May-Thurner Syndrome (and related topics) Glossary 1
|
|
|
- Vincent Gray
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 May-Thurner Syndrome (and related topics) Glossary 1 DISCLAIMER: This document is not the work of medical professionals and only contains information, not advice. It is intended to be used as quick reference guide to unfamiliar words and as a starting point for further research, including consulting with a licensed medical doctor. Any information contained herein should not be considered a replacement or used as a substitute for advice from a licensed medical doctor relating to diagnosis, treatment, management, or other issues arising out of any medical condition, including those listed below. Angioplasty: a procedure used to widen vessels using catheters containing balloons that are inflated to widen the vessel and/or stents. There are various types of these procedures and their names are associated with the type of vessel entry and equipment used. For example, percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA) describes entry through the skin (percutaneous) and navigates to the area of the vessel of interest through the same vessel or one that communicates with it (transluminal). Anticoagulant: Drugs used to prevent clot formation or to prevent a clot that has formed from enlarging. Anticoagulant drugs inhibit clot formation by blocking the action of clotting factors or platelets. Anticoagulants do not break up blood clots. They only help stop the body from making more/bigger ones while it breaks any existing clot down. Anticoagulant drugs fall into 4 groups: Factor Xa inhibitors are anticoagulants that block the activity of clotting factor Xa and prevents blood clots developing or getting worse. They include Xarelto, Eliquis, and Arixtra. Inhibitors of clotting factor synthesis: These anticoagulants inhibit the production of certain clotting factors (vitamin K) in the liver. One example is warfarin (Jantoven or Coumadin). Inhibitors of thrombin: These drugs interfere with blood clotting by blocking the activity of thrombin. They include heparins, Pradaxa, and lepirudin (Refludan). Antiplatelet drugs. These drugs interact with platelets, which is a type of blood cell, to block platelets from sticking together into harmful clots. They include aspirin, ticlopidine (Ticlid), clopidogrel (Plavix), tirofiban (Aggrastat), and eptifibatide (Integrilin). These are often prescribed for a short period of time after something has been implanted in the body. Antithrombin (AT): A small protein molecule that inhibits blood clotting. AT deficiencies can lead to clotting. The type most likely to cause problems is inherited, and a blood test of AT levels can diagnosis it. It should be noted that warfarin can increase AT levels, so any test done to rule it out should not be done while taking warfarin. Artery: a muscular vessel that carries oxygen and nutrient rich blood under high pressure from the heart to other parts of the body. Blood Thinners-see Anticoagulant
2 May-Thurner Syndrome (and related topics) Glossary 2 Chronic Venous Insufficiency-see Post Thrombosis Syndrome Chronic Venous Limb Disorder-see Post Thrombosis Syndrome Clot: a clump of platelets and blood proteins (also known as a thrombus) that form a plug at the site of an injured blood vessel to prevent excessive bleeding. A clot may also form inside a blood vessel and block that vessel, which is called a thrombosis or a blood clot. Collateral Veins: When there is an area in a vein that is blocked, the body responds by trying to bulk up tiny blood vessels to go around it. As the collateral vessels grow more muscular and interconnected, they begin to reroute some of the blood flow around the blockage. Cardiovascular exercise helps them grow quicker and larger. Overstressed collaterals can become painful. If they are superficial, they can be visible under the skin. Compression Stocking: a specialized socks, knee highs, thigh highs, or panty hose that provide graduated compression where most of the squeeze or pressure is at the foot and the least amount is at the top of the stocking. Therefore, the degree of compression is described by a range, example The higher number is the amount of pressure or squeeze at the foot and the lower number is the pressure at the top of the sock. This helps control swelling or edema (fluid) in the legs and feet. Compression stockings help treat symptoms but not really the underlying cause of the fluid accumulation. The edema can be a result of a very wide variety of conditions, and often the result of Post Thrombosis Syndrome (PTS). There is some research that shows they help reduce PTS, but the results are mixed on that at this time. *It is important to note that athletic compressions and TED type garments are generally not graduated and/or strong enough to help PTS and are not what is generally recommended by doctors following DVTs. Coumadin/Warfarin: an anticoagulant that inhibits the production of certain clotting factors (vitamin K) in the liver. Requires monitoring, by way of INR levels, to adjust dosage to stay in therapeutic range. See INR. Coumadin Induced Skin Necrosis-see Warfarin Induced Skin Necrosis CT Scan: Computerized tomography scan combines a series of X-ray views taken from many different angles and computer processing to create cross-sectional images of the bones and soft tissues inside your body. For visualizing blood vessels a contrast material has to be injected first. The contrast material blocks X-rays and appears white on images. There is a higher exposure to radiation than in a standard x-ray, so CT scans are not a routine procedure.
3 May-Thurner Syndrome (and related topics) Glossary 3 D-Dimer: a blood test that measures a substance that is released when a blood clot breaks up. Doctors order the d-dimer test, along with other lab tests and imaging scans, to help check for blood-clotting problems. A d-dimer test can also be used to check how well a treatment is working. A higher-than-normal d-dimer level might mean that there is a blood-clotting problem, but a higher level might be caused by some other health problem or by a normal healing process. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): a type of blood clot that forms in a major vein of the leg or, less commonly, in the arms, pelvis, or other large veins in the body. More likely to cause problems or result in a PE than a superficial clot. Distal DVT: Affects veins below the knee. Doppler Ultrasound-See Ultrasound Ecchymosis: Bleeding that occurs under the skin, a type of hematoma; larger than 1cm. Edema (Dropsy): A condition of excess fluid volume in the circulatory system. Results in swelling and discomfort or pain depending on severity. Can be caused by a variety of medical conditions (heart, kidney, liver, lymph node), medication, pregnancy, sunburn, salt intake, etc. Embolism: a condition where an object called an embolus is created in one part of the body, circulates throughout the body, and then blocks blood flowing through a vessel in another part of the body. Emboli are not to be confused with thrombi, which are clots that are formed and remain in one area of the body without being carried throughout the bloodstream. Emboli can be made up of many different materials including blood, clots, air, gas, amniotic fluid, fat, bacteria, or cholesterol. Factor V Leiden Thrombophilia: an inherited a specific gene mutation that causes thrombophilia, which is an increased tendency to form abnormal blood clots that can block blood vessels. It leads to a higher than average risk of developing DVTs. It is generally treated with lifetime anticoagulation medication. Fibrin/Fibrinogen: Fibrin (also called Factor Ia) is a threadlike protein that supports the formation of blood clots and provides the initial structure upon which new tissue can form at the site of an injury. Fibrinogen levels are high when there are active clots. They reduce as the clot goes down or stabilizes. Fragmin: a type of low molecular weight heparin injection. Hematologist: a physician who specializes in researching, diagnosing, and treating blood disorders.
4 May-Thurner Syndrome (and related topics) Glossary 4 Hematoma (bruise/contusion): A solid swelling of clotted blood that forms in the tissues or organs of the body as a result of a broken blood vessel. The types of hematoma depend on their size and location. Epidural hematomas are on the outside of the brain, subdural and intracerebral are on the inside. See petechial (tiny), purpura (small) and ecchymosis (bigger) for descriptions on size. Heparin: a blood thinner that interferes with blood clotting by blocking the activity of thrombin. Full strength (unfractured) heparin is generally administered in the hospital via IV. When broken down into a lower molecular weight, it is often self-administered at home. See Low Molecular Weight Heparin. Hypercoagulability: An increased tendency of the blood to coagulate (thicken) more rapidly than is normal. Can be due to things like pregnancy, medications, clotting disorders, sepsis, or cancer to name a few. Idiopathic DVT/PE (Unprovoked DVT/PE): Formation of venous blood clot with no known cause. Iliac Vein: The common iliac vein starts in the abdomen region of the fifth lumbar vertebrae. It divides into two branches. The internal iliac vein supplies blood to organs in the pelvic region. The external iliac connects to the femoral veins. Both veins join together to form the inferior vena cava. The external iliac vein is located in the lower leg. Inferior Vena Cava Filter (IVC filter): a small cone-shaped device that is implanted using a catheter in the inferior vena cava just below the kidneys. The filter is designed to capture blood clots that have broken loose from one of the deep veins in the legs on its way to the heart and lungs. IVC filters can be either permanent or optionally removable (temporary). Not all temporary ones end up being removable and it is considered safe to leave them in. INR (international normalized ratio): is a way of standardizing the results of prothrombin time tests, no matter the testing method. Generally used in the context to testing ranges for administering warfarin/coumadin. Normal INR is generally The warfarin (Coumadin) dose is changed so that the prothrombin time is longer than normal (by about 1.5 to 2.5 times the normal value - INR values 2 to 3). Intravascular Ultrasound (IVUS): an invasive procedure where a miniature sound probe (transducer) on the tip of a catheter is threaded through the vein or artery and, using high-frequency sound waves, produces detailed images of the vein walls and any clots or compression. This is the gold standard of imaging techniques for MTS. It is the only way to really know if there is compression or not. It will show compression that was not visible on a venogram, CT or regular external ultrasound.
5 May-Thurner Syndrome (and related topics) Glossary 5 Intervention Radiology (IR): a medical sub-specialty of radiology that uses minimally-invasive image-guided procedures to diagnose and treat diseases in nearly every part of the body. Interventional Radiologists: Doctors who diagnose and treat patients using the least invasive techniques to minimize risk to the patient and improve outcomes. IVUS-see Intravascular Ultrasound Lovenox (enoxaparin): a quick acting, short lasting blood thinner (a LMWH), generally administered through injections. Safe during pregnancy. Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH): LMWH is produced by chemically splitting heparin into one-third of its original size. It has fewer side effects than heparin and produces a more predictable anticoagulant response. Administered under the skin through a small needle, can be done at home. LMWHs include dalteparin (Fragmin), enoxaparin (Lovenox), tinzaparin (Innohep), and a few others. Lupus Anticoagulant: A clotting disorder, Lupus anticoagulants are antibodies against substances in the lining of cells. Those with these antibodies may have an abnormally high risk of blood clotting. It is generally treated with lifetime anticoagulation medication. May-Thurner Syndrome (MTS): when the left iliac vein is compressed by the right iliac artery. Also known as Iliac Vein compression Syndrome and Cockett's syndrome. Non-DVT MTS patients tend to have nonthrombotic iliac vein lesions (NIVL). Rarely this can occur on the right side, although the left side is much more common. MRI/MRA/MRV- Magnetic Resonance Imaging: a test that uses a magnetic field and pulses of radio wave energy to make pictures of organs and structures inside the body. Using MRI to look at blood vessels and the flow of blood through them is called Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA), or Magnetic Resonance Venography (MRV), which can find problems of the arteries and veins, such as an aneurysm, a blocked blood vessel, or the torn lining of a blood vessel (dissection). Sometimes contrast material is used to see the blood vessels more clearly, and will be administered through an IV. Note: for those with metal stents or filters, MRIs may not be recommended or they may have to be done with slightly different calibrations. Make sure you let your health care professions know you have a stent or filter if they mention MRI/MRA. There are no known harmful effects from the strong magnetic field used for MRI as long as you have no metal implants. More expensive than a CT, x-ray, or ultrasound and not available at all hospitals. MRIs may not always show compression from MTS.
6 May-Thurner Syndrome (and related topics) Glossary 6 Nonthrombotic Iliac vein lesions (NIVLs): Lesions in the iliac vein, such as webs and spurs, which have not led to thrombosis. However, this compression of the iliac vein may cause symptoms of venous obstruction for some people, who may require stenting of the iliac vein to relieve symptoms. Are common in the general population but clinically significant in people with MTS. Nutcracker Syndrome (NCS) (Left Renal Vein Entrapment): compression of the left renal vein, most commonly between the aorta and the superior mesenteric artery, with impaired blood outflow often accompanied by distention of the distal portion of the vein. NCS is associated with hematuria (which can lead to anemia) and abdominal pain/left flank pain. Since the left gonad drains via the left renal vein it can also result in left testicular pain in men or left lower quadrant pain in women. Nausea and vomiting can result due to compression of the splanchnic veins. Petechia(e): Bleeding that occurs under the skin, a type of hematoma; less than 3mm in diameter. Phlebitis-see Thrombophlebitis Platelet: a small cell fragment (also known as a thrombocyte) involved in the blood s clotting process Plethysmography: An instrument used to measure changes in volume in parts of the body. This can help check blood circulation and check for the presence of blood clots in arms and legs, or how much air you can hold. Post-Phlebitic Syndrome-See Post Thrombosis Syndrome Post Thrombosis Syndrome (PTS): Post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS), Post-phlebitic syndrome (PPS), Venous stasis syndrome (VSS), Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI), Venous stress disorder, or Chronic venous limb disorder is a condition that occurs in up to 40% of leg DVT patients following original DVT, and is severe in 4%. Onset is usually within 6 months of DVT, but may not start for up to 2 years. Symptoms include chronic extremity swelling, chronic (or waxing and waning) pain, unspecific discomfort of the extremity, diffuse aching, heaviness, tiredness and cramping of extremity, dark skin pigmentation, bluish discoloration of toes/fingers, foot/hand or diffusely of leg/arm, skin dryness, eczema, hardening of the skin, formation of varicose veins, skin ulcer (stasis ulcer), atrophie blanche or white atrophy (scar tissue forms in the skin without the development of ulcers, areas of white skin) and dermatoliposclerosis (the tightness of the swollen leg leads to destruction of the skin and fat tissues). Damaged valves or valve reflux may play a part in PTS. Treatment is elevation of extremity at rest and at night, compression stockings, grade 2, weight loss, increased exercise with strengthening of extremity muscles, pain management, compression pump, interventional radiology procedures: balloon opening and stenting of narrowed vein.
7 May-Thurner Syndrome (and related topics) Glossary 7 *Some studies have shown that true graduated compression stockings worn for at least 2 years post-dvt may reduce the likelihood of PTS, however there is not enough clear research to state that definitely. Post-Thrombotic Syndrome-See Post Thrombosis Syndrome Pradaxa: a newer blood thinner that blocks the activity of thrombin. Protein C deficiency: disorder characterized by an increased tendency to form blood clots. Protein S deficiency: disorder characterized by an increased tendency to form blood clots. Prothrombin G20210A: A genetic risk factor that doubles or triples the risk of forming blood clots in the veins. Prothrombin Time Test (PT or PTT): a blood test that measures how long it takes blood to clot. A prothrombin time test can be used to check for bleeding problems. PT is also used to check whether medicine to prevent blood clots is working. Normal PT is seconds. Provoked DVT: A DVT with clear possible cause(s). See Virchow s triad for more information. Proximal DVT: Affects veins above the knee. PTA-see angioplasty Pulmonary Embolism (PE): A clot in a vein that has detached from the blood vessel in which it formed and traveled through the heart to the lungs where it becomes wedged, preventing adequate blood flow. Can lead to major damage to lung tissue, preventing the transmission of oxygen to the body, up to the point of death. Purple Toe Syndrome: A rare adverse effect of warfarin characterized by painful blue or purple toes. Usually noticeable in the first weeks of warfarin therapy. This adverse reaction usually indicates the need to stop warfarin and find an alternative treatment option. Purpura: Bleeding that occurs under the skin, a type of hematoma; between 3mm and 1cm in diameter Rivaroxaban-See Xarelto Spider Veins: Enlargement of capillary blood vessels leading to the formation of red or blue threadlike lines visible on the surface of the skin. They are the same
8 May-Thurner Syndrome (and related topics) Glossary 8 as varicose veins, but on the smaller capillaries. Spider veins can be caused by the backup of blood. They can also be caused by hormone changes, exposure to the sun, and injuries. Spur (fibrous spur/venous spur): This is a fibrous obstructive lesion within the Left Common Iliac Vein that can develop from the chronic pulsatile compressive force of the Common Iliac Artery. This causes May-Thurner Syndrome and predisposes patient to thrombosis. Stent: small mesh tubes that usually are made of metal, but sometimes fabric, that are inserted into narrowed veins or arteries to widen them. Fabric stents, also called stent grafts, are used in larger arteries. Some stents are coated with medicine to prevent them from becoming blocked again, which is slowly and continuously released into the blood vessel. These stents are called drug-eluting stents. Superficial Clot/Thrombus: This is a blood clot forming in one or more veins located in the fatty tissue lying directly below the skin. These are usually rather small veins and the clot stops within these veins. If the blood clotting stops before it gets to the largest part of the major superficial vein (the saphenous vein) or before it goes to the deep veins, it generally will not cause much more than local pain, swelling, and redness over the vein. Thrombectomy: removal of a blood clot. There are two different ways to do it: Mechanical thrombectomy is the surgical removal of a blood clot using a long catheter tipped with a tiny suction cup, rotating device, high-speed fluid jet, or ultrasound device that physically breaks up the clot. Pharmacomechanical catheter-directed thrombolysis is a combination of the mechanical procedure with infused medications used to break up a clot. Thrombolysis: involves breaking up a clot using medication administered either in an IV, or through a catheter at or near the site of the clot. The most commonly used clot-busting drugs Eminase (anistreplase), Retavase (reteplase), Streptase (streptokinase, kabikinase), tpa (class of drugs that includes Activase), TNKase (tenecteplase), Abbokinase, Kinlytic (rokinase). Thrombophlebitis (Phlebitis): inflammation in a vein in an area where a blood clot has formed. Thrombosis: excess clotting, which may block veins or arteries. Thrombus/Thrombi: a clump of platelets and blood proteins (also known as a clot) that form a plug at the site of an injured blood vessel to prevent excessive bleeding. They can also form at sites of compression or where blood flow is slowed or reduced.
9 May-Thurner Syndrome (and related topics) Glossary 9 tpa (Tissue Plasminogen Activator, also known as IV rtpa): a medication that breaks up clots and is given through an IV in the arm or directly onto the clot through a catheter. Very expensive, not often used, but more and more studies are advocating for its use in DVT treatment. It may be something you have to ask for. Most often used when the DVT has extremely limited blood flow and patient presents with serious symptoms of pain and swelling. Ultrasound: (sonography or diagnostic medical sonography) an imaging method that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce relatively precise images of structures within your body. Doppler ultrasound tests use reflected sound waves to see how blood flows through a blood vessel. It helps doctors evaluate blood flow through major arteries and veins, such as those of the arms, legs, and neck. It can show blocked or reduced blood flow through narrowing veins or arteries. It is performed by a handheld instrument (transducer) that is passed lightly over the skin above a blood vessel. The transducer sends and receives sound waves that are amplified through a microphone. The sound waves bounce off solid objects, including blood cells. The movement of blood cells causes a change in pitch of the reflected sound waves. If there is no blood flow, the pitch does not change. Valve Reflux (also known as Venous Reflux Disease, Valvular Incompetency or Venous Insufficiency): a condition that develops when the valves (tiny flaps in the veins that open and close to keep blood from flowing backwards) that usually keep blood flowing out of your legs become damaged or diseased. These valves that normally force blood back towards the heart no longer function, causing blood to pool up in the legs, and the veins to the legs become distended. Superficial valve reflux can cause spider veins, varicose veins, and if left untreated, lead to other conditions such as leg swelling (edema), skin changes (hyperpigmentation), and open sores (venous ulcers). Common symptoms of superficial venous reflux include pain, swelling, leg heaviness and fatigue, as well as varicose veins in your legs. Superficial valve reflux can be treated surgically. Deep venous reflux occurs if the valves become damaged after a deep vein blood clot. It can lead to Post Thrombosis Syndrome. Deep venous reflux is not treatable, but symptoms can be managed. Pictures and links to video at: Valvular Incompetency-see Valve Reflux Varicose Vein: enlarged veins that can be blue, red, or flesh-colored. They often look like cords and appear twisted and bulging. They can be swollen and raised above the surface of the skin. Symptoms can also include aching pain that may get worse after sitting or standing for a long time, throbbing or cramping, heaviness, swelling, rash that s itchy or irritated, darkening of the skin (in severe cases) and restless legs. They can lead to sores or skin ulcers, bleeding, superficial thrombophlebitis, or DVTs.
10 May-Thurner Syndrome (and related topics) Glossary 10 Vascular Surgeon: Those who specialize in the diagnosis and management of disorders of the arterial, venous and lymphatic systems (but not intracranial vessels and the heart). In addition to experience with dissection and control of blood vessels that general surgery trainees gain vascular surgeons have significant experience with all aspects of treating patients with all types of vascular disease. Vein: a vessel that carries blood low in oxygen away from the body s organs and back to the heart. Vena Cava: two large veins (venous trunks) that return deoxygenated blood from the body, into the heart. The inferior vena cava travels up alongside the abdominal aorta with blood from the lower part of the body. The superior vena cava is above the heart, and forms from a convergence of the left and right brachiocephalic veins that contain blood from the head and the arms. Vena Cava Filter-see Inferior Vena Cava Filter Venous Insufficiency-see Valve Reflux Venous Reflux Disease-see Valve reflux Venous Stasis Syndrome-see Post Thrombosis Syndrome. Venous Stress Disorder-see Post Thrombosis Syndrome. Venous Thromboembolism: a clot that forms within a vein and may obstruct the flow of blood. Venogram: an X-ray test that takes pictures of blood flow through the veins in a certain area of the body. During a venogram, a special dye (contrast material) is put into your veins so they can be seen clearly on an X-ray picture. A venogram looks at the condition of your veins and the valves in your veins. It can show the veins in your legs, pelvis, or arm; the veins leading to the heart; or the veins leaving your kidneys. While venograms can show veins and blood flow and are often used as tool to diagnose MTS, they cannot always definitively show MTS related compression. False negatives for MTS are possible. Virchow s Triad: This describes the three broad factors that can lead to thrombosis: stasis (blood not moving, e.g. varicose veins, being bedbound, atrial fibrillation), hypercoagulability (blood disorder, pregnancy, hormones, etc.) and injury to the blood vessel. Warfarin-See Coumadin Warfarin Induced Skin Necrosis (WISN) (Coumadin Induced Skin Necrosis-CISN, Coumarin-Congener-Associated Skin Necrosis, Warfarin
11 May-Thurner Syndrome (and related topics) Glossary 11 Dermal Gangrene): A rare adverse effect of warfarin therapy characterized by a painful rash and usually noticeable in the first ten days of warfarin therapy. Occurs in % of Coumadin based medication users. In such rare cases, warfarin therapy is immediately discontinued. Xarelto (rivaroaxiban): a newer blood thinner that that blocks the activity of clotting factor Xa. Most entries are a combination of multiple sources. References include but aren t limited to: Web MD, MedlinePlus, drugs.com, United States National Institutes of Health, Mayo Clinic, Cleveland Clinic, and the following:
Tired, Aching Legs? Swollen Ankles? Varicose Veins?
 Tired, Aching Legs? Swollen Ankles? Varicose Veins? Healthy Legs 2006 http://healthylegs.com Page 1 Venous disorders are widespread Leg problems are widespread throughout the world, but what most people
Tired, Aching Legs? Swollen Ankles? Varicose Veins? Healthy Legs 2006 http://healthylegs.com Page 1 Venous disorders are widespread Leg problems are widespread throughout the world, but what most people
Tired, Aching Legs? Swollen Ankles? Varicose Veins? An informative guide for patients
 Tired, Aching Legs? Swollen Ankles? Varicose Veins? An informative guide for patients Are You at Risk? Leg problems are widespread throughout the world, but what most people don t know is that approximately
Tired, Aching Legs? Swollen Ankles? Varicose Veins? An informative guide for patients Are You at Risk? Leg problems are widespread throughout the world, but what most people don t know is that approximately
Confirmed Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
 Confirmed Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Information for patients What is deep vein thrombosis? Blood clotting provides us with essential protection against severe loss of blood from an injury to a vein or
Confirmed Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Information for patients What is deep vein thrombosis? Blood clotting provides us with essential protection against severe loss of blood from an injury to a vein or
INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia deep vein thrombosis DVT pulmonary embolism PE inherited thrombophilia
 INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia (Hypercoagulability) is a condition in which a person forms blood clots more than normal. Blood clots may occur in the arms or legs (e.g., deep vein thrombosis DVT), the lungs
INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia (Hypercoagulability) is a condition in which a person forms blood clots more than normal. Blood clots may occur in the arms or legs (e.g., deep vein thrombosis DVT), the lungs
Preventing Blood Clots After Hip or Knee Replacement Surgery or Surgery for a Broken Hip. A Review of the Research for Adults
 Preventing Blood Clots After Hip or Knee Replacement Surgery or Surgery for a Broken Hip A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: You are considering or planning to
Preventing Blood Clots After Hip or Knee Replacement Surgery or Surgery for a Broken Hip A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: You are considering or planning to
What Does Pregnancy Have to Do With Blood Clots in a Woman s Legs?
 Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning A Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning Drugs to Prevent Abnormal Blood
Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning A Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning Drugs to Prevent Abnormal Blood
INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia deep vein thrombosis DVT pulmonary embolism PE inherited thrombophilia
 INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia (Hypercoagulability) is a condition in which a person forms blood clots more than normal. Blood clots may occur in the arms or legs (e.g., deep vein thrombosis DVT), the lungs
INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia (Hypercoagulability) is a condition in which a person forms blood clots more than normal. Blood clots may occur in the arms or legs (e.g., deep vein thrombosis DVT), the lungs
Provided by the American Venous Forum: veinforum.org
 CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal
 Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
To provide an evidenced-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis.
 DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS: TREATMENT TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidenced-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis.
DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS: TREATMENT TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidenced-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis.
MCHENRY WESTERN LAKE COUNTY EMS SYSTEM OPTIONAL CE ADVANCED LEVEL (EMTP, PHRN, ECRN) August 2013. Anticoagulants
 MCHENRY WESTERN LAKE COUNTY EMS SYSTEM OPTIONAL CE ADVANCED LEVEL (EMTP, PHRN, ECRN) August 2013 Anticoagulants Anticoagulants are agents that prevent the formation of blood clots. Before we can talk about
MCHENRY WESTERN LAKE COUNTY EMS SYSTEM OPTIONAL CE ADVANCED LEVEL (EMTP, PHRN, ECRN) August 2013 Anticoagulants Anticoagulants are agents that prevent the formation of blood clots. Before we can talk about
Patient Information Understanding Varicose Veins
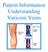 Patient Information Understanding Varicose Veins The Circulatory System Arteries carry oxygenated blood to your legs and the veins carry de-oxygenated blood away from your legs. The blood returns to the
Patient Information Understanding Varicose Veins The Circulatory System Arteries carry oxygenated blood to your legs and the veins carry de-oxygenated blood away from your legs. The blood returns to the
Provided by the American Venous Forum: veinforum.org
 CHAPTER 17 SURGICAL THERAPY FOR DEEP VALVE INCOMPETENCE Original author: Seshadri Raju Abstracted by Gary W. Lemmon Introduction Deep vein valvular incompetence happens when the valves in the veins (tubes
CHAPTER 17 SURGICAL THERAPY FOR DEEP VALVE INCOMPETENCE Original author: Seshadri Raju Abstracted by Gary W. Lemmon Introduction Deep vein valvular incompetence happens when the valves in the veins (tubes
A Patient s Guide to Primary and Secondary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Using Blood-Thinning (Anticoagulant) Drugs
 A Patient s Guide to Primary and Secondary Prevention of PATIENT EDUCATION GUIDE What Is Cardiovascular Disease? Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a broad term that covers any disease of the heart and circulatory
A Patient s Guide to Primary and Secondary Prevention of PATIENT EDUCATION GUIDE What Is Cardiovascular Disease? Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a broad term that covers any disease of the heart and circulatory
Surgical Options for Venous Disease. Sandra C Carr MD Vascular Surgery Meriter Wisconsin Heart
 Surgical Options for Venous Disease Sandra C Carr MD Vascular Surgery Meriter Wisconsin Heart Chronic Venous Disease Approximately 23% of adults in the US have varicose veins Estimated 22 million women
Surgical Options for Venous Disease Sandra C Carr MD Vascular Surgery Meriter Wisconsin Heart Chronic Venous Disease Approximately 23% of adults in the US have varicose veins Estimated 22 million women
Venous Thromboembolic Treatment Guidelines
 Venous Thromboembolic Treatment Guidelines About the NYU Venous Thromboembolic Center (VTEC) The center s mission is to deliver advanced screening, detection, care, and management services for patients
Venous Thromboembolic Treatment Guidelines About the NYU Venous Thromboembolic Center (VTEC) The center s mission is to deliver advanced screening, detection, care, and management services for patients
CHAPTER 15 SCLEROTHERAPY FOR VENOUS DISEASE
 Introduction CHAPTER 15 SCLEROTHERAPY FOR VENOUS DISEASE Original authors: Niren Angle, John J. Bergan, Joshua I. Greenberg, and J. Leonel Villavicencio Abstracted by Teresa L. Carman New technology has
Introduction CHAPTER 15 SCLEROTHERAPY FOR VENOUS DISEASE Original authors: Niren Angle, John J. Bergan, Joshua I. Greenberg, and J. Leonel Villavicencio Abstracted by Teresa L. Carman New technology has
Varicose Veins and Spider Veins
 page 1 Varicose Veins and Spider Veins Q: What are varicose veins and spider A: Varicose (VAR-i-kos) veins are enlarged veins that can be blue, red, or fleshcolored. They often look like cords and appear
page 1 Varicose Veins and Spider Veins Q: What are varicose veins and spider A: Varicose (VAR-i-kos) veins are enlarged veins that can be blue, red, or fleshcolored. They often look like cords and appear
Baby Your Legs! Get relief for: Heavy, tired or aching legs Swollen ankles and feet Varicose or spider veins. Managing leg health during pregnancy
 Baby Your Legs! Get relief for: Heavy, tired or aching legs Swollen ankles and feet Varicose or spider veins Managing leg health during pregnancy Common leg health problems during pregnancy Venous disorders
Baby Your Legs! Get relief for: Heavy, tired or aching legs Swollen ankles and feet Varicose or spider veins Managing leg health during pregnancy Common leg health problems during pregnancy Venous disorders
The veins of the lower limbs can be subdivided into three subtypes: deep veins, superficial veins, and connecting veins (figure 1).
 VEIN DISEASE Vein disease may seem insignificant and harmless at first, but if left untreated, it can develop into a major problem. It occurs when veins have trouble transporting blood back to the heart
VEIN DISEASE Vein disease may seem insignificant and harmless at first, but if left untreated, it can develop into a major problem. It occurs when veins have trouble transporting blood back to the heart
X-Plain Varicose Veins Reference Summary
 X-Plain Varicose Veins Reference Summary Introduction Varicose veins are very common, in both women and men. Varicose veins can be painful and unattractive. Vein doctors use non-invasive ultrasound imaging
X-Plain Varicose Veins Reference Summary Introduction Varicose veins are very common, in both women and men. Varicose veins can be painful and unattractive. Vein doctors use non-invasive ultrasound imaging
Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA) and Stenting For PVS Patients
 Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA) and Stenting For PVS Patients There are two types of blood vessels in the body arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood rich in oxygen from the heart to all
Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA) and Stenting For PVS Patients There are two types of blood vessels in the body arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood rich in oxygen from the heart to all
SEDICO Newsletter Issue 8. Varicose veins
 SEDICO Newsletter Issue 8 Definition: Varicose veins Varicose veins are veins that have become enlarged and twisted. The term commonly refers to the veins on the leg, although varicose veins occur elsewhere.
SEDICO Newsletter Issue 8 Definition: Varicose veins Varicose veins are veins that have become enlarged and twisted. The term commonly refers to the veins on the leg, although varicose veins occur elsewhere.
Preventing Blood Clots in Adult Patients. Information For Patients
 Preventing Blood Clots in Adult Patients Information For Patients 1 This leaflet will give you information on how to reduce the risk of developing blood clots during and after your stay in hospital. If
Preventing Blood Clots in Adult Patients Information For Patients 1 This leaflet will give you information on how to reduce the risk of developing blood clots during and after your stay in hospital. If
TREATMENT OF VARICOSE AND SPIDER VEINS Patient Info
 TREATMENT OF VARICOSE AND SPIDER VEINS Patient Info www.heartofthevillages.com TIRED & ACHING LEGS? If you suffer from varicose and spider veins, you are not alone. It is estimated that there are more
TREATMENT OF VARICOSE AND SPIDER VEINS Patient Info www.heartofthevillages.com TIRED & ACHING LEGS? If you suffer from varicose and spider veins, you are not alone. It is estimated that there are more
Varicose veins - 1 -
 Varicose veins - 1 - Varicose Veins About 3 in 10 adults develop varicose veins at some time in their life. Most people with varicose veins do not have an underlying disease and they usually occur for
Varicose veins - 1 - Varicose Veins About 3 in 10 adults develop varicose veins at some time in their life. Most people with varicose veins do not have an underlying disease and they usually occur for
Renovascular Disease. Renal Artery and Arteriosclerosis
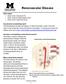 Other names: Renal Artery Stenosis (RAS) Renal Vascular Hypertension (RVH) Renal Artery Aneurysm (RAA) How does the normal kidney work? The blood passes through the kidneys to remove the body s waste.
Other names: Renal Artery Stenosis (RAS) Renal Vascular Hypertension (RVH) Renal Artery Aneurysm (RAA) How does the normal kidney work? The blood passes through the kidneys to remove the body s waste.
Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal
 Scan for mobile link. Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? In an inferior vena cava filter placement procedure, interventional radiologists
Scan for mobile link. Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? In an inferior vena cava filter placement procedure, interventional radiologists
VARICOSE VEINS. Information Leaflet. Your Health. Our Priority. VTE Ambulatory Clinic Stepping Hill Hospital
 VARICOSE VEINS Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 7 Varicose Veins There are no accurate figures for the number of people with varicose veins. Some studies suggest that 3 in 100 people
VARICOSE VEINS Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 7 Varicose Veins There are no accurate figures for the number of people with varicose veins. Some studies suggest that 3 in 100 people
treatment of varicose and spider veins patient information SAMPLE a publication by advancing vein care
 treatment of varicose and spider veins patient information a publication by advancing vein care Since most veins lie deep to the skin s surface, vein disorders are not always visible to the naked eye.
treatment of varicose and spider veins patient information a publication by advancing vein care Since most veins lie deep to the skin s surface, vein disorders are not always visible to the naked eye.
A Patient s Guide to Minimally Invasive Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair
 A Patient s Guide to Minimally Invasive Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair Table of Contents The AFX Endovascular AAA System............................................ 1 What is an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
A Patient s Guide to Minimally Invasive Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair Table of Contents The AFX Endovascular AAA System............................................ 1 What is an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
Understanding Varicose Veins
 Understanding Varicose Veins Professor Bruce Campbell Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT NOTICE This book is intended not as a
Understanding Varicose Veins Professor Bruce Campbell Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT NOTICE This book is intended not as a
Patient Information Booklet. Endovascular Stent Grafts: A Treatment for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms
 Patient Information Booklet Endovascular Stent Grafts: A Treatment for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 1 Glossary 2 Abdominal Aorta 4 Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm 5 Causes 6 Symptoms
Patient Information Booklet Endovascular Stent Grafts: A Treatment for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 1 Glossary 2 Abdominal Aorta 4 Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm 5 Causes 6 Symptoms
SCRIPT NUMBER 122 VARICOSE VEINS - 2 (TWO SPEAKERS)
 SCRIPT NUMBER 122 VARICOSE VEINS - 2 (TWO SPEAKERS) PROGRAM NAME: HEALTH NUGGETS PROGRAM TITLE: VARICOSE VEINS - 2 PROGRAM NUMBER: 122 SUBJECT: SYMPTOMS, CAUSES, TREATMENT, PREVENTION OF VARICOSE VEINS
SCRIPT NUMBER 122 VARICOSE VEINS - 2 (TWO SPEAKERS) PROGRAM NAME: HEALTH NUGGETS PROGRAM TITLE: VARICOSE VEINS - 2 PROGRAM NUMBER: 122 SUBJECT: SYMPTOMS, CAUSES, TREATMENT, PREVENTION OF VARICOSE VEINS
Ultrasound - Vascular
 Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Vascular Vascular ultrasound uses sound waves to evaluate the body s circulatory system and help identify blockages and detect blood clots. A Doppler ultrasound study
Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Vascular Vascular ultrasound uses sound waves to evaluate the body s circulatory system and help identify blockages and detect blood clots. A Doppler ultrasound study
Venous Reflux Disease and Current Treatments VN20-87-A 01/06
 Venous Reflux Disease and Current Treatments Leg Vein Anatomy Your legs are made up of a network of veins and vessels that carry blood back to the heart The venous system is comprised of: Deep veins Veins
Venous Reflux Disease and Current Treatments Leg Vein Anatomy Your legs are made up of a network of veins and vessels that carry blood back to the heart The venous system is comprised of: Deep veins Veins
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary
 X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
Treatment by LASER. Understanding Varicose veins and. Dr. Rajesh Mundhada (MD. DNB) Dr. Atul Rewatkar (MD)
 Understanding Varicose veins and Treatment by LASER Dr. Rajesh Mundhada (MD. DNB) Dr. Atul Rewatkar (MD) Orange city Hospital & Research Institute 19, Pandey Lay out, Veer Sawarkar Square, Nagpur 440015
Understanding Varicose veins and Treatment by LASER Dr. Rajesh Mundhada (MD. DNB) Dr. Atul Rewatkar (MD) Orange city Hospital & Research Institute 19, Pandey Lay out, Veer Sawarkar Square, Nagpur 440015
THE VEIN CENTER. State-of-the-Art Treatment for Varicose Veins and Spider Veins
 THE VEIN CENTER State-of-the-Art Treatment for Varicose Veins and Spider Veins Vein Disorders Nearly 50 percent of the adult population suffers from undesirable, sometimes painful vein disease. The most
THE VEIN CENTER State-of-the-Art Treatment for Varicose Veins and Spider Veins Vein Disorders Nearly 50 percent of the adult population suffers from undesirable, sometimes painful vein disease. The most
Venous and Lymphatic Disorders
 Venous and Lymphatic Disorders. ก. Venous and Lymphatic Disorders Varicose Veins Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Lymphedema What Is Varicose Veins? Latin: Varicose = Varix = twisted Abnormal venous dilatation
Venous and Lymphatic Disorders. ก. Venous and Lymphatic Disorders Varicose Veins Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Lymphedema What Is Varicose Veins? Latin: Varicose = Varix = twisted Abnormal venous dilatation
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO PULMONARY EMBOLISM TREATMENT
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO PULMONARY EMBOLISM TREATMENT This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get any side effects, talk to
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO PULMONARY EMBOLISM TREATMENT This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get any side effects, talk to
Understanding Coronary Artery Disease, Cardiac Catheterization, and Treatment Options. A Guide for Patients
 Understanding Coronary Artery Disease, Cardiac Catheterization, and Treatment Options A Guide for Patients Coronary Artery Disease If you or a member of your family has been diagnosed with coronary artery
Understanding Coronary Artery Disease, Cardiac Catheterization, and Treatment Options A Guide for Patients Coronary Artery Disease If you or a member of your family has been diagnosed with coronary artery
Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism
 P A T I E N T I N F O R M A T I O N G U I D E Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Information for Newly Diagnosed Patients CONTENTS A. Blood clot basics a. What is a blood clot? b. What causes
P A T I E N T I N F O R M A T I O N G U I D E Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Information for Newly Diagnosed Patients CONTENTS A. Blood clot basics a. What is a blood clot? b. What causes
A Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation
 Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation A Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation PATIENT EDUCATION GUIDE What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation
Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation A Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation PATIENT EDUCATION GUIDE What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation
What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms
 What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Interventions Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Radiology Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D.,
What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Interventions Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Radiology Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D.,
Provided by the American Venous Forum: veinforum.org
 CHAPTER 19 VASCULAR MALFORMATIONS Original authors: David H. Deaton, Byung Boong Lee, James Loredo, Richard F. Neville, William H. Pearce, and Heron E. Rodriguez Abstracted by Raghu Motaganahalli Introduction
CHAPTER 19 VASCULAR MALFORMATIONS Original authors: David H. Deaton, Byung Boong Lee, James Loredo, Richard F. Neville, William H. Pearce, and Heron E. Rodriguez Abstracted by Raghu Motaganahalli Introduction
Cook Celect and Günther Tulip Vena Cava Filter Patient Guide
 Cook Celect and Günther Tulip Vena Cava Filter Patient Guide www.cookmedical.com Filter patient guide Contents Pulmonary embolism 4 5 What is pulmonary embolism? What causes it? What are the symptoms of
Cook Celect and Günther Tulip Vena Cava Filter Patient Guide www.cookmedical.com Filter patient guide Contents Pulmonary embolism 4 5 What is pulmonary embolism? What causes it? What are the symptoms of
PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION
 PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION This booklet was designed to help you and the important people in your life understand the treatment of high dose chemotherapy with stem cell support: a procedure
PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION This booklet was designed to help you and the important people in your life understand the treatment of high dose chemotherapy with stem cell support: a procedure
Spotlight Series: Interventional Radiology. Varicose Veins and Venous Insufficiency
 Spotlight Series: Interventional Radiology Varicose Veins and Venous Insufficiency What is venous insufficiency? Spectrum of Disease Spider veins and telangiectasias Small reddish and purple veins near
Spotlight Series: Interventional Radiology Varicose Veins and Venous Insufficiency What is venous insufficiency? Spectrum of Disease Spider veins and telangiectasias Small reddish and purple veins near
DVT/PE Management with Rivaroxaban (Xarelto)
 DVT/PE Management with Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) Rivaroxaban is FDA approved for the acute treatment of DVT and PE and reduction in risk of recurrence of DVT and PE. FDA approved indications: Non valvular
DVT/PE Management with Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) Rivaroxaban is FDA approved for the acute treatment of DVT and PE and reduction in risk of recurrence of DVT and PE. FDA approved indications: Non valvular
Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in Children and Young Adults
 Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in MSRHTC P.O. Box 6507 Aurora, CO 80045-0507 (303) 724-0724 An Overview for Patients and Health Care Providers 2 15 GLOSSARY: venous thrombosis = a condition of
Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in MSRHTC P.O. Box 6507 Aurora, CO 80045-0507 (303) 724-0724 An Overview for Patients and Health Care Providers 2 15 GLOSSARY: venous thrombosis = a condition of
What are spider veins? What is the best treatment for spider veins?
 Laser Spider/Leg Vein Q & A What are spider veins? Millions of women and men are bothered by unsightly spider veins on their faces and legs. Spider veins or telangiectasias are those small red, blue and
Laser Spider/Leg Vein Q & A What are spider veins? Millions of women and men are bothered by unsightly spider veins on their faces and legs. Spider veins or telangiectasias are those small red, blue and
Varicose Vein Treatment (Endovenous Ablation of Varicose Veins)
 Scan for mobile link. Varicose Vein Treatment (Endovenous Ablation of Varicose Veins) Varicose vein treatment, also known as endovenous ablation, uses radiofrequency or laser energy to cauterize and close
Scan for mobile link. Varicose Vein Treatment (Endovenous Ablation of Varicose Veins) Varicose vein treatment, also known as endovenous ablation, uses radiofrequency or laser energy to cauterize and close
Thrombophilia. Steven R. Lentz, M.D. Ph.D. Carver College of Medicine The University of Iowa May 2003
 Thrombophilia Steven R. Lentz, M.D. Ph.D. Carver College of Medicine The University of Iowa May 2003 Thrombophilia Hereditary and acquired risk factors for thrombosis Venous thromboembolism Arterial thromboembolism
Thrombophilia Steven R. Lentz, M.D. Ph.D. Carver College of Medicine The University of Iowa May 2003 Thrombophilia Hereditary and acquired risk factors for thrombosis Venous thromboembolism Arterial thromboembolism
Varicose veins and spider veins
 Varicose veins and spider veins Summary Varicose veins are knobbly, twisted and darkish-blue in appearance, and are most commonly found on people s legs. Varicose veins are caused by faulty valves within
Varicose veins and spider veins Summary Varicose veins are knobbly, twisted and darkish-blue in appearance, and are most commonly found on people s legs. Varicose veins are caused by faulty valves within
Ischaemic stroke 85% (85 in every 100 strokes)
 UNDERSTANDING STROKE DUE TO INTRACEREBRAL HAEMORRHAGE This factsheet provides information for people who have had a stroke due to an intracerebral (bleed in the brain) and for their families and carers.
UNDERSTANDING STROKE DUE TO INTRACEREBRAL HAEMORRHAGE This factsheet provides information for people who have had a stroke due to an intracerebral (bleed in the brain) and for their families and carers.
OPERATION:... Proximal tibial osteotomy Distal femoral osteotomy
 AFFIX PATIENT DETAIL STICKER HERE Forename.. Surname NHS Organisation. Responsible surgeon. Job Title Hospital Number... D.O.B.././ No special requirements OPERATION:..... Proximal tibial osteotomy Distal
AFFIX PATIENT DETAIL STICKER HERE Forename.. Surname NHS Organisation. Responsible surgeon. Job Title Hospital Number... D.O.B.././ No special requirements OPERATION:..... Proximal tibial osteotomy Distal
Recurrent Varicose Veins
 Information for patients Recurrent Varicose Veins Sheffield Vascular Institute Northern General Hospital You have been diagnosed as having Varicose Veins that have recurred (come back). This leaflet explains
Information for patients Recurrent Varicose Veins Sheffield Vascular Institute Northern General Hospital You have been diagnosed as having Varicose Veins that have recurred (come back). This leaflet explains
Heart Attack: What You Need to Know
 A WorkLife4You Guide Heart Attack: What You Need to Know What is a Heart Attack? The heart works 24 hours a day, pumping oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to the body. Blood is supplied to the heart through
A WorkLife4You Guide Heart Attack: What You Need to Know What is a Heart Attack? The heart works 24 hours a day, pumping oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to the body. Blood is supplied to the heart through
V03 Varicose Veins Surgery
 V03 Varicose Veins Surgery What are varicose veins? Varicose veins are enlarged and twisted veins in the leg. They are common and affect up to 3 in 10 people. More women than men ask for treatment, with
V03 Varicose Veins Surgery What are varicose veins? Varicose veins are enlarged and twisted veins in the leg. They are common and affect up to 3 in 10 people. More women than men ask for treatment, with
Acute Myeloid Leukemia
 Acute Myeloid Leukemia Introduction Leukemia is cancer of the white blood cells. The increased number of these cells leads to overcrowding of healthy blood cells. As a result, the healthy cells are not
Acute Myeloid Leukemia Introduction Leukemia is cancer of the white blood cells. The increased number of these cells leads to overcrowding of healthy blood cells. As a result, the healthy cells are not
A Guide to Healthier Legs
 A Guide to Healthier Legs Are You at Risk? Keeping Your Legs Healthy Leg problems are widespread throughout the world. According to the American College of Phlebology, more than 80 million Americans suffer
A Guide to Healthier Legs Are You at Risk? Keeping Your Legs Healthy Leg problems are widespread throughout the world. According to the American College of Phlebology, more than 80 million Americans suffer
Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Treatment with Rivaroxaban
 Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Treatment with Rivaroxaban Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn: about venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism how the medicine Rivaroxaban
Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Treatment with Rivaroxaban Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn: about venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism how the medicine Rivaroxaban
Smoking and misuse of certain pain medicines can affect the risk of developing renal cell cancer.
 Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Information for patients who require Foam Sclerotherapy for Varicose Veins.
 Information for patients who require Foam Sclerotherapy for Varicose Veins. Why do I need this procedure? Everybody has two sets of veins in the legs. These include the superficial and deep veins. Their
Information for patients who require Foam Sclerotherapy for Varicose Veins. Why do I need this procedure? Everybody has two sets of veins in the legs. These include the superficial and deep veins. Their
Information for you Treatment of venous thrombosis in pregnancy and after birth. What are the symptoms of a DVT during pregnancy?
 Information for you Treatment of venous thrombosis in pregnancy and after birth Published in September 2011 What is venous thrombosis? Thrombosis is a blood clot in a blood vessel (a vein or an artery).
Information for you Treatment of venous thrombosis in pregnancy and after birth Published in September 2011 What is venous thrombosis? Thrombosis is a blood clot in a blood vessel (a vein or an artery).
Anticoagulant therapy
 Anticoagulation: The risks Anticoagulant therapy 1990 2002: 600 incidents reported 120 resulted in death of patient 92 deaths related to warfarin usage 28 reports related to heparin usage Incidents in
Anticoagulation: The risks Anticoagulant therapy 1990 2002: 600 incidents reported 120 resulted in death of patient 92 deaths related to warfarin usage 28 reports related to heparin usage Incidents in
F REQUENTLY A SKED Q UESTIONS. and Spider Veins
 page 1 Varicose Veins moves up the legs. If the one-way valves become weak, blood can leak back into the vein and collect there. This problem is called venous insufficiency. Pooled blood enlarges the vein
page 1 Varicose Veins moves up the legs. If the one-way valves become weak, blood can leak back into the vein and collect there. This problem is called venous insufficiency. Pooled blood enlarges the vein
The degree of liver inflammation or damage (grade) Presence and extent of fatty liver or other metabolic liver diseases
 ilearning about your health Liver Biopsy www.cpmc.org/learning What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a specially trained doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist, or gastroenterologist)
ilearning about your health Liver Biopsy www.cpmc.org/learning What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a specially trained doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist, or gastroenterologist)
Prevent Bleeding When Taking Blood Thinners
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Prevent Bleeding When Taking Blood Thinners Blood thinners are medicines used to keep harmful blood clots from forming in the body. Blood thinners can also
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Prevent Bleeding When Taking Blood Thinners Blood thinners are medicines used to keep harmful blood clots from forming in the body. Blood thinners can also
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
WHY DO MY LEGS HURT? Veins, arteries, and other stuff.
 WHY DO MY LEGS HURT? Veins, arteries, and other stuff. Karl A. Illig, MD Professor of Surgery Chief, Division of Vascular Surgery Mitzi Ekers, ARNP April 2013 Why do my legs hurt? CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
WHY DO MY LEGS HURT? Veins, arteries, and other stuff. Karl A. Illig, MD Professor of Surgery Chief, Division of Vascular Surgery Mitzi Ekers, ARNP April 2013 Why do my legs hurt? CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
Col league. SMMC Vascular Center Opens A PUBLICATION FOR SOUTHERN MAINE PHYSICIANS
 A PUBLICATION FOR SOUTHERN MAINE PHYSICIANS Col league 8 2012 SMMC Vascular Center Opens By Frank Lavoie, MD, Executive Vice President and Chief Operating Officer During the last year, Southern Maine Medical
A PUBLICATION FOR SOUTHERN MAINE PHYSICIANS Col league 8 2012 SMMC Vascular Center Opens By Frank Lavoie, MD, Executive Vice President and Chief Operating Officer During the last year, Southern Maine Medical
MEDICATION GUIDE ELIQUIS (ELL eh kwiss) (apixaban) tablets
 MEDICATION GUIDE ELIQUIS (ELL eh kwiss) (apixaban) tablets What is the most important information I should know about ELIQUIS? For people taking ELIQUIS for atrial fibrillation: People with atrial fibrillation
MEDICATION GUIDE ELIQUIS (ELL eh kwiss) (apixaban) tablets What is the most important information I should know about ELIQUIS? For people taking ELIQUIS for atrial fibrillation: People with atrial fibrillation
Horton General Hospital Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Information for patients
 Horton General Hospital Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Information for patients What is a Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)? A DVT is a blood clot which forms in a deep vein, usually in
Horton General Hospital Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Information for patients What is a Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)? A DVT is a blood clot which forms in a deep vein, usually in
ARTHROSCOPIC HIP SURGERY
 ARTHROSCOPIC HIP SURGERY Hip Arthroscopy is a relatively simple procedure whereby common disorders of the hip can be diagnosed and treated using keyhole surgery. Some conditions, which previously were
ARTHROSCOPIC HIP SURGERY Hip Arthroscopy is a relatively simple procedure whereby common disorders of the hip can be diagnosed and treated using keyhole surgery. Some conditions, which previously were
Registered Charity No: 326679 Caring for those with a rare, complex and lifelong disease www.behcets.org.uk
 Registered Charity No: 326679 Caring for those with a rare, complex and lifelong disease www.behcets.org.uk Behçet s Disease and the Kidneys How are the kidneys affected by Behçet s disease? Kidney disease
Registered Charity No: 326679 Caring for those with a rare, complex and lifelong disease www.behcets.org.uk Behçet s Disease and the Kidneys How are the kidneys affected by Behçet s disease? Kidney disease
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS TREATMENT
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS TREATMENT This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get any side effects, talk
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS TREATMENT This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get any side effects, talk
An abdominal ultrasound produces a picture of the organs and other structures in the upper abdomen.
 Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Abdomen Ultrasound imaging of the abdomen uses sound waves to produce pictures of the structures within the upper abdomen. It is used to help diagnose pain or distention
Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Abdomen Ultrasound imaging of the abdomen uses sound waves to produce pictures of the structures within the upper abdomen. It is used to help diagnose pain or distention
Planning: Patient Goals and Expected Outcomes The patient will: Remain free of unusual bleeding Maintain effective tissue perfusion Implementation
 Obtain complete heath history including allergies, drug history and possible drug Assess baseline coagulation studies and CBC Assess for history of bleeding disorders, GI bleeding, cerebral bleed, recent
Obtain complete heath history including allergies, drug history and possible drug Assess baseline coagulation studies and CBC Assess for history of bleeding disorders, GI bleeding, cerebral bleed, recent
How To Take Xarelto
 A patient's guide Your clinic's contact details are: Name: Contact number: Contents 2 Why have I been prescribed Xarelto? 2 What is Xarelto? 3 How do I take Xarelto? 3 What should I do if I miss a dose
A patient's guide Your clinic's contact details are: Name: Contact number: Contents 2 Why have I been prescribed Xarelto? 2 What is Xarelto? 3 How do I take Xarelto? 3 What should I do if I miss a dose
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services
 CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
Facts About Peripheral Arterial Disease (P.A.D.)
 Facts About Peripheral Arterial Disease (P.A.D.) One in every 20 Americans over the age of 50 has P.A.D., a condition that raises the risk for heart attack and stroke. Peripheral arterial disease, or P.A.D.,
Facts About Peripheral Arterial Disease (P.A.D.) One in every 20 Americans over the age of 50 has P.A.D., a condition that raises the risk for heart attack and stroke. Peripheral arterial disease, or P.A.D.,
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma)
 Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Understanding your Renal Stent Procedure. A patient Guide (COVER PAGE) TABLE OF CONTENTS (inside front page)
 Understanding your Renal Stent Procedure. A patient Guide (COVER PAGE) TABLE OF CONTENTS (inside front page) The Kidney and the Renal Arteries... 1 Renal Artery Disease... 2 Diagnosis of Renal.Artery Disease...
Understanding your Renal Stent Procedure. A patient Guide (COVER PAGE) TABLE OF CONTENTS (inside front page) The Kidney and the Renal Arteries... 1 Renal Artery Disease... 2 Diagnosis of Renal.Artery Disease...
GENERAL HEART DISEASE KNOW THE FACTS
 GENERAL HEART DISEASE KNOW THE FACTS WHAT IS Heart disease is a broad term meaning any disease affecting the heart. It is commonly used to refer to coronary heart disease (CHD), a more specific term to
GENERAL HEART DISEASE KNOW THE FACTS WHAT IS Heart disease is a broad term meaning any disease affecting the heart. It is commonly used to refer to coronary heart disease (CHD), a more specific term to
PARTICULAR ASPECTS OF ANTI-THROMBOTIC TREATMENT IN HIP ARTHROPLASTY
 1 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA PARTICULAR ASPECTS OF ANTI-THROMBOTIC TREATMENT IN HIP ARTHROPLASTY ABSTRACT Ph.D student DR. TRUŞCĂ PAUL TIBERIU SCIENTIFIC COORDONATOR PROF. DR.VALENTIN
1 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA PARTICULAR ASPECTS OF ANTI-THROMBOTIC TREATMENT IN HIP ARTHROPLASTY ABSTRACT Ph.D student DR. TRUŞCĂ PAUL TIBERIU SCIENTIFIC COORDONATOR PROF. DR.VALENTIN
Traditional anticoagulants
 TEGH Family Practice Clinic Day April 4, 03 Use of Anticoagulants in 03: What s New (and What Isn t) Bill Geerts, MD, FRCPC Director, Thromboembolism Program, Sunnybrook HSC Professor of Medicine, University
TEGH Family Practice Clinic Day April 4, 03 Use of Anticoagulants in 03: What s New (and What Isn t) Bill Geerts, MD, FRCPC Director, Thromboembolism Program, Sunnybrook HSC Professor of Medicine, University
The Circulatory System. Chapter 17 Lesson 1
 The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
PATIENT INFORMATION BOOKLET
 PATIENT INFORMATION BOOKLET Wingspan Stent System with Gateway PTA Balloon Catheter TABLE OF CONTENTS Definitions... 2 What is the Purpose of This Booklet?... 3 What is an Intracranial Lesion?... 3 Who
PATIENT INFORMATION BOOKLET Wingspan Stent System with Gateway PTA Balloon Catheter TABLE OF CONTENTS Definitions... 2 What is the Purpose of This Booklet?... 3 What is an Intracranial Lesion?... 3 Who
Lumbar Laminectomy and Interspinous Process Fusion
 Lumbar Laminectomy and Interspinous Process Fusion Introduction Low back and leg pain caused by pinched nerves in the back is a common condition that limits your ability to move, walk, and work. This condition
Lumbar Laminectomy and Interspinous Process Fusion Introduction Low back and leg pain caused by pinched nerves in the back is a common condition that limits your ability to move, walk, and work. This condition
Venefit treatment for varicose veins
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Venefit treatment for varicose veins Information for patients Your consultant has recommended that we treat your varicose veins with a procedure known as Venefit radio
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Venefit treatment for varicose veins Information for patients Your consultant has recommended that we treat your varicose veins with a procedure known as Venefit radio
What You Need to KnowWhen Taking Anticoagulation Medicine
 What You Need to KnowWhen Taking Anticoagulation Medicine What are anticoagulant medicines? Anticoagulant medicines are a group of medicines that inhibit blood clotting, helping to prevent blood clots.
What You Need to KnowWhen Taking Anticoagulation Medicine What are anticoagulant medicines? Anticoagulant medicines are a group of medicines that inhibit blood clotting, helping to prevent blood clots.
Session 3 Topics. Argatroban. Argatroban. Drug Use and Adverse Effects. Laboratory Monitoring of Anticoagulant Therapy
 ~~Marshfield Labs Presents~~ Laboratory Monitoring of Anticoagulant Therapy Session 3 of 4 Michael J. Sanfelippo, M.S. Technical Director, Coagulation Services Session 3 Topics Direct Thrombin Inhibitors:
~~Marshfield Labs Presents~~ Laboratory Monitoring of Anticoagulant Therapy Session 3 of 4 Michael J. Sanfelippo, M.S. Technical Director, Coagulation Services Session 3 Topics Direct Thrombin Inhibitors:
PATIENT CONSENT TO PROCEDURE - ROUX-EN-Y GASTRIC BYPASS
 As a patient you must be adequately informed about your condition and the recommended surgical procedure. Please read this document carefully and ask about anything you do not understand. Please initial
As a patient you must be adequately informed about your condition and the recommended surgical procedure. Please read this document carefully and ask about anything you do not understand. Please initial
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
RENAL ANGIOMYOLIPOMA EMBOLIZATION
 RENAL ANGIOMYOLIPOMA EMBOLIZATION The information about renal angiomyolipomas on the next several pages includes questions commonly asked about the embolization procedure. Please take a few moments to
RENAL ANGIOMYOLIPOMA EMBOLIZATION The information about renal angiomyolipomas on the next several pages includes questions commonly asked about the embolization procedure. Please take a few moments to
Tired legs, varicose veins
 Tired legs, varicose veins Everything you need to know What are varicose veins? Varicose veins are swollen, enlarged and twisted veins in the deep or superficial venous system of the legs, due to loss
Tired legs, varicose veins Everything you need to know What are varicose veins? Varicose veins are swollen, enlarged and twisted veins in the deep or superficial venous system of the legs, due to loss
Ureteroscopy with Laser Lithotripsy
 Ureteroscopy with Laser Lithotripsy Introduction Kidney stones are fairly common. Although kidney stones can be very painful, they are treatable, and in many cases preventable. Your doctor may recommend
Ureteroscopy with Laser Lithotripsy Introduction Kidney stones are fairly common. Although kidney stones can be very painful, they are treatable, and in many cases preventable. Your doctor may recommend
The Treatment of Varicose Veins and Spider Veins
 The Treatment of Varicose Veins and Spider Veins St. Joseph Vein Center Surgical Specialists of St. Joseph, P.C. Glen H. Hastings, M.D., F.A.C.S. 820 Lester Ave., Suite 105 St. Joseph, MI 49085 (269) 983-3368
The Treatment of Varicose Veins and Spider Veins St. Joseph Vein Center Surgical Specialists of St. Joseph, P.C. Glen H. Hastings, M.D., F.A.C.S. 820 Lester Ave., Suite 105 St. Joseph, MI 49085 (269) 983-3368
