Drug Name (Generic & Trade) - Classification - Drug Actions - Therapeutic Effect Clinical Indications - Nursing interventions -
|
|
|
- Calvin Wilcox
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Drug Name (Generic & Trade) - Ferrous Sulfate Classification - Enzimatic Mineral, Iron Drug Actions - Essential component in formation of Hgb, myoglobin & Enzimes. Therapeutic Effect: Prevents iron deficiency Clinical Indications - Prevention & treatment of Iron deficiency, Anemia Nursing interventions - Assess nutritional status, Assess for constipation, Check CBC Side effects/toxicity - Nausea, Constipation, GI Upset Contraindications - Hemochromatosis, Peptic Ulcers Aging/developmental considerations - Pregnancy Category A, Elderly: None Noted Patient Teaching - Expect stool color to darken Drug Name (Generic & Trade) - Gleevec / imatinib Mesylate Classification - tyrosine-kinase inhibitor used in the treatment of multiple cancers, most notably Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) chronic myelogenous leukemia Drug Actions - preventing a tyrosine kinase enzyme, in this case BCR-Abl, from phosphorylating subsequent proteins and initiating the signaling cascade necessary for cancer development, thus preventing the growth of cancer cells and leading to their death by apoptosis Clinical Indications - Leukimea OFF-LABEL: Treatment of desmoid tumors, Post stem cell transplant Nursing interventions - Assess CBC & BMP Side effects/toxicity - edema and, occasionally, serious fluid retention, Severe congestive heart failure and left ventricular dysfunction have been reported, Nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, headache, rash, musculoskeletal pain, muscle cramps, arthralgia Precautions - Hepatic/renal impairment, thyroidectomy pts, hypothyroidism. Gastric surgery pts Interactions: St. John s wort decreases concentration, Grapefruit products may increase concentration Lab values: May increase serum bilirubin, AST, ALT, creatinine. May decrease platelet count, WBC count, serum potassium, albumin, calcium, RBC. Nursing considerations - Obtain baseline CBC, serum chemistries, renal function. Monitor hepatic function tests before beginning treatment, monthly thereafter Intervention/evaluation - Assess periorbital area, lower extremities for early evidence of fluid retention. Monitor for unexpected, rapid weight gain Patient Teaching - Drink plenty of fluids and ensure a healthy diet, Avoid crowds, those with known infection Drug Name (Generic & Trade) - Lovenox / enoxaparin sodium Classification - Anticoagulant, Low molecular weight heparin Drug Actions - potentiates action of antithrombin III, inactivates coagulation factor Xa Therapeutic Effect: Produces anticoagulation. Does not significantly influence PT, aptt. Clinical Indications - Prevention of postop deep vein thrombosis (DVT) following hip or knee replacement surgery, abdominal surgery. Long-term DVT prevention following hip replacement surgery, nonsurgical acute illness. Treatment of acute coronary syndrome (ACS): unstable angina, non Q-wave MI, acute ST-segment elevation MI (STEMI). Acute DVT (with warfarin). Off-label: Prophylaxis/treatment of thromboembolism in children. DVT prophylaxis following moderate-risk general surgery, Gynecologic surgery; management of venous thromboembolism (vte) during pregnancy. Interactions: Antiplatelet agents, aspirin, NSAIDs, thrombolytics may increase risk of bleeding, Cat's claw, dong quai, evening primrose, feverfew, garlic, ginger, ginkgo, ginseng may increase antiplatelet action Side effects/toxicity - Bleeding complications, Injection site hematoma, nausea, peripheral edema Lab values - Increases serum alkaline phosphatase, AST, ALT. May decrease Hgb, Hct, RBCs Contraindications - Pork products, acute bleeding, hypersensitivity to heparin Antidote - Proramine sulfate Nursing interventions - Periodically monitor CBC, platelet count, stool for occult blood, Assess for any sign of bleeding Nursing considerations - Obtain baseline CBC. Note platelet count. Patient Teaching - May increase bleeding time, may make you bruise more easily
2 Drug Name (Generic & Trade) - dabigatran etexilate / Pradaxa Classification - Thrombin inhibitor Anticoagulant Drug Actions -Direct thrombin inhibitor, preventing the conversion of fibrinogen into fibrin during coagulation cascade. Therapeutic Effect: Produces anticoagulation, preventing development of thrombus Clinical Indications - Indicated to reduce risk of stroke, systemic embolism in pts with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation Precautions: Active major bleeding, patients with mechanical prosthetic heart valves, Renal / Heppatic impairment Interactions: Rifampin may decrease concentration. Antacids, proton pump inhibitors may decrease levels, effect. Antiplatelet agents, NSAIDs, other anticoagulants, thrombolytics may increase risk of bleeding, Feverfew, ginkgo biloba, green tea, red clover may increase risk of bleeding. St. John's wort may decrease concentration/effects, High-fat meal delays absorption approximately 2 hrs Lab Values: May increase aptt, PT, INR Side effects/toxicity - Dyspepsia (heartburn, nausea, indigestion), diarrhea, upper abdominal pain Antidote - Vitamin K. Amount based on INR, significance of bleeding. Nursing interventions - Assess any sign of bleeding (hematuria, stool, bleeding from gums, petechiae, bruising). Nursing considerations - Assess CBC, including platelet count. Check PT, PTT. Determine initial B/P Patient Teaching - Avoid alcohol, salicylates, drastic dietary changes. May increase bleeding time., Use electric razor, soft toothbrush to prevent bleeding Drug Name (Generic & Trade) - Aspirin (ASA) Classification - Nonsteroidal salicylate, Anti-inflammatory, Antipyretic, Anticoagulant Drug Actions - Inhibits prostaglandin synthesis, effects hypothalamus heat regulation, interferes with thromboxane A in platelet aggregation Clinical Indications - Treatment of mild to moderate pain, fever. Reduces inflammation related to rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile arthritis, osteoarthritis, rheumatic fever. As platelet aggregation inhibitor in the prevention of transient ischemic attacks, cerebral thromboembolism, MI or reinfarction. Adjunctive treatment of Kawasaki's disease. OFF-LABEL: Prevention of pre-eclampsia; alternative therapy for preventing thromboembolism associated with atrial fibrillation where warfarin cannot be used; pericarditis associated with MI; prosthetic valve thromboprophylaxis Side effects/toxicity - Toxic over 30mg/dl/day, GI distress (including abdominal distention, cramping, heartburn, mild nausea); allergic reaction (including bronchospasm, pruritus, urticaria). Precautions - Hypersensitivity to salicylates, NSAIDs; asthma; rhinitis; nasal polyps; inherited or acquired bleeding disorders; use in children for viral infections; pregnancy. Interactions: Alcohol, NSAIDs may increase risk of GI effects (e.g., ulceration). Antacids, urinary alkalinizers increase excretion. Anticoagulants, heparin, thrombolytics, rivaroxaban, ticagrelor increase risk of bleeding. Avoid cat's claw, dong quai, evening primrose, feverfew, garlic, ginger, ginkgo, ginseng, green tea, horse chestnut, red clover Lab values: May alter serum AST, ALT, alkaline phosphatase, uric acid; prolongs prothrombin time (PT), bleeding time. May decrease serum cholesterol, potassium, T3, T4. Nursing interventions - Assess type, location, duration of pain, inflammation. Inspect appearance of affected joints for Immobility, deformities, skin condition. Intervention/evaluation - Monitor urinary ph (sudden acidification, ph from 6.5 to 5.5, may result in toxicity). Assess skin for evidence of ecchymosis Patient Teaching - Don t drink alcohol while using this drug. Report any ringing in the ears (Tinnitus), Report tinnitus or persistent abdominal GI pain, bleeding
3 Drug Name (Generic & Trade) - Heparin/Hepalean Classification - Anticoagulant Drug Actions - Interferes with blood coagulation by blocking conversion of prothrombin to thrombin to thrombin and fibrinogen to fibrin. Prevents further extension of existing thrombi or new clot formation. No effect on existing clots Clinical Indications - Prophylaxis, treatment of thrombolitic disorders. Dosage and administration - IV units/kg Max 5000 Units, SQ 5000 Units Nursing interventions - Check dose with co-worker, Determine PTT before administration Side effects/toxicity - Bleeding complications, Puritus, Burning by vasospastic reaction Contraindications - Intercranial hemorrhage, severe hypotension, severe thrombocytopenia, uncontrolled bleeding Antidote - Protamine Sulfate Aging/developmental considerations - Pregnancy category C, Elderly more susceptible to hemorrhage Patient Teaching - Use a soft toothbrush and electric razor to prevent bleeding, report signs of dark or red urine Drug Name (Generic & Trade) - filgrastim/neupogen Classification - Biologic modifier CLINICAL: Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor Drug Actions - Stimulates production, maturation, activation of neutrophils. Therapeutic Effect: Increases migration, activation of neutrophils Clinical Indications - Decreases infection incidence in pts with malignancies receiving chemotherapy associated with severe neutropenia, fever OFF-LABEL: Treatment of AIDS-related neutropenia or hepatitis C treatment-associated neutropenia Lab Values: - May increase LDH, leukocyte alkaline phosphatase (LAP) scores, serum alkaline phosphatase, uric acid Nursing interventions - Monitor INR reports diligently. Assess Hct, platelet count, AST, ALT, urine/stool for occult blood. Be alert to complaints of abdominal/back pain, severe headache (may be sign of hemorrhage). Side effects - Nausea/vomiting, mild to severe bone pain, alopecia (18%), diarrhea, fever, fatigue Nursing considerations - CBC, platelet count should be obtained before therapy initiation and twice weekly thereafter. Intervention/evaluation: In septic pts, be alert for adult respiratory distress syndrome Patient Teaching - Report fever, chills, severe bone pain, chest pain, palpitations. Drug Name (Generic & Trade) - clopidogrel/ Plavix Classification - Thienopyridine derivative clinical: Antiplatelet Drug Actions - Inhibits binding of enzyme adenosine phosphate (ADP) to its platelet receptor and subsequent ADP-mediated activation of a glycoprotein complex. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits platelet aggregation. Clinical Indications - Reduction of atherosclerotic events (e.g., MI, stroke, vascular death) in pts with recent MI or stroke, or established peripheral artery disease (PAD). Treatment of acute coronary syndrome (ACS). Reduces rate of atherothrombotic events in pts with unstable angina (UA), non-st segment elevation MI (non-stemi), ST-segment elevation MI (STEMI), or with percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or CABG OFF-LABEL: Graft patency (saphenous vein), stable coronary artery disease (in combination with aspirin). Initial treatment of acute coronary syndrome in pts allergic to aspirin Lab Values: - May increase bilirubin, AST, ALT, serum cholesterol, uric acid. May decrease neutrophil count, platelet count. Side effects - Skin disorders, Upper respiratory tract infection, chest pain, flu-like symptoms, headache, dizziness, arthralgia. Nursing interventions - : Monitor platelet count for evidence of thrombocytopenia. Assess BUN, serum creatinine, bilirubin, AST, ALT, WBC, Hgb, Hct, signs/symptoms of hepatic insufficiency during therapy Nursing considerations - Obtain baseline chemistries, platelet count, PFA level Intervention/evaluation: In septic pts, be alert for adult respiratory distress syndrome Patient Teaching - Inform physicians, dentists if clopidogrel is being taken, esp. before surgery is scheduled or before taking any new drug.
4 Drug Name (Generic & Trade) - Warfarin/ Coumadin Classification - Coumarin derivative clinical: Anticoagulant Drug Actions - Interferes w/ hepatic synthesis of vita K dependent clotting factors, resulting in depletion of coagulation factors Therapeutic Effect: Prevents extension of formed existing clot; prevents new clots, secondary thromboembolic complications Clinical Indications - Prophylaxis, treatment of venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and thromboembolic disorders. Prophylaxis, treatment of thromboembolic complications associated with cardiac valve replacement or atrial fibrillation. Reduces risk of death, recurrent MI, stroke, embolization after MI. OFF-LABEL: Treatment adjunct in transient ischemic attacks Lab Values: - Watch INR, Therapeudic levela between Precautions: Hemorrhagic tendencies (e.g., cerebral aneurysms), surgery of eye or CNS, neurosurgical procedures, open wounds, severe hypertension, spinal puncture procedures, uncontrolled bleeding, ulcers, unreliable or noncompliant pt, unsupervised senile or psychotic pt, blood dyscrasias, pericarditis or pericardial effusion, pregnancy (except in women with mechanical heart valves at high risk for thromboembolism), bacterial endocarditis, threatened abortion. Interactions - Amiodarone, azole antifungals, cimetidine, disulfiram, fluvoxamine, sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim, levothyroxine, metronidazole, NSAIDs, omeprazole, platelet aggregation inhibitors, salicylates, thrombolytic agents, thyroid hormones may increase effect. Griseofulvin, hepatic enzyme inducers (e.g., rifampin), vitamin K may decrease effects. Alcohol may enhance anticoagulant effect, Cat's claw, dong quai, evening primrose, feverfew, garlic, ginger, ginkgo biloba, ginseng possess antiplatelet activity, may increase risk of bleeding. Ginseng, St. John's wort may decrease effect. Side Effects: GI distress Antidote: Vitamin K Nursing interventions - : Monitor INR reports diligently. Assess Hct, platelet count, AST, ALT, urine/stool for occult blood. Be alert to complaints of abdominal/back pain, severe headache (may be sign of hemorrhage). Decrease in B/P, increase in pulse rate may be sign of hemorrhage Nursing considerations - Determine INR before administration and daily following therapy initiation. Patient Teaching - Take medication at same time each day. Do not take, discontinue any other medication except on advice of physician. Avoid alcohol, aspirin, drastic dietary changes. Drug Name (Generic & Trade) - Erythropoietin/EPO/Procrit / epoetin alfa Classification - Glycoprotien clinical: Erythropoietin Drug Actions - Stimulates division, differentiation of erythroid progenitor cells in bone marrow. Therapeutic Effect: Induces erythropoiesis, releases reticulocytes from bone marrow. Clinical Indications - Treatment of anemia in pts receiving or who have received chemotherapy, those with chronic renal failure to decrease need for RBC transfusion, HIV-infected pts on zidovudine (AZT) therapy when endogenous erythropoietin levels 500 munits/ml or less, those scheduled for elective noncardiac, nonvascular surgery, reducing need for allogenic blood transfusions. Off-Label: Anemia in myelodysplastic syndromes. Lab Values: - May increase BUN, serum phosphorus, potassium, creatinine, uric acid, sodium. May decrease bleeding time, iron concentration, serum ferritin. Precautions: Pure red cell aplasia, uncontrolled hypertension. Cautions: History of seizures or hypertension. Cancer pts: Tumor growth, shortened survival may occur when Hgb levels of 11 g/dl or greater are achieved with epoetin alfa. Chronic kidney failure pts: Increased risk for serious cardiovascular reactions (e.g., stroke, MI) when Hgb levels greater than 11 g/dl are achieved with epoetin alfa. Interactions - Heparin, iron supplements dosage may need to be increased Side Effects: Fever, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, edema, Hypertension, arthralgia Nursing interventions - : Assess CBC routinely. Monitor Hgb, Hct. Monitor aggressively for increased B/P (25% of pts on medication require antihypertensive therapy, dietary restrictions). Monitor temperature, esp. Nursing considerations - Assess B/P before drug initiation (80% of pts with chronic renal failure have history of hypertension). B/P often rises during early therapy in pts with history of hypertension. Patient Teaching - void potentially hazardous activity during first 90 days of therapy (increased risk of seizures in pts with chronic renal failure during first 90 days).
5 Drug Name (Generic & Trade) - Sargramostim/Leukine Classification - Colony stimulating factor clinical: Hematopoietic, antineutropenic Drug Actions - Stimulates proliferation/differentiation of hematopoietic cells to activate mature granulocytes and macrophages Therapeutic Effect: Assists bone marrow in making new WBCs, increases their chemotactic, antifungal, antiparasidic activity. Increases cytoneplastic cells, activates neutrophiles to inhibit tumor cell growth Clinical Indications - Accelerates myloid recovery in Pts undergoing autologous or allogenic bone marrow transplant or in Pts who have undergonehematopoetic stem cell transplant folllowing myeloblative chemotherapy. Prolongs survival in patents that just went under a bone marroe transplant. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of aids-related neutropenia; chronic severe neutropenia, chronic, severe neutropenia, drug induced neutropenis, myledospastic syndrome Lab Values: - May increase serum biliruben, createnan, hepatic enzimes, may decrease serum albumin Precautions: 12hrs before/after radiation therapy, 24hrs before/after chemo therapy, excessive leukemic myeloid blasts in bone marrow or peripheral blood greater than 10% Interactions - None significant Side Effects: GI disturbance, arthalgia, myalgia, HA, malaise, rash, putitus Nursing interventions - : Monitor CBC with Diff, plateletes, rensl/hepatic and pulmonary function, VS, weight Nursing considerations - Baseline PFT, Weights, VS Patient Teaching - Monitor daily weights Drug Name (Generic & Trade) - Dipyridamole/Persantine Classification - Blood modifyer, platelet aggrigation inhibitor, coronary vasodiolator clinical: Antiplatelet, antianginal, diagnostic agent Drug Actions - Inhibits activity of sndenosine deaminase and phosphodiesterase, enzymes cauzing accumulation of adenosine, cyclic adenosen monophosphate (AMP) Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits platelet aggrigation, may cause coronary vasodilation Clinical Indications - Adjunct to warfarin (Coumadin) anticoagulant therapy in prevention of postoperative thromboembolitic complications of cardiac valve replacement OFF-LABEL: Reduces risk of reinfarction in pts recovering from MI, treatment of transient ischemic atacks (TIA) Lab Values: - none. Precautions: Hypertension, coronary artery disease (CAD). Interactions - Anticoagulants, ASA, Heparin, Salicylates, throbolytics may increase risk for bleeding. Cats Claw, Dong quai, Evening primrose, Garlic, Gensing may increase antiplatelet activity. Side Effects: Dizzieness, Abdominal distress, HA, Rash Nursing interventions - : Assist with ambulation, Assess B/P for Hypotension Nursing considerations - Assess for presense of CP, Obtain baseline B/P, Pulse. Patient Teaching - Use caustion when rising from a laying or sitting position Drug Name (Generic & Trade) - Apixaban /Eliquis Classification - Ce clinical: At Drug Actions - Inhibits clotting factor Xa Clinical Indications - For patients wit nonvalvular atrial fibrilation to reduce risk of stroke (CVA), Tx/prevention of DVT and PE Lab Values: - PT/INR, aptt Precautions: Risk related to spinal anesthesia, spinal tap Side Effects: Increased risk of bleeding Nursing interventions - Monitor renal function Nursing considerations - Monitor for S/S of bleeding Patient Teaching - Monitor for S/S of bleeding
6 Drug Name (Generic & Trade) - Heparin Classification - Sulfated polysaccharide, blood modifyer clinical: Anticoagulant Drug Actions - Interfears with blood coagulation by blocking conversion of prothrombin to thrombin and fibrinogen to fibrin. Therapeutic Effect: Prevents further extension of existing thrombi or new clot formation. No effect on existing clots Clinical Indications - Prophylaxis, treatment of thromboembolitic disorders, including venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, peripheral artery embolism, atrial fibrilation with embolism OFF-LABEL: Acute MI as adjunct to thrombolysis, percutaneous coronary intervention Lab Values: - May increase free fatty acids, serum AST, ALT, May decrease serum cholesterol Precautions: Intercranial Hemmorhage, severe hypotension, sever thrombocytopenia, subacute bacterial endocarditis, uncontrolled bleeding (unless secondary to DIC) Interactions - Antithyroid medications valproic acid may cause hypoprpthrombinemia. Platelet aggrigation inhibitors, throbolytics may increase risk of bleeding, Probenecid may increase effect Side Effects: Puritus, burning (prticularly on soles of feet) caused by vasospastic reaction Antidote: Protamine Sulfate Nursing interventions - : Monitor aptt (Therapeutic range at times normal) diligently. Assess Hct, platelet count, AST, ALT, Monitor urine and stool for occult blood. Assess B/P Nursing considerations - Crosscheck dose with coworker, determine aptt before administration and 24 hours following initiation of therapy then q24-48hrs for first week untill maintenance dosage is determined Patient Teaching - Use only electric razors to shave Drug Name (Generic & Trade) - Rivaroxaban/Xarelto Classification - Factor Xa inhibitor clinical: Anticoagulant Drug Actions - Selectively blocks active site of factor Xa, a key factor in the intrinsic and extrinsic pathway of blood coagulation cascade. Prevents new clot formation, secondary thromboembolic complications Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits blood coagulation Clinical Indications - Ptophylaxis of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in pts undergoing knee or hip replacement surgery. Reduces risk of thromboembolism/stroke in pts with nonvalular atrial fibrilation Lab Values: - May decrease platelets. May increase AST, ALT, bilirubin Precautions: Major active bleeding Interactions - Ketoconazole, itraconazole, clarithromycin, erythromycin, fluconazole, ritonavir may increase risk of bleeding. Anticoagulants, antiplatelets, NSAIDs may increase bleeding risk. St Johns Wart may decrease effect Side Effects: Wound secretion/oozing Nursing interventions - : Monitor CBC, CMP, CrCl, occult urine/stool Nursing considerations - Monitor VE, obtain EKG, Comprehensive Pt Hx. Patient Teaching - Do not abruptly stop taking medication, Avoid NSAIDs Drug Name (Generic & Trade) - Protamine Sulfate Classification - Protien clinical: Heparin agonist Antidote Drug Actions - Combines with heparin to form stable salt Therapeutic Effect: Reduces anticoagulation activity of heparin Clinical Indications - Treatment of severe heparin overdose (cauzing hemorrhage) Off-Label: Tx of low molecular weight heparin toxisity Lab Values: - PT/INR, aptt Precautions: Hx of alergy to shelfish Side Effects: Decreased BP, Dyspnea, N/V Nursing interventions - : Baseline assessment, check PT/INR, aptt, Hct, Assess for bleeding
7 Drug Name (Generic & Trade) - Abciximab / Reopro Classification - Glycoprotien IIb/IIIa receptor inhibitor clinical: Antiplatelet, antithrombotic Drug Actions - Rapidly inhibits platelet aggregation by preventing the binding of fibrinogen to GP IIb/IIIa receptor sites on platelets Therapeutic Effect: Prevents occlusion of trated coronary arteries. Prevents acute cardiac ischemic complications Clinical Indications - Adjunct to ASA and heparin therapy to prevent cardiac ischemic complications in patients undergoing percutanious coronary intervention (PCI) and those with unstable angina not responding to conventional medical therepy when PCI is planned within 24 hours OFF-LABEL: Support PCI durring ST-segment elevation, MI (STEMI) as an adjunct to half-dose thrombolytics Lab Values: - Increases activated clotting time (ACT) prothrombin time (PT) activated partial thromboplastin time (aptt), decreases platelet count Precautions: Active internal bleeding, arteriovenous malformation or aneurism, CVA with residual neurologic deficient, Hx of CVA (within 2 years) Interactions - Antiplatelet medications, heparin, thrombolitics, may increase risk of bleeding Side Effects: Nausea, Hypotension, Vomiting Nursing interventions - : Observe for AMS, Monitor for bleeding, Monitor ACT, PT, aptt, Platelet counts, Hgb, Hct Nursing considerations - Heparin should be discontinued 4hrs befor atrial sheeth is removed. Maintain Pt on bedrest 6-8hrs following procedure. Patient Teaching - Assess skin for bruising up to 3 days after infusion, report signs of bleeding Drug Name (Generic & Trade) - Vitamin K Classification - Fat-soluable vitamin clinical: Nutritional suppliment, antidote (drug-induces hypothrombinemia) Antihemmhoragic Drug Actions - Promotes hepatic formation of coagulation factors II, VII, IX, X Therapeutic Effect: Essential for normal clotting of blood Clinical Indications - Prevention, treatment of hemorrhagic states in neonates, antidote for hemorrhagic-induced by oral anticoagulants, hypothtombinemic states due to vitamin K deficiency. Will NOT counteract anticoagulation effects of heparin Lab Values: - INR Precautions: Renal impairment, newborns, Risk of jaundace via hyperbilirubinemia Interactions - Broad-spectrum antibiotics, high-dose salicylates may increase vitamin K requirements. Cholestyramine, coleestipol, minerla oil, sucraflate may decrease absorbtion. May decrease the effects of oral anticoagulants Side Effects: Pain, Soreness, Swelling, Puritic erythemia, facial flushing, altered taste Nursing interventions - : Monitor PT/INR routienly Nursing considerations - Assess for echymosis,petechiae, Bleeding in gums Patient Teaching - Use only an electric razor and soft tooth brush, and monitor for bleeding Drug Name (Generic & Trade) - Pentoxifylline/Trental Classification - Hemorrheologic agent clinical: Hemorrheologic Drug Actions - Alters flexibility of RBCs, inhibits production of tumor necrosis factor (TNF), neutrophil activation, platelet aggregation Therapeutic Effect: Reduces blood viscosity, improves blood flow Clinical Indications - Symptomatic treatment of intermittent claudication associated with occlusive peripheral vascular disease, diabetic angiopathies OFF-LABEL: Venous leg ulcers Lab Values: - None Precautions: Hx of intollerance to xanthine derivitives, such as caffeen, theophylline, thrombromine, recent cerebral/retinal hemorrhage Interactions - May intensify effects of antihypertensives Side Effects: Dizzieness, Nausea, altered taste, dyspepsia (Heartburn, epigastric pain, indigestion) Nursing interventions - : Assist with ambulation if dizzieness occurs. Assess for hand tremmors. Patient Teaching - Limit caffeen, Avoid tasks that require operation of heavy machenery such as driving
8 March 2014 pentoxifylline (pen-tox-i-fi-leen) (Albert, Apo-Pentoxifylline SR, Trental) CLASSIFICATION PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Hemorheologic agent. CLINICAL: Hemorheologic. Copyright 2015, 2014, 2013 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. ACTION Alters flexibility of RBCs; inhibits production of tumor necrosis factor (TNF), neutrophil activation, platelet aggregation. Therapeutic Effect: Reduces blood viscosity, improves blood flow. PHARMACOKINETICS Well absorbed after PO administration. Undergoes first-pass metabolism in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Unknown if removed by hemodialysis. USES Symptomatic treatment of intermittent claudication associated with occlusive peripheral vascular disease, diabetic angiopathies. OFF-LABEL: Venous leg ulcers. PRECAUTIONS History of intolerance to xanthine derivatives, such as caffeine, theophylline, theobromine; recent cerebral/retinal hemorrhage. INTERACTIONS DRUG: May increase effects of antihypertensives, warfarin, oral hypoglycemic agents. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant. SIDE EFFECTS Dizziness, nausea, altered taste, dyspepsia (heartburn, epigastric pain, indigestion). INTERVENTION/EVALUATION Assist with ambulation if dizziness occurs. Assess for hand tremor. Monitor for relief of symptoms of intermittent claudication (pain, aching, cramping in calf muscles, buttocks, thigh, feet). PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING Avoid tasks requiring alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. Limit caffeine.
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22 DIC underlying disorder systemic activation of coagulation widespread intracellular fibrin deposition consumption of platelets & clotting factors thrombosis and organ failure (severe) bleeding Inflamation Infection Coagulation TF Platelets Thrombin (IIa) PAI-1 Clot TAFI DIC Laboratory Tests tpa Fibrinolysis PT/INR Normal Values Prothrombin Time Seconds Internationalized Ratio PTT/APTT THROMBIN TIME FIBRINOGEN PLATELETS FSP/FDP* Partial Thromboplastin Time Seconds ACT Test Seconds Seconds Factor I X10 9 /L Fibrin Split Products Fibrin Degadation Products CLOTTING FACTOR ASSAYS D-DIMER ELISAs Chromogenic <250 Ecarin Clotting Time (ECT)
23 ANEMIAS Compare Fe, TIBC, Transferrin and Transferrin Saturation DISORDER IRON DEFICIENCY CHRONIC ILLNESS IRON Tx OVERLOAD Serum Fe (Iron) TIBC Trans-ferrin Feren Sat
MCHENRY WESTERN LAKE COUNTY EMS SYSTEM OPTIONAL CE ADVANCED LEVEL (EMTP, PHRN, ECRN) August 2013. Anticoagulants
 MCHENRY WESTERN LAKE COUNTY EMS SYSTEM OPTIONAL CE ADVANCED LEVEL (EMTP, PHRN, ECRN) August 2013 Anticoagulants Anticoagulants are agents that prevent the formation of blood clots. Before we can talk about
MCHENRY WESTERN LAKE COUNTY EMS SYSTEM OPTIONAL CE ADVANCED LEVEL (EMTP, PHRN, ECRN) August 2013 Anticoagulants Anticoagulants are agents that prevent the formation of blood clots. Before we can talk about
DVT/PE Management with Rivaroxaban (Xarelto)
 DVT/PE Management with Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) Rivaroxaban is FDA approved for the acute treatment of DVT and PE and reduction in risk of recurrence of DVT and PE. FDA approved indications: Non valvular
DVT/PE Management with Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) Rivaroxaban is FDA approved for the acute treatment of DVT and PE and reduction in risk of recurrence of DVT and PE. FDA approved indications: Non valvular
Planning: Patient Goals and Expected Outcomes The patient will: Remain free of unusual bleeding Maintain effective tissue perfusion Implementation
 Obtain complete heath history including allergies, drug history and possible drug Assess baseline coagulation studies and CBC Assess for history of bleeding disorders, GI bleeding, cerebral bleed, recent
Obtain complete heath history including allergies, drug history and possible drug Assess baseline coagulation studies and CBC Assess for history of bleeding disorders, GI bleeding, cerebral bleed, recent
Session 3 Topics. Argatroban. Argatroban. Drug Use and Adverse Effects. Laboratory Monitoring of Anticoagulant Therapy
 ~~Marshfield Labs Presents~~ Laboratory Monitoring of Anticoagulant Therapy Session 3 of 4 Michael J. Sanfelippo, M.S. Technical Director, Coagulation Services Session 3 Topics Direct Thrombin Inhibitors:
~~Marshfield Labs Presents~~ Laboratory Monitoring of Anticoagulant Therapy Session 3 of 4 Michael J. Sanfelippo, M.S. Technical Director, Coagulation Services Session 3 Topics Direct Thrombin Inhibitors:
ACUTE STROKE UNIT ORIENTATION
 ACUTE STROKE UNIT ORIENTATION 2014 TEACHING YOUR STROKE PATIENTS ABOUT THEIR MEDICATION Please refer to Module 8: Secondary Stroke Prevention for additional information Blood Pressure Medication Angiotensin
ACUTE STROKE UNIT ORIENTATION 2014 TEACHING YOUR STROKE PATIENTS ABOUT THEIR MEDICATION Please refer to Module 8: Secondary Stroke Prevention for additional information Blood Pressure Medication Angiotensin
COMPARISON OF NEW ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS AND FREQUENTLY- ASKED QUESTIONS FROM PATIENTS. TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals.
 COMPARISON OF NEW ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS AND FREQUENTLY- ASKED QUESTIONS FROM PATIENTS AND PHYSICIANS TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVES: To provide a comparison of the new
COMPARISON OF NEW ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS AND FREQUENTLY- ASKED QUESTIONS FROM PATIENTS AND PHYSICIANS TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVES: To provide a comparison of the new
Anticoagulant therapy
 Anticoagulation: The risks Anticoagulant therapy 1990 2002: 600 incidents reported 120 resulted in death of patient 92 deaths related to warfarin usage 28 reports related to heparin usage Incidents in
Anticoagulation: The risks Anticoagulant therapy 1990 2002: 600 incidents reported 120 resulted in death of patient 92 deaths related to warfarin usage 28 reports related to heparin usage Incidents in
Dabigatran (Pradaxa) Guidelines
 Dabigatran (Pradaxa) Guidelines Dabigatran is a new anticoagulant for reducing the risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation. Dabigatran is a direct thrombin inhibitor, similar to warfarin, without
Dabigatran (Pradaxa) Guidelines Dabigatran is a new anticoagulant for reducing the risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation. Dabigatran is a direct thrombin inhibitor, similar to warfarin, without
Anticoagulants in Atrial Fibrillation
 Anticoagulants in Atrial Fibrillation Starting and Stopping Them Safely Carmine D Amico, D.O. Overview Learning objectives Introduction Basic concepts Treatment strategy & options Summary 1 Learning objectives
Anticoagulants in Atrial Fibrillation Starting and Stopping Them Safely Carmine D Amico, D.O. Overview Learning objectives Introduction Basic concepts Treatment strategy & options Summary 1 Learning objectives
New Oral Anticoagulants. How safe are they outside the trials?
 New Oral Anticoagulants How safe are they outside the trials? Objectives The need for anticoagulant therapy Indications for anticoagulation Traditional anticoagulant therapies Properties of new oral anticoagulants
New Oral Anticoagulants How safe are they outside the trials? Objectives The need for anticoagulant therapy Indications for anticoagulation Traditional anticoagulant therapies Properties of new oral anticoagulants
Prescriber Guide. 20mg. 15mg. Simply Protecting More Patients. Simply Protecting More Patients
 Prescriber Guide 20mg Simply Protecting More Patients 15mg Simply Protecting More Patients 1 Dear Doctor, This prescriber guide was produced by Bayer Israel in cooperation with the Ministry of Health as
Prescriber Guide 20mg Simply Protecting More Patients 15mg Simply Protecting More Patients 1 Dear Doctor, This prescriber guide was produced by Bayer Israel in cooperation with the Ministry of Health as
Update on Antiplatelets and anticoagulants. Outlines. Antiplatelets and Anticoagulants 1/23/2013. Timir Paul, MD, PhD
 Update on Antiplatelets and anticoagulants Timir Paul, MD, PhD Antiplatelets Indications Doses Long term use (beyond 12 months) ASA and combination use of NSAIDS ASA resistance Plavix resistance Plavix
Update on Antiplatelets and anticoagulants Timir Paul, MD, PhD Antiplatelets Indications Doses Long term use (beyond 12 months) ASA and combination use of NSAIDS ASA resistance Plavix resistance Plavix
Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) by
 Essentia Health Med Moment Short Video Tune-Up A brief overview of a new medication, or important new medication information Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) by Richard Mullvain RPH BCPS (AQC) Current - August 2011
Essentia Health Med Moment Short Video Tune-Up A brief overview of a new medication, or important new medication information Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) by Richard Mullvain RPH BCPS (AQC) Current - August 2011
Dallas Neurosurgical and Spine Associates, P.A Patient Health History
 Dallas Neurosurgical and Spine Associates, P.A Patient Health History DOB: Date: Reason for your visit (Chief complaint): Past Medical History Please check corresponding box if you have ever had any of
Dallas Neurosurgical and Spine Associates, P.A Patient Health History DOB: Date: Reason for your visit (Chief complaint): Past Medical History Please check corresponding box if you have ever had any of
Interpretation of Laboratory Values
 Interpretation of Laboratory Values Konrad J. Dias PT, DPT, CCS Overview Electrolyte imbalances Renal Function Tests Complete Blood Count Coagulation Profile Fluid imbalance Sodium Electrolyte Imbalances
Interpretation of Laboratory Values Konrad J. Dias PT, DPT, CCS Overview Electrolyte imbalances Renal Function Tests Complete Blood Count Coagulation Profile Fluid imbalance Sodium Electrolyte Imbalances
Inpatient Anticoagulation Safety. To provide safe and effective anticoagulation therapy through a collaborative approach.
 Inpatient Anticoagulation Safety Purpose: Policy: To provide safe and effective anticoagulation therapy through a collaborative approach. Upon the written order of a physician, Heparin, Low Molecular Weight
Inpatient Anticoagulation Safety Purpose: Policy: To provide safe and effective anticoagulation therapy through a collaborative approach. Upon the written order of a physician, Heparin, Low Molecular Weight
More information for patients and caregivers can be accessed at http://www.xarelto-us.com/.
 Janssen Research & Development Submits Application to U.S. FDA for XARELTO (rivaroxaban) to Reduce Secondary Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome RARITAN, DECEMBER 29, 2011 -
Janssen Research & Development Submits Application to U.S. FDA for XARELTO (rivaroxaban) to Reduce Secondary Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome RARITAN, DECEMBER 29, 2011 -
TSOAC Initiation Checklist
 Task Establish appropriate dose based on anticoagulant selected, indication and patient factors such as renal function. Evaluate for medication interactions that may necessitate TSOAC dose adjustment.
Task Establish appropriate dose based on anticoagulant selected, indication and patient factors such as renal function. Evaluate for medication interactions that may necessitate TSOAC dose adjustment.
New Treatments for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation. John C. Andrefsky, MD, FAHA NEOMED Internal Medicine Review course May 5 th, 2013
 New Treatments for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation John C. Andrefsky, MD, FAHA NEOMED Internal Medicine Review course May 5 th, 2013 Classification Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF) Last < 7
New Treatments for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation John C. Andrefsky, MD, FAHA NEOMED Internal Medicine Review course May 5 th, 2013 Classification Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF) Last < 7
Anticoagulants. Anticoagulants Definition. When are blood clots GOOD? Where and why do blood clots occur? 6/12/2014
 Anticoagulants Steven R. Kayser, PharmD Professor Emeritus Department of Clinical Pharmacy UCSF Anticoagulants Definition A substance that hinders the clotting of blood Sometimes referred to as blood thinners
Anticoagulants Steven R. Kayser, PharmD Professor Emeritus Department of Clinical Pharmacy UCSF Anticoagulants Definition A substance that hinders the clotting of blood Sometimes referred to as blood thinners
Antiplatelet and Antithrombotics From clinical trials to guidelines
 Antiplatelet and Antithrombotics From clinical trials to guidelines Ashraf Reda, MD, FESC Prof and head of Cardiology Dep. Menofiya University Preisedent of EGYBAC Chairman of WGLVR One of the big stories
Antiplatelet and Antithrombotics From clinical trials to guidelines Ashraf Reda, MD, FESC Prof and head of Cardiology Dep. Menofiya University Preisedent of EGYBAC Chairman of WGLVR One of the big stories
Analyzing Clinical Trial Findings of the Efficacy and Safety Profiles of Novel Anticoagulants for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation
 Analyzing Clinical Trial Findings of the Efficacy and Safety Profiles of Novel Anticoagulants for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Drew Baldwin, MD Virginia Mason Seattle, Washington NCVH May 29,
Analyzing Clinical Trial Findings of the Efficacy and Safety Profiles of Novel Anticoagulants for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Drew Baldwin, MD Virginia Mason Seattle, Washington NCVH May 29,
Comparison between New Oral Anticoagulants and Warfarin
 Comparison between New Oral Anticoagulants and Warfarin Warfarin was the mainstay of oral anticoagulant therapy until the recent discovery of more precise targets for therapy. In recent years, several
Comparison between New Oral Anticoagulants and Warfarin Warfarin was the mainstay of oral anticoagulant therapy until the recent discovery of more precise targets for therapy. In recent years, several
East Kent Prescribing Group
 East Kent Prescribing Group Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) Safety Information Approved by the East Kent Prescribing Group. Approved by: East Kent Prescribing Group (Representing Ashford CCG, Canterbury and Coastal
East Kent Prescribing Group Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) Safety Information Approved by the East Kent Prescribing Group. Approved by: East Kent Prescribing Group (Representing Ashford CCG, Canterbury and Coastal
HERTFORDSHIRE MEDICINES MANAGEMENT COMMITTEE (HMMC) RIVAROXABAN RECOMMENDED see specific recommendations for licensed indications below
 Name: generic (trade) Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) HERTFORDSHIRE MEDICINES MANAGEMENT COMMITTEE (HMMC) RIVAROXABAN RECOMMENDED see specific recommendations for licensed indications below What it is Indications
Name: generic (trade) Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) HERTFORDSHIRE MEDICINES MANAGEMENT COMMITTEE (HMMC) RIVAROXABAN RECOMMENDED see specific recommendations for licensed indications below What it is Indications
What Does Pregnancy Have to Do With Blood Clots in a Woman s Legs?
 Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning A Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning Drugs to Prevent Abnormal Blood
Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning A Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning Drugs to Prevent Abnormal Blood
DABIGATRAN ETEXILATE TARGET Vitamin K epoxide reductase WARFARIN RIVAROXABAN APIXABAN
 TARGET SPECIFIC ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS (TSOACs) This document is intended as a guideline only and should not replace sound clinical judgment Please refer to UNMH formulary in Lexicomp for approved use(s)
TARGET SPECIFIC ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS (TSOACs) This document is intended as a guideline only and should not replace sound clinical judgment Please refer to UNMH formulary in Lexicomp for approved use(s)
Three new/novel oral anticoagulants (NOAC) have been licensed in Ireland since 2008:
 Key Points to consider when prescribing NOACs Introduction Three new/novel oral anticoagulants (NOAC) have been licensed in Ireland since 2008: Dabigatran Etexilate (Pradaxa ) 75mg, 110mg, 150mg. Rivaroxaban
Key Points to consider when prescribing NOACs Introduction Three new/novel oral anticoagulants (NOAC) have been licensed in Ireland since 2008: Dabigatran Etexilate (Pradaxa ) 75mg, 110mg, 150mg. Rivaroxaban
FDA Approved Oral Anticoagulants
 FDA Approved Oral Anticoagulants Generic (Trade Name) Warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven ) 1 FDA approved indication Prophylaxis and treatment of venous thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis and treatment of thromboembolic
FDA Approved Oral Anticoagulants Generic (Trade Name) Warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven ) 1 FDA approved indication Prophylaxis and treatment of venous thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis and treatment of thromboembolic
Reversal of Antiplatelet and Anticoagulant Therapy: What You Need To Know. Ronald Walsh, MD Chief Medical Officer Community Blood Services
 Reversal of Antiplatelet and Anticoagulant Therapy: What You Need To Know Ronald Walsh, MD Chief Medical Officer Community Blood Services HEMOSTATIC PROCESS Initiation and formation of the platelet plug
Reversal of Antiplatelet and Anticoagulant Therapy: What You Need To Know Ronald Walsh, MD Chief Medical Officer Community Blood Services HEMOSTATIC PROCESS Initiation and formation of the platelet plug
New Anticoagulants: Are we Ready to Replace Warfarin? Carole Goodine, RPh Horizon Health Network Stroke Conference 2011
 New Anticoagulants: Are we Ready to Replace Warfarin? Carole Goodine, RPh Horizon Health Network Stroke Conference 2011 Warfarin Decreases stroke risk by 60-70% Superior to ASA and ASA plus clopidogrel
New Anticoagulants: Are we Ready to Replace Warfarin? Carole Goodine, RPh Horizon Health Network Stroke Conference 2011 Warfarin Decreases stroke risk by 60-70% Superior to ASA and ASA plus clopidogrel
MEDICATION GUIDE. PROCRIT (PRO KRIT) (epoetin alfa)
 MEDICATION GUIDE PROCRIT (PROKRIT) (epoetin alfa) Read this Medication Guide: before you start PROCRIT. if you are told by your healthcare provider that there is new information about PROCRIT. if you are
MEDICATION GUIDE PROCRIT (PROKRIT) (epoetin alfa) Read this Medication Guide: before you start PROCRIT. if you are told by your healthcare provider that there is new information about PROCRIT. if you are
How To Compare The New Oral Anticoagulants
 Disclosures The New Oral Anticoagulants: Are they better than Warfarin? Alan P. Agins, Ph.D. does not have any actual or potential conflicts of interest in relation to this CE activity. Alan Agins, Ph.D.
Disclosures The New Oral Anticoagulants: Are they better than Warfarin? Alan P. Agins, Ph.D. does not have any actual or potential conflicts of interest in relation to this CE activity. Alan Agins, Ph.D.
What You Need to KnowWhen Taking Anticoagulation Medicine
 What You Need to KnowWhen Taking Anticoagulation Medicine What are anticoagulant medicines? Anticoagulant medicines are a group of medicines that inhibit blood clotting, helping to prevent blood clots.
What You Need to KnowWhen Taking Anticoagulation Medicine What are anticoagulant medicines? Anticoagulant medicines are a group of medicines that inhibit blood clotting, helping to prevent blood clots.
A Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation
 Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation A Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation PATIENT EDUCATION GUIDE What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation
Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation A Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation PATIENT EDUCATION GUIDE What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation
Daily aspirin therapy: Understand the benefits and risks
 Daily aspirin therapy: Understand the benefits and risks Is an aspirin a day the right thing for you? It's not as easy a decision as it sounds. Know the benefits and risks before considering daily aspirin
Daily aspirin therapy: Understand the benefits and risks Is an aspirin a day the right thing for you? It's not as easy a decision as it sounds. Know the benefits and risks before considering daily aspirin
News Release. Media contacts: Ernie Knewitz Tel: 908.927.2953 Mobile: 917.697.2318 eknewitz@its.jnj.com
 News Release Media contacts: Ernie Knewitz Tel: 908.927.2953 Mobile: 917.697.2318 eknewitz@its.jnj.com Shaun Mickus Phone: 908.927.2416 Mobile: 973.476.7144 smickus@its.jnj.com Investor contacts: Stan
News Release Media contacts: Ernie Knewitz Tel: 908.927.2953 Mobile: 917.697.2318 eknewitz@its.jnj.com Shaun Mickus Phone: 908.927.2416 Mobile: 973.476.7144 smickus@its.jnj.com Investor contacts: Stan
MEDICAL ASSISTANCE HANDBOOK PRIOR AUTHORIZATION OF PHARMACEUTICAL SERVICES. A. Prescriptions That Require Prior Authorization
 MEDICAL ASSISTANCE HBOOK PRI AUTHIZATION OF PHARMACEUTICAL SERVICES I. Requirements for Prior Authorization of Anticoagulants A. Prescriptions That Require Prior Authorization Prescriptions for Anticoagulants
MEDICAL ASSISTANCE HBOOK PRI AUTHIZATION OF PHARMACEUTICAL SERVICES I. Requirements for Prior Authorization of Anticoagulants A. Prescriptions That Require Prior Authorization Prescriptions for Anticoagulants
Antiplatelet and Antithrombotic Therapy. Dr Curry Grant Stroke Prevention Clinic Quinte Health Care
 Antiplatelet and Antithrombotic Therapy Dr Curry Grant Stroke Prevention Clinic Quinte Health Care Disclosure of Potential for Conflict of Interest Dr. F.C. Grant Atrial Fibrillation FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE:
Antiplatelet and Antithrombotic Therapy Dr Curry Grant Stroke Prevention Clinic Quinte Health Care Disclosure of Potential for Conflict of Interest Dr. F.C. Grant Atrial Fibrillation FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE:
Low Molecular Weight Heparin. All Wales Medicines Strategy Group (AWMSG) Recommendations and advice
 Low Molecular Weight Heparin All Wales Medicines Strategy Group (AWMSG) Recommendations and advice Starting Point Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH): Inhibits factor Xa and factor IIa (thrombin) Small
Low Molecular Weight Heparin All Wales Medicines Strategy Group (AWMSG) Recommendations and advice Starting Point Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH): Inhibits factor Xa and factor IIa (thrombin) Small
The Role of the Newer Anticoagulants
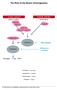 The Role of the Newer Anticoagulants WARFARIN = Coumadin DAGIBATRAN = Pradaxa RIVAROXABAN = Xarelto APIXABAN = Eliquis INDICATION DABIGATRAN (Pradaxa) RIVAROXABAN (Xarelto) APIXABAN (Eliquis) Stroke prevention
The Role of the Newer Anticoagulants WARFARIN = Coumadin DAGIBATRAN = Pradaxa RIVAROXABAN = Xarelto APIXABAN = Eliquis INDICATION DABIGATRAN (Pradaxa) RIVAROXABAN (Xarelto) APIXABAN (Eliquis) Stroke prevention
The author has no disclosures
 Mary Bradbury, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Specialist, Cardiac Surgery September 18, 2012 Mary.bradbury@inova.org This presentation will discuss unlabeled and investigational use of products The author
Mary Bradbury, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Specialist, Cardiac Surgery September 18, 2012 Mary.bradbury@inova.org This presentation will discuss unlabeled and investigational use of products The author
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO SECONDARY PREVENTION IN ACUTE CORONARY SYNDROME (ACS)
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO SECONDARY PREVENTION IN ACUTE CORONARY SYNDROME (ACS) This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO SECONDARY PREVENTION IN ACUTE CORONARY SYNDROME (ACS) This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get
Guideline for the Prescribing of Novel Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs): Dabigatran (Pradaxa ), Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ), Apixaban (Eliquis )
 Guideline for the Prescribing of Novel Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs): Dabigatran (Pradaxa ), Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ), Apixaban (Eliquis ) The contents of this CPG are to be used as a guide. Healthcare professionals
Guideline for the Prescribing of Novel Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs): Dabigatran (Pradaxa ), Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ), Apixaban (Eliquis ) The contents of this CPG are to be used as a guide. Healthcare professionals
Novel oral anticoagulant (NOAC) for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation Special situations
 Novel oral anticoagulant (NOAC) for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation Special situations Dardo E. Ferrara MD Cardiac Electrophysiology North Cascade Cardiology PeaceHealth Medical Group Which anticoagulant
Novel oral anticoagulant (NOAC) for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation Special situations Dardo E. Ferrara MD Cardiac Electrophysiology North Cascade Cardiology PeaceHealth Medical Group Which anticoagulant
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Xofigo Therapy. For metastatic prostate cancer. What is Xofigo? How does it work?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Xofigo Therapy For metastatic prostate cancer This handout explains how the drug Xofigo is used to treat metastatic prostate cancer. What is Xofigo? Xofigo is a radioactive
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Xofigo Therapy For metastatic prostate cancer This handout explains how the drug Xofigo is used to treat metastatic prostate cancer. What is Xofigo? Xofigo is a radioactive
Program Objectives. Why Use Anticoagulants? 6/5/2014
 Larry Reis RPh CGP FASCP Prepared June 2014 for NADONA REIS RXCARE CONSULTING Reisrxcare@comcast.net 1 Program Objectives Discuss complications of current anticoagulant Rx Identify risks of using anticoagulants
Larry Reis RPh CGP FASCP Prepared June 2014 for NADONA REIS RXCARE CONSULTING Reisrxcare@comcast.net 1 Program Objectives Discuss complications of current anticoagulant Rx Identify risks of using anticoagulants
Speaker Disclosure. Outline. Pharmacist Objectives. Patient Case. Outline 9/4/2014
 Speaker Disclosure Matthew K. Pitlick, Pharm.D., BCPS St. Louis College of Pharmacy/VA St. Louis HCS mpitlick@stlcop.edu Matthew K. Pitlick, Pharm.D., BCPS declares no conflicts of interest, real or apparent,
Speaker Disclosure Matthew K. Pitlick, Pharm.D., BCPS St. Louis College of Pharmacy/VA St. Louis HCS mpitlick@stlcop.edu Matthew K. Pitlick, Pharm.D., BCPS declares no conflicts of interest, real or apparent,
Anticoagulation Therapy Update
 Anticoagulation Therapy Update JUDY R. WALLING, FNP-BC ARRHYTHMIA MANAGEMENT MUSC CARDIOLOGY Outline Who do we anticoagulate? Review classes of Anticoagulants Review examples of Anticoagulants Review CHADS2
Anticoagulation Therapy Update JUDY R. WALLING, FNP-BC ARRHYTHMIA MANAGEMENT MUSC CARDIOLOGY Outline Who do we anticoagulate? Review classes of Anticoagulants Review examples of Anticoagulants Review CHADS2
Time of Offset of Action The Trial
 New Antithrombotic Agents DISCLOSURE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) Speaker Bureau - None Consultant Amgen Tom DeLoughery, MD FACP FAWM Oregon Health and Sciences University What I am Talking About
New Antithrombotic Agents DISCLOSURE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) Speaker Bureau - None Consultant Amgen Tom DeLoughery, MD FACP FAWM Oregon Health and Sciences University What I am Talking About
Use of Antithrombotic Agents In The Presence Of Neuraxial Anesthesia
 Use of Antithrombotic Agents In The Presence Of Neuraxial Anesthesia Insertion, removal or presence of a catheter in selected sites can place a patient who is antithrombotic agent at risk for a local bleeding
Use of Antithrombotic Agents In The Presence Of Neuraxial Anesthesia Insertion, removal or presence of a catheter in selected sites can place a patient who is antithrombotic agent at risk for a local bleeding
Management of Patients on Anticoagulants. Haemostasis. Coagulation cascade. Cell-based model 19/11/2013
 Management of Patients on Anticoagulants National Coal Mining Museum 11 Nov 2013 Navneet Lad StR Special Care Dentistry Aims: Discuss the different anti-platelet drugs available. Discuss the new generation
Management of Patients on Anticoagulants National Coal Mining Museum 11 Nov 2013 Navneet Lad StR Special Care Dentistry Aims: Discuss the different anti-platelet drugs available. Discuss the new generation
Blood-thinning medication after stroke
 Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Blood-thinning medication after stroke Blood-thinning medicines are drugs that help to prevent clots forming in your blood. They are often prescribed
Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Blood-thinning medication after stroke Blood-thinning medicines are drugs that help to prevent clots forming in your blood. They are often prescribed
Traditional anticoagulants
 TEGH Family Practice Clinic Day April 4, 03 Use of Anticoagulants in 03: What s New (and What Isn t) Bill Geerts, MD, FRCPC Director, Thromboembolism Program, Sunnybrook HSC Professor of Medicine, University
TEGH Family Practice Clinic Day April 4, 03 Use of Anticoagulants in 03: What s New (and What Isn t) Bill Geerts, MD, FRCPC Director, Thromboembolism Program, Sunnybrook HSC Professor of Medicine, University
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS TREATMENT
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS TREATMENT This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get any side effects, talk
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS TREATMENT This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get any side effects, talk
Sudden dizziness, trouble walking, loss of balance or coordination
 rivaroxaban (Xarelto) Patient Education Information Sheet Veterans Health System Pharmacy Service 119 What is rivaroxaban (Xarelto)? A new anticoagulant ( blood thinner ) that reduces the risk of stroke
rivaroxaban (Xarelto) Patient Education Information Sheet Veterans Health System Pharmacy Service 119 What is rivaroxaban (Xarelto)? A new anticoagulant ( blood thinner ) that reduces the risk of stroke
Enoxaparin for long term anticoagulation in patients unsuitable for oral anticoagulants
 Enoxaparin for long term anticoagulation in patients unsuitable for oral anticoagulants Traffic light classification- Amber 2 Information sheet for Primary Care Prescribers Relevant Licensed Indications
Enoxaparin for long term anticoagulation in patients unsuitable for oral anticoagulants Traffic light classification- Amber 2 Information sheet for Primary Care Prescribers Relevant Licensed Indications
New Oral Anticoagulants for VTE, A-fib, and ACS
 New Oral Anticoagulants for VTE, A-fib, and ACS KCUMB Fall CME 2014 September 18, 2014 Schoen W. Kruse, Ph.D. Assistant Dean Associate Professor of Pharmacology KCUMB An 82 y/o male presents to the ED
New Oral Anticoagulants for VTE, A-fib, and ACS KCUMB Fall CME 2014 September 18, 2014 Schoen W. Kruse, Ph.D. Assistant Dean Associate Professor of Pharmacology KCUMB An 82 y/o male presents to the ED
Rivaroxaban for the treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis in patients unsuitable for vitamin K antagonists
 Rivaroxaban for the treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis in patients unsuitable for vitamin K antagonists Traffic light classification- Amber 2 specialist initiation Information sheet for Primary Care Prescribers
Rivaroxaban for the treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis in patients unsuitable for vitamin K antagonists Traffic light classification- Amber 2 specialist initiation Information sheet for Primary Care Prescribers
Management for Deep Vein Thrombosis and New Agents
 Management for Deep Vein Thrombosis and New Agents Mark Malesker, Pharm.D., FCCP, FCCP, FASHP, BCPS Professor of Pharmacy Practice and Medicine Creighton University 5 th Annual Creighton Cardiovascular
Management for Deep Vein Thrombosis and New Agents Mark Malesker, Pharm.D., FCCP, FCCP, FASHP, BCPS Professor of Pharmacy Practice and Medicine Creighton University 5 th Annual Creighton Cardiovascular
The Brave New (Anticoagulant) World
 The Brave New (Anticoagulant) World Diane M. Birnbaumer, M.D., FACEP Emeritus Professor of Medicine University of California, Los Angeles Senior Clinical Educator Department of Emergency Medicine Harbor-UCLA
The Brave New (Anticoagulant) World Diane M. Birnbaumer, M.D., FACEP Emeritus Professor of Medicine University of California, Los Angeles Senior Clinical Educator Department of Emergency Medicine Harbor-UCLA
STROKE PREVENTION IN ATRIAL FIBRILLATION. TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: ABBREVIATIONS: BACKGROUND:
 STROKE PREVENTION IN ATRIAL FIBRILLATION TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To guide clinicians in the selection of antithrombotic therapy for the secondary prevention
STROKE PREVENTION IN ATRIAL FIBRILLATION TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To guide clinicians in the selection of antithrombotic therapy for the secondary prevention
Anticoagulation at the end of life. Rhona Maclean Rhona.maclean@sth.nhs.uk
 Anticoagulation at the end of life Rhona Maclean Rhona.maclean@sth.nhs.uk Content Anticoagulant Therapies Indications for anticoagulation Venous thromboembolism (VTE) Atrial Fibrillation Mechnical Heart
Anticoagulation at the end of life Rhona Maclean Rhona.maclean@sth.nhs.uk Content Anticoagulant Therapies Indications for anticoagulation Venous thromboembolism (VTE) Atrial Fibrillation Mechnical Heart
Analytical Specifications RIVAROXABAN
 Page 1 of 9 ANALYTE NAME AND STRUCTURE - RIVAROXABAN SYNONYMS Xarelto CATEGORY Anticoagulant TEST CODE PURPOSE Therapeutic Drug Monitoring GENERAL RELEVANCY BACKGROUND Xarelto (rivaroxaban) is an orally
Page 1 of 9 ANALYTE NAME AND STRUCTURE - RIVAROXABAN SYNONYMS Xarelto CATEGORY Anticoagulant TEST CODE PURPOSE Therapeutic Drug Monitoring GENERAL RELEVANCY BACKGROUND Xarelto (rivaroxaban) is an orally
Acute Myocardial Infarction (the formulary thrombolytic for AMI at AAMC is TNK, please see the TNK monograph in this manual for information)
 ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Alteplase (Tissue Plasminogen Activator (t-pa)), Activase in the Treatment
ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Alteplase (Tissue Plasminogen Activator (t-pa)), Activase in the Treatment
The new oral anticoagulants & the future of haemostasis laboratory testing. Alcohol: the good, the bad and the ugly
 The new oral anticoagulants & the future of haemostasis laboratory testing Emmanuel J Favaloro Diagnostic Haemostasis Laboratory, Institute of Clinical Pathology & Medical Research, ICPMR, Pathology West,
The new oral anticoagulants & the future of haemostasis laboratory testing Emmanuel J Favaloro Diagnostic Haemostasis Laboratory, Institute of Clinical Pathology & Medical Research, ICPMR, Pathology West,
MEDICAL ASSISTANCE HANDBOOK PRIOR AUTHORIZATION OF PHARMACEUTICAL SERVICES. A. Prescriptions That Require Prior Authorization
 MEDICAL ASSISTANCE HBOOK I. Requirements for Prior Authorization of Anticoagulants A. Prescriptions That Require Prior Authorization Prescriptions for Anticoagulants which meet any of the following conditions
MEDICAL ASSISTANCE HBOOK I. Requirements for Prior Authorization of Anticoagulants A. Prescriptions That Require Prior Authorization Prescriptions for Anticoagulants which meet any of the following conditions
Hepatitis C. Laboratory Tests and Hepatitis C
 Hepatitis C Laboratory Tests and Hepatitis C If you have hepatitis C, your doctor will use laboratory tests to check your health. This handout will help you understand what the major tests are and what
Hepatitis C Laboratory Tests and Hepatitis C If you have hepatitis C, your doctor will use laboratory tests to check your health. This handout will help you understand what the major tests are and what
Module 1: Orthopedic Surgery: Disease State
 XARELTO Product Brief ORS Rivaroxaban tablets Course Summary Module 1: Orthopedic Surgery: Disease State Orthopedic Surgery: Overview Pain and altered function of the hip and knee, due to conditions such
XARELTO Product Brief ORS Rivaroxaban tablets Course Summary Module 1: Orthopedic Surgery: Disease State Orthopedic Surgery: Overview Pain and altered function of the hip and knee, due to conditions such
LAMC Reversal Agent Guideline for Anticoagulants 2013. Time to resolution of hemostasis (hrs) Therapeutic Options
 LAMC Reversal Agent Guideline for Anticoagulants 2013 Medication resolution of hemostasis (hrs) Intervention Administration Instructions Heparin 3-4 Protamine 1mg IV for every 100 units of heparin Slow
LAMC Reversal Agent Guideline for Anticoagulants 2013 Medication resolution of hemostasis (hrs) Intervention Administration Instructions Heparin 3-4 Protamine 1mg IV for every 100 units of heparin Slow
Preoperative Laboratory and Diagnostic Studies
 Preoperative Laboratory and Diagnostic Studies Preoperative Labratorey and Diagnostic Studies The concept of standardized testing in all presurgical patients regardless of age or medical condition is no
Preoperative Laboratory and Diagnostic Studies Preoperative Labratorey and Diagnostic Studies The concept of standardized testing in all presurgical patients regardless of age or medical condition is no
To provide an evidenced-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis.
 DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS: TREATMENT TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidenced-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis.
DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS: TREATMENT TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidenced-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis.
PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION
 PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION This booklet was designed to help you and the important people in your life understand the treatment of high dose chemotherapy with stem cell support: a procedure
PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION This booklet was designed to help you and the important people in your life understand the treatment of high dose chemotherapy with stem cell support: a procedure
MEDICATION GUIDE ELIQUIS (ELL eh kwiss) (apixaban) tablets
 MEDICATION GUIDE ELIQUIS (ELL eh kwiss) (apixaban) tablets What is the most important information I should know about ELIQUIS? For people taking ELIQUIS for atrial fibrillation: People with atrial fibrillation
MEDICATION GUIDE ELIQUIS (ELL eh kwiss) (apixaban) tablets What is the most important information I should know about ELIQUIS? For people taking ELIQUIS for atrial fibrillation: People with atrial fibrillation
SCRN Medication Review. Susan M. Gaunt MS APRN ACNS-BC CCRN CNRN Gwinnett Medical Center
 SCRN Medication Review Susan M. Gaunt MS APRN ACNS-BC CCRN CNRN Gwinnett Medical Center Objectives To explain the indications, contraindications, interaction, timing, dosing, side effects of: Thrombolytics
SCRN Medication Review Susan M. Gaunt MS APRN ACNS-BC CCRN CNRN Gwinnett Medical Center Objectives To explain the indications, contraindications, interaction, timing, dosing, side effects of: Thrombolytics
Xarelto (rivaroxaban) Prescriber Guide
 Xarelto (rivaroxaban) Prescriber Guide May 2013 Simple Protection for More Patients 2 Xarelto Prescriber Guide Patient Alert Card 4 Dosing Recommendations 4 Dosing in patients with atrial fibrillation
Xarelto (rivaroxaban) Prescriber Guide May 2013 Simple Protection for More Patients 2 Xarelto Prescriber Guide Patient Alert Card 4 Dosing Recommendations 4 Dosing in patients with atrial fibrillation
To aid practitioners in prescribing unfractionated heparin and low-molecular-weight heparins to patients.
 UNFRACTIONATED HEPARIN AND LOW-MOLECULAR-WEIGHT HEPARIN TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To aid practitioners in prescribing unfractionated heparin and low-molecular-weight
UNFRACTIONATED HEPARIN AND LOW-MOLECULAR-WEIGHT HEPARIN TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To aid practitioners in prescribing unfractionated heparin and low-molecular-weight
3/25/14. To Clot or Not What s New In Anticoagulation? Clotting Cascade. Anticoagulant drug targets. Anita Ralstin, MS CNS CNP. Heparin.
 To Clot or Not What s New In Anticoagulation? Anita Ralstin, MS CNS CNP 1 Clotting Cascade 2 Anticoagulant drug targets Heparin XI VIII IX V X VII LMWH II Warfarin Fibrin clot 1 Who Needs Anticoagulation
To Clot or Not What s New In Anticoagulation? Anita Ralstin, MS CNS CNP 1 Clotting Cascade 2 Anticoagulant drug targets Heparin XI VIII IX V X VII LMWH II Warfarin Fibrin clot 1 Who Needs Anticoagulation
DOACs. What s in a name? or TSOACs. Blood Clot. Darra Cover, Pharm D. Clot Formation DOACs work here. Direct Oral AntiCoagulant
 DOACs NOACs or TSOACs Generic Name DOACs Brand Name Mechanism of Action Direct Xa Inhibitor Direct Thrombin Inhibitor Dabigatran Pradaxa X Rivaroxaban Xarelto X Darra Cover, Pharm D Apixaban Eliquis X
DOACs NOACs or TSOACs Generic Name DOACs Brand Name Mechanism of Action Direct Xa Inhibitor Direct Thrombin Inhibitor Dabigatran Pradaxa X Rivaroxaban Xarelto X Darra Cover, Pharm D Apixaban Eliquis X
Devang M. Desai, MD, FACC, FSCAI Chief of Interventional Cardiology Director of Cardiac Catheterization Lab St. Mary s Hospital and Regional Medical
 Devang M. Desai, MD, FACC, FSCAI Chief of Interventional Cardiology Director of Cardiac Catheterization Lab St. Mary s Hospital and Regional Medical Center A.Fib affects 2.2 million Americans. The lifetime
Devang M. Desai, MD, FACC, FSCAI Chief of Interventional Cardiology Director of Cardiac Catheterization Lab St. Mary s Hospital and Regional Medical Center A.Fib affects 2.2 million Americans. The lifetime
NHS FORTH VALLEY RIVAROXABAN AS TREATMENT FOR DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS AND PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN ADULTS
 NHS FORTH VALLEY RIVAROXABAN AS TREATMENT FOR DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS AND PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN ADULTS Date of First Issue 01/12/ 2012 Approved 15/11/2012 Current Issue Date 29/10/2014 Review Date 29/10/2016
NHS FORTH VALLEY RIVAROXABAN AS TREATMENT FOR DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS AND PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN ADULTS Date of First Issue 01/12/ 2012 Approved 15/11/2012 Current Issue Date 29/10/2014 Review Date 29/10/2016
QUICK REFERENCE. Mary Cushman 1 Wendy Lim 2 Neil A Zakai 1. University of Vermont 2. McMaster University
 QUICK REFERENCE Clinical Practice Guide on Antithrombotic Drug Dosing and Management of Antithrombotic Drug- Associated Bleeding Complications in Adults February 2014* Mary Cushman 1 Wendy Lim 2 Neil A
QUICK REFERENCE Clinical Practice Guide on Antithrombotic Drug Dosing and Management of Antithrombotic Drug- Associated Bleeding Complications in Adults February 2014* Mary Cushman 1 Wendy Lim 2 Neil A
Treatment with Rivaroxaban
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Treatment with Rivaroxaban Xarelto This handout explains the medicine rivaroxaban, a drug that helps prevent blood clots. What is rivaroxaban? Rivaroxaban (brand name Xarelto)
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Treatment with Rivaroxaban Xarelto This handout explains the medicine rivaroxaban, a drug that helps prevent blood clots. What is rivaroxaban? Rivaroxaban (brand name Xarelto)
Disclosure. New Agents for Treatment of DVT. Prevalence of DVT VTE. Normal Hemostasis 7/17/2015. Mark Oliver, MD, RVT, RPVI,FSVU
 New Agents for Treatment of DVT Disclosure PI Adopt and Amplify trials Mark Oliver, MD, RVT, RPVI,FSVU BMS and Pfizer Speaker VTE Venous Thromboembolism Recognized DVT s New : 170,000 Recurrent : 90,000
New Agents for Treatment of DVT Disclosure PI Adopt and Amplify trials Mark Oliver, MD, RVT, RPVI,FSVU BMS and Pfizer Speaker VTE Venous Thromboembolism Recognized DVT s New : 170,000 Recurrent : 90,000
CONTEMPORARY REVERSAL OF ANTICOAGULATION
 CONTEMPORARY REVERSAL OF ANTICOAGULATION Michael S. McHale, M.D., F.A.C.P. Avera Medical Group Hematology & Oncology Medications Coumadin / Warfarin Unfractionated Heparin Low Molecular Weight Heparin
CONTEMPORARY REVERSAL OF ANTICOAGULATION Michael S. McHale, M.D., F.A.C.P. Avera Medical Group Hematology & Oncology Medications Coumadin / Warfarin Unfractionated Heparin Low Molecular Weight Heparin
NHS FORTH VALLEY Rivaroxaban for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation
 NHS FORTH VALLEY Rivaroxaban for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Date of First Issue 06/06/2012 Approved 06/06/2012 Current Issue Date 29/10/2014 Review Date 29/10/2016 Version 1.4 EQIA Yes 01/06/2012
NHS FORTH VALLEY Rivaroxaban for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Date of First Issue 06/06/2012 Approved 06/06/2012 Current Issue Date 29/10/2014 Review Date 29/10/2016 Version 1.4 EQIA Yes 01/06/2012
SNAPSHOT OF ANTITHROMBOTIC THERAPY WITH A FOCUS
 SNAPSHOT OF ANTITHROMBOTIC THERAPY WITH A FOCUS ON THE PERIOPERATIVE PERIOD A PHARMACIST S PERSPECTIVE Katie Cinnamon, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacist DISCLOSURE The content of this presentation is based
SNAPSHOT OF ANTITHROMBOTIC THERAPY WITH A FOCUS ON THE PERIOPERATIVE PERIOD A PHARMACIST S PERSPECTIVE Katie Cinnamon, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacist DISCLOSURE The content of this presentation is based
Xarelto (rivaroxaban) Prescriber Guide
 Xarelto (rivaroxaban) Prescriber Guide Simple Protection For More Patients 2 Xarelto Prescriber Guide Patient Alert Card 4 Dosing Recommendations 4 Dosing in patients with atrial fibrillation 4 Patients
Xarelto (rivaroxaban) Prescriber Guide Simple Protection For More Patients 2 Xarelto Prescriber Guide Patient Alert Card 4 Dosing Recommendations 4 Dosing in patients with atrial fibrillation 4 Patients
Cardiology Medications New Drugs, New Guidelines
 Cardiology Medications New Drugs, New Guidelines Ken Kester, PharmD, JD Pharmacy Team Leader Nebraska Heart Hospital August 4, 2014 Cardiology Medications Objectives The attendee will understand Indications,
Cardiology Medications New Drugs, New Guidelines Ken Kester, PharmD, JD Pharmacy Team Leader Nebraska Heart Hospital August 4, 2014 Cardiology Medications Objectives The attendee will understand Indications,
New Anticoagulation Options for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation. Joy Wahawisan, Pharm.D., BCPS April 25, 2012
 New Anticoagulation Options for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Joy Wahawisan, Pharm.D., BCPS April 25, 2012 Stroke in Atrial Fibrillation % Stroke 1991;22:983. Age Range (years) CHADS 2 Risk
New Anticoagulation Options for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Joy Wahawisan, Pharm.D., BCPS April 25, 2012 Stroke in Atrial Fibrillation % Stroke 1991;22:983. Age Range (years) CHADS 2 Risk
Guideline for managing patients on a factor Xa inhibitor Apixaban (Eliquis ) or Rivaroxaban (Xarelto )
 Guideline [Optional heading here. Change font size to suit] Document Number # QH-GDL-950:2014-2 Guideline for managing patients on a factor Xa inhibitor Apixaban (Eliquis ) or Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) 1.
Guideline [Optional heading here. Change font size to suit] Document Number # QH-GDL-950:2014-2 Guideline for managing patients on a factor Xa inhibitor Apixaban (Eliquis ) or Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) 1.
New oral anticoagulants and antiplatelets: Where do they fit? Meredith Hollinger, PharmD BCPS
 New oral anticoagulants and antiplatelets: Where do they fit? Meredith Hollinger, PharmD BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Specialist, Cardiology September 2012 Objectives Describe the mechanisms of action for novel
New oral anticoagulants and antiplatelets: Where do they fit? Meredith Hollinger, PharmD BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Specialist, Cardiology September 2012 Objectives Describe the mechanisms of action for novel
2/17/2015 ANTICOAGULATION UPDATE OBJECTIVES BRIEF REVIEW: CLASSES OF ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS
 ANTICOAGULATION UPDATE C AR R I E P AL M E R, D N P, RN, AN P - BC OBJECTIVES At the end of the presentation, the NP will be able to: Identify new indications for target-specific oral anticoagulants (TSOACs),
ANTICOAGULATION UPDATE C AR R I E P AL M E R, D N P, RN, AN P - BC OBJECTIVES At the end of the presentation, the NP will be able to: Identify new indications for target-specific oral anticoagulants (TSOACs),
Warfarin. (Coumadin, Jantoven ) Taking your medication safely
 Warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven ) Taking your medication safely Welcome This booklet is designed to provide you with important information about warfarin to help you take this medication safely and effectively.
Warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven ) Taking your medication safely Welcome This booklet is designed to provide you with important information about warfarin to help you take this medication safely and effectively.
New Oral Anticoagulants
 New Oral Anticoagulants Tracy Minichiello, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Chief, San FranciscoVA Anticoagulation and Thrombosis Service Ansell, J. Hematology Copyright 2010 American Society of Hematology.
New Oral Anticoagulants Tracy Minichiello, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Chief, San FranciscoVA Anticoagulation and Thrombosis Service Ansell, J. Hematology Copyright 2010 American Society of Hematology.
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO PULMONARY EMBOLISM TREATMENT
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO PULMONARY EMBOLISM TREATMENT This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get any side effects, talk to
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO PULMONARY EMBOLISM TREATMENT This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get any side effects, talk to
An#- Coagulant An#- Thrombo#c An#- Platelet Drugs
 An#- Coagulant An#- Thrombo#c An#- Platelet Drugs 1 ANTICOAGULANT CLASSES INHIBITORS OF CLOTTING FACTOR SYNTHESIS WARFARIN (COUMADIN ) Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) INHIBITORS OF THROMBIN HEPARIN, LEPIRUDIN (REFLUDAN
An#- Coagulant An#- Thrombo#c An#- Platelet Drugs 1 ANTICOAGULANT CLASSES INHIBITORS OF CLOTTING FACTOR SYNTHESIS WARFARIN (COUMADIN ) Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) INHIBITORS OF THROMBIN HEPARIN, LEPIRUDIN (REFLUDAN
NHS FORTH VALLEY Rivaroxaban for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation
 NHS FORTH VALLEY Rivaroxaban for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Date of First Issue 06/06/2012 Approved 06/06/2012 Current Issue Date 06/06/2012 Review Date 06/06/2014 Version 1.1 EQIA Yes /
NHS FORTH VALLEY Rivaroxaban for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Date of First Issue 06/06/2012 Approved 06/06/2012 Current Issue Date 06/06/2012 Review Date 06/06/2014 Version 1.1 EQIA Yes /
Reversing the New Anticoagulants
 Reversing the New Anticoagulants Disclosure Susan C. Lambe, MD Assistant Clinical Professor Department of Emergency Medicine University of California, San Francisco Roadmap for today 1 Roadmap for today
Reversing the New Anticoagulants Disclosure Susan C. Lambe, MD Assistant Clinical Professor Department of Emergency Medicine University of California, San Francisco Roadmap for today 1 Roadmap for today
