Cornell Institute for Biology Teachers
|
|
|
- Gordon Small
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cornell Institute for Biology Teachers Copyright CIBT This work may be copied by the original recipient from CIBT to provide copies for users working under the direction of the original recipient. All other redistribution of this work without the written permission of the copyright holder is prohibited. Lab review date: 06/26/08 Title: Authors: Appropriate Level: Living Environment Abstract: Dissection of the Pregnant Cow Reproductive Tract Dave Frank, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY Nancy Wright, Honeoye Central School, Honeoye, NY Life Science, Biology, Honors, AP, and Tech prep, depending upon the level of discussion and types of questions asked. 4-Content: 4-Reproduction and Development: 4.1 a,e,f The instructor will dissect an early to mid-pregnant bovine reproductive tract. Data on crown rump length and fetal mass can be collected for use with CIBT s Fetal Development lab. Some appreciation of the form and function of the various organs should be developed by students. This exercise will also serve as a comparative reproduction lab and highlight some of the differences between human and bovine anatomy. Time Required: Teacher preparation time: Minimal. The uterus will need to thaw for about 24 hours before dissection. Plan on thawing time similar to a turkey of equivalent size. It can also be thawed by placing it into a sink full of water. This technique takes about an hour. Or, a final alternative would be to place it into a microwave on defrost. In class time: The exercise as scripted is designed to take 20 to 30 minutes (Time varies based on student involvement and questions). The exercise can be used as an introduction to the CIBT Fetal Development and/or Hormones of the Menstrual Cycle labs. Special Needs: Cow uterus (available from West Hill Biological Resources. See information at CIBT Bovine Uterus Dissection Teacher Section Page 1
2 Teacher Information Preparation Instructions On the day of the dissection, you will want to rinse the uterus (avoid splashing water off the uterus) and lay it out on the tray so that you have oriented yourself. It is good to spend a few minutes locating the major features, since the specimens are not consistent. Materials Large dissection tray or cafeteria tray. Additionally, a dishpan may be useful for catching the amniotic fluid, depending on the size of the uterus. Latex or rubber gloves for all participants handling the specimen One pregnant bovine reproductive tract Scalpel, dissecting needle, dissecting pan and forceps (optional) set of photographic slides of the dissection Space to gather entire class around the tract. Alternately, a video hook-up or flex cam could be used. Flex cams are available through the CIBT Lending Library. Safety Precautions The reproductive tracts used are harvested from cows being slaughtered for human consumption. The cows were not specifically killed to collect the reproductive tracts. No preservatives were used in the preparation of tissues. The cows passed USDA inspection; however, gloves should be used whenever handling animal tissue because accidental contamination of tissue can occur. Students should be instructed not to touch their faces or other clean surfaces with contaminated gloves. If they touched the preparation, they should thoroughly wash their hands with soap afterwards, even if they were wearing gloves. Good lab practices should be followed including: no food or drink in the lab. Helpful Hints It can be helpful to show slides of the dissection in advance to orient students to what they will see. You might want to write the terms you wish to introduce during the demonstration on the blackboard. This will help to give students an outline of what they should be seeing as well as a list of which vocabulary they would be responsible for. Alternately, these terms might be given to students in advance in the form of a glossary CIBT Bovine Uterus Dissection Teacher Section Page 2
3 Terms you might want to include: amnion/amniocentesis cotyledons caruncles DES (diethylstilbestrol) cervix umbilical cord chorion/chorionic villus sampling contralateral corpus luteum ipsilateral CVS prostaglandins myometrium/endometrium Observations This is an outline of topics you might want to discuss with students as you do the demonstration. External: Size and shape of uterus. Contrast human uterine shape (pear) to cow (Y), to pig (much bigger uterine horns). Relate this to number of offspring produced at one time. Animals that have multiple births have bigger uterine horns. Shape and structures of ovaries and their location in relation to the uterus. Can you tell which ovary has ovulated most recently? Corpus luteum. It will be a rounded, yellow body on the ovary. Determine if the implantation was ipsilateral (in the horn on the same side as where ovulation occurred) or contralateral (in the opposite horn from where ovulation occurred). Broad ligaments. They extend wing-like from the sides of the uterus to attach it to either side of the pelvic wall. Ovarian bursa and oviduct. The oviduct can be very difficult to find as it is a very tiny tube (about the width of a piece of yarn). Remind students that fertilization occurs in the oviduct. You may be able to point out the vascularization in this area. This allows for the transfer of prostaglandins from the uterus to the ovaries. Feel the uterus. Can you feel a fetus? How many fetuses are present? (Palpation is the most common way of checking for pregnancy in cows. Be careful if the uterus is not totally thawed, since ice chunks may be mistaken for a fetus.) Is the wall muscular? (Yes.) What type of muscle is present in the uterine wall? (Smooth.) Feel the cervix and examine its structure. Point out the pleated structure of the cervix. Discuss its function. You may be able to point out cervical mucus. Diethylstilbesterol (DES) and its effects on the cervix, role of cervix. Daughters of mothers who used DES have an increased rate of cervical deformities. This includes incompetent cervix that 2008 CIBT Bovine Uterus Dissection Teacher Section Page 3
4 results in the inability to carry a pregnancy to term. Internal: Chorion. Discuss chorionic villus sampling (CVS). This is an alternative to amniocentesis. It can be done earlier in pregnancy, but has an increased risk of miscarriage. Amnion. You will be able to locate this as a bag inside the chorion. Discuss amniocentesis: removal of a sample of the amniotic fluid. The fluid can then be used to make a karyotype for DNA profiling. Thickness of uterine wall and its layers. The myometrium is the muscle wall, the endometrium is the inner, lining layer that gets shed during menses. Caruncles (from the mother) and cotyledons (from the fetus). They are small round discs. The two sides attach together like velcro and function like the discoid placenta in humans. This type of placenta is referred to as a cotyledonary placenta. Embryo/fetus: umbilical cord (2 arteries and 1 vein). Remind students that the fetal circulation is separate from the mother. Note the fetal structures. These will vary depending upon the age of the fetus; hooves, eyes, ribs, the extent of calcification of the bones (they become harder and appear whiter). You may notice many small bumps on the umbilical cord as well as on the internal chorionic membrane. These are structures that did not totally form into cotyledons and are referred to as adventitious plantation. Extensions If you are lucky enough to get twins, you may want to discuss free martins. A free martin is a sterile female calf. This occurs with fraternal twins of the opposite sex. The transfer of male androgens to the female calf causes it to become sterile. This is probably related to the cotilydonary placenta that allows more intermingling of fetal blood. This does not happen in humans due to the presence of a discoid placenta. If the fetus is large enough, students may find it interesting to dissect it. The most obvious difference from a fetal pig will be the presence of the multiple stomachs in the calf. This might be a good alternative for students who object to the dissection of pigs for religious reasons. Ovarian vascular arrangement of the uterine vein and ovarian artery. Compare total mass of the pregnant uterus to the mass of the fetus. This could be compared to human weight gain during pregnancy, i.e., normal weight gain during pregnancy exceeds the mass of the neonate. Measure fetus to estimate fetal age from crown-rump length. Age(days) =2.46 x length(cm) Works for ages 56 to 200 days. Students could do research projects to study the effects of DES, amniocentesis, and karyotyping and CVS. If you plan to do the CIBT Fetal Development lab, be sure to measure and record the crown-rump 2008 CIBT Bovine Uterus Dissection Teacher Section Page 4
5 length as well as the mass of the fetus. Cow and Human Reproductive Anatomy: Differences Uterine Shape: The cow has a uterine body with two distinct uterine horns whereas the human uterus lacks distinct uterine horns. The human uterus resembles an upside down pear. This structural difference is due to the fact that humans typically have single babies, whereas multiple births are more common in cows. Animals such as pigs and mice that have litters of offspring have a Y shaped uterus with more distinct horns. The non-pregnant human uterus is about 7.5 cm long and the cow uterus is about 40 cm long. Type of placenta: Placental shapes vary by species. Humans, rats, mice, and primates have a discoid, or round placenta. Pigs and dogs have a zonary placenta. Ruminants have a cotyledonary placenta. In the ruminants placental transfer occurs at specific predetermined sites. These sites are visible as bumps on the endometrial surface and are called caruncles. There are many caruncles present on the endometrium. The embryonic chorion forms cotyledons and attaches to the caruncles forming a functional unit called a placentome. A normal cow will have placentomes. The placentomes are the functional equivalent of the disc shaped placenta in humans. Unlike humans, where a new placental attachment forms each pregnancy, these same maternal caruncles will be used for each pregnancy. The cotyledons should be visible as round, whitish, textured areas on the chorion, or outer fetal membrane. In older fetuses the chorion will actually be fused with the caruncles and it will be difficult to separate the layers. However, when peeled apart it will appear almost like Velcro. In humans the amnion and chorion fuse; however, in the cow you can see the amnion which will appear like a separate bag inside the chorion. Dairy Cattle Reproduction Domestic cattle breed year round. This is important for a constant milk supply and has been accomplished by selective breeding. Another important feature of dairy cattle reproduction is the lack of lactational anestrus. Dairy farmers strive to have a cow calf at 24 months of age and then once per year after that. To achieve this goal the cow must resume cycling and be bred at 85 days postpartum; this will allow a 305 day lactation to be followed by a 60 day dry period prior to the next calving. This takes excellent nutrition, careful management, and good care of the cows by the farmer. References Bobak, Irene and Jensen, Duncan and Marianne K. Zalar. (1989) Maternity and Gynecologic Care. C. V. Mosby Company, St. Louis, Missouri Hafez, E. S. E. (1993) Reproduction in Farm Animals, 6th ed. Lea & Febiger, Philadelphia, PA Van Tienohoven, Ari. (1983) Reproductive Physiology of Vertebrates, 2nd ed. Cornell University Press, Ithaca, NY 2008 CIBT Bovine Uterus Dissection Teacher Section Page 5
6 Standard 4: Living Environment New York State Learning Standards Pregnant Cow Dissection Key Idea 4: The continuity of life is sustained through reproduction and development Explain how organisms, including humans, reproduce their own kind a. Reproduction and development are necessary for the continuation of any species e. Human reproduction and development are influenced by factors such as gene expression, hormones, and the environment. The reproductive cycle in both males and females is regulated by hormones such as testosterone, estrogen and progesterone. f. The structures and functions of human female reproductive system, as in almost all other mammals, are designed to produce gametes in ovaries, allow for internal fertilization, support the internal development of the embryo and fetus in the uterus, and provide essential materials through the placenta and nutrition through milk for the newborn CIBT Bovine Uterus Dissection Teacher Section Page 6
ANS 3319C Reproductive Physiology and Endocrinology Pregnancy Diagnosis via Rectal Palpation in Cattle and Horses
 ANS 3319C Reproductive Physiology and Endocrinology Pregnancy Diagnosis via Rectal Palpation in Cattle and Horses Objectives 1) To introduce the management practice of rectal palpation for pregnancy diagnosis
ANS 3319C Reproductive Physiology and Endocrinology Pregnancy Diagnosis via Rectal Palpation in Cattle and Horses Objectives 1) To introduce the management practice of rectal palpation for pregnancy diagnosis
Page 1. 1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems
 1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on the diagram below of the female reproductive
1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on the diagram below of the female reproductive
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1
 Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
EVERY LIVING THING has a number of
 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems EVERY LIVING THING has a number of organ systems operating to perform specific functions. If you were to examine one of these systems, you would observe
Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems EVERY LIVING THING has a number of organ systems operating to perform specific functions. If you were to examine one of these systems, you would observe
Reproduction Multiple Choice questions
 Reproduction Multiple Choice questions 1. In mammals that are seasonal breeders, females are receptive only once a year. This is called A) a follicular cycle B) an estrous cycle C) a menstrual cycle D)
Reproduction Multiple Choice questions 1. In mammals that are seasonal breeders, females are receptive only once a year. This is called A) a follicular cycle B) an estrous cycle C) a menstrual cycle D)
Explore and Discover... Human growth. You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Teacher information
 You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Explore and Discover... Teacher information Gallery visited Human Biology Suitable for Key Stage 3 (ages 11 to
You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Explore and Discover... Teacher information Gallery visited Human Biology Suitable for Key Stage 3 (ages 11 to
Science 10-Biology Activity 15 The Development of the Human Embryo
 Science 10-Biology Activity 15 The Development of the Human Embryo 10 Name Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By NOTE: This worksheet is based on material from pages 379-380 in Science
Science 10-Biology Activity 15 The Development of the Human Embryo 10 Name Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By NOTE: This worksheet is based on material from pages 379-380 in Science
Female Reproductive System. Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued
 Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Human Embryonic Development. Human fetal development
 Human Embryonic Development Day 1: 1 st cleavage 1 cell becomes 2 (2-cell stage) Day 2: 2 nd cleavage 4-cell stage Day 3: 6-12 cell stage can test at this stage for genetic diseases if done by IVF Day
Human Embryonic Development Day 1: 1 st cleavage 1 cell becomes 2 (2-cell stage) Day 2: 2 nd cleavage 4-cell stage Day 3: 6-12 cell stage can test at this stage for genetic diseases if done by IVF Day
2. What muscle pulls the testis down into the scrotum during development?
 Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
Course: AG 534 Zoology - Science of Animal Reproduction
 Course: AG 53 Zoology - Science of Animal Reproduction Unit Objective CAERT Lesson Plan Library Unit Problem Area Les son Animal. Plant & Soil Science 1 1,2, 3 Introduction to Animal Science Match terms
Course: AG 53 Zoology - Science of Animal Reproduction Unit Objective CAERT Lesson Plan Library Unit Problem Area Les son Animal. Plant & Soil Science 1 1,2, 3 Introduction to Animal Science Match terms
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
The Menstrual Cycle. Model 1: Ovarian Cycle follicular cells
 The Menstrual Cycle REVIEW questions to complete before starting this POGIL activity 1. Gonads produce both gametes and sex steroid hormones. For the female, name the: A. gonads ovaries B. gametes oocyte/ovum/egg
The Menstrual Cycle REVIEW questions to complete before starting this POGIL activity 1. Gonads produce both gametes and sex steroid hormones. For the female, name the: A. gonads ovaries B. gametes oocyte/ovum/egg
A POWERFUL IN VITRO FERTILIZATION
 A POWERFUL During the past 50 years technological advances in the field of bovine reproduction have led to some dramatic changes in the way cattle look, reproduce, perform, and even taste. Artificial Insemination
A POWERFUL During the past 50 years technological advances in the field of bovine reproduction have led to some dramatic changes in the way cattle look, reproduce, perform, and even taste. Artificial Insemination
1. AMOUNT OF FSH PRESENT
 The Menstrual Cycle Name Date Period PRE-LAB 1. Write down three facts you know about the menstrual cycle. A. B. C. FOLLICULAR PHASE Within the ovaries are located many egg cells. Each egg is enclosed
The Menstrual Cycle Name Date Period PRE-LAB 1. Write down three facts you know about the menstrual cycle. A. B. C. FOLLICULAR PHASE Within the ovaries are located many egg cells. Each egg is enclosed
Avian (chicken) normal ovary
 1. Avian (chicken) normal ovary Page - 1 2. Bovine gravid uterus (fetus and placenta) Page - 2 3. Bovine normal 83-day fetus and placenta Page - 3 4. Bovine normal postpartum uterus Page - 4 5. Bovine
1. Avian (chicken) normal ovary Page - 1 2. Bovine gravid uterus (fetus and placenta) Page - 2 3. Bovine normal 83-day fetus and placenta Page - 3 4. Bovine normal postpartum uterus Page - 4 5. Bovine
Reproduction and its Hormonal Control
 Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Page 1 Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Different mammals have different patterns of reproduction Eg mammals, rats and mice can breed all year round, whereas
Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Page 1 Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Different mammals have different patterns of reproduction Eg mammals, rats and mice can breed all year round, whereas
CHAPTER 23: HUMAN GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT. 1. Define the term fertilization and name the site where fertilization typically occurs.
 1. Define the term fertilization and name the site where fertilization typically occurs. 2. Explain what is meant by capacitation of a sperm. 3. Describe the structure of a secondary oocyte when it is
1. Define the term fertilization and name the site where fertilization typically occurs. 2. Explain what is meant by capacitation of a sperm. 3. Describe the structure of a secondary oocyte when it is
Understanding Fertility
 Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE
 Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, the learner should be able to: Explain the importance of understanding the male and female reproductive
Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, the learner should be able to: Explain the importance of understanding the male and female reproductive
Artificial Insemination in Cattle
 Artificial Insemination in Cattle Introduction This slide show is designed to introduce students to artificial insemination in cattle. However, it is only a brief overview and further training is necessary
Artificial Insemination in Cattle Introduction This slide show is designed to introduce students to artificial insemination in cattle. However, it is only a brief overview and further training is necessary
Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum
 Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum Lesson title: In Vitro Fertilization Grade level: 9-12, with adaptation for younger students Subject area: Life Science Duration: Two class periods Objectives: Students
Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum Lesson title: In Vitro Fertilization Grade level: 9-12, with adaptation for younger students Subject area: Life Science Duration: Two class periods Objectives: Students
4.2 Meiosis. Meiosis is a reduction division. Assessment statements. The process of meiosis
 4.2 Meiosis Assessment statements State that meiosis is a reduction division of a diploid nucleus to form haploid nuclei. Define homologous chromosomes. Outline the process of meiosis, including pairing
4.2 Meiosis Assessment statements State that meiosis is a reduction division of a diploid nucleus to form haploid nuclei. Define homologous chromosomes. Outline the process of meiosis, including pairing
Sexual reproduction in humans
 Sexual reproduction in humans Name: WHY DO HUMANS NEED TO REPRODUCE? The reason humans reproduce is to have children so that our species can continue to exist. Humans reproduce sexually, which means like
Sexual reproduction in humans Name: WHY DO HUMANS NEED TO REPRODUCE? The reason humans reproduce is to have children so that our species can continue to exist. Humans reproduce sexually, which means like
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma)
 Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I
 Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I TOPIC: Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I SUBJECT: Life Skills TARGET AGE RANGE: 9 15 TIME: 45 minutes IDEAL NUMBER OF LEARNERS:
Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I TOPIC: Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I SUBJECT: Life Skills TARGET AGE RANGE: 9 15 TIME: 45 minutes IDEAL NUMBER OF LEARNERS:
Prenatal Testing Special tests for your baby during pregnancy
 English April 2006 [OTH-7750] There are a number of different prenatal (before birth) tests to check the development of your baby. Each test has advantages and disadvantages. This information is for people
English April 2006 [OTH-7750] There are a number of different prenatal (before birth) tests to check the development of your baby. Each test has advantages and disadvantages. This information is for people
Multiple Pregnancy and Birth: Twins, Triplets, and High-order Multiples
 Multiple Pregnancy and Birth: Twins, Triplets, and High-order Multiples A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
Multiple Pregnancy and Birth: Twins, Triplets, and High-order Multiples A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
Artificial insemination with donor sperm
 Artificial insemination with donor sperm Ref. 123 / 2009 Reproductive Medicine Unit Servicio de Medicina de la Reproducción Gran Vía Carlos III 71-75 08028 Barcelona Tel. (+34) 93 227 47 00 Fax. (+34)
Artificial insemination with donor sperm Ref. 123 / 2009 Reproductive Medicine Unit Servicio de Medicina de la Reproducción Gran Vía Carlos III 71-75 08028 Barcelona Tel. (+34) 93 227 47 00 Fax. (+34)
PRODUCERS can choose to use natural
 Artificial Insemination PRODUCERS can choose to use natural or artificial means of breeding their animals. Technology has advanced in the last 30 to 40 years to allow animal producers to use means other
Artificial Insemination PRODUCERS can choose to use natural or artificial means of breeding their animals. Technology has advanced in the last 30 to 40 years to allow animal producers to use means other
The Menstrual Cycle, Hormones and Fertility Treatment
 The Menstrual Cycle, Hormones and Fertility Treatment How many of us understand how our monthly cycle works? Every 28 days (or thereabouts), between the ages of around 13 and 51, a woman will release a
The Menstrual Cycle, Hormones and Fertility Treatment How many of us understand how our monthly cycle works? Every 28 days (or thereabouts), between the ages of around 13 and 51, a woman will release a
Anatomy and Physiology of Human Reproduction. Module 10a
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Endometriosis
 Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system.
 Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Menstruation
 Menstruation WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Menstruation is a normal and healthy part of growing up. The discharge of blood and tissue from the lining of your uterus each
Menstruation WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Menstruation is a normal and healthy part of growing up. The discharge of blood and tissue from the lining of your uterus each
Understanding Animal Reproduction Technology
 Lesson 251c Understanding Animal Reproduction Technology Core Area. Animal Science Unit 250. Genetics and Breeding Topic 251. Fertilization California Academic Standard. Science Grades 9 through 12 Biology/Life
Lesson 251c Understanding Animal Reproduction Technology Core Area. Animal Science Unit 250. Genetics and Breeding Topic 251. Fertilization California Academic Standard. Science Grades 9 through 12 Biology/Life
Reproductive System. from the Human Body System Series. catalog # 3322. Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING
 Reproductive System from the Human Body System Series catalog # 3322 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Reproductive System from the Human Body System Series catalog # 3322 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
OUTCOMES BASED LEARNING MATRIX
 OUTCOMES BASED LEARNING MATRIX Course: BIOL 206 Vertebrate Anatomy and Physiology II Department: Biology Course Description: This is the second part of an introductory course sequence in the comparative
OUTCOMES BASED LEARNING MATRIX Course: BIOL 206 Vertebrate Anatomy and Physiology II Department: Biology Course Description: This is the second part of an introductory course sequence in the comparative
SHEEP EYE DISSECTION PROCEDURES
 SHEEP EYE DISSECTION PROCEDURES The anatomy of the human eye can be better shown and understood by the actual dissection of an eye. One eye of choice for dissection, that closely resembles the human eye,
SHEEP EYE DISSECTION PROCEDURES The anatomy of the human eye can be better shown and understood by the actual dissection of an eye. One eye of choice for dissection, that closely resembles the human eye,
LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-6.3:
 GRADE 6 FETAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 2 FETAL DEVELOPMENT Lesson 2 GRADE 6 LEARNER OUTCOME W-6.3: Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth.
GRADE 6 FETAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 2 FETAL DEVELOPMENT Lesson 2 GRADE 6 LEARNER OUTCOME W-6.3: Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth.
Successful Timed AI Programs: Using Timed AI to Improve Reproductive Efficiency in High Producing Dairy Cattle
 Successful Timed Programs: Using Timed to Improve Reproductive Efficiency in High Producing Dairy Cattle Milo C. Wiltbank, Ph.D. Department of Dairy Science University of Wisconsin, Madison Introduction
Successful Timed Programs: Using Timed to Improve Reproductive Efficiency in High Producing Dairy Cattle Milo C. Wiltbank, Ph.D. Department of Dairy Science University of Wisconsin, Madison Introduction
The Rh Factor: How It Can Affect Your Pregnancy
 The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists f AQ FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS FAQ027 PREGNANCY The Rh Factor: How It Can Affect Your Pregnancy What is the Rh factor? How does a person get the
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists f AQ FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS FAQ027 PREGNANCY The Rh Factor: How It Can Affect Your Pregnancy What is the Rh factor? How does a person get the
The Endocrine System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 9 The Endocrine System Slides 9.1 9.48 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Endocrine System Second messenger
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 9 The Endocrine System Slides 9.1 9.48 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Endocrine System Second messenger
ANS 431 - Reproductive Physiology of Domestic Animals (Spring 2015)
 1 ANS 431 - Reproductive Physiology of Domestic Animals (Spring 2015) Instructor: Dr. Eduardo L. Gastal, DVM, MS, PhD Room: AG 129; Phone: 453-1774; E-mail: egastal@siu.edu Office hours: MWF 11-12 a.m.;
1 ANS 431 - Reproductive Physiology of Domestic Animals (Spring 2015) Instructor: Dr. Eduardo L. Gastal, DVM, MS, PhD Room: AG 129; Phone: 453-1774; E-mail: egastal@siu.edu Office hours: MWF 11-12 a.m.;
GLOSSARY. A Abstinence: having no vaginal, anal, or oral sex. It is the only method that is 100% effective in preventing pregnancy and STI s.
 WOMEN S HEALTH GLOSSARY We encourage you to learn the meanings behind these words for your personal health and to fully understand the words being used during your appointments at the Falcon Health Center.
WOMEN S HEALTH GLOSSARY We encourage you to learn the meanings behind these words for your personal health and to fully understand the words being used during your appointments at the Falcon Health Center.
Age and Fertility. A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES
 Age and Fertility A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
Age and Fertility A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
Each person normally has 23 pairs of chromosomes, or 46 in all. We inherit one chromosome per pair from our mother and one from our father.
 AP Psychology 2.2 Behavioral Genetics Article Chromosomal Abnormalities About 1 in 150 babies is born with a chromosomal abnormality (1, 2). These are caused by errors in the number or structure of chromosomes.
AP Psychology 2.2 Behavioral Genetics Article Chromosomal Abnormalities About 1 in 150 babies is born with a chromosomal abnormality (1, 2). These are caused by errors in the number or structure of chromosomes.
STAGES OF PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT
 STAGES OF PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT College of William and Mary Students for Life 2013 Germinal Period From conception to implantation Terms to Know Conception: the first stage in human development in which
STAGES OF PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT College of William and Mary Students for Life 2013 Germinal Period From conception to implantation Terms to Know Conception: the first stage in human development in which
Facts About Brucellosis
 Facts About Brucellosis 1. What is brucellosis? It is a contagious, costly disease of ruminant (E.g. cattle, bison and cervids) animals that also affects humans. Although brucellosis can attack other animals,
Facts About Brucellosis 1. What is brucellosis? It is a contagious, costly disease of ruminant (E.g. cattle, bison and cervids) animals that also affects humans. Although brucellosis can attack other animals,
How To Collect Blood From A Placenta
 UK Cord Blood and Tissue Procurement Protocol Only to be used by a person who has been trained & licensed by Cells4Life or has an HTA licence Important information In the event of a complicated delivery,
UK Cord Blood and Tissue Procurement Protocol Only to be used by a person who has been trained & licensed by Cells4Life or has an HTA licence Important information In the event of a complicated delivery,
Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: Cervix. Cervix. Nabothian cysts. cervical polyps. leiomyomas. Cervical stenosis
 Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Cervix Nabothian cysts result from chronic cervicitis most
Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Cervix Nabothian cysts result from chronic cervicitis most
Stem Cell Quick Guide: Stem Cell Basics
 Stem Cell Quick Guide: Stem Cell Basics What is a Stem Cell? Stem cells are the starting point from which the rest of the body grows. The adult human body is made up of hundreds of millions of different
Stem Cell Quick Guide: Stem Cell Basics What is a Stem Cell? Stem cells are the starting point from which the rest of the body grows. The adult human body is made up of hundreds of millions of different
Vertebrate Development Chapter 60
 Vertebrate Development Chapter 60 Copyright McGraw-Hill Companies Permission required for reproduction or display Raven - Johnson - Biology: 6th Ed. - All Rights Reserved - McGraw Hill Companies Stages
Vertebrate Development Chapter 60 Copyright McGraw-Hill Companies Permission required for reproduction or display Raven - Johnson - Biology: 6th Ed. - All Rights Reserved - McGraw Hill Companies Stages
Getting Pregnant: The Natural Approach Revealing the Secrets to Increase Your Fertility
 Getting Pregnant: The Natural Approach Revealing the Secrets to Increase Your Fertility Page 1 Contents Introduction 3 Part I Understanding Fertility and Infertility Chapter 1: What is Fertility? 4 - Signs
Getting Pregnant: The Natural Approach Revealing the Secrets to Increase Your Fertility Page 1 Contents Introduction 3 Part I Understanding Fertility and Infertility Chapter 1: What is Fertility? 4 - Signs
Embryo Clay Model Embryogenesis and Stem Cell Development
 Embryo Clay Model Embryogenesis and Stem Cell Development Objective: To identify stages and locations of early embryonic development To see at what point stem cells are totipotent, pluripotent, and multipotent
Embryo Clay Model Embryogenesis and Stem Cell Development Objective: To identify stages and locations of early embryonic development To see at what point stem cells are totipotent, pluripotent, and multipotent
INTRODUCTION TO ARTIFICIAL INSEMINATION APICHAI POONCHAI D.V.M.
 INTRODUCTION TO ARTIFICIAL INSEMINATION APICHAI POONCHAI D.V.M. In natural mating a bull mounts a cow & ejuculates his semen in her vagina INTRODUCTION In A.I. Semen is collected from a bull in an artificial
INTRODUCTION TO ARTIFICIAL INSEMINATION APICHAI POONCHAI D.V.M. In natural mating a bull mounts a cow & ejuculates his semen in her vagina INTRODUCTION In A.I. Semen is collected from a bull in an artificial
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Hormone Therapy
 Hormone Therapy WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 At menopause, a woman's body makes less estrogen and she stops having menstrual periods. This is a natural stage in a woman's
Hormone Therapy WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 At menopause, a woman's body makes less estrogen and she stops having menstrual periods. This is a natural stage in a woman's
Reproductive System. Anatomy of Male Reproductive System
 Function: producing offspring Reproductive System propagation of the species in terms of evolution the only reason all the other systems exist only major system that doesn t work continuously only activated
Function: producing offspring Reproductive System propagation of the species in terms of evolution the only reason all the other systems exist only major system that doesn t work continuously only activated
SYNCHRONIZATION OF CATTLE
 UNDER ESTRUS SYNCHRONIZATION OF CATTLE FS921C Robin Salverson, Extension Livestock Educator, Harding County, and George Perry, Extension Beef Reproduction and Management Specialist Reproductive failure
UNDER ESTRUS SYNCHRONIZATION OF CATTLE FS921C Robin Salverson, Extension Livestock Educator, Harding County, and George Perry, Extension Beef Reproduction and Management Specialist Reproductive failure
6. Pig Dissection I. BI102. B.K. Penney
 6. Pig Dissection I BACKGROUND To study the anatomy of vertebrates, we will be dissecting fetal pigs. Material for these labs is essentially from Term 1. The context for BI02 is that I want you to understand
6. Pig Dissection I BACKGROUND To study the anatomy of vertebrates, we will be dissecting fetal pigs. Material for these labs is essentially from Term 1. The context for BI02 is that I want you to understand
Human Embryology. Weeks 1-4
 Human Embryology Weeks 1-4 Week 1 Fertilisation to Implantation For this presentation embryonic age will be expressed as days or weeks from fertilisation. On this basis human pregnancy lasts about 266±3
Human Embryology Weeks 1-4 Week 1 Fertilisation to Implantation For this presentation embryonic age will be expressed as days or weeks from fertilisation. On this basis human pregnancy lasts about 266±3
STUDENT S WORKSHEETS. Eva M. Zamudio Zamudio
 STUDENT S WORKSHEETS January April 2009 HUMAN LIFE CYCLE HANDOUT 1 1. Write the name of each stage in the right order: retirement adolescence babyhood adulthood - childhood 2. What stage does it belong
STUDENT S WORKSHEETS January April 2009 HUMAN LIFE CYCLE HANDOUT 1 1. Write the name of each stage in the right order: retirement adolescence babyhood adulthood - childhood 2. What stage does it belong
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. 7 th edition Marieb, Elaine, 2003. Chapters 10-11. Lab Manual, 2 nd edition and coloring book, 7 th edition
 Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
Studies on cortisol and prolactin concentrations in umbilical cord blood, amniotic fluid, maternal blood, and breast milk related to perinatal factors
 Studies on cortisol and prolactin concentrations in umbilical cord blood, amniotic fluid, maternal blood, and breast milk related to perinatal factors Summary of the thesis Doctoral Course of Applied Life
Studies on cortisol and prolactin concentrations in umbilical cord blood, amniotic fluid, maternal blood, and breast milk related to perinatal factors Summary of the thesis Doctoral Course of Applied Life
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System
 Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface) sperm producing organs testes ducts that
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface) sperm producing organs testes ducts that
Why is prematurity a concern?
 Prematurity What is prematurity? A baby born before 37 weeks of pregnancy is considered premature. Approximately 12% of all babies are born prematurely. Terms that refer to premature babies are preterm
Prematurity What is prematurity? A baby born before 37 weeks of pregnancy is considered premature. Approximately 12% of all babies are born prematurely. Terms that refer to premature babies are preterm
Assisted Reproductive Technologies at IGO
 9339 Genesee Avenue, Suite 220 San Diego, CA 92121 858 455 7520 Assisted Reproductive Technologies at IGO Although IGO no longer operates an IVF laboratory or program as such, we work closely with area
9339 Genesee Avenue, Suite 220 San Diego, CA 92121 858 455 7520 Assisted Reproductive Technologies at IGO Although IGO no longer operates an IVF laboratory or program as such, we work closely with area
About the Uterus. Hysterectomy may be done to treat conditions that affect the uterus. Some reasons a hysterectomy may be needed include:
 Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
In - Vitro Fertilization Handbook
 In - Vitro Fertilization Handbook William F. Ziegler, D.O. Medical Director Scott Kratka, ELD, TS Embryology Laboratory Director Lauren F. Lucas, P.A.-C, M.S. Physician Assistant Frances Cerniak, R.N.
In - Vitro Fertilization Handbook William F. Ziegler, D.O. Medical Director Scott Kratka, ELD, TS Embryology Laboratory Director Lauren F. Lucas, P.A.-C, M.S. Physician Assistant Frances Cerniak, R.N.
bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks odyworks bodyworks bodywor bodyworks yworks bodyworks bodyworks bodywork bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks odyworks body
 Bodyworks Your guide to understanding reproduction orksody odyworks body bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks dyworks ork bodywor odyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodywork
Bodyworks Your guide to understanding reproduction orksody odyworks body bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks dyworks ork bodywor odyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodywork
Unit B: Understanding Animal Reproduction. Lesson 3: Understanding Animal Reproduction Technology
 Unit B: Understanding Animal Reproduction Lesson 3: Understanding Animal Reproduction Technology Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following
Unit B: Understanding Animal Reproduction Lesson 3: Understanding Animal Reproduction Technology Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following
Determining Pregnancy in Cattle
 B-1077 Determining Pregnancy in Cattle Texas Agricultural Extension Service Zerle L. Carpenter, Director The Texas A&M University System College Station, Texas Acknowledgments The authors express appreciation
B-1077 Determining Pregnancy in Cattle Texas Agricultural Extension Service Zerle L. Carpenter, Director The Texas A&M University System College Station, Texas Acknowledgments The authors express appreciation
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography
 Semester 1 Orientation - 101 This class is an introduction to sonography which includes a basic anatomy review, introduction to sonographic scanning techniques and physical principles. This curriculum
Semester 1 Orientation - 101 This class is an introduction to sonography which includes a basic anatomy review, introduction to sonographic scanning techniques and physical principles. This curriculum
First Trimester Screening for Down Syndrome
 First Trimester Screening for Down Syndrome What is first trimester risk assessment for Down syndrome? First trimester screening for Down syndrome, also known as nuchal translucency screening, is a test
First Trimester Screening for Down Syndrome What is first trimester risk assessment for Down syndrome? First trimester screening for Down syndrome, also known as nuchal translucency screening, is a test
Proceedings, Applied Reproductive Strategies in Beef Cattle September 11 and 12, 2007, Billings, Montana NEW TECHNOLOGIES FOR REPRODUCTION IN CATTLE
 Proceedings, Applied Reproductive Strategies in Beef Cattle September 11 and 12, 2007, Billings, Montana NEW TECHNOLOGIES FOR REPRODUCTION IN CATTLE George E. Seidel, Jr. Animal Reproduction and Biotechnology
Proceedings, Applied Reproductive Strategies in Beef Cattle September 11 and 12, 2007, Billings, Montana NEW TECHNOLOGIES FOR REPRODUCTION IN CATTLE George E. Seidel, Jr. Animal Reproduction and Biotechnology
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot
 Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
CONFIDENT CODING FOR OB/GYN CONFIDENT CODING FOR OB/GYN
 Arlene J. Smith, CPC AAPC National Advisory Board 2007-2009 1 So when exactly does the global period start? Unraveling the confusion in antepartum care coding Correct coding for multiple gestations! Vaginal
Arlene J. Smith, CPC AAPC National Advisory Board 2007-2009 1 So when exactly does the global period start? Unraveling the confusion in antepartum care coding Correct coding for multiple gestations! Vaginal
FAMILY LIFE EDUCATION ACPS Fifth Grade
 Table of Contents UNIT I FAMILY...2 Relatives and Family Friends...2 Similarities and Differences among Families...2 UNIT II PERSONAL AND SEXUAL SAFETY... 3 Sexual Safety Good and Bad Touching... 3 UNIT
Table of Contents UNIT I FAMILY...2 Relatives and Family Friends...2 Similarities and Differences among Families...2 UNIT II PERSONAL AND SEXUAL SAFETY... 3 Sexual Safety Good and Bad Touching... 3 UNIT
To familiarise students with the stages in the development of a human fetus.
 Bumps and Babies Lesson aim To familiarise students with the stages in the development of a human fetus. 3 Lesson objectives Students will be expected to: Work effectively within a group. Discuss within
Bumps and Babies Lesson aim To familiarise students with the stages in the development of a human fetus. 3 Lesson objectives Students will be expected to: Work effectively within a group. Discuss within
FERTILITY AND AGE. Introduction. Fertility in the later 30's and 40's. Am I fertile?
 FERTILITY AND AGE Introduction Delaying pregnancy is a common choice for women in today's society. The number of women in their late 30s and 40s attempting pregnancy and having babies has increased in
FERTILITY AND AGE Introduction Delaying pregnancy is a common choice for women in today's society. The number of women in their late 30s and 40s attempting pregnancy and having babies has increased in
Guidance For Research Involving Human Embryonic Stem Cells, Germ Cells, And Cells Obtained From Cord Blood
 Guidance For Research Involving Human Embryonic Stem Cells, Germ Cells, And Cells Obtained From Cord Blood Supreme Council of Health Department of Research Guidance Regarding Research Involving Human Embryonic
Guidance For Research Involving Human Embryonic Stem Cells, Germ Cells, And Cells Obtained From Cord Blood Supreme Council of Health Department of Research Guidance Regarding Research Involving Human Embryonic
Sex for the purposes of this class refers to 4 components
 Sex for the purposes of this class refers to 4 components Gonadal sex Gonads or where gametes are produced by meiosis Somatic sex Somatic cells are cells that undergo mitosis. They can be divided into
Sex for the purposes of this class refers to 4 components Gonadal sex Gonads or where gametes are produced by meiosis Somatic sex Somatic cells are cells that undergo mitosis. They can be divided into
THE WHY, HOW-TO, AND COST OF PROGRAMED AI BREEDING OF DAIRY COWS. J. S. Stevenson
 Dairy Day 1998 THE WHY, HOW-TO, AND COST OF PROGRAMED AI BREEDING OF DAIRY COWS J. S. Stevenson Summary Management of the estrous cycle is now more practical than it was a decade ago because of our understanding
Dairy Day 1998 THE WHY, HOW-TO, AND COST OF PROGRAMED AI BREEDING OF DAIRY COWS J. S. Stevenson Summary Management of the estrous cycle is now more practical than it was a decade ago because of our understanding
Acknowledgment The authors thank John R. Beverly, former Professor and Associate Vice Chancellor of the Agriculture Program at Texas A&M University,
 B-1077 11/08 Acknowledgment The authors thank John R. Beverly, former Professor and Associate Vice Chancellor of the Agriculture Program at Texas A&M University, for his work on the original B-1077 publication.
B-1077 11/08 Acknowledgment The authors thank John R. Beverly, former Professor and Associate Vice Chancellor of the Agriculture Program at Texas A&M University, for his work on the original B-1077 publication.
D. Pant, J.T. Choi, J.S. Luther, C. Navanukraw, P. Borowicz, R.M. Weigl, J. D. Kirsch, K.C.Kraft, D.A. Redmer, L.P. Reynolds and A.T.
 Comparison of Gravid Uterine Parameters in Naturally Bred Ewes and Ewes after Transfer of In Vitro Produced Embryos, and in Single, Twin and Triplet Pregnancies. D. Pant, J.T. Choi, J.S. Luther, C. Navanukraw,
Comparison of Gravid Uterine Parameters in Naturally Bred Ewes and Ewes after Transfer of In Vitro Produced Embryos, and in Single, Twin and Triplet Pregnancies. D. Pant, J.T. Choi, J.S. Luther, C. Navanukraw,
Organ Systems Overview
 E x e r c i s e 2 Organ Systems Overview Time Allotment: 1½ hours (rat dissection: 1 hour; if performing reproductive system dissection, ½ hour each for male and female; dissectible human torso model:
E x e r c i s e 2 Organ Systems Overview Time Allotment: 1½ hours (rat dissection: 1 hour; if performing reproductive system dissection, ½ hour each for male and female; dissectible human torso model:
Ovarian Cysts in Dairy Cattle
 AS-451-W Reviewed 2001 Purdue University Cooperative Extension Service West Lafayette, IN 47907 Ovarian Cysts in Dairy Cattle R. D. Allrich, Department of Animal Sciences Purdue University, West Lafayette,
AS-451-W Reviewed 2001 Purdue University Cooperative Extension Service West Lafayette, IN 47907 Ovarian Cysts in Dairy Cattle R. D. Allrich, Department of Animal Sciences Purdue University, West Lafayette,
From Menses to Menopause: How Hormones Can Affect Blood Glucose Levels. Christine Day, RN, MS, CNS-BC Lake Superior College
 From Menses to Menopause: How Hormones Can Affect Blood Glucose Levels Christine Day, RN, MS, CNS-BC Lake Superior College Overview Will review hormonal changes over the female lifespan Discuss the effects
From Menses to Menopause: How Hormones Can Affect Blood Glucose Levels Christine Day, RN, MS, CNS-BC Lake Superior College Overview Will review hormonal changes over the female lifespan Discuss the effects
A Guide to Hysteroscopy. Patient Education
 A Guide to Hysteroscopy Patient Education QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ABOUT HYSTEROSCOPY Your doctor has recommended that you have a procedure called a hysteroscopy. Naturally, you may have questions about
A Guide to Hysteroscopy Patient Education QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ABOUT HYSTEROSCOPY Your doctor has recommended that you have a procedure called a hysteroscopy. Naturally, you may have questions about
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System
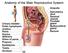 Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface)
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface)
OVARIAN CYSTS. Types of Ovarian Cysts There are many types of ovarian cysts and these can be categorized into functional and nonfunctional
 OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
Reproduction in Mammals
 Reproduction in Mammals A. Introduction 1. The organs of the male and female reproductive systems ensure the continuation of the species. 2. They do this by producing gametes and by providing a method
Reproduction in Mammals A. Introduction 1. The organs of the male and female reproductive systems ensure the continuation of the species. 2. They do this by producing gametes and by providing a method
Balanced. translocations. rarechromo.org. Support and Information
 Support and Information Rare Chromosome Disorder Support Group, G1, The Stables, Station Rd West, Oxted, Surrey. RH8 9EE Tel: +44(0)1883 723356 info@rarechromo.org I www.rarechromo.org Balanced Unique
Support and Information Rare Chromosome Disorder Support Group, G1, The Stables, Station Rd West, Oxted, Surrey. RH8 9EE Tel: +44(0)1883 723356 info@rarechromo.org I www.rarechromo.org Balanced Unique
Human Growth and Reproduction
 Human Growth and Reproduction Sperm reach ovum and cluster around it Only one sperm is allowed to penetrate egg When the sperm penetrates the egg, the egg immediately releases a chemical creating a hard
Human Growth and Reproduction Sperm reach ovum and cluster around it Only one sperm is allowed to penetrate egg When the sperm penetrates the egg, the egg immediately releases a chemical creating a hard
Abortion and Stem Cell Debate Background Information
 Abortion and Stem Cell Debate Background Information 1 Fetal Development 2 Terms Syngamy: fusion of two gametes in fertilization Zygote: name of the cell resulting from fertilization until it implants
Abortion and Stem Cell Debate Background Information 1 Fetal Development 2 Terms Syngamy: fusion of two gametes in fertilization Zygote: name of the cell resulting from fertilization until it implants
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Birth Control Pills
 Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle
 Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
ARTIFICIAL INSEMINATION
 ARTIFICIAL INSEMINATION Artificial insemination is the deposition of male reproductive cells (spermatozoa) in the female reproductive tract by mechanical means rather than by natural mating. The success
ARTIFICIAL INSEMINATION Artificial insemination is the deposition of male reproductive cells (spermatozoa) in the female reproductive tract by mechanical means rather than by natural mating. The success
BOER GOAT EMBRYO TRANSFER
 BOER GOAT EMBRYO TRANSFER Good management No shortcuts PLAN AHEAD AVOID STRESS Some examples of how stress is induced are: Mixing groups or individual animals together that have not previously been together.
BOER GOAT EMBRYO TRANSFER Good management No shortcuts PLAN AHEAD AVOID STRESS Some examples of how stress is induced are: Mixing groups or individual animals together that have not previously been together.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
 Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a disorder that affects as many as 5 10% of women. PCOS has three key features: 1) high levels of hormones called androgens; 2) irregular menstrual
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a disorder that affects as many as 5 10% of women. PCOS has three key features: 1) high levels of hormones called androgens; 2) irregular menstrual
