Older people s perceptions and experiences of a digital learning game
|
|
|
- Ronald Rice
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Older people s perceptions and experiences of a digital learning game H.H. Nap PhD a U. Diaz-Orueta PhD b M.F. González MSc c K. Lozar-Manfreda PhD d D. Facal PhD e V. Dolničar PhD f D. Oyarzun PhD g M-M. Ranga PhD h B. de Schutter PhD i a Smart Homes, The Netherlands, E: h.nap@vilans.nl; b Nesplora, Donostia-San Sebastian, Spain, E: undiaz@gmail.com; c Fundación Instituto Gerontológico Matia INGEMA, Spain, E: mari.feli.gonzalez@gmail.com; d University of Ljubljana, Slovenia, E: katja.lozar@fdv.uni-lj.si; e Fundación Instituto Gerontológico Matia INGEMA, University of Santiago de Compostela, Spain, E: david.facal@usc.es; f University of Ljubljana, Slovenia, E: vesna.dolnicar@fdv.uni-lj. si; g Vicomtech Research Centre, Spain, E: doyarzun@vicomtech.org; h 50plus Hellas, Greece, E: myrto.ranga@gmail.com; i CEHS AIMS Miami University, USA, E: b@bobdeschutter.be H.H. Nap, U. Diaz-Orueta, M.F. González, K. Lozar-Manfreda, D. Facal, V. Dolničar, D. Oyarzun, M-M. Ranga, B. de Schutter. Older people s perceptions and experiences of a digital learning game. Gerontechnology 2015;13(3): ; doi: /gt The paper describes the evaluation studies of a learning game for older adults using a multicultural European sample. The goal of the evaluation was to explore the acquisition of knowledge as a result of game play, the acceptance of two different game interaction systems by the seniors, their experiences while playing the game, and the accessibility of the game s user interface. Several qualitative and quantitative research methods were combined among older adults in the Netherlands, Spain and Greece. The tests revealed that (i) the accessibility of the game menus and interaction devices was high, (ii) the player experience in digital game play with a TV remote control and 3D sensor were mostly positive, and (iii) the older adults reported that they experienced learning. Overall, it can be concluded that the goals were met, offering a similar accessibility and player experience between the three different countries, and to provide a learning experience for older Europeans. Keywords: usability, acceptance, senior preferences, serious games, lifelong learning Digital games are becoming popular among older adults. People who are 50+ years of age represent 29% of the gamer market in the United States (US); which is a 20% increase in comparison to their 1999 report 1. Digital games have become a popular activity in the lives of many older adults in Western societies and scientific studies on older adults and games go hand in hand with the increasing popularity of digital game play among older adults. Studies trying to capture and reflect the motivational aspects facilitating older people s engagement with digital games are progressively increasing 2. De Schutter 3 found that the most popular playing motive among the older digital game audience was challenge, while social interaction proved to be the most important predictor for the time that respondents invested in playing digital games. Nap et al. 2 speculate that it is possible that there is an overlap between the motivations of older people to play digital games and those of young adults. However, senior specific lifetime experiences, world knowledge, age-related changes in perception, cognition, and motor control are likely to have an influence on specific gaming preferences, motivations and needs. Furthermore, various studies addressed game design requirements that are compatible with the older adults cognitive, motor, and perceptual abilities 4-6. As a consequence of both functional changes and a lack of technological experience, older adults are hurt more by usability problems than younger users
2 Digital games whenever compatible with older adults needs and abilities can provide a fun means to spend time and a way to meet others 2. In addition, digital games can also have a positive influence on older adults performance in a wide-range of executive control tasks, such as short-term memory, working memory, task switching, and inhibition. For example, Basak et al. 7 found significant benefits after 23.5 hours of strategy-based gaming on executive control functions following training. In the latest years, there is an increase of learning - or more specifically - of brain training games in the market and in our culture, like Nintendo s Brain Training by Dr. Kawashima, Big Brain Academy and the online Lumosity platform. Although brain training games are put to market, there is no evidence that these type of games make people smarter. In fact, the results from a recent study 8 supported by BBC Lab UK suggest that improved cognitive functioning by brain training games only hold for the cognitive tasks that are trained. They found no transfer to more general tests of cognition, even when those tasks were closely related to the trained task. Moreover, brain training games lack a number of qualities that most successful commercial games do offer like narration, a story line, appealing graphics, co- and multiplay, etc. In terms of cognitive skills, a recent meta-analysis 9 concluded that the spatial skills improvements derived from playing commercially available shooter video games are comparable to the effects of formal (high school and universitylevel) courses aimed at enhancing these same skills. These improvements can be obtained in a relatively brief period and its effects may last over an extended period of time, being the most crucial outcome their transfer to other spatial tasks outside the video game context. In terms of socialization, players seem to acquire important prosocial skills when they play games that are specifically designed to reward effective cooperation, support, and helping behaviors 10. One study that summarized international evidence from correlational, longitudinal, and experimental studies found that playing prosocial video games consistently related to, or predicted, prosocial behaviors 11. When it comes to make games closer and attractive to senior novel gamers, the challenge is higher than with regular high-skilled, younger players. A relatively recent study 12 explored the key factors and motivations that would engage senior users for them to show interest in playing digital games. In the focus groups conducted, the main interests shared among the participants were to highlight the social aspect of the gaming experience, to experience challenge in games, to combine cognitive and physical activity, and to acquire specific abilities or skills. Two components were commonly agreed on in the participating countries: Challenge (as a basic foundation for the game development, with participants asking for challenging, fun-to-play games with increasing difficulty) and socialization (i.e., participants clearly pointed that they wanted to play with others - not necessarily against others). These results are in line with those reported by Whitcomb 13, who suggested that seniors playing computer games for an extended period may receive stimulation on their social interaction, and, additionally, outcome benefits in eye-hand coordination and fine motor ability, as well as in basic movements and reaction time, with transfer of these skills to their daily routine such as household chores and automobile driving ability. Based on these requisites, this paper describes the accessibility and player experience evaluations of a learning game for older adults with a multicultural European sample, following requirements previously reported 12. The overall goal of the learning game is to activate and stimulate the aging body by mini-games that vary from brain training to physical exercise. The research was performed as part of the LEAGE (LEArning Games for older Europeans) project, partially funded by the Life-Long Learning European Program, with the goal developing a learning game for older adults. Method Participants In total eighteen older adults participated in the experimental Beta study, who individually performed menu- and game play tasks. Six older adults participated in The Netherlands (M age =78.4; SD age =8.4; 5 female) six older adults in Spain (M age =67.3; SD age =4.4; 3 female) also six older adults in Greece (M age =70.7; SD age =7.5; 4 female). For the selection of the participants in The Netherlands, the KBO (senior organization in the province of Noord-Brabant) was approached, in Spain the Senior Citizens Day Centre of Lasarte and in Greece the Senior Care Centres (KAPI). Respondents were required to be 60+ years of age and of good cognitive health in order to participate in the study. The mean subjective memory ability score measured by the Memory Assessment Clinics Self-Rating Scale (MAC-S 14 ) questionnaire on a 5-item Likert scale was 3.5 (SD MAC-S =0.27). The LEAGE game The evaluation study of the digital learning game for older people aims to gather data in the following domains: (i) the knowledge acquisition due to game play; (ii) the perceptions and acceptance of the digital learning game and sys
3 tem; (iii) the player experience when playing the game; and (iv) the accessibility of the game user interface (UI) and interaction devices. Prior to the study presented here, the potential success of the game was theorized to be determined by two key factors: (a) The continuous involvement of older adults in the game design and implementation stages; (b) The implementation on devices which have a low threshold of use for older adults (because they are already familiar with them (e.g., a TV remote control), or because the device is very intuitive (e.g., a Set-Top Box & 3D sensor-microsoft Kinect). Therefore, the LEAGE game is available in two versions, one played by means of a 3D-Microsoft Kinect sensor, and one played by means of a TV remote control on a Set-Top Box (from now on called the STB version of the game). The game aims to help older people improve their competences by practicing and expanding their knowledge on topics such as geography, history, health issues (first aid), nutrition and by motivating exercise and memory training. The LEAGE of European Travellers is a game about a road trip along several European countries. The goal of the game is to visit all countries and collect souvenirs (tokens). Each country is Figure 1. Screens from the LEAGE game: top-left the village square where players can select a challenge, top-right the narration part of the trivia game, center the Athens dancing game, bottom-left the recipe/cooking instructions, and on the bottom-right travel item selection game represented by three major cities, each with an important landmark or something distinctive (e.g. a famous recipe, person, dance, etc.) that makes the city worth visiting. Each city comprises of a narration (teaching) part and several challenges, each with a different educational goal. Countries and cities are presented on a map and are unlocked as the player proceeds. The rules imply that the player must complete a challenge to proceed to the next city, but can return to previous cities (challenges) in order to achieve a higher score. Each time the player completes a challenge s/he receives a souvenir (token) as feedback. Souvenirs are of three types (bronze, silver, or gold) according to the players score in the challenge. The player s score is based on the number of correct answers and the time (how fast a challenge is completed). Players also have the opportunity to voluntarily decide to play in pairs competing against each other in specific challenges. Each country comprises of specific challenges. In all countries challenges are of the same type, to enable a seamless experience to players regardless of their own country. More specifically, each country comprises three locations, and each location has three challenges which all start from the village/city square (Figure 1), in total nine per country, i.e. three sight-seeing, two recipes, two emergencies (first aid), and two exercises/dances. In Table 1, the various challenges per country are listed. A sightseeing challenge consisted of first a narration part with a video (both 3D graphics and images) about the sightseeing place (Figure 1) about the history of the particular location. After this, the player receives a number of multiple choice questions about the narration part (e.g., When was the Mill Network built? ; ; ). The recipe challenge consisted of an animated instruction about how a certain recipe should be prepared with the right ingredients (e.g., prepare Tzatziki at the Athens sight). The game could also be played by means of the 3D motion sensor Kinect, and then the actual movements of stirring, cutting, etc. had to be made. The emergency challenge is also a trivia game, yet, without a narration part. The exercise/
4 Figure 2. Participant in the Netherlands playing the Set-Top Box (left) LEAGE game in the experimental session, and participant in Spain (center) and Greece (right) playing the Kinect version of the LEAGE game dance consisted of an instruction video for the exercise and 3D animated person for the dance to train the player how to perform the actions. After that, players had to try it themselves and the Kinect monitored their behaviours and translated these into actual game behaviours. Procedure The participants were welcomed and an introduction was given by one of the experimenters to introduce the digital learning game under study (UI, controls etc.) and to provide information about the study procedure. After this, participants were asked to read and sign an informed consent form. The informed consent stated what was being studied, ensured anonymous analysis, announced that audio and image recordings were going to be made, and made clear to the participants that they could withdraw their consent and cooperation at any given point in time during or after the session. If necessary, the participants were supported by the experimenters in filling in the forms. Then, they filled a general questionnaire to gather the age, gender, etc. of the participants. The MAC-S was administered to ensure that all participants had sufficient abilities to (learn to) play the game. The game and controls were introduced the first time they started a game and they also received a manual. The participants had to perform game UI and game play tasks with the purpose of testing the usability of the interface, player experience, user acceptance, and learning. The participants filled in the IBM usability questions after they performed the UI tasks and after the game tasks. Then, an interview took place with each participant after he/she had finished the game. The interview provided users with means to step outside the box of pre-constructed questionnaires. The focus of the interview was about the preferences and user acceptance of the digital learning (LEAGE) game. The interviews lasted approximately 15 minutes for the experimental session and the whole experiment took about 1.5 hours. At the end of all sessions there was a gift for participation. Figure 2 shows the various experimental sessions at the 3 pilot sites. Game menu and play tasks As it has been said, the digital learning game is composed by a series of activities and puzzles that the player has to solve. The activities and puzzles are grouped, and each group takes place virtually in a European city, immersing the player in its historical and geographical context. Moreover, during the starting of the game, it includes some screens to configure the avatar of the player, specify his/her language, etc. The participants performed game menu tasks with the purpose of testing the usability of the interface and user acceptance. An example of a game menu task is: Create a new player. In ad- Table 1. The four game challenges in LEAGE, described per country and sightseeing place Country & sightseeing place Sightseeing / trivia Recipe Emergency Dance / Exercise Greece Athens Acropolis Tzatziki NI Syrtaki dance Epidavros Ancient theatre, Cheese pie Skin burn Not included history of theatre Santorini Akrotiri, wall Not included Earthquake Swimming paintings, Volcano Netherlands Amsterdam Ring of Canals, Anne Pepernoten Fire in hotel Not included Frank s house Kinderdijk-Elshout The Mill Network Not included Insect bite - tick Turn cap of windmill Delta Works Eastern Scheldt storm Zeeland mussels Not included Cycling surge barrier Spain Bilbao Guggenheim Cod stuffed with Sun burn Not included museum peppers Santiago de Compostella Saint James Cathedral Saint James cake Food poisoning Not included Barcelona Sagrada Familia Cathedral Mongetes seques con botifarra Not included Sardana dance
5 dition, participants performed game-play tasks to gather an insight into older adults player experience, user acceptance, and learning with the game. An example of a game play task is: Go to Greece, then to Athens (Acropolis), go to the monument and play the game. Tasks were provided on separate sheets of paper. Location & equipment The experimental sessions took place in a specific room in the designated institution in the Netherlands (Ananz Geldrop), Spain (Ingema s lab), and Greece (KAPI Day Center in Ilioupoli). Due to technical difficulties with the Microsoft Kinect in The Netherlands, the Kinect version of the game could not be tested there. Due to technical difficulties with the LEAGE STB in Spain and Greece, the STB version of the game could not be tested in these countries. It should be noted that the LEAGE game was in a Beta stage during the evaluations, a stage in which technical problems are common. In The Netherlands, the experimental sessions were conducted on an all-in-one PC (MSI Wind Top AE210) with an AMD Athlon dual core 3250e processor and with a 20.0 wide screen (1600x900-pixel resolution). To ensure the compatibility with the developed design of the game, the 20.0 screen was set to 1280x768-pixel resolution. The LEAGE STB was used as the platform on which the participants performed the UI and game tasks. For the STB version of LEAGE, a standard Microsoft Mediacenter Infra-Red remote and receiver was used. The tasks were written on paper. A stopwatch was used to measure task time. All instructions were read from premade printed cards. Audio and image recordings were made with a HTC Legend smartphone. an Intel processor, a beamer as well as an XBOX 360 USB Kinect. The projection on the wall was about 70 wide with a 1280x768 pixel resolution on a crème-white wall. Instructions were written on paper and read to the participants by the researchers. Image recordings and videos were made with a Samsung Galaxy smartphone. Measurements Learning Learning was assessed with qualitative data on perceived learning / knowledge acquisition from semi-structured interviews. In-game scores were also collected via log-files. Yet, a number of the log-files could not be identified and therefore the in-game scores were not used in the analyses. Player experience The player experience of the users was measured by the Game Experience Questionnaire (GEQ), which probes the players feelings and thoughts while playing the game 15. The questionnaires assess game experience as scores on seven components: immersion (e.g., I could use my fantasy in the game ), flow (e.g., While playing, I forgot everything around me ), competence (e.g., I was good at it ), positive affect (e.g., Playing the game was fun ), negative affect (e.g., I found it boring ), annoyance (e.g., I felt irritable ) and challenge (e.g., I had to put a lot of effort in the game ). The GEQ was administered during the experimental session where participants received it after a predefined play time (e.g., 5 minutes). Reliability is measured using Cronbach s alpha as a measure of internal consistency which is one possible dimension of scale reliability 16. Cronbach s alpha scores for the seven components of the game experience are shown in Table 2. In Spain, the experimental and open sessions were conducted on a PC (Acer Aspire Revo) with an Intel Atom processor D525 and with a 20.0 wide screen (1600x900-pixel resolution). The Kinect version of the LEAGE game was presented on a 51 wide screen TV. To ensure the compatibility with the developed design of the game, the screen was set to 1280x768-pixel resolution and to 1280x800-pixel resolution for the Kinect version of the game. The LEAGE Kinect game was used as the platforms on which the participants performed the UI and game tasks. For the Kinect version of LEAGE, an XBOX 360 USB Kinect was used. The tasks were written on paper. A stopwatch was used to measure task time. All instructions were read from pre-made printed cards. Audio and image recordings were made with a Samsung Galaxy smartphone. In Greece, the sessions were conducted with the use of a laptop computer (TURBO-X) with A Cronbach s alpha is used to measure the internal consistency reliability of the used questionnaire. A reliability of 0.70 or higher is considered good, 0.60 or higher as acceptable 17. As can be seen below, in our user studies at the various sites sometimes alpha scores were lower than this target value. This may be due to the relatively small Table 2. Cronbach s alpha scores for seven components of game experience by country; NL=Netherlands; ES=Spain; GR=Greece; zero scores (with asterisk) were removed from the analyses Component Country NL ES GR Positive affect Competence Challenge Annoyance * 0.00* Negative affect 0.00* * Immersion Flow
6 sample sizes and/or the fact that some participants scored unreliably. Especially the latest was probably the case, as the GEQ was developed mainly for young adults and also used on children samples 18-20, however a special version for older adults was not available. It is possible that some senior participants did not understand the items as were supposed to be understood. However, since we employed the in-game version of the GEQ, which only has two items per scale, deleting items was not an option. Moreover, the scales employed here have been validated based on studies with large sample sizes (n>250). We therefore decided to stick with the original scales. Results on the scales with zero internal consistencies (negative affect and annoyance) were removed from the analysis. In the FUGA project (EU FP6 project), player experience data was gathered per game genre, platform, etc. of about 400 younger to older players 20. This data can be used to compare or benchmark the player experience of the user groups in the Beta tests of the LEAGE game. The LEAGE game on both end-devices should rather provide a similar player experience for a specific game genre to the player experience FUGA threshold. The game genres of which player experience data is available from the FUGA project are: First Person Shooters (FPS), Role Playing Games (RPG), Sports/Racing Games, Puzzle & Quiz Games, Action Adventures, and Strategy Games. The LEAGE game is closest to a puzzle and quiz game, and therefore the FUGA data of the Puzzle & Quiz games were used to benchmark the LEAGE Beta player experience. User acceptance, perceived usability, preferences, and errors were gathered through interviews. An appropriate method to study user acceptance is by means of interviews to elicit in-depth information of the perceptions, opinions, beliefs, and attitudes. Key questions that were asked among others: Please share your learning experiences with the LEAGE game ; What were your feelings while playing the game? ; What are your opinions about playing the games together?. Probing questions followed to gather additional insight information. Accessibility of the UI The accessibility of the UI was studied using the interviews and by means of the IBM usability questionnaire 21. The IBM usability questionnaire was delivered in the language of participants (Greek, Spanish or Dutch) and usability experience assessed as scores on three components (system usefulness, information quality, and interface quality). The questionnaire contained nineteen usability items that had to be rated on a Table 3. Cronbach s alpha scores for three components of usability by country; NL=Netherlands; ES=Spain; GR=Greece Component Country NL ES GR System usefulness Information quality Interface quality item Likert scale. It measures system usefulness (e.g. It is simple to use this system ), information quality (e.g. The organization of information on the system screens is clear ), and interface quality (e.g., This system has all the functions and capabilities I expect it to have ). The interviewees could also comment on specific UI flaws, but also on their likes about certain aspects of the functionality of the system. Cronbach s alpha s were calculated (Table 3), and although one of the alpha s could not be calculated and one was negative, all components were used for the analyses since in general the internal consistency was high (Overall Usability had a Cronbach s alpha of 0.97). Results Qualitative data Results from the interviews are presented per discussion topic and interview question. The interviews were held in the mother language of the participant. The quotes have been translated into English for the purpose of this article. To prevent distortion of the original messages, the quotes have not been modified to create full sentences. Clarifications are presented above the quotes and between brackets within the quotes. Learning Please share your learning experiences with the LEAGE game Overall, most participants reported that they learned new facts about different cultures and history, and that they experienced the game play as a learning experience: I really liked the fact that I learn about history and culture of other countries. It is a game for grown-ups! (P1, Greece). I liked it. You learn something from it. Stuff is coming back to you [experiences/knowledge] (P6, The Netherlands). Yes, [I learned about] a couple of recipes. Certainly the information from Spain. The knowledge from The Netherlands was already in my head. It was certainly a learning experience (P2, The Netherlands). However, some of the participants (especially from Spain) reported that although the game was informative, it was also fast paced with small fonts. Because of this, they perceived learning as difficult or limited:
7 It is useful because it shows you things that you didn t know. The game is very fast and has a lot of text so it is difficult to remember the dates and places. At the end, you are not able to know the answers unless you are lucky. It s not possible to remember all the things [facts presented in the game]. (P7, Spain). What were your feelings and thoughts while playing the game? Some of the participants reported that they did not experience a game or playfulness, but rather memory training: Simple game, [it is] no game. It is more memory training that is how I see it. In a game you need to get to certain levels and it becomes more difficult. That is not the case here. Old-fashioned way (P1, The Netherlands). At the second or third time, you know how to use it. There is no motivation to lay alone with the remote control. There should be the option to practice more physical activity, it lacks something more playful (P7, Spain). Some of the participants experienced fun and had a positive player experience, yet, they did report that the text that was shown in the Trivia game was too fast and the font sizes too small: Good, it is easy. You do need to read the text very well. Sometimes a fact is double. Need to look carefully at the text (P3, The Netherlands). Cooking was fun. Text too fast. New screen, new sentence. Sometimes I missed something. Not synchronous. A lot of information in a short time. The Netherlands and Spain, general knowledge (P4, The Netherlands). [The game] is fun. Next time the results will be higher. It was very fast (P5, The Netherlands). At the beginning you feel a little bit clumsy, but at the second or third time it [the game] is more easy to use. When you hit the answer you feel a little joy. When you play with another person it is more fun because you can compete with him. It is easier to play with the remote control because you know where the buttons are (P15, Spain). User acceptance - replayability Did you keep playing LEAGE until the end of the pilot? If yes/no, why? Would you keep playing LEAGE after the pilot if possible? Overall, most participants reported that they would play it again if additional content would be provided: I would want to extend my knowledge. Every time a new version. Would play it at least one more time. New cities, extend it (P4, The Netherlands). Would like to continue playing with it if it would have more countries, cities more dynamic games (famous painters, agriculture, people, cities, sports, literature, etc.). I would like to have the same game with more contents (P7, Spain). Yes I would. Because I think it is interesting. Three cities, etc. more countries (P6, The Netherlands). I would play with it if I would have it and if it would include more contents and activities (P15, Spain). One participant reported that she would not play it again, since she experienced little challenge. However, increasing the difficulty level and adding more countries could enhance replayability: One time and another time [playing it twice] and that is it. There is no challenge. Having read the text three times and that is it. [The game should be] more difficult, more countries, more time (P1, The Netherlands). Social play What are your opinions about playing the games together (turn based, social play)? A considerable group of participants reported that they would play the LEAGE game together with other people and reported positively about this possibility: Playing together would be fun/ [a] laugh. [Would like] One time to try. Interesting, but no (P1, The Netherlands). Playing turns is always more fun (P4, The Netherlands). With my wife, taking turns. We always play together. IQ, dictation, etc. (P5, The Netherlands). The game is thought to play with other people. One of the strengths is that is good to compete with other people (P7, Spain). I guess playing it together with others would be more fun, as we will laugh with at each other s mistakes or movements (P2, Greece). Quantitative data Usability The results from the IBM usability questionnaires of the older adults in experimental sessions in respect to usability and player experience for the devices and countries are shown as means and standard deviations per country and usability component (Table 4). Ideally, usability should be above the scale mid-point of 4, should not differ between the countries, and should be similar on both end-devices. Multiple comparisons were run with a Bonferroni correction to account for chance capitalization. No significant differences were found between the devices and countries on the usability components. Player experience Positive player experience should rather be above the GEQ scale mid-point of 2. The enddevices should not significantly differ in their
8 Table 4. Usability Means (M) and Standard Deviations (SD) by country with end-device; NL=Netherlands; ES=Spain; GR=Greece; STB=Set- Top Box Country Player experience NL ES GR (STB) (Kinect) (Kinect) Overall usability M SD M Information quality SD Interface quality M SD System usefulness M SD player experience scores, as for the scores between the participating countries. From the data it seems that both the player experience for both devices and countries do not differ, except possibly challenge and flow which both seem to differ between the countries (Table 5). Again, multiple comparisons were run with a Bonferroni correction to account for chance capitalization. No significant differences were found between the devices and countries on the player experience components. Benchmark In respect to the benchmark scores, it is interesting to note that immersion was rated higher on the LEAGE game than the benchmark. Both negative player experiences annoyance and negative affect scored lower than the benchmark, which implies that the LEAGE game was less boring and frustrating than the benchmark. Yet, competence scores were lower for LEAGE than the benchmark (Table 5). Discussion & conclusion The evaluations of a digital learning game for older people provided rich in-depth data about older people s perception and experiences from a multi-cultural sample from The Netherlands, Table 5. Player experience Means (M) and Standard Deviations (SD) by country with end-device, and benchmark; NL=Netherlands; ES=Spain; GR=Greece; STB=Set-Top Box Country Player experience NL ES GR Benchmark (STB) (Kinect) (Kinect) Competence M SD Positive affect M SD Immersion M SD Flow M SD Challenge M SD Spain, and Greece. From the evaluations, both qualitative and quantitative data was gathered and the qualitative results showed that the majority of older adults learned new facts about different cultures and history and experienced the game play as a learning experience. Nevertheless, an important aspect of the player experience is positive affect or fun and some of the older adults reported a lack of fun and described LEAGE as training and did not experience game play. Therefore, the game mechanics, dynamics and aesthetics (MDA) should be enhanced. The MDA could - in potential - be enhanced by an additional game design iteration, possibly supported by game developers from the entertainment game industry. The findings do indicate that learning games in potential be a valuable tool for memory training purposes among older people. Overall, most participants would play the game again and found the game content interesting. One of the major achievements of the developed learning game is the ease-of-use of the game menu and input devices, although the narration text could be enlarged and the narration part is somewhat fast paced, which should be enhanced in a future version of the game. In The Netherlands, the STB (with remote control) to operate the game was perceived as easy, as the Kinect in Greece. The older adults further reported that they would play the game together with other people, indicating a positive social play possibility for digital learning games as LEAGE. Finally, older adults from The Netherlands, Spain, and Greece were positive about the design, usability and player experience of the game and suggestions for improvements were reported (e.g., slower game speed, enhanced Kinect responsiveness, larger fonts). The quantitative usability results showed per country and device that the satisfaction, information quality, interface quality, and system usefulness of the game menus and interaction devices were scored positively above the scale mid-point of 4. No significant differences were found on usability and player experience between the devices and countries. In respect to the player experience compared to the benchmark, the developed learning game seems to be competitive compared to existing puzzle and quiz games. Future evaluations will provide more insight in the player experience of the LEAGE game compared to exemplar games
9 Possible limitations of the study were the small sample size, unbalanced study design, and most importantly, the current stage of the game design. The game still needs to be polished in respect to usability issues (e.g., small fonts, narration speed, etc.) and an additional game design cycle is needed to enhance the game MDA. In addition, the Kinect and STB technology needs to be further improved to ensure stability of the software, and social and cooperative play should be made possible. Although all participants had no cognitive impairments and reported to be healthy, future studies should include auditoryand visual acuity measurements that could serve as inclusion criteria, or as moderator variables to gain more insight in the results. Furthermore, research in the field of senior gamers should put effort in the development and validation of a GEQ that is attuned to capture the player experience of seniors. Longitudinal research is needed to gather an insight in the re-playability of the LEAGE game. Continuous player experience data could be represented by and extracted from in-game achievements, and the frequency and duration of game play sessions. Future research is needed to which extent these measurements relate to the various player experience components. Overall, the results from the study represent data at one moment in time of a game at a Beta stage. In conclusion, the experimental evaluations provided us with a number of valuable and in-depth results. The usability of the game menus and interaction devices and the player experience Acknowledgements The authors thank the older adults who participated in the studies, Vivian Vergouwen from ANANZ (Geldrop, The Netherlands), KBO (Province of Noord- Brabant, The Netherlands), Senior Citizens Day Centre (Lasarte, Spain), and in Greece the Senior Care Centres (KAPI). We gratefully acknowledge support from the European Commission s Lifelong Learning Programme (LLP). In particular, the work reported here has been supported by the LEAGE project (part of the GRUNDTVIG Subprogramme Education and Culture DG). References 1. Entertainment Software Association (ESA). Essential Facts About the Computer and Video Game Industry: Sales, Demographics, and Usage data; 2011; pdf; retrieved February 7, Nap HH, Kort YAW de, IJsselsteijn WA. Senior Gamers: Preferences, Motivations & Needs. Gerontechnology 2009;8(4): ; doi: / gt Schutter B de. Never Too Old to Play: The Appeal of Digital Games to an Older Audience. Games and Culture 2010;6(2): ; in digital game play with the STB and Kinect were high. Older adults reported that they experienced learning and overall we can conclude that the game provided accessible and attractive game play for older Europeans. Research results also indicate that the learning game holds the potential to improve older people s quality of life by enhancing social interactions and enriching their leisure time. As stated in a recent review 22, caution is warranted for any gamified intervention in the health and education sciences, as very few of the games developed to improve health and learning outcomes are scientifically evaluated. Also in the case of LEAGE, we lack a control group to assure that the benefits can be implemented in the long term and, most important, transfer them to the daily life routine of senior gamers. As a result, for many games and also for LEAGE, further work is needed to examine how much more effective it can be to change behavioural and health outcomes than are conventional approaches. In addition, whenever a game as LEAGE will be deployed in real-life applications, several challenges will have to be addressed. For example re-playability, the availability and/or costs of ICT equipment to run the game, the accessibility of peripheral equipment and operating system, and the availability of specific selling channels that reach the intended stakeholders. As any game, the developed learning game is still open for improvements and deployment challenges will have to be addressed, yet, the LEAGE game shows potential for entertaining and accessible means to learning by digital game play for an older audience. doi: / Gerling KM, Schulte F, Smeddinck J, Masuch M. Game Design for Older Adults: Effects of Age-Related Changes on Structural Elements of Digital Games. Proceedings of the International Conference on Entertainment Computing (ICEC 12). Bremen; 2012; doi: / _20 5. Schutter B de, Abeele V vanden. Meaningful Play in Elderly Life. Proceedings of ICA 2008, Communication for social impact. Montreal; IJsselsteijn WA, Nap HH, Kort YAW de, Poels K. Digital Game Design for Elderly Users, Proceedings of Futureplay Toronto; 2007; pp 17-22; doi: / Basak C, Boot WR, Voss MW and Kramer AF. Can Training in a Real-Time Strategy Video Game Attenuate Cognitive Decline in Older Adults? Psychology and Aging 2008; 23(4): ; doi: /a Owen AM, Hampshire A, Grahn JA, Stenton R, Dajani S, Burns AS, Howard RJ, Ballard CG. Putting brain training to the test. Nature, 20 April 2010; 465(7299): ; doi: /nature
10 9. Uttal DH, Meadow NG, Tipton E, Hand LL, Alden AR, Warren C, Newcombe NS. The malleability of spatial skills: A meta-analysis of training studies. Psychology Bulletin 2013;139(2): ; doi: /a Ewoldsen DR, Eno CA, Okdie BM, Velez JA, Guadagno RE, DeCoster J. Effect of playing violent video games cooperatively or competitively on subsequent cooperative behavior. Cyberpsychology Behavior and Social Networks 2012;15(5): ; doi: /cyber Gentile DA, Anderson CA, Yukawa S, Ihori N, Saleem M, Ming LK, Sakamoto A. The effects of prosocial video games on prosocial behaviors: International evidence from correlational, longitudinal, and experimental studies. Personal and Social Psychology Bull 2009;35(6): ; doi: / Diaz-Orueta U, Facal D, Nap HH, Ranga MM. What is the key for older people to show interest in playing digital learning games? Initial qualitative findings from the LEAGE project on a multicultural European sample. Games for Health Journal 2012;1(2): ; doi: /g4h Whitcomb GR. Computer games for the elderly. ACM Sigcas Computers and Society 1990;20(3): ; doi: / Crook T, Larrabee H, Glenn J. A self-rating scale for evaluating memory in everyday life. Psychology and Aging 1990;5(1):48-57; doi: / IJsselsteijn WA, Kort YAW de, Poels K. The Game Experience Questionnaire: Development of a selfreport measure to assess the psychological impact of digital games. Personal communication 16. Kline P. The handbook of psychological testing. 2nd edition. London: Routledge; George D, Mallery P. SPSS for Windows step by step: A simple guide and reference update. 4th edition. Boston: Allyn & Bacon; Gajadhar BJ, Kort YAW de, IJsselsteijn WA. Rules of Engagement: Influence of Co-Player Presence on Player Involvement in Digital Games. International Journal of Gaming Medicine and Simulation 2009;1(3):14-27; doi: /jgcms Nacke LE, Drachen A, Kuikkaniemi K, Niesenhaus J, Korhonen HJ, Hoogen WM van den, Poels K, IJsselsteijn WA, Kort YAW de. Playability and Player Experience Research. DiGRA 2009, Breaking New Ground: Innovation in Games, Play, Practice and Theory, Brunel University, West London; September Poels K, IJsselsteijn WA, Kort YAW de. Development of the Kids Game Experience Questionnaire. Poster presented at the Meaningful Play Conference, East Lansing, USA, October 2008; Abstract in proceedings; Lewis JR. IBM Computer Usability Satisfaction Questionnaires: Psychometric Evaluation and Instructions for Use. International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction 1995;7(1):57-78; doi: / Granic I, Lobel A, Engels RC. The Benefits of Playing Video Games; 2013; journals/releases/amp-a pdf; retrieved February 9,
To Virtualize or Not? The Importance of Physical and Virtual Components in Augmented Reality Board Games
 To Virtualize or Not? The Importance of Physical and Virtual Components in Augmented Reality Board Games Jessica Ip and Jeremy Cooperstock, Centre for Intelligent Machines, McGill University, Montreal,
To Virtualize or Not? The Importance of Physical and Virtual Components in Augmented Reality Board Games Jessica Ip and Jeremy Cooperstock, Centre for Intelligent Machines, McGill University, Montreal,
Research and Digital Game- based Play: A Review of Martha Madison
 Research and Digital Game- based Play: A Review of Martha Madison White Paper Compiled by Anne Snyder, Ph.D. Second Avenue Learning is a certified women- owned business, specializing in the creation of
Research and Digital Game- based Play: A Review of Martha Madison White Paper Compiled by Anne Snyder, Ph.D. Second Avenue Learning is a certified women- owned business, specializing in the creation of
Mobile Apps: What Consumers Really Need and Want. A Global Study of Consumers Expectations and Experiences of Mobile Applications
 Mobile Apps: What Consumers Really Need and Want A Global Study of Consumers Expectations and Experiences of Mobile Applications The Difference Between a Mobile App and a Mobile Website Before we evaluate
Mobile Apps: What Consumers Really Need and Want A Global Study of Consumers Expectations and Experiences of Mobile Applications The Difference Between a Mobile App and a Mobile Website Before we evaluate
How To Use Gameup
 GAMEUP PROJECT DOCUMENT USER EVALUATION ANALYSIS Category: Deliverable Public Reference: D2.5 Version: 1.0 Date: 15 May 2015 Responsible: IBERNEX Participants: IBERNEX USE KLINIKEN VALENS NORUT PLUSPOINT
GAMEUP PROJECT DOCUMENT USER EVALUATION ANALYSIS Category: Deliverable Public Reference: D2.5 Version: 1.0 Date: 15 May 2015 Responsible: IBERNEX Participants: IBERNEX USE KLINIKEN VALENS NORUT PLUSPOINT
Leveraging the engagement of games to change energy behavior
 Leveraging the engagement of games to change energy behavior Byron Reeves, Ph.D. Stanford University Department of Communication Stanford, CA 94305 USA reeves@stanford.edu James J. Cummings Stanford University
Leveraging the engagement of games to change energy behavior Byron Reeves, Ph.D. Stanford University Department of Communication Stanford, CA 94305 USA reeves@stanford.edu James J. Cummings Stanford University
! " # $ % & ' # $ ( )*% (! (! " #$ "! % + $ 2
 !" #$% " &''( !" # $%&'# $( )*%(!(!" #$ "!%+ $ 2 & ' ( ) *+, - +,. / 0+, 22 3+ 4) "(5+#,60,+4),7$0,..(648 $594/,7$,0(,6,4/ ",0(:,;< +,=09;
!" #$% " &''( !" # $%&'# $( )*%(!(!" #$ "!%+ $ 2 & ' ( ) *+, - +,. / 0+, 22 3+ 4) "(5+#,60,+4),7$0,..(648 $594/,7$,0(,6,4/ ",0(:,;< +,=09;
Dr. Wei Wei Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology, Vietnam Campus January 2013
 Research Summary: Can integrated skills tasks change students use of learning strategies and materials? A case study using PTE Academic integrated skills items Dr. Wei Wei Royal Melbourne Institute of
Research Summary: Can integrated skills tasks change students use of learning strategies and materials? A case study using PTE Academic integrated skills items Dr. Wei Wei Royal Melbourne Institute of
Deploying a CRM system in practice Understanding the user experience Received (in revised form): 5th February, 2007
 Deploying a CRM system in practice Understanding the user experience Received (in revised form): 5th February, 2007 Yuksel Ekinci is one of the leading international academics in service quality and customer
Deploying a CRM system in practice Understanding the user experience Received (in revised form): 5th February, 2007 Yuksel Ekinci is one of the leading international academics in service quality and customer
Arkansas State PIRC/ Center for Effective Parenting
 Increasing Your Child s Motivation to Learn In order to be successful in school and to learn, students must stay involved in the learning process. This requires students to do many different activities
Increasing Your Child s Motivation to Learn In order to be successful in school and to learn, students must stay involved in the learning process. This requires students to do many different activities
Engagement and motivation in games development processes
 Engagement and motivation in games development processes Engagement and motivation in games development processes Summary... 1 Key findings... 1 1. Background... 2 Why do we need to engage with games developers?...
Engagement and motivation in games development processes Engagement and motivation in games development processes Summary... 1 Key findings... 1 1. Background... 2 Why do we need to engage with games developers?...
Research on consumer attitude and effectiveness of advertising in computer and video games
 Research on consumer attitude and effectiveness of advertising in computer and video games (Summary) Zhana Belcheva Master program Advertising Management, New Bulgarian University, Bulgaria In a world
Research on consumer attitude and effectiveness of advertising in computer and video games (Summary) Zhana Belcheva Master program Advertising Management, New Bulgarian University, Bulgaria In a world
Usability Evaluation with Users CMPT 281
 Usability Evaluation with Users CMPT 281 Outline Usability review Observational methods Interview methods Questionnaire methods Usability ISO 9241-11: The extent to which a product can be used by specified
Usability Evaluation with Users CMPT 281 Outline Usability review Observational methods Interview methods Questionnaire methods Usability ISO 9241-11: The extent to which a product can be used by specified
Ludology. Ludology: Psychology of fun. Remembering from last time. Thinking like a gamer
 Ludology: Psychology of fun Ludology The fundamental purpose of games is fun! So what makes them fun, exactly? Remembering from last time nobody wants to make a bad game. ( go to shaqfu.com) Famous game
Ludology: Psychology of fun Ludology The fundamental purpose of games is fun! So what makes them fun, exactly? Remembering from last time nobody wants to make a bad game. ( go to shaqfu.com) Famous game
Time Management Does Not Matter For Academic Achievement Unless You Can Cope
 DOI: 10.7763/IPEDR. 2014. V 78. 5 Time Management Does Not Matter For Academic Achievement Unless You Can Cope Azura Hamdan 1, Rohany Nasir 1, Rozainee Khairudin 1 and Wan Sharazad Wan Sulaiman 1 1 National
DOI: 10.7763/IPEDR. 2014. V 78. 5 Time Management Does Not Matter For Academic Achievement Unless You Can Cope Azura Hamdan 1, Rohany Nasir 1, Rozainee Khairudin 1 and Wan Sharazad Wan Sulaiman 1 1 National
AN INVESTIGATION OF THE US FAMILY REUNION TRAVEL MARKET: MOTIVATIONS AND ACTIVITIES
 AN INVESTIGATION OF THE US FAMILY REUNION TRAVEL MARKET: MOTIVATIONS AND ACTIVITIES A Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of Purdue University by Juyeon Yun Master of Science in Hospitality and Tourism Management
AN INVESTIGATION OF THE US FAMILY REUNION TRAVEL MARKET: MOTIVATIONS AND ACTIVITIES A Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of Purdue University by Juyeon Yun Master of Science in Hospitality and Tourism Management
Model for E-Learning in Higher Education of Agricultural Extension and Education in Iran
 Model for E-Learning in Higher Education of Agricultural Extension and Education in Iran Jafar Yaghoubi 1 and Iraj Malekmohammadi 2 1. Assistant Professor, Zanjan University, Iran, Jafar230@yahoo.com 2.
Model for E-Learning in Higher Education of Agricultural Extension and Education in Iran Jafar Yaghoubi 1 and Iraj Malekmohammadi 2 1. Assistant Professor, Zanjan University, Iran, Jafar230@yahoo.com 2.
The Impact of Aging on Access to Technology
 The Impact of Aging on Access to Technology Sara J. Czaja Department of Psychiatry and Behavior Sciences Center on Aging University of Miami Miller School of Medicine Introduction Two major demographic
The Impact of Aging on Access to Technology Sara J. Czaja Department of Psychiatry and Behavior Sciences Center on Aging University of Miami Miller School of Medicine Introduction Two major demographic
APPLYING THE TECHNOLOGY ACCEPTANCE MODEL AND FLOW THEORY TO ONLINE E-LEARNING USERS ACCEPTANCE BEHAVIOR
 APPLYING THE TECHNOLOGY ACCEPTANCE MODEL AND FLOW THEORY TO ONLINE E-LEARNING USERS ACCEPTANCE BEHAVIOR Su-Houn Liu, Chung Yuan Christian University, vandy@mis.cycu.edu.tw Hsiu-Li Liao, Chung Yuan Christian
APPLYING THE TECHNOLOGY ACCEPTANCE MODEL AND FLOW THEORY TO ONLINE E-LEARNING USERS ACCEPTANCE BEHAVIOR Su-Houn Liu, Chung Yuan Christian University, vandy@mis.cycu.edu.tw Hsiu-Li Liao, Chung Yuan Christian
ANALYSIS OF USER ACCEPTANCE OF A NETWORK MONITORING SYSTEM WITH A FOCUS ON ICT TEACHERS
 ANALYSIS OF USER ACCEPTANCE OF A NETWORK MONITORING SYSTEM WITH A FOCUS ON ICT TEACHERS Siti Rahayu Abdul Aziz 1, Mohamad Ibrahim 2, and Suhaimi Sauti 3 1 Universiti Teknologi MARA, Malaysia, rahayu@fskm.uitm.edu.my
ANALYSIS OF USER ACCEPTANCE OF A NETWORK MONITORING SYSTEM WITH A FOCUS ON ICT TEACHERS Siti Rahayu Abdul Aziz 1, Mohamad Ibrahim 2, and Suhaimi Sauti 3 1 Universiti Teknologi MARA, Malaysia, rahayu@fskm.uitm.edu.my
RADMIN remote control software. Product Overview. What is Radmin? Innovative screen capture technology
 What is Radmin? Radmin is a secure and reliable Windows-based remote control program, which allows you to work on several computers through a simple and familiar graphical interface. Radmin allows a user
What is Radmin? Radmin is a secure and reliable Windows-based remote control program, which allows you to work on several computers through a simple and familiar graphical interface. Radmin allows a user
Agent s Handbook. Your guide to satisfied customers
 Agent s Handbook Your guide to satisfied customers Introduction LiveChat is a tool that facilitates communication between a company and its customers. Agents who wield that tool use it to make customers
Agent s Handbook Your guide to satisfied customers Introduction LiveChat is a tool that facilitates communication between a company and its customers. Agents who wield that tool use it to make customers
Outline. Lecture 13: Web Usability. Top Ten Web Design Mistakes. Web Usability Principles Usability Evaluations
 Lecture 13: Web Usability Outline Web Usability Principles Usability Evaluations Wendy Liu CSC309F Fall 2007 1 2 What Makes Web Application Development Hard? Target audience can be difficult to define
Lecture 13: Web Usability Outline Web Usability Principles Usability Evaluations Wendy Liu CSC309F Fall 2007 1 2 What Makes Web Application Development Hard? Target audience can be difficult to define
What do you love to do? Retirement Activity Book
 What do you love to do? Retirement Activity Book Welcome to the AfterWorks Retirement Seminar Being able to do more of what you love is really what investing is all about. You may think that your financial
What do you love to do? Retirement Activity Book Welcome to the AfterWorks Retirement Seminar Being able to do more of what you love is really what investing is all about. You may think that your financial
Improvement of Visual Attention and Working Memory through a Web-based Cognitive Training Program
 . Improvement of Visual Attention and Working Memory through a Web-based Cognitive Training Program Michael Scanlon David Drescher Kunal Sarkar Context: Prior work has revealed that cognitive ability is
. Improvement of Visual Attention and Working Memory through a Web-based Cognitive Training Program Michael Scanlon David Drescher Kunal Sarkar Context: Prior work has revealed that cognitive ability is
Lean UX. Best practices for integrating user insights into the app development process. Best Practices Copyright 2015 UXprobe bvba
 Lean UX Best practices for integrating user insights into the app development process Best Practices Copyright 2015 UXprobe bvba Table of contents Introduction.... 3 1. Ideation phase... 4 1.1. Task Analysis...
Lean UX Best practices for integrating user insights into the app development process Best Practices Copyright 2015 UXprobe bvba Table of contents Introduction.... 3 1. Ideation phase... 4 1.1. Task Analysis...
Examining Science and Engineering Students Attitudes Toward Computer Science
 Examining Science and Engineering Students Attitudes Toward Computer Science Abstract Concerns have been raised with respect to the recent decline in enrollment in undergraduate computer science majors.
Examining Science and Engineering Students Attitudes Toward Computer Science Abstract Concerns have been raised with respect to the recent decline in enrollment in undergraduate computer science majors.
<ECE1778H> Submitted by: Jinyoung Kim (997864173) Rowa Karkokli (992424159)
 Submitted by: Jinyoung Kim (997864173) Rowa Karkokli (992424159) Date: April 12, 2011 EXECITIVE SUMMARY: Dementia is a cognitive disorder resulting in loss of memory, changes in personality,
Submitted by: Jinyoung Kim (997864173) Rowa Karkokli (992424159) Date: April 12, 2011 EXECITIVE SUMMARY: Dementia is a cognitive disorder resulting in loss of memory, changes in personality,
Evaluating Pedagogical Quality: An Integral Part of Course Development Strategy
 1 20th Annual Conference on Distance Teaching and Learning click here -> Evaluating Pedagogical Quality: An Integral Part of Course Development Strategy L Bagley, PhD Head of Learning Research and Development
1 20th Annual Conference on Distance Teaching and Learning click here -> Evaluating Pedagogical Quality: An Integral Part of Course Development Strategy L Bagley, PhD Head of Learning Research and Development
A study to investigate Students and Teachers attitudes towards the use of computer games in St Johns School, to assist learning.
 A study to investigate Students and Teachers attitudes towards the use of computer games in St Johns School, to assist learning. 1 Contents Page Abstract Page 3 Introduction Page 4 Methodology Page 5 and
A study to investigate Students and Teachers attitudes towards the use of computer games in St Johns School, to assist learning. 1 Contents Page Abstract Page 3 Introduction Page 4 Methodology Page 5 and
CREA: Defining future multiplatform interaction on TV shows through a user experience study
 CREA: Defining future multiplatform interaction on TV shows through a user experience study Abstract. Television programs use to involve a passive role by the viewer. The aim of the project described in
CREA: Defining future multiplatform interaction on TV shows through a user experience study Abstract. Television programs use to involve a passive role by the viewer. The aim of the project described in
Mobile Stock Trading (MST) and its Social Impact: A Case Study in Hong Kong
 Mobile Stock Trading (MST) and its Social Impact: A Case Study in Hong Kong K. M. Sam 1, C. R. Chatwin 2, I. C. Ma 3 1 Department of Accounting and Information Management, University of Macau, Macau, China
Mobile Stock Trading (MST) and its Social Impact: A Case Study in Hong Kong K. M. Sam 1, C. R. Chatwin 2, I. C. Ma 3 1 Department of Accounting and Information Management, University of Macau, Macau, China
Video Conferencing Display System Sizing and Location
 Video Conferencing Display System Sizing and Location As video conferencing systems become more widely installed, there are often questions about what size monitors and how many are required. While fixed
Video Conferencing Display System Sizing and Location As video conferencing systems become more widely installed, there are often questions about what size monitors and how many are required. While fixed
Understanding the User Model of the Elderly People While Using Mobile Phones
 Understanding the User Model of the Elderly People While Using Mobile Phones Hsien-Hui TANG Shih-An KAO DITL, The Graduate Institute of Industrial Design, Chang Gung University, Taiwan hhtang@mail.cgu.edu.tw
Understanding the User Model of the Elderly People While Using Mobile Phones Hsien-Hui TANG Shih-An KAO DITL, The Graduate Institute of Industrial Design, Chang Gung University, Taiwan hhtang@mail.cgu.edu.tw
BIG DATA: IT MAY BE BIG BUT IS IT SMART?
 BIG DATA: IT MAY BE BIG BUT IS IT SMART? Turning Big Data into winning strategies A GfK Point-of-view 1 Big Data is complex Typical Big Data characteristics?#! %& Variety (data in many forms) Data in different
BIG DATA: IT MAY BE BIG BUT IS IT SMART? Turning Big Data into winning strategies A GfK Point-of-view 1 Big Data is complex Typical Big Data characteristics?#! %& Variety (data in many forms) Data in different
Our Guide to Customer Journey Mapping
 Our Guide to Customer Journey Mapping Our Guides Our guides are here to help you understand a topic or to provide support for a particular task you might already be working on. Inside you ll find lots
Our Guide to Customer Journey Mapping Our Guides Our guides are here to help you understand a topic or to provide support for a particular task you might already be working on. Inside you ll find lots
Usability Test Plan Docutek ERes v. 5.0.05 University of Texas Libraries
 Usability Test Plan Docutek ERes v. 5.0.05 University of Texas Libraries Prepared for: INF 385p Usability (Dr. Randolph Bias) Prepared by: Laura Bright, Rachael Gilg and Heather Nodler Date: March 24,
Usability Test Plan Docutek ERes v. 5.0.05 University of Texas Libraries Prepared for: INF 385p Usability (Dr. Randolph Bias) Prepared by: Laura Bright, Rachael Gilg and Heather Nodler Date: March 24,
CORRALLING THE WILD, WILD WEST OF SOCIAL MEDIA INTELLIGENCE
 CORRALLING THE WILD, WILD WEST OF SOCIAL MEDIA INTELLIGENCE Michael Diederich, Microsoft CMG Research & Insights Introduction The rise of social media platforms like Facebook and Twitter has created new
CORRALLING THE WILD, WILD WEST OF SOCIAL MEDIA INTELLIGENCE Michael Diederich, Microsoft CMG Research & Insights Introduction The rise of social media platforms like Facebook and Twitter has created new
Why is the design of a computer game important?
 Why is the design of a computer game important? Arcade reaction speed Puzzle clever thinking / brain improvement (Angry Birds, Myst) Role Playing steer a character through a world Management build a empire
Why is the design of a computer game important? Arcade reaction speed Puzzle clever thinking / brain improvement (Angry Birds, Myst) Role Playing steer a character through a world Management build a empire
Postgraduate Computing at Goldsmiths
 Postgraduate Computing at Goldsmiths We aim to develop your creative as well as your technical skills. That s what makes computing at Goldsmiths so distinctive Key features Our range of Masters extend
Postgraduate Computing at Goldsmiths We aim to develop your creative as well as your technical skills. That s what makes computing at Goldsmiths so distinctive Key features Our range of Masters extend
UNDERSTANDING AND MOTIVATING ENERGY CONSERVATION VIA SOCIAL NORMS. Project Report: 2004 FINAL REPORT
 UNDERSTANDING AND MOTIVATING ENERGY CONSERVATION VIA SOCIAL NORMS Project Report: 2004 FINAL REPORT Robert Cialdini, Ph.D. Arizona State University Wesley Schultz, Ph.D. California State University, San
UNDERSTANDING AND MOTIVATING ENERGY CONSERVATION VIA SOCIAL NORMS Project Report: 2004 FINAL REPORT Robert Cialdini, Ph.D. Arizona State University Wesley Schultz, Ph.D. California State University, San
Standards for Certification in Early Childhood Education [26.110-26.270]
![Standards for Certification in Early Childhood Education [26.110-26.270] Standards for Certification in Early Childhood Education [26.110-26.270]](/thumbs/24/3436110.jpg) I.B. SPECIFIC TEACHING FIELDS Standards for Certification in Early Childhood Education [26.110-26.270] STANDARD 1 Curriculum The competent early childhood teacher understands and demonstrates the central
I.B. SPECIFIC TEACHING FIELDS Standards for Certification in Early Childhood Education [26.110-26.270] STANDARD 1 Curriculum The competent early childhood teacher understands and demonstrates the central
In this chapter you will find information on the following subjects:
 17 1. From XP to Vista Microsoft, the creator of Windows, has published various versions of the Windows operating system over the past two decades. Windows Vista is the latest version, the successor to
17 1. From XP to Vista Microsoft, the creator of Windows, has published various versions of the Windows operating system over the past two decades. Windows Vista is the latest version, the successor to
Paper Prototyping as a core tool in the design of mobile phone user experiences
 Paper Prototyping as a core tool in the design of mobile phone user experiences Introduction There is much competition in the mobile telecoms industry. Mobile devices are increasingly featurerich they
Paper Prototyping as a core tool in the design of mobile phone user experiences Introduction There is much competition in the mobile telecoms industry. Mobile devices are increasingly featurerich they
An Iterative Usability Evaluation Procedure for Interactive Online Courses
 An Iterative Usability Evaluation Procedure for Interactive Online Courses by Laurie P. Dringus ABSTRACT The Internet and World Wide Web (W3) have afforded distance learners simple links to access information.
An Iterative Usability Evaluation Procedure for Interactive Online Courses by Laurie P. Dringus ABSTRACT The Internet and World Wide Web (W3) have afforded distance learners simple links to access information.
Super Market TV A study about means and effects of (good) design
 Super Market TV A study about means and effects of (good) design Ursula Stalder, lic. phil I Head of Competence Center Online Communication University of Applied Sciences, Lucerne/Switzerland Seite 1 Question
Super Market TV A study about means and effects of (good) design Ursula Stalder, lic. phil I Head of Competence Center Online Communication University of Applied Sciences, Lucerne/Switzerland Seite 1 Question
CONSUMERLAB CONNECTED LIFESTYLES. An analysis of evolving consumer needs
 CONSUMERLAB CONNECTED LIFESTYLES An analysis of evolving consumer needs An Ericsson Consumer Insight Summary Report January 2014 Contents INTRODUCTION AND KEY FINDINGS 3 THREE MARKETS, THREE REALITIES
CONSUMERLAB CONNECTED LIFESTYLES An analysis of evolving consumer needs An Ericsson Consumer Insight Summary Report January 2014 Contents INTRODUCTION AND KEY FINDINGS 3 THREE MARKETS, THREE REALITIES
High School Psychology and its Impact on University Psychology Performance: Some Early Data
 High School Psychology and its Impact on University Psychology Performance: Some Early Data John Reece Discipline of Psychology School of Health Sciences Impetus for This Research Oh, can you study psychology
High School Psychology and its Impact on University Psychology Performance: Some Early Data John Reece Discipline of Psychology School of Health Sciences Impetus for This Research Oh, can you study psychology
Triple Bottom Line Values, Social Identification and Organic Food Consumption
 Triple Bottom Line Values, Social Identification and Organic Food Consumption Jos Bartels (PhD) and Marleen Onwezen (MSc) Wageningen University and Research Centre Agricultural Economics Research Institute,
Triple Bottom Line Values, Social Identification and Organic Food Consumption Jos Bartels (PhD) and Marleen Onwezen (MSc) Wageningen University and Research Centre Agricultural Economics Research Institute,
Qualitative data acquisition methods (e.g. Interviews and observations) -.
 Qualitative data acquisition methods (e.g. Interviews and observations) -. Qualitative data acquisition methods (e.g. Interviews and observations) ( version 0.9, 1/4/05 ) Code: data-quali Daniel K. Schneider,
Qualitative data acquisition methods (e.g. Interviews and observations) -. Qualitative data acquisition methods (e.g. Interviews and observations) ( version 0.9, 1/4/05 ) Code: data-quali Daniel K. Schneider,
The Game Development Process. Slides: largely based on Mark Claypool (WPI, USA) course on game development
 The Game Development Process Slides: largely based on Mark Claypool (WPI, USA) course on game development Outline Introduction Game Business Overview Stats Shape Game Companies Structure Timeline References
The Game Development Process Slides: largely based on Mark Claypool (WPI, USA) course on game development Outline Introduction Game Business Overview Stats Shape Game Companies Structure Timeline References
T3.1. Independent Living Applications Portfolio. Henk Herman Nap: h.h.nap@smart-homes.nl. Ad van Berlo: a.vberlo@smart-homes.nl
 T3.1 Independent Living Applications Portfolio Henk Herman Nap: h.h.nap@smart-homes.nl Ad van Berlo: a.vberlo@smart-homes.nl Richard Pasmans: r.pasmans@smart-homes.nl 2013 Roll-out with 7000 users in real
T3.1 Independent Living Applications Portfolio Henk Herman Nap: h.h.nap@smart-homes.nl Ad van Berlo: a.vberlo@smart-homes.nl Richard Pasmans: r.pasmans@smart-homes.nl 2013 Roll-out with 7000 users in real
CASE NOTES: SENPORTAL: INTERNET-BASED SERVICES FOR SENIOR CITIZENS
 CASE NOTES: SENPORTAL: INTERNET-BASED SERVICES FOR SENIOR CITIZENS Rossouw von Solms and Etienne de Lange, Institute for ICT Advancement, Nelson Mandela Metropolitan University, Port Elizabeth, South Africa,
CASE NOTES: SENPORTAL: INTERNET-BASED SERVICES FOR SENIOR CITIZENS Rossouw von Solms and Etienne de Lange, Institute for ICT Advancement, Nelson Mandela Metropolitan University, Port Elizabeth, South Africa,
Exploring Social Interaction in Co-located Multiplayer Games
 Exploring Social Interaction in Co-located Multiplayer Games Dennis L. Kappen dennis.kappen@uoit.ca John Gregory john.uoit@hotmail.com Daniel Stepchenko daniel.stepchenko@uoit.net Rina R. Wehbe University
Exploring Social Interaction in Co-located Multiplayer Games Dennis L. Kappen dennis.kappen@uoit.ca John Gregory john.uoit@hotmail.com Daniel Stepchenko daniel.stepchenko@uoit.net Rina R. Wehbe University
Guidelines for Using the Retrospective Think Aloud Protocol with Eye Tracking
 Guidelines for Using the Retrospective Think Aloud Protocol with Eye Tracking September, 2009 Short paper by Tobii Technology Not sure of how to design your eye tracking study? This document aims to provide
Guidelines for Using the Retrospective Think Aloud Protocol with Eye Tracking September, 2009 Short paper by Tobii Technology Not sure of how to design your eye tracking study? This document aims to provide
OCR LEVEL 3 CAMBRIDGE TECHNICAL
 Cambridge TECHNICALS OCR LEVEL 3 CAMBRIDGE TECHNICAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA IN IT COMPUTER GAME DESIGN H/502/5671 LEVEL 3 UNIT 32 GUIDED LEARNING HOURS: 60 UNIT CREDIT VALUE: 10 COMPUTER GAME DESIGN H/502/5671
Cambridge TECHNICALS OCR LEVEL 3 CAMBRIDGE TECHNICAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA IN IT COMPUTER GAME DESIGN H/502/5671 LEVEL 3 UNIT 32 GUIDED LEARNING HOURS: 60 UNIT CREDIT VALUE: 10 COMPUTER GAME DESIGN H/502/5671
La gent gran i les TIC Barcelona, 22 d Abril 2013. Les TIC per a la salut integral i la vida activa i independent
 La gent gran i les TIC Barcelona, 22 d Abril 2013 Les TIC per a la salut integral i la vida activa i independent Outline Active Independent Living at BDigital Ageing society, facts Ambient Assisted Living
La gent gran i les TIC Barcelona, 22 d Abril 2013 Les TIC per a la salut integral i la vida activa i independent Outline Active Independent Living at BDigital Ageing society, facts Ambient Assisted Living
Motivations of Play in Online Games. Nick Yee, Department of Communication, Stanford University. (in press in CyberPsychology and Behavior) Abstract
 Motivations of Play in Online Games Nick Yee, Department of Communication, Stanford University (in press in CyberPsychology and Behavior) Abstract An empirical model of player motivations in online games
Motivations of Play in Online Games Nick Yee, Department of Communication, Stanford University (in press in CyberPsychology and Behavior) Abstract An empirical model of player motivations in online games
OBL4HE: students' use of online learning resources and preferences for design and content. February 2012. Rebecca Reynolds
 Rebecca Section name OBL4HE: students' use of online learning resources and preferences for design and content February 2012 Rebecca Reynolds University of Reading 2012 Wednesday 8 August 2012 Page 1 Introduction
Rebecca Section name OBL4HE: students' use of online learning resources and preferences for design and content February 2012 Rebecca Reynolds University of Reading 2012 Wednesday 8 August 2012 Page 1 Introduction
The Importance and Impact of Nursing Informatics Competencies for Baccalaureate Nursing Students and Registered Nurses
 IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS) e-issn: 2320 1959.p- ISSN: 2320 1940 Volume 5, Issue 1 Ver. IV (Jan. - Feb. 2016), PP 20-25 www.iosrjournals.org The Importance and Impact of Nursing
IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS) e-issn: 2320 1959.p- ISSN: 2320 1940 Volume 5, Issue 1 Ver. IV (Jan. - Feb. 2016), PP 20-25 www.iosrjournals.org The Importance and Impact of Nursing
ASSESSMENT: Coaching Efficacy As Indicators Of Coach Education Program Needs
 March, 2003 Volume 5, Issue 1 ASSESSMENT: Coaching Efficacy As Indicators Of Coach Education Program Needs Lena Fung, Ph.D. Department of Physical Education Hong Kong Baptist University Hong Kong, SAR
March, 2003 Volume 5, Issue 1 ASSESSMENT: Coaching Efficacy As Indicators Of Coach Education Program Needs Lena Fung, Ph.D. Department of Physical Education Hong Kong Baptist University Hong Kong, SAR
GUIDE Gentle User Interfaces for Elderly People
 GUIDE Gentle User Interfaces for Elderly People Christoph Jung, Fraunhofer IGD christoph.jung@igd.fraunhofer.de GUIDE project in a nutshell GUIDE develops a software framework and toolbox for integration
GUIDE Gentle User Interfaces for Elderly People Christoph Jung, Fraunhofer IGD christoph.jung@igd.fraunhofer.de GUIDE project in a nutshell GUIDE develops a software framework and toolbox for integration
A DIGITAL SOLUTIONS AGENCY. 2212 Queen Anne Ave N. Ste. 337 Seattle WA, 98109 206.280.3422 info@peelinteractive.com www.peelinteractive.
 A DIGITAL SOLUTIONS AGENCY We are an Enteractive Agency! We are a full service digital production agency located in Seattle Washington. We specialize in developing digital marketing for the entertainment
A DIGITAL SOLUTIONS AGENCY We are an Enteractive Agency! We are a full service digital production agency located in Seattle Washington. We specialize in developing digital marketing for the entertainment
VIEWS OF STUDENTS IN THE DEPARTMENT OF RECREATION AND SPORT MANAGEMENT ON DISTANCE EDUCATION
 VIEWS OF STUDENTS IN THE DEPARTMENT OF RECREATION AND SPORT MANAGEMENT ON DISTANCE EDUCATION Asst.Prof.Dr.Gülten Hergüner Sakarya University Physical Education and Sports Teaching Department herguner@sakarya.edu.tr
VIEWS OF STUDENTS IN THE DEPARTMENT OF RECREATION AND SPORT MANAGEMENT ON DISTANCE EDUCATION Asst.Prof.Dr.Gülten Hergüner Sakarya University Physical Education and Sports Teaching Department herguner@sakarya.edu.tr
Assessing Online Asynchronous Discussion in Online Courses: An Empirical Study
 Assessing Online Asynchronous Discussion in Online Courses: An Empirical Study Shijuan Liu Department of Instructional Systems Technology Indiana University Bloomington, Indiana, USA shijliu@indiana.edu
Assessing Online Asynchronous Discussion in Online Courses: An Empirical Study Shijuan Liu Department of Instructional Systems Technology Indiana University Bloomington, Indiana, USA shijliu@indiana.edu
Evaluation of a Radiology Picture Archiving and Communication System Laboratory Exercise
 Current Developments in Technology-Assisted Education (2006) 1253 Evaluation of a Radiology Picture Archiving and Communication System Laboratory Exercise A. Tzavaras 1, E.Ventouras 1,* 1 Department of
Current Developments in Technology-Assisted Education (2006) 1253 Evaluation of a Radiology Picture Archiving and Communication System Laboratory Exercise A. Tzavaras 1, E.Ventouras 1,* 1 Department of
Adoption of Social Media by Fast-Growing Companies: Innovation Among the Inc. 500
 Adoption of Social Media by Fast-Growing Companies: Innovation Among the Inc. 500 Nora Ganim Barnes University of Massachusetts Dartmouth Stephanie Jacobsen University of Massachusetts Dartmouth This study
Adoption of Social Media by Fast-Growing Companies: Innovation Among the Inc. 500 Nora Ganim Barnes University of Massachusetts Dartmouth Stephanie Jacobsen University of Massachusetts Dartmouth This study
Involving Children and Young Adults With Complex Needs in Game Design
 Involving Children and Young Adults With Complex Needs in Game Design Kathrin Gerling kgerling@lincoln.ac.uk Conor Linehan clinehan@lincoln.ac.uk Jonathan Waddington WESC Foundation Exeter EX2 6HA, UK
Involving Children and Young Adults With Complex Needs in Game Design Kathrin Gerling kgerling@lincoln.ac.uk Conor Linehan clinehan@lincoln.ac.uk Jonathan Waddington WESC Foundation Exeter EX2 6HA, UK
Effects of Automated Transcription Delay on Non-native Speakers Comprehension in Real-time Computermediated
 Effects of Automated Transcription Delay on Non-native Speakers Comprehension in Real-time Computermediated Communication Lin Yao 1, Ying-xin Pan 2, and Dan-ning Jiang 2 1 Institute of Psychology, Chinese
Effects of Automated Transcription Delay on Non-native Speakers Comprehension in Real-time Computermediated Communication Lin Yao 1, Ying-xin Pan 2, and Dan-ning Jiang 2 1 Institute of Psychology, Chinese
Single Level Drill Down Interactive Visualization Technique for Descriptive Data Mining Results
 , pp.33-40 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijgdc.2014.7.4.04 Single Level Drill Down Interactive Visualization Technique for Descriptive Data Mining Results Muzammil Khan, Fida Hussain and Imran Khan Department
, pp.33-40 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijgdc.2014.7.4.04 Single Level Drill Down Interactive Visualization Technique for Descriptive Data Mining Results Muzammil Khan, Fida Hussain and Imran Khan Department
Quantitative Analysis of Desirability in User Experience
 Quantitative Analysis of Desirability in User Experience Sisira Adikari School of Information Systems and Accounting University of Canberra Canberra, Australia ACT 2617 Email: sisira.adikari@canberra.edu.au
Quantitative Analysis of Desirability in User Experience Sisira Adikari School of Information Systems and Accounting University of Canberra Canberra, Australia ACT 2617 Email: sisira.adikari@canberra.edu.au
Barriers & Incentives to Obtaining a Bachelor of Science Degree in Nursing
 Southern Adventist Univeristy KnowledgeExchange@Southern Graduate Research Projects Nursing 4-2011 Barriers & Incentives to Obtaining a Bachelor of Science Degree in Nursing Tiffany Boring Brianna Burnette
Southern Adventist Univeristy KnowledgeExchange@Southern Graduate Research Projects Nursing 4-2011 Barriers & Incentives to Obtaining a Bachelor of Science Degree in Nursing Tiffany Boring Brianna Burnette
Open innovation and agile project management in video game industry
 Open innovation and agile project management in video game industry RADIM ŠPICAR Department of Business Administration and Management University of West Bohemia Husova 11, 30614 Plzeň CZECH REPUBLIC rspicar@students.zcu.cz
Open innovation and agile project management in video game industry RADIM ŠPICAR Department of Business Administration and Management University of West Bohemia Husova 11, 30614 Plzeň CZECH REPUBLIC rspicar@students.zcu.cz
E-Commerce Web Sites Trust Factors: An Empirical Approach
 Contemporary Engineering Sciences, Vol. 6, 2013, no. 1, 1 7 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com E-Commerce Web Sites Trust Factors: An Empirical Approach Radwan M. Al-Dwairi Department of Computer Information
Contemporary Engineering Sciences, Vol. 6, 2013, no. 1, 1 7 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com E-Commerce Web Sites Trust Factors: An Empirical Approach Radwan M. Al-Dwairi Department of Computer Information
Android Box SNNPB73B
 Android Box SNNPB73B ANDROID EASE OF USE EXPERIENCE Very easy to use device, users can enjoy a tablet-like browsing experience. Enjoy the intuitive operation of Android KitKat 4.4 with thousands of productivity
Android Box SNNPB73B ANDROID EASE OF USE EXPERIENCE Very easy to use device, users can enjoy a tablet-like browsing experience. Enjoy the intuitive operation of Android KitKat 4.4 with thousands of productivity
The Computing Curriculum at Coston Primary
 Years Year 1 Year 2 1 and 2 Autumn We are learning about programming and computational thinking and in We are learning about programming and computational thinking and in Year 1 Food and farming Year 2
Years Year 1 Year 2 1 and 2 Autumn We are learning about programming and computational thinking and in We are learning about programming and computational thinking and in Year 1 Food and farming Year 2
Analysis of User Experience Quality on Responsive Web Design from its Informative Perspective
 , pp.53-62 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijseia.2014.8.5.06 Analysis of User Experience Quality on Responsive Web Design from its Informative Perspective Devita Mira Lestari, Dadan Hardianto and Achmad Nizar
, pp.53-62 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijseia.2014.8.5.06 Analysis of User Experience Quality on Responsive Web Design from its Informative Perspective Devita Mira Lestari, Dadan Hardianto and Achmad Nizar
Introduction to Video Game Design. The business of games Ludology Game Theory "Funativity" Abstract Rules Concrete Rules Scratch
 Introduction to Video Game Design The business of games Ludology Game Theory "Funativity" Abstract Rules Concrete Rules Scratch Video Games = Big Business U.S. video game sales 2009, $20.2 billion (i).
Introduction to Video Game Design The business of games Ludology Game Theory "Funativity" Abstract Rules Concrete Rules Scratch Video Games = Big Business U.S. video game sales 2009, $20.2 billion (i).
Web-Based Education in Secondary Schools in Cyprus A National Project
 Web-Based Education in Secondary Schools in Cyprus A National Project Aimilia Tzanavari, George A. Papadopoulos Department of Computer Science University Of Cyprus Nicosia, CYPRUS {aimilia, george}@cs.ucy.ac.cy
Web-Based Education in Secondary Schools in Cyprus A National Project Aimilia Tzanavari, George A. Papadopoulos Department of Computer Science University Of Cyprus Nicosia, CYPRUS {aimilia, george}@cs.ucy.ac.cy
Evaluation of an Electronic Charting System in the BCIT Nursing Simulation Lab
 Evaluation of an Electronic Charting System in the BCIT Nursing Simulation Lab Prepared by: Johanne Mattie Research Associate, Technology and Product Evaluation Group As part of the Stage 3 ehealth Go
Evaluation of an Electronic Charting System in the BCIT Nursing Simulation Lab Prepared by: Johanne Mattie Research Associate, Technology and Product Evaluation Group As part of the Stage 3 ehealth Go
Market Research: Friend or Foe to Christian Charities?
 Market Research: Friend or Foe to Christian Charities? by Redina Kolaneci Senior Fundraising & Stewardship Consultant McConkey Johnston international UK If you are ignorant of yourself, in addition to
Market Research: Friend or Foe to Christian Charities? by Redina Kolaneci Senior Fundraising & Stewardship Consultant McConkey Johnston international UK If you are ignorant of yourself, in addition to
Using Surveys for Data Collection in Continuous Improvement
 Innovation Insight Series Number 14 http://www.psu.edu/president/pia/innovation/ Across the University many people use data in assessment and decision-making. Data-based decision-making, an essential element
Innovation Insight Series Number 14 http://www.psu.edu/president/pia/innovation/ Across the University many people use data in assessment and decision-making. Data-based decision-making, an essential element
Outcomes of Preservice Teacher s Technology Use
 Outcomes of Preservice Teacher s Technology Use William F. Morrison, Assistant Professor, Bowling Green State University Tara L. Jeffs, Assistant Professor, East Carolina University Abstract: At a time
Outcomes of Preservice Teacher s Technology Use William F. Morrison, Assistant Professor, Bowling Green State University Tara L. Jeffs, Assistant Professor, East Carolina University Abstract: At a time
Rating vs. Preference: A comparative study of self-reporting
 Rating vs. Preference: A comparative study of self-reporting Georgios N. Yannakakis 1 and John Hallam 2 1 Center for Computer Games Research, IT University of Copenhagen, Rued Langgaards Vej 7, Copenhagen
Rating vs. Preference: A comparative study of self-reporting Georgios N. Yannakakis 1 and John Hallam 2 1 Center for Computer Games Research, IT University of Copenhagen, Rued Langgaards Vej 7, Copenhagen
Stock Market Challenge Maths, Business Studies and Key Skills Development. Dealing Room Game Teacher s Guide
 Stock Market Challenge Maths, Business Studies and Key Skills Development Dealing Room Game Teacher s Guide 10 Lane Learning 2010 Stock Market Challenge: Maths, Business Studies and Key Skills Development
Stock Market Challenge Maths, Business Studies and Key Skills Development Dealing Room Game Teacher s Guide 10 Lane Learning 2010 Stock Market Challenge: Maths, Business Studies and Key Skills Development
Top 5 best practices for creating effective dashboards. and the 7 mistakes you don t want to make
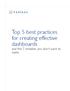 Top 5 best practices for creating effective dashboards and the 7 mistakes you don t want to make p2 Financial services professionals are buried in data that measure and track: relationships and processes,
Top 5 best practices for creating effective dashboards and the 7 mistakes you don t want to make p2 Financial services professionals are buried in data that measure and track: relationships and processes,
BUILDING LIFETIME VALUE WITH SEGMENTATION
 PRESENTS DATA DRIVEN BRAND MARKETING PART ONE YOUR DEFINITIVE GUIDE TO BUILDING LIFETIME VALUE WITH SEGMENTATION WHAT YOU D KNOW IF WE COULD TALK TO YOU Proving the Value of Marketing 1 2 3 4 5 6 SEE YOUR
PRESENTS DATA DRIVEN BRAND MARKETING PART ONE YOUR DEFINITIVE GUIDE TO BUILDING LIFETIME VALUE WITH SEGMENTATION WHAT YOU D KNOW IF WE COULD TALK TO YOU Proving the Value of Marketing 1 2 3 4 5 6 SEE YOUR
Miami University: Human Subjects Research General Research Application Guidance
 Miami University: Human Subjects Research General Research Application Guidance Use the accompanying Word template for completing the research description. You must provide sufficient information regarding
Miami University: Human Subjects Research General Research Application Guidance Use the accompanying Word template for completing the research description. You must provide sufficient information regarding
KSS Call Recorder KSS Call Manager KSS Call Control
 www.kelmar-software.com Product Range KSS Call Recorder KSS Call Manager KSS Call Control Kelmar Software Solutions, Genesys Court, Denton Drive, Northwich, Cheshire CW9 7LU W: www.kelmar-software.com
www.kelmar-software.com Product Range KSS Call Recorder KSS Call Manager KSS Call Control Kelmar Software Solutions, Genesys Court, Denton Drive, Northwich, Cheshire CW9 7LU W: www.kelmar-software.com
ESOMAR PRACTICAL GUIDE ON COOKIES JULY 2012
 ESOMAR PRACTICAL GUIDE ON COOKIES JULY 2012 Copyright ESOMAR 2012 TABLE OF CONTENTS 2 Objectives 2 Introduction 3 Definitions 4 SECTION 1: APPLICABLE LAW 4 SECTION 2: WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW SOME FAQs 5
ESOMAR PRACTICAL GUIDE ON COOKIES JULY 2012 Copyright ESOMAR 2012 TABLE OF CONTENTS 2 Objectives 2 Introduction 3 Definitions 4 SECTION 1: APPLICABLE LAW 4 SECTION 2: WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW SOME FAQs 5
Student diaries: using technology to produce alternative forms of feedback
 Student diaries: using technology to produce alternative forms of feedback NUZ QUADRI University of Hertfordshire PETER BULLEN University of Hertfordshire AMANDA JEFFERIES University of Hertfordshire 214
Student diaries: using technology to produce alternative forms of feedback NUZ QUADRI University of Hertfordshire PETER BULLEN University of Hertfordshire AMANDA JEFFERIES University of Hertfordshire 214
Soft Skills Requirements in Software Architecture s Job: An Exploratory Study
 Soft Skills Requirements in Software Architecture s Job: An Exploratory Study 1 Faheem Ahmed, 1 Piers Campbell, 1 Azam Beg, 2 Luiz Fernando Capretz 1 Faculty of Information Technology, United Arab Emirates
Soft Skills Requirements in Software Architecture s Job: An Exploratory Study 1 Faheem Ahmed, 1 Piers Campbell, 1 Azam Beg, 2 Luiz Fernando Capretz 1 Faculty of Information Technology, United Arab Emirates
Using Second Life in an English Course: Designing Class Activities to Address Learning Objectives
 Citation: Mayrath, M., Sanchez, J., Traphagan, T., Heikes, J. & Trivedi, A. Using Second Life in an English Course: Designing Class Activities to Address Learning Objectives Proceedings of World Conference
Citation: Mayrath, M., Sanchez, J., Traphagan, T., Heikes, J. & Trivedi, A. Using Second Life in an English Course: Designing Class Activities to Address Learning Objectives Proceedings of World Conference
AUSTRALIAN MULTI-SCREEN REPORT QUARTER 3 2014
 AUSTRALIAN MULTI-SCREEN REPORT QUARTER 3 TV AND OTHER VIDEO CONTENT ACROSS MULTIPLE SCREENS The edition of The Australian Multi-Screen Report provides the latest estimates of screen technology penetration
AUSTRALIAN MULTI-SCREEN REPORT QUARTER 3 TV AND OTHER VIDEO CONTENT ACROSS MULTIPLE SCREENS The edition of The Australian Multi-Screen Report provides the latest estimates of screen technology penetration
Understanding the Performance of an X550 11-User Environment
 Understanding the Performance of an X550 11-User Environment Overview NComputing's desktop virtualization technology enables significantly lower computing costs by letting multiple users share a single
Understanding the Performance of an X550 11-User Environment Overview NComputing's desktop virtualization technology enables significantly lower computing costs by letting multiple users share a single
Year 2 Evaluation of the Connecticut Clean Energy Climate Solutions Project
 Year 2 Evaluation of the Connecticut Clean Energy Climate Solutions Project Submitted to Clean Air-Cool Planet Prepared by Rucha Londhe, Ph.D. Irene F. Goodman, Ed.D. Margaret Tiedemann, B.A. October 2008
Year 2 Evaluation of the Connecticut Clean Energy Climate Solutions Project Submitted to Clean Air-Cool Planet Prepared by Rucha Londhe, Ph.D. Irene F. Goodman, Ed.D. Margaret Tiedemann, B.A. October 2008
Video Games and Academic Performance. Ronny Khadra. Cody Hackshaw. Leslie Mccollum. College of Coastal Georgia
 Video Games and Academic Performance Ronny Khadra Cody Hackshaw Leslie Mccollum College of Coastal Georgia Introduction and Background The development of video games goes back to the 1940s and 1950s. Computer
Video Games and Academic Performance Ronny Khadra Cody Hackshaw Leslie Mccollum College of Coastal Georgia Introduction and Background The development of video games goes back to the 1940s and 1950s. Computer
Serious Game as Educational Tool for Safety and Prevention
 Serious Game as Educational Tool for Safety and Prevention Maarten Vanhoucke 1, Cesar Vandevelde 1, Joost Ingels 2, Geoffrey Hamon 2, Jelle Saldien 1 1 Department of Industrial System and Product Design,
Serious Game as Educational Tool for Safety and Prevention Maarten Vanhoucke 1, Cesar Vandevelde 1, Joost Ingels 2, Geoffrey Hamon 2, Jelle Saldien 1 1 Department of Industrial System and Product Design,
Reading with Mobile Phone & Large Display
 Reading with Mobile Phone & Large Display Roswitha Gostner Computing Department Lancaster University, gostner@lancs.ac.uk Hans Gellersen Computing Department Lancaster University Lancaster, LA1 4WY, UK
Reading with Mobile Phone & Large Display Roswitha Gostner Computing Department Lancaster University, gostner@lancs.ac.uk Hans Gellersen Computing Department Lancaster University Lancaster, LA1 4WY, UK
BEST PRACTICES IN UTILIZING 360 DEGREE FEEDBACK
 BEST PRACTICES IN UTILIZING 360 DEGREE FEEDBACK Kenneth M. Nowack Ph.D. 3435 Ocean Park Blvd. Suite 214 Santa Monica, CA 90405 (310) 452-5130 (310) 450-0548 Fax www.envisialearning.com 2008 Envisia Learning
BEST PRACTICES IN UTILIZING 360 DEGREE FEEDBACK Kenneth M. Nowack Ph.D. 3435 Ocean Park Blvd. Suite 214 Santa Monica, CA 90405 (310) 452-5130 (310) 450-0548 Fax www.envisialearning.com 2008 Envisia Learning
Child Psychology and Education with Technology
 International Journal of Education and Information Studies. ISSN 2277-3169 Volume 4, Number 1 (2014), pp. 41-45 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Child Psychology and Education with
International Journal of Education and Information Studies. ISSN 2277-3169 Volume 4, Number 1 (2014), pp. 41-45 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Child Psychology and Education with
