Genetic Testing for Hearing Loss
|
|
|
- Shana Parker
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Genetic Testing for Hearing Loss S H O B A N A K U B E N D R A N, M B B S, M S, C G C G E N E T I C C O U N S E L O R A S S T P R O F E S S O R D E P T O F P E D I A T R I C S K U S M - W
2 Objectives Indications for a genetic evaluation for hearing loss Common genetic syndromes associated with hearing loss Benefits and limitations of genetic testing for hearing loss Genetic counseling for hearing loss
3 Why have a genetic evaluation? Why did it happen? Can it happen again? Will the hearing loss be stable or get worse? Syndromic or Non syndromic?
4 Etiology of Hearing Loss ACMG 2002 Genetic Evaluation Guidelines
5 Genes interact with the environment Completely genetic Mix of genetic And environmental Completely environmental Connexin 26 Usher syndrome Aminoglycoside Induced HL Noise Induced HL Meningitis Alcohol exposure TORCH CMV
6 40% of deafness is non-genetic BUT Teratogens known genetic susceptibility Congenital/perinatal infections not all that are exposed have effects; genetic variation? Prematurity hyperbilirubinemia low birthweight NICU, ventilation what is the underlying cause of LBW, neonatal distress? Ototoxic medications known genetic susceptibility Meningitis may be predisposed by anatomical abnormality
7 Terminology DFN (for DeaFNess) DFNA - autosomal dominant DFNB - autosomal recessive DFN - X-linked (e.g. DFNB1 = recessive hearing loss gene #1)
8 Genetic Causes of HL Genetic Syndromic 30% Nonsyndromic 70% Autosomal Recessive 75-80% Autosomal Dominant 20-25% X-linked or Mitochondrial 1-2% DFNB1/Connexin 26 50% Other DFNB 50%
9 Autosomal Recessive Nonsyndromic Hearing Loss Congenital severe to profound type is most common Genetic studies have identified >60 different loci, with genes identified for only some of the loci 90% born to parents with normal hearing
10 Genetic Causes of HL Genetic Syndromic 30% Nonsyndromic 70% Autosomal Recessive 75-80% Autosomal Dominant 20-25% X-linked or Mitochondrial 1-2% DFNB1/Connexin 26 50% Other DFNB 50%
11 DFNB1 GJB2 gene codes for Connexin 26 protein GJB6 gene codes for Connexin 30 protein Most common cause of nonsyndromic, autosomal recessive, congenital hearing loss (50%) Overall Connexin 26 mutations accounts for 20% of patients with nonsyndromic sensorineural hearing loss 98% of individuals with DFNB1 have two GJB2 mutations 2% have one GJB2 mutation and one GJB6 mutation
12 Compound Heterozygosity (Digeneic Inheritance) CX 26 CX 26 CX 30 CX 30 Hearing loss Hearing loss Hearing loss
13 Connexin 26 (DFNB1 / GJB2) Phenotype non-syndromic normal vision and vestibular function non-progressive (2/3) hearing loss = mild to profound with intra- and inter- familial variability few kindreds are progressive and asymmetric 2 common mutations : 35delG (85% N. Europeans) 167delT (Jewish) 235delC mutation (Chinese) Carrier rate ~3% of Caucasians 1 in % of Ashkenazi Jewish Epidemiology 1/2500-1/5000
14 DFNB1 testing strategy First screen for 35delG deletion in Connexin 26 If negative or find only one mutation DNA sequencing of Connexin 26 DFNB1 is not complete unless screening for the splice site mutation (exon 1 of GJB2) and the large GJB6-containing deletions is included If DNA sequencing of Connexin 26 is normal Targeted mutation analysis of Connexin 30 Two large deletions GJB6-D13S1830 and GJB6-D13S1854 GJB6-D13S1830 is the most common GJB6 mutation associated with DFNB1
15 Genetic Causes of HL Genetic Syndromic 30% Nonsyndromic 70% Autosomal Recessive 75-80% Autosomal Dominant 20-25% X-linked or Mitochondrial 1-2% DFNB1/Connexin 26 50% Other DFNB 50%
16 List of autosomal recessive hearing loss loci Locus Name Gene Symbol Onset Type DFNB1 GJB2 Prelingual 1 Usually stable GJB6 DFNB2 MYO7A Prelingual, postlingual Unspecified DFNB3 MYO15 Prelingual Severe to profound; stable DFNB4 SLC26A4 Prelingual, postlingual Stable, progressive DFNB6 TMIE Prelinqual Severe to profound; stable DFNB7/11 TMC1 DFNB8/10 TMPRSS3 Postlingual 2, Prelingual Progressive, stable DFNB9 OTOF Prelingual Usually severe to profound; stable DFNB12 CDH23 Prelingual Severe to profound; stable DFNB16 STRC Prelingual Severe to profound; stable DFNB18 USH1C Prelingual Severe to profound; stable DFNB21 TECTA Prelingual Severe to profound; stable DFNB22 OTOA Prelingual Severe to profound; stable DFNB23 PCDH15 Prelingual Severe to profound; stable DFNB24 RDX Prelingual Severe to profound; stable DFNB25 GRXCR1 Prelingual Moderate to profound; progressive DFNB28 TRIOBP Prelingual Severe to profound; stable DFNB29 CLDN14 Prelingual Severe to profound; stable DFNB30 MYO3A Prelingual Severe to profound; stable DFNB31 DFN31 Prelingual DFNB32/82 GPSM2 Prelingual Severe to profound; stable DFNB35 ESRRB Unknown Severe to profound DFNB36 ESPN Prelingual DFNB37 MYO6 Prelingual DFNB39 HGF Prelingual Severe to profound; downsloping DFNB49 MARVELD2 Prelingual Moderate to profound; stable DFNB53 COL11A2 Prelingual Severe to profound; stable DFNB59 PJVK Prelingual Severe to profound; stable DFNB61 SLC26A5 Prelingual Severe to profound; stable DFNB63 LRTOMT Prelingual Severe to profound; stable DFNB67 LHFPL5 Prelingual Severe to profound; stable DFNB73 BSND Prelingual Severe to profound; stable DFNB77 LOXHD1 Postlingual Moderate to profound; progressive DFNB79 TPRN Prelingual Severe to Profound; stable DFNB84 PTPRQ Prelingual Moderate to profound; progressive
17 Genetic Causes of HL Genetic Syndromic 30% Nonsyndromic 70% Autosomal Recessive 75-80% Autosomal Dominant 20-25% X-linked or Mitochondrial 1-2% DFNB1/Connexin 26 50% Other DFNB 50%
18 Autosomal Dominant NSHL Usually post-lingual Usually progressive (onset in 2nd or 3rd decades) Accounts for 15% of cases of nonsyndromic hearing loss In general, onset is postlingual and is progressive Some forms also include vestibular dysfunction Over 40 genes have been identified Many found in only one or two families
19 Genetic Causes of HL Genetic Syndromic 30% Nonsyndromic 70% Autosomal Recessive 75-80% Autosomal Dominant 20-25% X-linked or Mitochondrial 1-2% DFNB1/Connexin 26 50% Other DFNB 50%
20 Mitochondrial gene associated with HL 12S rrna gene mutation A1555G confers a sensitivity to aminoglycosides HL within days of even a single dose 40% of those not exposed develop HL by 30 years of age Isolated sensorineural hearing loss. Variable age of onset: congenital - 7th decade. Flat, sloping or high frequency hearing loss. Progressive hearing loss. Mild-to-profound sensorineural hearing loss with or without a history of aminoglycoside exposure, or Hearing loss that appears to be consistent with maternal inheritance.
21 Genetic Causes of HL Genetic Syndromic 30% Nonsyndromic 70% Autosomal Recessive 75-80% Autosomal Dominant 20-25% X-linked or Mitochondrial 1-2% DFNB1/Connexin 26 50% Other DFNB 50%
22 Syndromic Hearing Loss Is more than one organ system involved? Are there similar issues in family members? Is there a distinctive or characteristic appearance?
23 Genetic Syndromes with Hearing Loss as a Major Feature Alport Branchial-Oto-Renal Jervell and Lange-Nielsen Neurofibromatosis type 2 Pendred Stickler syndrome Waardenburg
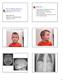
24 Branchio-oto-renal Syndrome (BOR) Estimated to occur in 2% of children with congenital hearing loss Ear: pits/tags, abnormalities of the external, middle, or inner ear Hearing loss: can be mild to profound, sensorineural, conductive, or mixed Branchial arch: sinus or cyst in neck Renal: agenesis, hypoplasia, or dysgenesis Patient picture
25 Characterized by cleft palate, micrognathia, severe myopia, retinal detachments, cataracts, short stature, and hypermobility SNHL in about 40%, conductive can also be seen Most autosomal dominant, although can be recessive Mutations in one of four collagen genes (COL2A1) At risk for retinal detachment, arthritis Stickler Syndrome
26 4 5 Thick glasses, hearing aids, joint prob Glasses Vision prob Deaf in one ear Seizures Accident HL, vision prob Epilepsy Detached retina Deaf in one ear 2 17m HL, cataract Dev delay
27 Waardenburg Syndrome Accounts for 3% of childhood hearing impairment Incidence is 1 in 4000 live births AD PAX 3 gene mutation May have unilateral or bilateral SNHL Pigmentary features include: white forelock heterochromia irides premature graying vitiligo Craniofacial features include: dystopia canthorum (lateral displacement of inner canthus of eye) broad nasal root and synophrys Patient picture (people may dye their hair therefore ask specifically about white forelock)
28 Alport Syndrome Hearing, vision, and renal involvement Blood in urine (hematuria) often first symptom Typically progresses to renal failure HL may not become evident until the second decade of life, 80-90% by age 40 Anterior lenticonus - eye finding 85% of cases are X-linked, with some dominant and recessive families
29 Neurofibromatosis Type 2 Affects 1 in 40,000 Hallmark feature is vestibular schwannoma - tumor on 8th nerve Symptoms include tinnitis, hearing loss, balance problems, occasional facial palsy Other features include tumors on brain or spinal cord, early cataracts Autosomal dominant, 50% de novo
30 Usher Syndrome Prevalence of 3.5 per 100,000 population; 1 in 70 carrier frequency Autosomal recessive 11 loci, 2 Association of hearing loss with retinitis pigmentosa At least 11 loci 2 identified Progressive vision loss - night blindness and loss of peripheral vision noted in second decade Electroretinography can identify abnormalities in younger children - Three subtypes Type 1: congenital bilateral profound HL and abnormal vestibular function Type 2: moderate HL and normal vestibular function Type 3: progressive HL and progressive loss of vestibular function
31 Pendred Syndrome ~1/7500 Congenital severeprofound SNHL Enlarged vestibular aqueduct or Mondini dysplasia on temporal bone CT Thyroid goiter - develops in adolescence or adulthood Autosomal recessive SLC26A4 gene Mutations in this gene may cause up to 5-10% of congenital hearing loss Patient picture
32 Jervell and Lange-Nielsen Syndrome Profound SNHL and syncopal episodes resulting from cardiac conduction defect ECG reveals large T waves and prolonged QT interval Can result in sudden death ECG should be done on all children with uncertain etiology of hearing loss Autosomal recessive inheritance fainting long QT 3 6 sudden death JLN
33 Evaluation for Syndromic Hearing Loss Family history Three generation family history Age onset hearing loss Description of hearing loss Heritable / non-heritable Conductive / neurosensory / mixed Unilateral / bilateral Symmetric / asymmetric Congenital / acquired Progressive / stable / fluctuant Isolated / syndromic
34 Evaluation for Syndromic Hearing Loss Visual anomalies : heterochromia, retinitis pigmentosa, myopia, retinal detachment, early cataracts, night blindness Dysmorphology: preauricular pits, ear anomalies, cleft lip/palate, dental anomalies, pits, lumps or fistulae on the neck Endocrine work up: thyroid disorders and diabetes Cardiac work up: syncope, sudden death, prolonged QT interval, fainting spells, CHD Renal abnormalities hematuria, proteinuria, structural defects Skin abnormalities abnormal pigmentation, premature graying, white forelock, dry skin/keratoderma Bone: arthritis, loose joints, joint swelling, dislocation, frequent broken bones
35 Medical Genetic Evaluation of Hearing Loss Smith et al 1998 Stage 1 o Medical Genetics o Audiology o Otolaryngology Stage 2 o Vestibular o Ophthalmology o CT of temporal bones o Urinalysis/serum creatinine o Serology Stage 3 o Perchlorate discharge (if CT abnormal) o DNA o Electrocardiogram o Electroretinogram
36 Genetic counseling for hearing loss "In contrast to the medical model which considers deafness to be a pathologic condition, many deaf people do not consider themselves to be handicapped but define themselves as being part of a distinct cultural group with its own language, customs, and beliefs. Strategies for effective genetic counseling to deaf people include the recognition that perception of risk is very subjective and that some deaf individuals may prefer to have deaf children." [Arnos et al 1991]
37 References Medical genetic evaluation for the etiology of hearing loss in children. Smith SD, Kimberling WJ, Schaefer GB, Horton MB, Tinley ST. J Commun Disord Sep-Oct;31(5):371-88; quiz Review. Genetics Evaluation Guidelines for the Etiologic Diagnosis of Congenital Hearing Loss. Genetic Evaluation of Congenital Hearing Loss Expert Panel. ACMG statement. ACMG.Genet Med May-Jun;4(3): Genetests.org A prospective, longitudinal study of the impact of GJB2/GJB6 genetic testing on the beliefs and attitudes of parents of deaf and hard-of-hearing infants. Palmer CG, Martinez A, Fox M, Zhou J, Shapiro N, Sininger Y, Grody WW, Schimmenti LA. Am J Med Genet A Jun;149A(6): Genetic counseling of the deaf. Medical and cultural considerations.arnos KS, Israel J, Cunningham M. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;630: Deaf adults' reasons for genetic testing depend on cultural affiliation: results from a prospective, longitudinal genetic counseling and testing study. Boudreault P, Baldwin EE, Fox M, Dutton L, Tullis L, Linden J, Kobayashi Y, Zhou J, Sinsheimer JS, Sininger Y, Grody WW, Palmer CG. Deaf Stud Deaf Educ Summer;15(3): Epub 2010 May 20. Attitudes of deaf adults toward genetic testing for hereditary deafness. Middleton A, Hewison J, Mueller RF. Am J Hum Genet Oct;63(4): Slide acknowledgementt 1. Dr.Bradley Schaefer, Geneticist, UAMS, KUSM-W 2. Allison Schreiber, MS, CGC, Genetic Counselor, Cleveland Clinic
G. Shashidhar Pai, MD MUSC Children s Hospital Department of Pediatrics Division of Genetics
 G. Shashidhar Pai, MD MUSC Children s Hospital Department of Pediatrics Division of Genetics One of every 500 newborns has bilateral permanent sensorineural hearing loss 40 db which makes it the most common
G. Shashidhar Pai, MD MUSC Children s Hospital Department of Pediatrics Division of Genetics One of every 500 newborns has bilateral permanent sensorineural hearing loss 40 db which makes it the most common
Jennifer A. Defant, M.S., C.G.C. Certified Genetic Counselor Division of Genetics and Metabolism University of Florida
 Jennifer A. Defant, M.S., C.G.C. Certified Genetic Counselor Division of Genetics and Metabolism University of Florida 60% of childhood hearing loss is genetic Syndromic Nonsyndromic 40% of childhood hearing
Jennifer A. Defant, M.S., C.G.C. Certified Genetic Counselor Division of Genetics and Metabolism University of Florida 60% of childhood hearing loss is genetic Syndromic Nonsyndromic 40% of childhood hearing
Objectives Role of Medical Genetics in Hearing Loss Evaluation. 5 y.o. boy with severe SNHL
 Objectives Role of Medical Genetics in Hearing Loss Evaluation Millan Patel, MD UBC Dept. of Medical Genetics October 22, 2010 Case presentation to illustrate importance of defining syndromic hearing loss
Objectives Role of Medical Genetics in Hearing Loss Evaluation Millan Patel, MD UBC Dept. of Medical Genetics October 22, 2010 Case presentation to illustrate importance of defining syndromic hearing loss
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Hereditary Hearing Loss
 Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Hereditary Hearing Loss File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_hereditary_hearing_loss 10/2013 8/2015 8/2016
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Hereditary Hearing Loss File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_hereditary_hearing_loss 10/2013 8/2015 8/2016
Single Gene and NextGen Panels
 Molecular Testing for Hearing Loss: Single Gene and NextGen Panels Honey V Reddi, PhD, FACMG Clinical Molecular Geneticist Prevention Genetics, Marshfield, WI www.preventiongenetics.com Outline of Presentation
Molecular Testing for Hearing Loss: Single Gene and NextGen Panels Honey V Reddi, PhD, FACMG Clinical Molecular Geneticist Prevention Genetics, Marshfield, WI www.preventiongenetics.com Outline of Presentation
BEST PRACTICES Pediatric Bilateral Sensorineural Hearing Loss
 BEST PRACTICES Pediatric Bilateral Sensorineural Hearing Loss Christina L. Runge, PhD, CCC-A Associate Professor Chief, Division of Communication Sciences Director, Koss Cochlear Implant Program Resources
BEST PRACTICES Pediatric Bilateral Sensorineural Hearing Loss Christina L. Runge, PhD, CCC-A Associate Professor Chief, Division of Communication Sciences Director, Koss Cochlear Implant Program Resources
The Genetics of Hearing Loss. Heidi L. Rehm, Ph.D. Harvard Medical School Boston, MA
 The Genetics of Hearing Loss Heidi L. Rehm, Ph.D. Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Faculty Disclosure Information In the past 12 months, I have not had a significant financial interest or other relationship
The Genetics of Hearing Loss Heidi L. Rehm, Ph.D. Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Faculty Disclosure Information In the past 12 months, I have not had a significant financial interest or other relationship
Genetic Testing for Hereditary Hearing Loss
 MEDICAL POLICY POLICY RELATED POLICIES POLICY GUIDELINES DESCRIPTION SCOPE BENEFIT APPLICATION RATIONALE REFERENCES CODING APPENDIX HISTORY Genetic Testing for Hereditary Hearing Loss Number 12.04.87 Effective
MEDICAL POLICY POLICY RELATED POLICIES POLICY GUIDELINES DESCRIPTION SCOPE BENEFIT APPLICATION RATIONALE REFERENCES CODING APPENDIX HISTORY Genetic Testing for Hereditary Hearing Loss Number 12.04.87 Effective
About The Causes of Hearing Loss
 About 1 in 500 infants is born with or develops hearing loss during early childhood. Hearing loss has many causes: some are genetic (that is, caused by a baby s genes) or non-genetic (such as certain infections
About 1 in 500 infants is born with or develops hearing loss during early childhood. Hearing loss has many causes: some are genetic (that is, caused by a baby s genes) or non-genetic (such as certain infections
SENSORINEURAL HEARING LOSS INVESTIGATION & REFERRAL
 Epidemiology NZ Hearing Screening Referral Pathway Important Services When to Investigate Initial Assessment Referrals Investigations Indications for Cochlear Transplant Acknowledgements References Epidemiology
Epidemiology NZ Hearing Screening Referral Pathway Important Services When to Investigate Initial Assessment Referrals Investigations Indications for Cochlear Transplant Acknowledgements References Epidemiology
Deafness and Hereditary Hearing Loss Overview
 Page 1 of 25 NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health. Pagon RA, Bird TD, Dolan CR, et al., editors. GeneReviews [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University
Page 1 of 25 NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health. Pagon RA, Bird TD, Dolan CR, et al., editors. GeneReviews [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University
Genetic Hearing Loss
 Genetic Hearing Loss Stephanie Cordes, MD Faculty Advisor: Norman Friedman, MD The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation April 2000 Introduction Deafness
Genetic Hearing Loss Stephanie Cordes, MD Faculty Advisor: Norman Friedman, MD The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation April 2000 Introduction Deafness
Patient Information. for Childhood
 Patient Information Genetic Testing for Childhood Hearing Loss Introduction This document describes the most common genetic cause of childhood hearing loss and explains the role of genetic testing. Childhood
Patient Information Genetic Testing for Childhood Hearing Loss Introduction This document describes the most common genetic cause of childhood hearing loss and explains the role of genetic testing. Childhood
Congenital Hearing Loss
 Congenital Hearing Loss A resident asks... Why would a primary care physician want to know about the genetics of hearing loss? Key Points: Newborn screening for hearing loss is being implemented in many
Congenital Hearing Loss A resident asks... Why would a primary care physician want to know about the genetics of hearing loss? Key Points: Newborn screening for hearing loss is being implemented in many
Genetic Testing for Hereditary Hearing Loss. Populations Interventions Comparators Outcomes Interventions of interest are: Genetic testing
 Protocol Genetic Testing for Hereditary Hearing Loss (20487) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 01/01/15 Next Review Date: 11/16 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 01/14, 11/14, 11/15 Preauthorization is
Protocol Genetic Testing for Hereditary Hearing Loss (20487) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 01/01/15 Next Review Date: 11/16 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 01/14, 11/14, 11/15 Preauthorization is
DURATION OF HEARING LOSS
 When your child is diagnosed with a hearing loss, it may be very overwhelming. This may be a difficult time for you and your family. However, gaining a greater knowledge in this area is crucial in helping
When your child is diagnosed with a hearing loss, it may be very overwhelming. This may be a difficult time for you and your family. However, gaining a greater knowledge in this area is crucial in helping
Special Needs. Establishment of a System. Special Needs. The New Genetics: Concepts We should know. Family. Friends. School. Community.
 The New Genetics: Concepts We should know Special Needs Used in clinical diagnostic and functional development to describe individuals who require assistance medical, mental, or psychological areas Luis
The New Genetics: Concepts We should know Special Needs Used in clinical diagnostic and functional development to describe individuals who require assistance medical, mental, or psychological areas Luis
Usher Syndrome Genetics
 Usher Syndrome Genetics October 2012 Page 1 of 20 Introduction Usher syndrome is a genetic or inherited condition that affects hearing, vision and balance The sight loss is caused by an eye condition known
Usher Syndrome Genetics October 2012 Page 1 of 20 Introduction Usher syndrome is a genetic or inherited condition that affects hearing, vision and balance The sight loss is caused by an eye condition known
Goals for Today. Clinical and Molecular Aspects of Genetic Hearing Loss. Case presentation. Case presentation continued. Case presentation continued
 Clinical and Molecular Aspects of Genetic Hearing Loss Kathleen Arnos, PhD Department of Science, Technology, & Mathematics Gallaudet University Washington, DC 20002 kathleen.arnos@gallaudet.edu Goals
Clinical and Molecular Aspects of Genetic Hearing Loss Kathleen Arnos, PhD Department of Science, Technology, & Mathematics Gallaudet University Washington, DC 20002 kathleen.arnos@gallaudet.edu Goals
Genetics Evaluation Guidelines for the Etiologic Diagnosis of Congenital Hearing Loss Genetic Evaluation of Congenital Hearing Loss Expert Panel
 ACMG statement May/June 2002 Vol. 4 No. 3 Genetics Evaluation Guidelines for the Etiologic Diagnosis of Congenital Hearing Loss Genetic Evaluation of Congenital Hearing Loss Expert Panel The advent of
ACMG statement May/June 2002 Vol. 4 No. 3 Genetics Evaluation Guidelines for the Etiologic Diagnosis of Congenital Hearing Loss Genetic Evaluation of Congenital Hearing Loss Expert Panel The advent of
Genetic Bases of Hearing Loss: Future Treatment Implications
 Genetic Bases of Hearing Loss: Future Treatment Implications Luis F. Escobar, MD Medical Director Medical Genetics & Neurodevelopmental Pediatrics of Indiana Peyton Manning Children s Hospital St. Vincent
Genetic Bases of Hearing Loss: Future Treatment Implications Luis F. Escobar, MD Medical Director Medical Genetics & Neurodevelopmental Pediatrics of Indiana Peyton Manning Children s Hospital St. Vincent
Title: Genetics and Hearing Loss: Clinical and Molecular Characteristics
 Session # : 46 Day/Time: Friday, May 1, 2015, 1:00 4:00 pm Title: Genetics and Hearing Loss: Clinical and Molecular Characteristics Presenter: Kathleen S. Arnos, PhD, Gallaudet University This presentation
Session # : 46 Day/Time: Friday, May 1, 2015, 1:00 4:00 pm Title: Genetics and Hearing Loss: Clinical and Molecular Characteristics Presenter: Kathleen S. Arnos, PhD, Gallaudet University This presentation
The Genomics of Hearing Loss
 The Genomics of Hearing Loss Ian Krantz, M.D. The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia and the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania Objectives 1. Understand the clinical and genetic
The Genomics of Hearing Loss Ian Krantz, M.D. The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia and the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania Objectives 1. Understand the clinical and genetic
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
 Sensorineural Hearing Loss 1. Review the patterns of hearing loss in hereditary hearing impairment. AL First, we must understand that genetic hearing loss seems to breach all categories of hearing loss,
Sensorineural Hearing Loss 1. Review the patterns of hearing loss in hereditary hearing impairment. AL First, we must understand that genetic hearing loss seems to breach all categories of hearing loss,
Medical Policy Manual. Date of Origin: October 2014. Topic: Genetic Testing for Hereditary Hearing Loss. Last Reviewed Date: December 2015
 Medical Policy Manual Topic: Genetic Testing for Hereditary Hearing Loss Section: Genetic Testing Policy No: 36 Date of Origin: October 2014 Last Reviewed Date: December 2015 Effective Date: February 1,
Medical Policy Manual Topic: Genetic Testing for Hereditary Hearing Loss Section: Genetic Testing Policy No: 36 Date of Origin: October 2014 Last Reviewed Date: December 2015 Effective Date: February 1,
Understanding the Genetics of Deafness
 Understanding the Genetics of Deafness A Guide for Patients and Families Harvard Medical School Center For Hereditary Deafness Understanding the Genetics of Deafness Understanding the Genetics of Deafness
Understanding the Genetics of Deafness A Guide for Patients and Families Harvard Medical School Center For Hereditary Deafness Understanding the Genetics of Deafness Understanding the Genetics of Deafness
1/26/2011. 50% of deafness and hearing impairment is avoidable through prevention, early diagnosis, and management.
 Hearing Impairment Roseann Mulligan, DDS, MS Herman Ostrow School of Dentistry of the University of Southern California 1 JAMA, July 4, 2007 Vol 298, No. 1 2 278 million - moderate to profound bilateral
Hearing Impairment Roseann Mulligan, DDS, MS Herman Ostrow School of Dentistry of the University of Southern California 1 JAMA, July 4, 2007 Vol 298, No. 1 2 278 million - moderate to profound bilateral
Why does my child have a hearing loss?
 Introduction This factsheet will tell you about the range of tests that can be carried out to try to find the cause of your child s hearing loss. The process to find out why a child is deaf is sometimes
Introduction This factsheet will tell you about the range of tests that can be carried out to try to find the cause of your child s hearing loss. The process to find out why a child is deaf is sometimes
Deafblind syndromes, diagnostic tools and treatment
 Deafblind syndromes, diagnostic tools and treatment Claes Möller Department of Audiology Örebro University Hospital Confusion Why is my child deaf? Why is my child clumsy? Why has my child problems at
Deafblind syndromes, diagnostic tools and treatment Claes Möller Department of Audiology Örebro University Hospital Confusion Why is my child deaf? Why is my child clumsy? Why has my child problems at
Neurofibromatosis Type 2: Information for Patients & Families by Mia MacCollin, M.D., Catherine Bove, R.N. Ed. & M. Priscilla Short, M.D.
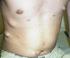 Neurofibromatosis Type 2: Information for Patients & Families by Mia MacCollin, M.D., Catherine Bove, R.N. Ed. & M. Priscilla Short, M.D. Neurofibromatosis Type 2 is a rare genetic disease, which causes
Neurofibromatosis Type 2: Information for Patients & Families by Mia MacCollin, M.D., Catherine Bove, R.N. Ed. & M. Priscilla Short, M.D. Neurofibromatosis Type 2 is a rare genetic disease, which causes
commentary Genetics IN Medicine 521 November/December 2004 Vol. 6 No. 6
 November/December 2004 Vol. 6 No. 6 commentary Genetic testing as part of the Early Hearing Detection and Intervention (EHDI) process Lisa A. Schimmenti, MD 1, Ariadna Martinez, MS, MS 2, Michelle Fox,
November/December 2004 Vol. 6 No. 6 commentary Genetic testing as part of the Early Hearing Detection and Intervention (EHDI) process Lisa A. Schimmenti, MD 1, Ariadna Martinez, MS, MS 2, Michelle Fox,
So, how do we hear? outer middle ear inner ear
 The ability to hear is critical to understanding the world around us. The human ear is a fully developed part of our bodies at birth and responds to sounds that are very faint as well as sounds that are
The ability to hear is critical to understanding the world around us. The human ear is a fully developed part of our bodies at birth and responds to sounds that are very faint as well as sounds that are
Causes of Birth Defects
 Causes of Birth Defects Some medical / genetic terms: congenital defects: visible defects present at birth (due to any cause (genetic, developmental error ). syndrome: the symptoms that characterize any
Causes of Birth Defects Some medical / genetic terms: congenital defects: visible defects present at birth (due to any cause (genetic, developmental error ). syndrome: the symptoms that characterize any
The future role of genetic screening to detect newborns at risk of childhood-onset hearing loss
 International Journal of Audiology 2013; 52: 124 133 Discussion Article The future role of genetic screening to detect newborns at risk of childhood-onset hearing loss Luan Linden Phillips *, Maria Bitner-Glindzicz,
International Journal of Audiology 2013; 52: 124 133 Discussion Article The future role of genetic screening to detect newborns at risk of childhood-onset hearing loss Luan Linden Phillips *, Maria Bitner-Glindzicz,
Chapter 176: Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Children. Patrick E. Brookhouser
 Chapter 176: Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Children Patrick E. Brookhouser Early identification of educationally significant sensorineural hearing impairment in young children, which varies in incidence
Chapter 176: Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Children Patrick E. Brookhouser Early identification of educationally significant sensorineural hearing impairment in young children, which varies in incidence
Molecular Genetic Testing in Public Health and Clinical Settings
 Molecular Genetic Testing in Public Health and Clinical Settings Ira M. Lubin, PhD, FACMG Division of Laboratory Systems NCPDCID, CCID Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Atlanta, Georgia Disclaimers
Molecular Genetic Testing in Public Health and Clinical Settings Ira M. Lubin, PhD, FACMG Division of Laboratory Systems NCPDCID, CCID Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Atlanta, Georgia Disclaimers
The Work-Up of Childhood Sensorineural Hearing Loss Jonathan M. Sherman, Eliot Shearer, Richard J.H. Smith, and Dana Suskind
 2 The Work-Up of Childhood Sensorineural Hearing Loss Jonathan M. Sherman, Eliot Shearer, Richard J.H. Smith, and Dana Suskind The Problem Hearing loss in children is common in the United States with an
2 The Work-Up of Childhood Sensorineural Hearing Loss Jonathan M. Sherman, Eliot Shearer, Richard J.H. Smith, and Dana Suskind The Problem Hearing loss in children is common in the United States with an
Cochlear Implantation for Children With GJB2-Related Deafness
 The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. 2004 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Cochlear Implantation for Children With GJB2-Related Deafness Robert D.
The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. 2004 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Cochlear Implantation for Children With GJB2-Related Deafness Robert D.
ALBINISM. Other Common Names. Causes/Etiology. Incidence. Characteristics. Hypopigmentation
 ALBINISM Other Common Names Hypopigmentation Causes/Etiology Incidence Most types of albinism are inherited when a child receives the albinism gene from both parents. There is an exception with one type
ALBINISM Other Common Names Hypopigmentation Causes/Etiology Incidence Most types of albinism are inherited when a child receives the albinism gene from both parents. There is an exception with one type
The Developing Person Through the Life Span 8e by Kathleen Stassen Berger
 The Developing Person Through the Life Span 8e by Kathleen Stassen Berger Chapter 3 Heredity and Environment PowerPoint Slides developed by Martin Wolfger and Michael James Ivy Tech Community College-Bloomington
The Developing Person Through the Life Span 8e by Kathleen Stassen Berger Chapter 3 Heredity and Environment PowerPoint Slides developed by Martin Wolfger and Michael James Ivy Tech Community College-Bloomington
Supervisors Prof.Dr.Ahmad Sameh Farid Professor of ENT and Audiology Faculty of Medicine Cairo University
 Connexin 26 gene in non-syndromic hearing loss Thesis Submitted for partial fulfillment of MD degree in Audiology by Mona Ahmed El-Akkad M.B, B.CH., MSc. Supervisors Prof.Dr.Ahmad Sameh Farid Professor
Connexin 26 gene in non-syndromic hearing loss Thesis Submitted for partial fulfillment of MD degree in Audiology by Mona Ahmed El-Akkad M.B, B.CH., MSc. Supervisors Prof.Dr.Ahmad Sameh Farid Professor
Hearing loss is an etiologically heterogeneous trait with
 The new england journal of medicine review article Current Concepts Newborn Hearing Screening A Silent Revolution Cynthia C. Morton, Ph.D., and Walter E. Nance, M.D., Ph.D. Hearing loss is an etiologically
The new england journal of medicine review article Current Concepts Newborn Hearing Screening A Silent Revolution Cynthia C. Morton, Ph.D., and Walter E. Nance, M.D., Ph.D. Hearing loss is an etiologically
Genetic Mutations Cause Many Birth Defects:
 Genetic Mutations Cause Many Birth Defects: What We Learned from the FORGE Canada Project Jan M. Friedman, MD, PhD University it of British Columbia Vancouver, Canada I have no conflicts of interest related
Genetic Mutations Cause Many Birth Defects: What We Learned from the FORGE Canada Project Jan M. Friedman, MD, PhD University it of British Columbia Vancouver, Canada I have no conflicts of interest related
CONGENITAL HEARING LOSS
 CONGENITAL HEARING LOSS Congenital hearing loss, for the purposes of this fact sheet, is defined as permanent and is bilateral or unilateral, is sensory or conductive, and averages 30 db or more in the
CONGENITAL HEARING LOSS Congenital hearing loss, for the purposes of this fact sheet, is defined as permanent and is bilateral or unilateral, is sensory or conductive, and averages 30 db or more in the
Genetics of Hearing Loss
 2 Genetics of Hearing Loss Ella Shalit and Karen B. Avraham 1. Introduction The revolution in genetics in the past decades has enabled identification of many of the genes associated with human hereditary
2 Genetics of Hearing Loss Ella Shalit and Karen B. Avraham 1. Introduction The revolution in genetics in the past decades has enabled identification of many of the genes associated with human hereditary
22/02/2015. Possible causes. Decisions decisions decisions. Challenging eye and ear conditions at underwriting and claim stage Dr Maritha van der Walt
 Challenges Underwriting symptoms rather than conditions- tinnitus, vertigo, blurred vision Requests for narrower rather than broad exclusions and consequences Pre existing condition and unrelated claims
Challenges Underwriting symptoms rather than conditions- tinnitus, vertigo, blurred vision Requests for narrower rather than broad exclusions and consequences Pre existing condition and unrelated claims
More information >>> HERE <<<
 More information >>> HERE http://urlzz.org/hearloss/pdx/dcli864/ Tags: ## best way to get cheapest natural methods to
More information >>> HERE http://urlzz.org/hearloss/pdx/dcli864/ Tags: ## best way to get cheapest natural methods to
Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Hereditary Hearing Loss
 Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Hereditary Hearing Loss Table of Contents Policy: Commercial Coding Information Information Pertaining to All Policies Policy: Medicare Description References Authorization
Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Hereditary Hearing Loss Table of Contents Policy: Commercial Coding Information Information Pertaining to All Policies Policy: Medicare Description References Authorization
Genetic Mutations. Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes.
 Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
Medical Evaluation of children with permanent unilateral hearing loss.
 Medical Evaluation of children with permanent unilateral hearing loss. Produced by the British Association of Audiovestibular Physicians and British Association of Paediatricians in Audiology August 2009
Medical Evaluation of children with permanent unilateral hearing loss. Produced by the British Association of Audiovestibular Physicians and British Association of Paediatricians in Audiology August 2009
Synopsis of Causation. Sensorineural Hearing Loss
 Ministry of Defence Synopsis of Causation Sensorineural Hearing Loss Author: Validator: Dr Adrian Roberts, Medical Author, Medical Text, Edinburgh Mr Kevin Gibbin, University Hospital, Queen s Medical
Ministry of Defence Synopsis of Causation Sensorineural Hearing Loss Author: Validator: Dr Adrian Roberts, Medical Author, Medical Text, Edinburgh Mr Kevin Gibbin, University Hospital, Queen s Medical
Genetic Aspects of Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities
 Prepared by: Chahira Kozma, MD Associate Professor of Pediatrics Medical Director/DCHRP Kozmac@georgetown.edu cck2@gunet.georgetown.edu Genetic Aspects of Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities
Prepared by: Chahira Kozma, MD Associate Professor of Pediatrics Medical Director/DCHRP Kozmac@georgetown.edu cck2@gunet.georgetown.edu Genetic Aspects of Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities
Attitudes toward genetic testing
 DOI 10.1515/jbcpp-2013-0063 J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 2013; 24(3): 165 170 Mini Review Natali Idan, Zippora Brownstein, Shaked Shivatzki and Karen B. Avraham* Advances in genetic diagnostics for hereditary
DOI 10.1515/jbcpp-2013-0063 J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 2013; 24(3): 165 170 Mini Review Natali Idan, Zippora Brownstein, Shaked Shivatzki and Karen B. Avraham* Advances in genetic diagnostics for hereditary
Learners Who are Deaf or Hard of Hearing Kalie Carlisle, Lauren Nash, and Allison Gallahan
 Learners Who are Deaf or Hard of Hearing Kalie Carlisle, Lauren Nash, and Allison Gallahan Definition Deaf A deaf person is one whose hearing disability precludes successful processing of linguistic information
Learners Who are Deaf or Hard of Hearing Kalie Carlisle, Lauren Nash, and Allison Gallahan Definition Deaf A deaf person is one whose hearing disability precludes successful processing of linguistic information
DISABILITY-RELATED DEFINITIONS
 DISABILITY-RELATED DEFINITIONS 1. The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) of 1990 is a civil rights law, which makes it unlawful to discriminate on the basis of disability. It covers employment in the
DISABILITY-RELATED DEFINITIONS 1. The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) of 1990 is a civil rights law, which makes it unlawful to discriminate on the basis of disability. It covers employment in the
GONCA SENNAROĞLU PhD LEVENT SENNAROĞLU MD. Department of Otolaryngology Hacettepe University ANKARA, TURKEY
 GONCA SENNAROĞLU PhD LEVENT SENNAROĞLU MD Department of Otolaryngology Hacettepe University ANKARA, TURKEY To present the audiological findings and rehabilitative outcomes of CI in children with cochlear
GONCA SENNAROĞLU PhD LEVENT SENNAROĞLU MD Department of Otolaryngology Hacettepe University ANKARA, TURKEY To present the audiological findings and rehabilitative outcomes of CI in children with cochlear
Neonatal Hypotonia. Clinical Approach to Floppy Baby
 Neonatal Hypotonia Clinical Approach to Floppy Baby Hypotonia in the newborn is a common presenting feature of systemic illness or neurologic dysfunction at any level of the central or peripheral nervous
Neonatal Hypotonia Clinical Approach to Floppy Baby Hypotonia in the newborn is a common presenting feature of systemic illness or neurologic dysfunction at any level of the central or peripheral nervous
A CASE FOR ETIOLOGIC FOCUS IN AUDIOLOGY GENETIC TESTING. Thesis
 A CASE FOR ETIOLOGIC FOCUS IN AUDIOLOGY GENETIC TESTING Thesis Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for The Masters in Speech and Hearing Science in the Graduate School of The Ohio State
A CASE FOR ETIOLOGIC FOCUS IN AUDIOLOGY GENETIC TESTING Thesis Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for The Masters in Speech and Hearing Science in the Graduate School of The Ohio State
The Newborn With a Congenital Disorder. Chapter 14. Copyright 2008 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
 The Newborn With a Congenital Disorder Chapter 14 Congenital Anomalies or Malformations May be caused by genetic or environmental factors Approximately 2% to 3% of all infants born have a major malformation
The Newborn With a Congenital Disorder Chapter 14 Congenital Anomalies or Malformations May be caused by genetic or environmental factors Approximately 2% to 3% of all infants born have a major malformation
 THE EYES IN CHARGE: FOR THE OPHTHALMOLOGIST Roberta A. Pagon, M.D. Division of Medical Genetics, CH-25, Children's Hospital /Medical Center, Box C5371, Seattle, WA 98105-0371 bpagon@u.washington.edu (206)
THE EYES IN CHARGE: FOR THE OPHTHALMOLOGIST Roberta A. Pagon, M.D. Division of Medical Genetics, CH-25, Children's Hospital /Medical Center, Box C5371, Seattle, WA 98105-0371 bpagon@u.washington.edu (206)
Less common vestibular disorders presenting with funny turns
 Less common vestibular disorders presenting with funny turns Charlotte Agrup, Department of Neuro-otology, The National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery, London Making the diagnosis Making the diagnosis
Less common vestibular disorders presenting with funny turns Charlotte Agrup, Department of Neuro-otology, The National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery, London Making the diagnosis Making the diagnosis
Optic Disc Drusen. Normal Enlarged view of Optic Disc. Lumpy Appearance of Optic Disc. Optic Disc Drusen With Drusen
 Optic Disc Drusen Your doctor has diagnosed you with optic disc drusen. Optic disc drusen are abnormal deposits of protein-like material in the optic disc the front part of the optic nerve. We do not know
Optic Disc Drusen Your doctor has diagnosed you with optic disc drusen. Optic disc drusen are abnormal deposits of protein-like material in the optic disc the front part of the optic nerve. We do not know
Enlarged Vestibular Aqueduct Syndrome
 PO BOX 13305 PORTLAND, OR 97213 FAX: (503) 229-8064 (800) 837-8428 INFO@VESTIBULAR.ORG WWW.VESTIBULAR.ORG Enlarged Vestibular Aqueduct Syndrome (EVAS) By Hamid, MD, PhD, EE, The Cleveland Hearing & Balance
PO BOX 13305 PORTLAND, OR 97213 FAX: (503) 229-8064 (800) 837-8428 INFO@VESTIBULAR.ORG WWW.VESTIBULAR.ORG Enlarged Vestibular Aqueduct Syndrome (EVAS) By Hamid, MD, PhD, EE, The Cleveland Hearing & Balance
Policy Product Variations Description/Background Rationale Definitions Benefit Variations Disclaimer Coding Information References Policy History
 Original Issue Date (Created): 4/1/2014 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): 11/24/2015 Effective Date: 2/1/2016 Policy Product Variations Description/Background Rationale Definitions Benefit Variations
Original Issue Date (Created): 4/1/2014 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): 11/24/2015 Effective Date: 2/1/2016 Policy Product Variations Description/Background Rationale Definitions Benefit Variations
Acute Profound Deafness
 Sensory Organ Disorders Acute Profound Deafness How much do we now know about the clinical condition? JMAJ 46(7): 285 290, 2003 Jin KANZAKI Director, International University of Health and Welfare Atami
Sensory Organ Disorders Acute Profound Deafness How much do we now know about the clinical condition? JMAJ 46(7): 285 290, 2003 Jin KANZAKI Director, International University of Health and Welfare Atami
Healthy Hearing Program. Medical Guidelines for Children born with a Permanent Hearing Loss
 Healthy Hearing Program Medical Guidelines for Children born with a Permanent Hearing Loss 1.0 Introduction Table of Contents 1.1 Background 5 1.2 Aims 5 1.3 Why investigate the cause of hearing loss 6
Healthy Hearing Program Medical Guidelines for Children born with a Permanent Hearing Loss 1.0 Introduction Table of Contents 1.1 Background 5 1.2 Aims 5 1.3 Why investigate the cause of hearing loss 6
Ulrika Löfkvist, Ass.Professor, SLP, LSLS cert. AVEd University of Oslo Arvika, 2016-05-13
 Medfödd Cytomegalovirusinfektion inte bara en vanlig orsak till hörselnedsättning utan även balanssvårigheter och kognitiva funktionsnedsättningar Ulrika Löfkvist, Ass.Professor, SLP, LSLS cert. AVEd University
Medfödd Cytomegalovirusinfektion inte bara en vanlig orsak till hörselnedsättning utan även balanssvårigheter och kognitiva funktionsnedsättningar Ulrika Löfkvist, Ass.Professor, SLP, LSLS cert. AVEd University
Common Cancers & Hereditary Syndromes
 Common Cancers & Hereditary Syndromes Elizabeth Hoodfar, MS, LCGC Regional Cancer Genetics Coordinator Kaiser Permanente Northern California Detect clinical characteristics of hereditary cancer syndromes.
Common Cancers & Hereditary Syndromes Elizabeth Hoodfar, MS, LCGC Regional Cancer Genetics Coordinator Kaiser Permanente Northern California Detect clinical characteristics of hereditary cancer syndromes.
Insights into Visual Impairments
 Insights into Visual Impairments Definition of Visual Impairment Washington State WAC 392 172A 01035 Child with a disability or student eligible for special education. (n) Visual impairment including blindness
Insights into Visual Impairments Definition of Visual Impairment Washington State WAC 392 172A 01035 Child with a disability or student eligible for special education. (n) Visual impairment including blindness
Clinical Policy Title: Genomic tests in sensorineural hearing loss
 Clinical Policy Title: Genomic tests in sensorineural hearing loss Clinical Policy Number: 02.01.18 Effective Date: January 1, 2016 Initial Review Date: September 16, 2015 Most Recent Review Date: September
Clinical Policy Title: Genomic tests in sensorineural hearing loss Clinical Policy Number: 02.01.18 Effective Date: January 1, 2016 Initial Review Date: September 16, 2015 Most Recent Review Date: September
TERATOGENESIS ONTOGENESIS
 TERATOGENESIS ONTOGENESIS Inborn developmental defects Occured during prenatal development Are present by delivery At about 3-5 % newborns are affected. Inborn developmental defects 1. CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATIONS
TERATOGENESIS ONTOGENESIS Inborn developmental defects Occured during prenatal development Are present by delivery At about 3-5 % newborns are affected. Inborn developmental defects 1. CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATIONS
Chromosomal Abnormalities
 Chromosomal Abnormalities George E Tiller, MD, PhD Regional Chief, Dept. Genetics Southern California Permanente Medical Group Los Angeles, CA Objectives of Lecture list several indications for karyotyping
Chromosomal Abnormalities George E Tiller, MD, PhD Regional Chief, Dept. Genetics Southern California Permanente Medical Group Los Angeles, CA Objectives of Lecture list several indications for karyotyping
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY OF JOINT COMMITTEE ON INFANT HEARING YEAR 2007 POSITION STATEMENT. Intervention Programs
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY OF JOINT COMMITTEE ON INFANT HEARING YEAR 2007 POSITION STATEMENT Principles and Guidelines for Early Hearing Detection and Intervention Programs The Joint Committee on Infant Hearing
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY OF JOINT COMMITTEE ON INFANT HEARING YEAR 2007 POSITION STATEMENT Principles and Guidelines for Early Hearing Detection and Intervention Programs The Joint Committee on Infant Hearing
REQUEST FOR IMAGe SYNDROME TESTING
 REQUEST FOR IMAGe SYNDROME TESTING Please provide the following information. We cannot perform your test without ALL of this information. PLEASE PRINT ALL ANSWERS PATIENT INFORMATION* FIRST NAME MI LAST
REQUEST FOR IMAGe SYNDROME TESTING Please provide the following information. We cannot perform your test without ALL of this information. PLEASE PRINT ALL ANSWERS PATIENT INFORMATION* FIRST NAME MI LAST
Developmental delay and Cerebral palsy. Present the differential diagnosis of developmental delay.
 Developmental delay and Cerebral palsy objectives 1. developmental delay Define developmental delay Etiologies of developmental delay Present the differential diagnosis of developmental delay. 2. cerebral
Developmental delay and Cerebral palsy objectives 1. developmental delay Define developmental delay Etiologies of developmental delay Present the differential diagnosis of developmental delay. 2. cerebral
GENETIC TESTING AND MARFAN SYNDROME
 GENETIC TESTING AND MARFAN SYNDROME Genetic testing for mutations in fibrillin-1 (FBN1) and other genes has become an important and reliable option to aid in the diagnosis of Marfan syndrome and related
GENETIC TESTING AND MARFAN SYNDROME Genetic testing for mutations in fibrillin-1 (FBN1) and other genes has become an important and reliable option to aid in the diagnosis of Marfan syndrome and related
Screening for Progressive Retinal Atrophy in Tibetan Terriers
 Screening for Progressive Retinal Atrophy in Tibetan Terriers What is PRA? Progressive retinal atrophy (PRA) is the name given to a group of conditions that are inherited and result in a progressive loss
Screening for Progressive Retinal Atrophy in Tibetan Terriers What is PRA? Progressive retinal atrophy (PRA) is the name given to a group of conditions that are inherited and result in a progressive loss
Diagnostic Scoring System for LQTS
 Medical Coverage Policy Genetic Testing: Congenital Long QT Syndrome Device/Equipment Drug Medical Surgery Test Other Effective Date: 2/15/2011 Policy Last Updated: 2/21/2012 Prospective review is recommended/required.
Medical Coverage Policy Genetic Testing: Congenital Long QT Syndrome Device/Equipment Drug Medical Surgery Test Other Effective Date: 2/15/2011 Policy Last Updated: 2/21/2012 Prospective review is recommended/required.
Obstetrical Ultrasound and Prenatal Diagnostic Center
 Obstetrical Ultrasound and Prenatal Diagnostic Center Prenatal Diagnosis: Options and Opportunities Learn about various screening options including Early Risk Assessment (ERA), now available to women of
Obstetrical Ultrasound and Prenatal Diagnostic Center Prenatal Diagnosis: Options and Opportunities Learn about various screening options including Early Risk Assessment (ERA), now available to women of
GENETIC CONSIDERATIONS IN CANCER TREATMENT AND SURVIVORSHIP
 GENETIC CONSIDERATIONS IN CANCER TREATMENT AND SURVIVORSHIP WHO IS AT HIGH RISK OF HEREDITARY CANCER? Hereditary Cancer accounts for a small proportion of all cancer or approximately 5-10% THE DEVELOPMENT
GENETIC CONSIDERATIONS IN CANCER TREATMENT AND SURVIVORSHIP WHO IS AT HIGH RISK OF HEREDITARY CANCER? Hereditary Cancer accounts for a small proportion of all cancer or approximately 5-10% THE DEVELOPMENT
A bout 1 in 1000 British children are born deaf.
 1of5 ELECTRONIC LETTER Genetic information but not termination: pregnant women s attitudes and willingness to pay for carrier screening for deafness genes M Ryan, Z Miedzybrodzka, L Fraser, M Hall... J
1of5 ELECTRONIC LETTER Genetic information but not termination: pregnant women s attitudes and willingness to pay for carrier screening for deafness genes M Ryan, Z Miedzybrodzka, L Fraser, M Hall... J
AGE Iowa Midwest Nation N % N % N % Total students 256 100.0 9272 100.0 37500 100.0 Information NOT reported 7 2.7 229 2.5 841 2.2
 202-651-5575 * 1-800-451-8834 ext 5575 Page 1 of 9 AGE Iowa Midwest Nation Information NOT reported 7 2.7 229 2.5 841 2.2 Total known information 249 100.0 9043 100.0 36659 100.0 Under 3 years 16 6.4 201
202-651-5575 * 1-800-451-8834 ext 5575 Page 1 of 9 AGE Iowa Midwest Nation Information NOT reported 7 2.7 229 2.5 841 2.2 Total known information 249 100.0 9043 100.0 36659 100.0 Under 3 years 16 6.4 201
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Fanconi Anemia
 Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Fanconi Anemia File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_fanconi_anemia 03/2015 3/2016 3/2017 3/2016 Description
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Fanconi Anemia File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_fanconi_anemia 03/2015 3/2016 3/2017 3/2016 Description
What Is Genetic Counseling? Helping individuals and families understand how genetics affects their health and lives
 What Is Genetic Counseling? Helping individuals and families understand how genetics affects their health and lives What does the career involve? Explore family histories to identify risks Reducing risks
What Is Genetic Counseling? Helping individuals and families understand how genetics affects their health and lives What does the career involve? Explore family histories to identify risks Reducing risks
Static Encephalopathy A Basis Explanation for Parents
 Static Encephalopathy A Basis Explanation for Parents Nancy J. Hitzfelder, M.D. Medical Director July 1999 This article may not be copied without the express written permission of Easter Seals of Greater
Static Encephalopathy A Basis Explanation for Parents Nancy J. Hitzfelder, M.D. Medical Director July 1999 This article may not be copied without the express written permission of Easter Seals of Greater
SPONDYLOEPIPHYSEAL DYSPLASIA, CONGENITA NATURAL HISTORY INTRODUCTION:
 SPONDYLOEPIPHYSEAL DYSPLASIA, CONGENITA NATURAL HISTORY Richard M. Pauli, M.D., Ph.D., Midwest Regional Bone Dysplasia Clinics revised 8/2009 INTRODUCTION: The following summary of the medical expectations
SPONDYLOEPIPHYSEAL DYSPLASIA, CONGENITA NATURAL HISTORY Richard M. Pauli, M.D., Ph.D., Midwest Regional Bone Dysplasia Clinics revised 8/2009 INTRODUCTION: The following summary of the medical expectations
Influences on Birth Defects
 Influences on Birth Defects FACTS About 150,000 babies are born each year with birth defects. The parents of one out of every 28 babies receive the frightening news that their baby has a birth defect There
Influences on Birth Defects FACTS About 150,000 babies are born each year with birth defects. The parents of one out of every 28 babies receive the frightening news that their baby has a birth defect There
Why is prematurity a concern?
 Prematurity What is prematurity? A baby born before 37 weeks of pregnancy is considered premature. Approximately 12% of all babies are born prematurely. Terms that refer to premature babies are preterm
Prematurity What is prematurity? A baby born before 37 weeks of pregnancy is considered premature. Approximately 12% of all babies are born prematurely. Terms that refer to premature babies are preterm
Vitreo-Retinal and Macular Degeneration Frequently Asked Questions
 Vitreo-Retinal and Macular Degeneration Frequently Asked Questions What is a Vitreo-Retinal specialist? Retinal specialists are eye physicians and surgeons who focus on diseases in the back of the eye
Vitreo-Retinal and Macular Degeneration Frequently Asked Questions What is a Vitreo-Retinal specialist? Retinal specialists are eye physicians and surgeons who focus on diseases in the back of the eye
Hearing Screening Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Pediatricians
 Hearing Screening Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Pediatricians While coding for hearing screening is relatively straightforward, ensuring that appropriate payment is received for such services is a
Hearing Screening Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Pediatricians While coding for hearing screening is relatively straightforward, ensuring that appropriate payment is received for such services is a
Patient Information. Ordering Physician Information. Indication for Testing (REQUIRED)
 EPILEPSY EXOME CLINICAL CHECKLIST REQUIRED Please check all clinical features that apply, and use the additional space provided at the bottom of the form if needed Patient Information Name: Last First
EPILEPSY EXOME CLINICAL CHECKLIST REQUIRED Please check all clinical features that apply, and use the additional space provided at the bottom of the form if needed Patient Information Name: Last First
UNIT 13 (OPTION) Genetic Abnormalities
 Unit 13 Genetic Abnormailities 1 UNIT 13 (OPTION) Genetic Abnormalities Originally developed by: Hildur Helgedottir RN, MN Revised (2000) by: Marlene Reimer RN, PhD, CCN (C) Associate Professor Faculty
Unit 13 Genetic Abnormailities 1 UNIT 13 (OPTION) Genetic Abnormalities Originally developed by: Hildur Helgedottir RN, MN Revised (2000) by: Marlene Reimer RN, PhD, CCN (C) Associate Professor Faculty
Overview of Genetic Testing and Screening
 Integrating Genetics into Your Practice Webinar Series Overview of Genetic Testing and Screening Genetic testing is an important tool in the screening and diagnosis of many conditions. New technology is
Integrating Genetics into Your Practice Webinar Series Overview of Genetic Testing and Screening Genetic testing is an important tool in the screening and diagnosis of many conditions. New technology is
ICD-10 Codes Utilized by Audiologists
 ICD-10 Codes Utilized by Audiologists Introduction Beginning with the first claim filed to all payers on or after October 1, 2015, the ICD-10 codes must be utilized in box 21 A-L on the CMS 1500 claim
ICD-10 Codes Utilized by Audiologists Introduction Beginning with the first claim filed to all payers on or after October 1, 2015, the ICD-10 codes must be utilized in box 21 A-L on the CMS 1500 claim
Genetic Counseling: A Profession in the Making. Jessica Hooks, MS Genetic Counselor University of South Carolina
 Genetic Counseling: A Profession in the Making Jessica Hooks, MS Genetic Counselor University of South Carolina Definition the process of helping people understand and adapt to the medical, psychological
Genetic Counseling: A Profession in the Making Jessica Hooks, MS Genetic Counselor University of South Carolina Definition the process of helping people understand and adapt to the medical, psychological
BIRTH DEFECTS IN MICHIGAN All Cases Reported and Processed by April 15, 2008
 MICHIGAN DEPARTMENT OF COMMUNITY HEALTH Division for Vital Records and Health Statistics MICHIGAN BIRTH DEFECTS SURVEILLANCE REGISTRY BIRTH DEFECTS IN MICHIGAN All Cases Reported and Processed by April
MICHIGAN DEPARTMENT OF COMMUNITY HEALTH Division for Vital Records and Health Statistics MICHIGAN BIRTH DEFECTS SURVEILLANCE REGISTRY BIRTH DEFECTS IN MICHIGAN All Cases Reported and Processed by April
Mendelian inheritance and the
 Mendelian inheritance and the most common genetic diseases Cornelia Schubert, MD, University of Goettingen, Dept. Human Genetics EUPRIM-Net course Genetics, Immunology and Breeding Mangement German Primate
Mendelian inheritance and the most common genetic diseases Cornelia Schubert, MD, University of Goettingen, Dept. Human Genetics EUPRIM-Net course Genetics, Immunology and Breeding Mangement German Primate
The Genetics of Early- Onset Breast Cancer. Cecelia Bellcross, Ph.D., M.S.,C.G.C. Department of Human Genetics Emory University School of Medicine
 The Genetics of Early- Onset Breast Cancer Cecelia Bellcross, Ph.D., M.S.,C.G.C. Department of Human Genetics Emory University School of Medicine All cancers are genetic BUT Not all cancers are hereditary
The Genetics of Early- Onset Breast Cancer Cecelia Bellcross, Ph.D., M.S.,C.G.C. Department of Human Genetics Emory University School of Medicine All cancers are genetic BUT Not all cancers are hereditary
Differential Diagnosis of Waardenburg Syndrome
 CHAPTER 4 Differential Diagnosis of Waardenburg Syndrome Chapter 1 described several ways that scientists diagnose genetic syndromes. This chapter addresses the specific application of these diagnostic
CHAPTER 4 Differential Diagnosis of Waardenburg Syndrome Chapter 1 described several ways that scientists diagnose genetic syndromes. This chapter addresses the specific application of these diagnostic
Neuromuscular diseases
 Neuromuscular diseases Spinal muscular atrophy - SMA characterized by degeneration of the anterior horn cells in the spinal cord and motor nuclei in the lower brainstem. SMA type 1, is also known as Werdnig-
Neuromuscular diseases Spinal muscular atrophy - SMA characterized by degeneration of the anterior horn cells in the spinal cord and motor nuclei in the lower brainstem. SMA type 1, is also known as Werdnig-
