis ImPACT St George s Hospital, London maria.lewis@stgeorges.nhs.uk CT scanner development Slice wars 1998 Increased z-coverage
Assessing Radiation Dose: How to Do It Right
 Assessing Radiation Dose: How to Do It Right Michael McNitt-Gray, PhD, DABR, FAAPM Professor, Department of Radiology Director, UCLA Biomedical Physics Graduate Program David Geffen School of Medicine
Assessing Radiation Dose: How to Do It Right Michael McNitt-Gray, PhD, DABR, FAAPM Professor, Department of Radiology Director, UCLA Biomedical Physics Graduate Program David Geffen School of Medicine
CT Protocol Optimization over the Range of CT Scanner Types: Recommendations & Misconceptions
 CT Protocol Optimization over the Range of CT Scanner Types: Recommendations & Misconceptions Frank N. Ranallo, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Medical Physics & Radiology University of Wisconsin School of
CT Protocol Optimization over the Range of CT Scanner Types: Recommendations & Misconceptions Frank N. Ranallo, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Medical Physics & Radiology University of Wisconsin School of
Chest CT protocols. Mannudeep K. Kalra, MD, DNB. Dianna D. Cody, PhD. Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School
 Chest CT protocols Mannudeep K. Kalra, MD, DNB Dianna D. Cody, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Specific principles Routine chest CT Lung nodule follow
Chest CT protocols Mannudeep K. Kalra, MD, DNB Dianna D. Cody, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Specific principles Routine chest CT Lung nodule follow
State-of-the-Art Technology in Cardiac CT
 1 2 Next Step Evolution or Revolution? State-of-the-Art Technology in Cardiac CT Stefan Ulzheimer, PhD Global Director of Collaborations CT Siemens Medical Solutions Major Innovations in CT Head The 80
1 2 Next Step Evolution or Revolution? State-of-the-Art Technology in Cardiac CT Stefan Ulzheimer, PhD Global Director of Collaborations CT Siemens Medical Solutions Major Innovations in CT Head The 80
Multi-slice Helical CT Scanning of the Chest
 Multi-slice Helical CT Scanning of the Chest Comparison of different low-dose acquisitions Lung cancer is the main cause of deaths due to cancer in human males and the incidence is constantly increasing.
Multi-slice Helical CT Scanning of the Chest Comparison of different low-dose acquisitions Lung cancer is the main cause of deaths due to cancer in human males and the incidence is constantly increasing.
Low-dose CT for Pulmonary Embolism
 Low-dose CT for Pulmonary Embolism Gautham Gautham P. P. Reddy, Reddy, MD, MD, MPH MPH University University of of Washington Washington Introduction Introduction CT CT accounts accounts for for > 50%
Low-dose CT for Pulmonary Embolism Gautham Gautham P. P. Reddy, Reddy, MD, MD, MPH MPH University University of of Washington Washington Introduction Introduction CT CT accounts accounts for for > 50%
American College of Radiology CT Accreditation Program. Testing Instructions
 American College of Radiology CT Accreditation Program Testing Instructions (Revised July 24, 2015) This guide provides all of the instructions necessary for clinical tests, phantom tests and general submission
American College of Radiology CT Accreditation Program Testing Instructions (Revised July 24, 2015) This guide provides all of the instructions necessary for clinical tests, phantom tests and general submission
Physics testing of image detectors
 Physics testing of image detectors Parameters to test Spatial resolution Contrast resolution Uniformity/geometric distortion Features and Weaknesses of Phantoms for CR/DR System Testing Dose response/signal
Physics testing of image detectors Parameters to test Spatial resolution Contrast resolution Uniformity/geometric distortion Features and Weaknesses of Phantoms for CR/DR System Testing Dose response/signal
2/28/2011. MIPPA overview and CMS requirements. CT accreditation. Today s agenda. About MIPPA. Computed Tomography
 Today s agenda Computed Tomography Presented by: Dina Hernandez, BSRT, RT (R), CT, QM Krista Bush, RT, MBA Leonard Lucey, JD ACR Quality & Safety MIPPA overview and CMS requirements CT accreditation How
Today s agenda Computed Tomography Presented by: Dina Hernandez, BSRT, RT (R), CT, QM Krista Bush, RT, MBA Leonard Lucey, JD ACR Quality & Safety MIPPA overview and CMS requirements CT accreditation How
R/F. Efforts to Reduce Exposure Dose in Chest Tomosynthesis Targeting Lung Cancer Screening. 3. Utility of Chest Tomosynthesis. 1.
 R/F Efforts to Reduce Exposure Dose in Chest Tomosynthesis Targeting Lung Cancer Screening Department of Radiology, National Cancer Center Hospital East Kaoru Shimizu Ms. Kaoru Shimizu 1. Introduction
R/F Efforts to Reduce Exposure Dose in Chest Tomosynthesis Targeting Lung Cancer Screening Department of Radiology, National Cancer Center Hospital East Kaoru Shimizu Ms. Kaoru Shimizu 1. Introduction
How To Improve Your Ct Image Quality
 Translating Protocols Between Scanner Manufacturer and Model Cynthia H. McCollough, PhD, FACR, FAAPM Professor of Radiologic Physics Director, CT Clinical Innovation Center Department of Radiology Mayo
Translating Protocols Between Scanner Manufacturer and Model Cynthia H. McCollough, PhD, FACR, FAAPM Professor of Radiologic Physics Director, CT Clinical Innovation Center Department of Radiology Mayo
The Challenge of CT Dose Records
 The Challenge of CT Dose Records Kimberly Applegate, MD, MS, FACR Professor of Radiology and Pediatrics Emory University *financial disclosures: -Springer Textbook contracts -AIM advisory board for patient
The Challenge of CT Dose Records Kimberly Applegate, MD, MS, FACR Professor of Radiology and Pediatrics Emory University *financial disclosures: -Springer Textbook contracts -AIM advisory board for patient
Imaging of Thoracic Endovascular Stent-Grafts
 Imaging of Thoracic Endovascular Stent-Grafts Tariq Hameed, M.D. Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, Indiana Disclosures: No relevant financial
Imaging of Thoracic Endovascular Stent-Grafts Tariq Hameed, M.D. Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, Indiana Disclosures: No relevant financial
The disclaimer on page 1 is an integral part of this document. 1. Copyright December 14, 2015 by AAPM. All rights reserved.
 DISCLAIMER: TO THE EXTENT ALLOWED BY LOCAL LAW, THIS INFORMATION IS PROVIDED TO YOU BY THE AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF PHYSICISTS IN MEDICINE, A NON-PROFIT ORGANIZATION ORGANIZED TO PROMOTE THE APPLICATION
DISCLAIMER: TO THE EXTENT ALLOWED BY LOCAL LAW, THIS INFORMATION IS PROVIDED TO YOU BY THE AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF PHYSICISTS IN MEDICINE, A NON-PROFIT ORGANIZATION ORGANIZED TO PROMOTE THE APPLICATION
Pediatric Hospitals Bring Low-dose CT to the Middle East
 Pediatric Hospitals ring Low-dose CT to the Middle East For years, radiologists have been cognizant of the importance of limiting pediatric patients exposure to radiation dose. uilding on the LR principle,
Pediatric Hospitals ring Low-dose CT to the Middle East For years, radiologists have been cognizant of the importance of limiting pediatric patients exposure to radiation dose. uilding on the LR principle,
Reliable versatility. Philips HD5 ultrasound system
 Reliable versatility Philips HD5 ultrasound system Affordability and features in one Designed to perform as you need it Every day, your patients come to you for high-quality care. Now, there s an ultrasound
Reliable versatility Philips HD5 ultrasound system Affordability and features in one Designed to perform as you need it Every day, your patients come to you for high-quality care. Now, there s an ultrasound
Tracking Radiation Exposure From Medical Diagnostic Procedures: Siemens Perspectives
 Tracking Radiation Exposure From Medical Diagnostic Procedures: Siemens Perspectives Gilbert W. Beebe Symposium The National Academies Katharine Grant, PhD Staff Scientist 8 December 2011 For internal
Tracking Radiation Exposure From Medical Diagnostic Procedures: Siemens Perspectives Gilbert W. Beebe Symposium The National Academies Katharine Grant, PhD Staff Scientist 8 December 2011 For internal
Spiral CT: Single and Multiple Detector Systems. AAPM Refresher Course Nashville, TN July 28,1999
 Spiral CT: Single and Multiple Detector Systems AAPM Refresher Course Nashville, TN July 28,1999 Mike McNitt-Gray, PhD, DABR Assistant Professor UCLA Radiological Sciences mmcnittgray@mednet.ucla.edu X-Ray
Spiral CT: Single and Multiple Detector Systems AAPM Refresher Course Nashville, TN July 28,1999 Mike McNitt-Gray, PhD, DABR Assistant Professor UCLA Radiological Sciences mmcnittgray@mednet.ucla.edu X-Ray
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Prepublication Requirements
 Issued Prepublication Requirements The Joint Commission has approved the following revisions for prepublication. While revised requirements are published in the semiannual updates to the print manuals
Issued Prepublication Requirements The Joint Commission has approved the following revisions for prepublication. While revised requirements are published in the semiannual updates to the print manuals
Cardiac CT for Calcium Scoring
 Scan for mobile link. Cardiac CT for Calcium Scoring Cardiac computed tomography (CT) for Calcium Scoring uses special x-ray equipment to produce pictures of the coronary arteries to determine if they
Scan for mobile link. Cardiac CT for Calcium Scoring Cardiac computed tomography (CT) for Calcium Scoring uses special x-ray equipment to produce pictures of the coronary arteries to determine if they
Practical exercise: Effective dose estimate in CT
 Practical exercise: Effective dose estimate in CT TRAINING COURCE PROGRAM 19 20 May 2011, Sofia, Bulgaria Virginia Tsapaki Medical Physics Dpt Konstantopoulio General Hospital email: virginia@otenet.gr
Practical exercise: Effective dose estimate in CT TRAINING COURCE PROGRAM 19 20 May 2011, Sofia, Bulgaria Virginia Tsapaki Medical Physics Dpt Konstantopoulio General Hospital email: virginia@otenet.gr
Computed Tomography Radiation Safety Issues in Ontario
 Computed Tomography Radiation Safety Issues in Ontario Healthcare Human Factors Group Centre for Global ehealth Innovation University Health Network Toronto, ON, Canada June 16, 2006 Table of Contents
Computed Tomography Radiation Safety Issues in Ontario Healthcare Human Factors Group Centre for Global ehealth Innovation University Health Network Toronto, ON, Canada June 16, 2006 Table of Contents
Brilliance CT 64-channel confi guration
 Brilliance CT 64-channel confi guration with Essence technology The Brilliance CT 64-channel confi guration is designed to help you conduct the most advanced multislice CT studies possible. These systems
Brilliance CT 64-channel confi guration with Essence technology The Brilliance CT 64-channel confi guration is designed to help you conduct the most advanced multislice CT studies possible. These systems
The Possibilities Tomosynthesis Brings to Lung Cancer Screening
 Special Report The Possibilities Brings to Lung Cancer Screening Low-dose is a Useful Tool in Lung Cancer Screening A Technical Evaluation of Low-dose with the SONIALVISION safire Joint Industrial-Academic
Special Report The Possibilities Brings to Lung Cancer Screening Low-dose is a Useful Tool in Lung Cancer Screening A Technical Evaluation of Low-dose with the SONIALVISION safire Joint Industrial-Academic
Advanced Molecular Imaging. Ingenuity TF PET/CT. Your scan, your way
 Advanced Molecular Imaging Ingenuity TF PET/CT Your scan, your way The results speak for themselves In today s rapidly evolving world of imaging, it can seem as though you need to compromise on virtually
Advanced Molecular Imaging Ingenuity TF PET/CT Your scan, your way The results speak for themselves In today s rapidly evolving world of imaging, it can seem as though you need to compromise on virtually
The disclaimer on page 1 is an integral part of this document. Copyright March 1, 2016 by AAPM. All rights reserved.
 DISCLAIMER: TO THE EXTENT ALLOWED BY LOCAL LAW, THIS INFORMATION IS PROVIDED TO YOU BY THE AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF PHYSICISTS IN MEDICINE, A NON-PROFIT ORGANIZATION ORGANIZED TO PROMOTE THE APPLICATION
DISCLAIMER: TO THE EXTENT ALLOWED BY LOCAL LAW, THIS INFORMATION IS PROVIDED TO YOU BY THE AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF PHYSICISTS IN MEDICINE, A NON-PROFIT ORGANIZATION ORGANIZED TO PROMOTE THE APPLICATION
GE Healthcare. DoseWatch. Gathering Radiation Dose Data
 GE Healthcare DoseWatch Gathering Radiation Dose Data Gathering Radiation Dose Data After your organization crosses the bridge of Why? for patient radiation dose management either due to regulation, risk
GE Healthcare DoseWatch Gathering Radiation Dose Data Gathering Radiation Dose Data After your organization crosses the bridge of Why? for patient radiation dose management either due to regulation, risk
Interim policy effective January 1, 2016, through December 31, 2017
 IMPORTANT NOTICE Interim policy announced for post-primary structured education requirement Interim policy relaxes exam content outline requirement (November 2, 205) The ARRT announces an interim policy
IMPORTANT NOTICE Interim policy announced for post-primary structured education requirement Interim policy relaxes exam content outline requirement (November 2, 205) The ARRT announces an interim policy
GE Healthcare. Revolution EVO. More than just high tech. Higher purpose.
 GE Healthcare Revolution EVO More than just high tech. Higher purpose. Revolution EVO. Designed with purpose. Today s healthcare environment is about creating new solutions to pressing needs. It s about
GE Healthcare Revolution EVO More than just high tech. Higher purpose. Revolution EVO. Designed with purpose. Today s healthcare environment is about creating new solutions to pressing needs. It s about
GE Healthcare. Discovery * CT750 HD Great care by design
 GE Healthcare Discovery * CT750 HD Great care by design At GE Healthcare, imag lie at the heart of every than 30 years, we ve d that enhance the ways and treat disease. Bett us to render the inner greater
GE Healthcare Discovery * CT750 HD Great care by design At GE Healthcare, imag lie at the heart of every than 30 years, we ve d that enhance the ways and treat disease. Bett us to render the inner greater
Comparison of radiation dose from X-ray, CT, and PET/ CT in paediatric patients with neuroblastoma using a dose monitoring program
 Comparison of radiation dose from X-ray, CT, and PET/ CT in paediatric patients with neuroblastoma using a dose monitoring program Poster No.: C-0591 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific
Comparison of radiation dose from X-ray, CT, and PET/ CT in paediatric patients with neuroblastoma using a dose monitoring program Poster No.: C-0591 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific
Master s Program in Medical Physics. Physics of Imaging Systems Basic Principles of Computer Tomography (CT) III. Prof. Dr. Lothar Schad.
 1 12/9/2008 Page 1 Master s Program in Medical Physics Physics of Imaging Systems Basic Principles of Computer Tomography (CT) III Chair in Faculty of Medicine Mannheim University of Heidelberg Theodor-Kutzer-Ufer
1 12/9/2008 Page 1 Master s Program in Medical Physics Physics of Imaging Systems Basic Principles of Computer Tomography (CT) III Chair in Faculty of Medicine Mannheim University of Heidelberg Theodor-Kutzer-Ufer
Moving Forward What does this mean for the Medical Physicist and the Imaging Community?
 Moving Forward What does this mean for the Medical Physicist and the Imaging Community? John M. Boone, Ph.D., FAAPM, FACR Professor and Vice Chairman of Radiology University of California Davis Medical
Moving Forward What does this mean for the Medical Physicist and the Imaging Community? John M. Boone, Ph.D., FAAPM, FACR Professor and Vice Chairman of Radiology University of California Davis Medical
Running head: OBESITY AND MEDICAL IMAGING 1. Obesity and Medical Imaging. November 13, 2012
 Running head: OBESITY AND MEDICAL IMAGING 1 Obesity and Medical Imaging November 13, 2012 OBESITY AND MEDICAL IMAGING 2 Abstract Obesity is a growing problem in the United States, and it affects the health
Running head: OBESITY AND MEDICAL IMAGING 1 Obesity and Medical Imaging November 13, 2012 OBESITY AND MEDICAL IMAGING 2 Abstract Obesity is a growing problem in the United States, and it affects the health
Low-dose CT Imaging. Edgar Fearnow, M.D. Section Chief, Computed Tomography, Lancaster General Hospital
 Lung Cancer Screening with Low-dose CT Imaging Edgar Fearnow, M.D. Section Chief, Computed Tomography, Lancaster General Hospital Despite recent declines in the incidence of lung cancer related to the
Lung Cancer Screening with Low-dose CT Imaging Edgar Fearnow, M.D. Section Chief, Computed Tomography, Lancaster General Hospital Despite recent declines in the incidence of lung cancer related to the
Cynthia H. McCollough b) and Michael R. Bruesewitz Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic College of Medicine, Rochester, Minnesota 55905
 The phantom portion of the American College of Radiology ACR Computed Tomography CT accreditation program: Practical tips, artifact examples, and pitfalls to avoid a Cynthia H. McCollough b) and Michael
The phantom portion of the American College of Radiology ACR Computed Tomography CT accreditation program: Practical tips, artifact examples, and pitfalls to avoid a Cynthia H. McCollough b) and Michael
The IAC Standards and Guidelines for CT Accreditation
 The IAC Standards and Guidelines for CT Accreditation Table of Contents All entries in Table of Contents are linked to the corresponding sections. Introduction... 4 Part A: Organization... 5 Section 1A:
The IAC Standards and Guidelines for CT Accreditation Table of Contents All entries in Table of Contents are linked to the corresponding sections. Introduction... 4 Part A: Organization... 5 Section 1A:
PET/CT-MRI First clinical experience
 20 th April 2013, Barcelona, Sp PET/CT-MRI First clinical experience Philippe Appenzeller, MD Staff Radiologist and Nuclear Medicine Physician Department Medical Imaging, University Hospital Zurich PET/CT-MR
20 th April 2013, Barcelona, Sp PET/CT-MRI First clinical experience Philippe Appenzeller, MD Staff Radiologist and Nuclear Medicine Physician Department Medical Imaging, University Hospital Zurich PET/CT-MR
Implementation of Cone-beam CT imaging for Radiotherapy treatment localisation.
 Implementation of Cone-beam CT imaging for Radiotherapy treatment localisation. Andrew Bridges Clinical Scientist Diagnostic Radiology & Radiation Protection Physics Overview What is CBCT? Use of CBCT
Implementation of Cone-beam CT imaging for Radiotherapy treatment localisation. Andrew Bridges Clinical Scientist Diagnostic Radiology & Radiation Protection Physics Overview What is CBCT? Use of CBCT
CT RADIATION DOSE REPORT FROM DICOM. Frank Dong, PhD, DABR Diagnostic Physicist Imaging Institute Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, OH
 CT RADIATION DOSE REPORT FROM DICOM Frank Dong, PhD, DABR Diagnostic Physicist Imaging Institute Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, OH CT Patient comes out... Patient goes in... Big Black Box Radiology
CT RADIATION DOSE REPORT FROM DICOM Frank Dong, PhD, DABR Diagnostic Physicist Imaging Institute Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, OH CT Patient comes out... Patient goes in... Big Black Box Radiology
OPTIMIZING PATIENT EXPOSURE TO IONIZING RADIATION (OPEIR) MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW 2015 PQRS OPTIONS FOR MEASURES GROUPS:
 OPTIMIZING PATIENT EXPOSURE TO IONIZING RADIATION (OPEIR) MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW 2015 PQRS OPTIONS F MEASURES GROUPS: 2015 PQRS MEASURES IN OPTIMIZING PATIENT EXPOSURE TO IONIZING RADIATION (OPEIR) MEASURES
OPTIMIZING PATIENT EXPOSURE TO IONIZING RADIATION (OPEIR) MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW 2015 PQRS OPTIONS F MEASURES GROUPS: 2015 PQRS MEASURES IN OPTIMIZING PATIENT EXPOSURE TO IONIZING RADIATION (OPEIR) MEASURES
Dose Modulation Technique in CT
 Content Dose Modulation Technique in CT Short Overview - Overview - Dose Saving Features - Take Home Point - Conclusions Senior Application specialist Siemens Limited, Taiwan For internal use only / Copyright
Content Dose Modulation Technique in CT Short Overview - Overview - Dose Saving Features - Take Home Point - Conclusions Senior Application specialist Siemens Limited, Taiwan For internal use only / Copyright
Techniques and Applications of Automatic Tube Current Modulation for CT 1
 Review Radiology Mannudeep K. Kalra, MD, DNB Michael M. Maher, MD, FFR (RCSI), FRCR Thomas L. Toth, DSc Bernhard Schmidt, PhD Bryan L. Westerman, PhD Hugh T. Morgan, PhD Sanjay Saini, MD Index terms: Computed
Review Radiology Mannudeep K. Kalra, MD, DNB Michael M. Maher, MD, FFR (RCSI), FRCR Thomas L. Toth, DSc Bernhard Schmidt, PhD Bryan L. Westerman, PhD Hugh T. Morgan, PhD Sanjay Saini, MD Index terms: Computed
Siemens Computed Tomography
 Siemens Computed Tomography Innovation Leader. The Cosmopolitan Information Topic Waltraud Winter Siemens Copyright Siemens AG 2011. All rights reserved. Page 1 October 2012 Waltraud Winter An Innovation
Siemens Computed Tomography Innovation Leader. The Cosmopolitan Information Topic Waltraud Winter Siemens Copyright Siemens AG 2011. All rights reserved. Page 1 October 2012 Waltraud Winter An Innovation
Cone Beam Reconstruction Jiang Hsieh, Ph.D.
 Cone Beam Reconstruction Jiang Hsieh, Ph.D. Applied Science Laboratory, GE Healthcare Technologies 1 Image Generation Reconstruction of images from projections. textbook reconstruction advanced acquisition
Cone Beam Reconstruction Jiang Hsieh, Ph.D. Applied Science Laboratory, GE Healthcare Technologies 1 Image Generation Reconstruction of images from projections. textbook reconstruction advanced acquisition
First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year
 First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year General Radiology (X-ray) Fluoroscopy Ultrasound (Sonography) Nuclear Medicine P.E.T. imaging Computed Tomography (CT scan) Magnetic
First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year General Radiology (X-ray) Fluoroscopy Ultrasound (Sonography) Nuclear Medicine P.E.T. imaging Computed Tomography (CT scan) Magnetic
RADIOLOGY SERVICES. By Dr Lim Eng Kok 1
 INTRODUCTION RADIOLOGY SERVICES By Dr Lim Eng Kok 1 Radiology is the branch of medicine that deals with the use of ionising (e.g. x- rays and radio-isotopes) and non-ionising radiation (e.g. ultrasound
INTRODUCTION RADIOLOGY SERVICES By Dr Lim Eng Kok 1 Radiology is the branch of medicine that deals with the use of ionising (e.g. x- rays and radio-isotopes) and non-ionising radiation (e.g. ultrasound
Scan Time Reduction and X-ray Scatter Rejection in Dual Modality Breast Tomosynthesis. Tushita Patel 4/2/13
 Scan Time Reduction and X-ray Scatter Rejection in Dual Modality Breast Tomosynthesis Tushita Patel 4/2/13 Breast Cancer Statistics Second most common cancer after skin cancer Second leading cause of cancer
Scan Time Reduction and X-ray Scatter Rejection in Dual Modality Breast Tomosynthesis Tushita Patel 4/2/13 Breast Cancer Statistics Second most common cancer after skin cancer Second leading cause of cancer
Diagnostic Exposure Tracking in the Medical Record
 Diagnostic Exposure Tracking in the Medical Record J.A. Seibert, Ph.D. Department of Radiology Sacramento, California USA Vancouver. British Columbia Relevant disclosures None Learning objectives Understand
Diagnostic Exposure Tracking in the Medical Record J.A. Seibert, Ph.D. Department of Radiology Sacramento, California USA Vancouver. British Columbia Relevant disclosures None Learning objectives Understand
DENTAL Cone beam 3D X-RAY SYSTEM with
 VERSATILE INTUITIVE efficient DENTAL Cone beam 3D X-RAY SYSTEM with dedicated panoramic imaging With thirty years of experience in designing and manufacturing state-of-the-art dental panoramic and tomographic
VERSATILE INTUITIVE efficient DENTAL Cone beam 3D X-RAY SYSTEM with dedicated panoramic imaging With thirty years of experience in designing and manufacturing state-of-the-art dental panoramic and tomographic
Improve your image. ClearVue 350 ultrasound system. The print quality of this copy is not an accurate representation of the original.
 Improve your image ClearVue 350 ultrasound system Not yet available in the U.S. Smart and intuitive The system looks sleek from the outside, but it s what s on the inside that you ll value most. ClearVue
Improve your image ClearVue 350 ultrasound system Not yet available in the U.S. Smart and intuitive The system looks sleek from the outside, but it s what s on the inside that you ll value most. ClearVue
The AAPM does not endorse any products, manufacturers, or suppliers. Nothing in this publication should be interpreted as implying such endorsement.
 DISCLAIMER: This publication is based on sources and information believed to be reliable, but the AAPM, the editors, and the publisher disclaim any warranty or liability based on or relating to the contents
DISCLAIMER: This publication is based on sources and information believed to be reliable, but the AAPM, the editors, and the publisher disclaim any warranty or liability based on or relating to the contents
Computed Tomography (CT) - Chest
 Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Chest Computed tomography (CT) of the chest uses special x-ray equipment to examine abnormalities found in other imaging tests and to help diagnose the
Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Chest Computed tomography (CT) of the chest uses special x-ray equipment to examine abnormalities found in other imaging tests and to help diagnose the
Patient sample criteria for the OPEIR Measures Group are all patients regardless of age, that have a specific CT procedure performed:
 OPTIMIZING PATIENT EXPOSURE TO IONIZING RADIATION (OPEIR) MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW 2016 PQRS OPTIONS F MEASURES GROUPS: 2016 PQRS MEASURES IN OPTIMIZING PATIENT EXPOSURE TO IONIZING RADIATION (OPEIR) MEASURES
OPTIMIZING PATIENT EXPOSURE TO IONIZING RADIATION (OPEIR) MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW 2016 PQRS OPTIONS F MEASURES GROUPS: 2016 PQRS MEASURES IN OPTIMIZING PATIENT EXPOSURE TO IONIZING RADIATION (OPEIR) MEASURES
X-ray (Radiography) - Bone
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Bone Bone x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of any bone in the body. It is commonly used to diagnose fractured bones or
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Bone Bone x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of any bone in the body. It is commonly used to diagnose fractured bones or
GE Healthcare. Optima* CT660
 GE Healthcare Optima* CT660 Your vision of quality care made The Optima CT660 system helps you deliver competent, personalized care that helps fulfill your mission and please your patients. One look at
GE Healthcare Optima* CT660 Your vision of quality care made The Optima CT660 system helps you deliver competent, personalized care that helps fulfill your mission and please your patients. One look at
The new generation in ECG interpretation
 The new generation in ECG interpretation Philips DXL ECG Algorithm, Release PH100B The Philips DXL ECG Algorithm, developed by the Advanced Algorithm Research Center, uses sophisticated analytical methods
The new generation in ECG interpretation Philips DXL ECG Algorithm, Release PH100B The Philips DXL ECG Algorithm, developed by the Advanced Algorithm Research Center, uses sophisticated analytical methods
Exploring the value of EPIQ premium ultrasound
 Exploring the value of EPIQ premium ultrasound Reducing cost of care through more definitive diagnoses Philips EPIQ offers a new level of premium performance ultrasound, and with it the opportunity to
Exploring the value of EPIQ premium ultrasound Reducing cost of care through more definitive diagnoses Philips EPIQ offers a new level of premium performance ultrasound, and with it the opportunity to
REGULATION: QUALITY ASSURANCE PROGRAMS FOR MEDICAL DIAGNOSTIC X-RAY INSTALLATIONS N.J.A.C. 7:28-22
 REGULATION: QUALITY ASSURANCE PROGRAMS FOR MEDICAL DIAGNOSTIC X-RAY INSTALLATIONS N.J.A.C. 7:28-22 New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection Bureau of Radiological Health PO Box 415 Trenton NJ
REGULATION: QUALITY ASSURANCE PROGRAMS FOR MEDICAL DIAGNOSTIC X-RAY INSTALLATIONS N.J.A.C. 7:28-22 New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection Bureau of Radiological Health PO Box 415 Trenton NJ
Improve your image. ClearVue 650 ultrasound system
 Improve your image ClearVue 650 ultrasound system Introducing the ClearVue 650 The Philips ClearVue 650 ultrasound system is as versatile as it is elegant. Use it in a variety of settings for many types
Improve your image ClearVue 650 ultrasound system Introducing the ClearVue 650 The Philips ClearVue 650 ultrasound system is as versatile as it is elegant. Use it in a variety of settings for many types
Patient Prep Information
 Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
A new way of thinking. Philips Sparq regional anesthesia and pain medicine ultrasound system
 A new way of thinking Philips Sparq regional anesthesia and pain medicine ultrasound system Introducing Philips Sparq Breakthrough technology should not make your life more complex. Quite the opposite.
A new way of thinking Philips Sparq regional anesthesia and pain medicine ultrasound system Introducing Philips Sparq Breakthrough technology should not make your life more complex. Quite the opposite.
Ultrasound. Your versatile performer to depend on. Philips ClearVue ultrasound family for women s health care
 Ultrasound ClearVue Your versatile performer to depend on Philips ClearVue ultrasound family for women s health care Over 70 countries More than 5,000 systems Touching 25 million lives every year For one
Ultrasound ClearVue Your versatile performer to depend on Philips ClearVue ultrasound family for women s health care Over 70 countries More than 5,000 systems Touching 25 million lives every year For one
Always in touch. Philips PageWriter TC50 cardiograph
 Always in touch Philips PageWriter TC50 cardiograph Intuitive and efficient You need to fit a lot into every day. That s why we ve fit a lot into the Philips PageWriter TC50 cardiograph. It s an affordable
Always in touch Philips PageWriter TC50 cardiograph Intuitive and efficient You need to fit a lot into every day. That s why we ve fit a lot into the Philips PageWriter TC50 cardiograph. It s an affordable
33-10-06-03. General requirements. 1. Administrative Controls.
 33-10-06-03. General requirements. 1. Administrative Controls. a. Registrant. The registrant shall be responsible for directing the operation of the x-ray systems which have been registered with the department.
33-10-06-03. General requirements. 1. Administrative Controls. a. Registrant. The registrant shall be responsible for directing the operation of the x-ray systems which have been registered with the department.
GE Healthcare. Great treasures in small places. BrightSpeed Elite
 GE Healthcare Great treasures in small places BrightSpeed Elite The BrightSpeed Elite brings you multi-detector CT capabilities with maximum convenience in an ultra-compact design. Built with LightSpeed
GE Healthcare Great treasures in small places BrightSpeed Elite The BrightSpeed Elite brings you multi-detector CT capabilities with maximum convenience in an ultra-compact design. Built with LightSpeed
Role of the Medical Physicist in Clinical Implementation of Breast Tomosynthesis
 Role of the Medical Physicist in Clinical Implementation of Breast Tomosynthesis Bob Liu, Ph.D. Department of Radiology Massachusetts General Hospital And Harvard Medical School Digital Breast Tomosynthesis
Role of the Medical Physicist in Clinical Implementation of Breast Tomosynthesis Bob Liu, Ph.D. Department of Radiology Massachusetts General Hospital And Harvard Medical School Digital Breast Tomosynthesis
Table of Contents. Scan acquisition and user interface basics. Dose modulation and reduction tools. Multi-Slice Detector Geometry
 Table of Contents Scan acquisition and user interface basics Dose modulation and reduction tools Multi-Slice Detector Geometry Image Reconstruction and Display Contrast Media Tools Multi-planar formats
Table of Contents Scan acquisition and user interface basics Dose modulation and reduction tools Multi-Slice Detector Geometry Image Reconstruction and Display Contrast Media Tools Multi-planar formats
Copyright March 1, 2016 by AAPM. All rights reserved.
 DISCLAIMER: TO THE EXTENT ALLOWED BY LOCAL LAW, THIS INFORMATION IS PROVIDED TO YOU BY THE AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF PHYSICISTS IN MEDICINE, A NON-PROFIT ORGANIZATION ORGANIZED TO PROMOTE THE APPLICATION
DISCLAIMER: TO THE EXTENT ALLOWED BY LOCAL LAW, THIS INFORMATION IS PROVIDED TO YOU BY THE AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF PHYSICISTS IN MEDICINE, A NON-PROFIT ORGANIZATION ORGANIZED TO PROMOTE THE APPLICATION
CONTENT SPECIFICATIONS FOR THE FLUOROSCOPY EXAMINATION
 CONTENT SPECIFICATIONS FOR THE FLUOROSCOPY EXAMINATION Publication Date: November 2010 Implementation Date: March 2011 The purpose of the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists Fluoroscopy Examination
CONTENT SPECIFICATIONS FOR THE FLUOROSCOPY EXAMINATION Publication Date: November 2010 Implementation Date: March 2011 The purpose of the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists Fluoroscopy Examination
Procedure Codes. RadConsult provides real-time decision support for physicians who order high-cost imaging procedures RADIATION THERAPY
 Procedure Codes 2011 RadConsult provides real-time decision support for physicians who order high-cost imaging procedures RADIATION THERAPY 2D3D Therapeutic radiology treatment planning; simple 77261 Therapeutic
Procedure Codes 2011 RadConsult provides real-time decision support for physicians who order high-cost imaging procedures RADIATION THERAPY 2D3D Therapeutic radiology treatment planning; simple 77261 Therapeutic
INTRODUCTION. A. Purpose
 New York State Department of Health Bureau of Environmental Radiation Protection Guide for Radiation Safety/Quality Assurance Programs Computed Radiography INTRODUCTION A. Purpose This guide describes
New York State Department of Health Bureau of Environmental Radiation Protection Guide for Radiation Safety/Quality Assurance Programs Computed Radiography INTRODUCTION A. Purpose This guide describes
MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY PhD course in Medical Imaging. Anne Günther Department of Radiology OUS Rikshospitalet
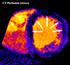 MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY PhD course in Medical Imaging Anne Günther Department of Radiology OUS Rikshospitalet CORONARY CT ANGIOGRAPHY (CTA) Accurate method in the assessment of possible
MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY PhD course in Medical Imaging Anne Günther Department of Radiology OUS Rikshospitalet CORONARY CT ANGIOGRAPHY (CTA) Accurate method in the assessment of possible
Radiation Safety Issues for Radiologic Technologists
 Radiation Safety Issues for Radiologic Technologists Greg Sackett, M.S., CHP Medical Physicist Radiation Worker Risks? 1 Patient Risks? Acute Effects? Delayed Effects? Patient Questions? Radiation Dose
Radiation Safety Issues for Radiologic Technologists Greg Sackett, M.S., CHP Medical Physicist Radiation Worker Risks? 1 Patient Risks? Acute Effects? Delayed Effects? Patient Questions? Radiation Dose
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Computed Tomography to Detect Coronary Artery Calcification File Name: computed_tomography_to_detect_coronary_artery_calcification Origination: 3/1994 Last CAP Review 11/2014 Next
Corporate Medical Policy Computed Tomography to Detect Coronary Artery Calcification File Name: computed_tomography_to_detect_coronary_artery_calcification Origination: 3/1994 Last CAP Review 11/2014 Next
CPT Radiology Codes Requiring Review by AIM Effective 01/01/2016
 CPT Radiology Codes Requiring Review by AIM Effective 01/01/2016 When a service is authorized only one test per group is payable. *Secondary codes or add-on codes do not require preauthorization or separate
CPT Radiology Codes Requiring Review by AIM Effective 01/01/2016 When a service is authorized only one test per group is payable. *Secondary codes or add-on codes do not require preauthorization or separate
Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition
 www.rcr.ac.uk Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition Breast cancer Faculty of Clinical Radiology www.rcr.ac.uk Contents Breast cancer 2 Clinical background 2 Who
www.rcr.ac.uk Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition Breast cancer Faculty of Clinical Radiology www.rcr.ac.uk Contents Breast cancer 2 Clinical background 2 Who
Development of SCENARIA New Version Software MEDIX VOL. 62 P.32 P.35
 Development of SCENAIA New Version Software Takayuki Kadomura Toshio Sakamoto Kana Tanaka Takatsugu Ito Yuuko Nishimura Naomi Maekawa MEDIX VOL. 62 P.32 P.35 Development of SCENAIA New Version Software
Development of SCENAIA New Version Software Takayuki Kadomura Toshio Sakamoto Kana Tanaka Takatsugu Ito Yuuko Nishimura Naomi Maekawa MEDIX VOL. 62 P.32 P.35 Development of SCENAIA New Version Software
SUBCHAPTER 22 QUALITY ASSURANCE PROGRAMS FOR MEDICAL DIAGNOSTIC X-RAY INSTALLATIONS
 Note: This is a courtesy copy and is not the official version of this rule. The official, legally effective version of this rule is available through www.lexisnexic.com/bookstore (Phone: (800) 223-1940).
Note: This is a courtesy copy and is not the official version of this rule. The official, legally effective version of this rule is available through www.lexisnexic.com/bookstore (Phone: (800) 223-1940).
University Children s Hospital Basel
 Cooperation Siemens International Reference Center Pediatric MRI www.siemens.com/skyra University Children s Hospital Basel Siemens International Reference Center Pediatric MRI Answers for life. Partnering
Cooperation Siemens International Reference Center Pediatric MRI www.siemens.com/skyra University Children s Hospital Basel Siemens International Reference Center Pediatric MRI Answers for life. Partnering
TISSUE MIMICKING GEL QUALITY LE PHANTOM SERIES DESIGN. performance the ultrasound labs ofand. icking material has the same attenuation mim-
 QUALITY Tissue Benefits Mimicking of s RMI recognized RMI as the ultrasound standard phantoms for quality are performance the ultrasound labs ofand hospitals, manufacturers. clinics Sophisticated and ultrasound
QUALITY Tissue Benefits Mimicking of s RMI recognized RMI as the ultrasound standard phantoms for quality are performance the ultrasound labs ofand hospitals, manufacturers. clinics Sophisticated and ultrasound
A d v a n c e d 1 2 8
 Advanced 128 SCENARIA Advanced 128 Hitachi Innovation at Work for You. Continuing its commitment to the SCENARIA scalable CT platform, Hitachi introduces cutting-edge 128-slice technology with the SCENARIA
Advanced 128 SCENARIA Advanced 128 Hitachi Innovation at Work for You. Continuing its commitment to the SCENARIA scalable CT platform, Hitachi introduces cutting-edge 128-slice technology with the SCENARIA
Computed Tomography, Head Or Brain; Without Contrast Material, Followed By Contrast Material(S) And Further Sections
 1199SEIU BENEFIT AND PENSION FUNDS High Tech Diagnostic Radiology and s # 1 70336 Magnetic Resonance (Eg, Proton) Imaging, Temporomandibular Joint(S) 2 70450 Computed Tomography, Head Or Brain; Without
1199SEIU BENEFIT AND PENSION FUNDS High Tech Diagnostic Radiology and s # 1 70336 Magnetic Resonance (Eg, Proton) Imaging, Temporomandibular Joint(S) 2 70450 Computed Tomography, Head Or Brain; Without
It understands your everyday
 Ultrasound Affiniti It understands your everyday Philips Affiniti ultrasound system for women s health care Affiniti ultrasound for women s health care Designed to set you ahead and help you stay ahead,
Ultrasound Affiniti It understands your everyday Philips Affiniti ultrasound system for women s health care Affiniti ultrasound for women s health care Designed to set you ahead and help you stay ahead,
Preface to Practice Standards
 0 0 0 0 Preface to Practice Standards A profession s practice standards serve as a guide for appropriate practice. The practice standards define the practice and establish general criteria to determine
0 0 0 0 Preface to Practice Standards A profession s practice standards serve as a guide for appropriate practice. The practice standards define the practice and establish general criteria to determine
In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer
 In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide, accounting for 15% of all new cancer cases. 1 Great strides have
In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide, accounting for 15% of all new cancer cases. 1 Great strides have
Cancer in North Carolina 2013 Report
 Cancer in North Carolina 2013 Report January 2014 Updated by Central Cancer Registry Cancer in North Carolina Purpose Cancer is the leading cause of death in North Carolina even though cancer mortality
Cancer in North Carolina 2013 Report January 2014 Updated by Central Cancer Registry Cancer in North Carolina Purpose Cancer is the leading cause of death in North Carolina even though cancer mortality
Test Request Tip Sheet
 With/Without Contrast CT, MRI Studies should NOT be ordered simultaneously as dual studies (i.e., with and without contrast). Radiation exposure is doubled and both views are rarely necessary. The study
With/Without Contrast CT, MRI Studies should NOT be ordered simultaneously as dual studies (i.e., with and without contrast). Radiation exposure is doubled and both views are rarely necessary. The study
Thinking ahead. Focused on life. REALIZED: GROUNDBREAKING RESOLUTION OF 80 µm VOXEL
 Thinking ahead. Focused on life. REALIZED: GROUNDBREAKING RESOLUTION OF 80 µm VOXEL X-ray ZOOM RECONSTRUCTION Flat Panel Detector (FPD) Automatic Positioning Function For ø 40 x H 40 mm, ø 60 x H 60 mm,
Thinking ahead. Focused on life. REALIZED: GROUNDBREAKING RESOLUTION OF 80 µm VOXEL X-ray ZOOM RECONSTRUCTION Flat Panel Detector (FPD) Automatic Positioning Function For ø 40 x H 40 mm, ø 60 x H 60 mm,
Radiology Management Program
 Highmark Blue Shield Radiology Management Program Prior Authorization Reference Guide* Effective with service dates of April 1, 2006, and beyond *Originally published December 2005; revised January 2007
Highmark Blue Shield Radiology Management Program Prior Authorization Reference Guide* Effective with service dates of April 1, 2006, and beyond *Originally published December 2005; revised January 2007
Acknowledgement. Diagnostic X-Ray Shielding. Nomenclature for Radiation Design Criteria. Shielding Design Goal (Air Kerma):
 Diagnostic X-Ray Shielding Multi-Slice CT Scanners Using NCRP 47 Methodology Melissa C. Martin, M.S., FAAPM, FACR Therapy Physics Inc., Bellflower, CA AAPM Annual Meeting, Orlando, FL Refresher Course
Diagnostic X-Ray Shielding Multi-Slice CT Scanners Using NCRP 47 Methodology Melissa C. Martin, M.S., FAAPM, FACR Therapy Physics Inc., Bellflower, CA AAPM Annual Meeting, Orlando, FL Refresher Course
Rb 82 Cardiac PET Scanning Protocols and Dosimetry. Deborah Tout Nuclear Medicine Department Central Manchester University Hospitals
 Rb 82 Cardiac PET Scanning Protocols and Dosimetry Deborah Tout Nuclear Medicine Department Central Manchester University Hospitals Overview Rb 82 myocardial perfusion imaging protocols Acquisition Reconstruction
Rb 82 Cardiac PET Scanning Protocols and Dosimetry Deborah Tout Nuclear Medicine Department Central Manchester University Hospitals Overview Rb 82 myocardial perfusion imaging protocols Acquisition Reconstruction
QUANTITATIVE IMAGING IN MULTICENTER CLINICAL TRIALS: PET
 Centers for Quantitative Imaging Excellence (CQIE) LEARNING MODULE QUANTITATIVE IMAGING IN MULTICENTER CLINICAL TRIALS: PET American College of Radiology Clinical Research Center v.1 Centers for Quantitative
Centers for Quantitative Imaging Excellence (CQIE) LEARNING MODULE QUANTITATIVE IMAGING IN MULTICENTER CLINICAL TRIALS: PET American College of Radiology Clinical Research Center v.1 Centers for Quantitative
MANCHESTER Lung Cancer Screening Program Dartmouth-Hitchcock Manchester 100 Hitchcock Way Manchester, NH 03104 (603) 695-2850
 LEBANON Lung Cancer Screening Program One Medical Center Drive Lebanon, NH 03756 (603) 650-4400 (866) 966-1601 Toll-free cancer.dartmouth.edu/lungscreening MANCHESTER Lung Cancer Screening Program Dartmouth-Hitchcock
LEBANON Lung Cancer Screening Program One Medical Center Drive Lebanon, NH 03756 (603) 650-4400 (866) 966-1601 Toll-free cancer.dartmouth.edu/lungscreening MANCHESTER Lung Cancer Screening Program Dartmouth-Hitchcock
Emory University RT to Bachelor of Medical Science Degree Medical Imaging
 Emory University RT to Bachelor of Medical Science Degree Medical Imaging Courses: All RT-BMSc students must complete all of the program s core courses and the courses specific to their selected minor
Emory University RT to Bachelor of Medical Science Degree Medical Imaging Courses: All RT-BMSc students must complete all of the program s core courses and the courses specific to their selected minor
