For lecture notes: Allied OSI Orthotic Lab. Demographics. Lecture Handout Courtesy Of:
|
|
|
- Carol Glenn
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 New Thoughts and Orthotic Strategies in the Treatment of Plantar Heel Pain Syndrome Lecture Handout Courtesy Of: Allied OSI Orthotic Lab Douglas H. Richie Jr., DPM Adjunct Associate Clinical Professor-Department of Applied Biomechanics California School of Podiatric Medicine at Samuel Merritt College Private Practice: Seal Beach Podiatry Group, Inc. 550 Pacific Coast Highway Suite 209 Seal Beach, California USA For lecture notes: Demographics Author Male Female Mean Age Wolgin (1994) Tisdel (1996) Pfeffer (1999) Martin (1998) Davis (1994) Mizel (1996) Gill (1996) TOTAL % 60% (47.5 YRS) Fig. 7. Conditions capable of producing chronic plantar pain can be differentiated by the area of maximal tenderness: (1) plantar fasciitis, (2) entrapment of the first branch of the lateral plantar nerve, (3) heel pain syndrome, and (4) fat pad disorders. 1
2 SUBCALCANEAL PAIN Nerve Entrapment? Medial calcaneal nerve Savastano,, 1985 Nerve to abd. dig. quint. brev. Baxter, 1984 Medial plantar a. & n. Posterior tibial n. Posterior tibial a. Medial calcaneal n. Nerve to Abductor digiti quinti m. Lateral plantar a. & n. Nerve to Abductor Digiti Quinnti m. Abductor Digiti Quinti m. Lateral Plantar n. Medial Plantar n. Flexor digitorum brevis / Abductor hallucis mm. Plantar fascia Skin incision Fig. 2. Neurovascular anatomy of the subcalcaneal region. (From Ward WG, Clippinger FW: Proximal medial longitudinal arch incision for plantar fascia release. Foot Ankle 8:155, American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle society 1987; with permission.) Figs. 4A and 4B. (A) Anatomic depiction described in Gray s Anatomy of the location of the nerve to the abductor digiti minimi. (B) Baxter s anatomic specimen dissections found that this branch actually comes off more proximally, implicating it in the painful heel syndrome. Causative Factors Of Heel Pain: Heel Pain Treatments Obesity O Brien, Shikoff, Tanz Pes Planus Bordelon, 1993 MULTIPLE Pes Cavus Culter, 1986 Tight Heel Cord Kibler, 1991 DISEASE Custom foot orthosis Heel pain Night splint NSAID OUTCOMES Pronation of STS Baxter, 1984 Gould, 1959 Hicks, 1954 Davis, 1990 PATHWAYS Shock McKenzie, 1985 Windlass Dysfunction Ellis,
3 Pathogenesis It is reasonably certain that a condition which has so many different theories of etiology and treatment does not have valid proof of any one cause. Snook and Chrisman Clin Orthop 82:163, 1972 Points of Confusion Pathomechanics of Plantar Fascia overload: Foot Pronation STJ Pronation MTJ Pronation Longitudinal axis Oblique axis 1 st Ray movement Arch Flattening IR 5.8 cm Fig. 15. Anatomic preparation of the foot with the plantar structures in view. Internal rotation is applied to the tibiotalar column and the foot is maintained in the plantigrade position. The height of the medial longitudinal arch measures 5.8 cm. It is lower as compared with a high arch situation measuring 7 cm. In the same specimen. The plantar aponeurosis (PA) and the abductor hallucis muscle (ABDH) are seen under tension. They are not undulant. Fig. 12. Anatomic preparation of the foot with the plantar structures in view. External rotation is applied to the tibiotalar column and the foot is maintained in a plantigrade position. The height of the medial longitudinal arch measures 7 cm. It has increased as compared with a low arch situation measuring 5.8 cm in the same specimen. The plantar aponeurosis (PA) and the abductor hallucis muscle (ABD.H.) are seen relaxed and undulant. P.A. ABD.H. PLANTAR FASCIITIS Pronation of Subtalar Joint : Cannot by itself cause strain of PF Can only influence PF thru MTJ 3
4 Scherer PR, The Biomechanics Graduate Research Group for 1988: Heel Spur Syndrome. Pathomechanics and non surgical treatment. Journal American Med Assoc 81:68, Patients, 118 painful heels Treatments: NSAIDS, Steroid injection, Tape strapping, Foot Orthoses 81% in group with tape strapping and orthoses achieved good results 80% of all patients had foot deformity compensated by supination of longitudinal axis of midtarsal joint Scherer PR, The Biomechanics Graduate Research Group for 1988: Heel Spur Syndrome. Pathomechanics and non surgical treatment. Journal American Med Assoc 81:68, % of all patients had foot deformity compensated by supination of longitudinal axis of midtarsal joint Out of 133 painful heels: 63 had forefoot valgus 33 had everted rearfoot 20 had plantarflexed first ray SUPP. OF MTJ LA Everted Calc. past perpend. Flexible FF valgus Plantarflexed 1st Ray In-Vitro Study Nine fresh frozen specimens Axial load in static stance N 6 degree wedges: Medial & Lateral, RF & FF Strain in plantar fascia measured with reluctance transducer Kogler GF, Veer FB, Solomonidis SE, Paul JP: The influence of medial and lateral placement of orthotic wedges on loading of the plantar aponeurosis. Journal Bone Joint Surgery 81-A:1403,
5 Kogler GF, Veer FB, Solomonidis SE, Paul JP: The influence of medial and lateral placement of orthotic wedges on loading of the plantar aponeurosis. Journal Bone Joint Surgery 81-A:1403, 1999 Plantar Fascia Strain Wedge under lateral forefoot decreased strain (p<0.05) Wedge under medial forefoot increased strain (p<0.05) Rearfoot wedges had no significant effect Kogler GF, Veer FB, Solomonidis SE, Paul JP: The influence of medial and lateral placement of orthotic wedges on loading of the plantar aponeurosis. Journal Bone Joint Surgery 81-A:1403, 1999 Kogler GF, Veer FB, Solomonidis SE, Paul JP: The influence of medial and lateral placement of orthotic wedges on loading of the plantar aponeurosis. Journal Bone Joint Surgery 81-A:1403, 1999 Fig. 7. The truss is a triangular structure. Under the load (W) the struts are under compression ( C ) and the tie-rod (AB) is under tension (T). Any joint, for example point A, is in vectorial equilibrium as indicated in the insert diagram. C compresses the point A and T tenses the same point. 5
6 Chimp Assembled Bonobo Assembled Orangutan Twisted Plate Theory FOOT VIEWED FROM BEHIND Twisted Plate Theory RAISE ARCH: Invert Rear Plate Evert Front Plate Rear Plate twisted clockwise (inversion) Front Plate twisted counter clockwise LOWER ARCH: Evert Rear Plate Invert Front Plate 6
7 Twisted Plate Theory RAISE ARCH: Invert Rear Plate Evert Front Plate LOWER ARCH: Evert Rear Plate Invert Front Plate 7
8 8
9 9
10 Load cell Mounting post Crosshead Beam Hole for locator pin DVRT Compression plate Shoe Shoe alignment plate Foot Orthosis Cancellous bone screws Figure 2. Diagramatic representation of the experimental set-up for testing the longitudinal arch support mechanism of foot orthoses. Kogler GF, Veer FB, Solomonidis SE, Paul JP: Biomechanics of longitudinal arch support mechanisms in foot orthoses and their effect on plantar aponeurosis strain. Clinical Biomech 11:243, 1996 FO 1 FO 4 FO 2 FO 5 FO 3 Figure 3. Illustrations of test orthoses for a left foot. FO no. 1, prefabricated stock orthosis; FO no2, custom viscoelastic orthosis; FO no. 3, custom semi-rigid orthosis; FO no. 4, custom rigid functional orthosis; FO no. 5, custom rigid UC-BL shoe insert Plantar Fascia Strain Effect of shoe inserts: 3 devices significantly reduced strain: 1.) UCBL 2.) Viscoelastic footbed 3.) Cork & rubber footbed 2 devices did not reduce strain: 1.) Custom rigid functional foot orthosis 2.) Pre-fabricated stock orthosis Kogler GF, Veer FB, Solomonidis SE, Paul JP: Biomechanics of longitudinal arch support mechanisms in foot orthoses and their effect on plantar aponeurosis strain. Clinical Biomech 11:243, FO 2 FO 3 FO 1 FO FO 5 LOAD (N) foot shoe RELATIVE STRAIN % Kogler GF, Veer FB, Solomonidis SE, Paul JP: Biomechanics of longitudinal arch support mechanisms in foot orthoses and their effect on plantar aponeurosis strain. Clinical Biomech 11:243, 1996 Fig. 7. The truss is a triangular structure. Under the load (W) the struts are under compression ( C ) and the tie-rod (AB) is under tension (T). Any joint, for example point A, is in vectorial equilibrium as indicated in the insert diagram. C compresses the point A and T tenses the same point. 10
11 One of the distinguishing features of the orthoses which decreased plantar aponeurosis strain was the surface contours of their medial and central regions and the angles related to their arch shape were more acute MAXIMUM MEDIAL ARCH HEIGHT OF TESTED FOOT ORTHOSES Kogler GF, Veer FB, Solomonidis SE, Paul JP: Biomechanics of longitudinal arch support mechanisms in foot orthoses and their effect on plantar aponeurosis strain. Clinical Biomech 11:243, 1996 Kogler GF, Veer FB, Solomonidis SE, Paul JP: Biomechanics of longitudinal arch support mechanisms in foot orthoses and their effect on plantar aponeurosis strain. Clinical Biomech 11:243, 1996 Elevate Heel? 12 cadaver limbs, static stance Strain transducer in central band PF 2 load levels: 337 N, 450N Heel Heights 2.0, 4.0, 6.0 cm Blocks: No significant difference in p.f. strain Shank contour platforms: sig. Decrease in p.f. Strain with elevation (p< 0.05) Kogler G.F., Veer F.B., Verhulst S.J., et. al. The effect of heel elevation on strain within the plantar apneurosis: : In Vitro Study. Foot and Ankle 22: , 439, Foot types with a normal arch do not have any medial tarsal bone contact with the shank profile interface. Therefore, structural repositioning of the foot most likely occurs from lateral skeletal segments that touch the shank profile surface. This suggests that an extended support zone, from just under the calcaneus to the cuboid, decreases the medial truss-like action of the foot by permitting the metatarsals to plantarflex slightly. Kogler G.F., Veer F.B., Verhulst S.J., et. al. The effect of heel elevation on strain within the plantar apneurosis: : In Vitro Study. Foot and Ankle 22: , 439,
12 Subcalcaneal Pain Footwear considerations 1. Heel height 2. Shank stability 3. Home shoe program Fig. 7. The truss is a triangular structure. Under the load (W) the struts are under compression ( C ) and the tie-rod (AB) is under tension (T). Any joint, for example point A, is in vectorial equilibrium as indicated in the insert diagram. C compresses the point A and T tenses the same point. Medial Truss Theory Reduce Plantar Fascia Strain: Plantarflex Distal Strut (1 st Ray) Dorsiflex Proximal Strut (Calcaneus) Elevate Junction of Struts (T-N Joint) Elevate Lateral Truss PROPOSED MECHANISM 1. 1st Ray dorsiflexes & inverts 2. MTJ supp. about long. axis 3. Eccentric cont. of abd. hallucis and FHB 4. Elongation strain of PF MECHANISM OF PLANTAR FASCIAL OVERLOAD FOREFOOT VALGUS OR PRONATED SUBTALAR JOINT CAUSING HEEL TO PRONATE PAST PERPENDICULAR ECCENTRIC CONTRACTION OF FLEXOR HALLUCIS BREVIS, ABDUCTOR HALLUCIS FIRST RAY DORSIFLEXES AND INVERTS MIDTARSAL JOINT SUPINATES ABOUT LONGITUDINAL AXIS MEDIAL COLUMN FLATTENING 5. Oblique MTJ pronation OVERLOAD OF PLANTAR FASCIA 12
13 First Ray Position 1. Same during gait vs. at rest? 2. Accurately depicted in neut susp cast? 3. Cast & orthotic modifications Based on activity? Dynamic Gait In terminal stance: Foot inverts 1 st ray plantar flexes below 2-5 Due to: Peroneus longus Plantar intrinsics Windlass Plantar Intrinsics No activity until 40% of gait cycle In pronated feet, activity at 10% Principal active role in arch stability No activity in standing feet Mann and Inman, JBJS, 1964 RELAXED STANCE 1. Extrinsic foot muscles inactive 2. Arch integrity maintained solely by plantar fascia Basmajian, 1963 Huang, 1993 Reeser, 1983 First Ray Position Static stance Plantar intrinsics and peroneus longus inactive Position 1 st ray dorsiflexed to at least level of 2 nd Met or to end ROM 13
14 Static Stance No windlass No plantar intrinsics No peroneus longus AOFAS Study Use of custom foot orthotics Standing less than 8 hrs. per day Standing more than 8 hrs. per day Rate of success Certain forms of treatment for the foot originated from the basis of thinking that only considers the foot as a static structure. Accommodative appliances and arch supports are typical examples of methods of treatment based upon static considerations. Such methods are relatively ineffective in comparison with methods designed to control function of the foot during kinetic stance. Pfeffer G et al: comparison of custom and prefabricated orthoses in the initial treatment of proximal plantar fasciitis. Foot & Ankle 20: 214, 1999 Root, ML, Orien, WP, Weed, JH: Clinical Biomechanics: Normal and Abnormal Function of the Foot, Vol 2. Los Angeles, Clinical Biomechanics Corp, Static stance stability of the foot is of minor clinical significance. In most feet that function abnormally during kinetic conditions, the static stance periods are probably not very traumatic to the foot. Therefore, static stance can be considered to be clinically insignificant except in feet that are severely subluxed and pronated. Most symptomatology and trauma to the foot is occasioned by instability of the foot that primarily develops during kinetic function. Therefore, the foot should be clinically evaluated and treatment consideration should be based primarily upon kinetic requirements of the foot. Treatment based upon static considerations has usually failed to provide more than partial relief of symptoms and that relief may be only temporary. Root, ML, Orien, WP, Weed, JH: Clinical Biomechanics: Normal and Abnormal Function of the Foot, Vol 2. Los Angeles, Clinical Biomechanics Corp,
15 First Ray Position Dynamic Gait Static stance with orthosis 1-5 valgus 2-5 varus No PF of 1 st Ray 1 st Ray plantarflexes below 2-5 Inverting Foot Theory 1. The alignment of the First Ray is different in a neutral suspension cast position than it is in a weight bearing static stance position. 2. A functional foot orthosis (Root design) affects First Ray position differently in dynamic gait than during static stance. First Ray Position Dynamic gait with orthosis 1-5 valgus 1 st plantar flexes First Ray Overload Orthosis too wide Supinated cast false FF Varus FF Varus post with no true FF Varus 2-5 varus with filler 15
16 Plantar Heel Pain Orthotic Treatment Proposal Goal: Prevent dorsiflexion overload of First Ray Strategy: Assure that the first metatarsal remains plantar to the plane of the lesser metatarsals during static stance and during gait Plantarflex First Ray 1. Push down on 1 st during Casting 2. Reverse Mortons Extension or External FF Valgus Wedge 3. Lite Filler between platforms 4. First Ray Cut Out ORTHOTIC STRATEGIES 16
17 Maximal Plantar Flexion Of First Ray Push down on First Ray During Casting Procedure Maximal Plantar Flexion Of First Ray Push down on First Ray During Casting Procedure Light Filler Between Balancing Platforms 17
18 Figure A & B: A, Reference marking for intrinsic forefoot balancing during the positive cast correction technique. B, Reference and corrective platforms for intrinsic balancing of the positive cast. Light Filler First Ray Cutout Vs First Met Accomodation 18
19 ABD ANAT ABD TENSION ABD TENSION Medial Truss Theory Reduce Plantar Fascia Strain: Plantarflex Distal Strut (1 st Ray) Dorsiflex Proximal Strut (Calcaneus) Elevate Junction of Struts (T-N Joint) Elevate Lateral Truss 19
20 Dorsiflex Calcaneus (Increase Calcaneal Pitch) 1. Decrease Load on Achilles Stretching Night Splint Heel Lift 2. Contoured heel seat of FO Fig. 7. The truss is a triangular structure. Under the load (W) the struts are under compression ( C ) and the tie-rod (AB) is under tension (T). Any joint, for example point A, is in vectorial equilibrium as indicated in the insert diagram. C compresses the point A and T tenses the same point. Heel Cord Tension Fig. 7. The truss is a triangular structure. Under the load (W) the struts are under compression ( C ) and the tie-rod (AB) is under tension (T). Any joint, for example point A, is in vectorial equilibrium as indicated in the insert diagram. C compresses the point A and T tenses the same point. 20
21 Subcalcaneal Pain Treatment recommendations 3. Decrease passive loading of heel cord: Heel elevation (footwear) Static stretching Night splint CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT Which treatment worked best? TREATMENT Stretching Rest NSAIDS Cushion Inserts RATING Wolgin et al. Conservative Treatment of Plantar Heel Pain : Long Term F/U Foot & Ankle :97, 1994 Powell M, Post WR, Keener J, Wearden S: Effective treatment of chronic plantar fasciitis with dorsiflexion night splints: A crossover prospective randomized outcome study. Foot and Ankle 19:10, 1998 Pt Total: 37 Sx Present: 6 mo. or more Tx: PF Night Splint 30 days Assessment: Physician exam/interview - Mayo Clinic Scoring System - AOFAS Ankle Hindfoot Rating Results: Satisfied 59% Satisfied with reservations 13% Dissatisfied 10% Could not wear splint 18% CONCLUSION: We believe dorsiflexion splints provide relief from the symptoms of recalcitrant plantar fasciitis in the majority of patients. Batt ME, Tanji JL, Skattum N: Plantar fasciitis: A prospective randomized clinical trial of the tension night splint. Clin Journal Sport Med 6:158, Patient total: 32 Sx present: 12.7 months Tx: 2 Groups 1. NSAID, viscoelastic heel stretch (control) 2. Tension plantar fascia night splint (custom fabricated) Assessment: Physician exam Results: Group Healed Time to Healing Control TNS Cross over 6/17 16/16 8/ weeks 12.5 weeks 13 weeks Conclusion: the TNS is an effective treatment for plantar fasciitis. 21
22 Subcalcaneal Pain Footwear considerations 1. Heel height 2. Shank stability 3. Home shoe program Heel Pain Treatments Success with Orthotics MULTIPLE Rated most successful of all treatment: DISEASE Custom foot orthosis Heel pain Night splint NSAID PATHWAYS OUTCOMES Martin, 1998 Wolgin, 1994 O Brien, 1985 Blake, 1985 Gross, 1991 Lynch, 1998 Ferguson,
23 Scherer PR, The Biomechanics Graduate Research Group for 1988: Heel Spur Syndrome. Pathomechanics and non surgical treatment. Journal American Med Assoc 81:68, Patient total: 73, 118 painful heels Sx present: not reported Tx: Tape Strapping, NSAID, Steroid Inj. Rigid foot orthosis Assessment: Patient evaluation of % of pain relief Results: Subgroup of strapping & orthosis only. Good 81% Fair 15% in 6 weeks Poor 4% 63 of 133 painful heels had forefoot valgus 20 had plantarflexed first 33 had everted heel (Thus, 80% had supp. long axis of MPJ) Scherer PR, The Biomechanics Graduate Research Group for 1988: Heel Spur Syndrome. Pathomechanics and non surgical treatment. Journal American Med Assoc 81:68, Conclusion: This study demonstrates that with or without initial short term antiinflammatory medication, mechanical control of the midtarsal joint is an effective treatment for heel spur syndrome. Lynch D, Goforth WP, Martin JE, Odom RD, Preece CK, Kotler MW: Conservative treatment of plantar fasciitis A prospective study. Journal American Pod Med Assoc. 88: 375, 1998 Patient total: 85 Sx present: 46 weeks Tx: 3 Categories 1. NSAID & Steroid Inj. 2. Viscoelastic heel cup 3. Low dye strapping / arch pad functional foot orthosis Assessment: Patient self-completed questionnaire, Physician evaluation, visualizing pain scale: 2,4,6 & 12 weeks Lynch D, Goforth WP, Martin JE, Odom RD, Preece CK, Kotler MW: Conservative treatment of plantar fasciitis A prospective study. Journal American Pod Med Assoc. 88: 375, 1998 Results: Starting visual analog pain = 6.4 Finish (all 3 groups) 12 weeks = % improvement Treatment failure: (no improvement or adverse reaction) 2.3% in Group 1 42% in Group 2 4% in Group 3 Final Pain/activity assessment: Group G F P Conclusion: A significant difference was noted between groups with taping and orthosis proving to be more effective than either anti-inflammatory or accommodative modalities. Mechanical vs. Accomodative Failure at 6 weeks Anti-inflammatory Accommodative Mechanical 23% 42% 4% Good-Excellent Results at 12 weeks 33% 30% 70% Lynch D.M., Goforth W.P., Martin J.E. et al: Conservative Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis. A Prospective Study. JAPMA 88 : 375,
24 Author Wolgin Tisdel Martin Duration of Treatment (mos) Outcome (%) G F P Ideal Subcalcaneal Pain Treatment Outcome Davis Mizel Scherer Lynch Absence of morning pain Absence of day/night pain Full work capacity Return to previous recreation Return to previous fitness No unacceptable footwear restrictions Restoration of strength flexibility Return to pre-injury mobility Yes No Plantar Fasciitis: Custom vs. Pre-fab Foot Orthoses RCT involving 135 participants Random assignment into three groups: Sham orthosis (soft foam) Prefabricated orthosis (firm foam) Custom orthosis (semi-rigid plastic) Duration of follow-up for each patient: 12 months Plantar Fasciitis: Custom vs. Pre-fab Foot Orthoses Results: Compared with sham orthoses: Mean pain score with pre-fab orthoses was 8.7 points better (P=.05) Mean pain score with custom orthoses was 7.4 points better (P=.10) Mean pain score with custom orthoses was 7.4 points better (P=.10) Mean function score was 7.5 points better for custom orthoses (P=.04) There were no differences between groups at the 12 month review. Landorf KB, Keenan AM, Herbert RD: Effectiveness of foot orthoses to treat plantar fasciitis. Arch Intern Med/ Vol 166, June 26th, 2006 pp Landorf KB, Keenan AM, Herbert RD: Effectiveness of foot orthoses to treat plantar fasciitis. Arch Intern Med/ Vol 166, June 26th, 2006 pp
25 Is a Formthotic a Prefabricated Orthosis??? Why was the pain score not significantly different between the 3 groups? Summary Of Heel Pain Treatment Studies 1. Patients have low expectation of achieving total permanent relief. 2. Acceptable time frame to achieve successful tx outcome? 3. Definition of success: Pain, patient satisfaction 4. Treatments deemed successful, yet: Significant # of pts still in pain Significant # of pts fail to comply & improve Significant length of time to achieve success 5. Multiple tx s yet Which worked best? 6. Physician assessment of success 7. Retrospective reviews Time Heals All Wounds 25
26 Martin RL, Irrgang JJ, and Conti SF: Outcome Study of Subjects with Insertional Plantar Fasciitis.. Foot & Ankle Int. 19:803, Time Wounds All Heels Duration of Sx: 30% > 12 mos. 54% > 6 mos. Less likely to have good outcome if symptoms present for > 12 mo. before treatment. P <.05 Martin RL, Irrgang JJ, Conti SF: Outcome study of subjects with insertional plantar fasciitis. Foot and Ankle 19:803, CONCLUSION: 2. This may add support to the observation that subjects with more chronic symptoms have a poorer outcome and that initiation of early, aggressive, non surgical therapy is appropriate and warranted. Subcalcaneal Pain Subjects with symptoms less than 12 months have the best outcome with non surgical treatment Furrey, 1975 O Brien, 1985 Shikoff, 1986 Arnis, 1988 Wolgin, 1994 Mizel, 1996 Martin, 1998 Heel Pain = What is a quality outcome? What is the overall cost? Ideal Subcalcaneal Pain Treatment Outcome 26
27 Absence of morning pain Absence of day/night pain Full work capacity Return to previous recreation Return to previous fitness No unacceptable footwear restrictions Restoration of strength flexibility Return to pre-injury mobility Yes No 27
28 Raise Medial Arch at T-N Joint 1. Twist the plate Evert FF Lateral FF wedge 2. Plaster expansion at T-N not a filler 3. Wider footplate at T-N narrower at 1 st Ray 28
29 CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT Which treatment worked best? TREATMENT Stretching Rest NSAIDS Cushion Inserts RATING Wolgin et al. Conservative Treatment of Plantar Heel Pain : Long Term F/U Foot & Ankle :97, 1994 Subcalcaneal Pain Treatment recommendations 4. Footwear program: Elevated heel Shank stability Home shoe use 29
30 Lecture Handout Courtesy Of: Allied OSI Orthotic Lab PATHOMECHANICS LEG LENGTH INEQUALITY PRONATION OF STJ RESTRICTED DORSIFLEX HIGH ARCH FOOT LOW ARCH FOOT HEEL STRIKE SHOCK Arch Elongation Varus FF Wedge 30
31 Valgus FF Wedge Fig. 7. The truss is a triangular structure. Under the load (W) the struts are under compression ( C ) and the tie-rod (AB) is under tension (T). Any joint, for example point A, is in vectorial equilibrium as indicated in the insert diagram. C compresses the point A and T tenses the same point. Raise Lateral Truss 1. FF Valgus Post 2. Minimal Plaster Fill at CC joint 3. Contoured Shank Footwear 31
32 Subcalcaneal Pain Treatment recommendations 1. Prevent overload (dorsiflexion) of first ray: Light filler between platforms Balance 2-5, 1 st ray cut out Avoid wide orthotic plate Don t capture a false FF varus Subcalcaneal Pain Treatment recommendations 2. Minimize supination of longitudinal Axis of MTJ: Prevent rearfoot eversion If present, capture FF valgus 32
33 33
34 34
35 Like the hand, the foot has three anatomical regions: (1) The seven bones of the tarsus form the ankle and proximal half of the foot. (2) The middle portion of the foot consists of five metatarsals. (3) Phalanges, the skeletal elements of the toes, have the same number and arrangement as in the fingers. The primary difference between the human and chimp foot is the contrast between prehensile functions of the ape foot and the anatomy of bipedal striding in the human. The chimpanzee foot has an opposable hallux and long phalanges. The human foot has greatly reduced digits, with all metatarsals parallel and an increase in the lever arm of the tarsus for striding. In the human foot, a longitudinal arch provides a shock absorbing and weight distribution system. The orientation of the ankle joint allows the tibia to take a straighter path over the foot during walking Dr. Meldrum has been investigating the ways monkeys, apes and human ancestors get around, or locomote, for nearly fifteen years. Some of his research has focused on the way in which the human foot has adapted to the habit of walking on two feet (bipedalism). His research compares and contrasts the anatomy and function of diverse primate feet -- the interaction of the muscles ligaments and bones, as well as the sole pad and skin ridges. He has also taught courses in comparative primate anatomy, the fossil record of primate and human evolution, and currently teaches human anatomy in the Health Professions Programs at Idaho State University. Representative Publications: Meldrum, DJ and Wunderlich, RE. (1998) Midtarsel flexibility in ape foot dynamics, early hominid footprints and bipedalism. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. Suppl 26. (In press) Hamrick, MW, Meldrum, DJ and Simons, EL (1995). Anthropoid phalanges from the Oligocene of Egypt. Journal of Human Evolution. 28: Meldrum, DJ (1993). On plantigrady and quadrupedalism. American Journal of Physical Anthropology 91: Jungers, WL, Meldrum, DJ and Stern, JT, Jr. (1993) Evolutionary and functional significance of the human peroneus tertius muscle. Journal of Human Evolution 25: Meldrum, DJ (1991). The kinematics of the cercopithecine foot on arboreal and terrestrial substrates with implications for the interpretation of hominid terrestrial adaptations. American Journal of Physical Anthropology 84:
36 36
37 Twisted Plate Theory RAISE ARCH: Invert Rear Plate Evert Front Plate LOWER ARCH: Evert Rear Plate Invert Front Plate Scherer PR, The Biomechanics Graduate Research Group for 1988: Heel Spur Syndrome. Pathomechanics and non surgical treatment. Journal American Med Assoc 81:68, Patient total: 73, 118 painful heels Sx present: not reported Tx: Tape Strapping, NSAID, Steroid Inj. Rigid foot orthosis Assessment: Patient evaluation of % of pain relief Results: Subgroup of strapping & orthosis only. Good 81% Fair 15% in 6 weeks Poor 4% 63 of 133 painful heels had forefoot valgus 20 had plantarflexed first 33 had everted heel (Thus, 80% had supp. long axis of MPJ) 84 Pts. Tx conservative for PF 115 of 133 feet had MTJ supination on longitudinal axis (86%) Scherer et al: JAPMA 81:68,
The Five Most Common Pathomechanical Foot Types (Rearfoot varus, forefoot varus, equinus, plantarflexed first ray, forefoot valgus)
 The Five Most Common Pathomechanical Foot Types (Rearfoot varus, forefoot varus, equinus, plantarflexed first ray, forefoot valgus) Pathomechanical foot types usually refer to structural deformities that
The Five Most Common Pathomechanical Foot Types (Rearfoot varus, forefoot varus, equinus, plantarflexed first ray, forefoot valgus) Pathomechanical foot types usually refer to structural deformities that
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE
 PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE Presenter Dr. Richard Coughlin AOFAS Lecture Series OBJECTIVES 1. ASSESS 2. DIAGNOSE 3. TREAT HISTORY TAKING Take a HISTORY What is the patient s chief complaint?
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE Presenter Dr. Richard Coughlin AOFAS Lecture Series OBJECTIVES 1. ASSESS 2. DIAGNOSE 3. TREAT HISTORY TAKING Take a HISTORY What is the patient s chief complaint?
Plantar fascia. Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot)
 ! Plantar fascia Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot) Plantar Fasciitis is the most common foot problem seen in runners and is often associated with an increase in running mileage. Typically
! Plantar fascia Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot) Plantar Fasciitis is the most common foot problem seen in runners and is often associated with an increase in running mileage. Typically
Clinical Analysis of Foot Problems
 Clinical Analysis of Foot Problems by Karen S. Seale, M.D. Introduction Orthotists are vital members of the foot care team. Their expertise and special interests in materials and biomechanics add a unique
Clinical Analysis of Foot Problems by Karen S. Seale, M.D. Introduction Orthotists are vital members of the foot care team. Their expertise and special interests in materials and biomechanics add a unique
The Best Treatments for Plantar Heel Pain
 CLINICAL PODIATRY The Best Treatments for Plantar Heel Pain Objectives 1) Understand the pathway to wound healing through the three phases of inflammatory, proliferative, and remodeling. 2) Introduce the
CLINICAL PODIATRY The Best Treatments for Plantar Heel Pain Objectives 1) Understand the pathway to wound healing through the three phases of inflammatory, proliferative, and remodeling. 2) Introduce the
Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies
 Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies David Lee, D.P.M., D. A.B.P.S. Purpose Identification of mechanical foot and ankle conditions Base treatments Knowing when to refer to a podiatrist
Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies David Lee, D.P.M., D. A.B.P.S. Purpose Identification of mechanical foot and ankle conditions Base treatments Knowing when to refer to a podiatrist
Using Might Splints in the Treatment
 Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1993, 2, 287-297 @ 1993 Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. Using Might Splints in the Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis in the Athlete David J. Pezzullo Plantar fasciitis is
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1993, 2, 287-297 @ 1993 Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. Using Might Splints in the Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis in the Athlete David J. Pezzullo Plantar fasciitis is
Pathology-Designed Custom Molded Foot Orthoses
 Pathology-Designed Custom Molded Foot Orthoses Kevin B. Rosenbloom, CPed KEYWORDS Foot orthoses Custom orthoses Orthotic devices Pathology-designed orthoses Orthosis design Treating patients with custom
Pathology-Designed Custom Molded Foot Orthoses Kevin B. Rosenbloom, CPed KEYWORDS Foot orthoses Custom orthoses Orthotic devices Pathology-designed orthoses Orthosis design Treating patients with custom
Structure & Function of the Ankle and Foot. A complicated model of simplicity that you really think little about until you have a problem with one.
 Structure & Function of the Ankle and Foot A complicated model of simplicity that you really think little about until you have a problem with one. The Foot and Ankle Terminology Plantar flexion Dorsi flexion
Structure & Function of the Ankle and Foot A complicated model of simplicity that you really think little about until you have a problem with one. The Foot and Ankle Terminology Plantar flexion Dorsi flexion
Outline. The Agony of the Foot: Disclosure. Plantar Fasciitis. Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care. Daniel Thuillier, M.D.
 The Agony of the Foot: Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care Daniel Thuillier, M.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Orthopaedics University of California San Francisco Plantar Fasciitis Achilles
The Agony of the Foot: Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care Daniel Thuillier, M.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Orthopaedics University of California San Francisco Plantar Fasciitis Achilles
Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understa
 Plantar Fasciitis Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understand why it occurs. Recognize the injury
Plantar Fasciitis Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understand why it occurs. Recognize the injury
Lower Back Spinal Fusion & Exercise
 & Exercise with Rick Kaselj, MS More FREE Information on Exercise & Injuries $299 Fitness Education Returning the Shoulder Back to Optimal Function Seminar Exercise Modification for the Sensitive Shoulder
& Exercise with Rick Kaselj, MS More FREE Information on Exercise & Injuries $299 Fitness Education Returning the Shoulder Back to Optimal Function Seminar Exercise Modification for the Sensitive Shoulder
.org. Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs. Anatomy. Cause
 Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Page ( 1 ) Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition
Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Page ( 1 ) Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition
Predislocation syndrome
 Predislocation syndrome Sky Ridge Medical Center, Aspen Building Pre-dislocation syndrome, capsulitis, and metatarsalgia are all similar problems usually at the ball of the foot near the second and third
Predislocation syndrome Sky Ridge Medical Center, Aspen Building Pre-dislocation syndrome, capsulitis, and metatarsalgia are all similar problems usually at the ball of the foot near the second and third
Functional Anatomy and Lower Extremity Biomechanics
 Functional Anatomy and Lower Extremity Biomechanics Eric Folmar, MPT, OCS Functional Lower Extremity Biomechanics The science of foot, ankle, knee and hip biomechanics and their relationships and interactions
Functional Anatomy and Lower Extremity Biomechanics Eric Folmar, MPT, OCS Functional Lower Extremity Biomechanics The science of foot, ankle, knee and hip biomechanics and their relationships and interactions
The Forefoot Valgus Foot-Type Joe Fox, MS, LAT June 10, 2014
 The Forefoot Valgus Foot-Type Joe Fox, MS, LAT June 10, 2014 Introduction BS Kinesiology Exercise Science and Athletic Training, University of Wisconsin-Madison MS in Exercise Science Athletic Training,
The Forefoot Valgus Foot-Type Joe Fox, MS, LAT June 10, 2014 Introduction BS Kinesiology Exercise Science and Athletic Training, University of Wisconsin-Madison MS in Exercise Science Athletic Training,
Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain)
 Discussion paper prepared for The Workplace Safety and Insurance Appeals Tribunal March 2003 Prepared by: Timothy Daniels, MD, FRCSC Division of Orthopaedic Surgery, St. Michael s Hospital, Toronto, Ontario
Discussion paper prepared for The Workplace Safety and Insurance Appeals Tribunal March 2003 Prepared by: Timothy Daniels, MD, FRCSC Division of Orthopaedic Surgery, St. Michael s Hospital, Toronto, Ontario
Steve Manning 2/10/2011
 Utilising Footwear Modification as a Treatment Modality Steve Manning Intraining Running Injury Clinic, Milton BHlSc Podiatry (Hons), Level IV Coach Athletics SMA Qld President, QUT Sports Medicine Clinic
Utilising Footwear Modification as a Treatment Modality Steve Manning Intraining Running Injury Clinic, Milton BHlSc Podiatry (Hons), Level IV Coach Athletics SMA Qld President, QUT Sports Medicine Clinic
Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries
 Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries Symptoms Related to Abnormal Foot Biomechanics & their Differential Diagnosis Daniel Pang BSc (Hon) P&O, Cped Certified Pedorthist (USA) Only 10% of foot having structure
Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries Symptoms Related to Abnormal Foot Biomechanics & their Differential Diagnosis Daniel Pang BSc (Hon) P&O, Cped Certified Pedorthist (USA) Only 10% of foot having structure
Page 2 of 6 plantar fascia. This is called the windlass mechanism. Later, we'll discuss how this mechanism is used to treat plantar fasciitis with str
 Page 1 of 6 Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain) Plantar fasciitis is a painful condition affecting the bottom of the foot. It is a common cause of heel pain and is sometimes called a heel spur. Plantar fasciitis
Page 1 of 6 Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain) Plantar fasciitis is a painful condition affecting the bottom of the foot. It is a common cause of heel pain and is sometimes called a heel spur. Plantar fasciitis
Plantar Heel Pain. By: Kevin Kleiner, M.B.S. New York College of Podiatric Medicine
 Plantar Heel Pain By: Kevin Kleiner, M.B.S. New York College of Podiatric Medicine Plantar Heel Pain: - Many Etiologies but few solutions Plantar heel pain more specifically: Heel pain felt in ones rear-foot
Plantar Heel Pain By: Kevin Kleiner, M.B.S. New York College of Podiatric Medicine Plantar Heel Pain: - Many Etiologies but few solutions Plantar heel pain more specifically: Heel pain felt in ones rear-foot
Heel pain and Plantar fasciitis
 A patient s guide Heel pain and Plantar fasciitis Fred Robinson BSc FRCS FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon Alex Wee BSc FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon. What causes
A patient s guide Heel pain and Plantar fasciitis Fred Robinson BSc FRCS FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon Alex Wee BSc FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon. What causes
Integra. Subtalar MBA and bioblock Implant SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 Integra Subtalar MBA and bioblock Implant SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Table of contents Introduction Description... 2 Indications... 2 Contraindications... 2 Surgical Technique Step 1: Incision and Dissection...3
Integra Subtalar MBA and bioblock Implant SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Table of contents Introduction Description... 2 Indications... 2 Contraindications... 2 Surgical Technique Step 1: Incision and Dissection...3
Current Concepts In Orthotic Therapy For Pes Cavus
 Current Concepts In Orthotic Therapy For Pes Cavus http://www.podiatrytoday.com/current-concepts-in-orthotic-therapy-for-pes-cavus Podiatry Today- Volume 21 - Issue 10 - October 2008 Author(s): By Paul
Current Concepts In Orthotic Therapy For Pes Cavus http://www.podiatrytoday.com/current-concepts-in-orthotic-therapy-for-pes-cavus Podiatry Today- Volume 21 - Issue 10 - October 2008 Author(s): By Paul
Heel Pain Syndromes DELLON INSTITUTES FOR PERIPHERAL NERVE SURGERY
 Heel Pain s 5 3333 N CALVERT ST, SUITE 370, BALTIMORE, MD 21218 T410 467 5400 F410 366 9826 delloninstitutes.com your complaints are Pain, numbness or burning in your heel. The timing of this pain and
Heel Pain s 5 3333 N CALVERT ST, SUITE 370, BALTIMORE, MD 21218 T410 467 5400 F410 366 9826 delloninstitutes.com your complaints are Pain, numbness or burning in your heel. The timing of this pain and
Dr Rick Robinson, DPM Director of Podiatric Services USPHS Hospital at Whiteriver, AZ 2015 IHS National Combined Council Winter Meeting Friday,
 Dr Rick Robinson, DPM Director of Podiatric Services USPHS Hospital at Whiteriver, AZ 2015 IHS National Combined Council Winter Meeting Friday, January 30, 2015 1 We are all athletes, the difference is
Dr Rick Robinson, DPM Director of Podiatric Services USPHS Hospital at Whiteriver, AZ 2015 IHS National Combined Council Winter Meeting Friday, January 30, 2015 1 We are all athletes, the difference is
Podiatric Management in Ice Skating. geographical location. A close cousin to ice skating is in-line skating, which is a similar biomechanical
 SPORTS PODIATRY Podiatric Management in Ice Skating Understanding the biomechanics of this sport can help you better treat skaters. By R. Neil Humble, D.P.M. This article is the second in a sevenpart sports
SPORTS PODIATRY Podiatric Management in Ice Skating Understanding the biomechanics of this sport can help you better treat skaters. By R. Neil Humble, D.P.M. This article is the second in a sevenpart sports
Hyperpronation and Foot Pain
 Hyperpronation and Foot Pain Steps Toward Pain-Free Feet Steven D. Stovitz, MD; J. Chris Coetzee, MD THE PHYSICIAN AND SPORTSMEDICINE - VOL 32 - NO. 8 - AUGUST 2004 For CME accreditation information, instructions
Hyperpronation and Foot Pain Steps Toward Pain-Free Feet Steven D. Stovitz, MD; J. Chris Coetzee, MD THE PHYSICIAN AND SPORTSMEDICINE - VOL 32 - NO. 8 - AUGUST 2004 For CME accreditation information, instructions
WALKING BOOTS WALKING BOOTS. AFO s: Provider vs Prescriber? Provider. Prescriber
 Douglas H. Richie, Jr., D.P.M. 550 Pacific Coast Highway Suite 209 Seal Beach, California 90740 562.493.2451 phone 562.596.3157 fax DRichieJr@aol.com WALKING BOOTS Definitions: L 4360 (defined by HCPS):
Douglas H. Richie, Jr., D.P.M. 550 Pacific Coast Highway Suite 209 Seal Beach, California 90740 562.493.2451 phone 562.596.3157 fax DRichieJr@aol.com WALKING BOOTS Definitions: L 4360 (defined by HCPS):
Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933
 Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933 www.grhsonline.org Important Notice The information contained in this document is for informational
Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933 www.grhsonline.org Important Notice The information contained in this document is for informational
Plantar Fasciitis. Plantar Fascia
 Plantar Fasciitis Introduction Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the thick band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. This thick band of tissue is called the plantar fascia. Plantar
Plantar Fasciitis Introduction Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the thick band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. This thick band of tissue is called the plantar fascia. Plantar
Plantar Fascia Release
 Plantar Fascia Release Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. If other treatments are unsuccessful,
Plantar Fascia Release Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. If other treatments are unsuccessful,
November 2012 Case Study. Authors: Kyle Nagle, MD, MPH; Karl Fry, PT, DPT, OCS; David Bernhardt, MD
 CC: Right foot pain November 2012 Case Study Authors: Kyle Nagle, MD, MPH; Karl Fry, PT, DPT, OCS; David Bernhardt, MD HPI: A 17 year old female cross country runner presents with right foot pain. At a
CC: Right foot pain November 2012 Case Study Authors: Kyle Nagle, MD, MPH; Karl Fry, PT, DPT, OCS; David Bernhardt, MD HPI: A 17 year old female cross country runner presents with right foot pain. At a
Plantar fasciitis is a common foot problem that occurs in 10%
 Review Article Plantar Fasciitis Heel Pain: Part 1 a Practical Management Plantar fasciitis is a common foot problem that occurs in 10% of the population. 1,2 The most involved age group is 40-50 3,4 Actually,
Review Article Plantar Fasciitis Heel Pain: Part 1 a Practical Management Plantar fasciitis is a common foot problem that occurs in 10% of the population. 1,2 The most involved age group is 40-50 3,4 Actually,
A Patient s Guide to Plantar Fasciitis. Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, P.C.
 A Patient s Guide to Plantar Fasciitis Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
A Patient s Guide to Plantar Fasciitis Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome)
 PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome) R. Amadeus Mason MD Description Plantar fascitis is characterized by stiffness and inflammation of the main fascia (fibrous connective [ligament-like] tissue) on the
PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome) R. Amadeus Mason MD Description Plantar fascitis is characterized by stiffness and inflammation of the main fascia (fibrous connective [ligament-like] tissue) on the
Arches. Foot Injuries. Medial Longitudinal Arch. Lateral Longitudinal Arch. Transverse Arch. Arch Strains
 Arches Foot Injuries Three arches in the foot: 1) Lateral longitudinal arch 2) Medial longitudinal arch 3) Transverse arch These arches are maintained and supported by the wedging of the interlocking tarsal
Arches Foot Injuries Three arches in the foot: 1) Lateral longitudinal arch 2) Medial longitudinal arch 3) Transverse arch These arches are maintained and supported by the wedging of the interlocking tarsal
HEEL PAIN. Differential diagnosis. 1. Insertional Plantar fascitis. 2. Enthesis. 3. Heel pad atrophy. 4. Tarsal tunnel syndrome
 HEEL PAIN Differential diagnosis 1. Insertional Plantar fascitis 2. Enthesis 3. Heel pad atrophy 4. Tarsal tunnel syndrome 5. Calcaneal stress fracture 6. Haglund s syndrome 7. Posterior ankle impingement
HEEL PAIN Differential diagnosis 1. Insertional Plantar fascitis 2. Enthesis 3. Heel pad atrophy 4. Tarsal tunnel syndrome 5. Calcaneal stress fracture 6. Haglund s syndrome 7. Posterior ankle impingement
PLANTAR FASCIITIS. Plantar Fasciitis. Plantar Fasciitis. Heel Pain - common causes. Plantar Fasciitis 1/16/2012. Robert A Erdin III, MD
 PLANTAR FASCIITIS Robert A Erdin III, MD Special thanks to the AOFAS and David Richardson MD for slide reproductions Most common symptom related to the foot leading a patient to seek professional care
PLANTAR FASCIITIS Robert A Erdin III, MD Special thanks to the AOFAS and David Richardson MD for slide reproductions Most common symptom related to the foot leading a patient to seek professional care
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Lateral Ankle Reconstruction
 UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Lateral Ankle Reconstruction The ankle is a very complex joint. There are actually three joints that make up the ankle complex: the tibiotalar
UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Lateral Ankle Reconstruction The ankle is a very complex joint. There are actually three joints that make up the ankle complex: the tibiotalar
Paediatric Flat Feet Why do we treat the way we do? By Kim McArthur and Adam Jones
 Paediatric Flat Feet Why do we treat the way we do? By Kim McArthur and Adam Jones Aims and Objectives As clinicians we regularly make decisions in clinics regarding the orthotic treatment plan of children.
Paediatric Flat Feet Why do we treat the way we do? By Kim McArthur and Adam Jones Aims and Objectives As clinicians we regularly make decisions in clinics regarding the orthotic treatment plan of children.
Posttraumatic medial ankle instability
 Posttraumatic medial ankle instability Alexej Barg, Markus Knupp, Beat Hintermann Orthopaedic Department University Hospital of Basel, Switzerland Clinic of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kantonsspital Baselland
Posttraumatic medial ankle instability Alexej Barg, Markus Knupp, Beat Hintermann Orthopaedic Department University Hospital of Basel, Switzerland Clinic of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kantonsspital Baselland
RX: Custom Thermoplastic AFO Compliance Documentation
 RX: Custom Thermoplastic AFO Compliance Documentation Doctor Name: Phone: Patient Name: HICN: DOB: Indicate Quality ARIZONA THERMOPLASTIC ARTICULATED AFO, DORSI-ASSIST CROW L4631 A bivalved custom molded
RX: Custom Thermoplastic AFO Compliance Documentation Doctor Name: Phone: Patient Name: HICN: DOB: Indicate Quality ARIZONA THERMOPLASTIC ARTICULATED AFO, DORSI-ASSIST CROW L4631 A bivalved custom molded
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle. Dr. Travis Kieckbusch August 7, 2014
 Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Dr. Travis Kieckbusch August 7, 2014 Foot and Ankle Injuries in Athletes Lateral ankle sprains Syndesmosis sprains high ankle sprain Achilles tendon injuries Lisfranc
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Dr. Travis Kieckbusch August 7, 2014 Foot and Ankle Injuries in Athletes Lateral ankle sprains Syndesmosis sprains high ankle sprain Achilles tendon injuries Lisfranc
Common Foot Pathologies
 Common Foot Pathologies Chondromalacia Patella (patellofemoral pain syndrome) Chondromalacia Patella (patellofemoral pain syndrome) What is it? Chondromalacia (of Greek origin meaning softening of the
Common Foot Pathologies Chondromalacia Patella (patellofemoral pain syndrome) Chondromalacia Patella (patellofemoral pain syndrome) What is it? Chondromalacia (of Greek origin meaning softening of the
PODIATRIC SURGERY INFORMATION GUIDE: MANAGEMENT OF PLANTAR FASCIITIS/HEEL PAIN
 PODIATRIC SURGERY INFORMATION GUIDE: MANAGEMENT OF PLANTAR FASCIITIS/HEEL PAIN What is Plantar Fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is pain in the heel and arch area of the foot. The plantar fascia is a strong
PODIATRIC SURGERY INFORMATION GUIDE: MANAGEMENT OF PLANTAR FASCIITIS/HEEL PAIN What is Plantar Fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is pain in the heel and arch area of the foot. The plantar fascia is a strong
Clinical outcome of surgical intervention for recalcitrant infero-medial heel pain
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 483-488 ORIGINAL STUDY Clinical outcome of surgical intervention for recalcitrant infero-medial heel pain Friedl SINNAEVE, Geoffroy VANDEPUTTE From the Heilig Hartziekenhuis
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 483-488 ORIGINAL STUDY Clinical outcome of surgical intervention for recalcitrant infero-medial heel pain Friedl SINNAEVE, Geoffroy VANDEPUTTE From the Heilig Hartziekenhuis
Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures
 Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures Fractures of the heel bone, or calcaneus, can be disabling injuries. They most often occur during high-energy collisions
Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures Fractures of the heel bone, or calcaneus, can be disabling injuries. They most often occur during high-energy collisions
By: Jerry Ryan, M.D., University of Wisconsin Medical School, Madison, Wisconsin
 UAmerican Family PhysicianU September 1995 Use of Posterior Night Splints in the Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis Plantar fasciitis is a frequent cause of heel pain in athletes, as well as in persons who
UAmerican Family PhysicianU September 1995 Use of Posterior Night Splints in the Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis Plantar fasciitis is a frequent cause of heel pain in athletes, as well as in persons who
BACK PAIN FROM THE GROUND UP: THE WINDLASS EFFECT. Dr. Marcus A. Kampfe, CCEP, FAKTR, PSC, PES, CES, GFS
 BACK PAIN FROM THE GROUND UP: THE WINDLASS EFFECT Dr. Marcus A. Kampfe, CCEP, FAKTR, PSC, PES, CES, GFS WINDLASS EFFECT Mech of Gait Heel raise to toe off Supination of the foot, Ext rot of contact leg
BACK PAIN FROM THE GROUND UP: THE WINDLASS EFFECT Dr. Marcus A. Kampfe, CCEP, FAKTR, PSC, PES, CES, GFS WINDLASS EFFECT Mech of Gait Heel raise to toe off Supination of the foot, Ext rot of contact leg
The WalkOn Range. Dynamic Lower Leg Orthoses. NeW. Information for physicians, orthotists and physiotherapists
 The WalkOn Range Dynamic Lower Leg Orthoses NeW Information for physicians, orthotists and physiotherapists One Range Many Different Applications The WalkOn product range allows you to address the specific
The WalkOn Range Dynamic Lower Leg Orthoses NeW Information for physicians, orthotists and physiotherapists One Range Many Different Applications The WalkOn product range allows you to address the specific
ADVANCEMENTS IN PLANTAR FASCIA SURGERY
 C H A P T E R 3 3 ADVANCEMENTS IN PLANTAR FASCIA SURGERY James L. Bouchard, DPM Andrea Cass, DPM INTRODUCTION It has been estimated that 90% of patients with plantar fasciitis and heel spur syndrome get
C H A P T E R 3 3 ADVANCEMENTS IN PLANTAR FASCIA SURGERY James L. Bouchard, DPM Andrea Cass, DPM INTRODUCTION It has been estimated that 90% of patients with plantar fasciitis and heel spur syndrome get
CUSTOM ORTHOTICS/SHOES FAQ AND GLOSSARY
 CUSTOM ORTHOTICS/SHOES FAQ AND GLOSSARY What is GSC s new orthotics and orthopedic shoe policy? Only certain health professionals can prescribe and provide you with custom orthotics, orthopedic shoes,
CUSTOM ORTHOTICS/SHOES FAQ AND GLOSSARY What is GSC s new orthotics and orthopedic shoe policy? Only certain health professionals can prescribe and provide you with custom orthotics, orthopedic shoes,
Foot Pain. Aching in arch of foot - worse after prolonged weight bearing
 1 Foot Pain "Pronatory Disorder" ICD-9-CM: 734 Flat foot (pes planus-acquired) Diagnostic Criteria History: Physical Exam: Aching in arch of foot - worse after prolonged weight bearing Excessive pronation
1 Foot Pain "Pronatory Disorder" ICD-9-CM: 734 Flat foot (pes planus-acquired) Diagnostic Criteria History: Physical Exam: Aching in arch of foot - worse after prolonged weight bearing Excessive pronation
Effect of Foot Orthoses as Treatment for Plantar Fasciitis or Heel Pain
 Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2013, 22, 130-136 2013 Human Kinetics, Inc. www.jsr-journal.com CRITICALLY APPRAISED TOPIC Effect of Foot Orthoses as Treatment for Plantar Fasciitis or Heel Pain Jordan
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2013, 22, 130-136 2013 Human Kinetics, Inc. www.jsr-journal.com CRITICALLY APPRAISED TOPIC Effect of Foot Orthoses as Treatment for Plantar Fasciitis or Heel Pain Jordan
.org. Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction. Anatomy. Cause. Symptoms
 Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Treatment of Recalcitrant Intermetatarsal Neuroma With 4% Sclerosing Alcohol Injection: A Pilot Study
 Treatment of Recalcitrant Intermetatarsal Neuroma With 4% Sclerosing Alcohol Injection: A Pilot Study Christopher F. Hyer, DPM,' Lynette R. Mehl, DPM,2 Alan J. Block, DPM, MS, FACFAS,3 and Robert B. Vancourt,
Treatment of Recalcitrant Intermetatarsal Neuroma With 4% Sclerosing Alcohol Injection: A Pilot Study Christopher F. Hyer, DPM,' Lynette R. Mehl, DPM,2 Alan J. Block, DPM, MS, FACFAS,3 and Robert B. Vancourt,
Knee Kinematics and Kinetics
 Knee Kinematics and Kinetics Definitions: Kinematics is the study of movement without reference to forces http://www.cogsci.princeton.edu/cgi-bin/webwn2.0?stage=1&word=kinematics Kinetics is the study
Knee Kinematics and Kinetics Definitions: Kinematics is the study of movement without reference to forces http://www.cogsci.princeton.edu/cgi-bin/webwn2.0?stage=1&word=kinematics Kinetics is the study
Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy
 Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain centralized around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. Health care providers
Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain centralized around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. Health care providers
RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION
 RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION Topics of Tonight s s Lecture Common Injuries and Treatments Causes of Common Injuries Measures to Avoid Injury Most Common Running Injuries Plantar Fascitis
RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION Topics of Tonight s s Lecture Common Injuries and Treatments Causes of Common Injuries Measures to Avoid Injury Most Common Running Injuries Plantar Fascitis
Field Evaluation and Management of Non-Battle Related Knee and Ankle Injuries by the ATP in the
 Field Evaluation and Management of Non-Battle Related Knee and Ankle Injuries by the ATP in the JF Rick Hammesfahr, MD Editor s Note: Part Three consists of ankle injury evaluation and taping. Part Two
Field Evaluation and Management of Non-Battle Related Knee and Ankle Injuries by the ATP in the JF Rick Hammesfahr, MD Editor s Note: Part Three consists of ankle injury evaluation and taping. Part Two
GET A HANDLE ON YOUR HEEL PAIN GUIDE
 GET A HANDLE ON YOUR HEEL PAIN GUIDE American Podiatric Medical Association www.apma.org/heelpain Take a Moment to Focus in on Your Feet. Does one (or even both) of your heels hurt? If so, you aren t alone.
GET A HANDLE ON YOUR HEEL PAIN GUIDE American Podiatric Medical Association www.apma.org/heelpain Take a Moment to Focus in on Your Feet. Does one (or even both) of your heels hurt? If so, you aren t alone.
A Guide to Heel Pain
 The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists A Guide to Heel Pain The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists Heel pain may be caused by a number of different problems; for effective treatment you need
The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists A Guide to Heel Pain The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists Heel pain may be caused by a number of different problems; for effective treatment you need
49 Plantar fasciitis. 49.1 Introduction. 49.2 Anatomy. OrthopaedicsOne Articles. Contents
 49 Plantar fasciitis Contents Introduction Anatomy Clinical Presentation Pathogenesis Physical Examination Imaging Conservative Treatment Operative Treatment Controversy References 49.1 Introduction Plantar
49 Plantar fasciitis Contents Introduction Anatomy Clinical Presentation Pathogenesis Physical Examination Imaging Conservative Treatment Operative Treatment Controversy References 49.1 Introduction Plantar
MODIFIED STRAYER GASTROCNEMIUS RECESSION: A Technique Guide for the Supine Positioned Patient
 C H A P T E R 4 5 MODIFIED STRAYER GASTROCNEMIUS RECESSION: A Technique Guide for the Supine Positioned Patient M. Jay Groves, IV, DPM Gastrosoleal equinus is a common deforming force on the foot and ankle.
C H A P T E R 4 5 MODIFIED STRAYER GASTROCNEMIUS RECESSION: A Technique Guide for the Supine Positioned Patient M. Jay Groves, IV, DPM Gastrosoleal equinus is a common deforming force on the foot and ankle.
Therapeutic shoes (for individuals with diabetes) and foot (in-shoe) orthotics are reimbursable under Plans administered by QualCare, Inc.
 Subject: Foot Orthotics and Diabetic Shoes* Effective Date: October 1, 1999 Department(s): Utilization Management Policy: Objective: Procedure: Therapeutic shoes (for individuals with diabetes) and foot
Subject: Foot Orthotics and Diabetic Shoes* Effective Date: October 1, 1999 Department(s): Utilization Management Policy: Objective: Procedure: Therapeutic shoes (for individuals with diabetes) and foot
How To Treat Heel Pain
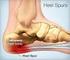 Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Heel Pain The Plantar Fasciitis Organization is dedicated to the understanding of Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, and all other forms of Heel Pain. Welcome to the Plantar
Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Heel Pain The Plantar Fasciitis Organization is dedicated to the understanding of Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, and all other forms of Heel Pain. Welcome to the Plantar
WHEN TO BE CONCERNED: Leg Bowing, Intoeing and Flat Feet.
 WHEN TO BE CONCERNED: Leg Bowing, Intoeing and Flat Feet. Understanding normal childhood development and recognizing signs of pathology WHAT IS NORMAL? Very important: the average and normal are not the
WHEN TO BE CONCERNED: Leg Bowing, Intoeing and Flat Feet. Understanding normal childhood development and recognizing signs of pathology WHAT IS NORMAL? Very important: the average and normal are not the
Deformities. Assessment of Foot. The majority of foot deformities occur in otherwise healthy infants. However most generalized.
 Assessment of Foot Deformities in the Infant By Maureen Baxter, MDCM, FRCS The majority of foot deformities occur in otherwise healthy infants. However most generalized neurologic disorders (spina bifida,
Assessment of Foot Deformities in the Infant By Maureen Baxter, MDCM, FRCS The majority of foot deformities occur in otherwise healthy infants. However most generalized neurologic disorders (spina bifida,
COMPLICATIONS OF PLANTAR FASCIA RELEASE
 C H A P T E R 8 COMPLICATIONS OF PLANTAR FASCIA RELEASE Michelle L. Butterworth, DPM INTRODUCTION Heel pain is one of the most common disorders that foot and ankle surgeons treat. Investigators have stated
C H A P T E R 8 COMPLICATIONS OF PLANTAR FASCIA RELEASE Michelle L. Butterworth, DPM INTRODUCTION Heel pain is one of the most common disorders that foot and ankle surgeons treat. Investigators have stated
The role of bone scintigraphy in determining the etiology of heel pain
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 16, No. 6, 395 401, 2002 The role of bone scintigraphy in determining the etiology of heel pain Hakan ÖZDEMI%R,* Aysun ÖZDEMI%R,** Yetkin SOYUNCU* and Mustafa
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 16, No. 6, 395 401, 2002 The role of bone scintigraphy in determining the etiology of heel pain Hakan ÖZDEMI%R,* Aysun ÖZDEMI%R,** Yetkin SOYUNCU* and Mustafa
Chapter 5. Objectives. Normal Ankle Range of Motion. Lateral Ankle Sprains. Lateral Ankle Sprains. Assessment of Lateral Ankle Sprains
 Objectives Chapter 5 Assessment of Ankle & Lower Leg Injuries Review the following components of injury assessment related to the ankle and lower leg Stress tests Special tests Normal Ankle Range of Motion
Objectives Chapter 5 Assessment of Ankle & Lower Leg Injuries Review the following components of injury assessment related to the ankle and lower leg Stress tests Special tests Normal Ankle Range of Motion
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. EXCISION OF RETROCALCANEAL SPUR BY A LATERAL APPROACH FOR RELIEF OF HEEL PAIN. Nandivada V.S. Kiran Kumar
 EXCISION OF RETROCALCANEAL SPUR BY A LATERAL APPROACH FOR RELIEF OF HEEL PAIN. Nandivada V.S. Kiran Kumar 1. Assistant Professor. Department of Orthopaedics, King George Hospital. Visakhapatnam. CORRESPONDING
EXCISION OF RETROCALCANEAL SPUR BY A LATERAL APPROACH FOR RELIEF OF HEEL PAIN. Nandivada V.S. Kiran Kumar 1. Assistant Professor. Department of Orthopaedics, King George Hospital. Visakhapatnam. CORRESPONDING
International Standards for the Classification of Spinal Cord Injury Motor Exam Guide
 C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
Understanding. Heel Pain
 Understanding Heel Pain What Causes Heel Pain? Heel pain is a common problem that occurs when the heel is placed under too much stress. Heel pain is most often caused by walking in ways that irritate tissues
Understanding Heel Pain What Causes Heel Pain? Heel pain is a common problem that occurs when the heel is placed under too much stress. Heel pain is most often caused by walking in ways that irritate tissues
Plantar Fasciitis - Ayurvedic Strain
 BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Department of Rehabilitation Services Physical Therapy Case Type / Diagnosis: (diagnosis specific, impairment/ dysfunction specific) ICD9-728.71 plantar fibromatosis Plantar
BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Department of Rehabilitation Services Physical Therapy Case Type / Diagnosis: (diagnosis specific, impairment/ dysfunction specific) ICD9-728.71 plantar fibromatosis Plantar
Osteoarthritis progresses slowly and the pain and stiffness it causes worsens over time.
 Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States. It can occur at any age, and literally means "pain within a joint." As a result, arthritis is a term used
Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States. It can occur at any age, and literally means "pain within a joint." As a result, arthritis is a term used
Pathomechanics, Gait Deviations, and Treatment of the Rheumatoid Foot
 Pathomechanics, Gait Deviations, and Treatment of the Rheumatoid Foot A Clinical Report PHYLLIS DIMONTE and HOLLIS LIGHT This article describes the five major foot deformities or problems often seen in
Pathomechanics, Gait Deviations, and Treatment of the Rheumatoid Foot A Clinical Report PHYLLIS DIMONTE and HOLLIS LIGHT This article describes the five major foot deformities or problems often seen in
Plantar Fasciitis Information Leaflet. Maneesh Bhatia. Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon
 Plantar Fasciitis Information Leaflet Maneesh Bhatia Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon What is plantar fasciitis? The plantar fascia is a strong band of tissue that stretches from the heel to the toes. It
Plantar Fasciitis Information Leaflet Maneesh Bhatia Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon What is plantar fasciitis? The plantar fascia is a strong band of tissue that stretches from the heel to the toes. It
Biomechanical Explanations for Selective Sport Injuries of the Lower Extremity
 Biomechanical Explanations for Selective Sport Injuries of the Lower Extremity DR. LEE S. COHEN Podiatric Consultant: Philadelphia Eagles Philadelphia 76ers Philadelphia Wings Understanding Normalcy What
Biomechanical Explanations for Selective Sport Injuries of the Lower Extremity DR. LEE S. COHEN Podiatric Consultant: Philadelphia Eagles Philadelphia 76ers Philadelphia Wings Understanding Normalcy What
AOBP with thanks to: Dawn Dillinger, DO Kyle Bodley, DO
 AOBP with thanks to: Dawn Dillinger, DO Kyle Bodley, DO Common maneuvers in some sports that can increase risk for injury Jumping Pivoting while running Sudden stopping while running Maneuvering a ball
AOBP with thanks to: Dawn Dillinger, DO Kyle Bodley, DO Common maneuvers in some sports that can increase risk for injury Jumping Pivoting while running Sudden stopping while running Maneuvering a ball
1/15/14. Walking vs Running. Normal Running Mechanics. Treadmill vs. Overground Are they the same? Importance of Gait Analysis.
 angle (deg) 1/1/14 Normal Running Mechanics Walking vs Running Irene Davis, PhD, PT, FACSM, FAPTA, FASB Director, Spaulding National Running Center Walking Periods of DOUBLE SUPPORT Running Periods of
angle (deg) 1/1/14 Normal Running Mechanics Walking vs Running Irene Davis, PhD, PT, FACSM, FAPTA, FASB Director, Spaulding National Running Center Walking Periods of DOUBLE SUPPORT Running Periods of
Chapter 140 Heel Pain
 Chapter 140 Heel Pain David R. Richardson, MD E. Greer Richardson, MD I. Overview and Epidemiology A. General characteristics Heel pain (subcalcaneal pain syndrome) is the most common foot-related symptom
Chapter 140 Heel Pain David R. Richardson, MD E. Greer Richardson, MD I. Overview and Epidemiology A. General characteristics Heel pain (subcalcaneal pain syndrome) is the most common foot-related symptom
12. Physical Therapy (PT)
 1 2. P H Y S I C A L T H E R A P Y ( P T ) 12. Physical Therapy (PT) Clinical presentation Interventions Precautions Activity guidelines Swimming Generally, physical therapy (PT) promotes health with a
1 2. P H Y S I C A L T H E R A P Y ( P T ) 12. Physical Therapy (PT) Clinical presentation Interventions Precautions Activity guidelines Swimming Generally, physical therapy (PT) promotes health with a
FORGET ME NOT: The Triple Arthrodesis
 C H A P T E R 1 5 FORGET ME NOT: The Triple Arthrodesis Andrea D. Cass, DPM INTRODUCTION The triple arthrodesis is a procedure that is performed much less commonly for the same conditions as it was 20
C H A P T E R 1 5 FORGET ME NOT: The Triple Arthrodesis Andrea D. Cass, DPM INTRODUCTION The triple arthrodesis is a procedure that is performed much less commonly for the same conditions as it was 20
How To Treat Turf Toe Injuries
 How To Treat Turf Toe Injuries Turf toe injuries can have a significant impact upon the playing time of professional athletes. Accordingly, this author reviews the etiology of these injuries and assesses
How To Treat Turf Toe Injuries Turf toe injuries can have a significant impact upon the playing time of professional athletes. Accordingly, this author reviews the etiology of these injuries and assesses
This is caused by muscle strain to the Achilles tendon in the heel of the foot.
 Foot Facts Our feet were designed to move across uneven earthy surfaces. The hard, inflexible surfaces that we regularly walk on today, such as concrete, tile or wood, leave our feet wanting in terms of
Foot Facts Our feet were designed to move across uneven earthy surfaces. The hard, inflexible surfaces that we regularly walk on today, such as concrete, tile or wood, leave our feet wanting in terms of
PATHOLOGIC GAIT -- MUSCULOSKELETAL. Focal Weakness. Ankle Dorsiflexion Weakness COMMON GAIT ABNORMALITIES
 Pathological Gait I: Musculoskeletal - 1 PATHOLOGIC GAIT -- MUSCULOSKELETAL Normal walking is the standard against which pathology is measured Efficiency is often reduced in pathology COMMON GAIT ABNORMALITIES
Pathological Gait I: Musculoskeletal - 1 PATHOLOGIC GAIT -- MUSCULOSKELETAL Normal walking is the standard against which pathology is measured Efficiency is often reduced in pathology COMMON GAIT ABNORMALITIES
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names
 Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
Screening Examination of the Lower Extremities BUY THIS BOOK! Lower Extremity Screening Exam
 Screening Examination of the Lower Extremities Melvyn Harrington, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Loyola University Medical Center BUY THIS BOOK! Essentials of Musculoskeletal Care
Screening Examination of the Lower Extremities Melvyn Harrington, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Loyola University Medical Center BUY THIS BOOK! Essentials of Musculoskeletal Care
Over-Supination and Peroneal Tendinosis
 Over-Supination and Peroneal Tendinosis Dani Martínez November 2013 Chicago, IL 1 Abstract This paper assesses the use of Pilates to decrease over-supination in the forefoot and thus alleviate associated
Over-Supination and Peroneal Tendinosis Dani Martínez November 2013 Chicago, IL 1 Abstract This paper assesses the use of Pilates to decrease over-supination in the forefoot and thus alleviate associated
Flat foot and lower back pain
 Flat foot and lower back pain Dr James Tang, MBA, BDS, LDS RCS General Dental Practitioner, NASM Corrective Exercise Specialist with special interest in postural dysfunction & lower back problems, Level
Flat foot and lower back pain Dr James Tang, MBA, BDS, LDS RCS General Dental Practitioner, NASM Corrective Exercise Specialist with special interest in postural dysfunction & lower back problems, Level
CAPPAGH NATIONAL ORTHOPAEDIC HOSPITAL, FINGLAS, DUBLIN 11. The Sisters of Mercy. Plantar Fascitis
 1.0 Policy Statement... 2 2.0 Purpose... 2 3.0 Scope... 2 4.0 Health & Safety... 2 5.0 Responsibilities... 2 6.0 Definitions and Abbreviations... 2 7.0 Guideline... 3 7.1 Assessment... 3 7.2 Treatment...
1.0 Policy Statement... 2 2.0 Purpose... 2 3.0 Scope... 2 4.0 Health & Safety... 2 5.0 Responsibilities... 2 6.0 Definitions and Abbreviations... 2 7.0 Guideline... 3 7.1 Assessment... 3 7.2 Treatment...
Review epidemiology of knee pain. Discuss etiology and the biomechanics of knee pain utilizing current literature/evidence
 Jenny Kempf, MPT Review epidemiology of knee pain Discuss etiology and the biomechanics of knee pain utilizing current literature/evidence Review commonly seen knee injuries Discuss treatment strategies
Jenny Kempf, MPT Review epidemiology of knee pain Discuss etiology and the biomechanics of knee pain utilizing current literature/evidence Review commonly seen knee injuries Discuss treatment strategies
Read a chapter on Angular Kinematics
 Read a chapter on Angular Kinematics Angular Kinematics Hamill & Knutzen (Ch 9) Hay (Ch. 4), Hay & Ried (Ch. 10), Kreighbaum & Barthels (Module Ι) or Hall (Ch. 11) Reporting Angles Measurement of Angles
Read a chapter on Angular Kinematics Angular Kinematics Hamill & Knutzen (Ch 9) Hay (Ch. 4), Hay & Ried (Ch. 10), Kreighbaum & Barthels (Module Ι) or Hall (Ch. 11) Reporting Angles Measurement of Angles
LATERAL PAIN SYNDROMES OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE
 C H A P T E R 3 LATERAL PAIN SYNDROMES OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE William D. Fishco, DPM The majority of patient encounters with the podiatrist are secondary to pain in the foot and/or ankle. If we draw an
C H A P T E R 3 LATERAL PAIN SYNDROMES OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE William D. Fishco, DPM The majority of patient encounters with the podiatrist are secondary to pain in the foot and/or ankle. If we draw an
Ankle Sports injuries. Ben Yates
 Ankle Sports injuries Ben Yates Common Extra-articular Conditions Lateral collateral ligament sprains (grades 1,2,3) Functional instability Mechanical instability Achilles tendonopathy (Achillodynia) superficial
Ankle Sports injuries Ben Yates Common Extra-articular Conditions Lateral collateral ligament sprains (grades 1,2,3) Functional instability Mechanical instability Achilles tendonopathy (Achillodynia) superficial
The Correlation Between Plantar Fascia Thickness and Symptoms of Plantar Fasciitis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES The Correlation Between Plantar Fascia Thickness and Symptoms of Plantar Fasciitis Sarah Mahowald, DPM* Bradford S. Legge, DPM John F. Grady, DPM* Background: The purpose of this study
ORIGINAL ARTICLES The Correlation Between Plantar Fascia Thickness and Symptoms of Plantar Fasciitis Sarah Mahowald, DPM* Bradford S. Legge, DPM John F. Grady, DPM* Background: The purpose of this study
.org. Achilles Tendinitis. Description. Cause. Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel.
 Achilles Tendinitis Page ( 1 ) Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your
Achilles Tendinitis Page ( 1 ) Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your
DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES. Anthony Hewitt
 DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES Anthony Hewitt Introduction Anatomy of the scaphoid Resembles a deformed peanut Articular cartilage covers 80% of the surface It rests in a plane 45 degrees to the longitudinal
DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES Anthony Hewitt Introduction Anatomy of the scaphoid Resembles a deformed peanut Articular cartilage covers 80% of the surface It rests in a plane 45 degrees to the longitudinal
